Page 1
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
SAA7240
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
2001 Oct 22
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
1.1 General
1.2 External interfaces
1.3 CPU-related features
1.4 MPEG-2 System Processor (MSP) features
1.5 Compatibility with other devices
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1 Limitation notes
2.2 IntegratedConditionalAccessModule(ICAM®)
licensing requirements
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
4 BLOCK DIAGRAMS
5 PINNING INFORMATION
5.1 Pinning
5.2 Pin description
5.3 Pin list in numerical order
6 LIMITING VALUES
7 HANDLING
8 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
9 DC CHARACTERISTICS
9.1 Power saving in Sleep and Coma modes
9.2 Maximum allowable load capacitance on
output pins
10 APPLICATION INFORMATION
10.1 Application examples of the multi-master mode
10.2 Memory configurations
11 PACKAGE OUTLINE
12 SOLDERING
12.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages
12.2 Reflow soldering
12.3 Wave soldering
12.4 Manual soldering
12.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for
wave and reflow soldering methods
13 DATA SHEET STATUS
14 DEFINITIONS
15 DISCLAIMERS
16 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
2001 Oct 22 2
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
1 FEATURES
1.1 General
• Conditional access descrambling Digital Video
Broadcasting (DVB) compliant, MULTI2 compliant and
(1)
ICAM
• Targeted to BSkyB 3.00 and Canal+basic box 3.02 and
web box 1.01 applications
• Stream demultiplexing: Transport Stream (TS),
Packetized Elementary Stream(PES), Program Stream
(PS) and Proprietary data streams
• Internal 32-bit MIPS RISC-based CPU, supporting
MIPS16 instruction set and running at 81 MHz
• Low-power Sleep modes supported across the chip
• Support for external co-processor
• 0.25 µm technology
• Power supply of 2.5 V for the core and 3.3 V for the
peripherals, to be TTL level compatible
• Comprehensive driver software and development tool
support
• Package: SQFP208.
1.2 External interfaces
The SAA7240 supports the following external interfaces:
• Versatile transport streaminput/output at 13.5 Mbytes/s
configurable in parallel or serial mode. Interfaces to
IEEE 1394 devices (such as Philips PDI 1394 chip-set)
in full-duplex mode and to external descramblers
through a Common Interface (CI) device. The following
interfaces are supported:
– 3 parallel TS input/output ports
– 2 parallel TS input/output ports and 3 serial TS ports
– 1 parallel TS input/output port and 5 serial TS ports
– 6 serial TS input/output ports.
• A microcontroller extension bus, supporting:
– 16-bit and 32-bit data buses
– Up to 64 Mbytes addressing range
– Synchronous Dynamic RAM (SDRAM) interface
– Dynamic RAM interface
– Read Only Memory (ROM) interface
– Flash memory interface
– Interface to various peripherals
compliant
– Synchronous interface to communicate with the
integrated MPEG Audio Video Graphics Decoder
(AVGD) SAA7215 at 40.5 MHz
– Large endian and small endian byte addressing
– A multi-master mode (master and slave modes).
• 2-channel Direct Memory Access (DMA) for fast block
move to/from any memory location
• Up to 12 chipselects available, some can be configured
as general purpose ports
• An IEEE 1284 interface (Centronics) with DMA engine
supporting master and slave modes. Usable as a
general purpose port
• TwoUART (RS232) dataports with DMAcapabilities (at
187.5 kbit/s), including hardware flow control signals
RXD, TXD, RTS and CTS for modem support
• A Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) to connect an
off-chip modem analog front-end
• An elementary UART with DMA capabilities, dedicated
to front panel devices for instance
• Two dedicated smart card reader interfaces (ISO 7816
compatible) with DMA capabilities. One interface is
intended for the conditional access and is shared with
the Integrated ConditionalAccess Module (ICAM) when
ICAM is enabled; the second interface may be used for
pay-per-view
• Two I2C-bus master/slave transceivers with DMA
capabilities, supporting the standard (100 kbit/s) and
fast (400 kbit/s) I2C-bus modes
• 32-bit general purpose port
• Eight interrupt inputs
• Parallel audio video interface to the MPEG AVGD
decoder SAA7215
• One Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) output with 8-bit
resolution
• An Extended JTAG (EJTAG) interface for board test
support.
(1) Integrated Conditional Access Module (ICAM
) is an
intellectual property of News Data System
Corporation.
2001 Oct 22 3
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
1.3 CPU-related features
The SAA7240 contains an embedded RISC CPU, which
incorporates the following features:
• A 32-bit PR3930 core, running at 81 MHz
• Support for large and small byte addressing modes; is
ready for Windows
(1)
CE and pSOS
(2)
operating
systems
• 8-kbyte 2-way set of associative instruction cache
• 4-kbyte 4-way set of associative data cache
• A programmable low-power mode, including wake-up
on interrupt
• A Memory Management Unit (MMU) with 32 odd/even
entries and variable page sizes
• Multiply/accumulate/divide unit with fast
multiply/accumulate for 16-bit and 32-bit operands
• Twofully independent 24-bit timers andone24-bit timer,
including watchdog facilities
• A real-time clock unit (active in Sleep mode)
• Built-in software debug support unit as part of extended
JTAG debug interface
• On-chip SRAM of 4 kbytes for storing code that needs
fast execution.
1.4 MPEG-2 System Processor (MSP) features
• A flexible re-router to support many combinations of the
transport stream input/output interfaces:
– Connection to serial or parallel Common Interface IC
– Connection to serial or parallel 1394 IC in full-duplex
mode
– Static dual front-end handling of channel decoders
– A maximum frequency of up to 13.5 Mbytes/s in
parallel mode and up to 81 Mbits/s in serial mode.
• A demultiplexer scheme, which is fully compliant with
Canal+ and BSkyB specifications:
– Hardware-based parsing of transport, program and
proprietary software data streams. The maximum
input rate is 13.5 Mbytes/s in parallel mode and
81 Mbits/s in serial mode
– Up to 40, 13-bit Packet Identifier (PID) filters applied
on the PID value. 32 PID filters can be dedicated to
filter packets containing sections; four PID filters to
filter transport packets header; four PID filters to
parse audio, video, teletext and subtitle data
(1) Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation
(2) pSOS is a registered trademark of Wind River Systems, Inc.
– 4 TS/PES packet header filters (filter condition of
3 bytes, including PID value for TS packet header
and specific filter condition for PES packet header)
– 32 section filters based on a flexible number of filter
conditions to retrieve PSI, SI, Private data and EPG,
etc. Each section filter supports 48 filters conditions
of 12 bytes; each filter condition can be negated or
masked on a bit level
– 7 ECM/EMM filters stored in on-chip RAM for ICAM
implementation (ECM/EMM packets are stored in
on-chip RAM)
– Flexible 40 channel DMA-based storage of the
32 section sub-streams and four TS/PES data
sub-streams and 4 TS/PES packet headers in
external memory
– System time base management with a double
counter mechanism for clock control and
discontinuity handling
– Two Presentation TimeStamp (PTS)/Decoding Time
Stamp (DTS) timers
– A General Purpose/High Speed (GP/HS)filter, which
can serve as an alternative input from IEEE 1394
devices, for example. The IEEE 1394 GP/HS mode
supports packet insertion and has an internal SRAM
for storing two packets. It can also output either
scrambled or descrambled TS to IEEE 1394 devices.
• A real time descrambler, supporting different
descrambler algorithms and consisting of four modules:
– A control word bank, containing 14 pairs (odd or
even) of control words and a default control word
– The DVB descrambler core, implementing the stream
decipher and block decipher algorithms
– The MULTI2 descrambler algorithm, implementing
the CBC and OFB mode descrambling functions.
In this mode, the maximum frequency is 9 Mbytes/s
(72 Mbits/s)
– The Integrated Conditional Access Module (ICAM),
including an ISO 7816 compliant UART to interface
the conditional access smart card.
1.5 Compatibility with other devices
The SAA7240 seamlessly interfaces to the integrated
MPEG AVGD decoder SAA7215HS. It is also backward
compatible with the other devices of the family. The
following modes/combinations are supported:
• SAA7240 with SAA7215HS seamless
• Pinning compatibility with the SAA7219HS.
2001 Oct 22 4
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAA7240 is a transport MPEG-2 source decoder
designed for application in set-top boxes in aDigital Video
Broadcast (DVB)environment.Itistargeted to BSkyB 3.00
and Canal+ basic box and web box applications. The
device is part of a comprehensive source decoding kit that
contains all the hardware and software required to receive
and decode MPEG-2 transport streams, including
descrambling and demultiplexing.
In addition, it includes a PR3930 core, which is a 32-bit
MIPS RISC-based CPU core supporting the MIPS16
instruction set (to reduce memory requirements) and
several peripheral interfaces such as UARTs, I2C-bus
units, an IEC 1883, and an IEEE 1284 (Centronics)
interface.The SAA7240 is thereforecapableof performing
all controller tasks in digital television applications.
Furthermore, the SAA7240 complies with DVB, ICAM and
MULTI2 descrambler standards.
The SAA7240 receives transport streams through a
versatile stream input interface capable of handling both
byte-parallel and bit-serial streams, in various formats,
supportingdatastreams up to and including13.5 Mbytes/s
in parallel mode and 81 Mbits/s in serial mode. The data
stream is first applied to an on-chip descrambler with a
DVB descrambling algorithm, on the basis of 14 control
word pairs stored in an on-chip RAM.
Demultiplexingis subsequently applied tothedata stream,
to separate up to 40 individual data streams. The
demultiplexer section includes clock recovery and
timebase management. Program Specific Information
(PSI), Service Information (SI), Conditional Access (CA)
messages and private data are selected and stored in
external memory, for subsequent off-line processing by
the internal PR3930 CPU core.
To support advanced board testing facilities,the SAA7240
includes Boundary Scan Test (BST) hardware, according
to the JTAG standard. The device features flexible
low-power Sleep modes, which independently control the
activity of each functional block and can sustain set-top
box standby functionality, thus eliminating the need for a
separate front-panel controller.
The SAA7240 requires a supply voltage of 3.3 V for the
I/O pads and a supply voltage of 2.5 V for the core.
2.1 Limitation notes
Althoughthemostadvanced techniques and sophisticated
tools are used during the design and validation phases,
some design limitations giving some restrictions for
specific applications might be discovered during the
characterization of the SAA7240 and during its life time.
If such an eventuality occurs, a limitation note will be
issued, describing the deviation against the specification
and the advised work-around if any. This limitation note,
alsosometimescalled ‘anomaly sheet’ or ‘buglist’,isgiven
to customers when they are in the initial design-in phase.
Once the design-in is in production phase, customers are
informed about any new limitation if the severity is
estimated to be high.
Please contact your nearest Philips Semiconductor sales
office for more information.
2.2 Integrated Conditional Access Module (ICAM
licensing requirements
Companies planning to use ICAMimplementation in any
final product must obtain a license from News Data
System Corporation before designing such products.
Additionalper-chip royalties mayberequired and aretobe
paid by the purchaser to News Data System Corporation.
For information on the Integrated Conditional Access
Module features, a non-disclosure agreement must be
signed with Philips Semiconductors to get the ICAM
specification.
Please contact your nearest Philips Semiconductor sales
office for more information.
®
)
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGE
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SAA7240 SQFP208 plasticshrink quad flat package, 208 leads (lead length 1.3 mm);
body 28 × 28 × 34 mm; high stand-off height
2001 Oct 22 5
SOT316-1
Page 6
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
u
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Oct 22 6
ll pagewidth
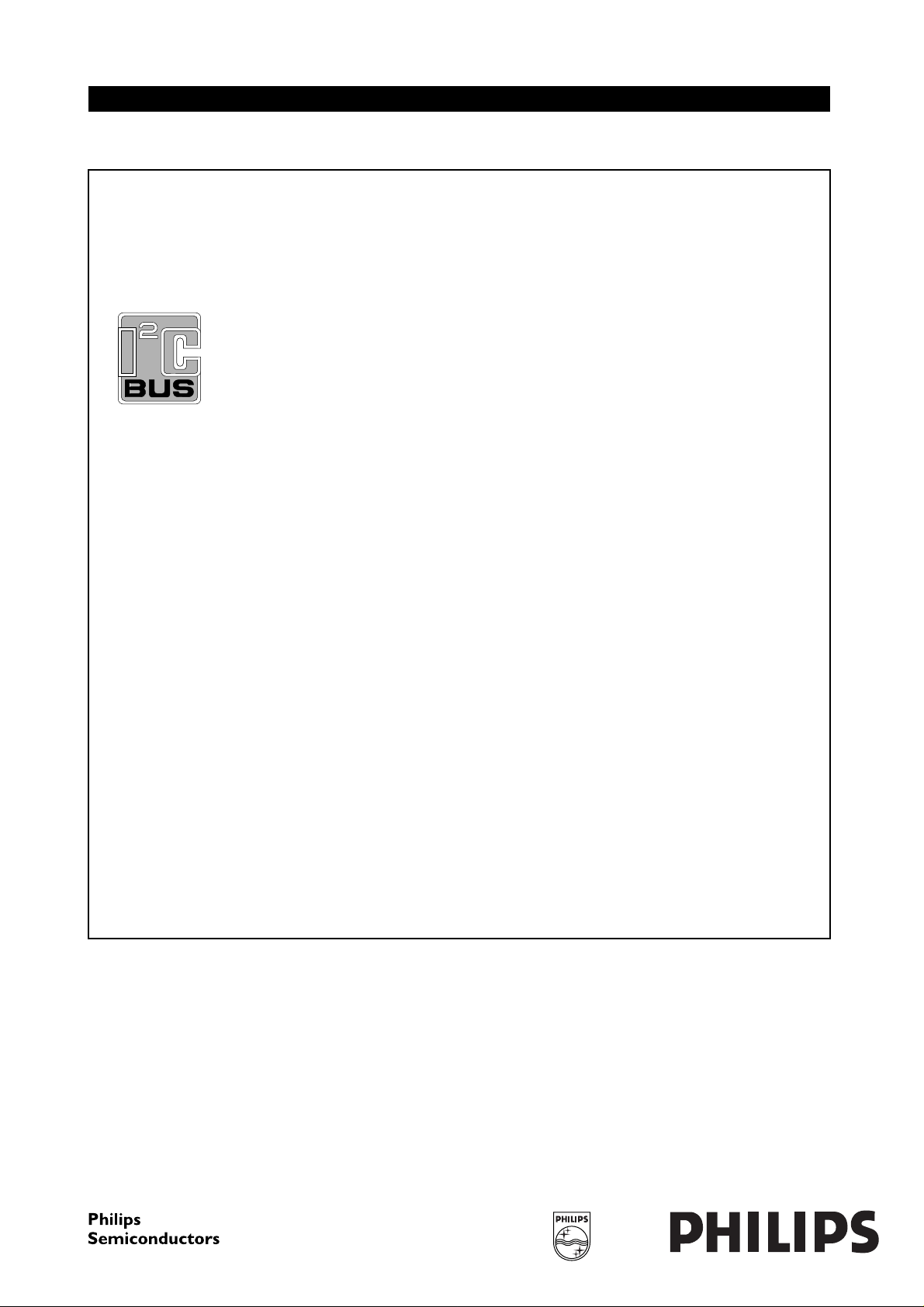
4 BLOCK DIAGRAMS
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
CPU section
MIPS
PR3930
CORE
DATA CACHE
INSTRUCTION CACHE
TIMER 1
TIMER 2
TIMER 3 (WATCHDOG)
DSU
EJTAG
SAA7240
S
PI-BUS
CTRL
EXTENSION BUS
CONTROLLER AND
GPDATA PKTDATA GPD
INPUT/OUTPUT ROUTER
MMU
PI-bus
SMM
CARD READER
DMA
UART
12
01 0 10
MM
SSI
PWM
PWM
DEMUX AND
DESCRAMBLERS
BUFFER POOL CONTROLLER
M
MS
PIO
INTERFACE
I2C-bus
IEEE
1284
MSP section
AUDIO AND
VIDEO
INTERFACE
SS S
RTC
32 kHz
INTERRUPT
CONTROLLER
(1)
AV PES
interface
RESETN
CLK
4-KBYTE
SRAM
JTAG
EJTAG
interface
M = master peripheral with embedded DMA channel
S = slave peripheral
(1) The MSP section is shown in more detail in Fig.2.
extension
bus
smart card
interface
UART
interface
SSI
interface
PIO
interface
Fig.1 Block diagram.
I2C-bus
interface
IEEE 1284
interface
Peripheral section
FCE811
Page 7
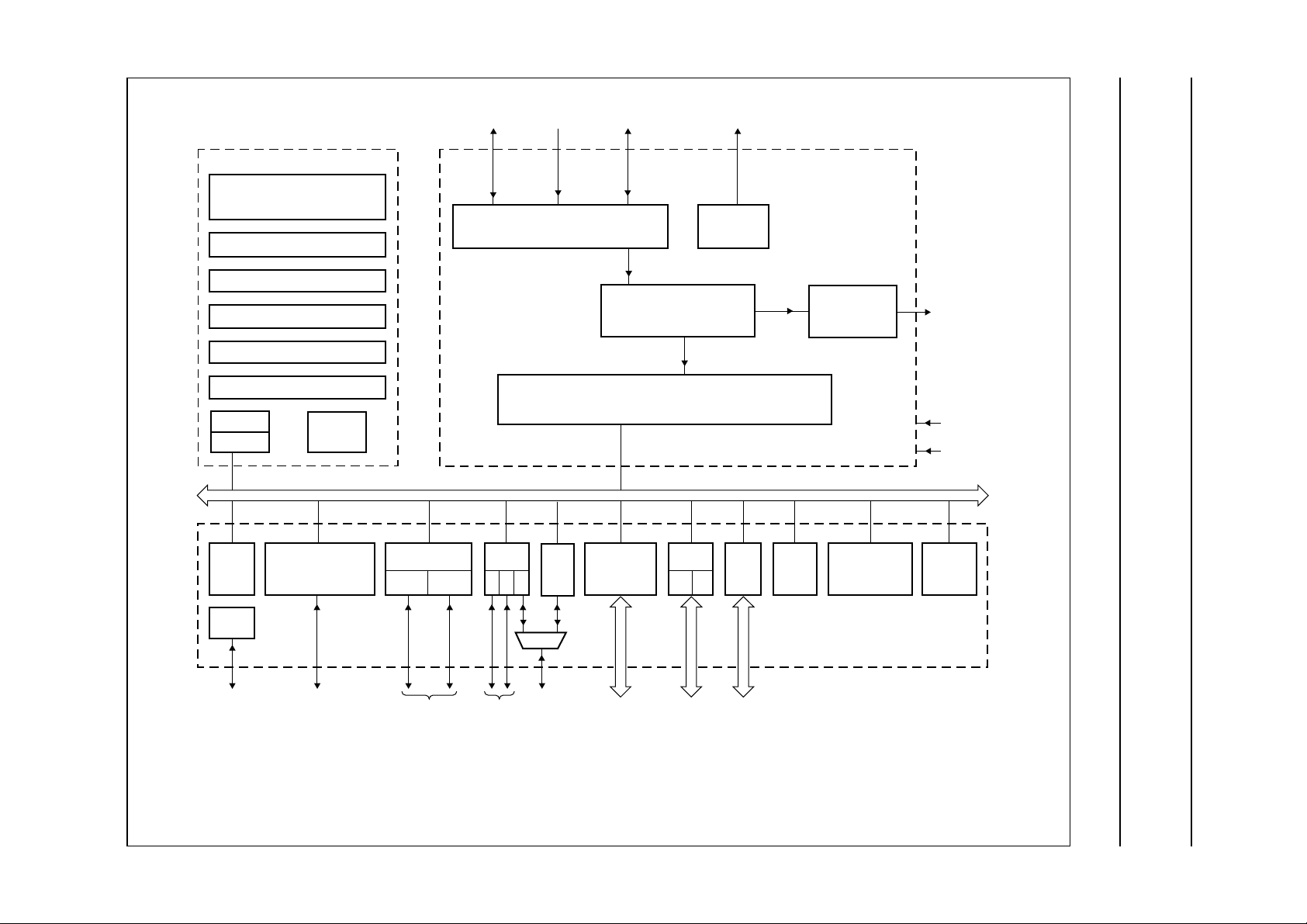
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
handbook, full pagewidth
smart
card
interface
INTERRUPT
HANDLER
BIST
CONTROLLERS
DVB
DESCRAMBLER
CA/UART
MODULE
ECM/EMM
FILTER
RAM
TO / FROM SERIAL OR PARALLEL PORTS
PKTDATA
INPUT / OUTPUT ROUTER
INPUT
INTERFACE
PID
FILTER
MULTI2
DESCRAMBLER
SECTION
FILTER
GP/HS
MPEG bus
TS-PES
PACKET
FILTER
GPD PWMGPDATA
PCR/SCR
TS-PES
HEADER
FILTER
4432
PWM
AV
INTERFACE
CONTROL &
STATUS
REGISTERS
AV PES
interface
BUFFER POOL CONTROLLER
WITH 40 DMA CHANNELS
PI-bus
Fig.2 MSP block diagram.
2001 Oct 22 7
PI
INTERFACE
FCE824
Page 8
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
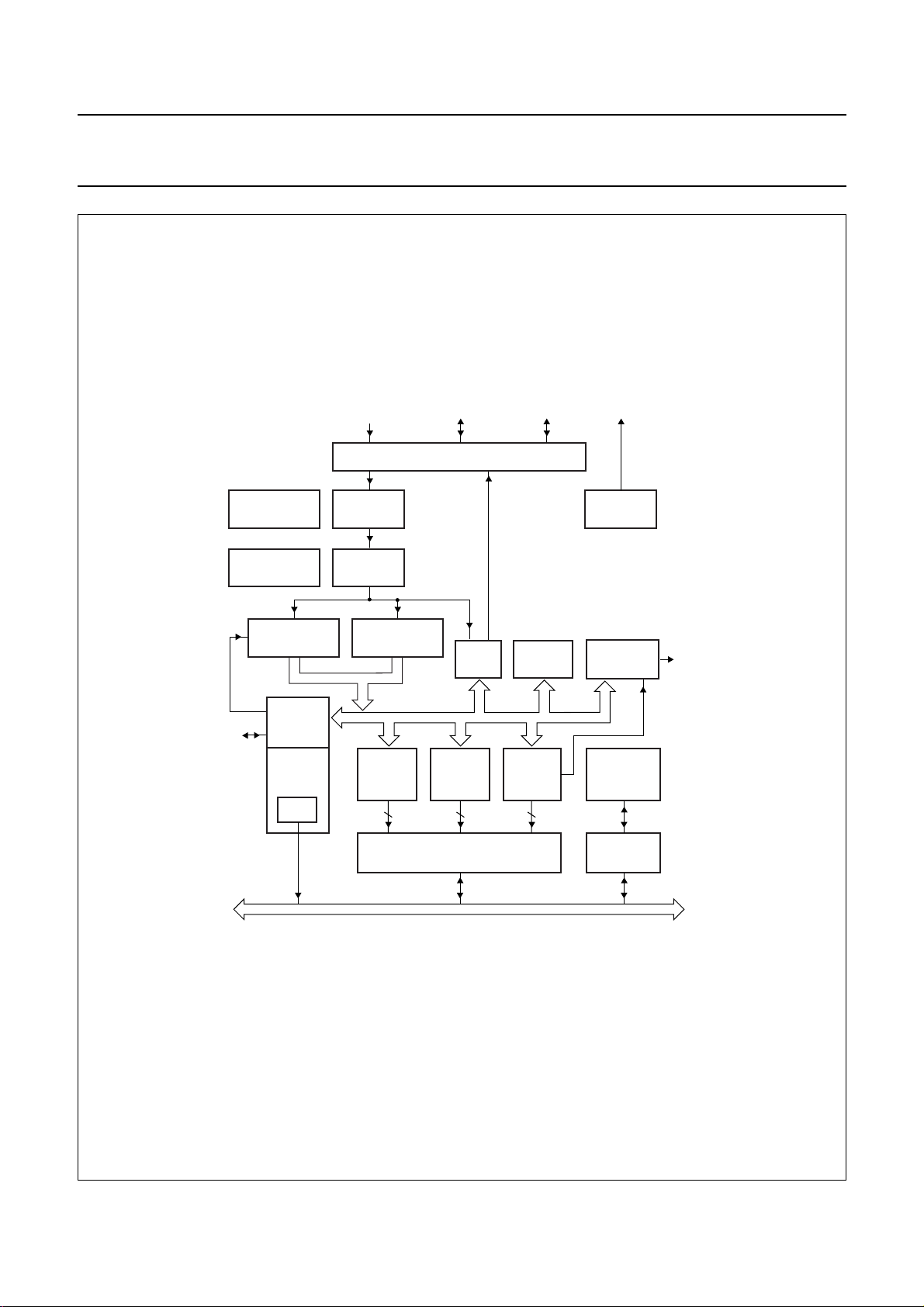
5 PINNING INFORMATION
5.1 Pinning
handbook, halfpage
208
1
SAA7240HS
52
53
Fig.3 Pin configuration.
157
104
156
105
FCE812
2001 Oct 22 8
Page 9
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Oct 22 9
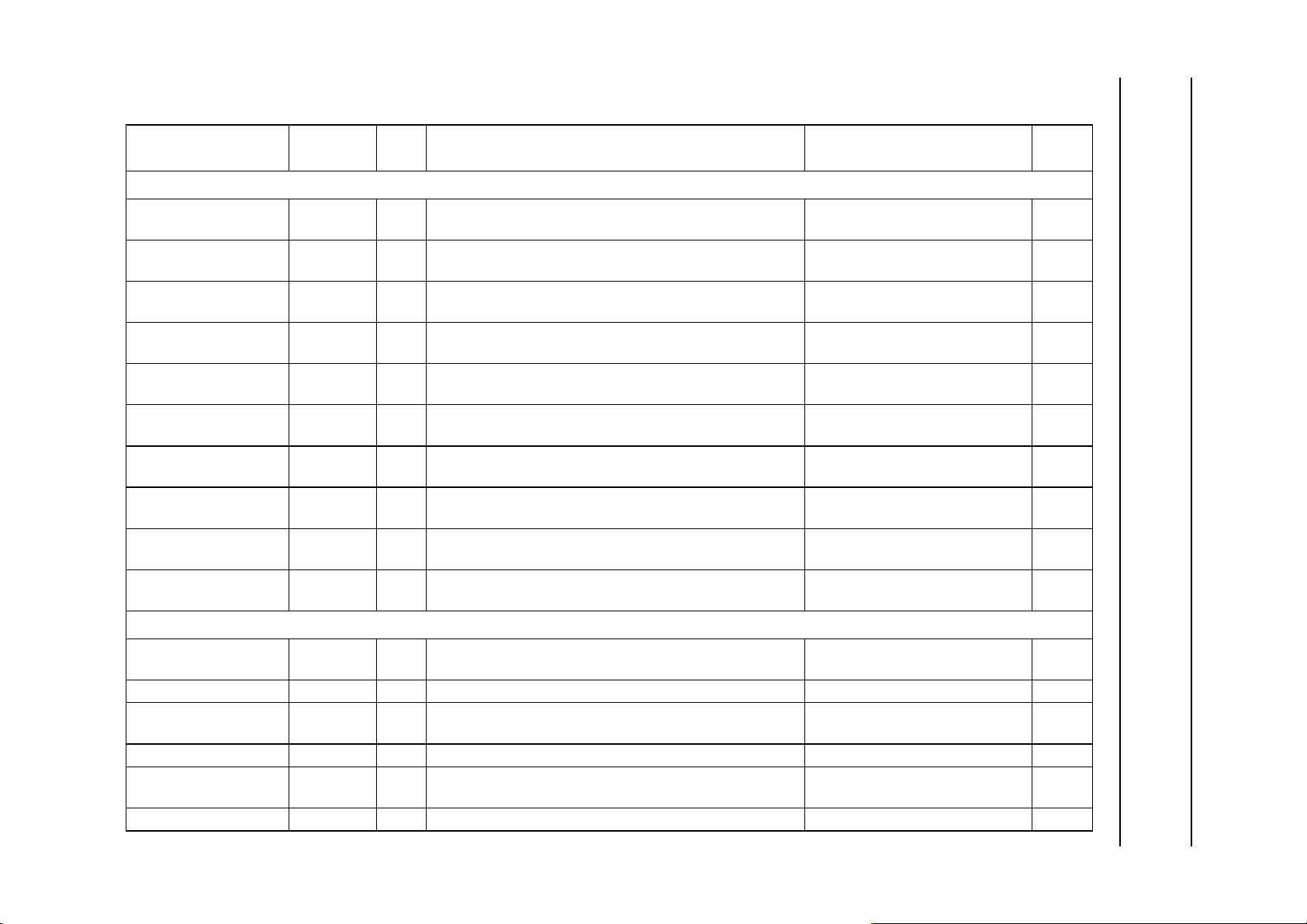
5.2 Pin description Table 1 Interface signal descriptions
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION BUFFER TYPE
Programmable input/output port
PIO[0:7]/INT[0:7] 105 to 112 I/O I/O lines or interrupt inputs bidirectional; CMOS input; 2 mA
output drive
PIO8 113 I/O I/O line bidirectional; CMOS input; 2 mA
output drive
PIO9 114 I/O I/O line bidirectional; CMOS input; 2 mA
output drive
PIO10/BPN 116 I/O I/O line or bus pre-empt; this requires the bus owner to
release the bus after the current transfer
PIO11/VPP 117 I/O I/O line or VPP; control signal for the supply voltage
(ICAM)
PIO12/C8 118 I/O I/O line or IO data for conditional access (ICAM) bidirectional; CMOS input;
PIO13/C4 119 I/O I/O line or IO data for conditional access (ICAM) bidirectional; 8 mA output drive;
PIO14/BRN 120 I/O I/O line or bus request input bidirectional; CMOS input; 2 mA
PIO15/BGN 121 I/O I/O line or bus grant output bidirectional; CMOS input; 2 mA
PIO[16:31]/D[16:31] 20 to 11,
9 to 4, 2
Extension bus interface
D[0:15] 41 to 28,
25 to 21
A[0:21] 63 to 90 O address bus 3-state output; 2 mA output drive LOW
A[22:25]
RAS0N 49 O row access strobe for DRAM and SDRAM bank 0 3-state output; 2 mA output drive HIGH
RAS1N/DCS1N 48 O row access strobe for DRAM and SDRAM bank 1 or
LCASN/LBA#/SIZE0 46 O column access strobe lower byte 3-state output; 2 mA output drive HIGH
(1)
I/O I/O lines or upper data bus in 32-bit configuration bidirectional; CMOS input;
I/O lower 16-bit data bus bidirectional; CMOS input;
n.a. address bus extension shared with the IEEE 1284
interface
SDRAM chip select bank 1
bidirectional; CMOS input; 2 mA
output drive
bidirectional; CMOS input; 2 mA
output drive
8 mA output drive; open-drain;
open-drain
output drive
output drive
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
n.a. n.a.
3-state output; 2 mA output drive HIGH
RESET
STATE
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Page 10
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Oct 22 10
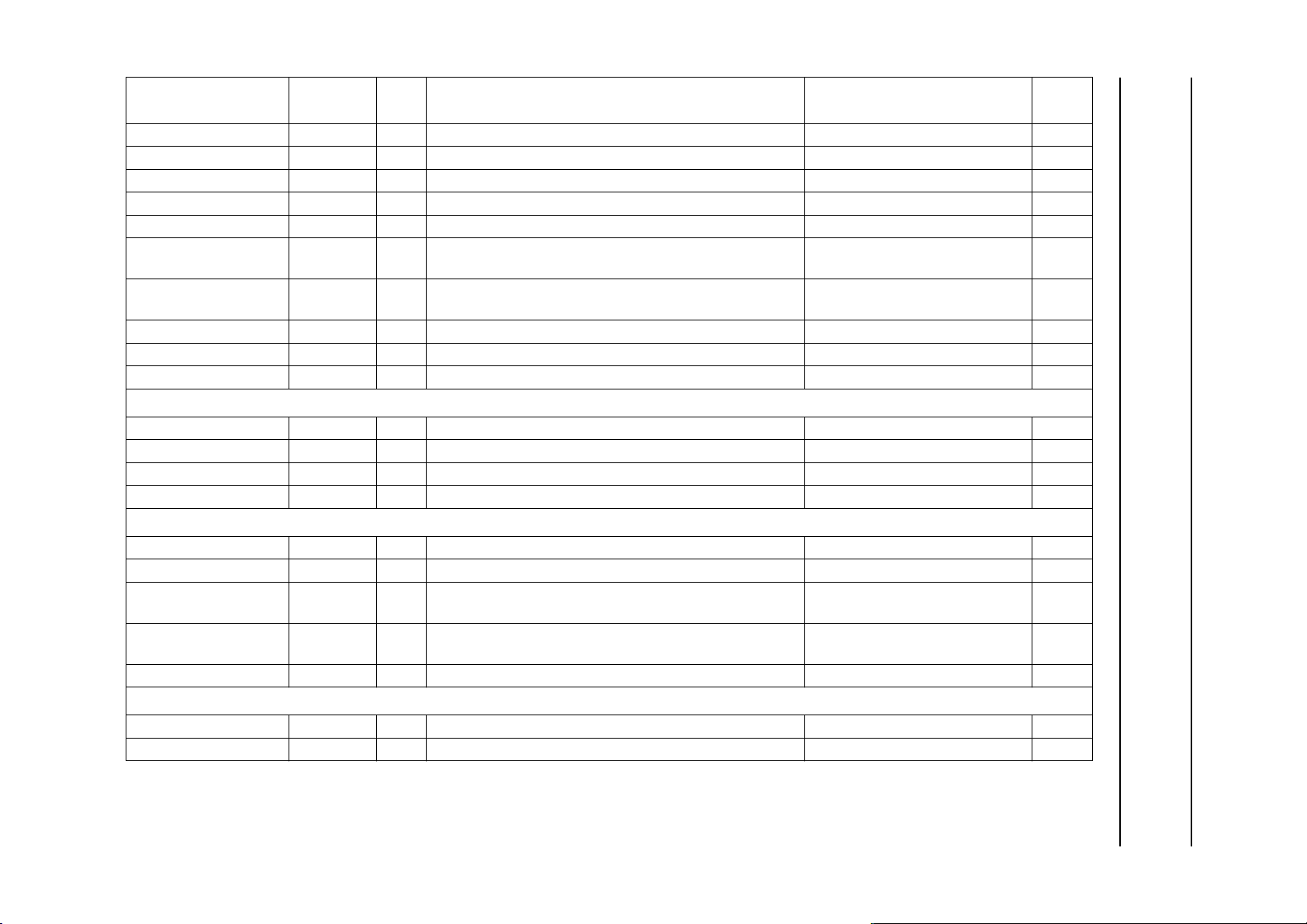
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION BUFFER TYPE
MLCASN/BAA#/SIZE1 45 O column access strobe mid lower byte 3-state output; 2 mA output drive HIGH
MUCASN/SIZE2 44 O column access strobe mid upper byte 3-state output; 2 mA output drive HIGH
UCASN 42 O column access strobe upper byte 3-state output; 2 mA output drive HIGH
WEN 62 O write enable 3-state output; 2 mA output drive HIGH
DCS0N 47 O chip select for SDRAM bank 0 3-state output; 2 mA output drive HIGH
CS[0:8]N 56 to 50,
O chip select 3-state output; 2 mA output drive HIGH
60, 61
CS[10:9]N
(1)
n.a. chip select extension shared with the IEEE 1284
n.a. n.a.
interface
OEN/TSN 58 O output enable or Transfer Start indication 3-state output; 2 mA output drive HIGH
DTACK 59 I data termination acknowledge CMOS input Z
CLK 91 O 40.5 MHz clock 2 mA output drive T
UART 0 interface
TXD0 142 O UART 0 transmit data line 2 mA output drive HIGH
RXD0 141 I UART0 receive data line CMOS input Z
RTSN0 143 O UART 0 request to send 2 mA output drive HIGH
CTSN0 144 I UART 0 clear to send CMOS input Z
UART 1 and SSI interface
TXD1/V34_TXD
RXD1/V34_RXD
RTSN1/V34_FS
CTSN1/V34_CLK
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
138 O transmit data line or transmit serial data to the CODEC 2 mA output drive HIGH
137 I receive data line or receive serial data from CODEC CMOS input Z
139 I/O request to send (output) or Frame synchronization
reference from CODEC (input)
140 I clear to send or serial input clock from CODEC (up to
bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
CMOS input Z
3.375 MHz)
MCLK 146 O master clock to the CODEC (up to 36.864 MHz) 2 mA output drive T
UART 2 interface
TXD2 136 O UART 2 transmit data line 2 mA output drive HIGH
RXD2 135 I UART2 receive data line CMOS input Z
RESET
STATE
HIGH
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
Page 11

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Oct 22 11
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION BUFFER TYPE
2
C-bus 0 interface
I
SDA0 150 I/O data line bidirectional; CMOS input;
open-drain; 8 mA output drive
SCL0 149 I/O clock line bidirectional; CMOS input;
open-drain; 8 mA output drive
2
C-bus 1 interface
I
SDA1 148 I/O data line bidirectional; CMOS input;
open-drain; 8 mA output drive
SCL1 147 I/O clock line bidirectional; CMOS input;
open-drain; 8 mA output drive
Smart card 0 interface
SC_I/O0 134 I/O I/O line bidirectional; CMOS input;
open-drain; 8 mA output drive
CLK_CARD0 128 O clock to the card 2 mA output drive LOW
CMDVCCN0 129 O command of the card power supply 2 mA output drive HIGH
RSTIN0 132 O reset of the card 2 mA output drive HIGH
OFFN0 133 I card presence detection CMOS input Z
Smart card 1 interface
SC_I/O1 126 I/O I/O line bidirectional; CMOS input;
open-drain; 8 mA output drive
CLK_CARD1 122 O clock to the card 2 mA output drive LOW
CMDVCCN1 123 O command of the card power supply 2 mA output drive HIGH
RSTIN1 124 O reset of the card 2 mA output drive HIGH
OFFN1 125 I card presence detection CMOS input Z
Parallel or serial transport input interface from the front-end
PKTDATA[0:7] 164 to 157 I 8-bit primary TS data input CMOS input Z
PKTSTROBE 154 I/O byte strobe or bit strobe bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
PKTVALID 156 I data valid or bit stream word select CMOS input Z
PKTSYNC 155 I packet synchronization Z
RESET
STATE
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
Page 12

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Oct 22 12
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION BUFFER TYPE
GP/HS interface (1 parallel port or 2 serial ports)
GPDATA[0:7] 174 to 166 I/O GP/HS data bus bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
GPSYNC 176 I/O GP/HS synchronization bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
GPVALID 175 I/O GP/HS valid bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
GPSTROBE 177 I/O GP/HS strobe bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
Audio/video interface
AVD0/STRAP0 103 I/O MPEG audio/video data stream output port 0; latched in
PIO_STRAP register during reset
AVD1/STRAP1 102 I/O MPEG audio/video data stream output port 1; latched in
PIO_STRAP register during reset
AVD2/STRAP2 101 I/O MPEG audio/video data stream output port 2; latched in
PIO_STRAP register during reset
AVD3/STRAP3 100 I/O MPEG audio/video data stream output port 3; latched in
PIO_STRAP register during reset
AVD4/BIG 99 I/O MPEG audio/video data stream output port 4; latched in
PIO_STRAP register during reset
AVD5/BOOTCS0 98 I/O MPEG audio/video data stream output port 5; latched in
PIO_STRAP register during reset
AVD6/BOOTW1 97 I/O MPEG audio/video stream data output port 6; latched in
PIO_STRAP register during reset
AVD7/BOOTW0 96 I/O MPEG audio/video stream data output port 7; latched in
PIO_STRAP register during reset
A_STROBE 94 O audio data strobe in the AVD stream 2 mA output drive LOW
V_STROBE 93 O video data strobe in the AVD stream 2 mA output drive LOW
AV_ERROR 95 O flag for bit stream error (active HIGH) 2 mA output drive LOW
bidirectional; CMOS input;
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
bidirectional; CMOS input;
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
bidirectional; CMOS input;
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
bidirectional; CMOS input;
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
bidirectional; CMOS input;
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
bidirectional; CMOS input;
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
bidirectional; CMOS input;
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
bidirectional; CMOS input;
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
RESET
STATE
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
Page 13

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Oct 22 13
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION BUFFER TYPE
IEEE 1284 or transport stream interface
GPD0/TS_DAT0 190 I/O parallel data bus or data for serial TSS2_in interface bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
GPD1/TS_SYN0 191 I/O parallel data bus or sync for serial TSS2_in interface bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
GPD2/TS_VAL0 192 I/O parallel data bus or data valid for serial TSS2_in interface bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
GPD3/TS_CK0 193 I/O parallel data bus or clock for serial TSS2_in interface bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
GPD4/TS_VAL1 194 I/O parallel data bus or data valid for serial CI_out interface bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
GPD5/TS_SYN1 195 I/O parallel data bus or sync for serial CI_out interface bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
GPD6/TS_DAT1 196 I/O parallel data bus or data for serial CI_out interface bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
GPD7/TS_CK1 197 I/O parallel data bus or clock for serial CI_out interface bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
NSELECTIN/TS_DAT2 199 I/O host to peripheral select line or data for serial CI_in
interface
NINIT/TS_SYN2 200 I/O host to peripheral control line or sync for serial CI_in
interface
NSTROBE/TS_VAL2 201 I/O host to peripheral strobe line or data valid for serial CI_in
interface
NACK/CS10N/TS_CK2 202 I/O peripheral acknowledge line or clock for serial CI_in
interface or chip select
BUSY/CS9N 203 I/O peripheral busy line or chip select bidirectional; CMOS input;
PERROR/A25 204 I/O peripheral error or address line bidirectional; CMOS input;
SELECT/A24 205 I/O peripheral on-line or address line bidirectional; CMOS input;
NAUTOF/A23 206 I/O peripheral error line or address line bidirectional; CMOS input;
bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
bidirectional; CMOS input;
2 mA output drive
bidirectional; CMOS input;
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
RESET
STATE
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Z
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
Page 14

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Oct 22 14
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION BUFFER TYPE
NFAULT/A22 207 I/O host to peripheral control line or address line bidirectional; CMOS input;
3-state output; 2 mA output drive
DIR1284 208 O direction control of the external buffers 2 mA output drive LOW
PWM interface
PWM0 165 O PWM output for VCXO control open-drain; 8 mA output drive LOW
System interface
RESETN 1 I/O general system reset; active LOW; the pad is asserted
LOW (if enabled) when the internal watch dog time-out is
detected
XTAL1 153 I 13.5 MHz crystal input oscillator input T
XTAL2 152 I/O 13.5 MHz crystal output or external clock input oscillator output T
JTAG and test interface
TDO 178 O test data output/target PC output 2 mA output drive Z
TDI 179 I test data input/debug interrupt CMOS input Z
TMS 180 I test mode select CMOS input Z
TRST 181 I test reset CMOS input Z
TCK 184 I test clock CMOS input Z
EJTAG interface
DSU_CLK 185 O DSU clock is equivalent to the processor clock; used to
capture address and data from pin TDO when PC trace
mode is on; is 3-stated when bit 0 or 15 of the
JTAG_Control_Register is LOW or logic 0
PCST[0:2] 186 to 189 O CPU status (debug mode, pipeline stall and occurrence
of exception)
bidirectional; CMOS input;
4 mA output drive open drain;
2 mA output drive Z
2 mA output drive Z
RESET
STATE
Z
LOW
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
Page 15

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Oct 22 15
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION BUFFER TYPE
Power supplies
V
V
DDA
DDC
151 S 2.5 V analog supply voltage for the PLL and oscillator n.a.
27,79,130,
S 2.5 V supply voltage for the core n.a.
182
V
DDP
3, 17, 31,
S 3.3 V supply voltage for interface I/O pads n.a.
43, 66, 80,
92, 115,
145, 187
V
SSC
26,78,131,
S ground for the core n.a.
183
V
SSP
10, 23, 37,
S ground for the interface pads n.a.
57, 72, 86,
104, 127,
170, 190
Notes
1. These signals are internal.
2. Shared with UART 1 and SSI.
RESET
STATE
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
5.3 Pin list in numerical order Table 2 Numbered list of SAA7240 pins
PIN NAME
1 RESETN
2 PIO31/D31
3, 17, 31, 43, 66, 80, 92,
V
DDP
115, 145, 187
4 PIO30/D30
5 PIO29/D29
6 PIO28/D28
7 PIO27/D27
8 PIO26/D26
9 PIO25/D25
10, 23, 37, 57, 72, 86, 104,
V
SSP
127, 170, 198
11 PIO24/D24
12 PIO23/D23
13 PIO22/D22
14 PIO21/D21
15 PIO20/D20
16 PIO19/D19
18 PIO18/D18
19 PIO17/D17
20 PIO16/D16
21 D15
22 D14
24 D13
25 D12
26, 78, 131, 183 V
27, 79, 130, 182 V
SSC
DDC
28 D11
29 D10
30 D9
32 D8
33 D7
34 D6
35 D5
36 D4
38 D3
39 D2
40 D1
41 D0
PIN NAME
42 UCASN
44 MUCASN/SIZE2
45 MLCASN/BAA#/SIZE1
46 LCASN/LBA#/SIZE0
47 DCS0N
48 RAS1N/DCS1N
49 RAS0N
50 CS6N
51 CS5N
52 CS4N
53 CS3N
54 CS2N
55 CS1N
56 CS0N
58 OEN/TSN
59 DTACK
60 CS7N
61 CS8N
62 WEN
63 A0
64 A1
65 A2
67 A3
68 A4
69 A5
70 A6
71 A7
73 A8
74 A9
75 A10
76 A11
77 A12
81 A13
82 A14
83 A15
84 A16
85 A17
87 A18
88 A19
89 A20
90 A21
2001 Oct 22 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
PIN NAME
91 CLK
93 V_STROBE
94 A_STROBE
95 AV_ERROR
96 AVD7/BOOTW0
97 AVD6/BOOTW1
98 AVD5/BOOTCS0
99 AVD4/BIG
100 AVD3/STRAP3
101 AVD2/STRAP2
102 AVD1/STRAP1
103 AVD0/STRAP0
105 PIO0/INT0
106 PIO1/INT1
107 PIO2/INT2
108 PIO3/INT3
109 PIO4/INT4
110 PIO5/INT5
111 PIO6/INT6
112 PIO7/INT7
113 PIO8
114 PIO9
116 PIO10/BPN
117 PIO11/VPP
118 PIO12/C8
119 PIO13/C4
120 PIO14/BRN
121 PIO15/BGN
122 CLK_CARD1
123 CMDVCCN1
124 RSTIN1
125 OFFN1
126 SC_I/O1
128 CLK_CARD0
129 CMDVCCN0
132 RSTIN0
133 OFFN0
134 SC_I/O0
135 RXD2
136 TXD2
137 RXD1/V34_RXD
PIN NAME
138 TXD1/V34_TXD
139 RTSN1/V34_FS
140 CTSN1/V34_CLK
141 RXD0
142 TXD0
143 RTSN0
144 CTSN0
146 MCLK
147 SCL1
148 SDA1
149 SCL0
150 SDA0
151 V
152 XTAL2
153 XTAL1
154 PKTSTROBE
155 PKTSYNC
156 PKTVALID
157 PKTDATA7
158 PKTDATA6
159 PKTDATA5
160 PKTDATA4
161 PKTDATA3
162 PKTDATA2
163 PKTDATA1
164 PKTDATA0
165 PWM0
166 GPDATA7
167 GPDATA6
168 GPDATA5
169 GPDATA4
171 GPDATA3
172 GPDATA2
173 GPDATA1
174 GPDATA0
175 GPVALID
176 GPSYNC
177 GPSTROBE
178 TDO
179 TDI
180 TMS
DDA
2001 Oct 22 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
PIN NAME
181 TRST
184 TCK
185 DSU_CLK
186 PCST0
188 PCST1
189 PCST2
190 GPD0/TS_DAT0
191 GPD1/TS_SYN0
192 GPD2/TS_VAL0
193 GPD3/TS_CK0
194 GPD4/TS_VAL1
195 GPD5/TS_SYN1
PIN NAME
196 GPD6/TS_DAT1
197 GPD7/TS_CK1
199 NSELECTIN/TS_DAT2
200 NINIT/TS_SYN2
201 NSTROBE/TS_VAL2
202 NACK/CS10N/TS_CK2
203 BUSY/CS9N
204 PERROR/A25
205 SELECT/A24
206 NAUTOF/A23
207 NFAULT/A22
208 DIR1284
2001 Oct 22 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
6 LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DDP
V
, V
DDC
V
I
P
tot
I
DDC
I
DDP
T
stg
T
amb
T
j
Notes
1. System designers should be aware that:
a) The IC junction temperature (Tj) is greatly influenced by the environment and the Printed-Circuit Board (PCB)
b) Table 3 gives some examples of theoretical maximum power dissipation supported by the package; thedesigner
2. This value represents the maximum current that the power track can carry without excessive voltage drop in the
internal chip. This value does not reflect the maximum current consumption of the core, which is far below this value.
3. This theoretical maximum value which should never be exceeded is determined when all output buffers are driving
their specified maximum static drive current. In a standard application, this worst case never occurs because the
output loads are mainly line capacitance and not resistive loads.
supply voltage for the I/O buffers −0.5 4.0 V
supply voltages for the core, PLL and oscillator −0.5 3.0 V
DDA
input voltage on any pin with respect to ground (VSS) −0.5 VDD+ 0.5 V
total power dissipation (based on package transfer, not IC power consumption) − P
core supply current − 500
supply current for the I/O buffers − 330
storage temperature −55 150 °C
ambient temperature 0 70 °C
junction temperature − 125 °C
layout thermal behaviour. Total allowable power P
characteristics;thermal resistance fromjunction to air;(R
P
tot(max)
=(T
j(max)
− T
)/R
amb
th(j-a)=PINT+PI/O
the power dissipation in the input and output buffers. P
in the customer application depends on its thermal
tot
,refer to Chapter 8)and ambient temperatureT
th(j-a)
. P
represents the internal device power (core and PLL). P
INT
depends on the user application and is limited by the
INT
maximum drive capability of the output buffers.
has to check that there is no I
maximum current violation.
DDP
tot(max)
(2)
(3)
(1)
W
mA
mA
I/O
amb
is
.
7 HANDLING
Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharges in normal handling. However, to be totally safe, it is
desirable to take normal precautions appropriate to handling CMOS integrated circuits.
8 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th(j-a)
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 35
(1)
°C/W
Note
1. When the device is soldered onto a PCB, the intrinsic thermal resistance of the package is improved. The R
th(j-a)
value depends on the PCB type; some typical values are given below:
a) For a standard PCB; R
b) For a 4-layer PCB; R
c) For a 4-layer PCB with thermal dissipation layer; R
th(j-a)
th(j-a)
=32°C/W.
=28°C/W.
th(j-a)
=24°C/W.
2001 Oct 22 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
Table 3 Theoretical package maximum power dissipation
THERMAL COEFFICIENT
(R
)
th(j-a)
P
tot(max)
at T
=70°CP
amb
tot
at T
=50°CP
amb
tot
at T
amb
=25°C
35 °C/W 1.57 W 2.14 W 2.85 W
32 °C/W 1.72 W 2.34 W 3.12 W
28 °C/W 1.96 W 2.67 W 3.57 W
24 °C/W 2.29 W 3.26 W 4.34 W
9 DC CHARACTERISTICS
V
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; V
DDP
respect to V
; unless otherwise specified.
SS
= 2.25 to 2.75 V; V
DDC
= 2.25 to 2.75 V; VSS=0V; T
DDA
= 0 to 70 °C; all voltages with
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
V
V
DDP
DDC
DDA
supply voltage for the I/O buffers 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
supply voltage for the core 2.25 2.5 2.75 V
analog supply voltage for PLL and
2.25 2.5 2.75 V
oscillator
I
DDP
supply current for the interface I/O
V
= 3.3 V − 30
DDP
(1)
− mA
pads
(2)
(2)
(2)
− mA
(2)
− mA
− mA
− mA
I
DDC
I
DDA
I
DDC(sleep)
I
DDC(coma)
core supply current V
analog supply current V
core supply current in Sleep mode values are measured at V
core supply current in Coma mode −
= 2.5 V − 220
DDC
= 2.5 V; f
DDA
f
= 13.5 MHz
clk
= 13.5 MHz − 2
clk
;
DD(max)
−
Inputs
V
IL
V
IH
LOW-level input voltage −−0.8 V
HIGH-level input voltage (except
2.0 − V
DDP
+ 0.5 V
XTAL1)
V
IH(XTAL1)
I
IL
I
IZ
I
IZ(off)
HIGH-level input voltage (XTAL1) 2.0 − 2.5 V
input leakage current VDD= 3.3 V; VSS<Vi<V
DD
−10 +1 +10 mA
3-state input current Vi= 2.4 or 0.4 V −10 +1 +10 mA
3-state (off-state) input current;
VDD=Vi= 3.6 V −10 +1 +10 mA
SDA, SCL and SC_I/O
Outputs
V
OH
V
OL
C
i
HIGH-level output voltage output drive current = I
LOW-level output voltage output sink current = I
OH(max)
OL(min)
2.4 −− V
−−0.4 V
input capacitance −−10 pF
Notes
1. Typical current measured on a test board running a set-top box-like application (bitstream decoding and a few
on-chip peripherals activated).
2. The typical current in Sleep and Coma modes is given in Table 4.
2001 Oct 22 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
9.1 Power saving in Sleep and Coma modes
Table 4 shows an example of typical current savings when either the Sleep mode or Coma mode is set. The
measurement is carried out on a test board running an application at room temperature with V
current consumption of the SAA7240 is measured with all peripherals enabled; this value is taken as a reference. Then,
the Sleep and Coma modes of the peripherals and CPU are set one at a time to measure the power consumption and
determine the relevant current saving.
Table 4 Typical current consumption for Sleep and Coma modes
MIPS
CONFIGURATION
REGISTER
PERIPHERAL
TYPICAL I
CURRENT (mA)
VALUE
0000H no shutdown; used for reference 220
(1)
0001H CPU core in Sleep mode and peripherals active 210 10
0002H CPU core in Coma mode and peripherals active 208 12
0004H peripheral section in Coma mode and CPU active 12 208
7FFFH everything down; including CPU 12 208
= 2.5 V. First, the total
DDC
DDC
SAVINGS
n.a.
(mA)
Note
1. This is the measured value used to determine the power savings.
9.2 Maximum allowable load capacitance on output pins
Table 5shows the maximumload capacitances thatare allowed on theoutput pins. Theseloads should notbe exceeded.
Table 5 Maximum output load capacitances
OUTPUT PIN MAXIMUM LOAD UNIT
SDA0, SCL0, SDA1 and SCL1 400 pF
D[15:0], A[21:0], LCASN, MLCASN, MUCASN, UCASN, WEN, OEN and
100 pF
PIO[31:16]/D[31:16]
CLK, MCLK, DSU_CLK and PCST[2:0] 25 pF
PKTSTROBE, GPDATA[7:0], GPSYNC, GPVALID, GPSTROBE, GPD0/TS_DAT0,
20 pF
GPD1/TS_SYN0, GPD2/TS_VAL0, GPD3/TS_CK0, GPD4/TS_VAL1,
GPD5/TS_SYN1, GPD6/TS_DAT1, GPD7/TS_CK1, NSELECTIN/TS_DAT2,
NINIT/TS_SYN2, NSTROBE/TS_VAL2 and NACK/CS10N/TS_CK2
All other outputs 50 pF
2001 Oct 22 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
10 APPLICATION INFORMATION
handbook, full pagewidth
Telco
interface
smart
cards
FRONT
PANEL
CONTROL
VXX
MODEM
TDA8004
16-Mbit
SDRAM
16-Mbit
SDRAM
(OPTIONAL)
2
I
C-bus
SAA7240
SAA7215
LR
RF-in
TDA8060
TDA5056
TUNER
2
SAA8044
(SDD)
MPEG-2
AV PES
BUFFERS
IEEE1394
L + PHY
IEEE 1284
RS232
IEEE 1394
FLASH
DRAM
(OPTIONAL)
ADAC
SWITCHING
SCART1 SCART2 SCART3
Fig.4 Set-top box example.
2001 Oct 22 22
CVBS/YC
RGB
FCE815
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
10.1 Application examples of the multi-master mode
The SAA7240 supports a multi-master mode. The SAA7240 is always the bus arbiter of the External Bus Interface Unit
(EBIU) bus. The possible configurations are depicted in Figs 5 and 6.
handbook, full pagewidth
16-Mbit
VIDEO
AV PES
16-Mbit
GRAPHICS
handbook, full pagewidth
SAA7240
EBIU BUS
ROM FLASH SDRAM PERIPHERAL
BPN
BGN
BRN
SAA7215
GATEWAY
CO-PROCESSOR
FCE813
Fig.5 Multi-master mode; EBIU bus is shared with a co-processor.
16-Mbit
VIDEO
AV PES
16-Mbit
GRAPHICS
SAA7240
EBIU BUS
ROM FLASH SDRAM PERIPHERAL
BPN
BGN
BRN
Fig.6 Multi-master mode; EBIU bus is split with a co-processor.
2001 Oct 22 23
SAA7215
GATEWAY
SAA7215 BUS
CO-PROCESSOR
FCE814
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
10.2 Memory configurations
Figures 7 and 8 show some examples of typical set-top box memory configurations.
handbook, full pagewidth
handbook, full pagewidth
16 8
DRAM/
SDRAM
PROM
FLASH RESERVED
SAA7240
16
SAA7215
1616
SDRAM
(MPEG)
FCE816
Fig.7 Typical low-end memory configuration; data bus is 16 bits wide.
32 32
DRAM/
SDRAM
PROM
FLASH-1 FLASH-2
SAA7240
16
SAA7215
Fig.8 Typical high-end configuration; data bus is 32 bits wide.
2001 Oct 22 24
1616
16
SDRAM
(MPEG)
SDRAM
GRAPHICS
FCE817
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
11 PACKAGE OUTLINE
SQFP208: plastic shrink quad flat package;
208 leads (lead length 1.3 mm); body 28 x 28 x 3.4 mm; high stand-off height
c
y
X
A
SOT316-1
157
208
156
105
104
Z
E
e
A
2
A
A
1
(A )
3
θ
L
p
b
w M
p
H
E
E
L
pin 1 index
1
w M
b
e
p
Z
D
H
D
53
52
v M
D
A
B
v M
B
detail X
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
mm
A
max.
4.10
0.50
0.25
3.6
3.2
0.25
UNIT A1A2A3b
cE
p
0.27
0.20
0.17
0.09
(1)
(1) (1)(1)
D
28.1
27.9
eH
H
28.1
27.9
0.5
30.9
30.3
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
OUTLINE
VERSION
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
REFERENCES
SOT316-1 MS-029
2001 Oct 22 25
D
E
30.9
30.3
LL
p
0.75
0.45
0.080.21.3 0.08
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
Z
D
1.39
1.11
Zywv θ
E
1.39
1.11
o
8
o
0
ISSUE DATE
99-12-27
00-01-25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
12 SOLDERING
12.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount packages
Thistext gives a very briefinsightto a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages”
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all surface
mount IC packages. Wave soldering can still be used for
certainsurfacemount ICs, but it isnotsuitablefor fine pitch
SMDs. In these situations reflow soldering is
recommended.
12.2 Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
tothe printed-circuit board byscreen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
convection or convection/infrared heating in a conveyor
type oven. Throughput times (preheating, soldering and
cooling) vary between 100 and 200 seconds depending
on heating method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C. The top-surface temperature of the
packages should preferable be kept below 220 °C for
thick/large packages, and below 235 °C for small/thin
packages.
12.3 Wave soldering
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended
forsurfacemount devices (SMDs) or printed-circuitboards
with a high component density, as solder bridging and
non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering
method was specifically developed.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be
observed for optimal results:
• Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a
turbulent wave with high upward pressure followed by a
smooth laminar wave.
• For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
– larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint
longitudinal axis is preferred to be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
– smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis
must be parallel to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the
downstream end.
• Forpackageswith leads on four sides,thefootprintmust
be placed at a 45° angle to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board. The footprint must incorporate
solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
During placement andbefore soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
12.4 Manual soldering
Fix the component by first soldering two
diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low voltage (24 V or
less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead.
Contact time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to
300 °C.
When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be
soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
2001 Oct 22 26
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
12.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for wave and reflow soldering methods
PACKAGE
WAVE REFLOW
(1)
BGA, HBGA, LFBGA, SQFP, TFBGA not suitable suitable
SOLDERING METHOD
HBCC, HLQFP, HSQFP, HSOP, HTQFP, HTSSOP, HVQFN, SMS not suitable
(3)
PLCC
, SO, SOJ suitable suitable
LQFP, QFP, TQFP not recommended
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO not recommended
(2)
(3)(4)
(5)
suitable
suitable
suitable
Notes
1. All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the maximum
temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal or external package
cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called popcorn effect). For details, refer to the
Drypack information in the
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods”
.
2. These packages are not suitable for wave soldering as a solder joint between the printed-circuit board and heatsink
(at bottom version) can not be achieved, and as solder may stick to the heatsink (on top version).
3. If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45° angle to the solder wave direction.
The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
4. Wave soldering is only suitable for LQFP, TQFP and QFP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.8 mm;
it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65 mm.
5. Wave soldering is only suitable for SSOP and TSSOP packageswith apitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.65 mm; it is
definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
2001 Oct 22 27
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
13 DATA SHEET STATUS
PRODUCT
DATA SHEET STATUS
Objective data Development This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product
Preliminary data Qualification This data sheet contains data from the preliminary specification.
Product data Production This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips
(1)
STATUS
(2)
DEFINITIONS
development. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to change the
specification in any manner without notice.
Supplementary data will be published at a later date. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification without
notice, in order to improve the design and supply the best possible
product.
Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes at any time in order
to improve the design, manufacturing and supply. Changes will be
communicated according to the Customer Product/Process Change
Notification (CPCN) procedure SNW-SQ-650A.
Notes
1. Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
2. The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was
published. The latest information is available on the Internet at URL http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
14 DEFINITIONS
Short-form specification The data in a short-form
specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the
same type number and title. For detailed information see
the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition Limiting values given are in
accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System
(IEC 60134). Stress above one or more of the limiting
values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device
atthese or at anyotherconditionsabove those given inthe
Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied.
Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Application information Applications that are
described herein for any of these products are for
illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make
norepresentationorwarranty that such applications willbe
suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
15 DISCLAIMERS Life support applications These products are not
designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result inpersonal injury. Philips
Semiconductorscustomersusingor selling these products
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and
agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes Philips Semiconductors
reserves the right to make changes, without notice, in the
products, including circuits, standard cells, and/or
software, described or contained herein in order to
improve design and/or performance. Philips
Semiconductors assumes no responsibility or liability for
theuseof any of these products,conveysnolicence or title
under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products,and makes no representationsorwarranties that
these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask
work right infringement, unless otherwise specified.
ICs with MPEG-2 functionality Use of this product in
any manner that complies with the MPEG-2 Standard is
expressly prohibited without a license under applicable
patents in the MPEG-2 patent portfolio, which license is
available from MPEG LA, L.L.C., 250 Steele Street, Suite
300, Denver, Colorado 80206.
2001 Oct 22 28
Page 29

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
16 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
Purchase of Philips I
components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I2C patent to use the
2001 Oct 22 29
Page 30

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
NOTES
2001 Oct 22 30
Page 31

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
MPEG-2 Transport RISC processor SAA7240
NOTES
2001 Oct 22 31
Page 32

Philips Semiconductors – a w orldwide compan y
Contact information
For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com. Fax: +31 40 27 24825
For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2001
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Printed in The Netherlands 753504/01/pp32 Date of release: 2001 Oct 22 Document order number: 9397 750 07749
SCA73
 Loading...
Loading...