Datasheet SAA7124H-01, SAA7124HZ-01, SAA7124WP-00, SAA7125H-01, SAA7125WP-01 Datasheet (Philips)
Page 1

DATA SH EET
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC22
1996 Nov 07
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
SAA7124; SAA7125
Digital Video Encoder
(ECO-DENC)
Page 2
1996 Nov 07 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
FEATURES
• Monolithic CMOS 5 V device
• Digital PAL/NTSC encoder
• System pixel frequency 13.5 MHz
• Accepts MPEG decoded data on 8-bit wide input port.
Input data format Cb, Y, Cr etc.
“(CCIR 656)”
• Four DACs for CVBS (10-bit resolution), RGB (9-bit
resolution) operating at 27 MHz; RGB sync on CVBS
• Optionally 2 times CVBS and Y, C (all 10-bit resolution)
available simultaneously
• Closed captioning encoding
• On-chip YUV to RGB dematrix optionally to be
by-passed for Cr, Y, Cb output on RGB DACs
• Fast I
2
C-bus control port (400 kHz)
• Encoder can be master or slave
• Programmable horizontal and vertical input
synchronization phase, via input pins or auxiliary codes
at MP data port
• Programmable horizontal sync output phase
• Internal 100/75 Colour Bar Generator (CBG)
• Macrovision Pay-per-View copy protection system as
option, also partly used for RGB output.
This applies to SAA7124 only. The device is protected
by USA patent numbers 4631603, 4577216 and
4819098 and other intellectual property rights. Use of
the Macrovision anti-copy process in the device is
licensed for non-commercial home use only.
Reverse engineering or disassembly is prohibited.
Please contact your nearest Philips Semiconductor
sales office for more information
• Controlled rise and fall times of output syncs and
blanking
• Down-mode of DACs
• LQFP64 (V1 devices only), QFP80 or PLCC84
package.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAA7124; SAA7125 encodes digital YUV video data
to an NTSC or PAL CVBS plus RGB or alternatively to
S-Video and CVBS output.
Optionally, the YUV to RGB dematrix can be by-passed
providing the digital-to-analog converted Cb, Y, Cr signals
instead of RGB.
The circuit accepts CCIR compatible YUV data with
720 active pixels per line in 4:2:2multiplexed formats,
for example MPEG decoded data.
It includes a sync/clock generator and on-chip
Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs).
ORDERING INFORMATION
Note
1. LQFP64 package for V1 devices only.
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
(1)
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SAA7124WP;
SAA7125WP
PLCC84 plastic leaded chip carrier; 84 leads SOT189-2
SAA7124HZ;
SAA7125HZ
LQFP64 plastic low profile quad flat package; 64 leads; body 10 × 10 × 1.4 mm SOT314-2
SAA7124H;
SAA7125H
QFP80 plastic quad flat package; 80 leads (lead length 2.35 mm);
body 14 × 20 × 2.8 mm
SOT318-3
Page 3
1996 Nov 07 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DDA
analog supply voltage 4.75 5.0 5.25 V
V
DDD
digital supply voltage 4.75 5.0 5.25 V
I
DDA
analog supply current − tbf 60 mA
I
DDD
digital supply current − tbf 100 mA
V
i
input signal voltage levels TTL compatible
V
o(p-p)
analog output signal voltages Y, C, CVBS and RGB without load
(peak-to-peak value)
− 2.0 − V
R
L
load resistance 80 −−Ω
ILE LF integral linearity error −−±4 LSB
DLE LF differential linearity error −−±1 LSB
T
amb
operating ambient temperature 0 − +70 °C
Page 4
1996 Nov 07 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
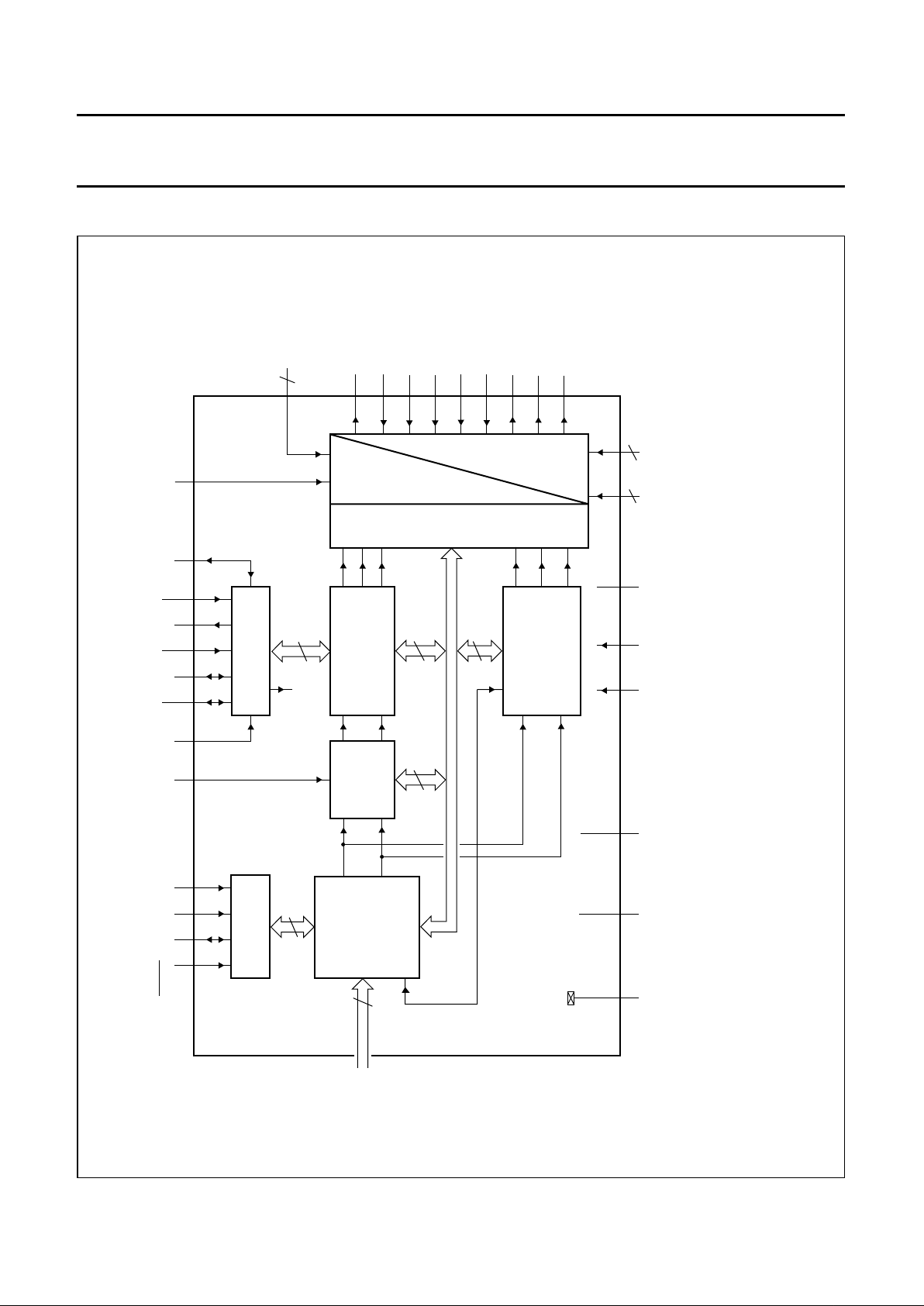
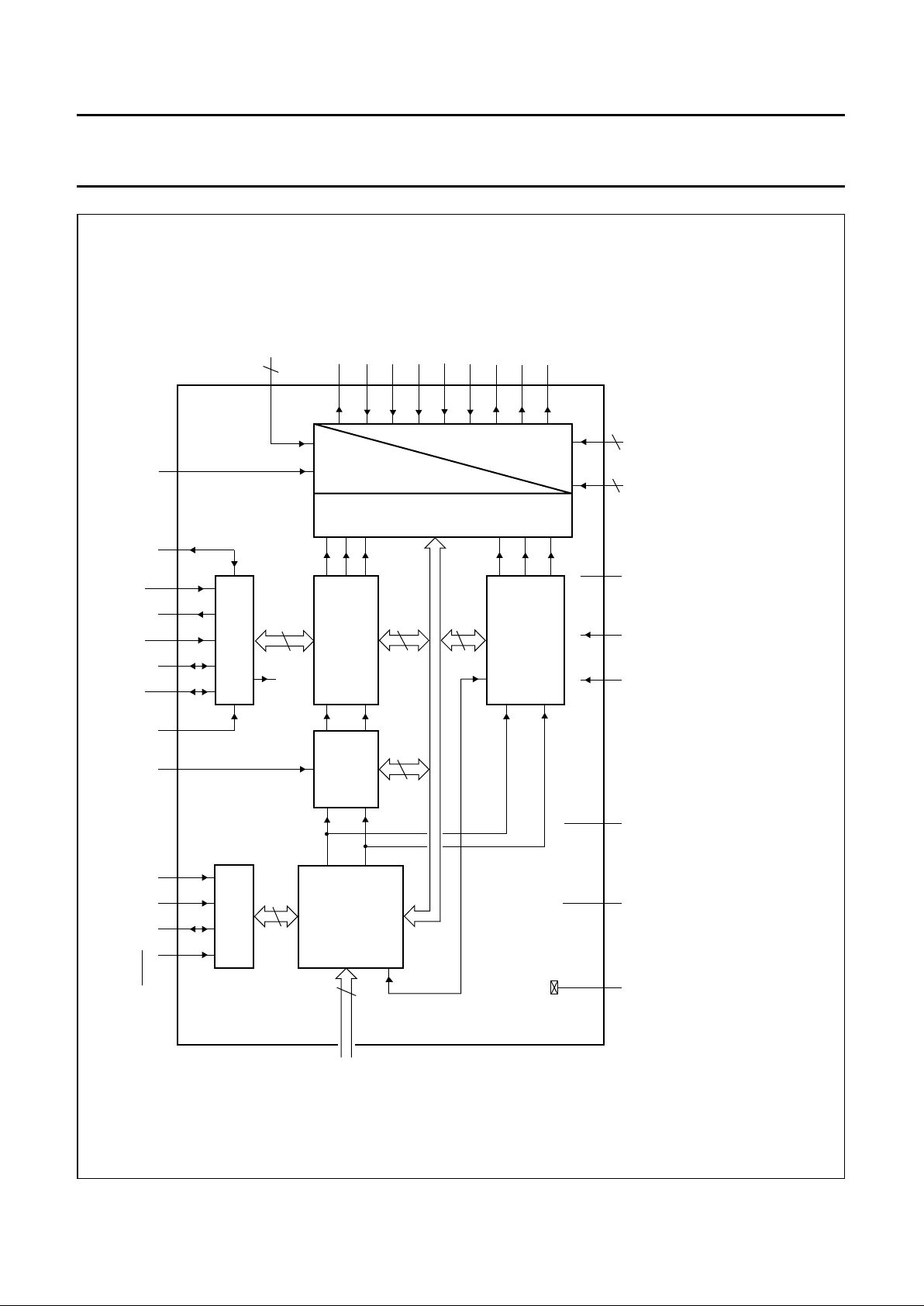
BLOCK DIAGRAM
ll pagewidth
MGG550
8
2
8
I
2
C-BUS
INTERFACE
I
2
C-bus
control
8
I
2
C-bus
control
8
I
2
C-bus
control
8
22
I
2
C-bus
control
I
2
C-bus
control
I
2
C-bus
control
8
I
2
C-bus
control
DATA
MANAGER
ENCODER
SYNC CLOCK
OUTPUT
INTERFACE
MODE
RGB
PROCESSOR
internal
control bus
CbCr
Y
C
clock
and timing
D
A
1
84
83
4
37 50
35
36
46
45 44
48
54, 57, 60,
64, 74
53, 75
73
67
62
59
56
65
61
58
55
63, 6852, 76
7778
3, 15, 24,
30, 39, 42,
51, 79, 81
5, 14, 22,
29, 38, 41,
49, 80, 82
2, 16 to 21, 23,
40, 43, 47, 66,
70, 72
Y
CbCr
25 to 28,
31 to 34
MP7
to
MP0
RESET
SDA
SCL
SA
RTCI
CDIR
RCV1
RCV2
V
DDDO
(5)
XTALO
XTALI
LLC
V
DDA1
to V
DDA5
V
refH1VrefH2
CVBS
(1)
V
SSA1
res
res
res
res
RED
(2)
GREEN
(3)
BLUE
(4)
CUR1
CUR2
V
refL1VrefL2
AP
69, 71
resSPn.c.
V
DDD1
to
V
DDD9
V
SSD1
to
V
SSD9
Y
SAA7124
SAA7125
Fig.1 Block diagram; PLCC84.
(1) Alternatively Y or CVBS.
(2) Alternatively CHROMA or Cr.
(3) Alternatively CVBS or Yin.
(4) Alternatively CVBS or Cb.
(5) V1 devices only.
Page 5
1996 Nov 07 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
ll pagewidth
MGG551
8
2
8
I
2
C-BUS
INTERFACE
I
2
C-bus
control
8
I
2
C-bus
control
8
I
2
C-bus
control
8
22
I
2
C-bus
control
I
2
C-bus
control
I
2
C-bus
control
8
I
2
C-bus
control
DATA
MANAGER
ENCODER
SYNC CLOCK
OUTPUT
INTERFACE
MODE
RGB
PROCESSOR
internal
control bus
CbCr
Y
C
clock
and timing
D
A
57
56
55
59
21 31
19
20
28
27 26
29
34, 36, 38,
41, 46
33, 47
45
42,
43
39
37
35
40, 4432, 48
4950
6, 8, 14,
23, 25, 51,
53, 58
5, 7, 13,
22, 24, 30,
52, 54, 60
Y
CbCr
9 to 12,
15 to 18
MP7
to
MP0
RESET
SDA
SCL
SA
RTCI
CDIR
RCV1
RCV2
V
DDDO
XTALO
XTALI
LLC
V
DDA1
to V
DDA5
V
refH1VrefH2
CVBS
(1)
V
SSA2
RED
(2)
GREEN
(3)
BLUE
(4)
CUR1
CUR2
V
refL1VrefL2
APSP
V
DDD1
to
V
DDD9
V
SSD1
to
V
SSD8
Y
SAA7124
SAA7125
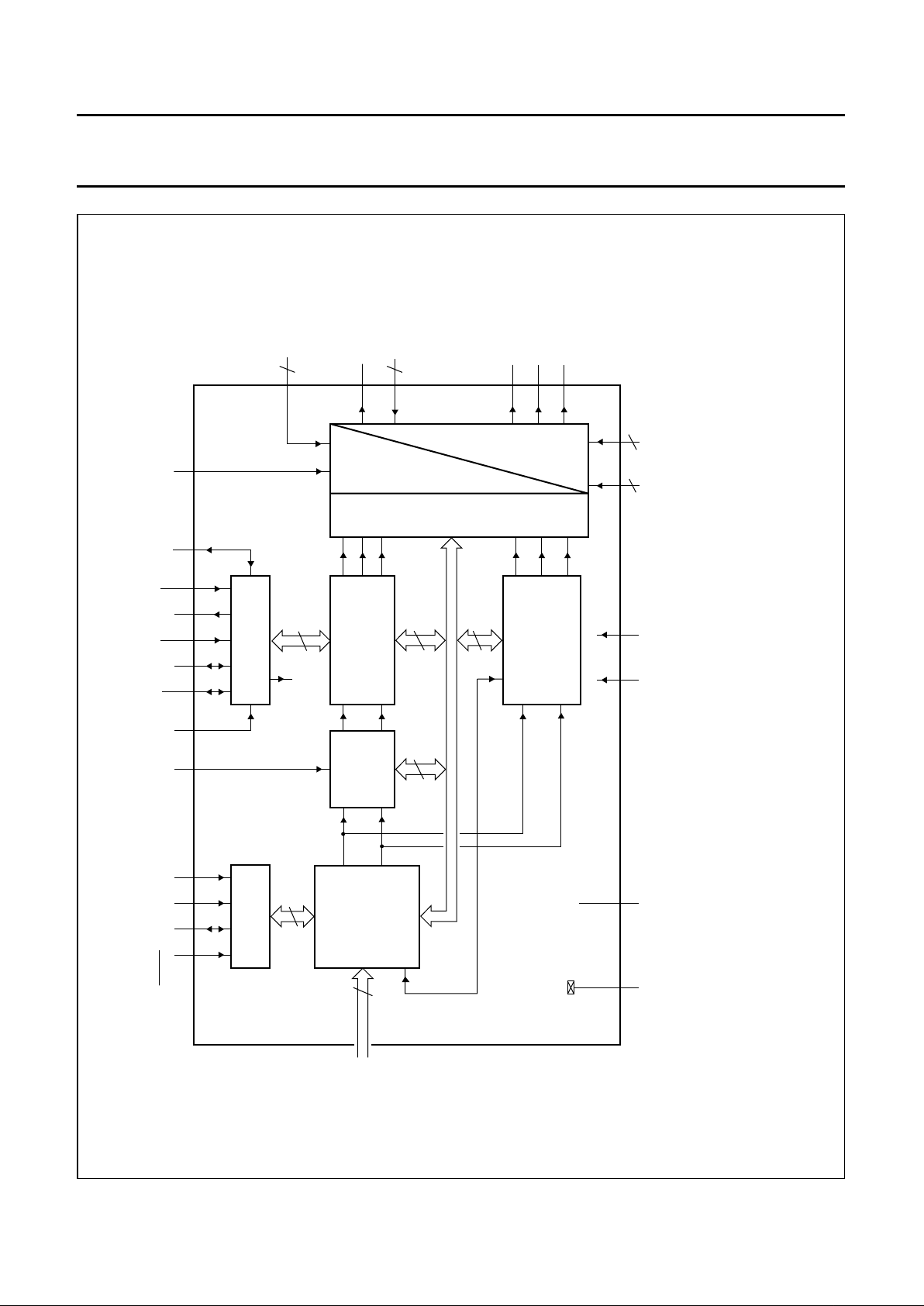
2
Fig.2 Block diagram; TQFP64, V1 devices only.
(1) Alternatively Y or CVBS.
(2) Alternatively CHROMA or Cr.
(3) Alternatively CVBS or Yin.
(4) Alternatively CVBS or Cb.
Page 6
1996 Nov 07 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
gewidth
MGG552
8
2
8
I
2
C-BUS
INTERFACE
I
2
C-bus
control
8
I
2
C-bus
control
8
I
2
C-bus
control
8
22
I
2
C-bus
control
I
2
C-bus
control
I
2
C-bus
control
8
I
2
C-bus
control
DATA
MANAGER
ENCODER
SYNC CLOCK
OUTPUT
INTERFACE
MODE
RGB
PROCESSOR
internal
control bus
CbCr
Y
C
clock
and timing
D
A
73
72
71
75
27 38
25
26
34
33 32
36
54, 57, 60,
64, 74
53, 75
61
55
54
51
48
45
50
47
44
52, 5641, 64
6566
6, 14, 20,
29, 31, 39,
67, 69, 74
5, 13, 19,
28, 30, 37,
68, 70, 76
7 to 12, 35, 40
58, 60
Y
CbCr
15 to 18,
21 to 24
MP7
to
MP0
RESET
SDA
SCL
SA
RTCI
CDIR
RCV1
RCV2
V
DDDO
(5)
XTALO
XTALI
LLC
V
DDA1
to V
DDA5
V
refH1VrefH2
CVBS
(1)
V
SSA1
res
res
res
res
RED
(2)
GREEN
(3)
BLUE
(4)
CUR1
CUR2
V
refL1VrefL2
AP
57, 59
resSPn.c.
V
DDD1
to
V
DDD9
V
SSD1
to
V
SSD9
Y
SAA7124
SAA7125
Fig.3 Block diagram; QFP80.
(1) Alternatively Y or CVBS.
(2) Alternatively CHROMA or Cr.
(3) Alternatively CVBS or Yin.
(4) Alternatively CVBS or Cb.
(5) V1 devices only.
Page 7
1996 Nov 07 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
PINNING
SYMBOL TYPE
PIN
DESCRIPTION
PLCC84 LQFP64 QFP80
RESET I 1 57 73 Reset input, active LOW. After reset is applied, all digital I/Os
are in input mode. The I2C-bus receiver waits for the START
condition.
n.c. − 2 −−not connected
V
SSD1
I 3 6 6 digital ground 1
SA I 4 59 75 The I
2
C-bus slave address select input pin. LOW: slave
address = 88H, HIGH = 8CH.
V
DDD1
I 5 5 5 digital supply voltage 1
TP1 O 6 61 77
Test pin outputs. Leave open for normal operation.
TP2 O 7 62 78
TP3 O 8 63 79
TP4 O 9 64 80
TP5 O 10 1 1
TP6 O 11 2 2
TP7 O 12 3 3
TP8 O 13 4 4
V
DDD2
I 14 7 13 digital supply voltage 2
V
SSD2
I 15 8 14 digital ground 2
n.c. − 16 − 7
not connected
n.c. − 17 − 8
n.c. − 18 − 9
n.c. − 19 − 10
n.c. − 20 − 11
n.c. − 21 − 12
V
DDD3
I 22 13 19 digital supply voltage 3
n.c. − 23 −−not connected
V
SSD3
I 24 14 20 digital ground 3
MP7 I 25 9 15
Upper 4 bits of MPEG port. It is an input for
“CCIR 656”
style
multiplexed Cb, Y, Cr data.
MP6 I 261016
MP5 I 27 11 17
MP4 I 281218
V
DDD4
I 29 22 28 digital supply voltage 4
V
SSD4
I 30 23 29 digital ground 4
MP3 I 311521
Lower 4 bits of MPEG port. It is an input for
“CCIR 656”
style
multiplexed Cb, Y, Cr data.
MP2 I 321622
MP1 I 331723
MP0 I 341824
RCV1 I/O 35 19 25 Raster Control 1 for video port. This pin receives/provides a
VS/FS/FSEQ signal.
Page 8
1996 Nov 07 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
RCV2 I/O 36 20 26 Raster Control 2 for video port. This pin provides an HS pulse
of programmable length or receives an HS pulse.
RTCI I 37 21 27 Real Time Control input. If the LLC clock is provided by an
SAA7111 or SAA7151B, RTCI should be connected to the
RTCO pin of the respective decoder to improve the signal
quality.
V
DDD5
I 38 24 30 digital supply voltage 5
V
SSD5
I 39 25 31 digital ground 5
n.c. − 40 − 35 not connected
V
DDD6
I 41 30 37 digital supply voltage 6
V
SSD6
I 42 51 39 digital ground 6
n.c. − 43 − 40 not connected
XTALI I 44 26 32 Crystal oscillator input (from crystal). If the oscillator is not
used, this pin should be connected to ground.
XTALO O 45 27 33 Crystal oscillator output (to crystal).
V
DDDO
I 46 28 34 digital supply voltage for the internal oscillator; note 1
n.c. − 47 −−not connected
LLC I/O 48 29 36 Line-Locked Clock. This is the 27 MHz master clock for the
encoder. The I/O direction is set by the CDIR pin.
V
DDD7
I 49 52 68 digital supply voltage 7
CDIR I 50 31 38 Clock direction. If CDIR input is HIGH, the circuit receives a
clock signal, otherwise if CDIR is LOW, LLC is generated by
the internal crystal oscillator.
V
SSD7
I 51 53 67 digital ground 7
V
refL1
I 52 32 41 Lower reference voltage 1 input for DACs; connect to analog
ground.
V
refH1
I 53 33 42 Upper reference voltage 1 input for DACs; connect via 100 nF
capacitor to analog ground.
V
DDA1
I 54 34 43 Analog supply voltage 1 for DACs.
BLUE O 55 35 44 Analog output of the BLUE component.
res I 56 − 45 reserved
V
DDA2
I 57 36 46 Analog supply voltage 2 for DACs.
GREEN O 58 37 47 Analog output of GREEN component.
res I 59 − 48 reserved
V
DDA3
I 60 38 49 Analog supply voltage 3 for DACs.
RED O 61 39 50 Analog output of RED component.
res I 62 − 51 reserved
CUR1 I 63 40 52 Current input 1 for RGB amplifiers; connect via 15 kΩ resistor
to V
DDA
.
V
DDA4
I 64 41 53 Analog supply voltage 4 for DACs.
res I 65 − 54 reserved
n.c. − 66 −−not connected
SYMBOL TYPE
PIN
DESCRIPTION
PLCC84 LQFP64 QFP80
Page 9
1996 Nov 07 9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Note
1. V1 devices only.
V
SSA1
I 67 42 55 Analog ground 1 for the DACs.
V
SSA2
I − 43 − Analog ground 2 for the DACs.
CUR2 I 68 44 56 Current input 2 for RGB amplifiers; connect via 15 kΩ resistor
to V
DDA
.
res O 69 − 57 reserved
n.c. − 70 − 58 not connected
res O 71 − 59 reserved
n.c. − 72 − 60 not connected
CVBS O 73 45 61 Analog output of the CVBS signal.
V
DDA5
I 74 46 62 Analog supply voltage 5 for DACs.
V
refH2
I 75 47 63 Upper reference voltage 2 input for DACs; connect via 100 nF
capacitor to analog ground.
V
refL2
I 76 48 64 Lower reference voltage 2 input for DACs; connect to analog
ground.
AP I 77 49 65 Test pin. Connected to digital ground for normal operation.
SP I 78 50 66 Test pin. Connected to digital ground for normal operation.
V
SSD8
I 79 58 69 digital ground 8
V
DDD8
I 80 54 70 digital supply voltage 8
V
SSD9
I81−74 digital ground 9
V
DDD9
I 82 60 76 digital supply voltage 9
SCL I 835571I
2
C-bus serial clock input.
SDA I/O 84 56 72 I
2
C-bus serial data input/output.
SYMBOL TYPE
PIN
DESCRIPTION
PLCC84 LQFP64 QFP80
Page 10
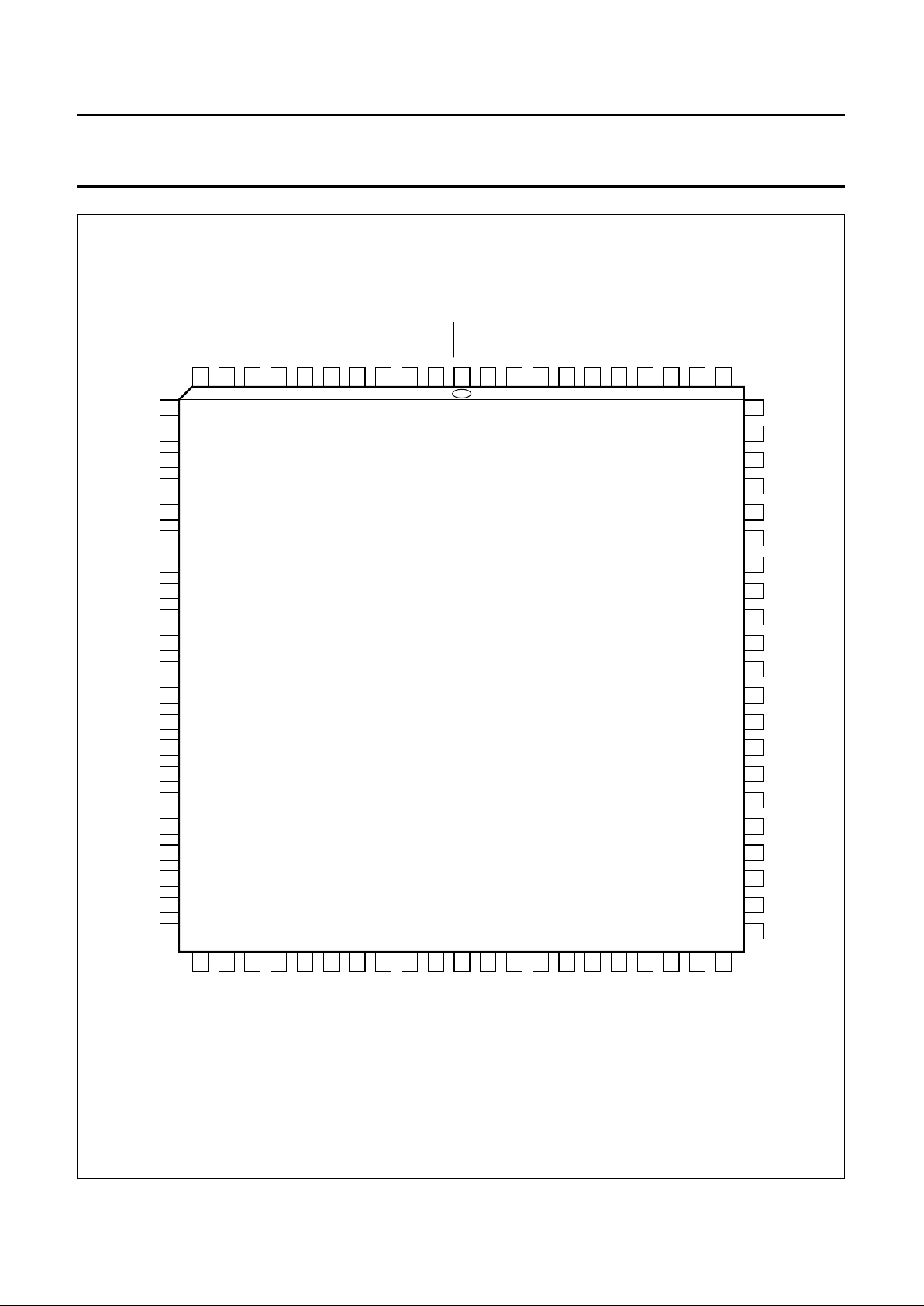
1996 Nov 07 10
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Fig.4 Pin configuration; PLCC84.
(1) V1 devices only.
handbook, full pagewidth
SAA7124
SAA7125
MGG548
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
TP6
TP5
TP4
TP3
TP2
TP1
V
DDD1
SA
V
SSD1
n.c.
RESET
SDA
SCL
V
DDD9VSSD9VDDD8VSSD8
SP
AP
V
refL2VrefH2
MP1
MP0
RCV1
RCV2
RTCI
V
DDD5
V
SSD5
n.c.
V
DDD6
V
SSD6
n.c.
XTALI
XTALO
V
DDDO
(1)
n.c.
LLC
V
DDD7
CDIR
V
SSD7
V
refL1
V
ref H1
V
DDA5
CVBS
n.c.
res
n.c.
res
CUR2
V
SSA1
n.c.
res
V
DDA4
CUR1
res
RED
V
DDA3
res
GREEN
V
DDA2
res
BLUE
V
DDA1
TP7
TP8
V
DDD2
V
SSD2
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
V
DDD3
n.c.
V
SSD3
MP7
MP6
MP5
MP4
V
DDD4
V
SSD4
MP3
MP2
Page 11
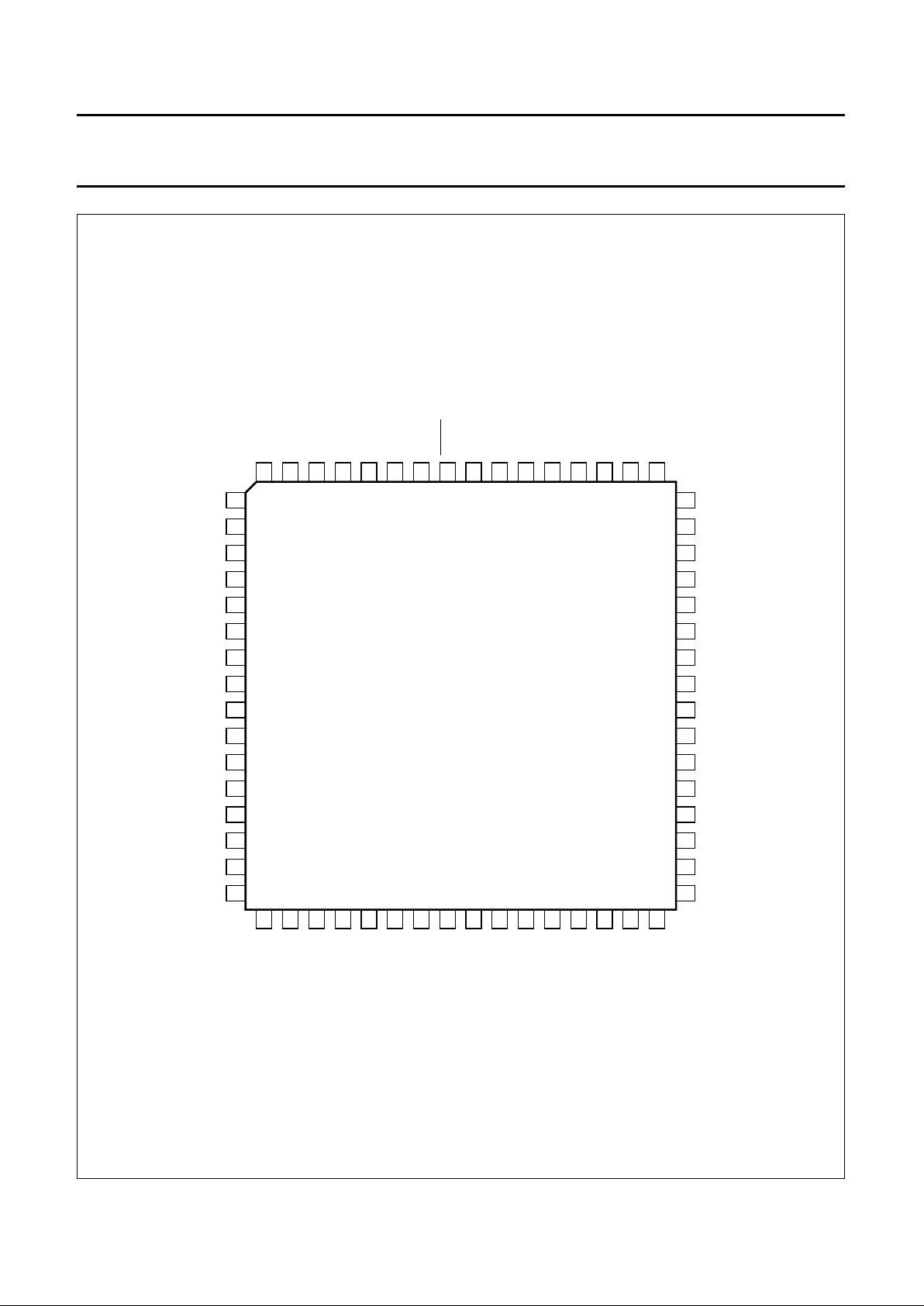
1996 Nov 07 11
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Fig.5 Pin configuration; LQFP64 (V1 devices only).
handbook, full pagewidth
SAA7124
SAA7125
MGG547
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
V
refL2
V
refH2
V
DDA5
CVBS
CUR2
V
SSA2
V
SSA1
V
DDA4
CUR1
RED
V
DDA3
GREEN
V
DDA2
BLUE
V
DDA1
V
refH1
TP5
TP6
TP7
TP8
V
DDD1
V
SSD1
V
DDD2
V
SSD2
MP7
MP6
MP5
MP4
V
DDD3
V
SSD3
MP3
MP2
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
TP4
TP3
TP2
TP1
V
DDD9
SA
V
SSD8
RESET
SDA
SCL
V
DDD8
V
SSD7
V
DDD7
V
SSD6
SP
AP
MP1
MP0
RCV1
RCV2
RTCI
V
DDD4
V
SSD4
V
DDD5
V
SSD5
XTALI
XTALO
V
DDDO
LLC
V
DDD6
CDIR
V
refL1
Page 12
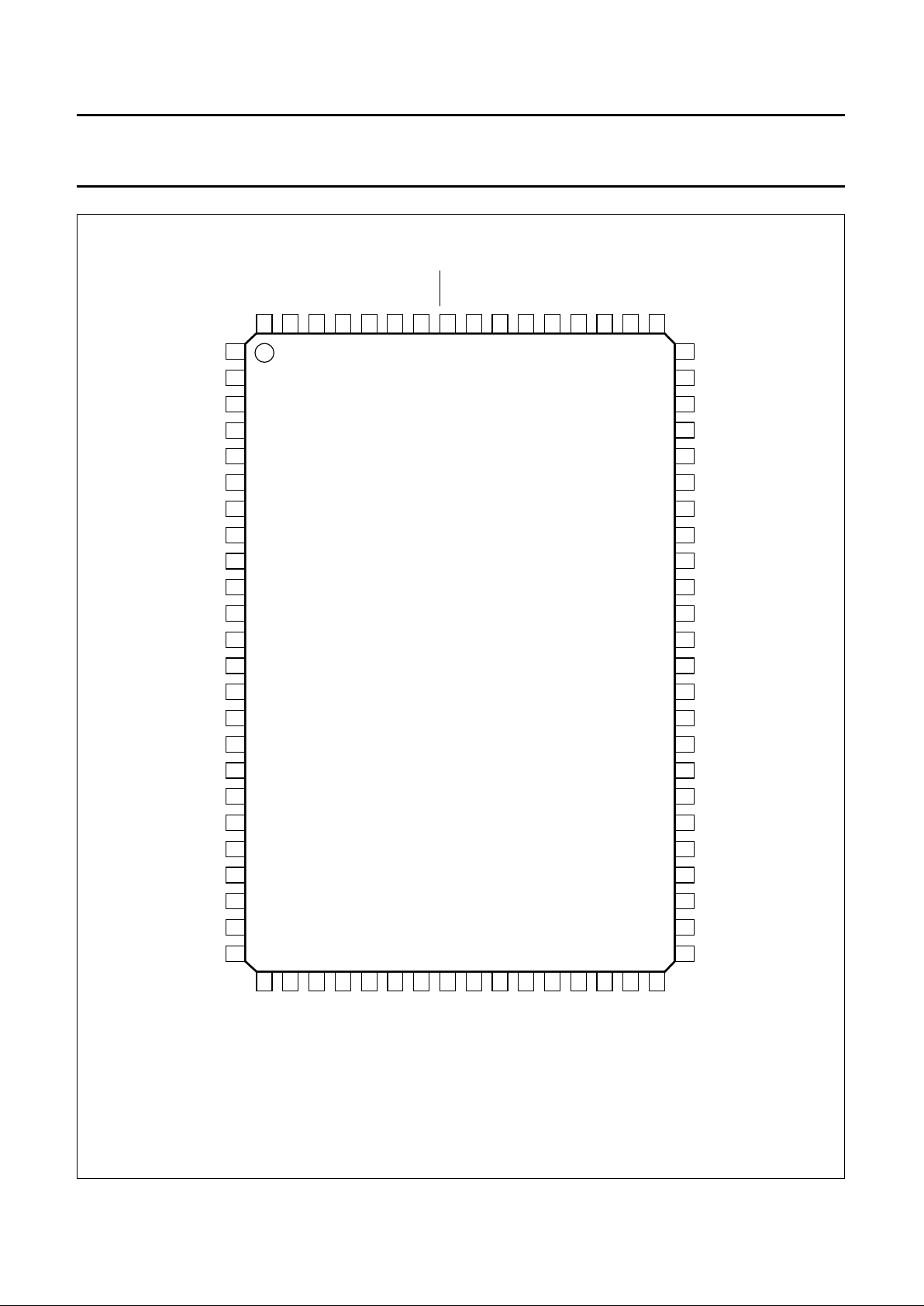
1996 Nov 07 12
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Fig.6 Pin configuration; QFP80.
(1) V1 devices only.
handbook, full pagewidth
SAA7124
SAA7125
MGG549
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
60
59
58
57
56
64
63
62
61
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
n.c.
res
n.c.
res
CUR2
V
refL2
V
refH2
V
DDA5
CVBS
V
SSA1
res
V
DDA4
CUR1
res
RED
V
DDA3
res
GREEN
V
DDA2
res
BLUE
V
DDA1
V
refH1
V
refL1
V
DDD1
V
SSD1
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
TP5
TP6
TP7
TP8
n.c.
n.c.
n.c.
V
DDD2
V
SSD2
MP7
MP6
MP5
MP4
V
DDD3
V
SSD3
MP3
MP2
MP1
MP0
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
RCV1
RCV2
RTCI
V
DDD4
V
SSD4
V
DDD5
V
SSD5
XTALI
XTALO
V
DDDO
(1)
n.c.
LLC
V
DDD6
CDIR
V
SSD6
n.c.
TP4
TP3
TP2
TP1
V
DDD9
SA
V
SSD9
RESET
SDA
SCL
V
DDD8VSSD8VDDD7VSSD7
SP
AP
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
Page 13

1996 Nov 07 13
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The digital video encoder (ECO-DENC) encodes digital
luminance and colour difference signals into analog CVBS
and simultaneously RGB signals. NTSC-M, PAL B/G
standards and sub-standards are supported.
Both interlaced and non-interlaced operation is possible
for all standards.
Optionally, the input Y, Cb and Cr data, digital-to-analog
converted, is available at the analog RGB outputs.
For applications that do not require RGB output, the device
can be configured in such a way that S-Video and twice
CVBS is available (Y at CVBS-DAC, C at R-DAC, and
CVBS at G-DAC and B-DAC).
The basic encoder function consists of subcarrier
generation, colour modulation and insertion of
synchronization signals. Luminance and chrominance
signals are filtered in accordance with the standard
requirements of
“RS-170-A”
and
“CCIR 624”
.
For ease of analog post filtering the signals are twice
oversampled with respect to the pixel clock before
digital-to-analog conversion.
For total filter transfer characteristics see
Figs 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12. The DACs for Y, C, and CVBS
are realized with full 10-bit resolution, DACs for RGB with
9-bit resolution.
The MPEG port (MP) accepts 8 line multiplexed Cb, Y, Cr
data.
The 8-bit multiplexed Cb-Y-Cr formats are
“CCIR 656”
(D1 format) compatible, but auxiliary codes such as SAV
and EAV are decoded optionally for trigger purposes.
A crystal-stable master clock (LLC) of 27 MHz, which is
twice the CCIR line-locked pixel clock of 13.5 MHz, needs
to be supplied externally. Optionally, a crystal oscillator
input/output pair of pins and an on-chip clock driver is
provided.
It is also possible to connect a Philips Digital Video
Decoder (SAA7111 or SAA7151B) in conjunction with a
CREF clock qualifier to ECO-DENC. Via the RTCI pin,
connected to RTCO of a decoder, information concerning
actual subcarrier, PAL-ID, and if connected to SAA7111,
definite subcarrier phase can be inserted.
The ECO-DENC synthesizes all necessary internal
signals, colour subcarrier frequency, and synchronization
signals, from that clock.
The encoder can be configured as slave with respect to
RCV trigger inputs or auxiliary
“CCIR 656”
codes, or can
be master to output horizontal and vertical trigger pulses.
The IC also contains Closed Caption and Extended Data
Services Encoding (Line 21), and supports anti-taping
signal generation in accordance with Macrovision.
A number of possibilities are provided for setting different
video parameters such as:
Black and blanking level control
Colour subcarrier frequency
Variable burst amplitude etc.
During reset (RESET = LOW) and after reset is released,
all digital I/O stages are set to input mode. A reset forces
the I2C-bus interface to abort any running bus transfer and
sets register 3A to 03H, register 61 to 06H and
registers 6BH and 6EH to 00H. All other control registers
are not influenced by a reset.
Data manager
In the data manager, real time arbitration on the data
stream to be encoded is performed.
Optionally, the device can operate as a 100/75 colour bar
test pattern generator without need for an external data
source.
Encoder
V
IDEO PATH
The encoder generates out of Y, U and V baseband
signals luminance and colour subcarrier output signals,
suitable for use as CVBS or separate Y and C signals.
Luminance is modified in gain and in offset (latter
programmable in a certain range to enable different black
level set-ups). After having been inserted a fixed
synchronization level, in accordance with standard
composite synchronization schemes, and blanking level,
programmable also in a certain range to allow for
manipulations with Macrovision anti-taping, additional
insertion of AGC super-white pulses, programmable in
height, is supported.
In order to enable easy analog post filtering, luminance is
interpolated from 13.5 MHz data rate to 27 MHz data rate,
providing luminance in 10-bit resolution. This filter is also
used to define smoothed transients for synchronization
pulses and blanking period. For transfer characteristic of
the luminance interpolation filter see Figs 9 and 10.
Page 14
1996 Nov 07 14
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Chrominance is modified in gain (programmable
separately for U and V), standard dependent burst is
inserted, before baseband colour signals are interpolated
from 6.75 MHz data rate to 27 MHz data rate. One of the
interpolation stages can be bypassed, thus providing a
higher colour bandwidth, which can be made use of for
Y and C output. For transfer characteristics of the
chrominance interpolation filter see Figs 7 and 8.
The amplitude of inserted burst is programmable in a
certain range, suitable for standard signals and for special
effects. Behind the succeeding quadrature modulator,
colour in 10-bit resolution is provided on subcarrier.
The numeric ratio between Y and C outputs is in
accordance with set standards.
C
LOSED CAPTION ENCODER
Using this circuit, data in accordance with the specification
of Closed Caption or Extended Data Service, delivered by
the control interface, can be encoded (Line 21).
Two dedicated pairs of bytes (two bytes per field), each
pair preceded by run-in clocks and framing code, are
possible.
The actual line number where data is to be encoded in, can
be modified in a certain range.
Data clock frequency is in accordance with definition for
NTSC-M standard 32 times horizontal line frequency.
Data LOW at the output of the DACs corresponds to 0 IRE,
data HIGH at the output of the DACs corresponds to
approximately 50 IRE.
It is also possible to encode Closed Caption Data for 50 Hz
field frequencies at 32 times horizontal line frequency.
A
NTI-TAPING (SAA7124 ONLY)
For more information contact your nearest Philips
Semiconductors sales office.
RGB processor
This block contains a dematrix in order to produce RED,
GREEN and BLUE signals to be fed to a SCART plug.
Before Y, Cb and Cr signals are de-matrixed, 2 times
oversampling for luminance and 4 times oversampling for
colour difference signals is performed. For transfer curves
of luminance and colour difference components of RGB
see Figs 11 and 12.
Output interface/DACs
In the output interface encoded both Y and C signals are
converted from digital-to-analog in 10-bit resolution.
Y and C signals are also combined to a 10-bit CVBS
signal.
RED, GREEN and BLUE signals (optionally Cr, Y, Cb) are
also converted from digital-to-analog, each providing a
9-bit resolution.
All output occurs with the same processing delay.
Absolute amplitudes at the input of the DAC for CVBS is
reduced by
15
⁄16with respect to Y and C DACs to make
maximum use of conversion ranges.
Depending on control bits YC_EN and DEMOFF, different
signal combinations are available at DACs #1 to #4.
YC_EN = DEMOFF = LOW is the default configuration
after reset.
Table 1 Control of DAC signals
Outputs of the DACs can be set together in two groups
(#1 and #2 by DOWNB, #3 and #4 by DOWNA) via
software control to minimum output voltage for either
purpose.
Synchronization
Synchronization of the ECO-DENC is able to operate in
two modes; slave mode and master mode.
In the slave mode, the circuit accepts synchronization
pulses at the bidirectional RCV1 port (or equivalently as
frame synchronization from
“CCIR 656”
data stream).
The timing and trigger behaviour related to RCV1 can be
influenced by programming the polarity and on-chip delay
of RCV1. Active slope of RCV1 defines the vertical phase
and optionally the odd/even and colour frame phase to be
initialized, it can be also used to set the horizontal phase.
If the horizontal phase is not to be influenced by RCV1, a
horizontal pulse needs to be supplied at the RCV2 pin
(or a horizontal synchronization from
“CCIR 656”
data
stream). Timing and trigger behaviour can also be
influenced for RCV2.
YC_EN DEMOFF DAC1 DAC2 DAC3 DAC4
0 0 CVBS R G B
0 1 CVBS Cr Y Cb
1 0 VBS C CVBS CVBS
1 1 VBS C CVBS CVBS
Page 15

1996 Nov 07 15
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
If there are missing pulses at RCV1 and/or RCV2, the time
base of ECO-DENC runs free, thus an arbitrary number of
synchronization slopes may miss, but no additional pulses
(with the incorrect phase) must occur.
If the vertical and horizontal phase is derived from RCV1,
RCV2 can be used for horizontal or composite blanking
input or output.
Alternatively, the device can be triggered by auxiliary
codes in a
“CCIR 656”
data stream at the MP port.
In the master mode, the time base of the circuit
continuously runs free. On the RCV1 port, the IC can
output:
• A Vertical Sync signal (VS) with 3 or 2.5 lines duration,
or;
• An ODD/EVEN signal which is LOW in odd fields, or;
• A field sequence signal (FSEQ) which is HIGH in the first
of 4, 8 fields respectively.
On the RCV2 port, the IC can provide a horizontal pulse
with programmable start and stop phase; this pulse can be
inhibited in the vertical blanking period to build up, for
example, a composite blanking signal.
The polarity of both RCV1 and RCV2 is selectable by
software control.
Field length is in accordance with to 50 Hz or 60 Hz
standards, including non-interlaced options; start and end
of its active part can be programmed. The active part of a
field always starts at the beginning of a line, If the standard
blanking option SBLBN is not set.
I
2
C-bus interface
The I2C-bus interface is a standard slave transceiver,
supporting 7-bit slave addresses and 400 kbits/s
guaranteed transfer rate. It uses 8-bit subaddressing with
an auto-increment function. All registers are write only,
except one readable status byte.
Two I2C-bus slave addresses are selected:
88H: LOW at pin SA
8CH: HIGH at pin SA.
Input levels and formats
ECO-DENC expects digital Y, Cb, Cr data with levels
(digital codes) in accordance with
“CCIR 601”
.
For C and CVBS outputs, deviating amplitudes of the
colour difference signals can be compensated by
independent gain control setting, while gain for luminance
is set to predefined values, distinguishable for 7.5 IRE
set-up or without set-up.
For RGB (or Y, Cb and Cr) outputs fixed amplification in
accordance with
“CCIR 601”
is provided.
Reference levels are measured with a colour bar,
100% white, 100% amplitude and 100% saturation.
T
RANSFORMATION
R = Y + 1.3707 × (Cr − 128)
G=Y−0.3365 × (Cb − 128) − 0.6982 × (Cr − 128)
B = Y + 1.7324 × (Cb − 128).
Representation of R, G and B at the output is 9 bits at
27 MHz.
Table 2 8-bit multiplexed format (similar to
“CCIR 656”
)
TIME
BITS
01224567
Sample Cb
0
Y
0
Cr
0
Y
1
Cb
2
Y
2
Cr
2
Y
3
Luminance pixel number 0123
Colour pixel number 0 2
Page 16

1996 Nov 07 16
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Bit allocation map
Table 3 Slave receiver (slave address 88H or 8CH)
REGISTER FUNCTION
SUB
ADDRESS
DATA BYTE
(1)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Null 00 00000000
↓
Null 39 00000000
I/O port control 3A CBENB 0 YC_EN SYMP DEMOFF 0 Y2C UV2C
Null 42 00000000
↓
Null 59 00000000
Chrominance phase 5A CHPS7 CHPS6 CHPS5 CHPS4 CHPS3 CHPS2 CHPS1 CHPS0
Gain U 5B GAINU7 GAINU6 GAINU5 GAINU4 GAINU3 GAINU2 GAINU1 GAINU0
Gain V 5C GAINV7 GAINV6 GAINV5 GAINV4 GAINV3 GAINV2 GAINV1 GAINV0
Gain U MSB, black level 5D GAINU8 0 BLCKL5 BLCKL4 BLCKL3 BLCKL2 BLCKL1 BLCKL0
Gain V MSB, blanking level,
decoder type
5E GAINV8 DECTYP BLNNL5 BLNNL4 BLNNL3 BLNNL2 BLNNL1 BLNNL0
Blanking level VBI 5F 0 0 BLNVB5 BLNVB4 BLNVB3 BLNVB2 BLNVB1 BLNVB0
Null 60 00000000
Standard control 61 DOWNB DOWNA INPI YGS 0 SCBW PAL FISE
RTC enable burst amplitude 62 RTCE BSTA6 BSTA5 BSTA4 BSTA3 BSTA2 BSTA1 BSTA0
Subcarrier 0 63 FSC07 FSC06 FSC05 FSC04 FSC03 FSC02 FSC01 FSC00
Subcarrier 1 64 FSC15 FSC14 FSC13 FSC12 FSC11 FSC10 FSC09 FSC08
Subcarrier 2 65 FSC23 FSC22 FSC21 FSC20 FSC19 FSC18 FSC17 FSC16
Subcarrier 3 66 FSC31 FSC30 FSC29 FSC28 FSC27 FSC26 FSC25 FSC24
Line 21 odd 0 67 L21O07 L21O06 L21O05 L21O04 L21O03 L21O02 L21O01 L21O00
Line 21 odd 1 68 L21O17 L21O16 L21O15 L21O14 L21O13 L21O12 L21O11 L21O10
Line 21 even 0 69 L21E07 L21E06 L21E05 L21E04 L21E03 L21E02 L21E01 L21E00
Line 21 even 1 6A L21E17 L21E16 L21E15 L21E14 L21E13 L21E12 L21E11 L21E10
RCV port control 6B SRCV11 SRCV10 TRCV2 ORCV1 PRCV1 CBLF ORCV2 PRCV2
Trigger control 6C HTRIG7 HTRIG6 HTRIG5 HTRIG4 HTRIG3 HTRIG2 HTRIG1 HTRIG0
Trigger control 6D HTRIG10 HTRIG9 HTRIG8 VTRIG4 VTRIG3 VTRIG2 VTRIG1 VTRIG0
Multi control 6E SBLBN 0 PHRES1 PHRES0 0 0 FLC1 FLCO
Page 17

1996 Nov 07 17
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Note
1. All bits marked 0 must be programmed to zero.
Closed caption 6F CCEN1 CCEN0 0 SCCLN4 SCCLN3 SCCLN2 SCCLN1 SCCLN0
RCV2 output start 70 RCV2S7 RCV2S6 RCV2S5 RCV2S4 RCV2S3 RCV2S2 RCV2S1 RCV2S0
RCV2 output end 71 RCV2E7 RCV2E6 RCV2E5 RCV2E4 RCV2E3 RCV2E2 RCV2E1 RCV2E0
MSBs RCV2 output 72 0 RCV2E10 RCV2E9 RCV2E8 0 RCV2S10 RCV2S9 RCV2S8
Null 73 00000000
Null 74 00000000
Null 75 00000000
Null 76 00000000
Null 77 00000000
Null 78 00000000
Null 79 00000000
First active line 7A FAL7 FAL6 FAL5 FAL4 FAL3 FAL2 FAL1 FAL0
Last active line 7B LAL7 LAL6 LAL5 LAL4 LAL3 LAL2 LAL1 LAL0
MSBs vertical 7C 0 LAL8 0 FAL8 0000
Null 7D 00000000
Null 7E 00000000
Null 7F 00000000
REGISTER FUNCTION
SUB
ADDRESS
DATA BYTE
(1)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Page 18

1996 Nov 07 18
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
I2C-bus format
Table 4 I
2
C-bus address; see Table 5
Table 5 Explanation of Table 4
Notes
1. X is the read/write control bit; X = logic 0 is order to write; X = logic 1 is order to read, no subaddressing with read.
2. If more than 1 byte DATA is transmitted, then auto-increment of the subaddress is performed.
Slave Receiver
Table 6 Subaddress 3A
S SLAVE ADDRESS ACK SUBADDRESS ACK DATA 0 ACK -------- DATA n ACK P
PART DESCRIPTION
S START condition
Slave address 1000100X or 1000110X (note 1)
ACK acknowledge, generated by the slave
Subaddress (note 2) subaddress byte
DATA data byte
-------- continued data bytes and ACKs
P STOP condition
DATA
BYTE
LOGIC
LEVEL
DESCRIPTION
UV2C 0 Cb, Cr data are two’s complement.
1 Cb, Cr data are straight binary. Default after reset.
Y2C 0 Y data is two’s complement.
1 Y data is straight binary. Default after reset.
DEMOFF 0 Y, Cb and Cr for RGB dematrix is active. Default after reset.
1 Y, Cb and Cr for RGB dematrix is bypassed.
SYMP 0 Horizontal and vertical trigger is taken from RCV2 and RCV1 respectively. Default after reset.
1 Horizontal and vertical trigger is decoded out of
“CCIR 656”
compatible data at MP port.
YC_EN 0 Output of CVBS and RGB signals. Default after reset.
1 Output of Y, C, and CVBS, CVBS signals.
CBENB 0 Data from input ports is encoded. Default after reset.
1 Colour bar with fixed colours is encoded. The LUTs are read in upward order from
index 0 to index 7.
Page 19

1996 Nov 07 19
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Table 7 Subaddress 5A
Table 8 Subaddress 5B and 5D
Notes
1. GAINU = −2.17 × nominal to +2.16 × nominal.
2. GAINU = −2.05 × nominal to +2.04 × nominal.
Table 9 Subaddress 5C and 5E
Notes
1. GAINV = −1.55 × nominal to +1.55 × nominal.
2. GAINV = −1.46 × nominal to +1.46 × nominal.
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION VALUE RESULT
CHPS phase of encoded colour
subcarrier (including burst)
relative to horizontal sync.
Can be adjusted in steps
of 360/256 degrees
tbf PAL-B/G and data from input ports
tbf PAL-B/G and data from look-up table
tbf NTSC-M and data from input ports
tbf NTSC-M and data from look-up table
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION CONDITIONS REMARKS
GAINU variable gain for Cb signal;
input representation
accordance with
“CCIR 601”
white-to-black = 92.5 IRE
(1)
GAINU = 0 output subcarrier of U contribution = 0
GAINU = 118 (76H) output subcarrier of U contribution = nominal
white-to-black = 100 IRE
(2)
GAINU = 0 output subcarrier of U contribution = 0
GAINU = 125 (7DH) output subcarrier of U contribution = nominal
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION CONDITIONS REMARKS
GAINV variable gain for Cr signal;
input representation
accordance with
“CCIR 601”
white-to-black = 92.5 IRE
(1)
GAINV = 0 output subcarrier of V contribution = 0
GAINV = 165 (A5H) output subcarrier of V contribution = nominal
white-to-black = 100 IRE
(2)
GAINV = 0 output subcarrier of V contribution = 0
GAINV = 175 (AFH) output subcarrier of V contribution = nominal
Page 20

1996 Nov 07 20
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Table 10 Subaddress 5D
Notes
1. Output black level/IRE = BLCKL × 25/63 + 24; recommended value: BLCKL = 60 (3CH) normal.
2. Output black level/IRE = BLCKL × 26/63 + 24; recommended value: BLCKL = 45 (2DH) normal.
Table 11 Subaddress 5E
Notes
1. Output black level/IRE = BLNNL × 25/63 + 17; recommended value: BLNNL = 58 (3AH) normal.
2. Output black level/IRE = BLNNL × 26/63 + 17; recommended value: BLNNL = 63 (3FH) normal.
Table 12 Subaddress 5F
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION CONDITIONS REMARKS
BLCKL variable black level; input
representation accordance
with
“CCIR 601”
white-to-sync = 140 IRE
(1)
BLCKL = 0 output black level = 24 IRE
BLCKL = 63 (3FH) output black level = 49 IRE
white-to-sync = 143 IRE
(2)
BLCKL = 0 output black level = 24 IRE
BLCKL = 63 (3FH) output black level = 50 IRE
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION CONDITIONS REMARKS
BLNNL variable blanking level white-to-sync = 140 IRE
(1)
BLNNL = 0 output blanking level = 17 IRE
BLNNL = 63 (3FH) output blanking level = 42 IRE
white-to-sync = 143 IRE
(2)
BLNNL = 0 output blanking level = 17 IRE
BLNNL = 63 (3FH) output blanking level = 43 IRE
DECTYP RTCI logic 0 real time control input from SAA7151B
logic 1 real time control input from SAA7111
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION
BLNVB variable blanking level during vertical blanking interval is typically identical to value of BLNNL
Page 21

1996 Nov 07 21
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Table 13 Subaddress 61
Table 14 Subaddress 62A
Table 15 Subaddress 62B
DATA BYTE LOGIC LEVEL DESCRIPTION
FISE 0 864 total pixel clocks per line; default after reset
1 858 total pixel clocks per line
PAL 0 NTSC encoding (non-alternating V component)
1 PAL encoding (alternating V component); default after reset
SCBW 0 enlarged bandwidth for chrominance encoding (for overall transfer characteristic of
chrominance in baseband representation see Figs 7 and 8)
1 standard bandwidth for chrominance encoding (for overall transfer characteristic of
chrominance in baseband representation see Figs 7 and 8); default after reset
YGS 0 luminance gain for white − black 100 IRE; default after reset
1 luminance gain for white − black 92.5 IRE including 7.5 IRE set-up of black
INPI 0 PAL switch phase is nominal; default after reset
1 PAL switch phase is inverted compared to nominal
DOWNA 0 DACs for G and B (Y and Cb or CVBS and CVBS) in normal operational mode;
default after reset
1 DACs for G and B (Y and Cb or CVBS and CVBS) forced to lowest output voltage
DOWNB 0 DACs for CVBS and R (CVBS and Cr or VBS and C) in normal operational mode;
default after reset
1 DACs for CVBS and R (CVBS and Cr or VBS and C) forced to lowest output
voltage
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION CONDITIONS REMARKS
BSTA amplitude of colour burst;
input representation in
accordance with
“CCIR 601”
white-to-black = 92.5 IRE;
burst = 40 IRE; NTSC encoding
recommended value:
BSTA = 102 (66H
BSTA = 0 to 1.25 × nominal
white-to-black = 92.5 IRE;
burst = 40 IRE; PALencoding
recommended value:
BSTA = 72 (48H)
BSTA = 0 to 1.76 × nominal
white-to-black = 100 IRE;
burst = 43 IRE; NTSC encoding
recommended value:
BSTA = 106 (6AH)
BSTA = 0 to 1.20 × nominal
white-to-black = 100 IRE;
burst = 43 IRE; PALencoding
recommended value:
BSTA = 75 (4BH)
BSTA = 0 to 1.67 × nominal
DATA BYTE LOGIC LEVEL DESCRIPTION
RTCE 0 no real time control of generated subcarrier frequency
1 real time control of generated subcarrier frequency through SAA7151B or SAA711 1
(timing see Fig.15)
Page 22

1996 Nov 07 22
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Table 16 Subaddress 63 to 66 (four bytes to program subcarrier frequency)
Note
1. Examples:
a) NTSC-M: f
fsc
= 227.5, f
llc
= 1716 → FSC = 569408543 (21F07C1FH).
b) PAL-B/G: f
fsc
= 283.7516, f
llc
= 1728 → FSC = 705268427 (2A098ACBH).
Table 17 Subaddress 67 to 6A
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION CONDITIONS REMARKS
FSC0 to FSC3 f
fsc
= subcarrier frequency
(in multiples of line
frequency);
f
llc
= clock frequency (in
multiples of line
frequency)
see note 1
FSC3 = most significant byte
FSC0 = least significant byte
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION REMARK
L21O0 first byte of captioning data, odd field LSB of the respective bytes are encoded immediately
after run-in and framing code, the MSBs of the
respective bytes have to carry the parity bit, in
accordance with the definition of Line 21 encoding
format
L21O1 second byte of captioning data, odd field
L21E0 first byte of extended data, even field
L21E1 second byte of extended data, even field
FSC round
f
fsc
f
llc
------- -
2
32
×
=
Page 23

1996 Nov 07 23
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Table 18 Subaddress 6B
Table 19 Logic levels and function of SRCV1
DATA BYTE LOGIC LEVEL DESCRIPTION
PRCV2 0 polarity of RCV2 as output is active HIGH, rising edge is taken when input,
respectively; default after reset
1 polarity of RCV2 as output is active LOW, falling edge is taken when input,
respectively
ORCV2 0 pin RCV2 is switched to input; default after reset
1 pin RCV2 is switched to output
CBLF 0 if ORCV2 = HIGH, pin RCV2 provides an HREF signal (Horizontal Reference pulse
that is defined by RCV2S and RCV2E, also during vertical blanking Interval); default
after reset
if ORCV2 = LOW and bit SYMP = LOW, signal input to RCV2 is used for horizontal
synchronization only (if TRCV2 = HIGH); default after reset
1 if ORCV2 = HIGH, pin RCV2 provides a ‘Composite-Blanking-Not’ signal, this is a
reference pulse that is defined by RCV2S and RCV2E, excluding Vertical Blanking
Interval, which is defined by FAL and LAL
if ORCV2 = LOW and bit SYMP = LOW, signal input to RCV2 is used for horizontal
synchronization (if TRCV2 = HIGH) and as an internal blanking signal
PRCV1 0 polarity of RCV1 as output is active HIGH, rising edge is taken when input; default
after reset
1 polarity of RCV1 as output is active LOW, falling edge is taken when input
ORCV1 0 pin RCV1 is switched to input; default after reset
1 pin RCV1 is switched to output
TRCV2 0 horizontal synchronization is taken from RCV1 port (at bit SYMP = LOW) or from
decoded frame sync of
“CCIR 656”
input (at bit SYMP = HIGH); default after reset
1 horizontal synchronization is taken from RCV2 port (at bit SYMP = LOW)
SRCV1 − defines signal type on pin RCV1; see Table 19
DATA BYTE
AS OUTPUT AS INPUT FUNCTION
SRCV11 SRCV10
0 0 VS VS vertical sync each field; default after reset
0 1 FS FS frame sync (odd/even)
1 0 FSEQ FSEQ field sequence, vertical sync every fourth field
(PAL = 0) or eighth field (PAL = 1)
1 1 not applicable not applicable −
Page 24

1996 Nov 07 24
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Table 20 Subaddress 6C and 6D
Table 21 Subaddress 6D
Table 22 Subaddress 6E
Table 23 Logic levels and function of PHRES
Table 24 Logic levels and function of FLC
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION
HTRIG sets the horizontal trigger phase related to signal on RCV1 or RCV2 input (or to decoded
“CCIR 656”
data)
values above 1715 (FISE = 1) or 1727 (FISE = 0) are not allowed
increasing HTRIG decreases delays of all internally generated timing signals
reference mark: analog output horizontal sync (leading slope) coincides with active edge of RCV
used for triggering at HTRIG = tbfH (tbfH)
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION
VTRIG sets the vertical trigger phase related to signal on RCV1 input (or to decoded
“CCIR 656”
data)
increasing VTRIG decreases delays of all internally generated timing signals, measured in half lines
variation range of VTRIG = 0 to 31 (1FH)
DATA BYTE LOGIC LEVEL DESCRIPTION
SBLBN 0 vertical blanking is defined by programming of FAL and LAL; default after reset
1 vertical blanking is forced in accordance with
“CCIR 624”
(50 Hz) or
“RS170A”
(60 Hz)
PHRES − selects the phase reset mode of the colour subcarrier generator; see Table 23
FLC − field length control; see Table 24
DATA BYTE
FUNCTION
PHRES1 PHRES0
0 0 no reset or reset via RTCI from SAA7111 if bit RTCE = 1; default after reset
0 1 reset every two lines
1 0 reset every eight fields
1 1 reset every four fields
DATA BYTE
FUNCTION
FLC1 FLC0
0 0 interlaced 312.5 lines/field at 50 Hz, 262.5 lines/field at 60 Hz; default after reset
0 1 non-interlaced 312 lines/field at 50 Hz, 262 lines/field at 60 Hz
1 0 non-interlaced 313 lines/field at 50 Hz, 263 lines/field at 60 Hz
1 1 non-interlaced 313 lines/field at 50 Hz, 263 lines/field at 60 Hz
Page 25

1996 Nov 07 25
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Table 25 Subaddress 6F
Table 26 Logic levels and function of CCEN
Table 27 Subaddress 70 to 72
Table 28 Subaddress 7A to 7C
S
UBADDRESSES
In subaddresses 5B, 5C, 5D, 5E and 62 all IRE values are rounded up.
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION
CCEN enables individual Line 21 encoding; see Table 26
SCCLN selects the actual line, where closed caption or extended data are encoded
line = (SCCLN + 4) for M-systems
line = (SCCLN + 1) for other systems
DATA BYTE
FUNCTION
CCEN1 CCEN0
0 0 line 21 encoding off
0 1 enables encoding in field 1 (odd)
1 0 enables encoding in field 2 (even)
1 1 enables encoding in both fields
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION
RCV2S start of output signal on RCV2 pin
values above 1715 (FISE = 1) or 1727 (FISE = 0) are not allowed
first active pixel at analog outputs (corresponding input pixel coinciding with RCV2) at
RCV2S = tbfH (tbfH)
RCV2E end of output signal on RCV2 pin
values above 1715 (FISE = 1) or 1727 (FISE = 0) are not allowed
last active pixel at analog outputs (corresponding input pixel coinciding with RCV2) at
RCV2E = tbfH (tbfH)
DATA BYTE DESCRIPTION
FAL first active line = FAL + 4 for M-systems, = FAL + 1 for other systems, measured in lines
FAL = 0 coincides with the first field synchronization pulse
LAL last active line = LAL + 3 for M-systems, = LAL for other system, measured in lines
LAL = 0 coincides with the first field synchronization pulse
Page 26

1996 Nov 07 26
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Slave Transmitter
Table 29 Slave transmitter (slave address 89H or 8DH)
Table 30 No subaddress
REGISTER
FUNCTION
SUBADDRESS
DATA BYTE
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Status byte − VER2 VER1 VER0 CCRDO CCRDE 0 FSEQ O_E
DATA BYTE LOGIC LEVEL DESCRIPTION
VER − Version identification of the device. It will be changed with all versions of the IC that
have different programming models. Current Version is 100 binary.
CCRDO 1 Closed caption bytes of the odd field have been encoded.
0 The bit is reset after information has been written to the subaddresses 67 and 68.
It is set immediately after the data has been encoded.
CCRDE 1 Closed caption bytes of the even field have been encoded.
0 The bit is reset after information has been written to the subaddresses 69 and 6A. It
is set immediately after the data has been encoded.
FSEQ 1 During first field of a sequence (repetition rate: NTSC = 4 fields, PAL = 8 fields.
0 Not first field of a sequence.
O_E 1 During even field.
0 During odd field.
Page 27

1996 Nov 07 27
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Fig.7 Chrominance transfer characteristic 1.
handbook, full pagewidth
6 8 10 12 14
6
0
024
MBE737
−6
−12
−18
−30
−24
−36
−42
−54
−48
f (MHz)
G
v
(dB)
(1) (2)
(1) SCBW = 1.
(2) SCBW = 0.
Fig.8 Chrominance transfer characteristic 2.
(1) SCBW = 1.
(2) SCBW = 0.
handbook, halfpage
0 0.4 0.8 1.6
2
0
−4
−6
−2
MBE735
1.2
f (MHz)
G
v
(dB)
(1)
(2)
Page 28

1996 Nov 07 28
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Fig.9 Luminance transfer characteristic 1.
(1) Total luminance of Y and CVBS.
handbook, full pagewidth
6 8 10 12 14
6
0
024
MGG556
−6
−12
−18
−30
−24
−36
−42
−54
−48
f (MHz)
G
v
(dB)
(1)
Fig.10 Luminance transfer characteristic 2.
handbook, halfpage
02
(1)
6
1
0
−1
−2
−3
−4
−5
MBE736
4
f (MHz)
G
v
(dB)
(1) Detailed luminance of Y and CVBS.
Page 29

1996 Nov 07 29
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Fig.11 Luminance transfer characteristic in RGB.
handbook, full pagewidth
6 8 10 12 14
6
0
024
MGB708
−6
−12
−18
−30
−24
−36
−42
−54
−48
f (MHz)
G
v
(dB)
Fig.12 Colour difference transfer characteristic in RGB.
handbook, full pagewidth
6 8 10 12 14
6
0
024
MGB706
−6
−12
−18
−30
−24
−36
−42
−54
−48
f (MHz)
G
v
(dB)
Page 30

1996 Nov 07 30
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
CHARACTERISTICS
V
DDD
= 4.75 to 5.25 V; T
amb
= 0 to +70 °C; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
V
DDA
analog supply voltage 4.75 5.25 V
V
DDD
digital supply voltage 4.75 5.25 V
I
DDA
analog supply current note 1 − 60 mA
I
DDD
digital supply current note 1 − 100 mA
Inputs
V
IL
LOW level input voltage
(except SDA, SCL, AP, SP and XTALI)
−0.5 +0.8 V
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage
(except LLC, SDA, SCL, AP, SP and XTALI)
2.0 V
DDD
+ 0.5 V
HIGH level input voltage (LLC) 2.4 V
DDD
+ 0.5 V
I
LI
input leakage current − 1 µA
C
i
input capacitance clocks − 10 pF
data − 8pF
I/Os at high
impedance
− 8pF
Outputs
V
OL
LOW level output voltage
(except SDA and XTALO)
note 2 0 0.6 V
V
OH
HIGH level output voltage
(except LLC, SDA, and XTALO)
note 2 2.4 V
DDD
+ 0.5 V
HIGH level output voltage (LLC) note 2 2.6 V
DDD
+ 0.5 V
I
2
C-bus; SDA and SCL
V
IL
LOW level input voltage −0.5 +1.5 V
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage 3.0 V
DDD
+ 0.5 V
I
i
input current Vi= LOW or HIGH −10 +10 µA
V
OL
LOW level output voltage (SDA) IOL=3mA − 0.4 V
I
o
output current during acknowledge 3 − mA
Clock timing (LLC)
T
LLC
cycle time note 3 34 41 ns
δ duty factor t
HIGH/TLLC
note 4 40 60 %
t
r
rise time note 3 − 5ns
t
f
fall time note 3 − 6ns
Input timing
t
SU;DAT
input data set-up time (any other except
CDIR, SCL, SDA, RESET, AP and SP)
6 − ns
t
HD;DAT
input data hold time (any other except
CDIR, SCL, SDA, RESET, AP and SP)
3 − ns
Page 31

1996 Nov 07 31
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Notes
1. At maximum supply voltage with highly active input signals.
2. The levels have to be measured with load circuits of 1.2 kΩ to 3.0 V (standard TTL load) and CL= 25 pF.
3. The data is for both input and output direction.
4. With LLC in input mode. In output mode, with a crystal connected to XTALO/XTALI duty factor is typically 50%.
5. If an internal oscillator is used, crystal deviation of nominal frequency is directly proportional to the deviation of
subcarrier frequency and line/field frequency.
6. For full digital range, without load, V
DDA
= 5.0 V. The typical voltage swing is 2.0 V, the typical minimum output
voltage (digital zero at DAC) is 0.2 V.
Crystal oscillator
f
n
nominal frequency (usually 27 MHz) 3rd harmonic − 30 MHz
∆f/f
n
permissible deviation of nominal frequency note 5 −50 +50 10
−6
CRYSTAL SPECIFICATION
T
amb
operating ambient temperature 0 70 °C
C
L
load capacitance 8 − pF
R
S
series resistance − 80 Ω
C
1
motional capacitance (typical) 1.5 − 20% 1.5 + 20% fF
C
0
parallel capacitance (typical) 3.5 − 20% 3.5 + 20% pF
Data and reference signal output timing
C
L
output load capacitance 7.5 40 pF
t
h
output hold time 4 − ns
t
d
output delay time − 25 ns
CHROMA, Y, CVBS and RGB outputs
V
o(p-p)
output signal voltage (peak-to-peak value) note 6 1.9 2.1 V
R
int
internal serial resistance 18 35 Ω
R
L
output load resistance 80 −Ω
B output signal bandwidth of DACs −3dB 10 − MHz
ILE LF integral linearity error of DACs −±4 LSB
DLE LF differential linearity error of DACs −±1 LSB
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
Page 32

1996 Nov 07 32
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Fig.13 Clock data timing.
handbook, full pagewidth
MBE742
LLC clock output
0.6 V
1.5 V
2.6 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.4 V
0.6 V
input data
output data
not valid
valid
valid
not valid
valid
valid
LLC clock input
0.8 V
1.5 V
2.4 V
t
HIGH
t
HD; DAT
T
LLC
t
HIGH
T
LLC
t
d
t
HD; DAT
t
HD; DAT
t
SU; DAT
t
f
t
f
t
r
t
r
Fig.14 Functional timing.
The data demultiplexing phase is coupled to the internal horizontal phase.
The phase of the RCV2 signal is programmed to 0F2H (110H for 50 Hz) in this example in output mode (RCV2S).
handbook, full pagewidth
MP(n)
LLC
Cb(0) Y(0) Cr(0) Y(1) Cb(2)
RCV2
MGB699
Page 33

1996 Nov 07 33
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
Fig.15 RTCI timing.
(1) Sequence bit:
PAL = logic 0 then (R − Y) line normal; PAL = logic 1 then (R − Y) line inverted.
NTSC = logic 0 then no change.
(2) Reserved bits: 235 with 50 Hz systems; 232 with 60 Hz systems.
(3) Only from SAA7111 decoder.
(4) SAAA7111 provides (22 : 0) bits, resulting in 3 reserved bits before sequence bit.
handbook, full pagewidth
128
13
14 19
6768
01
0 021
RTCI
HPLL
increment
FSCPLL increment (4)
H/L transition
count start
4 bits
reserved
valid
sample
invalid
sample
not used in
SAA7124/25
sequence
bit (1)
reset
bit (3)
5 bits
reserved
8/LLC
reserved (2)
MGG557
LOW
time slot:
Page 34

1996 Nov 07 34
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
APPLICATION INFORMATION
ndbook, full pagewidth
MGG553
15 kΩ
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
10 pF 10 pF
10 µH
1 nF
X1
27.0 MHz
3rd
harmonic
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
V
SSD
V
SSD
V
SSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSD
+5 V digital
+5 V digital
V
DDD1
V
DDD2VDDD3VDDD4VDDD5VDDD6VDDD7VDDD8VDDD9
5
14
22
29
38
41
49
80
82
12 Ω
75 Ω
73
35 Ω
(1)
74 Ω
75 Ω
61
35 Ω
(1)
74 Ω
75 Ω
58
35 Ω
(1)
74 Ω
75 Ω
55
35 Ω
(1)
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
+5 V analog
DAC1
DAC2
DAC3
DAC4
digital inputs
and outputs
XTALI XTALO
44
45
CVBS
1.23 V (p-p)
(2)
RED
0.7 V (p-p)
(2)
GREEN
0.7 V (p-p)
(2)
BLUE
0.7 V (p-p)
(2)
0.1 µF
V
SSD
V
SSA
V
DDDO
(4)
V
DDA4
V
refH
CUR
V
DDA1
V
DDA2
V
DDA3
V
DDA5
46 64 53, 75
63, 68
54
57 60
74
V
refL
52, 76
V
SSD1
to V
SSD9
V
SSA
3, 15, 24, 30, 39,
42, 51, 79, 81
SAA7124
SAA7125
67
V
SSA1
V
SSA
V
SSA
V
SSA
V
SSA
(3)
Fig.16 Application environment of the ECO-DENC; PLCC84.
(1) Typical value. (2) For
100
⁄
100
colour bar. (3) Philips 12NC ordering code: 9922 520 30003. (4) V1 devices only.
Page 35

1996 Nov 07 35
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
ook, full pagewidth
MGG554
15 kΩ
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
10 pF 10 pF
10 µH
1 nF
X1
27.0 MHz
3rd
harmonic
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
V
SSD
V
SSD
V
SSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSD
+5 V digital
+5 V digital
V
DDD1
V
DDD2VDDD3VDDD4VDDD5VDDD6VDDD7VDDD8VDDD9
5
7
13
22
24
30
52
54
60
12 Ω
75 Ω
45
35 Ω
(1)
74 Ω
75 Ω
39
35 Ω
(1)
74 Ω
75 Ω
37
35 Ω
(1)
74 Ω
75 Ω
35
35 Ω
(1)
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
+5 V analog
DAC1
DAC2
DAC3
DAC4
digital inputs
and outputs
XTALI XTALO
20
27
CVBS
1.23 V (p-p)
(2)
RED
0.7 V (p-p)
(2)
GREEN
0.7 V (p-p)
(2)
BLUE
0.7 V (p-p)
(2)
0.1 µF
V
SSD
V
SSA
V
DDDO
V
DDA4
V
refH
CUR
V
DDA1
V
DDA2
V
DDA3
V
DDA5
28 41 33, 47
40, 44
34
36 38
46
V
refL
32, 48
V
SSD1
to V
SSD8
V
SSA
6, 8, 14, 23, 25,
51, 53, 58
SAA7124
SAA7125
42, 43
V
SSA1
V
SSA
V
SSA
V
SSA
V
SSA
(3)
Fig.17 Application environment of the ECO-DENC; LQFP64 (V1 devices only).
(1) Typical value. (2) For
100
⁄
100
colour bar. (3) Philips 12NC ordering code: 9922 520 30003.
Page 36

1996 Nov 07 36
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
book, full pagewidth
MGG555
15 kΩ
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
10 pF 10 pF
10 µH
1 nF
X1
27.0 MHz
3rd
harmonic
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
V
SSD
V
SSD
V
SSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSDVSSD
+5 V digital
+5 V digital
V
DDD1
V
DDD2VDDD3VDDD4VDDD5VDDD6VDDD7VDDD8VDDD9
5
13
19
28
30
37
68
70
76
12 Ω
75 Ω
61
35 Ω
(1)
74 Ω
75 Ω
50
35 Ω
(1)
74 Ω
75 Ω
47
35 Ω
(1)
74 Ω
75 Ω
44
35 Ω
(1)
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
0.1 µF
V
SSA
+5 V analog
DAC1
DAC2
DAC3
DAC4
digital inputs
and outputs
XTALI XTALO
32
33
CVBS
1.23 V (p-p)
(2)
RED
0.7 V (p-p)
(2)
GREEN
0.7 V (p-p)
(2)
BLUE
0.7 V (p-p)
(2)
0.1 µF
V
SSD
V
SSA
V
DDDO
(4) V
DDA4
V
refH
CUR
V
DDA1
V
DDA2
V
DDA3
V
DDA5
34 53 42, 63
52, 56
43
46 49
62
V
refL
41, 64
V
SSD1
to V
SSD8
V
SSA
6, 14, 20, 29, 31
39, 67, 69, 74
SAA7124
SAA7125
55
V
SSA1
V
SSA
V
SSA
V
SSA
V
SSA
(3)
Fig.18 Application environment of the ECO-DENC; QFP80.
(1) Typical value. (2) For
100
⁄
100
colour bar. (3) Philips 12NC ordering code: 9922 520 30003. (4) V1 devices only.
Page 37

1996 Nov 07 37
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
PACKAGE OUTLINES
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.01 inches maximum per side are not included.
SOT189-2
5474
84
1
11
12 32
53
33
75
detail X
(A )
3
b
p
w M
A
1
A
A
4
L
p
b
1
β
k
1
k
X
y
e
E
B
D
H
E
H
v M
B
D
Z
D
A
Z
E
e
v M
A
pin 1 index
0 5 10 mm
scale
92-11-17
95-03-11
PLCC84: plastic leaded chip carrier; 84 leads
SOT189-2
UNIT A
A
min. max. max. max. max.
1
A
4
b
p
E
(1)
(1) (1)
eH
E
Z
ywv β
mm
4.57
4.19
0.51
3.30
0.53
0.33
0.021
0.013
1.27
0.51
2.16
45
o
0.18 0.100.18
DIMENSIONS (millimetre dimensions are derived from the original inch dimensions)
D
(1)
29.41
29.21
H
D
30.35
30.10
E
Z
2.16
D
b
1
0.81
0.66
k
1.22
1.07
k
1
0.180
0.165
0.020
0.13
A
3
0.25
0.01
0.05
0.020
0.085
0.007 0.0040.007
L
p
1.44
1.02
0.057
0.040
1.158
1.150
29.41
29.21
1.158
1.150
1.195
1.185
30.35
30.10
1.195
1.185
e
E
e
D
28.70
27.69
1.130
1.090
28.70
27.69
1.130
1.090
0.085
0.032
0.026
0.048
0.042
E
e
inches
D
e
Page 38

1996 Nov 07 38
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
UNIT
A
max.
A1A2A3b
p
cE
(1)
eH
E
LLpQZywv θ
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
mm
1.60
0.20
0.05
1.45
1.35
0.25
0.27
0.17
0.18
0.12
10.1
9.9
0.5
12.15
11.85
0.69
0.59
1.45
1.05
7
0
o
o
0.12 0.11.0 0.2
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
0.75
0.45
SOT314-2
94-01-07
95-12-19
D
(1) (1)(1)
10.1
9.9
H
D
12.15
11.85
E
Z
1.45
1.05
D
b
p
e
θ
E
A
1
A
L
p
Q
detail X
L
(A )
3
B
16
c
D
H
b
p
E
H
A
2
v M
B
D
Z
D
A
Z
E
e
v M
A
X
1
64
49
48 33
32
17
y
pin 1 index
w M
w M
0 2.5 5 mm
scale
LQFP64: plastic low profile quad flat package; 64 leads; body 10 x 10 x 1.4 mm
SOT314-2
Page 39

1996 Nov 07 39
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
UNIT A1A2A3b
p
cE
(1)
eH
E
LLpQZywv θ
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
mm
0.30
0.10
2.90
2.65
0.25
0.45
0.30
0.25
0.14
14.1
13.9
0.8 0.2
19.0
18.4
1.4
1.2
1.2
0.8
7
0
o
o
0.2 0.1
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
1.4
1.0
SOT318-3
95-02-04
95-04-25
D
(1) (1)(1)
20.1
19.9
H
D
25.0
24.4
E
Z
1.0
0.6
D
b
p
e
θ
E
A
1
A
L
p
Q
detail X
L
(A )
3
B
24
y
c
D
H
b
p
E
H
A
2
v M
B
D
Z
D
A
Z
E
e
v M
A
1
80
65
64 41
40
25
pin 1 index
2.35
X
w M
w M
0 5 10 mm
scale
QFP80: plastic quad flat package; 80 leads (lead length 2.35 mm); body 14 x 20 x 2.8 mm
SOT318-3
A
max.
3.25
Page 40

1996 Nov 07 40
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“IC Package Databook”
(order code 9398 652 90011).
Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering techniques are suitable for all PLCC and
QFP packages.
The choice of heating method may be influenced by larger
PLCC or QFP packages (44 leads, or more). If infrared or
vapour phase heating is used and the large packages are
not absolutely dry (less than 0.1% moisture content by
weight), vaporization of the small amount of moisture in
them can cause cracking of the plastic body. For more
information, refer to the Drypack chapter in our
“Quality
Reference Handbook”
(order code 9397 750 00192).
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several techniques exist for reflowing; for example,
thermal conduction by heated belt. Dwell times vary
between 50 and 300 seconds depending on heating
method. Typical reflow temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C.
Preheating is necessary to dry the paste and evaporate
the binding agent. Preheating duration: 45 minutes at
45 °C.
Wave soldering
PLCC
Wave soldering techniques can be used for all PLCC
packages if the following conditions are observed:
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave) soldering
technique should be used.
• The longitudinal axis of the package footprint must be
parallel to the solder flow.
• The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves at
the downstream corners.
QFP
Wave soldering is not recommended for QFP packages.
This is because of the likelihood of solder bridging due to
closely-spaced leads and the possibility of incomplete
solder penetration in multi-lead devices.
If wave soldering cannot be avoided, the following
conditions must be observed:
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave)
soldering technique should be used.
• The footprint must be at an angle of 45° to the board
direction and must incorporate solder thieves
downstream and at the side corners.
Even with these conditions, do not consider wave
soldering the following packages: QFP52 (SOT379-1),
QFP100 (SOT317-1), QFP100 (SOT317-2),
QFP100 (SOT382-1) or QFP160 (SOT322-1).
M
ETHOD (PLCC AND QFP)
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Maximum permissible solder temperature is 260 °C, and
maximum duration of package immersion in solder is
10 seconds, if cooled to less than 150 °C within
6 seconds. Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
Repairing soldered joints
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonallyopposite end leads. Use only a low voltage soldering iron
(less than 24 V) applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact
time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C. When
using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in
one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
Page 41

1996 Nov 07 41
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
DEFINITIONS
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I
2
C COMPONENTS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
Purchase of Philips I
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I2C patent to use the
components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
Page 42

1996 Nov 07 42
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
NOTES
Page 43

1996 Nov 07 43
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoder (ECO-DENC) SAA7124; SAA7125
NOTES
Page 44

Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company
© Philips Electronics N.V. 1996 SCA52
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 40 27 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +63 2 817 3474
Poland: Ul. Lukiska 10, PL 04-123 WARSZAWA,
Tel. +48 22 612 2831, Fax. +48 22 612 2327
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 247 9145, Fax. +7 095 247 9144
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 1231,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 7430 Johannesburg 2000,
Tel. +27 11 470 5911, Fax. +27 11 470 5494
South America: Rua do Rocio 220, 5th floor, Suite 51,
04552-903 São Paulo, SÃO PAULO - SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax. +55 11 829 1849
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 3 301 6312, Fax. +34 3 301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 632 2000, Fax. +46 8 632 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2686, Fax. +41 1 481 7730
Taiwan: PHILIPS TAIWAN Ltd., 23-30F, 66,
Chung Hsiao West Road, Sec. 1, P.O. Box 22978,
TAIPEI 100, Tel. +886 2 382 4443, Fax. +886 2 382 4444
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Talatpasa Cad. No. 5, 80640 GÜLTEPE/ISTANBUL,
Tel. +90 212 279 2770, Fax. +90 212 282 6707
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +380 44 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 181 730 5000, Fax. +44 181 754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 625 344, Fax.+381 11 635 777
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors, Marketing & Sales Communications,
Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218, 5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 34 Waterloo Road, NORTH RYDE, NSW 2113,
Tel. +61 2 9805 4455, Fax. +61 2 9805 4466
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213,
Tel. +43 1 60 101, Fax. +43 1 60 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 200 733, Fax. +375 172 200 773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: see South America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15th floor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 689 211, Fax. +359 2 689 102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +852 2319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Prags Boulevard 80, PB 1919, DK-2300 COPENHAGEN S,
Tel. +45 32 88 2636, Fax. +45 31 57 1949
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615800, Fax. +358 9 61580/xxx
France: 4 Rue du Port-aux-Vins, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 40 99 6161, Fax. +33 1 40 99 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 23 53 60, Fax. +49 40 23 536 300
Greece: No. 15, 25th March Street, GR 17778 TAVROS/ATHENS,
Tel. +30 1 4894 339/239, Fax. +30 1 4814 240
Hungary: see Austria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Shivsagar Estate, A Block, Dr. Annie Besant Rd.
Worli, MUMBAI 400 018, Tel. +91 22 4938 541, Fax. +91 22 4938 722
Indonesia: see Singapore
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax. +353 1 7640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, TEL AVIV 61180,
Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax. +972 3 649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS, Piazza IV Novembre 3,
20124 MILANO, Tel. +39 2 6752 2531, Fax. +39 2 6752 2557
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku, TOKYO 108,
Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5077
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381
Middle East: see Italy
Printed in The Netherlands 657021/1200/01/pp44 Date of release: 1996 Nov 07 Document order number: 9397 750 01467
 Loading...
Loading...