Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
PDIUSBH11
Universal Serial Bus Hub
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1997 Apr 17
1997 Aug 01
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH1 1Universal Serial Bus Hub
FEA TURES
•Complies with the Universal Serial Bus specification Rev. 1.0
•Four downstream ports with per packet connectivity
•Embedded function with two endpoints (control and interrupt)
•Integrated FIFO memory for hub and embedded function
•Automatic protocol handling
•Versatile I
2
C interface
•Allows software control of monitor
•Compliant with USB Human Interface and Display Device Class
•Single 3.3V supply with 5V tolerant I/O
DESCRIPTION
The Philips Semiconductors PDIUSBH1 1 is a compound USB hub
IC (hub plus embedded function).
It is used in a microcontroller based system and communicates with
the system microcontroller over the I
approach to implementing a hub and embedded function allows the
designer to maintain the system microcontroller of choice and retain
existing architecture. This cuts down development time and offers
the most cost-effective solution.
Ideal applications for the IC include computer monitors and
keyboards.
The PDIUSBH11 conforms to the USB specification 1.0 and I
serial interface specification. It is also compliant with the USB
Human Input Device and Monitor Control Class specifications.
2
C serial bus. This modular
The embedded function of the PDIUSBH11 appears as PORT1 to
the host system and the four downstream ports are numbered 2
through 5.
ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGES TEMPERATURE RANGE OUTSIDE NORTH AMERICA NORTH AMERICA PKG. DWG. #
32-pin plastic SO 0°C to +70°C PDIUSBH11 D PDIUSBH11 D SOT287-1
32-pin plastic SDIP 0°C to +70°C PDIUSBH11 NB PDIUSBH11 NB SOT232-1
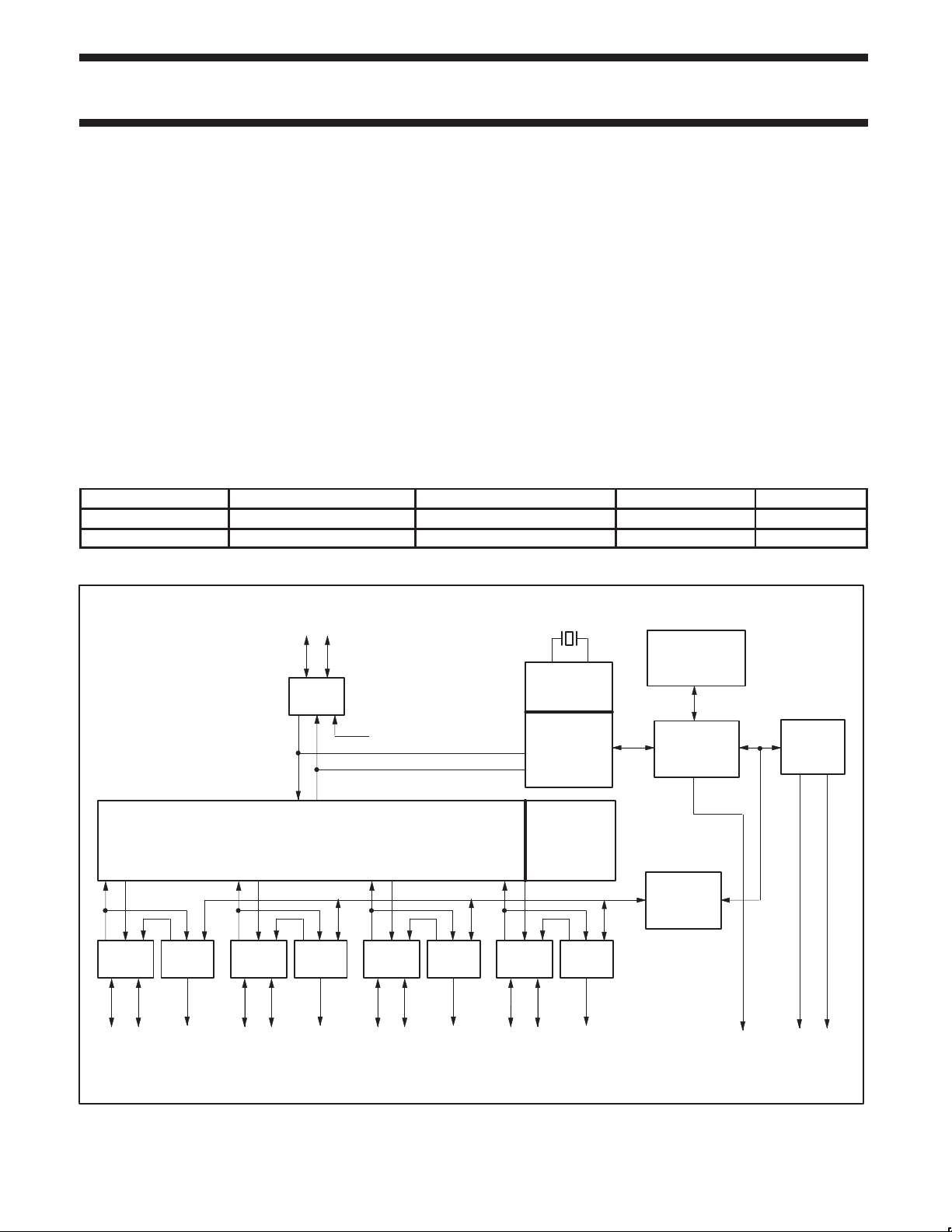
BLOCK DIAGRAM
UPSTREAM
PORT
D+
ANALOG
T
X/RX
D–
48 MHz
BIT CLOCK
RECOVERY
INTEGRATED
RAM
2
C
FULL SPEED
HUB
REPEATER
ANALOG
T
X/RX
D–D+
DOWNSTREAM
PORT 2
PORT
CONTROL
LED
ENABLE
ANALOG
T
X/RX
D–D+
DOWNSTREAM
PORT 3
PORT
CONTROL
LED
ENABLE
ANALOG
T
X/RX
D–D+
DOWNSTREAM
PORT 4
PORT
CONTROL
LED
ENABLE
ANALOG
T
X/RX
DOWNSTREAM
PORT 5
NOTE:
1. This is a conceptual block diagram and does not include each individual signal.
PHILIPS
SIE
END OF
FRAME
TIMERS
D–D+
PORT
CONTROL
LED
ENABLE
MEMORY
MANAGEMENT
UNIT
GENERAL
PORT
CONTROLLER
2
C
I
SLAVE
INTERFACE
INTERRUPT SDA SCL
SV00226
1997 Aug 01 853–1968 18238
2
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
HUB
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
Analog Transceivers
These transceivers interface directly to the USB cables through
some termination resistors. They are capable of transmitting and
receiving serial data at both “full speed” (12 Mbit/s) and “low speed”
(1.5 Mbit/s) data rates.
Hub Repeater
The hub repeater is responsible for managing connectivity on a per
packet basis. It implements packet signaling connectivity and
resume connectivity.
Low speed devices can be connected to downstream ports since the
repeater will not propagate upstream packets to downstream ports,
to which low speed devices are connected, unless they are
preceded by a PREAMBLE PID.
End of Frame Timers
This block contains the specified EOF1 and EOF2 timers which are
used to detect loss-of-activity and babble error conditions in the hub
repeater. The timers also maintain the low-speed keep-alive strobe
which is sent at the beginning of a frame.
General and Individual Port Controller
The general and individual port controllers together provide status
and control of individual downstream ports. Via the I
2
C-interface a
microcontroller can access the downstream ports and request or
change the status of each individual port.
Any change in the status or settings of the individual port will result
in an interrupt request. Via an interrupt register, the servicing
microcontroller can look up the downstream port which generated
ENDPOINT DESCRIPTIONS
The following table summarizes the endpoints supported by the PDIUSBH11.
FUNCTION
EMBEDDED
ENDPOINT
NUMBER
ENDPOINT TYPE TRANSFER TYPE DIRECTION
0 Default Control IN, OUT 8
1 Status change Interrupt IN 1
0 Default Control IN, OUT 8
1 Interrupt Interrupt IN 8
the interrupt and request its new status. Any port status change can
then be reported to the host via the hub status change (interrupt)
endpoint.
Bit Clock Recovery
The bit clock recovery circuit recovers the clock from the incoming
USB data stream using (4X) over-sampling principle. It is able to
track jitter and frequency drift specified by the USB spec.
Philips Serial Interface Engine (PSIE)
The Philips SIE implements the full USB protocol layer. It is
completely hardwired for speed and needs no firmware intervention.
The functions of this block include: synchronization pattern
recognition, parallel / serial conversion, bit stuffing / destuffing, CRC
checking / generation, PID verification / generation, address
recognition, handshake evaluation / generation.
Memory Management Unit (MMU) and Integrated RAM
The MMU and the integrated RAM is used to handle the large
difference in data-rate between USB, running in burst of 12 Mbit/s
and the I
This allows the microcontroller to read and write USB packets at its
own (low) speed through I
I
This block implements the necessary I
I
microcontroller whenever the PDIUSBH11 needs attention. As a
slave I
2
C interface to the microcontroller, running at 100 kbit/s.
2
C.
2
C Slave Interface
2
C allows for simple micro-coding. An interrupt is used to alert the
2
C device, the PDIUSBH11 I2C clock: SCL is an input and is
2
C interface protocol. A slave
controlled by the microcontroller.
MAXIMUM PACKET SIZE
(bytes)
PIN DESCRIPTION
The PDIUSBH11 has two modes of operation. The first mode
(Mode 0) enables the pins DNx_EN_N to power a LED indicating
the port is enabled. The second mode (Mode 1) utilizes the LED
enable pins as per port overcurrent condition pins.
1997 Aug 01
The voltage level at power up on the TEST1 and TEST2 pins
determine the PDIUSBH1 1 mode of operation. When both of the
pins are connected to Ground, Mode 0 is enabled. When pins
TEST1 and TEST2 are connected to Vcc, Mode 1 is enabled. Note
that in Mode 1 the pin DN2_EN_N remains an LED enable pin. Pin
TEST3 should always be connected to Ground at all times.
3
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
PIN DESCRIPTION (MODE 0)
PIN NO PIN SYMBOL I/O DRIVE NAME AND FUNCTION
1 TEST1 I Connect to Ground
2 TEST2 I Connect to Ground
3 TEST3 I Connect to Ground
4 RESET_N I ST Power-on reset
5 GND POWER Ground reference
6 XTAL1 I/O Crystal connection 1 (48MHz)
7 XTAL2 I/O Crystal connection 2 (48MHz)
8 CLK12MHZ O 2mA 12MHz output clock for external devices
9 V
10 OCURRENT_N I ST Over-current notice to the device
11 SWITCH_N O OD8 Enables power to downstream ports
12 SUSPEND O 4mA Device is in suspended state
13 DN2_EN_N O OD8 Downstream port 2 LED enable indicator
14 DN3_EN_N O OD8 Downstream port 3 LED enable indicator
15 DN4_EN_N O OD8 Downstream port 4 LED enable indicator
16 DN5_EN_N O OD8 Downstream port 5 LED enable indicator
17 INT_N O OD4 Connect to microcontroller interrupt
18 SDA I/O OD4 I2C bi-directional data
19 SCL I/O OD4 I2C bit-clock
20 GND POWER Ground reference
21 DN5_DP AI/O Downstream port 5 D+ connection
22 DN5_DM AI/O Downstream port 5 D– connection
23 DN4_DP AI/O Downstream port 4 D+ connection
24 DN4_DM AI/O Downstream port 4 D– connection
25 DN3_DP AI/O Downstream port 3 D+ connection
26 DN3_DM AI/O Downstream port 3 D– connection
27 DN2_DP AI/O Downstream port 2 D+ connection
28 DN2_DM AI/O Downstream port 2 D- connection
29 AGND POWER Analog Ground reference
30 AV
31 UP_DP AI/O Upstream D+ connection
32 UP_DM AI/O Upstream D- connection
CC
CC
POWER
POWER
Voltage supply 3.3V 0.3V
Analog voltage supply 3.3V 0.3V
1997 Aug 01
4
Page 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
PIN DESCRIPTION (MODE 1)
PIN NO PIN SYMBOL I/O DRIVE NAME AND FUNCTION
1 TEST1 I Connect to V
2 TEST2 I Connect to V
3 TEST3 I Connect to Ground
4 RESET_N I ST Power-on reset
5 GND POWER Ground reference
6 XTAL1 I/O Crystal connection 1 (48MHz)
7 XTAL2 I/O Crystal connection 2 (48MHz)
8 CLK12MHZ O 2mA 12MHz output clock for external devices
9 V
10 OCURRENT2_N I ST Downstream port 2 over-current notice
11 SWITCH_N O OD8 Enables power to downstream ports
12 SUSPEND O 4mA Device is in suspended state
13 DN2_EN_N O OD8 Downstream port 2 LED enable indicator
14 OCURRENT3_N I ST Downstream port 3 over-current notice
15 OCURRENT4_N I ST Downstream port 4 over-current notice
16 OCURRENT5_N I ST Downstream port 5 over-current notice
17 INT_N O OD4 Connect to microcontroller interrupt
18 SDA I/O OD4 I2C bi-directional data
19 SCL I/O OD4 I2C bit-clock
20 GND POWER Ground reference
21 DN5_DP AI/O Downstream port 5 D+ connection
22 DN5_DM AI/O Downstream port 5 D– connection
23 DN4_DP AI/O Downstream port 4 D+ connection
24 DN4_DM AI/O Downstream port 4 D- connection
25 DN3_DP AI/O Downstream port 3 D+ connection
26 DN3_DM AI/O Downstream port 3 D- connection
27 DN2_DP AI/O Downstream port 2 D+ connection
28 DN2_DM AI/O Downstream port 2 D- connection
29 AGND POWER Analog Ground reference
30 AV
31 UP_DP AI/O Upstream D+ connection
32 UP_DM AI/O Upstream D- connection
NOTES:
1. Signals ending in _N indicate active low signals.
ST: Schmitt Trigger
OD4, OD8: Open Drain with 4 or 8 mA drive
AI/O: Analog I/O
CC
CC
POWER
POWER
Voltage supply 3.3V 0.3V
Analog voltage supply 3.3V 0.3V
CC
CC
1997 Aug 01
5
Page 6
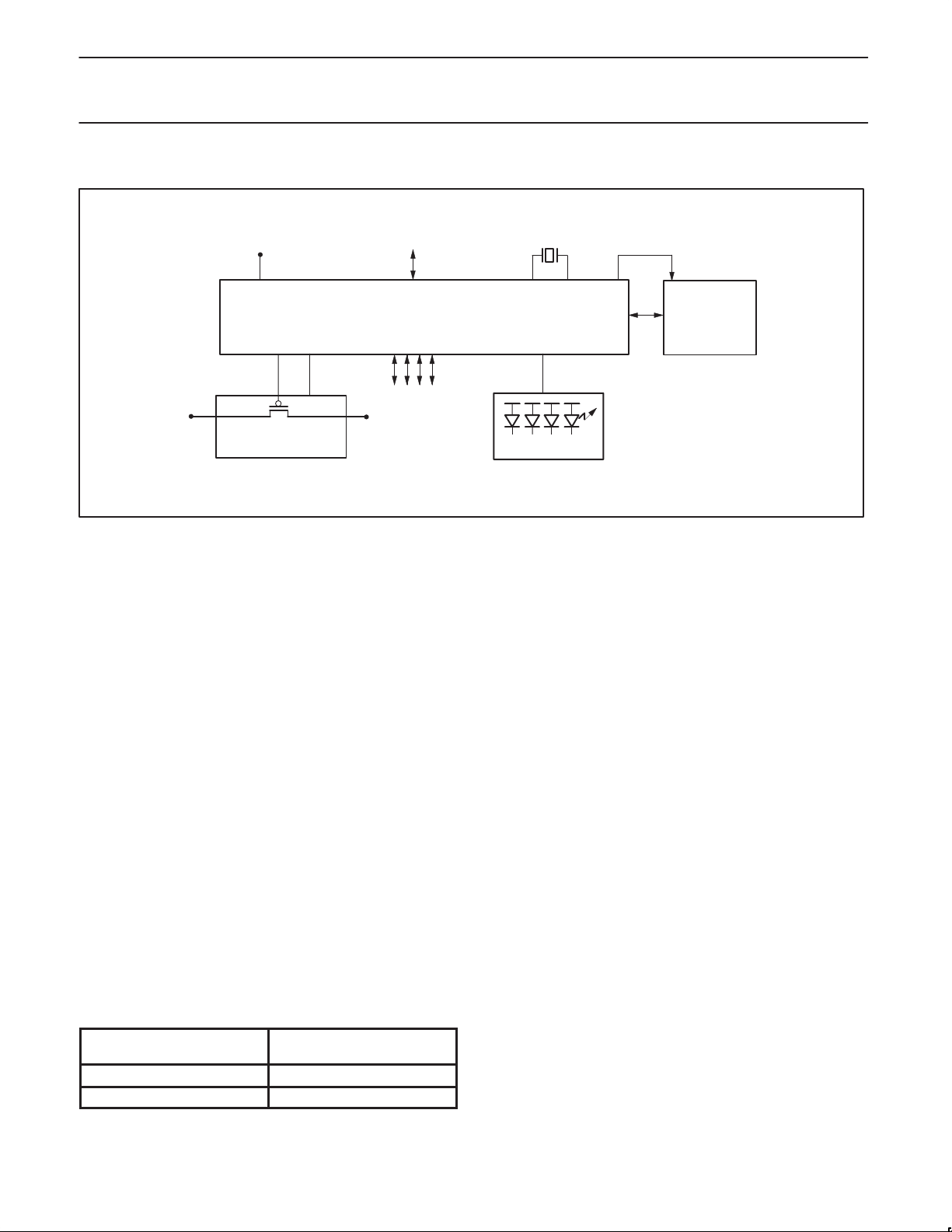
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
APPLICATION DIAGRAM
USB
3.3V
UPSTREAM
48MHz
12MHz
H11
USB
5V
POWER SWITCH
AND
OVERCURRENT CIRCUIT
I2C Interface.
2
The I
C bus is used to interface to an external microcontroller
DOWNSTREAM
SWITCHED
5V
needed to control the operation of the hub. For cost consideration,
the target system microcontroller can be shared and utilized for this
purpose. The PDIUSBH11 implements a slave I
2
C interface. When
the PDIUSBH11 needs to communicate with the microcontroller it
asserts an interrupt signal. The microcontroller services this
interrupt by reading the appropriate status register on the
PDIUSBH11 through the I
2
I
C serial bus, refer to the I2C handbook, Philips order number 9397
2
C bus. (For more information about the
750 00013).
2
The I
C interface on the PDIUSBH11 defines two types of
transactions :
1. command transaction
A command transaction is used to define which data (e.g., status
byte, buffer data, ...) will be read from / written to the USB
interface in the next data transaction. A data transaction usually
follows a command transaction.
2. data transaction
A data transaction reads data from / writes data to the USB
interface. The meaning of the data is dependent on the
command transaction which was sent before the data
transaction.
I2C
ENABLE LED
Protocol
2
An I
C transaction starts with a ‘Start Condition’, followed by an
µC
SV00227
address. When the address matches either the command or data
address the transaction starts and runs until a ‘Stop Condition’ or
another ‘Start Condition’ (repeated start) occurs.
The command address is write-only and is unable to do a read. The
next bytes in the message are interpreted as commands. Several
command bytes can be sent after one command address. Each of
the command bytes is acknowledged and passed on to the Memory
Management Unit inside the PDIUSBH11.
When the start condition address matches the data address, the
next bytes are interpreted as data. When the RW bit in the address
indicates a ‘master writes data to slave’ (=‘0’) the bytes are received,
acknowledged and passed on to the Memory Management Unit. If
the RW bit in the address indicates a ‘master reads data from slave’
(=‘1’) the PDIUSBH11 will send data to the master. The I
must acknowledge all data bytes except the last one. In this way the
2
I
C interface knows when the last byte has been transmitted and it
2
C-master
then releases the SDA line so that the master controller can
generate the STOP condition.
Repeated start support allows another packet to be sent without
generating a Stop Condition.
Two addresses are used to differentiate between command and
data transactions. Writing to the command address is interpreted as
a command, while reading from / writing to the data address is used
to transfer data between the PDIUSBH11 and the controller.
ADDRESS TABLE
TYPE OF ADDRESS
Command 0011 011 (binary)
Data 0011 010 (binary)
1997 Aug 01
PHYSICAL ADDRESS
(MSB to LSB)
Timing
When the master writes data to the PDIUSBH11, the data is
sampled 1 micro-second after the rising edge of SCL. When the
PDIUSBH11 writes data to the master, the data is driven 1
micro-second after the falling edge of SCL.
6
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
COMMAND SUMMARY
Some commands have the same command code (e.g., Read Buffer and Write Buffer). In these cases, the direction of the Data Phase (read or
write) indicates which command is executed.
COMMAND NAME
Initialization Commands
Set Address / Enable Hub D0h Write 1 byte
Set Endpoint Enable Hub + Embedded Function D8h Write 1 byte
Data Flow Commands
Read Interrupt Register F4h Read 1 byte
Select Endpoint Hub Control OUT 00h Read 1 byte (optional)
Embedded Function Control OUT 02h Read 1 byte (optional)
Embedded Function Control IN 03h Read 1 byte (optional)
Embedded Function Interrupt 04h Read 1 byte (optional)
Read Last Transaction Status Hub Control OUT 40h Read 1 byte
Embedded Function Control OUT 42h Read 1 byte
Embedded Function Control IN 43h Read 1 byte
Embedded Function Interrupt 44h Read 1 byte
Read Endpoint Status Hub Control OUT 80h Read 1 byte
Embedded Function Control OUT 82h Read 1 byte
Embedded Function Control IN 83h Read 1 byte
Embedded Function Interrupt 84h Read 1 byte
Read Buffer Selected Endpoint F0h Read n bytes
Write Buffer Selected Endpoint F0h Write n bytes
Set Endpoint Status Hub Control OUT 40h Write 1 byte
Embedded Function Control OUT 42h Write 1 byte
Embedded Function Control IN 43h Write 1 byte
Embedded Function Interrupt 44h Write 1 byte
Acknowledge Setup Selected Endpoint F1h None
Clear Buffer Selected Endpoint F2h None
Validate Buf fer Selected Endpoint FAh None
Hub Commands
Clear Port Feature Port 2 E0h Write 1 byte
Set Port Feature Port 2 E8h Write 1 byte
Get Port Status Port 2 E0h Read 1 or 2 bytes
Set Status Change Bits F7h Write 1 byte
General Commands
Send Resume F6h None
Read Current Frame Number F5h Read 1 or 2 bytes
RECIPIENT CODING DATA PHASE
Embedded Function D1h Write 1 byte
Hub Control IN 01h Read 1 byte (optional)
Hub Control IN 41h Read 1 byte
Hub Control IN 81h Read 1 byte
Hub Control IN 41h Write 1 byte
Port 3 E1h Write 1 byte
Port 4 E2h Write 1 byte
Port 5 E3h Write 1 byte
Port 3 E9h Write 1 byte
Port 4 EAh Write 1 byte
Port 5 EBh Write 1 byte
Port 3 E1h Read 1 or 2 bytes
Port 4 E2h Read 1 or 2 bytes
Port 5 E3h Read 1 or 2 bytes
1997 Aug 01
7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
COMMAND DESCRIPTIONS
Command Procedure
There are four basic types of commands: Initialization, Data, Hub Specific and General commands. Respectively, these are used t o initialize the
hub and embedded function; for data flow between the hub, embedded function and the host; some hub specific commands for controlling
individual downstream ports; and some general commands.
Initialization Commands
Initialization commands are used during the enumeration process of the USB network. These commands are used to enable the hub and
embedded function endpoints. They are also used to set the USB assigned address.
Set Address / Enable
Command : D0h (Hub), D1h (Embedded Function)
Data : Write 1 byte
This command is used to set the USB assigned address and enable the hub or embedded function respectively. The hub always powers up
disabled and should be enabled after a bus RESET.
706050403020100
0
ADDRESS THE VALUE WRITTEN BECOMES THE ADDRESS
ENABLE A ‘1’ ENABLES THIS FUNCTION
POWER ON VALUE
ADDRESS
ENABLE
SV00385
Set Endpoint Enable
Command : D8h
Data : Write 1 byte
Interrupt endpoints can only be enabled when the hub/function is enabled via the Set Address/Enable command.
7X6X5X4X3X20100
X
POWER ON VALUE
HUB’S INTERRUPT ENDPOINT
FUNCTION’S INTERRUPT ENDPOINT
RESERVED
1997 Aug 01
HUB’S INTERRUPT ENDPOINT A VALUE OF ‘1’ INDICATES THE HUB’S INTERRUPT ENDPOINT IS ENABLED.
FUNCTION’S INTERRUPT ENDPOINT A VALUE OF ‘1’ INDICATES THE EMBEDDED FUNCTION’S INTERRUPT ENDPOINT IS ENABLED.
SV00387
8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
Data Flow Commands
Data flow commands are used to manage the data transmission between the USB endpoints and the monitor. Much of the data flow is initiated
via an interrupt to the microcontroller. The microcontroller utilizes these commands to access and determine whether the endpoint FIFOs have
valid data.
Read Interrupt Register
Command : F4h
Data : Read 1 byte
This command indicates the origin of an interrupt. A “1” indicates an interrupt occurred at this endpoint. The bits are cleared by reading the
endpoint status register through Read Endpoint Status command.
After a bus reset an interrupt will be generated, however all bits in the interrupt register will be 0. The interrupt is internally cleared by reading
the interrupt register. A bus reset is completely identical to the hardware reset through the RESET_N pin with the sole difference of interrupt
notification.
The hub interrupt endpoint is handled internally by the PDIUSBH11 hardware without the need of microcontroller intervention.
7X6X50403020100
X
POWER ON VALUE
HUB CONTROL OUT ENDPOINT
HUB CONTROL IN ENDPOINT
FUNCTION CONTROL OUT ENDPOINT
FUNCTION CONTROL IN ENDPOINT
FUNCTION INTERRUPT ENDPOINT
RESERVED
SV00505
Select Endpoint
Command : 00–04h
Data : Optional Read 1 byte
The Select Endpoint command initializes an internal pointer to the start of the Selected buffer. Optionally, this command can be followed by a
data read, which returns 0 if the buffer is empty and 1 if the buffer is full.
7X6X5X4X3X2X100
X
POWER ON VALUE
FULL / EMPTY
1997 Aug 01
RESERVED
FULL / EMPTY A ‘1’ INDICATES THE BUFFER IS FULL, ‘0’ INDICATES AN EMPTY BUFFER
SV00506
9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
Read Last Transaction Status
Command : 40–44h
Data : Read 1 byte
The
Read Last Transaction Status
command also resets the corresponding interrupt flag in the interrupt register, and clears the status, indicating that it was read.
This command is useful for debugging purposes. Since it keeps track of every transaction, the status information is overwritten for each new
transaction.
706050403020100
0
command is followed by one data read that returns the status of the last transaction of the endpoint. This
POWER ON VALUE
DATA RECEIVE / TRANSMIT SUCCESS
ERROR CODE (SEE TABLE 1)
SETUP PACKET
DATA 0/1 PACKET
PREVIOUS STATUS NOT READ
DATA RECEIVE / TRANSMIT SUCCESS A ‘1’ INDICATES DATA HAS BEEN RECEIVED OR TRANSMITTED SUCCESSFULLY
ERROR CODE SEE TABLE 1
SETUP PACKET A ‘1’ INDICATES THE LAST RECEIVED PACKET HAD A SETUP TOKEN (THIS ALWAYS READ ‘0’ FOR IN BUFFERS.
DATA 0/1 PACKET A ‘1’ INDICATES THAT THE LAST RECEIVED OR SENT PACKET HAD A DATA1 PID
PREVIOUS STATUS NOT READ A ‘1’ INDICATES A SECOND EVENT OCCURRED BEFORE THE PREVIOUS STATUS WAS READ.
Table 1.
ERROR CODE RESULT
0000 No Error
0001 PID Encoding Error, Bits 7–4 are not the inversion of bits 3–0
0010 PID Unknown, encoding is valid, but PID does not exist
0011 Unexpected Packet, Packet is not of the type expected (= token, data or acknowledge), or SETUP token to a
0100 Token CRC Error
0101 Data CRC Error
0110 Time Out Error
0111 Babble Error
1000 Unexpected End of Packet
1001 Sent or Received NAK
1010 Sent Stall, a token was received, but the endpoint was stalled
1011 Overflow Error, the received packet was longer than the available buffer space
1101 Bitstuff Error
1111 Wrong DATA PID, the received DATA PID was not the expected one
SV00507
non-control endpoint
1997 Aug 01
10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
Read Endpoint Status
Command : 80–84h
Data : Read 1 byte
0
070605040302010
POWER ON VALUE
RESERVED
SETUP PACKET
STALL
DATA 0/1 PACKET
BUFFER FULL
RESERVED
SETUP PACKET A ‘1’ INDICATES THE LAST RECEIVED PACKET WAS A SETUP TOKEN
STALL A ‘1’ INDICATES THE ENDPOINT IS STALLED
DATA 0/1 PACKET A ‘1’ INDICATES THAT THE LAST RECEIVED OR SENT PACKET HAD A DATA1 PID
BUFFER FULL A ‘1’ INDICATES THAT THE BUFFER IS FULL
SV00508
Read Buffer
Command : F0h
Data : Read multiple bytes (max 10)
The Read Buffer command is followed by a number of data reads, which return the contents of the selected endpoint data buffer. After each
read, the internal buffer pointer is incremented by 1.
The buffer pointer is not reset to the buffer start by the Read Buffer command. This means that reading or writing a buf fer can be interrupted by
any other command (except for Select Endpoint), or can be done by more than one I2C transaction (read the first 2 bytes to get the number of
data bytes, then read the rest in other transactions).
The data in the buffer are organized as follows:
•byte 0: reserved: can have any value
•byte 1: Number / length of data bytes
•byte 2: Data byte 1
•byte 3: Data byte 2
Write Buffer
Command : F0h
Data : Write multiple bytes (max 10)
The Write Buffer command is followed by a number of data writes, which load the endpoints buffer. The data must be organized in the same
way as described in the Read Buffer command. The first byte (reserved) should always be 0. As in the Read Buffer command, the data can be
split up into different I2C data transactions.
WARNING
There is no protection against writing or reading over a buffer’s boundary or against writing into an OUT buffer or reading from an IN buffer. Any
of these actions could cause an incorrect operation. Data in an OUT buffer are only meaningful after a successful transaction.
1997 Aug 01
11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
Clear Buffer
Command : F2h
Data : None
When a packet is received completely, an internal endpoint buffer full flag is set. All subsequent packets will be refused by returning a NACK.
When the microcontroller has read the data, it should free the buffer by the Clear Buffer command. When the buffer is cleared new packets will
be accepted.
V alidate Buffer
Command : FAh
Data : None
When the microprocessor has written data into an IN buffer, it should set the buffer full flag by the Validate Buffer command. This indicates that
the data in the buffer are valid and can be sent to the host when the next IN token is received.
Set Endpoint Status
Command : 40–44h
Data : Write 1 byte
A stalled control endpoint is automatically unstalled when it receives a SETUP token, regardless of the content of the packet. If the endpoint
should stay in its stalled state, the microcontroller can re–stall it.
When a stalled endpoint is unstalled (either by the Set Endpoint Status command or by receiving a SETUP token), it is also re–initialized. This
flushes the buffer and if it is an OUT buffer it waits for a DATA 0 PID, if it is an IN buffer it writes a DATA 0 PID.
Even when unstalled, writing Set Endpoint Status to ‘0’ initializes the endpoint.
X7X6X5X4X3X2X100POWER ON VALUE
STALLED
RESERVED
STALLED A ‘1’ INDICATES THE ENDPOINT IS STALLED
SV00509
Acknowledge Setup
Command : F1h
Data : None
The arrival of a SETUP packet flushes the IN buffer and disables the Validate Buffer
endpoints.
The microcontroller needs to re–enable these commands by the
in the buffer and no packet can be sent back to the host until the microcontroller has acknowledged explicitly that it has seen the SETUP packet.
The microcontroller must send the Acknowledge Setup
Acknowledge Setup command. This ensures that the last SETUP packet stays
command to both the IN and OUT endpoints.
and Clear Buffer commands for both IN and OUT
1997 Aug 01
12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
Hub Commands
Hub commands are used to report connectivity and power status between the hub and the host. These commands allow the host to enable
each port individually and get any change of status such as new connectivity information.
Clear/Set Port Feature
Command : E0–E3h (Clear) and E8h–EBh (Set)
Data : Write 1 byte
When the controller receives a
•The request applies to port 1, the embedded port. In this case the request should be handled internally by the controller.
•If the request applies to ports 2 through 5, the controller should translate the request into a Set Feature or Clear Feature command towards
the PDIUSBH11.
When the PDIUSBH11 is configured in mode 0, there is only one power switch output and one overcurrent input. This means that th e
F_PORT_POWER and C_PORT_OVERCURRENT features are not port specific. For these features, any of the Set / Clear Feature commands
can be used. The specific port assignment is ignored.
When the PDIUSBH11 is configured in mode 1, there is still only one power switch output but there are four individual overcurrent input pins
corresponding to each port. This means that the F_PORT_POWER feature is port specific and the C_PORT_OVERCURRENT feature is not
port specific.
Setting the F_PORT_POWER feature turns the power on when it is off and turns the overcurrent detection on only when the power is already
on. This allows to have a short period of overcurrent condition at the moment that power is switched on. For this reason, the F_PORT_POWER
feature needs to be set twice. Clearing this feature turns both the power and the overcurrent detection off.
The data written in the data phase is the feature code described in Table 2.
Set Feature or a Clear Feature request, there are two possibilities:
Table 2.
FEATURE FEATURE CODE SET CLEAR
F_PORT_ENABLE 0 Enables a port Disables a port
F_PORT_SUSPEND 1 Suspends a port Resumes a port
FC_PORT_RESET 2 Resets a port Clears a port Reset Change bit
F_PORT_POWER 3 Powers all ports Unpowers all ports
C_PORT_CONNECTION 4 – Clears a port Connection Change bit
C_PORT_ENABLE 5 – Clears a port Enable Change bit
C_PORT_SUSPEND 6 – Clears a port Suspend Change bit
C_PORT_OVERCURRENT 7 – Clears a port (Mode 1) or hub (Mode 0) Overcurrent Change bit
1997 Aug 01
13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
Get Port Status
Command : E0h–E3h
Data : Read 1 or 2 bytes
The Get Port Status Command can be followed by one or two data reads. The first byte returned contains the port status. The second byte
returned is the port status change byte.
PORT STATUS BYTE
706050403020100
X
POWER ON VALUE
CONNECT
ENABLED
SUSPEND
OVER-CURRENT
RESET
POWER
LOW SPEED
RESERVED
CONNECT A ‘1’ INDICATES THAT A DEVICE IS CONNECTED ON THIS PORT OF THE HUB
ENABLED A ‘1’ INDICATES THAT THIS PORT IS ENABLED
SUSPEND A ‘1’ INDICATES THAT THIS PORT IS SUSPENDED
OVERCURRENT A ‘1’ INDICATES THAT OVERCURRENT CONDITION EXISTS ON THIS PORT.
RESET A ‘1’ INDICATES THAT BUS RESET ON THIS PORT IS IN PROGRESS.
POWER A ‘1’ INDICATES THAT POWER IS SUPPLIED TO DOWNSTREAM PORTS.
LOW SPEED A ‘1’ INDICATES THAT LOW SPEED DEVICE IS CONNECTED TO THIS PORT.
IN MODE 0 OF OPERATION, THIS BIT IS THE SAME FOR ALL PORTS.
IN MODE 1, INDIVIDUAL PORT OVERCURRENT INDICATION IS POSSIBLE.
WHEN RESET IS COMPLETED (NORMAL DURATION OF 10MS), THIS BIT INDICATES A ‘0’.
SINCE THE PDIUSBH11 SUPPORTS GANG MODE POWER SWITCHING,
THIS BIT IS THE SAME FOR ALL PORTS.
THIS BIT IS ONLY VALID WHEN CONNECT BIT IS A ‘1’.
SV00503
Port Status Change Byte
The description for the Port Status Change Byte is similar to the Port Status Byte except that the value of the bits are ‘1’ only when a change
has occurred.
0
X7X6X5040302010
POWER ON VALUE
CONNECT
ENABLED
SUSPEND
OVERCURRENT
RESET
1997 Aug 01
RESERVED
SV00510
14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
Set Status Change Bits
Command : F7h
Data : Write 1 byte
For assembling the hub’s status change register, the device needs some additional information from the controller, i.e. the Local Power Status
Change bit and the embedded function Status Change bit.
These are provided by the Set Status Change Bits command. This command is always followed by one data write which contains the Local
Power Status Change bit at the LSB and the embedded function Status Change bit at position 1. All other bits should be 0.
0
X7X6X5X4X3X2010
POWER ON VALUE
LOCAL POWER
EMBEDDED FUNCTION
RESERVED
SV00511
GENERAL COMMANDS
Send Resume
Command : F6h
Data : None
Sends an upstream resume signal for 10 ms. This command is normally issued when the device is in suspend. The RESUME command is not
followed by a data read or write.
The PDIUSBH11 automatically sends a RESUME command when an event occurs downstream.
Read Current Frame Number
Command : F5h
Data : Read 1 or 2 bytes
This command is followed by one or two data reads and returns the frame number of the last successfully received SOF. The frame number is
returned Least Significant Byte first.
7X6X5X4X3X2X1X0
X
7X6X5X4X3X2X1X0
X
LEAST SIGNIFICANT BYTE
MOST SIGNIFICANT BYTE
SV00512
EMBEDDED FUNCTION
The USB host sees no difference between the embedded function and a function connected to one of the downstream ports. Some of the port
commands sent by the host must be handled appropriately by the embedded function to appear as any other downstream port.
The micro controller maintains a series of status and status change bits for the embedded function as described in the Get Port Status
command section. From these bits, the Status Change bit for the embedded function is derived (i.e. the port specific Status Change bits). This
Status Change bit is then provided to the PDIUSBH11 by the Set Status Change Bits command.
1997 Aug 01
15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
UNIT
MIN.MAX
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
Host Requests
SetFeature PORT_RESET
Reinitialize the embedded function and set the Reset Change bit to indicate that the reset has completed. Reset the Enable Status bit, enable
the embedded function and set its address to 0 by the Set embedded function Address / Enable command. Disable the embedded function
interrupt endpoint by the Set Endpoint Enable command.
SetFeature PORT_ENABLE
Enable the function by the Set embedded function Address / Enable command. Set the Enable Status bit.
SetFeature PORT_SUSPEND
Disable the function by the Set embedded function Address / Enable command. Reset the Enable Status bit and set the Suspend Status bit.
ClearFeature PORT_ENABLE
Disable the function by the Set embedded function Address / Enable command. Reset the Enable Status bit.
ClearFeature PORT_SUSPEND
Enable the function by the Set embedded function Address / Enable command. Set the Enable Status bit, reset the Suspend Status bit; set the
Resume Status Change bit to indicate that the resume has completed.
ClearFeature any Change Indicator
Clear the corresponding status change bit.
Babbling Condition
When the embedded function causes a babbling condition, the function is automatically disabled by the PDIUSBH11. As soon as the micro
controller detects the babbling error , it must set the Enable Status Change bit and reset the Enable Status bit.
Remote WakeUp
There are three scenarios a remote wakeup can occur. The following describes the course of actions for each of the cases:
1. The device is not suspended and the embedded port is suspended
– Enable back the function by setting the enable bit in the Set Address/Enable register and update the following status bits in the
micro–controller program: reset the Suspend Status bit, set the Enable Status bit and set the Suspend Status Change bit.
2. The device is suspended and the embedded port is suspended.
– Send an upstream Resume using the Send Resume command, enable back the function by setting the enable bit in the Set
Address/Enable register and update the following status bits in the micro–controller program: reset the Suspend Status bit, set the Enable
Status bit and set the Suspend Status Change bit.
3. The device is suspended and the embedded port is enabled
– Send an upstream resume using the Send Resume command
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
LIMITS
.
V
T
V
V
CC
V
I/O
AI/O
V
amb
DC supply voltage 3.0 3.6 V
DC Input voltage range 0 5.5 V
I
DC input range for I/O 0 5.5 V
DC input range for analog I/O 0 V
DC output voltage range 0 V
O
Operating ambient temperature range in
free air
See DC and AC characteristics
per device
0 +70 °C
CC
CC
V
V
1997 Aug 01
16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
UNIT
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
1
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134) Voltages are referenced to GND (ground = 0V)
LIMITS
MIN MAX
I
GND
V
I
V
I
V
I
I
T
P
DC supply voltage –0.5 +4.6 V
CC
DC input diode current VI < 0 – -50 mA
IK
V
DC input voltage Note 2 –0.5 +5.5 V
I
DC input voltage range for I/O’s –0.5 V
I/O
DC output diode current VO > VCC or VO < 0 –
OK
DC output voltage Note 2 –0.5 VCC +0.5 V
O
DC output source or sink current for digital
O
pins
DC output source or sink current for D+/D–
O
pins
, I
DC VCC or GND current –
CC
Storage temperature range –60 +150 °C
stg
Power dissipation per package mW
tot
VO = 0 to V
VO = 0 to V
CC
CC
–
–
CC
100
+0.5 V
50
15
50
mA
mA
mA
mA
NOTES:
1. Stresses beyond those listed may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to
absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability .
2. The input and output voltage ratings may be exceeded if the input and output clamp current ratings are observed.
1997 Aug 01
17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PARAMETER
VOLLOW level out ut
V
VOHHIGH level out ut
V
PARAMETER
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
DC CHARACTERISTICS (DIGIT AL PINS)
LIMITS
MIN TYP MAX
Input Levels:
V
V
VTLH LOW to HIGH threshold voltage ST (Schmitt Trigger) pins 80 %V
VTHL HIGH to LOW threshold voltage ST (Schmitt Trigger) pins 20 %V
VHYS Hysteresis voltage ST (Schmitt Trigger) pins 1.1 V
Output Levels:
Leakage Current:
I
OZ
I
LOW level input voltage 0.9 V
IL
HIGH level input voltage 2.5 V
IH
I
= rated drive 0.4
p
p
OL
IOL = 20µA 0.1
I
= rated drive VCC –0.4
OH
IOH = 20µA VCC –0.1
OFF-state current OD (Open Drain) pins
Input leakage current
I
5
1
CC
CC
µA
µA
DC CHARACTERISTICS (AI/O PINS)
LIMITS
MIN MAX
Leakage Current:
I
LO
Input Levels:
VDI Differential input sensitivity |(D+) – (D–)|
VCM Differential common mode range Includes VDI range 0.8 2.5 V
VSE Single ended receiver threshold 0.8 2.0 V
Output Levels:
V
OL
V
OH
Capacitance:
C
IN
Output Resistance:
ZDRV
NOTES:
1. D+ is the generic symbol for the USB positive data pins: UP_DP, DN2_DP, DN3_DP, DN4_DP, DN5_DP. D– is the generic symbol for the
USB negative data pins: UP_DM, DN2_DM, DN3_DM, DN4_DM, DN5_DM.
2. Includes external resistors of 24 1% each on D+ and D–.
Hi–Z state data line leakage 0V < VIN < 3.3V
1
Static output LOW
Static output HIGH
Transceiver capacitance
2
Driver output resistance Steady state drive 28 43
RL of 1.5K to 3.6V
RL of 15K to GND
Pin to GND 20 pF
0.2 V
2.8 3.6 V
10
0.3 V
µA
1997 Aug 01
18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
UNIT
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
LOAD FOR D+/D–
V
TEST POINT
CC
D. U. T .
CL = 50pF, FULL SPEED
= 50 pF, LOW SPEED (MIN TIMING)
C
L
= 350pF, LOW SPEED (MAX TIMING)
C
L
* 1.5K OHM ON D– (LOW SPEED) OR D+ (FULL SPEED) ONLY
24 OHM
15K OHM
AC CHARACTERISTICS (AI/O PINS. FULL SPEED)
Driver Characteristics:
Transition time:
T
V
T
R
T
RFM
CRS
Rise time
Fall tIme
F
Rise/Fall tIme matching (TR/TF) 90 110 %
Output signal crossover voltage 1.3 2.0 V
Driver Timings:
T
T
EOPT
DEOP
Source EOP width Figure 1 160 175 ns
Differential data to EOP transition skew Figure 1 –2 5 ns
Receiver Timings:
Receiver data jitter tolerance
T
JR1
T
JR2
To next transition
For paired transitions
EOP width at receiver
T
EOPR1
T
EOPR2
Must reject as EOP
Must accept
Hub Timings:
T
HDD
T
SOP
T
EOPDR
T
HESK
Hub differential data delay Figure 2 40 ns
Data bit width distortion after SOP Figure 2 –5 3 ns
Hub EOP delay relative to T
Hub EOP output width skew Figure 3 –15 +15 ns
HDD
CL = 50pF;
= 1.5KΩ on D+ to V
R
pu
Between 10% and 90%
Characterized and not Tested.
Guaranteed by Design.
Figure 1
CL = 50pF;
= 1.5KΩ on D+ to V
R
pu
Figure 3 0 15 ns
S1
C
L
1.5K OHM*
TEST
D–/LS
D+/LS
D–/FS
D+/FS
S1
CLOSE
OPEN
OPEN
CLOSE
SV00237
LIMITS
MIN MAX
CC
4
4
–18.5
–9
40
20
20
18.5
9
ns
ns
ns
82
CC
1997 Aug 01
19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
UNIT
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
AC CHARACTERISTICS (AI/O PINS. LOW SPEED)
LIMITS
MIN MAX
Driver Characteristics:
CL = 50pF and 350pF;
= 1.5KΩ on D– to V
R
pu
CC
Transition time:
V
T
LR
T
LF
LCRS
Rise time
Fall tIme
Output signal crossover voltage 1.3 2.0 V
Driver Timings:
T
LEOPT
T
LDEOP
Source EOP width Figure 1 1.25 1.50 ns
Differential data to EOP transition skew Figure 1 –40 100 ns
Receiver Timings:
EOP width at receiver
T
LEOPR1
T
LEOPR2
Must reject as EOP
Must accept
Hub Timings:
T
LHDD
T
LSOP
T
LEOPDR
T
LHESK
Hub differential data delay Figure 2 300 ns
Data bit width distortion after SOP Figure 2 –65 45 ns
Hub EOP delay relative to T
Hub EOP output width skew Figure 3 –300 +300 ns
HDD
Between 10% and 90%
= 50pF
C
L
= 350pF
C
L
= 50pF
C
L
= 350pF
C
L
Figure 1
75
75
330
300
300
ns
ns
675
CL = 50pF and 350pF;
= 1.5KΩ on D– to V
R
pu
CC
Figure 3 0 200 ns
DIFFERENTIAL
DATA LINES
T
PERIOD
CROSSOVER
CROSSOVER
POINT
DIFFERENTIAL DATA TO
SEO/EOP SKEW
N* T
PERIOD
+ T
DEOP
POINT EXTENDED
SOURCE EOP WIDTH: T
RECEIVER EOP WIDTH: T
Figure 1. Differential Data to EOP Transition Skew and EOP Width
EOPT
EOPR1
, T
EOPR2
SV00513
1997 Aug 01
20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
V
DD
UPSTREAMDIFFERENTIAL
DATA
V
SS
DOWNSTREAMDIFFERENTIAL
DATA
V
SS
A. DOWNSTREAM HUB DELAY B. UPSTREAM HUB DELAY
SOP DISTORTION
= T
T
SOP
HDD
LOW SPEED TIMINGS ARE DETERMINED IN THE SAME WAY FOR:
T
AND T
LHDD
(SOP) – T
LSOP
CROSSOVER
POINT
Hub Delay
Downstream
T
(NEXT J)
HDD
HDD
CROSSOVER
POINT
DOWNSTREAM
DIFFERENTIAL
DATA
UPSTREAM
DIFFERENTIAL
DATA
Figure 2. Hub Differential Data Delay and SOP Distortion
CROSSOVER
POINT
Hub Delay
Upstream
T
HDD
CROSSOVER
POINT
SV00514
V
DD
UPSTREAMDIFFERENTIAL
DATA
V
SS
DOWNSTREAMDIFFERENTIAL
DATA
V
SS
DOWNSTREAM
PORT
UPSTREAM
END OF CABLE
T
EOP–
T
EOP–
T
EOP+
CROSSOVER
POINT
EXTENDED
CROSSOVER
POINT
EXTENDED
A. DOWNSTREAM EOP DELAY B. UPSTREAM EOP DELAY
EOP DELAY
= T
T
EOPD
EOP–
EOP DELAY RELATIVE TO T
= T
= T
, T
EOPD
EOP+
LEOPDR
– T
– T
, AND T
T
EOPDR
EOP SKEW
T
HESK
LOW SPEED TIMINGS ARE DETERMINED IN THE SAME WAY FOR:
T
LEOPD
HDD
EOP–
HDD
LHESK
Figure 3. Hub EOP Delay and EOP Skew
T
EOP+
CROSSOVER
POINT
EXTENDED
CROSSOVER
POINT
EXTENDED
SV00515
1997 Aug 01
21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
UNIT
PDIUSBH11Universal Serial Bus Hub
AC CHARACTERISTICS (I2C)
All timing values are valid within the operating supply voltage and ambient temperature range and reference to VIL and VIH with an input voltage
swing of V
I2C-bus timing (see Figure ; Note )
1. A detailed description of the I2C-bus specification, with applications, is given in brochure ‘‘
may be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
f
SCL
t
SP
t
BUF
t
SU;STA
t
HD;STA
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
r
t
f
t
SU;DAT
t
HD;DAT
t
VD;DAT
t
SU;STO
and VDD.
SS
LIMITS
MIN TYP MAX
SCL clock frequency – – 100 kHZ
Tolerable spike width on bus – – 100 ns
Bus free time 4.7 – – µs
Start condition set-up time 4.7 – – µs
Start condition hold time 4.0 – – µs
SCL LOW time 4.7 – – µs
SCL HIGH time 4.0 – – µs
SCL and SDA rise times – – 1.0 µs
SCL and SDA fall times – – 0.3 µs
Data set-up time 250 – – ns
Data hold time 0 – – ns
SCL LOW to data out valid – – 3.4 µs
Stop condition set-up time 4.0 – – µs
The I2C-bus and how to use it
”. This brochure
PROTOCOL
SCL
SDA
START
CONDITION
(S)
t
SU;STA
t
BUF
t
HD;STA
t
LOW
BIT 7
MSB
(A7)
t
HIGH
t
r
t
f
t
SU;DAT
BIT 6
(A6)
1/f
SCL
t
HD;DAT
BIT 0
LSB
(R/W)
ACKNOWLEDGE
(A)
t
VD:DAT
Figure 4. I2C-bus timing diagram; rise and fall times refer to VIL and V
IH
STOP
CONDITION
(P)
t
SU;STO
SV00756
1997 Aug 01
22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH1 1Universal Serial Bus Hub
SO32: plastic small outline package; 32 leads; body width 7.5mm SOT287-1
1997 Aug 01
23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH1 1Universal Serial Bus Hub
SDIP32: plastic shrink dual in-line package; 32 leads (400 mil) SOT232-1
1997 Aug 01
24
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH1 1Universal Serial Bus Hub
NOTES
1997 Aug 01
25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
PDIUSBH1 1Universal serial bus hub
DEFINITIONS
Data Sheet Identification Product Status Definition
Objective Specification
Preliminary Specification
Product Specification
Formative or in Design
Preproduction Product
Full Production
Philips Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation reserve the right to make changes, without notice, in the products,
including circuits, standard cells, and/or software, described or contained herein in order to improve design and/or performance. Philips
Semiconductors assumes no responsibility or liability for the use of any of these products, conveys no license or title under any patent, copyright,
or mask work right to these products, and makes no representations or warranties that these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask
work right infringement, unless otherwise specified. Applications that are described herein for any of these products are for illustrative purposes
only. Philips Semiconductors makes no representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for the specified use without further testing
or modification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICA TIONS
Philips Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation Products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices,
or systems where malfunction of a Philips Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation Product can reasonably be expected
to result in a personal injury. Philips Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation customers using or selling Philips
Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation Products for use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully
indemnify Philips Semiconductors and Philips Electronics North America Corporation for any damages resulting from such improper use or sale.
Philips Semiconductors
811 East Arques Avenue
P.O. Box 3409
Sunnyvale, California 94088–3409
Telephone 800-234-7381
This data sheet contains the design target or goal specifications for product development. Specifications
may change in any manner without notice.
This data sheet contains preliminary data, and supplementary data will be published at a later date. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes at any time without notice in order to improve design
and supply the best possible product.
This data sheet contains Final Specifications. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes
at any time without notice, in order to improve design and supply the best possible product.
Copyright Philips Electronics North America Corporation 1997
All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
1997 Apr 17
26
 Loading...
Loading...