Page 1
DATA SH EET
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of 1998 Feb 18
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1998 Sep 07
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
SAA7212
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder
Page 2

1998 Sep 07 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
FEATURES
General features
• Single external Synchronous DRAM organized
as1M×16 interfacing at 81 MHz. Due to efficient
memory use in MPEG decoding, more than 1 Mbit
available for graphics
• Fast 16-bit data + 8-bit address interface with external
controller on 27 MHz. Sustained data rate to external
SDRAM ≤9 Mbytes/s in bursts of 128 bytes
• Dedicated input for audio and video in PES or ES in byte
wide. Data input rate: ≤9 Mbytes/s in byte mode.
Accompanying strobe signals distinguish between audio
and video data
• Dedicated compressed data input compatible with the
VLSI VES2020/2030 demultiplexers; video is received
in byte format and audio serially
• Audio and/or video can also be input via the CPU
interface in PES/ES in 8 or 16-bit parallel format up to a
peak data rate of 9 Mbytes/s
• Single 27 MHz external clock for time base reference
and internal processing. Internal system time base at
90 kHz can be synchronized via CPU port. All required
decoding and presentation clocks are generated
internally
• Flexible memory allocation under control of the external
CPU enables optimized partitioning of memory for
different tasks
• Boundary scan testing implemented
• External SDRAM self test
• Supply voltage 3.3 V
• Package QFP160.
CPU related features
• 16 bits data, 8 bits address, or 16 bits multiplexed bus.
Motorola 68xxx and Intel x 86 compatible.
• Support fast DMA transfer
• Flexible bidirectional interface to external SDRAM.
Minimum sustained rate is 9 Mbytes/s
• Enhanced block mover allows 3 D data move in the
external SDRAM. Picture move/Graphic bit maps
construction can be done with minimum CPU support.
MPEG2 system features
• Parsing of MPEG2 PES and MPEG1 packet streams
• Double system time clock counters
• Stand-alone or supervised audio/video synchronization
• Processing of errors flagged by channel decoding
section
• Support for retrieval of PES header.
MPEG2 video features
• Decoding of MPEG2 video up to main level, main profile
• Output picture format: CCIR-601 4:2:2 interlaced
pictures. Picture format 720 × 576 at 50 Hz or 720 × 480
at 60 Hz
• Support of constant and variable bit rates up to
15 Mbits/s
• Stand-alone or CPU controlled mode for
decoding/display processes
• Stand-alone mode can be used by applications requiring
still pictures manipulations
• Output interface at 8-bit wide, 27 MHz UYVY
multiplexed bus
• Horizontal and vertical pan and scan allows the
extraction of a window from the coded picture
• Flexible horizontal scaling from 0.5 up to 4 allows easy
aspect ratio conversion including support
for 2.21 : 1 aspect ratio movies. In case of shrinking an
anti-aliasing pre-filter is applied
• Vertical scaling with fixed factors 0.5, 1 or 2. Factor 0.5,
realizing picture shrink. Factor 2 can be used for
up-conversion of pictures with 288 (240) lines or less.
• Vertical down-scaling with 0.75 factor, realizing letter
box conversion
• Horizontal and vertical scaling can be combined to scale
pictures to
1
⁄4 their original size, thus freeing up screen
space for graphic applications like electronic program
guides
• Non full screen MPEG pictures will be displayed in a box
of which position and background colour are adjustable
by the external microcontroller
• Nominal video input buffer size for ml@mp 2.7 Mbit
• Video output may be slaved to internally (master)
generated or externally (slave) supplied HV
synchronization signals. The position of active video is
programmable. Display phase is not affected by MPEG
timebase changes.
Page 3

1998 Sep 07 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
• Video output direct connectable to SAA718x encoder
family
• Various trick modes under control of external
microcontroller in stand-alone mode:
– Freeze field/frame on I or P pictures; restart on I
picture
– Freeze field on B pictures; restart on the next I or P
picture.
– Scanning and decoding of I or I + P pictures in a IBP
sequence
– Single step mode
– Repeat/skip field for time base correction.
MPEG2 audio features
• Decoding of 2 channels, layer I and II MPEG audio.
Support for mono, stereo, intensity stereo and dual
channel mode.
• Constant and variable bit rates up to 448 kbit/s
• Supported audio sampling frequencies: 48, 44.1, 32, 24,
22.05 and 16 kHz
• CRC error detection
• 3 decoding modes for dual channel streams: decoding
of CH1 only, decoding of CH2 only and decoding of both
CH1 and CH2
• Storage of last 54 bytes in ancillary data field
• Dynamic Range Control (DRC) at output
• Independent channel volume control and programmable
inter channel crosstalk through a baseband audio
processing unit
• Muting possibility via external controller. Automatic
muting in case of errors or data lack.
• Generation of ‘beeps’ with programmable tone height,
duration and amplitude
• Serial two channel digital audio output with 16, 18, 20 or
22 bits per sample, compatible either to I
2
S or Japanese
formats. Output can be set to high-impedance mode via
the external controller.
• Serial SPDIF audio output. Output can be set to
high-impedance mode.
• Clock output 256 or 384 × fs for external DA converter.
Output can be set to high-impedance mode.
• Audio FIFO in external SDRAM. Programmable buffer
size, at least 64 kbit is available.
• Synchronization modes: PTS controlled, PTS free
running, software controlled, buffer controlled
• PTS register can be set via external controller
• Programmable processing delay compensation
• Software controlled stop and restart functions.
Graphics features
• Graphics are presented in boxes independent of video
format
• Screen arrangement of boxes is determined by display
list mechanism which allows for multiple boxes,
background loading, fast switching, scrolling and fading
of regions
• Support of 2, 4, 8-bit/pixel in fixed bit maps format or
coded in accordance to the DVB variable/run length
standard for region based graphics
• Display colours are obtained via colour look up tables.
CLUT output is YUVT at 8-bit for each signal component
thus enabling 16 M different colours and 6-bit for T
which gives 64 mixing levels with video,
(T = transparency).
• Bit-map table mechanism to specify a sub set of entries
if the CLUT is larger than required by the coded bit
pattern. Supported bit-map tables are 16 to 256,
4 to 256 and 4 to 16.
• Graphics boxes may not overlap vertically. If 256 entry
CLUT has to be down loaded, a vertical separation of
1 line is mandatory.
• Optimized memory utilization in MPEG video decoding
allows for a storage capacity of 1.2 Mbit for graphics bit
maps. Flexibility in memory control enables larger
capacity in a lot of applications. Moreover variable
length/run length encoding makes better use of
available memory capacity for graphics bit maps thus
making full screen graphics at 8-bit/pixel feasible.
• Fast CPU access (9 Mbytes/s) enables full 1.2 Mbit bit
map update within 20 ms
• Internal support for fast block moves in external SDRAM
• Graphics mechanism can be used for signal generation
in the vertical blanking interval. Useful for teletext, wide
screen signalling, closed caption, etc.
• Support for a single down loadable cursor of 1k pixel
with programmable shape. Supported shapes are
8 × 128 pixels, 16 × 64 pixels, 32 × 32 pixels,
64 × 16 pixels and 128 × 8 pixels.
• Cursor colours obtained via 4 entry CLUT with YUVT at
6,4,4 respectively 2 bits. Mixing of cursor with
video + graphics in 4 levels.
• Cursor can be moved freely across the screen without
overlapping restrictions.
Page 4

1998 Sep 07 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
APPLICATIONS
• Tbf.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAA7212 is an MPEG2 source decoder which combines audio decoding and video decoding. Additionally to these
basic MPEG functions it also provides means for enhanced graphics and/or on-screen display (OSD). Due to an
optimized architecture for audio and video decoding, maximum capacity in external memory and processing power from
the external CPU is available for graphics support.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
ORDERING INFORMATION
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DD
functional supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
I
DD(tot)
total supply current; VDD= 3.3 V − tbf − mA
f
clk
device clock frequency −30 ppm 27.0 +30 ppm MHz
TYPE NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SAA7212H QFP160 plastic quad flat package; 160 leads (lead length 1.95 mm);
body 28 × 28 × 3.4 mm; high stand-off height
SOT322-1
Page 5
1998 Sep 07 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
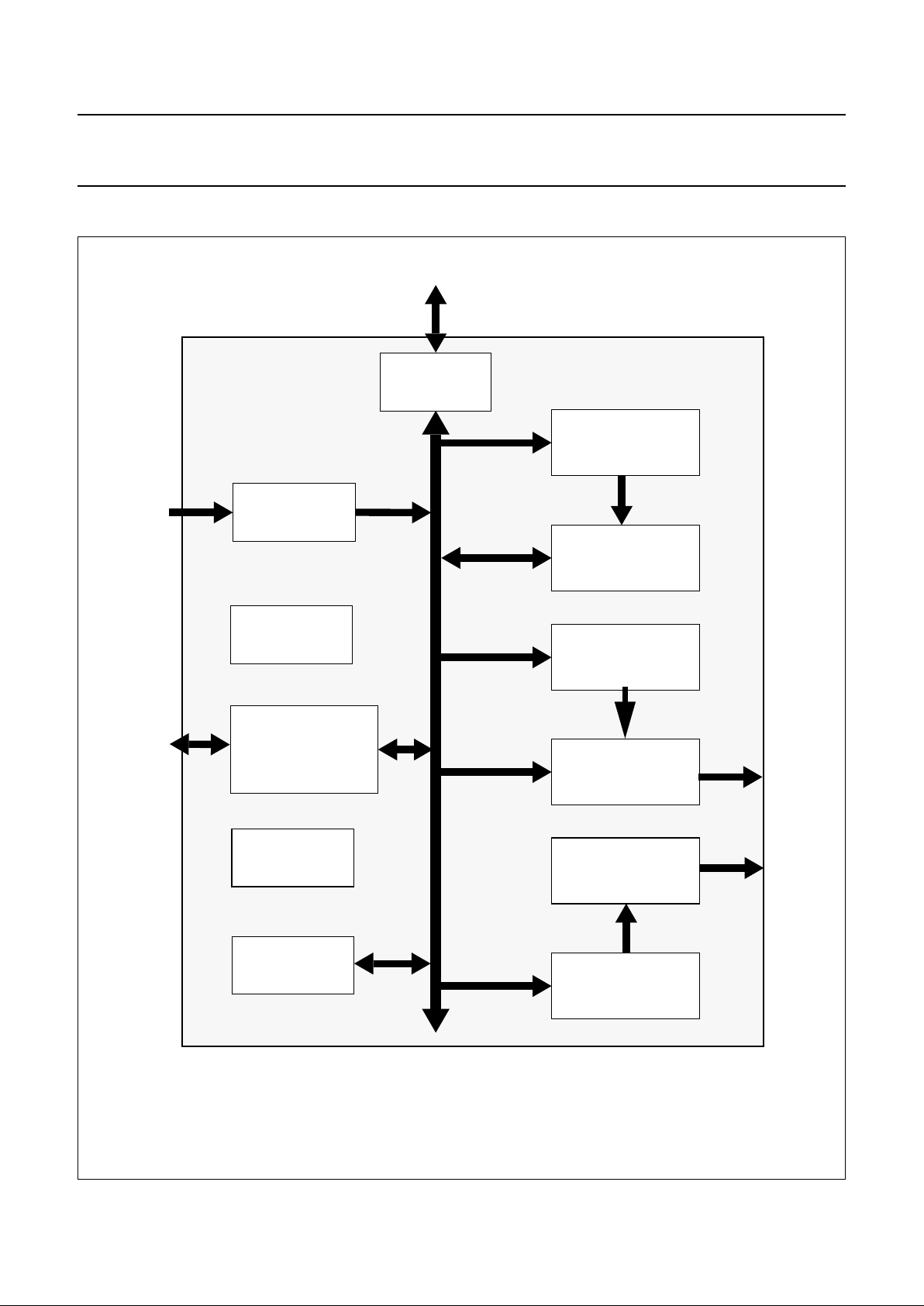
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Fig.1 Block diagram.
Memory
interface
Audio/video
interface
SDRAM
to/from
to
digital
encoder
Display
to
audio
DAC
Decoder
Audio
System time
base unit
Graphics
unit
CPU
unit
external
Decoder
Video
Clock
JTAG
generation
buffer and sync
Video input
from
Demux
buffer and sync
Audio input
Host interface
SDRAM access
unit
Page 6
1998 Sep 07 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
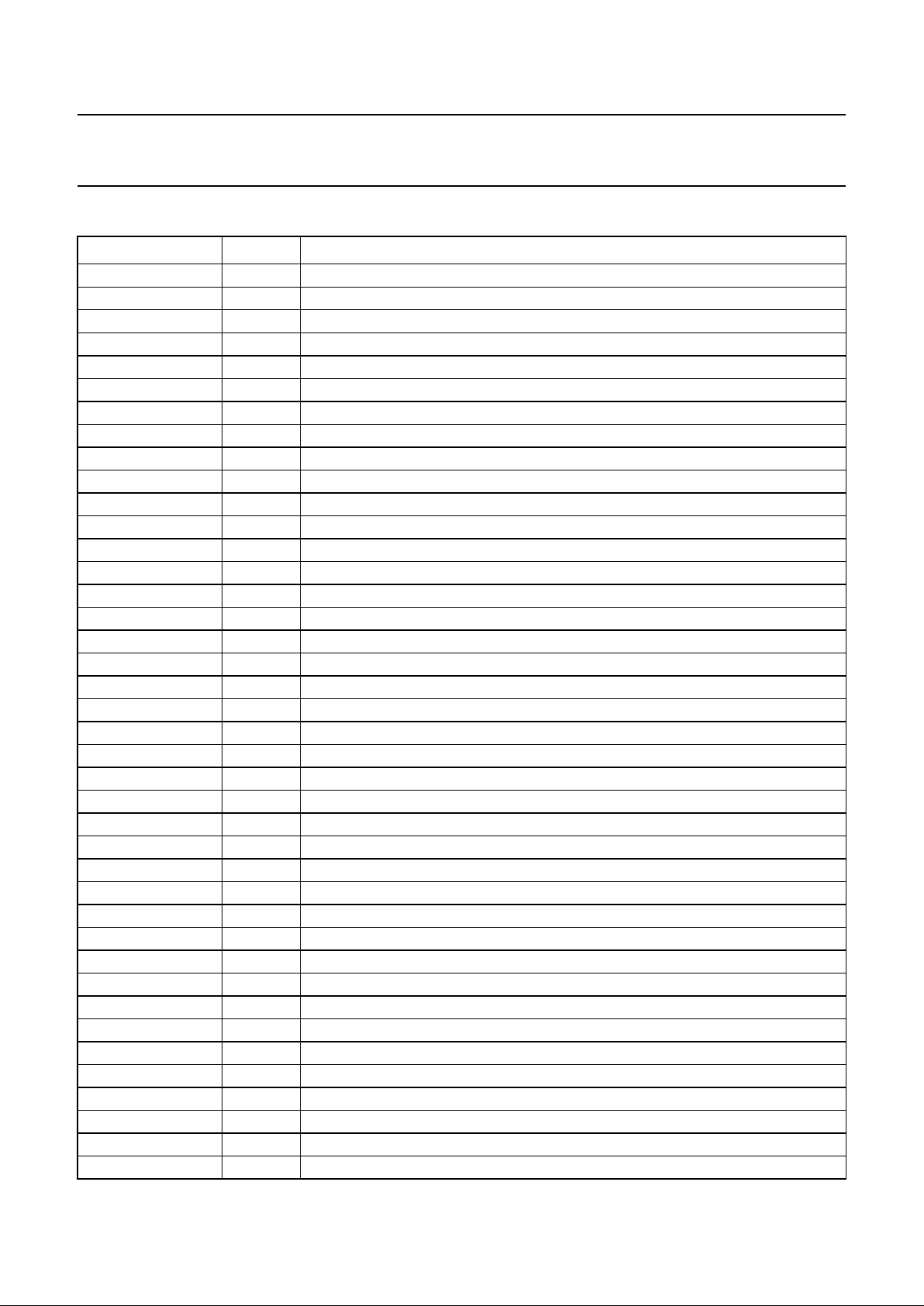
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
MUX 1 multiplexed/non multiplexed bus
CPU_TYPE 2 Intel/Motorola selection
DMA_ACK 3 DMA acknowledge
DMA_REQ 4 DMA request
DMA_DONE 5 DMA end
DMA_RDY 6 DMA ready
V
SS
7 ground for pad ring
CS 8 chip select.
DS 9 data strobe
AS 10 address strobe
RWN 11 read/write
DTACK 12 data acknowledge
V
DD
13 3.3 V supply for pad ring
IRQ 0 14 individually maskable interrupts
IRQ 1 15 individually maskable interrupts
V_REQ 16 compressed video data request
A_REQ 17 compressed audio data request
V
SS
18 ground for pad ring
V
SSCO
19 ground for core logic
V
DDCO
20 3.3 V supply for core logic
DATA 0 21 CPU data interface
DATA 1 22 CPU data interface
DATA 2 23 CPU data interface
DATA 3 24 CPU data interface
V
DD
25 3.3 V supply for pad ring
DATA 4 26 CPU data interface
DATA 5 27 CPU data interface
DATA 6 28 CPU data interface
DATA 7 29 CPU data interface
V
SS
30 ground for pad ring
DATA 8 31 CPU data interface
DATA 9 32 CPU data interface
DATA 10 33 CPU data interface
DATA 11 34 CPU data interface
V
DD
35 3.3 V supply for pad ring
DATA 12 36 CPU data interface
DATA 13 37 CPU data interface
DATA 14 38 CPU data interface
DATA 15 39 CPU data interface
V
SS
40 ground for pad ring
Page 7

1998 Sep 07 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
ADDRESS 1 41 CPU address interface
ADDRESS 2 42 CPU address interface
ADDRESS 3 43 CPU address interface
ADDRESS 4 44 CPU address interface
V
DD
45 3.3 V supply for pad ring
ADDRESS 5 46 CPU address interface
ADDRESS 6 47 CPU address interface
ADDRESS 7 48 CPU address interface
ADDRESS 8 49 CPU address interface
V
SS
50 ground for pad ring
V
SSCO
51 ground for core logic
V
DDCO
52 3.3 V supply for core logic
SDRAM_DATA 0 53 SDRAM data
SDRAM_DATA 15 54 SDRAM data
SDRAM_DATA 1 55 SDRAM data
V
DD
56 3.3 V supply for pad ring
SDRAM_DATA 14 57 SDRAM data
SDRAM_DATA 2 58 SDRAM data
SDRAM_DATA 13 59 SDRAM data
V
SS
60 ground for pad ring
SDRAM_DATA 3 61 SDRAM data
SDRAM_DATA 12 62 SDRAM data
SDRAM_DATA 4 63 SDRAM data
V
DD
64 3.3 V supply for pad ring
SDRAM_DATA 11 65 SDRAM data
SDRAM_DATA 5 66 SDRAM data
SDRAM_DATA 10 67 SDRAM data
V
SS
68 ground for pad ring
SDRAM_DATA 6 69 SDRAM data
SDRAM_DATA 9 70 SDRAM data
SDRAM_DATA 7 71 SDRAM data
V
DD
72 3.3 V supply for pad ring
SDRAM_DATA 8 73 SDRAM data
SDRAM_WE 74 SDRAM write enable
SDRAM_CAS 75 SDRAM column address strobe
V
SS
76 ground for pad ring
SDRAM_RAS 77 SDRAM row address strobe
SDRAM_UDQ 78 SDRAM write mask
V
DD
79 3.3 V supply for pad ring
READ_IN 80 read command in
READ_OUT 81 read command out
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
Page 8

1998 Sep 07 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
V
SS
82 ground for pad ring
CP81MEXT 83 81 MHz SDRAM clock return path
CP81M 84 81 MHz SDRAM memory clock
V
DD
85 3.3 V supply for pad ring
SDRAM_ADDR 8 86 SDRAM address
SDRAM_ADDR 9 87 SDRAM address
SDRAM_ADDR 11 88 SDRAM address
V
SS
89 ground for pad ring
SDRAM_ADDR 7 90 SDRAM address
SDRAM_ADDR 10 91 SDRAM address
SDRAM_ADDR 6 92 SDRAM address
V
DD
93 3.3 V supply for pad ring
SDRAM_ADDR 0 94 SDRAM address
SDRAM_ADDR 5 95 SDRAM address
SDRAM_ADDR 1 96 SDRAM address
V
SS
97 ground for pad ring
SDRAM_ADDR 4 98 SDRAM address
SDRAM_ADDR 2 99 SDRAM address
SDRAM_ADDR 3 100 SDRAM address
V
SSCO
101 ground for core logic
V
DDCO
102 3.3 V supply for core logic
V
DD
103 3.3 V supply for pad ring
Test 5 104 IC test interface (see note 2)
Test 6 105 IC test interface (see note 2)
HS 106 horizontal synchronization
VS 107 vertical synchronization
V
SS
108 ground for pad ring
YUV 0 109 YUV video output at 27 MHz
YUV 1 110 YUV video output at 27 MHz
YUV 2 111 YUV video output at 27 MHz
YUV 3 112 YUV video output at 27 MHz
V
DD
113 3.3 V supply for pad ring
YUV 4 114 YUV video output at 27 MHz
YUV 5 115 YUV video output at 27 MHz
YUV 6 116 YUV video output at 27 MHz
YUV 7 117 YUV video output at 27 MHz
Test 4 118 IC test interface (see note 3)
GRPH 119 indicator for graphics information
Test 3 120 IC test interface (see note 4)
V
DDAN
121 3.3 V supply for analog blocks
V
SSAN
122 ground for analog blocks
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
Page 9

1998 Sep 07 9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
V
SS
123 ground for pad ring
CLK 124 27 MHz Clock input
V
SS
125 ground for pad ring
TCK 126 boundary scan test clock
TRST 127 boundary scan test reset
TMS 128 boundary scan test mode select
TDO 129 boundary scan test data output
TDI 130 boundary scan test data input
V
DD
131 3.3 V supply for pad ring
Test 0 132 IC test interface (see note 4)
Test 1 133 IC test interface (see note 4)
Test 2 134 IC test interface (see note 4)
AUDDEN 135 synchronization of the serial audio input (A_DATA)
A_DATA 136 serial audio input
V
DD
137 3.3 V supply for pad ring
RESET 138 hard reset input, active LOW
FSCLK 139 256 or 384f
s
(audio sampling)
V
DDCO
140 3.3 V supply for core logic
V
SSCO
141 ground for core logic
SCK 142 serial audio clock
SD 143 serial audio data output
V
SS
144 ground for pad ring
WS 145 word select
SPDIF 146 digital audio output
ERROR 147 flag for bitstream error.
V_STROBE 148 video strobe
V
DD
149 3.3 V supply for pad ring
AV_DATA 0 150 MPEG stream input port
AV_DATA 1 151 MPEG stream input port
AV_DATA 2 152 MPEG stream input port
AV_DATA 3 153 MPEG stream input port
V
SS
154 ground for pad ring
AV_DATA 4 155 MPEG stream input port
AV_DATA 5 156 MPEG stream input port
AV_DATA 6 157 MPEG stream input port
AV_DATA 7 158 MPEG stream input port
A_STROBE 159 audio strobe
V
DD
160 3.3 V supply for pad ring
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
Page 10

1998 Sep 07 10
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
Notes
1. 5 V tolerant outputs swing between VSS and VDD but 5 V tolerant input can receive signal swinging between VSS and
3.3 V or VSS and 5 V.
2. Should be left open in normal mode.
3. Should be tied up to VDD in normal mode.
4. Should be tied down to ground in normal mode.
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
handbook, halfpage
SAA7212H
1
160
121
41
80
40
120
81
MGL400
Page 11

1998 Sep 07 11
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
HANDLING
Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharges in normal handling. However, to be totally safe, it is
desirable to take normal precautions appropriate to handling integrated circuits.
CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DD
supply voltage −0.5 +5 tbf V
V
n(max)
voltage on all pins 0 5 tbf V
P
tot
total power dissipation T
amb
=25°C − 1 tbf W
T
stg
IC storage temperature −55 150 tbf °C
T
amb
operating ambient temperature 0 70 tbf °C
SYMBOL PARAMETER VALUE UNIT
R
th(j-a)
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 30 K/W
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
DD
functional supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
I
DD(tot)
total supply current; VDD= 3.3 V − tbf − mA
Inputs
V
IH(5V tolerant)
input voltage HIGH 2.0 − 6.5 V
V
IH
input voltage HIGH 0.7V
DD
− VDD+2.0 V
V
IL(5V tolerant)
input voltage LOW −0.5 − 0.8 V
V
IL
input voltage LOW −0.5 − 0.3V
DD
V
I
L
leakage current −−20 µA
C
i
input capacitance 0 − 10 pF
Outputs
V
OH(5V tolerant)
output voltage HIGH 2.4 −− V
V
OH
output voltage HIGH VDD− 0.4 −− V
V
OL(5V tolerant)
output voltage LOW −−0.4 V
V
OL
output voltage LOW −−0.4 V
DC timing
T
cy
cycle time − 37.037 − ns
δ duty factor 40 − 60 %
Page 12

1998 Sep 07 12
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Fig.3 Application diagram
CVBS
H,V
YUV
I2S
AUDIO
D/A
L
R
8
valid
Strobe
SAA7212
27 MHz
4-Mbit
DRAM
16-Mbit
SDRAM
TTX/TTXRQ
high
data
4-Mbit
EPROM
speed
27.0 MHz
I2C-bus
16
16
H,V,FP
SAA7183
Y/C
RGB
(euro-denc)
8+3
Irq
12
ctrldataaddr
2
4
CPU + DEMUX
Page 13

1998 Sep 07 13
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
Fig.4 Connection SAA7212 SDRAM.
SDRAM 16-Mbit
DQ0
DQ15
....
A7
A0
....
CAS
A11
A10
A9
A8
RAS
CS
WE
UDQM
LDQM
CKE
CLK
TSSOP II
50 pins
400 mil
SDRAM_DATA0
SDRAM_DATA15
.......
SDRAM_ADDR7
SDRAM_ADDR0
....
SDRAM_CAS
SDRAM_ADDR11
SDRAM_ADDR10
SDRAM_ADDR9
SDRAM_ADDRA8
SDRAM_RAS
SDRAM_CS
SDRAM_WE
SDRAM_UDQ
CP81M
READ_IN
READ_OUT
CP81MEXT
The board should be designed to insure a similar load on the CP81M and READ_OUT pins as well as a similar fly time between the CP81M and
CP81MEXT pins on one side and the READ_OUT and READ_IN pins on the other side.
Page 14

1998 Sep 07 14
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
PACKAGE OUTLINE
UNIT A1A2A3b
p
cE
(1) (1) (1)
eH
E
LL
p
Zywv θ
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
mm
0.40
0.25
3.70
3.15
0.25
0.40
0.25
0.23
0.13
28.1
27.9
0.65 0.31.95
32.2
31.6
1.5
1.1
8
0
o
o
0.15 0.1
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
1.1
0.7
SOT322-1 MO112DD1
95-02-04
97-08-04
D
(1)
28.1
27.9
H
D
32.2
31.6
E
Z
1.5
1.1
D
pin 1 index
b
p
e
θ
E
A
1
A
L
p
detail X
L
(A )
3
B
40
c
D
H
b
p
E
H
A
2
v M
B
D
Z
D
A
Z
E
e
v M
A
X
1
160
121
120
81
80
41
y
w M
w M
0 5 10 mm
scale
SOT322-1
160 leads (lead length 1.95 mm); body 28 x 28 x 3.4 mm; high stand-off height
QFP160: plastic quad flat package;
A
max.
3.95
Page 15

1998 Sep 07 15
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages”
(order code 9398 652 90011).
Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering techniques are suitable for all QFP
packages.
The choice of heating method may be influenced by larger
plastic QFP packages (44 leads, or more). If infrared or
vapour phase heating is used and the large packages are
not absolutely dry (less than 0.1% moisture content by
weight), vaporization of the small amount of moisture in
them can cause cracking of the plastic body. For details,
refer to the Drypack information in the
“Data Handbook
IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing
Methods”
.
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
infrared/convection heating in a conveyor type oven.
Throughput times (preheating, soldering and cooling) vary
between 50 and 300 seconds depending on heating
method. Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C.
Wave soldering
Wave soldering is not recommended for QFP packages.
This is because of the likelihood of solder bridging due to
closely-spaced leads and the possibility of incomplete
solder penetration in multi-lead devices.
If wave soldering cannot be avoided, for QFP
packages with a pitch (e) larger than 0.5 mm, the
following conditions must be observed:
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave)
soldering technique should be used.
• The footprint must be at an angle of 45° to the board
direction and must incorporate solder thieves
downstream and at the side corners.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Maximum permissible solder temperature is 260 °C, and
maximum duration of package immersion in solder is
10 seconds, if cooled to less than 150 °C within
6 seconds. Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
Repairing soldered joints
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonallyopposite end leads. Use only a low voltage soldering iron
(less than 24 V) applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact
time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C. When
using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in
one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
CAUTION
Wave soldering is NOT applicable for all QFP
packages with a pitch (e) equal or less than 0.5 mm.
Page 16

1998 Sep 07 16
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
DEFINITIONS
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
Page 17

1998 Sep 07 17
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
NOTES
Page 18

1998 Sep 07 18
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
NOTES
Page 19

1998 Sep 07 19
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
NOTES
Page 20

Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company
© Philips Electronics N.V. 1998 SCA60
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Middle East: see Italy
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 4027 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Pakistan: see Singapore
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC,MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +632 817 3474
Poland: Ul. Lukiska 10, PL 04-123 WARSZAWA,
Tel. +48 22 612 2831, Fax.+48 22612 2327
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 755 6918, Fax.+7 095755 6919
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 319762,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 7430 Johannesburg 2000,
Tel. +27 11 470 5911, Fax.+27 11470 5494
South America: Al. Vicente Pinzon, 173, 6th floor,
04547-130 SÃO PAULO, SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax.+55 11821 2382
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 93 301 6312, Fax.+34 93301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 5985 2000, Fax. +46 85985 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2741 Fax. +41 1 488 3263
Taiwan: Philips Semiconductors, 6F, No. 96, Chien Kuo N. Rd., Sec. 1,
TAIPEI, Taiwan Tel. +886 2 2134 2865, Fax. +886 2 2134 2874
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Talatpasa Cad. No. 5, 80640 GÜLTEPE/ISTANBUL,
Tel. +90 212 279 2770, Fax. +90 212 282 6707
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +38044 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 181 730 5000, Fax.+44 181754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 625 344, Fax.+38111 635777
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors,
International Marketing & Sales Communications, Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218,
5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 34 Waterloo Road, NORTH RYDE, NSW 2113,
Tel. +61 2 9805 4455, Fax. +61 29805 4466
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213, Tel. +43 160 1010,
Fax. +43 160 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 200 733, Fax. +375 172 200773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: see South America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15th floor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 689 211, Fax. +359 2689 102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +8522319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Prags Boulevard 80, PB 1919, DK-2300 COPENHAGEN S,
Tel. +45 32 88 2636, Fax. +45 31 57 0044
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615800, Fax. +358 9 61580920
France: 51 Rue Carnot, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 40 99 6161, Fax. +33 1 4099 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 23 53 60, Fax. +4940 23536 300
Greece: No. 15, 25th March Street, GR 17778 TAVROS/ATHENS,
Tel. +30 1 4894 339/239, Fax. +30 14814 240
Hungary: see Austria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Band Box Building, 2nd floor,
254-D, Dr. Annie BesantRoad, Worli, MUMBAI 400 025,
Tel. +91 22 493 8541, Fax.+91 22493 0966
Indonesia: PT Philips Development Corporation, Semiconductors Division,
Gedung Philips, Jl. Buncit Raya Kav.99-100, JAKARTA 12510,
Tel. +62 21 794 0040 ext.2501, Fax. +6221 7940080
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax.+353 17640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, PO Box 18053,
TEL AVIV 61180, Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax.+972 3649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS, Piazza IV Novembre 3,
20124 MILANO, Tel. +39 2 6752 2531, Fax. +39 2 6752 2557
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku,
TOKYO 108-8507, Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5077
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 7574880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381
Printed in The Netherlands 545104/750/02/pp20 Date of release: 1998 Sep 07 Document order number: 9397 750 04068
 Loading...
Loading...