Page 1
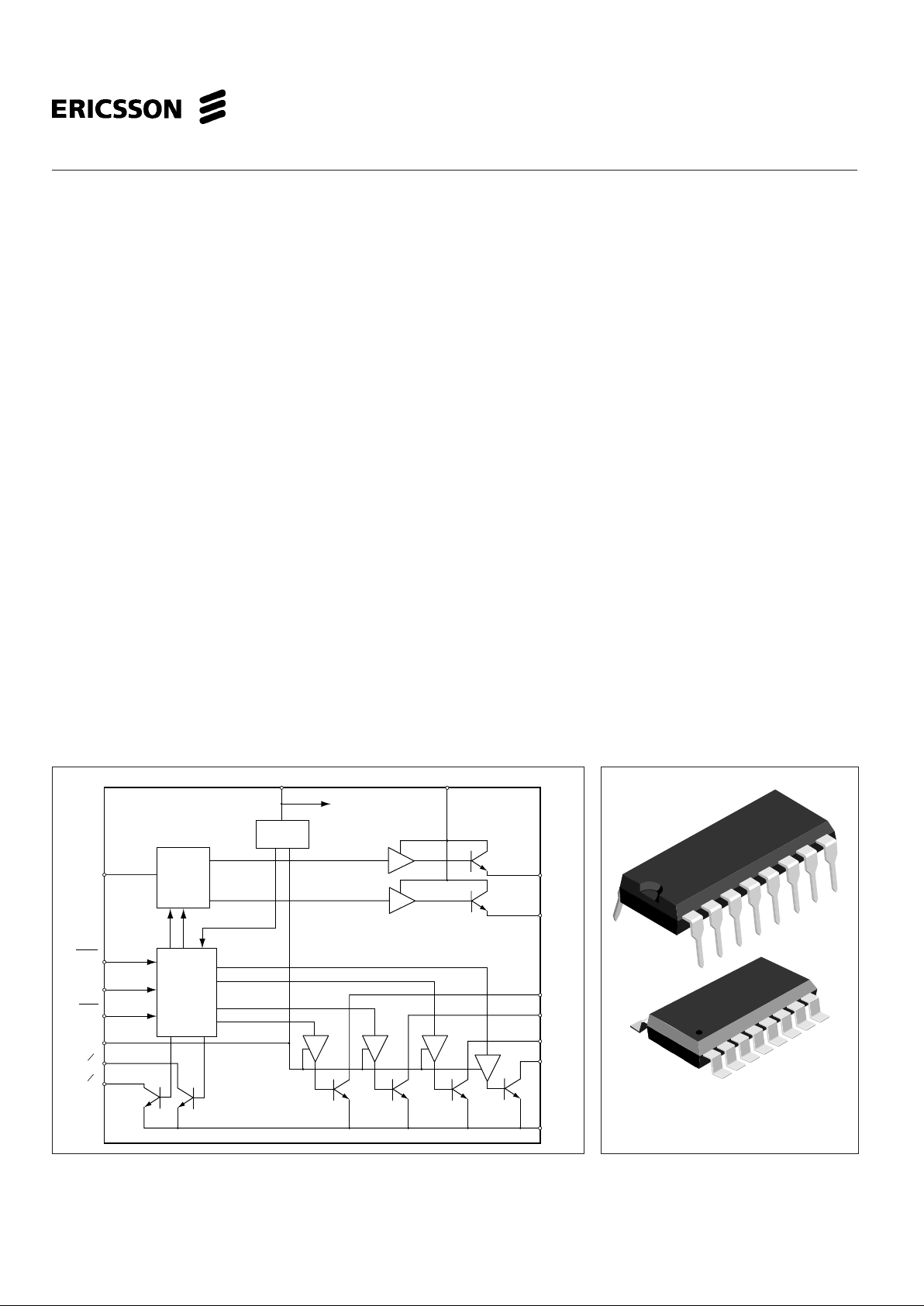
PBD 3517/1
Stepper Motor
Drive Circuit
Figure 1. Block diagram.
February 1999
16-pin plastic DIP
16-pin SO (wide body)
RC
STEP
DIR
HSM
INH
O
A
OB
L
A
L
B
P
B2
P
B1
P
A2
P
A1
GND
V
CC
V
SS
PBD 3517/1
PQR
Mono
F - F
Phase
Logic
P
A
P
B
Description
PBD 3517/1 is a bipolar, monolithic, integrated circuit, intended to drive a stepper motor
in a unipolar, bilevel way.
One PBD 3517/1 and a minimum of external components form a complete control
and drive unit for LS-TTL- or microprocessor-controlled stepper motor system for
currents up to 500mA. The driver is suited for applications requiring least-posssible RFI.
Motor performance can be increased by operating in a bilevel drive mode. This
means that a high voltage pulse is applied to the motor winding at the beginning of a
step, in order to give a rapid rise of current.
Key Features
• Complete driver and phase logic on
chip
• 2 x 350 mA continuous-output current
• Half- and full-step mode generation
• LS-TTL-compatible inputs
• Bilevel drive mode for high step rates
• Voltage-doubling drive possibilities
• Half-step position-indication output
• Minimal RFI
• 16-pin plastic DIP package or 16 pin
small outline wide body
PBD 3517/1
PBD 3517/1
1
Page 2
PBD 3517/1
2
Maximum Ratings
Parameter Pin No. Symbol Min Max Unit
Voltage
Logic supply 16 V
CC
07V
Second supply 15 V
SS
045V
Logic input 6, 7, 10, 11 VI -0.3 6 V
Current
Phase output 1, 2, 4, 5 I
P
0 500 mA
Second-level output 13, 14 I
L
-500 0 mA
Logic input 6, 7, 10, 11 I
I
-10 mA
The zero output 8, 9 I
Ο
6mA
Temperature
Operating junction temperature T
J
-40 +150 °C
Storage temperature T
S
-55 +150 °C
Power Dissipation (Package Data)
Power dissipation at TA = 25°C, DIP package. Note 2. P
D
1.6 W
Power dissipation, SO package. Note 3. P
D
1.3 W
Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Logic supply voltage V
CC
4.75 5 5.25 V
Second-level supply voltage V
SS
10 40 V
Phase output current I
P
0 350 mA
Second-level output current I
L
-350 0 mA
Operating junction temperature T
J
-20 +125 °C
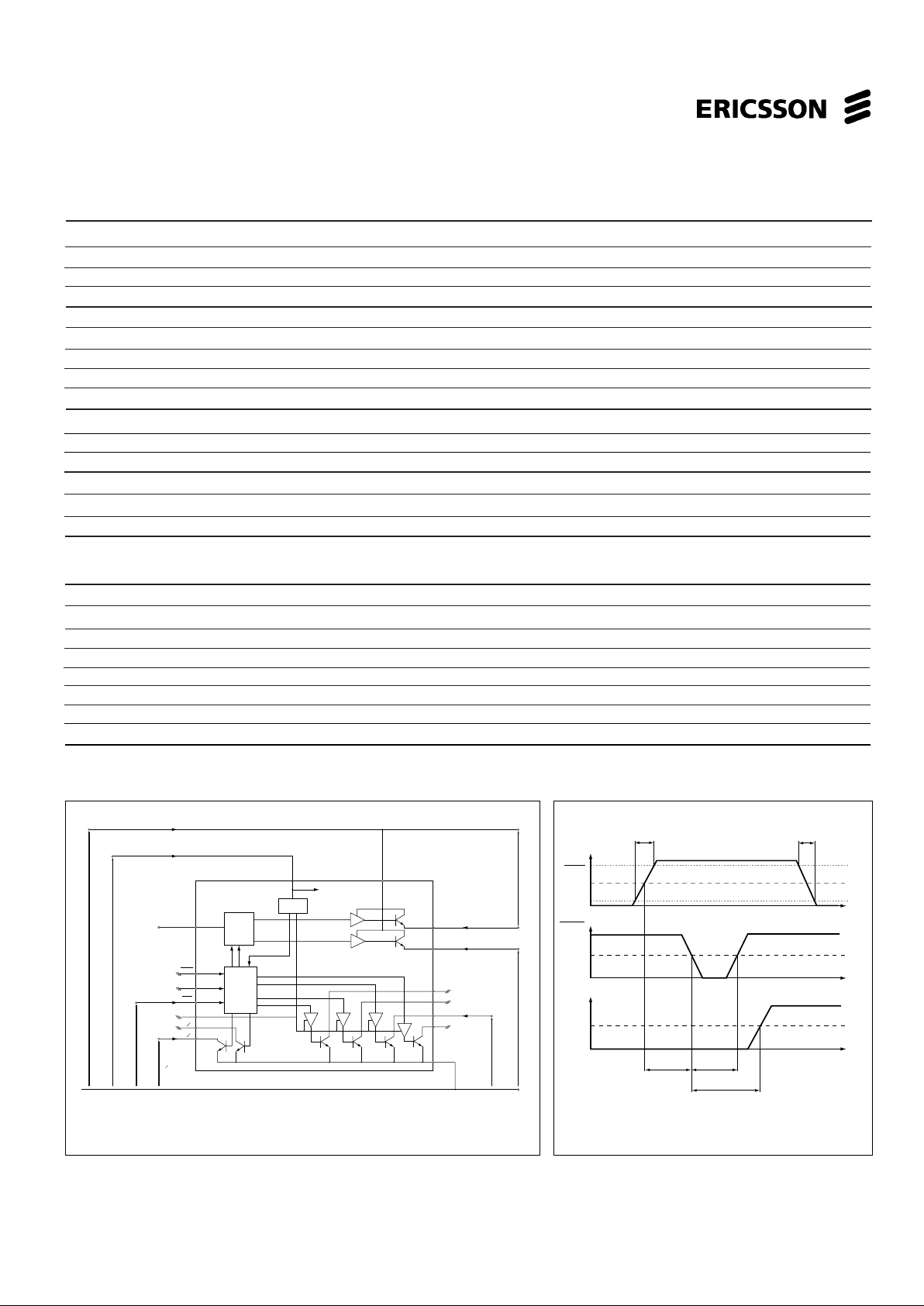
Set-up time t
s
400 ns
Step-pulse duration t
p
800 ns
Figure 2. Definition of symbols.
HSM
or
DIR
V
I
STEP
I
P
t
t
t
t
r
t
f
t
s
t
p
t
d
Figure 3. Timing diagram
.
RC 12
STEP 7
DIR 6
HSM 10
INH 11
O
A
9
OB 8
13 L
A
14 L
B
1 P
B2
2 P
B1
5 P
A2
4 P
A1
3 GND
V
CC
16
V
SS
15
PBD 3517/1
PQR
Mono
F - F
Phase
Logic
P
A
P
B
V
CC
V
SS
V
I
V
IH
V
IL
V
OCE Sat
V
LCE Sat
V
L
V
PCE Sat
V
P
IPI
PL
I
LL
I
L
IIIILI
IH
I
SS
I
CC
Page 3
PBD 3517/1
3
Electrical Characteristics
Electrical characteristics at TA = +25°C, VCC = +5.0 V, VMM = +40 V, VSS = +40 V unless otherwise specified.
Ref.
Parameter Symbol Fig. Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Supply current I
CC
2 INH = LOW 45 60 mA
2 INH = HIGH 12 mA
Phase outputs
Saturation voltage V
PCE Sat
4IP = 350 mA 0.85 V
Leakage current I
PL
2VP = 0 V 500 µA
Turn on, turn off t
d
3 +70°C3µs
t
d
3 +125°C6µs
Second-level outputs
Saturation voltage V
LCE Sat
4IL = -350 mA 2.0 V
Leakage current I
LL
2VL = 0 V -500 µA
On time t
On
11 (note 4) 220 260 300 µs
Logic inputs
Voltage level, HIGH V
IH
2 2.0 V
Voltage level, LOW V
IL
2 0.8 V
Input current, low I
IL
2VI = 0.4 V -400 µA
Input current, high I
IH
2VI = 2.4 V 20 µA
Logic outputs
Saturation voltage V
ØCE Sat
5IØ = 1.6 mA 0.4 V
Notes
1. All voltages are with respect to ground. Current are positive into, negative out of specified terminal.
2 Derates at 12,8 mW/°C above +25°C.
3. Derates at 10.4 mW/°C above +25°C.
4. R
T
= 47 kΩ, CT = 10 nF.
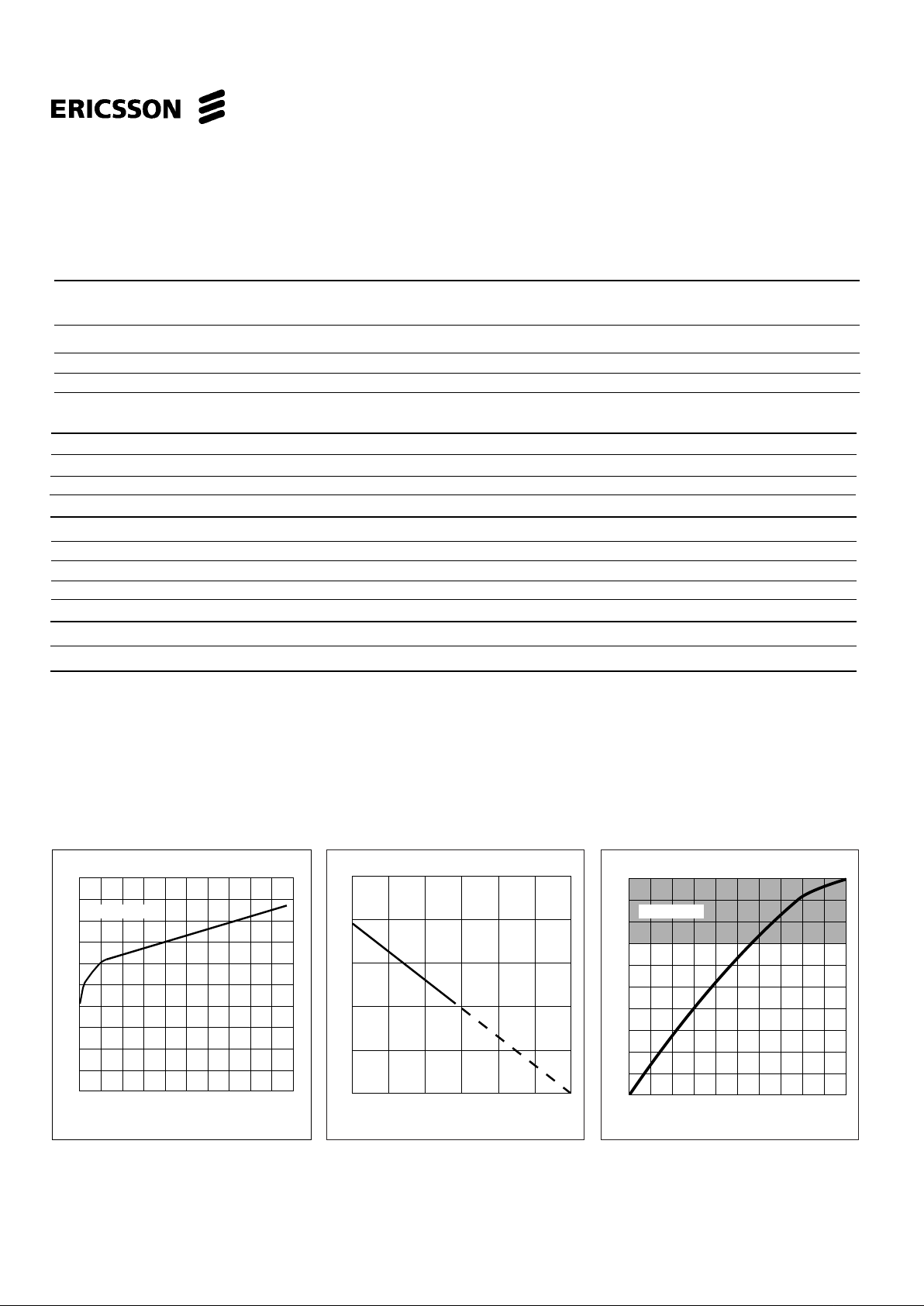
Figure 5. Typical second level saturation
voltage vs output current.
Figure 4. Typical phase output saturation
voltage vs. output current.
Figure
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0,5
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.50.40.3
V
LCE
sat [V]
I
L
[A]
TA= +25° C
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0,5
0
0 50 100 150
Allowable power dissipation [W]
Ambient temrature [°C]
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 0.2 0.4 1.00.80.6
Output Current [A]
Output Voltage [V]
TA= +25° C
Page 4

PBD 3517/1
4
Diagrams
How to use the diagrams:
1. What is the maximum motor current
in the application?
• The ambient temperature sets the
maximum allowable power
dissipation in the IC, which
relates to the motor currents and
the duty cycle of the bilevel
function. For PBD 3517/1, without
any measures taken to reduce
the chip temperature via
heatsinks, the power dissipation
vs. temperature follows the curve
in figure 4.
• Figures 9 and 10 give the
relationship between motor
currents and their dissipations.
The sum of these power dissipations must never exceed the
previously-established value, or
life expectancy will be drastically
shortened.
• When no bilevel or voltage
doubling is utilized, the maximum
motor current can be found
directly in figure 9.
2. How to choose timing components.
• Figure 7 shows the relationship
between C
T
, RT, and tOn. Care
must be taken to keep the tOn time
short, otherwise the current in the
winding will rise to a value many
times the rated current, causing
an overheated IC or motor.
3. What is the maximum t
On
pulse-width
at a given frequency?
• Figure 8 shows the relationship
between duty cycle, pulse width,
and step frequency. Check
specifications for the valid
operating area.
4. Figures 4, 5 and 6 show typical
saturation voltages vs. output current
levels for different output transistors.
5. Shaded areas represent operating
conditions outside the safe operating
area.
Figure 7. Typical IØ vs. V
ØCE Sat
. “Zero
output” saturation.
Figure 8. Typical t
On
vs. CT/RT. Output
pulse width vs. capacitance/resistance.
Figure 9. Typical tOn vs. fs/dc. Output pulse
width vs. step frequency/duty cycle
.
Figure 10. Typical PDP vs. IP. Power
dissipation without second-level supply
(includes 2 active outputs = FULL STEP)
.
Figure 11. Typical PDI vs. II. Power
dissipation in the bilevel pulse when
raising to the II value. One active output.
Figure 12 . Motor Current 1p.
TA= +25° C
10
8
6
4
2
0
0 0.2 0.4 1.00.80.6
Output Current [A]
Output Voltage [V]
1
10
-1
10
-6
0.01 0.1 1 100010010
Output Pulse Width [s]
Ct Capacitance [nF]
10
-2
10
-3
10
-4
10
-5
TA= +25° C
Rt = 10M
Rt = 100k
Rt = 10k
Rt = 1k
1
10
-1
10
-6
0.001 0.01 0.1 100101
Output Pulse Width [s]
fs Step frequency [kHz]
10
-2
10
-3
10
-4
10
-5
TA= +25° C
50%
25%
Dutycykle
100%
0.1%
1%
10%
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 0.2 0.4 1.00.80.6
Output Current [A]
Power Dissipation [W]
TA= +25° C
(II = 0)
-0.5
-0.4
-0.3
-0.2
-0.1
0
0 0.2 0.4 1.00.80.6
Output Current [A]
Power Dissipation [W]
TA= +25° C
(Ip = 0)
10% 50% 100%
350
Motor Current [mA]
t
ON
Time
Normal
Bilevel
Bilevel without
time limit
Page 5

PBD 3517/1
5
Pin Description
DIP SO-pack. Symbol Description
11 PB2Phase output 2, phase B. Open collector output capable of sinking max 500 mA.
22 P
B1
Phase output 1, phase B. Open collector output capable of sinking max 500 mA.
3 3 GND Ground and negative supply for both V
CC
and VSS.
44 P
A1
Phase output 1, phase A.
55 P
A2
Phase output 2, phase A.
6 6 DIR Direction input. Determines in which rotational direction steps will be taken.
7 7 STEP Stepping pulse. One step is generated for each negative edge of the step signal.
8 8 ØB Zero current half step position indication output for phase B.
9 9 ØA Zero current half step position indication output for phase A.
10 10 HSM Half-step mode. Determines whether the motor will be operated in half or full-step
mot. When pulled low, one step pulse will correspond to a half step of the motor.
11 11 INH A high level on the inhibit input turns all phase output off.
12 12 RC Bilevel pulse timing pin. Pulse time is approximately t
on
= 0.55 • RT • C
T
13 13 LA Second level (bilevel) output, phase A.
14 14 LB Second level (bilevel) output, Phase B.
15 15 V
SS
Second level supply voltage, +10 to +40 V.
16 16 V
CC
Logic supply voltage, nominally +5 V.
Figure 13. Pin configuration.
B2
B1
GND
A1
A2
DIR
STEP
B
V
V
L
L
R
INH
HSM
Ø
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
P
P
P
P
A
C
A
B
SS
CC
Ø
B2
B1
GND
A1
A2
DIR
STEP
B
V
V
L
L
R
INH
HSM
Ø
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
P
P
P
P
A
C
A
B
SS
CC
Ø
PBD
3517/1N
PBD
3517/1SO
Page 6

PBD 3517/1
6
determined by VSS voltage and motor
data, the L/R time-constant.
In a low-voltage system, where high
motor performance is needed, it is also
possible to double the motor voltage by
adding a few external components, see
figure 14.
The time the circuit applies the higher
voltage to the motor is controlled by a
monostable flip-flop and determined by
the timing components RT and CT.
The circuit can also drive a motor in
traditional unipolar way.
An inhibit input (INH) is used to switch
off the current completely.
Logic inputs
All inputs are LS-TTL compatible. If any
of the logic inputs are left open, the
circuit will accept it as a HIGH level. PBD
3517/1 contains all phase logic
necessary to control the motor in a
proper way.
Functional Description
The circuit, PBD 3517/1, is a high
perform-ance motor driver, intended to
drive a stepper motor in a unipolar, bilevel
way. Bilevel means that during the first
time after a phase shift, the voltage
across the motor is increased to a second
voltage supply, VSS, in order to obtain a
more-rapid rise of current, see figure 11.
The current starts to rise toward a
value which is many times greater than
the rated winding current. This compensates for the loss in drive current and loss
of torque due to the back emf of the
motor.
After a short time, tOn, set by the
monostable, the bilevel output is switched
off and the winding current flows from the
VMM supply, which is chosen for rated
winding current. How long this time must
be to give any increase in performance is
STEP — Stepping pulse
One step is generated for each negative
edge of the STEP signal. In half-step
mode, two pulses will be required to move
one full step. Notice the set up time, t
s
, of
DIR and HSM signals. These signals
must be latched during the negative edge
of STEP, see timing diagram, figure 3.
DIR — Direction
DIR determines in which direction steps
will be taken. Actual direction depends on
motor and motor connections. DIR can be
changed at any time, but not simultaneously with STEP, see timing diagram,
figure 3.
HSM determines whether the motor will
be controlled in full-step or half-step
mode. When pulled low, a step-pulse will
correspond to a half step of the motor.
HSM can be changed at any time, but not
simultaneously with STEP, see timing
diagram, figure 3.
Figure 15. Voltage
doubling with
external
transistors.
Figure 14.
Typical
application.
RC 12
STEP 7
DIR 6
HSM 10
INH 11
O
A
9
OB 8
13 L
A
14 L
B
1 P
B2
2 P
B1
5 P
A2
4 P
A1
3 GND
V
CC
16
V
SS
15
PBD 3517/1
PQR
Mono
F - F
Phase
Logic
P
A
P
B
STEP
CW / CCW
HALF / FULL STEP
NORMAL /INHIBIT
(Optional Sensor)
GND
V
CC
CMOS, TTL-LS
Input / Output-Device
V
SS
+ 5V
GND (V
CC
)
V
MM
R9 R8
R
T
C
T
C3C4C
5
+++
R11 R10
D2 D1
MOTOR
D3-D6
D3-D6 are
UF 4001 or
BYV 27
trr < 100 ns
GND (VMM,VSS)
D3
+
RC 12
STEP 7
DIR 6
HSM 10
INH 11
O
A
9
OB 8
13 L
A
14 L
B
1 P
B2
2 P
B1
5 P
A2
4 P
A1
3 GND
V
CC
16
V
SS
15
PBD 3517/1
PQR
Mono
F - F
Phase
Logic
P
A
P
B
STEP
CW / CCW
HALF / FULL STEP
NORMAL /INHIBIT
(Optional Sensor)
GND
V
CC
CMOS, TTL-LS
Input / Output-Device
V
MM
+ 5V
GND (V
CC
)
R9 R8
R
T
C
T
C3C
4
++
R10
D1
1/2 MOTOR
GND (V
MM,VSS
)
R1
R2
Q1
Q3
C1
R12 R13
R4
R5
Q5
Q6
Equal to
Phase A
Page 7

PBD 3517/1
7
Purpose of external components
For figures 14 and 15. Note that “Larger than …” is normally the vice versa of “Smaller
than … .”
Component Purpose Value Larger than value Smaller than value
D1, D2 Passes low power to
motor and prevents
high power from
shorting through low
power supply
If = 1A
1N4001, UF4001
Increases price Decreases max
current capability
D3 … D6 Inductive current
supressor
Increases price Decreases current
turn-off capability
trr = 100nS
e.g. BYV27
UF4001
RGPP10G
RGPP30D
Slows down turnoff time. Voltage
at anode might
exceed voltage
breakdown
Speeds up turn-
off time.
R1 Base drive current
limitter
R = 20ohm
2
Slows down Q1’s
turn-on and Q4’s
turn-off time.
Speeds up Q1’s
turn-on and Q4’s
turn-off time.
R2, R3 Base discharge resistor R = 240ohm
2
Slows down Q1’s
turn-off and Q4’s
turn-on time.
Speeds up Q1’s
turn-off and Q4’s
turn-on time.
R4 … R7 External transistor base
driver
Vmm - Vbe - V
ce
R =
P > (I4)2 • R4
Check hfe.
Decreases ext.
transistor IC max.
Lowers 3517
power dissipation.
Increases ext.
transistor IC max.
Increases 3517
power dissipation.
R8, R9 ØA, ØB pull-up
resistors
R = 5ohm @ pull-up
voltage = 5V.
Increases noise
sensitivity, worse
logic-level
definition
Increases noise
immunity, better
logic-level
definition.
Less stress on ØA,
ØB output
transistors
Stress on ØA, ØB
output
transistors.
R10, R11 Limit max. motor
current. Resistors may
be omitted. (Check
motor specifications
first.)
Vmm -V
Motor
-V
CESat
R =
I
Motor max
Decreases motor
current.
Increases motor
current.
R12 … R15 External transistor base
discharge.
V
be
R =
ª 15
W
I
12
P > Vbe • I
12
Slows down
external transistor
turn-off time.
Lowers 3517
power dissipation
Speeds up
external transistor
turn-off time.
Increases 3517
power dissipation
RT, CT Sets LA and LB on time
when triggered by
STEP.
R = 47kohm, C = 10nf
P < 250mW
Increases on time. Decreases on time.
C1, C2 Stores the doubling
voltage.
C = 100µF
VC ≥ 45V
Increases effective
on-time during
voltage doubling
Decreases
effective on-time
during voltage
doubling.
C3 … C5 Filtering of supply-
voltage ripple and takeup of energy feedback
from D3 … D6
C µF Increases price,
better filtering,
decreases risk of
IC breakdown
Decreases price,
more compact
solution.
V
Rated
>Vmm,Vss or VccIncreases price Risk for capacitor
breakdown.
Q1, Q2 Activation transistor of
voltage doubling.
IC as motor requires. Increases price. Decreases max I
m
during voltage
doubling.
Q3, Q4 Charging of voltage
doubling capacitor
Q5 … Q8 Motor current drive
transistor. PNP power trans.
Increases max
current capability.
Decreases max
current capability.
If = 1A
V
mm
P = R1
)
R1 + R
2
(
V
mm
P = R1
)
R1 + R
2
(
V
be
I4 -
)
R12
(
(VCC)
2
P =
R
(V
mm
- Vf -VCE) • C1
IC =
(
- 0.55 • RT • C
T
1
f
Step
)
IC as motor requires.
10≥
INH — Inhibit
A HIGH level on the INH input,turns off all
phase outputs to reduce current
consumption.
Reset
An internal Power-On Reset circuit
connected to Vcc resets the phase logic
and inhibits the outputs during power up,
to prevent false stepping.
Output Stages
The output stage consists of four opencollector transistors. The second highvoltage supply contains Darlington
transistors.
Phase Outputs
The phase outputs are connected directly
to the motor as shown in figure 14.
Bilevel Technique
The bilevel pulse generator consists of
two monostables with a common RC
network.
The internal phase logic generates a
trigger pulse every time the phase
changes state. The pulse triggers its own
monostable which turns on the output
transistors for a precise period of time:
t
On
= 0.55 • CT • RT.
See pulse diagrams, figures 16 through
20.
Bipolar Phase Logic Output
The ØA and ØB outputs are generated
from the phase logic and inform an
external device if the A phase or the B
phase current is internally inhibited.
These outputs are intended to support if it
is legal to correctly go from a half-step
mode to a full-step mode without loosing
positional information.
The PBD 3517/1 can act as a controller
IC for 2 driver ICs, the PBL 3770A. Use
PA1 and PB1 for phase control, and ØA and
ØB for I0 and I1 control of current turn-off.
Applications Information
Logic inputs
If any of the logic inputs are left open, the
circuit will treat it as a high-level input.
Unused inputs should be connected to
proper voltage levels in order to get the
highest noise immunity.
Phase outputs
Page 8

PBD 3517/1
8
Phase outputs use a current-sinking
method to drive the windings in a unipolar
way. A common resistor in the center tap
will limit the maximum motor current.
Fast free-wheeling diodes must be
used to protect output transistors from
inductive spikes. Alternative solutions are
shown in figures 21 through 25 on pages
6 - 10.
Series diodes in VMM supply, prevent
VSS voltage from shorting through the V
MM
power supply. However, these may be
omitted if no bilevel is used. The VSS pin
must not be connected to a lower voltage
than VMM, but can be left unconnected.
Zero outputs
Ø
A
and ØB, “zero A” and “zero B,” are
open-collector outputs, which go high
when the corresponding phase output is
inhibited by the half-step-mode circuitry. A
pull-up resistor should be used and
connected to a suitable supply voltage (5
kohms for 5V logic). See “Bipolar phase
logic output.”
Interference
To avoid interference problems, a good
idea is to route separate ground leads to
each power supply, where the only
common point is at the 3517/1’s GND pin.
Decoupling of V
SS
and VMM will improve
performance. A 5 kohm pull-up resistor at
logic inputs will improve level definitions,
especially when driven by open-collector
outputs.
Input and Output Signals for
Different Drive Modes
The pulse diagrams, figures 16 through
20, show the necessary input signals and
the resulting output signals for each drive
mode.
On the left side are the input and output
signals, the next column shows the state
of each signal at the cursor position
marked “C.”
STEP is shown with a 50% duty cycle,
but can, of course, be with any duty cycle,
as long as pulse time (tp) is within
specifications.
PA and PB are displayed with low level,
showing current sinking.
LA and LB are displayed with high level,
showing current sourcing.
Figure 16. Full-step mode, forward. 4-step sequence. Gray-code +90° phase shift.
Figure 17. Full-step mode, reverse. 4-step sequence. Gray-code -90° phase shift.
Figure 20. Half-step mode, inhibit.
Figure 18. Half-step mode, forward. 8-step sequence.
DIR
INH
HSM
STEP
OB
LB
PB1
PB2
PA1
PA2
LA
OA
H
L
H
P
L
P
P
P
P
P
P
L
DIR
INH
HSM
STEP
OB
LB
PB1
PB2
PA1
PA2
LA
OA
H
L
L
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
C
DIR
INH
HSM
STEP
OB
LB
PB1
PB2
PA1
PA2
LA
OA
L
L
L
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
C
DIR
INH
HSM
STEP
OB
LB
PB1
PB2
PA1
PA2
LA
OA
L
H
L
P
P
P
H
H
H
H
P
P
C
Figure 19. Half-step mode, reverse. 8-step sequence.
DIR
INH
HSM
STEP
OB
LB
PB1
PB2
PA1
PA2
LA
OA
H
L
H
P
L
P
P
P
P
P
P
L
Page 9

PBD 3517/1
9
V
Z
R
R
Ext
i
Figure 24. Power return turn-off circuit. Figure 25. Power return turn-off circuit for
bilevel .
Figure 22. Resistance turn-off circuit.
Figure 23. Zener diode turn-off circuit.
Figure 21. Diode turn-off circuit.
7. To change actual motor rotation
direction, exchange motor connections at PA1 and PA2 (or PB1 and PB2).
8. Half-stepping. in the half-step mode,
the power input to the motor alternates between one or two phase
windings. In half-step mode, motor
resonances are reduced. In a twophase motor, the electrical phase
shift between the windings is 90
degrees. The torque developed is the
vector sum of the two windings
energized. Therefore, when only one
winding is energized, which is the
case in half-step mode for every
second step, the torque of the motor
is reduced by approximately 30%.
This causes a torque ripple.
9. Ramping. Every drive system has
inertia which must be considered in
the drive scheme. The rotor and load
inertia plays a big role at higher
speeds. Unlike the DC motor, the
stepper motor is a synchronous
motor and does not change speed
due to load variations. Examination of
typical stepper motors’ torque versus
speed curves indicates a sharp
torque drop-off for the start-stop
without error curve. The reason for
this is that the torque requirements
increase by the cube of the speed
change. As it can be seen, for good
motor performance, controlled
acceleration and deceleration should
be considered.
User Hints
1. Never disconnect ICs or PC-boards
when power is supplied.
2. If second supply is not used, disconnect and leave open V
SS
, LA, LB, and
RC. Preferably replace the V
MM
supply diodes (D1, D2) with a straight
connection.
3. Remember that excessive voltages
might be generated by the motor,
even though clamping diodes are
used.
4. Choice of motor. Choose a motor
that is rated for the current you need
to establish desired torque. A high
supply voltage will gain better
stepping performance. If the motor is
not specified for the V
MM
voltage, a
current limiting resistor will be
necessary to connect in series with
center tap. This changes the L/R
time constant.
5. Never use L
A
or LB for continuous
output at high currents. L
A
and LB ontime can be altered by changing the
RC net. An alternative is to trigger
the mono-flip-flop by taking a STEP
and then externally pulling the RC
pin (12) low (0V) for the desired ontime.
6. Avoid V
MM
and VSS power supplies
with serial diodes (without filter
capacitor) and/or common ground
with V
CC
. The common place for
ground should be as close as
possible to the IC’s ground pin (pin
3).
V
1
V
2
C
S
0V
Power supply
Page 10

PBD 3517/1
10
Zener diode T O C (figure 23)
Relatively high VZ gives:
— Relatively fast current decay
— Energy lost mainly in V
Z
— Potential cooling problems
Power return T O C for unipolar drive
(figure 24)
Relatively high V
Z
gives:
— Relatively fast current decay
— Energy returned to power supply
— Only small energy losses
— Winding leakage flux must be
considered
— Potential cooling problems
Power return to T O C for bilevel drive
(figure 25)
— Very fast current decay
— Energy returned to power supply
— Only small energy losses
— Winding leakage flux must be
considered
Common Fault Conditions
•VMM supply not connected, or V
MM
supply not connected through diodes.
• The inhibit input not pulled low or
floating. Inhibit is active high.
• A bipolar motor without a center tap is
used. Exchange motor for unipolar
version. Connect according to figure
14.
• External transistors connected without
proper base-current supply resistor.
• Insufficient filtering capacitors used.
• Current restrictions exceeded.
•L
A
and LB used for continuous output at
high currents. Use the RC network to
set a proper duty cycle according to
specifications, see figures 6 through
11.
• A common ground wire is used for all
three power supplies. If possible, use
separate ground leads for each supply
to minimize power interference.
Ericsson Components AB
SE-164 81 Kista-Stockholm, Sweden
Telephone: +46 8 757 50 00
Specifications subject to change without
notice.
1522-PBD 3517/1 Uen Rev. C
© Ericsson Components AB 1999
Information given in this data sheet is believed to be
accurate and reliable. However no responsibility is
assumed for the consequences of its use nor for any
infringement of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent
rights of Ericsson Components. These products are
sold only according to Ericsson Components' general
conditions of sale, unless otherwise confirmed in
writing.
Drive Circuits
If high performance is to be achieved from
a stepper motor, the phase must be
energized rapidly when turned on and
also de-energize rapidly when turned off.
In other words, the phase current must
increase/decrease rapidly at phase shift.
Phase Turn-off
Considerations
When the winding current is turned off the
induced high voltage spike will damage
the drive circuits if not properly suppressed. Different turn-off circuits
are used; e. g. :
Diode turn-off circuit (figure 21)
— Slow current decay
— Energy lost mainly in winding
resistance
— Potential cooling problems.
Resistance T O C (figure 22)
— Somewhat faster current decay
— Energy lost mainly in R-Ext
— Potential cooling problems
Ordering Information
Package Part No.
DIP Tube PBD 3517/1NS
SO Tube PBD 3517/1SOS
SO Tape & Reel PBD 3517/1SOT
 Loading...
Loading...