Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
PCB8517
Stand-alone OSD for monitor
applications
Objective specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1997 Mar 03
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
FEATURES
Interface with microcontroller
• 3-wire high speed (maximum 2.5 Mbits/s) serial
interface with three types of transmission sequence.
On-Screen Display (OSD)
• On-chip PLL oscillator to generate the OSD dot clock
frequency which is 384 × horizontal sync frequency
• Horizontal sync frequency range of 10 to 100 kHz
• 10 rows of 24 characters display buffer
• 128 character fonts
• 12 × 16 character matrix
• Programmable height of displayed character (from
16 to 63 scan-lines); frame basis
• 4 types of character size; single/double character
height/width; row basis
• Horizontal starting position: 32 different positions
(6 dots for each step)
• Vertical starting position: 64 different positions
(4 scan-lines for each step)
• 8 foreground character colours: selection of only 2 out of
the 8 (outside the window) and 4 out of the of 8 (in the
window) in the same row
• 3 character shadowing modes:
– No shadow
– Shadowing
– Bordering shadow
• 3 fully programmable background windows with
overlapping capability and presetting priorities (for
multi-level application). The window colour can be
selected from 1 out of 8
• Half tone in background window supported
• Single 5 V power supply
• Available in DIP16 package.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PCB8517 is a stand-alone OSD which is used to
display the adjustment/status information on the screen of
an auto-sync monitor for menu driving application.
The display operation of the device is controlled by a
microcontroller which programs the internal 273 bytes of
RAM via a 3-wire high-speed serial interface. The on-chip
PLL oscillator and programmable character height are
used to keep the same character size displayed on the
screen in different display modes, VGA, SVGA and XGA
for example.
The OSD of the PCB8517 provides display buffers of
10 rows with 24 characters each. These display buffers
can select from 128 customized character fonts (with
12 × 16 bit resolution) to be displayed. The characters
displayed on the screen can be specified double height,
double width, different colour and with/without shadowing.
Three positional background windows are provided for
multi-level application.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
PCB8517P DIP16 plastic dual in-line package; 16 leads (300 mil) SOT38-4
1997 Mar 03 2
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE
Page 3
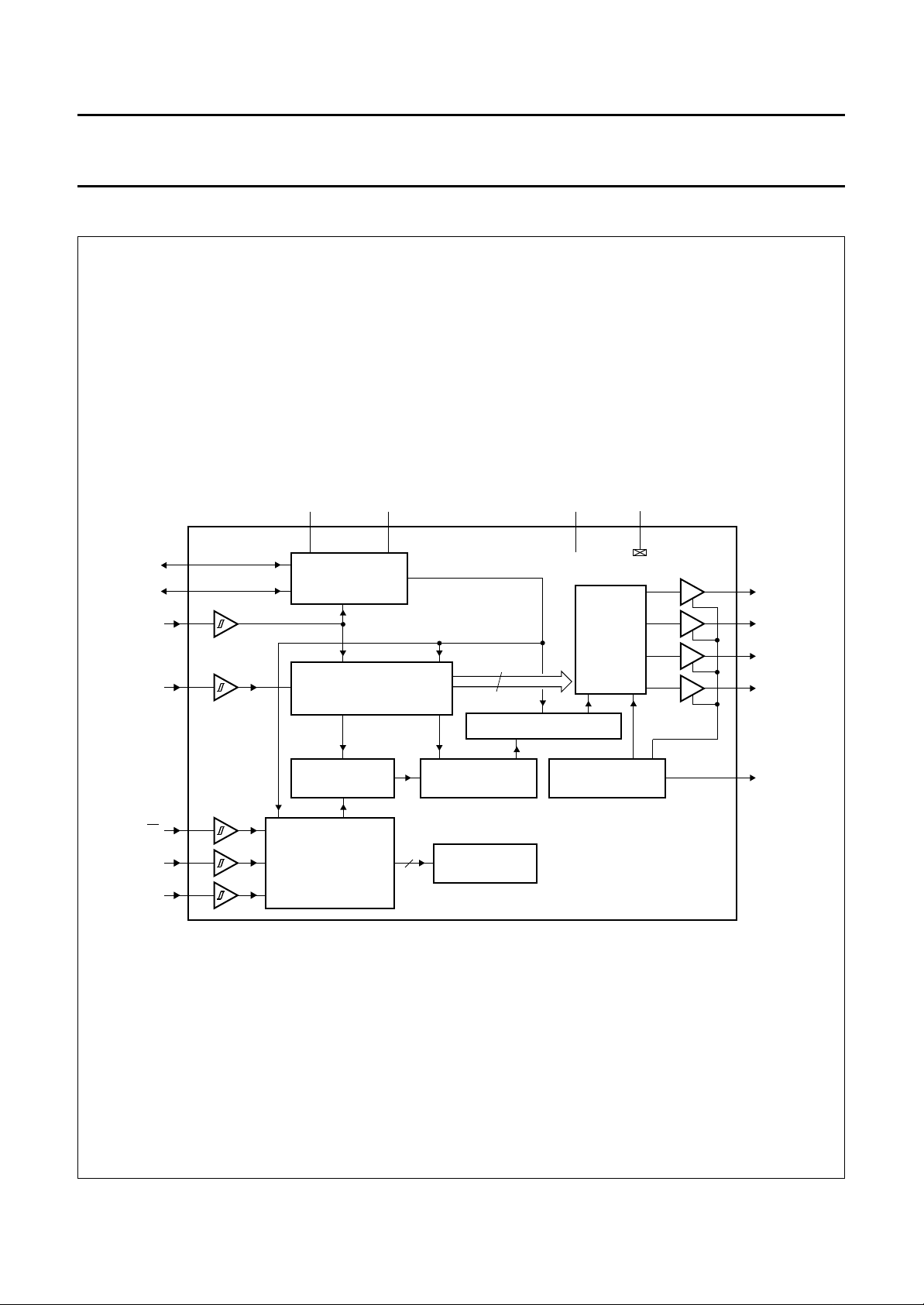
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
VCO
BIAS
HFLB
VFLB
EN
SDI
SCK
V
DDA
4
2
3
5
10
6
7
8
+
OSCILLATOR
−
DISPLAY CONTROL
DISPLAY BUFFER
24 × 10 RAM
HIGH SPEED SERIAL
I/O INTERFACE
PLL
V
SSA
1
CHARACTER FONTS
3
VCLK
4
12-STAGE SHIFT REGISTER
128 FONT ROM
CONTROL
REGISTERS
V
DDD
916
WINDOW AND
FRAME CONTROL
COLOUR
ENCODER
V
SSD
OSDEN
15
RED
14
GREEN
13
BLUE
12
FB
11
HTONE
MGD762
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1997 Mar 03 3
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
V
SSA
VCO 2 DC control voltage input/output to regulate the internal PLL oscillator frequency; a low-pass filter
BIAS 3 bias input/output to regulate the bias current of internal current control oscillator to resonate at a
V
DDA
HFLB 5 horizontal sync input signal from flyback circuit with negative polarity
EN 6 active LOW input to enable serial interface
SDI 7 data input of serial interface
SCK 8 clock input of serial interface
V
DDD
VFLB 10 vertical sync input signal from flyback circuit with negative polarity
HTONE 11 half tone control which outputs a logic 1 during windowing except characters are displayed; it is
FB 12 fast blanking output of OSD; active HIGH and high impedance when OSD is disabled
BLUE 13 blue colour output of OSD; active HIGH and high impedance when OSD is disabled
GREEN 14 green colour output of OSD; active HIGH and high impedance when OSD is disabled
RED 15 red colour output of OSD; active HIGH and high impedance when OSD is disabled
V
SSD
1 analog ground
circuit is connected to this pin
specific dot frequency
4 analog power supply
9 digital power supply
used to lower the external RED, GREEN and BLUE amplifier gain to achieve a transparent
windowing effect
16 digital ground
handbook, halfpage
V
SSA
VCO
BIAS
V
DDA
HFLB
SDI
SCK
EN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PCB8517
MGD760
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
V
SSD
RED
GREEN
BLUE
FB
HTONE
VFLB
V
DDD
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
1997 Mar 03 4
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
3-wire high speed serial interface (HSSI)
The 3-wire (
EN, SDI and SCK) high speed serial interface
of the PCB8517 is write only and is used to write data from
the microcontroller to the internal 273 bytes of RAM (see
Section “Internal RAM organization (see Fig.4)”) to control
the OSD. The RAM is organized into 11 rows of
32 columns (see Fig.4) and can be programmed by three
types of sequence (see Section “Data sequence and
format”).
ATA PROTOCOL
D
Figure 3 shows the protocol of HSSI. To initiate HSSI
transmission, pin EN must be LOW to enable the
PCB8517 to accept data. The EN input must be pulled
LOW prior to the occurrence of SCK and remain LOW until
after the last SCK clock pulse. The rising edge of SCK
facilitates the input data of SDI being shifted into an 8-bit
shift register. When the shift register is full this data will be
loaded into a row address register, column address
register or into one of the internal RAM bytes.
Table 1 shows the switching characteristics when the
HFLB pin has a pulse presented, but when there is no
horizontal sync pulse present on the HFLB pin, the
transmission bit rate will be slowed down to 500 kbit/s.
Table 1 Switching characteristics (under operating
conditions)
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
t
su(EN)
t
h(EN)
t
SCKL
t
SCKH
t
su(SDI)
t
h(SDI)
EN to SCK set-up time 200 − ns
EN to SCK hold time 100 − ns
SCK LOW time 200 − ns
SCK HIGH time 200 − ns
SDI data set-up time 200 − ns
SDI data hold time 100 − ns
handbook, full pagewidth
EN
SCK
SDI
t
su(EN)
B7
MSB
t
SCKH
first byte
t
SCKL
t
su(SDI)
t
h(SDI)
B0 B7B7 B0 B7 B0
LSB
last byte
Fig.3 3-wire serial interface protocol.
t
h(EN)
MGD764
1997 Mar 03 5
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
DATA SEQUENCE AND FORMAT
The PCB8517 provides the following 3 types of
transmission sequence:
• Sequence A: R ⇒ CA ⇒ D ⇒ R ⇒ CA ⇒ D etc.
• Sequence B: R ⇒ CA ⇒ D ⇒ CA ⇒ D ⇒ CA ⇒ D etc.
• Sequence C: R ⇒ CB ⇒ D ⇒ D ⇒ D ⇒ D etc.
Where: R = row address,
CA = column address A, CB = column address B,
D = data of RAM.
The column address will be increased by 1 automatically
after each bit of data has been stored into the RAM.
In sequence C, if the column address of the last data is
1FH, the row address will also be increased by 1.
The sequence A is particularly suitable for updating small
amounts of data between different rows. However, if the
current information byte has the same row address as the
previous one, sequence B is recommended. For a greater
information update, such as a power-up situation,
sequence C should be used.
Table 2 Data format
ADDRESS
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Row address 1 X X X R3 R2 R1 R0
Column address A 0 0 X C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
Column address B 0 1 X C4 C3 C2 C1 C0
Bit B7 in Table 2 is used to distinguish between row or
column address and bit B6 is used to distinguish between
column address A or B. When A or B sequence is
transmitted, the column address should be formatted as
column address A, and the data format of column
address B is used for sequence C. There are some
limitations on using mixed formats during a single
transmission, for example when pin
LOW once.
Allowed:
• From A to B or C
• From B to A.
Not allowed:
• From C to A or B.
DATA BYTE
(1)
EN has been pulled to
Note
1. X = don’t care.
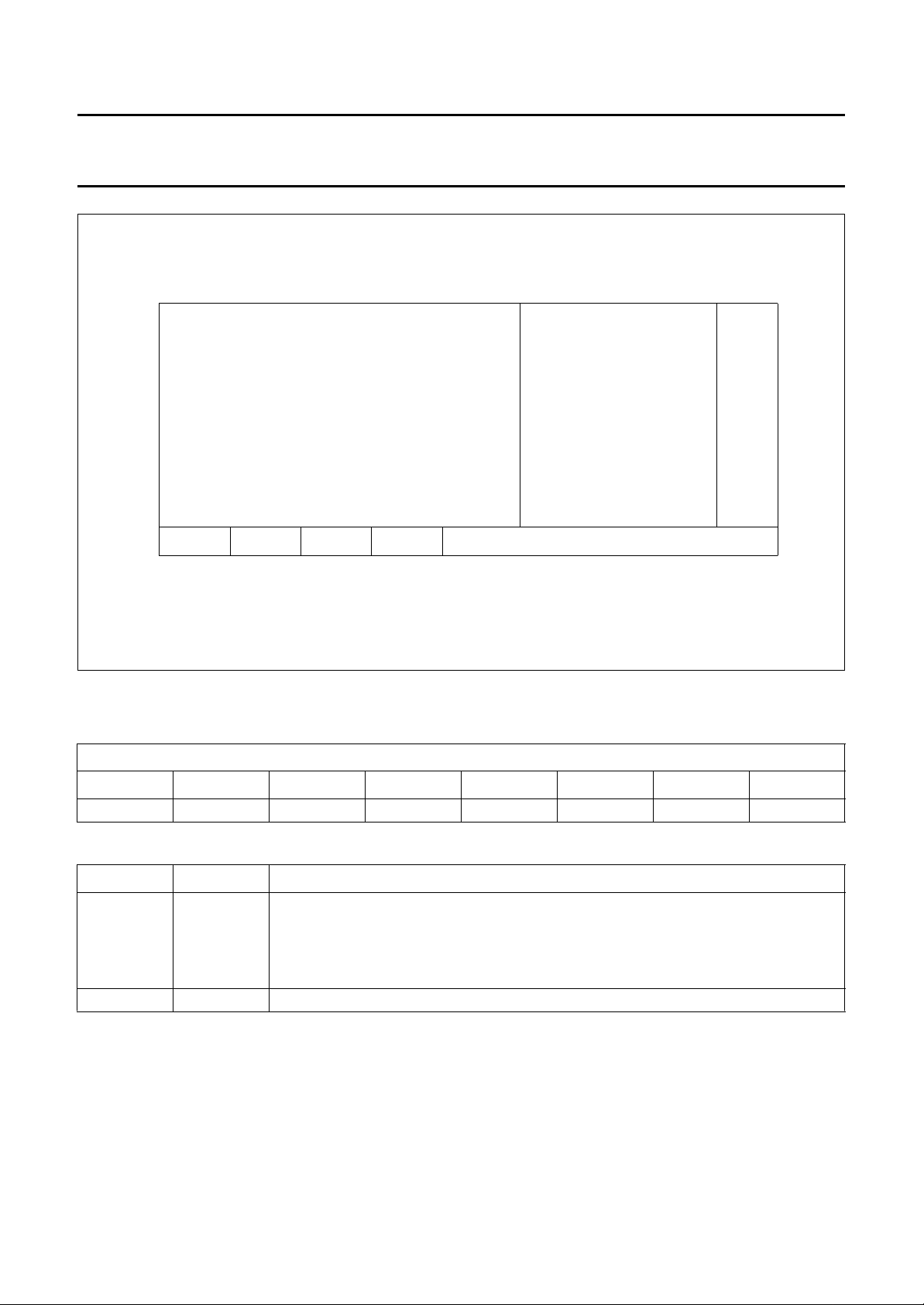
Internal RAM organization (see Fig.4)
The internal RAM is addressed with rows 0 to 10 and columns 0 to 31. The OSD character display buffers are located in
columns 0 to 23 of rows 0 to 9. Each display buffer contains a character ROM address and the colour control bit
corresponding to a display location on the monitor screen.
Each row data is associated with two control registers which are located at columns 30 and 31 of their respective row.
Also three window control registers for three windows together with three frame control register occupy the first
13 columns of row 10.
1997 Mar 03 6
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
handbook, full pagewidth
0
ROW CHARACTER DISPLAY BUFFERS RESERVED
9
WINDOW 1
10
CONTROL
02356891213 31
WINDOW 2
CONTROL
WINDOW 3
CONTROL
COLUMN
230 24 29 30 31
FRAME
CONTROL
Fig.4 Internal RAM map.
DISPLAY BUFFERS
ROW
CONTROL
RESERVED
MGD763
Table 3 Display buffers; see Table 4
DATA BYTE
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
CCS0 CA6 CA5 CA4 CA3 CA2 CA1 CA0
Table 4 Explanation of Table 3
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7 CCS0 This bit defines the characters colour. When the character has no window background
with it, colour 0 is selected if CCS0 = 0, otherwise colour 1 is selected. When the
character is inside a window and the CCS1 bit of the corresponding windows control
register is 0, the colour selection is the same as no window background, and if
CCS1 = 1, colour 2 is selected when CCS0 = 0, otherwise colour 3 is selected.
6 to 0 CA6 to CA0 These 7 bits define 1 of 128 character symbols to be displayed in this position.
1997 Mar 03 7
Page 8
Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
ROW CONTROL REGISTERS
Table 5 Column 30
DATA BYTE
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
R0 G0 B0 R1 G1 B1 CHS CWS
Table 6 Explanation of Table 5
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7 to 5 R0, G0, B0 colour definition of colour 0
4 to 2 R1, G1, B1 colour definition of colour 1
1 CHS This bit defines the height of the display character; when CHS = 1 double height is
selected.
(1)
0 CWS This bit defines the width of the display character; when CWS = 1 double width
selected.
is
Note
1. When the display row is selected to be double width, only even column characters will be displayed on the screen
and the odd column characters will not appear.
Table 7 Column 31
DATA BYTE
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
R2 G2 B2 R3 G3 B3 reserved
Table 8 Explanation of Table 7
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7 to 5 R2, G2, B2 colour definition of colour 2
4 to 2 R3, G3, B3 colour definition of colour 3
WINDOW CONTROL REGISTERS
There are three control registers for each window. Window 1 occupies columns 0 to 2 of row 10, columns 3 to 5 of
row 10 are occupied by window 2 and columns 6 to 8 of row 10 are occupied by window 3. If window overlapping occurs,
the highest priority window will cover the lowest. Window 1 has the highest priority and window 3 the lowest.
Table 9 Columns 0, 3 and 6 of row 10
DATA BYTE
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
MSB row start address LSB MSB row end address LSB
1997 Mar 03 8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
Table 10 Explanation of Table 9
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7to4 − These bits specify which row is the start of window.
3to0 − These bits specify which row is the end of window.
Table 11 Columns 1, 4 and 7 of row 10
DATA BYTE
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
MSB column start address LSB WEN CCS1 reserved
Table 12 Explanation of Table 11
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7to3 − These bits specify which column is the start of the window.
2 WEN When this bit is set to logic 1 the corresponding window background is enabled.
1 CCS1 When this bit is set to logic 1, the characters resided within this particular window can
have two extra colour selections (i.e. colour 2 and colour 3); see Section “Display
buffers”.
Table 13 Columns 2, 5 and 8 of row 10
DATA BYTE
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
MSB column end address LSB WR WG WB
Table 14 Explanation of Table 13
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7to3 − These bits specify which column is the end of the window.
2 to 0 WR, WG, WB These bits define the colour of the window.
RAME CONTROL REGISTERS
F
Table 15 Column 9 of row 10
DATA BYTE
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
reserved MSB vertical start position LSB
1997 Mar 03 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
Table 16 Explanation of Table 15
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
5to0 − These bits specify the vertical starting position of OSD. The counting starts from the
falling edge of the VFLB signal (e.g. enter vertical flyback period) and each increment
represents four scan line movement to the bottom. 64 positions are provided.
The default value is 4 after power-up. The time from the falling edge of the VFLB signal
to starting display is:
= (vertical start position) × 4 × t
t
v
Where t
= one horizontal line display time.
h-sync
h-sync+th-sync
Table 17 Column 10 of row 10
DATA BYTE
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
reserved MSB horizontal start position LSB
.
Table 18 Explanation of Table 17
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
4to0 − These bits specify the horizontal starting position of OSD. The counting starts from the
falling edge of the HFLB signal (e.g. enter horizontal flyback period) and each increment
represents six dots movement to the right. 32 positions are provided. The default value
is 15 after power-up. The time from the falling edge of the HFLB signal to starting
display is:
= (horizontal start position) × 6 × t
t
h
Where t
= one pixel display time (e.g. one horizontal line display time/384).
dot
+61×t
dot
dot
.
A horizontal display line consists of 384 dots, which include 288 dots (e.g. 12 dots × 24 characters) for display character,
and 96 dots for the blank region.
Table 19 Column 11 of row 10
DATA BYTE
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
reserved CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1 CH0
Table 20 Explanation of Table 19
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
5 to 0 CH5 to CH0 These bits specify the height of displayed characters. Table 21 shows the lines to be
repeated.
The height of character can be specified from 16 to 63 scan lines. For example, when
CH5 to CH0 = 00 0010, the height of character will be 18 scan lines, the 4th and 12th
line will be double scanned but others will be scanned once.
1997 Mar 03 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
Table 21 The repeat line of character
CH5 to CH0
LINE NUMBER
0123456789101112131415
CH0 = 1 −−−−−−−−V−−−−−−−
CH1 = 1 −−−−V−−−−−−−V−−−
CH2 = 1 −−V−−−V−−−V−−−V−
CH4 = 1 − V − V − V − V − V − V − V − V
CH5 and CH4 = 0X all sixteen lines scanned once
CH5 and CH4 = 10 all sixteen lines scanned twice
CH5 and CH4 = 11 all sixteen lines scanned three times
Note
1. V indicates which line of the character will be repeated one more time.
Table 22 Column 12 of row 10
(1)
DATA BYTE
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
OSDEN BSEN SHSE reserved FBC
Table 23 Explanation of Table 22
BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7 OSDEN The OSD circuit is active when this bit is set to logic 1. The outputs of R, G, B and FB
will be high impedance when OSD is disabled.
6 BSEN The bordering or shadowing effect is enabled when this bit is set to logic 1.
5 SHSE The shadowing of characters is selected if this bit is set to logic 1, otherwise bordering
of characters is chosen.
0 FBC This bit defines the output configuration of the FB pin. If this bit is set to logic 0, then the
output of FB will be logic HIGH when displaying character or window, otherwise the
output of FB is logic HIGH only when displaying characters.
1997 Mar 03 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
Character ROM
The character ROM contains 128 character fonts. Each
font consists of a 12 × 16 dot matrix.
Bordering and shadowing of characters
The characters displayed on the screen can be specified
with or without shadowing or with border shadowing by
setting the BSEN and SHSE bits of frame control register
“Column 11 of row 10”. If shadowing is specified, there is
black shadow on the right and bottom sides of character,
and if border shadowing is specified, the black shadowing
will surround both internal and external sides of characters
(see Fig.5). The characters shadow will not appear if it is
outside the display area of character (i.e. 12 × 16 dots).
Combination of two or more character fonts to
formulate a new symbol
User can combine two (or more) character fonts to
formulate a new higher resolution symbol in a horizontal
direction, but the combination of two fonts in a vertical
direction could cause the shadowing or bordering shadow
of upper font to be missed if shadowing or bordering is
applied.
PLL clock generator
By tracing the signal on the HFLB pin, the on-chip PLL
circuit generates the clock (VCLK) which is used for both
system clock and dot clock of the OSD. The frequency of
VCLK signal is determined by following equation:
f
VCLK=fHFLB
× 384 (i.e. the frequency range of VCLK
signal is from 3.84 to 38.4 MHz).
When there is no horizontal sync pulse present on the
HFLB pin, the PLL circuit will generate a 2.5 MHz
(approximate) clock for the system clock, and the RED,
GREEN, BLUE and FB pins will be high impedance.
handbook, full pagewidth
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
no shadow
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
shadowing
Fig.5 Character shadowing and bordering.
1997 Mar 03 12
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
bordering shadow
MGD759
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
PCB8517P/001 character fonts
dbook, full pagewidth
Fig.6 Character fonts 00H to 1FH.
1997 Mar 03 13
MGD755
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
dbook, full pagewidth
Fig.7 Character fonts 20H to 3FH.
1997 Mar 03 14
MGD756
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
dbook, full pagewidth
Fig.8 Character fonts 40H to 5FH.
1997 Mar 03 15
MGD757
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
dbook, full pagewidth
Fig.9 Character fonts 60H to 7FH.
1997 Mar 03 16
MGD758
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DDX
V
i
T
stg
T
amb
DC CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
DDX
I
DDX
digital supply voltage −0.3 +7.0 V
input voltage (all inputs) −0.3 V
DDX
+ 0.3 V
storage temperature −55 +125 °C
operating ambient temperature 0 70 °C
digital supply voltage 4.75 5.0 5.25 V
digital supply current VI=V
DDX
;
−−25 mA
no load on outputs
Inputs
V
IH
V
IL
Outputs
I
OH(source)
I
OL(sink)
HIGH level input voltage 2.0 − V
LOW level input voltage V
HIGH level output current (source) VO≥ V
− 0.8 5.0 −−mA
DDX
− 0.3 − 0.8 V
SSX
DDX
+ 0.3 V
LOW level output current (sink) VO≤ 0.5 5.0 −−mA
1997 Mar 03 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
APPLICATION INFORMATION
R, G and B video signals
handbook, full pagewidth
from PC or work station
horizontal sync from
deflection circuit
vertical sync from
deflection circuit
MICROCONTROLLER
HFLB
VFLB
EN
SDI
SCK
10
PCF8517
6
7
8
155
14
13
12
11
2
3
RED
GREEN
BLUE
FB
HTONE
(2)
VCO
5.6 kΩ
(2)
BIAS
MIXER
(1)
1 MΩ
0.01 µF
5.6 kΩ10 kΩ
0.01 µF
R, G and B outputs
to video circuit
MGD761
The analog power and ground pins should be separated from other circuits.
(1) Only connected when half tone is applied.
(2) The recommended circuit or value of components connected to VCO and BIAS could be changed in a different printed-circuit board layout.
Fig.10 Application circuit.
1997 Mar 03 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
PACKAGE OUTLINE
DIP16: plastic dual in-line package; 16 leads (300 mil)
D
seating plane
L
Z
16
pin 1 index
e
b
SOT38-4
M
E
A
2
A
A
1
w M
b
1
b
2
9
E
c
(e )
1
M
H
1
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
A
A
A
UNIT
max.
mm
inches
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT38-4
12
min.
max.
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
b
1.73
1.30
0.068
0.051
b
1
0.53
0.38
0.021
0.015
b
1.25
0.85
0.049
0.033
REFERENCES
cD E e M
2
0.36
0.23
0.014
0.009
19.50
18.55
0.77
0.73
1997 Mar 03 19
8
(1) (1)
6.48
6.20
0.26
0.24
L
e
1
M
3.60
8.25
3.05
7.80
0.14
0.32
0.12
0.31
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
E
10.0
8.3
0.39
0.33
H
0.2542.54 7.62
0.010.10 0.30
ISSUE DATE
92-11-17
95-01-14
w
max.
0.764.2 0.51 3.2
0.0300.17 0.020 0.13
(1)
Z
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“IC Package Databook”
Soldering by dipping or by wave
The maximum permissible temperature of the solder is
260 °C; solder at this temperature must not be in contact
with the joint for more than 5 seconds. The total contact
time of successive solder waves must not exceed
5 seconds.
DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
(order code 9398 652 90011).
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but
the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling
may be necessary immediately after soldering to keep the
temperature within the permissible limit.
Repairing soldered joints
Apply a low voltage soldering iron (less than 24 V) to the
lead(s) of the package, below the seating plane or not
more than 2 mm above it. If the temperature of the
soldering iron bit is less than 300 °C it may remain in
contact for up to 10 seconds. If the bit temperature is
between 300 and 400 °C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
stg max
). If the
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
1997 Mar 03 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
NOTES
1997 Mar 03 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
NOTES
1997 Mar 03 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Objective specification
Stand-alone OSD for monitor applications PCB8517
NOTES
1997 Mar 03 23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 34 Waterloo Road, NORTH RYDE, NSW 2113,
Tel. +61 2 9805 4455, Fax. +61 2 9805 4466
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213,
Tel. +43 1 60 101, Fax. +43 1 60 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 200 733, Fax. +375 172 200 773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: seeSouth America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15thfloor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 689 211, Fax. +359 2 689 102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +852 2319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Prags Boulevard 80, PB 1919, DK-2300 COPENHAGEN S,
Tel. +45 32 88 2636, Fax. +45 31 57 1949
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615800, Fax. +358 9 61580/xxx
France: 4 Rue du Port-aux-Vins, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 40 99 6161, Fax. +33 1 40 99 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 23 53 60, Fax. +49 40 23 536 300
Greece: No. 15, 25th March Street, GR 17778 TAVROS/ATHENS,
Tel. +30 1 4894 339/239, Fax. +30 1 4814 240
Hungary: seeAustria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Shivsagar Estate, A Block, Dr. Annie Besant Rd.
Worli, MUMBAI 400 018, Tel. +91 22 4938 541, Fax. +91 22 4938 722
Indonesia: see Singapore
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax. +353 1 7640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, TEL AVIV 61180,
Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax. +972 3 649 1007
Italy: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS, Piazza IV Novembre 3,
20124 MILANO, Tel. +39 2 6752 2531, Fax. +39 2 6752 2557
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku, TOKYO 108,
Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5077
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381
Middle East: see Italy
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 40 27 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +63 2 817 3474
Poland: Ul. Lukiska 10, PL 04-123 WARSZAWA,
Tel. +48 22 612 2831, Fax. +48 22 612 2327
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 755 6918, Fax. +7 095 755 6919
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 1231,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 7430 Johannesburg 2000,
Tel. +27 11 470 5911, Fax. +27 11 470 5494
South America: Rua do Rocio 220, 5th floor, Suite 51,
04552-903 São Paulo, SÃO PAULO - SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax. +55 11 829 1849
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 3 301 6312, Fax. +34 3 301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 632 2000, Fax. +46 8 632 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2686, Fax. +41 1 481 7730
Taiwan: Philips Semiconductors, 6F, No. 96, Chien Kuo N. Rd., Sec. 1,
TAIPEI, Taiwan Tel. +886 2 2134 2870, Fax. +886 2 2134 2874
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Talatpasa Cad. No. 5, 80640 GÜLTEPE/ISTANBUL,
Tel. +90 212 279 2770, Fax. +90 212 282 6707
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +380 44 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 181 730 5000, Fax. +44 181 754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 625 344, Fax.+381 11 635 777
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors, Marketing & Sales Communications,
Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218, 5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
© Philips Electronics N.V. 1997 SCA53
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
Printed in The Netherlands 547047/1200/01/pp24 Date of release: 1997 Mar 03 Document order number: 9397 75001017
 Loading...
Loading...