Page 1
CMOS Quad
a
FEATURES
Four Independent Sample-and-Holds
Internal Hold Capacitors
High Accuracy: 12 Bit
Very Low Droop Rate: 2 mV/s typ
Output Buffers Stable for C
TTL/CMOS Compatible Logic Inputs
Single or Dual Supply Applications
Monolithic Low Power CMOS Design
APPLICATIONS
Signal Processing Systems
Multichannel Data Acquisition Systems
Automatic Test Equipment
Medical and Analytical Instrumentation
Event Analysis
DAC Deglitching
≤ 500 pF
L
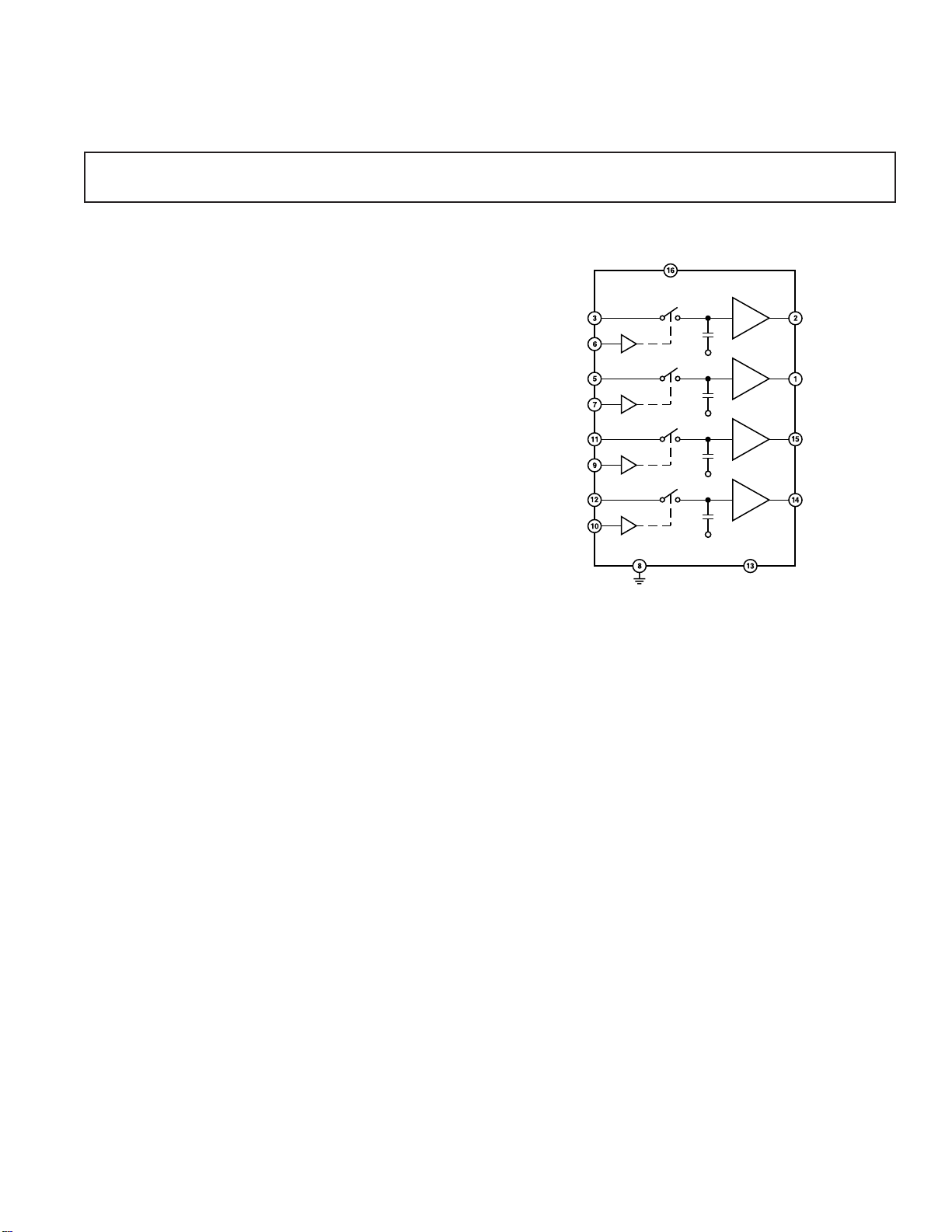
Sample-and-Hold Amplifier
SMP04*
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
V
DD
SMP04
V
S/H
V
S/H
V
S/H
V
S/H
IN1
1
V
SS
IN2
2
V
SS
IN3
3
IN4
4
V
SS
V
SS
V
V
V
V
OUT1
OUT2
OUT3
OUT4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SMP04 is a monolithic quad sample-and-hold; it has four
internal precision buffer amplifiers and internal hold capacitors.
It is manufactured in ADI’s advanced oxide isolated CMOS
technology to obtain the high accuracy, low droop rate and fast
acquisition time required by data acquisition and signal processing systems. The device can acquire an 8-bit input signal to
±1/2 LSB in less than four microseconds. The SMP04 can
operate from single or dual power supplies with TTL/CMOS
logic compatibility. Its output swing includes the negative supply.
The SMP04 is ideally suited for a wide variety of sample-andhold applications, including amplifier offset or VCA gain adjustments. One or more can be used with single or multiple DACs
to provide multiple setpoints within a system.
V
DGND
SS
The SMP04 offers significant cost and size reduction over
equivalent module or discrete designs. It is available in a
16-lead hermetic or plastic DIP and surface mount SOIC
packages. It is specified over the extended industrial tem-
perature range of –40°C to +85°C.
*Protected by U.S. Patent No. 4,739,281.
REV. D
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 1998
Page 2
SMP04–SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(@ VDD = +12.0 V, VSS = DGND = 0 V, RL = No Load, TA = Operating Temperature Range
specified in Absolute Maximum Ratings, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Linearity Error 0.01 %
V
Buffer Offset Voltage V
Hold Step V
Droop Rate ∆V/∆tV
Output Source Current
Output Sink Current
1
1
OS
HS
I
SOURCE
I
SINK
Output Voltage Range OVR R
LOGIC CHARACTERISTICS
Logic Input High Voltage V
Logic Input Low Voltage V
Logic Input Current I
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Acquisition Time
Acquisition Time
Hold Mode Settling Time t
Slew Rate
3
3
4
2
Capacitive Load Stability C
INH
INL
IN
t
AQ
t
AQ
H
SR R
L
Analog Crosstalk 0 V to 10 V Step –80 dB
SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS
Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR 10.8 V ≤ V
Supply Current I
Power Dissipation P
DD
DIS
= 6 V –10 ±2.5 +10 mV
IN
VIN = 6 V, T
= 6 V, T
V
IN
= 6 V, T
IN
= +25°C to +85°C2.54mV
A
= –40°C5mV
A
= +25°C 2 25 mV/s
A
VIN = 6 V 1.2 mA
VIN = 6 V 0.5 mA
= 20 kΩ 0.06 10.0 V
L
R
= 10 kΩ 0.06 9.5 V
L
2.4 V
0.8 V
0.5 1 µA
T
= +25°C, 0 V to 10 V Step to 0.1% 3.5 4.25 µs
A
–40°C ≤ T
T
= +25°C, 0 V to 10 V Step to 0.01% 9 µs
A
≤ +85°C 3.75 5.25 µs
A
To 1 mV 1 µs
= 20 kΩ 34 V/µs
L
<30% Overshoot 500 pF
≤ 13.2 V 60 75 dB
DD
47 mA
84 mW
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(@ VDD = +5.0 V, VSS = –5.0 V, DGND = 0.0 V, RL = No Load, TA = Operating Temperature
Range specified in Absolute Maximum Ratings, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Linearity Error 0.01 %
V
Buffer Offset Voltage V
Hold Step V
OS
HS
Droop Rate ∆V/∆tV
Output Resistance R
Output Source Current
Output Sink Current
1
1
OUT
I
SOURCE
I
SINK
Output Voltage Range OVR R
LOGIC CHARACTERISTICS
Logic Input High Voltage V
Logic Input Low Voltage V
Logic Input Current I
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Acquisition Time
Acquisition Time
Hold Mode Settling Time t
Slew Rate
3
3
5
2
Capacitive Load Stability C
INH
INL
IN
t
AQ
t
AQ
H
SR R
L
SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS
Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR ±5 V ≤ V
Supply Current I
Power Dissipation P
NOTES
1
Outputs are capable of sinking and sourcing over 20 mA, but linearity and offset are guaranteed at specified load levels.
2
All input control signals are specified with tR = tF = 5 ns (10% to 90% of +5 V) and timed from a voltage level of 1.6 V.
3
This parameter is guaranteed without test.
4
Slew rate is measured in the sample mode with a 0 V to 10 V step from 20% to 80%.
5
Slew rate is measured in the sample mode with a –3 V to +3 V step from 20% to 80%.
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
DD
DIS
= 0 V –10 ±2.5 +10 mV
IN
VIN = 0 V, T
= 0 V, T
V
IN
= 0 V, T
IN
= +25°C to +85°C2.54mV
A
= –40°C5mV
A
= +25°C 2 25 mV/s
A
1 Ω
VIN = 0 V 1.2 mA
VIN = 0 V 0.5 mA
= 20 kΩ –3.0 +3.0 V
L
2.4 V
0.8 V
0.5 1 µA
–3 V to +3 V Step to 0.1% 3.6 11 µs
–3 V to +3 V Step to 0.01% 9 µs
To 1 mV 1 µs
= 20 kΩ 3V/µs
L
<30% Overshoot 500 pF
≤ ±6 V 60 75 dB
DD
3.5 5.5 mA
55 mW
–2–
REV. D
Page 3
SMP04
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(T
= +25°C unless otherwise noted)
A
VDD to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V, 17 V
V
to VSS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.7 V, 17 V
DD
to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V, V
V
LOGIC
VIN to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VSS, V
V
to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VSS, V
OUT
DD
DD
DD
Analog Output Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±20 mA
(Not Short-Circuit Protected)
Digital Input Voltage to DGND . . . . . . . –0.3 V, V
+ 0.3 V
DD
Operating Temperature Range
EQ, EP, ES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .+150°C
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . .+300°C
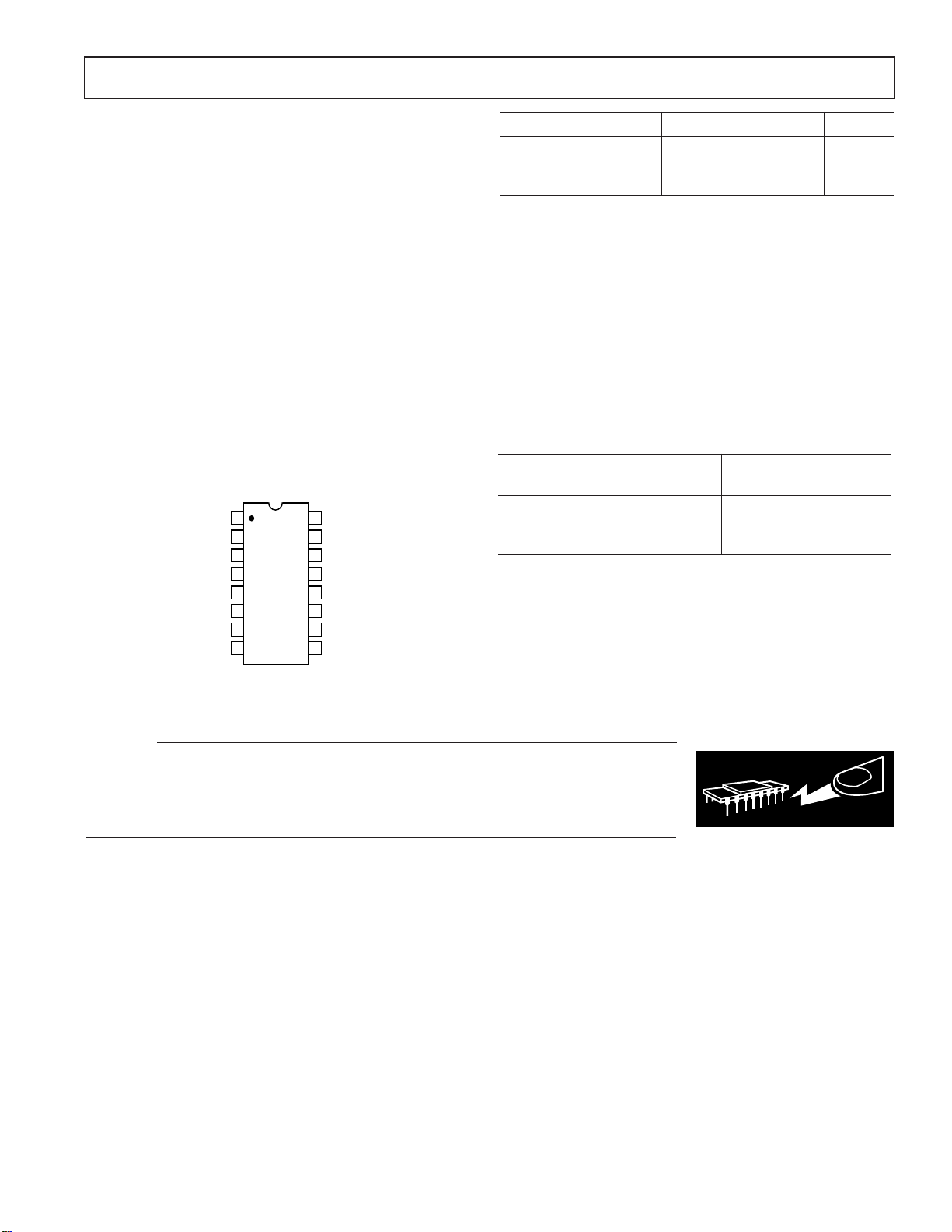
PIN CONNECTIONS
16-Lead Cerdip
16-Lead Plastic DIP
16-Lead SO
V
1
OUT2
2
V
OUT1
3
V
IN1
NC
4
V
5
IN2
S/H
6
1
S/H
7
2
DGND
8
NC = NO CONNECT
SMP04
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
V
16
DD
V
15
OUT3
V
14
OUT4
V
13
SS
V
12
IN4
V
11
IN3
10
S/H
4
9
S/H
3
Package Type JA*
JC
Units
16-Lead Cerdip 94 12 °C/W
16-Lead Plastic DIP 76 33 °C/W
16-Lead SO 92 27 °C/W
*JA is specified for worst case mounting conditions, i.e., JA is specified for device
in socket for cerdip and plastic DIP packages;
to printed circuit board for SO package.
is specified for device soldered
JA
CAUTION
1. Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; function operation
at or above this specification is not implied. Exposure to the above maximum
rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2. Digital inputs and outputs are protected; however, permanent damage may
occur on unprotected units from high energy electrostatic fields. Keep units in
conductive foam or packaging at all times until ready to use. Use proper antistatic
handling procedures.
3. Remove power before inserting or removing units from their sockets.
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package Package
Model Range Description Options*
SMP04EQ –40°C to +85°C Cerdip-16 Q-16
SMP04EP –40°C to +85°C PDIP-16 N-16
SMP04ES –40°C to +85°C SO-16 R-16A
*Q = Cerdip; N = Plastic DIP; R = Small Outline.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the SMP04 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
REV. D
–3–
Page 4
SMP04
OUT2
DGND
2
V
V
OUT3
DD
V
OUT4
S/H3S/H
V
SS
V
IN4
V
IN3
4
V
V
S/H
V
IN1
IN2
1
OUT1
V
S/H
Dice Characteristics
Die Size: 0.80 x 0.120 mil = 9,600 sq. mil
(2.032 x 3.048mm = 6.193 sq. mm)
WAFER TEST LIMITS
(@ VDD = +12 V, VSS = DGND = 0 V, RL = No Load, TA = +25ⴗC, unless otherwise noted.)
SMP04G
Parameter Symbol Conditions Limits Units
V
Buffer Offset Voltage V
Hold Step V
OS
HS
Droop Rate ∆V/∆tV
Output Source Current I
Output Sink Current I
SOURCE
SINK
Output Voltage Range OVR R
= +6 V ±10 mV max
IN
V
= +6 V ±4 mV max
IN
= +6 V 25 mV/s max
IN
VIN = +6 V 1.2 mA min
VIN = +6 V 0.5 mA min
= 20 kΩ 0.06/10.0 V min/max
L
R
= 10 kΩ 0.06/9.5 V min/max
L
LOGIC CHARACTERISTICS
Logic Input High Voltage V
Logic Input Low Voltage V
Logic Input Current I
INH
INL
IN
2.4 V min
0.8 V max
1 µA max
SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS
Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR 10.8 V ≤ V
Supply Current I
Power Dissipation P
NOTE
Electrical tests are performed at wafer probe to the limits shown. Due to variations in assembly methods and normal yield loss, yield after packaging is not guaranteed
for standard product dice. Consult factory to negotiate specifications based on dice lot qualifications through sample lot assembly and testing.
DD
DIS
≤ 13.2 V 60 dB min
DD
7 mA max
84 mW max
–4–
REV. D
Page 5
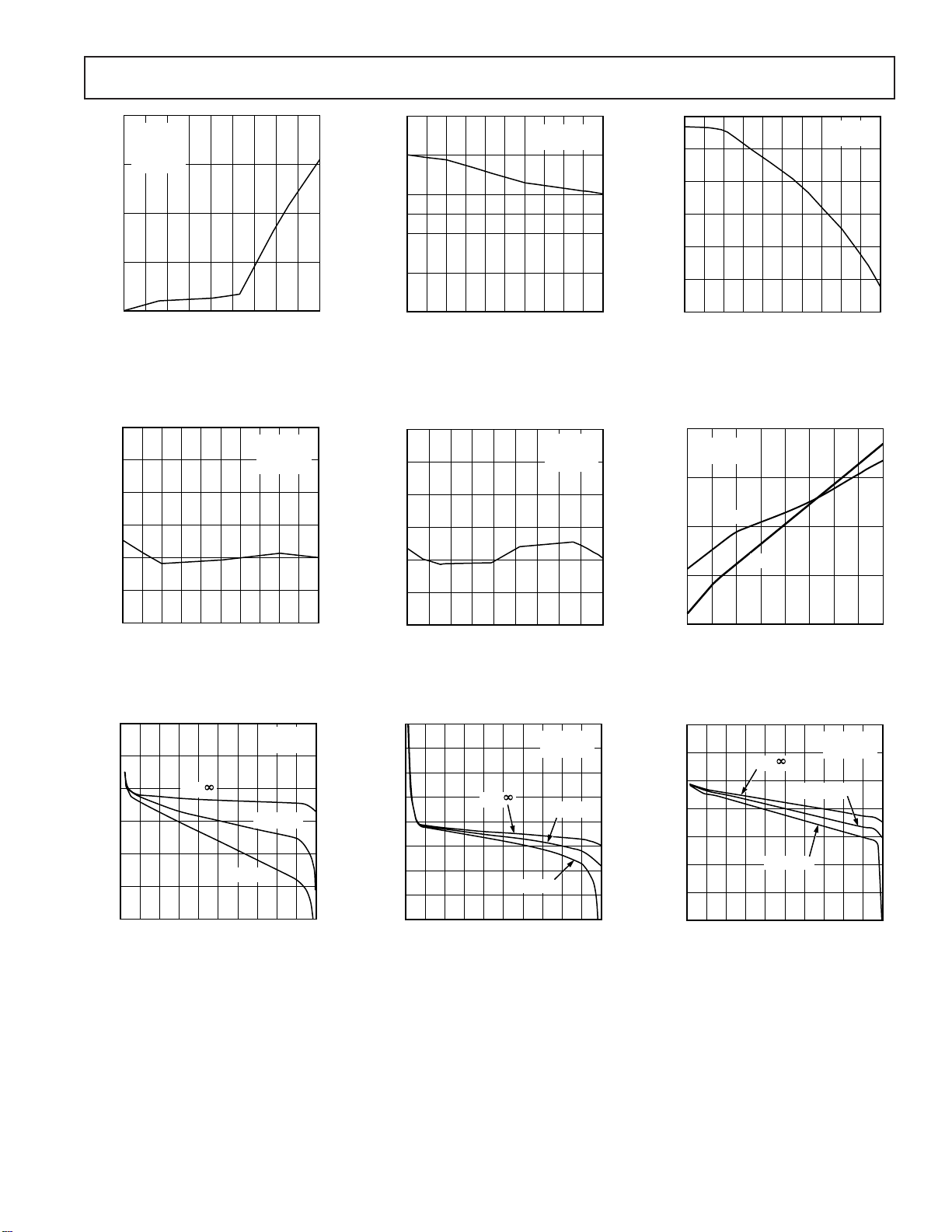
Typical Performance Characteristics–SMP04
INPUT VOLTAGE – Volts
DROOP RATE – mV/s
1800
1200
600
01 10
23456789
1600
1400
1000
800
VDD = +12V
V
SS
= 0V
10000
VDD = +12V
V
= 0V
SS
VIN = +5V
1000
= 10kV
R
L
100
DROOP RATE – mV/s
10
0
–55 –35 125
–15 5 25 65 85 10545
TEMPERATURE – 8C
Figure 1. Droop Rate vs. Temperature
3
2
1
0
–1
HOLD STEP – mV
–2
TA = +258C
V
= +12V
DD
V
= 0V
SS
5
3
1
0
–1
DROOP RATE – mV/s
–3
–5
01 10
23456789
INPUT VOLTAGE – Volts
VDD = +12V
V
= 0V
SS
Figure 2. Droop Rate vs. Input
Voltage (T
3
2
1
0
–1
HOLD STEP – mV
–2
= +25°C)
A
VDD = +12V
V
= 0V
SS
V
= +5V
IN
Figure 3. Droop Rate vs. Input
Voltage (T
7
TA = +258C
VSS = 0V
6
5
SLEW RATE – V/ms
4
= +125°C)
A
–SR
+SR
–3
01 10
23456789
INPUT VOLTAGE – Volts
Figure 4. Hold Step vs. Input Voltage
2
1
0
–1
–2
OFFSET VOLTAGE – mV
–3
–4
01 10
RL =
23456789
INPUT VOLTAGE – Volts
RL = 20kV
RL = 10kV
VDD = +12V
V
= 0V
SS
Figure 7. Offset Voltage vs. Input
Voltage (T
= +25°C)
A
–3
–55 –35 125
–15 5 25 65 85 10545
TEMPERATURE – 8C
Figure 5. Hold Step vs. Temperature
20
15
10
5
0
–5
–10
OFFSET VOLTAGE – mV
–15
–20
01 10
RL =
23456789
INPUT VOLTAGE – Volts
VDD = +12V
V
RL = 10kV
= 0V
SS
RL = 20kV
Figure 8. Offset Voltage vs. Input
Voltage (T
= +125°C)
A
3
10 11 18
Figure 6. Slew Rate vs. V
4
2
0
–2
–4
–6
OFFSET VOLTAGE – mV
–8
–10
12 13 14 15 16 17
V
– Volts
DD
DD
VDD = +12V
V
= 0V
RL =
RL = 10kV
01 10
23456789
INPUT VOLTAGE – Volts
SS
RL = 20kV
Figure 9. Offset Voltage vs. Input
Voltage (T
= –55°C)
A
REV. D
–5–
Page 6

SMP04
FREQUENCY – Hz
REJECTION RATIO – dB
90
80
0
10 100 1M1k 10k 100k
40
30
20
10
70
50
60
+PSSR
–PSSR
VDD = +12V
V
SS
= 0V
VIN = +6V
0
–1
–2
–3
OFFSET VOLTAGE – mV
–4
–5
–55 –33 125
–15 5 25 65 85 10545
TEMPERATURE – 8C
VDD = +12V
V
= 0V
SS
V
= +5V
IN
R
= 10kV
L
Figure 10. Offset Voltage vs.
Temperature
2
1
0
–1
–2
GAIN – dB
–3
–4
–5
100 1k 10M
10k 100k 1M
FREQUENCY – Hz
PHASE
GAIN
Figure 13. Gain, Phase Shift vs.
Frequency
SUPPLY CURRENT – mA
Figure 11. Supply Current vs. V
90
45
0
–45
–90
–135
PHASE SHIFT – Degrees
–180
–225
OUTPUT IMPEDANCE – V
Figure 14. Output Impedance vs.
Frequency
7
VSS = 0V
RL =
6
5
4
3
2
1
46 18
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
10 100 1M
+1258C
+258C
–558C
8 10121416
VDD – Volts
1k 10k 100k
FREQUENCY – Hz
DD
Figure 12. Sample Mode
Power Supply Rejection
15
12
9
6
3
PEAK-TO-PEAK OUTPUT – Volts
0
10k 100k 10M
FREQUENCY – Hz
TA = +258C
V
DD
V
SS
1M
= +6V
= –6V
Figure 15. Maximum Output Voltage
vs. Frequency
–6–
REV. D
Page 7

SMP04
GENERAL INFORMATION
The SMP04 is a quad sample-and-hold with each track-andhold having its own input, output, control, and on-chip hold
capacitor. The combination of four high performance track-andhold capacitors on a single chip greatly reduces board space and
design time while increasing reliability.
After the device selection, the primary considerations in using
track-and-holds are the hold capacitor and layout. The SMP04
eliminates most of these problems by having the hold capacitors
internal, eliminating the problems of leakage, feedthrough,
guard ring layout and dielectric absorption.
POWER SUPPLIES
The SMP04 is capable of operating with either single or dual
supplies over a voltage range of 7 to 15 volts. Based on the
supply voltages chosen, V
and VSS establish the output volt-
DD
age range, which is:
V
+ 0.05 V ≤ V
SS
OUT
≤ V
DD
–2 V
Note that several specifications, including acquisition time,
offset and output voltage compliance will degrade for a total
supply voltage of less than 7 V. Positive supply current is typically 4 mA with the outputs unloaded. The SMP04 has an internally regulated TTL supply so that TTL/CMOS compatibility
will be maintained over the full supply range.
Single Supply Operation Grounding Considerations
In single supply applications, it is extremely important that the
V
(negative supply) pin be connected to a clean ground. This
SS
is because the hold capacitor is internally tied to V
. Any noise
SS
or disturbance in the ground will directly couple to the output of
the sample-and-hold, degrading the signal-to-noise performance.
It is advisable that the analog and digital ground traces on the
circuit board be physically separated to reduce digital switching
noise from entering the analog circuitry.
Power Supply Bypassing
For optimum performance, the VDD supply pin must also be
bypassed with a good quality, high frequency ceramic capacitor.
The recommended value is 0.1 µF. In the case where dual sup-
plies are used, V
(negative supply) bypassing is particularly
SS
important. Again this is because the internal hold capacitor is
tied to V
. Good bypassing prevents high frequency noise from
SS
entering the sample-and-hold amplifier. A 0.1 µF ceramic bypass
capacitor is generally sufficient. For high noise environments,
adding a 10 µF tantalum capacitor in parallel with the 0.1 µF
provides additional protection.
Power Supply Sequencing
It may be advisable to have the VDD turn on prior to having logic
levels on the inputs. The SMP04 has been designed to be resistant to latch-up, but standard precautions should still be taken.
OUTPUT BUFFERS (Pins 1, 2, 14 and 15)
The buffer offset specification is ±10 mV; this is less than 1/2 LSB
of an 8-bit DAC with 10 V full scale. Change in offset over the
output range is typically 3 mV. The hold step is the magnitude
of the voltage step caused when switching from sample-to-hold
mode. This error is sometimes referred to as the pedestal
error or sample-to-hold offset, and is about 2 mV with little
variation. The droop rate of a held channel is 2 µV/ms typical
and ±25 µV/ ms maximum.
The buffers are designed primarily to drive loads connected to
ground. The outputs can source more than 1.2 mA each, over
the full voltage range and maintain specified accuracy. In split
supply operation, symmetrical output swings can be obtained by
restricting the output range to 2 V from either supply.
On-chip SMP04 buffers eliminate potential stability problems
associated with external buffers; outputs are stable with capacitive loads up to 500 pF. However, since the SMP04’s buffer
outputs are not short-circuit protected, care should be taken to
avoid shorting any output to the supplies or ground.
SIGNAL INPUT (Pins 3, 5, 11 and 12)
The signal inputs should be driven from a low impedance
voltage source such as the output of an op amp. The op amp
should have a high slew rate and fast settling time if the SMP04’s
fast acquisition time characteristics are to be maintained. As
with all CMOS devices, all input voltages should be kept within
range of the supply rails (V
≤ VIN ≤ V
SS
) to avoid the possibil-
DD
ity of setting up a latch-up condition.
The internal hold capacitance is typically 60 pF and the internal
switch ON resistance is 2 kΩ.
If single supply operation is desired, op amps such as the OP183
or AD820, that have input and output voltage compliances
including ground, can be used to drive the inputs. Split sup-
plies, such as ±7.5 V, can be used with the SMP04 and the
above mentioned op amps.
APPLICATION TIPS
All unused digital inputs should be connected to logic LOW
and the analog inputs connected to analog ground. For connectors or driven analog inputs that may become temporarily disconnected, a resistor to V
or analog ground should be used
SS
with a value ranging from 0.2 MΩ to 1 MΩ.
Do not apply signals to the SMP04 with power off unless the
input current’s value is limited to less than 10 mA.
Track-and-holds are sensitive to layout and physical connections.
For the best performance, the SMP04 should not be socketed.
REV. D
–7–
Page 8

SMP04
FREQUENCY DOMAIN PERFORMANCE
The SMP04 has been characterized in the frequency domain for
those applications that require capture of dynamic signals. See
Figure 16a for typical 86.1 kHz sample rate and an 8 kHz input
signal. Typically, the SMP04 can sample at rates up to 85 kHz.
In addition to the maximum sample rate, a minimum sample
pulsewidth will also be acceptable for a given design. Our testing
shows a drop in performance as the sample pulsewidth becomes
less than 4 µs.
10 dB/DIV RANGE 15.0 dBm 6.0 dBm
START 1 000.0 Hz STOP 100 000.0 Hz
a.
10 dB/DIV RANGE 15.0 dBm 6.3 dBm
START 1 000.0 Hz STOP 100 000.0 Hz
b.
Figure 16. Spectral Response at a Sampling Frequency of
86 kHz. Photo (a) Shows a 20 kHz Carrier Frequency and
Photo (b) Shows an 8 kHz Frequency.
Optimizing Dynamic Performance of the SMP04
Various operating parameters such as input voltage amplitude,
sampling pulsewidth and, as mentioned before, supply bypassing and grounding all have an effect on the signal-to-noise ratio.
Table I shows the SNR versus input level for the SMP04.
Distortion of the SMP04 is reduced by increasing the supply
voltage. This has the effect of increasing the positive slew rate.
Table II shows data taken at 12.3 kHz sample rate and 2 kHz
input frequency. Total harmonic distortion is dominated by the
second and third harmonics.
Table III shows the effect of sampling pulsewidth on the SNR of
the SMP04. The recommended operating pulsewidth should be
a minimum of 5 µs to achieve a good balance between acqui-
sition time and SNR for the 1.4 V p-p signal shown. For larger
swings the pulsewidth will need to be larger to account for
the time required for the signal to slew the additional voltage.
This could be used as a method of measuring acquisition
time indirectly.
Table I. SNR vs. V
IN
Input
Voltage SNR
(V p-p) (dB)
1 –61
2 –53
3 –50
4 –47
5 –45
6 –44
Conditions: V
fIN = 1.8 kHz, t
= ±6 V, f
S
= 10 µs.
PW
= 14.4 kHz,
S
Table II. SNR vs. Supply Voltage
Supply
Voltage 2nd 3rd
(V) (dB) (dB)
10 –49 –62
12 –55 –71
14 –60 –80
15 –62 <–80
16 –63 <–83
17 –65 <–85
Table III. SNR vs. Sample Pulsewidth
Sample
Pulsewidth SNR
(s) (dB)
1 –37
2 –44
3 –50
4 –54
5 –54.9
6 –55
7 –55.3
Conditions: V
fS = 14.4 kHz, fIN = 1.8 kHz.
= ±6 V, V
S
= 1.4 V p-p,
IN
–8–
REV. D
Page 9

SMP04
Sample-Mode Distortion Characteristics
Although designed as a sample-and-hold, the SMP04 may be
used as a straight buffer amplifier by configuring it in a continuous sample mode. This is done by connecting the S/H control
pin to a logic LOW. Its buffer bandwidth is primarily limited by
the distortion content as the signal frequency increases. Figure
17 shows the distortion characteristics of the SMP04 versus
frequency. It maintains less than 1% total harmonic distortion
over a voiceband of 8 kHz. Output spot noise voltage measures
4 nV/√Hz at f = 1 kHz.
10
VS = 66V
V
= 4Vp-p
IN
1
0.1
THD + NOISE – %
0.010
0.001
0.0005
20 100k
100 1k 10k
FREQUENCY – Hz
200k
Figure 17. THD+N vs. Frequency
Sampled Data Dynamic Performance
In continuous sampled data applications such as voice digitization or communication circuits, it is important to analyze the
spectral response of a sample-and-hold. Figures 16a and 16b
show the SMP04 sampling at a frequency of 86 kHz with a
1.4 V p-p pure sine wave input of 20 kHz and 8 kHz respectively. The photos include the sampling carrier frequency as
well as its multiplying frequencies. In the case of the 20 kHz
carrier frequency, the second harmonic measures 41 dB down
from the fundamental, because the second is dominant, the
signal-to-noise ratio is –40.9 dB. The 8 kHz case produces an
improved S/N performance of –48 dB.
In the V.32 and V.33 modem environment, where a 1.8 kHz
carrier signal frequency is applied to the SMP04, Figure 18
compares the spectral responses of the SMP04 under three
different sampling frequencies of 14.4 kHz, 9.6 kHz and
7.2 kHz. The signal-to-noise ratios measure 58.2 dB, 59.3 dB
and 60 dB respectively.
Figure 19 depicts SMP04’s spectral response operating with
voice frequency of 3 kHz sampling at a 15.7 kHz rate. Under
this condition, the signal-to-noise measures 53 dB.
10 dB/DIV RANGE 15.0 dBm 5.9 dBm
START 1 000.0 Hz STOP 20 000.0 Hz
Figure 19. SMP04 Spectral Response with an Input Carrier
Frequency of 3 kHz and the Sampling Frequency of 15.7 kHz
Sampled Data Dynamic Performance
In continuous sampled data applications such as voice digitization or communication circuits, it is important to analyze the
spectral response of a sample-and-hold. Figures 16a and 16b
show the SMP04 sampling at a frequency of 86 kHz with a
1.4 V p-p pure sine wave input of 20 kHz and 8 kHz respectively. The photos include the sampling carrier frequency as well
as its multiplying frequencies. In the case of the 20 kHz carrier
frequency, the second harmonic measures 41 dB down from the
fundamental, because the second is dominant, the signal-tonoise ratio is –40.9 dB. The 8 kHz case produces an improved
S/N performance of –48 dB.
In the V.32 and V.33 modem environment, where a 1.8 kHz
carrier signal frequency is applied to the SMP04, Figure 18
compares the spectral responses of the SMP04 under three
different sampling frequencies of 14.4 kHz, 9.6 kHz and
7.2 kHz. The signal-to-noise ratios measure 58.2 dB, 59.3 dB
and 60 dB respectively.
10 dB/DIV RANGE 15.0 dBm 5.9 dBm
CENTER 10 500.0 Hz SPAN 19 000.0 Hz
a.
10 dB/DIV RANGE 15.0 dBm 5.7 dBm
START 1 000.0 Hz STOP 12 000.0 Hz
b.
10 dB/DIV RANGE 15.0 dBm 5.2 dBm
START 1 000.0 Hz STOP 12 000.0 Hz
c.
Figure 18. SMP04 Spectral Response with a 1.8 kHz Carrier Frequency. (a) Shows the Sampling Frequency at 14.4 kHz;
it Exhibits a S/N Ratio of 58.2 dB. (b) Shows a 59.3 dB S/N at a Sampling Frequency of 8.6 kHz. (c) Shows a 60 dB S/N at
7.2 kHz.
REV. D
–9–
Page 10

SMP04
APPLICATIONS
MULTIPLEXED QUAD DAC (Figure 20)
The SMP04 can be used to demultiplex a single DAC converter’s
output into four separate analog outputs. The circuit is greatly
simplified by using a voltage output DAC such as the DAC8228.
To minimize output voltage perturbation, 5 µs should be allowed
to settle to its final voltage before a sample signal is asserted.
Each sample-and-hold amplifier must be refreshed every second
or less in order to assure the droop does not exceed 10 mV or
1/2 LSB.
+12V
0.1mF
WR
CS
DIGITAL
INPUTS
ADDRESS
INPUTS
REF02
+5V
V
Z
1/2 DAC8228
V
REF
+12V
V
DD
GND
5V TO 10V
V
O
CHANNEL
DECODE
S/H
S/H
S/H
S/H
1
2
3
4
Figure 20. Multiplexed Quad DAC
+12V
DGND
1mF
+
SMP04
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
V
V
V
OUT1
OUT2
OUT3
OUT4
–10–
REV. D
Page 11

SMP04
V
(63.5V)
RESET
PD/H
POSITIVE
PD/H
NEGATIVE
AMPLIFIER A
+5V
1/2 OP221
IN
–5V
AMPLIFIER B
1/2 OP221
R1
20kV
D
1
1N914
R3
20kV
D
3
1N914
D
SD214
D
SD214
V
DD
2
R2
100V
G
D
Q
1
S
1/2 SMP04
4
R4
100V
G
D
Q
2
S
DGND
–5V+5V
V
SS
V
OUT
POSITIVE
V
SS
V
OUT
NEGATIVE
V
SS
Figure 21. Positive and Negative Peak Detector with Hold Control
POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE PEAK DETECTOR WITH
HOLD CONTROL (Figure 21)
In this application the top amplifier (Amplifier A) is the positive
peak detector and the bottom amplifier (Amplifier B) is the
negative peak detector. Operation can be analyzed as follows:
Assume that the S/H switch is closed. As a positive increasing
voltage is applied to V
, D2 turns on, and D1 turns off, closing
IN
the feedback loop around Amplifier A and the SMP04, causing
the output to track the input. Conversely, in the negative peak
detector circuit at the bottom, D
turns off and D3 turns on,
4
holding the last most negative input voltage on the SMP04.
This voltage is buffered to the V
As V
falls in voltage the above conditions reverse, causing the
IN
most positive peak voltage to be held at V
O(NEG)
output.
O(POS)
output. This
voltage will be held until the input has a more positive voltage
than the previously held peak voltage, or a reset condition is
applied.
An optional HOLD control can be used by applying a logic HIGH
to the PD/H inputs. This HOLD mode further reduces leakage
current through the reverse-biased diodes (D
and D4) during
2
peak hold.
GAIN OF 10 SAMPLE-AND-HOLD (Figure 22)
This application places the SMP04 in a feedback loop of an
amplifier. Because the SMP04 has no sign inversion and the
amplifier has very high open-loop gain, the gain of the circuit is set
by the ratio of the sum of the source and feedback resistances
8.66kV 340V
+12V
V
V
OUT
0V TO
10V
SS
1kV
V
0V TO
1.0V
S/H
1N914
+12V
1/4 OP490
IN
100kV
1/4 SMP04
Figure 22. Gain of 10 Sample-and-Hold Amplifier
to the source resistance. When a logic LOW is applied to the
S/H control input, the loop is closed around the OP490,
yielding a gain of 10 (in the example shown) amplifier. When
the S/H control goes HIGH, the loop opens and the SMP04
holds the last sampled voltage. The loop remains open and the
output is unaffected by the input until a logic LOW is reapplied
to the S/H control. The pair of back-to-back diodes from the
output of the op amp to the output of the track-and-hold prevents the op amp from saturating when the track-and-hold is in
the hold mode and the loop is open.
REV. D
–11–
Page 12

SMP04
+12V
V
1
V
2
VIN (0V TO 8V)
d
t
S/H
S/H (DELAYED)
2
0
0
t
t
1
V
1/2 SMP04
DD
V
SS
V
SS
DGND
Figure 23. Time Delta Sample-and-Difference Measurement
SAMPLE AND DIFFERENCE AMPLIFIER (Figure 23)
This circuit uses two sample-and-holds to measure the voltage
difference of a signal between two time points, t
and t2. The
1
sampled voltages are fed into the differential inputs of the AMP02
instrumentation amplifier. A single resistor R
sets the gain of
G
this instrumentation amplifier. Using two channels of the
SMP04 in this application has the advantage of matched
sample-and-hold performance, since they are both on the same
chip.
INSTRUMENTATION AMP
V
SS
V
1
R
G
V
2
+12V
AMP02
–5V OR –12V
= G(V1–V2)
V
OUT
50kV
G = +1
R
G
SINGLE SUPPLY, SAMPLING, INSTRUMENTATION
AMPLIFIER (Figure 24)
This application again uses two channels of the SMP04 and an
instrumentation amplifier to provide a sampled difference signal.
The sample-and-hold signals in this circuit are tied together to
sample at the same point in time. The other two parts of the
SMP04 are used as amplifiers by grounding their control lines
so they are always sampling. One section is used to drive a
guard to the common-mode voltage and the other to generate a
+6 V reference to serve as an offset for single supply operation.
+ INPUT
– INPUT
S/H
GUARD
GUARD
GUARD
DRIVE
1/4
SMP04
1/4
SMP04
SMP04
+12V
1/4
+12V
20kV
20kV
50kV
50kV
SMP04
0.01mF
1/4
+12V
AMP02
R
G
Figure 24. +12 V Single Supply Sampling Instrumentation Amplifier with Guard Drive
50kV
GAIN =
REFERENCE
+6V REFERENCE
R
0.1mF
+1
G
V
OUT
–12–
REV. D
Page 13

+15V
SMP04
0.1mF
V
OUT
WR
10-BIT
COUNTER
CLOCK
GENERATOR
+5V
DB2–DB
DB
DB
DB
9
9
DB
2
ANALOG
RETURN
DIGITAL
RETURN
0
1
A
A
1
0
MSB
LSB
V
SS
V
DD
1/4 DAC8426
AGND DGND
1/4 AD7432
DEGLITCH LOGIC
Figure 25. DAC Deglitcher
D/A CONVERTER DEGLITCHER
Most D/A converters output an appreciable amount of glitch
energy during a transition from one code to another. The glitch
amplitude can range from several millivolts to hundreds of millivolts. This may become unacceptable in many applications. By
selectively delaying the DAC’s output transition, the SMP04
can be used to smooth the output waveform. Figure 25 shows
the schematic diagram of such a deglitcher circuit. Two simple
logic gates (an OR and a NAND gate) provide the proper timing
sequence for the DAC WR strobe and the S/H control signal to
the SMP04. In this example a linear ramp signal is generated by
feeding the most significant eight bits of the 10-bit binary
counter to the DAC. The two least significant bits are used to
produce the delayed WR strobe and the S/H control signals.
Referring to Figure 26a, new data to the DAC input is set up at
the S/H’s falling edge, but the DAC output does not change
until a WR strobe goes active. During this period, the SMP04 is
in a sample mode whose output tracks the DAC output. When
S/H goes HIGH, the current DAC output voltage is held by the
SMP04. After 1.2 µs settling, the WR strobe goes LOW to allow
the DAC output to change. Any glitch that occurs at the DAC
output is effectively blocked by the SMP04. As soon as the WR
strobe goes HIGH, the digital data is latched; at the same time
the S/H goes LOW, allowing the SMP04 to track to the new
DAC output voltage.
Figure 26b shows the deglitching operation. The top trace
shows the DAC output during a transition, while the bottom
trace shows the deglitched output of the SMP04.
REF
DAC C
1/4 AD7400
OUT
0.1mF–1mF CERAMIC
V
IN
S/H
1/4 SMP04
DGND
V
5V
V
OUT
V
SS
DD
1mF
AGND
+15V
DB
0
DB
1
WR
1ms
S/H
a.
DLY
50m
627.4
1ms
m
s
b.
Figure 26. (a) Shows the Logic Timing of the Deglitcher.
The Top Two Traces Are the Two Least Significant Bits,
and DB1, Respectively. These Are Used to Generate
DB
0
WR
the
and S/H Signals Which Are Shown in the Bottom
Two Traces. (b) Shows the Typical Glitch Amplitude of a
DAC (Top Trace) and the Deglitched Output of the AMP04
(Bottom Trace).
REV. D
–13–
Page 14

SMP04
V
DD
V
V
IN
V
DD
N-CH
P-CH
C
H
OUT
LOAD
S/H
V
DGND
LOGIC
SS
V
SS
Figure 27. Simplified Schematic of One Channel
V
DD
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
+15V
R1
10V
C1
10mF
+
D
1
C2
1mF
R2
R2
10kV
10kV
R3
4kV
R2
10kV
R4
1kV
1
2
3
SMP04
5
R2
6
10kV
7
89
Figure 28. Burn-In Circuit
–14–
REV. D
Page 15

OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm).
16-Lead Cerdip
(Q-16)
SMP04
0.005 (0.13) MIN
0.200 (5.08)
MAX
0.200 (5.08)
0.125 (3.18)
0.210 (5.33)
MAX
0.160 (4.06)
0.115 (2.93)
0.080 (2.03) MAX
16
1
0.840 (21.34) MAX
0.023 (0.58)
0.014 (0.36)
PIN 1
0.100
(2.54)
BSC
9
0.310 (7.87)
0.220 (5.59)
8
0.070 (1.78)
0.030 (0.76)
0.060 (1.52)
0.015 (0.38)
16-Lead Plastic DIP
(N-16)
0.840 (21.34)
0.745 (18.92)
16
18
PIN 1
0.022 (0.558)
0.014 (0.356)
0.100
(2.54)
BSC
9
0.280 (7.11)
0.240 (6.10)
0.060 (1.52)
0.015 (0.38)
0.070 (1.77)
0.045 (1.15)
0.150
(3.81)
MIN
SEATING
PLANE
0.130
(3.30)
MIN
SEATING
PLANE
0.320 (8.13)
0.290 (7.37)
15°
0°
0.325 (8.26)
0.300 (7.62)
0.015 (0.381)
0.008 (0.204)
C3131–0–4/98
0.015 (0.38)
0.008 (0.20)
0.195 (4.95)
0.115 (2.93)
REV. D
0.1574 (4.00)
0.1497 (3.80)
0.0098 (0.25)
0.0040 (0.10)
SEATING
PLANE
16-Lead SO
(R-16A)
0.3937 (10.00)
0.3859 (9.80)
16 9
PIN 1
0.0192 (0.49)
0.0500
(1.27)
0.0138 (0.35)
BSC
0.2440 (6.20)
81
0.2284 (5.80)
0.0688 (1.75)
0.0532 (1.35)
0.0099 (0.25)
0.0075 (0.19)
–15–
0.0196 (0.50)
0.0099 (0.25)
8°
0°
0.0500 (1.27)
0.0160 (0.41)
x 45°
PRINTED IN U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...