Page 1

ICs for Consumer Electronics
VPS-Decoder
SDA 5642-6/X
Data Sheet 02.97
Page 2
SDA 5642-6/X
Revision History: Current Version: 02.97
Previous Version:
Page
(in previous
Version)
Page
(in current
Version)
Subjects (major changes since last revision)
Edition 02.97
This edition was realized using the software system FrameMaker
Published by Siemens AG,
Bereich Halbleiter, MarketingKommunikation, Balanstraße 73,
81541 München
.
© Siemens AG 1997.
All Rights Reserved.
Attention please!
As far as patents or other rights of third parties are concerned, liability is only assumed for components, not for applications, processes
and circuits implemented within components or assemblies.
The information describes the type of component and shall not be considered as assured characteristics.
Terms of delivery and rights to change design reserved.
For questions on technology, delivery and prices please contact the Semiconductor Group Offices in Germany or the Siemens Companies
and Representatives worldwide (see address list).
Due to technical requirements components may contain dangerous substances. For information on the types in question please contact
your nearest Siemens Office, Semiconductor Group.
Siemens AG is an approved CECC manufacturer.
Packing
Please use the recycling operators known to you. We can also help you – get in touch with your nearest sales office. By agreement we
will take packing material back, if it is sorted. You must bear the costs of transport.
For packing material that is returned to us unsorted or which we are not obliged to accept, we shall have to invoice you for any costs incurred.
Components used in life-support devices or systems must be expressly authorized for such purpose!
Critical components1 of the Semiconductor Group of Siemens AG, may only be used in life-support devices or systems
written approval of the Semiconductor Group of Siemens AG.
1 A critical component is a component used in a life-support device or system whose failure can reasonably be expected to cause the
failure of that life-support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness of that device or system.
2 Life support devices or systems are intended (a) to be implanted in the human body, or (b) to support and/or maintain and sustain hu-
man life. If they fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health of the user may be endangered.
2
with the express
Page 3

SDA 5642-6/X
Table of Contents Page
1 General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.2 Pin Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.3 Pin Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.4 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2 System Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1 Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2 I
2.2.1 General Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.2.2 Chip Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.2.3 Write Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.2.4 Read Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.3 Order of Data Output on the I
2.4 Description of DAVN and EHB Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2
C Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2
C Bus and Bit Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3 Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4 VPS-Receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5 Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
5.1 Control Register Write (I
5.2 Data Register Read (I
2
C-Bus Write) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2
C-Bus Read) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
5.3 DAVN and EHB Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
5.4 Position of VPS Data Lines within the Vertical Blanking Interval . . . . . . . . . 23
5.5 Definition of Voltage Levels for VPS Data Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.6 Data Format of Programme Delivery Data in the Dedicated TV Line (VPS) 24
6 Package Outlines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Purchase of Siemens I2C components conveys the license under the Philips I2C patent to use the components
2
in the I
Semiconductor Group 3 02.97
C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specifications defined by Philips.
Page 4

VPS-Decoder SDA 5642-6/X
MOS
1 General Description
The SDA 5642-6 VPS decoder chip receives all VPS
data.
1.1 Features
• On chip data slicer
• Low external component count
2
C-Bus interface
• I
communication with external microcontroller
• 5 V supply voltage
• Video input signal level: 0.7 Vpp to 2.0 Vpp
• Technology: CMOS
• P-DIP-14-1 and P-DSO-20-1 package
P-DIP-14-1
P-DSO-20-1
Type Ordering Code Package
SDA 5642-6 Q67100-H5182 P-DIP-14-1
SDA 5642-6X Q67106-H5183 P-DSO-20-1 (SMD)
Semiconductor Group 4 02.97
Page 5
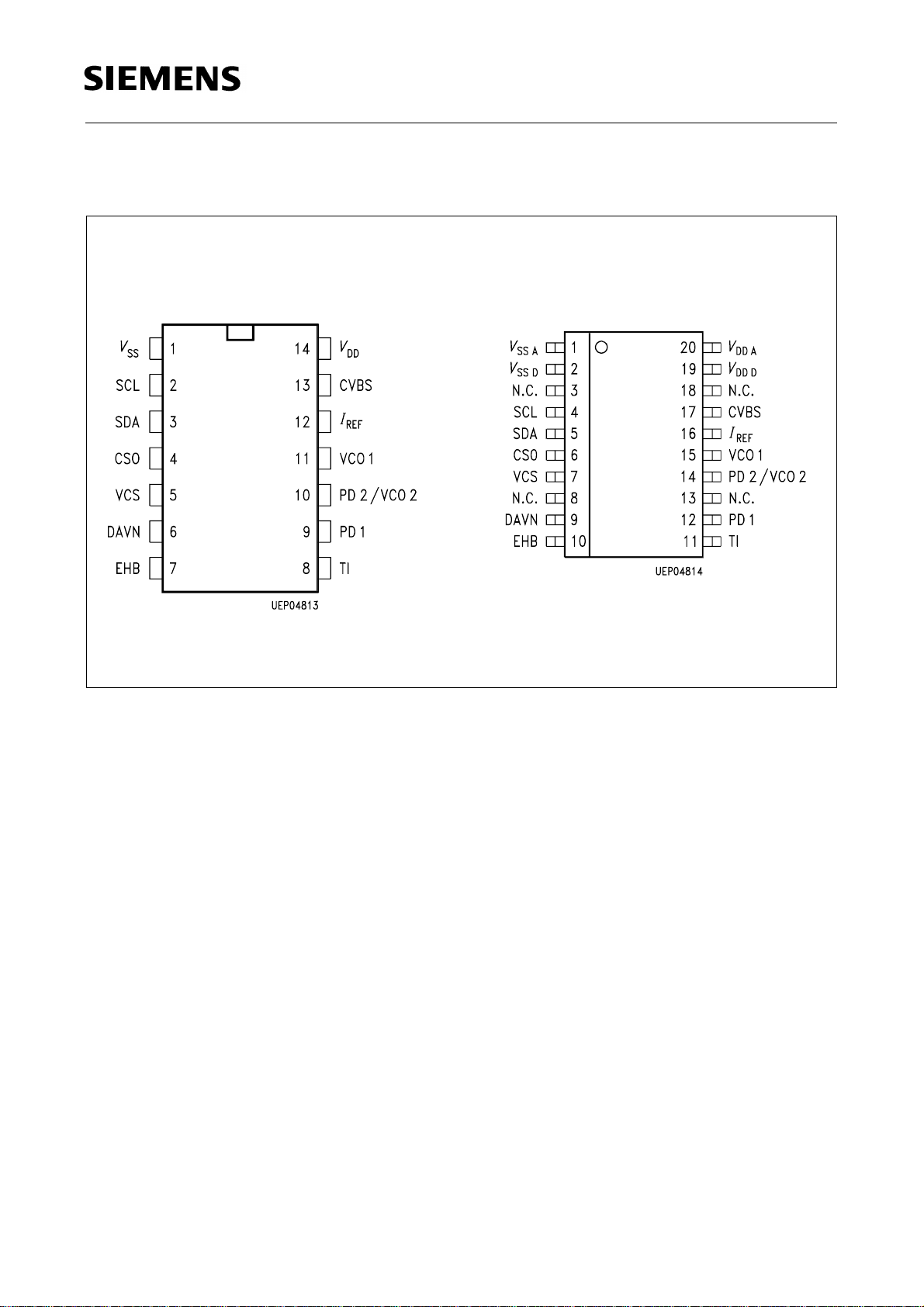
1.2 Pin Configurations
P-DIP-14-1 P-DSO-20-1
SDA 5642-6/X
Figure 1
Semiconductor Group 5 02.97
Page 6

1.3 Pin Description
Pin No. Symbol Function
P-DIP-14-1 P-DSO-20-1
SDA 5642-6/X
1 V
1
2
V
V
SS
SSA
SSD
Ground (0 V)
Analog ground (0 V)
Digital ground (0 V)
3, 8, 13, 18 N.C. Not connected
2 4 SCL Serial clock input of I
3 5 SDA Serial data input of I
4 6 CS0 Chip select input determining the I
20
/ 21H, when pulled low
H
22
/ 23H, when pulled high.
H
2
C Bus.
2
C Bus.
2
C-Bus addresses:
5 7 VCS Video Composite Sync output from sync slicer used
for PLL based clock generation.
6 9 DAVN Data available output active low, when VPS data is
received.
7 10 EHB Output signaling the presence of the first field active
high.
8 11 TI Test input; activates test mode when pulled high.
Connect to ground for operating mode.
9 12 PD1 Phase detector/charge pump output of data PLL
(DAPLL).
10 14 PD2/
Connector of the loop filter for the SYSPLL.
VCO2
11 15 VCO1 Input to the voltage controlled oscillator #1 of the
DAPLL.
12 16
I
REF
Reference current input for the on-chip analog circuit.
13 17 CVBS Composite video signal input.
14
19
V
V
DD
DDD
Positive supply voltage (+ 5 V nom.).
Positive supply voltage for the digital circuits
(+ 5 V nom.).
20
V
DDA
Positive supply voltage for the analog circuits
(+ 5 V nom.).
Semiconductor Group 6 02.97
Page 7
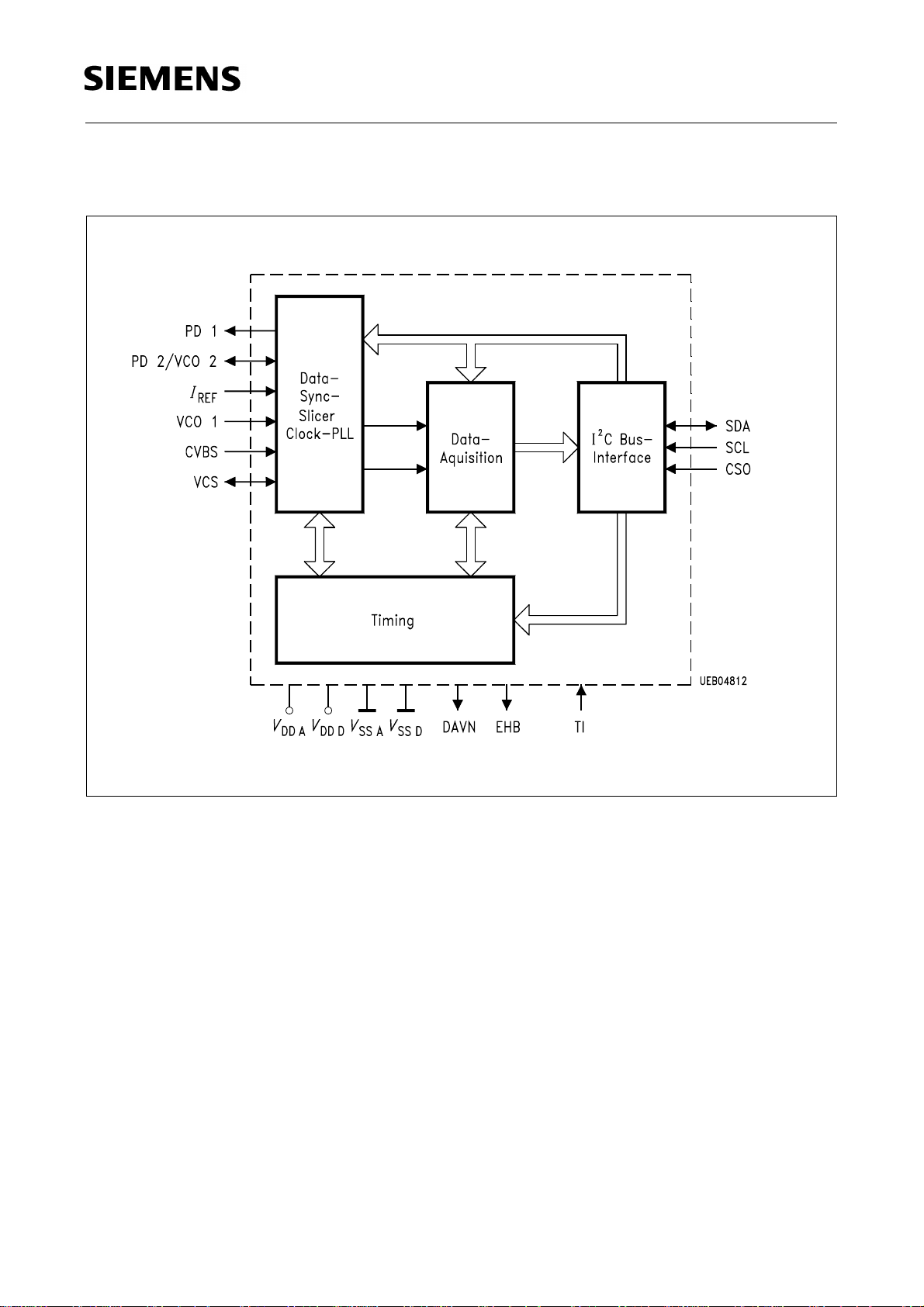
1.4 Block Diagram
SDA 5642-6/X
Figure 2
Semiconductor Group 7 02.97
Page 8

SDA 5642-6/X
2 System Description
2.1 Functions
Referring to the functional block diagram of the VPS decoder, the composite video signal
with negative going sync pulses is coupled to the pin CVBS through a capacitor which is
used for clamping the bottom of the sync pulses to an internally fixed level. The signal is
passed on to the slicer, an analogue circuitry separating the sync and the data parts of
the CVBS signal, thus yielding the digital composite sync signal VCS and a digital data
signal for further processing by comparing those signals to internally generated slicing
levels.
The output of the sync separator is forwarded, on one hand, to the output pin VCS, and
on the other hand, to the clock generator and the timing block. The VCS signal
represents a key signal that is used for deriving a system clock signal by means of a PLL
and all other timing signal.
The data slicer separates the data signal from the CVBS signal by comparing the video
voltage to an internally generated slicing level which is found by averaging the data
signal during TV line no. 16.
The clock generator delivers the system clock needed for the basic timing as well as for
the regeneraton of the dataclock. It is based on two phase locked loops (PLL’s) all parts
of which are integrated on chip with the exception of the loop filter components. Each of
the PLL’s is composed of a voltage controlled relaxation oscillator (VCO), a phase/
frequency detector (PFD), and a charge pump which converts the digital output signals
of the PFD to an analogue current. That current is transformed to a control voltage for
the VCO by the off-chip loop filter. The generated VCO frequency is 10 MHz.
All signals necessary for the control of sync and data slicing as well as for the data
acquisition are generated by the Timing block.
The extracted data bits of TV line no. 16 are checked for biphase errors. With no biphase
errors encountered, the acquired bytes are stored in the transfer register to the I
2
C Bus.
That transfer is signalled by a H/L transition of the DAVN output.
Data are updated when a new data line has been received, provided that the chip is not
accessed via the I2C Bus at the same time.
2
A micro controller can read the stored bytes via the I
C-Bus interface at any time.
However, one must be aware that the storage of new data from the acquisition interface
is inhibited as long as the VPS decoder is being accessed via the I
2
C Bus.
Semiconductor Group 8 02.97
Page 9
SDA 5642-6/X
2.2 I2C Bus
2.2.1 General Information
2
The I
i.e., both reading from and writing to the VPS decoder is possible. The clock line SCL is
controlled only by the bus master usually being a micro controller, whereas the SDA line
is controlled either by the master or by the slave. A data transfer can only be initiated by
the bus master when the bus is free, i.e., both SDA and SCL lines are in a high state. As
a general rule for the I
The only exception to that rule are the Start Condition and the Stop Condition. Further
Details are given below. The following abbreviations are used:
START: Start Condition generated by master
AS: Acknowledge by slave
AM: Acknowledge by master
NAM: No Acknowledge by master
STOP: Stop condition generated by master
C-Bus interface implemented on the VPS decoder is a slave transmitter/receiver,
2
C Bus, the SDA line changes state only when the SCL line is low.
2.2.2 Chip Address
There are two pairs of chip addresses, which are selected by the CS0-input pin
according to the following table:
CS0 Input Write Mode Read Mode
Low 20 (hex) 21 (hex)
High 22 (hex) 23 (hex)
Semiconductor Group 9 02.97
Page 10

SDA 5642-6/X
2.2.3 Write Mode
For writing to the VPS decoder, the following format has to be used:
Start Chipaddress and Write Mode AS Byte to set Control Register AS Stop
Description of Data Transfer (Write Mode)
Step1: In order to start a data transfer the master generates a Start Condition on the
bus by pulling the SDA line low while the SCL line is held high.
Step 2: The bus master puts the chip address on the SDA line during the next eight
SCL pulses.
Step 3: The master releases the SDA line during the ninth clock pulse. Thus the slave
can generate an acknowledge (AS) by pulling the SDA line to a low level.
Step 4: The controller transmits the data byte to set the Control register
Step 5: The slave acknowledges the reception of the byte.
Step 6: The master concludes the data communication by generating a Stop
Condition.
2
The write mode is used to set the I
C-Bus control register which determines the
operating mode:
Control Register:
Bit Number: 76543210
T7 T6 T5 T4 T3 T2 T1 T0
Default: All bits are set to 0 on power-up.
The bits T4 through T7 are used for test purposes and must not be changed for normal
operation by user software! (0 = normal operation)
You may write 00H, 01H, 02H, 03H, 04H, 05H, 06H, 07H, 08H, 09H, 0AH, 0BH, 0CH,
0DH, 0EH, 0FH to the register without efect. This enables the SDA 5642-6 to be used
for VPS decoding instead of the SDA 5050 or SDA 5649 without software problems.
Semiconductor Group 10 02.97
Page 11

SDA 5642-6/X
2.2.4 Read Mode
For reading from the VPS decoder, the following format has to be used
Start Chipaddress Read Mode AS 1st Byte AM ..... Last Byte NAM Stop
:
The contents of up to 16 registers (bytes) can be read starting with byte 1 bit 7 (refer to
2
the table Order of Data Output on the I
operating mode.
Description of Data Transfer (Read Mode)
Step1: To start a data transfer the master generates a Start Condition on the bus by
pulling the SDA line low while the SCL line is held high. The byte address
counter in the decoder is reset and points to the first byte to be output.
Step 2: The bus master puts the chip address on the SDA line during the next eight
SCL pulses.
C Bus and...) depending on the selected
Step 3: The master releases the SDA line during the ninth clock pulse. Thus the slave
can generate an acknowledge (AS) by pulling the SDA line to a low level. At
this moment, the slave switches to transmitting mode.
Step 4: During the next eight clock pulses the slave puts the addressed data byte
onto the SDA line.
Step 5: The reception of the byte is acknowledged by the master device which, in
turn, pulls down the SDA line during the next SCL clock pulse. By
acknowledging a byte, the master prompts the slave to increment its internal
address counter and to provide the output of the next data byte.
Step 6: Steps no. 4 and no. 5 are repeated, until the desired amount of bytes have
been read.
Step 7: The last byte is output by the slave since it will not be acknowledged by the
master.
Step 8: To conclude the read operation, the master doesn’t acknowledge the last byte
to be received. A No Acknowledge by the master (NAM) causes the slave to
switch from transmitting to receiving mode. Note that the master can
prematurely cease any reading operation by not acknowledging a byte.
Step 9: The master gains control over the SDA line and concludes the data transfer
by generating a Stop Condition on the bus, i. e., by producing a low/high
transition on the SDA line while the SCL line is in a high state. With the SDA
2
and the SCL lines being both in a high state, the I
C Bus is free and ready for
another data transfer to be started.
Semiconductor Group 11 02.97
Page 12

2.3 Order of Data Output on the I2C Bus and Bit Allocation
2
I
C Bus VPS Mode
t
Byte 1 bit 7
byte 11 bit 0
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
SDA 5642-6/X
Byte 2 bit 7
Byte 3 bit 7
Byte 4 bit 7
byte 12 bit 0
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
byte 13 bit 0
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
byte 14 bit 0
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1)
Transmission bit number
Semiconductor Group 12 02.97
Page 13

SDA 5642-6/X
2.3 Order of Data Output on the I
2
I
C Bus VPS Mode
Byte 5 bit 7
byte 5 bit 0
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Byte 6 bit 7
byte 15 bit 0
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
2
C Bus and Bit Allocation (cont’d)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Byte 7 bit 7
1)
Transmission bit number
– set to “1”
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
– set to “1”
– set to “1”
– set to “1”
– set to “1”
– set to “1”
– set to “1”
– set to “1”
Semiconductor Group 13 02.97
Page 14

2.4 Description of DAVN and EHB Outputs
DAVN (Data Valid active low)
EHB (First Field active high)
Signal Output VPS Mode
DAVN
SDA 5642-6/X
H/L-transition
in line 16 when valid VPS data is received
(set low)
L/H-transition
at the start of line 16
(set high)
always set high on power-up or during I
2
C-Bus accesses when the
bus master doesn’t acknowledge in order to
generate the stop condition
EHB
L/H-transition at the beginning of the first field
H/L-transition at the beginning of the second field
In test mode (i.e. TI = high), both DAVN and EHB are controlled by the CS0 pin and
reproduce the state of the CS0 input.
Semiconductor Group 14 02.97
Page 15

SDA 5642-6/X
3 Electrical Characteristics
Absolute Maximum Ratings
T
= 25 °C
A
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test
min. typ. max.
Condition
Ambient temperature
Storage temperature
Total power dissipation
Power dissipation per
T
T
P
P
A
stg
tot
DQ
070°C in operation
– 40 125 °C by storage
300 mW
10 mW
output
Input voltage
Supply voltage
Thermal resistance
V
V
R
IM
DD
th SU
– 0.3 6 V
– 0.3 6 V
80 K/W
Note: Maximum ratings are absolute ratings; exceeding any one of these values may
cause irreversible damage to the integrated circuit.
Operating Range
Supply voltage
Supply current
V
I
DD
DD
4.5 5 5.5 V
515mA
Ambient temperature
T
A
070°C
range
Note: In the operating range the functions given in the circuit description are fulfilled.
Semiconductor Group 15 02.97
Page 16

SDA 5642-6/X
Electrical Characteristics
T
= 25 °C
A
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
min. typ. max.
Input Signals SDA, SCL, CS0
H-input voltage
L-input voltage
Input capacitance
Input current
V
V
C
I
Input Signal TI
H-input voltage V
L-input voltage
Input capacitance
Input current
V
C
I
Input Signals CVBS
(pos. Video, neg. Sync)
Video input signal
V
level
IH
IL
I
IM
IH
IL
I
IM
CVBS
0.7 × V
DD
V
DD
V
0 0.3 × VDDV
10 pF
10 µA
0.9 × V
DD
V
DD
V
0 0.1 × VDDV
10 pF
10 µA
0.7 1.0 2.0 V 2 Vpp with
0.8 V
1.2 V
V
SYNC
V
DAT
and
Synchron signal
amplitude
V
SYNC
0.15 0.3 0.8 (1.0) V 1.0 V only related
to VCS signal
generation
Data amplitude
Coupling capacitor
H-input current
L-input current
Source impedance
Leakage resistance
V
C
I
I
R
R
DAT
IH
IL
S
C
0.25
1.5 ×
C
V
SYNC
0.5 1.2 V
33 nF
10 µA VI=5V
– 1000 – 400 – 100 µA VI=0V
250 Ω
0.91 1 1.2 MΩ
at coupling capacitor
Semiconductor Group 16 02.97
Page 17

SDA 5642-6/X
Electrical Characteristics (cont’d)
T
= 25 °C
A
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
min. typ. max.
Output Signals DAVN, EHB, VCS
H-output voltage
L-output voltage
V
V
QH
QL
V
– 0.5 V IQ= – 100 µA
DD
0.4 V IQ= 1.6 mA
Output Signals SDA (Open-Drain-Stage)
L-output voltage V
Permissible output
QL
0.4 V IQ= 3.0 mA
5.5 V
voltage
PLL-Loop Filter Components (see application circuit)
Resistance at PD2/
R
1
6.8 kΩ
VCO2
Resistance at VCO1
Attenuation
R
R
2
3
1200 kΩ
6.8 kΩ
resistance
Resistance at PD2/
R
5
1200 kΩ
VCO2
Integration capacitor
Integration capacitor
C
C
1
3
2.2 nF
33 nF
VCO – Frequence Range Adjustment
Resistance at IREF
R
4
100 kΩ
(for bias current
adjustment)
Note: The listed characteristics are ensured over the operating range of the integrated
circuit. Typical characteristics specify mean values expected over the production
spread. If not otherwise specified, typical characteristics apply at
T
= 25°C and
A
the given supply voltage.
Semiconductor Group 17 02.97
Page 18

SDA 5642-6/X
Figure 3
2
I
C-Bus Timing
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
min. max.
Clock frequency f
Inactive time prior to new transmission start-up
Hold time during start condition
Low-period of clock
High-period of clock
Set-up time for data
Rise time for SDA and SCL signal
Fall time for SDA and SCL signal
Set-up time for SCL clock during stop condition
V
All values referred to
and VIL levels.
IH
SCL
t
BUF
t
HD; STA
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
SU;DAT
t
TLH
t
THL
t
SU; STO
0 100 kHz
4.7 µs
4.0 µs
4.7 µs
4.0 µs
250 ns
1 µs
300 ns
4.7 µs
Semiconductor Group 18 02.97
Page 19

4 VPS-Receiver
SDA 5642-6/X
Figure 4
Semiconductor Group 19 02.97
Page 20

5 Appendix
5.1 Control Register Write (I
2
C-Bus Write)
SDA 5642-6/X
Figure 5
Semiconductor Group 20 02.97
Page 21

5.2 Data Register Read (I2C-Bus Read)
SDA 5642-6/X
Figure 6
Semiconductor Group 21 02.97
Page 22

5.3 DAVN and EHB Timing
SDA 5642-6/X
Figure 7
Semiconductor Group 22 02.97
Page 23

SDA 5642-6/X
5.4 Position of VPS Data Lines within the Vertical Blanking Interval
Figure 8
1)
(shown for first field)
5.5 Definition of Voltage Levels for VPS Data Line
Figure 9
Semiconductor Group 23 02.97
Page 24

SDA 5642-6/X
5.6 Data Format of Programme Delivery Data in the Dedicated TV Line (VPS)
Figure 10
Semiconductor Group 24 02.97
Page 25

SDA 5642-6/X
Figure 11
Semiconductor Group 25 02.97
Page 26

6 Package Outlines
P-DIP-14-1
(Plastic Dual In-line Package)
SDA 5642-6/X
Sorts of Packing
Package outlines for tubes, trays etc. are contained in our
Data Book “Package Information”.
GPD05005
Dimensions in mm
Semiconductor Group 26 02.97
Page 27

P-DSO-20-1
(Plastic Dual Small Outline Package)
SDA 5642-6/X
Sorts of Packing
Package outlines for tubes, trays etc. are contained in our
Data Book “Package Information”.
SMD = Surface Mounted Device
GPS05094
Dimensions in mm
Semiconductor Group 27 02.97
 Loading...
Loading...