Page 1
DATA SH EET
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC01
1997 Aug 11
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
SAA7335
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM
systems
Page 2
1997 Aug 11 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
FEATURES
• Compatibility with CD-I, CD-ROM, MPEG-video
DVD-ROM and DVD-video applications
• Designed for very high playback speeds
• Typical CD-ROM operation up to n = 12, DVD-ROM to
n = 1.9, maximum rates (tbf)
• Matched filtering, quad-pass error correction
(C1-C2-C1-C2), overspeed audio playback function
included (up to 3 kbytes buffer)
• Lock-to-disc playback, Constant Angular Velocity
(CAV), pseudo-Constant Linear Velocity (CLV) and CLV
motor control loops
• Interface to 32 kbytes SRAM for DVD error correction
and de-interleave
• Sub-code/ header processing for DVD and CD formats
• Programmable HF equalizer
• In DVD mode it is still compatible with Philips block
decoders
• Sub-CPU interface can be parallel or fast I
2
C-bus
• On-chip clock multiplier.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
This device is a high-end combined Compact Disc (CD)
and Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) compatible decoding
device. The device operates with an external 32 kbytes
S-RAM memory for de-interleaving operations. The device
provides quad-pass error correction for CD-ROM
applications (C1-C2-C1-C2) and operates in lock-to-disk,
CAV, pseudo CLV and CLV modes.
In DVD modes double-pass C1-C2 error correction is used
which is capable of correcting up to 5 C1 frame errors and
16 C2 frame errors.
The SAA7335 contains all the functions required to
decode an EFM or EFM+ HF signal directly from the laser
pre-amplifier, including analog front-end, PLL data
recovery, demodulation and error correction. The spindle
motor interface provides both motor control signals from
the demodulator and, in addition, contains a tachometer
loop that accepts tachometer pulses from the motor unit.
The SAA7335 has two independent microcontroller
interfaces. The first is a serial I
2
C-bus and the second is a
standard 8-bit multiplexed parallel interface. Both of these
interfaces provide access to a total of 32 × 8-bit registers
for control and status.
This data sheet contains an descriptive overview of the
device together with electrical and timing characteristics.
For a detailed description of the device refer to the user
guide
“SAU/UM96018”
.
Supply of this CD/DVD IC does not convey an implied
license under any patent right to use this IC in any CD or
DVD application.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DDD
digital supply voltage 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
I
DDD
digital supply current − 70 300 mA
V
DDA
analog supply voltage 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
I
DDA
analog supply current − 70 300 mA
f
xtal
crystal input frequency 4 25 tbf MHz
T
amb
operating ambient temperature −20 − +70 °C
T
stg
storage temperature −55 − +125 °C
Page 3
1997 Aug 11 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
ORDERING INFORMATION
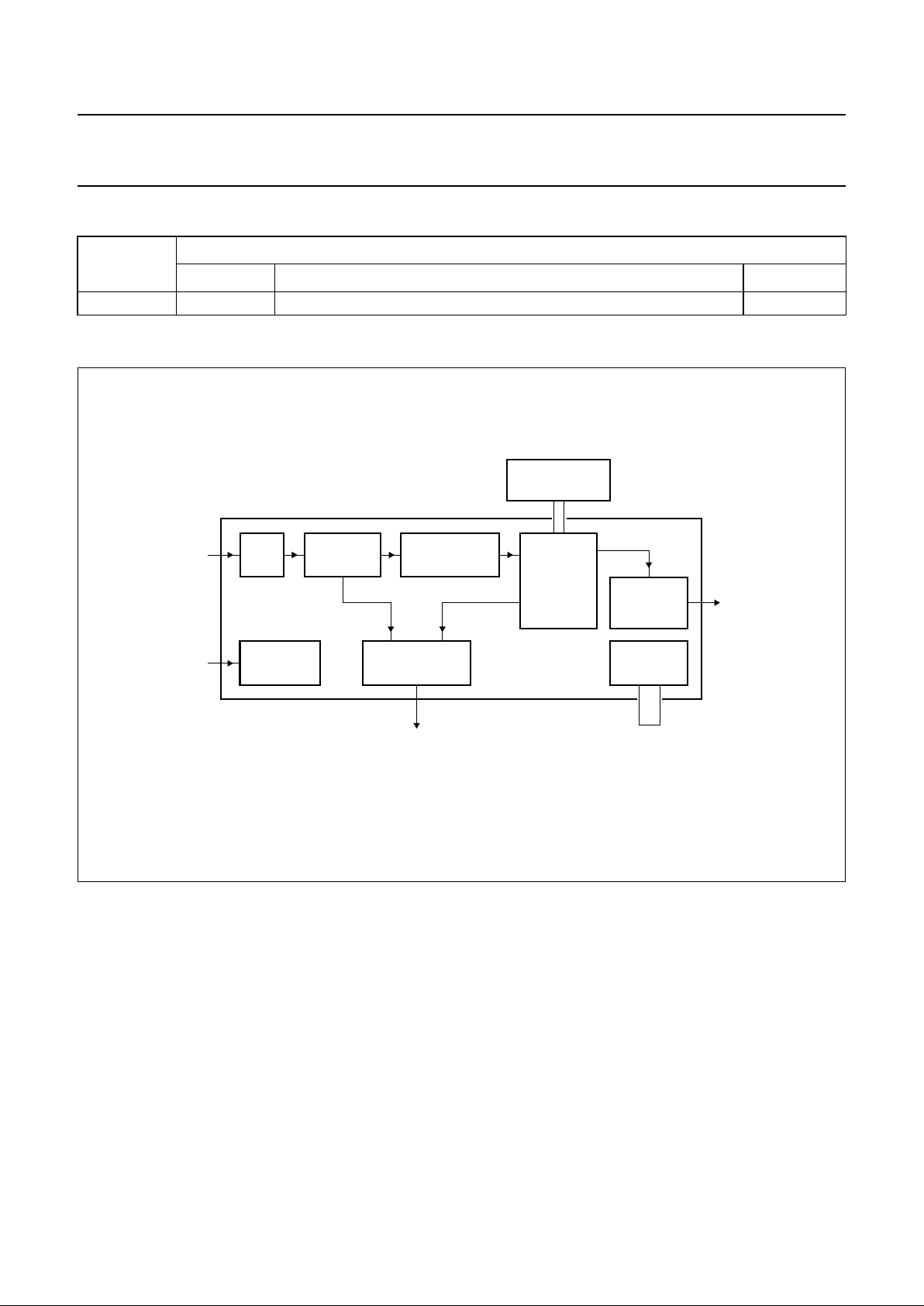
BLOCK DIAGRAM
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SAA7335GP LQFP100 plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 × 14 × 1.4 mm SOT407-1
Fig.1 Simplified block diagram.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGK242
DEMODULATOR
EFM/EFM+
PLL BIT
DETECTOR
SRAM
32 KBYTES
SPINDLE
MOTOR CONTROL
motor control
SAA7335
CLOCK
GENERATOR
SUB-CPU
INTERFACE
ADCHF input
clock input
DECODER
block
decoder
output
I2S-BUS
OUTPUT
INTERFACE
Page 4
1997 Aug 11 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
V
SSA1
1 supply analog ground 1
I
ref
2 I analog current reference input for ADC
REFLo 3 I analog low reference input for ADC
REFHi 4 I analog high reference input for ADC
VREF 5 I analog negative input
HFIN 6 I analog positive input
V
SSA2
7 supply analog ground 2
AGCOUT 8 O analog test pin output
V
DDA2
9 supply analog supply voltage 2
V
DDD1
10 supply digital supply voltage 1
V
SSD1
11 supply digital ground 1
OTD 12 I off track detect input
MOTO1 13 O 3-state motor control output
n.c. 14 − not connected, reserved
MOTO2/T3 15 I/O motor control output/tachometer 3 input
n.c. 16 − not connected, reserved
T1 17 I tachometer 1 input
T2 18 I tachometer 2 input
V
DDD2
19 supply digital supply voltage 2
V
SSD2
20 supply digital ground 2
TEST1 21 I test input 1
TEST2 22 I test input 2
POR 23 I power-on reset input
MUXSWICH 24 I use clock multiplier input
n.c. 25 − not connected, reserved
CL1 26 O divided clock output
BCAIN 27 I BCA input
SDA 28 I/O sub-CPU I
2
C-bus serial data input/output
SCL 29 I sub-CPU I
2
C-bus serial clock input
INT 30 O sub-CPU interrupt output (open-drain)
V
DDD3
31 supply digital supply voltage 3
V
SSD3
32 supply digital ground 3
da7 33 I/O sub-CPU data bus bit 7 input/output (parallel)
da6 34 I/O sub-CPU data bus bit 6 input/output (parallel)
da5 35 I/O sub-CPU data bus bit 5 input/output (parallel)
n.c. 36 − not connected, reserved
da4 37 I/O sub-CPU data bus bit 4 input/output (parallel)
n.c. 38 − not connected, reserved
da3 39 I/O sub-CPU data bus bit 3 input/output (parallel)
da2 40 I/O sub-CPU data bus bit 2 input/output (parallel)
Page 5

1997 Aug 11 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
da1 41 I/O sub-CPU data bus bit 1 input/output (parallel)
n.c. 42 − not connected, reserved
da0 43 I/O sub-CPU data bus bit 0 input/output (parallel)
V
DDD4
44 supply digital supply voltage 4
V
SSD4
45 supply digital ground 4
WRi 46 I sub-CPU write enable input (active LOW)
RDi 47 I sub-CPU read enable input (active LOW)
ALE 48 I sub-CPU address latch enable input
CSi 49 I sub-CPU chip select input (active HIGH)
STOPCLOCK 50 O stop clock output
n.c. 51 − not connected, reserved
V4 52 O serial subcode output (for CD)
EBUOUT 53 O digital audio output
SYNC 54 O I
2
S-bus sector sync output
FLAG 55 O I
2
S-bus correction flag output
DATA 56 O I
2
S-bus serial data output
BCLK 57 I/O I
2
S-bus bit serial clock input/output
WCLK 58 I/O I
2
S-bus word clock input/output
V
DDD5
59 supply digital supply voltage 5
V
SSD5
60 supply digital ground 5
RAMRW 61 O RAM read/write control output
n.c. 62 − not connected, reserved
RAMDA7 63 I/O RAM data bus bit 7 input/output
RAMDA6 64 I/O RAM data bus bit 6 input/output
RAMDA5 65 I/O RAM data bus bit 5 input/output
RAMDA4 66 I/O RAM data bus bit 4 input/output
RAMDA3 67 I/O RAM data bus bit 3 input/output
RAMDA2 68 I/O RAM data bus bit 2 input/output
n.c. 69 − not connected, reserved
RAMDA1 70 I/O RAM data bus bit 1 input/output
RAMDA0 71 I/O RAM data bus bit 0 input/output
V
DDD6
72 supply digital supply voltage 6
V
SSD6
73 supply digital ground 6
RAMAD0 74 O RAM address bit 0 output
RAMAD1 75 O RAM address bit 1 output
RAMAD2 76 O RAM address bit 2 output
RAMAD3 77 O RAM address bit 3 output
RAMAD4 78 O RAM address bit 4 output
RAMAD5 79 O RAM address bit 5 output
RAMAD6 80 O RAM address bit 6 output
V
DDD7
81 supply digital supply voltage 7
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
Page 6
1997 Aug 11 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
V
SSD7
82 supply digital ground 7
RAMAD7 83 O RAM address bit 7 output
RAMAD8 84 O RAM address bit 8 output
RAMAD9 85 O RAM address bit 9 output
n.c. 86 − not connected, reserved
RAMAD10 87 O RAM address bit 10 output
RAMAD11 88 O RAM address bit 11 output
RAMAD12 89 O RAM address bit 12 output
RAMAD13 90 O RAM address bit 13 output
RAMAD14 91 O RAM address bit 14 output
V
DDD8
92 supply digital supply voltage 8
V
SSD8
93 supply digital ground 8
CRIN 94 I analog crystal input
CROUT 95 O analog crystal output
CFLG 96 O correction statistics output
MEAS1 97 O front-end telemetry output
V
DDD9
98 supply digital supply voltage 9
V
SSD9
99 supply digital ground 9
V
DDA1
100 supply analog supply voltage 1
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
Page 7
1997 Aug 11 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
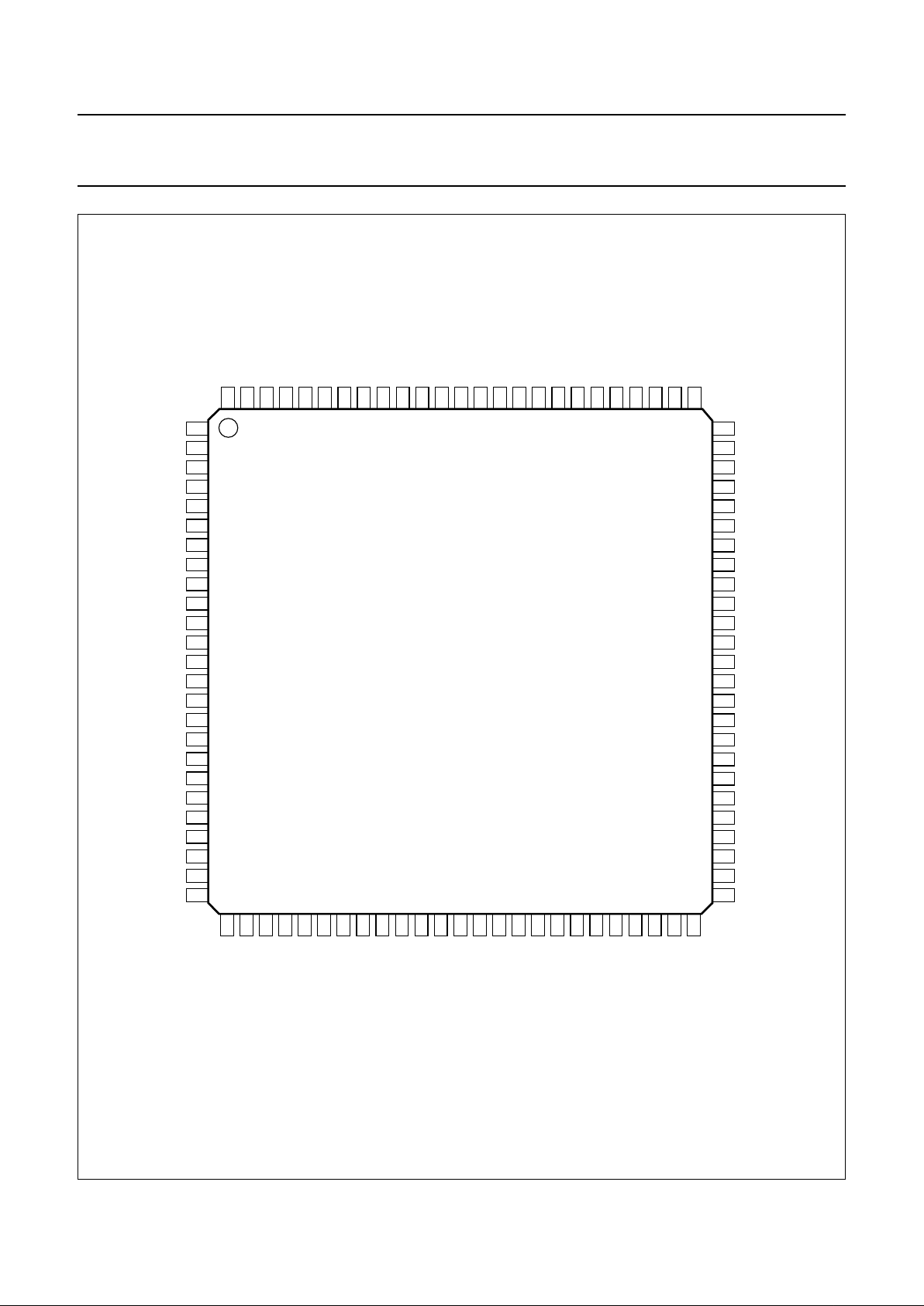
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
handbook, full pagewidth
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
8079787776
RAMAD1
RAMAD0
V
SSD6
V
DDD6
RAMDA0
RAMDA1
n.c.
RAMDA2
RAMDA3
RAMDA4
RAMDA5
RAMDA6
RAMDA7
n.c.
RAMRW
V
SSD5
V
DDD5
WCLK
BCLK
DATA
FLAG
SYNC
EBUOUT
V4
n.c.
MGK241
V
SSA1
I
ref
REFLo
REFHi
VREF
HFIN
V
SSA2
AGCOUT
V
DDA2
V
DDD1
V
SSD1
OTD
MOTO1
n.c.
MOTO2/T3
n.c.
T1
T2
V
DDD2
V
SSD2
TEST1
TEST2
POR
MUXSWICH
n.c.
RAMAD6
RAMAD5
RAMAD4
RAMAD3
RAMAD2
V
DDA1VSSD9VDDD9
MEAS1
CFLG
CROUT
CRIN
V
SSD8VDDD8
RAMAD14
RAMAD13
RAMAD12
RAMAD11
RAMAD10
n.c.
RAMAD9
RAMAD8
RAMAD7
V
SSD7VDDD7
V
DDD3
V
SSD3
da7
da6
da5
n.c.
da4
n.c.
da3
da2
da1
n.c.
da0
V
DDD4
V
SSD4
WRi
RDi
ALE
CSi
STOPCLOCK
CL1
BCAIN
SDA
SCL
INT
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
100
99989796959493929190898887868584838281
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
50
SAA7335
Page 8

1997 Aug 11 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Analog front-end
This block converts the HF input to the digital domain using
an 8-bit ADC proceeded by an AGC circuit to obtain the
optimum performance from the convertor. This block is
clocked by ADCCLK which is set by the external crystal
frequency plus a flexible clock multiplier and divider block.
PLL and bit detector
This subsystem recovers the data from the channel
stream. The block corrects asymmetry, performs noise
filtering and equalisation and finally recovers the bit clock
and data from the channel using a digital PLL.
The equalizer and the data slicer are programmable.
Digital logic
All the digital system logic is clocked from the master ADC
clock (ADCCLK) described above.
Advanced bit detector
The advanced bit detector offers improved data recovery
for multi-layer discs and contains two extra detection
circuits to increase the margins in the bit recovery block:
1. Adaptive slicer: adds a second stage slicer with higher
bandwidth
2. Run length 2 push-back: all T2 run lengths are pushed
back to T3, thereby automatically determining the
erroneous edge and shifting the transitions on that
edge.
Demodulator
F
RAME SYNC PROTECTION CD MODE
This circuit detects the frame synchronization signals.
Two synchronization counters are used in the SAA7335:
1. The coincidence counter: this is used to detect the
coincidence of successive syncs. It generates a sync
coincidence signal if 2 syncs are 588 ±1 EFM clocks
apart.
2. The main counter: this is used to partition the EFM
signal into 17-bit words. This counter is reset when:
a) A sync coincidence is generated
b) A sync is found within ±6 EFM clocks of its
expected position.
The sync coincidence signal is also used to generate the
lock signal which will go active HIGH when 1 sync
coincidence is found. It will reset to LOW when, during
61 consecutive frames, no sync coincidence is found.
FRAME SYNC PROTECTION DVD MODE
This circuit detects the frame synchronization signals.
Two synchronization counters are used in the SAA7335:
1. The coincidence counter: this is used to detect the
coincidence of successive syncs. It generates a sync
coincidence signal if 2 syncs are 1488 ±3 EFM+
clocks apart.
2. The main counter: this is used to partition the EFM+
signal into 16-bit words. This counter is reset when:
a) A sync coincidence is generated
b) A sync is found within ±10 EFM+ clocks of its
expected position.
The sync coincidence signal is also used to generate the
lock signal which will go active HIGH when 1 sync
coincidence is found. It will reset to LOW when, during
61 consecutive frames, no sync coincidence is found.
EFM/EFM+ demodulation
The 14-bit EFM (16-bit EFM+) data and subcode words
are decoded into 8-bit symbols.
Page 9

1997 Aug 11 9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Microcontroller interface
The SAA7335 has two microcontroller interfaces, one
serial I2C-bus and one parallel (8051 microcontroller
compatible).
The two communication modes may be operated at the
same time, the modes are described below:
1. Parallel mode: protocol compatible with 8052
multiplexed bus:
a) da0 to da7 = address/data bus
b) ALE = Address Latch Enable, latches the address
information on the bus
c)
WRi = active LOW write signal for write to
SAA7335
d) RDi = active LOW read signal for read from
SAA7335
e) CSi = active HIGH Chip Select signal (this signal
gates the RDi and WRi signals).
2. I2C-bus mode: I2C-bus protocol where SAA7335
behaves as slave device where:
a) SDA = I2C-bus data
b) SCL = I2C-bus clock
c) I2C-bus slave address (write mode) = 3EH
d) I2C-bus slave address (read mode) = 3FH
e) Maximum data transfer rate = 400 kbits/s.
M
ICROCONTROLLER INTERFACE (I
2
C-BUS MODE)
Bytes are transferred over the interface in single bytes of
which there are two types; write data commands and read
data commands.
The sequence for a write data command (1 data byte) is as
follows:
• Send START condition
• Send address 3EH (write)
• Write command address byte
• Write data byte
• Send STOP condition.
The sequence for a read data command (that reads 1 data
byte) is as follows:
• Send START condition
• Send address 3EH (write)
• Write status address byte
• Send STOP condition
• Send START condition
• Send address 3FH (read)
• Read data byte
• Send STOP condition.
R
EADING AND WRITING DATA TO THE SAA7335
The SAA7335 has 32 × 8-bit configuration and status
registers as shown in Table 1. Not all locations are
currently defined and some remain reserved for future
upgrades. These can be written to or read from via the
microcontroller interface using either the serial or parallel
control bus.
Page 10
1997 Aug 11 10
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
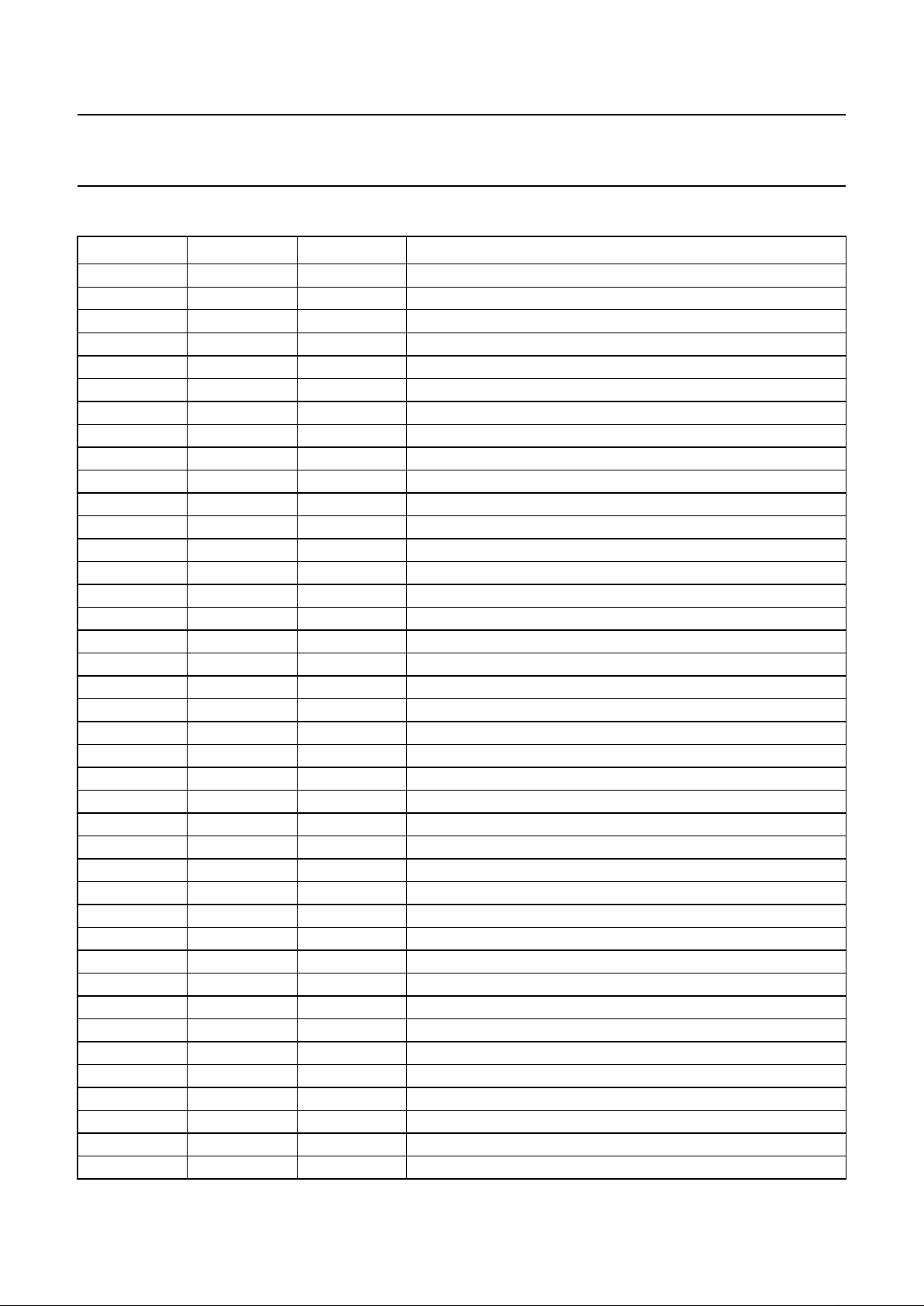
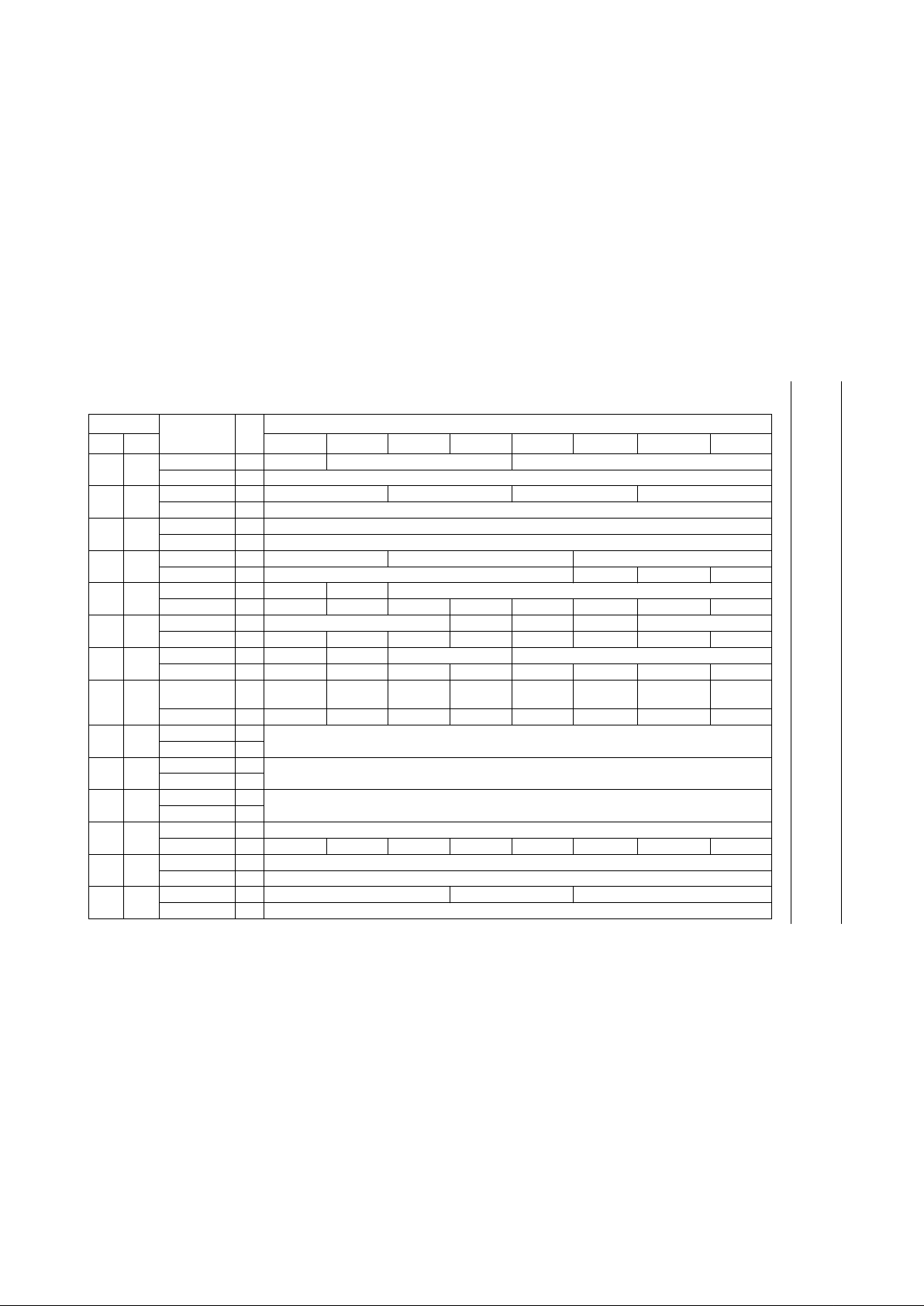
REGISTER MAP
Table 1 SAA7335 microcontroller register map
ADDRESS
NAME R/W
BIT
DEC HEX 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 0 PLL_LOCK W Lock Oride Pha_Oset PLL_Force_L
PLL_Freq_R R PLL measured frequency (bits 9 to 2)
1 1 PLL_SET W SliceBW Integ_F0 PLLBW_F1 LP_BW_F3
PLL_ASSYM R PLL asymmetry value (8 bits)
2 2 PLL_FREQ W PLL frequency (8 MSBs)
PLL_Jit R jitter value (bits 9 to 2)
3 3 PLL_EQU W PLL frequency (2 LSBs) equalizer tap α 1 equaliser tap α 2
PLL_Lock_In R reserved Long_Symb F_Lock In_Lock
4 4 PLL_F_MEAS W RL3_EN reserved EFM nominal setting (101110)
reserved R −−−−−− − −
5 5 OUTPUT1 W Fmat(3 to 1) WCLK_Op BCLK_Op Fmat (0) SyncSwap (1 and 0)
reserved R −−−−−− − −
6 6 OUTPUT2 W EBU_Valid EBU_On EBU control bits 28, 29 EBU control bits (1 to 4)
reserved R −−−−−− − −
7 7 OUTPUT3 W WCLK_H_
Left
Descr_On Interp_On CD_ROM_
Header_On
Flag_Pin Kill Data On Kill EBU_On CD_ROM_
Scrb_On
reserved R −−−−−− − −
8 8 SEMA1 W general purpose semaphore register
R
9 9 SEMA2 W general purpose semaphore register
R
10 A SEMA3 W general purpose semaphore register
R
11 B INTEN W hardware pin interrupt enable bits (map to status bits)
Status R Fl_S1 Fl_S2 Fl_S3 PLL lock DVD rdy Mot Ov Tacho reserved
12 C MOTOR1 W frequency set point
SLICE1 R slice compensation value
13 D MOTOR2 W G(2 to 0) Ki Kf
EYE_Open R eye opening value
Page 11
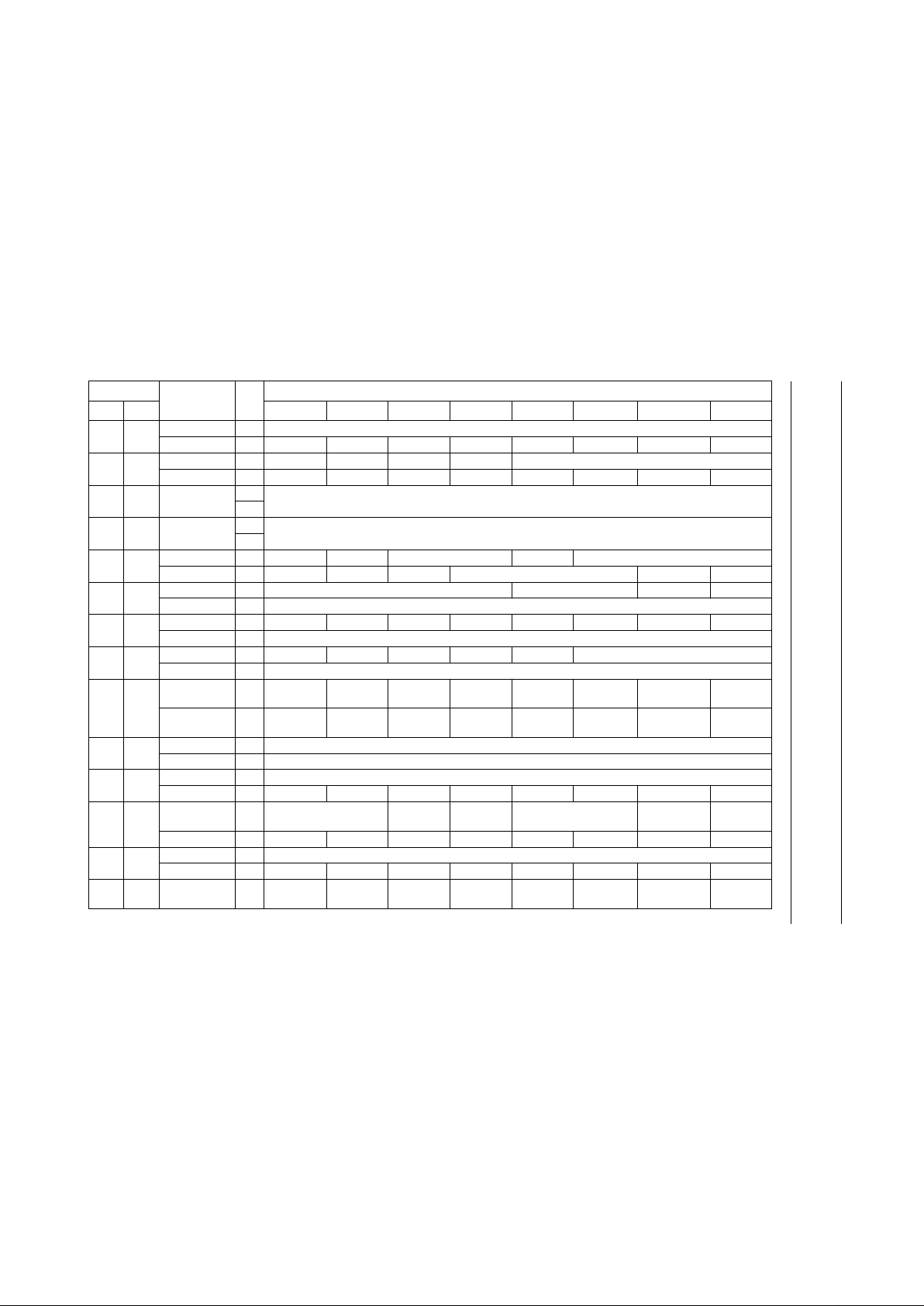
1997 Aug 11 11
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
14 E MOTOR3 W FIFO set point
MTR_F R −−−−−− − −
15 F MOTO4 W PWM_PDM OVF_SW SW2 SW1 motor servo control (3 to 0)
reserved R −−−−−− − −
16 10 MTR_INTG_L W motor integrator value (7 to 0)
R
17 11 MTR_INTG_H W motor integrator value (15 to 8)
R
18 12 CLOCKPRE W CL1Div BCLKG_En Div1 (2 to 0) Mux 2 Div2 (2 to 0)
SUB_C_STAT R ready busy CRC_OK err (2 to 0) cor fail reserved
19 13 DECMODE W mode reserved read TOC reserved
SUB_C_DATA R subcode data (7 to 0)
20 14 reserved W −−−−−− − −
SUB_C_End R no meaning (register read used as a signal)
21 15 ANASET W AGC_En gain set gain up gain down AGC_On reserved
FIFOFILL_L R number of C1 frames in FIFO
22 16 VITSET W slice ON AdDet ON FEndAutoS
ON
BCA_STAT R Buff_
Loaded
sync Buff_ORun
23 17 TACHO1 W tachometer multiplier frequency KTacho (7to0)
BCA_DATA R BCA data (7 to 0)
24 18 TACHO2 W tachometer interrupt trip frequency tachometer trip (7 to 0)
reserved R −−−−−− − −
25 19 TACHO3 W servo control source Tacho
FRes
Moto2_T3 Fsam TachoInt_LF reserved
reserved R −−−−−− − −
26 1A BCASET W BCA_Freq (7 to 0)
reserved R −−−−−− − −
27 to311B to1Freserved −−−−−− − −
ADDRESS
NAME R/W
BIT
DEC HEX 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Page 12

1997 Aug 11 12
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
READING STATUS INFORMATION FROM THE SAA7335
There are several internal status signals which can be made available on the INT line (see Table 2).
Table 2 Internal status signals; note 1
Note
1. The status signal to be output is selected by interrupt control register.
SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
Fl_S1 change in semaphore register 1 detected
Fl_S2 change in semaphore register 2 detected
Fl_S3 change in semaphore register 3 detected
PLLlock channel data PLL lock (not latched) indicates in-lock condition
DVDrdy DVD header or subcode block is available, reset when SUBREADEND register is read
MotOv motor overflow, (not latched) indicates when a motor overflow is occurring
Tacho motor speed is higher (or lower depending on TACHO3 bit 2) than motor set point (defined in
TACHO2) this signal is not latched
Subcode data/DVD header processing
Q-
CHANNEL PROCESSING
The 96-bit Q-channel word is accumulated in an internal
buffer. Sixteen bits are used to perform a Cyclic
Redundancy Check (CRC). Subcode is available via the
V4 output and, in addition, the Q channel code can also be
read via the SUBREADDATA register.
DVD
HEADER
The DVD header processor accumulates a selection of
bytes from the beginning of the DVD sector. Two header
modes are defined, one for reading the normal sector
headers and one for filtering the disk physical format
information (from the control data block in the lead-in area)
This is controlled by the READ_TOC bit in the DECMODE
register.
O
THER SUBCODE CHANNELS
Data of the other subcode channels (Q-to-W) may be read
via the V4 pin, this is only valid in CD modes.
The data on the V4 pin is clocked on the WCLK edges with
a fixed delay and so may be clocked by external circuitry
running off the WCLK edges, i.e. at twice the WCLK
frequency.The subcode data is also available in the EBU
output (DOBM) in a similar format.
Crystal oscillator
The crystal oscillator is a conventional 2 pin design. This
oscillator is capable of operating with ceramic resonators
and with both fundamental and third overtone crystals.
External components should be used to suppress the
fundamental output of the third overtone crystals as shown
in Figs 3 and 4. Typical oscillation frequencies required
are 8.462, 16.9344 or 22.57 MHz depending on the
internal clock settings used and whether or not the clock
multiplier is enabled.
Error corrector
The error corrector can operate in a number of modes; CD
single-pass, CD dual-pass and DVD mode. In the CD
single-pass mode the error corrector performs 2 error
corrections per frame (C1 and C2). In the CD dual-pass
mode up to 4 symbol corrections per frame are possible
(C1-C2 then C1-C2 again). For the DVD mode full depth
PI and PO error correction is performed allowing
5 corrections per PI row and full depth (2t + e)
≤16 correction to be performed per PO column. The error
corrector also contains a flag controller. Flags are
assigned to symbols when the error corrector cannot
ascertain if the symbols are definitely good. C1 generates
output flags which are read (after de-interleaving) by C2,
to help in the generation of C2 output flags. The C2 output
flags are used by the interpolator for concealment of
non-correctable errors. They are also output via the EBU
signal (DOBM) and the MISC output via the I
2
S-bus for
CD-ROM applications.
The flags output pin CFLG provides information on the
state of all error correction and concealment flags.
Page 13

1997 Aug 11 13
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Fig.3 8.4672 MHz fundamental configuration.
handbook, halfpage
MGK243
330 Ω
100 kΩ
22
pF
22
pF
8.4672 MHz
CRINCROUT
OSCILLATOR
SAA7335
Fig.4 22.57 MHz overtone configuration.
handbook, halfpage
MGK244
330 Ω
100 kΩ
3.3 µH
10
pF
10
pF
22.57 MHz
1 nF
CRINCROUT
OSCILLATOR
SAA7335
Fig.5 Concealment mechanism.
Interpolation Hold Interpolation
MGA372
OK Error OK Error Error Error OK OK
Page 14

1997 Aug 11 14
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Audio functions
C
ONCEALMENT
A 1-sample linear interpolator becomes active if a single
sample is flagged as erroneous but cannot be corrected.
The erroneous sample is replaced by a level midway
between the preceding and following samples. Left and
right channels have independent interpolators.
If more than one consecutive non-correctable sample is
found the last good sample is held. A 1-sample linear
interpolation is then performed before the next good
sample (see Fig.5).
DAC Interface
The SAA7335 is compatible with a wide range of ROM
block decoders and Digital-to-Analog Converters DACs.
The seven main formats that are supported are given in
Table 3.
Table 3 DAC interface formats (notes 1, 2 and 3)
Notes
1. EIAJ is the abbreviation for Electronic Industries
Associated of Japan.
2. Number of BCLK periods per half WCLK period
(i.e. bits per sample).
3. Clock gating must be DISABLED for format mode 7.
MODE BITS/WORD FORMAT
1 16 Philips I
2
S-bus
2 16 EIAJ
3 24 Philips I
2
S-bus
4 24 EIAJ
5 32 Philips I
2
S-bus
6 32 EIAJ
7 variable Philips I
2
S-bus
Fig.6 Philips I2S-bus data format 1 (16-bit word length).
handbook, full pagewidth
MGK245
D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14
BCLK
DATA
MISC
WCLK
SYNC
flag-MSB (1 is unreliable) flag-LSB flag-MSB
right
left
Page 15

1997 Aug 11 15
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Fig.7 EIAJ (‘S’) data format 2 (16-bit word length).
handbook, full pagewidth
MGK246
D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14
BCLK
DATA
MISC
WCLK
SYNC
flag-MSB (1 is unreliable) flag-LSB flag-MSB
left
right
Fig.8 Philips I2S-bus data format 3 (24-bit word length).
handbook, full pagewidth
MGK247
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14
BCLK
DATA
MISC
WCLK
SYNC
flag-MSB (1 is unreliable) flag-LSB flag-MSB
right
left
Fig.9 EIAJ (‘S’) data format 4 (24-bit word length).
handbook, full pagewidth
MGK248
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
D15 D14
BCLK
DATA
MISC
WCLK
SYNC
flag-MSB (1 is unreliable)
flag-LSB flag-MSB
left
right
Page 16

1997 Aug 11 16
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
MGK249
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14
BCLK
DATA
MISC
WCLK
SYNC
flag-MSB (1 is unreliable) flag-LSB flag-MSB
right
left
Fig.10 Philips I2S-bus data format 5 (32-bit word length).
MGK250
D15 D14 D15 D14D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
BCLK
DATA
MISC
WCLK
SYNC
flag-MSB (1 is unreliable) flag-LSB flag-MSB
left
right
Fig.11 EIAJ (‘S’) data format 6 (24-bit word length).
Page 17

1997 Aug 11 17
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Fig.12 Philips I2S-bus data format (variable word length).
handbook, full pagewidth
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
D15 D14
BCLK
DATA
FLAG
WCLK
SYNC
flag-MSB (1 is unreliable) flag-LSB
variable number of clocks
flag-MSB
right
MGK251
left
EBU interface
The biphase-mark digital output signal at pin DOBM is in
accordance with the format defined by the
“IEC 958”
specification.
Three different modes can be selected via the EBU output
control register (address 1010).
F
ORMAT
The digital audio output consists of 32-bit words
(subframes) transmitted in biphase-mark code
(2 transitions for a logic 1 and one transition for a logic 0).
Words are transmitted in blocks of 384 (see Table 4).
S
YNC
The sync word is formed by violation of the biphase rule
and therefore does not contain any data. Its length is
equivalent to 4 data bits. The three different sync patterns
indicate the following situations:
• Sync B: start of a block (384 words), word contains left
sample
• Sync M: word contains left sample (no block start)
• Sync W: word contains right sample.
A
UDIO SAMPLE
Left and right samples are transmitted alternately.
V
ALIDITY FLAG
Audio samples are flagged (bit 28 = logic 1) if an error has
been detected but was non-correctable. This flag remains
the same even if data is taken after concealment.
U
SER DATA
Subcode bits Q-to-W from the subcode section are
transmitted via the user data bit. This data is asynchronous
with the block rate.
C
HANNEL STATUS
The channel status bit is the same for left and right words.
Therefore a block of 384 words contains 192 channel
status bits. The category code is always CD. The bit
assignment is given in Table 5.
Page 18

1997 Aug 11 18
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Table 4 EBU word format
Table 5 EBU channel status
WORD BITS FUNCTION
Sync 0 to 3 −
Auxiliary 4 to 7 not used; normally zero
Error flags 4 CFLG error and interpolation flags when bit 3 of EBU control register is set
to logic 1
Audio sample 8 to 27 first 4 bits not used (always zero)
Validity flag 28 valid = logic 0
User data 29 used for subcode data (Q-to-W)
Channel status 30 control bits and category code
Parity bit 31 even parity for bits 4 to 30
WORD BITS FUNCTION
Consumer/professional 0 always zero
Control 1 to 4 copied from bits 3 to 0 of register OUTPUT2, normally should be set to a
copy of CRC checked Q-channel control bits 0 to 3; bit 2 is logic 1 when
copy permitted; bit 3 is logic 1 when recording has pre-emphasis
Reserved 5 to 7 always zero
Category code 8 to 15 CD; bit 8 = logic 1, all other bits = logic 0
Reserved 16 to 27 always zero
Clock accuracy 28 to 29 set by OUTPUT2 control register bits 5 and 4; 00 = level II, 01 = level III
Remaining 30 to 191 always zero
Spindle motor control
The spindle motor speed is controlled by a fully integrated
digital servo. Address information from the internal
±8 frame FIFO and disc speed information are used to
calculate the motor control output signals.
Several output modes are supported:
1. Pulse density, 1-line,
2. Pulse density, 2-line (true complement output) (cannot
be used with tachometer control)
3. PWM output, 2-line.
The modes are selected via the motor output configuration
register.
P
ULSE DENSITY MODE
In the pulse density mode the motor output (pin MOTO1)
is the pulse density modulated motor output signal. A 50%
duty cycle corresponds with the motor not actuated, higher
duty cycles mean acceleration, lower mean braking.
In this mode, the MOTO2 signal is the inverse of the
MOTO1 signal. Both signals change state only on the
edges of a internal clock signal.
Possible application diagrams are shown in Fig.13.
PWM
MODE,2-LINE
In the PWM mode the motor acceleration signal is put in
pulse-width modulation form on the MOTO1 output and
the motor braking signal is pulse-width modulated on the
MOTO2 output.
Figure 14 illustrates the PWM mode timing and Fig.15
illustrates a typical PWM mode application diagram.
Page 19

1997 Aug 11 19
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
OPERATIONAL MODES
The motor servo has a number of operational modes controlled by the motor mode register MOTOR4.
P
OWER LIMIT
To start and stop the spindle motor, a fixed positive or negative voltage is applied to the motor. This voltage can be
programmed as a percentage of the maximum possible voltage via the motor output configuration register (MOTOR4) to
limit current drain during start and stop. The following power limits are possible:
• 100% of maximum (no power limit)
• 75% of maximum
• 50% of maximum
• 37% of maximum.
L
OOP CHARACTERISTICS
The gain and crossover frequencies of the motor control loop can be programmed via the motor gain and bandwidth
register MOTOR2.
MGA363 - 1
MOTO2
V
DD
V
SS
MOTO1
M
22 kΩ
10 nF
+
–
22 kΩ
10 nF
+
–
V
SS
V
SS
MOTO1
M
22 kΩ
10 nF
+
–
22 kΩ
22 kΩ
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
22 kΩ
22 kΩ
Fig.13 Motor pulse density application diagrams.
Page 20

1997 Aug 11 20
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Fig.14 Motor 2-line PWM mode timing.
rep
t = 45 µs
t 240 ns
dead
Accelerate Brake
MOTO1
MOTO2
MGA366
MGA365 - 2
V
SS
+
M
MOTO1 MOTO2
10 Ω
100 nF
Fig.15 Motor 2-line PWM mode application diagram.
Page 21

1997 Aug 11 21
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Flags output (CFLG) (open-drain output)
A 1-bit flag signal is available at the CFLG pin, this contains 11 bits running off the ADCCLK, each bit period is 7 ADCCLK
periods. This signal shows the status of the error corrector and interpolator and is updated every frame.
Table 6 Definition of flag bits
Notes
1. For DVD mode read PI for C1 and PO for C2.
2. This flag refers to the previous correction frame.
3. This flag refers to the previous correction frame (is not valid i.e. always logic 0 in DVD mode).
4. Bit order of root count is 9, then 6 to 8 for root count (3 to 0).
A
BSOLUTE TIME SYNC
The sync signal is the absolute time sync signal. In the CD mode it is the FIFO-passed subcode sync and relates the
position of the subcode sync to the audio data (DAC output). In the DVD mode it indicates the start of a new sector
header.
The flag may be used for special purposes such as synchronization of different players.
BIT
NUMBER
VALUE DESCRIPTION
0 1 START bit
1 to 3 000 C1 first or C1 last; note 1
001 C2 first, CD mode reserved, DVD mode; note 1
010 reserved; note 1
011 C2 last; note 1
100 corrector not active; note 1
all others reserved
4 core fail failure flag set because correction impossible; note 2
5 flag fail; note 3
9, 6 to 8 root count (3 to 0) this indicates the number of errors corrected; note 4
10 0 STOP bit
Fig.16 Flags output format.
handbook, halfpage
START
bit
data bitspause
MGK252
Page 22

1997 Aug 11 22
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
Notes
1. This maximum value has an absolute maximum of 6.5 V independent of the supply voltage.
2. The human body model ESD simulation is equivalent to discharging a 100 pF capacitor via a 1.5 kΩ resistor, which
produces a single discharge transient. Reference
“Philips Semiconductors Test Method UZW-BO/FQ-A302 (similar
to MIL-STD 883C method 3015.7)”
.
3. The machine model ESD simulation is equivalent to discharging a 200 pF capacitor via a resistor and series inductor
with effective dynamic values of 25 Ω and 2.5 µH, which produces a damped oscillating discharge. Reference
“Philips Semiconductors Test Method UZW-BO/FQ-B302 (similar to EIAJ IC-121 Test Method 20 condition C)”
.
QUALITY
This device will meet the requirements of the
“Philips Semiconductors General Quality Specification UZW-BO/FQ-0601”
in accordance with
“Quality Reference Handbook (order number 9397 750 00192)”
. This details the acceptance criteria
for all Q & R tests applied to the product.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DDD
digital supply voltage −0.3 +6.5 V
V
DDA
analog supply voltage −0.3 +6.5 V
V
i(max)
maximum input voltage (any input) note 1 −0.3 VDD+ 0.5 V
V
o(max)
maximum output voltage (any output) note 1 − VDD+ 0.5 V
I
o(max)
maximum output current (each output) −±10 mA
T
amb
operating ambient temperature −20 +70 °C
T
stg
storage temperature −55 +125 °C
V
ESD
electrostatic handling
human body model note 2 −2000 +2000 V
machine model note 3 −200 +200 V
Page 23

1997 Aug 11 23
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
DC CHARACTERISTICS
V
DDD=VDDA
= 5 to 5.5 V; V
SSD=VSSA
=0V; T
amb
= −20 to +70 °C; unless otherwise specified.
Note
1. These inputs are analog, V
IL
and VIH values are quoted as a guide for digital RGB users.
AC CHARACTERISTICS
V
DDD=VDDA
= 4.5 to 5.5 V; V
SSD=VSSA
=0V; T
amb
= −20 to +70 °C; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
V
DDD
digital supply voltage 4.5 − 5.5 V
V
DDA
analog supply voltage 4.5 − 5.5 V
I
DD(tot)
total supply current at 25 MHz clock − 60 − mA
Inputs
D
IGITAL INPUTS (TTL LEVEL); note 1
V
IL
LOW-level input voltage −−0.8 V
V
IH
HIGH-level input voltage 2.0 −−V
V
OL
LOW-level output voltage 0.8 −−V
V
OH
HIGH-level output voltage −−2.4 V
ANALOG INPUTS
V
I(max)(p-p)
maximum input voltage
(peak-to-peak value)
−−2V
V
I(nom)(p-p)
nominal input voltage
(peak-to-peak value)
− 1 − V
DR dynamic range 41 −−dB
B −3 dB bandwidth 0 to 12 dB gain −−−MHz
12 to 20 dB gain −−−MHz
I
I(AGC)
AGC input current − 1 − mA
I
I(ADC)
ADC input current − 24 − mA
I
I(buf)
output buffer input current − 3 − mA
I
I(tot)
total input current −−28 mA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
V
DDD
digital supply voltage 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
I
DDD
digital supply current V
DDD
=5V − 60 165 mA
V
DDA
analog supply voltage 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
I
DDA
analog supply current V
DDA
=5V − 60 165 mA
Page 24

1997 Aug 11 24
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Analog front-end (V
DDA
= 4.5 to 5.5 V); HFIN
f
chan
channel frequency −−50 MHz
Digital inputs
V
IL
LOW-level input voltage −−0.8 V
V
IH
HIGH-level input voltage 2.0 −− V
I
LI
input leakage current Vi= 0 to V
DDD
−10 − +10 µA
C
i
input capacitance −−10 pF
Open-drain output; pin INT
V
OL
LOW-level output voltage IOL= 1 mA 0 − 0.4 V
I
OL
LOW-level output current −−0mA
C
L
load capacitance −−50 pF
t
o(f)
output fall time CL= 20 pF; note 1 −−15 ns
3-state outputs
V
OL
LOW-level output voltage IOL= 0 mA 0 − 0.4 V
V
OH
HIGH-level output voltage IOH= −8 mA 2.4 −− V
C
L
load capacitance −−50 pF
t
o(r)
output rise time CL= 20 pF; note 1 −−15 ns
t
o(f)
output fall time CL= 20 pF; note 1 −−15 ns
I
LI(Z)
3-state leakage current Vi= 0 to V
DDD
−10 − +10 µA
3-state outputs; pins MOTO1, MOTO2 and DOBM
V
OL
LOW-level output voltage V
DDD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V;
IOL=10mA
0 − 0.8 V
V
OH
HIGH-level output voltage V
DDD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V;
IOH= −10 mA
−1 − +2.4 V
C
L
load capacitance −−50 pF
t
o(r)
output rise time CL= 20 pF; note 1 −−10 ns
t
o(f)
output fall time CL= 20 pF; note 1 −−10 ns
I
LI(Z)
3-state leakage current Vi= 0 to V
DDD
−10 − +10 µA
Digital input/outputs (V
DDD
= 4.5 to 5.5 V)
I
NPUT/OUTPUT: SDA (INPUT/OPEN-DRAIN I
2
C-BUS OUTPUT)
V
IL
LOW-level input voltage −−1.5 V
V
IH
HIGH-level input voltage 3.0 −− V
V
OL
LOW-level output voltage IOL= 2 mA;
I
sink
=3mA
−−0.4 V
I
OL
LOW-level output current −−− mA
C
SDA
serial data line capacitance −−10 pF
C
SCL
serial clock line capacitance −−10 pF
N
marL
LOW-level noise margin − 0.1V
DDD
−
N
marH
HIGH-level noise margin − 0.2V
DDD
−
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Page 25

1997 Aug 11 25
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
R
s
series resistance on the SDA and
SCL lines
− 300 −Ω
C
bus(max)
maximum bus capacitance per wire − 400 − pF
INPUT: SCL (CMOS INPUT)
V
IL
LOW-level input voltage −0.3 − 0.3V
DDD
V
V
IH
HIGH-level input voltage 0.7V
DDD
− V
DDD
+ 0.3 V
I
LI
input leakage current Vi=0−V
DDD
−10 − +10 µA
C
i
input capacitance −−10 pF
Crystal oscillator input CRIN (external clock)
g
m
mutual conductance at start-up − 4 − mS
R
o
output resistance at start-up − 11 − kΩ
C
i
input capacitance −−10 pF
I
LI
input leakage current −10 − +10 µA
Crystal oscillator output CROUT (see Figs 3 and 4)
f
xtal
crystal frequency 4 25 − MHz
C
fb
feedback capacitance −−5pF
C
o
output capacitance −−10 pF
I
2
S-bus timing
CLOCK OUTPUT SCLK (see Fig.17)
T
cy
output clock period set by CLKPRE1
register
− 472.4 − ns
t
SCLKH
clock HIGH time −−− ns
−−− ns
−−− ns
t
SCLKL
clock LOW time −−− ns
−−− ns
−−− ns
t
su(SCLK)
set-up time − tbf − ns
− tbf − ns
− tbf − ns
t
h(SCLK)
hold time − tbf − ns
− tbf − ns
− tbf − ns
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Page 26

1997 Aug 11 26
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Notes
1. Timing reference voltage levels are 0.8 V and V
DDD
− 0.8 V.
2. Negative set-up time means that data may change after clock transition.
External RAM timing (see Figs 18 and 20)
t
AV-DV
address valid to data valid − tbf − ns
t
OE-DV
output enable to data valid − tbf − ns
t
W(W)
write pulse width − tbf − ns
t
su(A)
address set-up before start of write − tbf − ns
t
h(A)
address hold after end of write − tbf − ns
t
su(D-EW)
data set-up to end of write − tbf − ns
t
h(D-EW)
data hold after end of write − tbf − ns
t
OE-DA
output enable to data active − tbf − ns
t
OD-DI
output disable to data inactive − tbf − ns
Microcontroller interface timing (see Figs 18 and 20)
I
NPUT ALE
t
su(A-ALE)
address set-up before ALE LOW 25 −− ns
t
h(A-ALE)
address hold after ALE LOW 25 −− ns
t
ALEL
input LOW time 1 × ADC
CLK+15
−− ns
t
ALEH
input HIGH time 1 × ADC
CLK+15
−− ns
t
d(ALEL-WRL)
delay time ALE LOW to WR LOW −−− ns
t
r
rise time −−− ns
t
f
fall time −−240 ns
INPUTS RDI AND WRI
t
IL(R/W)
input LOW time 1 × ADC
CLK+15
−− ns
t
IH(R/W)
input HIGH time 1 × ADC
CLK+15
−− ns
t
r
rise time −−− ns
t
f
fall time −−240 ns
READ MODE
t
d(RLDV)
delay time RD LOW to DA0 to DA7
valid
2 × ADC
CLK+35
−− ns
t
d(RHDX)
delay time RD HIGH to DA0 to DA7
high-impedance
15 −− ns
WRITE MODE
t
su(QVWX)
set-up time WR LOW to
DA0 to DA7
−−− ns
t
h(WHQX)
hold time WR HIGH to DA0 to DA7
3-state
2 × ADC
CLK+25
−− ns
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Page 27

1997 Aug 11 27
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Fig.17 I2S-bus timing.
DD
V – 0.8 V
0.8 V
DD
V – 0.8 V
0.8 V
t
SCLKH
MGL507
t
SCKL
T
cy
SCLK
WCLK
DATA
MISC
t
h(SCLK)
t
su(SCLK)
Fig.18 Microcontroller interface timing; parallel read mode.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGK253
ALE
RDi
DA0
to
DA7
t
ALEL
3
DATA OUT
A0 to A7
9
t
d(RHDX)
13
t
d(RLDV)
t
su(A-ALE)
t
h(A-ALE)
t
IH(R/W)
t
ALEH
Page 28

1997 Aug 11 28
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Fig.19 Microcontroller interface timing; parallel write mode.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGK254
ALE
WRi
DA0
to
DA7
DATA IN
A0 to A7
9
t
d(ALEL-WRL)
t
IH(R/W)
t
su(A-ALE)
t
su(QVWX)
t
h(A-ALE)
t
h(WHDX)
Fig.20 External RAM timing.
handbook, full pagewidth
MBH995
ADDRESS
DATA
WE
OE
A0
t
su(A)
t
su(D-EW)
t
su(D-EW)
t
AD-DV
t
h(A)
t
OE-DA
A1 A2 A3 A4
D1
write cycle write cycleread cycle
X D2 D1
t
OE-DV
t
W(W)
t
OD-DI
Page 29

1997 Aug 11 29
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
APPLICATION INFORMATION
The complete data path chipset consists of two ICs, the CD decoder (or DSP) device and the block decoder/host
interface manager. In addition to these components a general purpose microcontroller and tracking servo is necessary
to produce a complete controller system for a DVD mechanism. The DSP, block decoder and microcontroller are shown
highlighted in Fig.21. An ADC application circuit is illustrated in Fig.22.
Fig.21 Basic DVD player block diagram.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGK255
CD-DSP
DEMODULATION
C1-C2 ERROR CORRECTOR
BLOCK
DECODER
(FOR CD-ROM
COMPATIBILITY)
AND
HOST
INTERFACE
AUDIO DAC
PC host
interface
RAM BUFFER
SYSTEM
CONTROLLER
PRE-
AMPLIFIER
RAM BUFFER
SERVO CONTROL
PD TRACKING
(3 BEAM OPTIONAL FOR
BACKWARD CD-ROM
COMPATIBILITY)
SLED/FOCUS
ACTUATORS
spindle
motor
laser
MECHANISM/SERVO SUBSYSTEM DECODER/DATA PATH SUBSYSTEM
audio L/R
output
user
key
switches
Page 30

1997 Aug 11 30
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
Fig.22 ADC application circuit.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGK256
100 kΩ
10 kΩ
R14
4.7 Ω
R25
4.7 Ω
47 µF (50 V)
C11
47 µF
(50 V)
C15
47 µF
(50 V)
C14
100 nF
AGND1
AGND1
V
CC
V
CC
C10
100
nF
98
97
100
123456789
99
AGND1
TP5
TP1
R28
C18
22
nF
C17
22
nF
C19
SAA7335
TP6
R29
2.2 nF
C16X6
HF input
AGND1
Page 31

1997 Aug 11 31
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
PACKAGE OUTLINE
UNIT
A
max.
A1A2A3bpcE
(1)
eH
E
LL
p
Zywv θ
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
mm
1.6
0.20
0.05
1.5
1.3
0.25
0.28
0.16
0.18
0.12
14.1
13.9
0.5
16.25
15.75
1.15
0.85
7
0
o
o
0.12 0.10.21.0
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
0.75
0.45
SOT407-1
95-12-19
97-08-04
D
(1) (1)(1)
14.1
13.9
H
D
16.25
15.75
E
Z
1.15
0.85
D
b
p
e
θ
E
A
1
A
L
p
detail X
L
(A )
3
B
25
c
D
H
b
p
E
H
A
2
v M
B
D
Z
D
A
Z
E
e
v M
A
X
1
100
76
75
51
50
26
y
pin 1 index
w M
w M
0 5 10 mm
scale
LQFP100: plastic low profile quad flat package; 100 leads; body 14 x 14 x 1.4 mm
SOT407-1
Page 32

1997 Aug 11 32
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“IC Package Databook”
(order code 9398 652 90011).
Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering techniques are suitable for all LQFP
packages.
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several techniques exist for reflowing; for example,
thermal conduction by heated belt. Dwell times vary
between 50 and 300 seconds depending on heating
method. Typical reflow temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C.
Preheating is necessary to dry the paste and evaporate
the binding agent. Preheating duration: 45 minutes at
45 °C.
Wave soldering
Wave soldering is not recommended for LQFP packages.
This is because of the likelihood of solder bridging due to
closely-spaced leads and the possibility of incomplete
solder penetration in multi-lead devices.
If wave soldering cannot be avoided, the following
conditions must be observed:
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave)
soldering technique should be used.
• The footprint must be at an angle of 45° to the board
direction and must incorporate solder thieves
downstream and at the side corners.
Even with these conditions, do not consider wave
soldering LQFP packages LQFP48 (SOT313-2),
LQFP64 (SOT314-2) or LQFP80 (SOT315-1).
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Maximum permissible solder temperature is 260 °C, and
maximum duration of package immersion in solder is
10 seconds, if cooled to less than 150 °C within
6 seconds. Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
Repairing soldered joints
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonallyopposite end leads. Use only a low voltage soldering iron
(less than 24 V) applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact
time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C. When
using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in
one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
Page 33

1997 Aug 11 33
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
DEFINITIONS
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
PURCHASE OF CD/DVD DEVICES
Supply of this CD/DVD IC does not convey an implied license under any patent right to use this IC in any CD or DVD
application.
PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I
2
C COMPONENTS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
Purchase of Philips I
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I2C patent to use the
components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
Page 34

1997 Aug 11 34
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
NOTES
Page 35

1997 Aug 11 35
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DSP for CD and DVD-ROM systems
SAA7335
NOTES
Page 36

Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company
© Philips Electronics N.V. 1997 SCA55
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 40 27 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +63 2 817 3474
Poland: Ul. Lukiska 10, PL 04-123 WARSZAWA,
Tel. +48 22 612 2831, Fax. +48 22 612 2327
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 755 6918, Fax. +7 095 755 6919
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 1231,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 7430 Johannesburg 2000,
Tel. +27 11 470 5911, Fax. +27 11 470 5494
South America: Rua do Rocio 220, 5th floor, Suite 51,
04552-903 São Paulo, SÃO PAULO - SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax. +55 11 829 1849
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 3 301 6312, Fax. +34 3 301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 632 2000, Fax. +46 8 632 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2686, Fax. +41 1 481 7730
Taiwan: Philips Semiconductors, 6F, No. 96, Chien Kuo N. Rd., Sec. 1,
TAIPEI, Taiwan Tel. +886 2 2134 2865, Fax. +886 2 2134 2874
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Talatpasa Cad. No. 5, 80640 GÜLTEPE/ISTANBUL,
Tel. +90 212 279 2770, Fax. +90 212 282 6707
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +380 44 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 181 730 5000, Fax. +44 181 754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 625 344, Fax.+381 11 635 777
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors, Marketing & Sales Communications,
Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218, 5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 34 Waterloo Road, NORTH RYDE, NSW 2113,
Tel. +61 2 9805 4455, Fax. +61 2 9805 4466
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213, Tel. +43 160 1010,
Fax. +43 160 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 200 733, Fax. +375 172 200 773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: see South America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15th floor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 689 211, Fax. +359 2 689 102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +852 2319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Prags Boulevard 80, PB 1919, DK-2300 COPENHAGEN S,
Tel. +45 32 88 2636, Fax. +45 31 57 0044
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615800, Fax. +358 9 61580920
France: 4 Rue du Port-aux-Vins, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 40 99 6161, Fax. +33 1 40 99 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 23 53 60, Fax. +49 40 23 536 300
Greece: No. 15, 25th March Street, GR 17778 TAVROS/ATHENS,
Tel. +30 1 4894 339/239, Fax. +30 1 4814 240
Hungary: see Austria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Band Box Building, 2nd floor,
254-D, Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli, MUMBAI 400 025,
Tel. +91 22 493 8541, Fax. +91 22 493 0966
Indonesia: see Singapore
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax. +353 1 7640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, PO Box 18053,
TEL AVIV 61180, Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax. +972 3 649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS, Piazza IV Novembre 3,
20124 MILANO, Tel. +39 2 6752 2531, Fax. +39 2 6752 2557
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku, TOKYO 108,
Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5077
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381
Middle East: see Italy
Printed in The Netherlands 547027/1200/01/pp36 Date of release: 1997 Aug 11 Document order number: 9397 750 01764
 Loading...
Loading...