Page 1
PC901V
PC901V
Digital Output Type OPIC
Photocoupler
■ Features
1. Normal-ON operation, open collector out put
2. Operating supply voltage (V : 3 to 15V
CC
3. TTL and LSTTL compatible output
4. High isolation voltage between input and
output (V
: 5 000V
iso
5. High sensitivity (I
Ta= 25˚C
)
)
rms
: MAX. 2.0mA at
FLH
6. Recognized by UL, file No. 64380
■ Applications
1. Isolation between logic circuits
2. Logic level shifters
3. Line receivers
4. Replacements for relays and pulse trans formers
5. Noise reduction
■ Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Rating Unit
Forward current I
*1
Input
Output
*1 Pulse width<=100µs, Duty ratio : 0.001
*2 40 to 60% RH, AC for 1 minute
*3 For 10 seconds
Peak forward current I
Reverse voltage V
Power dissipation P 70 mW
Supply voltage V
High level output voltage V
Low level output current I
Power dissipation P
Total power dissipation P
*2
Isolation voltage V
Operating temperature T
Storage temperature T
*3
Soldering temperature T
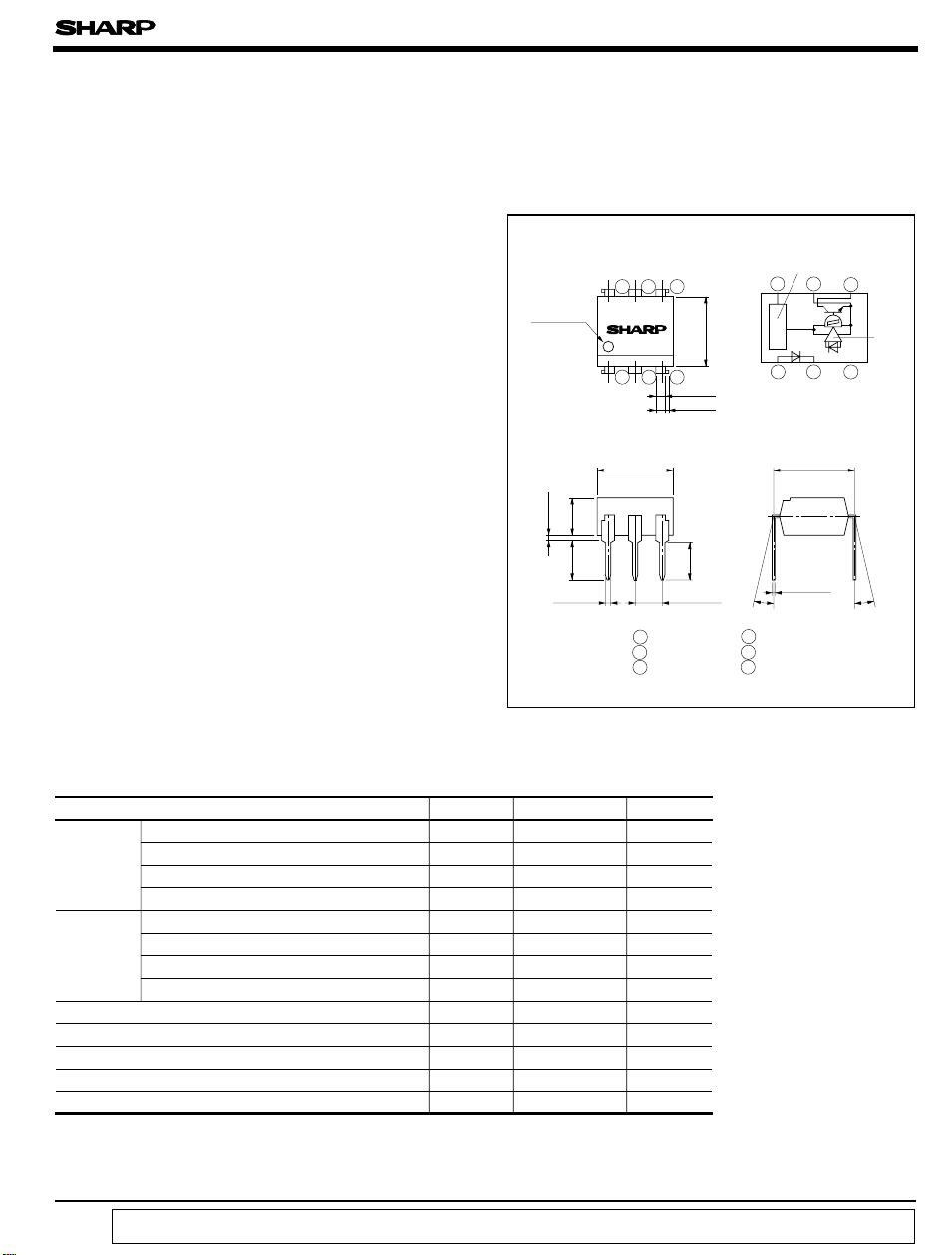
■ Outline Dimensions
)
Anode
mark
7.12
± 0.5
TYP.
3.5
0.5
± 0.5
3.7
± 0.1
0.5
* “ OPIC ” (Optical IC) is a trademark of the SHARP Corporation.
An OPIC consists of a light-detecting element and signal processing circuit integrated onto a single chip.
F
FM
R
CC
OH
OL
O
tot
iso
opr
stg
sol
50 mA
1A
6V
16 V
16 V
50 mA
150 mW
170 mW
5 000
- 25 to + 85 ˚C
- 40 to + 125 ˚C
260 ˚C
456
PC901V
123
± 0.5
2.54
1 Anode
2 Cathode
3 NC
(
Ta= 25˚C
V
rms
0.9
1.2
± 0.5
6.5
± 0.2
± 0.3
± 0.5
± 0.25
3.35
)
4 V
5 GND
6 V
(
Unit : mm
Internal connection
diagram
Voltage regulator
123
± 0.3
7.62
θ
= 0 to 13 ˚
± 0.1
0.26
θ
O
CC
)
456
Amp
θ
“ In the absence of confirmation by device specification sheets, SHARP takes no responsibility for any defects that occur in equipment using any of SHARP's devices, shown in catalogs,
data books, etc. Contact SHARP in order to obtain the latest version of the device specification sheets before using any SHARP's device.”
Page 2
PC901V
■ Electro-optical Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Forward voltage V
Input
Output
Transfer
charac-
teristics
*4 I
represents forward current when output goes from low to high.
FLH
*5 I
represents forward current when output goes from high to low.
FHL
*6 Hysterisis stands for I
*7 Test circuit for response time is shown below.
*8 Test circuit for CM
Reverse current I
Terminal capacitance C
Operating supply voltage V
Low level output voltage V
High level output current I
Low level supply current I
High level supply current I
“L→H” threshold input
*4
current
“H→L” threshold input
*5
current
*6
Hysteresis
Isolation resistance R
“L→H ” propagation delay time
“H→L ” propagation delay time
Rise time
time
Response
Fall time
*7
Instantaneous common mode rejec-
*8
tion voltage (High level output
Instantaneous common mode rejec-
*8
tion voltage (Low level output
FHL/IFLH
H,CML shown below.
)
(
Ta= 0 to + 70˚C unless otherwise specified
IF= 4mA - 1.1 1.4
F
I
= 0.3mA 0.7 1.0 -
F
Ta= 25˚C, V
R
Ta= 25˚C, V= 0, f = 1kHz - 30 250 pF
t
CC
OLIOL
OH
CCL
CCH
I
FLH
I
FHL
I
FHL/IFLH
ISO
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
r
t
f
CM
CM
)
= 16mA, VCC= 5V, I
VO=VCC= 15V, I
VCC= 5V, IF= 0 - 2.5 5.0 mA
VCC= 5V, IF= 4mA - 2.7 5.5 mA
Ta= 25˚C, VCC= 5V, RL= 280Ω
V
= 5V, RL= 280Ω - - 4.0
CC
Ta= 25˚C, VCC= 5V, RL= 280Ω
= 5V, RL= 280Ω
V
CC
VCC= 5V, RL= 280Ω 0.5 0.7 0.9 Ta = 25˚C, DC500V, 40 to 60% RH
Ta= 25˚C
= 5V, IF= 4mA
V
CC
R
= 280Ω
L
VCM= 600V(peak), V
H
= 4mA, RL= 280Ω, Ta= 25˚C
I
F
VCM= 600V(peak), V
L
= 0, RL= 280Ω, Ta = 25˚C
I
F
=4V
R
(
O
= 4mA
F
=0
F
(
MIN.)=2V
O
MAX.)= 0.8V
--10µA
3 - 15 V
- 0.2 0.4 V
- - 100 µ A
- 1.1 2.0
0.4 0.8 -
0.3 - -
5x101010
11
- Ω
-13
-26
- 0.1 0.5
- 0.05 0.5
- - 2000 - V/ µ s
- 2000 - V/ µ s
)
V
mA
mA
µs
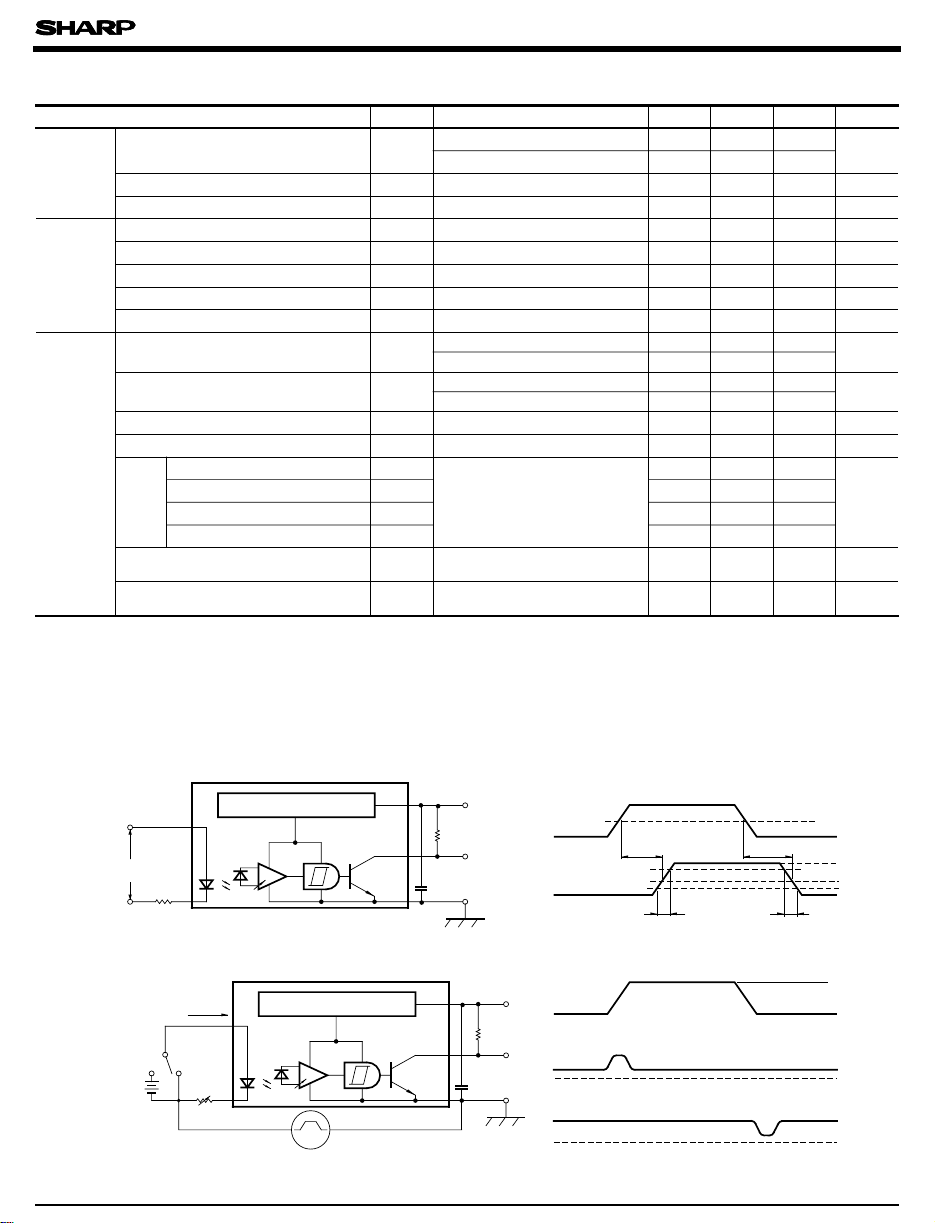
Test Circuit for Response Time
= tf= 0.01µs
t
r
= 50Ω
Z
O
V
IN
47Ω
Test Circuit for CMH, CM
Switch for
Infrared LED
A
B
I
F
Voltage regulator
Amp.
L
Voltage regulator
Amp.
+
V
CM
5V
V
280Ω
V
O
0.1µF
280Ω
0.1µ F
-
IN
V
O
V
5V
CM
Switch for Infrared LED at A (IF=0
V
O
Switch for Infrared LED at B (I
t
PLH
1.5V
V
(
V
MIN.)=2.0V
O
(
O
t
r
MAX.)=0.8V
=4mA
F
t
)
PHL
50%
V
OH
90%
10%
V
OL
t
f
600V
V
OL
GND
)
GND
Page 3

PC901V
Fig. 1 Forward Current vs. Ambient
Temperature
60
50
)
40
mA
(
F
30
20
Forward current I
10
0
- 25 0 25 50 75 10085
)
Ambient temperature T
a
(˚C
Fig. 3 Forward Current vs. Forward Voltage
500
= 75˚C
T
a
200
)
100
mA
(
50
F
20
10
5
Forward current I
2
1
0
50˚C
25˚C
0˚C
- 25˚C
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
Forward voltage V
)
(V
F
Fig. 2 Power Dissipation vs. Ambient
Temperature
200
P
tot
P
O
)
mW
(
, P
170
150
tot
100
O
50
Power dissipation P
0
0 25507510085
-25
Ambient temperature Ta (˚C
)
Fig. 4 Relative Threshold Input Current vs.
Supply Voltage
1.4
Ta= 25˚C
I
= 1 at VCC=5V
FLH
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
Relative threshold input current
0.4
0.2
I
FLH
I
FHL
510 20015
Supply voltage VCC (V
)
Fig. 5 Relative Threshold Input Current vs.
Ambient Temperature
1.6
V
=5V
CC
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
Relative threshold input current
0.2
0
0 25 50 100-25 75
I
FLH
I
FHL
I
= 1 at Ta= 25˚C
FLH
Ambient temperature Ta (˚C
)
Fig. 6 Low Level Output Voltage vs.
Low Level Output Current
1.0
0.5
)
V
(
OL
0.2
0.1
0.05
Low level output voltage V
0.02
0.01
=5V
V
CC
I
=0
F
T
= 25˚C
a
1
2 5 10 1005020
Low level output current IOL (mA
)
Page 4

PC901V
Fig. 7 Low Level Output Voltage vs.
Ambient Temperature
0.5
)
VCC=5V
0.4
V
(
OL
I
OL
= 30mA
0.3
16mA
0.2
0.1
Low level output voltage V
5mA
0
- 25 0 25 50 100
Ambient temperature T
75
(˚C)
a
Fig. 9 High Level Output Current vs.
Ambient Temperature
2
)
µA
(
1
OH
0.5
0.2
0.1
High level output current I
0.05
- 25 0 25 50 75 100
Ambient temperature T
VCC=VO= 15V
I
= 4mA
F
(˚C)
a
Fig.11 Propagation Delay Time vs.
Forward Current
6
=5V
V
CC
R
= 280Ω
L
)
T
= 25˚C
a
5
µs
(
PLH
, t
4
PHL
3
t
PHL
Fig. 8 High Level Output Current vs.
Forward Current
10
V
=5V
CC
= 25˚C
T
)
µA
(
OH
a
5
2
1
0.5
High level output current I
0.2
0.1
0
10 60
20 30 40 50
Forward current I
F
(mA)
Fig.10 Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
9
8
7
)
mA
(
6
CC
5
4
3
Supply current I
Ta=
{
- 25˚C
2
25˚C
{
{
1
85˚C
I
CCH
I
CCL
I
CCH
I
CCL
I
CCH
I
CCL
0
48 18012
Supply voltage V
10 1462
CC
16
(V)
Fig.12 Rise Time, Fall Time vs.
Load Resistance
0.6
VCC=5V
I
= 4mA
F
0.5
)
T
= 25˚C
µs
(
f
, t
r
a
0.4
0.3
2
1
Propagation delay time t
0
10 20 30 40 60050
Forward current I
F
(mA)
0.2
Rise time, fall time t
t
PLH
0.1
0
0.2 0.5 1 2 5 10 20
Load resistance R
t
r
t
f
(kΩ)
L
Page 5

■ Precautions for Use
(1)
It is recommended that a by-pass capacitor of more than 0.01µF is added between V
GND near the device in order to stabilize power supply line.
(2)
Handle this product the same as with other integrated circuits against static electricity.
(3)
As for other general cautions, please refer to the chapter “Precautions for Use ”
CC
PC901V
and
 Loading...
Loading...