Page 1
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
SAA7348GP
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE)
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC22
1997 Jul 11
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
4 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
6 PINNING
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1 Analog front-end
7.1.1 Decoder front-end
7.1.2 Servo front end
7.2 Decoder functions
7.3 Servo functions
7.3.1 Signal conditioning
7.3.2 Focus control
7.3.3 Radial control
7.3.4 Off-track counting
7.3.5 Off-track detection
7.3.6 Shock detection
7.3.7 Defect detection
7.3.8 Driver interface
7.3.9 Laser interface
7.4 Subcode interface
7.5 Digital output
7.5.1 Format
7.6 S2B interface
7.7 Audio support
7.7.1 Serial audio data interface
7.8 CD-ROM support
7.8.1 Serial CD-ROM data interface
7.9 Reset
7.10 External ROM support
8 MICROCONTROLLER INTERFACE
8.1 Microcontroller applications registers
8.1.1 CLK generate register (CLKgen)
8.1.2 Port Servo Register (PSR)
8.1.3 Servo Control Register (SCR)
8.1.4 Servo Status Register (STR)
8.1.5 Motor Output QCLV Register (MOQ; address
0XF2H and 0XF3H)
8.1.6 P3 Register
8.1.7 Decoder Status Register (DSR)
8.1.8 Motor Setpoint Register (MSR; address
0XF9H)
8.1.9 Motor Gain QCLV Register (address 0XFAH)
8.1.10 Data Direction Registers (DDR0, DDR2 and
DDR3)
8.1.11 Configuration Control Register (CCR)
8.1.12 A second serial interface
8.1.13 Memory map access to the servo
8.1.14 PLL Registers
8.1.15 DIV17 Register (address 0X9FH)
8.2 Memory map
8.3 Summary of the functions controlled by
decoder registers 0 to F
8.4 Summary of servo commands
8.4.1 Summary of servo command parameters
9 LIMITING VALUES
10 CHARACTERISTICS
10.1 General characteristics
10.2 Subcode interface timing characteristics
10.3 I2S timing characteristics
11 PACKAGE OUTLINE
12 SOLDERING
12.1 Introduction
12.2 Reflow soldering
12.3 Wave soldering
12.4 Repairing soldered joints
13 DEFINITIONS
14 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
1997 Jul 11 2
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
1 FEATURES
• Focus servo loop
• Radial servo loop
• Built-in access procedure with fast track count
possibilities
• Sledge motor servo loop with pulsed sledge support
• High speed error correction, up to sixteen times
over-speed
• Supports three different over-speed ranges with only
one external crystal
• Lock-to-disc mode
• Full turntable motor control
• Full error correction strategy, t = 2 ande=4
• All standard decoder functions implemented digitally
• Adaptive digital HF equalizer
• FIFO overflow concealment for rotational shock
resistance
• Digital audio interface (EBU), audio and data
• 2 and 4 times oversampling integrated digital filter,
including fs mode
• Audio data peak level detection
• Kill interface for DAC deactivation during digital silence
• All TDA1301 (DSIC2) digital servo functions
• Low focus noise
• Improved playability on ABEX TCD-721R, TCD-725 and
TCD-714 discs
• Automatic closed loop gain control available for focus
and radial loops
• On chip clock multiplier allows the use of 8.4672 MHz
crystal
• S2B serial interface with host controller
• Double speed servo
• Integrated engine controller (high speed embedded
80C51)
• External program support.
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAA7348 All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) combines
the functionality of a CD decoder (LO9585), a digital servo
(OQ8868) and a microcontroller core (80C51 based) on a
single chip. It was developed for high speed CD-ROM
applications but, due to the large scale integration, can
also be used in other CD applications. The internal
microcontroller makes it possible to develop other
applications quickly. The microcontroller can operate with
internal or external ROM.
Additional features include:
• High level integration
• Improved communication speed.
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SAA7348GP LQFP100 plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 × 14 × 1.4 mm SOT407-1
1997 Jul 11 3
PACKAG0E
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
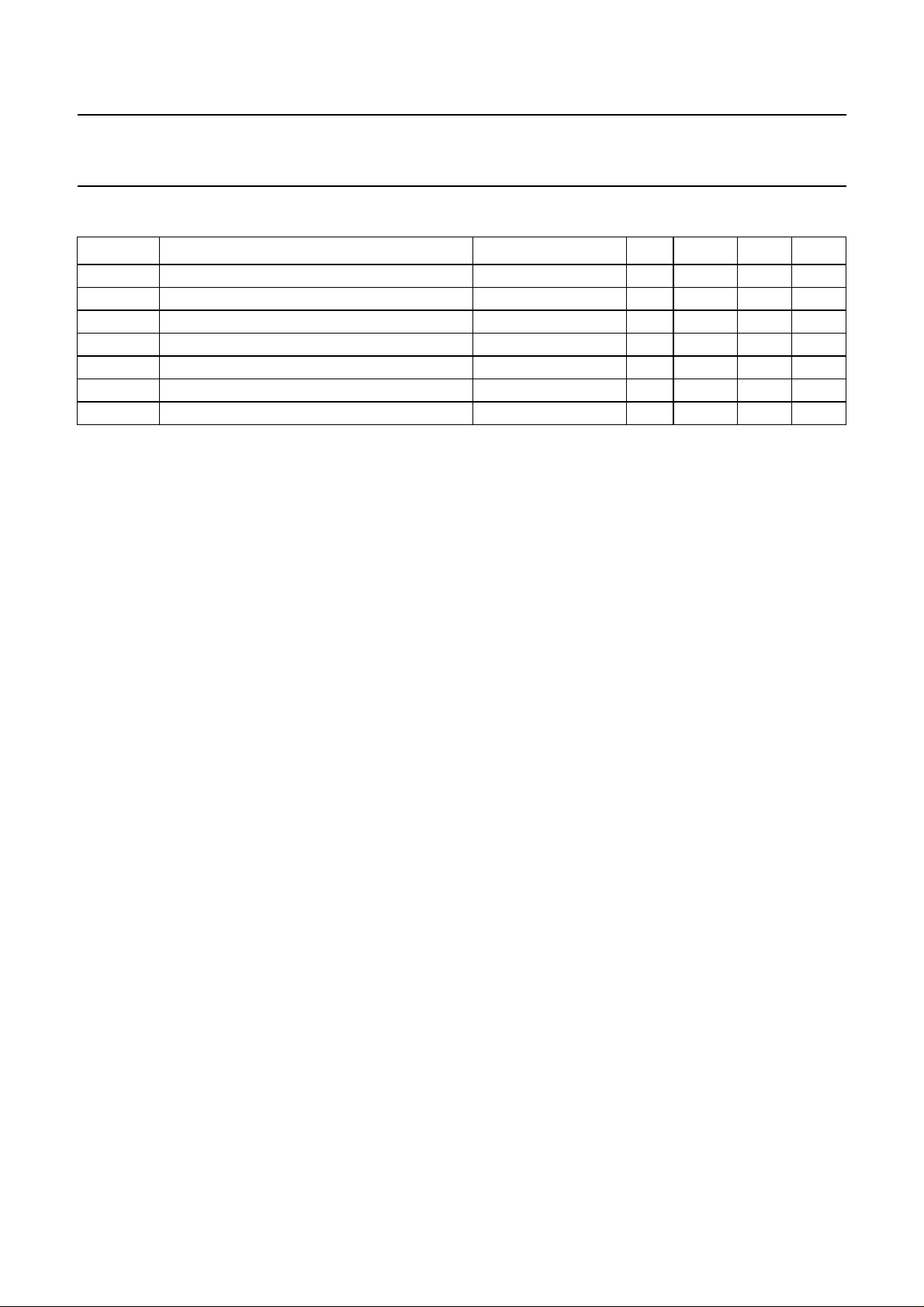
4 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DDD(pads)
V
DDD(core)
V
DDA
I
DD
f
xtal
T
amb
T
stg
Note
1. The analog and digital core supply pins (V
The core and pads can operate at different voltages and should never be connected together directly.
digital supply voltage for pad cells 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
digital supply voltage for the core note 1 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
analog supply voltage note 1 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
supply current n = 8 mode − 90 − mA
crystal frequency 8 8.4672 35 MHz
operating ambient temperature 0 − 70 °C
storage temperature −55 − +125 °C
DDA
and V
DDD(core)
) must be connected to the same external supply.
1997 Jul 11 4
Page 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
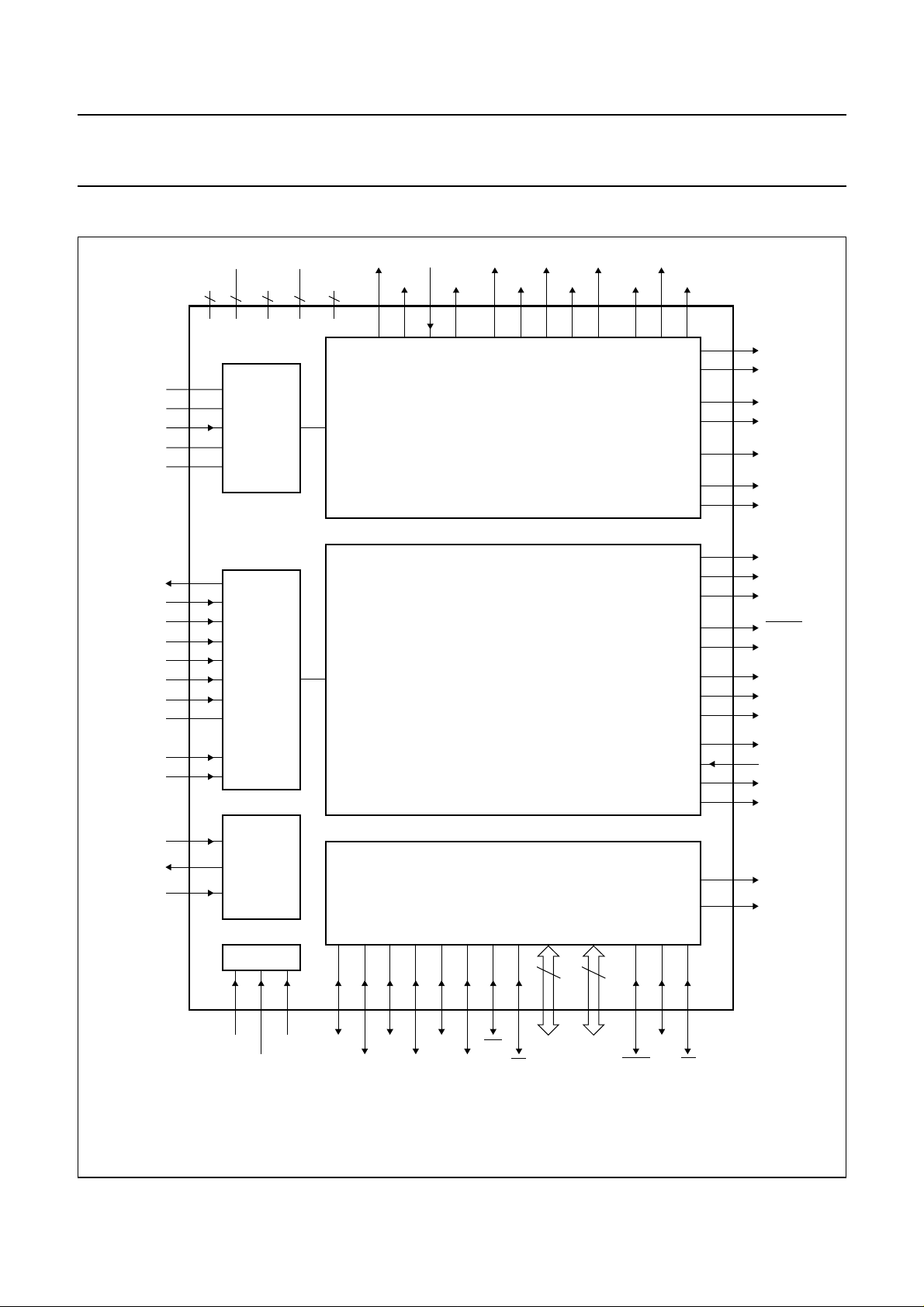
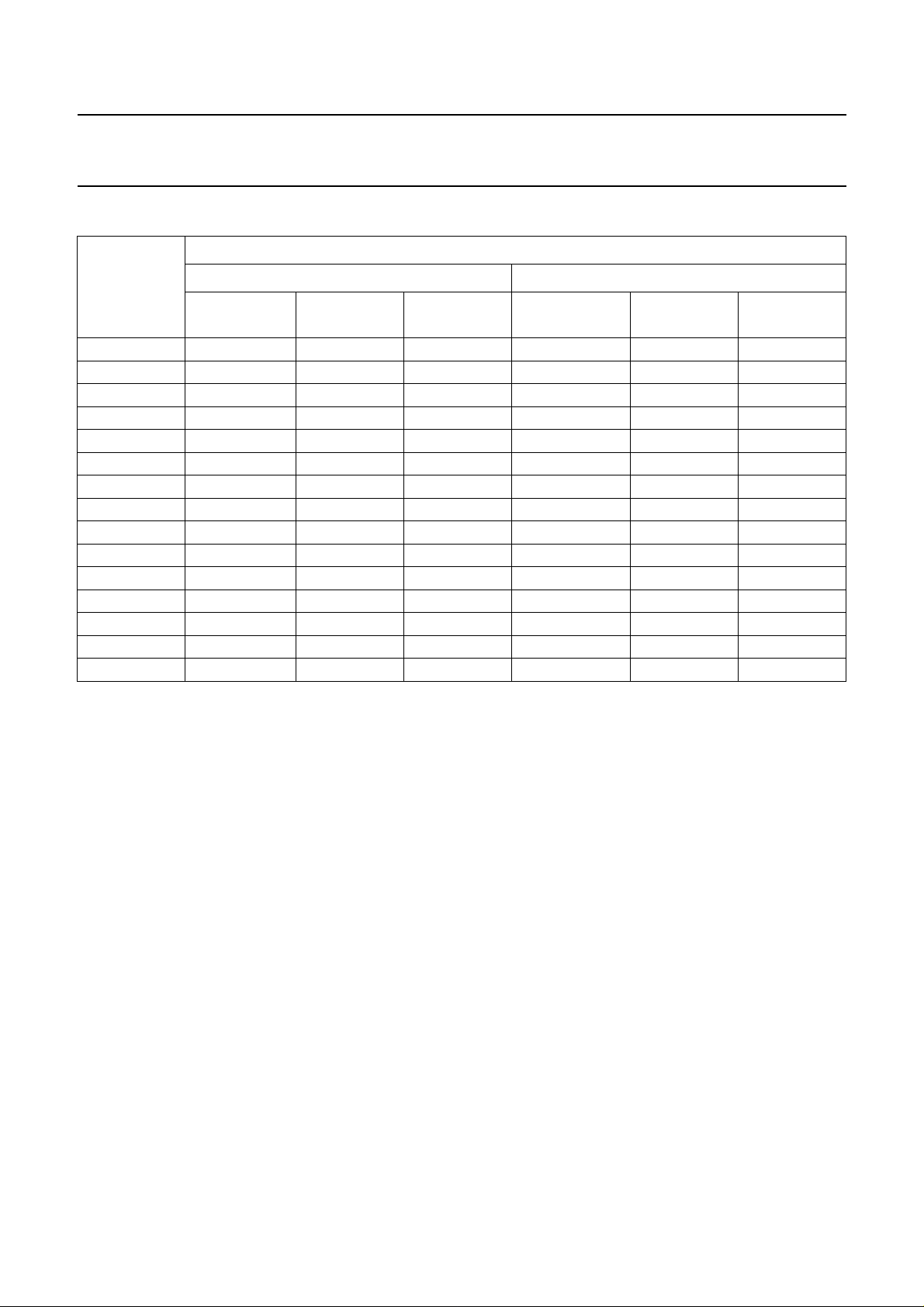
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
MIDLAD
REFLCA
HFIN
REFHCA
I
ref
V
RH
D1
D2
D3
D4
S1
S2
I
refT
FTC
H
FTC
L
V
DDD(core)
HF
V
V
SSA
V
DDA
2 2 2 9 3
(1) (2) (3) (4)
7
8
9
FRONT-END
10
11
SAA7348GP
14
15
16
17
20
21
22
23
24
25
LF
FRONT-END
SSD
V
DDD(pads)
(5)
SBSY RCK VALID
SFSY SUB DAC WCLK DACCLK
92
93
94 95 65 66 67 68 69 62 97 96
DECODER
DIGITAL SERVO
DATA SCLK KILL
DEEM
100
89
71
73
72
91
86
85
84
83
82
74
75
78
79
80
90
98
99
DOBM
SUBQW
MOTOV
MOTOS
FB
C2FAIL
CFLG
FOK
TL
RP
DSDEN
CLO
RA
FO
SL
OTD
DEFI
DEFO
LDON
XTALI
XTALO
SELPLL
(1) Pins 13 and 19.
(2) Pins 12 and 18.
(3) Pins 39 and 88.
(4) Pins 29, 38, 51, 61,
63, 70, 76, 81 and
87.
(5) Pins 52, 64 and 77.
28
27
26
CLOCK
PLL
TEST
1 2 3 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 48
TS1 TS3
TS2
R
XD0
T
XD0
INT0
INT1
R
XD1
T
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1997 Jul 11 5
XD1
80C51
8
40 to4753 to
A8 to
A15
AD0 to
AD7
5
TPWM
6
TEN
8
60
49 50
ALE
PSENWREARD
MGK498
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
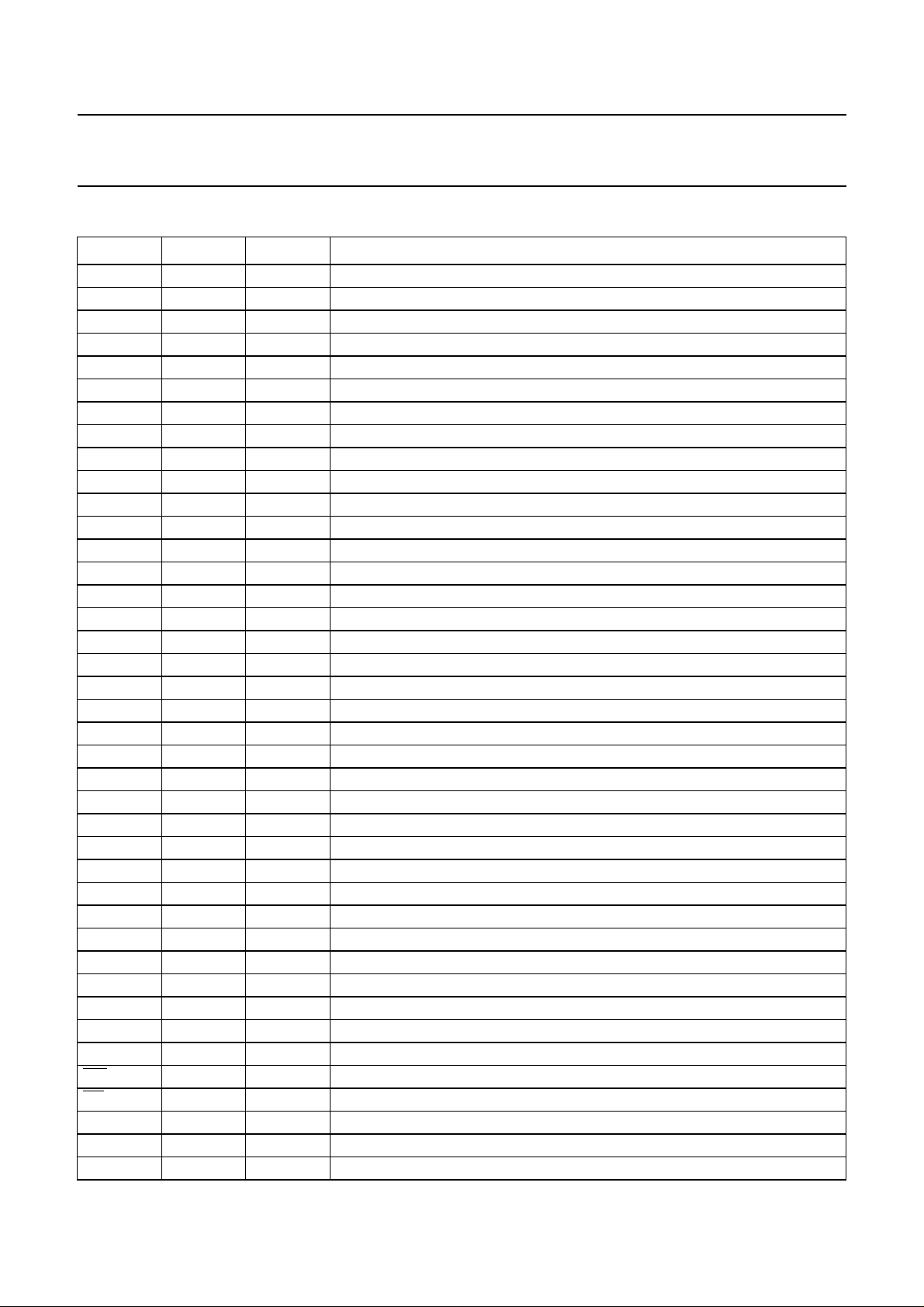
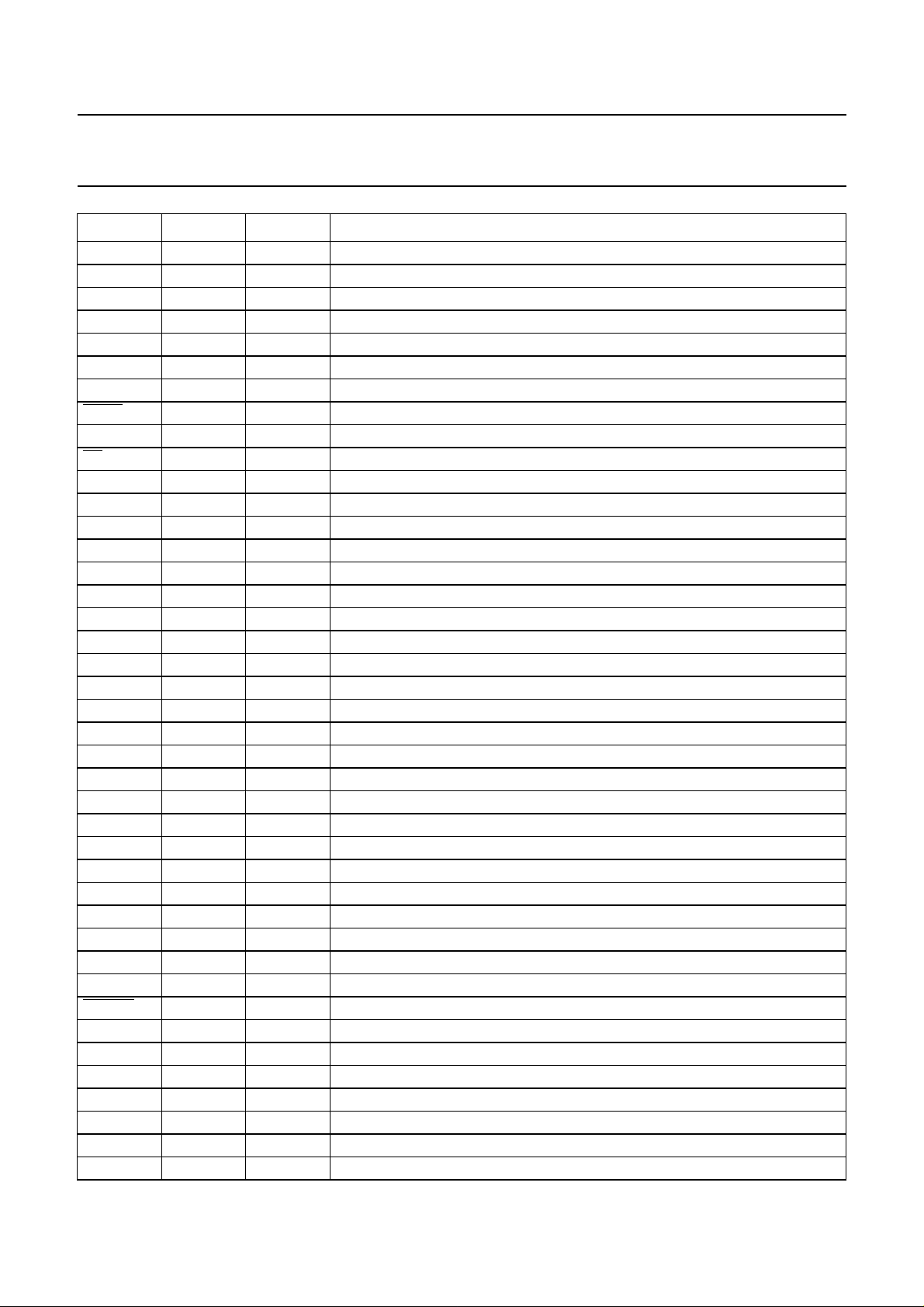
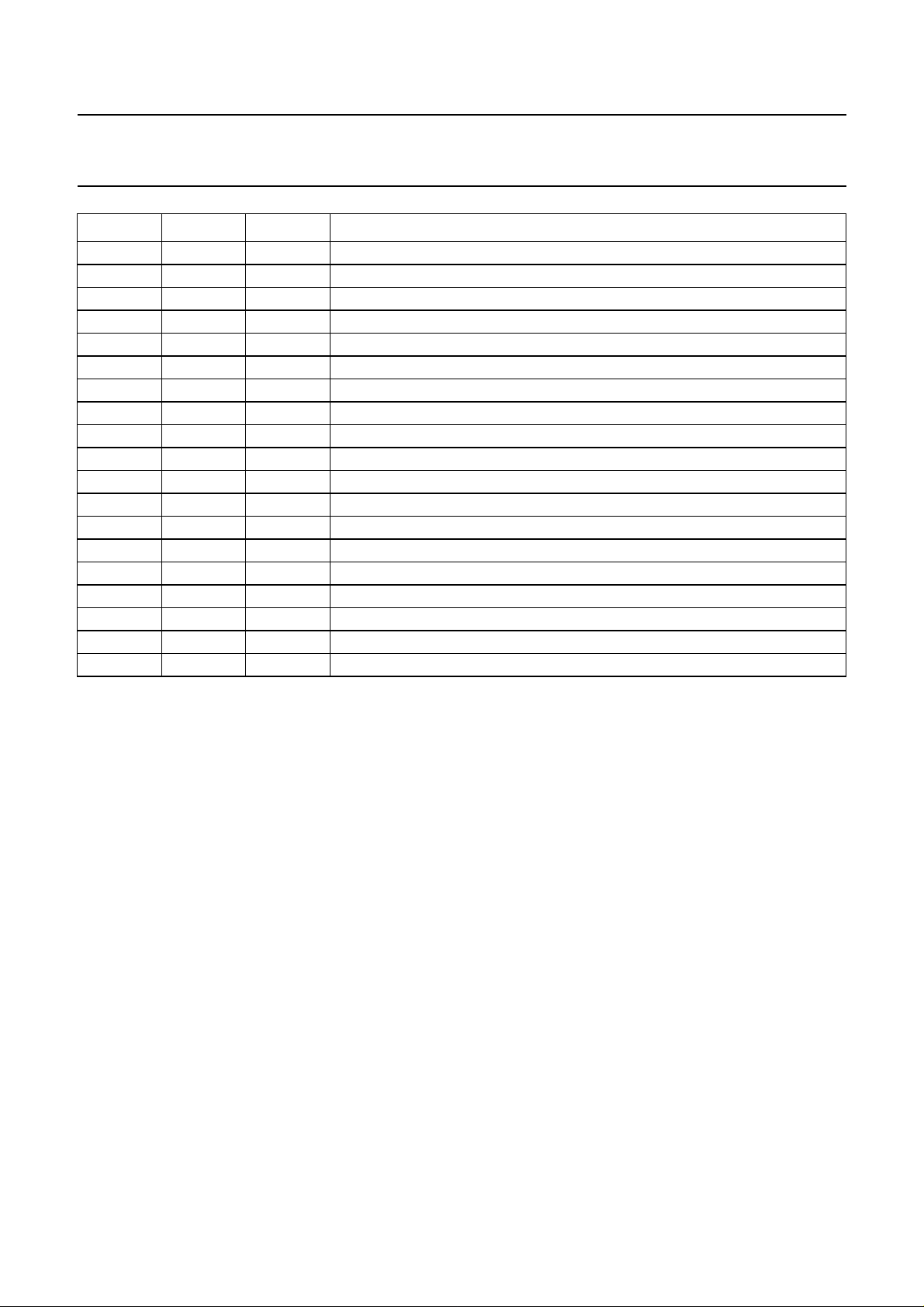
6 PINNING
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
(1)
DESCRIPTION
TS1 1 I test control input; this pin should be tied LOW
TS2 2 I test control input; this pin should be tied LOW
TS3 3 I test control input; this pin should be tied LOW
RST 4 I power-on reset input
TPWM 5 O tray PWM output
TEN 6 O tray enable output
MIDLAD 7 A ladder middle decoupling of High Frequency (HF) ADC
REFLCA 8 A ladder low decoupling of HF ADC
HFIN 9 A HF input
REFHCA 10 A ladder high decoupling of HF ADC
I
ref
V
V
V
SSA1
DDA1
RH
11 A reference current input
12 S analog ground 1 for HF front-end
13 S analog supply voltage 1 for HF front-end (3.3 V)
14 A calibrated reference voltage output from ADC
D1 15 A unipolar current input (central diode signal input)
D2 16 A unipolar current input (central diode signal input)
D3 17 A unipolar current input (central diode signal input)
V
V
SSA2
DDA2
18 S analog ground 2 for LF front-end
19 S analog supply voltage 2 for LF front-end (3.3 V)
D4 20 A unipolar current input (central diode signal input)
S1 21 A unipolar current input (satellite diode signal input)
S2 22 A unipolar current input (satellite diode signal input)
I
refT
FTC
FTC
H
L
23 A current reference, for input range of LF front-end ADCs
24 A fast track counter comparator (+) input
25 A fast track counter comparator (−) input
SELPLL 26 I enables internal clock multiplier PLL
XTALO 27 A crystal output
XTALI 28 A crystal input
V
R
T
SSD1
XD0
XD0
29 S digital ground 1
30 B P3.0
31 B P3.1
INT0 32 B P3.2 (interrupt 0)
INT1 33 B P3.3 (interrupt 1)
R
XD1
T
XD1
34 B P3.4
35 B P3.5
WR 36 B P3.6; active LOW
RD 37 B P3.7; active LOW
V
SSD2
V
DDD1(core)
38 S digital ground 2
39 S digital supply voltage 1 for the core (3.3 V)
A8 40 B P2.0 (address or I/O)
1997 Jul 11 6
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
(1)
DESCRIPTION
A9 41 B P2.1 (address or I/O)
A10 42 B P2.2 (address or I/O)
A11 43 B P2.3 (address or I/O)
A12 44 B P2.4 (address or I/O)
A13 45 B P2.5 (address or I/O)
A14 46 B P2.6 (address or I/O)
A15 47 B P2.7 (address or I/O)
PSEN 48 B program store enable (pull-up; active LOW)
ALE 49 B address latch enable (pull-up)
EA 50 B external ROM select (active LOW); enhanced hooks
V
SSD3
V
DDD1(pads)
51 S digital ground 3
52 S digital supply voltage 1 for the pads (5 V); pins 26 to 60
AD0 53 B P0.0 (data, address or I/O)
AD1 54 B P0.1 (data, address or I/O)
AD2 55 B P0.2 (data, address or I/O)
AD3 56 B P0.3 (data, address or I/O)
AD4 57 B P0.4 (data, address or I/O)
AD5 58 B P0.5 (data, address or I/O)
AD6 59 B P0.6 (data, address or I/O)
AD7 60 B P0.7 (data, address or I/O)
V
SSD4
61 S digital ground 4
DACCLK 62 T BCC-DAC clock output
V
SSD5
V
DDD2(pads)
63 S digital ground 5
64 S digital supply voltage 2 (level shifter) for the pads (5 V)
VALID 65 T data validity flag; C2 error flag; (3-state)
DAC 66 T serial audio data output to DAC (3-state)
DATA 67 T serial data output to block decoder (3-state)
WCLK 68 T word clock output (3-state)
SCLK 69 T serial bit clock output (3-state)
V
SSD6
70 S digital ground 6
SUBQW 71 O subcode output; Q to W subcode bits
MOTOS 72 T motor output, sign
MOTOV 73 T motor output, value
DSDEN 74 O DSD enable output (active LOW)
CLO 75 O clock output
V
SSD7
V
DDD3(pads)
76 S digital ground 7
77 S digital supply voltage 3 for the pads (5 V); pins 1 to 6 and 65 to 100
RA 78 T radial actuator output
FO 79 T focus actuator output
SL 80 T sledge control output
V
SSD8
81 S digital ground 8
1997 Jul 11 7
Page 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
(1)
DESCRIPTION
RP 82 OD radial polarity signal (open drain)
TL 83 OD track loss signal (open drain)
FOK 84 OD focus OK signal or decoder measurement signal (open drain)
CFLG 85 OD correction flag output (open drain)
C2FAIL 86 OD indication of correction failure (open drain)
V
SSD9
V
DDD2(core)
87 S digital ground 9
88 S digital supply voltage 2 for the core (3.3 V)
DOBM 89 T EBU bi-phase mark output (externally buffered) (3-state)
OTD 90 O off-track detect
FB 91 OD FIFO boundary, motor overflow (open drain)
SBSY 92 T subcode block sync (3-state)
SFSY 93 T subcode frame sync (3-state)
RCK 94 I subcode clock input
SUB 95 T P to W subcode bits (3-state)
DEEM 96 O deemphasis active output
KILL 97 OD kill output (open drain)
DEFI 98 I defect detector input
DEFO 99 O defect detector output
LDON 100 OD laser drive on output (open drain)
Note
1. Pin type abbreviations: O = Output, I = Input, S = power Supply, A = Analog function, OD = Open Drain,
B = Bidirectional, T = 3-state output. All supply pins must be connected directly to their respective external power
supply voltages.
1997 Jul 11 8
Page 9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
handbook, full pagewidth
DDD3(pads)
SSD7
V
V
75
CLO
74
DSDEN
MOTOV
73
MOTOS
72
71
SUBQW
V
70
SSD6
SCLK
69
68
WCLK
67
DATA
DAC
66
VALID
65
V
64
DDD2(pads)
V
63
SSD5
DACCLK
62
V
61
SSD4
AD7
60
59
AD6
AD5
58
AD4
57
AD3
56
AD2
55
AD1
54
AD0
53
V
52
DDD1(pads)
V
51
SSD3
TS1
TS2
TS3
RST
TPWM
TEN
MIDLAD
REFLCA
HFIN
REFHCA
I
ref
V
SSA1
V
DDA1
V
RH
D1
D2
D3
V
SSA2
V
DDA2
D4
S1
S2
I
refT
FTC
FTC
DDD2(core)
LDON
DEFO
DEFI
KILL
DEEM
SUB
RCK
SFSY
SBSYFBOTD
99989796959493929190898887868584838281
100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
H
25
L
SAA7348GP
DOBM
V
SSD9
V
C2FAIL
CFLG
FOKTLRP
SSD8
SLFORA
V
8079787776
26
XTALO
SELPLL
XTALI
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
RD
SSD1
V
XD0
R
XD0
T
INT0
INT1
XD1TXD1
R
WR
30
29
28
27
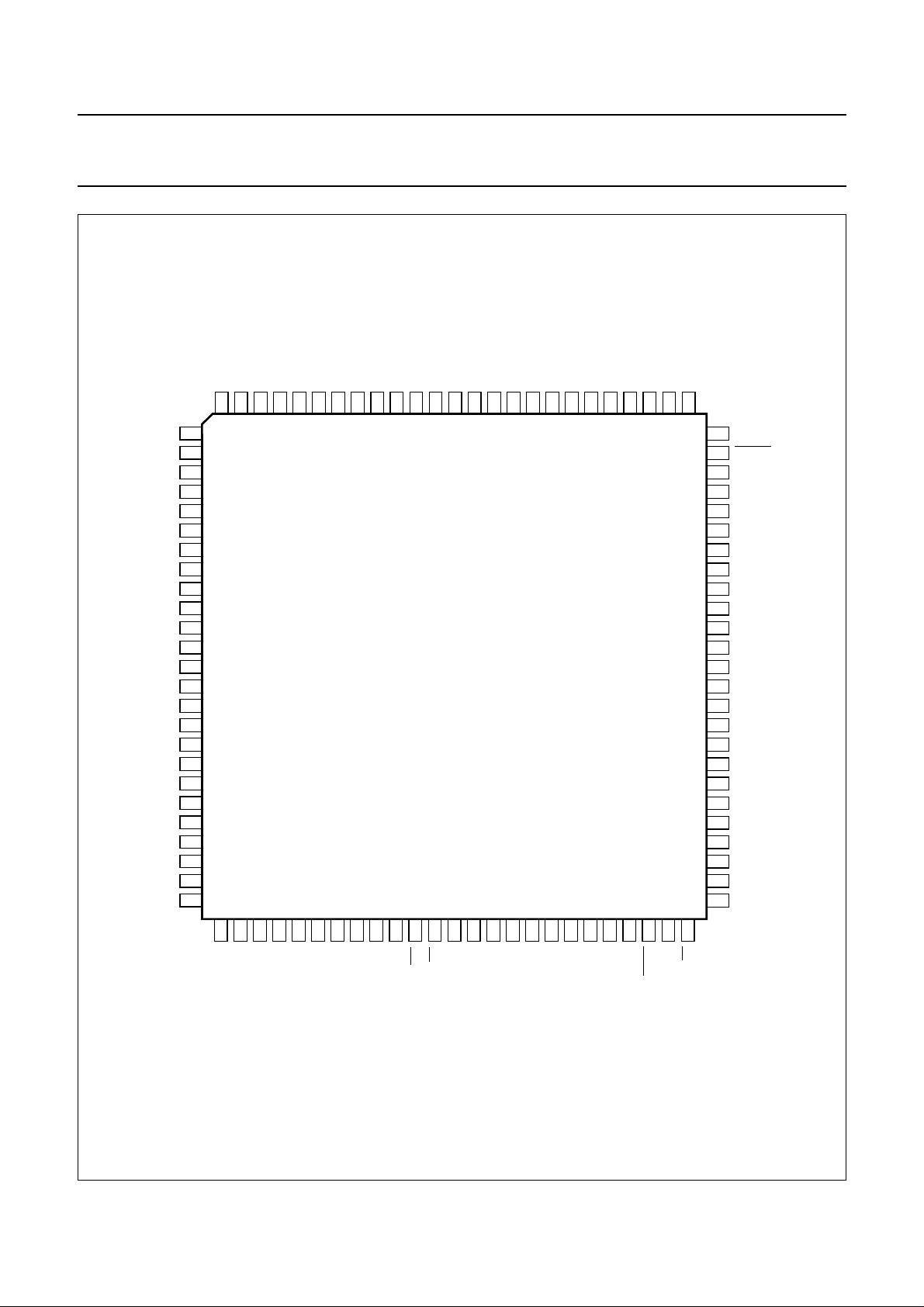
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
1997 Jul 11 9
SSD2
V
DDD1(core)
V
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
PSEN
ALE
50
EA
MGK497
Page 10
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The ACE combines the functionality of a DSICS
(OQ8868), a CD65 (LO9585) and an 80C51-based
microcontroller (83C654). In addition, a large part of the
glue logic has been integrated to help minimize the
number of external components required in CD-ROM
applications.
7.1 Analog front-end
The front-end circuit can be split into two parts:
1. The decoder input (HF front-end)
2. The servo input (LF front-end).
Each is powered by a separate power supply pin pair.
7.1.1 D
ECODER FRONT-END
The EFM signal is fed to the decoder through an ADC,
which is preceded by an AGC stage. In order to make full
use of the digital front-end resolution, the gain control
amplifier should deliver a constant 1.4 V p-p output signal.
The gain range of the AGC is 16 dB and is controlled in
steps of 1.0 dB. The gain of the variable gain amplifier is
controlled by an on-chip digital gain control block. This
block allows for both automatic and microcontroller gain
control.
The internal HF detector is sensitive to any disturbance on
the HF signal; a clean (good signal-to-noise ratio) EFM
signal is necessary since high frequency components can
disturb the HF detector. The input range of the HF
front-end varies from 2.3 V p-p down to 0.35 V p-p. If in the
lower range the signal level is between 25% and 75% of
the ADC range, the HF detector will signal NO HF (In this
range an ADC LSB translates into 5.5 mV, so half the
range equals 175 mV. If the total offset was equal to
6 LSBs, the signal range would be reduced by 2 × 33 mV.
In this case a signal of less than 109 mV would signal NO
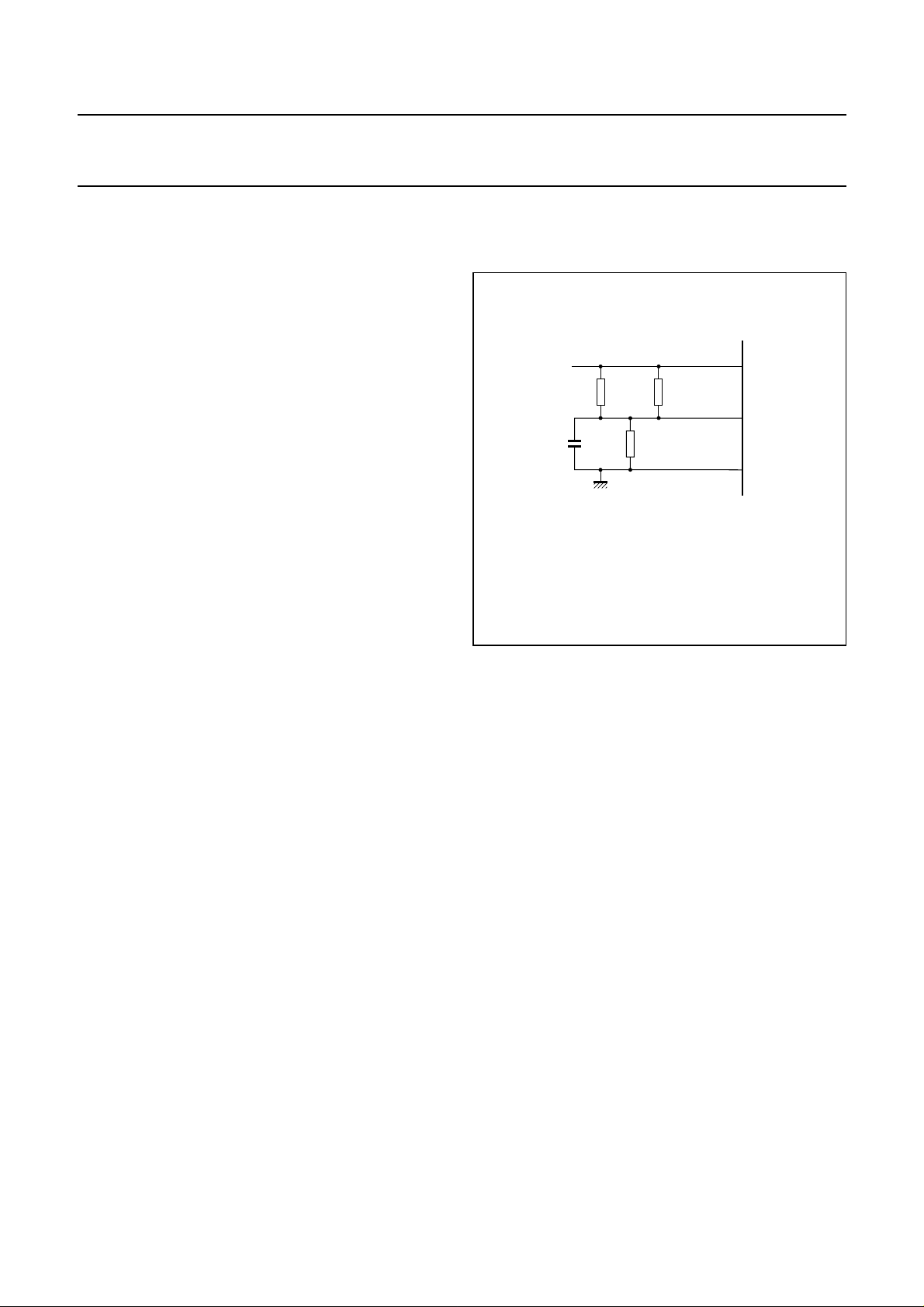
HF). To ensure the AGC offset is minimized when the AGC
gain is high, it is necessary to connect a resistor divider to
MIDLAD, as shown in Fig.3.
The SAA7348 contains an on-chip digital equalizer and
data slicer. The equalizer is adaptive; actual equalization
depends on the disc speed. The data slicer has a
microcontroller programmable bandwidth. A fully digital
internal PLL is used to regenerate the bit clock.
The bandwidth and equalization of the PLL can be
programmed by the microcontroller. An off-track input is
necessary for certain applications. If the off-track input flag
is HIGH, the SAA7348 will assume that the servo is
following on the wrong track, and will flag all incoming HF
data as incorrect. The off-track input is connected
internally to the servo section.
handbook, halfpage
+3.3 V
820 Ω 820 Ω
10 nF
820 Ω
V
DDA1
MIDLAD
V
SSA1
MGK500
13
7
12
Fig.3 Front-end offset compensation.
7.1.2 SERVO FRONT END
The servo front end contains six current-input ADCs (four
for focus and two for the radial signals). The ADCs do not
require external capacitors, unlike the OQ8868 or CD7
(SAA7370). For high performance radial access, a
comparator input is available for the FTC (Fast Track
Count) signal.
The dynamic range of the ADC input currents can be
adjusted over a range dependent on the value of an
external resistor connected to I
. The maximum input
refT
current for the central and satellite diodes, respectively, is
given below:
I
i(central) max()
I
i satellite()max()
V
is generated internally. The value of VRH is dependent
RH
2.4 106×
----------------------- R
1.2 106×
----------------------- R
µ A()=
IrefT
µ A()=
IrefT
upon the spread of internal capacitors and on the value of
the reference current generated by the external resistor on
I
. Typical input currents for a range of resistance values
refT
are given in Table 1.
1997 Jul 11 10
Page 11
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
Table 1 Typical input currents for a range of values of R
IrefT
TYPICAL CURRENT INPUT RANGE
R
IrefT
(kΩ)
D1, D2, D3, D4
(µA)
(1)
f
= 4.2336 MHz f
sys
S1, S2
(µA)
V
(V)
RH
D1, D2, D3, D4
(µA)
(1)
= 8.4672 MHz
sys
S1, S2
(µA)
V
(V)
RH
200 12.000 6.000 1.891 12.000 6.000 0.946
220 10.909 5.455 1.719 10.909 5.455 0.860
240 10.000 5.000 1.576 10.000 5.000 0.788
270 8.889 4.444 1.396 8.889 4.444 0.698
300 8.000 4.000 1.261 8.000 4.000 0.631
330 7.273 3.636 1.146 7.273 3.636 0.573
360 6.667 3.333 1.051 6.667 3.333 0.526
390 6.154 3.077 0.970 6.350 3.175 0.500
430 5.581 2.791 0.880 −−−
470 5.106 2.553 0.805 −−−
510 4.706 2.353 0.742 −−−
560 4.286 2.143 0.675 −−−
620 3.871 1.935 0.610 −−−
680 3.529 1.765 0.556 −−−
750 3.200 1.600 0.504 −−−
Note
1. f
is always equal to ; see Table 9.
sys
servo clock
------------------------------2
The preset latch command can be used to select this
method of V
automatic adjustment.
RH
Alternatively, the dynamic range of the input currents can
be made dependent on the ADC reference voltage, V
RH
In this case, the maximum input current for the central and
satellite diodes, respectively, is:
I
i(central) max()
I
i(satellite) max()
where f
sys
f
× 1.10× 106–×µA()=
sysVRH
f
× 0.55× 106–×µA()=
sysVRH
= 4.2336 MHz.
VRH can be set to any one of 32 pre-defined levels,
selectable under software control. VRH is initially set to
2.5 V using the preset latch command, then incremented
or decremented one level at a time by repeatedly
resending the same commend.
7.2 Decoder functions
The SAA7348 is a multi-speed decoding device with an
internal phase locked loop clock multiplier. Several
playback speeds can be selected, depending on the
crystal frequency and the internal clock settings;
see Table 2.
The following functions are performed in the decoder
.
block:
• Demodulation (includes sync protection circuit);
converts the 14-bit EFM data and subcode words into
8-bit symbols.
• Subcode data processing.
• Error correction; a t = 2, e = 4 type is used on both C1
(32 symbol) and C2 (28 symbol) frames. The error
corrector can correct up to 2 errors on the C1 level and
up to 4 errors on the C2 level. The error corrector also
contains a flag processor. Flags are assigned to
symbols when the error corrector cannot ascertain if the
symbols are definitely good. C1 generates output flags
that are used by C2. The C2 output flags are used by the
interpolator to conceal uncorrectable errors for audio
output; they are also output via the EBU signal (DOBM)
and the VALID output with I
2
S for CD-ROM applications.
1997 Jul 11 11
Page 12
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
• Motor control; the spindle motor is controlled by a fully
integrated digital servo. Address information from the
internal 8 frame FIFO and disc speed information are
used to calculate the motor control output signals.
Several output modes are supported:
– Pulse density, 2-line (true complement output),
1 × n MHz sample frequency
– PWM-output, 2-line, 22.05 × n kHz modulation
frequency
– CDV motor mode
– Brushless motor control mode.
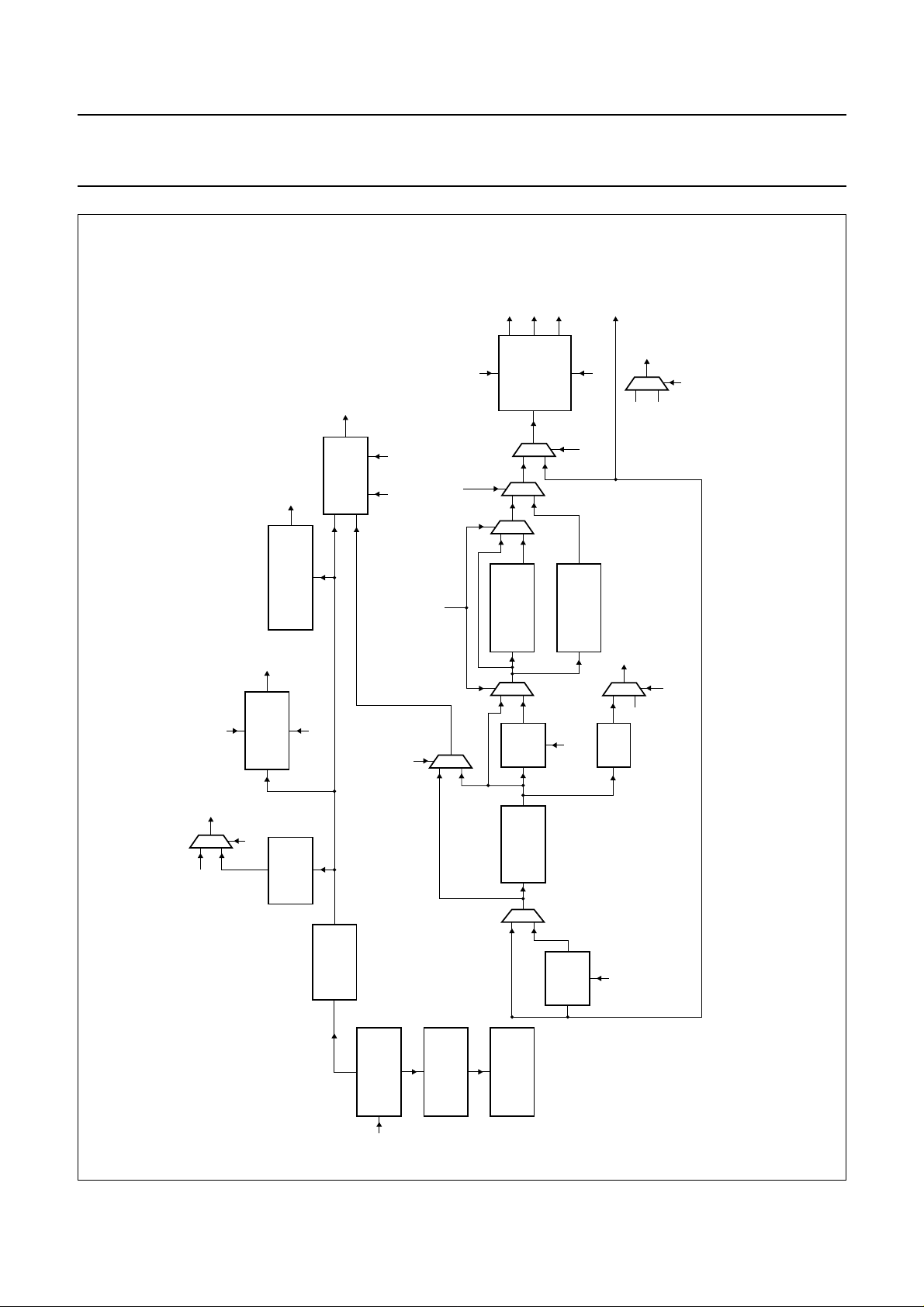
A simplified illustration of the data flow through the
decoder is shown in Fig.4.
Table 2 Decoder playback speeds; note 1
INTERNAL FREQUENCY (MHz)
REGISTER B REGISTER E
67.7376
(2)
50.8032
(2)
33.8688
(2)(3)
16.9344
00XX 0XXX n = 2 n = 1.5 n = 1 −
00XX 1XXX n = 8 n = 6 n = 4 n = 2
01XX 0XXX −−−n=1
01XX 1XXX −−−n=4
10XX 0XXX n = 4 n = 3 n = 2 −
10XX 1XXX n= 16 n = 12 n = 8 −
11XX 0XXX −−−n=2
Notes
1. X = don’t care.
2. With an 8.4672 MHz crystal, and only if SELPLL = 1 (i.e. clock multiplier enabled; see also Section 8.1.1).
3. Can use external 33.8688 MHz crystal.
4. Can use external 16.9344 MHz crystal.
(4)
1997 Jul 11 12
Page 13
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
SCLK
WCLK
DAC
DATA
VALID
DEEM
handbook, full pagewidth
RCK
SUBQW
INTERFACE
MICROCONTROLLER
SBSY
SFSY
SUB
INTERFACE
CD GRAPHICS
reg F
DOBM
EBU
INTERFACE
registers 3, 7 and E
reg A reg E
0 : no pre-emphasis detected
OR reg D = 0xxx
1 : pre-emphasis detected
AND reg D = 1xxx
mode)
s
(1f
1 : reg 3 = xx10
0
1
0 : reg A = xx0x
1 : reg A = xx1x
S-BUS
2
I
INTERFACE
1
0
0
1
1
0
PHASE
COMPENSATION
1
0
FILTER
DIGITAL
reg 3
0 : reg 3 = 101x
(CD-ROM modes)
FILTER
DE-EMPHASIS
1
reg 3
KILL
1
0
1
0
1 : pre-emphasis detected AND reg D = 0xxx
OR reg D = 11xx
MGK499
KILL
0
0
0 : reg 0 = x000/reg 3 = 101x/reg 7 = 00xx/reg E = x0xx
1
0
0 : reg D = xx0x
SUBCODE
INTERFACE
0 : reg D = xx10
1 : reg D = xx11
SUBCODE
PROCESSOR
FIFO
DEMODULATOR
DIGITAL PLL AND
EFM
1997 Jul 11 13
FADE/MUTE/
INTERPOLATE
1
0
ERROR
CORRECTOR
1 : reg 7 = 11xx or 00xx
MONO
reg 7
FUNCTION
Fig.4 SAA7348 decoder function: simplified data flow.
Page 14
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
7.3 Servo functions
7.3.1 S
IGNAL CONDITIONING
The digital codes retrieved from the ADCs are applied to
logic circuitry to obtain various control signals. The signals
from the central aperture diodes are processed to obtain a
normalised focus error signal:
FE
n
D1 D2–
---------------------D1 D2+
D3 D4–
–=
---------------------D3 D4+
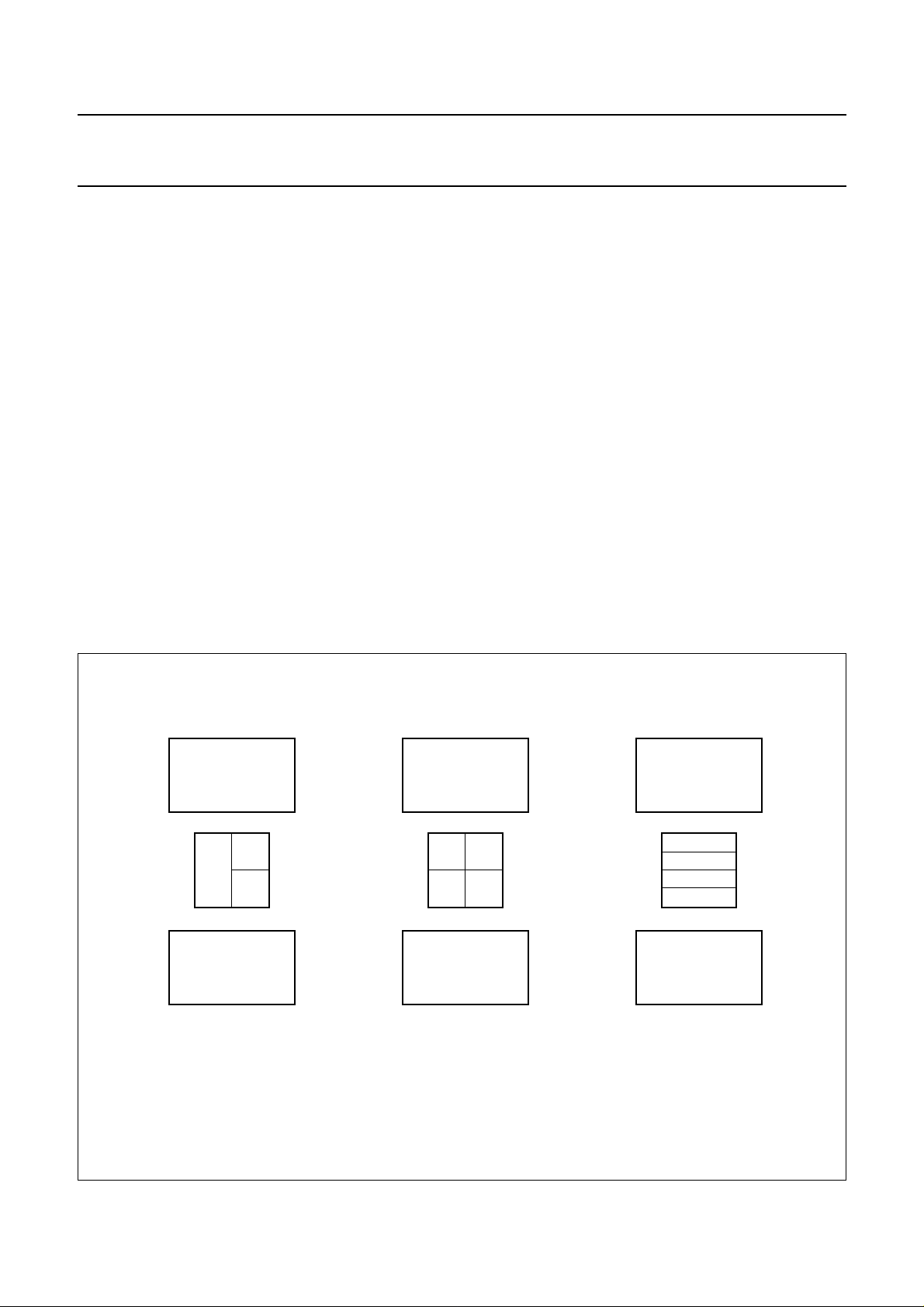
where the detector set-up illustrated in Fig.5 is assumed.
For single Foucault focusing, signal conditioning can be
switched under software control such that:
D1 D2–
FE
The error signal, FE
×=
2
n
---------------------D1 D2+
, is further processed by a
n
Proportional Integral and Differential (PID) filter section.
A Focus OK (FOK) flag is generated by means of the
central aperture signal and an adjustable reference level.
This signal is used to provide extra protection for
Track-Loss (TL) generation, drop out detection and the
focus start-up procedure.
The radial or tracking error signal is generated by the
satellite detector signals R1 and R2. The radial error signal
can be formulated as follows:
RE
= (R1 − R2) × re_gain + (R1 − R2) × re_offset
s
where the index ‘s’ indicates the automatic scaling
operation performed on the radial error signal. This scaling
is necessary to avoid non-optimal dynamic range usage in
the digital representation and to reduce the radial
bandwidth spread. Furthermore, the radial error signal will
be free of offset during disc start-up.
The four signals from the central aperture detectors,
together with the satellite detector signals, generate a
track position signal (TPI), which can be formulated as
follows:
TPI = sign [(D1 + D2 + D3 + D4) − (R1 + R2) × sum_gain]
where the weighting factor sum_gain is generated
internally by the SAA7348 during initialization.
handbook, full pagewidth
SATELLITE
DIODE R1
D1
D3
D2
SATELLITE
DIODE R2
single Foucault astigmatic focus double Foucault
SATELLITE
DIODE R1
D1
D2
D3
D4
SATELLITE
DIODE R2
SATELLITE
DIODE R1
D1
D2
D3
D4
SATELLITE
DIODE R2
Fig.5 Detector arrangement.
MBG422
1997 Jul 11 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
7.3.2 Focus control
The SAA7348 performs the following focus servo function:
• Focus start-up
• Focus position control loop
• Drop-out detection
• Focus loss detection and fast restart
• Focus loop gain switching
• Focus automatic gain control loop.
7.3.3 R
ADIAL CONTROL
The SAA7348 performs the following radial servo
functions:
• Level initialization
• Radial position control loop
• Sledge control
• Tracking control
• Access with or without track loss information
• Radial automatic gain control loop.
7.3.4 O
FF-TRACK COUNTING
The track position signal (TPI) is a flag used to indicate
whether the radial spot is positioned on the track with a
margin of ±0.25 of the track pitch. One of the following
three counting states is selected:
• Protected state
• Slow counting state
• Fast counting state.
7.3.5 O
FF-TRACK DETECTION
The Off-Track Detection (OTD) signal flags off-track
conditions; the polarity of this signal is programmable.
7.3.6 S
HOCK DETECTION
A shock detector can be switched on during normal track
following. Within an adjustable frequency range, it detects
whether disturbances in the radial spot relative to the track
exceed a programmable level. Every time the Radial
tracking Error (RE) exceeds this level, the radial control
bandwidth is switched to twice its original bandwidth and
the loop gain is increased by a factor of 4.
switched off, applied only to focus control, or applied to
both focus and radial controls under software control.
The actions of the circuit can be monitored on the DEFO
pin (active HIGH).
An external defect detector can be added by removing the
connection between DEFO and DEFI (normal operation)
and inserting the necessary circuitry.
7.3.8 D
RIVER INTERFACE
The control signals (pins RA, FO and SL) for the
mechanism actuators are pulse density modulated.
The modulating frequency can be set to either
servo clock
----------------------------- 8
servo clock
or MHz. An analog representation
----------------------------- 4
of the output signals can be generated by connecting a first
order low-pass filter to the outputs.
During reset (i.e. RST pin held HIGH) the RA, FO and SL
pins are high impedance.
7.3.9 L
ASER INTERFACE
The LDON pin (open-drain output) is used to turn the laser
on and off. When the laser is on, the output is high
impedance. The action of the LDON pin is controlled by the
xtra_preset parameter; the pin is automatically driven if the
focus control loop is active.
7.4 Subcode interface
There are two subcode interfaces:
• One which conforms to
“EIAJ CP-2401”
(using SBSY,
SFSY, RCK and SUB) and can be configured as either
a 3- or 4-wire interface. The interface formats are
illustrated in Fig.6.
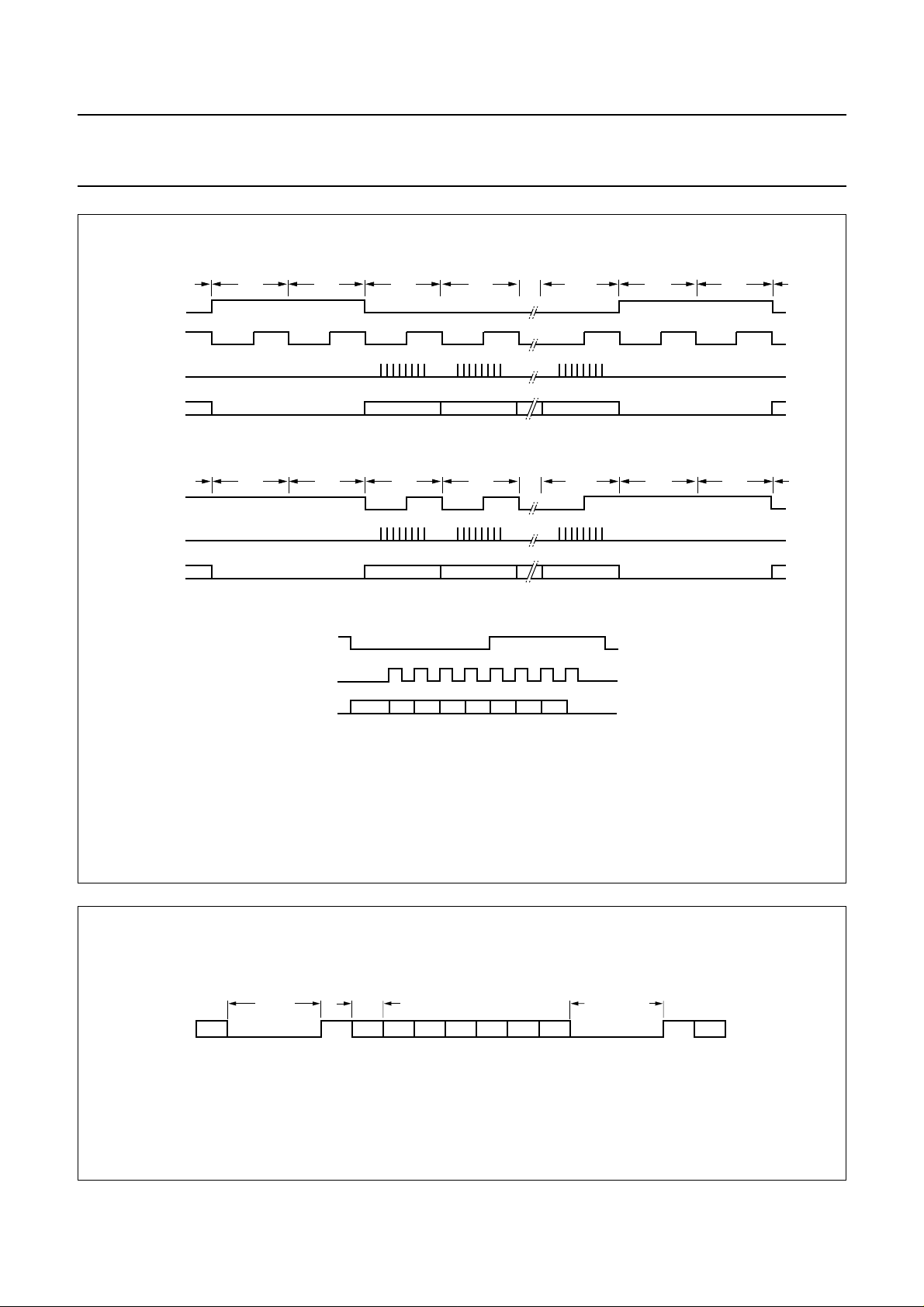
• An RS232 like format on SUBQW as illustrated in Fig.7.
The subcode sync word is formed by a pause of µs
200
--------- n
minimum. Each subcode byte starts with a 1 followed by
7 bits (Q to W). The gap between bytes can vary
between and µs. Note that SUBQW is not
11.3
----------n
90
-----n
valid in lock-to-disc mode (includes QLLV).
The subcode data is also available at the EBU output
(DOBM).
7.3.7 D
EFECT DETECTION
A defect detection circuit is incorporated into the
SAA7348. If a defect is detected, the circuit can hold all
radial and focus controls. The defect detector can be
1997 Jul 11 15
Page 16
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
handbook, full pagewidth
SBSY
SFSY
RCK
SUB
SFSY
RCK
SUB
SF0 SF1
SF0 SF1 SF2 SF3 SF97 SF0 SF1
SFSY
RCK
SUB
SF2 SF3 SF97 SF0 SF1
P-W P-W P-W
EIAJ 4-wire subcode interface
P-W P-W P-W
EIAJ 3-wire subcode interface
PQRSTUVW
MBG410
Fig.6 EIAJ subcode (CD graphics) interface format.
11.3/n
µs
(1) n = disc speed.
200/n µs
min
W96 1 Q1 R1 S1 T U1 V W1 1 Q2
Fig.7 Subcode format and timing on SUBQW pin.
1997 Jul 11 16
11.3/n µs min
90/n µs max
MGK501
Page 17
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
7.5 Digital output
The AES/EBU signal on pin DOBM is in accordance with
the format defined in
“IEC 958”
. This signal is only
available in the decoder’s CLV modes if audio features are
enabled (not in QCLV modes). Three different modes can
be selected:
• DOBM pin held LOW
• Data taken before concealment, mute and fade (must
• Data taken after concealment, mute and fade (can only
be used for audio modes).
7.5.1 F
ORMAT
The digital audio output consists of 32-bit words
(‘subframes’) transmitted in bi-phasemark code (two
transitions for a logic 1 and one transition for a logic 0).
Words are transmitted in blocks of 384.
always be used for CD-ROM modes)
Table 3 32-bit digital audio output format
FUNCTION BITS DESCRIPTION
Sync 0 to 3 note 1
Auxiliary 4 to 7 not used; normally zero
Error flags 4 CFLG error and interpolation flags when selected by register A
Audio sample
Validity flag
User data
(3)
(4)
Channel status
(2)
(5)
8 to 27 first 4 bits not used (always zero); two’s complement; LSB = bit 12, MSB = bit 27
28 valid = logic 0
29 used for subcode data (Q to W)
30 control bits and category code
Parity bit 31 even parity for bits 4 to 30
Notes
1. The sync word is formed in violation of the bi-phase rule and, therefore, does not contain any data. Its length is
equivalent to 4 data bits. The 3 different sync patterns indicate the following situations:
a) Sync B: word contains left sample (start of a block, 384 words).
b) Sync M: word contains left sample (no block start).
c) Sync W: word contains right sample.
2. Left and right samples are transmitted alternately.
3. Audio samples are flagged (bit 28 = 1) if an error was detected but could not be corrected. This flag remains the same
even if data is taken after concealment.
4. Subcode bits Q to W from the subcode section are transmitted via the user data bit. This data is asynchronous with
the block rate.
5. The channel status bit is the same for both left and right words. Therefore, a block of 384 words contains 192 channel
status bits. The category code is always CD. The bit assignment is shown in Table 4.
1997 Jul 11 17
Page 18
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
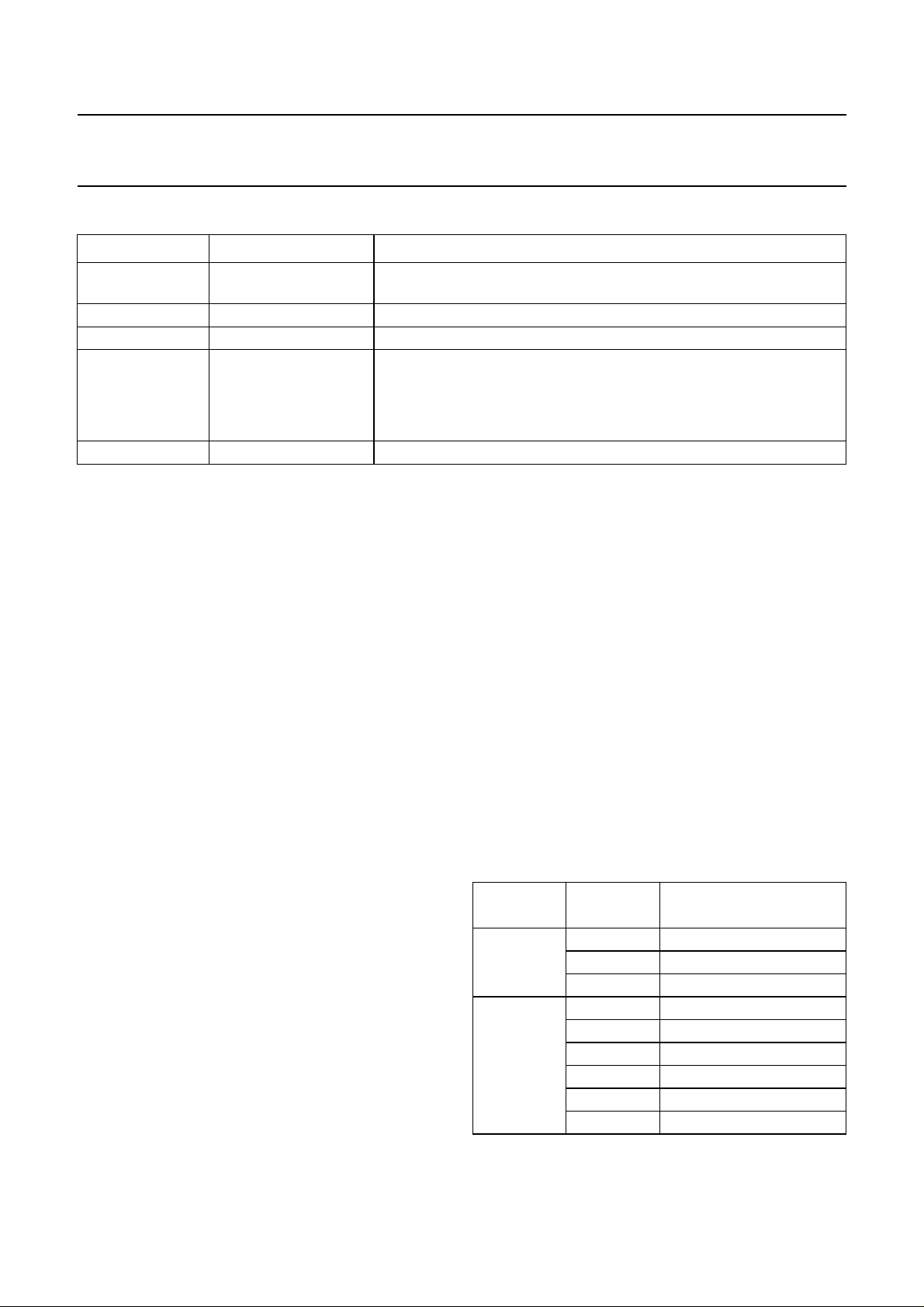
Table 4 Channel status bit assignment
FUNCTION BIT DESCRIPTION
Control 0 to 3 copy of CRC checked Q-channel control bits 0 to 3; bit 2 is logic 1 when
copy permitted; bit 3 is logic 1 when recording has pre-emphasis
Reserved mode 4 to 7 always zero
Category code 8 to 15 CD: bit 8 = logic 1, all other bits = logic 0
Clock accuracy 28 and 29 set by register A:
10 = class 1 crystal (<50 ppm)
00 = class 2 crystal (<1000 ppm)
01 = class 3 crystal (>1000 ppm)
Remaining 16 to 27 and 30 to 191 always zero
7.6 S2B interface
This interface is in accordance with the
Description”
. It's a serial interface with a high level
“S2B Interface
command set for controlling a CD-ROM engine.
7.7 Audio support
Audio support consists of several parts:
• Serial data interface.
• Deemphasis control (DEEM). This signal is HIGH if the
subcode info of a track defines it to be recorded with
deemphasis.
• Kill control (KILL). This signal tests for digital silence in
the right and left channel before the digital filter.
The output is switched active LOW if silence has been
detected for at least 250 ms, if mute is active, or in
CD-ROM modes.
• Output clock for BCC-DAC applications (DACCLK).
• Oversampled output. The SAA7348 contains a
2 to 4 times oversampling IIR (Infinite
Impulse-Response) filter, and a selectable deemphasis
filter (if the de-emphasis signal is selected to come out
of DEEM then the filter is bypassed; see Table 31).
• Concealment, mute, attenuation and fade. In audio
modes a 1-sample linear interpolator becomes active if
a single sample is flagged as erroneous; left and right
channels have independent interpolators. A digital level
converter performs the following functions:
– soft mute (signal reduced to 0 in a maximum of
128 steps)
– full-scale (signal ramped back to 0 dB level)
– attenuation (signal scaled by −12 dB)
– fade (activates a 128 stage counter which allows the
signal to be scaled up or down in 0.07 dB steps)
– peak detector (measures highest audio level;
absolute level for left and right channels; the 8 MSBs
of each are output in the Q-channel data).
• Mono output selection. Either channel can be selected
to be output over both left and right channels.
7.7.1 S
ERIAL AUDIO DATA INTERFACE
The serial data interface can be switched between two
modes: Philips I2S and the EIAJ format.
In each case, the serial data is transferred through a 3-wire
interface. The I2S signal contains three components:
WCLK (word select), SCLK (serial clock) and DAC (serial
data). The polarity of WCLK and of the data can be
inverted.
The oversampling frequency and format are selected as
shown in Table 5. The serial data output is separate from
the CD-ROM output. In CD-ROM mode the DAC serial
data output pin will be muted.
Table 5 Oversampling frequency select
MODE
I2S18 4f
EIAJ 18 4f
NUMBER
OF BITS
SAMPLE FREQUENCY
18 2f
16 f
18 2f
18 f
16 4f
16 2f
16 f
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
1997 Jul 11 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
7.8 CD-ROM support
The principle difference between the ACE and its
predecessors with regard to CD-ROM support is the
provision of a separate serial data pin, which removes the
need for external components. The format can be I2S or
EIAJ.
7.8.1 S
The serial data signal contains three components: WCLK
(word select), SCLK (serial clock) and DATA (serial data).
The polarity of WCLK and of the data can be inverted.
WCLK and SCLK are common with the audio serial data
output. The VALID signal is used to flag errors in either the
LSB or MSB of the 16-bit data word.
7.9 Reset
The RST pin on the SAA7348 is an active HIGH Schmitt
trigger. For a valid reset, the signal should be HIGH for a
period of 12 XTALI clock cycles, during which time the
power supply must be within specification on all power
ERIAL CD-ROM DATA INTERFACE
supply pins. To ensure that the SAA7348 resets fully it is
necessary to do one of the following:
• Connect SELPLL to DSDEN (rather than VDD). This
allows the internal clock multiplier to start immediately
after reset. Note that the internal clocks are not
guaranteed to operate at the correct frequencies for the
first 200 µs after reset. Note also that the operating
speed of the microcontroller is reduced in Idle mode
(and that baud rates change with the processor clock).
• Connect SELPLL to an inverted reset signal.
The internal clock multiplier starts after reset, but during
Idle mode the microcontroller speed is normal.
7.10 External ROM support
Since the ACE incorporates an 80C51 core it can, like any
microcontroller, run a program from external ROM.
EA pin should be tied to VSS in this case. For security
The
reasons, this pin is only sampled during reset, so a
program cannot be run partly from external ROM. Signal
relationships for external program execution are shown in
Fig.8. Timing specification can be found in Table 6.
1997 Jul 11 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
Table 6 Timing specifications for external program memory search
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
t
LHLL
t
AVLL
t
LLAX
t
LLPL
t
PLPH
t
PLIV
t
PXIX
t
PXIZ
t
AVIV
t
PLAZ
t
RLRH
t
WLWH
t
RLDV
t
RHDX
t
RHDZ
t
LLDV
t
AVDV
t
LLWL
t
AVWL
t
QVWX
t
WHQX
t
RLAZ
t
WHLH
ALE pulse width 60 − ns
address valid to ALE LOW 15 − ns
address hold after ALE LOW 21 − ns
ALE LOW to PSEN LOW 25 − ns
PSEN pulse width 80 − ns
PSEN LOW to valid instruction in − 65 ns
input instruction hold after PSEN 0 − ns
input instruction float after PSEN − 30 ns
address to valid instruction in − 130 ns
PSEN LOW to address float − 6ns
read pulse width 170 − ns
write pulse width 170 − ns
RD LOW to valid data in − 135 ns
data hold after RD − 50 ns
data float after RD 0 − ns
ALE LOW to valid data in − 235 ns
address to valid data in − 260 ns
ALE LOW to RD or WR LOW 80 115 ns
address valid to RD or WR LOW 115 − ns
data valid to WR transition 20 − ns
data hold to WR 20 − ns
RD LOW to address float − 0ns
RD or WR HIGH to ALE HIGH 20 40 ns
In addition to external program memory, external RAM and I/O can be accessed. Timing relationships for an external
data read are shown in Fig.9, and for an external data write in Fig.10.
1997 Jul 11 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
handbook, full pagewidth
t
LHLL
ALE
PSEN
LA0 to LA7
A8 to A15
t
AVLLtLLPL
t
LLAX
t
AVIV
t
PLAZ
t
PLIV
t
PLPH
t
PXIX
Fig.8 Timing for an external program memory fetch.
t
PXIZ
MGK502
handbook, full pagewidth
ALE
PSEN
RD
LA0 to LA7
A8 to A15
t
AVLL
t
t
AVWL
t
LLWL
LLAX
t
AVDV
t
LLDV
Fig.9 Timing for an external data read.
1997 Jul 11 21
t
RLRH
t
WHLH
t
RHDZ
MGK503
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
handbook, full pagewidth
ALE
PSEN
WR
LA0 to LA7
A0 to A15
t
WHLH
t
AVLL
t
t
AVWL
t
LLWL
LLAX
t
WLWH
t
QVWX
t
WHQX
Fig.10 Timing for an external data write.
MGK504
1997 Jul 11 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8 MICROCONTROLLER INTERFACE
This section describes the microcontroller application
registers, the memory map, the decoder registers and the
servo commands.
8.1 Microcontroller applications registers
8.1.1 CLK GENERATE REGISTER (CLKgen)
The CLK generate register is used to select clock multiplier
PLL frequencies and dividers and to switch the servo clock
between single and double frequency. The register is byte
addressable; R/W.
The on-chip clock multiplier (programmable: 4×, 6× or 8×)
allows an external 8.4672 MHz crystal to be used. This
Table 7 CLK generate register (address 0X9EH)
765 4 3 2 1 0
CLKgen.7 CLKgen.6 CLKgen.5 clock_servohi clock_seldiv2 clock_seldiv1 clock_selpll2 clock_selpll1
Table 8 Description of CLKgen bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 CLKgen.7 not used
6 CLKgen.6
5 CLKgen.5
4 clock_servohi selects single or 2 × servo clock
3 clock_seldiv2 these bits select the clock divider for the 80C51 core and servo; see Table 9
2 clock_seldiv1
1 clock_selpll2 these bits select the clock multiplier frequency; see Table 9
0 clock_selpll1
generates a single internal master clock from which all
other clock signals are derived.
Note that both the microcontroller and the servo are
designed for a 50% duty factor input clock.
For a 16× decoder speed, the internal master clock must
be 67.7376 MHz (i.e. clock multiplier set to 8×).
The 16.9344 MHz signal can be generated by setting the
clock divider to 4, resulting in a standard 50% duty factor
clock. For a 12× decoder speed, the internal master clock
must be 50.8032 MHz (i.e. clock multiplier set to 6×).
A divide factor of 3 will generate the 16.9344 MHz signal,
resulting in a 66% duty factor clock.
The clock divider values set by means of the CLKgen
register are shown in Table 9.
1997 Jul 11 23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
Table 9 Divider selection
MASTER
CLOCK
(MHz)
33.8688 16.9344
50.8032 16.9344
67.7376 16.9344 1
33.8688 16.9344 1
µP
CLOCK
(MHz)
REGISTER CLKgen BIT SERVO
CLOCK
01234
0000
0101
(1)
(1)
(1)
0
(1)
1
10
10
0 8.4672 4 100
1 16.9344 2 200
0 8.4672 6 100
1 16.9344 3 200
0 8.4672 8 100
1 16.9344 4 200
0 8.4672 4 100
1 16.9344 2 200
(MHz)
Note
1. The internal clock multiplier PLL operates at the same frequency for both these options.
DIVIDE
FACTOR
OVER-SPEED
SERVO
(%)
1997 Jul 11 24
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.2 PORT SERVO REGISTER (PSR)
The Port Servo Register is the internal bus used to communicate with the servo. The register is bit addressable; R/W.
The operation of the handshake bits used for serial communications with the servo is outlined in Table 12.
Table 10 Port servo register (address 0XD8H to 0XDFH)
765 4 3 2 1 0
Tray_en Tray_pwm Srv_rdy Srv_dacc Srv_sild Srv_sicl Srv_sida Srv_intreqn
Table 11 Description of PSR bits
BIT SYMBOL ADDRESS DESCRIPTION
7 Tray_en 0XDFH signal to enable tray driver
6 Tray_pwm 0XDEH PWM signal to tray driver
5 Srv_rdy 0XDDH RDY; see Table 12
4 Srv_dacc 0XDCH DAC; see Table 12
3 Srv_sild 0XDBH SILD
2 Srv_sicl 0XDAH SICL
1 Srv_sida 0XD9H SIDA
0 Srv_intreqn 0XD8H INTREQN
Table 12 Servo serial communication handshake signals
DAC RDY DESCRIPTION
0 0 transmit register full; the microcontroller can read a byte or send a new command
0 1 idle state, transmit register empty; the microcontroller can transmit a parameter relating
to the new command
1 0 received one byte, waiting for EOT
1 1 receive register full
1997 Jul 11 25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.3 SERVO CONTROL REGISTER (SCR)
The Servo Control Register is used for reading and writing internal control signals. The register is byte addressable; R/W.
Table 13 Servo control register (address 0XD9H)
76543210
Srv_frc_flock Srv_frc_lock Srv_otd Srv_da Srv_cl Srv_rab Srv_startup Serv_halt
Table 14 Description of SCR bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 Srv_frc_flock force_flock: coarse PLL lock indicator control; a HIGH indicates ±6% of disc speed
6 Srv_frc_lock force_lock; a HIGH indicates frequency lock
5 Srv_otd OTD controller: off-track signal generated by the controller input for the OTD
multiplexer; a HIGH indicates laser is off track
4 Srv_da DA (used only with direct decoder communication)
3 Srv_cl CL (used only with direct decoder communication)
2 Srv_rab RAB (used only with direct decoder communication)
1 Srv_startup 16 kHz pulse (start new servo processor execution sequence); pulse is latched; latch is
cleared by a write operation
0 Serv_halt servo halt; halts servo processor execution
1997 Jul 11 26
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.4 SERVO STATUS REGISTER (STR)
The Servo Status Register holds high level status information on the servo system. The information is latched into a
register and cleared whenever the register is read. This information could be a trigger to initiate a recovery. The register
is byte addressable; read only.
Table 15 Servo status register (address 0XE9H)
7654 3210
Srv_tl1 Srv_tl0 Srv_shock Srv_hf_present Srv_FIFO_ov Srv_fock Srv_otd_inp Srv_subc
Table 16 Description of STR bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 Srv_tl1 internal servo signal; see Table 17
6 Srv_tl0 internal servo signal; see Table 17
5 Srv_shock shock: decoder status signal; Motstart2 + PLL_phase_lock + Motor-ov + FOCOK +
OTD
4 Srv_hf_present HF_present: internal decoder signal; indicates if laser spot is in a recorded area
3 Srv_FIFO_ov FIFO_OV: decoder status signal; FIFO overflow occurred
2 Srv_fock FOCOK: servo output signal; focus OK/
1 Srv_otd_inp OTD: servo output signal; laser spot on/off track
0 Srv_subc subcode found: decoder status signal; subcode present in servo buffer
OK
The Srv_tl0 and Srv_tl1 signals can be used to determine in which direction the servo is counting during a jump
execution.
Table 17 Servo jump modes
Srv_tl1 Srv_tl0 DESCRIPTION
0 0 protected mode
0 1 fast jump_1
1 0 slow jump
1 1 fast jump_2
1997 Jul 11 27
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.5 MOTOR OUTPUT QCLV REGISTER (MOQ; address 0XF2H and 0XF3H)
The Motor Output QCLV register holds the sixteen bits of the filtered (−3 dB, 300 Hz) motor error signal. This signal is
updated at a frequency of 16.537 kHz. Address 0XF3H holds the eight most significant bits, address 0XF2H the eight
least significant bits. Refreshing rule: if the low byte is read, the high byte is locked to avoid mixing up two successive
samples. If the high byte has been read, the low byte will be refreshed. The register is byte addressable; read only.
8.1.6 P3 R
EGISTER
The P3 register is used in the same way as in the standard 80C51. It contains a second UART, however, whose input
and output pins are R
XD1
and T
respectively. Direction control is by DDROUT3 (SFR address 0XFD; see Table 25
XD1
and Section 8.1.12). The register is bit addressable; R/W.
Table 18 P3 register (address 0XB0H to 0XB7H)
76543210
WRN RDN TXD1 RXD1 INT1 INT0 TXD0 RXD0
Table 19 Description of P3 register bits
BIT SYMBOL ADDRESS DESCRIPTION
7 WRN 0XB7H WRN
6 RDN 0XB6H WDN
5 TXD1 0XB5H TXD1: serial buffer 1; transmit
4 RXD1 0XB4H RXD1: serial buffer 1; receive
3 INT1 0XB3H INT1: external Interrupt 1
2 INT0 0XB2H INT0: external Interrupt 0
1 TXD0 0XB1H TXD0: serial buffer 0; transmit
0 RXD0 0XB0H RXD0: serial buffer 0; receive
1997 Jul 11 28
Page 29

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.7 DECODER STATUS REGISTER (DSR)
The decoder status register provides decoder status information. The register is byte addressable; read only.
Table 20 Decoder status register (address 0XEBH)
765 4 3 2 1 0
Decoder_stat.7 TX_full Dec_motov Dec_pll_flock Dec_pll_lock Dec_motstop Dec_motstart_2 Dec_motstart_1
Table 21 Description of DSR bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 Decoder_stat.7 −
6 TX_full communication buffer to decoder is full
5 Dec_motov motor-overflow: decoder status signal; motor output saturates
4 Dec_pll_flock PLL_flock: decoder internal signal; can be forced by µP
3 Dec_pll_lock PLL_lock: decoder internal signal; can be forced by µP
2 Dec_motstop motstop: decoder status signal; speed <12%
1 Dec_motstart_2 motstart 2: decoder status signal; speed >50%
0 Dec_motstart_1 motstart 1: decoder status signal; speed >75%
1997 Jul 11 29
Page 30

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.8 MOTOR SETPOINT REGISTER (MSR; address
0XF9H)
The motor setpoint register is used to set the speed of the
motor in Quasi CLV mode. QCLV motor control is switched
off by making the setpoint equal 00100000. See Table 22
Table 22 Speed measurements
SFR
SETPOINT
00100000 1.8
00100010 1.9
00100011 2.0
00100101 2.1
00100111 2.2
00101000 2.3
00101010 2.4
00101100 2.5
00101101 2.6
00101111 2.7
00110000 2.8
00110010 2.9
00110011 3.0
00110101 3.1
00110111 3.2
00111000 3.3
00101010 3.4
00111100 3.5
00111110 3.6
00111111 3.7
01000000 3.8
01000010 3.9
01000011 4.0
01000101 4.1
01000111 4.2
01001001 4.3
01001011 4.4
01001100 4.5
01001110 4.6
01001111 4.7
01010001 4.8
01010010 4.9
MEASURED
SPEED
for setpoint/speed values. Note that these are measured
values. They were measured using the motor control
bread board. This bread board was hooked onto a ROM
65000 loader 12.66 application. The filter in the config
control (Cnf_filter) was switched off. A motor gain of 5 was
used. The register is byte addressable; R/W.
SFR
SETPOINT
01010100 5.0
01010110 5.1
01010111 5.2
01011001 5.3
01011011 5.4
01011100 5.5
01011110 5.6
01011111 5.7
01100001 5.8
01100010 5.9
01100100 6.0
01100110 6.1
01100111 6.2
01101001 6.3
01101011 6.4
01101100 6.5
01101110 6.6
01101111 6.7
01110001 6.8
01110010 6.9
01110100 7.0
01110110 7.1
01110111 7.2
01111001 7.3
01111011 7.4
01111100 7.5
01111110 7.6
10000000 7.7
01111111 7.7
10000001 7.8
10000011 7.9
10000100 8.0
MEASURED
SPEED
1997 Jul 11 30
Page 31

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.9 MOTOR GAIN QCLV REGISTER (address 0XFAH)
The motor_gain_QCLV register is used to set the gain of
the motor control signal. It can be used in quasi as well as
in CLV mode. Only the 6 least significant bits are used (see
Table 23 Loop gain
GAIN
SFR SETTING
FILTER ON FILTER OFF
00000000 1 0.125
00111111 2 0.25
00111110 3 0.375
00111101 4 0.5
00111100 5 0.625
00111011 6 0.75
00111010 7 0.875
00111001 8 1
00111000 9 1.125
00110111 10 1.25
00110110 11 1.375
00110101 12 1.5
00110100 13 1.625
00110011 14 1.75
00110010 15 1.875
00110001 16 2
00110000 17 2.125
00101111 18 2.25
00101110 19 2.375
00101101 20 2.5
00101100 21 2.625
00101011 22 2.75
00101010 23 2.875
00101001 24 3
00101000 25 3.125
00100111 26 3.25
00100110 27 3.375
00100101 28 3.5
00100100 29 3.625
00100011 30 3.75
00100010 31 3.875
00100001 32 4
Table 23 for values). The actual gain depends on the filter
in the config register (Cnf_filter). If the filtering is switched
on, the gain is reduced by a factor of 8. The register is byte
addressable; R/W.
GAIN
SFR SETTING
FILTER ON FILTER OFF
00100000 33 4.125
00011111 34 4.25
00011110 35 4.375
00011101 36 4.5
00011100 37 4.625
00011011 38 4.75
00011010 39 4.875
00011001 40 5
00011000 41 5.125
00010111 42 5.25
00010110 43 5.375
00010101 44 5.5
00010100 45 5.625
00010011 46 5.75
00010010 47 5.875
00010001 48 6
00010000 49 6.125
00001111 50 6.25
00001110 51 6.375
00001101 52 6.5
00001100 53 6.625
00001011 54 6.75
00001010 55 6.875
00001001 56 7
00001000 57 7.125
00000111 58 7.25
00000110 59 7.375
00000101 60 7.5
00000100 61 7.625
00000011 62 7.75
00000010 63 7.875
1997 Jul 11 31
Page 32

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.10 DATA DIRECTION REGISTERS (DDR0, DDR2 AND DDR3)
The data direction registers are used to control the direction of data flow at the port pins (P0, P2 and P3). DDR0 controls
P0; DDR2 controls P2; DDR3 controls P3. A logic 0 written to a bit makes the relevant port an input port. A logic 1 makes
it an output port. The register is byte addressable; R/W.
Table 24 Data direction registers (address DDR0: 0XFBH; DDR2: 0XFCH; DDR3: 0XFDH); note 1
76543210
Srv_frc_flock Srv_frc_lock Srv_otd Srv_da Srv_cl Srv_rab Srv_startup Serv_halt
Table 25 Description of DDR bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 DDROUTX7 controls direction of PX.7
6 DDROUTX6 controls direction of PX.6
5 DDROUTX5 controls direction of PX.5
4 DDROUTX4 controls direction of PX.4
3 DDROUTX3 controls direction of PX.3
2 DDROUTX2 controls direction of PX.2
1 DDROUTX1 controls direction of PX.1
0 DDROUTX0 controls direction of PX.0
(1)
Note to Tables 24 and 25
1. X = 0, 2 or 3, depending on register selected (DDR0, DDR2 or DDR3).
1997 Jul 11 32
Page 33

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.11 CONFIGURATION CONTROL REGISTER (CCR)
The Config_cntrl register is used to control internal multiplexers. Note that the motor output configuration register in the
decoder is used to choose between the decoder motor control and the QCLV motor control. The register is byte
addressable; R/W.
Table 26 Description of CCR bits (address 0XFEH)
BIT
POSITION
READ WRITE
7 7 Config_cntrl.7 not used
6 6 Cnf_dac_clk_sel
5 1 Cnf_AGC_bypass AGC decoder bypass; Cnf_AGC_bypass = 1: bypass; Cnf_AGC_bypass = 0:
4 5 Cnf_lock_over Lock_over_rule; Cnf_lock_over = 1: overrules the decoder signals force_lock,
3 4 Cnf_uPotd selects OTD input; Cnf_uPotd = 1: controller; Cnf_uPotd = 0: DSICS
2 3 Cnf_sign_mag selects PWM output mode; Cnf_sign_mag = 1: sign magnitude;
1 2 Cnf_filter selects the filter in the QCLV motor control; Cnf_filter = 1: enable;
0 0 Cnf_dircom selects decoder communication mode; Cnf_dircom = 1: direct;
(1)
SYMBOL FUNCTION
selects clock to DAC; Cnf_dac_clk_sel = 1: ;
Cnf_dac_clk_sel = 0:
use AGC
force_flock
Cnf_sign_mag = 0: two’s complement
Cnf_filter = 0: disable
Cnf_dircom = 0: indirect (via the servo)
master clock
--------------------------------3
master clock
--------------------------------2
Note
1. Note that the function of bit positions 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 depends on whether the register is being written to or read from.
1997 Jul 11 33
Page 34

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.12 A SECOND SERIAL INTERFACE
A second serial interface is implemented using the
following registers:
• SCON2: 0XC0
• SBUF2: 0XC1.
This is of course an interrupt function. Bit 6 of the
IE register is used to enable this function. Bit 6 of the
IP register is used to define this interrupt to the highest
Table 27 Servo memory map
ADDRESS (HEX) CONTENTS
0X100 time_keeper
0X101 focus_stat
0X102 rad_stat
0X103 mem_sledge1_hi
0X104 offtrack_hi_rb
0X105 offtrack_lo_rb
0X106 mem_sledge1_lo
0X107 rad_int_hi
0X108 rad_int_lo
0X109 rad_offset_hi
0X10A rad_error_gain_mem_hi
0X10B tpi_gain_hi
0X10C focus_error_mem
0X10D rad_error_mem
0X10E speed_hi
0X10F speed_lo
0X110 focus_int_hi
0X111 focus_int_lo
0X112 drop_out_code
0X113 foc_prop_mem
0X114 FOCUS_PROP_MULT
0X115 FOCUS_INT_GAIN
0X116 RAMP_MEAN_VALUE
0X117 slee_mult_mem
0X118 RAMP_HEIGTH
0X119 FE_LEVEL
0X11A timer1
0X11B acc_stat_mem
0X11C rad_prop_mult_mem
0X11D rad_error_acc_mem
priority level. The new vector address of the interrupt could
be 0033H.
8.1.13 M
Since the performance of a basic engine is largely
determined by the subcode retrieval speed, fast access to
the subcode buffer is desirable. The servo RAM is mapped
onto the AUX RAM of the microcontroller. In this way it is
possible to directly access the servo RAM registers; see
Table 27.
ADDRESS (HEX) CONTENTS
EMORY MAP ACCESS TO THE SERVO
0X11E rad_int_gain_mem
0X11F speed_mult_mem
0X120 rad_offset_lo
0X121 rad_error_gain_mem_lo
0X122 tpi_gain_lo
0X123 sp_mem_lo
0X124 sp_mem_hi
0X125 speed_setpoint
0X126 tpi_signal_mem
0X127 rad_ctrl_1_mem2
0X128 rad_ctrl_1_mem
0X129 rad_ctrl_2_mem
0X12A rad_gain_mem
0X12B stack 5
0X12C stack 4
0X12D stack 3
0X12E stack 2
0X12F stack 1
0X130 stack 0
0X131 oldcom
0X132 state_mult_mem
0X133 mem_sledge2_lo
0X134 mem_sledge2_h
0X135 RAMP_GAIN
0X136 slede_mult_mem2
0X137 FAST_SPEED
0X138 mem_sledge2_lo_lo
0X139 gain_filter2_mem_lo
0x13A gain_filter2_mem_hi
0x13B gain_filter1_mem
1997 Jul 11 34
Page 35

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
ADDRESS (HEX) CONTENTS
0x13C low_gain_mem
0x13D gain_drempel_mem
0x13E rad_ctrl_1_mem3
0x13F focus_int_mem1
0x140 interruptreg
0x141 cd6statmem
0x142 HiState
0x143 MotorStatTime
0x144 mem_sledge1_drempel_lo
0x145 mem_sledge1_drempel_hi
0x146 sledge_pulse_mem
0x147 sledge_time_ou
0x148 speed_drempel_mem
0x149 hold_mult_mem
0x14A xtra_preset
0x14B cd6subadr
0x14C cd6cmd1
0x14D cd6cmd2
0x14E asec
0x14F asecold
0x150 aframe
0x151 aframemeold
0x152 playwatchtimer
0x153 interruptmask
0x154 playwatchtimer
0x155 trackcount1
0x156 timer2
0x157 jumpwatchtime
0x158 sledge_long_brake
0x159 radwatchstat
0x15A sledge_power_mem
0x15B rad_mem_part1
0x15C StateTimerHi
0x15D StateTimerLo
ADDRESS (HEX) CONTENTS
0x15E FocusStartTime
0x15F MotorStartTime1
0x160 MotorStartTime2
0x161 RadInitTime
0x162 BrakeTime
0x163 RadialStartStat
0x164 sledge_pulse_height
0x165 focus_inject
0x166 radial_inject
0x167 detphase
0x168 oscinc
0x169 injectlevel1
0x16A injectlevel2
0x16B osc
0x16C agcgainmem
0x16D agcgainlo
0x16E focus_offset
0x16F inject_lo
0x170 offtrack_hi
0x171 oftrack_lo
0x172 not used
0x173 not used
0x174 subcode byte 0
0x175 subcode byte 1
0x176 subcode byte 2
0x177 subcode byte 3
0x178 subcode byte 4
0x179 subcode byte 5
0x17A subcode byte 6
0x17B subcode byte 7
0x17C subcode byte 8
0x17D subcode byte 9
0x17E peak level left
0x17F peak level right
1997 Jul 11 35
Page 36

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.14 DIGITAL PLL REGISTERS
The behaviour of the digital PLL can be monitored and
controlled using the following registers:
1. PLL Frequency Register (address 0XECH):
This register holds the 8 MSBs of the PLL frequency.
The register is byte addressable; read only.
2. PLL DC Offset Register (address 0XEDH):
This register holds the 8-bit asymmetry signal in two’s
complement form. The register is byte addressable;
read only.
3. PLL Jitter Register (address 0XEE):
This register holds the 8 MSBs of the 10 jitter bits.
The register is byte addressable; read only.
4. PLL Int Inp Register (address 0XFF):
Presets the 8 MSBs of the PLL frequency to a certain
value. The register is byte addressable; R/W.
1997 Jul 11 36
Page 37

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.1.15 DIV17 REGISTER (address 0X9FH)
This register can be used to generate the serial communication baud rate. If this method is chosen, the baud rate will be
62259 × P. The 5 LSBs of DIV17 hold the value of P. The 2 MSBs connect this baud rate generator to UART 1 or UART 2
(see Table 28). The register is byte addressable; R/W.
Table 28 Baud rate to UART connection
BIT 7 BIT 6 DESCRIPTION
0 0 baud rate generator not selected
0 1 select baud rate generator only for UART1
1 0 select baud rate generator only for UART2
1 1 select baud rate generator for UART1 and UART2
Of course in ACE it is still possible to use timers 1 and 2 to generate the baud rate. Table 29 provides an overview of
how various baud rates can be generated using timer 1, timer 2, and DIV17.
Table 29 Baud rate selection, timer based; note 1
BAUD RATE
kBAUD
1411.20 16.9344 0 XXXX
996.14 16.9344 X 1 X X 16
529.20 16.9344 2 1 X X X
498.07 16.9344 X 1 X X 8
373.55 16.9344 X 1 X X 6
264.60 16.9344 2 0 X X X
249.04 16.9344 X 1 X X 4
186.78 16.9344 X 1 X X 3
124.52 16.9344 X 1 X X 2
88.20 16.9344 1 1 0XFF X X
66.15 16.9344 1 X X 0XFFF0 X
62.26 16.9344 X 1 X X 1
44.10 16.9344 1 0 0XFF X X
33.08 16.9344 1 X X 0XFFE8 X
9.80 16.9344 1 1 0XF7 X X
Note
1. X = don’t care.
µPCLK
(MHz)
MODE SMOD
RELOAD
TIMER 1
RELOAD
TIMER 2
DIV17
(ACE)
1997 Jul 11 37
Page 38

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.2 Memory map
Table 30 Memory map
ADDRESS
LOWER ↓ 89ABCDE F
(1)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
PO P1 P2 P3 SCON2 PSW ACC B
SP SBUF2
DPL MOTQCLVL
DPH MOTQCLVH
RSV
PCON RSV
TCON SCON1 IE IP T2CON PSR RSV RSV
TMOD SBUF RSV RSV T2MOD SCR SSR MOTSETP
TL0 RCAP2L MOTGAIN
TL1 RCAP2H DSR DDR0
TH0 TL2 PLLFREQ DDR2
TH1 TH2 PLLOFS DDR3
CLKgen PLLJITT CONFIG
DIV17 PLLINT
UPPER →
Note
1. For example, hex address A8 = IE.
1997 Jul 11 38
Page 39

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.3 Summary of the functions controlled by decoder registers 0 to F
The decoder uses 16 programmable registers, accessible under internal microcontroller control. The addresses of these
registers are given in Table 31, along with a summary of the functions performed. The INITIAL column shows the
power-on reset state.
Table 31 Decoder Registers 0 to F
REGISTER ADDRESS DATA FUNCTION INITIAL
0
(Fade and
attenuation)
1
(Motor mode)
2
(Status control)
0000 X000 mute reset
X01X attenuate −
X001 full scale −
X100 step down −
X101 step up −
0XXX DACCLK operating −
1XXX DACCLK 3-stated reset
0001 X000 motor off mode reset
X001 motor brake mode 1 −
X010 motor brake mode 2 −
X011 motor start mode 1 −
X100 motor start mode 2 −
X101 motor jump mode −
X111 motor play mode −
X110 motor jump mode 1 −
1XXX anti-windup active −
0XXX anti-windup off reset
0010 0000 status = SUBQREADY-I reset
0001 status = MOTSTART1 −
0010 status = MOTSTART2 −
0011 status = MOTSTOP −
010X status = PLL lock −
011X status = MOTOR-OV −
1X00 status = FIFO overflow −
1X01 status = shock detect −
1X10 status = latched shock detect −
1X11 status = latched shock detect reset −
(1)
1997 Jul 11 39
Page 40

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
REGISTER ADDRESS DATA FUNCTION INITIAL
3
(DAC output)
4
(Motor gain)
0011 1010 I2S-bus; CD-ROM mode −
1011 EIAJ; CD-ROM mode −
110X I
1111 I
1110 I
000X EIAJ; 16-bit; 4f
0011 EAIJ; 16-bit; 2f
0010 EIAJ; 16-bit; f
010X EIAJ; 18-bit; 4f
0111 EIAJ; 18-bit; 2f
0110 EIAJ; 18-bit; f
2
S-bus; 18-bit; 4fs mode reset
2
S-bus; 18-bit; 2fs mode −
2
S-bus; 16-bit; fs mode −
s
s
s
s
s
s
0100 X000 motor gain G = 3.2 reset
X001 motor gain G = 4.0 −
X010 motor gain G = 6.4 −
X011 motor gain G = 8.0 −
X100 motor gain G = 12.8 −
X101 motor gain G = 16.0 −
X110 motor gain G = 25.6 −
X111 motor gain G = 32.0 −
0XXX new motor control reset
1XXX standard CD6 motor control −
5
(Motor
bandwidth)
0101 XX00 motor f4 = 0.5 × n Hz reset
XX01 motor f4 = 0.7 × nHz −
XX10 motor f4 = 1.4 × nHz −
XX11 motor f4 = 2.8 × nHz −
00XX motor f3 = 0.85 × n Hz reset
01XX motor f3 = 1.71 × nHz −
10XX motor f3 = 3.42 × nHz −
6
(Motor output
configuration)
0110 XX00 motor power maximum 37% reset
XX01 motor power maximum 50% −
XX10 motor power maximum 75% −
XX11 motor power maximum 100% −
00XX MOTOS, MOTOV pins 3-state reset
01XX motor PWM mode −
10XX motor PDM mode −
11XX motor CDV mode −
(1)
−
−
−
−
−
−
1997 Jul 11 40
Page 41

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
REGISTER ADDRESS DATA FUNCTION INITIAL
7
(DAC output
control)
8
(PLL loop filter
bandwidth)
9
(PLL
equalization)
A
(EBU output)
0111 xxx0 DAC data normal value reset
xxx1 DAC data inverted value −
xx0x left channel first at DAC (WCLK normal) reset
xx1x right channel first at DAC (WCLK inverted) −
11xx stereo output at DAC reset
10xx left mono out at DAC −
01xx right mono out at DAC −
00xx both DAC channels killed −
see Table 32
1001 0111 equalization = −60 ns −
0110 equalization = −45 ns −
0101 equalization = −30 ns −
0100 equalization = −15 ns −
0011 equalization=0ns reset
0010 equalization = 15 ns −
0001 equalization = 30 ns −
0000 equalization = 45 ns −
1111 equalization = 60 ns −
1110 equalization = 75 ns −
1101 equalization = 90 ns −
1100 equalization = 105 ns −
1011 equalization = 120 ns −
1010 equalization = 135 ns −
1001 equalization = 150 ns −
1000 equalization = 165 ns −
1010 xx0x DOBM data before concealment −
xx1x DOBM data after concealment and fade reset
x1x1 DOBM off; output LOW −
x0x1 class 1 crystal (<50 ppm) −
x0x0 class 2 crystal (<1000 ppm) reset
x1x0 class 3 crystal (>1000 ppm) -
0xxx flags to DOBM off reset
1xxx flags to DOBM on −
(1)
1997 Jul 11 41
Page 42

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
REGISTER ADDRESS DATA FUNCTION INITIAL
B
(Speed control)
C
(Data slicer and
AGC control)
D
(Versatile pins
interface)
E 1110 0xxx bit controls operating speed mode, see register B reset
1011 x0xx 33.8688 MHz crystal present,
or 8.4672 MHz crystal with SELPLL set HIGH
x1xx 16.9344 MHz crystal present −
0xxx single speed mode (if register E = 0xxx)
four times speed mode (if register E = 1xxx); note 2
1xxx double speed mode (if register E = 0xxx)
eight times speed mode (if register E = 1xxx); note 2
xx00 standby 1: ‘CD-STOP’ mode reset
xx10 standby 2: ‘CD-PAUSE’ mode −
xx11 operating mode −
1100 1xxx
01xx
00xx
xx0x digital equalizer enabled −
xx1x digital equalizer disabled reset
xxx0 AGC active reset
xxx1 AGC inactive (on hold) −
1101 xx01 subcode channels Q-W at SUBQW −
xx10 SUBQW = 0 −
xx11 SUBQW = 1 reset
01xx de-emphasis signal at DEEM, no internal
10xx DEEM = 0 −
11xx DEEM = 1 reset
x0xx audio features disabled −
x1xx audio features enabled reset
xx0x lock-to-disc mode disabled reset
xx1x lock-to-disc mode enabled −
xxx0 low-stop = 0; motor brakes to 12% reset
xxx1 low-stop = 1; motor brakes to 6% −
slicer bandwidth or Hz
slicer bandwidth or Hz
slicer bandwidth or Hz
de-emphasis filter
255
--------- n
112
--------- n
27
-----n
112
--------- n
56
-----n
13
-----n
reset
reset
reset
−
−
−
−
(1)
1997 Jul 11 42
Page 43

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
REGISTER ADDRESS DATA FUNCTION INITIAL
F
(Subcode
interface)
Notes
1. The initial column shows the power-on reset state.
2. Speed can be set to (1.5×, 3×, 6× and 12×) or (2×, 4×, 8× and 16×) via the microcontroller application register
CLKgen.
Table 32 Loop filter bandwidth
REGISTER ADDRESS DATA
8
(PLL loop filter
bandwidth)
1111 x0xx subcode interface off reset
x1xx subcode interface on −
0xxx 4-wire subcode reset
1xxx 3-wire subcode −
xx10 decrease AGC gain 1 step, when AGC off (register C) −
xx10 increase AGC gain 1 step, when AGC off (register C) −
FUNCTION
INTERNAL
BANDWIDTH
(Hz)
1000 0000 1640 × n 525 × n 8400 × n −
0001 3279 × n 263 × n 16800 × n −
0010 6560 × n 131 × n 33600 × n −
0100 1640 × n 1050 × n 8400 × n −
0101 3279 × n 525 × n 16800 × n −
0110 6560 × n 263× n 33600 × n −
1000 1640 × n 2101 × n 8400 × n −
1001 3279 × n 1050 × n 16800 × n reset
1010 6560 × n 525 × n 33600 × n −
1100 1640 × n 4200 × n 8400 × n −
1101 3279 × n 2101 × n 16800 × n −
1110 6560 × n 1050 × n 33600 × n −
BANDWIDTH
(Hz)
LOW-PASS
BANDWIDTH
(Hz)
INITIAL
(1)
(1)LOOP
Note
1. The initial column shows the power-on reset state.
1997 Jul 11 43
Page 44

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.4 Summary of servo commands
The servo commands are listed in Table 33.
Table 33 Servo commands
COMMANDS CODE BYTES PARAMETERS
Write commands
Preset_Latch 81H 1 <chip_init>
Write_focus_coefs1 17H 7 <foc_parm_3> <foc_int> <ramp_incr> <ramp_height> <ramp_offset>
<FE_start> <foc_gain>
Write_focus_coefs2 27H 7 <defect_parm> <rad_parm_jump> <vel_parm2> <vel_parm1>
<foc_parm_1> <foc_parm_2> <CA_drop>
Write_focus_command 33H 3 <foc_mask> <foc_stat> <shock_level>
Focus_gain_up 42H 2 <foc_gain> <foc_parm_1>
Focus_gain_down 62H 2 <foc_gain> <foc_parm_1>
Write_radial coefs 57H 7 <rad_length_lead> <rad_int> <rad_parm_play> <rad_pole_noise>
<rad_gain> <sledge_parm_2> <sledge_parm_1>
Preset_init 93H 3 <RE_offset> <RE_gain> <sum_gain>
Radial_off C1H 1 1Ch
Radial_init C1H 1 3Ch
Short_jump C3H 3 <offtrack_hi> <offtrack_lo> <rad_stat>
Long_jump C5H 5 <brake_dist_max> <sledge_U_max> <offtrack_hi> <offtrack_lo>
<rad_stat>
Steer_sledge B1H 1 <sledge_Uout>
Write_decoder_reg D1H 1 <deccmd>
Write_parameter A2H 2 <param_ram_addr> <param_data>
Read commands
Read_status 70H up to 5 <foc_stat> <rad_stat> <rad_int_lpf> <offtrack_hi> <offtrack_lo>
Read_aux_status F0H up to 3 <RE_offset> <RE_gain> <sum_gain> <foc_error> <rad_error>
Read_Q_subcode 0H up to 12 <Q_sub1 to 10> <peak_l> <peak_r>
Read_hilevel_status E0H up to 4 <intreq> <decstat> <seqstat> <motorstarttime>
1997 Jul 11 44
Page 45

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
8.4.1 SUMMARY OF SERVO COMMAND PARAMETERS
Table 34 Servo command parameters
PARAMETER
foc_parm_1 − focus PID − end of focus lead
foc_parm_2 − focus PID − focus low-pass
foc_parm_3 − focus PID − focus lead length
foc_int 14H focus PID − focus integrator crossover frequency
foc_gain 15H focus PID 70H focus PID loop gain
CA_drop 12H focus PID − sensitivity of drop-out detector
ramp_offset 16H focus ramp − asymmetry of focus ramp
ramp_height 18H focus ramp − p-p value of ramp voltage
ramp_incr − focus ramp − slope of ramp voltage
FE_start 19H focus ramp − minimum value of focus error
RE_offset − radial initialization − initial value for RE_offset
RE_gain − radial initialization − initial value for RE_gain
sum_gain − radial initialization − initial value for sum_gain
rad_parm_play 28H radial PID − end of radial lead
rad_pole_noise 29H radial PID − radial low-pass
rad_length_lead 1CH radial PID − length of radial lead
rad_int 1EH radial PID − radial integrator crossover frequency
rad_gain 2AH radial PID 70H radial loop gain
rad_parm_jump 27H radial jump − filter during jump
vel_parm1 1FH radial jump − PI controller crossover frequencies
vel_parm2 32H radial jump − jump pre-defined profile
speed_thres 48H radial jump − maximum speed in fast track mode
act_sled 49H radial jump 00H electronic damping of radial actuator
brake_dist_max 21H radial jump − max sledge distance allowed in fast
sledge_brake_dist 58H radial jump 7FH brake distance of sledge
offtrack_hi − radial jump − two’s complement MSB of number of tracks
offtrack_lo − radial jump − two’s complement LSB of number of tracks
rad_stat − radial/sledge − radial and sledge control
sledge_Umax − sledge − voltage on sledge during long jump
sledge_Uout − sledge − voltage on sledge when steered
RAM
ADDRESS
AFFECTS POR VALUE DETERMINES
defect detector enabling
OTD polarity
focus error normalising
minimum light level
sledge bandwidth during jump
actuator steered mode
to jump
to jump
1997 Jul 11 45
Page 46

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
PARAMETER
sledge_parm_1 36H sledge − sledge integrator crossover frequency
sledge_parm_2 17H sledge − sledge low-pass frequencies
pulse_time 46H pulsed sledge − control pulse width
pulse_height 64H pulsed sledge − control pulse height
defect_parm − defect detector − defect detector setting
shock_level − shock detector − shock detector operation
playwatchtime 54H watchdog − radial on-track watchdog time
jumpwatchtime 57H watchdog − radial jump watchdog time-out
wradcontrol 59H watchdog − enable/disable automatic radial off feature
chip_init − set-up − V
xtra_preset 4AH set-up 38H laser on/off
deccmd 4DH decoder interface − send commands to decoder
interruptmask 53H STATUS pin − enabled interrupts
seq_state 42H autosequencer − autosequencer control
FocusStartTime 5EH autosequencer − focus start time
MotorStartTime1 5FH autosequencer − motorstart1 time
MotorStartTime2 60H autosequencer − motorstart2 time
RadialInitTime 61H autosequencer − radial initialisation time
BrakeTime 62H autosequencer − brake time
RadCmdByte 63H autosequencer − radial command byte
osc_frequency 68H focus/radial AGC − AGC control
detect_phase 67H focus/radial AGC − phase shift of injected signal
injectlevel1 69H focus/radial AGC − amplitude of signal injected
injectlevel2 6AH focus/radial AGC − amplitude of signal injected
agc_gain 6CH focus/radial AGC − focus/radial gain
RAM
ADDRESS
AFFECTS POR VALUE DETERMINES
shock filter
sledge gain
sledge operation mode
level setting
RH
enable/disable decoder interface
decoder interface speed
interrupt request polarity
fast radial brake
RA, FO, SL PDM modulating frequency
enable/disable fast brake
fast jumping circuit on/off
frequency of injected signal
1997 Jul 11 46
Page 47

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
9 LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNITS
V
DDD(pads)
V
DDD(core)
V
DDA
V
I
V
O
∆V
DDA-DDD(core)
I
O
I
I(d)
T
amb
T
stg
V
es
digital supply voltage for pad cells notes 1 and 2 −0.5 +6.5 V
digital supply voltage for the core notes 2 and 3 −0.5 +4.0 V
analog supply voltage notes 2 and 3 −0.5 +4.0 V
input voltage (any input) −0.5 VDD+ 0.5 V
output voltage (any output) −0.5 +6.5 V
supply voltage difference
between the analog and digital (core) supply
−±0.25 V
voltages
output current (continuous) −±20 mA
diode DC input current (continuous) −±20 mA
operating ambient temperature 0 70 °C
storage temperature −55 +125 °C
electrostatic handling note 4 −2000 +2000 V
note 5 −200 +200 V
Notes
1. All pad supply pins (V
DDDn(pads)
) must be connected externally to the same power supply.
2. All VSS pins must be connected to the same external voltage.
3. All analog and digital core supply pins (V
DDA
and V
DDDn(core)
) must be connected externally to the same power
supply.
4. Equivalent to discharging a 100 pF capacitor via a 1.5 kΩ series resistor with a rise time of 15 ns.
5. Equivalent to discharging a 200 pF capacitor via a 2.5 µH series inductor.
1997 Jul 11 47
Page 48

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
10 CHARACTERISTICS
10.1 General characteristics
V
DDD(pads)
= 4.5 to 5.5 V; V
DDD(core)
specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
DDD(pads)
digital supply voltage for pad
cells
V
DDD(core)
digital supply voltage for the
core
V
DDA
I
DD
Servo analog section (V
P
INS: D1, D2, D3, D4, S1, S2, V
C
int
analog supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
supply current n = 8 mode − 90 − mA
DDD(pads)
internal capacitor D1, D2, D3,
D4, S1 and S2
I
IrefT
R
I
D
IrefT
input current for I
external resistor on I
input current for central diode
input signal
I
S(max)
maximum input current for
satellite diode input signal
I
IrefT
R
I
cd
IrefT
input current for I
external resistor on I
input current for central diode
input signal
I
sd
input current for satellite diode
input signal
V
IrefT
V
D1-D4, S1, S2
voltage on current input I
voltage on current inputs D1,
D2, D3, D4, S1 and S2
V
GAP
V
RH
t
ch(VRH)
band gap voltage − 1.2 − V
HIGH level reference voltage note 4 0.5 − 2.5 V
charge time VRH buffer −− 50 ns
(THD+N)/S total harmonic
distortion-plus-noise to signal
ratio
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; V
= 5.0 V; V
RH,IrefT
, FTC
refT
refT
refT
refT
refT
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; VSS= 0; T
DDA
= 0 to 70 °C; unless otherwise
amb
4.5 5.0 5.5 V
3.0 3.3 3.6 V
DDD(core)
AND FTC
L
= 3.3 V; V
H
= 3.3 V; VSS= 0; T
DDA
amb
=25°C)
100 −−pF
f
= 4.2336 MHz;
sys
1.99 − 5.95 µA
notes 1 and 2
f
= 4.2336 MHz;
sys
202 − 603 kΩ
notes 1 and 2
f
= 4.2336 MHz;
sys
3.97 − 11.91 µA
notes 2 and 3
f
= 4.2336 MHz;
sys
1.99 − 5.95 µA
notes 2 and 3
f
= 8.4672 MHz;
sys
3.97 − 11.91 µA
notes 1 and 2
f
= 8.4672 MHz;
sys
101 − 302 kΩ
notes 1 and 2
f
= 8.4672 MHz;
sys
7.94 − 23.81 µA
notes 2 and 3
f
= 8.4672 MHz;
sys
3.97 − 11.91 µA
notes 2 and 3
− virtual V
− virtual V
GAP
SSA
− V
− V
at 0 dB; note 5 −−50 −45 dB
1997 Jul 11 48
Page 49

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
S/N signal-to-noise ratio − 55 − dB
PSRR power supply ripple rejection at
V
DDA
G
tol
gain tolerance notes 2 and 7 −12 0 +12 %
∆G variation of gain between
channels
α
cs
V
offset(FTC)
Decoder analog front-end (V
P
INS: MIDLAD, REFLCA, HFIN, REFHCA AND I
f
clk
B
AGC
V
offset
G
) AGC gain:
v(AGC
channel separation − 60 − dB
comparator FTC offset −10 − +10 mV
DDD(pads)
= 5.0 V; V
ADC clock frequency n = 16 67 −−MHz
AGC bandwidth (−3 dB) n = 12/16 18/24 −−MHz
total offset voltage −7 0 +7 lsb
range −4.4 − +12.1 dB
step − 1.1 − dB
V
i(AGC)(p-p))
AGC input signal range;
peak-to-peak value
V
i(ADC)
input range ADC plus buffer − 1.4 − V
THD total harmonic distortion f
S/N signal-to-noise ratio − 33 − dB
Z
in
input impedance HFIN − 10 − kΩ
Digital inputs
note 6 − 45 − dB
−− 2%
DDD(core)
ref
= 3.3 V; V
= 3.3 V; VSS= 0; T
DDA
amb
=25°C)
0.4 − 2.3 V
= 5 MHz −−36 − dB
s
f
= 10 MHz −−30 − dB
s
= 18 MHz −−25 − dB
f
s
I
NPUT: DEFI; CMOS INPUT WITH PULL-DOWN
V
V
R
C
IL
IH
pd(int)
i
LOW-level input voltage −0.3 − 0.3 × VDDV
HIGH-level input voltage 0.7 × V
internal pull-down resistance VI=0 − 50 − kΩ
input capacitance −− 10 pF
Input: RST; CMOS input with hysteresis
V
th(r)
V
th(f)
V
hys
C
i
switching threshold rising −− 0.8 × VDDV
switching threshold falling 0.2 × V
hysteresis voltage − 0.33 × V
input capacitance −− 10 pF
INPUTS: RCK AND SELPLL; CMOS INPUTS
V
IL
V
IH
I
LI
C
i
LOW-level input voltage −0.3 − 0.3 × VDDV
HIGH-level input voltage 0.7 × V
input leakage current VI=0−V
input capacitance −− 10 pF
1997 Jul 11 49
DD
− VDD+ 0.3 V
DD
−−V
DD
− V
DD
− VDD+ 0.3 V
DD
−10 − +10 µA
Page 50

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Digital output
OUTPUTS: TPWM, TEN, SUBQW, DSDEN, CLO, DEEM, DEFO AND OTD
V
OL
V
OH
C
L
t
o(r)
t
o(f)
Open drain outputs
O
UTPUTS: RP, FOK, CFLG, C2FAIL, FB, TL, KILL AND LDON; OPEN DRAIN OUTPUTS
V
OL
I
OL
C
L
t
o(f)
LOW-level output voltage IOL= 2 mA 0 − 0.4 V
HIGH-level output voltage IOH= −2 mA VDD− 0.4 − V
DD
V
load capacitance −− 25 pF
output rise time 10% to 90% levels;
− 23 − ns
CL=20pF
output fall time 90% to 10% levels;
− 27 − ns
CL=20pF
LOW-level output voltage IOL=+4mA 0 − 0.4 V
LOW-level output current −− 4mA
load capacitance −− 25 pF
output fall time 90% to 10% levels;
− 27 − ns
CL=20pF
3-state outputs
O
UTPUTS: DACCLK, VALID, DAC, DATA, WCLK, SCLK, MOTOS, MOTOV, RA, FO, SL, DOBM, SBSY,
SFSY AND SUB
V
V
C
t
OL
OH
L
o(r)
LOW-level output voltage IOL=4mA 0 − 0.4 V
HIGH-level output voltage IOH= −4mA VDD− 0.4 − V
load capacitance −− 50 pF
output rise time 10% to 90% level;
− 24 − ns
CL=20pF
t
o(f)
output fall time 90% to 10% levels;
− 28 − ns
CL=20pF
I
LI
3-state leakage current VI=0−V
DD
−10 − +10 µA
Digital Input/Output
I
NPUTS/OUTPUTS: PSEN, ALE AND EA; CMOS INPUT/OUTPUT WITH PULL-UP
V
V
V
V
t
IL
IH
OL
OH
o(r)
LOW-level input voltage −0.3 − 0.3 × VDDV
HIGH-level input voltage 0.7 × V
− VDD+ 0.3 V
DD
LOW-level output voltage IOL=2mA 0 − 0.4 V
HIGH-level output voltage IOH= −2mA VDD− 0.4 − V
output rise time 10% to 90% levels;
− 24 − ns
CL=20pF
t
o(f)
output fall time 90% to 10% levels;
− 28 − ns
CL=20pF
C
L
C
i
R
pu
load capacitance −− 50 pF
input capacitance −− 10 pF
input pull-up resistance VI=0 − 50 − kΩ
DD
DD
V
V
1997 Jul 11 50
Page 51

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
NPUTS/OUTPUTS: AD0 TO AD7, A8 TO A15, R
I
V
V
V
V
I
t
t
C
C
IL
IH
OL
OH
L
o(r)
o(f)
L
i
LOW-level input voltage −0.3 − 0.3 × VDDV
HIGH-level input voltage 0.7 × V
LOW-level output voltage IOL=2mA 0 − 0.4 V
HIGH-level output voltage IOH= −2mA VDD− 0.4 − V
3-state leakage current VIN=0−V
output rise time 10% to 90% levels;
output fall time 90% to 10% levels;
load capacitance −− 50 pF
input capacitance −− 10 pF
INPUT: XTALI (EXTERNAL CLOCK)
V
IL
V
IH
t
IH
I
LI
C
i
LOW-level input voltage −0.3 − +0.5 V
HIGH-level input voltage −2.0 − VDD+ 0.3 V
input HIGH time relative to period 45 − 55 %
input leakage current −10 − +10 µA
input capacitance −− 10 pF
OUTPUT: XTALO
f
xtal
g
m(mutual)
G
v
C
F
C
o
crystal frequency note 8 8 8.4672 35 MHz
mutual transconductance at 100 kHz − 10 − mA/V
small signal voltage gain AV=gm×R
feedback capacitance −− 5pF
output capacitance −− 10 pF
Notes
XD0,TXD0
CL=20pF
CL=20pF
, INT0, INT1, R
DD
O
XD1,TXD1
, WR AND RD
− VDD+ 0.3 V
DD
DD
−10 − +10 µA
− 24 − ns
− 28 − ns
− 18 −
V
is always equivalent to ; see Section 10.2.
1. f
sys
servo clock
----------------------------- 2
2. Current input range (resistor range) can be extended by 25% (minimum and maximum) but gain tolerance in this
region is 25%.
V
×
I
3. for unipolar A/D converter. For D1, D2, D3 and D4, C
i max()
C
= 0.5 × C
ref
GAPCDAC
=
----------------------------------R
extCref
DAC
×
ref=CDAC.
For S1 and S2,
4. Internal reference source with 32 different output voltages. Selection is made during a calibration period or via the
v
-----------
serial interface. The values given are for an unloaded V
. The output voltage , where
RH
V
RH
0.5 10
44.4
×=
v=0to31.
5. V
6. f
7. Gain tolerance is determined by the accuracy of the external resistor R
= 2.5 V, measuring bandwidth: 200 Hz to 20 kHz, f
RH
ripple
= 1 kHz, V
= 0.5 V peak-to-peak.
ripple
i(ADC)
= 1 kHz.
ext
.
8. It is recommended that the series resistance of the crystal or ceramic resonator is ≤60 Ω.
1997 Jul 11 51
Page 52

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
10.2 Subcode interface timing characteristics
V
DDD(pads)
= 4.5 to 5.5 V; V
DDD(core)
specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Subcode interface timing (single speed × n); note 1; see Fig.11
I
NPUT: RCK
t
clkH
t
clkL
t
r
t
f
t
d(SFSY-RCK)
input clock HIGH time µs
input clock LOW time µs
input clock rise time
input clock fall time
delay time SFSY to RCK
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; V
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; VSS= 0; T
DDA
= 0 to 70 °C; unless otherwise
amb
2
-- n
2
-- n
4
-- n
4
-- n
−−
−−
10
-----n
−
6
-- n
6
-- n
80
-----n
80
-----n
20
-----n
ns
ns
µs
OUTPUTS: SBSY, SFSY AND SUB (CL=20pF)
T
cy(block)
t
W(SBSY)
T
cy(frame)
t
W(SFSY)
t
SFSYH
t
SFSYL
t
d(SFSY-SUB)
t
d(RCK-SUB)
t
h(RCK-SUB)
block cycle time ms
SBSY pulse width
frame cycle time µs
SFSY pulse width (3-wire mode only)
SFSY HIGH time
SFSY LOW time
delay time SFSY to SUB (P data) valid
delay time RCK falling to SUB
hold time RCK to SUB
12.0
----------n
13.3
----------n
−−
122
--------- n
136
--------- n
−−
−−
−−
−−
−−0
−−
Note
1. The subcode timing is directly related to the over-speed factor, n, in normal operating mode;
n is replaced by the disc speed factor, d, in lock-to-disc mode.
14.7
----------n
300
--------- -
n
150
--------- -
n
366
--------- -
n
66
------
n
84
------
n
1
-- -
n
0.7
------- -
n
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
1997 Jul 11 52
Page 53

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
handbook, full pagewidth
SBSY
SFSY
(4-wire mode)
SFSY
(3-wire mode)
SFSY
RCK
SUB
0.8 V
t
W(SBSY)
t
W(SFSY)
t
d(SFSY−RCK)
t
d(SFSY−SUB)
t
cy(frame)
t
r
t
h(RCK−SUB)
t
SFSYL
t
SFSYH
t
f
V
DD
– 0.8 V
T
cy(block)
t
d(RCK−SUB)
0.8 V
V
DD
0.8 V
– 0.8 V
MBG414
Fig.11 Subcode interface timing.
1997 Jul 11 53
Page 54

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
10.3 I2S timing characteristics
V
DDD(pads)
= 4.5 to 5.5 V; V
DDD(core)
specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
2
I
S Timing (single speed × n); note 1; see Fig.12
CLOCK OUTPUT: SCLK (CL=20pF)
T
cy(clk)
t
clkH
t
clkL
output clock period sample rate = f
clock HIGH time sample rate = f
clock LOW time sample rate = f
OUTPUTS: WCLK, DATA, VALIDAND DAC (CL=20pF)
t
su
t
h
set-up time sample rate = f
hold time sample rate = f
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; V
sample rate = 2f
sample rate = 4f
sample rate = 2f
sample rate = 4f
sample rate = 2f
sample rate = 4f
sample rate = 2f
sample rate = 4f
sample rate = 2f
sample rate = 4f
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; VSS= 0; T
DDA
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
= 0 to 70 °C; unless otherwise
amb
− 472.4/n − ns
− 236.2/n − ns
− 118.1/n − ns
166/n −−ns
83/n −−ns
42/n −−ns
166/n −−ns
83/n −−ns
42/n −−ns
95/n −−ns
48/n −−ns
24/n −−ns
95/n −−ns
48/n −−ns
24/n −−ns
Note
2
S timing is directly related to the over-speed factor, n, in normal operating mode;
1. I
n is replaced by the disc speed factor, d, in lock-to-disc mode.
SCLK
WCLK
DATA
DAC
VALID
clock period T
cy(clk)
t
CLKL
t
h
t
su
VDD − 0.8 V
0.8 V
Fig.12 I2S Timing.
t
CLKH
VDD − 0.8 V
0.8 V
MGK505
1997 Jul 11 54
Page 55

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
11 PACKAGE OUTLINE
LQFP100: plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 x 14 x 1.4 mm
c
y
100
X
75
76
pin 1 index
1
e
w M
b
p
D
H
D
51
50
Z
E
26
25
Z
D
b
B
e
w M
p
v M
v M
A
H
E
E
A
B
A
2
A
A
1
detail X
SOT407-1
Q
(A )
3
θ
L
p
L
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
mm
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT407-1
A
A1A2A3b
max.
0.20
1.6
0.05
cE
p
1.5
1.3
0.28
0.16
0.18
0.12
0.25
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
UNIT
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
(1)
(1) (1)(1)
D
14.1
13.9
REFERENCES
eH
H
14.1
13.9
0.5
16.25
15.75
1997 Jul 11 55
D
LLpQZywv θ
E
16.25
15.75
0.75
0.45
0.70
0.57
0.12 0.10.21.0
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
Z
D
1.15
1.15
0.85
0.85
ISSUE DATE
95-12-19
E
o
7
o
0
Page 56

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
12 SOLDERING
12.1 Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
“IC Package Databook”
our
12.2 Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering techniques are suitable for all QFP
packages.
The choice of heating method may be influenced by larger
plastic QFP packages (44 leads, or more). If infrared or
vapour phase heating is used and the large packages are
not absolutely dry (less than 0.1% moisture content by
weight), vaporization of the small amount of moisture in
them can cause cracking of the plastic body. For more
information, refer to the Drypack chapter in our
Reference Handbook”
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several techniques exist for reflowing; for example,
thermal conduction by heated belt. Dwell times vary
between 50 and 300 seconds depending on heating
method. Typical reflow temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C.
(order code 9398 652 90011).
“Quality
(order code 9397 750 00192).
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave)
soldering technique should be used.
• The footprint must be at an angle of 45° to the board
direction and must incorporate solder thieves
downstream and at the side corners.
Even with these conditions, do not consider wave
soldering the following packages: QFP52 (SOT379-1),
QFP100 (SOT317-1), QFP100 (SOT317-2),
QFP100 (SOT382-1) or QFP160 (SOT322-1).
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Maximum permissible solder temperature is 260 °C, and
maximum duration of package immersion in solder is
10 seconds, if cooled to less than 150 °C within
6 seconds. Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
12.4 Repairing soldered joints
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonallyopposite end leads. Use only a low voltage soldering iron
(less than 24 V) applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact
time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C. When
using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in
one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
Preheating is necessary to dry the paste and evaporate
the binding agent. Preheating duration: 45 minutes at
45 °C.
12.3 Wave soldering
Wave soldering is not recommended for QFP packages.
This is because of the likelihood of solder bridging due to
closely-spaced leads and the possibility of incomplete
solder penetration in multi-lead devices.
If wave soldering cannot be avoided, the following
conditions must be observed:
1997 Jul 11 56
Page 57

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
13 DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
14 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
1997 Jul 11 57
Page 58

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
NOTES
1997 Jul 11 58
Page 59

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
All Compact Disc Engine (ACE) SAA7348GP
NOTES
1997 Jul 11 59
Page 60

Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 34 Waterloo Road, NORTH RYDE, NSW 2113,
Tel. +61 2 9805 4455, Fax. +61 2 9805 4466
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213, Tel. +43 160 1010,
Fax. +43 160 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 200 733, Fax. +375 172 200 773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: see South America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15th floor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 689 211, Fax. +359 2 689 102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +852 2319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Prags Boulevard 80, PB 1919, DK-2300 COPENHAGEN S,
Tel. +45 32 88 2636, Fax. +45 31 57 0044
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615800, Fax. +358 9 61580920
France: 4 Rue du Port-aux-Vins, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 40 99 6161, Fax. +33 1 40 99 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 23 53 60, Fax. +49 40 23 536 300
Greece: No. 15, 25th March Street, GR 17778 TAVROS/ATHENS,
Tel. +30 1 4894 339/239, Fax. +30 1 4814 240
Hungary: see Austria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Band Box Building, 2nd floor,
254-D, Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli, MUMBAI 400 025,
Tel. +91 22 493 8541, Fax. +91 22 493 0966
Indonesia: see Singapore
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax. +353 1 7640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, PO Box 18053,
TEL AVIV 61180, Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax. +972 3 649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS, Piazza IV Novembre 3,
20124 MILANO, Tel. +39 2 6752 2531, Fax. +39 2 6752 2557
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku, TOKYO 108,
Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5077
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381
Middle East: see Italy
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 40 27 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +63 2 817 3474
Poland: Ul. Lukiska 10, PL 04-123 WARSZAWA,
Tel. +48 22 612 2831, Fax. +48 22 612 2327
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 755 6918, Fax. +7 095 755 6919
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 1231,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 7430 Johannesburg 2000,
Tel. +27 11 470 5911, Fax. +27 11 470 5494
South America: Rua do Rocio 220, 5th floor, Suite 51,
04552-903 São Paulo, SÃO PAULO - SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax. +55 11 829 1849
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 3 301 6312, Fax. +34 3 301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 632 2000, Fax. +46 8 632 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2686, Fax. +41 1 481 7730
Taiwan: Philips Semiconductors, 6F, No. 96, Chien Kuo N. Rd., Sec. 1,
TAIPEI, Taiwan Tel. +886 2 2134 2865, Fax. +886 2 2134 2874
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Talatpasa Cad. No. 5, 80640 GÜLTEPE/ISTANBUL,
Tel. +90 212 279 2770, Fax. +90 212 282 6707
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +380 44 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 181 730 5000, Fax. +44 181 754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 625 344, Fax.+381 11 635 777
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors, Marketing & Sales Communications,
Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218, 5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
© Philips Electronics N.V. 1997 SCA55
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
Printed in The Netherlands 657027/1200/01/pp60 Date of release: 1997 Jul 11 Document order number: 9397 750 02136
 Loading...
Loading...