Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of 2000 Jan 31
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
2001 Mar 28
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
FEATURES
General features
• Integrated MPEG AVGD decoder: audio, video and
graphics decoding and digital video encoding
• 5 planes display chain:background colour, background
plane, MPEG display plane, graphics plane and cursor
plane
• 16-Mbit or 32-Mbit external Synchronous DRAM
(SDRAM) for MPEG audio and video decoding and
graphics data storage
• Single or double external SDRAM organized as
1M×16 or 2 × 1M×16 (two independent 16-bit data
bus) interfacing at 81 MHz. Due to efficient memory use
in MPEG decoding, more than 1 Mbit is available for
graphics in the single SDRAM configuration whereas
17 Mbits are available in the double SDRAM
configuration.
• All basic operations of the AVGD decoder are possible
in both 16- and 32-Mbit configuration; enhanced
performance is achieved by the use of 32-Mbit external
SDRAM
• Targeted to BSkyB 3.0 and Canal+ basic box and web
box specifications
• Fast 16-bit data + 22-bit address synchronous or
asynchronous interface with external controller at up to
40.5 MHz
• Dedicated input for compressed audio and video in
Packetized Elementary Stream (PES) or Elementary
Stream (ES) in byte wide or bit serial format.
Accompanyingstrobesignalsdistinguishbetweenaudio
and video data. Transport stream error correction
available.
• Audio and/or video can also be input via the CPU
interface in PES or ES in 8 or 16-bit parallel format
• Single 27 or 40.5 MHz external clock for time base
reference and internal processing. Internal system time
base at 90 kHz can be synchronized via CPU port.
All required decoding and presentation clocks are
generated internally.
• Flexible memory allocation under control of the external
CPU enables optimized partitioning of memory for
different tasks
• Optimum compatibility with T-MIPS controller family
(SAA7214, SAA7219 and successors)
• Boundary scan testing implemented
• External SDRAM self test
• Supply voltage: 3.3 V; package: SQFP208.
CPU related features
• 16-bit data, 22-bit address, Chip Select, Data Strobe
and DaTa ACKnowledge external control protocol
• Fast 16-bit data plus 22-bit address synchronous
interface with the SAA7214, SAA7219 family at up to
40.5 MHz
• Asynchronous interface possible with external
microcontroller
• Support of fast DMA transfer
• Flexible bidirectional interface to external SDRAM
• High speed/low latency interface with second graphics
SDRAM
• Byte access to the full SDRAM in the upper 16-Mbit
address range
• Independent memory mapping of SDRAM and control
registers
• Two programmable independent interrupt lines
available
• Supports Motorola 68xxx interfaces as well as LSI
L64108 interface.
MPEG-2 system features
• Parsing of MPEG-2 PES and MPEG-1 packet streams
• Double system time clock counters
• Stand-alone or supervised audio/video synchronization
• Processing of errors flagged by channel decoding
section.
MPEG-2 video features
• Decodingof MPEG-2 video upto main level, main profile
• Output picture format: CCIR-601 4 : 2 : 2 interlaced
pictures.Pictureformat720 × 576at 50 Hz or 720 × 480
at 60 Hz.
• Support of constant and variable bit rates up to
15 Mbits/s for the elementary stream
• Horizontal and vertical pan and scan allows the
extraction of a window from the coded picture
• Flexible horizontal scaling from 0.5 up to 4 allows easy
aspect ratio conversion including support for 2.21 : 1
aspect ratio movies; in case of shrinking an anti-aliasing
pre-filter is applied
2001 Mar 28 2
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
• Vertical scaling with fixed factors 0.5, 0.75, 1 or 2;
factor 0.5 realizes picture shrink. Factor 2 can be used
for up-conversion of pictures with 288 (240) lines or
less; factor 0.75 is used for letterbox presentation.
• Horizontaland vertical scaling can be combinedtoscale
pictures to1⁄4of their original size, thus freeing up
screen space for graphic applications like electronic
program guides
• Non full screen MPEG pictures can be displayed in a
box of which position and background colour are
adjustable by the external microcontroller; structured
background is available as part of the graphic features
• Nominal video input buffer size for MP at ML 2.7-Mbit
• Video output may be slaved to internally (master)
generated or externally (slave) supplied
HV synchronization signals or CCIR-656 contained
synchronization signals. The position of active video is
programmable. Display phase is not affected by MPEG
timebase changes.
• Decoding and presentation can be independently
handled under CPU control
• Various trick modes under control of external
microcontroller:
– Freeze field/frame on I- or P-frames; restart on
I-picture
– Freeze field on B-frames; restart at any moment
– Scanning and decoding of I- or I- and P-frames in a
IBP sequence
– Single step mode
– Repeat/skip field for time base correction
– Repeat/skip frame for display parity integrity.
• Synchronization modes: DTS controlled, DTS free
running, software controlled, buffer controlled
• DTS register can be set via external controller;
programmable processing delay compensation.
MPEG-2 audio features
• Supported audio sampling frequencies:
48, 44.1, 32, 24, 22.05 and 16 kHz
• Independentchannelvolumecontrolandprogrammable
inter-channel crosstalk through a baseband audio
processing unit
• MPEG audio decoder
– Decoding of 2 channels, layer I and IIMPEG-1 audio
and low sampling frequency extension of MPEG-2
– Supports for mono, stereo, intensity stereo and dual
channel mode
– CRC error detection with automatic mute
– Constant and variable bit rates up to 448 kbit/s
– Selectable output channel in dual channel mode
– Storage of last 54 bytes in ancillary data field
– Dynamic range control at output.
• Muting possibility via external controller; automatic
muting in case of errors
• Generation of ‘beeps’ with programmable tone height,
duration and amplitude
• Linear PCM decoding
– Support for up to 8 channels linear PCM elementary
audio streams
– Supports for 8, 16, 20 and 24 bit/sample
– Supports for bit rates up to 6.144 Mbit/s
– 96 kHz LPCM samples will be mapped to a 48 kHz
multi-channel format
– Volume control for linear PCM samples in three
steps: −6, −12 and −18 dB.
• Burst-formatting for interconnection with an external
multi-channel decoder
– AC-3 elementary streams (IEC1937)
– MPEG-2 multi-channel streams in ES or PES format
– Output via the digital audio output or the IEC 958
output.
• Output stage
– Global control for volume and balance
– Serial multi-channel digital audio output with 16, 18,
20 or 22 bits per sample, compatible either to I2Sor
Japanese formats; output can be set to high
impedance mode via the external controller
– IEC958 (Serial SPDIF) audio output; output can be
set to high impedance mode
– Clock output 256 or 384 × fs for external
DA converter or clock input; output can be set to high
impedance mode.
• Audio FIFO in external SDRAM; programmable buffer
size, at least 64 kbit is available
• Synchronization modes: PTS controlled, PTS free
running, software controlled, buffer controlled
• PTS register can be set via external controller;
programmable processing delay compensation.
Background colour
• 24 bit YCbCr colour.
2001 Mar 28 3
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
Graphics features
2 nearly identical graphics planes: the first graphics plane
commonly called the background plane and the second
graphics plane commonly called foreground plane.
The following features apply for both planes.
• Graphics is presented in boxes independent of video
format
• Boxes can be up to full screen allowing double buffer
display mechanism
• Two independent data paths with RGB 4 :4:4 and
YCbCr 4 : 2 : 2 formats available with independent
mixing
• RGB path transparent to YCbCr format
• Conversion matrices available to allow any format on
any different data path (RGB or YCbCr)
• Screen arrangement of boxes is determined by display
list mechanism which allows for multiple boxes,
background loading, fast switching, scrolling,
overlapping and fading of regions
• Real-time anti-flickering performed in hardware;
programmable hardware available for off-line
anti-flickering
• Hard edged or soft edged wiping of regions available
• Support of 2, 4, 8, 16 bit/pixel infixed bit maps format or
coded in accordance to the DVB variable/run length
standard for region based graphics
• Chrominance down-sampling filter switched per region
• Display colours are obtained via colour look up tablesor
directly from bitmap; CLUT output can be YCbCrT at
8-bit for each signal component thus enabling 16 M
different colours and 6-bit for T which gives 64 mixing
levels with video; CLUT output can also be RGBT with
same resolutions; non linear processing available by
means of LUTs
• Map table mechanism to specify a sub set of entries if
the CLUT is larger than required by the coded bit
pattern; supported map tables are 16 to 256, 4 to 256
and4to16
• Up to 4 graphics boxes may overlap vertically even
inside one graphics layer thanks to the use of flexible
chained descriptors
• Graphics mechanism can be used for signal generation
in the vertical blanking interval; useful for teletext, wide
screen signalling, closed caption etc.
In addition to the previous listed features, the second
graphics plane sustains:
• Teletext insertion with automatic teletext data retrieving
from the external SDRAM.
Data manipulation unit
• Powerful 3D block move with different patterns for
source and destination area
• Dedicated events for video synchronization
• Scaling, format conversion and bit manipulation from a
chained list of instructions.
Cursor
• Size of 1024 pixels
• Programmable shape (8 × 128, 16 × 64, 32 × 32,
64 × 16 and 128 × 8)
• 16 colours available with a 4 level transparency mixing
with video and graphics
• Cursor colours obtained via two 16 entry CLUTs with
YCbCrTat6, 4, 4respectively 2 bits and RGBT at 4, 4, 4
respectively 4 bits (or 4, 5, 3, respectively 4 bits)
• Cursor can be moved freely across the screen without
overlapping restrictions.
Digital output
• Programmable selection for the mixed graphics planes
with video for the CVBS and RGB outputs
• Digital video input/output interface on 8 bit,
27 MHz (CbYCrY multiplexed bus), at a CCIR-656
format.
Analog output
• Analog video output interface on both the RGB and
Y/C/CVBS formats available simultaneously
• PAL/NTSC/SECAM encoding (SAA7221HS only)
• Two DACs for CVBS, Y and C, CVBS running at
27 MHz 10-bit resolution
• Three DACs for R (Y), G (Cb) and B (Cr) running at
27 MHz; 9-bit resolution connected to a 10-bit inputDAC
• Closed captioning and teletext encoding on CVBS
• Macrovision 7.01 and 6.1 encoding capability on
Y or CVBS and C or CVBS (SAA7216HS only).
2001 Mar 28 4
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
APPLICATIONS
The SAA7215 integrated MPEG AVGD decoder is aimed
at being used in MPEG digital TV applications. This
decoder is primarily designed to be connected to a
SAA7214 transport stream descrambler/demultiplexer/
microcontroller by means of glueless interfaces even
though connections to other market demultiplexers and/or
microcontrollers are possible. Compatibility is also
targeted with the SAA7219 and with the successor of the
T-MIPS family.
The SAA7215 can be used in any system where high-end
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAA7215HS, SAA7216HS, SAA7221H is a MPEG-2
sourcedecoderwhichcombinesaudiodecodingandvideo
decoding. Additionally to these basic MPEG functions it
also provides means for enhanced graphics, background
display and/or on-screen display as well as encoding of
output video. Due to an optimized architecture for audio
and video decoding, maximum capacity in external
memory and processing power from the external CPU is
available for graphics support.
Possible options are indicated in Table 1.
graphics are needed (associated SDRAM can be
extended to 32-Mbit) as well as in low cost systems (all
functions can be enabled with only 16-Mbit of associated
SDRAM).
Table 1 Possible options
TYPE NUMBER MACROVISION SECAM
SAA7215HS/C2 no no
SAA7216HS/C1 yes no
SAA7221HS/C1 no yes
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DD
I
DD
functional supply voltage range 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
total supply current; VDD= 3.3 V − tbf − mA
CLK device clock input frequency (2 solutions are possible) −30 ppm +27 +30 ppm MHz
−30 ppm +40.5 +30 ppm MHz
ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGE
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SAA7215HS/C2 SQFP208 plastic shrink quad flat package; 208 leads (lead length 1.3 mm);
SAA7216HS/C1
body 28 × 28 × 3.4 mm
SOT316-1
SAA7221HS/C1
2001 Mar 28 5
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
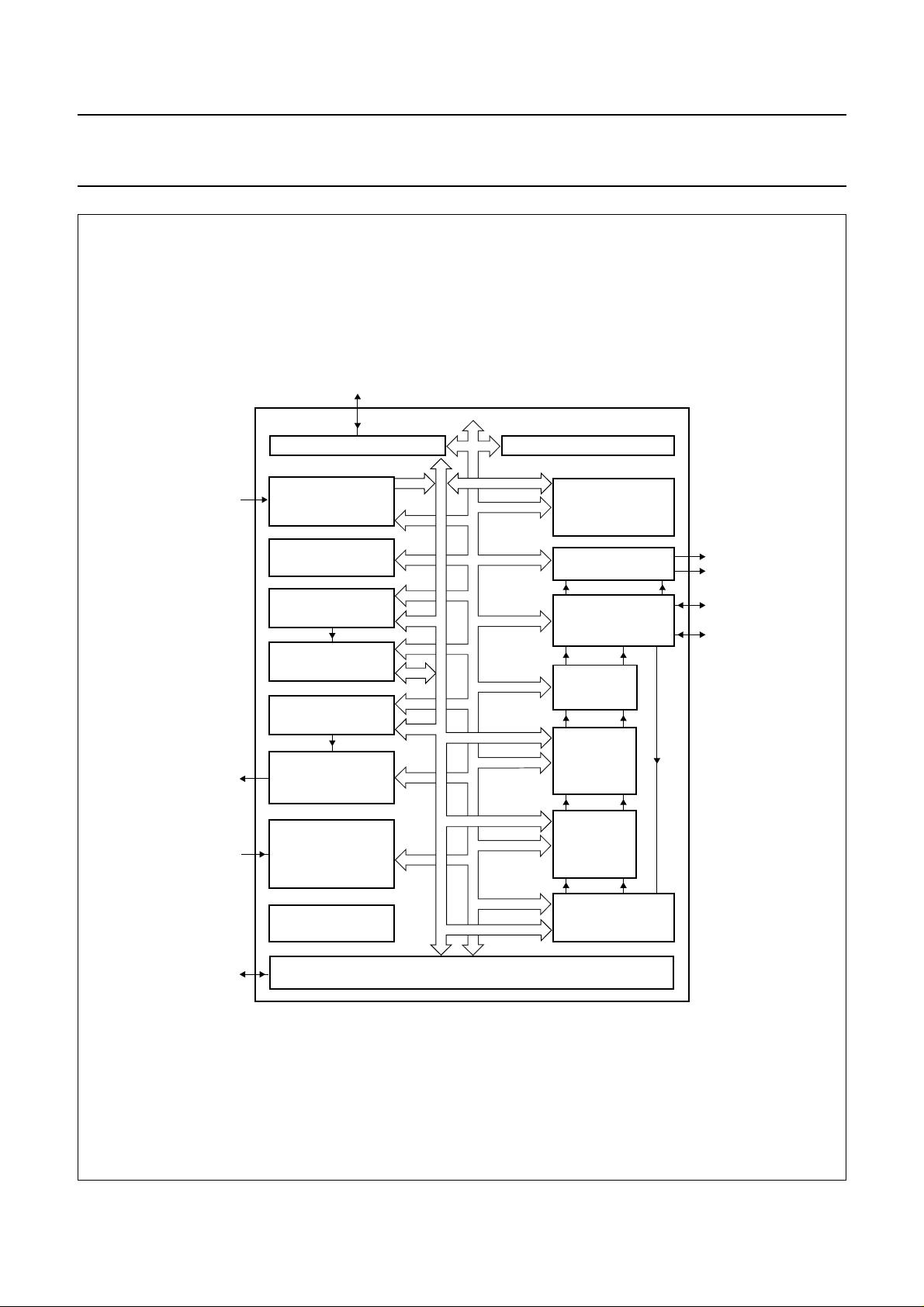
BLOCK DIAGRAMS
handbook, full pagewidth
MPEG
data
audio
DACs
16-Mbit SDRAM
(compulsory)
MEMORY INTERFACE 1 MEMORY INTERFACE 2
AUDIO/VIDEO
INTERFACE
SYSTEM TIME
BASE UNIT
VIDEO INPUT BUFFER
& SYNCHRONIZATION
VIDEO DECODER
AUDIO INPUT BUFFER
& SYNCHRONIZATION
AUDIO DECODER
data
data
16-Mbit SDRAM
(optional)
DATA MANIPULATION
DIGITAL ENCODER
DIGITAL VIDEO
SYNCHRONIZATION
CURSOR UNIT
GRAPHICS
UNIT 2
UNIT
analog
video
digital
video
CLK
CPU
CLOCK GENERATION
JTAG
HOST INTERFACE
Fig.1 Block diagram.
2001 Mar 28 6
control
GRAPHICS
UNIT 1
DISPLAY UNIT
FCE107
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
handbook, full pagewidth
MPEG
data
audio
DACs
16-Mbit SDRAM
MEMORY INTERFACE 1 MEMORY INTERFACE 2
AUDIO/VIDEO
INTERFACE
SYSTEM TIME
BASE UNIT
VIDEO INPUT BUFFER
& SYNCHRONIZATION
VIDEO DECODER
AUDIO INPUT BUFFER
& SYNCHRONIZATION
AUDIO DECODER
data
DATA MANIPULATION
DIGITAL ENCODER
DIGITAL VIDEO
SYNCHRONIZATION
CURSOR UNIT
GRAPHICS
UNIT 2
UNIT
analog
video
digital
video
CLK
CPU
CLOCK GENERATION
JTAG
HOST INTERFACE
Fig.2 Block diagram with preferred use in 16-Mbit configuration.
2001 Mar 28 7
control
GRAPHICS
UNIT 1
DISPLAY UNIT
FCE108
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
handbook, full pagewidth
MPEG
data
audio
DACs
16-Mbit SDRAM
(MPEG)
MEMORY INTERFACE 1 MEMORY INTERFACE 2
AUDIO/VIDEO
INTERFACE
SYSTEM TIME
BASE UNIT
VIDEO INPUT BUFFER
& SYNCHRONIZATION
VIDEO DECODER
AUDIO INPUT BUFFER
& SYNCHRONIZATION
AUDIO DECODER
data
data
16-Mbit SDRAM
(Graphics)
DATA MANIPULATION
DIGITAL ENCODER
DIGITAL VIDEO
SYNCHRONIZATION
CURSOR UNIT
GRAPHICS
UNIT 2
UNIT
analog
video
digital
video
CLK
CPU
CLOCK GENERATION
JTAG
HOST INTERFACE
Fig.3 Block diagram with preferred use in 32-Mbit configuration.
2001 Mar 28 8
control
GRAPHICS
UNIT 1
DISPLAY UNIT
FCE109
Page 9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
PINNING
Pinning table (listed numerically)
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
V
SS
1 S ground for pad ring
(1)
DESCRIPTION
DATA(4) 2 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 4); note 2
DATA(5) 3 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 5); note 2
DATA(6 4 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 6); note 2
DATA(7) 5 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 7); note 2
DATA(8) 6 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 8); note 2
DATA(9) 7 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 9); note 2
V
DD
8 S supply voltage for pad ring
DATA(10) 9 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 10); note 2
DATA(11) 10 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 11); note 2
DATA(12) 11 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 12); note 2
DATA(13) 12 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 13); note 2
DATA(14) 13 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 14); note 2
DATA(15) 14 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 15); note 2
V
SS
15 S ground for pad ring
SDRAM_ADDR1(3) 16 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 3)
SDRAM_ADDR1(2) 17 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 2)
SDRAM_ADDR1(4) 18 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 4)
SDRAM_ADDR1(1) 19 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 1)
SDRAM_ADDR1(5) 20 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 5)
SDRAM_ADDR1(0) 21 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 0)
V
DD
22 S supply voltage for pad ring
SDRAM_ADDR1(6) 23 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 6)
SDRAM_ADDR1(10) 24 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 10)
SDRAM_ADDR1(7) 25 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 7)
V
SS(CO)
V
DD(CO)
26 S ground for core logic
27 S supply voltage for digital core logic
SDRAM_ADDR1(11) 28 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 11)
SDRAM_ADDR1(9) 29 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 9)
SDRAM_ADDR1(8) 30 O SDRAM address 1 output (bit 8)
V
SS
31 S ground for pad ring
SDRAM_UDQ1 32 O SDRAM write mask 1 output
SDRAM_RAS1 33 O SDRAM row address strobe1 output
SDRAM_CAS1 34 O SDRAM column address 1 output
SDRAM_WE1 35 O SDRAM write enable 1 output
V
DD
36 S supply voltage for pad ring
SDRAM_DATA1(8) 37 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 8)
SDRAM_DATA1(7) 38 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 7)
2001 Mar 28 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
(1)
DESCRIPTION
SDRAM_DATA1(9) 39 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 9)
SDRAM_DATA1(6) 40 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 6)
SDRAM_DATA1(10) 41 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 10)
SDRAM_DATA11(5) 42 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 5)
V
SS
43 S ground for pad ring
SDRAM_DATA1(11) 44 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 11)
SDRAM_DATA1(4) 45 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 4)
SDRAM_DATA1(12) 46 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 12)
SDRAM_DATA1(3) 47 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 3)
SDRAM_DATA1(13) 48 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 13)
SDRAM_DATA1(2) 49 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 2)
V
DD
50 S supply voltage for pad ring
SDRAM_DATA1(14) 51 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 14)
SDRAM_DATA1(1) 52 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 1)
SDRAM_DATA1(15) 53 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 15)
SDRAM_DATA1(0) 54 I/O SDRAM data 1 input or output (bit 0)
READ_OUT1 55 O read command 1 output
READ_IN1 56 I read command 1 input
V
SS
57 S ground for pad ring
CP81MEXT 58 I 81 MHz SDRAM clock memory input
CP81M 59 O 81 MHz SDRAM clock return path output
V
DD
60 S supply voltage for pad ring
READ_IN2 61 I read command 2 input
READ_OUT2 62 O read command 2 output
SDRAM_DATA2(0) 63 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 0)
SDRAM_DATA2(15) 64 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 15)
SDRAM_DATA2(1) 65 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 1)
SDRAM_DATA2(14) 66 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 14)
V
SS
67 S ground for pad ring
SDRAM_DATA2(2) 68 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 2)
SDRAM_DATA2(13) 69 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 13)
SDRAM_DATA2(3) 70 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 3)
SDRAM_DATA2(12) 71 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 12)
SDRAM_DATA2(4) 72 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 4)
SDRAM_DATA2(11) 73 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 11)
V
DD
74 S supply voltage for pad ring
SDRAM_DATA2(5) 75 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 5)
SDRAM_DATA2(10) 76 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 10)
SDRAM_DATA2(6) 77 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 6)
V
SS(CO)
V
DD(CO)
78 S ground for core logic
79 S supply voltage for digital core logic
2001 Mar 28 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
(1)
DESCRIPTION
SDRAM_DATA2(9) 80 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 9)
SDRAM_DATA2(7) 81 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 7)
SDRAM_DATA2(8) 82 I/O SDRAM data 2 input or output (bit 8)
V
SS
83 S ground for pad ring
SDRAM_WE2 84 O SDRAM write enable 2 output
SDRAM_CAS2 85 O SDRAM column address 2 output
SDRAM_RAS2 86 O SDRAM row address strobe2 output
SDRAM_UDQ2(0) 87 O SDRAM write mask 2 (0) output
SDRAM_UDQ2(1) 88 O SDRAM write mask 2 (1) output
V
DD
89 S supply voltage for pad ring
SDRAM_ADDR2(8) 90 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 8)
SDRAM_ADDR2(9) 91 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 9)
SDRAM_ADDR2(11) 92 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 11)
SDRAM_ADDR2(7) 93 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 7)
SDRAM_ADDR2(10) 94 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 10)
SDRAM_ADDR2(6) 95 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 6)
V
SS
96 S ground for pad ring
SDRAM_ADDR2(0) 97 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 0)
SDRAM_ADDR2(5) 98 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 5)
SDRAM_ADDR2(1) 99 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 1)
SDRAM_ADDR2(4) 100 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 4)
SDRAM_ADDR2(2) 101 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 2)
SDRAM_ADDR2(3) 102 O SDRAM address 2 output (bit 3)
V
DD
103 S supply voltage for pad ring
TDI 104 I boundary scan test data input; note 2
TDO 105 O/Z boundary scan test data output; note 2
TMS 106 I boundary scan test mode select input; note 2
TRST 107 I boundary scan test data input; note 2
TCK 108 I boundary scan test clock input
V
DD(AN)
109 S 3.3 V supply for analog blocks(PLL)
IDUMP2 110 − analog sink2
B 111 − analog video (blue)
G 112 − analog video (green)
AV
DD3
113 S analog supply 3
R 114 − analog video (red)
AV
DD2
115 S analog supply 2
Y/CVBS 116 − analog luminance/analog composite video
C/CVBS 117 − analog chrominance/analog composite video
IDUMP1 118 − analog sink1
AV
SS
119 S analog supply ground
RSET 120 − analog reference
2001 Mar 28 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
AV
DD1
V
SS
121 S analog supply 1
122 S ground for pad ring
(1)
DESCRIPTION
GRPH 123 O/Z indicator for graphics information output; note 2
VS 124 I/O vertical synchronization input or output; note 2
HS 125 I/O horizontal synchronization input or output; note 2
CP27 126 O 27 MHz video presentation clock output; note 2
V
DD
127 S supply voltage for pad ring
YUV(0) 128 I/O YUV video input or output (bit 0);at 27 MHz; note 2
V
SS(CO)
V
DD(CO)
129 S ground for core logic
130 S supply voltage for digital core logic
YUV(1) 131 I/O YUV video input or output (bit 1); at 27 MHz; note 2
YUV(2) 132 I/O YUV video input or output (bit 2); at 27 MHz; note 2
YUV(3) 133 I/O YUV video input or output (bit 3); at 27 MHz; note 2
YUV(4) 134 I/O YUV video input or output (bit 4); at 27 MHz; note 2
YUV(5) 135 I/O YUV video input or output (bit 5); at 27 MHz; note 2
YUV(6) 136 I/O YUV video input or output (bit 6); at 27 MHz; note 2
YUV(7) 137 I/O YUV video input or output (bit 7); at 27 MHz; note 2
V
SS
138 S ground for pad ring
SPDIF 139 O/Z digital audio output; note 2
WS 140 O/Z word select output; note 2
WB 141 O/Z word begin output; note 2
SD 142 O/Z serial audio data output; note 2
SCK 143 O/Z serial audio clock output; note 2
FSCLK 144 I/O 256 or 384 x f
clock input or output;
s
RESET 145 I hard reset input; note 2
TTX 146 I teletext data input; note 2
TTXRQ/CPU_SEL(1) 147 I/O teletext data request or CPU data interface selection (1); note 2; note 3
V
DD
148 S supply voltage for pad ring
IRQ(1) 149 O/Z individually maskable interrupt (1) output; note 2
IRQ(0) 150 O/Z individually maskable interrupt (0) output; note 2
V_REQ 151 O/Z video data request output; note 2
A_REQ 152 O/Z audio data request output; note 2
AUDDEN 153 I byte synchronisation of serial audio input A_DATA; note 2
A_DATA 154 I MPEG audio stream serial port input; note 2
AV_DATA(0) 155 I MPEG stream port input (bit 0); note 2
AV_DATA(1) 156 I MPEG stream port input (bit 1); note 2
AV_DATA(2) 157 I MPEG stream port input (bit 2); note 2
AV_DATA(3) 158 I MPEG stream port input (bit 3); note 2
AV_DATA(4) 159 I MPEG stream port input (bit 4); note 2
AV_DATA(5) 160 I MPEG stream port input (bit 5); note 2
AV_DATA(6) 161 I MPEG stream port input (bit 6); note 2
2001 Mar 28 12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
(1)
DESCRIPTION
AV_DATA(7) 162 I MPEG stream port input (bit 7); note 2
ERROR 163 I flag for bitstream error; note 2
A_STROBE 164 I audio data strobe for AV_DATA and A_DATA inputs; note 2
V_STROBE 165 I video data strobe for AV_DATA and A_DATA inputs; note 2
V
(gate input) 166 S ground for pad ring
SS
CPU_SEL(0) 167 I CPU data interface selection (0) input; note 2; note 3
CLK 168 I 27 or 40.5 MHz clock input; note 2
V
SS
169 S ground for pad ring
SIZ(1) 170 I size of data on bus DATA (1) input; note 2
SIZ(0) 171 I size of data on bus DATA (0) input; note 2
ADDRESS(20) 172 I CPU address input (bit 20); note 2
ADDRESS(19) 173 I CPU address input (bit 19); note 2
ADDRESS(18) 174 I CPU address input (bit 18); note 2
ADDRESS(17) 175 I CPU address input (bit 17); note 2
ADDRESS(16) 176 I CPU address input (bit 16); note 2
ADDRESS(15) 177 I CPU address input (bit 15); note 2
ADDRESS(14) 178 I CPU address input (bit 14); note 2
ADDRESS(13) 179 I CPU address input (bit 13); note 2
ADDRESS(12) 180 I CPU address input (bit 12); note 2
ADDRESS(11) 181 I CPU address input (bit 11); note 2
V
SS(CO)
V
DD(CO)
V
DD
182 S ground for core logic
183 S supply voltage for digital core logic
184 S supply voltage for pad ring
ADDRESS(10) 185 I CPU address input (bit 10); note 2
ADDRESS(9) 186 I CPU address input (bit 9); note 2
ADDRESS(8) 187 I CPU address input (bit 8); note 2
ADDRESS(7) 188 I CPU address input (bit 7); note 2
ADDRESS(6) 189 I CPU address input (bit 6); note 2
ADDRESS(5) 190 I CPU address input (bit 5); note 2
ADDRESS(4) 191 I CPU address input (bit 4); note 2
ADDRESS(3) 192 I CPU address input (bit 3); note 2
ADDRESS(2) 193 I CPU address input (bit 2); note 2
ADDRESS(1) 194 I CPU address input (bit 1); note 2
ADDRESS(0) 195 I CPU address input (bit 0); note 2
R/
W 196 I read or write input; note 2
DMA_RDY 197 O/Z DMA ready output; note 2
DMA_DONE 198 I DMA end input; note 2
DMA_REQ 199 I/O DMA request input or output; note 2
DMA_ACK 200 I DMA acknowledge input; note 2
CS
RG
201 I chip select for control register access input; note 2
CSSD/ADDRESS(21) 202 I chip select for SDRAM access or CPU address (bit 21) input; note 2
2001 Mar 28 13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
DATACK 203 O/Z data acknowledge output; note 2
DS/TS 204 I data strobe or transfer start input; note 2
DATA(0) 205 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 0); note 2
DATA(1) 206 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 1); note 2
DATA(2) 207 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 2); note 2
DATA(3) 208 I/O CPU data input or output (bit 3); note 2
Notes
1. Pin type abbreviations: I = Input, O = Output, I/O = Input or Output, O/Z = high impedance Output and
S = Supply voltage.
2. 5 V tolerant outputs swing between VSSand VDD. 5 V tolerant inputs can receive signals swinging between VSSand
3.3 V or VSS and 5 V.
3. SignalCPU_SEL(1)is used only after a global hardware resetisappliedon external input line RESET for determining
the type of the microcontroller connected to SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221 and therefore apply the proper
communication protocol. This microcontroller type must be given by means of weak pull-up or pull-down externally
connected to CPU_SEL(1). During normal operation, the pin TTXRQ/CPU_SEL(1) is used for implementing the
Teletext Data Request protocol and must not be disturbed by the microcontroller type setting.
(1)
DESCRIPTION
2001 Mar 28 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
Pin configuration
handbook, halfpage
208
1
SAA7215HS
SAA7216HS
SAA7221HS
52
53
Fig.4 Pin configuration.
157
104
156
105
FCE351
2001 Mar 28 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
Pinning table (listed by function)
PIN SYMBOL TYPE
166 V
168 CLK I − 5.0 V tolerant rising edge
145 RESET I − 5.0 V tolerant low level
162 AV_DATA(7) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
161 AV_DATA(6) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
160 AV_DATA(5) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
159 AV_DATA(4) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
158 AV_DATA(3) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
157 AV_DATA(2) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
156 AV_DATA(1) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
155 AV_DATA(0) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
154 A_DATA I − 5.0 V tolerant low level
153 AUDDEN I − 5.0 V tolerant high level
164 A_STROBE I − 5.0 V tolerant program level
165 V_STROBE I − 5.0 V tolerant program level
152 A_REQ O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant program level
151 V_REQ O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant program level
163 ERROR I − 5.0 V tolerant program level
142 SD O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
143 SCK O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant edge
140 WS O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
141 WB O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
139 SPDIF O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
144 FSCLK I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant edge
126 CP27 O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant rising edge
137 YUV(7) I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
136 YUV(6) I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
135 YUV(5) I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
134 YUV(4) I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
133 YUV(3) I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
132 YUV(2) I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
131 YUV(1) I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
128 YUV(0) I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
125 HS I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant program level
124 VS I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant program level
123 GRPH O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant high level
114 R/CVBS −− − analog
112 G −− − analog
111 B −− − analog
116 Y/CVBS −− − analog
(gate input) S − 0V −
SS
(1)
DRIVE VOLTAGE ACTIVITY
2001 Mar 28 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
PIN SYMBOL TYPE
117 C/CVBS −− − analog
53 SDRAM_DATA1(15) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
51 SDRAM_DATA1(14) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
48 SDRAM_DATA1(13) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
46 SDRAM_DATA1(12) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
44 SDRAM_DATA1(11) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
41 SDRAM_DATA1(10) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
39 SDRAM_DATA1(9) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
37 SDRAM_DATA1(8) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
38 SDRAM_DATA1(7) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
40 SDRAM_DATA1(6) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
42 SDRAM_DATA1(5) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
45 SDRAM_DATA1(4) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
47 SDRAM_DATA1(3) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
49 SDRAM_DATA1(2) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
52 SDRAM_DATA1(1) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
54 SDRAM_DATA1(0) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
28 SDRAM_ADDR1(11) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
24 SDRAM_ADDR1(10) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
29 SDRAM_ADDR1(9) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
30 SDRAM_ADDR1(8) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
25 SDRAM_ADDR1(7) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
23 SDRAM_ADDR1(6) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
20 SDRAM_ADDR1(5) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
18 SDRAM_ADDR1(4) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
16 SDRAM_ADDR1(3) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
17 SDRAM_ADDR1(2) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
19 SDRAM_ADDR1(1) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
21 SDRAM_ADDR1(0) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
33 SDRAM_RAS1 O 2 mA 3.3 V low level
34 SDRAM_CAS1 O 2 mA 3.3 V low level
35 SDRAM_WE1 O 2 mA 3.3 V low level
32 SDRAM_UDQ1 O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
59 CP81M O 8 mA 3.3 V edge
58 CP81MEXT I − 3.3V edge
55 READ_OUT1 O 2 mA 3.3 V low level
56 READ_IN1 I − 3.3 V low level
64 SDRAM_DATA2(15) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
66 SDRAM_DATA2(14) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
69 SDRAM_DATA2(13) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
71 SDRAM_DATA2(12) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
(1)
DRIVE VOLTAGE ACTIVITY
2001 Mar 28 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
PIN SYMBOL TYPE
73 SDRAM_DATA2(11) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
76 SDRAM_DATA2(10) I/O 2mA 3.3 V direct level
80 SDRAM_DATA2(9) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
82 SDRAM_DATA2(8) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
81 SDRAM_DATA2(7) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
77 SDRAM_DATA2(6) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
75 SDRAM_DATA2(5) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
72 SDRAM_DATA2(4) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
70 SDRAM_DATA2(3) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
68 SDRAM_DATA2(2) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
65 SDRAM_DATA2(1) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
63 SDRAM_DATA2(0) I/O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
92 SDRAM_ADDR2(11) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
94 SDRAM_ADDR2(10) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
91 SDRAM_ADDR2(9) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
90 SDRAM_ADDR2(8) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
93 SDRAM_ADDR2(7) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
95 SDRAM_ADDR2(6) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
98 SDRAM_ADDR2(5) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
100 SDRAM_ADDR2(4) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
102 SDRAM_ADDR2(3) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
101 SDRAM_ADDR2(2) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
99 SDRAM_ADDR2(1) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
97 SDRAM_ADDR2(0) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
86 SDRAM_RAS2 O 2 mA 3.3 V low level
85 SDRAM_CAS2 O 2 mA 3.3 V low level
84 SDRAM_WE2 O 2 mA 3.3 V low level
88 SDRAM_UDQ2(1) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
87 SDRAM_UDQ2(0) O 2 mA 3.3 V direct level
62 READ_OUT2 O 2 mA 3.3 V low level
61 READ_IN2 I − 3.3 V low level
147 TTXRQ/CPU_SEL(1) I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
167 CPU_SEL(0) I − 5.0 V tolerant level
146 TTX I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
14 DATA(15) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
13 DATA(14) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
12 DATA(13) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
11 DATA(12) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
10 DATA(11) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
9 DATA(10) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
7 DATA(9) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
(1)
DRIVE VOLTAGE ACTIVITY
2001 Mar 28 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
PIN SYMBOL TYPE
(1)
DRIVE VOLTAGE ACTIVITY
6 DATA(8) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
5 DATA(7) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
4 DATA(6) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
3 DATA(5) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
2 DATA(4) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
208 DATA(3) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
207 DATA(2) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
206 DATA(1) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
205 DATA(0) I/O 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
172 ADDRESS(20) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
173 ADDRESS(19) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
174 ADDRESS(18) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
175 ADDRESS(17) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
176 ADDRESS(16) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
177 ADDRESS(15) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
178 ADDRESS(14) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
179 ADDRESS(13) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
180 ADDRESS(12) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
181 ADDRESS(11) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
185 ADDRESS(10) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
186 ADDRESS(9) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
187 ADDRESS(8) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
188 ADDRESS(7) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
189 ADDRESS(6) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
190 ADDRESS(5) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
191 ADDRESS(4) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
192 ADDRESS(3) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
193 ADDRESS(2) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
194 ADDRESS(1) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
195 ADDRESS(0) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
170 SIZ(1) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
171 SIZ(0) I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
201
202
204
196 R/
203
CS
RG
I − 5.0 V tolerant low level
CSSD/ADDRESS(21) I − 5.0 V tolerant low level
DS I − 5.0 V tolerant low level
WI−5.0 V tolerant direct level
DTACK O/Z 6 mA 5.0 V tolerant low level
199 DMA_REQ I/O 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant program level
200 DMA_ACK I − 5.0 V tolerant program level
197 DMA_RDY O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant program level
198 DMA_DONE I − 5.0 V tolerant program level
2001 Mar 28 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
PIN SYMBOL TYPE
(1)
DRIVE VOLTAGE ACTIVITY
149 IRQ(1) O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant program level
150 IRQ(0) O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant program level
104 TDI I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
105 TDO O/Z 3 mA 5.0 V tolerant direct level
106 TMS I − 5.0 V tolerant direct level
108 TCK I − 5.0 V tolerant edge
107 TRST I − 5.0 V tolerant low level
121 AV
115 AV
113 AV
DD1
DD2
DD3
S −− −
S −− −
S −− −
118 IDUMP1 −− − −
110 IDUMP2 −− − −
120 RSET −− − −
119 AV
27 V
79 V
130 V
183 V
8V
22 V
36 V
50 V
60 V
74 V
89 V
103 V
127 V
148 V
184 V
109 V
26 V
78 V
129 V
182 V
1V
15 V
31 V
43 V
57 V
67 V
83 V
SS
DD(CO)
)S−3.3 V −
DD(CO
)S−3.3 V −
DD(CO
DD(CO)
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD(AN)
SS(CO)
SS(CO)
)S−0V −
SS(CO
SS(CO)
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
S −− −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 3.3 V −
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
2001 Mar 28 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
PIN SYMBOL TYPE
96 V
122 V
138 V
169 V
SS
SS
SS
SS
(1)
DRIVE VOLTAGE ACTIVITY
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
S − 0V −
Notes
1. Pin type abbreviations: I = Input, O = Output, I/O = Input or Output, O/Z = high impedance Output and
S = Supply voltage.
2001 Mar 28 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
APPLICATION INFORMATION
handbook, full pagewidth
TS-in
(pktdata)
UART
13.5 MHz
PIO
SAA7214
(T-MIPS)
2
I
C
AV data
Strobe
IRQ
ERROR
Extension bus
EPROM
8
2
2
40.5 MHz
DRAM FLASH
(OPTIONAL)
ctrl
ctrl
16-Mbit
SDRAM
16-Mbit
SDRAM
16 12 4 5 12
addr
data
SAA7215
SAA7216
SAA7221
MPEG-2AVGD
DECODER
16 21
data
addr
FCE111
addr
DS
R/W
CS
CS
16
SD
RG
data
2
1
8
1
2
3
6
DTACK
HS, VS
CP27
CCIR-656
GRPH
Y/C/CVBS
RGB
Audio
DAC
Fig.5 Set-top box example.
2001 Mar 28 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
PACKAGE OUTLINE
SQFP208: plastic shrink quad flat package;
208 leads (lead length 1.3 mm); body 28 x 28 x 3.4 mm; high stand-off height
c
y
X
A
SOT316-1
157
208
156
105
104
Z
E
e
H
E
E
w M
b
p
A
2
A
A
1
(A )
3
θ
L
p
L
pin 1 index
1
w M
b
e
p
Z
D
H
D
53
52
v M
D
A
B
v M
B
detail X
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
mm
A
max.
4.10
0.50
0.25
3.6
3.2
0.25
UNIT A1A2A3b
cE
p
0.27
0.20
0.17
0.09
(1)
(1) (1)(1)
D
28.1
27.9
eH
28.1
27.9
0.5
30.9
30.3
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
OUTLINE
VERSION
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
REFERENCES
SOT316-1 MS-029
2001 Mar 28 23
E
30.9
30.3
LL
p
0.75
0.45
0.080.21.3 0.08
H
D
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
Z
1.39
1.11
D
Zywv θ
E
1.39
1.11
o
8
o
0
ISSUE DATE
99-12-27
00-01-25
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
SOLDERING
Introduction to soldering surface mount packages
Thistextgivesavery brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages”
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all surface
mount IC packages. Wavesoldering is not always suitable
for surface mount ICs, or for printed-circuit boards with
high population densities. In these situations reflow
soldering is often used.
Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
tothe printed-circuit board by screen printing,stencillingor
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
infrared/convection heating in a conveyor type oven.
Throughput times (preheating, soldering and cooling) vary
between 100 and 200 seconds depending on heating
method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C. The top-surface temperature of the
packages should preferable be kept below 230 °C.
• Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a
turbulent wave with high upward pressure followed by a
smooth laminar wave.
• For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
– larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint
longitudinal axis is preferred to be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
– smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis
must be parallel to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the
downstream end.
• Forpackageswithleadsonfoursides,the footprint must
be placed at a 45° angle to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board. The footprint must incorporate
solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
Manual soldering
Wave soldering
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended
forsurfacemountdevices(SMDs)orprinted-circuit boards
with a high component density, as solder bridging and
non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering
method was specifically developed.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be
observed for optimal results:
Fix the component by first soldering two
diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low voltage (24 V or
less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead.
Contact time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to
300 °C.
When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be
soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
2001 Mar 28 24
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
Suitability of surface mount IC packages for wave and reflow soldering methods
PACKAGE
WAVE REFLOW
(1)
BGA, SQFP not suitable suitable
SOLDERING METHOD
HLQFP, HSQFP, HSOP, HTSSOP, SMS not suitable
(3)
PLCC
, SO, SOJ suitable suitable
LQFP, QFP, TQFP not recommended
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO not recommended
(2)
(3)(4)
(5)
suitable
suitable
suitable
Notes
1. All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the maximum
temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal or external package
cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called popcorn effect). For details, refer to the
Drypack information in the
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods”
.
2. These packages are not suitable for wave soldering as a solder joint between the printed-circuit board and heatsink
(at bottom version) can not be achieved, and as solder may stick to the heatsink (on top version).
3. If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45° angle to the solder wave direction.
The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
4. Wave soldering is only suitable for LQFP, TQFP and QFP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.8 mm;
it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65 mm.
5. Wave soldering is only suitable for SSOP and TSSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.65 mm; it is
definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
2001 Mar 28 25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
DATA SHEET STATUS
PRODUCT
DATA SHEET STATUS
Objective data Development This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product
Preliminary data Qualification This data sheet contains data from the preliminary specification.
Product data Production This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips
(1)
STATUS
(2)
DEFINITIONS
development. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to change the
specification in any manner without notice.
Supplementary data will be published at a later date. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification without
notice, in order to improve the design and supply the best possible
product.
Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes at any time in order
to improve the design, manufacturing and supply. Changes will be
communicated according to the Customer Product/Process Change
Notification (CPCN) procedure SNW-SQ-650A.
Notes
1. Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
2. The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was
published. The latest information is available on the Internet at URL http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
DEFINITIONS
Short-form specification The data in a short-form
specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the
same type number and title. For detailed information see
the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition Limiting values given are in
accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System
(IEC 60134). Stress above one or more of the limiting
values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device
attheseor at any other conditions above those given inthe
Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied.
Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Application information Applications that are
described herein for any of these products are for
illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make
norepresentationorwarrantythatsuchapplicationswillbe
suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
DISCLAIMERS
Life support applications These products are not
designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected toresult in personal injury. Philips
Semiconductorscustomersusingorsellingtheseproducts
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and
agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes Philips Semiconductors
reserves the right to make changes, without notice, in the
products, including circuits, standard cells, and/or
software, described or contained herein in order to
improve design and/or performance. Philips
Semiconductors assumes no responsibility or liability for
theuseofanyoftheseproducts,conveys no licence or title
under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products,andmakes no representations or warranties that
these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask
work right infringement, unless otherwise specified.
ICs with MPEG-2 functionality Use of this product in
any manner that complies with the MPEG-2 Standard is
expressly prohibited without a license under applicable
patents in the MPEG-2 patent portfolio, which license is
available from MPEG LA, L.L.C., 250 Steele Street, Suite
300, Denver, Colorado 80206.
2001 Mar 28 26
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVGD decoders SAA7215; SAA7216; SAA7221
NOTES
2001 Mar 28 27
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors – a w orldwide compan y
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 3 Figtree Drive, HOMEBUSH, NSW 2140,
Tel. +61 2 9704 8141, Fax. +61 2 9704 8139
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213,
Tel. +43 1 60 101 1248, Fax. +43 1 60 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 20 0733, Fax. +375 172 20 0773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: see South America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15th floor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 68 9211, Fax. +359 2 68 9102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381, Fax. +1 800 943 0087
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +852 2319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Sydhavnsgade 23, 1780 COPENHAGEN V,
Tel. +45 33 29 3333, Fax. +45 33 29 3905
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615 800, Fax. +358 9 6158 0920
France: 7 - 9 Rue du Mont Valérien, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 4728 6600, Fax. +33 1 4728 6638
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 2353 60, Fax. +49 40 2353 6300
Hungary: Philips Hungary Ltd., H-1119 Budapest, Fehervari ut 84/A,
Tel: +36 1 382 1700, Fax: +36 1 382 1800
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Band Box Building, 2nd floor,
254-D, Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli, MUMBAI 400 025,
Tel. +91 22 493 8541, Fax. +91 22 493 0966
Indonesia: PT Philips DevelopmentCorporation, Semiconductors Division,
Gedung Philips, Jl. Buncit Raya Kav.99-100, JAKARTA 12510,
Tel. +62 21 794 0040 ext. 2501, Fax. +62 21 794 0080
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax. +353 1 7640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, PO Box 18053,
TEL AVIV 61180, Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax. +972 3 649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS, ViaCasati, 23 - 20052 MONZA (MI),
Tel. +39 039 203 6838, Fax +39 039 203 6800
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku,
TOKYO 108-8507, Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5057
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381, Fax +9-5 800 943 0087
Middle East: see Italy
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 40 27 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Pakistan: see Singapore
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +63 2 817 3474
Poland: Al.Jerozolimskie 195 B, 02-222 WARSAW,
Tel. +48 22 5710 000, Fax. +48 22 5710 001
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 755 6918, Fax. +7 095 755 6919
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 319762,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 58088 Newville 2114,
Tel. +27 11 471 5401, Fax. +27 11 471 5398
South America: Al. Vicente Pinzon, 173, 6th floor,
04547-130 SÃO PAULO, SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax. +55 11 821 2382
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 93 301 6312, Fax. +34 93 301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 5985 2000, Fax. +46 8 5985 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2741 Fax. +41 1 488 3263
Taiwan: Philips Semiconductors, 5F, No. 96, Chien Kuo N. Rd., Sec. 1,
TAIPEI, Taiwan Tel. +886 2 2134 2451, Fax. +886 2 2134 2874
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
60/14 MOO 11, Bangna Trad Road KM. 3, Bagna, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 361 7910, Fax. +66 2 398 3447
Turkey: Yukari Dudullu, Org. San. Blg., 2.Cad. Nr. 28 81260 Umraniye,
ISTANBUL, Tel. +90 216 522 1500, Fax. +90 216 522 1813
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +380 44 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 208 730 5000, Fax. +44 208 754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381, Fax. +1 800 943 0087
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 3341 299, Fax.+381 11 3342 553
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors,
Marketing Communications, Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218, 5600 MD EINDHOVEN,
The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
© Philips Electronics N.V. SCA
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
2001
Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
72
Printed in The Netherlands 753504/03/pp28 Date of release: 2001 Mar 28 Document order number: 9397750 08179
 Loading...
Loading...