Page 1
®
OPA177
OPA177
Precision
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
OPA177
FEATURES
● LOW OFFSET VOLTAGE: 25µV max
● LOW DRIFT: 0.3
µV/°C
● HIGH OPEN-LOOP GAIN: 130dB min
● LOW QUIESCENT CURRENT: 1.5mA typ
● REPLACES INDUSTRY-STANDARD OP
AMPS: OP-07, OP-77, OP-177, AD707,
ETC.
DESCRIPTION
The OPA177 precision bipolar op amp feature very
low offset voltage and drift. Laser-trimmed offset,
drift and input bias current virtually eliminate the need
for costly external trimming. The high performance
and low cost make them ideally suited to a wide range
of precision instrumentation.
The low quiescent current of the OPA177 dramatically reduce warm-up drift and errors due to thermo-
V+
7
Trim
1
14kΩ
Trim
8
APPLICATIONS
● PRECISION INSTRUMENTATION
● DATA ACQUISITION
● TEST EQUIPMENT
● BRIDGE AMPLIFIER
● THERMOCOUPLE AMPLIFIER
electric effects in input interconnections. It provides
an effective alternative to chopper-stabilized amplifiers. The low noise of the OPA177 maintains accuracy.
OPA177 performance gradeouts are available. Packaging options include 8-pin plastic DIP
and SO-8 surface-mount packages.
25Ω
30Ω
500Ω
+In
3
500Ω
–In
2
20µA
V–
4
International Airport Industrial Park • Mailing Address: PO Box 11400, Tucson, AZ 85734 • Street Address: 6730 S. Tucson Blvd., Tucson, AZ 85706 • Tel: (520) 746-1111 • Twx: 910-952-1111
Internet: http://www.burr-brown.com/ • FAXLine: (800) 548-6133 (US/Canada Only) • Cable: BBRCORP • Telex: 066-6491 • FAX: (520) 889-1510 • Immediate Product Info: (800) 548-6132
©
1990 Burr-Brown Corporation PDS-1081E Printed in U.S.A. August, 1997
V
O
6
Page 2
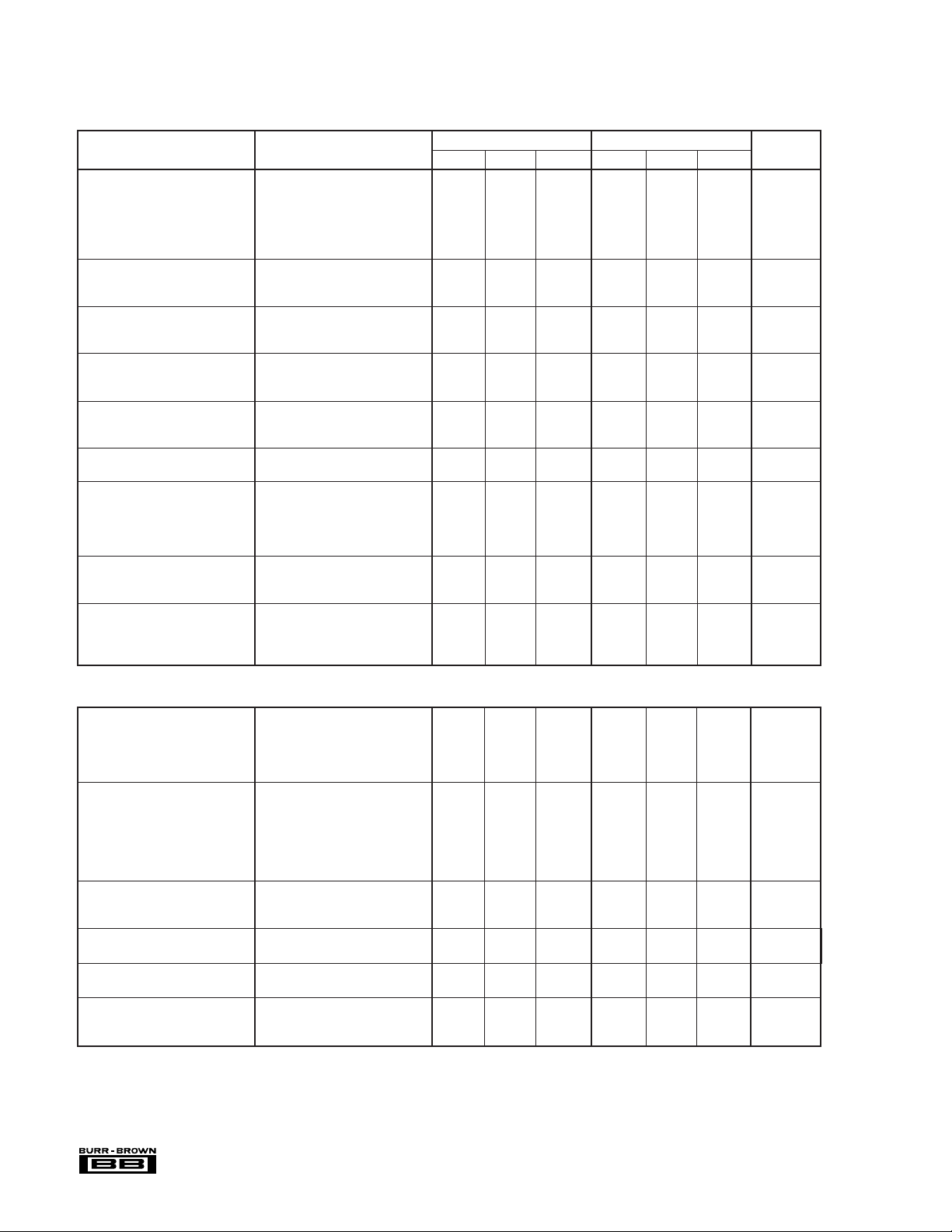
OPA177 SPECIFICATIONS
At VS = ±15V, TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.
OPA177F OPA177G
PARAMETER CONDITION MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX UNITS
OFFSET VOLTAGE
Input Offset Voltage 10 25 20 60 µV
Long-Term Input Offset
Voltage Stability
Offset Adjustment Range R
Power Supply Rejection Ratio V
INPUT BIAS CURRENT
Input Offset Current 0.3 1.5 ✻ 2.8 nA
Input Bias Current 0.5 ±2 ✻ ±2.8 nA
NOISE
Input Noise Voltage 1Hz to 100Hz
Input Noise Current 1Hz to 100Hz 4.5 ✻ pArms
INPUT IMPEDANCE
Input Resistance Differential Mode
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE
Common-Mode Input Range
Common-Mode Rejection V
OPEN-LOOP GAIN R
Large Signal Voltage Gain V
OUTPUT
Output Voltage Swing R
Open-Loop Output Resistance 60 ✻ Ω
FREQUENCY RESPONSE
Slew Rate R
Closed-Loop Bandwidth G = +1 0.4 0.6 ✻✻ MHz
POWER SUPPLY
Power Consumption V
Supply Current V
(1)
= 20kΩ±3 ✻mV
P
= ±3V to ±18V 115 125 110 120 dB
S
(2)
(3)
26 45 18.5 ✻ MΩ
0.3 0.4 µV/Mo
85 150 ✻✻nVrms
Common-Mode 200 ✻ GΩ
(4)
= ±13V 130 140 115 ✻ dB
CM
≥ 2kΩ
L
(5)
= ±10V
O
≥ 10kΩ±13.5 ±14 ✻✻ V
L
R
≥ 2kΩ±12.5 ±13 ✻✻ V
L
R
≥ 1kΩ±12 ±12.5 ✻✻ V
L
≥ 2kΩ 0.1 0.3 ✻✻ V/µs
L
= ±15V, No Load 40 60 ✻✻ mW
S
V
= ±3V, No Load 3.5 4.5 ✻✻ mW
S
= ±15V, No Load 1.3 2 ✻✻ mA
S
±13 ±14 ✻✻ V
5110 12,000 2000 6000 V/mV
At VS = ±15V, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C, unless otherwise noted.
OFFSET VOLTAGE
Input Offset Voltage 15 40 20 100 µV
Average Input Offset 0.1 0.3 0.7 1.2 µV/°C
Voltage Drift
Power Supply Rejection Ratio V
= ±3V to ±18V 110 120 106 115 dB
S
INPUT BIAS CURRENT
Input Offset Current 0.5 2.2 ✻ 4.5 nA
Average Input Offset Current 1.5 40 ✻ 85 pA/°C
(6)
Drift
Input Bias Current 0.5 ±4 ✻ ±6nA
Average Input Bias Current 8 40 15 60 pA/°C
(6)
Drift
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE
Common-Mode Input Range ±13 ±13.5 ✻✻ V
Common-Mode Rejection V
= ±13V 120 140 110 ✻ dB
CM
OPEN-LOOP GAIN
Large Signal Voltage Gain R
≥ 2kΩ, VO= ±10V 2000 6000 1000 4000 V/mV
L
OUTPUT
Output Voltage Swing R
≥ 2kΩ±12 ±13 ✻✻ V
L
POWER SUPPLY
Power Consumption V
Supply Current V
= ±15V, No Load 60 75 ✻✻ mW
S
= ±15V, No Load 2 25 ✻✻ mA
S
✻ Same as specification for product to left.
NOTES: (1) Long-Term Input Offset Voltage Stability refers to the averaged trend line of V
the initial hour of operation, changes in V
by CMRR test condition. (5) To insure high open-loop gain throughout the ±10V output range, A
during the first 30 operating days are typically less than 2µV. (2) Sample tested. (3) Guaranteed by design. (4) Guaranteed
OS
(6) Guaranteed by end-point limits.
vs time over extended periods after the first 30 days of operation. Excluding
OS
is tested at –10V ≤ VO ≤ 0V, 0V ≤ VO ≤ +10V, and –10V ≤ VO ≤ +10V.
OL
®
OPA177
2
Page 3
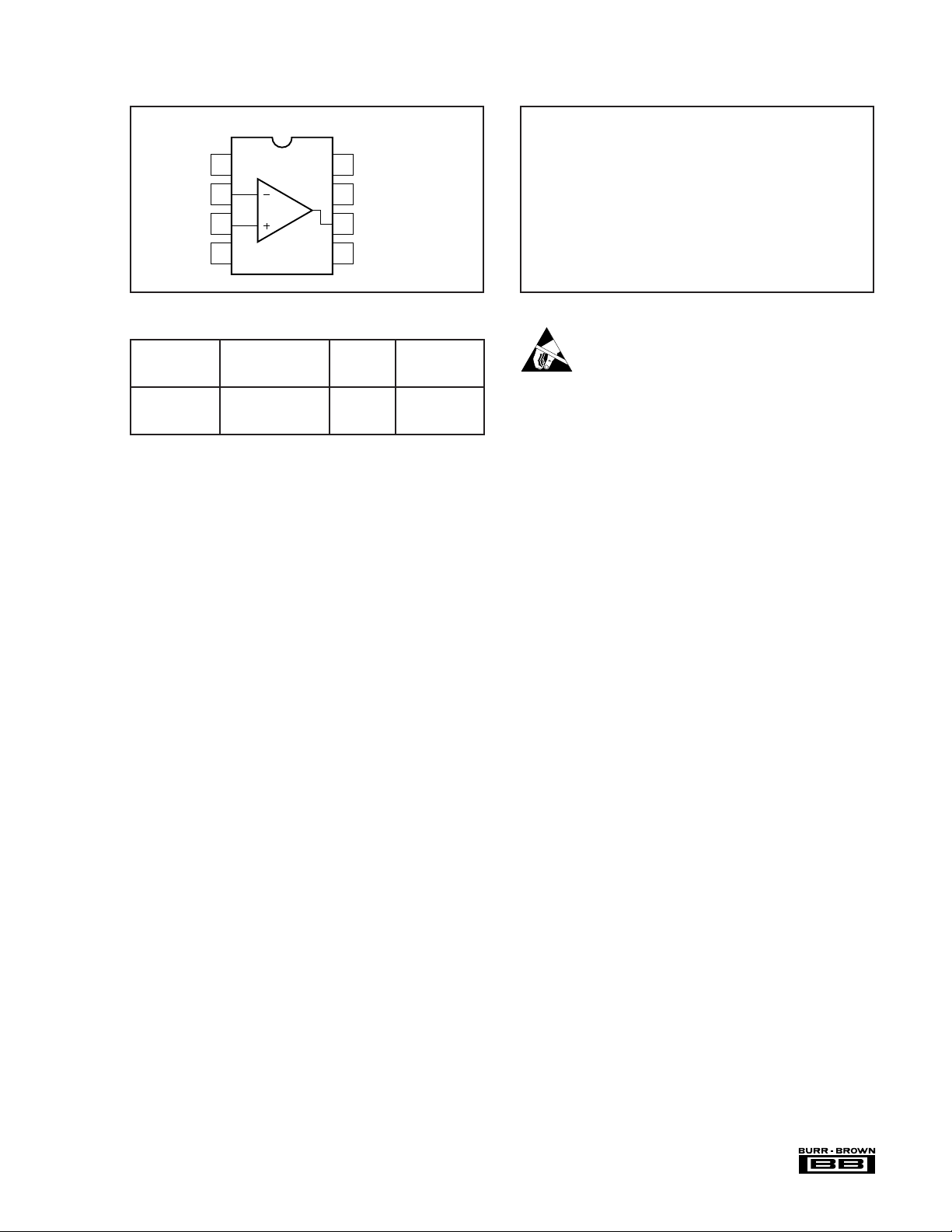
PIN CONFIGURATION
Top View DIP/SOIC
Offset Trim
–In
+In
V–
1
2
3
4
Offset Trim
8
V+
7
V
6
O
No Internal Connection
5
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Power Supply Voltage .......................................................................±22V
Differential Input Voltage ...................................................................±30V
Input Voltage ....................................................................................... ±V
Output Short Circuit .................................................................Continuous
Operating Temperature:
Plastic DIP (P), SO-8 (S) .............................................. –40°C to +85°C
θ
(PDIP) ................................................................................. 100°C/W
JA
θ
(SOIC) ................................................................................. 160°C/W
JA
Storage Temperature:
Plastic DIP (P), SO-8 (S) ............................................ –65°C to +125°C
Junction Temperature.................................................................... +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) P packages ........................... +300°C
(soldering, 3s) S package ............................... +260°C
S
PACKAGE/ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGE
DRAWING TEMPERATURE
PRODUCT PACKAGE NUMBER
OPA177FP 8-Pin Plastic DIP 006 –40°C to +85°C
OPA177GP 8-Pin Plastic DIP 006 –40°C to +85°C
OPA177GS SO-8 Surface-Mount 182 –40°C to +85°C
NOTE: (1) For detailed drawing and dimension table, please see end of data
sheet, or Appendix C of Burr-Brown IC Data Book.
(1)
RANGE
ELECTROSTATIC
DISCHARGE SENSITIVITY
Any integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Burr-Brown
recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with
appropriate precautions. ESD can cause damage ranging
from subtle performance degradation to complete device
failure. Precision integrated circuits may be more susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes
could cause the device not to meet published specifications.
Burr-Brown’s standard ESD test method consists of five
1000V positive and negative discharges (100pF in series
with 1.5kΩ) applied to each pin.
Failure to observe proper handling procedures could result
in small changes to the OPA177’s input bias current.
The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; however, BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies or omissions. BURR-BROWN assumes
no responsibility for the use of this information, and all use of such information shall be entirely at the user’s own risk. Prices and specifications are subject to change
without notice. No patent rights or licenses to any of the circuits described herein are implied or granted to any third party. BURR-BROWN does not authorize or warrant
any BURR-BROWN product for use in life support devices and/or systems.
3
OPA177
®
Page 4

TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
At TA = +25°C, VS = ±15V, unless otherwise noted.
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION AND NOISE
vs FREQUENCY
1
A = 20dB, 3Vrms, 10kΩ load
0.1
THD + N (%)
0.01
Noninverting
30kHz low pass filtered
0.001
1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
MAXIMUM V
(Positive Swing)
OUT
vs I
OUT
17.5
15
VS = ±18V
12.5
VS = ±15V
VS = ±12V
(V)
OUT
V
10
7.5
5
2.5
VS = ±15V
0
0 6 12 18 24 30 36
I
(mA)
OUT
Inverting
MAXIMUM V
(Negative Swing)
OUT
vs I
OUT
–17.5
VS = ±18V
VS = ±15V
VS = ±12V
(V)
OUT
V
–15
–12.5
–10
–7.5
–5
–2.5
VS = ±15V
0
0 –2 –4 –6 –8 –10 –12
–I
(mA)
OUT
WARM-UP OFFSET VOLTAGE DRIFT
3
2
1
0
–1
Offset Voltage Change (µV)
–2
–3
0 30 60 90 120
15 45 75 105
Time from Power Supply Turn-On (s)
30
Device Immersed in 70°C Inert Liquid
25
20
15
10
Offset Voltage (µV)
Absolute Change in Input
5
Plastic DIP
0
10 30 50 700204060
®
OPA177
OFFSET VOLTAGE CHANGE
DUE TO THERMAL SHOCK
Time (s)
100
CLOSED-LOOP RESPONSE vs FREQUENCY
80
60
40
20
Closed-Loop Gain (dB)
0
–20
80
10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
Frequency (Hz)
4
Page 5

TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES (CONT)
2
1
0
–1
–2
–40 –15 10 35 60 85
Temperature (°C)
INPUT BIAS AND INPUT OFFSET CURRENT
vs TEMPERATURE
Input Bias and Input Offset Current (nA)
I
B
I
OS
At TA = +25°C, VS = ±15V, unless otherwise noted.
160
140
120
100
80
60
Open-Loop Gain (dB)
40
20
0
150
130
110
90
OPEN-LOOP GAIN/PHASE vs FREQUENCY
Gain
0.01 1 10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M0.1
Frequency (Hz)
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION
vs FREQUENCY
Phase
0
45
90
135
Phase Shift (Degrees)
180
150
140
130
120
110
CMRR (dB)
100
90
80
1 10 100 1k 10k 100k
CMRR vs FREQUENCY
Frequency (Hz)
70
Power Supply Rejection (dB)
50
10
1
0.1
RMS Noise (µV)
0.01
100 1k 10k 100k
1 10 100 1k 10k0.1
Frequency (Hz)
TOTAL NOISE vs BANDWIDTH
(0.1Hz to Frequency Indicated)
Bandwidth (Hz)
Input Noise Voltage (nV/√Hz)
INPUT NOISE VOLTAGE DENSITY vs FREQUENCY
1k
100
10
1
1
10 100 1k 10k
R = 0
S
Frequency (Hz)
R = R = 200k
S1 S2
Thermal noise of
source resistors
included.
Ω
®
5
OPA177
Page 6

TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES (CONT)
At TA = +25°C, VS = ±15V, unless otherwise noted.
32
28
24
20
16
12
Peak-to-Peak Amplitude (V)
20
15
10
MAXIMUM OUTPUT SWING vs FREQUENCY
G = +1
R = 2k
L
8
4
0
1k 10k 100k 1M
Frequency (Hz)
MAXIMUM OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs LOAD RESISTANCE
Positive
Output
Negative
Output
100
Ω
10
Power Consumption (mW)
40
35
30
25
POWER CONSUMPTION vs POWER SUPPLY
1
0 10203040
Total Supply Voltage (V)
OUTPUT SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENT vs TIME
I +
SC
Maximum Output (V)
5
0
100 10k
Load Resistance to Ground ( )
1k
Ω
20
I –
SC
Output Short-Circuit Current (mA)
15
01234
Time from Output Being Shorted (min)
®
OPA177
6
Page 7

APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
The OPA177 is unity-gain stable, making it easy to use and
free from oscillations in the widest range of circuitry. Applications with noisy or high impedance power supply lines
may require decoupling capacitors close to the device pins.
In most cases 0.1µF ceramic capacitors are adequate.
The OPA177 has very low offset voltage and drift. To
achieve highest performance, circuit layout and mechanical
conditions must be optimized. Offset voltage and drift can
be degraded by small thermoelectric potentials at the op amp
inputs. Connections of dissimilar metals will generate thermal potential which can mask the ultimate performance of
the OPA177. These thermal potentials can be made to cancel
by assuring that they are equal in both input terminals.
1. Keep connections made to the two input terminals close
together.
2. Locate heat sources as far as possible from the critical
input circuitry.
3. Shield the op amp and input circuitry from air currents
such as cooling fans.
OFFSET VOLTAGE ADJUSTMENT
The OPA177 has been laser-trimmed for low offset voltage
and drift so most circuits will not require external adjustment. Figure 1 shows the optional connection of an external
potentiometer to adjust offset voltage. This adjustment should
not be used to compensate for offsets created elsewhere in a
system since this can introduce excessive temperature drift.
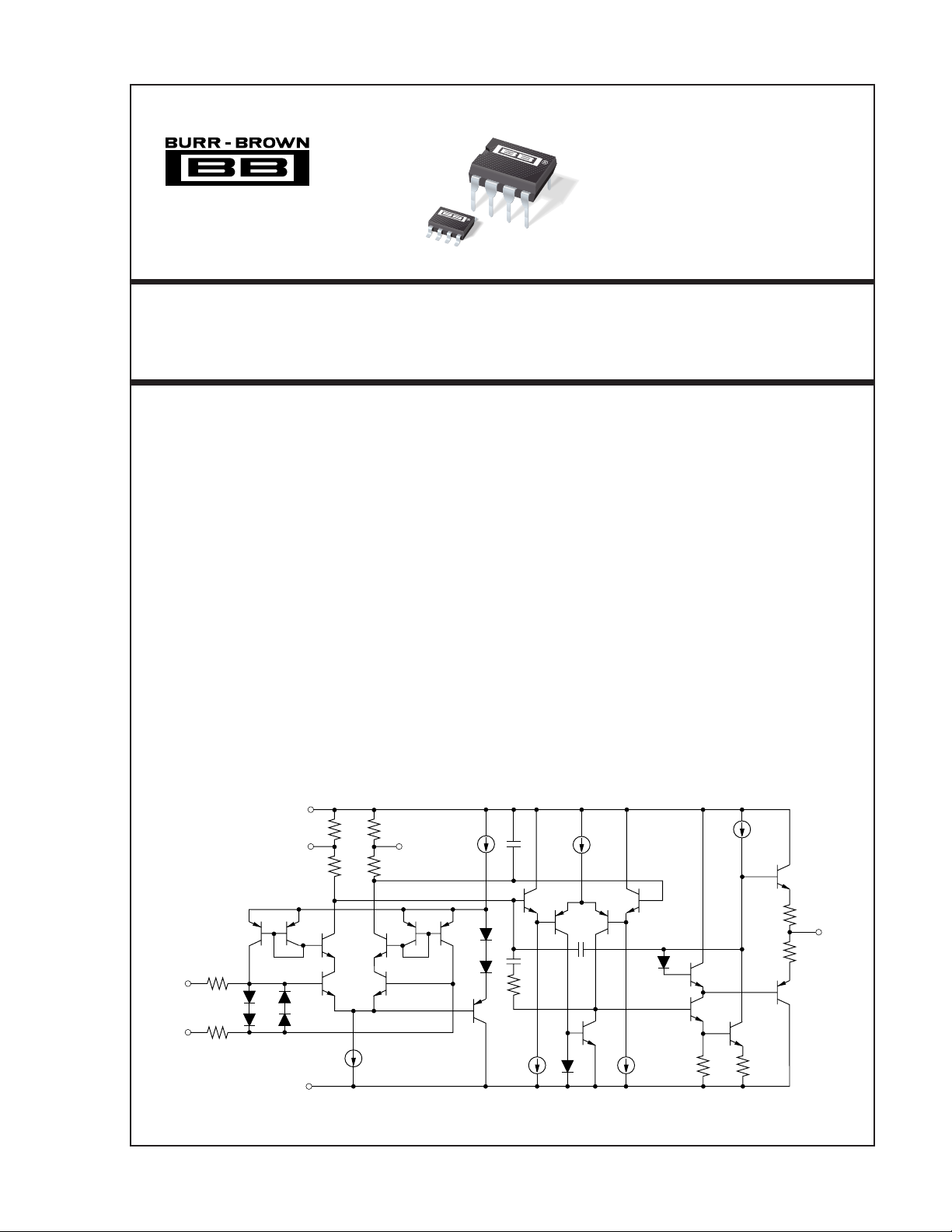
INPUT PROTECTION
The inputs of the OPA177 are protected with 500Ω series
input resistors and diode clamps as shown in the simplified
circuit diagram. The inputs can withstand ±30V differential
inputs without damage. The protection diodes will, of course,
conduct current when the inputs are overdriven. This may
disturb the slewing behavior of unity-gain follower applications, but will not damage the op amp.
V+
20kΩ
1
2
V
IN
Trim Range is approximately ±3.0mV
3
OPA177
8
V
OUT
FIGURE 1. Optional Offset Nulling Circuit.
NOISE PERFORMANCE
The noise performance of the OPA177 is optimized for
circuit impedances in the range of 2kΩ to 50kΩ. Total noise
in an application is a combination of the op amp’s input
voltage noise and input bias current noise reacting with
circuit impedances. For applications with higher source
impedance, the OPA627 FET-input op amp will generally
provide lower noise. For very low impedance applications,
the OPA27 will provide lower noise.
INPUT BIAS CURRENT CANCELLATION
The input stage base current of the OPA177 is internally
compensated with an equal and opposite cancellation current. The resulting input bias current is the difference
between the input stage base current and the cancellation
current. This residual input bias current can be positive or
negative.
When the bias current is cancelled in this manner, the input
bias current and input offset current are approximately the
same magnitude. As a result, it is not necessary to balance
the DC resistance seen at the two input terminals (Figure 2).
A resistor added to balance the input resistances may actually increase offset and noise.
R
2
R
1
Conventional op amp with
external bias current
cancellation resistor.
R
= R
B
Op Amp
|| R
2
(a)
1
FIGURE 2. Input Bias Current Cancellation.
R
2
R
1
OPA177 with no external
bias current cancellation
resistor.
7
OPA177
No bias current
cancellation resistor needed
(b)
®
OPA177
 Loading...
Loading...