
PIC18F8722 Family
Data Sheet
64/80-Pin, 1-Mbit,
Enhanced Flash Microcontrollers
with 10-Bit A/D and nanoWatt Technology
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C

Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the
intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our
knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchip’s Data
Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not
mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection features of our
products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts
allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and t he lik e is provided only for your convenience
and may be su perseded by upda t es . It is y our responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
MICROCHIP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WHETHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, WRITTEN OR ORAL, STATUTORY OR
OTHERWISE, RELATED TO THE INFORMATION,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ITS CONDITION,
QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR PURPOSE. Microchip disclaims all liability
arising from this information and its use. Use of Microchip
devices in life supp ort and/or safety ap plications is entir ely at
the buyer’s risk, and the buyer agrees to defend, indemnify and
hold harmless M icrochip from any and all dama ges, claims,
suits, or expenses re sulting from such use. No licens es are
conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any Microchip
intellectual property rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, Accuron,
dsPIC, K
EELOQ, KEELOQ logo, MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro,
PICSTART, rfPIC, SmartShunt and UNI/O are registered
trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the
U.S.A. and other countries.
FilterLab, Linear Active Thermistor, MXDEV, MXLAB,
SEEVAL, SmartSensor and The Embedded Control Solutions
Company are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Application Maestro, CodeGuard,
dsPICDEM, dsPICDEM.net, dsPICworks, dsSPEAK, ECAN,
ECONOMONITOR, FanSense, In-Circuit Serial
Programmin g , IC SP, ICEPIC, Mindi, MiW i , MPASM, MPLAB
Certified logo, MPLIB, MPLINK, mTouch, PICkit, PICDEM,
PICDEM.net, PICtail, PIC
32
logo, PowerCal, PowerInfo,
PowerMate, PowerT ool, REAL ICE, rfLAB, Select Mode, Total
Endurance, WiperLock and ZENA are trademarks of
Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other
countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2008, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received ISO/TS-16949:2002 certification for its worldwide
headquarters, design and wafer fabrication facilities in Chandler and
Tempe, Arizona; Gresham, Oregon and design centers in California
and India. The Company’s quality system processes and procedures
are for its PIC
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals, nonvolatile memory and
analog products. In addition, Microchip’s quality system for the design
and manufacture of development systems is ISO 9001:2000 certified.
®
MCUs and dsPIC® DSCs, KEELOQ
®
code hopping
DS39646C-page ii © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
64/80-Pin, 1-Mbit, Enhanced Flash Microcontrollers with
10-Bit A/D and nanoWatt Technology
Power Management Features:
• Run: CPU On, Peripherals On
• Idle: CPU Off, Peripherals On
• Sleep: CPU Off, Peripherals Off
• Ultra Low 50 nA Input Leakage
• Run mode Currents Down to 25 μA Typical
• Idle mode Currents Dow n to 6.8μA Typical
• Sleep mode Current Down to 120 nA Typical
• Timer1 Oscillator: 900 nA, 32 kHz, 2V
• Watchdog Timer: 1.6 μA, 2V Typical
• Two-Speed Oscillator Start-up
Flexible Oscillator Struc ture:
• Four Crystal modes, up to 40 MHz
• 4x Phase Lock Loop (PLL) – Available for Crystal
and Internal Oscillators
• Internal Oscillator Block:
- Fast wake from Sleep and Idle, 1 μs typical
- Provides a complete range of clock speeds
from 31 kHz to 32 MHz when used with PLL
- User-tunable to compensate for frequency drift
• Secondary oscillator using Timer1 @ 32 kHz
• Fail-Safe Clock Monitor:
- Allows for safe shutdown if peripheral clock stops
Peripheral Highlights:
• High-Current Sink/Source 25 mA/25 mA
• Three Programmable External Interrupts
• Four Input Change Interrupts
• Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM (ECCP)
module (40/44-pin devices only):
- One, two or four PWM outputs
- Programmable dead time
- Auto-shutdown and auto-restart
Peripheral Highlight s (Continued):
• Up to 2 Capture/Compare/PWM (CCP) modules,
one with Auto-Shutdown (28-pin devices)
• Master Synchronous Serial Port (MSSP) module
Supporting 3-Wire SPI (all 4 modes) and I
Master and Slave modes
• Enhanced Addressable USART module:
- Supports RS-485, RS-232 and LIN/J2602
- RS-232 operation using internal oscillator
block (no external crystal required)
• 10-Bit, up to 13-Channel Analog-to-Digital (A/D)
Converter module:
- Conversion available during Sleep
• Dual Analog Comparators with Input Multiplexing
• Programmable 16-Level High/Low-Voltage
Detection (HLVD) module
2
C™
Special Microcontroller Features:
• C Compiler Optimized Arch itecture
• 100,000 Erase/Write Cycle Enhanced Flash
Program Memory Typical
• 1,000,000 Erase/Write Cycle Data EEPROM
Memory Typical
• Flash/Data EEPROM Retention: 100 Y ears Typical
• Self-Programmable under Software Control
• Priority Levels for Interrupts
• 8 x 8 Single-Cycle Hardware Multiplier
• Extended Watchdog Timer (WDT):
- Programmable period from 4 ms to 131s
• Single-Supply 5V In-Circuit Se rial Programming™
(ICSP™) via Two Pins
• In-Circuit Debug (ICD) via Two Pins
• Wide Operating Voltage Range: 2.0V to 5.5V
• Programmable Brown-out Reset (BOR) with
Software Enable Option
Program Memory
Device
PIC18F6527 48K 24576 3936 1024 54 12 2/3 2 Y Y 2 2 2/3 N
PIC18F6622 64K 32768 3936 1024 54 12 2/3 2 Y Y 2 2 2/3 N
PIC18F6627 96K 49152 3936 1024 54 12 2/3 2 Y Y 2 2 2/3 N
PIC18F6722 128K 65536 3936 1024 54 12 2/3 2 Y Y 2 2 2/3 N
PIC18F8527 48K 24576 3936 1024 70 16 2/3 2 Y Y 2 2 2/3 Y
PIC18F8622 64K 32768 3936 1024 70 16 2/3 2 Y Y 2 2 2/3 Y
PIC18F8627 96K 49152 3936 1024 70 16 2/3 2 Y Y 2 2 2/3 Y
PIC18F8722 128K 65536 3936 1024 70 16 2/3 2 Y Y 2 2 2/3 Y
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 1
Flash
(bytes)
# Single-Word
Instructions
Data Memory
SRAM
EEPROM
(bytes)
(bytes)
I/O
10-Bit
A/D
(ch)
CCP/
ECCP
(PWM)
MSSP
SPI
Master
2
C™
I
Timers
EUSART
Comparators
8/16-Bit
External Bus

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Note 1: The ECCP2/P2A pin placement is determined by the CCP2MX Configuration bit.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
38
37
36
35
34
33
50 49
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
RE2/CS/P2B
RE3/P3C
RE4/P3B
RE5/P1C
RE6/P1B
RE7/ECCP2
(1)
/P2A
(1)
RD0/PSP0
VDDVSS
RD1/PSP1
RD2/PSP2
RD3/PSP3
RD4/PSP4/SDO2
RD5/PSP5/SDI2/SDA2
RD6/PSP6/SCK2/SCL2
RD7/PSP7/SS2
RE1/WR/P2C
RE0/RD
/P2D
RG0/ECCP3/P3A
RG1/TX2/CK2
RG2/RX2/DT2
RG3/CCP4/P3D
RG5/MCLR
/VPP
RG4/CCP5/P1D
VSS
VDD
RF7/SS1
RF6/AN11
RF5/AN10/CV
REF
RF4/AN9
RF3/AN8
RF2/AN7/C1OUT
RB0/INT0
RB1/INT1
RB2/INT2
RB3/INT3
RB4/KBI0
RB5/KBI1/PGM
RB6/KBI2/PGC
V
SS
OSC2/CLKO/RA6
OSC1/CLKI/RA7
V
DD
RB7/KBI3/PGD
RC4/SDI1/SDA1
RC3/SCK1/SCL1
RC2/ECCP1/P1A
RF0/AN5
RF1/AN6/C2OUT
AV
DD
AVSS
RA3/AN3/VREF+
RA2/AN2/V
REF-
RA1/AN1
RA0/AN0
V
SS
VDD
RA4/T0CKI
RA5/AN4/HLVDIN
RC1/T1OSI/ECCP2
(1)
/P2A
(1)
RC0/T1OSO/T13CKI
RC7/RX1/DT1
RC6/TX1/CK1
RC5/SDO1
15
16
31
40
39
27 28 29 30 32
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
54 53 52 5158 57 56 5560 5964 63 62 61
64-Pin TQFP
PIC18F6527
PIC18F6622
PIC18F6627
PIC18F6722
Pin Diagrams
DS39646C-page 2 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8527
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
64 63 62 61
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
RE2/AD10/CS/P2B
RE3/AD11/P3C
(2)
RE4/AD12/P3B
(2)
RE5/AD13/P1C
(2)
RE6/AD14/P1B
(2)
RE7/AD15/ECCP2
(1)
/P2A
(1)
RD0/AD0/PSP0
VDDVSS
RD1/AD1/PSP1
RD2/AD2/PSP2
RD3/AD3/PSP3
RD4/AD4/PSP4/SDO2
RD5/AD5/PSP5/SDI2/SDA2
RD6/AD6/PSP6/SCK2/SCL2
RD7/AD7/PSP7/SS2
RE1/AD9/WR/P2C
RE0/AD8/RD
/P2D
RG0/ECCP3/P3A
RG1/TX2/CK2
RG2/RX2/DT2
RG3/CCP4/P3D
RG5/MCLR
/VPP
RG4/CCP5/P1D
V
SS
VDD
RF7/SS1
RB0/INT0
RB1/INT1
RB2/INT2
RB3/INT3/ECCP2
(1)
/P2A
(1)
RB4/KBI0
RB5/KBI1/PGM
RB6/KBI2/PGC
V
SS
OSC2/CLKO/RA6
OSC1/CLKI/RA7
V
DD
RB7/KBI3/PGD
RC4/SDI1/SDA1
RC3/SCK1/SCL1
RC2/ECCP1/P1A
RF0/AN5
RF1/AN6/C2OUT
AV
DD
AVSS
RA3/AN3/VREF+
RA2/AN2/V
REF-
RA1/AN1
RA0/AN0
V
SS
VDD
RA4/T0CKI
RA5/AN4/HLVDIN
RC1/T1OSI/ECCP2
(1)
/P2A
(1)
RC0/T1OSO/T13CKI
RC7/RX1/DT1
RC6/TX1/CK1
RC5/SDO1
RJ0/ALE
RJ1/OE
RH1/A17
RH0/A16
1
2
RH2/A18
RH3/A19
17
18
RH7/AN15/P1B
(2)
RH6/AN14/P1C
(2)
RH5/AN13/P3B
(2)
RH4/AN12/P3C
(2)
RJ5/CE
RJ4/BA0
37
RJ7/UB
RJ6/LB
50
49
RJ2/WRL
RJ3/WRH
19
20
33 34
35 36
38
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
60
59
68 67 66 6572 71 70 6974 7378 77 76 757980
80-Pin TQFP
Note 1: The ECCP2/P2A pin placement is determined by the CCP2MX Configuration bit and Processor mode settings.
2: P1B, P1C, P3B and P3C pin placement is determined by the ECCPMX Configuration bit.
RF5/AN10/CVREF
RF4/AN9
RF3/AN8
RF2/AN7/C1OUT
RF6/AN11
PIC18F8622
PIC18F8627
PIC18F8722
Pin Diagrams (Continued)
PIC18F8722 FAMILY
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 3

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Table of Contents
1.0 Device Overview ..........................................................................................................................................................................7
2.0 Oscillator Configurations............................................................................................................................................................ 31
3.0 Power-Managed Modes........................................................................... .... ....... .... .. .... .. ........................................................... 41
4.0 Reset..........................................................................................................................................................................................49
5.0 Memory Organization.................................................................................................................................................................63
6.0 Flash Pro g ram Memory.............................................................. ................................................................................................87
7.0 External Memory Bus.................................................................................................................................................................97
8.0 Data EEPR OM Mem o ry................ .................................................................. ......................................................................... 111
9.0 8 x 8 Hardware Multip lier.............................. ........................... ........................................ ......................................................... 117
10.0 Interrupts..................................................................................................................................................................................119
11.0 I/O Ports.............................................................................................................. ..................................................................... 135
12.0 Timer0 Module ......................................................................................................................................................................... 161
13.0 Timer1 Module ......................................................................................................................................................................... 165
14.0 Timer2 Module ......................................................................................................................................................................... 171
15.0 Timer3 Module ......................................................................................................................................................................... 173
16.0 Timer4 Module ......................................................................................................................................................................... 177
17.0 Capture/Compare/PWM (CCP) Modules ................................................................................................................................. 179
18.0 Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM (ECCP) Module................................................................................................................187
19.0 Master Synchronous Serial Port (MSSP) Module ....................................................................................................................205
20.0 Enhanced Universal Synchronous Receiver Transmitter (EUSART)....................................................................................... 247
21.0 10-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (A/D) Module ......................................................................... ............................................ 271
22.0 Comparator Module................................................................................................. .. .... ...........................................................281
23.0 Comparator Voltage Reference Module....................................................... ......... .... .. .... ......... .. .............................................. 287
24.0 High/Low-Voltage Detect (HLVD)............................................................................................................................................. 291
25.0 Special Features of the CPU.................................................................. ..................................................................................297
26.0 Instruction Set Summary..........................................................................................................................................................321
27.0 Development Support. .............................................................................................................................................................. 371
28.0 Electrical Characteristics.......................................................................................................................................................... 375
29.0 Packaging Information..... .................................................... .....................................................................................................419
Appendix A: Revision History............................................................................................................................................................. 425
Appendix B: Device Differences......................................................................................................................................................... 425
Appendix C: Conversion Considerations ........................................................... .... ....... .... .... .. .... ....................................................... 426
Appendix D: Migration From Baseline to Enhanced Devices............................................................................................................. 426
Appendix E: Migration From Mid-Range to Enhanced Devices......................................................................................................... 427
Appendix F: Migration From High-End to Enhanced Devices.................................................................. .. ........................................ 427
Index .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 429
The Microchip Web Site.................. ................................................................................................................................................... 441
Customer Change Notification Service .............................................................................................................................................. 441
Customer Support..............................................................................................................................................................................441
Reader Response.............................................................................................................................................................................. 442
PIC18F8722 Family Product Identification System............................................................................................................................443
DS39646C-page 4 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TO OUR VALUED CUSTOMERS
It is our intention to provide our valued customers with the best documentation possible to ensure successful use of your Microchip
products. To this end, we will continue to improve our publications to better suit your needs. Our publications will be refined and
enhanced as new volumes and updates are introduced.
If you have any questions or c omm ents regarding t his publication, please contact the Marketing Communications Department via
E-mail at docerrors@.microchip.com or fax the Reader Response Form in the back of this data sheet to (480) 792-4150. We
welcome your feedback.
Most Current Data Sheet
To obtain the most up-to-date version of this data sheet, please register at our Worldwide Web site at:
http://www.microchip.com
You can determine the version of a data sheet by examining its literature number found on the bottom outside corner of any page.
The last character of the literature number is the version number, (e.g., DS30000A is version A of document DS30000).
Errata
An errata sheet, describing minor operational differences from the data sheet and recommended workarounds, may exist for current
devices. As device/documentation issues become known to us, we will publish an errata sheet. The errata will specify the revision
of silicon and revision of document to which it applies.
To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please check with one of the following:
• Microchip’s Worldwide Web site; http://www.microchip.com
• Your local Microchip sales office (see last page)
When contacting a sales office, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include literature number) you are
using.
Customer Notification System
Register on our web site at www.microchip.com to receive the most current information on all of our products.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 5

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
NOTES:
DS39646C-page 6 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
1.0 DEVICE OVERVIEW
This document co nta i ns dev ic e spec if i c in for m at ion fo r
the following devices:
• PIC18F6527 • PIC18LF6527
• PIC18F6622 • PIC18LF6622
• PIC18F6627 • PIC18LF6627
• PIC18F6722 • PIC18LF6722
• PIC18F8527 • PIC18LF8527
• PIC18F8622 • PIC18LF8622
• PIC18F8627 • PIC18LF8627
• PIC18F8722 • PIC18LF8722
This family offers the advantages of all PIC18 microcontrollers – namely, high computa tional performance at
an economical price – with the addition of highendurance, Enhanced Flash program memory . On top of
these features, the PIC18F8722 family introduces
design enhancements that make these microcontrollers
a logical choice for many high-performance, power
sensitive applications.
1.1 New Core Features
1.1.1 nanoWatt TECHNOLOGY
All of the devices in the PIC18 F8722 fami ly incorp orate
a range of features that can significantly reduce power
consumption during operation. Key items include:
• Alternate Run Modes: By clocking the controller
from the Timer1 source or the internal oscillator
block, power consumption during code execution
can be significantly redu ce d.
• Multiple Idle Modes: The controller can also run
with its CPU core disabled but the peripherals still
active. In these st ates, powe r consumpt ion can be
reduced even further.
• On-the-fly Mode Switching: The powermanaged modes a re invo ked b y user code durin g
operation, allowing the user to incorporate powersaving ideas into their application’s software
design.
• Low Consumption in Key Modules: The
power requirements for both Timer1 and the
Watchdog Timer are minimized. See
Section 28.0 “Electrical Characteristics”
for values.
1.1.2 EXPANDED MEMORY
The PIC18F8722 family provides ample room for
application code and includes members with 48, 64,
96 or 128 Kbytes of code space.
• Data RAM and Data EEPROM: The PIC18F872 2
family also p rov ide s ple nty o f room for applicati on
data. The devices have 3936bytes of data RAM,
as well as 1024 bytes of data EEPROM, for long
term retention of nonvolatile data.
• Memory Endurance: The Enhanced Flash cells
for both program memory and data EEPROM are
rated to last for many thousands of erase/write
cycles, up to 100,000 for program memory and
1,000,000 for EEPROM. Data retention without
refresh is conservatively estimated to be greater
than 40 years.
1.1.3 MULTIPLE OSCILLATOR OPTIONS
AND FEATURES
All of the devices in the PIC18F8722 family offer ten
different osci llator option s, all owin g users a w ide range
of choices in developing application hardware. These
include:
• Four Crystal modes, using crystals or ceramic
resonators
• Two External Clock modes, offering the option of
using two pins (oscillator input and a divide-by-4
clock output) or one pin (oscillator input, with the
second pin reassigned as general I/O)
• Two External RC Oscillator modes with the same
pin options as the External Clock modes
• An internal oscillator block which provides an
8 MHz clock and an INTRC source (approximately 31 kHz), as well as a range of 6 user
selectable cl ock fre quenc ies, be tween 125 kHz to
4 MHz, for a total of 8 clock frequencies. This
option frees the two oscillator pins for use as
additional general purpose I/O.
• A Phase Lock Loop (PLL) frequency multiplier,
available to both the high-speed crystal and internal oscillator m odes, which a llows clo ck speeds o f
up to 40 MHz. Used with the internal oscillator, the
PLL gives users a complete selection of clock
speeds, from 31 kHz to 32 MHz – all without us ing
an external crystal or clock circuit.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 7

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Besides its availability as a clock source, the internal
oscillator block provides a stable reference source that
gives the family additional features for robust operation:
• Fail-Safe Clock Monitor: This option co nst ant ly
monitors the m ai n c l oc k source against a reference
signal provide d by th e internal osci ll at or. If a cl oc k
failure occu rs , t he co nt rol le r i s s witc h ed to th e
internal oscillator block, allowing for continued
low-speed operation or a safe application shutdown.
• Two-Speed Start-up: This option allows the
internal oscillator to serve as the clock source
from Power-on Reset, or wake-up from Sleep
mode, until the primary clock source is available.
1.1.4 EXTERNAL MEMORY INTERFACE
In the unlikely event that 128 Kbytes of program
memory is inadequate for an application, the
PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 members of the family
also implement an external memory interface. This
allows the controller’s internal program counter to
address a memory space of up to 2 Mbytes,
permitting a level of data access that few 8-bit devices
can claim.
With the addition of new operat ing mod es, the ext erna l
memory interface offers many new options, including:
• Operating the microcontrol le r entirel y from
external memory
• Using combinations of on-chip and external
memory, up to the 2-Mbyte limit
• Using external Flash memory for reprogrammable
application code or large data tables
• Using external RAM devices for storing large
amounts of variable data
1.1.5 EASY MIGRATION
Regardless of the memory size, all devices share the
same rich set of peripherals, allowing for a smooth
migration path as applications grow and evolve.
The consistent pinout scheme used throughout the
entire family also aids in migrating to the next larger
device. Thi s is true when mo ving between the 64-pin
members, between the 80-pin members, or even
jumping from 64-pin to 80-pin devices.
1.2 Other Special Features
• Communications: The PIC18F8722 family
incorporates a range of serial communication
peripherals, including 2 independent Enhanced
USARTs and 2 Master SSP modules capable of
both SPI and I
operation. Also, one of the general purpose I/O
ports can be reconfigured as an 8-bit Parallel
Slave Port for direct processor-to-processor
communications.
• CCP Modules: All devices in the family
incorporate two Capture/Compare/PWM (CCP)
modules and three Enhanced CCP (ECCP)
modules to maximize flexibility in control
applications. Up to four different time bases may
be used to perform severa l di f fe rent operations at
once. Each of the three ECCP modul es offer up to
four PWM outputs, allowing for a total of
12 PWMs. The ECCPs also offer many beneficial
features, including polarity selection,
Programmable Dead-Time, Auto-Shutdown and
Restart and Half-Bridge and Full-Bridge
Output modes.
• Self-Programmability: These devices can write
to their own program memory spaces under
internal software control. By using a bootloader
routine located in the protected boot block at the
top of program memory, it becomes possible to
create an application that can update itself in the
field.
• Extended Instruction Set: The PIC18F8722
family introduces an optional extension to the
PIC18 instruction set, which adds 8 new instructions and an Indexed Addressing mode. This
extension, enabled as a device configuration
option, has been specifi cally des igned to opti mize
re-entrant applica tion code original ly deve loped in
high-level language s, su ch as C.
• 10-bit A/D Converter: This module incorporates
programmable acquisition time, allowing for a
channel to be selected and a conversion to be
initiated without w ait ing for a sampling period and
thus, reduce code overhead.
• Extended Watchdog Timer (WDT): This
enhanced version in corpora tes a 16 -bit pre scale r,
allowing an exte nded time-o ut rang e that is s ta ble
across operating voltage and temperature. See
Section 28.0 “Electrical Characteristics” for
time-out periods.
2
C (Master and Slave) modes of
DS39646C-page 8 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
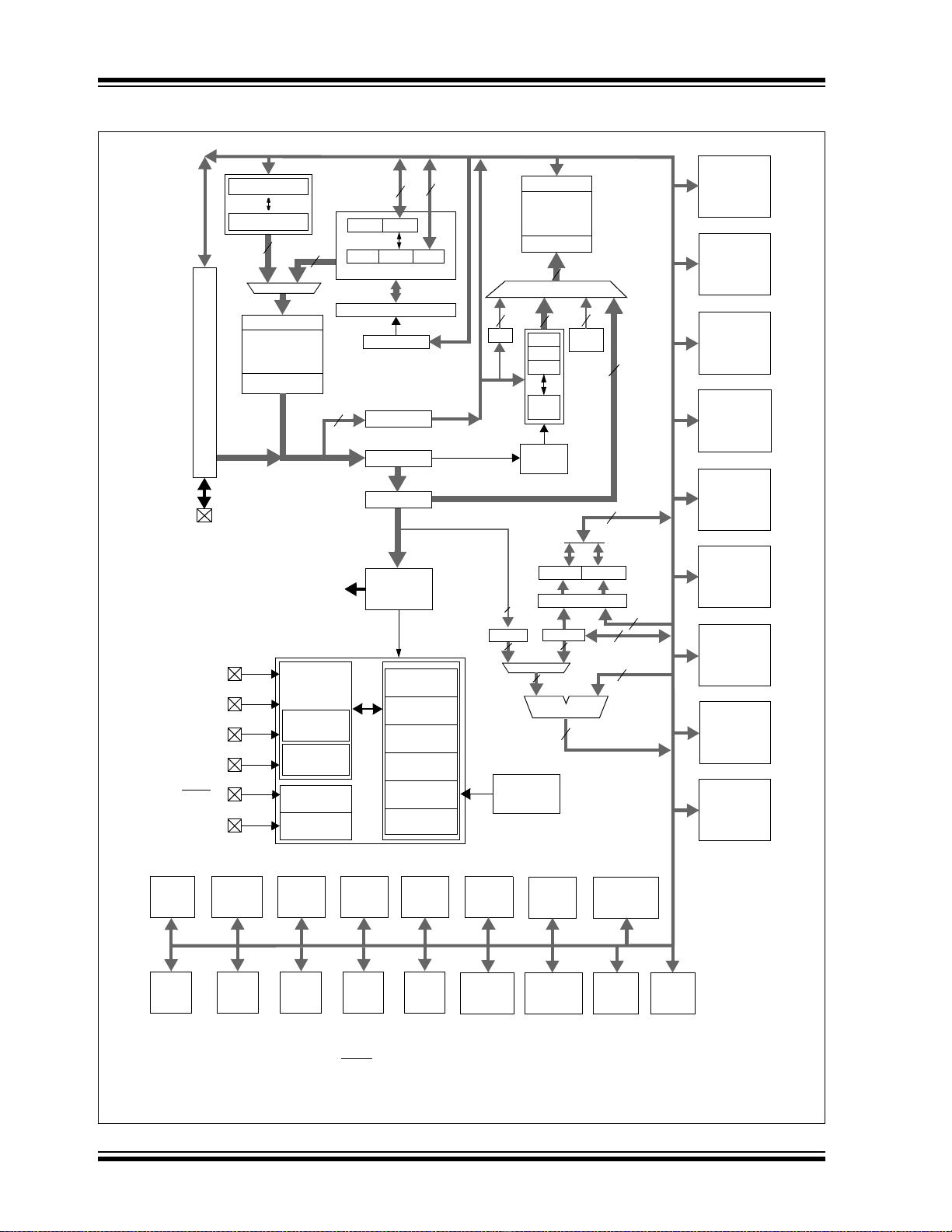
1.3 Details on Individual Family Members
Devices in the PIC18F8722 family are available in
64-pin and 80-pin packages. Block diagrams for the
two groups are shown in Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2.
The devices are differentiated from each other in five
ways:
1. Flash program memory (48 Kbytes for
PIC18F6527/8527 devices, 64 Kbytes for
PIC18F6622/8622 devices, 96 Kbytes for
PIC18F6627/8627 devices and 128 Kbytes for
All other features fo r device s in this family are identi cal.
These are summarized in Table1-2 and Table 1-2.
The pinouts for all devices are listed in Table 1-3 and
Table 1-4.
Like all Microchip PIC18 devices, members of the
PIC18F8722 family are available as both standard and
low-voltage devices. Standard devices with Enhanced
Flash memory, designated with an “F” in the part
number (such as PIC18F6627), accommodate an
operating V
DD range of 4.2V to 5.5V. Low-voltage
parts, designated by “LF” (such as PIC18LF6627),
function over an extended VDD range of 2.0V to 5.5V.
PIC18F6722/8722).
2. A/D channels (12 for 64-pin devices, 16 for
80-pin devices).
3. I/O ports (7 bidirectional por ts on 64-pin de vices,
9 bidirectional ports on 80-pin devices).
4. External Memory Bus, configurable for 8 and
16-bit operation, is available on PIC18F8527/
8622/8627/8722 devices.
T ABLE 1-1: DEVICE FEATURES (PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722)
Features PIC18F6527 PIC18F6622 PIC18F6627 PIC18F6722
Operating Frequency DC – 40 MHz DC – 40 MHz DC – 40 MHz DC – 40 MHz
Program Memory (Bytes) 48K 64K 96K 128K
Program Memory (Instructions) 24576 32768 49152 65536
Data Memory (Bytes) 3936 3936 3936 3936
Data EEPROM Memory (Bytes) 1024 1024 1024 1024
Interrupt Sources 28282828
I/O Ports Ports A, B, C, D, E, F, G Ports A, B, C, D, E, F, G Ports A, B, C, D, E, F, G Ports A, B, C, D, E, F, G
Timers 5 5 5 5
Capture/Co mp a re/PWM
Modules
Enhanced Capture/Compare/
PWM Modules
Enhanced USART 2 2 2 2
Serial Communications MSSP,
Parallel Communications (PSP) Y es Y es Ye s Yes
10-bit Analog-to-Digit al Modul e 12 Input Channels 12 Input Channels 12 In put Cha nnel s 12 Input Chann els
Resets (and Delays) POR, BOR,
RESET Instruction,
Underflow (PWRT , OST),
MCLR
Programmable
High/Low-Voltage Detect
Programmable Brown-out
Reset
Instruction Set 75 Instructions;
Instruction Set enabled
Packages 64-pin TQFP 64-pin TQFP 64-pin TQFP 64-pin TQFP
2222
3333
MSSP,
Enhanced USART
Enhanced USART
POR, BOR,
RESET Instruction,
Stack Full, Stack
(optional), WDT
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes
83 with Extended
Stack Full, Stack
Underflow (PWRT , OST),
(optional), WDT
MCLR
75 Instructions;
83 with Exten ded
Instruction Set enabled
Underflow (PWRT , OST),
MSSP,
Enhanced USART
POR, BOR,
RESET Instruction,
Stack Full, Stack
(optional), WDT
MCLR
75 Instructions;
83 with Extended
Instruction Set enabled
MSSP,
Enhanced USART
POR, BOR,
RESET Instruction,
Stack Full, Stack
Underflow (PWRT , OST),
(optional), WDT
MCLR
75 Instructions;
83 with Extended
Instruction Set enabled
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 9

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 1-2: DEVICE FEATURES (PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722)
Features PI C18 F8 527 PIC18F8622 PIC18F8627 PIC18F8722
Operating Frequency DC – 40 MHz DC – 40 MHz DC – 40 MHz DC – 40 MHz
Program Memory (Bytes) 48K 64K 96K 128K
Program Memory (Instructions) 24576 32768 49152 65536
Data Memory (Bytes) 3936 3936 3936 3936
Data EEPROM Memo ry (Byte s) 1024 1024 1024 1024
Interrup t Sou r ce s 29 29 29 29
I/O Ports Ports A, B, C, D, E,
F, G, H, J
Timers 5 5 5 5
Capture/Compare/PWM
Modules
Enhanced Capture/Comp are/
PWM Modules
Enhanced USART 2 2 2 2
Serial Communications MSSP,
Parallel Communications
(PSP)
10-bit Analog-to-Digit al Modul e 16 Input Channels 16 Input Chann els 16 Input Channels 16 Input Channels
Resets (and Delays) POR, BOR,
2222
3333
Enhanced USART
Yes Yes Yes Yes
RESET Instruction,
Stack Full, Stack
Underflow (PWRT , OST),
(optional), WDT
MCLR
Programmable
High/Low-Voltage Detect
Programmable Brown-out
Reset
Instruction Set 75 Instructions;
Instruction Set enabled
Packages 80-pin TQFP 80-pin TQFP 80-pin TQFP 80-pin TQFP
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes
83 with Extended
Ports A, B, C, D, E,
F, G, H, J
MSSP,
Enhanced USART
POR, BOR,
RESET Instruction,
Stack Full, Stack
Underflow (PWRT , OST),
(optional), WDT
MCLR
75 Instructions;
83 with Extended
Instruction Set enabled
Ports A, B, C, D, E,
F, G, H, J
MSSP,
Enhanced USART
POR, BOR,
RESET Instruction,
Stack Full, Stack
Underflow (PWRT , OST),
(optional), WDT
MCLR
75 Instructions;
83 with Extended
Instruction Set e nabled
Ports A, B, C, D, E,
F, G, H, J
MSSP,
Enhanced USART
POR, BOR,
RESET Instruction,
Stack Full, Stack
Underflow (PWRT , OST),
(optional), WDT
MCLR
75 Instructions;
83 with Exten ded
Instruction Set enabled
DS39646C-page 10 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Instruction
Decode and
Control
PORTA
Data Latch
Data Memory
(3.9Kbytes)
Address Latch
Data Address< 12>
12
Access
BSR
FSR0
FSR1
FSR2
inc/dec
logic
Address
4
12
4
PCH PCL
PCLATH
8
31-Level Stack
Program Counter
PRODLPRODH
8 x 8 Multiply
8
BITOP
8
8
ALU<8>
Address Latch
Program Memory
(48/64/96/128
Data Latch
20
8
8
T able Pointer<21>
inc/dec logic
21
8
Data Bus<8>
Table Latch
8
IR
12
3
PCLATU
PCU
Note 1: See Table 1-3 for I/O port pin descriptions.
2: RG5 is only available when MCLR
functionality is disabled.
3: OSC1/CLKI and OSC2/CLKO are only available in select oscillator modes and when these pins are not being used as
digital I/O. Refer to Section 2.0 “Oscillator Configurations” for additional information.
EUSART1
Comparators
MSSP1
Timer2Timer1 Timer3Timer0
HLVD
ECCP1
BOR
ADC
10-bit
W
Instruction Bus <16>
STKPTR
Bank
8
State M achine
Control Signals
Decode
8
8
Power-up
Timer
Oscillator
Start-up Timer
Power-on
Reset
Watchdog
Timer
OSC1
(3)
OSC2
(3)
VDD,
Brown-out
Reset
Internal
Oscillator
Fail-Safe
Clock Monitor
Precision
Reference
Band Gap
V
SS
MCLR
(2)
Block
INTRC
Oscillator
8 MHz
Oscillator
Single-Supply
Programming
In-Circuit
Debugger
T1OSI
T1OSO
EUSART2
ECCP2
ROM Latch
ECCP3
MSSP2CCP4 CCP5
PORTC
PORTD
PORTE
PORTF
PORTG
RA0:RA7
(1)
RC0:RC7
(1)
RD0:RD7
(1)
RE0:RE7
(1)
RF0:RF7
(1)
RG0:RG5
(1)
PORTB
RB0:RB7
(1)
Timer4
Kbytes)
FIGURE 1-1: PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722 (64-PIN) BLOCK DIAGRAM
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 11
PIC18F8722 FAMILY
PRODLPRODH
8 x 8 Multiply
8
BITOP
8
8
ALU<8>
8
8
3
W
8
8
8
Power-up
Timer
Oscillator
Start-up Timer
Power-on
Reset
Watchdog
Timer
OSC1
(3)
OSC2
(3)
VDD,
Brown-out
Reset
Internal
Oscillator
Fail-Safe
Clock Monitor
Precision
Reference
Band Gap
V
SS
MCLR
(2)
Block
INTRC
Oscillator
8 MHz
Oscillator
Single-Supply
Programming
In-Circuit
Debugger
T1OSI
T1OSO
Instruction
Decode &
Control
Data Latch
Data Memory
(3.9 Kbytes)
Address Lat ch
Data Address<12>
12
Access
BSR
FSR0
FSR1
FSR2
inc/dec
logic
Address
4124
PCH PCL
PCLATH
8
31-Level Stack
Program Counter
Address Latch
Program Memory
(48/64/96/ 128
Data Latch
20
T able Pointer<21>
inc/dec logic
21
8
Data Bus<8>
T able Latch
8
IR
12
ROM Latch
PCLATU
PCU
Instruction Bus <16>
STKPTR
Bank
State Machine
Control Signals
Decode
System Bus Interface
AD15:AD0, A19:A16
(Multiplexed with PORTD,
PORTE and PORTH)
PORTA
PORTC
PORTD
PORTE
PORTF
PORTG
RA0:RA7
(1)
RC0:RC7
(1)
RD0:RD7
(1)
RE0:RE7
(1)
RF0:RF7
(1)
RG0:RG5
(1)
PORTB
RB0:RB7
(1)
PORTH
RH0:RH7
(1)
PORTJ
RJ0:RJ7
(1)
EUSART1
Comparators
MSSP1
Timer2Timer1 Timer3Timer0
HLVD
ECCP1
BOR
ADC
10-bit
EUSART2
ECCP2 ECCP3
MSSP2CCP4 CCP5
Timer4
Note 1: See Table 1-4 for I/O port pin descriptions.
2: RG5 is only available when MCLR
functionality is disabled.
3: OSC1/CLKI and OS C2/CLKO are only available i n sele ct os ci llat or mo des and when the s e p ins ar e no t be i ng u sed as
digital I/O. Refer to Section 2.0 “Oscillator Configurations” for additional information.
Kbytes)
FIGURE 1-2: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 (80-PI N) BLOCK DIAGRAM
DS39646C-page 12 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
T ABLE 1-3: PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
RG5/MCLR
RG5
MCLR
VPP
OSC1/CLKI/RA7
OSC1
CLKI
RA7
OSC2/CLKO/RA6
OSC2
CLKO
RA6
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
Note 1: Default assignment for ECCP2 when Conf iguration bit, CCP2MX, is set.
/VPP
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
2: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared.
39
40
7
I
I
P
I
I
CMOS
I/O
O
O
I/O
2
C™ = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Master Clear (input) or programming voltage (input).
ST
ST
ST
TTL
—
—
TTL
Digital input.
Master Clear (Reset) input. This pin is an active-low
Reset to the device.
Programming voltage input.
Oscillator crystal or external clock input.
Oscillator crystal input or external clock source input.
ST buffer when configured in RC mode, CMOS
otherwise.
External clock source input. Always associated
with pin function OSC1. (See related OSC1/CLKI,
OSC2/CLKO pins.)
General purpose I/O pin.
Oscillator crystal or clock output.
Oscillator crystal output. Connects to crystal or
resonator in Crystal Oscillator mode.
In RC mode, OSC2 pin outputs CLKO, which has
1/4 the frequency of OSC1 and denotes the
instruction cycle rate.
General purpose I/O pin.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 13

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 1-3: PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTA is a bidirectional I/O port.
RA0/AN0
RA0
AN0
RA1/AN1
RA1
AN1
RA2/AN2/V
RA2
AN2
V
RA3/AN3/V
RA3
AN3
V
RA4/T0CKI
RA4
T0CKI
RA5/AN4/HLVDIN
RA5
AN4
HLVDIN
RA6 See the OSC2/CLKO/RA6 pin.
RA7 See the OSC1/CLKI/RA7 pin.
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
Note 1: Default assignment for ECCP2 when Conf iguration bit, CCP2MX, is set.
REF-
REF-
REF+
REF+
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
2: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared.
24
23
22
21
28
27
I/O
I
I/O
I
I/O
I
I
I/O
I
I
I/O
I
I/O
I
I
2
TTL
Analog
TTL
Analog
TTL
Analog
Analog
TTL
Analog
Analog
ST
ST
TTL
Analog
Analog
C™ = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Digital I/O.
Analog input 0.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 1.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 2.
A/D reference voltage (low) input.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 3.
A/D reference voltage (high) input.
Digital I/O.
Timer0 external clock input.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 4.
High/Low-Voltage Detect input.
DS39646C-page 14 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
T ABLE 1-3: PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
RB0/INT0/FLT0
RB0
INT0
FLT0
Pin Number
TQFP
48
Pin
Type
I/O
I
I
Buffer
Type
TTL
ST
ST
Description
PORTB is a bidirectional I/O port. PORTB can be software
programmed for internal weak pull-ups on all inputs.
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 0.
PWM Fault input for ECCPx.
RB1/INT1
RB1
INT1
RB2/INT2
RB2
INT2
RB3/INT3
RB3
INT3
RB4/KBI0
RB4
KBI0
RB5/KBI1/PGM
RB5
KBI1
PGM
RB6/KBI2/PGC
RB6
KBI2
PGC
RB7/KBI3/PGD
RB7
KBI3
PGD
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Default assignment for ECCP2 when Conf iguration bit, CCP2MX, is set.
2: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared.
47
46
45
44
43
42
37
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
2
TTL
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
C™ = I2C/SMBus input buffer
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 1.
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 2.
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 3.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
Low-Voltage ICSP™ Programming enable pin.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
In-Circuit Debugger and ICSP programming clock pin.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
In-Circuit Debugger and ICSP programming data pin.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 15

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 1-3: PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTC is a bidirectional I/O port.
RC0/T1OSO/T13CKI
RC0
T1OSO
T13CKI
RC1/T1OSI/ECCP2/P2A
RC1
T1OSI
(1)
ECCP2
(1)
P2A
RC2/ECCP1/P1A
RC2
ECCP1
P1A
RC3/SCK1/SCL1
RC3
SCK1
SCL1
RC4/SDI1/SDA1
RC4
SDI1
SDA1
RC5/SDO1
RC5
SDO1
30
29
33
34
35
36
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
ST
—
I
I
I
ST
ST
CMOS
ST
—
ST
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
—
Digital I/O.
Timer1 oscillator output.
Timer1/Timer3 external clock input.
Digital I/O.
Timer1 oscillator input.
Enhanced Capture 2 input/Compare 2 output/
PWM 2 output.
ECCP2 PWM output A.
Digital I/O.
Enhanced Capture 1 input/Compare 1 output/
PWM 1 output.
ECCP1 PWM output A.
Digital I/O.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for SPI mode.
Synchron ous serial clock input/ou tput for I
Digital I/O.
SPI data in.
2
C data I/O.
I
Digital I/O.
SPI data out.
2
C™ mode.
RC6/TX1/CK1
RC6
TX1
CK1
RC7/RX1/DT1
RC7
RX1
DT1
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Default assignment for ECCP2 when Conf iguration bit, CCP2MX, is set.
2: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared.
31
32
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I
I/O
2
C™ = I2C/SMBus input buffer
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
ST
Digital I/O.
EUSART1 asynchronous transmit.
EUSART1 synchronous clock (see related RX1/DT1).
Digital I/O.
EUSART1 asynchronous receive.
EUSART1 synchronous data (see related TX1/CK1).
DS39646C-page 16 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
T ABLE 1-3: PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTD is a bidirectional I/O port.
RD0/PSP0
RD0
PSP0
RD1/PSP1
RD1
PSP1
RD2/PSP2
RD2
PSP2
RD3/PSP3
RD3
PSP3
RD4/PSP4/SDO2
RD4
PSP4
SDO2
RD5/PSP5/SDI2/SDA2
RD5
PSP5
SDI2
SDA2
RD6/PSP6/SCK2/SCL2
RD6
PSP6
SCK2
SCL2
58
55
54
53
52
51
50
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
—
ST
TTL
I
ST
2
C/SMB
I
ST
TTL
ST
2
I
C/SMB
Digital I/O.
Parallel Slave Port data.
Digital I/O.
Parallel Slave Port data.
Digital I/O.
Parallel Slave Port data.
Digital I/O.
Parallel Slave Port data.
Digital I/O.
Parallel Slave Port data.
SPI data out.
Digital I/O.
Parallel Slave Port data.
SPI data in.
I2C™ data I/O.
Digital I/O.
Parallel Slave Port data.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for SPI mode.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for I2C mode.
RD7/PSP7/SS2
RD7
PSP7
SS2
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Default assignment for ECCP2 when Conf iguration bit, CCP2MX, is set.
2: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 17
49
I/O
I/O
I
2
C™ = I2C/SMBus input buffer
ST
TTL
TTL
Digital I/O.
Parallel Slave Port data.
SPI slave select input.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 1-3: PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTE is a bidirectional I/O port.
RE0/RD
RE0
RD
P2D
RE1/WR
RE1
WR
P2C
RE2/CS
RE2
CS
P2B
RE3/P3C
RE3
P3C
RE4/P3B
RE4
P3B
RE5/P1C
RE5
P1C
RE6/P1B
RE6
P1B
/P2D
/P2C
/P2B
64
63
62
61
60
2
I/O
I
O
1
I/O
I
O
I/O
I
O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
O
ST
TTL
—
ST
TTL
—
ST
TTL
—
ST
—
ST
—
ST
—
ST
—
Digital I/O.
Read control for Parallel Slave Port.
ECCP2 PWM output D.
Digital I/O.
Write control for Parallel Slave Port.
ECCP2 PWM output C.
Digital I/O.
Chip select control for Parallel Slave Port.
ECCP2 PWM output B.
Digital I/O.
ECCP3 PWM output C.
Digital I/O.
ECCP3 PWM output B.
Digital I/O.
ECCP1 PWM output C.
Digital I/O.
ECCP1 PWM output B.
RE7/ECCP2/P2A
RE7
(2)
ECCP2
(2)
P2A
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Default assignment for ECCP2 when Conf iguration bit, CCP2MX, is set.
2: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared.
59
I/O
I/O
O
2
C™ = I2C/SMBus input buffer
ST
ST
—
Digital I/O.
Enhanced Capture 2 input/Compare 2 output/
PWM 2 output.
ECCP2 PWM output A.
DS39646C-page 18 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
T ABLE 1-3: PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTF is a bidirectional I/O port.
RF0/AN5
RF0
AN5
RF1/AN6/C2OUT
RF1
AN6
C2OUT
RF2/AN7/C1OUT
RF2
AN7
C1OUT
RF3/AN8
RF3
AN8
RF4/AN9
RF4
AN9
RF5/AN10/CV
RF5
AN10
CVREF
RF6/AN11
RF6
AN11
REF
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
ST
I
Analog
ST
I
Analog
—
ST
I
Analog
—
ST
I
Analog
ST
I
Analog
ST
I
Analog
Analog
ST
I
Analog
Digital I/O.
Analog input 5.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 6.
Comparator 2 output.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 7.
Comparator 1 output.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 8.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 9.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 10.
Comparator reference voltage output.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 11.
RF7/SS1
RF7
SS1
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Default assignment for ECCP2 when Conf iguration bit, CCP2MX, is set.
2: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared.
11
I/O
I
2
C™ = I2C/SMBus input buffer
ST
TTL
Digital I/O.
SPI slave select input.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 19

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 1-3: PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTG is a bidirectional I/O port.
RG0/ECCP3/P3A
RG0
ECCP3
P3A
RG1/TX2/CK2
RG1
TX2
CK2
RG2/RX2/DT2
RG2
RX2
DT2
RG3/CCP4/P3D
RG3
CCP4
P3D
RG4/CCP5/P1D
RG4
CCP5
P1D
RG5 See RG5/MCLR
SS 9, 25, 41, 56 P — Ground reference for logic and I/O pins.
V
VDD 10, 26, 38, 57 P — Positive supply for logic and I/O pins.
AVSS 20 P — Ground reference for analog modules.
DD 19 P — Positive supply for analog modules.
AV
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Default assignment for ECCP2 when Conf iguration bit, CCP2MX, is set.
2: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared.
3
I/O
I/O
O
4
I/O
O
I/O
5
I/O
I
I/O
6
I/O
I/O
O
8
I/O
I/O
O
2
C™ = I2C/SMBus input buffer
ST
ST
—
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
—
ST
ST
—
Digital I/O.
Enhanced Capture 3 input/Compare 3 output/
PWM 3 output.
ECCP3 PWM output A.
Digital I/O.
EUSART2 asynchronous transmit.
EUSART2 synchronous clock (see related RX2/DT2).
Digital I/O.
EUSART2 asynchronous receive.
EUSART2 synchronous data (see related TX2/CK2).
Digital I/O.
Capture 4 input/Compare 4 output/PWM 4 output.
ECCP3 PWM output D.
Digital I/O.
Capture 5 input/Compare 5 output/PWM 5 output.
ECCP1 PWM output D.
/VPP pin.
DS39646C-page 20 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
T ABLE 1-4: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
RG5/MCLR
RG5
MCLR
VPP
OSC1/CLKI/RA7
OSC1
CLKI
RA7
OSC2/CLKO/RA6
OSC2
CLKO
RA6
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
Note 1: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared (all operating modes except
/VPP
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Microcontroller mode).
2: Default assignment fo r ECCP2 in all operating modes (CCP2MX is set).
3: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when CCP2MX is cleared (Microcontroller mode only).
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is set).
5: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is clear).
49
50
9
I
I
P
I
I
CMOS
I/O
O
O
I/O
2
C™/SMB = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Master Clear (input) or programming voltage (input).
ST
ST
ST
TTL
—
—
TTL
Digital input.
Master Clear (Reset) input. This pin is an active-low
Reset to the device.
Programming voltage input.
Oscillator crystal or external clock input.
Oscillator crystal input or external clock source input.
ST buffer when configured in RC mode, CMOS
otherwise.
External clock source input. Always associated with
pin function OSC1. (See related OSC1/CLKI,
OSC2/CLKO pins.)
General purpose I/O pin.
Oscillator crysta l or clock output.
Oscillator crystal output. Connects to crystal or
resonator in Crystal Oscillator mode.
In RC mode, OSC2 pin out put s CLKO, whi ch has 1/4 the
frequency of OSC1 and denotes the
instruction cycle rate.
General purpose I/O pin.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 21

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 1-4: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTA is a bidirectional I/O port.
RA0/AN0
RA0
AN0
RA1/AN1
RA1
AN1
RA2/AN2/V
RA2
AN2
V
RA3/AN3/V
RA3
AN3
V
RA4/T0CKI
RA4
T0CKI
RA5/AN4/HLVDIN
RA5
AN4
HLVDIN
RA6 See the OSC2/CLKO/RA6 pin.
RA7 See the OSC1/CLKI/RA7 pin.
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
Note 1: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared (all operating modes except
REF-
REF-
REF+
REF+
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Microcontroller mode).
2: Default assignment fo r ECCP2 in all operating modes (CCP2MX is set).
3: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when CCP2MX is cleared (Microcontroller mode only).
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is set).
5: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is clear).
30
29
28
27
34
33
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/OIST/ODSTDigital I/O. Open-drain when configured as output.
I/O
TTL
I
Analog
TTL
I
Analog
TTL
I
Analog
I
Analog
TTL
I
Analog
I
Analog
TTL
I
Analog
I
Analog
2
C™/SMB = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Digital I/O.
Analog input 0.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 1.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 2.
A/D reference voltage (low) input.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 3.
A/D reference voltage (high) input.
Timer0 external clock input.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 4.
High/Low-Voltage Detect inpu t.
DS39646C-page 22 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
T ABLE 1-4: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
RB0/INT0/FLT0
RB0
INT0
FLT0
Pin Number
TQFP
58
Pin
Type
I/O
I
I
Buffer
Type
TTL
ST
ST
Description
PORTB is a bidirectional I/O port. PORTB can be software
programmed for internal weak pull-ups on all inputs.
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 0.
PWM Fault input for ECCPx.
RB1/INT1
RB1
INT1
RB2/INT2
RB2
INT2
RB3/INT3/ECCP2/P2A
RB3
INT3
(1)
ECCP2
(1)
P2A
RB4/KBI0
RB4
KBI0
RB5/KBI1/PGM
RB5
KBI1
PGM
RB6/KBI2/PGC
RB6
KBI2
PGC
RB7/KBI3/PGD
RB7
KBI3
PGD
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared (all operating modes except
Microcontroller mode).
2: Default assignment fo r ECCP2 in all operating modes (CCP2MX is set).
3: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when CCP2MX is cleared (Microcontroller mode only).
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is set).
5: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is clear).
57
56
55
54
53
52
47
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
TTL
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
2
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
—
—
TTL
TTL
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
C™/SMB = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 1.
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 2.
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 3.
Enhanced Capture 2 input/Compare 2 output/
PWM 2 output .
ECCP2 PWM output A.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
Low-V o lt ag e ICSP™ Prog rammi ng ena ble pin.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
In-Circuit Debugger and ICSP™ programming clock pin.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
In-Circuit Debugger and ICSP programming data pin.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 23
PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 1-4: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTC is a bidirectional I/O port.
RC0/T1OSO/T13CKI
RC0
T1OSO
T13CKI
RC1/T1OSI/ECCP2/P2A
RC1
T1OSI
(2)
ECCP2
(2)
P2A
RC2/ECCP1/P1A
RC2
ECCP1
P1A
RC3/SCK1/SCL1
RC3
SCK1
SCL1
RC4/SDI1/SDA1
RC4
SDI1
SDA1
RC5/SDO1
RC5
SDO1
RC6/TX1/CK1
RC6
TX1
CK1
36
35
43
44
45
46
37
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
ST
—
I
I
I
ST
ST
CMOS
ST
—
ST
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
—
ST
—
ST
Digital I/O.
Timer1 oscillator output.
Timer1/Timer3 external clock input.
Digital I/O.
Timer1 oscillator input.
Enhanced Capture 2 input/Compare 2 output/
PWM 2 output .
ECCP2 PWM output A.
Digital I/O.
Enhanced Capture 1 input/Compare 1 output/
PWM 1 output .
ECCP1 PWM output A.
Digital I/O.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for SPI mode.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for I
Digital I/O.
SPI data in.
2
C data I/O.
I
Digital I/O.
SPI data out.
Digital I/O.
EUSART1 asynchronous transmit.
EUSART1 synchronous clock (see related RX1/DT1).
2
C™ mode.
RC7/RX1/DT1
RC7
RX1
DT1
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared (all operating modes except
Microcontroller mode).
2: Default assignment fo r ECCP2 in all operating modes (CCP2MX is set).
3: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when CCP2MX is cleared (Microcontroller mode only).
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is set).
5: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is clear).
DS39646C-page 24 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
38
I/O
I
I/O
2
ST
ST
ST
C™/SMB = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Digital I/O.
EUSART1 asynchronous receive.
EUSART1 synchronous data (see related TX1/CK1).

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
T ABLE 1-4: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTD is a bidirectional I/O port.
RD0/AD0/PSP0
RD0
AD0
PSP0
RD1/AD1/PSP1
RD1
AD1
PSP1
RD2/AD2/PSP2
RD2
AD2
PSP2
RD3/AD3/PSP3
RD3
AD3
PSP3
RD4/AD4/PSP4/SDO2
RD4
AD4
PSP4
SDO2
RD5/AD5/PSP5/
SDI2/SDA2
RD5
AD5
PSP5
SDI2
SDA2
RD6/AD6/PSP6/
SCK2/SCL2
RD6
AD6
PSP6
SCK2
SCL2
72
69
68
67
66
65
64
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
—
ST
TTL
TTL
I
ST
2
C/SMB
I
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
2
C/SMB
I
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 0.
Parallel Slave Port data.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 1.
Parallel Slave Port data.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 2.
Parallel Slave Port data.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 3.
Parallel Slave Port data.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 4.
Parallel Slave Port data.
SPI data out.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 5.
Parallel Slave Port data.
SPI data in.
2
C™ data I/O.
I
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 6.
Parallel Slave Port data.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for SPI mode.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for I2C mode.
RD7/AD7/PSP7/SS2
RD7
AD7
PSP7
SS2
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared (all operating modes except
Microcontroller mode).
2: Default assignment fo r ECCP2 in all operating modes (CCP2MX is set).
3: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when CCP2MX is cleared (Microcontroller mode only).
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is set).
5: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is clear).
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 25
63
I/O
I/O
I/O
I
2
ST
TTL
TTL
TTL
C™/SMB = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 7.
Parallel Slave Port data.
SPI slave select input.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 1-4: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTE is a bidirectional I/O port.
RE0/AD8/RD
RE0
AD8
RD
P2D
RE1/AD9/WR
RE1
AD9
WR
P2C
RE2/AD10/CS
RE2
AD10
CS
P2B
RE3/AD11/P3C
RE3
AD11
P3C
RE4/AD12/P3B
RE4
AD12
P3B
RE5/AD13/P1C
RE5
AD13
P1C
/P2D
(4)
(4)
(4)
/P2C
/P2B
78
77
76
75
4
I/O
I/O
I
O
3
I/O
I/O
I
O
I/O
I/O
I
O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
ST
TTL
TTL
—
ST
TTL
TTL
—
ST
TTL
TTL
—
ST
TTL
—
ST
TTL
—
ST
TTL
—
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 8.
Read control for Parallel Slave Port.
ECCP2 PWM output D.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 9.
Write control for Parallel Slave Port.
ECCP2 PWM output C.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 10.
Chip select control for Parallel Slave Port.
ECCP2 PWM output B.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 11.
ECCP3 PWM output C.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 12.
ECCP3 PWM output B.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 13.
ECCP1 PWM output C.
RE6/AD14/P1B
RE6
AD14
(4)
P1B
RE7/AD15/ECCP2/P2A
RE7
AD15
(3)
ECCP2
(3)
P2A
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared (all operating modes except
Microcontroller mode).
2: Default assignment fo r ECCP2 in all operating modes (CCP2MX is set).
3: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when CCP2MX is cleared (Microcontroller mode only).
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is set).
5: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is clear).
DS39646C-page 26 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
74
73
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
2
ST
TTL
—
ST
TTL
ST
—
C™/SMB = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 14.
ECCP1 PWM output B.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 15.
Enhanced Capture 2 input/Compare 2 output/
PWM 2 output.
ECCP2 PWM output A.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
T ABLE 1-4: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTF is a bidirectional I/O port.
RF0/AN5
RF0
AN5
RF1/AN6/C2OUT
RF1
AN6
C2OUT
RF2/AN7/C1OUT
RF2
AN7
C1OUT
RF3/AN8
RF3
AN8
RF4/AN9
RF4
AN9
RF5/AN10/CV
RF5
AN10
CVREF
RF6/AN11
RF6
AN11
REF
24
23
18
17
16
15
14
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
ST
I
Analog
ST
I
Analog
—
ST
I
Analog
—
ST
I
Analog
ST
I
Analog
ST
I
Analog
Analog
ST
I
Analog
Digital I/O.
Analog input 5.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 6.
Comparator 2 output.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 7.
Comparator 1 output.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 8.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 9.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 10.
Comparator reference voltage output.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 11.
RF7/SS1
RF7
SS1
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared (all operating modes except
Microcontroller mode).
2: Default assignment fo r ECCP2 in all operating modes (CCP2MX is set).
3: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when CCP2MX is cleared (Microcontroller mode only).
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is set).
5: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is clear).
13
I/O
I
2
ST
TTL
C™/SMB = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Digital I/O.
SPI slave select input.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 27

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 1-4: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTG is a bidirectional I/O port.
RG0/ECCP3/P3A
RG0
ECCP3
P3A
RG1/TX2/CK2
RG1
TX2
CK2
RG2/RX2/DT2
RG2
RX2
DT2
RG3/CCP4/P3D
RG3
CCP4
P3D
RG4/CCP5/P1D
RG4
CCP5
P1D
RG5 See RG5/ MC LR
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared (all operating modes except
Microcontroller mode).
2: Default assignment fo r ECCP2 in all operating modes (CCP2MX is set).
3: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when CCP2MX is cleared (Microcontroller mode only).
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is set).
5: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is clear).
10
5
I/O
I/O
O
6
I/O
O
I/O
7
I/O
I
I/O
8
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
2
ST
ST
—
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
—
ST
ST
—
C™/SMB = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Digital I/O.
Enhanced Capture 3 input/Compare 3 output/
PWM 3 output .
ECCP3 PWM output A.
Digital I/O.
EUSART2 asynchronous transmit.
EUSART2 synchronous clock (see related RX2/DT2).
Digital I/O.
EUSART2 asynchronous receive.
EUSART2 synchronous data (see related TX2/CK2).
Digital I/O.
Capture 4 input/Compare 4 output/PWM 4 output.
ECCP3 PWM output D.
Digital I/O.
Capture 5 input/Compare 5 output/PWM 5 output.
ECCP1 PWM output D.
/VPP pin.
DS39646C-page 28 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
T ABLE 1-4: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTH is a bidirectional I/O port.
RH0/A16
RH0
A16
RH1/A17
RH1
A17
RH2/A18
RH2
A18
RH3/A19
RH3
A19
RH4/AN12/P3C
RH4
AN12
(5)
P3C
RH5/AN13/P3B
RH5
AN13
(5)
P3B
RH6/AN14/P1C
RH6
AN14
(5)
P1C
79
80
22
21
20
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
1
I/O
I/O
2
I/O
I/O
I/O
I
O
I/O
I
O
I/O
I
O
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
Analog
—
ST
Analog
—
ST
Analog
—
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 16.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 17.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 18.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 19.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 12.
ECCP3 PWM output C.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 13.
ECCP3 PWM output B.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 14.
ECCP1 PWM output C.
RH7/AN15/P1B
RH7
AN15
(5)
P1B
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared (all operating modes except
Microcontroller mode).
2: Default assignment fo r ECCP2 in all operating modes (CCP2MX is set).
3: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when CCP2MX is cleared (Microcontroller mode only).
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is set).
5: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is clear).
19
I/O
I
O
2
ST
Analog
—
C™/SMB = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Digital I/O.
Analog input 15.
ECCP1 PWM output B.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 29

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 1-4: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
TQFP
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
PORTJ is a bidirectional I/O port.
RJ0/ALE
RJ0
ALE
RJ1/OE
RJ1
OE
RJ2/WRL
RJ2
WRL
RJ3/WRH
RJ3
WRH
RJ4/BA0
RJ4
BA0
RJ5/CE
RJ4
CE
RJ6/LB
RJ6
LB
RJ7/UB
RJ7
UB
VSS 11, 31, 51, 70 P — Groun d reference for logic an d I/O pins.
DD 12, 32, 48, 71 P — Positive supply for logic and I/O pins.
V
AVSS 26 P — Ground reference for analog modules.
AVDD 25 P — Positive supply for analog modules.
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog= Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P= Power I
Note 1: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when Configuration bit, CCP2MX, is cleared (all operating modes except
Microcontroller mode).
2: Default assignment fo r ECCP2 in all operating modes (CCP2MX is set).
3: Alternate assignment for ECCP2 when CCP2MX is cleared (Microcontroller mode only).
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is set).
5: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C (ECCPMX is clear).
62
61
60
59
39
40
41
42
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
O
2
ST
—
ST
—
ST
—
ST
—
ST
—
ST
—
ST
—
ST
—
C™/SMB = I2C/SMBus input buffer
Digital I/O.
External memory address latch enable.
Digital I/O.
External memory output enable.
Digital I/O.
External memory write low control.
Digital I/O.
External memory write high control.
Digital I/O.
External memory byte address 0 control.
Digital I/O
External memory chip enable control.
Digital I/O.
External memory low byte control.
Digital I/O.
External memory high byte control.
DS39646C-page 30 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Note 1: See Table 2-1 and Table2-2 for initial values of
C1 and C2.
2: A series resistor (R
S) may be required for AT
strip cut crystals.
3: R
F varies with the oscillator mode chosen.
C1
(1)
C2
(1)
XTAL
OSC2
OSC1
RF
(3)
Sleep
To
Logic
PIC18FXXXX
RS
(2)
Internal
2.0 OSCILLATOR CONFIGURATIONS
2.1 Oscillator Types
The PIC18F8722 family of devices can be operated in
ten different oscillator modes. The user can program the
Configuration bits, FOSC<3:0>, in Configuration
Register 1H to select one of these ten modes:
1. LP Low-Power Crystal
2. XT Crystal/Resonator
3. HS High-Speed Crystal/Resonator
4. HSPLL High-Speed Crystal/Resonator
with PLL enabled
5. RC External Resistor/Capacitor with
F
OSC/4 output on RA6
6. RCIO External Resistor/Capacitor with I/O
on RA6
7. INTIO1 Internal Oscillator with F
on RA6 and I/O on RA7
8. INTIO2 Internal Oscillator with I/O on RA6
and RA7
9. EC External Clock with F
10. ECIO External Clock with I/O on RA6
OSC/4 output
OSC/4 output
FIGURE 2-1: CRYSTAL/CERAMIC
RESONATOR OPERATION
(XT, LP, HS OR HSPLL
CONFIGURATION)
T ABLE 2-1: CAPACITOR SELECTION FOR
CERAMIC RESONATORS
Typical Capacitor Values Used:
Mode Freq OSC1 OSC2
2.2 Crystal Oscilla tor/Ceramic Resonators
In XT, LP, HS or HSPLL Oscillator modes, a crystal or
ceramic resonator is connected to the OSC1 and
OSC2 pins to establish oscillation. Figure 2-1 shows
the pin connections.
The oscillator design requires the use of a parallel cut
crystal.
Note: Use of a series cut crystal may give a
frequency out of the crystal ma nufacturer’s
specifications.
XT 3.58 MHz 22 pF 22 pF
Capacitor values are for design guidance only.
Different cap acitor values may be required to prod uce
acceptable oscillator operation. The user should test
the performance of the oscillator over the expected
DD and temperature range for the application. Refer
V
to the following applicat ion notes for oscil lator specific
information:
®
• AN588 – PI C
Microcontroller Oscillator Design
Guide
• AN826 – Crystal Oscillator Basics and Crystal
Selection for rfPIC
• AN849 – Basic PIC
• AN943 – Practical PIC
®
and PIC® Devices
®
Oscillator Design
®
Oscillator Analysis and
Design
• AN949 – Making Your Oscillator Work
See the notes following Table 2-2 for additional
information.
Note: When using resonators with frequencies
above 3.5 MHz, the use of HS mode,
rather than XT mode, is recommended.
HS mode may be used at any V
which the controller is rated. If HS is
selected, it is possible that the gain of the
oscillator will overdrive the resonator.
Therefore, a series resistor may be placed
between the OSC2 pin and the resonator.
As a good starting point, the
recommended value of R
S is 330Ω.
DD for
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 31

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
OSC1
OSC2
Open
Clock from
Ext. System
PIC18FXXXX
(HS Mode)
OSC1/CLKI
OSC2/CLKO
F
OSC/4
Clock from
Ext. System
PIC18FXXXX
OSC1/CLKI
I/O (OSC2)
RA6
Clock from
Ext. System
PIC18FXXXX
TABLE 2-2: CAPACITOR SELECTION FOR
QUARTZ CRYSTALS
Osc T y pe
Crystal
Freq
LP 32 kHz 22 pF 22 pF
XT 1 MHz
4 MHz
HS 4 MHz
10 MHz
20 MHz
25 MHz
Capacitor values are for design guidance only.
Different capa citor values may be required to produc e
acceptable oscillator operation. The user should test
the performance of the oscillator over the expected
VDD and temperature range for the application. Refer
to the following a pplicati on not es for os cillator specifi c
information:
®
• AN588 – PIC
Microcontroller Oscillator Design
Guide
• AN826 – Crystal Oscillator Basics and Crystal
Selection for rfPIC
• AN849 – Basic P IC
• AN943 – Practical PIC
Design
• AN949 – Making Your Oscillator Work
See the notes following this table for additional
information.
T ypical Cap acitor V alues
C1 C2
22 pF
22 pF
22 pF
22 pF
22 pF
22 pF
®
and PIC® Devices
®
Oscillator Design
®
Oscillator Analysis and
Tested:
22 pF
22 pF
22 pF
22 pF
22 pF
22 pF
An external clock source may also be connected to the
OSC1 pin in the HS mode, as shown in Figure 2-2.
When operated in this mode, parameters D033 and
D043 apply.
FIGURE 2-2: EXTERNAL CLOCK INPUT
OPERATION (HS OSC
CONFIGURATION)
2.3 External Clock Input
The EC and ECIO Oscillator mode s require an externa l
clock source to be conn ected to the OSC1 pi n. There is
no oscillator start-up time required after a Power-on
Reset or after an exit from Sleep mode.
In the EC Oscillator mode, the oscillator frequency
divided by 4 is available on the OSC2 pin. This signal
may be used f or t est pu r pos es or t o sy nc hr o niz e o t he r
logic. Figure 2-3 shows the pin connections for the EC
Oscillator mode.
FIGURE 2-3: EXTERNAL CLOCK
INPUT OPERATION
(EC CONFIGURATION)
Note 1: Hi gher capac itance inc reases the st abilit y
of the oscillator but also increases the
start-up time.
2: When operating below 3V V
DD, or when
using certain ceramic resonators at any
voltage, it may be necessary to use the
HS mode or switch to a crystal oscillator.
3: Since each resonator/crystal has its own
characteristics, the user should consult
the resonator/crystal manufacturer for
appropriate values of external
components.
4: Rs may be required to avoid overd riving
crystals with low driv e lev e l spe ci fic ati on.
5: Alw ays verify os ci lla tor pe rform an ce ov er
DD and temperature range that is
the V
expected for the application.
The ECIO Oscillator mo de func tio ns lik e t he EC mod e,
except that the OSC2 pin becomes an additional
general purpose I/O pin. The I/O pin becomes bit 6 of
PORTA (RA6). Figure 2-4 shows the pin connections
for the ECIO Oscillator mode. When operated in this
mode, parameters D033A and D043A apply.
FIGURE 2-4: EXTERNAL CLOCK
INPUT OPERATION
(ECIO CONFIGURATION)
DS39646C-page 32 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
OSC2/CLKO
CEXT
REXT
PIC18FXXXX
OSC1
F
OSC/4
Internal
Clock
VDD
VSS
Recommended values: 3 kΩ ≤ REXT ≤ 100 kΩ
20 pF ≤ C
EXT ≤ 300 pF
CEXT
REXT
PIC18FXXXX
OSC1
Internal
Clock
VDD
VSS
Recommended values: 3 kΩ ≤ REXT ≤ 100 kΩ
20 pF ≤ C
EXT ≤ 300 pF
I/O (OSC2)
RA6
MUX
VCO
Loop
Filter
Crystal
Osc
OSC2
OSC1
PLL Enable
F
IN
FOUT
SYSCLK
Phase
Comparator
HS Oscillator Enable
÷4
(from Configuration Register 1H)
HS Mode
2.4 RC Oscillator
For timing insensitive applications, the RC and RCIO
Oscillator modes offer additional cost savings. The
actual oscillator frequency is a function of several
factors:
• supply voltage
• values of the external resistor (R
capacitor (C
EXT)
• operating temperature
Given the same device, operating voltage and temperature and component values, there will also be unit-to-unit
frequency variations. These are due to factors such as:
• normal manufacturing variation
• difference in lead frame capacitance between
package types (especially for low C
• variati ons within th e tolerance of limits of R
EXT
and C
In the RC Oscillator mode, the oscillator frequency
divided by 4 is available on the OSC2 pin. This signal
may be used f or t est pu r pos es or t o sy nc hr o niz e o t he r
logic. Figure 2-5 shows how the R/C combination is
connected.
FIGURE 2-5: RC OSCILLATOR MODE
EXT) and
EXT values)
EXT
2.5 PLL Frequency Multiplier
A Phase Locked Loop (PLL) circuit is provided as an
option for users who wish to use a lower frequency
oscillator circuit or to clock the device up to its highest
rated frequency from a crystal oscillator. This may be
useful for customers who are concerned with EMI due
to high-frequency crystals or users who require higher
clock speeds from an internal oscillator.
2.5.1 HSPLL OSCILLATOR MODE
The HSPLL mode make s use of the HS mode osc illator
for frequencies up t o 10 MHz. A PLL then multipl ies the
oscillator output frequency by 4 to produce an internal
clock frequency up to 40 MHz. The PLLEN bit is not
available when this mode is configured as the primary
clock source.
The PLL is only available to the crystal oscillator when
the FOSC<3:0> Configurati on bits are progra mmed for
HSPLL mode (= 0110).
FIGURE 2-7: HSPLL BLOCK DIAGRAM
The RCIO Oscillator mode (Figure 2-6) functions like
the RC mode, except that the OSC2 pin becomes an
additional general purpose I/O pin. The I/O pin
becomes bit 6 of PORTA (RA6).
FIGURE 2-6: RCIO OSCILLATOR MODE
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 33
2.5.2 PLL AND INTOSC
The PLL is also ava ilabl e to th e inte rnal os cill ator bl ock
when the internal oscillator block is configured as the
primary clock source. In this configuration, the PLL is
enabled in sof tware and g enerate s a c lock output of u p
to 32 MHz. The operation of INTOSC with the PLL is
described in Section 2.6.4 “PLL in INTOSC Modes”.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
PIC18FXXXX
OSC2
F
OSC/4
I/O (OSC1)
RA7
PIC18FXXXX
I/O (OSC2)
RA6
I/O (OSC1)
RA7
MUX
VCO
Loop
Filter
OSC2
PLLEN
F
IN
FOUT
SYSCLK
Phase
Comparator
8 or 4 MHz
÷4
(OSCTUNE<6>)
MUX
RA6
CLKO
INTOSC
2.6 Internal Oscillator Block
The PIC18F8722 family of devices includes an int erna l
oscillator block which generates two different clock
signals; either can be used as the microcontroller’s
clock source. This may eliminate the need for external
oscillator circuits on the OSC1 and/or OSC 2 pins.
The main output (INTOSC) is an 8MHz clock source,
which can be used to directly drive the device clock. It
also drives a postscaler, which can provide a range of
clock frequencies from 31 kHz to 4 MHz. The INTOSC
output is enabled when a clock fre quency from 12 5 kHz
to 8 MHz is selected. The INTOSC output can also be
enabled when 31 kHz is selected, depending on the
INTSRC bit (OSCTUNE<7>).
The other clock source is the internal RC oscillator
(INTRC), which provides a nominal 31 kHz output.
INTRC is enabled if it is selected as the device clock
source; it is also ena bled autom atically when an y of the
following are enabled:
• Power-up Timer
• Fail-Safe Clock Monitor
• Watchdog Timer
• Two-Speed Start-up
These features are discussed in greater detail in
Section 25.0 “Special Features of the CPU”.
The clock source frequency (INTOSC direct, INTRC
direct or INTOSC postscaler) is selected by configuring
the IRCF bits of the OSCCON register (page 39).
2.6.1 INTIO MODES
Using the internal oscillator as the clock source eliminates the need for up to two external oscillator pins,
which can then be used for digital I/O. Two distinct
configurations are available:
• In INTIO1 mode, the OSC2 pin outputs F
while OSC1 functions as RA7 (s ee Fig ure 2-8) for
digital input and output.
• In INTIO2 mode, OSC1 functions as RA7 and
OSC2 functions as RA6 (see Figure2-9), both for
digital input and output.
OSC/4,
2.6.2 INTOSC OUTPUT FREQUENCY
The internal oscillator block is calibrated at the factory
to produce an INTOSC output frequency of 8 MHz.
The INTRC oscillator operates independently of the
INTOSC source. Any changes in INTOSC across
voltage and temperature are not necessarily reflected
by changes in INTRC or vice versa.
2.6.3 OSCTUNE REGISTER
The INTOSC output has been calibrated at the
factory but can be adjusted in the user’s application.
This is done by writing to TUN<4:0>
(OSCTUNE<4:0>) in the OSCTUNE register
(Register ).
When the OSCTUNE regis ter is mo di fied , the IN T O SC
frequency will begin shifting to the new frequency. The
INTOSC clock will stabilize within 1 ms. Code execution continues during this shift. There is no indication
that the shift has occurred. The INTRC is not affected
by OSCTUNE.
The OSCTUNE register also implements the INTSRC
(OSCTUNE<7>) and PLLEN (OSCTUNE<6>) bits,
which control certain features of the internal oscillator
block. The INTSRC bit allows users to select which
internal oscillator provides the clock source when the
31 kHz frequenc y o ptio n is selected. This is co vered in
greater detail in Section 2.7.1 “Oscillator Control
Register”.
The PLLEN bit controls the operation of the Phase
Locked Loop (PLL) in internal oscillator modes (see
Figure 2-10).
FIGURE 2-10: INTOSC AND PLL BLOCK
DIAGRAM
FIGURE 2-8: INTIO1 OSCILLATOR MODE
FIGURE 2-9: INTIO2 OSCILLATOR MODE
DS39646C-page 34 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
2.6.4 PLL IN INTOSC MODES
The 4x Phase Locked Loop (PLL) ca n be used with the
internal oscillator block to produce faster device clock
speeds than are normally possible with the internal
oscillator sources. When enabled, the PLL produces a
clock speed of 16 MHz or 32 MHz.
Unlike HSPLL mode, the PLL is controlled through
software. The control bit, PLLEN (OSCTUNE<6>), is
used to enable or disable its operation.
The PLL is available when the device is configured to
use the internal oscillator block as its primary clock
source (FOSC<3:0> = 1001 or 1000). Additionally, the
PLL will only function when the selected output frequency is either 4 MHz or 8 MHz (OSCCON<6:4> = 111
or 110). If both of these conditions are not met, the PLL
is disabled and the PLLEN bit remains clear (writes are
ignored).
2.6.5 INTOSC FREQUENCY DRIFT
The factory calibrates the internal oscillator block
output (INTOSC) for 8 MHz. However, this frequency
may drift as V
affect the controller operation in a variety of ways. It is
possible to adjust the INTOSC frequency by modifying
the value in the OSCTUNE register. Depending on the
device, this may have no effect on the INTRC clock
source frequency.
Tuning the INTOSC source requires knowing when to
make the adjustment, in which direction it should be
made and in some cases, how large a change is
needed. Three compensation techniques are discus sed
in Section 2.6.5.1 “Compensating with the
EUSART”, Section 2.6.5.2 “Compensating with the
Timers” and Section 2.6.5.3 “Compe nsa tin g w it h th e
CCP Module in Capture Mode” but other techniques
may be used.
DD or temperature changes and can
REGISTER 2-1: OSCTUNE: OSCILLATOR TUNING REGISTER
R/W-0 R/W-0 U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
INTSRC PLLEN
bit 7 bit 0
(1)
— TUN4 TUN3 TUN2 TUN1 TUN0
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
-n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
bit 7 INTSRC: Internal Oscillator Low-Frequency Source Select bit
1 = 31.25 kHz device clock derived from 8 MHz INTOSC source (divide-by-256 enabled)
0 = 31 kHz device clock derived directly from INTRC internal oscillator
bit 6 PLLEN: Frequency Multiplier PLL for INTOSC Enable bit
1 = PLL enabled for INTOSC (4 MHz and 8 MHz only)
0 = PLL disabled
bit 5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4-0 TUN<4:0>: Frequency Tuning bits
01111 = Maximum frequency
• •
• •
00001
00000 = Center frequency. Oscillator module is running at the calibrated frequency.
11111
• •
• •
10000 = Minimum frequency
Note 1: Available only in certain oscillator configurations; otherwise, this bit is unavailable and reads as ‘0’. See
Section 2.6.4 “PLL in INTOSC Modes” for details.
(1)
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 35

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
2.6.5.1 Compensating with the EUSART
An adjustment may be required when the EUSART
begins to generate frami ng errors or rec eive s dat a with
errors while in Asynchronous mode. Framing errors
indicate that the device clock frequency is too high. To
adjust for this, decrement the value in OSCTUNE to
reduce the clock frequency. On the other hand, errors
in data may sugge st that the clock speed is to o low. To
compensate, increment OSCTUNE to increase the
clock frequency.
2.6.5.2 Compensating with the Timers
This technique compares device clock speed to some
reference clock. Two timers may be used; one timer is
clocked by the peripheral clock, while the other is
clocked by a fixed reference source, such as the
Timer1 oscillat or.
Both timers are cleared, but the timer clocked by the
reference generates interrupts. When an interrupt
occurs, the internally clocked timer is read and both
timers are cleared. If the internally clocked timer value
is much greater than expected, then the internal
oscillator block is running too fast. To adjust for this,
decrement the OSCTUNE register.
2.6.5.3 Compensating with the CCP Module
in Capture Mode
A CCP module can use free running Timer1 (or
Timer3), cl oc ked by the internal oscillator block and an
external event with a known period (i.e., AC power
frequency). The ti me of the first ev ent is capt ured in the
CCPRxH:CCPRxL registers and is recorded for use
later. When the second event causes a capture, the
time of the first event is su btra cte d fro m the tim e of th e
second event. Since the period of the external event is
known, the time difference between events can be
calculated.
If the measured time is much greater than the
calculated time, the inte rnal oscillator block is running
too fast. To compensate, decrement the OSCTUNE
register. If the measured time is much less than the
calculated time, the inte rnal oscillator block is running
too slow. To compensate, increment the OSCTUNE
register.
DS39646C-page 36 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722/8527/8622/8627/8722
4 x PLL
FOSC<3:0>
Secondary Oscillator
T1OSCEN
Enable
Oscillator
T1OSO
T1OSI
Clock Source Option
for other Modules
OSC1
OSC2
Sleep
HSPLL, INTOSC/PLL
LP, XT, HS, RC, EC
T1OSC
CPU
Peripherals
IDLEN
Postscaler
MUX
MUX
8 MHz
4 MHz
2 MHz
1 MHz
500 kHz
125 kHz
250 kHz
OSCCON<6:4>
111
110
101
100
011
010
001
000
31 kHz
INTRC
Source
Internal
Oscillator
Block
WDT, PWRT, FSCM
8 MHz
Internal Oscillator
(INTOSC)
OSCCON<6:4>
Clock
Control
OSCCON<1:0>
Source
8 MHz
31 kHz (INTRC)
OSCTUNE<6>
0
1
OSCTUNE<7>
and Two-Speed Start-up
Primary Oscillator
2.7 Clock Sources and Oscillator Switching
The PIC18F8722 family of devices includes a feature
that allows the devic e clock so urce to be sw itched fro m
the main oscillator to an alternate clock source. These
devices also offer two alternate clock sources. When
an alternate clock source is enabled, the various
power-managed operating modes are available.
Essentially, there are three clock sources for these
devices:
• Primary oscillators
• Secondary oscillators
• Internal oscillator block
The primary oscillators include the Ex ternal Crystal
and Resonator modes, the External RC modes, the
External Clock modes and the internal oscillator block.
The particular mode is defined by the FOSC<3:0>
Configuration bits. The details of these modes are
covered earlier in this chapter.
The se condary oscillators are those external sources
not connected to the OSC1 or OSC2 pins. These
sources may continue to operate even after the
controller is placed in a power-managed mode.
The PIC18F8722 family of devices offers the Timer1
oscillator as a secon dary oscilla tor . This osc illator , in all
power-managed modes, is often the time base for
functions such as a real-time cloc k.
Most often, a 32.768 kHz watch crystal is connected
between the RC0/T1OSO/T13CKI and RC1/T1OSI
pins. Like the LP mode oscillator circuit, loading
capacitors are also connected from each pin to ground.
The Timer1 oscillator is discussed in greater detail in
Section 13.3 “Timer1 Oscillator”.
In addition to being a prim ary clock source, the internal
oscillator block is available as a power-managed
mode clock source. T he IN TR C s ource is also used as
the clock source for several special features, such as
the WDT and Fail-Safe Clock Monitor.
The clock sources for the PIC18F8722 famil y of devic es
are shown in Figure 2-11. See Section 25.0 “Special
Features of the CPU” for Configuration register details.
FIGURE 2-11: PIC18F8722 FAMILY CLOCK DIAGRAM
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 37

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
2.7.1 OSCILLATOR CONTROL REGISTER
The OSCCON register (Register 2-2) controls several
aspects of the device clock’s operation, both in full
power operation and in power-managed modes.
The System Clock Select bits, SCS<1:0>, select the
clock source. The available clock sources are the
primary clock (defined by the FOSC<3:0> Configuration bits), the secondary clock (Timer1 oscillator) and
the internal oscillator block. The clock source changes
immediately after either of the SCS<1:0> bits are
changed, following a brief clock transition interval. The
SCS bits are reset on all forms of Reset.
The Internal Oscillator Frequency Select bits
(IRCF<2:0>) select the fr equenc y output of th e interna l
oscillator block to drive the device clock. The choices
are the INTRC source (31 kHz), the INTOSC source
(8 MHz) or one of the frequencies derived from the
INTOSC postscaler (31.25 kHz to 4 MHz). If the
internal oscillator block is supplying the device clock,
changing the states of these bits will have an immediate change on the internal oscillator’s output. On
device Resets, the default output frequency of the
internal oscillator block is set at 1 MHz.
When a nominal ou tput frequenc y of 31 kHz is selected
(IRCF<2: 0> = 000), users may choose which internal
oscillator acts as the source. This is done with the
INTSRC bit in the OSCTUNE register (OSCTUNE<7>).
Setting this bit selects INTOSC as a 31.25 kHz clock
source derived from the INTOSC postscaler. Clearing
INTSRC selects INTRC (nominally 31 kHz) as the
clock source and disables the INTOSC to reduce
current consumption.
This option allows users to select the tunable and more
precise INTOSC as a clock source, while maintaining
power savings wit h a very low clock speed . Additionally , the IN T OSC so urce w ill alread y be sta ble s hould a
switch to a higher frequency be needed quickly.
Regardless of the setting of INTSRC, INTRC always
remains the clock source for features such as the
Watchdog Timer and the Fail-Safe Clock Monitor.
The OSTS, IOFS and T1RUN bits indicate which cl ock
source is currently providing the device clock. The
OSTS bit indicates that the Oscillator Start-up Timer
and PLL St art-up T im er (if enable d) have timed o ut and
the primary clock is providing the device clock in
primary clock modes. The IOFS bit indicates when the
internal oscillator block has stabilized and is providing
the device clock in RC Clock modes. The T1RUN bit
(T1CON<6>) indicates when the Timer1 oscillator is
providing the device clock in secondary clock modes.
In power-managed modes, only one of the se thre e bits
will be set at any time. If none of these bits are set, the
INTRC is providing the clock or the internal oscillator
block has just started and is not yet stable.
The IDLEN bit controls whether the device goes into
Sleep mode or one of the Idle modes when the SLEEP
instruction is executed.
The use of the flag and control bits in the OSCCON
register is discussed in more detail in Section 3.0
“Power-Managed Modes”.
Note 1: The Timer1 oscillator must be enabled to
select the secondary clock source. The
Timer1 osc illator is enabled by s etting the
T1OSCEN bit in the Timer1 Control re gister (T1CON<3>). If the Timer1 oscillator
is not enabled, then any at tem pt to se lec t
a secondary clock source will be ignore d.
2: It is recommended that the Timer1
oscillator be operating and stable before
selecting the secondary clock source or a
very long delay may occur while the
Timer1 oscillator starts.
2.7.2 OSCILLATOR TRANSITIONS
The PIC18F8722 family of d ev ic es c on t ai ns circuitry to
prevent clock “glitches” when switching between clock
sources. A short pause in the device clock occurs during the clock switch. The length o f this p ause is th e sum
of two cycles of the old clock source and three to four
cycles of the new clock source. This formula assumes
that the new clock source is stable.
Clock transitions are discussed in greater detail in
Section 3.1.2 “Entering Power-Managed Modes”.
DS39646C-page 38 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
REGISTER 2-2: OSCCON: OSCILLATOR CONTROL REGISTER
(1)
(1)
R-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
(5)
(2)
R/W-0 R/W-1 R/W-0 R/W-0 R
IDLEN IRCF2 IRCF1 IRCF0 OSTS IOFS SCS1 SCS0
bit 7 bit 0
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
-n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
bit 7 IDLEN: Idle Enable bit
1 = Device enters an Idle mode when a SLEEP instruction is executed
0 = Device enters Sleep mode when a SLEEP instruction is executed
bit 6-4 IRCF<2:0>: Internal Oscillator Frequency Select bits
111 = 8 MHz (INTOSC drives clock directly)
110 = 4MHz
101 = 2MHz
100 = 1MHz
011 = 500 kHz
010 = 250 kHz
001 = 125 kHz
000 = 31 kHz (from either INTOSC/256 or INTRC directly)
bit 3 OSTS: Oscillator Start-up Time-out Status bit
1 = Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST) time-out has expired; primary oscillator is running
0 = Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST) time-out is running; primary oscillator is not ready
bit 2 IOFS: INTOSC Frequency Stable bit
1 = INTOSC frequency is stable
0 = INTOSC frequency is not stable
bit 1-0 SCS<1:0>: System Clock Select bits
1x = Internal oscillator block
01 = Secondary (Timer1) oscillator
00 = Primary oscillator
(3)
(4)
Note 1: Reset state depends on state of the IESO Configuration bit.
2: Source selected by the INTSRC bit (OSCTUNE<7>), see text.
3: Default output frequency of INTOSC on Reset.
4: Modifying the SCS<1:0> bits will cause an immediate clock source switch.
5: Modifying the IRCF<3:0> bits will cause an immediate clock frequency switch if the internal oscillator is
providing the device clock s.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 39

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
2.8 Effects of Power-Managed Modes on the Various Clock Sources
When PRI_IDLE mode is selected, the configured
oscillator continues to run without interruption. For all
other power-managed modes, the oscillator using the
OSC1 pin is disa bled. The OSC1 pin (a nd OSC2 pin in
crystal oscillator modes) will stop oscillating.
In secondary clock modes (SEC_RUN and
SEC_IDLE), the Timer1 oscillator is operating and
providing the device clock. The Timer1 oscillator may
also run in all power-managed modes if required to
clock Timer1 or Timer3.
In internal oscillator modes (RC_RUN and RC_IDLE),
the internal oscillator block provides the device clock
source. The 31kHz INTRC output can be used dire ctly
to provide the clock and may be enabled to support
various special features, regardless of the powermanaged mode (see Section 25.2 “Watchdog Timer
(WDT)” and Section 25.4 “Fail-Safe Clock Monitor”
for more information). The INTOSC output at 8 MHz
may be used directly to clock the device or may be
divided down by the postscaler. The INTOSC output is
disabled if the clock is provi ded directly from the INTRC
output. The I NTOSC output is also enab led for TwoSpeed Start-up at 1 MHz after Resets and when
configured for wake from Sleep mode.
If the Sleep mode is selected, all clock sources are
stopped. Since all the transistor switching currents
have been stopped, Sleep mode achieves the lowest
current consumption of the device (only leakage
currents).
Enabling any on-chip feature that will operate during
Sleep will increas e the current cons umed during S leep.
The INTRC is required to support WDT operation. The
Timer1 oscillator may be operating to support a realtime clock. Other features m ay be op erating th at do not
require a device clock source (i.e., SSP slave, PSP,
INTx pins and others). Peripherals that may add
significant current consumption are listed in
Section 28.2 “DC Charac teristics”.
2.9 Power-up Delays
Power-up delays are controlled by two or three timers,
so that no external Reset circuitry is required for most
applications. The delays ensure that the device is kept
in Reset until the device power supply is stable under
normal circumstances and the primary clock is operating and stable. For additional information on power-up
delays, see Section 4.5 “Device Reset Timers”.
The first timer is the Power-up Timer (PWRT) which
provides a fixed delay on power-up (parameter 33,
Table 28-12). It is enabled by clearing (= 0) the
PWRTEN
2.9.1 DELAYS FOR POWER-UP AND
The second timer is the Oscillator Start-up Timer
(OST), intended to delay execution until the crystal
oscillator is stable (LP, XT and HS modes). The OST
does this by counting 1024 oscillator cycles before
allowing the oscillator to clock the device.
When the HSPL L Oscillator m ode is selected, a third
timer delays execution for an additional 2 ms following
the HS mode OST delay, so the PLL can lock to the
incoming clock frequency. At the end of these delays,
the OSTS bit (OSCCON<3>) is set.
There is a delay of interval T
Table 28-12), once execution is allowed to start, when
the controller becomes ready to execute instructions.
This delay runs concurrently with any other delays.
This may be the only delay that occurs when any of the
EC, RC or INTIO modes are us ed as the primary clock
source.
Configuration bit (CONFIG2L<0>).
RETURN TO PRIMARY CLOCK
CSD (parameter 38,
TABLE 2-3: OSC1 AND OSC2 PIN STATES IN SLEEP MODE
OSC Mode OSC1 Pin OSC2 Pin
RC, INTIO1 Floating, external resistor pulls high At logic low (clock/4 output)
RCIO Floating, external resistor pulls high Configured as PORTA, bit 6
INTIO2 Configured as PORTA, bit 7 Configured as PORTA, bit 6
ECIO Floating, driven by external clock Configured as PORTA, bit 6
EC Floating, driven by external clock At logic low (clock/4 output)
LP, XT and HS Feedback inverter disabled at quiescent
voltage level
Note: See Table 4-2 in Section 4.0 “Reset” for time-outs due to Sleep and MCLR
DS39646C-page 40 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
Feedback inverter disabled at quiescent
voltage level
Reset.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
3.0 POWER-MANAGED MODE S
The PIC18F8722 family of devices offers a total of
seven operating modes for more efficient power management. These modes prov ide a vari ety of options for
selective power conservation in applications where
resources may be limited (i.e., battery-powered
devices).
There are three categories of power-managed modes:
• Run modes
• Idle modes
• Sleep mode
These categories define which portions of the device
are clocked and some times , what sp eed. The R un and
Idle modes may use any of the three available clock
sources (primary, secondary or internal oscillator
block); the Sleep mode does not use a clock source.
The power-managed modes include several powersaving features of fe red on previ ous P IC
is the clock switching feature, offered in other PIC18
devices, allowing the controller to use the Timer1 oscillator in place of the primary oscillator. Also included is
the Sleep mode, offered by all PIC devices, where all
device clocks are stopped.
3.1 Selecting Power-Managed Modes
Selecting a power-managed mode requires two
decisions: if the CPU is to be clocked or not and the
selection of a clock source. The IDLEN bit
(OSCCON<7>) controls CPU clocking, while the
SCS<1:0> bits (OSCCON<1:0>) select the clock
source. The individual modes, bit settings, clock sources
and affected modules are summarized in Table 3-1.
®
devices. One
3.1.1 CLOCK SOURCES
The SCS1:SCS0 bits allow the sele ction of one o f three
clock sources for power-managed modes. They are:
• the primary clock, as defined by the FOSC<3:0>
Configuration bits
• the secondary clock (the Timer1 oscillator)
• the internal oscillator block (for INTOSC modes)
3.1.2 ENTERING POWER-MANAGED
MODES
Switching from one power-managed mode to another
begins by loading the OSCCON register. The
SCS<1:0> bits select the clock source and determine
which Run or Idle mode is to be used. Changing these
bits causes an immediate switch to the new clock
source, assuming that it is running. The switch may
also be sub ject to clock tr ansition delays. T hese are
discussed in Section 3.1.3 “Clock Transitions and
Status Indicators” and subsequent sections.
Entry to the power-managed Idle or Sleep modes is
triggered by the execution of a SLEE P instruction. The
actual mode that results depends on the status of the
IDLEN bit.
Depending on the current mode and the mode being
switched to, a change to a power-managed mode does
not always require setting all of these bits. Many
transitions may be done by changing the oscillator s elect
bits, or changing the IDLEN bit, prior to issuing a SLEEP
instruction. If the IDLEN bit is already configured
correctly, it may only be necessary to perform a SLEEP
instruction to switch to the desired mode.
TABLE 3-1: POWER-MANAGED MODES
Mode
Sleep 0 N/A Off Off None – All clocks are disabled
PRI_RUN N/A 00 Clocked Clocked Primary – LP, XT, HS, HSPLL, RC, EC and
SEC_RUN N/A 01 Clocked Clocked Secondary – Timer1 Oscillator
RC_RUN N/A 1x Clocked Clocked Internal Oscillator Block
PRI_IDLE 100Off Clocked Primary – LP, XT, HS, HSPLL, RC, EC
SEC_IDLE 101Off Clocked Secondary – Timer1 Oscillator
RC_IDLE 11xOff Clocked Internal Oscillator Block
Note 1: IDLEN reflects its value when the SLEEP instruction is executed.
2: Includes INTOSC and INTOSC postscaler, as well as the INTRC source.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 41
OSCCON Bits Module Clocking
IDLEN<7>
(1)
SCS<1:0> CPU Peripherals
Available Clock and Oscillator Source
(2)
Internal Oscillator Block
This is the normal full power execution mode.
.
(2)
(2)

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
3.1.3 CLOCK TRANSITI ONS AND S TATUS INDICATORS
The length of the transition between clock sources is
the sum of two cycles o f the old clo ck so urce an d three
to four cycles of the ne w clock source. Thi s formula
assumes that the new clock source is stable.
Three bits indicate the current clock source and its
status. They are:
• OSTS (OSCCON<3>)
• IOFS (OSCCON<2>)
• T1RUN (T1CON<6>)
In general, only one of these bits will be set while in a
given power-managed mode. When the OSTS bit is
set, the primary clock is providing the device clock.
When the IOFS bit is set, the INTOSC output is
providing a stable 8 MHz clock source to a divider that
actually drives the device clock. When the T1RUN bit is
set, the Timer1 oscillator is providing the clock. If none
of these bits are set, then either the INTRC clock
source is cloc ki ng t he dev ic e, o r th e INTOSC source is
not yet stable.
If the internal oscillator block is configured as the primary clock source by the FOSC<3:0> Configuration
bits, then both the OSTS and IOFS bits may be set
when in PRI_RUN or PRI_IDLE modes. This indicates
that the primary clock (INTOSC output) is genera tin g a
stable 8 MHz output. Entering another INTOSC po wermanaged mode at the sam e fre quency would clear the
OSTS bit.
Note 1: Caution should be us ed when modifyi ng a
single IRCF bit. I f V
possible to select a higher clock speed
than is supported by the low VDD.
Improper device operation may result if
DD/FOSC specifications are violated.
the V
2: Executing a SLEEP instruction does not
necessarily place the device into Sleep
mode. It acts as the trigger to place the
controller into either the Sleep mode or
one of the Idle modes, depending on the
setting of the IDLEN bit.
DD is less than 3V, it is
3.1.4 MULTIPLE SLEEP COMMANDS
The power-managed mode that is invoked with the
SLEEP instruction is determined by the setting of the
IDLEN bit at the time the instruction is executed. If
another SLEEP instruction is executed, the device will
enter the power-ma nag ed mo de s pe ci fie d by ID L EN at
that time. If IDLEN has changed, the device will enter
the new power-managed mode specified by the new
setting.
3.2 Run Modes
In the Run modes, clocks to both the core and
peripherals are active. The difference between these
modes is the clock source.
3.2.1 PRI_RUN MODE
The PRI_RUN mode is the normal, full power execution
mode of the microcontroller. This is also the default
mode upon a devi ce Reset, u nless T wo- Sp eed S tart-u p
is enabled (see Section 25.3 “Two-Speed Start-up”
for details). In this m ode, the OSTS bi t is set. Th e IOFS
bit may be set if the internal oscillator block is the
primary clock source (see Section 2.7.1 “Oscillator
Control Register”).
3.2.2 SEC_RUN MODE
The SEC_RUN mode is the compatible mode to the
“clock switching” feature offered in other PIC18
devices. In this mode, the CPU and peripherals are
clocked from the T imer1 os cillator. This gives users the
option of lower power consumption w hile still u sing a
high accuracy clock source.
SEC_RUN mode is entered by setting the SCS<1:0>
bits to ‘01’. The device clock source is switched to the
Timer1 oscillator (see Figure 3-1), the primary oscillator is shut down, the T1RUN bit (T1CON<6>) is set and
the OSTS bit is cleared.
Note: The Timer1 oscillator should already be
running prior to entering SEC_RU N mode.
If the T1OSCEN bit is not set when the
SCS<1:0> bits are set to ‘01’, entry to
SEC_RUN mode will not occur. If the
Timer1 oscillator is enabled, but not yet
running, devic e cloc ks will be de layed u ntil
the oscillator has started; in such situations, initial oscillator operation is far from
stable and unpredictable operation may
result.
On transitions from SEC_RUN mode to PRI_RUN, the
peripherals and CPU continue to be clocked from the
Timer1 oscillator while the primary clock is started.
When the primary clo ck bec omes r eady, a clock switch
back to the primary clock occurs (see Figure 3-2).
When the clock switch is complete, the T1RUN bit is
cleared, the OSTS bit is set and the primary clock is
providing the clock. The IDLEN and SCS bits are not
affected by the wake-up; the Timer1 oscillator
continues to run.
DS39646C-page 42 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Q4Q3Q2
OSC1
Peripheral
Program
Q1
T1OSI
Q1
Counter
Clock
CPU
Clock
PC + 2PC
123 n-1n
Clock Transition
(1)
Q4Q3Q2 Q1 Q3Q2
PC + 4
Note 1: Clock transition typically occurs within 2-4 T
OSC.
Q1 Q3 Q4
OSC1
Peripheral
Program
PC
T1OSI
PLL Clock
Q1
PC + 4
Q2
Output
Q3 Q4 Q1
CPU Clock
PC + 2
Clock
Counter
Q2 Q2 Q3
Note 1:TOST = 1024 TOSC; TPLL = 2 ms (approx). These intervals are not shown to scale.
2: Clock transition typically occurs within 2-4 T
OSC.
SCS1:SCS0 bits Changed
TPLL
(1)
12 n-1n
Clock
OSTS bit Set
Transition
(2)
TOST
(1)
FIGURE 3-1: TRANSITION TIMING FOR ENTRY TO SEC_RUN MODE
FIGURE 3-2: TRANSITION TIMING FROM SEC_RUN MODE TO PRI_RUN MODE (HSPLL)
3.2.3 RC_RUN MODE
In RC_RUN mode, the CPU and peripherals are
clocked from the internal oscillator block using the
INTOSC multiplexer. In this mode, the primary clock is
shut down. When using the INTRC source, this mode
provides the best power conservation of all the Run
modes, while still executing code. It works well for user
applications whi ch are n ot h igh ly tim in g-s ens it ive or d o
not require high-speed clocks at all times.
If the primary clock source is the internal oscillator
block (either INTRC or INTOSC), there are no distinguishable differences between PRI_RUN and
RC_RUN modes during execution. Howe ver, a clock
switch delay will occur during entry to and exit from
RC_RUN mode. Therefore, if the primary clock source
is the internal oscillator block, the use of RC_RUN
mode is not recommended.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 43
This mode is entered by setting the SCS1 bit to ‘1’.
Although it is ignored, it is rec ommended that the SCS0
bit also be cleared; this is to maintain software compatibility with future devices. When the clock source is
switched to the INTOSC multiplexer (see Figure 3-3),
the primary oscillator is shut down and the OSTS bit is
cleared. The IRCF bits may be modified at any time to
immediately change the clock speed.
Note: Caution should be used when modifying a
single IRCF bit. If V
DD is less than 3V, it is
possible to select a higher clock speed
than is supported by the low V
Improper device operation may result if
DD/FOSC specifications are violated.
the V
DD.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Q4Q3Q2
OSC1
Peripheral
Program
Q1
INTRC
Q1
Counter
Clock
CPU
Clock
PC + 2PC
123 n-1n
Clock Transition
(1)
Q4Q3Q2 Q1 Q3Q2
PC + 4
Note 1: Clock transition typically occurs within 2-4 T
OSC.
Q1
Q3 Q4
OSC1
Peripheral
Program
PC
INTOSC
PLL Clock
Q1
PC + 4
Q2
Output
Q3
Q4
Q1
CPU Clock
PC + 2
Clock
Counter
Q2
Q2
Q3
Note 1: TOST = 1024 TOSC; TPLL = 2 ms (approx). These intervals are not shown to scal e.
2: Clock transition typically occurs within 2-4 T
OSC.
SCS1:SCS0 bits Changed
TPLL
(1)
12 n-1n
Clock
OSTS bit Set
Transition
(2)
Multiplexer
TOST
(1)
If the IRCF bits and the INTSRC bit are all clear, the
INTOSC output is not enabled and the IOFS bit will
remain clear; there will be no indication of the current
clock source. The INTRC source is providing the
device clocks.
If the IRCF bits are changed from all clear (thus,
enabling the INTOSC output) or if INTSRC is set, the
IOFS bit becomes set after the INTOSC output
becomes stable. Clocks to the device continue while
the INTOSC source stabilizes after an interval of
IOBST (parameter 39, Table 28-12).
T
On transitions from RC_RUN mode to PRI_RUN mode,
the device continues to be clocked from the INTOSC
multiplexer whil e the prim ary clock is st arted. W hen the
primary clock becomes ready, a clock switch to the
primary clock occurs (see Figure 3-4). When the clock
switch is complete, the IOFS bit is cleared, the OSTS
bit is set and the primary clock is providing the device
clock. The IDLEN and SCS bits are not af fe cte d by the
switch. The INTRC source will continue to run if either
the WDT or the Fail-Safe Clock Monitor is enabled.
If the IRCF bits w ere prev io us ly at a no n-z ero val ue, or
if INTSRC was set before setting SCS1 and the
INTOSC source was already stable, the IOFS bi t will
remain set.
FIGURE 3-3: TRANSITION TIMING TO RC_RUN MODE
FIGURE 3-4: TRANSITION TIMING FROM RC_RUN MODE TO PRI_RUN MODE
DS39646C-page 44 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Q4Q3Q2
OSC1
Peripheral
Sleep
Program
Q1Q1
Counter
Clock
CPU
Clock
PC + 2PC
Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2
OSC1
Peripheral
Program
PC
PLL Clock
Q3 Q4
Output
CPU Clock
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2
Clock
Counter
PC + 6
PC + 4
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
Wake Event
Note 1:T
OST = 1024 TOSC; TPLL = 2 ms (approx). These intervals are not shown to scale.
TOST
(1)
TPLL
(1)
OSTS bit Set
PC + 2
3.3 Sleep Mode
The power-managed Sleep mode in the PIC18F8722
family of devices is identical to the legacy Sleep mode
offered in all other PIC de vices. It is enter ed by clearing
the IDLEN bit (the default state on device Reset) and
executing the SLEEP instruction. This shuts down the
selected oscillator (Figure 3-5). All clock source status
bits are cleared.
Entering the Sleep m ode from any other mo de does not
require a clock switch. This is because no clocks are
needed once the controller has entered Sleep. If the
WDT is selected, the INTRC source will continue to
operate. If the Timer1 oscillator is enabled, it will also
continue to run.
When a wake ev ent occurs i n Sleep mo de (by int errupt,
Reset or WDT time-out), the device will not be clocked
until the clock source selected by the SCS<1:0> bits
becomes ready (see Figure 3-6), or it will be clocked
from the internal osc illator block if e ither the T wo-S peed
Start-up or the Fail-Safe Clock Monitor are enabled
(see Sectio n 25.0 “Spe cial Features o f the CPU”). In
either case, the OS TS bit i s set wh en the p rimary cloc k
is providing the device cl ocks. The IDLEN and SCS bit s
are not affected by the w ake-up.
3.4 Idle Modes
The Idle modes allow the controller’s CPU to be
selectively shut down while the peripherals continue to
operate. Selecting a particular Idle mode allows users
to further manage power consumption.
If the IDLEN bit i s set to a ‘1’ when a SLEEP inst ruction is
executed, the periph erals will be cloc ked fro m the cloc k
source selecte d using the SCS< 1:0> bits; howev er, the
CPU will not be clocked. The clock source status bits are
not affected. Setting IDLEN and executing a SLEEP
instruction pr ovides a quick method of switchi ng from a
given Run mo de to its correspon ding Idle mode.
If the WDT is selected, the INTRC source will continue
to operate. If the T imer1 oscill ator is enable d, it will also
continue to run.
Since the CPU is not executing instructions, the only
exits from any of the Idle modes are by interrupt, WDT
time-out or a Reset. When a wa ke even t occur s, CPU
execution is delayed by an interval of T
(parameter 38, Table 28-12) while it becomes ready to
execute code. When the CPU begins executing code,
it resumes with the same clock source for the current
Idle mode. For example, when waking from RC_IDLE
mode, the internal oscillator block will clock the CPU
and peripherals (in other words, RC_RUN mode). The
IDLEN and SCS bits are not affected by the wake-up.
While in any Idle mode or the S leep mode, a WDT
time-out will result in a WDT wake-up to the Run mode
currently specified by the SCS<1:0> bits.
CSD
FIGURE 3-5: TRANSITION TIMING FOR ENTRY TO SLEEP MODE
FIGURE 3-6: TRANSITION TIMING FOR WAKE FROM SLEEP (HSPLL)
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 45

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Q1
Peripheral
Program
PC PC + 2
OSC1
Q3
Q4
Q1
CPU Clock
Clock
Counter
Q2
OSC1
Peripheral
Program
PC
CPU Clock
Q1 Q3 Q4
Clock
Counter
Q2
Wake Event
TCSD
3.4.1 PRI_IDLE MODE
This mode is uni que among the thre e low-power Idle
modes, in that it does not disable the primary device
clock. For timing sensitive applications, this allows for
the fastest resump tion of devic e operation w ith its mo re
accurate pri mary clock source, si nce the cl ock source
does not have to “warm-up” or transition from another
oscillator.
PRI_IDLE mode is entered from PRI_RUN mode by
setting the IDLEN bit and executing a SLEEP instruction. If the device is in another Run mode, set IDLEN
first, then clear the SCS bits and execute SLEEP.
Although the CPU i s disab led, th e peri pherals cont inue
to be clocked from the primary clock source specified
by the FOSC< 3:0> Configuration bi ts. The OSTS bit
remains set (see Figure3-7).
When a wake event occurs, the CPU is clocked from the
primary clock source. A delay of interval T
(parameter 39, Table 28-12) is required between the
wake event and when code execution starts. This is
required to allow the CPU to become ready to ex ecute
instructions. After the wake-up, the OSTS bit remains
set. The IDLEN and SCS b its are not affected by the
wake-up (see Figure 3-8).
CSD
3.4.2 SEC_IDLE MODE
In SEC_IDLE mode, the CPU is disabled but the
peripherals continue to be clocked from the Timer1
oscillator. This mode is entered from SEC_RUN by setting the IDLEN bit and executi ng a SLEEP instruction. If
the device is in another Run mode, set the IDLEN bit
first, then set the SCS<1:0> bits to ‘01’ and execute
SLEEP . When the clock source is switched to the
Timer1 oscillato r, the primary osci llator is shut down,
the OSTS bit is cleared and the T1RUN bit is set.
When a wake event occurs, the peripherals continue to
be clocked from the Timer1 oscillator. After an interval
CSD following the wake event, the CPU b egins exe-
of T
cuting code being cloc ked by the T im er1 oscil lator . Th e
IDLEN and SCS bits are not affected by the wake-up;
the Timer1 oscillator continues to run (see Figure3-8).
Note: The Timer1 oscillator should already be
running prior to entering SEC_IDLE mod e.
If the T1OSCEN bit is not set when the
SLEEP instruction is executed, the SLEEP
instruction will be ignored and entry to
SEC_IDLE mode will not occur. If the
Timer1 oscillator is enabled but not yet
running, peripheral clocks will be delayed
until the oscillator has started. In such
situations, initial oscillator operation is far
from stable and unpredictable operation
may result.
FIGURE 3-7: TRANSITION TIMING FOR ENTRY TO IDLE MODE
FIGURE 3-8: TRANSITION TIMING FOR WAKE FROM IDLE TO RUN MODE
DS39646C-page 46 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
3.4.3 RC_IDLE MODE
In RC_IDLE mode, t he C PU is d is abl ed but th e p erip herals continue to b e c loc ke d fro m the internal oscilla t or
block using the INTOSC multiplexer. This mode allows
for controllable power cons ervation during Idl e periods .
From RC_RUN, this mode is entered by setting the
IDLEN bit and executing a SLEEP instruction. If the
device is in a nother Run mode, first s et IDLEN, th en set
the SCS1 bit and execute SLEEP. Although its value is
ignored, it is reco mmended that SCS0 also be cle ared;
this is to maintain software compatibility with future
devices. The INTOSC multiplexer may be used to
select a higher clock frequency by modifying the IRCF
bits before exec uti ng th e SLEEP instruction. When the
clock source is switched to the INTOSC mult iplexer , the
primary oscillator is shut down and the OSTS bit is
cleared.
If the IRCF bits are set to any non-zero value, or the
INTSRC bit is set, the INTOSC output is enabled. The
IOFS bit becomes set, after the INTOSC output
becomes stable, after an interval of T
(parameter 39, Table 28-12). Clocks to the peripherals
continue while the INTOSC source stabilizes. If the
IRCF bits were previously at a non-zero value, or
INTSRC was set before the SLEEP instruction was ex ecuted and the INTOSC source was already stable, the
IOFS bit will remain set. If the IRCF bits and INTSRC
are all clear , the INT OSC output will n ot be enabled, the
IOFS bit will remain c lear and there will be no ind ication
of the current clock source .
When a wake event o ccurs, the pe ripherals co ntinue to
be clocked from the INTOSC multiplexer. After a delay
CSD (parameter 38, Table 28-12) following the wake
of T
event, the CPU begins executing code being clocked
by the INTOSC multiplexer. The IDLEN and SCS bits
are not affec ted by the wake-up. T he INTRC sou rce will
continue to run if eith er the WDT or th e Fail-Sa fe Cloc k
Monitor is enabled.
IOBST
3.5 Exiting Idle and Sleep Modes
An exit from Sleep mode or any of the Idle modes is
triggered b y an interrupt , a Reset or a WDT time-out.
This section discusses the triggers that cause exits
from power-managed modes. The clocking subsystem
actions are discussed in each of the power-managed
modes (see Section 3.2 “Run Modes”, Section 3.3
“Sleep Mode” and Section 3.4 “Idle Modes”).
3.5.1 EXIT BY INTERRUPT
Any of the available interrupt sources can cause the
device to exit from an Idle mode or the Sleep mode to
a Run mode. To enable this functionality, an interrupt
source must be enab led by s etti ng i t s en able bit in one
of the INTCON or PIE registers. The exit sequence is
initiated when the c orresponding interrupt flag bit is set.
On all exits from Idle or Sl eep modes by interrupt, code
execution branches to the interrupt vector if the GIE/
GIEH bit (INTCON<7>) is set. Otherwise, code execution continues or resumes without branching (see
Section 10.0 “Interrupts”).
A fixed delay of inter val T
is required when leaving Sleep and Idle modes. This
delay is required for the CPU to prepare for execution.
Instructio n execution r esumes on th e first clock c ycle
following this delay.
CSD following th e wake event
3.5.2 EXIT BY WDT TIME-OUT
A WDT time-out will cause different actions depending
on which power-managed mode the device is in when
the time-out occurs.
If the device i s not exec uti ng code (al l Idle mode s and
Sleep mode), the time-out will res ul t in a n ex it fro m th e
power-managed mode (see Section 3.2 “Run
Modes” and Section 3.3 “Sleep Mode”). If the device
is executing code (all Run modes), the time-out will
result in a WDT Reset (see Section 25.2 “Watchdog
Timer (WDT)”).
The WDT timer and postscaler are cleared by
executing a SL EE P or CLRWDT instruction, the loss of a
currently selected clock source (if the Fail-Safe Clock
Monitor is enabled) and modifying the IRCF bits in the
OSCCON register if the internal oscillator block is the
device clock source.
3.5.3 EXIT BY RESET
Normally, the device is held in Reset by the Oscillator
Start-up Timer (OST) until the primary clock becomes
ready. At that time, the OSTS bit is set and the device
begins executing code. If the internal osc il lat or bl oc k i s
the new clock source, the IOFS bit is set instead.
The exit delay time from Reset to the start of code
execution depends on both the clock sources before
and after the wake-up and the type of oscillator if the
new clock source is the primary clock. Exit delays are
summarized in Table 3-2.
Code execution can begin before the primary clock
becomes ready. If either the Two-Speed Start-up (see
Section 25.3 “Two-Speed Start-up”) or Fail-Safe
Clock Monitor (see Section 25.4 “Fail-Safe Clock
Monitor”) is enabled, the device may begin execution
as soon as the Reset source ha s cle are d. Execution is
clocked by the INTO SC mu lti ple xe r driv en b y th e internal oscillator bloc k. Executi on is clo cked by the interna l
oscillator block until either the primary clock becomes
ready or a power-mana ged mo de is e ntered b efore th e
primary clock beco mes re ady; the pri mary clo ck is then
shut down.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 47

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
3.5.4 EXIT WITHOUT AN OSCILLATOR START-UP DELAY
Certain exits from power-managed modes do not
invoke the OST at all. There are two cases:
• PRI_IDLE mode, where the primary clock source
is not stopped and
• the primary clock source is not any of the LP, XT,
HS or HSPLL modes.
In these instances, the primary clock source either
does not require an oscillator start-up delay since it is
already running (PRI_IDLE), or normally does not
require an oscillator start-up delay (RC, EC and INTIO
Oscillator modes). However, a fixed delay of interval
CSD following the wake event is still required when
T
leaving Sleep and Idle modes to allow the CPU to
prepare for execution. Instruction execution resumes
on the first clock cycle following this delay.
TABLE 3-2: EXIT DELAY ON WAKE-UP BY RESET FROM SLEEP MODE OR ANY IDLE MODE
(BY CLOCK SOURCES)
Clock Source
before Wake-up
Primary Device Clo ck
(PRI_IDLE mode)
T1OSC or IN TRC
INTOSC
(Sleep mode)
Note 1: TCSD (parameter 38, Table 28-12) is a required delay when w aking from Sle ep and all Idle modes and run s
concurrently with any other required delays (see Section 3.4 “Idle Modes”).
2: Includes both the INTOSC 8MHz source and postscaler deriv ed frequ encie s. On Res et, INT OSC defau lt s
to 1 MHz.
3: T
(parameter F12, Table 28-7); it is also designated as T
4: Execution continues during T
(2)
None
OST is the Oscillator Start-up Timer (parameter 32, Table 28-12). t
Clock Source
after Wake-up
Exit Delay
Clock Ready Status
Bit (OSCCON)
LP, XT, HS
HSPLL
EC, RC
INTOSC
(2)
LP, XT, HS TOST
EC, RC TCSD
INTOSC
(2)
LP, XT, HS TOST
EC, RC TCSD
INTOSC
(2)
LP, XT, HS TOST
EC, RC TCSD
INTOSC
IOBST (parameter 39, Table 28-12), the INTOSC stabilization period.
(2)
PLL.
(1)
CSD
T
(3)
(3)
rc
(1)
(4)
TIOBST
(4)
(3)
rc
(1)
None IOFS
(3)
(3)
rc
(1)
(4)
TIOBST
is the PLL Lock-out Timer
rc
OSTS
IOFS
OSTSHSPLL TOST + t
IOFS
OSTSHSPLL TOST + t
OSTSHSPLL TOST + t
IOFS
DS39646C-page 48 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
External Reset
MCLR
VDD
OSC1
WDT
Time-out
V
DD Rise
Detect
OST/PWRT
INTRC
(1)
POR Pulse
OST
10-bit Ripple Counter
PWRT
11-Bit Ripple Counter
Enable OST
(2)
Enable PWRT
Note 1: This is the INTRC source from the internal oscillator block and is separate from the RC oscillator of the CLKI pin.
2: See Table 4-2 for time-out situations.
Brown-out
Reset
BOREN
RESET
Instruction
Stack
Pointer
Stack Full/Underflow Reset
Sleep
( )_IDLE
1024 Cycles
64 ms
31 μs
MCLRE
S
R
Q
Chip_Reset
4.0 RESET
A simplified block di agram of the On-Chip Reset Circu it
is shown in Figure 4-1.
The PIC18F8722 family of devices differentiates
between various kinds of Reset:
a) Power-on Reset (POR)
b) MCLR
Reset during normal operation
c) MCLR Reset during power-managed modes
d) Watchdog Timer (WDT) Reset (during
execution)
e) Programmable Brown-out Reset (BOR)
f) RESET Instruction
g) Stack Full Reset
h) Stack Underflow Reset
This section discusses Resets generated by MCLR
POR and BOR and covers the ope rati on o f the various
start-up timers. Stack Reset events are covered in
Section 5.1.3.4 “Stack Full and Underflow Resets”.
WDT Resets are co v ere d i n Section 25.2 “Watchdog
,
4.1 RCON Register
Device Reset events are tracked through the RCON
register (Register 4-1). The lower five bits of the register indicate that a specif ic Reset eve nt has occu rred. In
most cases, thes e bits c an only be cl eared by the e vent
and must be set by the ap pli ca tio n af ter the event. The
state of these flag bits, taken together, can be read to
indicate the type of Reset that just occurred. This is
described in more detail in Section 4. 6 “Reset State
of Registers”.
The RCON register also has control bits for setting
interrupt priority (IPEN) and software control of the
BOR (SBOREN). Interrupt priority is discussed in
Section 10.0 “Interrupts”. BOR is covered in
Section 4.4 “Brown-out Reset (BOR)”.
Timer (WDT)”.
FIGURE 4-1: SIMPLIFIED BLOCK DIAGRAM OF ON-CHIP RESET CIRCUIT
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 49

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
REGISTER 4-1: RCON: RESET CONTROL REGISTER
R/W-0 R/W-1
IPEN SBOREN
bit 7 bit 0
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
-n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
bit 7 IPEN: Interrupt Priority Enable bit
1 = Enable priority levels on interrupts
0 = Disable priority levels on interrupts (PIC16CXXX Compatibility mode)
bit 6 SBOREN: BOR Software Enable bit
If BOREN
1 = BOR is enabled
0 = BOR is disabled
If BOREN
Bit is disabled and read as ‘0’
bit 5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4 RI: RESET Instruction Flag bit
1 = The RESET instru cti on was not exe cu ted (set by firmware only)
0 = The RESET instruction was executed causing a device Reset (must be set in software after a
bit 3 TO: Watchdog Time-out Flag bit
1 = Set by power-up, CLRWDT instruction or SLEEP instruction
0 = A WDT time-out occurred
bit 2 PD
1 = Set by power-up or by the CLRWDT instruction
0 = Set by execution of the SLEEP instruction
bit 1 POR
1 = A Power-on Reset has not occurred (set by firmware only)
0 = A Power-on Reset occurred (must be set in software after a Power-on Reset occurs)
bit 0 BOR
1 = A Brown-out Reset has not occurred (set by firmware only)
0 = A Brown-out Reset occurred (must be set in software after a Brown-out Reset occurs)
(1)
<1:0> = 01:
<1:0> = 00, 10 or 11:
Brown-out Reset occurs)
: Power-down Detection Flag bit
: Power-on Reset Status bit
: Brown-out Reset Status bit
U-0 R/W-1 R-1 R-1 R/W-0
—RITO PD POR BOR
(2)
(1)
(2)
R/W-0
Note 1: If SBOREN is enabled, its Reset state is ‘1’; otherwise, it is ‘0’.
2: The actual Reset value of POR
register and Section 4.6 “Reset State of Registers” for additional information.
Note 1: It is recommended that the POR bi t be se t af te r a Power-on Reset has been det ect ed s o th at s ub seq ue nt
Power-on Resets may be detected.
2: Brown-out Reset is said to have occurred when BOR
‘1’ by software immediately after POR).
DS39646C-page 50 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
is determined by the type of device Reset. See the notes following this
is ‘0’ and POR is ‘1’ (assuming that POR was set to

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Note 1: External Power- on Reset circuit is required
only if the V
DD power-up slope is too slow.
The diode D helps discharge the capacitor
quickly when V
DD powers down.
2: R < 40 kΩ is recommended to make sure that
the voltage drop across R does not violate
the device’s electrical specification.
3: R1 ≥ 1 kΩ will limit any current flowing into
MCLR
from external capacitor C, in the event
of MCLR
/VPP pin breakdown, due to
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) or Electrical
Overstress (EOS).
C
R1
(3)
R
(2)
D
V
DD
MCLR
PIC18FXXXX
VDD
4.2 Master Clear (MCLR)
The MCLR pin provides a method for triggering an
external Reset of the device. A Reset is generated by
holding the pin low. Thes e device s have a no ise filter i n
the MCLR
Reset path which detects and ignores small
pulses.
The MCLR
pin is not drive n low by any inter nal Reset s,
including the WDT.
In the PIC18F8722 family of devices, the MCLR
input
can be disabled with the MCLRE Configuration bit.
When MCLR is disabled, the pin becomes a digital
input. See Section 11.5 “PORTE, TRISE and LATE
Registers” for more information.
4.3 Power-on Reset (POR)
A Power-on Reset pulse is generated on-chip
whenever V
allows the device to start in the initialized state when
VDD is adequate for operation.
T o t ake advantage o f the POR circuitry , tie the MCLR
through a resistor (1 kΩ to 10 kΩ) to V
eliminate external RC components usually needed to
create a Power-on Reset delay . A minimum ri se rate for
DD is specified (parameter D004, “Section 28.2 “DC
V
Characteristics: Power-Down and Supply Current”).
For a slow rise time, see Figure 4-2.
When the device st arts normal operati on (i.e ., ex its the
Reset condition), device operating parameters (voltage, frequency, temperature, etc.) must be met to
ensure operation. If these conditions are not met, the
device must be held in Reset until the operating
conditions are met.
POR events are captured by the POR
The state of th e bit is set to ‘0’ wh enever a POR occurs;
it does not change for any other Reset event. POR is
not reset to ‘1’ by any hardware event. To capture
multiple events, the user manually resets the bit to ‘1’
in software following any POR.
DD rises above a certain threshold. This
pin
DD. This will
bit (RCON<1>).
FIGURE 4-2: EXTERNAL POWER-ON
RESET CIRCUIT (FOR
SLOW V
DD POWER-UP)
(1)
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 51

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
4.4 Brown-out Reset (BOR)
The PIC18F 87 22 f am il y of de vi ces im p lem en ts a BO R
circuit that provides the user with a number of configuration and power-saving options. The BOR is
controlled by the BORV<1:0> and BOREN<1:0>
Configuration bits. There are a total of four BOR
configurations which are summarized in Table 4-1.
The BOR threshold is set by the BORV<1:0> bits. If
BOR is enabled (any values of BOREN<1:0>, except
‘00’), any drop of V
Section 28. 1 “DC Characteris tics”) for greater than
TBOR (parameter 35, Table 28-12) will reset the device.
A Reset may or may not occur if V
for less tha n TBOR. The chip will remain in Br own-o ut
Reset until V
If the Power-up T imer is enab led, it will be inv oked after
DD rises above VBOR; it then will keep the chip in
V
Reset for an additional time delay, T
(parameter 33, Table 28-12). If VDD drops below VBOR
while the Power-up Timer is running, the chip will go
back into a Brown-out Reset and the Power-up Timer
will be initialized. Once VDD rises above VBOR, the
Power-up Timer will execute the additional time delay.
BOR and the Power-on Timer (PWRT) are
independently configured. Enabling BOR Reset does
not automat ically enable the PWRT.
4.4.1 SOF TWARE ENABLED BOR
When BOREN<1:0> = 01, the BOR can be enabled or
disabled by the user in software. This is done with the
control bit, SBOREN (RCON<6>). Setting SBOREN
enables the BOR to function as previously described.
Clearing SBOREN disables the BOR entirely. The
SBOREN bit operates only in this mode; otherwise it i s
read as ‘0’.
DD below VBOR (parameter D005,
DD falls below VBOR
DD rises abov e VBOR.
PWRT
Placing the BOR under software control gives the user
the additional flexibility of tailoring the application to its
environment withou t ha vi ng to reprogram the devi ce to
change the BOR configuration. It also allows the user
to tailor device power consumption in software by
eliminating the incremental current that the BOR consumes. While the BOR current is typically very small, it
may have some impact in low-power applications.
Note: Even when BOR is under software control,
the BOR Reset voltage level is still set by
the BORV<1:0> Configuration bits. It
cannot be changed in software.
4.4.2 DETECTING BOR
When BOR is enabl ed, the BOR bit always resets to ‘0’
on any BOR or P OR event. This makes it d ifficult to
determine if a BOR event has occurre d jus t by reading
the state of BOR
simultaneously check the state of both POR
This assumes that the POR
immediately after any POR event. If BOR
POR
is ‘1’, it can be reliably assum ed that a BOR event
has occurred.
alone. A more reliable method is to
and BOR.
bit is reset to ‘1’ in software
is ‘0’ while
4.4.3 DISABLING BOR IN SLEEP MODE
When BOREN<1:0> = 10 , the BOR remains under
hardware control and operates as previously
described. Whenever the device enters Sleep mode,
however , the BOR is au tom ati ca lly dis abl ed . When the
device returns to any other operating mode, BOR is
automatically re-enabled.
This mode allows for applications to recover from
brown-out situations, while actively executing code,
when the device requires BOR protection the most. At
the same time, it save s additional po wer in Sleep mod e
by eliminating the small incremental BOR current.
TABLE 4-1: BOR CONFIGURATIONS
BOR Configuration Status of
BOREN1 BOREN0
00Unavailable BOR disabled; must be enabled by reprogramming the Configuration bits.
01Available BOR enabled in software; operation controlled by SBOREN.
10Unavailable BOR enabled in hardware in Run and Idle modes, disabled during
11Unavailable BOR enabled in hardware; must be disabled by reprogramming the
DS39646C-page 52 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
SBOREN
(RCON<6>)
Sleep mode.
Configuration bit s.
BOR Operation

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
4.5 Device Reset Timers
The PIC18F8722 family of devices incorporates three
separate on-chip timers that help regulate the Power-on
Reset process. Their main function is to ensure that the
device clock is stable before code is executed. These
timers are:
• Power-up Timer (PWRT)
• Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST)
• PLL Lock Time-out
4.5.1 POWER-UP TIMER (PWRT)
The Power-up Timer (PWRT) of the PIC18F8722
family of devices is an 11-bit counter which uses the
INTRC source as the clock input. While the PWRT is
counting, the device is held in Reset.
The power-up time delay depe nd s on the INTRC cl oc k
and will vary from chip-to-chip due to temperature and
process variation. See DC parameter 33 in Table 28-12
for details.
The PWRT is enabled by clearing the PWRTEN
Configuration bit.
4.5.2 OSCILLATOR START-UP TIMER
(OST)
The Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST) provides a 1024
oscillator cycle (from OSC1 input) delay after the
PWRT delay is over (parameter 33, Table 28-12). This
ensures that the crystal oscillator or resonator has
started and stabilized.
The OST time-out is invoked only for XT, LP, HS and
HSPLL modes and only on Power-on Reset, or on exit
from most power-manag ed modes.
4.5.3 PLL LOCK TIME-OUT
With the PLL enabled in its PLL mode, the time-out
sequence following a Power-on Reset is slightly different from other oscillator modes. A separate timer is
used to provide a fixed time-out tha t i s su f f i cient for the
PLL to lock to the main oscillator frequency. This PLL
lock time-o ut (T
PLL) is typically 2 ms and follows the
oscillator start-up time-out.
4.5.4 TIME-OUT SEQUENCE
On power-up, the time-out sequence is as follows:
1. After the POR pulse has cleared, PWR T time-out
is invoked (if enabled).
2. Then, the OST is activated.
The total time-out will vary based on oscillator configuration and the status of the PWRT. Figure 4-3,
Figure 4-4, Figure 4-5, Figure 4-6 and Figure 4-7 all
depict time-out sequences on power-up, with the
Power-up Timer enabled and the device operating in
HS Oscillator mode. Figure s 4-3 through 4-6 also apply
to devices operating in XT or LP m odes. F or devi ces i n
RC mode and with the PWRT disabled, on the other
hand, there will be no time-out at all.
Since the time-outs occur from the POR pulse, if MC LR
is kept low long e nough, all ti me -out s will e xpire. Brin ging MCLR
(Figure 4-5). This is useful for testing purposes or to
synchronize more than one PIC18F8722 family device
operating in parallel.
high will begin execution immediately
TABLE 4-2: TIME-OUT IN VARIOUS SITUATIONS
(2)
Oscillator
Configuration
HSPLL T
PWRTEN
(1)
PWRT
+ 1024 TOSC + TPLL
HS, XT, LP TPWRT
EC, ECIO TPWRT
RC, RCIO T
INTIO1, INTIO2 T
Power-up
= 0 PWRTEN = 1
(1)
+ 1024 TOSC 1024 TOSC 1024 TOSC
(1)
(1)
PWRT
(1)
PWRT
Note 1: See parameter 33, Table28-12.
2: 2 ms is the nominal time required for the PLL to lock.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 53
and Brown-out
(2)
1024 TOSC + TPLL
Exit from
Power-Managed Mode
(2)
1024 TOSC + TPLL
(2)
——
——
——

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TPWRT
TOST
VDD
MCLR
INTERNAL POR
PWRT TIME-OUT
OST TIME-OUT
INTERNAL RESET
TPWRT
TOST
VDD
MCLR
INTERNAL POR
PWRT TI ME-OUT
OST TIME-OUT
INTERNAL RESET
VDD
MCLR
INTERNAL POR
PWRT TIME-OUT
OST TIME-OUT
INTERNAL RESET
TPWRT
TOST
FIGURE 4-3: TIME-OUT SEQUENCE ON POWER-UP (MCLR TIED TO VDD, VDD RISE < TPWRT)
FIGURE 4-4: TIME-OUT SEQUENCE ON POWER-UP (MCLR
FIGURE 4-5: TIME-OUT SEQUENCE ON POWER-UP (MCLR
NOT TIED TO VDD): CASE 1
NOT TIED TO VDD): CASE 2
DS39646C-page 54 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
VDD
MCLR
INTERNAL POR
PWRT TIME-OUT
OST TIME-OUT
INTERNAL RESET
TPWRT
TOST
TPWRT
TOST
VDD
MCLR
INTERNAL POR
PWRT TIME-OUT
OST TIME-OUT
INTERNAL RESET
PLL TIME-OUT
TPLL
Note: TOST = 1024 clock cycles.
T
PLL ≈ 2 ms is the nominal time required for the PLL to lock.
FIGURE 4-6: SLOW RISE TIME (MCLR TIED TO VDD, VDD RISE > TPWRT)
FIGURE 4-7: TIME-OUT SEQUENCE ON POR w/PLL ENABLED (MCLR
TIED TO VDD)
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 55

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
4.6 Reset State of Registers
Most registers are unaffected by a Reset. Their status
is unknown on POR and unchanged by all other
Table 4-4 describes the Reset states for all of the
Special Function Registers. These are categorized by
Power-on and Brown-out Resets, Master Clear and
WDT Resets and WDT wake-ups.
Resets. All othe r reg is ters are forced to a “Reset state”
depending on the type of Reset that occurred.
Most registers are not affected by a WDT wake-up,
since this is viewed as the resumption of normal operation. Status bits from the RCON register, RI
POR
and BOR, are set or cleare d dif ferently i n dif ferent
, TO, PD,
Reset situations, as indicated in Table4-3. These bits
are used in software to determine the nature of the
Reset.
TABLE 4-3: STATUS BITS, THEIR SIGNIFICANCE AND THE INITIALIZATION CONDITION
FOR RCON REGISTER
Condition
Program
Counter
SBOREN RI TO PD POR BOR STKFUL STKUNF
Power-on Reset 0000h 1 11100 0 0
RESET Instruction 0000h u
Brown-out Reset 0000h u
during Power-Managed
MCLR
0000h u
(2)
(2)
(2)
Run Modes
MCLR during Power-Managed
0000h u
(2)
Idle Modes and Sleep Mode
WDT Time-out during Full Power
0000h u
(2)
or Power-Managed Run Mode
MCLR during Full Power
0000h u
(2)
Execution
Stack Full Reset (STVREN = 1) 0000h u
Stack Underflow Reset
0000h u
(2)
(2)
(STVREN = 1)
Stack Underflow Error (not an
0000h u
(2)
actual Reset, STVREN = 0)
WDT Time-out during
PC + 2 u
(2)
Power-Managed Idle or
Sleep Modes
Interrupt Exit from
PC + 2
(1)
(2)
u
Power-Managed Modes
Legend: u = unchanged
Note 1: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEH or GIEL bits are set, the PC is loaded with the
interrupt vector (008h or 0018h).
2: Reset state is ‘1’ for POR and unchanged for all other Resets when software BOR is enabled
(BOREN<1:0> Configuration bits = 01 and SBOREN = 1). Otherwise, the Reset state is ‘0’.
RCON Register STKPTR Register
0uuuu u u
111u0 u u
u1uuu u u
u10uu u u
u0uuu u u
uuuuu u u
uuuuu 1 u
uuuuu u 1
uuuuu u 1
u00uu u u
uu0uu u u
DS39646C-page 56 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 4-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS
MCLR
Register Applicable Devices
TOSU 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 ---0 0000 ---0 0000 ---0 uuuu
TOSH 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TOSL 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
STKPTR 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22
PCLATU 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 ---0 0000 ---0 0000 ---u uuuu
PCLATH 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PCL 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 PC + 2
TBLPTRU 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
TBLPTRH 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TBLPTRL 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TABLAT 6X27 6X22 8X2 7 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PRODH 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PRODL 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
INTCON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 000x 0000 000u uuuu uuuu
INTCON2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
INTCON3 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1100 0000 1100 0000 uuuu uuuu
INDF0 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
POSTINC0 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
POSTDEC0 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
PREINC0 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
PLUSW0 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
FSR0H 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 ---- 0000 ---- 00 0 0 ---- uuuu
FSR0L 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
WREG 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
INDF1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
POSTINC1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
POSTDEC1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
PREINC1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
PLUSW1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
Legend: u = unchanged, x = unknown, - = unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’, q = value depends on condition.
Shaded cells indicate conditions do not apply for the designated device.
Note 1: One or more bits in the INTCONx or PIRx registers will be affected (to cause wake-up).
2: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the PC is loaded with the interrupt vector
(0008h or 0018h).
3: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the TOSU, TOSH and TOSL are updated with
the current value of the PC. The STKPTR is modified to point to the next location in the hardware stack.
4: See Table4-3 for Reset value for specific condition.
5: Bits 6 and 7 of PORTA, LATA and TRISA are enabled, depending on the oscillator mode selected. When not enabled
as PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’.
Power-on Reset,
Brown-out Reset
RESET Instruction,
00-0 0000 uu-u uuuu
Resets,
WDT Reset,
Stack Resets
Wake-up via WDT
or Interrupt
uu-u uuuu
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(2)
(1)
(1)
(1)
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 57

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 4-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED)
MCLR
Register Applicable Devices
FSR1H 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22
FSR1L 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
BSR 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 ---- 0000 ---- 0000 ---- uuuu
INDF2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
POSTINC2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
POSTDEC2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
PREINC2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
PLUSW2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 N/A N/A N/A
FSR2H 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22
FSR2L 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
STATUS 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 ---x xxxx ---u uuuu ---u uuuu
TMR0H 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TMR0L 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
T0CON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
OSCCON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22
HLVDCON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0-00 0101 0-00 01 01 u-uu uuuu
WDTCON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 ---- ---0 ---- -- -0 ---- ---u
(4)
RCON
TMR1H 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
TMR1L 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
T1CON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 u0uu uuuu uuuu uuuu
TMR2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PR2 6X27 6X22 8 X27 8X22 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
T2CON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 -000 0000 -000 0000 -uuu uuuu
SSP1BUF 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
SSP1ADD 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
SSP1STAT 6X27 6X22 8X2 7 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
SSP1CON1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
SSP1CON2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
Legend: u = unchanged, x = unknown, - = unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’, q = value depends on condition.
Note 1: One or more bits in the INTCONx or PIRx registers will be affected (to cause wake-up).
Shaded cells indicate conditions do not apply for the designated device.
2: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the PC is loaded with the interrupt vector
(0008h or 0018h).
3: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the TOSU, TOSH and TOSL are updated with
the current value of the PC. The STKPTR is modified to point to the next location in the hardware stack.
4: See Table4-3 for Reset value for specific condition.
5: Bits 6 and 7 of PORTA, LATA and TRISA are enabled, depending on the oscillator mode selected. When not enabled
as PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’.
6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0q-1 11q0 0q-q qquu uq-u qquu
Power-on Reset,
Brown-out Reset
RESET Instruction,
---- 0000 ---- 0000
---- 0000 ---- 0000
0100 q000 0100 q000 uuuu uuqu
Resets,
WDT Reset,
Stack Resets
Wake-up via WDT
or Interrupt
---- uuuu
---- uuuu
DS39646C-page 58 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 4-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED)
MCLR
Register Applicable Devices
ADRESH 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
ADRESL 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
ADCON0 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
ADCON1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
ADCON2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0-00 0000 0-00 0000 u-uu uuuu
CCPR1H 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCPR1L 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCP1CON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
CCPR2H 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCPR2L 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCP2CON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
CCPR3H 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCPR3L 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCP3CON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
ECCP1AS 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
CVRCON 6X 27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
CMCON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0111 0000 0111 uuuu uuuu
TMR3H 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
TMR3L 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
T3CON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PSPCON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 ---- 0000 ---- uuuu ----
SPBRG1 6X27 6 X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
RCREG1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TXREG1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TXSTA1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0010 0000 0010 uuuu uuuu
RCSTA1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 000x 0000 000x uuuu uuuu
EEADRH 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 ---- --00 ---- --00 ---- --uu
EEADR 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
EEDATA 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
EECON2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
EECON1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xx-0 x000 uu-0 u000 uu-u uuuu
Legend: u = unchanged, x = unknown, - = unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’, q = value depends on condition.
Shaded cells indicate conditions do not apply for the designated device.
Note 1: One or more bits in the INTCONx or PIRx registers will be affected (to cause wake-up).
2: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the PC is loaded with the interrupt vector
(0008h or 0018h).
3: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the TOSU, TOSH and TOSL are updated with
the current value of the PC. The STKPTR is modified to point to the next location in the hardware stack.
4: See Table4-3 for Reset value for specific condition.
5: Bits 6 and 7 of PORTA, LATA and TRISA are enabled, depending on the oscillator mode selected. When not enabled
as PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’.
Power-on Reset,
Brown-out Reset
RESET Instruction,
Resets,
WDT Reset,
Stack Resets
Wake-up via WDT
or Interrupt
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 59

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 4-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED)
MCLR
Register Applicable Devices
Power-on Reset,
Brown-out Reset
RESET Instruction,
IPR3 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
PIR3 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PIE3 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
IPR2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 11-1 1111 11-1 1111 uu-u uuuu
PIR2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 00-0 0000 00-0 0000 uu-u uuuu
PIE2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 00-0 0000 00-0 0000 uu-u uuuu
IPR1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
PIR1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PIE1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
MEMCON
6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0-00 --00 0-00 --00 u-uu --uu
OSCTUNE 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 00-0 0000 00-0 0000 uu-u uuuu
TRISJ
TRISH
6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISG 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 ---1 1111 ---1 1111 ---u uuuu
TRISF 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISE 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISD 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISC 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISB 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISA
(5)
6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111
(5)
LATJ 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATH
6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATG 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 --xx xxxx --uu uuuu --uu uuuu
LATF 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATE 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATD 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATC 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATB 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATA
(5)
6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx
(5)
PORTJ 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PORTH
6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PORTG 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 --xx xxxx --uu uuuu --uu uuuu
PORTF 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 x000 0000 u000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PORTE 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PORTD 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PORTC 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PORTB 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
Legend: u = unchanged, x = unknown, - = unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’, q = value depends on condition.
Shaded cells indicate conditions do not apply for the designated device.
Note 1: One or more bits in the INTCONx or PIRx registers will be affected (to cause wake-up).
2: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the PC is loaded with the interrupt vector
(0008h or 0018h).
3: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the TOSU, TOSH and TOSL are updated with
the current value of the PC. The STKPTR is modified to point to the next location in the hardware stack.
4: See Table4-3 for Reset value for specific condition.
5: Bits 6 and 7 of PORTA, LATA and TRISA are enabled, depending on the oscillator mode selected. When not enabled
as PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’.
Resets,
WDT Reset,
Stack Resets
1111 1111
uuuu uuuu
Wake-up via WDT
or Interrupt
(5)
(5)
uuuu uuuu
uuuu uuuu
(1)
(1)
(1)
(5)
(5)
DS39646C-page 60 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 4-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED)
MCLR
Register Applicable Devices
(5)
PORTA
SPBRGH1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu u uuu
BAUDCON1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 01-0 0-00 01-0 0-00 uu-u u-uu
SPBRGH2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu u uuu
BAUDCON2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 01-0 0-00 01-0 0-00 uu-u u-uu
ECCP1DEL 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TMR4 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PR4 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
T4CON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 -000 0000 -000 0000 -uuu uuuu
CCPR4H 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCPR4L 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCP4CON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
CCPR5H 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCPR5L 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCP5CON 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
SPBRG2 6X27 6 X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
RCREG2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuu u u uuu
TXREG2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu u uuu
TXSTA2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0010 0000 0010 uuuu u uuu
RCSTA2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 000x 0000 000x uuuu uuuu
ECCP3AS 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuu u uuuu
ECCP3DEL 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
ECCP2AS 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuu u uuuu
ECCP2DEL 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
SSP2BUF 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
SSP2ADD 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuu u uuuu
SSP2STAT 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
SSP2CON1 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuu u uuuu
SSP2CON2 6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuu u uuuu
Legend: u = unchanged, x = unknown, - = unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’, q = value depends on condition.
Shaded cells indicate conditions do not apply for the designated device.
Note 1: One or more bits in the INTCONx or PIRx registers will be affected (to cause wake-up).
2: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the PC is loaded with the interrupt vector
(0008h or 0018h).
3: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the TOSU, TOSH and TOSL are updated with
the current value of the PC. The STKPTR is modified to point to the next location in the hardware stack.
4: See Table4-3 for Reset value for specific condition.
5: Bits 6 and 7 of PORTA, LATA and TRISA are enabled, depending on the oscillator mode selected. When not enabled
as PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’.
6X27 6X22 8X27 8X22 xx0x 0000
Power-on Reset,
Brown-out Reset
(5)
RESET Instruction,
Resets,
WDT Reset,
Stack Resets
uu0u 0000
Wake-up via WDT
or Interrupt
(5)
uuuu uuuu
(5)
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 61

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
NOTES:
DS39646C-page 62 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
5.0 MEMORY ORGANIZATION
There are three types of memory in PIC18 Enhanced
microcontroller devices:
• Program Memory
• Data RAM
• Data EEPROM
As Harvard architecture dev ices, the dat a and progra m
memories use separate busses; this allows for concurrent access of the two memory spaces. The data
EEPROM, for practical purposes, can be regarded as
a peripheral device, since it is addresse d and accessed
through a set of control registers.
Additional detailed information on the operation of the
Flash program memory is provided in Section 6.0
“Flash Program Memory”. Data EEPROM is
discussed s eparately in Section 8.0 “Data EEPROM
Memory”.
5.1 Program Memory Organization
PIC18 microcontrollers implement a 21-bit program
counter, which is capable of addressing a 2-Mbyte
program memory space. Accessing a location between
the upper boundary of the physically implemented
memory and the 2-Mbyte address will return all ‘0’s (a
NOP instruction).
The PIC18F6527 and PIC18F8527 each have 48 Kbytes
of Flash memory an d can sto re up to 24, 576 sing le-wor d
instructions.
The PIC18F6622 and PIC18F8622 each have 64 Kbytes
of Flash memory an d can sto re up to 32, 768 sing le-wor d
instructions.
The PIC18F6627 a nd PIC18F86 27 each hav e 96 Kbytes
of Flash memory an d can sto re up to 49, 152 sing le-wor d
instructions.
The PIC18F6722 and PIC18F8722 each have
128 Kbytes of Flash memory and can store up to
65,536 single-word instructions.
PIC18 devices have two interrupt vectors. The Reset
vector address is at 0000h and the interrupt vector
addresses are at 0008h and 0018h.
The program memory map for the PIC18F8722 family
of devices is shown in Figure 5-1.
5.1.1 PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PROGRAM MEMORY MODES
PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 devices differ significantly from their PIC18 pred ecesso rs in their util izatio n
of program memory. In addition to available on-chip
Flash program memory, these controllers can also
address up to 2 Mbytes of external program memory
through the external memory interface. There are four
distinct operating modes available to the controllers:
• Microprocessor (MP)
• Microprocessor with Boot Block (MPBB)
• Extended Microcontroller (EMC)
• Microcontroller (MC)
The program memory mode is determined by setting
the two Least Significant bits of the Configuration
Register 3L (CONFIG3L) as shown in Register 25-4
(see Section 25.1 “Configuration Bits” for additional
details on the device Configuration bits).
The program memory modes operate as follows:
•The Microprocessor Mode permits access only
to external program memory; the contents of the
on-chip Flash memory are ignored. The 21-bit
program counter permits access to a 2-Mbyte
linear program memory space.
• The Microprocessor with Boot Block Mode
accesses on-chip Flash memory from the boot
block. Above this, external program memory is
accessed all the way up to the 2-Mbyte limit.
Program execution automatically switches
between the two memories as required. The boot
block is configurable to 1, 2 or 4 Kbytes.
• The Microcontroller Mode accesses only
on-chip Flash memory. Attempts to read above the
physical limit of the on-chip Flash (0BFFFh for the
PIC18F8527, 0FFFFh for the PIC18F8622,
17FFFh for the PIC18F8627, 1FFFFh for the
PIC18F8722) causes a read of all ‘0’s (a NOP
instruction).
The Microcontroller mode is also the only operating
mode available to PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722
devices.
•The Extended Microcontroller Mode allows
access to both internal and external program
memories as a single block. The device can
access its entire on-chip Flash memory; above
this, the device accesses external program
memory up to the 2-Mbyte program space limit.
As with Boot Block mode, ex ecution a utomatica lly
switches between the two memories as required.
In all modes, the microcontroller has complete access
to data RAM and EEPROM.
Figure 5-2 comp are s t he me mo ry m aps of the dif fere nt
program memory modes. The differences between
on-chip and external memory access limitations are
more fully explained in Table 5-1.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 63

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
PC<20:0>
Stack Level 1
•
Stack Level 31
Reset Vector
•
•
CALL,RCALL,RETURN
RETFIE,RETLW
21
0000h
0018h
On-Chip
Program Memory
High-Priority Interrupt Vector
0008h
User Memory Space
01FFFFh
018000h
017FFFh
1FFFFFh
PIC18FX627
PIC18FX722
On-Chip
Program Memory
Read ‘0’
On-Chip
Program Memory
0C000h
0BFFFh
PIC18FX527
PIC18FX622
On-Chip
Program Memory
Read ‘0’
Low-Priority Interrupt Vector
Read ‘0’
10000h
0FFFFh
FIGURE 5-1: PROGRAM MEMORY MAP AND STACK FOR PIC18F8722 FAMILY DEVICES
T ABLE 5-1: MEMORY ACCESS FOR PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 PROGRAM MEMORY MODES
Operating Mode
Microprocessor No Access No Access No Access Yes Yes Yes
Microprocessor
w/ Boot Block
Microcontroller Yes Yes Yes No Access No Access No Access
Extended
Microcontroller
Internal Program Memory External Program Memory
Execution
From
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Table Read
From
Table Write To
Execution
From
Table Read
From
Table Wri te To
DS39646C-page 64 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Microprocessor
Mode
000000h
1FFFFFh
External
Program
Memory
External
Program
Memory
1FFFFFh
000000h
On-Chip
Program
Memory
Extended
Microcontroller
Mode
Microcontroller
Mode
(5)
000000h
External
On-Chip
Program Space Execution
On-Chip
Program
Memory
1FFFFFh
Reads
000800h
(6)
or
1FFFFFh
0007FFh
(6)
or
Microprocessor
with Boot Block
Mode
000000h
On-Chip
Program
Memory
External
Program
Memory
Memory Flash
On-Chip
Program
Memory
(No
access)
‘0’s
External
On-Chip
Memory Flash
On-Chip
Flash
External
On-Chip
Memory
Flash
0FFFFh
(2)
0BFFFh
(1)
01FFFFh
(4)
017FFFh
(3)
Note 1: PIC18F6527 and PIC18F8527.
2: PIC18F6622 and PIC18F8622.
3: PIC18F6627 and PIC18F8627.
4: PIC18F6722 and PIC18F8722.
5: This is the only mode available on PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722 devices.
6: Boot block size is determined by the BBSIZ<1:0> bits in CONFIG4L.
000FFFh
(6)
or
001FFFh
(6)
001000h
(6)
or
002000h
(6)
010000h
(2)
0C000h
(1)
020000h
(4)
018000h
(3)
0FFFFh
(2)
0BFFFh
(1)
01FFFFh
(4)
017FFFh
(3)
010000h
(2)
0C000h
(1)
020000h
(4)
018000h
(3)
FIGURE 5-2: MEMORY MAPS FOR PIC18F8722 FAMILY PROGRAM MEMORY MODES
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 65

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
00011
001A34h
11111
11110
11101
00010
00001
00000
00010
Return Address Stack <20:0>
Top-of-Stack
000D58h
TOSLTOSHTOSU
34h1Ah00h
STKPTR<4:0>
T op -of-Stack Registers Stack Pointer
5.1.2 PROGRAM COUNTER
The Program Counter (PC ) specifies the address of th e
instruction to fetch for execu tion. The PC is 21 bits wide
and is contained in three separate 8-bit registers. The
low byte, known as the PCL register, is both readable
and writable. The high byt e, or PCH re gister, contains
the PC<15:8> bits; i t is not directly re adable or writ able.
Updates to the PCH register are perfo rmed through the
PCLATH register. The upper byte is called PCU. This
register contains the PC<20:16> bits; it is also not
directly readable or writable. Updates to the PCU
register are performed through the PCLATU register.
The contents of PCLATH and PCLATU are transferred
to the program counter by any operation that writes
PCL. Similarly, the upper two bytes of the program
counter are transferred to P CLATH and PCLATU by an
operation that reads PCL. This is useful for computed
offsets to the PC (see Section 5.1.5.1 “Computed
GOTO”).
The PC addresses bytes in the program memory. To
prevent the PC from becoming misaligned with word
instructions, the Least Significant bit of PCL is fixed to
a value of ‘0’. The PC increments by 2 to address
sequential instructions in the program memory.
The CALL, RCALL, GOTO and program branch
instructions write to the program counter directly. For
these instructions, the contents of PCLATH and
PCLATU are not transferred to the program counter.
5.1.3 RETURN ADDRESS STACK
The return address s tack allows any co mb ination of up
to 31 program calls and interrupts to occur. The PC is
pushed onto th e stac k when a CALL or RCALL instruction is executed or an interrupt is Acknowledged. The
PC value is pulled off the stack on a RETURN, RETLW
or a RETFIE instruction. PCLATU and PCLATH are not
affected by any of the RETURN or CALL instructions.
The stack operates as a 31-word by 21-bit RAM and a
5-bit Stack Pointer, STKPTR. The stac k space is not
part of either program or da ta sp ace. The Stack Point er
is readable and writable and the address on the top of
the stack is readable and writable through the top-ofstack Special File Registers. Data can also be pushed
to, or popped from the stack, using these registers.
A CALL type instru ctio n cau ses a pu sh ont o the stack;
the Stack Pointer is first incremented and the location
pointed to by the Stack Pointer is written with the
contents of the PC (already pointing to the instruction
following the CALL). A RETURN type instruction causes
a POP from the stack; the contents of the location
pointed to by the STKPTR are transferred to the PC
and then the Stack Pointer is decremented.
The Stack Pointer is initialized to ‘00000’ after all
Resets. There is no RAM associated with the location
corresponding to a Stack Pointer value of ‘00000’; this
is only a Reset value. Stat us bit s in dic ate if the stack is
full or has overflowed or has underflowed.
5.1.3.1 Top-of-Stack Access
Only the top of the return address stack (TOS) is
readable and writable. A set of three registers,
TOSU:TOSH:TOSL, hold the content s of the stack location pointed to by the STKPTR register (Figure5-3). This
allows users to implement a software stack if nec essary.
After a CALL, RCALL or interrupt, the software can read
the pushed value by reading the TOSU:TOSH:TOSL
registers. These values can be placed on a use r defined
software stack. At return time, the software can return
these values to TOSU:TOSH:TOSL and do a return.
The user must disable the global interrupt enable bits
while accessing the stack to prevent inadvertent stack
corruption.
FIGURE 5-3: RETURN ADDRESS STACK AND ASSOCIATED REGISTERS
DS39646C-page 66 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
5.1.3.2 Return Stack Pointer (STKPTR)
The STKPTR register (Register5-1) contains the St ack
Pointer value, the STKFUL (Stack Full) status bit and
the STKUNF (Stack Underflow) status bits. The value
of the Stack Pointer can be 0 through 31. The Stack
Pointer increments before values are pushed onto the
stack and decrements after values are popped off the
stack. On Reset, the Stack Pointer value will be zero.
The user may read and write the Stack Pointer value.
This feature can be used by a Real-Time Operating
System (RTOS) for return stack maintenance.
After the PC is pu sh ed ont o the s ta ck 31 time s (witho ut
popping any values off the stack), the STKFUL bit is
set. The STKFUL bit is cleared by software or by a
POR.
The action that takes place when the stack becomes
full depends on the state of the STVREN (Stack Overflow Reset Enable) Configuration bit. (Refer to
Section 25.1 “Configuration Bit s” for a descrip tion of
the device Configuration bits.) If STVREN is set
(default) , the 31st PUSH will push the (PC + 2) value
onto the stack, set the STKFUL bit and reset the
device. The STKFUL bit will remain set and the Stack
Pointer will be set to zero.
If STVREN is cleared, the STKFUL bi t will be set on the
31st PUSH and the Stack Pointer will increment to 31.
Any additional pushes will not overwrite the 31st PUSH
and STKPTR will remain at 31.
When the stack has been popped enough times to
unload the stack, the next POP will return a value of
zero to the PC and set the STKUNF bit, wh ile the S t ack
Pointer remains at zero. The STKUNF bit will remain
set until cleared by software or until a POR occurs.
Note: Returning a value of zero to the PC on an
underflow has the effect of vectoring the
program to the Reset vector, where the
stack conditions can be verified and
appropriate actions can be taken. This is
not the same as a Reset, as the contents
of the SFRs are not affected.
5.1.3.3 PUSH and POP Instructions
Since the Top-of-Stack is readable and writable, the
ability to push value s on to the st ac k an d pul l values off
the stack without disturbing normal program execution
is a desirable feature. The PIC18 instruction set
includes two instructions, PUSH and POP, that permit
the TOS to be manipulated under software control.
TOSU, TOSH and T OS L can be m odifie d to plac e dat a
or a return address on the stack.
The PUSH instruction places the current PC value onto
the stack. This increments the Stack Pointer and loads
the current PC value onto the stack.
The POP instruction discards the current TOS by decrementing the Stack Pointer. The previous value pushed
onto the stack then becomes the TOS value.
REGISTER 5-1: STKPTR: STACK POINTER REGISTER
R/C-0 R/C-0 U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
STKFUL
bit 7 bit 0
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
-n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
bit 7 STKFUL: Stack Full Flag bit
bit 6 STKUNF: Stack Underflo w Flag bit
bit 5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4-0 SP<4:0>: Stack Pointer Location bits
Note 1: Bit 7 and bit 6 are cleared by user software or by a POR.
(1)
STKUNF
1 = Stack became full or overflowed
0 = Stack has not become full or overflowed
1 = Stack underflow occurred
0 = Stack underflow did not occur
(1)
— SP4 SP3 SP2 SP1 SP0
(1)
(1)
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 67

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
CALL SUB1, FAST ;STATUS, WREG, BSR
;SAVED IN FAST REGISTER
;STACK
•
•
SUB1 •
•
RETURN, FAST ;RESTORE VALUES SAVED
;IN FAST REGISTER STACK
MAIN: ORG 0x0000
MOVLW 0x00
CALL TABLE
…
ORG 0x8000
TABLE MOVF PCL, F ; A simple read of PCL will update PCLATH, PCLATU
RLNCF W, W ; Multiply by 2 to get correct offset in table
ADDWF PCL ; Add the modified offset to force jump into table
RETLW ‘A’
RETLW ‘B’
RETLW ‘C’
RETLW ‘D’
RETLW ‘E’
END
5.1.3.4 Stack Full and Underflow Resets
Device Resets on stack overflow and stack underflow
conditions are enabled by setting the STVREN bit in
Configuration Register 4L. When STVREN is set, a ful l
or underflow will set the appropriate STKFUL or
STKUNF bit and then cause a device Reset. When
STVREN is cleared, a full or underflow condi tion will set
the appropriate STKFUL or STKUNF bit, but not caus e
a device Reset. The STKFUL or STKUNF bits are
cleared by the user software or a Power-on Reset.
5.1.4 FAST REGISTER STACK
A fast register stack is provided for the STATUS,
WREG and BSR registers, to provide a “fast return”
option for interrupts. The stack for each register is onl y
one level deep and is neith er readable no r writable. It is
loaded with the curre nt val ue of the corres pondi ng register when the processor vectors for an interrupt. All
interrupt sources will push values into the Stack registers. The values in the registers are then loaded back
into their associated registers if the RETFIE, FAST
instruction is used to return from the interrupt.
If both low and high-priority interrupts are enabled, the
stack registers cannot be used reliably to return from
low-priority interrupts. If a high-priority interrupt occurs
while servicing a low-priority interrupt, the Stack register values stored by the low-priority interrupt will be
overwritten. In these cases, users must save the key
registers in software during a low-priority interrupt.
If interrupt priority is not used, all interrupts ma y use the
fast register stack for returns from interrupt. If no interrupts are used, the fast register stack can be used to
restore the STATUS, WREG and BSR registers at the
end of a subroutine call. To use the fast register stack
for a subroutine call, a CALL label, FAST instruction
must be executed to save the STATUS, WREG and
BSR registers to the fast register stack. A
RETURN, FAST instruction is then executed to restore
these registers from the fast register stack.
Example 5-1 shows a source code example that uses
the fast register stack during a subroutine call and return.
EXAMPLE 5-1: FAST REGISTER STACK
CODE EXAMPLE
5.1.5 LOOK-UP TABLES IN PROGRAM MEMORY
There may be programming situations that require the
creation of data structures, or look-up tables, in
program memory. For PIC18 devices, look-up tables
can be implemented in two ways:
• Computed GOTO
• Table Reads
5.1.5.1 Computed GOTO
A computed GOTO is accompli shed by adding an offset
to the program counter. An example is shown in
Example 5-2.
A look-up table can be formed with an ADDWF PCL
instruction and a group of RETLW nn instructions. The W
register is load ed with an of fset in to the t able bef ore executing a call to that table. The first instruction of the called
routine is the ADDWF PCL instruction. The next instruction
executed will be one of th e RETLW nn instru ctions that
returns the valu e ‘nn’ to t he calling func tio n.
The offset value (in WREG) specifies the number of
bytes that the program counter should advance and
should be multiples of 2 (LSb = 0).
In this method, only one data byte may be stored in
each instruction location and room on the return
address stack is required.
Note: The “ADDWF PCL” instruction does not
update the PCLATH and PCLATU registers.
A read operation on PCL must be performed
to update PCLATH and PCLA TU.
EXAMPLE 5-2: COMPUTED GOTO USING AN OFFSET VALUE
DS39646C-page 68 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Q1
Q2 Q3 Q4
Q1
Q2 Q3 Q4
Q1
Q2 Q3 Q4
OSC1
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
PC
OSC2/CLKO
(RC mode)
PC PC + 2 PC + 4
Fetch INST (PC)
Execute INST (PC – 2)
Fetch INST (PC + 2)
Execute INST (PC)
Fetch INST (PC + 4)
Execute INST (PC + 2)
Internal
Phase
Clock
All instructions are single cycle, except for any program branche s. These tak e two cycles since the fetch instruct ion
is “flushed” from the pipeline while the new instruction is being fetched and then executed.
TCY0TCY1TCY2TCY3TCY4TCY5
1. MOVLW 55h
Fetch 1 Execute 1
2. MOVWF PORTB
Fetch 2 Execute 2
3. BRA SUB_1
Fetch 3 Execute 3
4. BSF PORTA, BIT3 (Forced NOP)
Fetch 4 Flush (NOP)
5. Instruction @ address SUB_1
Fetch SUB_1 Execute SUB_1
5.1.5.2 Table Reads and Table Writes
A better method of storing data in program memory
allows two bytes of dat a to be stored in each instruction
location.
Look-up table data may be stored two bytes per program word by using table reads and writes. The Table
Pointer (TBLPTR) register specifies the byte address
and the Table Latch (TABLAT) register contains the
data that is read from or wr itten to progr am memory.
Data is transferred to or from program memory one
byte at a time.
Table read and table write operations are discussed
further in Section 6.1 “Table Reads and Table
Writes”.
5.2 PIC18 Instruction Cycle
5.2.1 CLOCKING SCHEME
The microcontroller clock input, whether from an internal
or external source, is internally divided by four to generate four non-overlapping quadrature clocks (Q1, Q2, Q3
and Q4). Internally, the program counter is incremented
on every Q1; the instruction is fetched from the program
FIGURE 5-4: CLOCK/INSTRUCTION CYCLE
memory and latched into the instruction register during
Q4. The instruction is decoded and executed during the
following Q1 through Q4. The clocks and instruction
execution flow are shown in Figure 5-4.
5.2.2 INSTRUCTION FLOW/PIPELINING
An “Instruction Cycle” consists of four Q cycles: Q1
through Q4. The instruction fetch and execute are
pipelined in such a manner that a fetch takes one
instruction cycle, while the decode and execute take
another instruction cycle. However, due to the pipelining, each instruction effectively executes in one
cycle. If a n instruc tion caus es the pro gram coun ter to
change (e.g., GOTO), then two cycles are required to
complete the instruction (Example 5-3).
A fetch cycle begins with the program counter
incrementing in Q1.
In the execution cy cle, the fetch ed instruction i s latched
into the Instruction Register (IR) in cycle Q1. This
instruction is then decoded and executed during the
Q2, Q3 and Q4 c ycles. Dat a m emory is read during Q2
(operand read) and written during Q4 (destination
write).
EXAMPLE 5-3: INSTRUCTION PIPELINE FLOW
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 69

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Word Address
LSB = 1 LSB = 0 ↓
Program Memory
Byte Locations
→
000000h
000002h
000004h
000006h
Instruction 1: MOVLW 055h 0Fh 55h 000008h
Instruction 2: GOTO 0006h EFh 03 h 00000Ah
F0h 00h 00000Ch
Instruction 3: MOVFF 123h, 456h C1h 23h 00000Eh
F4h 56h 000010h
000012h
000014h
5.2.3 INSTRUCTIONS IN PROGRAM MEMORY
The program memory is addressed in bytes. Instructions are stored as two bytes or four bytes in program
memory. The Least Significant Byte of an instruction
word is always stored in a program memory location
with an even address (LSb = 0). To maintain alignment
with instruction bo undaries , the PC incr ements in step s
of 2 and the LSb wi ll always read ‘0’ (see Section 5.1.2
“Program Counter”).
Figure 5-5 shows an ex am ple of h ow in st ruc tion w ord s
are stored in the program memory.
The CALL and GOTO instructions have the absolute program memory address embedded into the instruction.
Since instructions are always stored on word boundaries, the data contained in the instruction is a word
address. The word address is written to PC<20:1>,
which accesses the desired byte address in program
memory. Instruction #2 in Figure 5-5 shows how the
instruction GOTO 0006h is encoded in the program
memory. Program branch instructions, which encode a
relative address offset, operate in the same ma nner. The
offset value stored in a branch instruction represents the
number of single-word instructions that the PC will be
offset by. Section 26.0 “Instruction Set Summary”
provides further details of the instruction set.
FIGURE 5-5: INSTRUCTIONS IN PROGRAM MEMORY
DS39646C-page 70 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
5.2.4 TWO-WORD INSTRUCTIONS
The standard PIC18 instruction set has 8 two-word
instructions: CALL, MOVFF, GOTO, LSFR, ADDULNK,
CALLW, MOVSS and SUBULNK. In all cases, the
second word of th e instructi ons always ha s ‘1111’ as
its four Most Signi fican t bit s; the oth er 12 bit s are li teral
data, usually a data memory address.
The use of ‘1111’ in the 4 MSbs of an instruction specifies a special form of NOP. If the instruction is executed
in proper sequence – immed iate ly af ter the first word –
the data in the s econd w ord is ac cessed an d used by
the instruction seq ue nce . If the first word is skipped for
some reason and the se cond word is ex ecuted by itsel f,
a NOP is executed instead. This is necessary for cases
when the two-word instruction is preceded by a conditional instruction that changes the PC. Example 5-4
shows how this works.
Note: See Section 5.6 “PIC18 Instruction
Execution and the Extended Instruction Set” for information on two-word
instructions in the extended instruction set.
EXAMPLE 5-4: TWO-WORD INSTRUCTIONS
CASE 1:
Object Code Source Code
0110 0110 0000 0000 TSTFSZ REG1 ; is RAM location 0?
1100 0001 0010 0011 MOVFF REG1, REG2 ; No, skip this word
1111 0100 0101 0110 ; Execute this word as a NOP
0010 0100 0000 0000 ADDWF REG3 ; continue code
CASE 2:
Object Code Source Code
0110 0110 0000 0000 TSTFSZ REG1 ; is RAM location 0?
1100 0001 0010 0011 MOVFF REG1, REG2 ; Yes, execute this word
1111 0100 0101 0110 ; 2nd word of instruction
0010 0100 0000 0000 ADDWF REG3 ; continue code
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 71

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
5.3 Data Memory Organization
Note: The operation of some aspects of data
memory are changed when the PIC18
extended instruction set is enabled. See
Section 5.5 “Data Memory and the
Extended Instruction Set” for more
information.
The data memory in PIC18 devices is implemented as
static RAM. Each register in the data memory has a
12-bit address, allowing up to 4096 bytes of data
memory . The m emory sp ace is div ided into as many as
16 banks that con tain 256 by tes each; the PIC18F 8722
family of devices implements all 16 banks. Figure 5-6
shows the data memory organization for the
PIC18F8722 family of devices.
The data memory contains Special Function Registers
(SFRs) and General Purpose Registers (GPRs). The
SFRs are used for control and status of the controller
and peripheral functio ns, while GPRs are us ed for data
storage and scratchpad operations in the user’s
application. Any re ad of an unimpl emented location will
read as ‘0’s.
The instruction set and architecture allow operations
across all banks. The entire data memory may be
accessed by Direct, Indirect or Indexed Addressing
modes. Addressing modes are discussed later in this
subsection.
To ensure that commonly used registers (SFRs and
select GPRs) c an b e ac ce ssed in a si ngle cyc le, PI C18
devices impl em ent an Ac ce ss Ba nk . Th is i s a 256-byte
memory space that pr ovid es fa st acc ess to SFRs a nd
the lower portion of GPR Bank 0 without using the
BSR. Section 5.3.2 “Access Bank” provides a
detailed description of the Access RAM.
5.3.1 BANK SELECT REGISTER (BSR)
Large areas of data memory require an efficient
addressing scheme to make rapid access to any
address possible. Ideally, this means that an entire
address does not need to be provided for each read or
write operation. For PIC18 devices, this is accomplished with a RAM banking scheme. This divides the
memory space into 16 contiguous banks of 256 bytes.
Depending on the instruction, each location can be
addressed directly by its full 12-bit address, or an 8-bit
low-order address and a 4-bit Bank Pointer.
Most instruct ions in th e PIC18 in struct ion set ma ke use
of the Bank Pointer , known as the Ba nk Select Reg ister
(BSR). This SFR holds the 4 Most Significant bits of a
location’s address; the instruction itself includes the
8 Least Significant bits. Only the four lower bits of the
BSR are implemented (BSR<3:0>). Th e upper four bit s
are unused; they will always read ‘0’ and cannot be
written to. The BSR can be l oaded direc tly b y using the
MOVLB instruction.
The value of the BSR indicates the bank in data
memory; the 8 bits in the instruction show the location
in the bank and can be thought of as an o f fs et from th e
bank’s lower boundary. The relationship between the
BSR’s value and the bank division in data memory is
shown in Figure 5-7.
Since up to 16 reg isters m ay sh are the same l ow-ord er
address, the user must alway s be careful to ensure that
the proper bank is selected before performing a data
read or write. For example, writing what should be
program data to an 8 -bi t ad dres s of F 9h w h il e th e BSR
is 0Fh will end up resetting the program counter.
While any bank can be s el ec ted, only those banks th at
are actually implemented can be read or written to.
Writes to unimplemented banks are ignored, while
reads from unimplemented banks will return ‘0’s. Even
so, the STATUS register will still be affected as if the
operation was successful. The data memory map in
Figure 5-6 indicates which banks are implemented.
In the core PIC18 instruction set, only the MOVFF
instruction fully specifies the 12-bit address of the
source and target registers. This i nstruction ig nores the
BSR completely when it ex ecutes. All o ther instructi ons
include only the low-order address as an operand and
must use either the BSR or the Access Bank to locate
their target registers.
DS39646C-page 72 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Bank 0
Bank 1
Bank 14
Bank 15
Data Memory Map
BSR<3:0>
= 0000
= 0001
= 1111
060h
05Fh
F60h
FFFh
00h
5Fh
60h
FFh
Access Bank
When ‘a’ =
0:
The BSR is ignored an d the
Access Bank is used.
The first 96 bytes are
general purpose RAM
(from Bank 0).
The second 160 bytes are
Special Function Registers
(from Bank 15).
When ‘a’ =
1:
The BSR specifies the Ban k
used by the instruction.
F5Fh
F00h
EFFh
1FFh
100h
0FFh
000h
Access RAM
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
GPR
GPR
SFR
Access RAM High
Access RAM Low
Bank 2
= 0110
= 0010
(SFRs)
2FFh
200h
3FFh
300h
4FFh
400h
5FFh
500h
6FFh
600h
7FFh
700h
8FFh
800h
9FFh
900h
AFFh
A00h
BFFh
B00h
CFFh
C00h
DFFh
D00h
E00h
Bank 3
Bank 4
Bank 5
Bank 6
Bank 7
Bank 8
Bank 9
Bank 10
Bank 11
Bank 12
Bank 13
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
GPR
FFh
00h
= 0011
= 0100
= 0101
= 0111
= 1000
= 1001
= 1010
= 1011
= 1100
= 1101
= 1110
GPR
GPR
GPR
GPR
GPR
GPR
GPR
GPR
GPR
GPR
GPR
GPR
GPR
FIGURE 5-6: DATA MEMORY MAP FOR THE PIC18F8722 FAMILY OF DEVICES
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 73

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Note 1: The Access RAM bit of the instruction can be used to force an override of the selected bank (BSR<3:0>) to
the registers of the Access Bank.
2: The
MOVFF instruction embeds the entire 12-bit address in the instruction.
Data
Memory
Bank Select
(2)
7
0
From Opcode
(2)
0000
000h
100h
200h
300h
F00h
E00h
FFFh
Bank 0
Bank 1
Bank 2
Bank 14
Bank 15
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
Bank 3
through
Bank 13
0011
11111111
7
0
BSR
(1)
FIGURE 5-7: USE OF THE BANK SELECT REGISTER (DIRECT ADDRESSING)
5.3.2 ACCESS BANK
While the use of the BSR with an embedded 8-bit
address allows users to address the entire range of
data memory, it also means th at the user must a lways
ensure that the correct bank is selected. Otherwise,
data may be read from or written to the wrong location.
This can be disastrous if a GPR is the intended target
of an operation, but an SFR is written to instead.
Verifying and/or changing the BSR for each read or
write to data memory can become very inefficient.
memory locations, the data memory is configured with
an Access Bank, which allows users to access a
mapped block of memory without specifying a BSR.
The Access Bank consists of the first 96 bytes of
T o stre amline acces s for the most commonl y used data
memory (00h-5Fh) in Bank 0 and the last 160 bytes of
memory (60h-FFh) in Block 15 . The lower half is known
as the “Access RAM” and is composed of GPRs. This
upper half is also where the device’s SFRs are
mapped. These two areas are mapped contiguously in
the Access Bank and can be addressed in a linear
fashion by an 8-bit address (Figure 5-6).
The Access Bank is used by core PIC18 instructions
that inclu de the Acce ss RAM bit ( the ‘a’ parame ter in
the instruction). When ‘a’ is equal to ‘1’, the instru ct ion
uses the BSR and the 8-bit address included in the
opcode for the data memory address. When ‘a’ is ‘0’,
however, the instruction is forced to use the Access
Bank address map; the current value of the BSR is
ignored entirely.
Using this “forced” addressing allows the instruction to
operate on a data address in a single cycle, without
updating the BSR first. For 8-bit addresses of 60h and
above, this mean s that use rs can ev aluate an d operate
on SFRs more efficiently. The Access RAM below 60h
is a good place for da ta values that the user might need
to access rapidly, such as immediate computational
results or common program variables. Access RAM
also allows for faster and more code efficient context
saving and switching of variables.
The mapping of the Access Bank is slightly different
when the extended instruction set is enabled (XINST
Configuration bit = 1). This is discussed in more deta il
in Section 5.5.3 “Mapping the Access Bank in
Indexed Literal Offset Mode”.
5.3.3 GENER AL PURPOSE REGISTER FILE
PIC18 devices may have banked memory in the GPR
area. This is data RAM, which is available for use by all
instructions. GPRs start at the bottom of Bank 0
(address 000h) and grow upwards towards the bottom of
the SFR area. GPRs are not initialized by a Power-on
Reset and are unchanged on all other Resets.
DS39646C-page 74 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
5.3.4 SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTERS
The Special Function Registers (SFRs) are registers
used by the CPU and p eripheral modul es for controllin g
the desired operation of the device. These reg isters are
implemented as static RAM. SFRs start at the top of
data memory (FF Fh) an d extend downw ard to oc cupy
the top half of Bank 15 (F60h to FFFh). A list of these
registers is given in Table 5-2 and Table 5-3.
The SFRs can be classified into two sets: those
associated with the “core” device functionality (ALU,
Resets and interrupts) and those related to the
peripheral functions. The Reset and interrupt registers
are described in their respective chapters, while the
ALU’s STATUS register is described later in this section. Registers related to the operation of a peripheral
feature are described in the chapter for that pe riphera l.
The SFRs are typically distributed among the
peripherals whose fun cti ons th ey c ontr ol. U nus ed SFR
locations are unimplemented and read as ‘0’s.
TABLE 5-2: SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER MAP FOR THE PIC18F8722 FAMILY OF DEVICES
Address Name Address Name Address Name Address Name Address Name
FFFh TOSU FDFh INDF2
FFEh TOSH FDEh POSTINC2
FFDh TOSL FDDh POSTDEC2
FFCh STKPTR FDCh PREINC2
FFBh PCLATU FDBh PLUSW2
FFAh PCLATH FDAh FSR2H FBAh CCP2CON F9Ah TRISJ
FF9h PCL FD9h FSR2L FB9h CCPR3H F99h TRISH
FF8h TBLPTRU FD8h STATUS FB8h CCPR3L F98h TRISG F78h TM R4
FF7h TBLPTRH FD7h TMR0H FB7h CCP3CON F97h TRISF F77h PR4
FF6h TBLPTRL FD6h TMR0L FB6h ECC P1A S F96h TRISE F76h T4CON
FF5h TABLAT FD5h T0CON FB5h CVRCON F95h TRISD F75h CCPR4H
FF4h PRODH FD4h
FF3h PRODL FD3h OSCCON FB3h TMR3H F93h TRISB F73h CCP4CON
FF2h INTCON FD2h HLVDCON F B2h TMR3L F92h TRISA F72h CCP R5H
FF1h INTCON2 FD1h WDTCON FB1h T3CON F91h LATJ
FF0h INTCON3 FD0h RCON FB 0h PSPCON F90h LATH
(1)
FEFh INDF0
FEEh POSTINC0
FEDh POSTDEC0
FECh PREINC0
FEBh PLUSW0
FCFh TMR1H FAFh SPBRG1 F8Fh LATG F6Fh SPBRG2
(1)
FCEh TMR1L FAEh RCREG1 F8Eh LATF F 6Eh RCREG2
(1)
FCDh T1CON FADh TXREG1 F8Dh LATE F6Dh TXREG2
(1)
(1)
FCCh TMR2 FACh TXSTA1 F8Ch LATD F6Ch TXSTA2
FCBh PR2 FABh RCSTA1 F8Bh LATC F6Bh RCSTA2
FEAh FSR0H FCAh T2CON FAAh EEADRH F8Ah LATB F6Ah ECCP3AS
FE9h FSR0L FC9h SSP1BUF FA9h EEADR F89h LATA F69h ECCP3DEL
FE8h WREG FC8h SSP1ADD FA8h EEDATA F88h PORTJ
FE7h INDF1
FE6h POSTINC1
FE5h POSTDEC1
FE4h PREINC1
FE3h PLUSW1
(1)
(1)
(1)
FC7h SSP1STAT FA7h EECON2
(1)
FC6h SSP1CON1 FA6h EECON1 F86h PORTG F66h SSP2BUF
(1)
FC5h SSP1CON2 FA5h IPR3 F85h PORTF F65h SSP2ADD
FC4h ADRESH FA4h PIR3 F84h PORTE F64h SSP2S TAT
FC3h ADRESL FA3h PIE3 F83h PORTD F63h SSP2CON1
FE2h FSR1H FC2h ADCON0 FA2h IPR2 F82h PORTC F62h SSP2CON2
FE1h FSR1L FC1h ADCON1 FA1h PIR2 F81h PORTB F61h
FE0h BSR FC0h ADCON2 FA0h PIE2 F80h PORTA F60h —
Note 1: T his is not a physical register.
2: Unimplemented registers are read as ‘0’.
3: This register is not available on 64-pin devices.
(1)
FBFh CCPR1H F9Fh IPR1 F7Fh SPBRGH1
(1)
FBEh CCPR1L F9Eh PIR1 F7Eh BAUDCON1
(1)
(1)
(1)
(2)
—
FBDh CCP1CON F9Dh PIE1 F7Dh SPBRGH2
FBCh CCPR2H F9Ch MEMCON F7Ch BAUDCON2
FBBh CCPR2L F9Bh OSC T UNE F7Bh —
(3)
(3)
F7Ah —
F79h ECCP1DEL
FB4h CMCON F94h TRISC F74h CCPR4L
(3)
(3)
(3)
(1)
F87h PORTH
(3)
F71h CCPR5L
F70h CCP5CON
F68h ECCP2AS
F67h ECCP2DEL
—
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 75

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 5-3: REGISTER FILE SUMMARY
File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TOSU
TOSH Top-of-Stack High Byte (TOS<15:8>) 0000 0000 57, 66
TOSL Top-of-Stack Low Byte (TOS<7:0>) 0000 0000 57, 66
STKPTR STKFUL
PCLATU
PCLATH Hol d ing R egist er for PC< 15: 8> 0000 0000 57, 66
PCL PC Low Byte (PC<7:0>) 0000 0000 57, 66
TBLPTRU
TBLPTRH Program Memory Table Pointer High Byte (TBLPTR<15:8>) 0000 0000 57, 90
TBLPTRL Program Memory Table Pointer Low Byte (TBLPTR<7:0>) 0000 0000 57, 90
TABLAT Program Memory Table Latch 0000 0000 57, 90
PRODH Product Register High Byte xxxx xxxx 57, 117
PRODL Product Register Low Byte xxxx xxxx 57, 117
INTCON GIE/GIEH PEIE/GIEL TMR0IE INT0IE RBIE TMR0IF INT0IF RBIF 0000 000x 57, 121
INTCON2 RBPU
INTCON3 INT2IP INT1IP INT3IE INT2IE INT1IE INT3IF INT2IF INT1IF 1100 0000 57, 123
INDF0 Uses contents of FSR0 to address data memory – value of FSR0 not changed (not a physical register) N/A 57, 82
POSTINC0 Uses contents of FSR0 to address data memory – value of FSR0 post-incremented (not a physical register) N/A 57, 82
POSTDEC0 Uses contents of FSR0 to address data memory – value of FSR0 post-decremented (not a physical register) N/A 57, 82
PREINC0 Uses contents of FSR0 to address data memory – value of FSR0 pre-incremented (not a physical register) N/A 57, 82
PLUSW0 Uses contents of FSR0 to address data memory – value of FSR0 pre-incremented (not a physical register) –
FSR0H
FSR0L Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 0 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 57, 82
WREG Working Regi st er xxxx xxxx 57
INDF1 Uses contents of FSR1 to address data memory – value of FSR1 not changed (not a physical register) N/A 57, 82
POSTINC1 Uses contents of FSR1 to address data memory – value of FSR1 post-incremented (not a physical register) N/A 57, 82
POSTDEC1 Uses contents of FSR1 to address data memory – value of FSR1 post-decremented (not a physical register) N/A 57, 82
PREINC1 Uses contents of FSR1 to address data memory – value of FSR1 pre-incremented (not a physical register) N/A 57, 82
PLUSW1 Uses contents of FSR1 to address data memory – value of FSR1 pre-incremented (not a physical register) –
FSR1H
FSR1L Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 1 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 58, 82
BSR
INDF2 Uses contents of FSR2 to address data memory – value of FSR2 not changed (not a physical register) N/A 58, 82
POSTINC2 Uses contents of FSR2 to address data memory – value of FSR2 post-incremented (not a physical register) N/A 58, 82
POSTDEC2 Uses contents of FSR2 to address data memory – value of FSR2 post-decremented (not a physical register) N/A 58, 82
PREINC2 Uses contents of FSR2 to address data memory – value of FSR2 pre-incremented (not a physical register) N/A 58, 82
PLUSW2 Uses contents of FSR2 to address data memory – value of FSR2 pre-incremented (not a physical register) –
FSR2H
FSR2L Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 2 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 58, 82
Legend: x = unknown , u = unchanged, - = unimplemented, q = value depends on condition
Note 1: The SBOREN bit is only available when the BOREN<1:0> Configuration bits = 01; otherwise, this bit reads as ‘0’.
2: These registers and/or bits are not implemented on 64-pin devices and are read as
3: The PLLEN bit is only available in specific oscillator configuration; otherwise, it is disabled and reads as
4: RA6/RA7 and their associated latch and direction bits are individually configured as port pins based on various primary oscillator modes.
5: RG5 and LATG5 are only available when Master Clear is disabled (MCLRE Configuration bit = 0); otherwise, RG5 and LATG5 read as
6: Bit 7 and Bit 6 are cleared by user software or by a POR.
7: Bit 21 of TBLPTRU allows access to the device Configuration bits.
— — — Top-of-Stack Upper Byte (TOS<20:16>) ---0 0000 57, 66
(6)
— — — Holding Register for PC<20:16> ---0 0000 57, 66
— —bit 21
value of FSR0 offset by W
— — — — Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 0 High ---- 0000 57, 82
value of FSR1 offset by W
— — — — Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 1 High ---- 0000 58, 82
— — — — Bank Select Register ---- 0000 58, 72
value of FSR2 offset by W
— — — — Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 2 High ---- 0000 58, 82
(6)
STKUNF
INTEDG0 INTEDG1 INTEDG2 INTEDG3 TMR0IP INT3IP RBIP 1111 1111 57, 122
— SP4 SP3 SP2 SP1 SP0 00-0 0000 57, 67
(7)
Program Memory Table Pointer Upper Byte (TBLPTR<20:16>) --00 0000 57, 90
‘0’. Reset values are shown for 80-pin devices;
individual unimplemented bits should be interpreted as ‘-’.
‘0’. See Section2.6.4 “PLL in
INTOSC Modes”.
When disabled, these bits read as ‘0’.
Value on
POR, BOR
N/A 57, 82
N/A 57, 82
N/A 58, 82
Details
on page:
‘0’.
DS39646C-page 76 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 5-3: REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED)
File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
STATUS — — —NOVZDCC---x xxxx 58, 80
TMR0H Timer0 Register High Byte 0000 0000 58, 163
TMR0L Timer0 Register Low Byte xxxx xxxx 58, 163
T0CON TMR0ON T08BIT T0CS T0SE PSA T0PS2 T0PS1 T0PS0 1111 1111 58, 161
OSCCON IDLEN IRCF2 IRCF1 IRCF0 OSTS IOFS SCS1 SCS0 0100 q000 39, 58
HLVDCON VDIRMAG
WDTCON
RCON IPEN SBOREN
TMR1H Timer1 Register High Byte xxxx xxxx 58, 169
TMR1L Timer1 Register Low Byte xxxx xxxx 58, 169
T1CON RD16 T1RUN T1CKPS1 T1CKPS0 T1OSCEN T1SYNC
TMR2 Timer2 Register 0000 0000 58, 172
PR2 Timer2 Period Register 1111 1111 58, 172
T2CON
SSP1BUF MSSP1 Receive Buffer/Transmit Register xxxx xxxx 58, 169,
SSP1ADD MSSP1 Address Register in I
SSP1STAT SMP CKE D/A
SSP1CON1 WCOL SSPOV SSPEN CKP SSPM3 SSPM2 SSPM1 SSPM0 0000 0000 58, 163,
SSP1CON2 GCEN ACKSTAT ACKDT ACKEN RCEN PEN RSEN SEN 0000 0000 58, 173
ADRESH A/D Result Register High Byte xxxx xxxx 59, 280
ADRESL A/D Result Register Low Byte xxxx xxxx 59, 280
ADCON0
ADCON1
ADCON2 ADFM
CCPR1H Enha nced Captur e/Compare/PWM Register 1 High Byte xxxx xxxx 59, 180
CCPR1L Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Register 1 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 59, 180
CCP1CON P1M1 P1M0 DC1B1 DC1B0 CCP1M3 CCP1M2 CCP1M1 CCP1M0 0000 0000 59, 187
CCPR2H Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Register 2 High Byte xxxx xxxx 59, 180
CCPR2L Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Register 2 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 59, 180
CCP2CON P2M1 P2M0 DC2B1 DC2B0 CCP2M3 CCP2M2 CCP2M1 CCP2M0 0000 0000 59, 179
CCPR3H Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Register 3 High Byte xxxx xxxx 59, 180
CCPR3L Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Register 3 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 59, 180
CCP3CON P3M1 P3M0 DC3B1 DC3B0 CCP3M3 CCP3M2 CCP3M1 CCP3M0 0000 0000 59, 179
ECCP1AS ECCP1ASE ECCP1AS2 ECCP1AS1 ECCP1AS0 PSS1AC1 PSS1AC0 PSS1BD1 PSS1BD0 0000 0000 59, 201
CVRCON CVREN CVROE CVRR CVRSS CVR3 CVR2 CVR1 CVR0 0000 0000 59, 287
CMCON C2OUT C1OUT C2INV C1INV CIS CM2 CM1 CM0 0000 0111 59, 289
TMR3H Timer3 Register High Byte xxxx xxxx 59, 175
TMR3L Timer3 Register Low Byte xxxx xxxx 59, 175
T3CON RD16 T3CCP2 T3CKPS1 T3CKPS0 T3CCP1 T3SYNC
Legend: x = unknown , u = unchanged, - = unimplemented, q = value depends on condition
Note 1: The SBOREN bit is only available when the BOREN<1:0> Configuration bits = 01; otherwise, this bit reads as ‘0’.
2: These registers and/or bits are not implemented on 64-pin devices and are read as
3: The PLLEN bit is only available in specific oscillator configuration; otherwise, it is disabled and reads as
4: RA6/RA7 and their associated latch and direction bits are individually configured as port pins based on various primary oscillator modes.
5: RG5 and LATG5 are only available when Master Clear is disabled (MCLRE Configuration bit = 0); otherwise, RG5 and LATG5 read as
6: Bit 7 and Bit 6 are cleared by user software or by a POR.
7: Bit 21 of TBLPTRU allows access to the device Configuration bits.
— — — — — — —SWDTEN--- ---0 58, 313
— T2OUTPS3 T2OUTPS2 T2OUTPS1 T2OUTPS0 TMR2ON T2CKPS1 T2CKPS0 -000 0000 58, 171
— — CHS3 CHS2 CHS1 CHS0 GO/DONE ADON --00 0000 59, 271
— — VCFG1 VCFG0 PCFG3 PCFG2 PCFG1 PCFG0 --00 0000 59, 272
individual unimplemented bits should be interpreted as ‘-’.
INTOSC Modes”.
When disabled, these bits read as ‘0’.
— IRVST HLVDEN HLVDL3 HLVDL2 HLVDL1 HLVDL0 0-00 0101 58, 291
(1)
—RITO PD POR BOR 0q-1 11q0 50, 56,
TMR1CS TMR1ON 0000 0000 58, 165
2
C™ Slave mode. MSSP1 Baud Rate Reload Register in I2C Master mode. 0000 0000 58, 170
PSR/WUA BF 0000 0000 58, 162,
— ACQT2 ACQT1 ACQT0 ADCS2 A DCS1 ADCS0 0-00 0000 59, 273
TMR3CS TMR3ON 0000 0000 59, 173
‘0’. Reset values are shown for 80-pin devices;
‘0’. See Section2.6.4 “PLL in
Value on
POR, BOR
Details
on page:
58, 133
170
171
172
‘0’.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 77

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 5-3: REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED)
File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PSPCON IBF OBF IBOV PSPMODE — — — — 0000 ---- 59, 252
SPBRG1 EUSART1 Baud Rate Generator Register Low Byte 0000 0000 59, 252
RCREG1 EUSART1 Receive Register 0000 0000 59, 260
TXREG1 EUSART1 Transmit Register 0000 0000 59, 257
TXSTA1 CSRC TX9 TXEN SYNC SENDB BRGH TRMT TX9D 0000 0010 59, 248
RCSTA1 SPEN RX9 SREN CREN ADDEN FERR OERR RX9D 0000 000x 59, 249
EEADRH
EEADR EEPROM Address Register Low Byte 0000 0000 59, 111
EEDATA EEPROM Data Register 0000 0000 59, 111
EECON2 EEPROM Control Register 2 (not a physical register) 0000 0000 59, 88
EECON1 EEPGD CFGS
IPR3 SSP2IP BCL2IP RC2IP TX2IP TMR4IP CCP5IP CCP4IP CCP3IP 1111 1111 60, 131
PIR3 SSP2IF BCL2IF RC2IF TX2IF TMR4IF CCP5IF CCP4IF CCP3IF 0000 0000 60, 125
PIE3 SSP2IE BCL2IE RC2IE TX2IE TMR4IE CCP5IE CCP4IE CCP3IE 0000 0000 60, 129
IPR2 OSCFIP CMIP
PIR2 OSCFIF CMIF
PIE2 OSCFIE CMIE
IPR1 PSPIP ADIP RC1IP TX1IP SSP1IP CCP1IP TMR2 IP TMR1IP 1111 1111 60, 130
PIR1 PSPIF ADIF RC1IF TX1IF SSP1IF CCP1IF TMR2IF TMR1IF 0000 0000 60, 124
PIE1 PSPIE ADIE RC1IE TX1 IE SSP1IE CCP1IE TMR2IE T MR1 IE 0000 0000 60, 127
MEMCON
OSCTUNE INTSRC PLLEN
TRISJ
TRISH
TRISG
TRISF TRISF7 TRISF6 TRISF5 TRISF4 TRISF3 TRISF2 TRISF1 TRISF0 1111 1111 60, 150
TRISE TRISE7 TRISE6 TRISE5 TRISE4 TRISE3 TRISE2 TRISE1 TRISE0 1111 1111 60, 148
TRISD TRISD7 TRISD6 TRISD5 TRISD4 TRISD3 TRISD2 TRISD1 TRISD0 1111 1111 60, 143
TRISC TRISC7 TRISC6 TRISC5 TRISC4 TRISC3 TRISC2 TRISC1 TRISC0 1111 1111 60, 140
TRISB TRISB7 TRISB6 TRISB5 TRISB4 TRISB3 TRISB2 TRISB1 TRISB0 1111 1111 60, 137
TRISA TRISA7
LATJ
LATH
LATG
LATF LATF7 LATF6 LATF5 LATF4 LATF3 LATF2 LATF1 LATF0 xxxx xxxx 60, 149
LATE LATE7 LATE6 LATE5 LATE4 LATE3 LATE2 LATE1 LATE0 xxxx xxxx 60, 146
LATD LATD7 LATD6 LATD5 LATD4 LATD3 LATD2 LATD1 LATD0 xxxx xxxx 60, 143
LATC LATC7 LATC6 LATC5 LATC4 LATC3 LATC2 LATC1 LATC0 xxxx xxxx 60, 140
LATB LATB7 LATB6 LATB5 LATB4 LATB3 LATB2 LATB1 LATB0 xxxx xxxx 60, 137
LATA LATA7
Legend: x = unknown , u = unchanged, - = unimplemented, q = value depends on condition
Note 1: The SBOREN bit is only available when the BOREN<1:0> Configuration bits = 01; otherwise, this bit reads as ‘0’.
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
2: These registers and/or bits are not implemented on 64-pin devices and are read as
3: The PLLEN bit is only available in specific oscillator configuration; otherwise, it is disabled and reads as
4: RA6/RA7 and their associated latch and direction bits are individually configured as port pins based on various primary oscillator modes.
5: RG5 and LATG5 are only available when Master Clear is disabled (MCLRE Configuration bit = 0); otherwise, RG5 and LATG5 read as
6: Bit 7 and Bit 6 are cleared by user software or by a POR.
7: Bit 21 of TBLPTRU allows access to the device Configuration bits.
— — — — — — EEPROM Address
— FREE WRERR WREN WR RD xx-0 x000 59, 89
— EEIP BCL1IP HLVDIP TMR3IP CCP2IP 11-1 1111 60, 131
— EEIF BCL1IF HLVDIF TMR3IF CCP2IF 00-0 0000 60, 125
— EEIE BCL1IE HLVDIE TMR3IE CCP2IE 00-0 0000 60, 128
EBDIS —WAIT1WAIT0— —WM1WM00-00 --00 60, 96
TRISJ7 TRISJ6 TRISJ5 TRISJ4 TRISJ3 TRISJ2 TRISJ1 TRISJ0 1111 1111 60, 157
TRISH7 TRISH6 TRISH5 TRISH4 TRISH3 TRISH2 TRISH1 TRISH0 1111 1111 60, 155
— — — TRISG4 TRISG3 TRISG2 TRISG1 TRISG0 ---1 1111 60, 153
(4)
LATJ7LATJ6LATJ5LATJ4LATJ3LATJ2LATJ1LATJ0xxxx xxxx 60, 156
LATH7 LATH6 LATH5 LATH4 LATH3 LATH2 LATH1 LATH0 xxxx xxxx 60, 154
— —LATG5
(4)
TRISA6
LATA6
(3)
(4)
(4)
— TUN4 TUN3 TUN2 T UN1 TUN0 00-0 0000 35, 60
TRISA5 TRISA4 TRISA3 TRISA2 TRISA1 TRISA0 1111 1111 60, 135
(5)
LATG4 LATG3 LATG2 LATG1 LATG0 --xx xxxx 60, 151
LATA5 LATA4 LATA3 LATA2 LATA1 LATA0 xxxx xxxx 60, 135
Register High Byte
‘0’. Reset values are shown for 80-pin devices;
individual unimplemented bits should be interpreted as ‘-’.
‘0’. See Section2.6.4 “PLL in
INTOSC Modes”.
When disabled, these bits read as ‘0’.
Value on
POR, BOR
---- --00 59, 111
Details
on page:
‘0’.
DS39646C-page 78 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLE 5-3: REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED)
File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
(2)
PORTJ
(2)
PORTH
PORTG
PORTF RF7 RF6 RF5 RF4 RF3 RF2 RF1 RF0 x000 0000 60, 149
PORTE RE7 RE6 RE5 RE4 RE3 RE2 RE1 RE0 xxxx xxxx 60, 146
PORTD RD7 RD6 RD5 RD4 RD3 RD2 RD1 RD0 xxxx xxxx 60, 143
PORTC RC7 RC6 RC5 RC4 RC3 RC2 RC1 RC0 xxxx xxxx 60, 140
PORTB RB7 RB6 RB5 RB4 RB3 RB2 RB1 RB0 xxxx xxxx 60, 137
PORTA RA7
SPBRGH1 EUSART1 Baud Rate Generator Register High Byte 0000 0000 61, 252
BAUDCON1 ABDOVF RCIDL
SPBRGH2 EUSART2 Baud Rate Generator Register High Byte 0000 0000 61, 252
BAUDCON2 ABDOVF RCIDL
ECCP1DEL P1RSEN P1DC6 P1DC5 P1DC4 P1DC3 P1DC2 P1DC1 P1D C0 0000 0000 61, 200
TMR4 Timer4 Register 0000 0000 61, 178
PR4 Timer4 Period Register 1111 1111 61, 178
T4CON
CCPR4H Capture/Co mpar e/P W M Register 4 High Byte xxxx xxxx 61, 180
CCPR4L C ap tur e/Co mpar e/P W M Register 4 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 61, 180
CCP4CON
CCPR5H Capture/Co mpar e/PW M Regi s ter 5 Hig h Byte xxxx xxxx 61, 180
CCPR5L C ap tur e/Co mpar e/P W M Register 5 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 61, 180
CCP5CON
SPBRG2 EUSART2 Baud Rate Generator Register Low Byte 0000 0000 61, 252
RCREG2 EUSART2 Receive Register 0000 0000 61, 260
TXREG2 EUSART2 Transmit Register 0000 0000 61, 257
TXSTA2 CSRC TX9 TXEN SYNC SENDB BRGH TRMT TX9D 0000 0010 61, 248
RCSTA2 SPEN RX9 SREN CREN ADDEN FERR OERR RX9D 0000 000x 61, 249
ECCP3AS ECCP3ASE ECCP3AS2 ECCP3AS1 ECCP3AS0 PSS3AC1 PSS3AC0 PSS3BD1 PSS3BD0 0000 0000 61, 201
ECCP3DEL P3RSEN P3DC6 P3DC5 P3DC4 P3DC3 P3DC2 P3DC1 P3D C0 0000 0000 61, 200
ECCP2AS ECCP2ASE ECCP2AS2 ECCP2AS1 ECCP2AS0 PSS2AC1 PSS2AC0 PSS2BD1 PSS2BD0 0000 0000 61, 201
ECCP2DEL P2RSEN P2DC6 P2DC5 P2DC4 P2DC3 P2DC2 P2DC1 P2D C0 0000 0000 61, 200
SSP2BUF MSSP2 Receive Buffer/Transmit Register xxxx xxxx 61, 170
SSP2ADD MSSP2 Address Register in I
SSP2STAT SMP CKE D/A
SSP2CON1 WCOL SSPOV SSPEN CKP SSPM3 SSPM2 SSPM1 SSPM0 0000 0000 61, 217
SSP2CON2 GCEN ACKSTAT ACKDT ACKEN RCEN PEN RSEN SEN 0000 0000 61, 218
Legend: x = unknown , u = unchanged, - = unimplemented, q = value depends on condition
Note 1: The SBOREN bit is only available when the BOREN<1:0> Configuration bits = 01; otherwise, this bit reads as ‘0’.
2: These registers and/or bits are not implemented on 64-pin devices and are read as
3: The PLLEN bit is only available in specific oscillator configuration; otherwise, it is disabled and reads as
4: RA6/RA7 and their associated latch and direction bits are individually configured as port pins based on various primary oscillator modes.
5: RG5 and LATG5 are only available when Master Clear is disabled (MCLRE Configuration bit = 0); otherwise, RG5 and LATG5 read as
6: Bit 7 and Bit 6 are cleared by user software or by a POR.
7: Bit 21 of TBLPTRU allows access to the device Configuration bits.
RJ7 RJ6 RJ5 RJ4 RJ3 RJ2 RJ1 RJ0 xxxx xxxx 60, 156
RH7 RH6 RH5 RH4 RH3 RH2 RH1 RH0 0000 xxxx 60, 154
— —RG5
(4)
— T4OUTPS3 T4OUTPS2 T4OUTPS1 T4OUTPS0 TMR4ON T4CKPS1 T4CKPS0 -000 0000 61, 178
— — DC4B1 DC4B0 CCP4M3 CCP4M2 CCP4M1 CCP4M0 --00 0000 61, 179
— — DC5B1 DC5B0 CCP5M3 CCP5M2 CCP5M1 CCP5M0 --00 0000 61, 179
RA6
(4)
(5)
RA5 RA4 RA3 RA2 RA1 RA0 xx0x 0000 61, 135
— SCKP BRG16 —WUEABDEN01-0 0-00 61, 250
— SCKP BRG16 —WUEABDEN01-0 0-00 61, 250
2
C™ Slave mode. MSSP2 Baud Rate Reload Register in I2C Master mode. 0000 0000 61, 170
RG4 RG3 RG2 RG1 RG0 --xx xxxx 60, 151
PSR/WUA BF 0000 0000 61, 216
‘0’. Reset values are shown for 80-pin devices;
individual unimplemented bits should be interpreted as ‘-’.
‘0’. See Section2.6.4 “PLL in
INTOSC Modes”.
When disabled, these bits read as ‘0’.
Value on
POR, BOR
Details
on page:
‘0’.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 79

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
5.3.5 STATUS REGISTER
The STATUS register, shown in Register 5-2, contains
the arithmetic status of the ALU. As wi th any other SFR,
it can be the operand for any instruction.
If the STA TUS register is the destination for an instruction
that affects the Z, DC, C, OV or N bits, the results of the
instruction are not written; instead, the STATUS register
is updated a ccording to the i nstructio n perfor med. There fore, the result of an inst ruction with th e STATUS registe r
as its destinat ion may b e differe nt than inten ded. As an
example, CLRF STATUS will set the Z bit and leave the
remaining Status bits unchanged (‘000u u1uu’).
It is recommended that only BCF, BSF, SWAPF , MOVFF
and MOVWF instructions are used to alter the STATUS
register , b ecaus e thes e ins tructi ons d o not af fect t he Z,
C, DC, OV or N bits in the STATUS register.
For other instructions that do not aff ect Status bi t s , se e
the instruction set summaries in Table 26-2 and
Table 26-3.
Note: The C and DC bits operate as the borrow
and digit borrow bits, respectively, in
subtraction.
REGISTER 5-2: STATUS: ARITHMETIC STATUS REGISTER
U-0 U-0 U-0 R/W-x R/W-x R/W-x R/W-x R/W-x
— — —NOVZDC
bit 7 bit 0
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
-n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
(1)
(2)
C
bit 7-5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4 N: Negative bit
This bit is used for signed arithmetic (2’s complement). It indicates whether the result was
negative (ALU MSB = 1).
1 = Result was negative
0 = Result was positive
bit 3 OV: Overflow bit
This bit is used for signed arithmetic (2’s complement). It indicates an overflow of the 7-bit
magnitude which causes the sign bit (bit 7 of the result) to change state.
1 = Overflow occurred for signed arithmetic (in this arithmetic operation)
0 = No overflow occurred
bit 2 Z: Zero bit
1 = The result of an arithmetic or logic operation is zero
0 = The result of an arithmetic or logic operation is not zero
(1)
bit
(2)
bit
bit 1 DC: Digit Carry/borrow
For ADDWF, ADDLW, SUBLW and SUBWF instructions:
1 = A carry-out from the 4th low-order bit of the result occurred
0 = No carry-out from the 4th low-order bit of the result
bit 0 C: Carry/borrow
For ADDWF, ADDLW, SUBLW and SUBWF instructions:
1 = A carry-out from the Most Significant bit of the result occurred
0 = No carry-out from the Most Significant bit of the result occurred
Note 1: For borrow,
operand. For rotate (RRF, RLF) instructions, this bit is lo ade d with either bit 4 or bit 3 of the sourc e re gis ter.
2: For borrow,
operand. For rotate (RRF, RLF) instructions, this bit is loaded with either the high or low-order bit of the
source register.
the polarity is reversed. A subtractio n is execu ted by adding th e 2’scomplement of the second
the polarity is reversed. A subtractio n is execu ted by adding th e 2’scomplement of the second
DS39646C-page 80 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
LFSR FSR0, 100h ;
NEXT CLRF POSTINC0 ; Clear INDF
; register then
; inc pointer
BTFSS FSR0H, 1 ; All done with
; Bank1?
BRA NEXT ; NO, clear next
CONTINUE ; YES, continue
5.4 Data Addressing Modes
Note: The execution of some instructions in the
core PIC18 instruction set are changed
when the PIC18 extended instruction set is
enabled. See Section 5.5 “Data Memory
and the Extended Instruction Set” for
more information.
The data memory space can be addr essed in se veral
ways. For most instructions, the addressing mode is
fixed. Other instructions may use up to three modes,
depending on whic h operands are used and whe ther or
not the extended instruction set is enabled.
The addressing modes are:
• Inherent
• Literal
•Direct
•Indirect
An additional addressing mode, Indexed Literal Offset,
is available when the extended instruction set is
enabled (XINST Configuration bit = 1). Its operation is
discussed in greater detail in Section 5.5.1 “Indexed
Addressing with Literal Offset”.
5.4.1 INHERENT AND LITERAL ADDRESSING
Many PIC18 control instructions do not need any argument at all; they either perform an operation that globally
affects the device or they operate implicitly on one
register. This addressing mode is known as Inherent
Addressing. Examples include SLEEP, RESET and DAW.
Other instructions work in a similar way but require an
additional explicit argument in the opcode. This is
known as Literal Addressing mode because they
require some literal value as an argument. Examples
include ADDLW and MOVLW, which respectively, add or
move a literal value to the W register. Other examples
include CALL and GOTO, which include a 20-bit
program memory address.
5.4.2 DIRECT ADDRESSING
Direct Addressing specifies all or part of the source
and/or destination address of the operation within the
opcode itself. The options are specified by the
arguments accompanying the instruction.
In the core PIC18 inst ruct ion se t, bit-ori ented and by teoriented instructions use some version of Direct
Addressing by default. All of these instructions include
some 8-bit literal address as their Least Significant
Byte. This address spec ifies either a re gister address in
one of the banks of d ata RAM ( Section 5.3.3 “General
Purpose Register File”) or a location in the Access
Bank (Section 5.3.2 “Access Bank”) as the data
source for the instruction.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 81
The Access RAM bit ‘a’ determines how the a ddre ss i s
interpreted. When ‘a’ is ‘1’, the contents of the BSR
(Section 5.3.1 “Bank Select Register (BSR)”) are
used with the address t o determin e the comple te 12-bit
address of the reg ister. When ‘a’ is ‘0’, the address is
interpreted as being a register in the Access Bank.
Addressing that uses the Access RAM is sometimes
also known as Direct Forced Addressing mode.
A few instructions, such as MOVFF, include the entire
12-bit address (either source or destination) in their
opcodes. In these cases, the BSR is ignored entirely.
The destination of the operati on’s results is determined
by the destination bit ‘d ’. Wh en ‘d’ is ‘1’, the results are
stored back in th e s o ur c e re g is ter, overw rit i n g i ts or i ginal contents. When ‘d’ is ‘0’, the results are stored in
the W register. Instructions without the ‘d’ argument
have a destin ation tha t is i mplicit in the inst ruction; their
destination is either the target register being operated
on or the W register.
5.4.3 INDIRECT ADDRESSING
Indirect Addressin g allows the u ser to access a l ocation
in data memory without giving a fixed address in the
instruction. This is done by using File Select Registers
(FSRs) as pointers to the location s to be read or written
to. Since the FSRs are themselves located in RAM as
Specia l File Regi sters, the y can als o be di rectly mani pulated under program control. This makes FSRs very
useful in imp lem ent ing data str uct ures , s uch as tabl es
and arrays in data memory.
The registers for Indirect Addressing are also
implemented with Indirect File Operands (INDFs) that
permit automatic mani pulati on of the poi nter value with
auto-incrementing, auto-decrementing or offsetting
with another va lue . Th is al lo ws f or e fficient code, us ing
loops, such as the example of clearing an entire RAM
bank in Example5-5.
EXAMPLE 5-5: HOW TO CLEAR RAM
(BANK 1) USING
INDIRECT ADDRESSING

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
FSR1H:FSR1L
0
7
Data Memory
000h
100h
200h
300h
F00h
E00h
FFFh
Bank 0
Bank 1
Bank 2
Bank 14
Bank 15
Bank 3
through
Bank 13
ADDWF, INDF1, 1
07
Using an instruction with one of the
Indirect Addressing registers as the
operand....
...uses the 12-bit address stored in
the FSR pair associated with that
register....
...to determine the data memory
location to be used in that operation.
In this case, the FSR1 pair contains
ECCh. This means the contents of
location ECCh will be added to that
of the W register and stored back in
ECCh.
xxxx1110 11001100
5.4.3.1 FSR Registers and the
INDF Operand
At the core of Indirect Addressing are three sets of
registers: FSR0, FSR1 and FSR2. Each represents a
pair of 8-bit registers, FSRnH and FSRnL. The four
upper bits of the FSRnH register are not used so each
FSR pair holds a 12-bi t va lue. T his repre sen ts a val ue
that can address the entire range of the data memory
in a linear fashion. The FSR register pairs, then, serve
as pointers to data memory locations.
Indirect Addressing is accomplished with a set of
Indirect File Operands, INDF0 through INDF2. These
can be thought of as “virtual” registers: they are
mapped in the SFR space but are not physically implemented. Reading or writin g to a particular INDF reg ister
actually accesses its corresponding FSR register pair.
A read from INDF1, for example, reads the data at the
address indi cated by FSR 1H:FSR1L. Instructi ons that
use the IND F registers a s operands actu ally use the
contents of th eir co rrespon ding FS R as a poin ter to th e
instruction’s target. The INDF operand is just a
convenient way of using the pointer.
Because Indirect Ad dressing uses a fu ll 12-bit addr ess,
data RAM banking is not necessary. Thus, the current
contents of the BSR and the Access RAM bit have no
effect on determining the target address.
5.4.3.2 FSR Registers and POSTI NC,
POSTDEC, PREINC and PLUSW
In addition to the IND F operand, eac h FSR register pair
also has four additional indirect operands. Like INDF,
these are “virtual” registers that cannot be indirectly
read or written to. Accessing these registers actually
accesses the associated FSR register pair, but also
performs a specifi c action on it s stored v alue. They ar e:
• POSTDEC: accesses the FSR value, then
automatically decrements it by 1 afterwards
• POSTINC: accesses the FSR value, then
automatically increments it by 1 afterwards
• PREINC: increments the FSR value by 1, then
uses it in the operation
• PLUSW: adds the signed value of the W register
(range of -127 to 128) t o that of th e FSR and uses
the new value in the operation.
In this context, accessing an INDF register uses the
value in the FSR registers without changing them.
Similarly, accessing a PLUSW register gives the FSR
value offset by the valu e in the W register; neithe r value
is actually changed in the operation. Accessing the
other virtual registers changes the value of the FSR
registers.
Operations on the FSRs with POSTDEC, POSTINC
and PREINC affect the entire register pair; that is, rollovers of the FSRnL register from FFh to 00h ca rry over
to the FSRnH register. On the other hand, results of
these operations do not change the value of any flags
in the STATUS register (e.g., Z, N, OV, etc.).
FIGURE 5-8: INDIRECT ADDRESSING
DS39646C-page 82 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
The PLUSW register can be used to implement a form
of Indexed Addressing in the data memory space. By
manipulating the value in the W register, users can
reach addresses that are fixed offsets from pointer
addresses. In some applications, this can be used to
implement some powerful program control structure,
such as software stacks, inside of data memory.
5.4.3.3 Operations by FSRs on FSRs
Indirect Addressing operations that target other FSRs
or virtual registers represent special cases. For example, using an FSR to point to on e of the virtual regis ters
will not result in successful operations. As a specific
case, assume that FSR0H:FSR0L contains FE7h, the
address of INDF1. Attempts to read the value of the
INDF1 using INDF0 as an operand will return 00h.
Attempts to write to INDF1 using I NDF0 as the operan d
will result in a NOP.
On the other ha nd, u sing the v irtual reg isters to w rite to
an FSR pair may n ot oc cur as plan ned. I n t hese cases ,
the value will be written to the FSR p air bu t withou t an y
incrementing or decrementing. Thus, writing to INDF2
or POSTDEC2 will write the same value to the
FSR2H:FSR2L.
Since the FSRs are physical registers mapped in the
SFR space, they can be manipulated through all direct
operations. Users should proceed cautiously when
working on these registers, particularly if their code
uses Indirect Addressing.
Similarly, operations by Indirect Addressing are generally permitted on all other SFRs. U sers shoul d exercise
the appropriate caution that they do not inadvertently
change settings that might affect the operation of the
device.
5.5 Data Memory and the Extended Instruction Set
Enabling the PIC18 extended instruction set (XINST
Configuration bit = 1) significantly changes certain
aspects of data memory and its addressing. Specifically, the use of the Access Bank for many of the core
PIC18 instructions is different; this is due to the
introduction of a new addressing mode for the data
memory space.
What does not change is just as im po rtant. The size of
the data memory space is unchanged, as well as its
linear addressing. The SFR map remains the same.
Core PIC18 instructions can still operate in both Direct
and Indirect Addressing mode; inherent and literal
instructions do not change at all. Indirect Addressing
with FSR0 and FSR1 also remain unchanged.
5.5.1 INDEXED ADDRESSING WITH LITERAL OFFSET
Enabling the PIC18 extended instruction set changes
the behavior of Indirect Addressing using the FSR2
register pair within Access RAM. Under the proper
conditions, instruc tions that us e the Access Ban k – that
is, most bit-oriented and byte-oriented instructions –
can invoke a form of Indexed Addressing using an
offset specified in the in structi on. Thi s spe cial a ddress ing mode is known as Indexed Addressing with Literal
Offset, or Indexed Literal Offset mode.
When using the extended instruction set, this
addressing mode requires the following:
• The use of the Access Ban k i s forced (‘a’ = 0) and
• The file address arg um ent is less than or e qua l to
5Fh.
Under these conditions, the file address of the instruction is not interpreted as the lower byte of an address
(used with the BSR in Direct Addres sing), or as an 8-bit
address in the Access Bank. Instead, the value is
interpreted as an offset value to an address pointer,
specified by FSR2. The offset and the contents of
FSR2 are added to obtain the target address of the
operation.
5.5.2 INSTRUCTIONS AFFECTED BY INDEXED LITERAL OFFSET MODE
Any of the core PIC18 instructions that can use Direct
Addressing are potentially affected by the Indexed
Literal Offset Addressing mode. This includes all
byte-oriented and bit-oriented instructions, or almost
one-half of the standard PIC18 instruction set.
Instructions that onl y use Inherent or Literal Addr essing
modes are unaffecte d.
Additionally, byte-oriented and bit-oriented instructions
are not affected if they do not use the Access Bank
(Access RAM bit is ‘1’), or include a fi le ad dres s of 60 h
or above. Instructions meeting these criteria will
continue to execute as be fore. A comp aris on of the di fferent possible addressing modes when the extended
instruction set is enabled in shown in Figure 5-9.
Those who desire to use byte-oriented or bit-oriented
instructions in the Indexed Literal Offset mode should
note the changes to assembler syntax for this mode.
This is described in more detail in Section 26.2.1
“Extended Instruction Syntax”.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 83

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
EXAMPLE INSTRUCTION: ADDWF, f, d, a (Opcode: 0010 01da ffff ffff)
When ‘a’ = 0 and f ≥ 60h:
The instruction executes in
Direct Forced mode. ‘f’ is interpreted as a location in the
Access RAM between 060h
and 0FFh. This is the sam e as
locations 060h to 07Fh
(Bank 0) and F80h to FFFh
(Bank 15) of data memory.
Locations below 60h are not
available in this addressing
mode.
When ‘a’ = 0 and f ≤ 5Fh:
The instruction executes in
Indexed Literal Offset mode. ‘f’
is interpreted as an offset to the
address value in FSR2. The
two are added together to
obtain the address of the target
register for the instruction. The
address can be anywhere in
the data memory space.
Note that in this mode, the
correct syntax is now:
ADDWF [k], d
where ‘k’ is the same as ‘f’.
When ‘a’ = 1 (all values of f):
The instruction executes in
Direct mode (also known as
Direct Long mode). ‘f’ is interpreted as a location in one of
the 16 banks of the data
memory space. The bank is
designated by the Bank Sel ect
Register (BSR). The address
can be in any implemented
bank in the data memory
space.
000h
060h
100h
F00h
F80h
FFFh
Valid range
00h
60h
80h
FFh
Data Memory
Access RAM
Bank 0
Bank 1
through
Bank 14
Bank 15
SFRs
000h
080h
100h
F00h
F80h
FFFh
Data Memory
Bank 0
Bank 1
through
Bank 14
Bank 15
SFRs
FSR2H FSR2L
ffffffff001001da
ffffffff001001da
000h
080h
100h
F00h
F80h
FFFh
Data Memory
Bank 0
Bank 1
through
Bank 14
Bank 15
SFRs
for ‘f’
BSR
00000000
080h
FIGURE 5-9: COMPARING ADDRESSING OPTIONS FOR BIT-ORIENTED AND
BYTE-ORIENTED INSTRUCTIONS (EXTENDED INSTRUCTION SET ENABLED)
DS39646C-page 84 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Data Memory
000h
100h
200h
F80h
F00h
FFFh
Bank 1
Bank 15
Bank 2
through
Bank 14
SFRs
05Fh
ADDWF f, d, a
FSR2H:FSR2L = 120h
Locations in the region
from the FSR2 Pointer
(120h) to the pointer plus
05Fh (17Fh) are mapped
to the bottom of the
Access RAM (000h-05Fh).
Locations in Bank 0 from
060h to 07Fh are mapped,
as usual, to the middle half
of the Access Bank.
Special File Registers at
F80h through FFFh are
mapped to 80h through
FFh, as usual.
Bank 0 addresses below
5Fh can still be addressed
by using the BSR.
Access Bank
00h
80h
FFh
7Fh
Bank 0
SFRs
Bank 1 “Window”
Bank 0
Bank 0
Window
Example Situation:
07Fh
120h
17Fh
5Fh
Bank 1
5.5.3 MAPPING THE ACCESS BANK IN INDEXED LITERAL OFFSET MODE
The use of Indexed Literal Offset Addressing mode
effectively chan ges how the first 96 locati ons of Access
RAM (00h to 5Fh) are m ap ped . R at her tha n c on taining
just the contents of the bottom half of Bank 0, this mode
maps the contents from Bank 0 and a user defined
“window” that can be located anywhere in the data
memory space. The value of FSR2 establishes the
lower boundary of the addresses mapped into the
window, while the upper boundary is defined by FSR2
plus 95 (5Fh). Addresses in the Access RAM above
Remapping of the Access Bank applies only to operations using the I ndexed Lite ral Offs et mode. Ope rations
that use the BSR (Access RAM bit is ‘1’) will continue
to use Direct Addressing as before.
5.6 PIC18 Instruction Execution and the Extended Instruction Set
Enabling the extended instruction set adds eight
additional commands to the existing PIC18 instruction
set. These instructions are executed as described in
Section 26.2 “Extended Instruction Set”.
5Fh are mapped as previously described (see
Section 5.3.2 “Access Ban k”). An example of Access
Bank remapping in this addressing mode is shown in
Figure 5-10.
FIGURE 5-10: REMAPPING THE ACCESS BANK WITH INDEXED LITERAL
OFFSET ADDRESSING
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 85

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
NOTES:
DS39646C-page 86 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Table Pointer
(1)
Table Latch (8-bit)
Program Memory
TBLPTRH TBLPTRL
TABLAT
TBLPTRU
Instruction: TBLRD*
Note 1:Table Pointer register points to a byte in program memory.
Program Memory
(TBLPTR)
6.0 FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY
The Flash program memory is readable, writable and
erasable during normal operation over the entire V
range.
A read from program memory is executed on one byte
at a time. A write to program memory is executed on
blocks of 64 bytes at a time. Program memory is
erased in blocks of 64 bytes at a time. A bulk erase
operation may not be issued from user code.
Writing or erasing program memory will cease
instruction fetches until the operation is complete. The
program memory cannot be accessed during the write
or erase, therefore, code cannot execute. An internal
programming timer terminates program memory writes
and erases.
A value written to progra m memory does not nee d to be
a valid instruction. Executing a program memory
location that forms an invalid instruction results in a
NOP.
DD
6.1 Table Reads and Table Writes
In order to read and write program memory, there are
two operations that allow the processor to move bytes
between the program memory sp ace and the dat a RAM:
• Table Read (TBLRD)
• Table Write (TBLWT)
The program memory space is 16 bits wide, while the
data RAM space is 8 bits wide. Table reads and table
writes move data between these two memory spaces
through an 8-bit register (TABLAT).
Table read operations retrieve data from program
memory and place it into the data RAM space.
Figure 6-1 shows the operation of a table read with
program memory and data RAM.
Table write opera tions s tor e data from t he da ta memo ry
space into holding registers in program memory. The
procedure to write the contents of the holding registers
into program memory is detailed in Section 6.5 “Writin g
to Flash Program Memory”. Figure6-2 shows the
operation of a table write with program memory and data
RAM.
Table operations work with byte entities. A table block
containing data, rather than program instructions, is not
required to be word aligned. Therefore, a table block can
start and end at any byte address. If a t able write is being
used to write executable code into program memory,
program instructions will need to be word aligned.
FIGURE 6-1: TABLE READ OPERATION
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 87

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
Table Pointer
(1)
Table Latch (8-bit)
TBLPTRH TBLPTRL
TABLAT
Program Memory
(TBLPTR)
TBLPTRU
Instruction: TBLWT*
Note1: Table Pointer actually points to one of 64 holding registers, the address of which is determined by
TBLPTRL<5:0>. The process for physically writing data to the program memor y array is discusse d in
Section 6.5 “Writing to Flash Program Memor y ”.
Holding Registers
Program Memory
FIGURE 6-2: TABLE WRITE OPERATION
6.2 Control Registers
Several control registers are used in conjunction with
the TBLRD and TBLWT instructions. These include the:
• EECON1 register
• EECON2 register
• TABLAT register
• TBLPTR registers
6.2.1 EECON1 AND EECON2 REGISTERS
The EECON1 register (Register 6-1) is the control
register for memory acce sses. The EECO N2 register is
not a physical register; it is used exclusively in the
memory write and erase sequences. Reading
EECON2 will read all ‘0’s.
The EEPGD control bit determines if th e access will be
a program or data EEPROM memory access. When
clear, any subsequent operations will operate on the
data EEPROM memory. When set, any subsequent
operations will operate on the program memory.
The CFGS control bit determines if the access will be
to the Configuration/C alib ration re giste rs or to pro gram
memory/data EEPROM memory. When set,
subsequent operations will operate on Configuration
registers regardless of EEPGD (see Section 25.0
“Special Featur es of the CPU”). When clear , memor y
selection access is determined by EEPGD.
The FREE bit, when set, will allow a program memory
erase operation. When FREE is set, the erase
operation is initiated on the next WR command. When
FREE is clear , only wr ite s are enab led .
The WREN bit, when set, will allow a write operation.
On power-up, the WREN bit is c lear . The WRERR bit is
set in hardware when the WR bit is set and cleared
when the internal programming timer expires and the
write operation is complete.
Note: During normal operation, the WRERR is
read as ‘1’. This can indicate that a write
operation was prematurely terminated by
a Reset, or a write operation was
attempted improperly.
The WR control bit initiates write operations. The bit
cannot be cleared, only set, in software; it is cleared in
hardware at the completion of the write operation.
Note: The EEIF interrupt flag bit (PIR2<4>) is set
when the write is complete. It must be
cleared in software.
DS39646C-page 88 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
REGISTER 6-1: EECON1: EEPROM CONTROL REGISTER 1
R/W-x R/W-x U-0 R/W-0 R/W-x R/W-0 R/S-0 R/S-0
EEPGD CFGS
bit 7 bit 0
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
-n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
bit 7 EEPGD: Flash Program or Data EEPROM Memory Select bit
1 = Access Flash program memory
0 = Access data EEPROM memory
bit 6 CFGS: Flash Program/Data EEPROM or Configuration Select bit
1 = Access Configuration registers
0 = Access Flash program or data EEPROM memory
bit 5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4 FREE: Flash Row Erase Enable bit
1 = Erase the program memory row addressed by TBLPTR on the next WR command
(cleared by completion of erase operation)
0 = Perform write only
bit 3 WRERR: Flash Program/Data EEPROM Error Flag bit
1 = A write operation is prematurely terminated (any Reset during self-timed programming in normal
operation, or an improper write attempt)
0 = The write operation completed
bit 2 WREN: Flash Program/Data EEPROM Write Enable bit
1 = Allows write cycles to Flash program/data EEPROM
0 = Inhibits write cycles to Flash program/data EEPROM
bit 1 WR: Write Control bit
1 = Initiates a data EEPROM erase/write cycle or a program memory erase cycle or write cycle.
(The operation is self-timed and the bit is cleared by hardware once write is complete.
The WR bit can only be set (not cleared) in software.)
0 = Write cycle to the EEPROM is complete
bit 0 RD: Read Control bit
1 = Initiates an EEPROM read (Read takes one cycle. RD is cleared in hardware. The RD bit can only
be set (not cleared) in software. RD bit cannot be set when EEPGD = 1 or CFGS = 1.)
0 = Does not initiate an EEPROM read
— FREE WRERR
(1)
WREN WR RD
(1)
Note 1: When a WRERR occurs, the EEPGD and CFGS bits are not cleared.
This allows tracing of the error cond ition.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 89

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
21 16 15 87 0
TABLE ERASE/WRITE
TABLE WRITE
TABLE READ – TBLPTR<21:0>
TBLPTRLTBLPTRH
TBLPTRU
TBLPTR<5:0>TBLPTR<21:6>
6.2.2 TABLAT – TABLE LATCH REGISTER
The Table Latch (TABLAT) is an 8-bit register mapped
into the SFR space. The Table Latch register is used to
hold 8-bit data during data transfers between program
memory and data RAM.
6.2.3 TBLPTR – TABLE POINTER REGISTER
The Table Poin ter (T BLPTR ) re gis ter add res se s a byte
within the program memory. The TBLPTR is comprised
of three SFR registers : Table Pointer Upper Byte, Table
Pointer High Byte and Table Pointer Low Byte
(TBLPTRU:TBLPTRH:TBLPTRL). These three registers join to form a 22-bit wide po inter. The low-o rder
21 bits allow the device to address up to 2 Mbytes of
program memory sp ace. Th e 22nd b it allow s acce ss to
the device ID, the user ID and the Configuration bits.
The Table Pointer register, TBLPTR, is used by the
TBLRD and TBLWT instructi ons . T hes e i ns truc tio ns ca n
update the TBLPTR in one of four ways based on the
table operation. These operations are shown in
T abl e 6-1. These op erations on the TBLPT R only af fect
the low-order 21 bits.
6.2.4 TABLE POINTER BOUNDARIES
TBLPTR is used in reads, writes and erases of the
Flash program memory.
When a TBLRD is executed, al l 22 bits of th e T BLPT R
determine which byte is read from program memory
into TABL AT.
When a TBLWT is executed, the six LSbs of the Table
Pointer register (TBLPTR<5:0>) determine which of
the 64 program memory holding registers is written to.
When the timed write to program memory begins (via
the WR bit), the 16 MSbs of the TBLPTR
(TBLPTR<21:6>) determine which program memory
block of 64 bytes is written to. For more detail, see
Section 6.5 “Writing to Flash Program Memory”.
When an erase of program memory is executed, the
16 MSbs of the Table Pointer register (TBLPTR<21:6>)
point to the 64-byte block that will be erased. The Least
Significant bits (TBLPTR<5:0>) are ignored.
Figure 6-3 describes the relevant boundaries of
TBLPTR based on Flash program memory operations.
TABLE 6-1: TABLE POINTER OPERATIONS WITH TBLRD AND TBLWT INSTRUCTIONS
Example Operation on Table Pointer
TBLRD*
TBLWT*
TBLRD*+
TBLWT*+
TBLRD*TBLWT*-
TBLRD+*
TBLWT+*
TBLPTR is incremented after the read/write
TBLPTR is decremented after the read/write
TBLPTR is incremented before the read/write
TBLPTR is not modified
FIGURE 6-3: TABLE POINTER BOUNDARIES BASED ON OPERATION
DS39646C-page 90 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
(Even Byte Address)
Program Memory
(Odd Byte Address)
TBLRD
TABLAT
TBLPTR = xxxxx1
FETCH
Instruction Register
(IR)
Read Register
TBLPTR = xxxxx0
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_UPPER ; Load TBLPTR with the base
MOVWF TBLPTRU ; address of the word
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_HIGH
MOVWF TBLPTRH
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF TBLPTRL
READ_WORD
TBLRD*+ ; read into TABLAT and increment
MOVF TABLAT, W ; get data
MOVWF WORD_EVEN
TBLRD*+ ; read into TABLAT and increment
MOVF TABLAT, W ; get data
MOVF WORD_ODD
6.3 Reading the Flash Program Memory
The TBLRD instruction is used to retrieve data from
program memory and places it into data RAM. Table
reads from program memory are pe rformed one by te at
a time.
TBLPTR poi nts to a byte address in pro gram space.
Executing TBLRD places the byte pointed to into
TABLAT. In addition, TBLPTR can be modified
automatically for the next table read operation.
The internal program memory is typically organize d by
words. The Least Sig nificant b it of th e address selects
between the high and low bytes of the word. Figure 6-4
shows the interface between the internal program
memory and the TABLAT.
FIGURE 6-4: READS FROM FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY
EXAMPLE 6-1: READING A FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY WORD
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 91

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_UPPER ; load TBLPTR with the base
MOVWF TBLPTRU ; address of the memory block
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_HIGH
MOVWF TBLPTRH
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF TBLPTRL
ERASE_ROW
BSF EECON1, EEPGD ; point to Flash program memory
BCF EECON1, CFGS ; access Flash program memory
BSF EECON1, WREN ; enable write to memory
BSF EECON1, FREE ; enable Row Erase operation
BCF INTCON, GIE ; disable interrupts
Required MOVLW 55h
Sequence MOVWF EECON2 ; write 55h
MOVLW 0AAh
MOVWF EECON2 ; write 0AAh
BSF EECON1, WR ; start erase (CPU stall)
BSF INTCON, GIE ; re-enable interrupts
6.4 Erasing Flash Program Memory
The minimum eras e block is 32 wo rds or 64 b ytes. Only
through the use of an external programmer, or through
ICSP control, can larger blocks of program memory be
bulk erased. Word erase in the Flash array is not
supported.
When initiating an erase sequence from the microcontroller itself, a blo ck of 64 bytes of program memo ry
is erased. The Most Significant 16 bits of the
TBLPTR<21:6> point to the block being erased.
TBLPTR<5:0> are ignored.
The EECON1 register comma nds the erase operation.
The EEPGD bit must be set to point to the Flash
program memory. The WREN bit must be set to enable
write operations. The F REE bit is set to select an erase
operation.
For protection, the wri te i ni tiat e s equ enc e f or EECO N2
must be used.
A long write is nec essa ry for erasin g the i nternal Flash.
Instruction execution is halted while in a long write
6.4.1 FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY ERASE SEQUENCE
The sequence of events for erasing a block of internal
program memory location is:
1. Load Table Pointer register with address of row
being erased.
2. Set the EECON1 register for the erase operation:
• set EEPGD bit to point to program memory;
• clear the CFGS bit to access program memory;
• set WREN bit to enable writes;
• set FREE bit to enable the erase.
3. Disable interrupts.
4. Write 55h to EECON2.
5. Write 0AAh to EECON2.
6. Set the WR bit. This will begin the row erase
cycle.
7. The CPU will stall for duration of the erase for
TIW (see parameter D1 33 A).
8. Re-enable interrupts.
cycle. The long write will be terminated by the internal
programming timer.
EXAMPLE 6-2: ERASING A FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY ROW
DS39646C-page 92 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
TABLAT
TBLPTR = xxxx3FTBLPTR = xxxxx1TBLPTR = xxxxx0
Write Register
TBLPTR = xxxxx2
Program Memory
Holding Register Holding Register Holding Register Holding Register
8
8 8 8
6.5 Writing to Flash Program Memory
The minimum programming block is 32 words or
64 bytes. Word or byte programming is not supported.
Table writes are used internally to load the holding
registers needed to program the Flash memory. There
are 64 holding registers used by the table writes for
programming.
Since the Table Latch (TABLAT) is only a single byte, the
TBLWT instruction may need to be executed 64 times for
each programming operation. All of the t able w rite ope rations will essentially be short writes because only the
holding registers are written. At the end of updating the
64 holding registers, the EECON1 register must be
written to in order to start the programming operation
with a long write.
The long write is necessary for programming the internal Flash. Instruc tion exe cution is halted wh ile in a long
write cycle. The long write will be terminated by the
internal programming timer.
The EEPROM on-chip timer controls the write time.
The write/erase voltages are generated by an on-chip
charge pump, rated to operate over the voltage range
of the device.
Note: The default value of the holding registers on
device Resets and aft er write op eratio ns is
FFh. A write of FFh to a holding register
does not modify that byte. T his mea ns th at
individual bytes of program memory may be
modified, provided that the change does not
attempt to change any bi t from a ‘0’ to a ‘1’.
When modifying individual bytes, it is not
necessary to load all 64 holding registers
before executing a write ope ration.
FIGURE 6-5: TABLE WRITES TO FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY
6.5.1 FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY WRITE SEQUENCE
The sequence of events for programming an internal
program memory location should be:
1. Read 64 bytes into RAM.
2. Update data values in RAM as necessary.
3. Load Table Pointer register with address being
erased.
4. Execute the row erase procedure.
5. Load Table Pointer register with address of first
byte being written.
6. Write the 64 bytes into the ho lding regis ters wi th
auto-increment.
7. Set the EECON1 register for the write operatio n:
• set EEPGD bit to point to program memory;
• clear the CFGS bit to access program memory;
• set WREN to enable byte writes.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 93
8. Disable interrupts.
9. Write 55h to EECON2.
10. Write 0AAh to EECON2.
1 1. Set the WR bit. This will begin the write cycl e.
12. The CPU will stall for duration of the write for T
(see parameter D133A).
13. Re-enable interrupts.
14. Verify the memory (table read).
An example of the required code is shown in
Example 6- 3 on the following page.
Note: Before setting the WR bit, the Table
Pointer address needs to be within the
intended address range of the 64 bytes in
the holding register.
IW

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
MOVLW D'64' ; number of bytes in erase block
MOVWF COUNTER
MOVLW BUFFER_ADDR_HIGH ; point to buffer
MOVWF FSR0H
MOVLW BUFFER_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF FSR0L
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_UPPER ; Load TBLPTR with the base
MOVWF TBLPTRU ; address of the memory block
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_HIGH
MOVWF TBLPTRH
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF TBLPTRL
READ_BLOCK
TBLRD*+ ; read into TABLAT, and inc
MOVF TABLAT, W ; get data
MOVWF POSTINC0 ; store data
DECFSZ COUNTER ; done?
BRA READ_BLOCK ; repeat
MODIFY_WORD
MOVLWD ATA_ADDR_HIGH ; point to buffer
MOVWF FSR0H
MOVLW DATA_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF FSR0L
MOVLW NEW_DATA_LOW ; update buffer word
MOVWF POSTINC0
MOVLW NEW_DATA_HIGH
MOVWF INDF0
ERASE_BLOCK
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_UPPER ; load TBLPTR with the base
MOVWF TBLPTRU ; address of the memory block
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_HIGH
MOVWF TBLPTRH
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF TBLPTRL
BSF EECON1, EEPGD ; point to Flash program memory
BCF EECON1, CFGS ; access Flash program memory
BSF EECON1, WREN ; enable write to memory
BSF EECON1, FREE ; enable Row Erase operation
BCF INTCON, GIE ; disable interrupts
MOVLW 55h
Required MOVWF EECON2 ; write 55h
Sequence MOVLW 0AAh
MOVWF EECON2 ; write 0AAh
BSF EECON1, WR ; start erase (CPU stall)
BSF INTCON, GIE ; re-enable interrupts
TBLRD*- ; dummy read decrement
MOVLW BUFFER_ADDR_HIGH ; point to buffer
MOVWF FSR0H
MOVLW BUFFER_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF FSR0L
WRITE_BUFFER_BACK
MOVLW D'64' ; number of bytes in holding register
MOVWF COUNTER
WRITE_BYTE_TO_HREGS
MOVFF POSTINC0, WREG ; get low byte of buffer data
MOVWF TABLAT ; present data to table latch
TBLWT+* ; write data, perform a short write
; to internal TBLWT holding register.
DECFSZ COUNTER ; loop until buffers are full
BRA WRITE_WORD_TO_HREGS
EXAMPLE 6-3: WRITING TO FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY
DS39646C-page 94 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
PROGRAM_MEMORY
BSF EECON1, EEPGD ; point to Flash program memory
BCF EECON1, CFGS ; access Flash program memory
BSF EECON1, WREN ; enable write to memory
BCF INTCON, GIE ; disable interrupts
MOVLW 55h
Required MOVWF EECON2 ; write 55h
Sequence MOVLW 0AAh
MOVWF EECON2 ; write 0AAh
BSF EECON1, WR ; start program (CPU stall)
BSF INTCON, GIE ; re-enable interrupts
BCF EECON1, WREN ; disable write to memory
EXAMPLE 6-3: WRITING TO FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY (CONTINUED)
6.5.2 WRITE VERIFY
Depending on the application, good programming
practice may dictate that the value written to the
memory should be verified against the original value.
This should be used in applications where excessive
writes can stress bits near the specification limit.
6.5.3 UNEXPECTED TERMINATION OF WRITE OPERATION
If a write is termin ate d b y a n u npl anned event, such as
loss of power or an unexpected Reset, the memory
location just pr ogrammed shou ld be verifi ed and repr ogrammed if needed. If the wr ite operatio n is interrupte d
by a MCLR
normal operation, the user can check the WRERR bit
and rewrite the location(s) as needed.
Reset or a WDT Time-out Reset during
TABLE 6-2: REGISTERS ASSOCIATED WITH PROGRAM FLASH MEMORY
Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TBLPTRU
TBPLTRH Program Memory Table Pointer High Byte (TBLPTR<15:8>) 57
TBLPTRL Program Memory Table Pointer Low Byte (TBLPTR<7:0>) 57
TABLAT Program Memory Table Latch 57
INTCON GIE/GIEH PEIE/GIEL TMR0IE INT0IE RBIE TMR0IF INT0IF RBIF 57
EECON2 EEPROM Control Register 2 (not a physical register) 59
EECON1 EEPGD CFGS
IPR2
PIR2
PIE2
Legend: — = unimplemented, read as ‘0’. Shaded cells are not used during Flash/EEPROM access.
Note 1: Bit 21 of TBLPTRU allows access to the device Configuration bits.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 95
— —bit 21
OSCFIP CMIP — EEIP BCL1IP HLVDIP TMR3IP CCP2IP 60
OSCFIF CMIF — EEIF BCL1IF HLVDIF TMR3IF CCP2IF 60
OSCFIE CMIE — EEIE BCL1IE HLVDIE TMR3IE CCP2IE 60
6.5.4 PROTECTION AGAINST SPURIOUS WRITES
To protect against spurious writes to Flash program
memory, the write initiate sequence must also be
followed. See Section 25.0 “Special Features of the
CPU” for more detail.
6.6 Flash Program Operation During
Code Protection
See Section 25.5 “Program Verification and Code
Protection” for details on code protection of Flash
program memory.
Reset
Values on
page
(1)
Program Memory T able Pointer Upper Byte (TBLPTR<20:16>) 57
— FREE WRERR WREN WR RD 59

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
NOTES:
DS39646C-page 96 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
7.0 EXTERNAL MEMORY BUS
Note: The External Memory Bus is not imple-
mented on PIC18F6527/6622/6627/6722
(64-pin) devices.
The External Memory Bus (EMB) allows the device to
access external memory devices (such as Flash,
EPROM, SRAM , etc.) as pro gram or data mem ory. It
supports both 8-bit and 16-bit Data Width modes and
four address widths from 8 to 20 bits.
The bus is implemented with 28 pins, multiplexed
across four I/O ports. Three ports (PORTD, PORTE
and PORTH) are m ultiplexed with th e address/dat a bus
for a total of 20 available lines, while PORTJ is
multiplexed with the bus cont rol sig nal s.
A list of the pins and their functions is provided in
Table 7-1.
T ABLE 7-1: PIC18F8527/8622/8627/8722 EXTERNAL BUS – I/O PORT FUNCTIONS
Name Port Bit External Memory Bus Function
RD0/AD0 PORTD 0 Address bit 0 or Data bit 0
RD1/AD1 PORTD 1 Address bit 1 or Data bit 1
RD2/AD2 PORTD 2 Address bit 2 or Data bit 2
RD3/AD3 PORTD 3 Address bit 3 or Data bit 3
RD4/AD4 PORTD 4 Address bit 4 or Data bit 4
RD5/AD5 PORTD 5 Address bit 5 or Data bit 5
RD6/AD6 PORTD 6 Address bit 6 or Data bit 6
RD7/AD7 PORTD 7 Address bit 7 or Data bit 7
RE0/AD8 PORTE 0 Address bit 8 or Data bit 8
RE1/AD9 PORTE 1 Address bit 9 or Data bit 9
RE2/AD10 PORTE 2 Address bit 10 or Data b it 10
RE3/AD11 PORTE 3 Address bit 11 or Data bit 11
RE4/AD12 PORTE 4 Address bit 12 or Data b it 12
RE5/AD13 PORTE 5 Address bit 13 or Data b it 13
RE6/AD14 PORTE 6 Address bit 14 or Data b it 14
RE7/AD15 PORTE 7 Address bit 15 or Data b it 15
RH0/A16 PORTH 0 Address bi t 16
RH1/A17 PORTH 1 Address bi t 17
RH2/A18 PORTH 2 Address bi t 18
RH3/A19 PORTH 3 Address bi t 19
RJ0/ALE PORTJ 0 Address Latch Enable (ALE) Control pin
RJ1/OE
RJ2/WRL
RJ3/WRH
RJ4/BA0 POR TJ 4 Byte Address bit 0 (BA0)
RJ5/CE
RJ6/LB
RJ7/UB
Note: For the sake of clarity, only I/O port and external bus assign ment s a re show n he re. One or more additi onal
multiplexed features may be available on some pins.
PORTJ 1 Output Enable (OE) Control pin
PORTJ 2 Write Low (WRL) Control pin
PORTJ 3 Write High (WRH) Control pin
PORTJ 5 Chip Enable (CE) Control pin
PORTJ 6 Lower Byte Enable (LB) Control pin
PORTJ 7 Upper Byte Enable (UB) Control pin
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS39646C-page 97

PIC18F8722 FAMILY
7.1 External Memory Bus Control
The operation of the interface is controlled by the
MEMCON register (Register 7-1). This register is
available in all program memory operating modes
except Microcontrol le r mode. In this mode, the reg is ter
is disabled and cannot be written to.
The EBDIS bit (MEMCON<7>) controls the operation
of the bus and related port functions. Clearing EBDIS
enables the interface and disables the I/O functions of
the ports, as well as any other functions multiplexed to
those pins. Setting the bit enables the I/O ports and
other functions but allows the interface to override
everything else on the pins when an external memory
operation i s required. By def ault, the external bus is
always enabled and disables all other I/O.
The operation of the EBDIS bit is also influenc ed by the
program memory mode being used. This is discussed
in more detail in Section 7.4 “Program Memory
Modes and the External Memory Bus”.
The WAIT bits allow for the addition of wait states to
external memory operations. The use of these bits is
discussed in Section 7.3 “Wait States”.
The WM bits select th e p artic ular ope rating m ode use d
when the bu s is o peratin g in 16 -bit D ata Width mode.
These are discussed in more detail in Section 7.5
“16-Bit Data Width Modes”. Thes e bits have no ef fect
when an 8-bit Data Width mode is selected.
WM<1:0>: TBLWT Operation with 16-Bit Data Bus
Width Select bits
1x = Word Write mode: TABLA T0 and TABLAT1 word
output, WRH
01 = Byte Select mode: TABLAT data copied on both
MSB and LSB; WRH and (UB or LB) will activate
active when TABLAT1 written
REGISTER 7-1: MEMCON: EXTERNAL MEMORY BUS CONTROL REGISTER
R/W-0 U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 U-0 U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
EBDIS —WAIT1WAIT0— —WM1WM0
bit 7 bit 0
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
-n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
bit 7 EBDIS: External Bus Disable bit
1 = External bus enabled when microcontroller accesses external memory;
otherwise, all external bus drivers are mapped as I/O ports
0 = External bus always enabled, I/O ports are disabled
bit 6 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 5-4 WAIT<1:0>: Table Reads and Writes Bus Cycle Wait Count bits
11 = Table reads and writes will wait 0 T
10 = Table reads and writes will wait 1 TCY
01 = Table reads and writes will wait 2 TCY
00 = Table reads and writes will wait 3 TCY
bit 3-2 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 1-0 WM<1:0>: TBLWT Operation with 16-Bit Data Bus Width Select bits
1 = Result was negative
0 = Result was positive
CY
DS39646C-page 98 © 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...