Page 1

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband
Processor Data Sheet
Revision 1.02
Apr 07, 2008
Page 2

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Revision History
Revision Date Comments
1.00 Sept 18, 2007 First Release
1.01
1.02 Apr 07, 2008
Dec 13, 2007 1. Update GPIO10 GPIO11 mode definition
2. Update ch8 audio front end and ch13 analog front end & analog blocks for PMU ball name
change (VMC,VSW_A, VCAMERA) > (VBT, VCAM_A, VCAM_D)
1. Update RGU, MCU, RTC, SIM, EMI, GLCON, TG, System Overview, and Product
Description
2/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 3

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Revision History......................................................................................................................................2
Preface......................................................................................................................................................5
1. System Overview.............................................................................................................. .................6
Platform Features................................................................................................................................................................. 9
1.1 MODEM Features.....................................................................................................................................................11
1.2 Multi-Media Features............................................................................................................................................... 12
1.3 General Description ................................................................................................................................................. 13
2 Product Description......................................................... ............................................................... 15
2.1 Pin Outs.................................................................................................................................................................... 15
2.2 Top Marking Definition ........................................................................................................................................... 18
2.3 DC Characteristics ................................................................................................................................................... 19
2.4 Pin Description......................................................................................................................................................... 20
2.5 Power Description.................................................................................................................................................... 32
3 Micro-Controller Unit Subsystem.................................................................................................40
3.1 Processor Core ......................................................................................................................................................... 41
3.2 Memory Management .............................................................................................................................................. 41
3.3 Bus System............................................................................................................................................................... 44
3.4 Direct Memory Access............................................................................................................................................. 48
3.5 Interrupt Controller .................................................................................................................................................. 66
3.6 BUS Monitor (BM) .................................................................................................................................................. 82
3.7 External Memory Interface (6235)........................................................................................................................... 93
4 Microcontroller Peripherals ........................................................................................................104
4.1 Security Engine with JTAG control ....................................................................................................................... 104
4.2 EFUSE Controller (efusec) .................................................................................................................................... 107
4.3 Pulse-Width Modulation Outputs............................................................................................................................111
4.4 SIM Interface ......................................................................................................................................................... 150
4.5 Keypad Scanner ..................................................................................................................................................... 159
4.6 General Purpose Inputs/Outputs ............................................................................................................................ 162
4.7 General Purpose Timer........................................................................................................................................... 181
4.8 UART..................................................................................................................................................................... 184
4.9 IrDA Framer........................................................................................................................................................... 199
4.10 Real Time Clock..................................................................................................................................................... 208
4.11 Auxiliary ADC Unit ............................................................................................................................................... 216
4.12 I2C / SCCB Controller ........................................................................................................................................... 220
5 Microcontr oller Coprocessors .....................................................................................................232
5.1 Divider ................................................................................................................................................................... 232
5.2 CSD Accelerator .................................................................................................................................................... 234
5.3 FCS Codec ............................................................................................................................................................. 246
5.4 GPRS Cipher Unit.................................................................................................................................................. 248
6 MCU/DSP Interface...................................................... ..... ...... .. ...... ..... ... ..... ..... ... ..... ...... .. ... ........ 252
6.1 MCU/DSP Shared Registers .................................................................................................................................. 254
6.2 MCU/DSP Shared RAM ........................................................................................................................................ 261
6.3 AHB-to-DDMA Bridge.......................................................................................................................................... 263
7 Multi-Media Subsystem ...............................................................................................................268
7.1 LCD Interface ........................................................................................................................................................ 268
7.2 Capture Resize ....................................................................................................................................................... 292
3/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 4

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
7.3 NAND FLASH interface ....................................................................................................................................... 300
7.4 USB 2.0 High-Speed Dual-Role Controller........................................................................................................... 320
7.5 Memory Stick and SD Memory Card Controller ................................................................................................... 358
7.6 2D acceleration ...................................................................................................................................................... 383
7.7 Camera Interface .................................................................................................................................................... 410
8 Audio Front-End...........................................................................................................................422
8.1 General Description ............................................................................................................................................... 422
8.2 Register Definitions ............................................................................................................................................... 425
8.3 DSP Register Definitions ....................................................................................................................................... 439
8.4 Programming Guide............................................................................................................................................... 444
9 Radio Interface Control........................................................................................................ ....... 446
9.1 Baseband Serial Interface....................................................................................................................................... 446
9.2 Baseband Parallel Interface.................................................................................................................................... 454
9.3 Automatic Power Control (APC) Unit ................................................................................................................... 457
9.4 Automatic Frequency Control (AFC) Unit ............................................................................................................ 464
10 Baseband Front End..................................................................................................................... 467
10.1 Baseband Serial Ports............................................................................................................................................. 468
10.2 Downlink Path (RX Path) ...................................................................................................................................... 472
10.3 Uplink Path (TX Path) ........................................................................................................................................... 480
11 Timing Generator............................................................................................ .. ...........................487
11.1 TDMA timer........................................................................................................................................................... 487
11.2 Slow Clocking Unit................................................................................................................................................ 499
12 Power, Clocks and Reset ......................................................... ..... ... ..... ..... ... ..... ...... .. ...... ..... .. ......503
12.1 Clocks .................................................................................................................................................................... 503
12.2 Reset Generation Unit (RGU)................................................................................................................................ 507
12.3 Global Configuration Registers...............................................................................................................................511
13 Analog Front-end & Analog Blocks............................................................................ ... .............526
13.1 General Description ............................................................................................................................................... 526
13.2 MCU Register Definitions ..................................................................................................................................... 537
13.3 Programming Guide............................................................................................................................................... 579
14 Digital Pin Electrical Characteristics..........................................................................................593
4/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 5

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Preface
Acronym for Register Type
R/W
RO
RC
WO
W1S
W1C
Capable of both read and write access
Read only
Read only. After reading the register bank, each bit which is HIGH(1) will be cleared to LOW(0 )
automatically.
Write only
Write only. When writing data bits to register bank, each bit which is HIGH(1) will cause the
corresponding bit to be set to 1. Data bits which are LOW(0) has no effect on the corresponding bit.
Write only. When writing data bits to register bank, each bit which is HIGH(1) will cause the
corresponding bit to be cleared to 0. Data bits which are LOW(0) has no effect on the corresponding bit.
5/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 6

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
1. System Overview
MT6235 is a highly-integrated and extremely powerful
single-chip solution for GSM/GPRS/EDGE mobile phones.
TM
Based on the 32-bit ARM926EJ-S
RISC processor,
MT6235’s superb processing power, along with high
bandwidth architecture and dedicated hardware support,
provides an unprecedented platform for high performance
GPRS/EDGE Class 12 MODEM application. Overall,
MT6235 presents a revolutionary platform for mobile
devices.
Typical application diagram is shown in Figure 1.
Platform
MT6235 is capable of running the ARM926EJ-S
TM
RISC
processor at up to 208 MHz, thus providing fast data
processing capabilities. In addition to the high clock
frequency, separate CODE and DATA caches are also
included to further improve the overall system efficiency.
For large amounts of data transfer, high performance DMA
(Direct Memory Access) with hardware flow control is
implemented, which greatly enhances the data movement
speed while reducing MCU processing load.
Targeted as a high performance platform for mobile
applications, hardware flash content protection is also
provided to prevent unauthorized porting of the software
load to protect the manufacturer’s development
investment.
Memory
To provide the greatest capacity for expansion and
maximum bandwidth for data intensive applications such
as multimedia features, MT6235 supports up to 4 external
state-of-the-art devices through its 8/16-bit host interface.
High performance devices such as Mobile SDRAM and
Cellular RAM are supported for maximum bandwidth.
Traditional devices such as burst/page mode flash, page
mode SRAM, and Pseudo SRAM are also supported. For
greatest compatibility, the memory interface can also be
used to connect to legacy devices such as Color/Parallel
LCD, and multi-media companion chips are all supported
through this interface. To minimize power consumption
and ensure low noise, this interface is designed for flexible
I/O voltage and allows lowering of the supply voltage
down to 1.8V. The driving strength is configurable for
signal integrity adjustment.
Multi-media
The MT6235 multi-media subsystem provides a
connection to a CMOS image sensor and supports a
resolution up to 2.0 Mpixels. With its high performance
application platform, MT6235 allows efficient processing
of image and video data.
In addition to image and video features, MT6235 utilizes
high resolution DAC, digital audio, and audio synthesis
technology to provide superior audio features for all future
multi-media needs.
Connectivity and Storage
To take advantage of its incredible multimedia strengths,
MT6235 incorporates myriads of advanced connectivity
and storage options for data storage and communication.
MT6235 supports UART, Fast IrDA, USB 2.0, SDIO,
Bluetooth, Touch Screen Controller, WIFI Interface, and
MMC/SD/MS/MS Pro storage systems. These interfaces
provide MT6235 users with the highest degree of
flexibility in implementing solutions suitable for the
targeted application.
To achieve a complete user interface, MT6235 also brings
together all the necessary peripheral blocks for a
multi-media GSM/GPRS/EDGE phone. The peripheral
blocks include the Keypad Scanner with the capability to
detect multiple key presses, SIM Controller, Alerter, Real
Time Clock, PWM, Serial LCD Controller, and General
Purpose Programmable I/Os.
Furthermore, to provide much better configurability and
bandwidth for multi-media products, an additional 18-bit
parallel interface is incorporated. This interface enables
connection to LCD panels as well as NAND flash devices
for additional multi-media data storage.
Audio
6/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 7

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Using a highly integrated mixed-signal Audio Front-End,
the MT6235 architecture allows for easy audio interfacing
with direct connection to the audio transducers. The
audio interface integrates D/A and A/D Converters for
Voice band, as well as high resolution Stereo D/A
Converters for Audio band. In addition, MT6235 also
provides Stereo Input and Analog MUX.
MT6235 supports AMR codec to adaptively optimize
speech and audio quality. Moreover, HE-AAC codec is
implemented to deliver CD-quality audio at low bit rates.
On the whole, MT6235’s audio features provide a rich
solution for multi-media applications.
Radio
MT6235 integrates a mixed-signal baseband front-end in
order to provide a well-organized radio interface with
flexibility for efficient customization. The front-end
contains gain and offset calibration mechanisms, and filters
with programmable coefficients for comprehensive
compatibility control on RF modules. This approach
allows the usage of a high resolution D/A Converter for
controlling VCXO or crystal, reducing the need for an
expensive TCVCXO. MT6235 achieves great MODEM
performance by utilizing a 14-bit high resolution A/D
Converter in the RF downlink path. Furthermore, to
reduce the need for extra external current-driving
component, the driving strength of some BPI outputs is
designed to be configurable.
advanced low leakage CMOS process, hence providing an
overall ultra low leakage solution.
Package
The MT6235 device is offered in a 13mm×13mm, 362-ball,
0.5 mm pitch, TFBGA package.
Debug Function
The JTAG interface enables in-circuit debugging of the
software program with the ARM926EJ-S core. With this
standardized debugging interface, MT6235 provides
developers with a wide set of options in choosing ARM
development kits from different third party vendors.
Power Management
The MT6235 offers various low-power features to help
reduce system power consumption. These features
include a Pause Mode of 32 KHz clocking in Standby State,
Power Down Mode for individual peripherals, and
Processor Sleep Mode. MT6235 is also fabricated in an
7/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 8
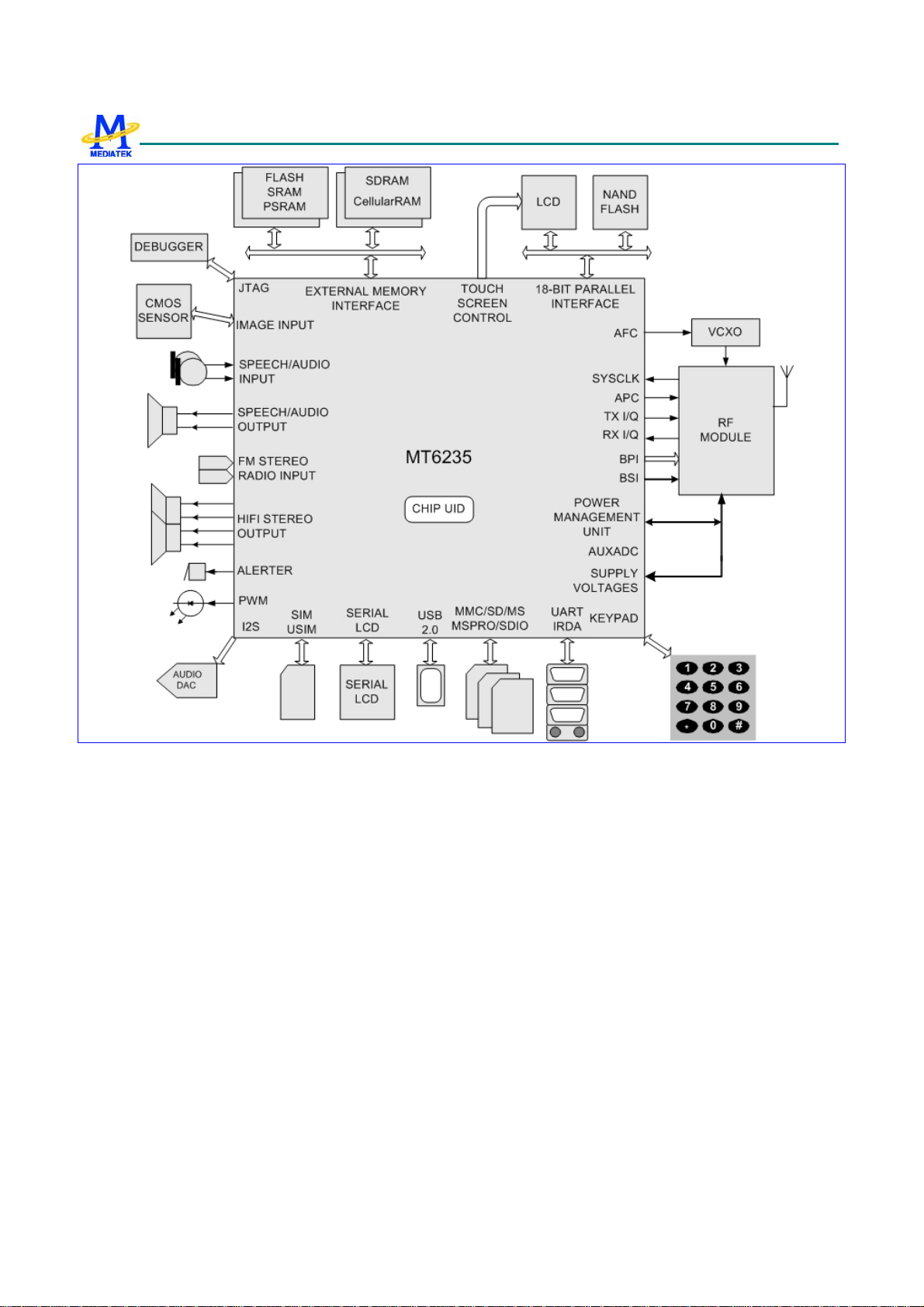
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Figure 1 Typical application of MT6235
8/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 9
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Platform Features
General
z Integrated voice-band, audio-band and base-band
analog front ends
z TFBGA 13mm×13mm, 362-ball, 0.5 mm pitch
package
MCU Subsystem
z ARM926EJ-S 32-bit RISC processor
z High performance multi-layer AMBA bus
z Java hardware acceleration for fast Java-based
games and applets
z Operating frequency: 26/52/104/208 MHz
z Dedicated DMA bus
z 14 DMA channels
z 512K bits on-chip SRAM
z 384K bits Instruction-TCM
z 640K bits Data-TCM
z 128K bits Instruction-Cache
z 128K bits Data-Cache
z On-chip boot ROM for Factory Flash
Programming
z Supports Flash and SRAM/PSRAM with page
mode or burst mode
z Industry standard Parallel LCD interface
z Supports multi-media companion chips with 8/16
bits data width
z Flexible I/O voltage of 1.8V ~ 2.8V for memory
interface
z Configurable driving strength for memory
interface
User Interfaces
z 8-row × 8-column keypad controller with
hardware scanner
z Supports multiple key presses for gaming
z SIM/USIM controller with hardware T=0/T=1
protocol control
z Real Time Clock (RTC) operating with a separate
power supply
z General Purpose I/Os (GPIOs)
z 4 sets of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) output
z Alerter output with Enhanced PWM or PDM
z 8 external interrupt lines
z Watchdog timer for system crash recovery
z 3 sets of General Purpose Timer
z Circuit Switch Data coprocessor
z Division coprocessor
z PPP Framer coprocessor
External Memory Interface
z Supports up to 4 external memory devices
z Supports 8-bit or 16-bit memory components with
maximum size of up to 128M Bytes each
z Supports Mobile SDRAM and Cellular RAM
9/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Security
z Supports security key and 126 bit chip unique ID
Connectivity
z 3 UARTs with hardware flow control and speeds
z IrDA modulator/demodulator with hardware
z USB 2.0 capability
z Multi Media Card, Secure Digital Memory Card,
up to 921600 bps
framer. Supports SIR/MIR/FIR operating speeds.
Memory Stick, Memory Stick Pro host controller
with flexible I/O voltage power
Page 10

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
z Supports SDIO interface for SDIO peripherals as
well as WIFI connectivity
z DAI/PCM and I2S interface for Audio application
Power Management
z Power Down Mode for analog and digital circuits
z Processor Sleep Mode
z Pause Mode of 32 KHz clocking in Standby State
z 4-channel Auxiliary 10-bit A/D Converter for
charger and battery monitoring and photo sensing
Test and Debug
z Built-in digital and analog loop back modes for
both Audio and Baseband Front-End
z DAI port complying with GSM Rec.11.10
z JTAG port for debugging embedded MCU
10/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 11

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
1.1 MODEM Features
Radio Interface and Baseband Front End
z GMSK modulator with analog I and Q channel
outputs
z 10-bit D/A Converter for uplink baseband I and Q
signals
z 14-bit high resolution A/D Converter for downlink
baseband I and Q signals
z Calibration mechanism of offset and gain
mismatch for baseband A/D Converter and D/A
Converter
z 10-bit D/A Converter for Automatic Power
Control
z 13-bit high resolution D/A Converter for
Automatic Frequency Control
z Programmable Radio RX filter
z 2 channels Baseband Serial Interface (BSI) with
3-wire control
z Bi-directional BSI interface. RF chip register
read access with 3-wire or 4-wire interface.
z 10-Pin Baseband Parallel Interface (BPI) with
programmable driving strength
z GSM/GPRS quad vocoders for adaptive multirate
(AMR), enhanced full rate (EFR), full rate (FR)
and half rate (HR)
z GSM channel coding, equalization and A5/1, A5/2
and A5/3 ciphering
z GPRS GEA1, GEA2 and GEA3 ciphering
z Programmable GSM/GPRS/EDGE modem
z Packet Switched Data with CS1/CS2/CS3/CS4
coding schemes
z GSM Circuit Switch Data
z GPRS/EDGE Class 12
Voice Interface and Voice Front End
z Two microphone inputs sharing one low noise
amplifier with programmable gain and automatic
gain control (AGC) mechanisms
z Voice power amplifier with programmable gain
nd
order Sigma-Delta A/D Converter for voice
z 2
uplink path
z D/A Converter for voice downlink path
z Supports half-duplex hands-free operation
z Multi-band support
Voice and Modem CODEC
z Dial tone generation
z Voice memo
z Noise reduction
z Echo suppression
z Advanced sidetone Oscillation Reduction
z Digital sidetone generator with programmable
gain
z Two programmable acoustic compensation filters
11/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
z Compliant with GSM 03.50
Page 12
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
1.2 Multi-Media Features
LCD/NAND Flash Interface
z Dedicated Parallel Interface supports 3 external
devices with 8-/16-bit NAND flash interface,
8-/9-/16-/18-bit Parallel interface, and Serial
interface for LCM
z Built-in NAND Flash Controller with 1-bit ECC
for mass storage
LCD Controller
z Supports simultaneous connection to up to 3
parallel LCD and 2 serial LCD modules
z Supports LCM format: RGB332, RGB444,
RGB565, RGB666, RGB888
z Supports LCD module with maximum resolution
up to 800x600 at 24bpp
z Per pixel alpha channel
z True color engine
z Supports hardware display rotation
z Capable of combining display memories with up to
6 blending layers
Image Signal Processor
z 8 bit YUV format image input
z Capable of processing image of size up to 2.0 M
pixels
z Horizontal scaling in averaging method
z Vertical scaling in bilinear method
z YUV and RGB color space conversion
z Boundary padding
2D Accelerator
z Supports 32-bpp ARGB8888, 24-bpp RGB888,
16-bpp RGB565, and 8-bpp index color modes
z Supports SVG Tiny
z Rectangle gradient fill
z BitBlt: multi-BitBlt with 7 rotation, 16 binary ROP
z Alpha blending with 7 rotation
z Line drawing: normal line, dotted line,
anti-aliasing
z Circle drawing
z Bezier curve drawing
z Triangle flat fill
z Font caching: normal font, italic font
z Command queue with max depth of 2047
Audio CODEC
z Supports HE-AAC codec decode
z Supports AAC codec decode
z IEEE Std 1180-1990 IDCT standards compliance
z Supports progressive image processing to
minimize storage space requirement
z Supports reload-able DMA for VLD stream
Image Data Processing
z Supports Digital Zoom
z Supports RGB888/565, YUV444 image
processing
z High throughput hardware scaler. Capable of
tailoring an image to an arbitrary size.
12/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
z Wavetable synthesis with up to 64 tones
z Advanced wavetable synthesizer capable of
generating simulated stereo
z Wavetable including GM full set of 128
instruments and 47 sets of percussions
z PCM Playback and Record
z Digital Audio Playback
Audio Interface and Audio Front End
z Supports I2S interface
Page 13

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
z High resolution D/A Converters for Stereo Audio
playback
z Analog multiplexer for stereo audio
z Stereo to mono conversion
z Stereo analog input for stereo audio source
1.3 General Description
Figure 2 depicts the block diagram of MT6235. Based on a dual-processor architecture, MT6235 integrates both an
ARM926EJ-S core and a digital signal processor core. ARM926EJ-S is the main processor responsible for running
high-level GSM/GPRS protocol software as well as multi-media applications. The digital signal processor manages the
low-level MODEM as well as advanced audio functions. Except for a few mixed-signal circuitries, the other building
blocks in MT6235 are connected to either the microcontroller or the digital signal processor.
MT6235consists of the following subsystems:
z Microcontroller Unit (MCU) Subsystem: includes an ARM926EJ-S RISC processor and its accompanying
memory management and interrupt handling logics;
z Digital Signal Processor (DSP) Subsystem: includes a DSP and its accompanying memory, memory controller, and
interrupt controller;
z MCU/DSP Interface: the junction at which the MCU and the DSP exchange hardware and software information;
z Microcontroller Peripherals: includes all user interface modules and RF control interface modules;
z Microcontroller Coprocessors: runs computing-intensive processes in place of the Microcontroller;
z DSP Peripherals: hardware accelerators for GSM/GPRS/EDGE channel codec;
z Multi-media Subsystem: integrates several advanced accelerators to support multi-media applications;
z Voice Front End: the data path for converting analog speech to and from digital speech;
z Audio Front End: the data path for converting stereo audio from an audio source;
z Baseband Front End: the data path for converting a digital signal to and from an analog signal from the RF
modules;
z Timing Generator: generates the control signals related to the TDMA frame timing; and,
z Power, Reset and Clock Subsystem: manages the power, reset, and clock distribution inside MT6235.
Details of the individual subsystems and blocks are described in the following chapters.
13/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 14
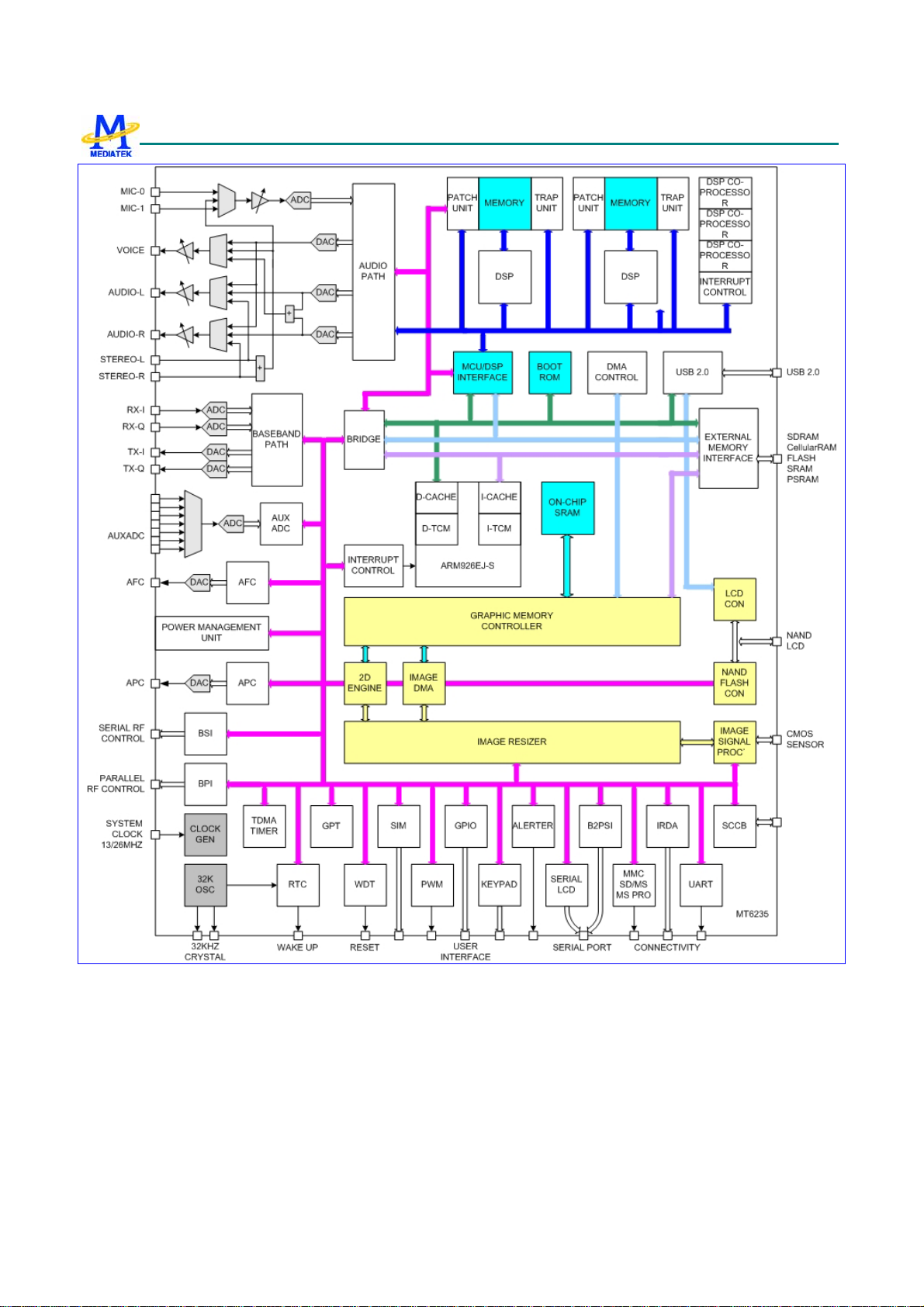
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Figure 2 MT6235 block diagram.
14/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 15

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
2 Product Description
2.1 Pin Outs
One type of package for this product, TFBGA 13mm*13mm, 362-ball, 0.5 mm pitch package, is offered.
Pin-outs and the top view are illustrated in Figure 3 for this package. Outline and dimension of package is illustrated in
Figure 4, while the definition of package is shown in Table 1.
15/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 16

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Figure 3 Top view of MT6235 TFBGA 13mm*13mm, 362-ball, 0.5 mm pitch package
Notes: RFU is reserved for future use and leave as NC in normal operation.
16/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 17

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Figure 4 Outlines and dimension of TFBGA 13mm*13mm, 362-ball, 0.5 mm pitch package
Body Size Ball Count Ball Pitch Ball Dia. Package Thk. Stand Off Substrate Thk.
D E N e b A (MAX) A1(NOM) C
13 13 362 0.5 0.3 1.2 0.21 0.36
Table 1 Definition of TFBGA 13mm*13mm, 362-ball, 0.5 mm pitch package (Unit: mm)
17/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 18

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
2.2 Top Marking Definition
MT6235A
DDDD-###
LLLLL
S
MT6235A: Part No.
DDDD: Date Code
###: Subcontractor Code
LLLLL: U1 Die Lot No.
S: Special Code
18/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 19
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
2.3 DC Characteristics
2.3.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Prolonged exposure to absolute maximum ratings may reduce device reliability. Functional operation at these maximum
ratings is not implied.
Item Symbol Min Max Unit
IO power supply VDD33 -0.3 VDD33+0.3 V
I/O input voltage VDD33 -0.3 VDD33+0.3 V
Operating temperature Topr -20 80 Celsius
Storage temperature Tstg -55 125 Celsius
19/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 20

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
2.4 Pin Description
Ball
Name Dir
13X13
Description
Mode0 Mode1 Mode2 Mode3
PU/PDRese
t
G4 JTRST_B I JTAG test port reset input PD PD
G3 JTCK I JTAG test port clock input PU PU
G2 JTDI I JTAG test port data input PU PU
G1 JTMS I JTAG test port mode switch PU PU
H1 JTDO IO JTAG test port data output
H2 JRTCK IO JTAG test port returned clock output
AE6 BPI_BUS0 IO RF hard-wire control bus 0
AD7 BPI_BUS1 IO RF hard-wire control bus 1
JTAG Port
RF Parallel Control Unit
AC7 BPI_BUS2 IO RF hard-wire control bus 2
AC6 BPI_BUS3 IO RF hard-wire control bus 3
AE8 BPI_BUS4 IO RF hard-wire control bus 4
AD8 BPI_BUS5 IO RF hard-wire control bus 5
AC8 BPI_BUS6 IO RF hard-wire control bus 6
AB8 BPI_BUS7 IO RF hard-wire control bus 7
20/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
GPIO19
GPIO20
GPIO21
BPI_BUS3 PU/PDPD
BPI_BUS6 PU/PDPD
BPI_BUS7 PU/PDPD
Page 21

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
AE9 BPI_BUS8 IO RF hard-wire control bus 8
AD9 BPI_BUS9 IO RF hard-wire control bus 9
AC9 BSI_CS0 IO RF 3-wire interface chip select 0
AE10 BSI_DATA IO RF 3-wire interface data output
AD10 BSI_CLK IO RF 3-wire interface clock output
AC10 PWM0 IO Pulse width modulated signal 0
AB10 PWM1 IO Pulse width modulated signal 1
RF Serial Control Unit
PWM Interface
GPIO22
GPIO23
GPIO39
GPIO40
BPI_BUS8 PU/PDPD
BPI_BUS9 BSI_CS1 PU/PDPD
PWM0 PU/PDPD
PWM1 BSI_RFIN PU/PDPD
AC5 PWM2 IO Pulse width modulated signal 2
AE5 PWM3 IO Pulse width modulated signal 3
AE4 SCL IO
AD5 SDA IO
AC11 LSCK IO Serial display interface data output
U11 LSA0 IO Serial display interface address output
Camera Control Interface
Serial LCD/PM IC Interface
GPIO17
GPIO18
GPIO15
GPIO16
GPIO24
GPIO25
PWM2 D2_TID5 PU/PDPD
PWM3 D2_TID6 PU/PDPD
SCL D2_TID3 PU/PDPU
SDA D2_TID4 PU/PDPU
LSCK DSP_GPO2 IRQ0 PU/PDPD
LSA0 DSP_GPO3 IRQ1 PU/PDPD
21/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 22
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
AD12 LSDA IO Serial display interface clock output
AE12 LSCE0B IO Serial display interface chip select 0
output
LSCE1B IO
AC12
AB12 LPCE1B IO
U12 LPCE0B IO
AE13 LPTE IO
AC13 LRSTB IO Parallel display interface Reset Signal
AD13 LRDB IO Parallel display interface Read Strobe
U13 LPA0 IO
AE14 LWRB IO Parallel display interface Write Strobe
AD14 NLD17 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 17
AC14 NLD16 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 16
AB14 NLD15 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 15 PD
U14 NLD14 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 14 PD
AE15 NDL13 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 13 PD
AD15 NLD12 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 12 PD
AC15 NLD11 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 11 PD
AB15 NLD10 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 10 PD
AE16 NLD9 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 9 PD
AD16 NLD8 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 8 PD
AC16 NLD7 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 7 PD
AB16 NLD6 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 6 PD
U16 NLD5 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 5 PD
AE17 NLD4 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 4 PD
AD17 NLD3 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 3 PD
AC17 NLD2 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 2 PD
AE18 NLD1 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 1 PD
AD18 NLD0 IO Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Data 0 PD
AC18 NRNB IO NAND-Flash Read/Busy Flag GPIO33
AB18 NCLE IO NAND-Flash Command Latch Signal GPIO34
AE19 NALE IO NAND-Flash Address Latch Signal GPIO35
AD19 NWEB IO NAND-Flash Write Strobe GPIO36
AC19 NREB IO NAND-Flash Read Strobe GPIO37
Serial display interface chip select 1
output
Parallel LCD/NAND-Flash Interface
Parallel display interface chip select 1
output
Parallel display interface chip select 0
output
Parallel display interface address
output
GPIO26
GPIO27
GPIO28
GPIO29
GPIO30
GPIO31
GPIO32
LSDA CLKM1 TDTIRQ PU/PDPD
LSCE0B CLKM2 TCTIRQ2 PU/PDPU
LSCE1B LPCE2B TCTIRQ1
LPCE1B NCE1B TEVTVAL
LPTE
NLD17
NLD16
NRNB
NCLE
NALE
NWEB
NREB
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU
PU
PD
PD
PD
PU
22/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 23
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
AB19 NCEB IO NAND-Flash Chip select output GPIO38
F25 SYSRST_B I System reset input active low PU PU
G23 WATCHDOG IO Watchdog reset output
U10 SRCLKENAN IO
AE11 SRCLKENA IO
AD11 SRCLKENAI IO External TCXO enable input
B14 TESTMODE I TESTMODE enable input PD PD
Y4 VCCQ I
AA1 FSOURCE I
AD6 SECU_EN I
AE7 XBOOT I PD PD
A22 KCOL7 IO Keypad column 7
B22 KCOL6 IO Keypad column 6
A21 KCOL5 IO Keypad column 5
B21 KCOL4 IO Keypad column 4
C21 KCOL3 IO Keypad column 3
D21 KCOL2 IO Keypad column 2
A20 KCOL1 IO Keypad column 1
B20 KCOL0 IO Keypad column 0
C20 KROW7 IO Keypad row 7
D20 KROW6 IO Keypad row 6
A19 KROW5 IO Keypad row 5
B19 KROW4 IO Keypad row 4
C19 KROW3 IO Keypad row 3
A18 KROW2 IO Keypad row 2
B18 KROW1 IO Keypad row 1
C18 KROW0 IO Keypad row 0
F24 EINT0 IO External interrupt 0 PU PU
F23 EINT1 IO External interrupt 1 PU PU
E25 EINT2 IO External interrupt 2 PU PU
E24 EINT3 IO External interrupt 3
E23 EINT4 IO External interrupt 4
D23 EINT5 IO External interrupt 5
D25 EINT6 IO External interrupt 6
D24 EINT7 IO External interrupt 7
Miscellaneous
External TCXO enable output active
low
External TCXO enable output active
high
Keypad Interface
External Interrupt Interface
GPIO42
GPIO41
GPIO43
GPIO55
GPIO56
GPIO57
GPIO58
GPIO44
GPIO45
GPIO46
GPIO47
GPIO48
NCE0B
SRCLKEN
AN
SRCLKEN
A
SRCLKEN
AI
KCOL7 IRDA_PDN
KCOL6
PU PU
PU PU
PU PU
PU PU
PU PU
PU PU
KROW7 CLKM4
KROW6
EINT3
EINT4 DRF_EN CLKM3
EINT5 EDICK
EINT6 EDIWS
EINT7 EDIDAT
DRF_DAT
A
IRQ2
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PD
PU
PU
PD
PD
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
23/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 24
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
K17 MFIQ IO Interrupt to MCU
G24 ED0 IO External memory data bus 0
G22 ED1 IO External memory data bus 1
G25 ED2 IO External memory data bus 2
H24 ED3 IO External memory data bus 3
H23 ED4 IO External memory data bus 4
J23 ED5 IO External memory data bus 5
J24 ED6 IO External memory data bus 6
K22 ED7 IO External memory data bus 7
H25 ED8 IO External memory data bus 8
J25 ED9 IO External memory data bus 9
K23 ED10 IO External memory data bus 10
K24 ED11 IO External memory data bus 11
K25 ED12 IO External memory data bus 12
L17 ED13 IO External memory data bus 13
L23 ED14 IO External memory data bus 14
L24 ED15 IO External memory data bus 15
M25 ERD_B IO External memory read strobe
N17 EWR_B IO External memory write strobe
L25 ECS0_B IO External memory chip select 0
M17 ECS1_B IO External memory chip select 1
M23 ECS2_B IO External memory chip select 2
M24 ECS3_B IO External memory chip select 3
R25 EWAIT IO
N25 ECAS_B IO MobileRAM column address
P24 ERAS_B IO MobileRAM row address
P23 ECKE IO MobileRAM clock enable
N22 ED_CLK O MobileRAM clock
T17 EADMUX IO GPIO65
R17 EDQM1 IO
P25 EDQM0 IO
P17 EADV_B O
N24 EC_CLK O
T23 EA0 IO External memory address bus 0
T22 EA1 IO External memory address bus 1
T24 EA2 IO External memory address bus 2
T25 EA3 IO External memory address bus 3
U23 EA4 IO External memory address bus 4
U24 EA5 IO External memory address bus 5
U25 EA6 IO External memory address bus 6
V23 EA7 IO External memory address bus 7
V24 EA8 IO External memory address bus 8
V25 EA9 IO External memory address bus 9
W22 EA10 IO External memory address bus 10
External Memory Interface
Flash, PSRAM and CellularRAM data
ready
Flash, PSRAM and CellularRAM
address valid
Flash, PSRAM and CellularRAM
clock
GPIO66
PD
:nFIQ CLKM7
EADMUX
CLKM6
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU
24/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 25
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
W23 EA11 IO External memory address bus 11
W24 EA12 IO External memory address bus 12
W25 EA13 IO External memory address bus 13
Y23 EA14 IO External memory address bus 14
Y24 EA15 IO External memory address bus 15
Y25 EA16 IO External memory address bus 16
AA23 EA17 IO External memory address bus 17
AA24 EA18 IO External memory address bus 18
AA25 EA19 IO External memory address bus 19
AB24 EA20 IO External memory address bus 20
AB25 EA21 IO External memory address bus 21
AC23 EA22 IO External memory address bus 22
AC24 EA23 IO External memory address bus 23
AC25 EA24 IO External memory address bus 24
AD24 EA25 IO External memory address bus 25
AD25 EA26 IO External memory address bus 26 GPIO64
AD20 USB_XTALI IO
AE20 USB_XTALO IO
AE21 VSSCA_USB IO
AD22 VSSCD_USB IO
AC21 VRT IO
AD23 VSS33_USB IO
AE22 USB_DP IO USB D+ Input/Output
AE23 USB_DM IO USB D- Input/Output
B16 MCCM0 IO SD Command/MS Bus State Output
C16 MCDA0 IO
D16 MCDA1 IO SD Serial Data IO 1
J16 MCDA2 IO SD Serial Data IO 2
C15 MCDA3 IO SD Serial Data IO 3
D15 MCCK IO
J15 MCPWRON IO SD Power On Control Output
C14 MCWP IO SD Write Protect Input
D14 MCINS IO SD Card Detect Input
C25 URXD1 IO UART 1 receive data PU
C24 UTXD1 IO UART 1 transmit data
C23 UCTS1 IO UART 1 clear to send GPIO49
B25 URTS1 IO UART 1 request to send GPIO50
USB Interface
Memory Card Interface
SD Serial Data IO 0/MS Serial Data
IO
SD Serial Clock/MS Serial Clock
Output
UART/IrDA I nterface
GPIO67
GPIO68
GPIO69
GPIO70
GPIO71
GPIO72
GPIO73
GPIO74
GPIO75
EA26
MC0CM0
MC0DA0
MC0DA1
MC0DA2 TDMA_FS
MC0DA3
MC0CK
MC0PWR
ON
MC0WP CLKM9
MC0INS
UCTS1
URTS1
CLKM5
TDMA_CK PU/
TDMA_D1 PU/
TDMA_D0 PU/
CLKM8
UCTS2
URTS2
PU/
PD
PD
PD
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
25/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 26
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
PD
A24 URXD2 IO UART 2 receive data
B24 UTXD2 IO UART 2 transmit data
A23 URXD3 IO UART 3 receive data
B23 UTXD3 IO UART 3 transmit data
D18 DAICLK IO DAI clock output
A17 DAIPCMOUT IO DAI pcm data out
B17 DAIPCMIN IO DAI pcm data input
C17 DAIRST IO DAI reset signal input
D17 DAISYNC IO
AA2 CMRST IO CMOS sensor reset signal output
AA3 CMPDN IO CMOS sensor power down control
AB3 CMVREF IO Sensor vertical reference signal input
AB2 CMHREF IO
AA4 CMPCLK IO CMOS sensor pixel clock input
AB6 CMMCLK IO CMOS sensor master clock output
AC2 CMDAT7 IO CMOS sensor data input 7
AC3 CMDAT6 IO CMOS sensor data input 6
AC1 CMDAT5 IO CMOS sensor data input 5
AD1 CMDAT4 IO CMOS sensor data input 4
AE2 CMDAT3 IO CMOS sensor data input 3
AD3 CMDAT2 IO CMOS sensor data input 2
AD4 CMDAT1 IO CMOS sensor data input 1
AE3 CMDAT0 IO CMOS sensor data input 0
AC4 CMFLASH IO
J1 AU_MOUTL O Audio analog output left channel
Digital Audio Interface
DAI frame synchronization signal
output
CMOS Sensor Interf ace
Sensor horizontal reference signal
input
Analog Interface
GPIO51
GPIO52
GPIO53
GPIO54
GPIO59
GPIO60
GPIO61
GPIO62
GPIO63
GPIO0
GPIO1
GPIO2
GPIO3
GPIO4
GPIO5
GPIO6
GPIO7
GPIO8
GPIO9
GPIO10
GPIO11
GPIO12
GPIO13
GPIO14
URXD2 UCTS3
UTXD2 URTS3
URXD3
UTXD3
DAICLK
DAIPCMO
UT
DAIPCMI
N
DAIRST
DAISYNC
CMRST CLKM0
CMPDN
CMVREF TBTXEN D1_TID0
CMHREF TBTXFS
CMPCLK TBRXEN D1_TID1
CMMCLK TBRXFS
CMDAT7 D1ICK
CMDAT6
CMDAT5 D1IMS
CMDAT4 D2ICK
CMDAT3 D2ID
CMDAT2 D2IMS
CMDAT1 D2_TID0
CMDAT0 D2_TID1
CMFLASH D2_TID2
IRDA_RX
D
IRDA_TX
D
D1ID
DSP_GPO0 PU/
DSP_GPO1 PU/
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PD
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU/
PD
PU
PU
PU
PU
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
PD
26/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 27
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
J2 AU_MOUTR O Audio analog output right channel
K4 AU_FMINL I FM radio analog input left channel
K3 AU_FMINR I FM radio analog input right channel
K2 AU_OUT0_N O Earphone 0 amplifier output (-)
K1 AU_OUT0_P O Earphone 0 amplifier output (+)
L2
AU_MICBIAS
_P
L1
AU_MICBIAS
_N
M2 AU_VREF_N O Audio reference voltage (-)
M1 AU_VREF_P O Audio reference voltage (+)
N1 AU_VIN0_P I Microphone 0 amplifier input (+)
N2 AU_VIN0_N I Microphone 0 amplifier input (-)
N3 AU_VIN1_N I Microphone 1 amplifier input (-)
N4 AU_VIN1_P I Microphone 1 amplifier input (+)
P1 BDLAQP I
P2 BDLAQN I
R1 BDLAIN I
R2 BDLAIP I
T3 APC I Automatic power control DAC output
T4 AUXADIN0 I Auxiliary ADC input 0
U2 AUXADIN1 I Auxiliary ADC input 1
U4 AUXADIN2 I Auxiliary ADC input 2
V2 AUXADIN3 I Auxiliary ADC input 3
U1 AUX_REF I Auxiliary ADC reference voltage input
U3 XP I
V1 XM I
W3 YP I
V3 YM I
V4 AFC O
W2 AFC_BYP O Automatic frequency control DAC
B1 BATDET I
C2 VRF_SENSE I
C1 VRF I
E3 VTCXO I
F2 VREF I
C12 VIBRATOR O
D11 LED O
A11 VCORE I
C11 VCORE_FB I
B11
BAT_BACKU
P
F1 VA
A9 VM I
D10 VM_SENSE I
O Microphone bias supply (+)
O Microphone bias supply (-)
Quadrature input (Q+) baseband codec
downlink
Quadrature input (Q-) baseband codec
downlink
In-phase input (I+) baseband codec
downlink
In-phase input (I-) baseband codec
downlink
Automatic frequency control DAC
output
bypass capacitance
I
27/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 28
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
C10 VCAM_D II
D8
VCAM_A_SE
NSE
A7 VCAM_A
C8 VBT I
A6 VIO I
C7 VUSB I
A5 VSIM I
C5 SIO IO
C6 PWRKEY I
D5 ISENSE I
A4 VMSEL I
B4 GATEDRV I
C4 CHRIN I
A3 SCLK I
B3 BATSENSE I
C3 SRST O
A2 RESET I
B2 RSTCAP IO
Y1 SYSCLK I 13MHz or 26MHz system clock input
A14 XIN I 32.768 KHz crystal input
A15 XOUT O 32.768 KHz crystal output
B13 BBWAKEUP IO Baseband power on/off control
H3 VDDK Supply voltage of internal logic
AB7 VDDK Supply voltage of internal logic
AB20 VDDK Supply voltage of internal logic
Y22 VDDK Supply voltage of internal logic
F22 VDDK Supply voltage of internal logic
J14 VDDK Supply voltage of internal logic
AB23 VDD33_EMI
V22 VDD33_EMI
R22 VDD33_EMI
M22 VDD33_EMI
J22 VDD33_EMI
AD2 VDD33_CAM
AB13 VDD33_LCD
AB17 VDD33_LCD
AC22 VDD33_USB
AB21 VDDC_USB
D13 VDD33_MC
I
I
VCXO Interface
RTC Interface
Supply V oltages
Supply voltage of memory interface
driver
Supply voltage of memory interface
driver
Supply voltage of memory interface
driver
Supply voltage of memory interface
driver
Supply voltage of memory interface
driver
28/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 29
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
H4 VDD33
AB9 VDD33
E22 VDD33
D19 VDD33 Supply voltage of drivers except
F4 VSS33
Y3 VSS33
AB5 VSS33
AB11 VSS33
U15 VSS33
AC20 VSS33
AE24 VSS33
AA22 VSS33
U22 VSS33
P22 VSS33
L22 VSS33
H22 VSS33
C22 VSS33
A16 VSS33
A13 VSS33
L9 VSS33
L11 VSS33
L12 VSS33
L13 VSS33
L14 VSS33
L15 VSS33
Supply voltage of drivers except
memory interface, USB and
MS/MMC/SD
Supply voltage of drivers except
memory interface, USB and
MS/MMC/SD
Supply voltage of drivers except
memory interface, USB and
MS/MMC/SD
memory interface, USB and
MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
29/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 30
MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
M9 VSS33
M11 VSS33
M15 VSS33
N11 VSS33
N13 VSS33
N15 VSS33
P9 VSS33
P11 VSS33
P15 VSS33
R9 VSS33
R11 VSS33
R12 VSS33
R13 VSS33
R14 VSS33
R15 VSS33
T9 VSS33
W1 AVCC12_PLL
Y2 AVSS12_PLL
B15 VRTC Supply voltage for Real Time Clock
J4
AVDD28_MB
UF
J3
AVSS28_MBU
F
K9 AVDD28_BUF
L3 AVSS28_BUF GND for voice band transmit section
L4 AVDD28_AFE
M3 AGND28_AFE
N9 AVSS28_AFE GND for voice band receive section
P4 AGND28_RFE
P3
AVSS28_GSM
RFTX
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Ground of drivers except memory
interface, USB and MS/MMC/SD
Analog Supplies
Supply Voltage for Audio band section
GND for Audio band section
Supply voltage for voice band transmit
section
Supply voltage for voice band receive
section
GND reference voltage for voice band
section
GND reference voltage for baseband
section, APC, AFC and AUXADC
GND for baseband transmit section
30/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 31

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
R3
AVDD28_GS
MRFTX
T2 AVSS28_RFE
T1 AVDD28_RFE
D1 VBAT_VRF
D3 AGND_VRF
E4 GND_LDOS
E2 VBAT_VA
E1 VBAT_VA
F3 AGND_VA
D12 GND_DRV
A12 GND_VCORE
A10
VBAT_VCOR
E
B10 VBAT_LDOS1
B9 VBAT_LDOS1
B8 VBAT_LDOS2
D7 GND_LDOS
B7 VBAT_LDOS2
B6 VBAT_LDOS3
D6 GND_LDOS
D9 GND_LDOS
Supply voltage for baseband transmit
section
GND for baseband receive section,
APC, AFC and AUXADC
Supply voltage for baseband receive
section, APC, AFC and AUXADC
Table 2 Pin Descriptions (Bolded types are functions at reset)
31/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 32

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
2.5 Power Description
BALL NAME IO SUPPLY IO GND CORE SUPPLY CORE GND REMARK
B1 BATDET
C2 VRF_SENSE
C1 VRF
D1 VBAT_VRF
D3 AGND_VRF
E4 GND_LDOS
E3 VTCXO
E2 VBAT_VA
F1 VA
E1 VBAT_VA
F2 VREF
F3 AGND_VA
G4 JTRST_B VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
F4 VSS33
G3 JTCK VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
G2 JTDI VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
G1 JTMS VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
H1 JTDO VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
H3 VDDK
H2 JRTCK VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
H4 VDD33
J4 AVDD28_MBUF
J2 AU_MOUTR
J3 AVSS28_MBUF
J1 AU_MOUTL
K3 AU_FMINR
K4 AU_FMINL
K9 AVDD28_BUF
K2 AU_OUT0_N
K1 AU_OUT0_P
L3 AVSS28_BUF
L2 AU_MICBIAS_P
L1 AU_MICBIAS_N
L4 AVDD28_AFE
M2 AU_VREF_N
M1 AU_VREF_P
M3 AGND28_AFE
N1 AU_VIN0_P
N2 AU_VIN0_N
N3 AU_VIN1_N
N4 AU_VIN1_P
N9 AVSS28_AFE
P3 AVSS28_GSMRFTX
P4 AGND28_RFE
R3 AVDD28_GSMRFTX
32/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 33

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
P1 BDLAQP
P2 BDLAQN
R1 BDLAIN
R2 BDLAIP
T3 APC
T1 AVDD28_RFE
U1 AUX_REF
T4 AUXADIN0
U2 AUXADIN1
T2 AVSS28_RFE
U3 XP
U4 AUXADIN2
V1 XM
V2 AUXADIN3
V3 YM
V4 AFC
W3 YP
W2 AFC_BYP
W1 AVCC12_PLL
Y1 SYSCLK AVCC12_PLL AVSS12_PLL AVCC12_PLL AVSS12_PLL
Y2 AVSS12_PLL
Y3 VSS33
Y4 VCCQ
AA1 FSOURCE
AA2 CMRST VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AA3 CMPDN VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB3 CMVREF VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB2 CMHREF VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AA4 CMPCLK VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB6 CMMCLK VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC2 CMDAT7 VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC3 CMDAT6 VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC1 CMDAT5 VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD2 VDD33_CAM
AD1 CMDAT4 VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE2 CMDAT3 VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD3 CMDAT2 VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD4 CMDAT1 VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE3 CMDAT0 VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC4 CMFLASH VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB7 VDDK
AE4 SCL VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD5 SDA VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC5 PWM2 VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE5 PWM3 VDD33_CAM VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB5 VSS33
AD6 SECU_EN VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE7 XBOOT VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE6 BPI_BUS0 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
33/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 34

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
AD7 BPI_BUS1 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC7 BPI_BUS2 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC6 BPI_BUS3 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE8 BPI_BUS4 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD8 BPI_BUS5 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC8 BPI_BUS6 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB8 BPI_BUS7 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE9 BPI_BUS8 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB9 VDD33
AD9 BPI_BUS9 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC9 BSI_CS0 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE10 BSI_DATA VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD10 BSI_CLK VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC10 PWM0 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB10 PWM1 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
U10 SRCLKENAN VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE11 SRCLKENA VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD11 SRCLKENAI VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB11 VSS33
AC11 LSCK VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
U11 LSA0 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD12 LSDA VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE12 LSCE0B VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC12 LSCE1B VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB12 LPCE1B VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
U12 LPCE0B VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE13 LPTE VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC13 LRSTB VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD13 LRDB VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB13 VDD33_LCD
U13 LPA0 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE14 LWRB VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD14 NLD17 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC14 NLD16 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB14 NLD15 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
U14 NLD14 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE15 NLD13 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD15 NLD12 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC15 NLD11 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
U15 VSS33
AB15 NLD10 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE16 NLD9 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD16 NLD8 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC16 NLD7 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB16 NLD6 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
U16 NLD5 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE17 NLD4 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD17 NLD3 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC17 NLD2 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
34/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 35

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
AB17 VDD33_LCD
AE18 NLD1 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD18 NLD0 VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC18 NRNB VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB18 NCLE VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AE19 NALE VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD19 NWEB VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC19 NREB VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB19 NCEB VDD33_LCD VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB20 VDDK
AC20 VSS33
AD20 USB_XTALI
AE20 USB_XTALO
AE21 VSSCA_USB
AD22 VSSCD_USB
AB21 VDDC_USB
AC21 VRT
AD23 VSS33_USB
AC22 VDD33_USB
AE22 USB_DP
AE23 USB_DM
AE24 VSS33
AD25 EA26 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AD24 EA25 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC25 EA24 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC24 EA23 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AC23 EA22 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB25 EA21 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AA22 VSS33
AB24 EA20 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AA25 EA19 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AA24 EA18 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
AB23 VDD33_EMI
AA23 EA17 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
Y25 EA16 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
Y22 VDDK
Y24 EA15 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
Y23 EA14 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
W25 EA13 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
W24 EA12 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
V22 VDD33_EMI
W23 EA11 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
W22 EA10 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
V25 EA9 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
V24 EA8 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
V23 EA7 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
U25 EA6 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
U24 EA5 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
U23 EA4 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
35/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 36

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
T25 EA3 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
U22 VSS33
T24 EA2 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
T22 EA1 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
T23 EA0 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
T17 EADMUX VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
R25 EWAIT VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
R17 EDQM1 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
P25 EDQM0 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
P24 ERAS_B VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
N25 ECAS_B VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
R22 VDD33_EMI
P17 EADV_B VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
N22 ED_CLK VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
P22 VSS33
N24 EC_CLK VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
P23 ECKE VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
N17 EWR_B VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
M25 ERD_B VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
M24 ECS3_B VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
M23 ECS2_B VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
M17 ECS1_B VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
L25 ECS0_B VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
L24 ED15 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
M22 VDD33_EMI
L23 ED14 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
L17 ED13 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
K25 ED12 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
L22 VSS33
K24 ED11 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
K23 ED10 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
J25 ED9 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
H25 ED8 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
K22 ED7 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
J24 ED6 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
J23 ED5 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
H23 ED4 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
H24 ED3 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
J22 VDD33_EMI
G25 ED2 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
G22 ED1 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
G24 ED0 VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
K17 MFIQ VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
G23 WATCHDOG VDD33_EMI VSS33 VDDK VSS33
H22 VSS33
F22 VDDK
F25 SYSRST_B VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
F24 EINT0 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
F23 EINT1 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
36/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 37

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
E25 EINT2 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
E24 EINT3 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
E23 EINT4 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
D23 EINT5 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
D25 EINT6 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
D24 EINT7 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
E22 VDD33
C25 URXD1 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
C24 UTXD1 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
C23 UCTS1 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
B25 URTS1 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
A24 URXD2 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
B24 UTXD2 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
A23 URXD3 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
B23 UTXD3 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
C22 VSS33
A22 KCOL7 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
B22 KCOL6 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
A21 KCOL5 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
B21 KCOL4 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
C21 KCOL3 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
D21 KCOL2 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
A20 KCOL1 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
B20 KCOL0 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
C20 KROW7 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
D20 KROW6 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
A19 KROW5 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
D19 VDD33
B19 KROW4 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
C19 KROW3 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
A18 KROW2 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
B18 KROW1 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
C18 KROW0 VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
D18 DAICLK VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
A17 DAIPCMOUT VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
B17 DAIPCMIN VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
C17 DAIRST VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
A16 VSS33
D17 DAISYNC VDD33 VSS33 VDDK VSS33
B16 MCCM0 VDD33_MC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
C16 MCDA0 VDD33_MC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
D16 MCDA1 VDD33_MC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
J16 MCDA2 VDD33_MC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
C15 MCDA3 VDD33_MC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
D15 MCCK VDD33_MC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
J15 MCPWRON VDD33_MC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
C14 MCWP VDD33_MC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
J14 VDDK
D14 MCINS VDD33_MC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
37/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 38

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
D13 VDD33_MC
B15 VRTC
A15 XOUT VRTC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
A14 XIN VRTC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
B13 BBWAKEUP VRTC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
B14 TESTMODE VRTC VSS33 VDDK VSS33
A13 VSS33
C12 VIBRATOR
D12 GND_DRV
D11 LED
A12 GND_VCORE
A11 VCORE
C11 VCORE_FB
A10 VBAT_VCORE
B11 BAT_BACKUP
A9 VM
D10 VM_SENSE
B10 VBAT_LDOS1
C10 VCAM_D
B9 VBAT_LDOS1
D9 GND_LDOS
D8 VCAM_A_SENSE
A7 VCAM_A
C8 VBT
B8 VBAT_LDOS2
A6 VIO
D7 GND_LDOS
C7 VUSB
B7 VBAT_LDOS2
A5 VSIM
C5 SIO
C6 PWRKEY
B6 VBAT_LDOS3
D6 GND_LDOS
D5 ISENSE
A4 VMSEL
B4 GATEDRV
C4 CHRIN
A3 SCLK
B3 \BATSENSE
C3 SRST
A2 RESET
B2 RSTCAP
L9 VSS33
L11 VSS33
L12 VSS33
L13 VSS33
L14 VSS33
L15 VSS33
38/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 39

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
M9 VSS33
M11 VSS33
M15 VSS33
N11 VSS33
N13 VSS33
N15 VSS33
P9 VSS33
P11 VSS33
P15 VSS33
R9 VSS33
R11 VSS33
R12 VSS33
R13 VSS33
R14 VSS33
R15 VSS33
T9 VSS33
Table 3 Power Descriptions
39/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 40

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
3 Micro-Controller Unit Subsystem
Figure 5 illustrates the block diagram of the Micro-Controller Unit Subsystem in MT6235.The subsystem utilizes a main
32-bit ARM926EJ-S RISC processor, which plays the role of the main bus master controlling the whole subsystem. The
ARM926EJ-S RISC is equipped with instruction cache, instruction TCM, data cache, and data TCM. The size of instruction
cache and data cache are both 16KB. The size of instruction TCM is 48KB. The size of data TCM is 80KB. If the requested
content is found in TCM or in cache, no bus transaction is required. If the code cache hit rate is high enough, bus traffic can
be effectively reduced and processor core performance maximized.
The bus comprises of two-level system buses: Advanced High-Performance Bus (AHB) and Advanced Peripheral Bus
(APB). All bus transactions originate from bus masters, while slaves can only respond to requests from bus masters.
Before data transfer can be established, the bus master must ask for bus ownership, accomplished by request-grant
handshaking protocol between masters and arbiters.
Two levels of bus hierarchy are designed to provide optimum usage for different performance requirements. Specifically,
AHB Bus, the main system bus, is tailored toward high-speed requirements and provides 32-bit data path with multiplex
scheme for bus interconnections. The APB Bus, on the other hand, is designed to reduce interface complexity for lower
data transfer rate, and so it is isolated from high bandwidth AHB Bus by APB Bridge. APB Bus supports 16-bit
addressing and both 16-bit and 32-bit data paths. APB Bus is also optimized for minimal power consumption by turning
off the clock when there is no APB bus activity.
During operation, if the target slave is located on AHB Bus, the transaction is conducted directly on AHB Bus. However,
if the target slave is a peripheral and is attached to the APB bus, then the transaction is conducted between AHB and APB
bus through the use of APB Bridge.
The MT6235 MCU subsystem supports only memory addressing method. Therefore all components are mapped onto the
MCU 32-bit address space. A Memory Management Unit is employed to allow for a central decode scheme. The MMU
generates appropriate selection signals for each memory-addressed module on the AHB Bus.
In order to off-load the processor core, a DMA Controller is designated to act as a master and share the bus resources on
AHB Bus to perform fast data movement between modules. This controller provides fourteen DMA channels.
The Interrupt Controller provides a software interface to manipulate interrupt events; it can handle up to 50 interrupt
sources asserted at the same time. In general, the controller generates 2 levels of interrupt requests, FIQ and IRQ, to the
processor.
A 64K Byte SRAM is provided as system memory for high-speed data access. For factory programming purposes, a Boot
ROM module is also integrated. These two modules use the same Internal Memory Controller to connect to AHB Bus.
External Memory Interface supports both 8-bit and 16-bit devices. This interface supports both synchronous and
asynchronous components, such as Flash, SRAM, SDRAM and parallel LCD. This interface supports page and burst
mode type of Flash, Cellular RAM, as well as high performance MobileRAM. Since AHB Bus is 32-bit wide, all data
transfers are converted into several 8-bit or 16-bit cycles depending on the data width of the target device.
40/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 41

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
AHB Masters
Graphic
LCD Controller
AHB Layer 1
AHB Layer 2
AHB Layer 3
AHB Layer 4
APB Bus
48KB ITCM 80KB DTCM
ARM926EJ-S
16KB
ICACHE
System RAM
System ROM
(64KB)
16KB
DCACHE
Other AHB
Masters (DMA ,
USB, ...)
AHB/APB
Bridge
APB
APB
Peripherals
APB
Peripherals
Peripherals
Figure 5 Block Diagram of the Micro-Controller Unit Subsystem in MT6235
EMI Controller
AHB Slaves
APB Slaves
3.1 Processor Core
3.1.1 General Description
The Micro-Controller Unit Subsystem in MT6235 uses the 32-bit ARM926EJ-S RISC processor that is based on the Von
Neumann architecture with a single 32-bit data bus carrying both instructions and data. The memory interface of
ARM926EJ-S is totally compliant with the AMBA based bus system, which allows direct connection to the AHB Bus.
3.2 Memory Management
3.2.1 General Description
The processor core of MT6235 supports only a memory addressing method for instruction fetch and data access. The core
manages a 32-bit address space that has addressing capability of up to 4 GB. System RAM, System ROM, Registers,
MCU Peripherals and external components are all mapped onto such 32-bit address space, as depicted in Figure 6.
41/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 42

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
BANK Base Address Description
BANK0 0000_0000h EMI Band 0 / Boot Code
BANK1 1000_0000h EMI Bank 1
BANK2 2000_0000h EMI Bank 2
BANK3 3000_0000h EMI Bank 3
BANK4
BANK5 5000_0000h TCM
BANK6 6000_0000h USB
BANK7 7000_0000h Reserved
BANK8 8000_0000h APB Peripheral
BANK9 9000_0000h LCD
BANK10 A000_0000h CPU-DSP Share RAM 1
BANK11 B000_0000h Reserved
BANK12 C000_0000h Reserved
BANK13 D000_0000h Reserved
BANK14 E000_0000h Reserved
BANK15 F000_0000h Reserved
4000_0000h System RA M
4800_0000h System ROM
6100_0000h Virtual FIFO Slave
A100_0000h CPU-DSP Share RAM2
A200_ 0000h DSP IDMA Port 1
A300_ 0000h DSP IDMA Port 2
Figure 6 The Memory Layout of MT6235
The address space is organized into blocks of 256 MB each. The block number is uniquely selected by address line
A31-A28 of the internal system bus.
3.2.1.1 External Access
To allow external access, the MT6235 can output 27bits (A26-A0) of address lines along with 4 selection signals that
correspond to the associated memory blocks. That is, MT6235 can support up to 4 MCU addressable external components.
The data width of internal system bus is fixed at 32-bit wide, while the data width of the external components is either 16–
bit or 8-bit.
Since devices are usually available with varied operating grades, adaptive configurations for different applications are
needed. MT6235 provides software programmable registers to configure their wait-states to adapt to different operating
conditions.
3.2.1.2 Memory Re-mapping Mechanism
To permit more flexible system configuration, a memory re-mapping mechanism is provided. The mechanism allows
software program to swap BANK0 (ECS0#) and BANK1 (ECS1#) dynamically. Whenever the bit value of RM0 in
register EMI_REMAP is changed, these two banks are swapped accordingly. Furthermore, it allows system to boot from
System ROM as detailed in 3.2.1.3 Boot Sequence.
42/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 43

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
3.2.1.3 Boot Sequence
Since the ARM926EJ-S core always starts to fetch instructions from the lowest memory address at 00000000h after system
has been reset, the system is designed to have a dynamic mapping architecture capable of associating Boot Code, external
Flash or external SRAM with the memory block 0000_0000h – 0fff_ffffh.
By default, the Boot Code is mapped onto 0000_0000h – 0fff_ffffh after a system reset. In this special boot mode,
External Memory Controller does not access external memory; instead, the EMI Controller send predefined Boot Code
back to the ARM926EJ-S core, which instructs the processor to execute the program in System ROM. This configuration
can be changed by programming bit value of RM1 in register EMI_REMAP directly.
MT6235 system provides one boot up scheme:
z Start up system of running codes from Boot Code for factory programming or NAND flash boot.
3.2.1.3.1 Boot Code
The Boot Code is placed together with Memory Re-Mapping Mechanism in External Memory Controller, and comprises of
just two words of instructions as shown below. A jump instruction leads the processor to run the code starting at address
48000000h where the System ROM is placed.
ADDRESS BINARY CODE ASSEMBLY
00000000h E51FF004h LDR PC, 0x4
00000004h 48000000h (DATA)
3.2.1.3.2 Factory Programming
The configuration for factory programming is shown in Figure 7. Usually the Factory Programming Host connects with
MT6235 via the UART interface. The download speed can be up to 921K bps while MCU is running at 26MHz.
After the system has reset, the Boot Code guides the processor to run the Factory Programming software placed in System
ROM. Then, MT6235 starts and polls the UART1 port until valid information is detected. The first information received
on the UART1 is used to configure the chip for factory programming. The Flash downloader program is then transferred
into System RAM or external SRAM.
Further information is detailed in the MT6235 Software Programming Specification.
UART
MT6235
External
Memory
Interface
FLASH
Factory
Programming
Host
Figure 7 System configuration required for factory programming
43/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 44

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
3.2.1.3.3 NAND Flash Booting
If MT6235 cannot receive data from UART1 for a certain amount of time, the program in System ROM checks if any valid
boot loader exists in NAND flash. If found, the boot loader code is copied from NAND flash to RAM (internal or external)
and executed to start the real application software. If no valid boot loader can be found in NAND flash, MT6235 starts
executing code in EMI bank0 memory. The whole boot sequence is shown in the following figure.
Boot from
Boot from
System ROM
System ROM
Check UART
Check UART
input
input
Y
Y
Receive
Receive
from UART
from UART
N
N
Valid loader
Valid loader
on NAND
on NAND
Y
Y
N
N
Boot from
Boot from
EMI bank 0
EMI bank 0
Factory
Factory
programming
programming
Copy loader from
Copy loader from
NAND to RAM
NAND to RAM
Boot from
Boot from
loader in RAM
loader in RAM
Figure 8 Boot sequence
3.2.1.4 Little Endian Mode
The MT6235 system always treats 32-bit words of memory in Little Endian format. In Little Endian mode, the lowest
numbered byte in a word is stored in the least significant position, and the highest numbered byte in the most significant
position. Byte 0 of the memory system is therefore connected to data lines 7 through 0.
3.3 Bus System
3.3.1 General Description
Two levels of bus hierarchy are employed in the Micro-Controller Unit Subsystem of MT6235. As depicted in Figure 5,
AHB Bus and APB Bus serve as system backbone and peripheral buses, while an APB bridge connects these two buses.
Both AHB and APB Buses operate at the same or half the clock rate of processor core.
The APB Bridge is the only bus master residing on the APB bus. All APB slaves are mapped onto memory block MB8 in
the MCU 32-bit addressing space. A central address decoder is implemented inside the bridge to generate select signals
for individual peripherals. In addition, since the base address of each APB slave is associated with select signals, the
address bus on APB contains only the value of offset address.
44/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 45

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
The maximum address space that can be allocated to a single APB slave is 64 KB, i.e. 16-bit address lines. The width of
the data bus is mainly constrained to 16 bits to minimize the design complexity and power consumption while some use
32-bit data buses to accommodate more bandwidth. In the case where an APB slave needs large amount of transfers, the
device driver can also request DMA channels to conduct a burst of data transfer. The base address and data width of each
peripheral are listed in Table 4.
Base Address Description
8001_0000h EFUSE Control 32 EFUSEC Base
8001_0000h
Configuration Registers
(Clock, Power Down, Version and Reset)
8002_0000h General Purpose Inputs/Outputs 16 GPIO Base
8003_0000h Reset Generation Unit 16 RGU Base
8100_0000h External Memory Interface 32 EMI Base
8101_0000h Interrupt Controller 32 CIRQ Base
8102_0000h DMA Controller 32 DMA Base
8103_0000h UART 1 16 UART1 Base
8104_0000h UART 2 16 UART2 Base
8105_0000h UART 3 16 UART3 Base
8106_0000h General Purpose Timer 16 GPT Base
8107_0000h Reserved 16 Reserved
8108_0000h Keypad Scanner 16 KP Base
8109_0000h Pulse-Width Modulation Outputs 32 PWM Base
810a_0000h SIM Interface 16 SIM Base
810b_0000h Reserved
810c_0000h Real Time Clock 16 RTC Base
810d_0000h Secure Engine 32 SEJ Base
810e_0000h Bus Monitor 32 BM Base
810f_0000h IrDA 16 IRDA Base
8110_0000h I2C 16 I2C Base
8111_0000h MS/SD Controller 32 MSDC Base
8112_0000h NAND Flash Interface 32 NFI Base
8113_0000h Reserved
8114_0000h Second MS/SD Interface 16 MSDC2 Base
8200_0000h TDMA Timer 32 TDMA Base
8201_0000h Base-Band Serial Interface 32 BSI Base
8202_0000h Base-Band Parallel Interface 16 BPI Base
8203_0000h Automatic Frequency Control Unit 16 AFC Base
8204_0000h Automatic Power Control Unit 32 APC Base
8205_0000h Auxiliary ADC Unit 16 AUXADC Base
8206_0000h Divider/Modulus Coprocessor 32 DIVIDER Base
Data
Width
Software Base ID
16 CONFG Base
45/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 46

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
8207_0000h Frame Check Sequence 16 FCS Base
8208_0000h GPRS Cipher Unit 32 GCU Base
8209_0000h CSD Format Conversion Coprocessor 32 CSD_ACC Base
820a_0000h MCU-DSP Shared Register 1 16 SHARE1 Base
820b_0000h IRDBG1 16 IRDBG Base
820c_0000h MCU-DSP Shared Register 2 16 SHARE2 Base
820d_0000h IRDBG2 16 IRDBG2 Bas3
820e_0000h DSP Patch Unit 16 PATCH Base
820f_0000h Audio Front End 16 AFE Base
8210_0000h Base-Band Front End 16 BFE Base
8211_0000h Reserved
8212_0000h Reserved
8300_0000h PLL / Clock square configuration 16 PLL_CLKSQ Base
8301_0000h Analog Chip Interface Controller 16 ACIF Base
8302_0000h Reserved
8400_0000h Graphics Memory Controller 32 GMC Base
8401_0000h 2D Accelerator 32 G2D Base
8402_0000h 2D Command Queue 32 GCMQ Base
8403_0000h Reserved
8404_0000h Reserved
8405_0000h Reserved
8406_0000h Reserved
8407_0000h Reserved
8408_0000h Reserved
8409_0000h Reserved
840a_0000h Reserved
840b_0000h Camera Interface 32 CAM Base
840c_0000h Reserved
840d_0000h Reserved
840e_0000h Capture Resizer 32 CRZ Base
840f_0000h Reserved
8410_0000h Reserved
8411_0000h Reserved
Table 4 Register Base Addresses for MCU Peripherals
REGISTER ADDRESS REGISTER NAME SYNONYM
CONFG + 0000h Hardware Version Register HW_VER
CONFG + 0004h Software Version Register SW_VER
CONFG + 0008h Hardware Code Register HW_CODE
46/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 47

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
CONFG + 0404h APB Bus Control Register APB_CON
CONFG + 0500h IRWIN Control Register IRWIN_CON
Table 5 APB Bridge Register Map
3.3.2 Register Definitions
CONFG+0000h Hardware Version Register HW_VERSION
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EXTP MAJREV MINREV
Type RO RO RO RO
Reset 8 A 0 0
This register is used by software to determine the hardware version of the chip. The register contains a new value
whenever each metal fix or major step is performed. All values are incremented by a step of 1.
MINREV Minor Revision of the chip
MAJREV Major Revision of the chip
EXTP This field shows the existence of Hardware Code Register that presents the Hardware ID while the value is other
than zero.
CONFG+0004h Software Version Register SW_VERSION
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EXTP MAJREV MINREV
Type RO RO RO RO
Reset 8 A 0 0
This register is used by software to determine the software version used with this chip. All values are incremented by a
step of 1.
MINREV Minor Revision of the Software
MAJREV Major Revision of the Software
EXTP This field shows the existence of Software Code Register that presents the Software ID when the value is other
than zero.
CONFG+0008h Hardware Code Register HW_CODE
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CODE3 CODE2 CODE1 CODE0
Type RO RO RO RO
Reset 6 2 3 5
This register presents the Hardware ID.
CODE This version of chip is coded as 6235h.
CONFG+0404h APB Bus Control Register APB_CON
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1
APBW4 APBW3 APBW2 APBW1 APBW
0
APBR4 APBR3 APBR2 APBR1 APBR
0
47/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 48

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
This register is used to control the timing of Read Cycle and Write Cycle on APB Bus. Note that APB Bridge 2 is
different from other bridges: the access time is varied, and access is not complete until an acknowledge signal from APB
slave is asserted.
APBR0-APBR6 Read Access Time on APB Bus
0 1-Cycle Access
1 2-Cycle Access
APBW0-APBW6 Write Access Time on APB Bus
0 1-Cycle Access
1 2-Cycle Access
3.4 Direct Memory Access
3.4.1 General Description
A generic DMA Controller is placed on Layer 2 AHB Bus to support fast data transfers and to off-load the processor. With
this controller, specific devices on AHB or APB buses can benefit greatly from quick completion of data movement from or
to memory modules such as Internal System RAM or External SRAM, excluding TCM. TCM is invisible for DMA
engine.. Such Generic DMA Controller can also be used to connect any two devices other than memory module as long as
they can be addressed in memory space.
Figure 9 Variety Data Paths of DMA Transfers
Up to fourteen channels of simultaneous data transfers are supported. Each channel has a similar set of registers to be
configured to different scheme as desired. If more than fourteen devices are requesting the DMA resources at the same
time, software based arbitration should be employed. Once the service candidate is decided, the responsible device driver
should configure the Generic DMA Controller properly in order to conduct DMA transfers. Both Interrupt and Polling
based schemes in handling the completion event are supported. The block diagram of such generic DMA Controller is
illustrated in Figure 10.
48/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 49

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Figure 10 Block Diagram of Direct memory Access Module
3.4.1.1 Full-Size & Half-Size DMA Channels
There are three types of DMA channels in the DMA controller. The first one is called a full-size DMA channel, the second
one is called a half-size DMA channel, and the last is Virtual FIFO DMA. Channels 1 through 3 are full-size DMA
channels; channels 4 through 10 are half-size ones; and channels 11 through 14 are Virtual FIFO DMAs. The difference
between the first two types of DMA channels is that both source and destination address are programmable in full-size
DMA channels, but only the address of one side can be programmed in half-size DMA channel. In half-size channels,
only either the source or destination address can be programmed, while the addresses of the other side is preset. Which
preset address is used depends on the setting of MAS in DMA Channel Control Register. Refer to the Register Definition
section for more detail.
3.4.1.2 Ring Buffer & Double Buffer Memory Data Movement
DMA channels 1 through 10 support ring-buffer and double-buffer memory data movement. This can be achieved by
programming DMA_WPPT and DMA_WPTO, as well as setting WPEN in DMA_CON register to enable. Figure 11
illustrates how this function works. Once the transfer counter reaches the value of WPPT, the next address jumps to the
WPTO address after completing the WPPT data transfer. Note that only one side can be configured as ring-buffer or
double-buffer memory, and this is controlled by WPSD in DMA_CON register.
49/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 50

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Figure 11 Ring Buffer and Double Buffer Memory Data Movement
3.4.1.3 Unaligned Word Access
The address of word access on AHB bus must be aligned to word boundary, or the 2 LSB is truncated to 00b. If
programmers do not notice this, it may cause an incorrect data fetch. In the case where data is to be moved from
unaligned addresses to aligned addresses, the word is usually first split into four bytes and then moved byte by byte. This
results in four read and four write transfers on the bus.
To improve bus efficiency, unaligned-word access is provided in DMA4~10. While this function is enabled, DMAs move
data from unaligned address to aligned address by executing four continuous byte-read access and one word-write access,
reducing the number of transfers on the bus by three.
Figure 12 Unaligned Word Accesses
50/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 51

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
3.4.1.4 Virtual FIFO DMA
Virtual FIFO DMA is used to ease UART control. The difference between the Virtual FIFO DMAs and the ordinary
DMAs is that Virtual FIFO DMA contains additional FIFO controller. The read and write pointers are kept in the Virtual
FIFO DMA. During a read from the FIFO, the read pointer points to the address of the next data. During a write to the
FIFO, the write pointer moves to the next address. If the FIFO is empty, a FIFO read is not allowed. Similarly, data is
not written into the FIFO if the FIFO is full. Due to UART flow control requirements, an alert length is programmed.
Once the FIFO Space is less than this value, an alert signal is issued to enable UART flow control. The type of flow
control performed depends on the setting in UART.
Each Virtual FIFO DMA can be programmed as RX or TX FIFO. This depends on the setting of DIR in DMA_CON
register. If DIR is “0”(READ), it means TX FIFO. On the other hand, if DIR is “1”(WRITE), the Virtual FIFO DMA is
specified as a RX FIFO.
Virtual FIFO DMA provides an interrupt to MCU. This interrupt informs MCU that there is data in the FIFO, and the
amount of data is over or under the value defined in DMA_COUNT register. With this, MCU does not need to poll DMA
to know when data must be removed from or put into the FIFO.
Note that Virtual FIFO DMAs cannot be used as generic DMAs, i.e. DMA1~10.
Figure 13 Virt u al FIFO D M A
DMA number Address of Virtual FIFO Access Port Associated UART
DMA11 6100_0000h UART1 RX / ALL UART TX
DMA12 6100_0100h UART2 RX / ALL UART TX
DMA13 6100_0200h UART3 RX / ALL UART TX
DMA14 6100_0300h ALL UART TX
Table 6 Virtual FIFO Access Port
DMA number Type Ring Buffer
Double
Buffer
Burst Mode
Unaligned Word
Access
DMA1 Full Size
DMA2 Full Size
51/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 52

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
DMA3 Full Size
DMA4 Half Size
DMA5 Half Size
DMA6 Half Size
DMA7 Half Size
DMA8 Half Size
DMA9 Half Size
DMA10 Half Size
DMA11 Virtual FIFO
DMA12 Virtual FIFO
DMA13 Virtual FIFO
DMA14 Virtual FIFO
Table 7 Function List of DMA channels
REGISTER ADDRESS REGISTER NAME SYNONYM
DMA + 0000h DMA Global Status Register DMA_GLBSTA
DMA + 0028h DMA Global Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA_GLBLIMITER
DMA + 0100h DMA Channel 1 Source Address Register DMA1_SRC
DMA + 0104h DMA Channel 1 Destination Address Register DMA1_DST
DMA + 0108h DMA Channel 1 Wrap Point Address Register DMA1_WPPT
DMA + 010Ch DMA Channel 1 Wrap To Address Register DMA1_WPTO
DMA + 0110h DMA Channel 1 Transfer Count Register DMA1_COUNT
DMA + 0114h DMA Channel 1 Control Register DMA1_CON
DMA + 0118h DMA Channel 1 Start Register DMA1_START
DMA + 011Ch DMA Channel 1 Interrupt Status Register DMA1_INTSTA
DMA + 0120h DMA Channel 1 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA1_ACKINT
DMA + 0124h DMA Channel 1 Remaining Length of Current Transfer DMA1_RLCT
DMA + 0128h DMA Channel 1 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA1_LIMITER
DMA + 0200h DMA Channel 2 Source Address Register DMA2_SRC
DMA + 0204h DMA Channel 2 Destination Address Register DMA2_DST
DMA + 0208h DMA Channel 2 Wrap Point Address Register DMA2_WPPT
DMA + 020Ch DMA Channel 2 Wrap To Address Register DMA2_WPTO
DMA + 0210h DMA Channel 2 Transfer Count Register DMA2_COUNT
DMA + 0214h DMA Channel 2 Control Register DMA2_CON
DMA + 0218h DMA Channel 2 Start Register DMA2_START
DMA + 021Ch DMA Channel 2 Interrupt Status Register DMA2_INTSTA
DMA + 0220h DMA Channel 2 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA2_ACKINT
DMA + 0224h DMA Channel 2 Remaining Length of Current Transfer DMA2_RLCT
DMA + 0228h DMA Channel 2 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA2_LIMITER
52/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 53

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
DMA + 0300h DMA Channel 3 Source Address Register DMA3_SRC
DMA + 0304h DMA Channel 3 Destination Address Register DMA3_DST
DMA + 0308h DMA Channel 3 Wrap Point Address Register DMA3_WPPT
DMA + 030Ch DMA Channel 3 Wrap To Address Register DMA3_WPTO
DMA + 0310h DMA Channel 3 Transfer Count Register DMA3_COUNT
DMA + 0314h DMA Channel 3 Control Register DMA3_CON
DMA + 0318h DMA Channel 3 Start Register DMA3_START
DMA + 031Ch DMA Channel 3 Interrupt Status Register DMA3_INTSTA
DMA + 0320h DMA Channel 3 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA3_ACKINT
DMA + 0324h DMA Channel 3 Remaining Length of Current Transfer DMA3_RLCT
DMA + 0328h DMA Channel 3 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA3_LIMITER
DMA + 0408h DMA Channel 4 Wrap Point Address Register DMA4_WPPT
DMA + 040Ch DMA Channel 4 Wrap To Address Register DMA4_WPTO
DMA + 0410h DMA Channel 4 Transfer Count Register DMA4_COUNT
DMA + 0414h DMA Channel 4 Control Register DMA4_CON
DMA + 0418h DMA Channel 4 Start Register DMA4_START
DMA + 041Ch DMA Channel 4 Interrupt Status Register DMA4_INTSTA
DMA + 0420h DMA Channel 4 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA4_ACKINT
DMA + 0424h DMA Channel 4 Remaining Length of Current Transfer DMA4_RLCT
DMA + 0428h DMA Channel 4 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA4_LIMITER
DMA + 042Ch DMA Channel 4 Programmable Address Register DMA4_PGMADDR
DMA + 0508h DMA Channel 5 Wrap Point Address Register DMA5_WPPT
DMA + 050Ch DMA Channel 5 Wrap To Address Register DMA5_WPTO
DMA + 0510h DMA Channel 5 Transfer Count Register DMA5_COUNT
DMA + 0514h DMA Channel 5 Control Register DMA5_CON
DMA + 0518h DMA Channel 5 Start Register DMA5_START
DMA + 051Ch DMA Channel 5 Interrupt Status Register DMA5_INTSTA
DMA + 0520h DMA Channel 5 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA5_ACKINT
DMA + 0524h DMA Channel 5 Remaining Length of Current Transfer DMA5_RLCT
DMA + 0528h DMA Channel 5 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA5_LIMITER
DMA + 052Ch DMA Channel 5 Programmable Address Register DMA5_PGMADDR
DMA + 0608h DMA Channel 6 Wrap Point Address Register DMA6_WPPT
DMA + 060Ch DMA Channel 6 Wrap To Address Register DMA6_WPTO
DMA + 0610h DMA Channel 6 Transfer Count Register DMA6_COUNT
DMA + 0614h DMA Channel 6 Control Register DMA6_CON
DMA + 0618h DMA Channel 6 Start Register DMA6_START
DMA + 061Ch DMA Channel 6 Interrupt Status Register DMA6_INTSTA
DMA + 0620h DMA Channel 6 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA6_ACKINT
DMA + 0624h DMA Channel 6 Remaining Length of Current Transfer DMA6_RLCT
53/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 54

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
DMA + 0628h DMA Channel 6 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA6_LIMITER
DMA + 062Ch DMA Channel 6 Programmable Address Register DMA6_PGMADDR
DMA + 0708h DMA Channel 7 Wrap Point Address Register DMA7_WPPT
DMA + 070Ch DMA Channel 7 Wrap To Address Register DMA7_WPTO
DMA + 0710h DMA Channel 7 Transfer Count Register DMA7_COUNT
DMA + 0714h DMA Channel 7 Control Register DMA7_CON
DMA + 0718h DMA Channel 7 Start Register DMA7_START
DMA + 071Ch DMA Channel 7 Interrupt Status Register DMA7_INTSTA
DMA + 0720h DMA Channel 7 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA7_ACKINT
DMA + 0724h DMA Channel 7 Remaining Length of Current Transfer DMA7_RLCT
DMA + 0728h DMA Channel 7 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA7_LIMITER
DMA + 072Ch DMA Channel 7 Programmable Address Register DMA7_PGMADDR
DMA + 0808h DMA Channel 8 Wrap Point Address Register DMA8_WPPT
DMA + 080Ch DMA Channel 8 Wrap To Address Register DMA8_WPTO
DMA + 0810h DMA Channel 8 Transfer Count Register DMA8_COUNT
DMA + 0814h DMA Channel 8 Control Register DMA8_CON
DMA + 0818h DMA Channel 8 Start Register DMA8_START
DMA + 081Ch DMA Channel 8 Interrupt Status Register DMA8_INTSTA
DMA + 0820h DMA Channel 8 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA8_ACKINT
DMA + 0824h DMA Channel 8 Remaining Length of Current Transfer DMA8_RLCT
DMA + 0828h DMA Channel 8 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA8_LIMITER
DMA + 082Ch DMA Channel 8 Programmable Address Register DMA8_PGMADDR
DMA + 0908h DMA Channel 9 Wrap Point Address Register DMA9_WPPT
DMA + 090Ch DMA Channel 9 Wrap To Address Register DMA9_WPTO
DMA + 0910h DMA Channel 9 Transfer Count Register DMA9_COUNT
DMA + 0914h DMA Channel 9 Control Register DMA9_CON
DMA + 0918h DMA Channel 9 Start Register DMA9_START
DMA + 091Ch DMA Channel 9 Interrupt Status Register DMA9_INTSTA
DMA + 0920h DMA Channel 9 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA9_ACKINT
DMA + 0924h DMA Channel 9 Remaining Length of Current Transfer DMA9_RLCT
DMA + 0928h DMA Channel 9 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA9_LIMITER
DMA + 092Ch DMA Channel 9 Programmable Address Register DMA9_PGMADDR
DMA + 0A08h DMA Channel 10 Wrap Point Address Register DMA10_WPPT
DMA + 0A0Ch DMA Channel 10 Wrap To Address Register DMA10_WPTO
DMA + 0A10h DMA Channel 10 Transfer Count Register DMA10_COUNT
DMA + 0A14h DMA Channel 10 Control Register DMA10_CON
DMA + 0A18h DMA Channel 10 Start Register DMA10_START
DMA + 0A1Ch DMA Channel 10 Interrupt Status Register DMA10_INTSTA
DMA + 0A20h DMA Channel 10 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA10_ACKINT
54/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 55

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
DMA + 0A24h
DMA Channel 10 Remaining Length of Current
Transfer
DMA + 0A28h DMA Channel 10 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA10_LIMITER
DMA + 0A2Ch DMA Channel 10 Programmable Address Register DMA10_PGMADDR
DMA + 0B10h DMA Channel 11 Transfer Count Register DMA11_COUNT
DMA + 0B14h DMA Channel 11 Control Register DMA11_CON
DMA + 0B18h DMA Channel 11 Start Register DMA11_START
DMA + 0B1Ch DMA Channel 11 Interrupt Status Register DMA11_INTSTA
DMA + 0B20h DMA Channel 11 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA11_ACKINT
DMA + 0B28h DMA Channel 11 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA11_LIMITER
DMA + 0B2Ch DMA Channel 11 Programmable Address Register DMA11_PGMADDR
DMA + 0B30h DMA Channel 11 Write Pointer DMA11_WRPTR
DMA + 0B34h DMA Channel 11 Read Pointer DMA11_RDPTR
DMA + 0B38h DMA Channel 11 FIFO Count DMA11_FFCNT
DMA + 0B3Ch DMA Channel 11 FIFO Status DMA11_FFSTA
DMA + 0B40h DMA Channel 11 Alert Length DMA11_ALTLEN
DMA + 0B44h DMA Channel 11 FIFO Size DMA11_FFSIZE
DMA + 0C10h DMA Channel 12 Transfer Count Register DMA12_COUNT
DMA + 0C14h DMA Channel 12 Control Register DMA12_CON
DMA + 0C18h DMA Channel 12 Start Register DMA12_START
DMA + 0C1Ch DMA Channel 12 Interrupt Status Register DMA12_INTSTA
DMA + 0C20h DMA Channel 12 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA12_ACKINT
DMA + 0C28h DMA Channel 12 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA12_LIMITER
DMA + 0C2Ch DMA Channel 12 Programmable Address Register DMA12_PGMADDR
DMA + 0C30h DMA Channel 12 Write Pointer DMA12_WRPTR
DMA + 0C34h DMA Channel 12 Read Pointer DMA12_RDPTR
DMA + 0C38h DMA Channel 12 FIFO Count DMA12_FFCNT
DMA + 0C3Ch DMA Channel 12 FIFO Status DMA12_FFSTA
DMA + 0C40h DMA Channel 12 Alert Length DMA12_ALTLEN
DMA + 0C44h DMA Channel 12 FIFO Size DMA12_FFSIZE
DMA + 0D10h DMA Channel 13 Transfer Count Register DMA13_COUNT
DMA + 0D14h DMA Channel 13 Control Register DMA13_CON
DMA + 0D18h DMA Channel 13 Start Register DMA13_START
DMA + 0D1Ch DMA Channel 13 Interrupt Status Register DMA13_INTSTA
DMA + 0D20h DMA Channel 13 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA13_ACKINT
DMA + 0D28h DMA Channel 13 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA13_LIMITER
DMA + 0D2Ch DMA Channel 13 Programmable Address Register DMA13_PGMADDR
DMA + 0D30h DMA Channel 13 Write Pointer DMA13_WRPTR
DMA + 0D34h DMA Channel 13 Read Pointer DMA13_RDPTR
DMA + 0D38h DMA Channel 13 FIFO Count DMA13_FFCNT
DMA10_RLCT
55/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 56

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
DMA + 0D3Ch DMA Channel 13 FIFO Status DMA13_FFSTA
DMA + 0D40h DMA Channel 13 Alert Length DMA13_ALTLEN
DMA + 0D44h DMA Channel 13 FIFO Size DMA13_FFSIZE
DMA + 0E10h DMA Channel 14 Transfer Count Register DMA14_COUNT
DMA + 0E14h DMA Channel 14 Control Register DMA14_CON
DMA + 0E18h DMA Channel 14 Start Register DMA14_START
DMA + 0E1Ch DMA Channel 14 Interrupt Status Register DMA14_INTSTA
DMA + 0E20h DMA Channel 14 Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMA14_ACKINT
DMA + 0E28h DMA Channel 14 Bandwidth Limiter Register DMA14_LIMITER
DMA + 0E2Ch DMA Channel 14 Programmable Address Register DMA14_PGMADDR
DMA + 0E30h DMA Channel 14 Write Pointer DMA14_WRPTR
DMA + 0E34h DMA Channel 14 Read Pointer DMA14_RDPTR
DMA + 0E38h DMA Channel 14 FIFO Count DMA14_FFCNT
DMA + 0E3Ch DMA Channel 14 FIFO Status DMA14_FFSTA
DMA + 0E40h DMA Channel 14 Alert Length DMA14_ALTLEN
DMA + 0E44h DMA Channel 14 FIFO Size DMA14_FFSIZE
Table 8 DMA Controller Register Map
3.4.2 Register Definitions
Register programming tips:
z Start registers shall be cleared, when associated channels are being programmed.
z PGMADDR, i.e. programmable address, only exists in half-size DMA channels. If DIR in Control Register is
high, PGMADDR represents Destination Address. Conversely, If DIR in Control Register is low, PGMADDR
represents Source Address.
z Functions of ring-buffer and double-buffer memory data movement can be activated on either source side or
destination side by programming DMA_WPPT & and DMA_WPTO, as well as setting WPEN in DMA_CON
register high. WPSD in DMA_CON register determines the activated side.
DMA+0000h DMA Global Status Register DMA_GLBSTA
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IT14
Type RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IT8 RUN8 IT7 RUN7 IT6 RUN6 IT5 RUN5 IT4 RUN4 IT3 RUN3 IT2 RUN2 IT1 RUN1
Type RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
RUN1
4
This register helps software program keep track of the global status of DMA channels.
IT13
RUN1
3
IT12
RUN1
2
IT11
RUN1
1
IT10
RUN1
0
IT9 RUN9
RUN
DMA channel n status
N
56/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 57

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
0 Channel n is stopped or has completed the transfer already.
1 Channel n is currently running.
Interrupt status for channel n
IT
N
0 No interrupt is generated.
1 An interrupt is pending and waiting for service.
DMA+0028h DMA Global Bandwidth limiter Register
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name GLBLIMITER
Type WO
Reset 0
DMA_GLBLIMIT
ER
Please refer to the expression in DMAn_LIMITER for detailed note. The value of DMA_GLBLIMITER is set to all
DMA channels, from 1 to 14.
DMA+0n00h DMA Channel n Source Address Register DMAn_SRC
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name SRC[31:16]
Type R/W
Reset 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name SRC[15:0]
Type R/W
Reset 0
The above registers contain the base or current source address that the DMA channel is currently operating on. Writing to
this register specifies the base address of transfer source for a DMA channel. Before programming these registers, the
software program should make sure that STR in DMAn_START is set to 0; that is, the DMA channel is stopped and
disabled completely. Otherwise, the DMA channel may run out of order. Reading this register returns the address value
from which the DMA is reading.
Note that n is from 1 to 3 and SRC can’t be TCM address. TCM is not accessible by DMA..
SRC SRC[31:0] specifies the base or current address of transfer source for a DMA channel, i.e. channel 1, 2 or 3.
WRITE Base address of transfer source
READ Address from which DMA is reading
DMA+0n04h DMA Channel n Destination Address Register DMAn_DST
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name DST[31:16]
Type R/W
Reset 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name DST[15:0]
Type R/W
Reset 0
57/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 58

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
The above registers contain the base or current destination address that the DMA channel is currently operating on..
Writing to this register specifies the base address of the transfer destination for a DMA channel. Before programming
these registers, the software should make sure that STR in DMAn_START is set to ‘0’; that is, the DMA channel is stopped
and disabled completely. Otherwise, the DMA channel may run out of order. Reading this register returns the address
value to which the DMA is writing.
Note that n is from 1 to 3 and DST can’t be TCM address. TCM is not accessible by DMA.
DST DST[31:0] specifies the base or current address of transfer destination for a DMA channel, i.e. channel 1, 2 or 3.
WRITE Base address of transfer destination.
READ Address to which DMA is writing.
DMA+0n08h DMA Channel n Wrap Point Count Register DMAn_WPPT
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name WPPT[15:0]
Type R/W
Reset 0
The above registers are to specify the transfer count required to perform before the jump point. This can be used to
support ring buffer or double buffer style memory accesses. To enable this function, two control bits, WPEN and WPSD,
in DMA control register must be programmed. See the following register description for more details. If the
transfercounter in the DMA engine matches this value, an address jump occurs, and the next address is the address specified
in DMAn_WPTO. Before programming these registers, the software should make sure that STR in DMAn_START is set
to ‘0’, that is the DMA channel is stopped and disabled completely. Otherwise, the DMA channel may run out of order.
To enable this function, WPEN in DMA_CON is set. Note that the total size of data specify in the wrap point count in a
DMA channel is determined by LEN together with the SIZE in DMAn_CON, i.e. WPPT x SIZE.
Note that n is from 1 to 10.
WPPT WPPT[15:0] specifies the amount of the transfer count from start to jumping point for a DMA channel, i.e.
channel 1 – 10.
WRITE Wrap point transfer count.
READ Value set by the programmer.
DMA+0n0Ch DMA Channel n Wrap To Address Register DMAn_WPTO
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name WPTO[31:16]
Type R/W
Reset 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name WPTO[15:0]
Type R/W
Reset 0
The above registers specify the address of the jump destination of a given DMA transfer to support ring buffer or double
buffer style memory accesses. To enable this function, set the two control bits, WPEN and WPSD, in the DMA control
register . See the following register description for more details. Before programming these registers, the software
58/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 59

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
should make sure that STR in DMAn_START is set to ‘0’, that is the DMA channel is stopped and disabled completely.
Otherwise, the DMA channel may run out of order. To enable this function, WPEN in DMA_CON should be set.
Note that n is from 1 to 10.
WPTO WPTO[31:0] specifies the address of the jump point for a DMA channel, i.e. channel 1 – 10.
WRITE Address of the jump destination.
READ Value set by the programmer.
DMA+0n10h DMA Channel n Transfer Count Register DMAn_COUNT
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LEN
Type R/W
Reset 0
This register specifies the amount of total transfer count that the DMA channel is required to perform. Upon completion,
the DMA channel generates an interrupt request to the processor while ITEN in DMAn_CON is set as ‘1’. Note that the
total size of data being transferred by a DMA channel is determined by LEN together with the SIZE in DMAn_CON, i.e.
LEN x SIZE.
For virtual FIFO DMA, this register is used to configure the RX threshold and TX threshold. Interrupt is triggered while
FIFO count >= RX threshold in RX path or FIFO count =< TX threshold in TX path. Note that ITEN bit in DMA_CON
register shall be set, or no interrupt is issued.
Note that n is from 1 to 14.
LEN The amount of total transfer count
DMA+0n14h DMA Channel n Control Register DMAn_CON
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name MAS DIR WPEN WPSD
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name ITEN BURST B2W DRQ DINC SINC SIZE
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
This register contains all the available control schemes for a DMA channel that is ready for software programmer to
configure. Note that all these fields cannot be changed while DMA transfer is in progress or an unexpected situation may
occur.
Note that n is from 1 to 14.
SIZE Data size within the confine of a bus cycle per transfer.
These bits confines the data transfer size between source and destination to the specified value for individual bus
cycle. The size is in terms of byte and has maximum value of 4 bytes. It is mainly decided by the data width of
a DMA master.
00 Byte transfer/1 byte
59/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 60

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
01 Half-word transfer/2 bytes
10 Word transfer/4 bytes
11 Reserved
SINC Incremental source address. Source addresses increase every transfer. If the setting of SIZE is Byte, Source
addresses increase by 1 every single transfer. If Half-Word, increase by 2; and if Word, increase by 4.
0 Disable
1 Enable
DINC Incremental destination address. Destination addresses increase every transfer. If the setting of SIZE is Byte,
Destination addresses increase by 1 every single transfer. If Half-Word, increase by 2; and Iif Word, increase by
4.
0 Disable
1 Enable
DREQ Throttle and handshake control for DMA transfer
0 No throttle control during DMA transfer or transfers occurred only between memories
1 Hardware handshake management
The DMA master is able to throttle down the transfer rate by way of request-grant handshake.
B2W Word to Byte or Byte to Word transfer for the applications of transferring non-word-aligned-address data to
word-aligned-address data. Note that BURST is set to 4-beat burst while enabling this function, and the SIZE is
set to Byte.
NO effect on channel 1 – 3 & 11 - 14.
0 Disable
1 Enable
BURST Transfer Type. Burst-type transfers have better bus efficiency. Mass data movement is recommended to use this
kind of transfer. However, note that burst-type transfer does not stop until all of the beats in a burst are
completed or transfer length is reached. FIFO threshold of peripherals must be configured carefully while being
used to move data from/to the peripherals.
What transfer type can be used is restricted by the SIZE. If SIZE is 00b, i.e. byte transfer, all of the four transfer
types can be used. If SIZE is 01b, i.e. half-word transfer, 16-beat incrementing burst cannot be used. If SIZE is
10b, i.e. word transfer, only single and 4-beat incrementing burst can be used.
NO effect on channel 11 - 14.
000 Single
001 Reserved
010 4-beat incrementing burst
011 Reserved
100 8-beat incrementing burst
101 Reserved
110 16-beat incrementing burst
111 Reserved
ITEN DMA transfer completion interrupt enable.
0 Disable
1 Enable
WPSD The side using address-wrapping function. Only one side of a DMA channel can activate address-wrapping
function at a time.
NO effect on channel 11 - 14.
60/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 61

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
0 Address-wrapping on source .
1 Address-wrapping on destination.
WPEN Address-wrapping for ring buffer and double buffer. The next address of DMA jumps to WRAP TO address
when the current address matches WRAP POINT count.
NO effect on channel 11 - 14.
0 Disable
1 Enable
DIR Directions of DMA transfer for half-size and Virtual FIFO DMA channels, i.e. channels 4~14. The direction is
from the perspective of the DMA masters. WRITE means read from master and then write to the address
specified in DMA_PGMADDR, and vice versa.
NO effect on channel 1 - 3.
0 Read
1 Write
MAS Master selection. Specifies which master occupies this DMA channel. Once assigned to certain master, the
corresponding DREQ and DACK are connected. For half-size and Virtual FIFO DMA channels, i.e. channels 4 ~
14, a predefined address is assigned as well.
00000 SIM
00001 MSDC
00010 IrDA TX
00011 IrDA RX
00100 Reserved
00101 Reserved
00110 Reserved
00111 Reserved
01000 UART1 TX
01001 UART1 RX
01010 UART2 TX
01011 UART2 RX
01100 UART3 TX
01101 UART3 RX
01110 DSP-DMA1
01111 NFI TX
10000 NFI RX
10001 DSP-DMA2
10010 I2C TX
10011 I2C RX
10100 Reserved
10101 Reserved
OTHERS Reserved
DMA+0n18h DMA Channel n Start Register DMAn_START
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
61/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 62

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name STR
Type R/W
Reset 0
This register controls the activity of a DMA channel. Note that prior to setting STR to “1”, all the configurations should
be done by giving proper value to the registers. Note also that once the STR is set to “1”, the hardware does not clear it
automatically no matter if the DMA channel accomplishes the DMA transfer or not. In other works, the value of STR
stays “1” regardless of the completion of DMA transfer. Therefore, the software program should be sure to clear STR to
“0” before restarting another DMA transfer. If this bit is cleared to “0” during DMA transfer is active, software should
polling MDDMA_GLBSTA RUN
after this bit is cleared to ensure current DMA transfer is terminated by DMA engine.
N
Note that n is from 1 to 14.
STR Start control for a DMA channel.
0 The DMA channel is stopped.
1 The DMA channel is started and running.
DMA+0n1Ch DMA Channel n Interrupt Status Register DMAn_INTSTA
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name INT
Type RO
Reset 0
This register shows the interrupt status of a DMA channel. It has the same value as DMA_GLBSTA.
Note that n is from 1 to 14.
INT Interrupt Status for DMA Channel
0 No interrupt request is generated.
1 One interrupt request is pending and waiting for service.
DMA+0n20h DMA Channel n Interrupt Acknowledge Register DMAn_ACKINT
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name ACK
Type WO
Reset 0
This register is used to acknowledge the current interrupt request associated with the completion event of a DMA channel
by software program. Note that this is a write-only register, and any read to it returns a value of “0”.
Note that n is from 1 to 14.
ACK Interrupt acknowledge for the DMA channel
0 No effect
62/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 63

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
1 Interrupt request is acknowledged and should be relinquished.
DMA+0n24h DMA Channel n Remaining Length of Current Transfer DMAn_RLCT
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RLCT
Type RO
Reset 0
This register is to reflect the left count of the transfer. Note that this value is transfer count not the transfer data size.
Note that n is from 1 to 10.
DMA+0n28h DMA Bandwidth limiter Register DMAn_LIMITER
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LIMITER
Type R/W
Reset 0
This register is to suppress the Bus utilization of the DMA channel. The value is from 0 to 255. 0 means no limitation,
and 255 means totally banned. The value between 0 and 255 means certain DMA can have permission to use AHB every
(4 X n) AHB clock cycles.
Note that it is not recommended to limit the Bus utilization of the DMA channels because this increases the latency of
response to the masters, and the transfer rate decreases as well. Before using it, programmer must make sure that the bus
masters have some protective mechanism to avoid entering the wrong states.
Note that n is from 1 to 14.
LIMITER from 0 to 255. 0 means no limitation, 255 means totally banned, and others mean Bus access permission
every (4 X n) AHB clock.
DMA+0n2Ch DMA Channel n Programmable Address Register
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name PGMADDR[31:16]
Type R/W
Reset 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name PGMADDR[15:0]
Type R/W
Reset 0
DMAn_PGMADD
R
The above registers specify the address for a half-size DMA channel. This address represents a source address if DIR in
DMA_CON is set to 0, and represents a destination address if DIR in DMA_CON is set to 1. Before being able to
63/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 64

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
program these register, the software should make sure that STR in DMAn_START is set to ‘0’, that is the DMA channel is
stopped and disabled completely. Otherwise, the DMA channel may run out of order.
Note that n is from 4 to 14 and PGMADDR can’t be TCM address. TCM is not accessible by DMA.
PGMADDR PGMADDR[31:0] specifies the addresses for a half-size or a Virtual FIFO DMA channel, i.e. channel 4 – 14.
WRITE Base address of transfer source or destination according to DIR bit
READ Current address of the transfer.
DMA+0n30h DMA Channel n Virtual FIFO Write Pointer Register DMAn_WRPTR
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name WRPTR[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name WRPTR[15:0]
Type RO
Note that n is from 11 to 14.
WRPTR Virtual FIFO Write Pointer.
DMA+0n34h DMA Channel n Virtual FIFO Read Pointer Register DMAn_RDPTR
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name RDPTR[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RDPTR[15:0]
Type RO
Note that n is from 11 to 14.
RDPTR Virtual FIFO Read Pointer.
DMA+0n38h DMA Channel n Virtual FIFO Data Count Register DMAn_FFCNT
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name FFCNT
Type RO
Note that n is from 11 to 14.
FFCNT To display the number of data stored in FIFO. 0 means FIFO empty, and FIFO is full if FFCNT is equal to
FFSIZE.
DMA+0n3Ch DMA Channel n Virtual FIFO Status Register DMAn_FFSTA
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name ALT
64/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
EMPT
Y
FULL
Page 65

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Type RO RO RO
Reset 0 1 0
Note that n is from 11 to 14.
FULL To indicate FIFO is full.
0 Not Full
1 Full
EMPTY To indicate FIFO is empty.
0 Not Empty
1 Empty
ALT To indicate FIFO Count is larger than ALTLEN. DMA issues an alert signal to UART to enable UART flow
control.
0 Not reach alert region.
1 Reach alert region.
DMA+0n40h DMA Channel n Virtual FIFO Alert Length Register DMAn_ALTLEN
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name ALTLEN
Type R/W
Reset 0
Note that n is from 11 to 14.
ALTLEN Specifies the Alert Length of Virtual FIFO DMA. Once the remaining FIFO space is less than ALTLEN, an
alert signal is issued to UART to enable flow control. Normally, ALTLEN shall be larger than 16 for UART
application.
DMA+0n44h DMA Channel n Virtual FIFO Size Register DMAn_FFSIZE
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name FFSIZE
Type R/W
Reset 0
Note that n is from 11 to 14.
FFSIZE Specifies the FIFO Size of Virtual FIFO DMA.
65/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 66

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
3.5 Interrupt Controller
3.5.1 General Description
Figure 14 outlines the major functionality of the MCU Interrupt Controller. The interrupt controller processes all
interrupt sources coming from external lines and internal MCU peripherals. Since ARM9EJ-S core supports two levels of
interrupt latency, this controller generates two request signals: FIQ for fast, low latency interrupt request and IRQ for more
general interrupts with lower priority.
31 (hex)
Figure 15 Block Diagram of the Interrupt Controller
One and only one of the interrupt sources can be assigned to FIQ Controller and have the highest priority in requesting
timing critical service. All the others share the same IRQ signal by connecting them to IRQ Controller. The IRQ
Controller manages up 50 interrupt lines of IRQ0 to IRQ31 with fixed priority in descending order.
The Interrupt Controller provides a simple software interface by mean of registers to manipulate the interrupt request shared
system. IRQ Selection Registers and FIQ Selection Register determine the source priority and connecting relation among
sources and interrupt lines. IRQ Source Status Register allows software program to identify the source of interrupt that
generates the interrupt request. IRQ Mask Register provides software to mask out undesired sources some time. End of
Interrupt Register permits software program to indicate to the controller that a certain interrupt service routine has been
finished.
Binary coded version of IRQ Source Status Register is also made available for software program to helpfully identify the
interrupt source. Note that while taking advantage of this, it should also take the binary coded version of End of Interrupt
Register coincidently.
The essential Interrupt Table of ARM926EJ-S core is shown as Table 9.
66/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 67

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Address Description
00000000h System Reset
00000018h IRQ
0000001Ch FIQ
Table 10 Interrupt Table of ARM926EJ-S
3.5.1.1 Interrupt Source Masking
Interrupt controller provides the function of Interrupt Source Masking by the way of programming MASK register. Any
of them can be masked individually.
However, because of the bus latency, the masking takes effect no earlier than 3 clock cycles later. In this time, the
to-be-masked interrupts could come in and generate an IRQ pulse to MCU, and then disappear immediately. This IRQ
forces MCU going to Interrupt Service Routine and polling Status Register (IRQ_STA(IRQ_STAH+IRQ_STAL) or
IRQ_STA2), but the register shows there is no interrupt. This might cause MCU malfunction.
There are two ways for programmer to protect their software.
1. Return from ISR (Interrupt Service Routine) immediately while the Status register shows no interrupt.
2. Set I bit of MCU before doing Interrupt Masking, and then clear it after Interrupt Masking done.
Both avoid the problem, but the first item recommended to have in the ISR.
3.5.1.2 External Interrupt
This interrupt controller also integrates an External Interrupt Controller that can support up to 8 interrupt requests coming
from external sources, the EINT0~7, and 4 WakeUp interrupt requests, i.e. EINT8-B, coming from peripherals. All external
interrupts can inform system to resume the system clock.
The eight external interrupts can be used for different kind of applications, mainly for event detections: detection of hand
free connection, detection of hood opening, detection of battery charger connection.
Since the external event may be unstable in a certain period, a de-bounce mechanism is introduced to ensure the
functionality. The circuitry is mainly used to verify that the input signal remains stable for a programmable number of
periods of the clock. When this condition is satisfied, for the appearance or the disappearance of the input, the output of
the de-bounce logic changes to the desired state. Note that, because it uses the 32 KHz slow clock for performing the
de-bounce process, the parameter of de-bounce period and de-bounce enable takes effect no sooner than one 32 KHz clock
cycle (~31.25us) after the software program sets them. When the sources of External Interrupt Controller are used to
resume the system clock in sleep mode, the de-bounce mechanism must be enabled. However, the polarities of EINTs are
clocked with the system clock. Any changes to them take effect immediately.
67/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 68

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Figure 16 Block Diagram of External Interrupt Controller
EINT
EINT0
EINT1
EINT2
EINT3
EINT4
EINT5
EINT6
EINT7
EINT8
3.5.1.3 External Interrupt Input Pins
Edge / Level
HW Debounce
Edge / Level
Yes
Edge / Level
Yes
Edge / Level
Yes
Edge / Level
Yes
Edge / Level
Yes
Edge / Level
Yes
Edge / Level
Yes
Edge / Level
Yes
Edge / Level
Yes
SOURCE PIN SUPPLEMENT
EINT0
1. GPIOs should
be in the input
EINT1
mode and are
effected by GPIO
EINT2
if(GPIO44_M==1) then EINT3=EINT3
else EINT3=1
if(GPIO45_M==1) then EINT4=EINT4
else EINT4=1
if(GPIO46_M==1) then EINT5=EINT5
else EINT5=1
if(GPIO47_M==1) then EINT6=EINT6
else EINT6=1
if(GPIO48_M==1) then EINT7=EINT7
data input
inversion
registers.
2. GPIOxx_M is
the GPIO mode
control registers,
please refer to
GPIO segment.
else EINT7=1
PMIC Charge Detection (Low Active)
EINT9
68/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Edge / Level
Yes
URXD1
Page 69

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
EINTA
EINTB
Edge / Level
Yes
Edge / Level
Yes
URXD2
URXD3
REGISTER ADDRESS REGISTER NAME SYNONYM
CIRQ + 0000h IRQ Selection 0 Register IRQ_SEL0
CIRQ + 0004h IRQ Selection 1 Register IRQ_SEL1
CIRQ + 0008h IRQ Selection 2 Register IRQ_SEL2
CIRQ + 000Ch IRQ Selection 3 Register IRQ_SEL3
CIRQ + 0010h IRQ Selection 4 Register IRQ_SEL4
CIRQ + 0014h IRQ Selection 5 Register IRQ_SEL5
CIRQ + 0018h IRQ Selection 6 Register IRQ_SEL6
CIRQ + 001ch IRQ Selection 7 Register IRQ_SEL7
CIRQ + 0020h IRQ Selection 8 Register IRQ_SEL8
CIRQ + 0034h FIQ Selection Register FIQ_SEL
CIRQ + 0038h IRQ Mask Register (LSB) IRQ_MASKL
CIRQ + 003ch IRQ Mask Register (MSB) IRQ_MASKH
CIRQ + 0040h IRQ Mask Clear Register (LSB) IRQ_MASK_CLRL
CIRQ + 0044h IRQ Mask Clear Register (MSB) IRQ_MASK_CLRH
CIRQ + 0048h IRQ Mask Set Register (LSB) IRQ_MASK_SETL
CIRQ + 004ch IRQ Mask Set Register (MSB) IRQ_MASK_SETH
CIRQ + 0050h IRQ Status Register (LSB) IRQ_STAL
CIRQ + 0054h IRQ Status Register (MSB) IRQ_STAH
CIRQ + 0058h IRQ End of Interrupt Register (LSB) IRQ_EOIL
CIRQ + 005ch IRQ End of Interrupt Register (MSB) IRQ_EOIH
CIRQ + 0060h IRQ Sensitive Register (LSB) IRQ_SENSL
CIRQ + 0064h IRQ Sensitive Register (MSB) IRQ_SENSH
CIRQ + 0068h IRQ Software Interrupt Register (LSB) IRQ_SOFTL
CIRQ + 006ch IRQ Software Interrupt Register (MSB) IRQ_SOFTH
CIRQ + 0070h FIQ Control Register FIQ_CON
CIRQ + 0074h FIQ End of Interrupt Register FIQ_EOI
CIRQ + 0078h Binary Coded Value of IRQ_STATUS IRQ_STA2
CIRQ + 007ch Binary Coded Value of IRQ_EOI IRQ_EOI2
CIRQ + 0080h Binary Coded Value of IRQ_SOFT IRQ_SOFT2
CIRQ + 0100h EINT Status Register EINT_STA
CIRQ + 0104h EINT Mask Register EINT_MASK
CIRQ + 0108h EINT Mask Disable Register EINT_MASK_DIS
CIRQ + 010Ch EINT Mask Enable Register EINT_MASK_EN
69/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 70

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
CIRQ + 0110h EINT Interrupt Acknowledge Register EINT_INTACK
CIRQ + 0114h EINT Sensitive Register EINT_SENS
CIRQ + 0120h EINT0 De-bounce Control Register EINT0_CON
CIRQ + 0130h EINT1 De-bounce Control Register EINT1_CON
CIRQ + 0140h EINT2 De-bounce Control Register EINT2_CON
CIRQ + 0150h EINT3 De-bounce Control Register EINT3_CON
CIRQ + 0160h EINT4 De-bounce Control Register EINT4_CON
CIRQ + 0170h EINT5 De-bounce Control Register EINT5_CON
CIRQ + 0180h EINT6 De-bounce Control Register EINT6_CON
CIRQ + 0190h EINT7 De-bounce Control Register EINT7_CON
CIRQ + 01a0h EINT8 De-bounce Control Register EINT8_CON
CIRQ + 01b0h EINT9 De-bounce Control Register EINT9_CON
CIRQ + 01c0h EINTA De-bounce Control Register EINT10_CON
CIRQ + 01d0h EINTB De-bounce Control Register EINT11_CON
Table 11 Interrupt Controller Register Map
3.5.2 Register Definitions
CIRQ+0000h IRQ Selection 0 Register IRQ_SEL0
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ4 IRQ3 IRQ2
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x4 0x3
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x2 0x1 0x0
CIRQ+0004h IRQ Selection 1 Register IRQ_SEL1
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ9 IRQ8 IRQ7
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x9 0x8
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ7 IRQ6 IRQ5
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x7 0x6 0x5
CIRQ+0008h IRQ Selection 2 Register IRQ_SEL2
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQE IRQD IRQC
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0xe 0xD
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQC IRQB IRQA
Type R/W R/W R/W
70/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 71

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Reset 0xc 0xb 0xa
CIRQ+000ch IRQ Selection 3 Register IRQ_SEL3
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ13 IRQ12 IRQ11
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x13 0x12
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ11 IRQ10 IRQF
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x11 0x10 0xf
CIRQ+0010h IRQ Selection 4 Register IRQ_SEL4
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ18 IRQ17 IRQ16
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x18 0x17
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ16 IRQ15 IRQ14
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x16 0x15 0x14
CIRQ+0014h IRQ Selection 5 Register IRQ_SEL5
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ1D IRQ1C IRQ1B
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x1d 0x1c
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ1B IRQ1A IRQ19
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x1b 0x1a 0x19
CIRQ+0018h IRQ Selection 6 Register IRQ_SEL6
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ22 IRQ21 IRQ20
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x22 0x21
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ20 IRQ1F IRQ1E
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x20 0x1f 0x1e
CIRQ+001ch IRQ Selection 7 Register IRQ_SEL7
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ27 IRQ26 IRQ25
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x27 0x26
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ25 IRQ24 IRQ23
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x25 0x24 0x23
71/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 72

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
CIRQ+0020h IRQ Selection 8 Register IRQ_SEL8
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ2C IRQ2B IRQ2A
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x2c 0x2b
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ2A IRQ29 IRQ28
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x2a 0x29 0x28
CIRQ+0024h IRQ Selection 9 Register IRQ_SEL9
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ31 IRQ30 IRQ2F
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x31 0x30
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ2F IRQ2E IRQ2D
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0x2f 0x2e 0x2d
CIRQ+0034h FIQ Selection Register FIQ_SEL
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name FIQ
Type R/W
Reset 0
The IRQ/FIQ Selection Registers provide system designers with a flexible routing scheme to make various mappings of
priority among interrupt sources possible. The registers allow the interrupt sources to be mapped onto interrupt requests
of either FIQ or IRQ. While only one interrupt source can be assigned to FIQ, the other ones share IRQs by mapping
them onto IRQ0 to IRQ1F connected to IRQ controller. The priority sequence of IRQ0~IRQ31 is fixed, i.e. IRQ0 > IRQ1 >
IRQ2 > … > IRQ30 > IRQ31. During the software configuration process, the Interrupt Source Code of desired interrupt
source should be written into source field of the corresponding IRQ_SEL0-IRQ_SEL9/FIQ_SEL. Six-bit Interrupt Source
Codes for all interrupt sources are fixed and defined.
Interrupt Source STA2 (Hex) STAH_STAL
GPI_FIQ 0 000_00000001
TDMA_CTIRQ1 1 000_00000002
TDMA_CTIRQ2 2 000_00000004
DSP2CPU 3 000_00000008
SIM 4 000_00000010
DMA 5 000_00000020
72/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 73

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
TDMA 6 000_00000040
UART1 7 000_00000080
KeyPad 8 000_00000100
UART2 9 000_00000200
GPTimer a 000_00000400
EINT b 000_00000800
USB MC c 000_00001000
MSDC d 000_00002000
RTC e 000_00004000
IrDA f 000_00008000
LCD 10 000_00010000
UART3 11 000_00020000
GPI0 12 000_00040000
WDT 13 000_00080000
Reserved 14 000_00100000
Reserved 15 000_00200000
NFI 16 000_00400000
Reserved 17 000_00800000
Reserved 18 000_01000000
Reserved 19 000_02000000
Reserved 1a 000_04000000
I2C 1b 000_08000000
G2D 1c 000_10000000
Reserved 1d 000_20000000
CAM 1e 000_40000000
Reserved 1f 000_80000000
Reserved 20 001_00000000
Reserved 21 002_00000000
Reserved 22 004_00000000
Reserved 23 008_00000000
Resizer_crz 24 010_00000000
Reserved 25 020_00000000
Reserved 26 040_00000000
Reserved 27 080_00000000
DSPINT 28 100_00000000
USB DMA 29 200_00000000
PWM 2A 400_00000000
GPI1 2B 800_00000000
GPI2 2C 1000_00000000
IRDebug1 2D 2000_00000000
73/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 74

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
IRDebug2 2E 4000_00000000
Reserved 2F 8000_00000000
Reserved 30 10000_00000000
AUXADC 31 20000_00000000
Table 12 Interrupt Source Code for Interrupt Sources
FIQ, IRQ0-31 The 5-bit content of this field corresponds to an Interrupt Source Code shown above.
CIRQ+0038h IRQ Mask Register (LSB) IRQ_MASKL
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ1F IRQ1E IRQ1D IRQ1C IRQ1B IRQ1A IRQ19 IRQ18 IRQ17 IRQ16 IRQ15 IRQ14 IRQ13 IRQ12 IRQ11 IRQ10
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQF IRQE IRQD IRQC IRQB IRQA IRQ9 IRQ8 IRQ7 IRQ6 IRQ5 IRQ4 IRQ3 IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
CIRQ+003ch IRQ Mask Register (MSB) IRQ_MASKH
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ31 IRQ30
Type R/W R/W
Reset 1 1
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ2F IRQ2E IRQ2D IRQ2C IRQ2B IRQ2A IRQ29 IRQ28 IRQ27 IRQ26 IRQ25 IRQ24 IRQ23 IRQ22 IRQ21 IRQ20
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
This register contains a mask bit for each interrupt line in IRQ Controller. The register allows each interrupt source IRQ0
to IRQ1F to be disabled or masked separately under software control. After a system reset, all bit values are set to 1 to
indicate that interrupt requests are prohibited.
IRQ0-31 Mask control for the associated interrupt source in the IRQ controller
0 Interrupt is enabled.
1 Interrupt is disabled.
CIRQ+0040h IRQ Mask Clear Register (LSB)
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ1F IRQ1E IRQ1D IRQ1C IRQ1B IRQ1A IRQ19 IRQ18 IRQ17 IRQ16 IRQ15 IRQ14 IRQ13 IRQ12 IRQ11 IRQ10
Type W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQF IRQE IRQD IRQC IRQB IRQA IRQ9 IRQ8 IRQ7 IRQ6 IRQ5 IRQ4 IRQ3 IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
Type W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C
74/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
IRQ_MASK_CL
RL
Page 75

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
CIRQ+0044h IRQ Mask Clear Register (MSB)
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ31 IRQ30
Type W1C W1C
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ2F IRQ2E IRQ2D IRQ2C IRQ2B IRQ2A IRQ29 IRQ28 IRQ27 IRQ26 IRQ25 IRQ24 IRQ23 IRQ22 IRQ21 IRQ20
Type W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C
IRQ_MASK_CL
RH
This register is used to clear bits in IRQ Mask Register. When writing to this register, the data bits that are HIGH cause
the corresponding bits in IRQ Mask Register to be cleared. Data bits that are LOW have no effect on the corresponding
bits in IRQ Mask Register.
IRQ0-31 Clear corresponding bits in IRQ Mask Register.
0 No effect.
1 Disable the corresponding MASK bit.
CIRQ+0048h IRQ Mask SET Register (LSB)
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ1F IRQ1E IRQ1D IRQ1C IRQ1B IRQ1A IRQ19 IRQ18 IRQ17 IRQ16 IRQ15 IRQ14 IRQ13 IRQ12 IRQ11 IRQ10
Type W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQF IRQE IRQD IRQC IRQB IRQA IRQ9 IRQ8 IRQ7 IRQ6 IRQ5 IRQ4 IRQ3 IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
Type W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S
IRQ_MASK_SET
L
CIRQ+004ch IRQ Mask SET Register (MSB)
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ31 IRQ30
Type W1S W1S
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ2F IRQ2E IRQ2D IRQ2C IRQ2B IRQ2A IRQ29 IRQ28 IRQ27 IRQ26 IRQ25 IRQ24 IRQ23 IRQ22 IRQ21 IRQ20
Type W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S
IRQ_MASK_SET
H
This register is used to set bits in the IRQ Mask Register. When writing to this register, the data bits that are HIGH cause
the corresponding bits in IRQ Mask Register to be set. Data bits that are LOW have no effect on the corresponding bits in
IRQ Mask Register.
IRQ0-31 Set corresponding bits in IRQ Mask Register.
0 No effect.
1 Enable corresponding MASK bit.
CIRQ+0050h IRQ Source Status Register (LSB) IRQ_STAL
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ1F IRQ1E IRQ1D IRQ1C IRQ1B IRQ1A IRQ19 IRQ18 IRQ17 IRQ16 IRQ15 IRQ14 IRQ13 IRQ12 IRQ11 IRQ10
Type RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQF IRQE IRQD IRQC IRQB IRQA IRQ9 IRQ8 IRQ7 IRQ6 IRQ5 IRQ4 IRQ3 IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
75/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 76

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Type RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CIRQ+0054h IRQ Source Status Register (MSB) IRQ_STAH
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ31 IRQ30
Type RO RO
Reset 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ2F IRQ2E IRQ2D IRQ2C IRQ2B IRQ2A IRQ29 IRQ28 IRQ27 IRQ26 IRQ25 IRQ24 IRQ23 IRQ22 IRQ21 IRQ20
Type RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
This Register allows software to poll which interrupt line has generated an IRQ interrupt request. A bit set to 1 indicates a
corresponding active interrupt line. Only one flag is active at a time. The IRQ_STA is type of read-clear; write access
has no effect on the content.
IRQ0-31 Interrupt indicator for the associated interrupt source.
0 The associated interrupt source is non-active.
1 The associated interrupt source is asserted.
CIRQ+0058h IRQ End of Interrupt Register (LSB) IRQ_EOIL
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ1F IRQ1E IRQ1D IRQ1C IRQ1B IRQ1A IRQ19 IRQ18 IRQ17 IRQ16 IRQ15 IRQ14 IRQ13 IRQ12 IRQ11 IRQ10
Type WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQF IRQE IRQD IRQC IRQB IRQA IRQ9 IRQ8 IRQ7 IRQ6 IRQ5 IRQ4 IRQ3 IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
Type WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CIRQ+005ch IRQ End of Interrupt Register (MSB) IRQ_EOIH
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ31 IRQ30
Type WO WO
Reset 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ2F IRQ2E IRQ2D IRQ2C IRQ2B IRQ2A IRQ29 IRQ28 IRQ27 IRQ26 IRQ25 IRQ24 IRQ23 IRQ22 IRQ21 IRQ20
Type WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
This register provides a mean for software to relinquish and to refresh the interrupt controller. Writing a 1 to a specific bit
position results in an End of Interrupt command issued internally to the corresponding interrupt line.
IRQ0-31 End of Interrupt command for the associated interrupt line.
0 No service is currently in progress or pending.
1 Interrupt request is in-service.
CIRQ+0060h IRQ Sensitive Register (LSB) IRQ_SENSL
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ1F IRQ1E IRQ1D IRQ1C IRQ1B IRQ1A IRQ19 IRQ18 IRQ17 IRQ16 IRQ15 IRQ14 IRQ13 IRQ12 IRQ11 IRQ10
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
76/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 77

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQF IRQE IRQD IRQC IRQB IRQA IRQ9 IRQ8 IRQ7 IRQ6 IRQ5 IRQ4 IRQ3 IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CIRQ+0064h IRQ Sensitive Register (MSB) IRQ_SENSH
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ31 IRQ30
Type R/W R/W
Reset 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ2F IRQ2E IRQ2D IRQ2C IRQ2B IRQ2A IRQ29 IRQ28 IRQ27 IRQ26 IRQ25 IRQ24 IRQ23 IRQ22 IRQ21 IRQ20
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
All interrupt lines of IRQ Controller, IRQ0~IRQ31 can be programmed as either edge or level sensitive. By default, all
the interrupt lines are edge sensitive and should be active LOW. Once a interrupt line is programmed as edge sensitive, an
interrupt request is triggered only at the falling edge of interrupt line, and the next interrupt is not accepted until the EOI
command is given. However, level sensitive interrupts trigger is according to the signal level of the interrupt line. Once
the interrupt line become from HIGH to LOW, an interrupt request is triggered, and another interrupt request is triggered if
the signal level remain LOW after an EOI command. Note that in edge sensitive mode, even if the signal level remains
LOW after EOI command, another interrupt request is not triggered. That is because edge sensitive interrupt is only
triggered at the falling edge.
IRQ0-31 Sensitivity type of the associated Interrupt Source
0 Edge sensitivity with active LOW
1 Level sensitivity with active LOW
CIRQ+0068h IRQ Software Interrupt Register (LSB) IRQ_SOFTL
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ1F IRQ1E IRQ1D IRQ1C IRQ1B IRQ1A IRQ19 IRQ18 IRQ17 IRQ16 IRQ15 IRQ14 IRQ13 IRQ12 IRQ11 IRQ10
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQF IRQE IRQD IRQC IRQB IRQA IRQ9 IRQ8 IRQ7 IRQ6 IRQ5 IRQ4 IRQ3 IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CIRQ+006ch IRQ Software Interrupt Register (MSB) IRQ_SOFTH
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name IRQ31 IRQ30
Type R/W R/W
Reset 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name IRQ2F IRQ2E IRQ2D IRQ2C IRQ2B IRQ2A IRQ29 IRQ28 IRQ27 IRQ26 IRQ25 IRQ24 IRQ23 IRQ22 IRQ21 IRQ20
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Setting “1” to the specific bit position generates a software interrupt for corresponding interrupt line before mask. This
register is used for debug purpose.
77/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 78

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
IRQ0-IRQ31 Software Interrupt
CIRQ+0070h FIQ Control Register FIQ_CON
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name SENS MASK
Type R/W R/W
Reset 0 1
This register provides a means for software program to control the FIQ controller.
MASK Mask control for the FIQ Interrupt Source
0 Interrupt is enabled.
1 Interrupt is disabled.
SENS Sensitivity type of the FIQ Interrupt Source
0 Edge sensitivity with active LOW
1 Level sensitivity with active LOW
CIRQ+0074h FIQ End of Interrupt Register FIQ_EOI
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EOI
Type WO
Reset 0
This register provides a means for software to relinquish and to refresh the FIQ controller. Writing a ‘1’ to the specific bit
position results in an End of Interrupt command issued internally to the corresponding interrupt line.
EOI End of Interrupt command
CIRQ+0078h Binary Coded Value of IRQ_STATUS IRQ_STA2
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name
Type RC RC
Reset 0 0
This Register is a binary coded version of IRQ_STA. It is used by the software program to poll which interrupt line has
generated the IRQ interrupt request in a much easier way. Any read to it has the same result as reading IRQ_STA. The
IRQ_STA2 is also read-only and read-clear; write access has no effect on the content. Note that IRQ_STA2 should be
coupled with IRQ_EOI2 while using it.
STS Binary coded value of IRQ_STA
78/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
NOIR
Q
STS
Page 79

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
NOIRQ Indicating if there is an IRQ or not. If there is no IRQ, this bit is HIGH, and the value of STS is 00_0000b.
CIRQ+007ch Binary Coded Value of IRQ_EOI IRQ_EOI2
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EOI
Type WO
Reset 0
This register is a binary coded version of IRQ_EOI. It provides an easier way for software program to relinquish and to
refresh the interrupt controller. Writing a specific code results in an End of Interrupt command issued internally to the
corresponding interrupt line. Note that IRQ_EOI2 should be coupled with IRQ_STA2 while using it.
EOI Binary coded value of IRQ_EOI
CIRQ+0080h Binary Coded Value of IRQ_SOFT IRQ_SOFT2
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name SOFT
Type WO
Reset 0
This register is a binary coded version of IRQ_SOFT.
SOFT Binary Coded Value of IRQ_SOFT
CIRQ+0100h EINT Interrupt Status Register EINT_STA
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EINTB EINTA EINT9 EINT8 EINT7 EINT6 EINT5 EI NT4 E INT3 EINT2 EINT1 EINT0
Type RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO RO
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
This register keeps up with current status that which EINT Source generates the interrupt request. If EINT sources are set
to edge sensitivity, EINT_IRQ is de-asserted while this register is read.
EINT0-EINTB Interrupt status
0 No interrupt request is generated.
1 Interrupt request is pending.
CIRQ+0104h EINT Interrupt Mask Register EINT_MASK
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
79/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 80

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EINTB EINTA EINT9 EINT8 EINT7 EINT6 EINT5 EI NT4 E INT3 EINT2 EINT1 EINT0
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
This register controls whether or not EINT Source is allowed to generate an interrupt request. Setting a “1” to
the specific bit position prohibits the external interrupt line from becoming active.
EINT0-EINTB Interrupt Mask
0 Interrupt request is enabled.
1 Interrupt request is disabled.
CIRQ+0108h EINT Interrupt Mask Clear Register
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EINTB EINTA EINT9 EINT8 EINT7 EINT6 EINT5 EI NT4 E INT3 EINT2 EINT1 EINT0
Type W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C W1C
EINT_MASK_CL
R
This register is used to clear individual mask bits. Only the bits set to 1 are in effect, and interrupt masks for which the
mask bit is set are cleared (set to 0). Otherwise the interrupt mask bit retains its original value.
EINT0-EINTB Disable mask for the associated external interrupt source.
0 No effect.
1 Disable the corresponding MASK bit.
CIRQ+010Ch EINT Interrupt Mask Set Register
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EINTB EINTA EINT9 EINT8 EINT7 EINT6 EINT5 EI NT4 E INT3 EINT2 EINT1 EINT0
Type W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S W1S
EINT_MASK_SE
T
This register is used to set individual mask bits. Only the bits set to 1 are in effect, and interrupt masks for which the mask
bit is set are set to 1. Otherwise the interrupt mask bit retains its original value.
EINT0-EINTB Disable mask for the associated external interrupt source.
0 No effect.
1 Enable corresponding MASK bit.
CIRQ+0110h EINT Interrupt Acknowledge Register EINT_INTACK
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EINTB EINTA EINT9 EINT8 EINT7 EINT6 EINT5 EI NT4 E INT3 EINT2 EINT1 EINT0
Type WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO WO
80/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 81

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Writing “1” to the specific bit position acknowledge the interrupt request correspondingly to the external interrupt line
source.
EINT0-EINTB Interrupt acknowledgement
0 No effect
1 Interrupt request is acknowledged.
CIRQ+0114h EINT Sensitive Register EINT_SENS
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EINTB EINTA EINT9 EINT8 EINT7 EINT6 EINT5 EI NT4 EINT3 EINT2 EINT1 EINT 0
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Sensitivity type of external interrupt source.
EINT0-B Sensitivity type of the associated external interrupt source.
0 Edge sensitivity with active LOW.
1 Level sensitivity with active LOW.
CIRQ+01m0h EINTn De-bounce Control Register EINTn_CON
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EN POL CNT
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0
These registers control the de-bounce logic for external interrupt sources in order to minimize the possibility of false
activations. Note that n is from 0 to 11, and m is n + 2. When the external interrupt sources is used to resume the system
clock from the sleep mode, the De-bounce control circuit must be enabled.
CNT De-bounce duration in terms of number of 32 KHz clock cycles.
POL Activation type of the EINT source
0 Negative polarity
1 Positive polarity
EN De-bounce control circuit
0 Disable
1 Enable
81/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 82

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
3.6 BUS Monitor (BM)
3.6.1 General Description
MT6235 contains 4-layer AHB BUS. Most of them contain AHB master and slave modules. BUS Monitor (BM) provides
an interface to provide the BUS access usage to help analyze system performance. In BM, only EN is cleared to 0 after
reset. Other registers do not effect by reset.
3.6.2 Register Definitions
BM+0000h BM control BM_CON
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CLR EN
Type WO R/W
Reset 0
EN Enable the BM. BM is off after reset. You have to turn on it by write EN =1.
0 BM is disabled.
1 BM is enabled.
CLR All statistics recorded in BM is going to clear if you write CLR=1. CLR is a one-shot control bit.
BM+0004h Layer-2 AHB master filter
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
Type
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name MASEN
Type R/W
MASEN Master enable filter.
0 Disable the logging when the transaction is caused by the corresponding master.
1 Enable the logging when the transaction is caused by the corresponding master.
bit0 VFF Port
bit1 DMA
bit2 Wavetable
bit3 USB
bit4 IRDBG1
bit5 IRDBG2
82/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
BM_LYR2_HMA
STER
Page 83

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
bit6 IRDA
bit7 PWM
BM+0008h BM cycle count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name CYCLE_CNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CYCLE_CNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_CYCLE_CN
CYCLE_CNT CYCLE_CNT indicates how many cycles passed when EN=1.
CYCLE_CNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
BM+0010h Layer-1 AHB active cycle count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR1_ACCNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR1_ACCNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_LYR1_ACC
NT
LYR1_ACCNT LYR1_ACCNT indicates how many cycles HTRANS is (non-IDLE and non-BUSY) and increments in
every cycle when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ).
LYR1_ACCNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
T
BM+0014h Layer-1 AHB transaction count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR1_TCNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR1_TCNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_LYR1_TCN
LYR1_TCNT LYR1_TCNT indicates transaction accumulation and increments in every cycle when (EN=1) and
(HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ) and (HREADY=1).
LYR1_ACNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
BM+0018h Layer-1 AHB word count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR1_WCNT[31:16]
83/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
BM_LYR1_WCN
T
T
Page 84

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR1_WCNT[15:0]
Type RO
LYR1_WCNT LYR1_WCNT indicates transaction of word counts been transferred and increases depends HSIZE in
every cycle when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ) and (HREADY=1). A word means 4 bytes (32-bit)
in this document. The total data counts transferred less then 1 word is truncated. (For example, the BUS transfers
33 bytes after EN=1. you will get 8 in WCNT. The last byte count is ignored.)
LYR1_WCNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
HSIZE=00 8-bit data. WCNT increases 1.
HSIZE=01 16-bit data. WCNT increases 2.
HSIZE=10 32-bit data. WCNT increases 4.
OTHER Not supported.
BM+0020h Layer-1 AHB status FIFO 0~3
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR1_HDY3 LYR1_HSEL3 LYR1_HDY2 LYR1_HSEL2
Type RO RO RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR1_HDY1 LYR1_HSEL1 LYR1_HDY0 LYR1_HSEL0
Type RO RO RO RO
BM+0024h Layer-1 AHB status FIFO 4~7
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR1_HDY7 LYR1_HSEL7 LYR1_HDY6 LYR1_HSEL6
Type RO RO RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR1_HDY5 LYR1_HSEL5 LYR1_HDY4 LYR1_HSEL4
Type RO RO RO RO
BM+0028h Layer-1 AHB status FIFO 8~11
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR1_HDY11 LYR1_HSEL11 LYR1_HDY10 LYR1_HSEL10
Type RO RO RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR1_HDY9 LYR1_HSEL9 LYR1_HDY8 LYR1_HSEL8
Type RO RO RO RO
BM_LYR1_FIFO
BM_LYR1_FIFO
BM_LYR1_FIFO
0
4
8
BM+002ch Layer-1 AHB status FIFO 12~15
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR1_HDY15 LYR1_HSEL15 LYR1_HDY14 LYR1_HSEL14
84/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
BM_LYR1_FIFO
C
Page 85

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Type RO RO RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR1_HDY13 LYR1_HSEL13 LYR1_HDY12 LYR1_HSEL12
Type RO RO RO RO
BM keeps FIFOs internal recording HSEL and HREADY status on BUS for each layer. 0th is the latest one and 15th is the
oldest. The FIFO only shifts when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=SEQ or NON-SEQ) and (HREADY=0) and (slaves’ HREADYs
differ from HDY0). If all above conditions meet, then (HRDY0=current HREADY on BUS) and (HRDY1=HRDY0) and
(HRDY2=HRDY1) and … and (HRDY15=HRDY14). HSEL follows the same rules.
th
HSELx The x
HSEL status on BUS
bit0 EMI
bit1 System memory
bit2 LCD
th
HRDYx The x
HREADY status on BUS
bit0 EMI
bit1 System memory
bit2 LCD
BM+0030h Layer-2 AHB active cycle count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_ACCNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_ACCNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_LYR2_ACC
NT
LYR2_ACCNT LYR2_ACCNT indicates how many cycles HTRANS is (non-IDLE and non-BUSY) and increments in
every cycle when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ).
LYR2_ACCNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
BM+0034h Layer-2 AHB transaction count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_TCNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_TCNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_LYR2_TCN
LYR2_TCNT LYR2_TCNT indicates transaction accumulation and increments in every cycle when (EN=1) and
(HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ) and (HREADY=1).
LYR2_ACNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
T
85/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 86

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
BM+0038h Layer-2 AHB word count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_WCNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_WCNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_LYR2_WCN
LYR2_WCNT LYR2_WCNT indicates transaction of word counts been transferred and increases depends HSIZE in
every cycle when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ) and (HREADY=1). A word means 4 bytes (32-bit)
in this document. The total data counts transferred less then 1 word is truncated. (For example, the BUS transfers
33 bytes after EN=1. you will get 8 in WCNT. The last byte count is ignored.)
LYR2_WCNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
HSIZE=00 8-bit data. WCNT increases 1.
HSIZE=01 16-bit data. WCNT increases 2.
HSIZE=10 32-bit data. WCNT increases 4.
OTHER Not supported.
BM+0040h Layer-2 AHB status FIFO 0~1
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_HDY1 LYR2_HSEL1
Type RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_HDY0 LYR2_HSEL0
Type RO RO
BM_LYR2_FIFO
T
0
BM+0044h Layer-2 AHB status FIFO 2~3
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_HDY3 LYR2_HSEL3
Type RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_HDY2 LYR2_HSEL2
Type RO RO
BM+0048h Layer-2 AHB status FIFO 4~5
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_HDY5 LYR2_HSEL5
Type RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_HDY4 LYR2_HSEL4
Type RO RO
86/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
BM_LYR2_FIFO
BM_LYR2_FIFO
2
4
Page 87

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
BM+004ch Layer-2 AHB status FIFO 6~7
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_HDY7 LYR2_HSEL7
Type RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_HDY6 LYR2_HSEL6
Type RO RO
BM+0050h Layer-2 AHB status FIFO 8~9
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_HDY9 LYR2_HSEL9
Type RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_HDY8 LYR2_HSEL8
Type RO RO
BM+0054h Layer-2 AHB status FIFO 10~11
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_HDY11 LYR2_HSEL11
Type RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_HDY10 LYR2_HSEL10
Type RO RO
BM_LYR2_FIFO
BM_LYR2_FIFO
BM_LYR2_FIFO
6
8
A
BM+0058h Layer-2 AHB status FIFO 12~13
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_HDY13 LYR2_HSEL13
Type RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_HDY12 LYR2_HSEL12
Type RO RO
BM+005ch Layer-2 AHB status FIFO 14~15
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_HDY15 LYR2_HSEL15
Type RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_HDY14 LYR2_HSEL14
Type RO RO
BM_LYR2_FIFO
C
BM_LYR2_FIFO
E
BM keeps FIFOs internal recording HSEL and HREADY status on BUS for each layer. 0th is the latest one and 15th is the
oldest. The FIFO only shifts when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=SEQ or NON-SEQ) and (HREADY=0) and (slaves’ HREADYs
87/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 88

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
differ from HDY0). If all above conditions meet, then (HRDY0=current HREADY on BUS) and (HRDY1=HRDY0) and
(HRDY2=HRDY1) and … and (HRDY15=HRDY14). HSEL follows the same rules.
th
HSELx The x
HSEL status on BUS
bit0 APB
bit1 SHARE1
bit2 SHARE2
bit3 IDMA1
bit4 IDMA2
th
HRDYx The x
HREADY status on BUS
bit0 APB
bit1 SHARE1
bit2 SHARE2
bit3 IDMA1
bit4 IDMA2
BM+0060h Layer-2 AHB master FIFO 0~7
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_MSEL7 LYR2_MSEL6 LYR2_MSEL5 LYR2_MSEL4
Type RO RO RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_MSEL3 LYR2_MSEL2 LYR2_MSEL1 LYR2_MSEL0
Type RO RO RO RO
BM+0064h Layer-2 AHB master FIFO 8~15
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR2_MSEL15 LYR2_MSEL14 LYR2_MSEL13 LYR2_MSEL12
Type RO RO RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR2_MSEL11 LYR2_MSEL10 LYR2_MSEL9 LYR2_MSEL8
Type RO RO RO RO
BM_LYR2_MFIF
O0
BM_LYR2_MFIF
O8
BM keeps a specific FIFO for layer-2 AHB to record HMASTER. 0th is the latest one and 15th is the oldest. The FIFO only
shifts when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=SEQ or NON-SEQ) and (HREADY=1) and (the bus transaction is caused by master
which is enabled in LYR2_HMASTER).
If all above conditions meet, then (MSEL0=current HMASTER_ENC) and (MSEL1=MSEL0) and (MSEL2=MSEL1)
and … and (MSEL15=MSEL14).
MSELx The x
th
MSEL status on BUS.
000 Vitua l FI FO
001 DMA
010 Wavetable
011 USB
88/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 89

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
100 IRDGB1
101 IRDBG2
110 IRDA
111 PWM
BM+0070h Layer-3 AHB active cycle count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR3_ACCNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR3_ACCNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_LYR3_ACC
NT
LYR3_ACCNT LYR3_ACCNT indicates how many cycles HTRANS is (non-IDLE and non-BUSY) and increments in
every cycle when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ).
LYR3_ACCNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
BM+0074h Layer-3 AHB transaction count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR3_TCNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR3_TCNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_LYR3_TCN
LYR3_TCNT LYR3_TCNT indicates transaction accumulation and increments in every cycle when (EN=1) and
(HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ) and (HREADY=1).
LYR3_ACNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
T
BM+0078h Layer-3 AHB word count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR3_WCNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR3_WCNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_LYR3_WCN
LYR3_WCNT LYR3_WCNT indicates transaction of word counts been transferred and increases depends HSIZE in
every cycle when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ) and (HREADY=1). A word means 4 bytes (32-bit)
in this document. The total data counts transferred less then 1 word is truncated. (For example, the BUS transfers
33 bytes after EN=1. you will get 8 in WCNT. The last byte count is ignored.)
LYR3_WCNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
HSIZE=00 8-bit data. WCNT increases 1.
89/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
T
Page 90

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
HSIZE=01 16-bit data. WCNT increases 2.
HSIZE=10 32-bit data. WCNT increases 4.
OTHER Not supported.
BM+0090h Layer-4 AHB active cycle count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR4_ACCNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR4_ACCNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_LYR4_ACC
NT
LYR4_ACCNT LYR4_ACCNT indicates how many cycles HTRANS is (non-IDLE and non-BUSY) and increments in
every cycle when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ).
LYR4_ACCNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
BM+0094h Layer-4 AHB transaction count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR4_TCNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR4_TCNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_LYR4_TCN
LYR4_TCNT LYR4_TCNT indicates transaction accumulation and increments in every cycle when (EN=1) and
(HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ) and (HREADY=1).
LYR4_ACNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
T
BM+0098h Layer-4 AHB word count
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR4_WCNT[31:16]
Type RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR4_WCNT[15:0]
Type RO
BM_LYR4_WCN
LYR4_WCNT LYR4_WCNT indicates transaction of word counts been transferred and increases depends HSIZE in
every cycle when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=NON-SEQ or SEQ) and (HREADY=1). A word means 4 bytes (32-bit)
in this document. The total data counts transferred less then 1 word is truncated. (For example, the BUS transfers
33 bytes after EN=1. you will get 8 in WCNT. The last byte count is ignored.)
LYR4_WCNT is only cleared by CLR and is not affected by RESET.
HSIZE=00 8-bit data. WCNT increases 1.
HSIZE=01 16-bit data. WCNT increases 2.
90/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
T
Page 91

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
HSIZE=10 32-bit data. WCNT increases 4.
OTHER Not supported.
BM+00a0h Layer-4 AHB FIFO 0~3
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR4_HDY3 LYR4_HSEL3 LYR4_HDY2
Type RO RO RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR4_HDY1 LYR4_HSEL1 LYR4_HDY0
Type RO RO RO RO
BM+00a4h Layer-4 AHB FIFO 4~7
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR4_HDY7 LYR4_HSEL7 LYR4_HDY6
Type RO RO RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR4_HDY5 LYR4_HSEL5 LYR4_HDY4
Type RO RO RO RO
BM+00a8h Layer-4 AHB FIFO 8~11
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR4_HDY11
Type RO RO RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR4_HDY9 LYR4_HSEL9 LYR4_HDY8
Type RO RO RO RO
LYR4_HSEL1
1
LYR4_HDY10
BM_LYR4_FIFO
LYR4_HSEL
LYR4_HSEL
BM_LYR4_FIFO
LYR4_HSEL
LYR4_HSEL
BM_LYR4_FIFO
LYR4_HSEL
LYR4_HSEL
0
2
0
4
6
4
8
10
8
BM+00ach Layer-4 AHB FIFO 12~15
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name LYR4_HDY15
Type RO RO RO RO
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LYR4_HDY13
Type RO RO RO RO
LYR4_HSEL1
5
LYR4_HSEL1
3
LYR4_HDY14
LYR4_HDY12
BM_LYR4_FIFO
C
LYR4_HSEL
14
LYR4_HSEL
12
BM keeps FIFOs internal recording HSEL and HREADY status on BUS for each layer. 0th is the latest one and 15th is the
oldest. The FIFO only shifts when (EN=1) and (HTRANS=SEQ or NON-SEQ) and (HREADY=0) and (slaves’ HREADYs
91/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 92

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
differ from HDY0). If all above conditions meet, then (HRDY0=current HREADY on BUS) and (HRDY1=HRDY0) and
(HRDY2=HRDY1) and … and (HRDY15=HRDY14). HSEL follows the same rules.
th
HSELx The x
HSEL status on BUS
bit0 EMI
bit1 System memory
th
HRDYx The x
HREADY status on BUS
bit0 EMI
bit1 System memory
92/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 93

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
3.7 External Memory Interface (6235)
3.7.1 General Description
MT6235 incorporates a powerful and flexible memory controller, External Memory Interface, to connect with a variety of
memory components. This controller provides one generic access scheme for FLASH Memory, SRAM, PSRAM and. Up to
4 memory banks can be supported simultaneously, BANK0-BANK3, with a maximum size of 128MB each. This controller
also provides another access scheme for DRAM (SDR), and only one bank can be supported, with a maximum size of
128MB.
The software program can treat different components by simply specifying certain predefined parameters. All these
parameters are based on cycle time of system clock.
The interface definition based on such scheme is listed in Table 13. Note that, this interface always operates data in Little
Endian format for all types of accesses.
Signal Name Type Description
XADMUX I Define ADMUX or not in NOR flash / PSRAM
EWAIT I Wait Signal Input
ED[15:0] I/O Data Bus
EA[26:0] I/O Address Bus
ECS# [3:0] O BANK3~BANK0 Selection Signal
EWR# O Write Enable Strobe
ERD# O Read Enable Strobe
EDQM[1:0]# O Data mask
EADV# O Burst Mode FLASH Memory Address Latch Signal
ERAS# O Row address latch signal (SDR DRAM)
ECAS# O Column address latch signal (SDR DRAM)
ECKE# O CLOK enable signal (SDR DRAM)
EC_CLK O Burst Mode FLASH/PSRAM Memory Clock Signal
ED_CLK O DRAM clock signal
Table 13 External Memory Interface of MT6235
REGISTER ADDRESS REGISTER NAME SYNONYM
EMI + 0000h PSRAM controller register for BANK0 EMI_CONA
EMI + 0008h PSRAM controller register for BANK1 EMI_CONB
EMI + 0010h PSRAM controller register for BANK2 EMI_CONC
EMI + 0018h PSRAM controller register for BANK3 EMI_COND
EMI + 0040h DRAM MR/EMR EMI_CONI
EMI + 0048h DRAM controller timing configuration I EMI_CONJ
93/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 94

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
EMI + 0050h DRAM controller timing configuration II EMI_CONK
EMI + 0058h DRAM controller read data path configuration EMI_CONL
EMI + 0060h DRAM controller read delay timing configuration EMI_CONM
EMI + 0068h DRAM controller function configuration EMI_CONN
EMI + 0070h EMI General Control Register A EMI_GENA
EMI + 0078h EMI General Control Register B EMI_GENB
EMI + 0080h EMI General Control Register C EMI_GENC
EMI + 0088h EMI General Control Register D EMI_GEND
Table 14 External Memory Interface Register Map
3.7.2 Registers
+0000h ~ 0018h Register EMI_CONA~D
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
SRAM
AD_M
Name PSIZE WPLO
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 7 1 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name WR_WAIT_1ST RD_WAIT_1ST AS_ADV AS_SET
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset F F 3 3 0 3
_16
PSIZE : Page size for page read mode
PSIZE 00 01 10
Sram_16 = 1 8 byte 16 byte 32 byte
Sram_16 = 0 4 byte 8 byte 16 byte
WPOL :
1: Wait polarity change
0: Wait polarity not change
SRAM_16 :
1: Data bit [15:0]
0: Data bit [ 7:0]
ADMUX:
1: ADMUX type memory
0: Non ADMUX type memory
ADVEN:
1: ADV enable in asynchronous read / write
0: ADV disable in asynchronous read / write
ADV_ENAS_RD AS_WR AP_R
UX
D
AS_WAIT CS_END SY_SET
WAIT_
EN
RESE
RVED
AS_HOLD
94/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 95

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
AS_RD:
1: Turn on asynchronous read
0: Turn off asynchronous read
AS_WR:
1: Turn on asynchronous write
0: Turn off asynchronous write
AP_RD:
1: Turn on asynchronous page read (burst-page read)
0: Turn off asynchronous page read(burst-page read)
AS_WAIT:
Adjust wait time in every transaction of asynchronous mode ( 0: 1clk , 1: 2clk ……)
CS_END:
Adjust CS disable time in the end of every transaction ( 0: 1clk , 1: 2clk ……)
SY_SET:
Adjust init set up time in every transaction of synchronous mode ( 0: 1clk , 1: 2clk ……)
WR_WAIT_1st:
Adjust first write wait time in every transaction of page read mode ( 0: 1clk , 1: 2clk ……)
RD_WAIT_1st:
Adjust first read wait time in every transaction of page read mode ( 0: 1clk , 1: 2clk ……)
For synchronous mode, RD_WAIT_1st[1:0] is used to adjust read wait time in every transaction
AS_ADV:
Adjust ADV time in every transaction of asynchronous mode ( 0: 1clk , 1: 2clk ……)
AS_SET:
Adjust init set up time in every transaction of asynchronous mode ( 0: 1clk , 1: 2clk ……)
WAIT_EN:
1: Pass XWAIT signal from external memory to controller
0: Skip XWAIT signal and pass 1 to controller
AS_HOLD:
Adjust hold time in every transaction of asynchronous and synchronus mode ( 0: 1clk , 1: 2clk ……)
95/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 96

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
+0040h Register EMI_CONI
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name MBA1 MBA0 MA12 MA11 MA10 MA9 MA8 MA7 MA6 MA5 MA4 MA3 MA2 MA1 MA0
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EBA1 EBA0
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
EBA12 EBA11 EBA1
0
EBA9 EBA8 EBA7 EBA6 EBA5 EBA4 EBA3 EBA2 EBA1 EBA0
MBA1~0 : DRAM bank address setting when load mode register to DRAM
MA12~0 : DRAM mode register value
EBA1~0 : DRAM bank address setting when load extended mode register to DRAM
EA12~0 : DRAM extended mode register value
+0048h Register EMI_CONJ
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name E_ES PRAL_CYC REF_CYC EXIT_SREF_CYC LDMR_CYC
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name ACT_RC_CYC ACT_RR_CYC
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0
WR_WAIT_C
YC
RD_WAIT_C
YC
E_ES : Extend EXIT_SREF_CYC
PRAL_CYC : DRAM pre-charge cycle time ( TRP)
REF_CYC : DRAM refresh cycle time (TRFC)
EXIT_SREF_CYC : DRAM exit self refresh to first valid command cycle time (TXSR)
LDMR_CYC : DRAM load mode/e-mode register cycle time (TMRD)
ACT_RC_CYC : DRAM active to read/write command delay cycle time (TRCD)
ACT_RR_CYC : DRAM active bank A to active bank b delay cycle time (TRRD)
WR_WAIT_CYC : DRAM write recovery cycle time (TWR)
RD_WAIT_CYC : DRAM read command to pre-charge delay cycle time ( adjust final read command to
pre-charge command delay cycle time
96/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 97

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
+0050h Register EMI_CONK
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name REEP_CYC
Type R/W
Reset 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name
Type R/W R/W
Reset 0 0
REFP_CYC : Auto refresh period cycle time ( TREF )
PW_EN : Power on wait-count enable
PW_CYC : Power on wait cycle time
PW_E
N
PW_CYC
+0058h Register EMI_CONL
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name DW_PSEL DPD_CYC
Type R/W R/W
Reset 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RAS_MIN_CYC PATH_SEL RD_DEL_SEL
Type R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0
DW_PSEL : Define EMI output clock to DRAM phase select
DW_PSEL[5:0] : Adjust phase delay --- > 1 tape (0.3~0.5 ns)
DPD_CYC : Enter and exit DRAM power down state cycle time
RAS_MIN_CYC : Active to pre-charge minimum cycle time
PATH_SEL : Data input path select from external memory
RD_DEL_SEL : Read data delay cycle time to read command (SDR SDRAM), include CAS latency, IO pad delay,
PCB delay
+0060h Register EMI_CONM
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name
97/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 98

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
Type
Reset
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RD_PDEL_SEL_BY1 RD_PDEL_SEL_BY0
Type R/W R/W
Reset 0 0
RD_PDEL_SEL_BY1 : Read phase delay for DRAM input data bit [15:8]
RD_PDEL_SEL_BY0 : Read phase delay for DRAM input data bit [ 7:0]
+0068h Register EMI_CONN
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
PRAL
AREF
AREF
LDMR
Name
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0
_EN
1_EN
2_EN
_EN
LDEM
R_EN
ADDR_TYPE DGB_EN
REF_
SREF
_ST
PDN_STSREF
_EN
PDN_
EN
CNT_
EN
DRA
M_EN
PRAL_EN : Single pre-charge all enable ( for DRAM initialize)
ARF1_EN : Single auto-refresh-1 enable ( for DRAM initialize)
ARF2_EN : Single auto-refresh-2 enable ( for DRAM initialize)
LDMR_EN : Single load mode register enable ( for DRAM initialize)
LDEM_EN : Single load extended mode register enable ( for DRAM initialize)
ADDR_TYPE : DRAM address type
ADDR_TYPE Row address bits Bank address bits Column address bits
000 11 1 8
001 11 2 8
010 12 2 8
011 12 2 9
100 13 2 9
101 13 2 10
110 14 2 10
DBG_EN :
00 : Normal mode
Others : Internal debug mode, and do not set!
98/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 99

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
SREF_ST :
1 : DRAM in self refresh status
0 : DRAM exit self refresh status
PDN_ST :
1 : DRAM in power down status
0 : DRAM exit power down status
SREF_EN :
1 : DRAM enter self refresh
0 : DRAM exit self refresh
PDN_EN :
1 : DRAM enter power down, when dram controller is IDLE ( the controller will exit power down status,
and exercise auto refresh step to keep data correctable in DRAM, if the refresh time is end)
0 : DRAM will not enter power down .
REF_CNT_EN :
1 : Enable auto refresh
0 : Disable auto refresh
DRAM_EN :
1 : Enable DRAM controller
0 : Disable DRAM controller
+0070h Register EMI_GENA
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
CRE_
SYW_
CRE_
Name SW_PSEL
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SDAT
SWAI
A_NL
AT_E
N
CRATE SCLK
_EN
Name HDD
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
T_NL
AT_E
N
DCLK
_EN
SDAT
_DLA
T_EN
EN
SDAT
_NDA
T_EN
VALU
E
AS_A
P_RD
_D
ACTIV
E_WR
WTD
_DIS
SYR_
WRPS LSS EST
WTD
ACTIV
E_RD
_DIS
M1_T
OP
M0_T
OP
SW_PSEL : Define EMI output clock to PSRAM phase select
SW_PSEL[5:0] : Adjust phase delay --- > 1 tape (0.3~0.5 ns)
CRE_EN
1: Assign EA26 as GPIO function for PSRAM CRE
0: disable
CRE_VALUE
Assign CRE output value
L2_E
N
RM1 RM0
99/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
Page 100

MT6235 GSM/GPRS Baseband Processor Data Sheet Revision 1.02
SYW_WTD :
1: Wait signal delay 1 more cycle at synchronous write mode of PSRAM
0: disable
SYR_WTD :
1: Wait signal delay 1 more cycle at synchronous read mode of PSRAM
0: disable
WRPS :
1: WRAP mode only PSRAM ( The PSRAM cannot support continues access mode)
0: disable
LSS :
1: Low speed PSRAM ( clock rate of EMI to PSRAM is 2:1)
0: disable
EST :
1: Extended PSRAM AS_WAIT timing 1 bit.
0: disable
L2_EN :
1: Resolve data consistence problem from L2.
0: disable
HDD :
1: Enable DRAM access at enough bus data rate without concern FIFO condition.
0: disable
SWAIT_NLAT_EN :
1: Latch XWAIT signal by negative edge of HCLK_CK enable (for low speed operation , especially in FPGA ENV)
0: disable
SDATA_NLAT_EN :
1: Latch XDATA(DEMUX) or XADDR(ADMUX) signal by negative edge of HCLK_CK enable
(for low speed operation , especially in FPGA ENV)
0: disable
CRATE:
1: If HDD is enable
0: disable
SCLKEN :
: SRAM controller clock out enable
1: Enable
0: Disable
DCLKEN :
DRAM controller clock out enable
1: Enable
0: Disable
SDAT_DLAT_EN:
SRAM input data sampled by DLAT_CLK positive edge like DRAM
100/599 MediaTek Inc. Confidential
 Loading...
Loading...