Page 1
DATA SH EET
Objective specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC17
1998 Apr 27
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
Low cost; low power DECT
baseband controllers (ABC-PRO)
Page 2

1998 Apr 27 2
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
5 PINNING INFORMATION
5.1 Pinning
5.2 Pin description
6 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
6.1 DECT baseband controller system
7 PACKAGE OUTLINES
8 SOLDERING
8.1 Introduction
8.2 Reflow soldering
8.3 Wave soldering
8.4 Repairing soldered joints
9 DEFINITIONS
10 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
11 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
Page 3

1998 Apr 27 3
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
1 FEATURES
• The PCD50912 is designed for GAP compatible DECT
handsets
• The PCD50922 is designed for GAP compatible DECT
base stations serving up to six handsets
• Fully static 80C51 microcontroller
• Emulation supported for 80C51 program development
• Four 8-bit ports (P0, P1, P2 and P3), 32 I/O lines
• Dedicated port pins for keyboard, I2C-bus, interrupt
sources and/or external memory
• Fifteen interrupt sources (including those from TICB,
BML and DSP) with two priority levels
• I
2
C-bus interface
• UART with IrDA-compatible Data Transmission Mode
• 256 bytes of microcontroller main RAM
• 3 kbytes of microcontroller AUX RAM
• 1 kbyte of shared System Data RAM
• 64 kbytes of mask programmable ROM
• 128 kbyte address space for external ROM access,
maximum 192 kbytes together with internal ROM
• 128 kbytes of external RAM addressable
• Embedded DSP with 6.912, 13.824 or 27.648 Mips
• Speech and IOM-2 interface
• BML for TDMA frame (de)multiplexing. Transmission or
reception can be programmed for any slot
• Ciphering, scrambling, CRC checking/generation,
protected B-fields
• Local call and B-field loop-back
• Automatic receiver delay adjustment programmable per
slot to correct for terminal mobility
• Phase error measurement and phase error correction by
hardware
• Serial interface to synthesizer for frequency
programming
• Programmable timing and polarity of radio-control
signals
• Easy interfacing with radio circuits, operating at different
supply voltages
• GMSK pulse shaper with two different pulse shapes
(BT = 0.5 and BT = 0.8)
• Comparator for use as bit-slicer
• 3 channel time-multiplexed 8-bit ADC for RSSI, battery
and general input voltage measurement
• Battery management supported by programmable
current source for temperature or charge current
measurement
• On-chip 8-bit DAC for various purposes
• Low power crystal oscillator at 13.824 MHz
• Programmable on-chip capacitors for frequency
adjustment to 13.824 MHz with large pulling range
• High performance DAC and ADC for dynamic earpiece
and dynamic or electret microphone
• Analog-to-digital path switchable sensitivity for
microphone or line interface input
• On-chip reference voltage and supply for electret
microphone
• Very low ohmic buzzer output
• Pulse density modulated or pulse width modulated
buzzer output signal
• Power-on-reset
• Low power operation optimized for 2 battery cells in
handset
• Long standby time due to reduced digital supply voltage
and reduced activity in idle-locked mode
• Flexible supply voltage concept due to use of level
shifters between each supply voltage domain
• Eight independent supply voltage domains:
– 1.8 to 3.6 V for digital core, microcontroller ports P0
and P2, and also P1 and P3
– 1.8 to 3.6 V for buzzer, oscillator and battery
– 2.7 to 3.6 V for RF interface and analog circuits
• CMOS technology
• Small and flat LQFP80 package.
Page 4
1998 Apr 27 4
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PCD509x2 family is designed for low power GAP
compatible DECT handset (PP) and base station (FP)
applications. The circuit includes the audio interface, the
DSP, the microcontroller and the Burst Mode Logic, and
contains all functionality to convert speech and data
signals from/to the analog side (microphone and earpiece
or line interface circuit) to/from the radio side
(1.152 Mbits/s data).
This circuit is a member of the ABC family, where A stands
for ‘ADPCM codec’, B for ‘Burst Mode Logic’ and C for
‘microController’. The name ABC-PRO stands for
PROfessional ABC.
The PCD509x2/zuu/v contains on-chip ROM for the
embedded DSP code and on-chip ROM for the embedded
microcontroller code. It is these ROM codes that
differentiate between various chip derivatives. For each
DSP code a separate DSP user manual is published.
Please contact Philips Semiconductors for more
information.
This family specification contains the hardware description
that is independent of the used ROM codes.
The numerical digit ‘x’ in PCD509x2 determines the
intended application area (e.g. PCD50912 for use in
handsets or PCD50922 for use in simple base stations,
etc.). The last numerical digit ‘2’ is used to denote
hardware derivatives. The extension digits ‘z’ (A to Z) and
‘uu’ (00 to 99) denote the DSP and the microcontroller
software version, respectively. The extension ‘v’ denotes
the hardware version updates of the circuit.
Although the microcontroller ROM code is present on-chip,
an external program memory for the microcontroller code
can be used. This is not the case for the DSP ROM code
which is fixed by the chip version.
Throughout this family specification the term PCD509x2 is
used to cover all sub types and versions. If any specific
feature or parameter is connected to a certain sub type or
version this will be specifically written. Until otherwise
stated this family specification is valid for hardware
version 1 (v = 1).
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PCD50912H LQFP80 plastic low profile quad flat package; 80 leads; body 12 × 12 × 1.4 mm SOT315-1
PCD50922H
Page 5
1998 Apr 27 5
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
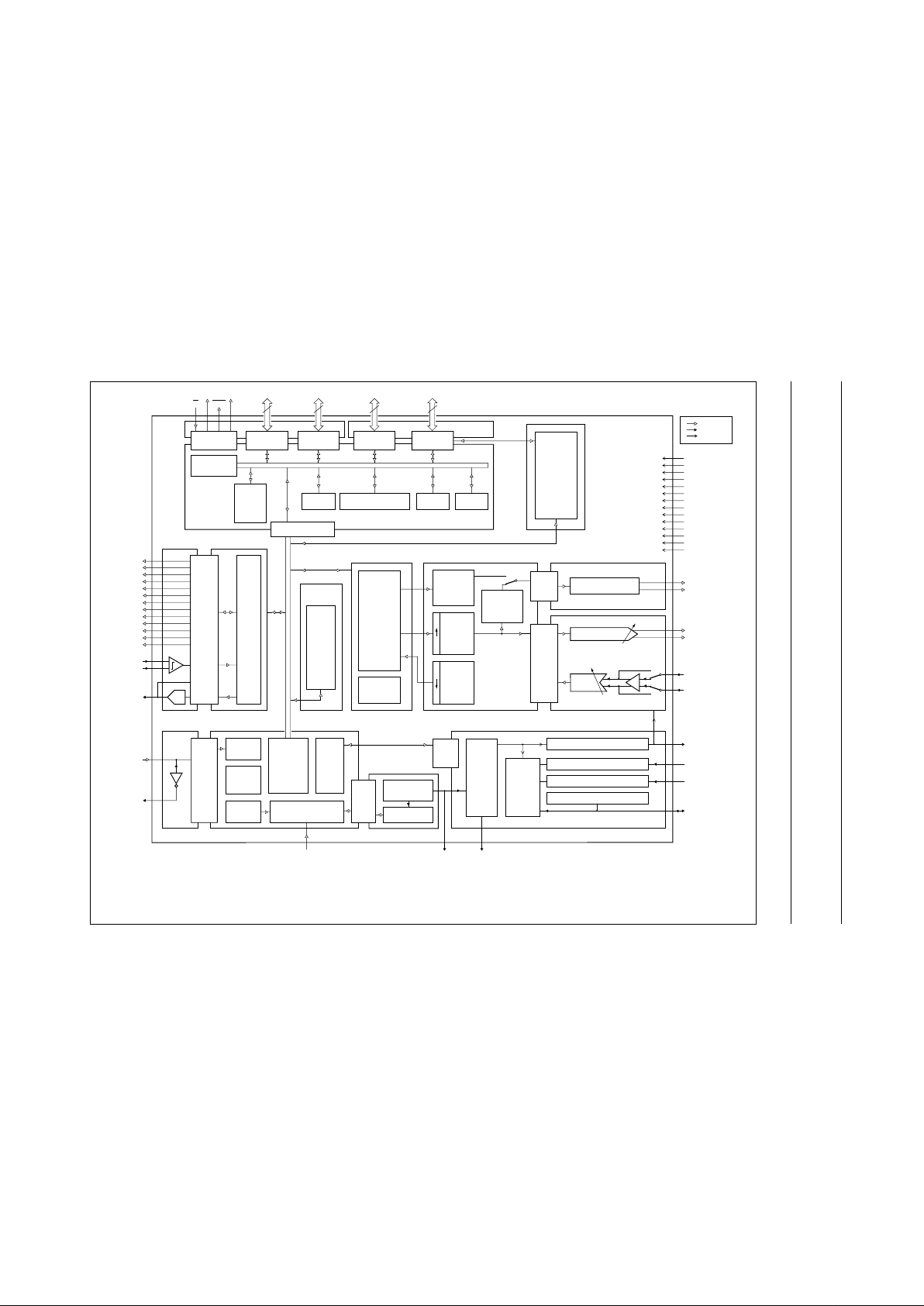
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
o
k, full pagewidth
MGM858
R_DATAM
R_DATAP
REF_CLK
SLICE_CTR
R_PWR
R_ENABLE
S_PWR
S_CLK
S_DATA
S_ENABLE
GPP
T_PWR
T_ENABLE
ANT_SW1
ANT_SW0
LEVEL
SHIFTER
AGM
BURST
MODE
LOGIC
(BML)
CLOCK
GENERATOR
(CLG)
TIMING
CONTROL
BLOCK
(TICB)
WATCHDOG
TIMER
(WDT)
ISB
RESET
GENERATOR
(RGE)
DIGITAL
CONTROL
OF
ANALOG
(DCA)
80CL51 CORE
ROM
(64 kBYTES)
AB-MICROCONTROLLER
INTERFACE (ABCIF)
LEVEL SHIFTER
PORT 0
8
8 8 8
LEVEL SHIFTER
PORT 2
LEVEL SHIFTER
PORT 1
LEVEL SHIFTER
PORT 3
AUX-RAM
(3 kBYTES)
MICROCONTROLLER-RAM
(256 BYTES)
I2C-BUS UART
SYSTEM
DATA
RAM
(SDR)
(1 kBYTE)
DIGITAL
SIGNAL
PROCESSOR
(DSP)
MEMORY
DIGITAL
DECIMATING
FILTER
(DDF)
DIGITAL
NOISE
SHAPER
(DNS)
DIGITAL
PULSE
SHAPER
(DPS)
DIGITAL
PULSE
SHAPER
(DPS)
LEVEL
SHIFTER
DIGITAL
RECEIVE
FILTER
(DRF)
ANALOG VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
(AVR)
POWER-ON-RESET
(POR)
ANALOG
VOLTAGE
SOURCE
(AVS)
AUXILIARY
ADC
(AAD)
Σ ∆
1-BIT ADC
ATS
1-BIT DAC (ARD)
AMP
V
ref
BUZZER BUFFER
(ABB)
CODEC
V
DDD
V
DDD
V
DDD
V
DD(BZ)
V
DDD
V
DDA
V
DD(RF)
V
DDD
ALE A16
V
DD(OSC)
V
DDD
V
DD(BAT)
V
DDA
T_GSMK/
T_DATA
XTAL1
XTAL2
M_RESET
VBGP
VANLO
MICM/LIFP
MICP/LIFM
EARM
EARP
BZM
BZP
ANALOG SWITCH (ASW)
V
ref
ANALOG SUBTRACTOR (ASU)
V
DD(BAT)
ANALOG RSSI TREATMENT (ART)
RSSI_AN
ADJUSTABLE CURRENT SOURCE (ACS)
VANLI
V
DDD
P0 P2 P3
(1)
P1
(1)
V
DDD
V
DD(P0, P2)
V
DD(P1, P3)
MICROCONTROLLER
PCD509x2
IB BUS
LEVEL
SHIFTER
EA
PSEN
digital pins
supply pins
analog pins
V
SSD
V
DD(P1, P3)
V
DD(P0, P2)
V
SS(P0, P2)
V
DD(BZ)
V
SS(BZ)
V
DD(RF)
V
SS(RF)
V
DDA
V
SSA
V
DD(OSC)
V
SS(OSC)
V
DD(BAT)
LEVEL
SHIFTER
LEVEL
SHIFTER
LEVEL
SHIFTER
LEVEL
SHIFTER
LEVEL
SHIFTER
SPEECH
INTERFACE
IOM
ADPCM
(SPI)
ISB BUS
CONTROLLER
(IBC)
Fig.1 Block diagram.
(1) Ports 1 and 3 are shared with alternative functions.
Page 6

1998 Apr 27 6
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
5 PINNING INFORMATION
5.1 Pinning
Fig.2 Pin configuration (LQPF80).
ndbook, full pagewidth
PCD509x2/zuu/v
MGM857
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
P1.1/INT3
P1.0/INT2
M_RESET
ANT_SW0
ANT_SW1
T_ENABLE
T_PWR
GPP
S_ENABLE
S_DATA
S_CLK
S_PWR
R_ENABLE
R_PWR
SLICE_CTR
V
DD(RF)
V
SS(RF)
REF_CLK
RSSI_AN
T_GSMK/T_DATA 20
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
P1.2/INT4/DI
P1.3/INT5/DO
P1.4/INT6/DCK
P1.5/INT7/FS1
P1.6/INT8/SCL
P1.7/INT9/SDA
V
DD(P1, P3)VDDDVSSD
P3.0/RXD
P3.1/TXD
P3.4/T0
P3.5/T1
P0.0
P0.1
R_DATAP
R_DATAM
V
DD(OSC)
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
SS(OSC)
V
DD(BAT)
VANLI
VANLO
V
DDA
EARM
EARP
V
SSA
VBGP
V
ref
MICM/LIFP
MICP/LIFM
V
DD(BZ)
BZM
BZP
P0.2
P0.3
P0.4
P0.5
P0.6
P0.7
ALE
PSEN
V
DD(P0, P2)
V
SS(P0, P2)
A16
P2.7
P2.6
P2.5
P2.4
P2.3
P2.2
P2.1
P2.0
V
SS(BZ)
P3.7/RD
P3.6/WR
P3.2/INT0
P3.3/INT1/IrDA
EA
Page 7

1998 Apr 27 7
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
5.2 Pin description
Table 1 LQFP80 package
SYMBOL PIN I/O
STATE
AFTER
RESET
(1)
SUPPLY
DOMAIN
DESCRIPTION
P1.1/INT3 1 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/external interrupt 3
P1.0/INT2 2 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/external interrupt 2
M_RESET 3 I − V
DDD
master reset input (Schmitt trigger)
ANT_SW0 4 O HIGH V
DD(RF)
antenna switch 0
ANT_SW1 5 O HIGH V
DD(RF)
antenna switch 1
T_ENABLE 6 O HIGH V
DD(RF)
enable transmitter
T_PWR 7 O LOW V
DD(RF)
switch transmitter power
GPP 8 O LOW V
DD(RF)
general purpose pin used for the following:
CLK100
VCO_BND_SW
GP_CLK7
GP_CLK3
GP_CLK05
R_SLICED
on/of
100 Hz signal related to DECT frame timing
VCO band switch
6.912 MHz general purpose clock
3.456 MHz general purpose clock
576 kHz general purpose clock
ABS bitslice comparator output
static high/low.
S_ENABLE 9 O LOW V
DD(RF)
synthesizer enable
S_DATA 10 O LOW V
DD(RF)
serial synthesizer data
S_CLK 11 O LOW V
DD(RF)
clock for serial synthesizer interface
S_PWR 12 O LOW V
DD(RF)
switch synthesizer power
R_ENABLE 13 O HIGH V
DD(RF)
enable receiver
R_PWR 14 O HIGH V
DD(RF)
switch receiver power
SLICE_CTR 15 O LOW V
DD(RF)
switch slicer time constant
V
DD(RF)
16 −− − positive supply voltage for RF interface pins
V
SS(RF)
17 −− − negative supply voltage for RF interface pins
REF_CLK 18 O running V
DD(RF)
programmable reference clock for synthesizer
RSSI_AN 19 I − V
DD(RF)
analog input for RSSI measurement
T_GMSK/T_DATA 20 O off V
DD(RF)
transmitter data output, filtered/digital
R_DATAP 21 I − V
DD(RF)
positive input for receiver data
R_DATAM 22 I − V
DD(RF)
negative input for receiver data
V
DD(OSC)
23 −− − positive supply for crystal oscillator
XTAL2 24 O running V
DD(OSC)
crystal oscillator output
XTAL1 25 I − V
DD(OSC)
crystal oscillator input
Page 8

1998 Apr 27 8
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
V
SS(OSC)
26 −− − negative supply for crystal oscillator
V
DD(BAT)
27 I −−positive battery supply voltage
VANLI 28 I/O − V
DDA
analog input to ADC, current output
VANLO 29 O off V
DDA
analog output from DAC
V
DDA
30 −− − positive supply voltage for analog circuits
EARM 31 O off V
DDA
negative output to earpiece
EARP 32 O off V
DDA
positive output to earpiece
V
SSA
33 −− − negative supply voltage for analog circuits
VBGP 34 O 1.2 V V
DD(BAT)
bandgap output voltage (+1.2 V)
V
ref
35 O off V
DDA
reference voltage, microphone supply (+2 V)
MICM/LIFP 36 I off V
DDA
negative/positive input from microphone/line
MICP/LIFM 37 I off V
DDA
positive/negative input from microphone/line
V
DD(BZ)
38 −− − positive supply voltage for buzzer
BZM 39 O LOW V
DD(BZ)
negative buzzer output
BZP 40 O LOW V
DD(BZ)
positive buzzer output
V
SS(BZ)
41 −− − negative supply voltage for buzzer
P2.0 42 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
bidirectional Port 3 pins (80C51)
P2.1 43 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P2.2 44 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P2.3 45 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P2.4 46 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P2.5 47 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P2.6 48 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P2.7 49 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
A16 50 O LOW V
DD(P0,P2)
A16 address select
V
SS(P0,P2)
51 −− − negative supply voltage
V
DD(P0,P2)
52 −− − positive supply voltage for periphery pins
PSEN 53 O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
program store enable (80C51), active LOW
ALE 54 O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
address latch enable (80C51)
P0.7 55 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
bidirectional Port 0 pins (80C51)
P0.6 56 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P0.5 57 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P0.4 58 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P0.3 59 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P0.2 60 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P0.1 61 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
P0.0 62 I/O HIGH V
DD(P0,P2)
SYMBOL PIN I/O
STATE
AFTER
RESET
(1)
SUPPLY
DOMAIN
DESCRIPTION
Page 9

1998 Apr 27 9
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
Note
1. In the ‘State After Reset’ column the following symbols are used:
a) HIGH means active HIGH, for BUPxSW pin types this means weak pull-up
b) LOW means active LOW
c) ‘running’ means the clock signal is active
d) ‘off’ means the high-impedance state.
EA 63 I − V
DD(P0,P2)
external access (80C51), active LOW
P3.7/
RD 64 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/Read data, active LOW
P3.6/
WR 65 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/Write data, active LOW
P3.5/T1 66 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/Timer 1 input
P3.4/T0 67 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/Timer 0 input
P3.3/
INT1/IrDA 68 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/external interrupt 1/IrDA clock
P3.2/
INT0 69 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/external interrupt 0
P3.1/TXD 70 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/UART transmit data
P3.0/RXD 71 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/UART receive data
V
SSD
72 −− − negative supply voltage for digital core
V
DDD
73 −− − positive supply voltage for digital core
V
DD(P1,P3)
74 −− − positive supply voltage for periphery pins
P1.7/INT9/SDA 75 I/O off V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/external interrupt 9/I2C-bus data
P1.6/INT8/SCL 76 I/O off V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/external interrupt 8/I2C-bus clock
P1.5/INT7/FS1 77 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/external interrupt 7/SPI Frame Sync
P1.4/INT6/DCK 78 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/external interrupt 6/SPI Data Clock
P1.3/INT5/DO 79 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/external interrupt 5/SPI Data Out
P1.2/INT4/DI 80 I/O HIGH V
DD(P1,P3)
80C51 port pin/external interrupt 4/SPI Data In
SYMBOL PIN I/O
STATE
AFTER
RESET
(1)
SUPPLY
DOMAIN
DESCRIPTION
Page 10

1998 Apr 27 10
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
6 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
6.1 DECT baseband controller system
The PCD509x2 is a family of baseband controllers,
designed for use in Digital Enhanced Cordless
Telecommunications systems (DECT). The family is
designed for minimal component-count and minimal power
consumption for very long standby times. All baseband
controllers include an embedded 80C51 microcontroller
with on-chip memory, including an IrDA (Infrared Data
Association) compatible UART and I
2
C-bus. The Burst
Mode Logic performs the time-critical MAC layer functions
for applications in DECT handsets and base stations.
The implemented RF Interface is compatible with the
Philips Burst Mode Controller PCD504x. The ADPCM
transcoding is in compliance with the CCITT
Recommendation G.726. Also included is an on-chip
codec with receive and transmit filters, complying with
CCITT Recommendation G.712. Power-on-reset logic and
power management functions further reduce power
consumption and external components.
The chip is intended to support stand-alone systems only
(see Fig.3). There are no provisions to build clusters of
base stations. There are no provisions for external
controllers to exert control over the embedded 80C51.
There are no provisions for external controllers to have
direct access to the on-chip data memories. There are no
provisions to allow handsets to receive from two
unsynchronised base stations simultaneously, but a
handset can operate in a multi base station environment
as long as they are synchronous base stations.
Refer to the block diagram in Fig.1. The DECT Controller
consists of a number of functional blocks that operate
more or less autonomously and communicate with each
other via the System Data RAM (SDR). Blocks have
access to SDR via the Internal System Bus (ISB). The ISB
consists of an 8-bit data bus, a 10-bit address bus and a
number of bus-request/bus-grant signals. Access to the
ISB is controlled by ISB Bus Controller (IBC). The IBC
acknowledges bus requests on the basis of a priority
scheme. The embedded 80C51 controller is to be
programmed by the user. It must contain DECT software
from Man-Machine Interface (MMI) to the DECT protocols
TBC, CBC and DBC (refer to
“Figures 10 to 13, in
Section 6 of prETS 300 175-3: June
1996”). Software is
available from Philips Semiconductors.
Hardware state machines in the Burst Mode Logic (BML)
and the Speech Interface (SPI) execute the lower blocks in
the TBC, CBC and DBC. The 80C51 has control over the
BML and the SPI via tables in SDR. The BML saves serial
data, received via R_DATAP/M, in buffer areas in SDR.
The position of the buffers in SDR is fixed by the 80C51
software by means of the tables previously mentioned.
A-fields and B-fields are stored in separate buffers. In this
way, two traffic bearers, each with their private A-fields,
can share the same B-field buffer as is required in case of
bearer hand-over or local call. The DSP and Codec
support speech processing functions like analog-to-digital
and digital-to-analog conversion, filtering, ADPCM
encoding and decoding, 8-bit µ-law PCM to 14-bit linear
PCM conversion and its reverse, echo cancelling, tone
generation etc.
Fig.3 Block diagram examples of DECT systems with PCD509xy.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGM859
PCD50922
LINE
INTERFACE
(e.g. PCA1070)
a/b line
RADIO
CIRCUITS
handbook, full pagewidth
MGM860
PCD50912
MICROPHONE
EARPIECE
RADIO
CIRCUITS
a. Handset.
b. Base station.
Page 11

1998 Apr 27 11
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
7 PACKAGE OUTLINE
UNIT
A
max.
A1A2A3bpcE
(1)
eH
E
LL
p
Zywv θ
REFERENCES
OUTLINE
VERSION
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
mm
1.6
0.16
0.04
1.5
1.3
0.25
0.27
0.13
0.18
0.12
12.1
11.9
0.5
14.15
13.85
1.45
1.05
7
0
o
o
0.15 0.10.21.0
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
0.75
0.30
SOT315-1
97-07-15
95-12-19
D
(1) (1)(1)
12.1
11.9
H
D
14.15
13.85
E
Z
1.45
1.05
D
b
p
e
θ
E
A
1
A
L
p
detail X
L
(A )
3
B
20
c
D
H
b
p
E
H
A
2
v M
B
D
Z
D
A
Z
E
e
v M
A
X
1
80
61
60 41
40
21
y
pin 1 index
w M
w M
0 5 10 mm
scale
LQFP80: plastic low profile quad flat package; 80 leads; body 12 x 12 x 1.4 mm
SOT315-1
Page 12

1998 Apr 27 12
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
8 SOLDERING
8.1 Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages”
(order code 9398 652 90011).
8.2 Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering techniques are suitable for all LQFP
packages.
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
infrared/convection heating in a conveyor type oven.
Throughput times (preheating, soldering and cooling) vary
between 50 and 300 seconds depending on heating
method. Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C.
8.3 Wave soldering
Wave soldering is not recommended for LQFP packages.
This is because of the likelihood of solder bridging due to
closely-spaced leads and the possibility of incomplete
solder penetration in multi-lead devices.
CAUTION
Wave soldering is NOT applicable for all LQFP
packages with a pitch (e) equal or less than 0.5 mm.
If wave soldering cannot be avoided, for LQFP
packages with a pitch (e) larger than 0.5 mm, the
following conditions must be observed:
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave)
soldering technique should be used.
• The footprint must be at an angle of 45° to the board
direction and must incorporate solder thieves
downstream and at the side corners.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Maximum permissible solder temperature is 260 °C, and
maximum duration of package immersion in solder is
10 seconds, if cooled to less than 150 °C within
6 seconds. Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
8.4 Repairing soldered joints
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonallyopposite end leads. Use only a low voltage soldering iron
(less than 24 V) applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact
time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C. When
using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in
one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
Page 13

1998 Apr 27 13
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
9 DEFINITIONS
10 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
11 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I
2
C COMPONENTS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Short-form specification The data in this specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the same type
number and title. For detailed information see the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
Purchase of Philips I
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I2C patent to use the
components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
Page 14

1998 Apr 27 14
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
NOTES
Page 15

1998 Apr 27 15
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Low cost; low power DECT baseband
controllers (ABC-PRO)
PCD509x2/zuu/v family
NOTES
Page 16

Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company
© Philips Electronics N.V. 1998 SCA59
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Middle East: see Italy
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 40 27 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Pakistan: see Singapore
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +63 2 817 3474
Poland: Ul. Lukiska 10, PL 04-123 WARSZAWA,
Tel. +48 22 612 2831, Fax. +48 22 612 2327
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 755 6918, Fax. +7 095 755 6919
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 319762,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 7430 Johannesburg 2000,
Tel. +27 11 470 5911, Fax. +27 11 470 5494
South America: Al. Vicente Pinzon, 173, 6th floor,
04547-130 SÃO PAULO, SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax. +55 11 821 2382
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 3 301 6312, Fax. +34 3 301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 5985 2000, Fax. +46 8 5985 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2741 Fax. +41 1 488 3263
Taiwan: Philips Semiconductors, 6F, No. 96, Chien Kuo N. Rd., Sec. 1,
TAIPEI, Taiwan Tel. +886 2 2134 2865, Fax. +886 2 2134 2874
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Talatpasa Cad. No. 5, 80640 GÜLTEPE/ISTANBUL,
Tel. +90 212 279 2770, Fax. +90 212 282 6707
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +380 44 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 181 730 5000, Fax. +44 181 754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 625 344, Fax.+381 11 635 777
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors,
International Marketing & Sales Communications, Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218,
5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 34 Waterloo Road, NORTH RYDE, NSW 2113,
Tel. +61 2 9805 4455, Fax. +61 2 9805 4466
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213, Tel. +43 160 1010,
Fax. +43 160 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 200 733, Fax. +375 172 200 773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: seeSouth America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15thfloor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 689 211, Fax. +359 2 689 102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +852 2319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Prags Boulevard 80, PB 1919, DK-2300 COPENHAGEN S,
Tel. +45 32 88 2636, Fax. +45 31 57 0044
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615800, Fax. +358 9 61580920
France: 51 Rue Carnot, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 40 99 6161, Fax. +33 1 40 99 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 23 53 60, Fax. +49 40 23 536 300
Greece: No. 15, 25th March Street, GR 17778 TAVROS/ATHENS,
Tel. +30 1 4894 339/239, Fax. +30 1 4814 240
Hungary: seeAustria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Band Box Building, 2nd floor,
254-D, Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli, MUMBAI 400 025,
Tel. +91 22 493 8541, Fax. +91 22 493 0966
Indonesia: PT Philips Development Corporation, Semiconductors Division,
Gedung Philips, Jl. Buncit Raya Kav.99-100, JAKARTA 12510,
Tel. +62 21 794 0040 ext. 2501, Fax. +62 21 794 0080
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax. +353 1 7640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, PO Box 18053,
TEL AVIV 61180, Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax. +972 3 649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS, Piazza IV Novembre 3,
20124 MILANO, Tel. +39 2 6752 2531, Fax. +39 2 6752 2557
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku, TOKYO 108,
Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5077
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381
Printed in The Netherlands 435102/1200/01/pp16 Date of release: 1998 Apr 27 Document order number: 9397 750 03527
 Loading...
Loading...