Page 1
PC929
(
❈ TÜV
VDE 0884) approved type is also available as an option.
PC929
Shortcircuit Protector Circuit
Built-in Photocoupler Suitable
for Inverter-Driving MOS-FET/IGBT
■
Features
1. Built-in IGBT shortcircuit protector circuit
2. Built-in direct drive circuit for IGBT drive
(Peak output current ... I
3. High speed response (t
4. High isolation voltage (V
O1P, IO2P : MAX. 0.4A)
, t
: MAX. 0.5µs)
PLH
PHL
: 4000V
iso
)
rms
5. Half lead pin pitch (p=1.27 mm) package type
6. Recognized by UL, file NO. E64380
■
Application
1. IGBT control for inverter drive
■
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter
*1
Forward current
Input
Reverse voltage V
Supply voltage V
O1 output current
*4
peak output current
O
1
O2 output current
*4
peak output current
O
2
Output
output voltage
O
1
*2
Power dissipation
Overcurrent detecting voltage
Overcurrent detecting current
Error signal output voltage
Error signal output current
*3
Total power dissipation
*5
Isolation voltage
Operating temperature T
Storage temperature T
Soldering temperature T
*1, 2, 3 Decrease in the ambient temperature range of the Absolute Max. Rating : Shown in Figs 1 and 2.
*4 Pulse width<=0.15µs, Duty ratio=0.01
*5 40 to 60% RH, AC for 1 minute, Ta=25˚C
(Ta=Topr unless otherwise specified)
Symbol
I
I
V
V
V
Rating Unit
I
F
R
CC
I
O1
O1P
I
O2
O2P
O1
P
O
V
C VCC
I
C
FS VCC
I
FS
P
tot
iso
opr
stg
sol
20 mA
6 (Ta=25˚C) V
35 V
0.1 A
0.4 A
0.1 A
0.4 A
35 V
500 mW
30 mA
20 mA
550 mW
4 000 Vrms
-25to +80
-55to +125
260 (for 10 sec)
V
V
˚C
˚C
˚C
■
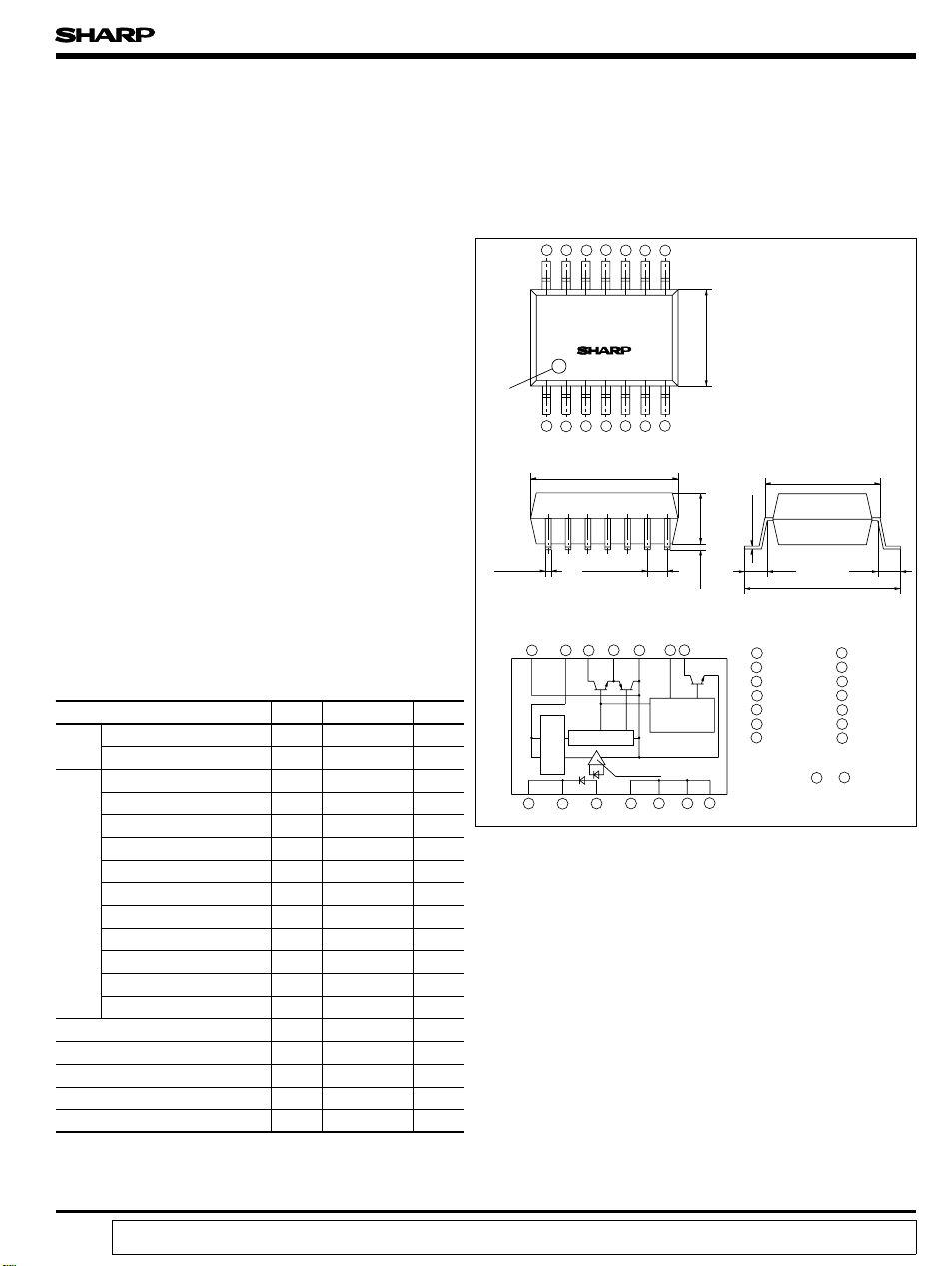
Outline Dimensions
1011121314
89
PC929
Primary
side mark
* "OPIC" (Optical IC) is a trademark of the SHARP Corporation.
An OPIC consists of a light-detecting element and signal processing circuit
integrated onto a single chip.
1234567
9.22
14-
0.6
Internal connection diagram
1234567
Interface
Constant
voltage circuit
12-
1.27
1011121314
Amp.
6.5
0.35 3.5
89
IGBT protector
circuit
0.26
1.0 1.0
1 Cathode
2 Cathode
3 Anode
4NC
5NC
6NC
7NC
Terminals 4 to 7 :
Shortcircuit in element
Operation truth table is shown on the next page.
7.62
10.0
8FS
9C
10
11
12
13
14
(Unit : mm)
GND
O
2
O
1
V
CC
GND
“In the absence of confirmation by device specification sheets, SHARP takes no responsibility for any defects that occur in equipment using any of SHARP's devices, shown in catalogs,
data books, etc. Contact SHARP in order to obtain the latest version of the device specification sheets before using any SHARP's device.”
Page 2
PC929
Electro-optical Characteristics (1)
■
(Ta=Topr unless otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Forward voltage
Reverse current I
Input
V
V
Terminal capacitance C
Operating supply voltage
O1 low level output voltage
O
high level output voltage
2
O
low level output voltage
2
Output
O leak current
High level supply current I
Low level supply current I
*7
"Low→High"
threshold input current
V
V
V
V
V
CCH
CCL
I
FLH
Isolation resistance R
"Low→High" propagation delay time
"High→Low" propagation delay time
t
PLH
t
PHL
Rise time t
Response time
Instantaneous common mode rejection
voltage "Output : High level"
Transfer characteristics
Instantaneous common mode rejection
voltage "Output : Low level"
*6 When measuring output and transfer characteristics, connect a bypass capacitor (0.01µ F or more) between V 13 and GND 14 near the device.
*7 I represents forward current when output goes from "Low" to "High".
FLH
*8 FS=OPEN, V =0V
C
Fall time t
CM
CM
Ta= 25˚C, IF= 10mA - 1.6 1.75 V -
F1
Ta= 25˚C, IF= 0.2mA 1.2 1.5 - V -
F2
Ta= 25˚C, VR=5V - - 10 µA-
R
Ta= 25˚C, V= 0, f= 1kHz - 30 250 pF -
t
Ta= - 10 to 60˚C 15 - 30 V
CC
V
= 12V, V
O1L
O2H
O2L
O1L
CC1
I
= 0.1A, IF= 5mA
O1
V
CC=VO1
I
= 5mA
F
VCC=VO1= 24V, IO2= 0.1A, IF= 0mA
Ta= 25˚C, VCC=VO1= 35V, IF= 0mA
Ta= 25˚C, VCC=VO1= 24V, IF= 5mA
VCC=VO1= 24V, IF= 5mA
Ta= 25˚C, VCC=VO1= 24V, IF= 0mA
VCC=VO1= 24V, IF= 0mA
Ta= 25˚C, VCC=VO1= 24V
VCC=VO1= 24V
Ta= 25˚C, DC500V, 40 to60% RH
ISO
Ta= 25˚C, VCC=VO1= 24V
RG=47Ω, CG= 3 000pF, IF= 5mA
r
f
Ta= 25˚C, VCC=VO1= 24V, IF= 5mA
H
L
= 600V(peak), ∆ V
V
CM
Ta= 25˚C, VCC=VO1= 24V, IF= 0mA
= 600V(peak), ∆ V
V
CM
- 15 - 24 V
= - 12V
CC2
= 24V, IO2= - 0.1A
- 0.2 0.4 V
*8
20 22 - V
*8
- 1.2 2.0 V
*8
- - 500 µ A
*8
-1017mA
*8
- - 19 mA
*8
-1118mA
*8
- - 20 mA
*8
0.3 1.5 3.0 mA
*8
0.2 - 5.0 mA
*8
5x10101x10
11
- 0.3 0.5 µs
- 0.3 0.5 µs
- 0.2 0.5 µs
*8
- 0.2 0.5 µs
O2H
O2L
= 2.0V
= 2.0V
CC
- 1 500
*8
1 500
*8
--V/µs
--V/µs
Measuring
circuit
-
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(
)
6
(5)
--Ω
(8)
(
)
7
Truth Table
■
Input
ON
OFF
Output FS OutputC Input/Output
O
2
Low level High level High level
High level Low level Low level
Low level Low level High level
High level Low level High level
For protective operation
Page 3

PC929
Electro-optical Characteristics (2)
■
Parameter Symbol Conditions Unit
*9
*9
*9
*9 When measuring overcurrent, protective output and error signal output characteristics, connect a bypass capacitor (0.01µ F or more) between V 13 and GND 14 near the device.
*10 V represents C-terminal voltage when O output goes from "High" to "Low".
*10
Overcurrent detecting voltage
Overcurrent detecting voltage
detection
hysteresis width
Overcurrent
O2 "High→Low" delay time
at protection from overcurrent
O2 fall time at protection
from overcurrent
O2 output voltage at protection
from overcurrent
Protective output
Low level error
signal voltage
High level error
signal current
Error signal "High→Low"
delay time
Error signal output
Error signal output pulse width
CTH 2
V
CTH
V
CHIS
t
PCOHL
t
PCOtf
V
V
I
FSH
t
PCFHL
∆ t
OE
FSL
T
= 25˚C, IF= 5mA
a
VCC=V01= 24V, RG=47Ω
= 3 000pF, FS= OPEN
C
G
Ta= 25˚C
V
C
C
= 24V, IF= 5mA
CC=V01
= 3 000pF, RG=47Ω
G
= 1 000pF, RC=1kΩ
P
FS= OPEN
T
= 25˚C, IF= 5mA, IFS= 10mA
a
VCC=VO1= 24V, RG=47Ω, CG= 3 000pF,
C = OPEN
T
= 25˚C, IF= 5mA, VFS= 24V
a
V
= 24V, RG=47Ω, CG= 3 000pF,
CC=VO1
VC=0V
Ta= 25˚C, RFS= 1.8kΩ
V
CG= 3 000pF, RG=47Ω
FS
C
= 24V, IF= 5mA
CC=VO1
= 1 000pF, RC=1kΩ
P
(Ta=Topr unless otherwise specified)
MIN. TYP. MAX.
V
-
VCC-
6.0
VCC-
5.5
V
CC
6.5
123V
-410
µs
25-µs
--2V
- 0.2 0.4 V
- - 100 µ A(12
-15µs
20 35 - µs
CC
Test circuit
(9)
(13)
(10)
(11)
)
(14)
Fig. 1 Forward Current vs. Ambient
Temperature
60
50
40
(mA)
F
30
20
Forward current I
10
0
0 25 50 75 80 100 125-25
Ambient temperature Ta (˚C)
Fig. 2 Power Dissipation vs. Ambient
Temperature
600
550
500
400
300
200
100
Power dissipation Ptot, Po (mW)
0
0 25 50 75 80 100 125-25
Ambient temperature Ta (˚C)
Page 4

Test Circuit Diagram
■
PC929
(1)(
3
↑ I
F
1
(
)(
3
3
↑ I
F
1
(
)(
5
3
↑ V
I
F
variable
1
(
)(
7
A
VCMwaveform
CM
, VO2waveform
H
SW at A, I
F
CM
, VO2waveform
L
SW at B, IF= 0mA
SW
B
= 5mA
3
1
PC929
2
PC929
2
PC929
2
PC929
2
+-
V
CM
13
12
11
10
14
9
8
13
12
11
10
14
9
8
13
12
11
10
14
9
8
13
12
11
10
14
9
8
∆ V
O2L
V ↑
V
O1L
V
V ↑
O2L
V
O2
V
V
O2
∆ V
I
O2H
O1
V
CC1
V
CC2
V
CC
I
O2
V
CC
V
CC
(Peak)
V
CM
GND
V
O2H
V
O2L
GND
)
2
3
↑ I
F
1
)
4
3
↑
I
F
1
)
6
3
↑
I
F
1
)
8
3
1
V
V
IN
V
OUT
tr= tf= 0.01 µ s
Pulse width : 5 µ s
IN
Duty ratio=50%
waveform
waveform
PC929
2
PC929
2
PC929
2
PC929
2
13
12
11
10
14
9
8
13
12
11
10
14
9
8
13
12
11
10
14
9
8
13
12
11
10
14
9
8
pLH
t
pHL
t
r
t
↑
I
O2
V
CC
V
O2H
V
A
I
O1L
V
OUT
50%
t
f
I
R
A
CC
G
90%
50%
10%
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
C
G
(
)(
9
3
↑ V
I
F
1
PC929
2
13
12
11
10
14
9
8
V
R
OUT
V
CC
G
C
G
V
V
CTH
)
10
3
↑ V
I
PC929
F
14
1
2
13
12
11
10
9
8
V
R
CC
G
R
C
V
OE
C
F
L
G
V
C
Page 5

Test Circuit Diagram
■
PC929
(11)
↑ I
(13)
tr= tf= 0.01 µs
Pulse width : 25µ s
V
IN
Duty ratio=25%
(12)
13
3
F
1
2
3
1
12
11
PC929 PC929
10
14
9
8
13
12
11
PC929 PC929
10
14
2
9
8
V ↓V
FSLIFS
V
C
P
R
V
G
CC
C
G
V
OUT
R
G
V
CC
C
G
R
C
↑ I
(14)
tr= tf= 0.01µ s
Pulse width : 25µ s
V
IN
Duty ratio=25%
3
F
1
2
3
1
13
12
11
10
14
9
8
13
12
11
10
14
2
9
8
R
V
G
CC
C
G
V
I
FSH
A
FS
R
C
R
G
V
CC
C
G
R
FS
V
I
F
(Input current)
V
O2
(O2 output voltage)
C
(Detecting terminal)
FS
(Error signal output)
10%
t
pCFHL
t
pCOTF
90%
50%
10%
t
pCOHL
90%
50% 50%
OE
V
Error detecting threshold voltage (V
∆ t
FS
CTH
)
Page 6

Operations of Shortcircuit Protector Circuit
■
Anode
Cathode
TTL, microcomputer, etc.
Light emitting diode
3
1
Photodiode
Constant voltage circuit
PC929
Amp.
Interface
IGBT protector circuit
GND
14
V
CC
13
O
1
12
O
2
11
R
G
C
9
FS
8
GND
10
Feedback to primary side
V
CC
IGBT
R
C
C
P
V
EE
1. Detection of increase in VCE (sat) of IGBT due to overcurrent by means of C-terminal 9 terminal)
2. Reduction of the IGBT gate voltage, and suppression of the collector current.
3. Simultaneous output of signals to indicate the shortcircuit condition (FS signal) from FS terminal to the microcomputer
4. Judgement and processing by the microcomputer
In the case of instantaneous shortcircuit, run continues.
At fault, input to the photocoupler is cut off, and IGBT is turned OFF.
PC929
Precautions for Operation
1. It is recommended that a capacitor of about 1000pF is added between C-terminal and GND in order to prevent
malfunction of C-terminal due to noise. In the case of capacitor added, rise of the detecting voltage is delayed.
Thus, use together a resistance of about 1kΩ set between Vcc and C-terminal.
The C-terminal rise time varies with the time constant of CR added. Check sufficiently before use.
2.
The light-detecting element used for this product is provided with a parasitic diode between each terminal and GND.
When a terminal happens to reach electric potential lower than GND potential even in a moment, malfunction
or rupture may result. Design the circuit so that each terminal will be kept at electric potential lower than the
GND potential at all times.
 Loading...
Loading...