Datasheet MT28F322D18FH-804B, MT28F322D18FH-804BET, MT28F322D18FH-804T, MT28F322D18FH-704TET, MT28F322D18FH-705B Datasheet (MICRON)
...Page 1
1
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
PRODUCTS AND SPECIFICATIONS DISCUSSED HEREIN ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE BY MICRON WITHOUT NOTICE.
FLASH MEMORY
MT28F322D20
MT28F322D18
Low Voltage, Extended Temperature
0.18µm Process Technology
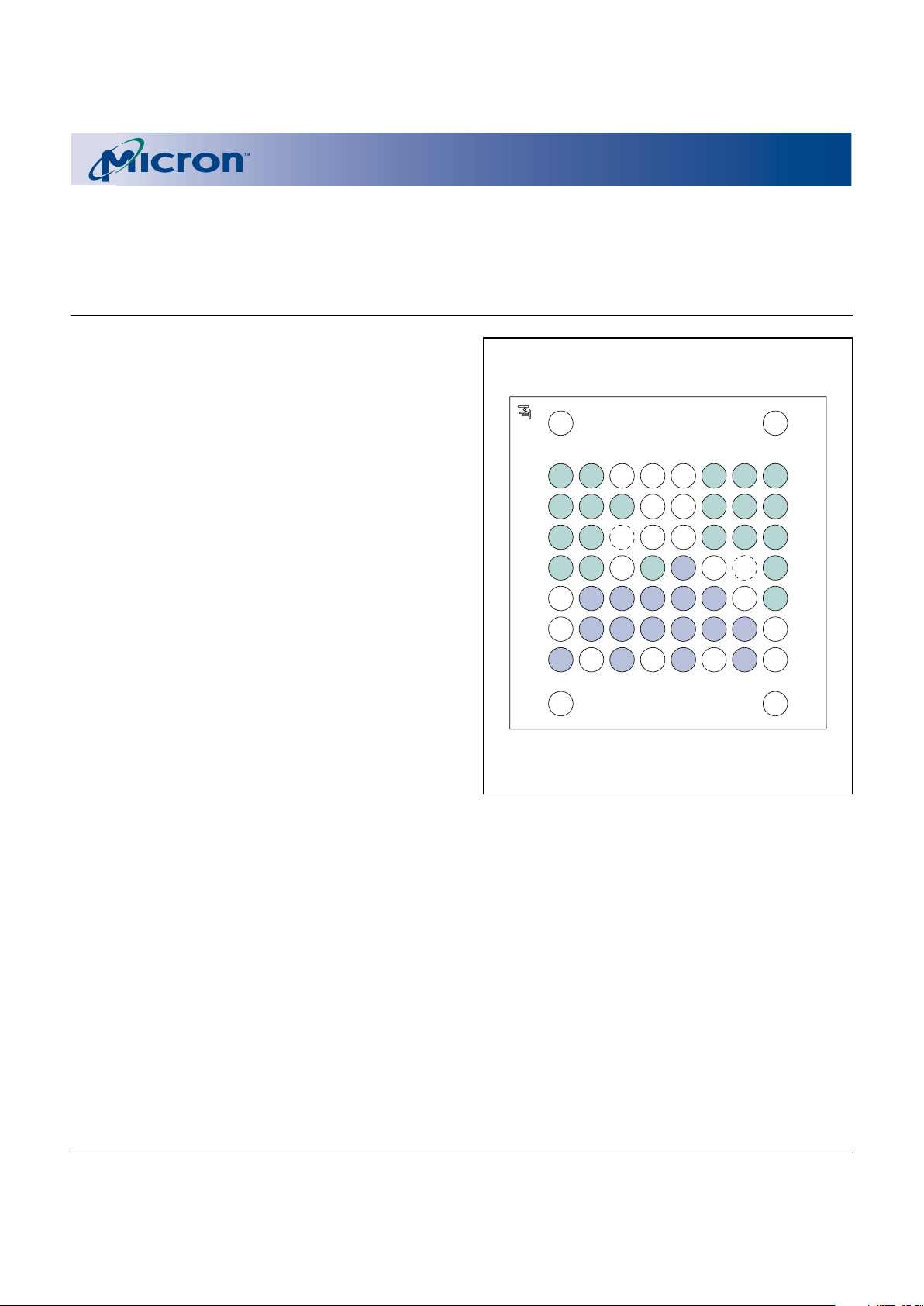
BALL ASSIGNMENT
58-Ball FBGA
FEATURES
• Flexible dual-bank architecture
– Support for true concurrent operation with zero
latency
– Read bank a during program bank b and vice versa
– Read bank a during erase bank b and vice versa
• Basic configuration:
Seventy-one erasable blocks
– Bank a (8Mb for data storage)
– Bank b (24Mb for program storage)
•VCC, VCCQ, VPP voltages
– 1.70V (MIN), 1.90V (MAX) VCC, VCCQ
(MT28F322D18 only)
– 1.80V VCC, VCCQ (MIN); 2.20V VCC (MAX)and 2.25V
VCCQ (MAX) (MT28F322D20 only)
– 0.9V (TYP) VPP (in-system PROGRAM/ERASE)
– 12V ±5% (HV) VPP tolerant (factory programming
compatibility)
• Random access time: 70ns/80ns @ 1.70V VCC
• Burst Mode read access (MT28F322D20)
– MAX clock rate: 54 MHz (tCLK = 18.5ns)
– Burst latency: 70ns @ 1.80V VCC and 54 MHz
–tACLK: 17ns @ 1.80V VCC and 54 MHz
• Page Mode read access
1
– Eight-word page
– Interpage read access: 70ns/80ns @ 1.80V
– Intrapage read access: 30ns @ 1.80V
• Low power consumption (VCC = 2.20V)
– Asynchronous READ < 15mA (MAX)
– Standby < 50µA
– Automatic power saving feature (APS)
• Enhanced write and erase suspend options
– ERASE-SUSPEND-to-READ within same bank
– PROGRAM-SUSPEND-to-READ within same bank
– ERASE-SUSPEND-to-PROGRAM within same bank
• Dual 64-bit chip protection registers for security
purposes
• Cross-compatible command support
– Extended command set
– Common flash interface
• PROGRAM/ERASE cycle
– 100,000 WRITE/ERASE cycles per block
NOTE: 1. Data based on MT28F322D20 device.
2. A “5” in the part mark represents two different
frequencies: 54 MHz (MT28F322D20) or 52 MHz
(MT28F322D18)
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Top View
(Ball Down)
A11
A12
A13
A15
V
CC
Q
V
SS
DQ7
A18
A17
A19
WP#
DQ1
DQ9
V
CC
Q
V
PP
RST#
WE#
DQ12
DQ2
DQ10
DQ3
V
SS
A20
WAIT#
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
OE#
V
SS
Q
A6
A5
A7
CE#
DQ0
DQ8
A8
A9
A10
A14
DQ15
DQ14
V
SS
Q
V
CC
CLK
ADV#
A16
DQ4
DQ11
V
CC
NOTE: See page 7 for Ball Description Table.
See page 43 for mechanical drawing.
OPTIONS MARKING
• Timing
70ns access -70
80ns access -80
• Frequency
54 MHz 5
2
40 MHz 4
No burst operation None
• Boot Block Configuration
Top T
Bottom B
• Package
58-ball FBGA (8 x 7 ball grid) FH
• Operating Temperature Range
Extended (-40ºC to +85ºC) ET
Part Number Example:
MT28F322D20FH-804 BET
Page 2
2
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MT28F322D20 and MT28F322D18 are highperformance, high-density, nonvolatile Flash memory
solutions that can significantly improve system performance. This new architecture features a two-memorybank configuration that supports dual-bank operation
with no latency.
A high-performance bus interface allows a fast burst
or page mode data transfer; a conventional asynchronous bus interface is provided as well.
The devices allow soft protection for blocks, as readonly, by configuring soft protection registers with dedicated command sequences. For security purposes, two
64-bit chip protection registers are provided.
The embedded WORD WRITE and BLOCK ERASE
functions are fully automated by an on-chip write state
machine (WSM). Two on-chip status registers, one for
each of the two memory partitions, can be used to monitor the WSM status and to determine the progress of the
program/erase task.
The erase/program suspend functionality allows
compatibility with existing EEPROM emulation software
packages.
The devices are manufactured using 0.18µm process
technology.
Please refer to the Micron Web site (www.micron.com/
flash) for the latest data sheet.
ARCHITECTURE AND MEMORY
ORGANIZATION
The Flash devices contain two separate banks of
memory (bank a and bank b) for simultaneous READ and
WRITE operations and are available in the following bank
segmentation configuration:
• Bank a is one-fourth of the memory containing
8 x 4K-word parameter blocks, while the remainder
of bank a is split into 15 x 32K-word blocks.
• Bank b represents three-fourths of the memory, is
equally sectored, and contains 48 x 32K-word blocks.
Figures 2 and 3 show the bottom and top memory
organizations.
DEVICE MARKING
Due to the size of the package, Micron’s standard part
number is not printed on the top of each device. Instead,
an abbreviated device mark comprised of a five-digit
alphanumeric code is used. The abbreviated device marks
are cross referenced to the Micron part numbers in
Table 1.
Table 1
Cross Reference for Abbreviated Device Marks
PRODUCT SAMPLE MECHANICAL
PART NUMBER MARKING MARKING SAMPLE MARKING
MT28F322D20FH-705 TET FW546 FX546 FY546
MT28F322D20FH-705 BET FW547 FX547 FY547
MT28F322D20FH-804 TET FW548 FX548 FY548
MT28F322D20FH-804 BET FW549 FX549 FY549
MT28F322D18FH-705 TET FW558 FX558 FY558
MT28F322D18FH-705 BET FW559 FX559 FY559
MT28F322D18FH-804 TET FW543 FX543 FY543
MT28F322D18FH-804 BET FW542 FX542 FY542
Page 3
3
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
PART NUMBERING INFORMATION
Micron’s low-power devices are available with sev-
eral different combinations of features (see Figure 1).
Table 2
Valid Part Number Combinations
BOOT BLOCK BURST OPERATING
ACCESS STARTING FREQUENCY TEMPERATURE
PART NUMBER TIME (ns) ADDRESS (MHz) RANGE
MT28F322D20FH-705 BET 70 Bottom 54 -40oC to +85oC
MT28F322D20FH-705 TET 70 Top 54 -40oC to +85oC
MT28F322D20FH-804 BET 80 Bottom 40 -40oC to +85oC
MT28F322D20FH-804 TET 80 Top 40 -40oC to +85oC
MT28F322D18FH-705 BET 70 Bottom 52 -40oC to +85oC
MT28F322D18FH-705 TET 70 Top 52 -40oC to +85oC
MT28F322D18FH-804 BET 80 Bottom 40 -40oC to +85oC
MT28F322D18FH-804 TET 80 Top 40 -40
o
C to +85oC
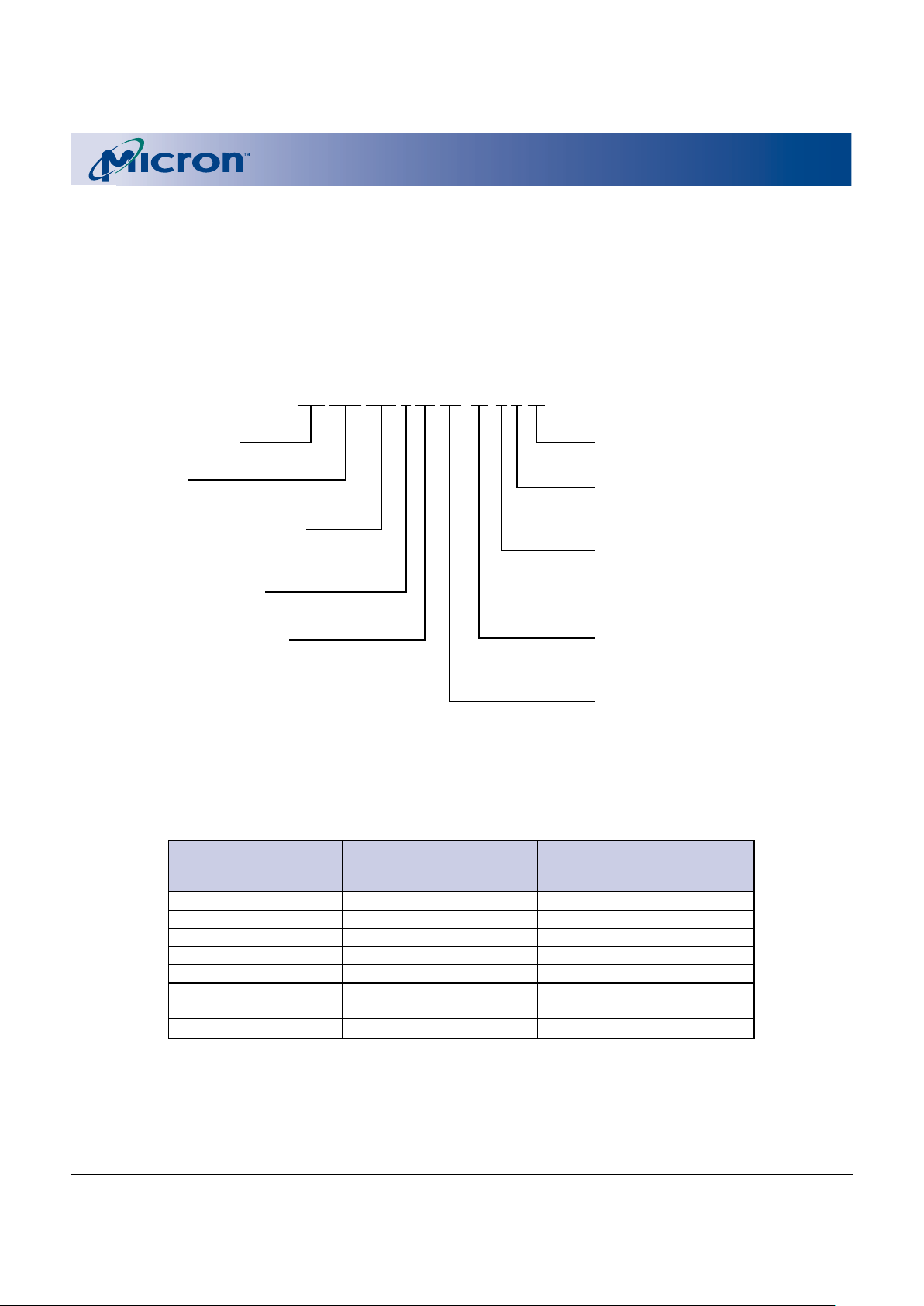
Figure 1
Part Number Chart
Valid combinations of features and their corresponding
part numbers are listed in Table 2.
MT 28F 322 D20 FH-80 4 B ET
Micron Technology
Flash Family
28F = Dual-Supply Flash
Density/Organization/Banks
322 = 32Mb (2,048K x 16)
bank a = 1/4; bank b = 3/4
Access Time
-70 = 70ns
-80 = 80ns
Read Mode Operation
D = Asynchronous/Page/Burst Read
Package Code
FH = 58-ball FBGA (8 x 7 grid)
Operating Temperature Range
ET = Extended (-40ºC to +85ºC)
Burst Mode Frequency
Blank = None
4 = 40 MHz
5 = 54 MHz (MT28F322D20) or
52 MHz (MT28F322D18)
Boot Block Starting Address
B = Bottom boot
T = Top boot
Operating Voltage Range
18 = 1.70V–1.90V
20 = 1.80V–2.20V V
CC
20 = 1.80V–2.25V VCCQ
Page 4
4
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
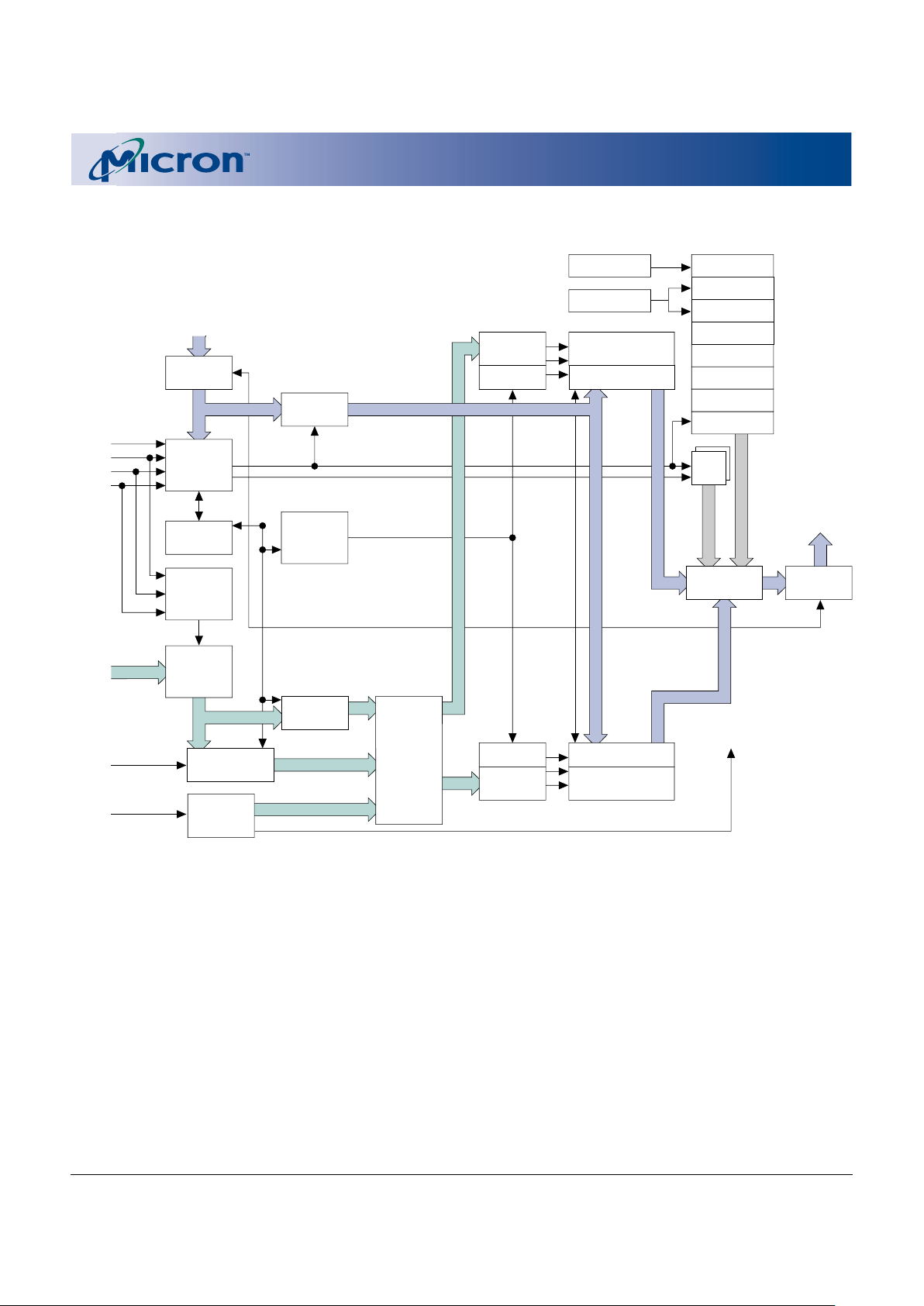
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Address
Input
Buffer
BSM
X DEC
Y/Z DEC
Data Input
Buffer
Output
Multiplexer
Address
CNT WSM
Output
Buffer
Status
Reg.
WSM
Program/
Erase
Pump Voltage
Generators
Address Latch
DQ0–DQ15
DQ0–DQ15
CSM
RST#
ADV#
WAIT#
CLK
CE#
X DEC
Y/Z DEC
WE#
OE#
I/O Logic
A0–A20
Address
Multiplexer
Bank 2 Blocks
Y/Z Gating/Sensing
Data
Register
Bank 1 Blocks
Y/Z Gating/Sensing
ID Reg.
RCR
Block Lock
Device ID
Manufacturer’s ID
OTP
Query
PR Lock
Query/OTP
PR Lock
Page 5
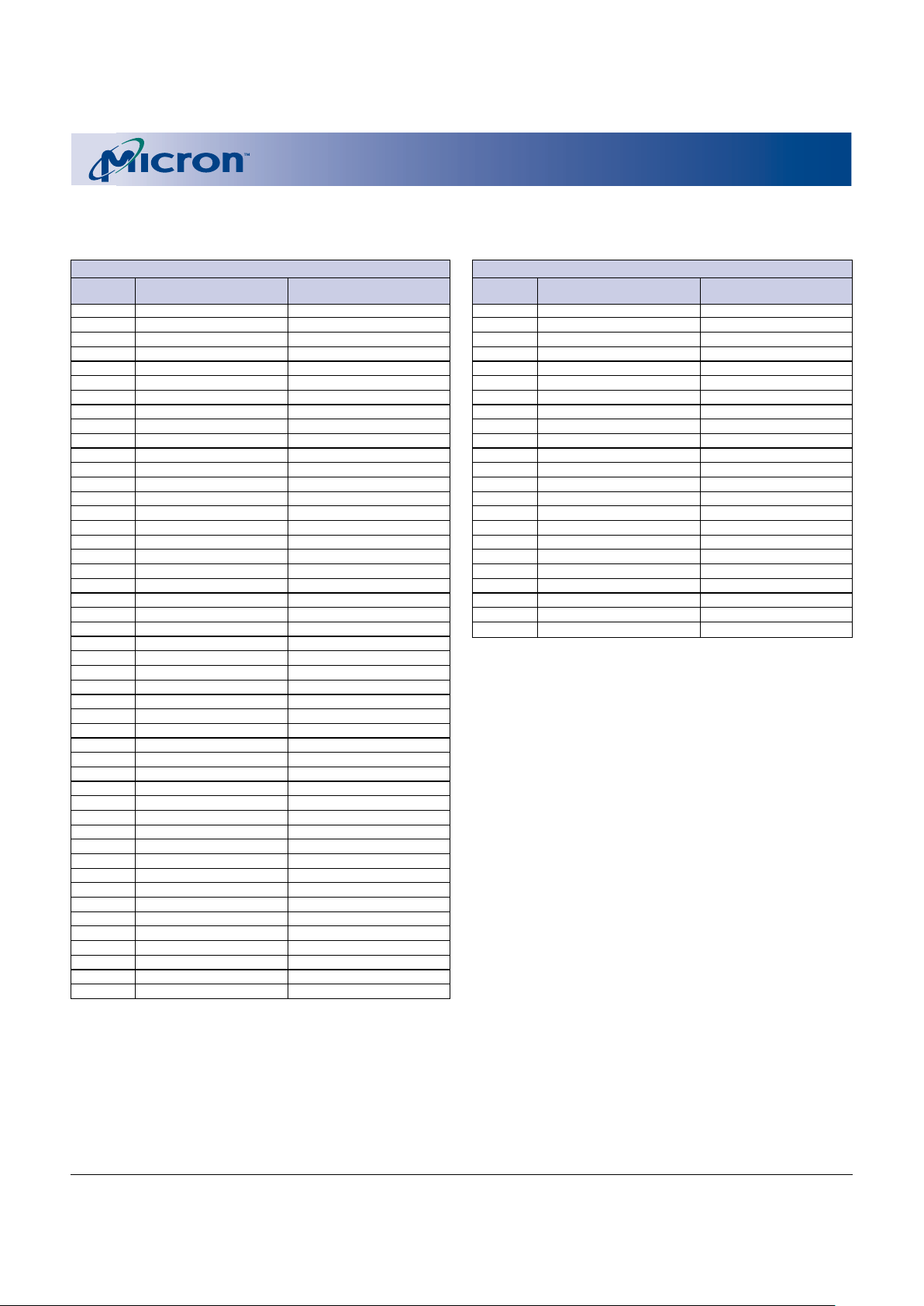
5
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
Bank b = 24Mb
Block Block Size Address Range
(K-bytes/K-words) (x16)
70 64/32 1F8000h-1FFFFFh
69 64/32 1F0000h-1F7FFFh
68 64/32 1E8000h-1EFFFFh
67 64/32 1E0000h-1E7FFFh
66 64/32 1D8000h-1DFFFFh
65 64/32 1D0000h-1D7FFFh
64 64/32 1C8000h-1CFFFFh
63 64/32 1C0000h-1C7FFFh
62 64/32 1B8000h-1BFFFFh
61 64/32 1B0000h-1B7FFFh
60 64/32 1A8000h-1AFFFFh
59 64/32 1A0000h-1A7FFFh
58 64/32 198000h-19FFFFh
57 64/32 190000h-197FFFh
56 64/32 188000h-18FFFFh
55 64/32 180000h-187FFFh
54 64/32 178000h-17FFFFh
53 64/32 170000h-177FFFh
52 64/32 168000h-16FFFFh
51 64/32 160000h-167FFFh
50 64/32 158000h-15FFFFh
49 64/32 150000h-157FFFh
48 64/32 148000h-14FFFFh
47 64/32 140000h-147FFFh
46 64/32 138000h-13FFFFh
45 64/32 130000h-137FFFh
44 64/32 128000h-12FFFFh
43 64/32 120000h-127FFFh
42 64/32 118000h-11FFFFh
41 64/32 110000h-117FFFh
40 64/32 108000h-10FFFFh
39 64/32 100000h-107FFFh
38 64/32 0F8000h-0FFFFFh
37 64/32 0F0000h-0F7FFFh
36 64/32 0E8000h-0EFFFFh
35 64/32 0E0000h-0E7FFFh
34 64/32 0D8000h-0DFFFFh
33 64/32 0D0000h-0D7FFFh
32 64/32 0C8000h-0CFFFFh
31 64/32 0C0000h-0C7FFFh
30 64/32 0B8000h-0BFFFFh
29 64/32 0B0000h-0B7FFFh
28 64/32 0A8000h-0AFFFFh
27 64/32 0A0000h-0A7FFFh
26 64/32 098000h-097FFFh
25 64/32 090000h-097FFFh
24 64/32 088000h-087FFFh
23 64/32 080000h-087FFFh
Bank a = 8Mb
Block Block Size Address Range
(K-bytes/K-words) (x16)
22 64/32 078000h-07FFFFh
21 64/32 070000h-077FFFh
20 64/32 068000h-067FFFh
19 64/32 060000h-067FFFh
18 64/32 058000h-05FFFFh
17 64/32 050000h-057FFFh
16 64/32 048000h-04FFFFh
15 64/32 040000h-047FFFh
14 64/32 038000h-03FFFFh
13 64/32 030000h-037FFFh
12 64/32 028000h-02FFFFh
11 64/32 020000h-027FFFh
10 64/32 018000h-01FFFFh
9 64/32 010000h-017FFFh
8 64/32 008000h-00FFFFh
7 8/4 007000h-007FFFh
6 8/4 006000h-006FFFh
5 8/4 005000h-005FFFh
4 8/4 004000h-004FFFh
3 8/4 003000h-003FFFh
2 8/4 002000h-002FFFh
1 8/4 001000h-001FFFh
0 8/4 000000h-000FFFh
Figure 2
Bottom Boot Block Device
Page 6
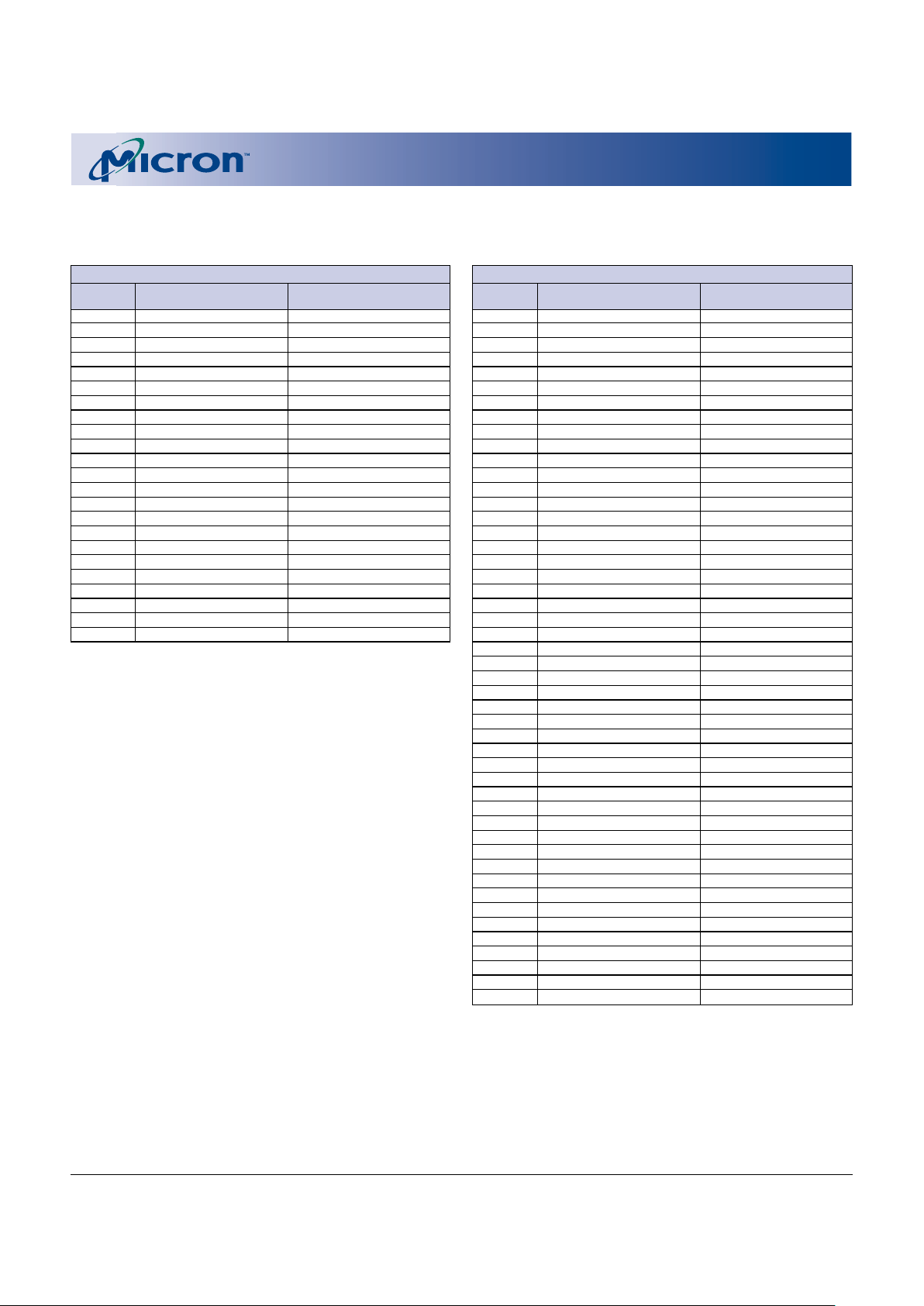
6
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
Bank b = 24Mb
Block Block Size Address Range
(K-bytes/K-words) (x16)
47 64/32 178000h-17FFFFh
46 64/32 170000h-177FFFh
45 64/32 168000h-16FFFFh
44 64/32 160000h-167FFFh
43 64/32 158000h-15FFFFh
42 64/32 150000h-157FFFh
41 64/32 148000h-14FFFFh
40 64/32 140000h-147FFFh
39 64/32 138000h-13FFFFh
38 64/32 130000h-137FFFh
37 64/32 128000h-12FFFFh
36 64/32 120000h-127FFFh
35 64/32 118000h-11FFFFh
34 64/32 110000h-117FFFh
33 64/32 108000h-10FFFFh
32 64/32 100000h-107FFFh
31 64/32 0F8000h-0FFFFFh
30 64/32 0F0000h-0F7FFFh
29 64/32 0E8000h-0EFFFFh
28 64/32 0E0000h-0E7FFFh
27 64/32 0D8000h-0DFFFFh
26 64/32 0D0000h-0D7FFFh
25 64/32 0C8000h-0CFFFFh
24 64/32 0C0000h-0C7FFFh
23 64/32 0B8000h-0BFFFFh
22 64/32 0B0000h-0B7FFFh
21 64/32 0A8000h-0AFFFFh
20 64/32 0A0000h-0A7FFFh
19 64/32 098000h-09FFFFh
18 64/32 090000h-097FFFh
17 64/32 088000h-08FFFFh
16 64/32 080000h-087FFFh
15 64/32 078000h-07FFFFh
14 64/32 070000h-077FFFh
13 64/32 068000h-06FFFFh
12 64/32 060000h-067FFFh
11 64/32 058000h-05FFFFh
10 64/32 050000h-057FFFh
9 64/32 048000h-04FFFFh
8 64/32 040000h-047FFFh
7 64/32 038000h-03FFFFh
6 64/32 030000h-037FFFh
5 64/32 028000h-02FFFFh
4 64/32 020000h-027FFFh
3 64/32 018000h-01FFFFh
2 64/32 010000h-017FFFh
1 64/32 008000h-00FFFFh
0 64/32 000000h-007FFFh
Bank a = 8Mb
Block Block Size Address Range
(K-bytes/K-words) (x16)
70 8/4 1FF000h-1FFFFFh
69 8/4 1FE000h-1FEFFFh
68 8/4 1FD000h-1FDFFFh
67 8/4 1FC000h-1FCFFFh
66 8/4 1FB000h-1FBFFFh
65 8/4 1FA000h-1FAFFFh
64 8/4 1F9000h-1F9FFFh
63 8/4 1F8000h-1F8FFFh
62 64/32 1F0000h-1F7FFFh
61 64/32 1E8000h-1EFFFFh
60 64/32 1E0000h-1E7FFFh
59 64/32 1D8000h-1DFFFFh
58 64/32 1D0000h-1D7FFFh
57 64/32 1C8000h-1CFFFFh
56 64/32 1C0000h-1C7FFFh
55 64/32 1B8000h-1BFFFFh
54 64/32 1B0000h-1B7FFFh
53 64/32 1A8000h-1AFFFFh
52 64/32 1A0000h-1A7FFFh
51 64/32 198000h-19FFFFh
50 64/32 190000h-197FFFh
49 64/32 188000h-18FFFFh
48 64/32 180000h-187FFFh
Figure 3
Top Boot Block Device
Page 7
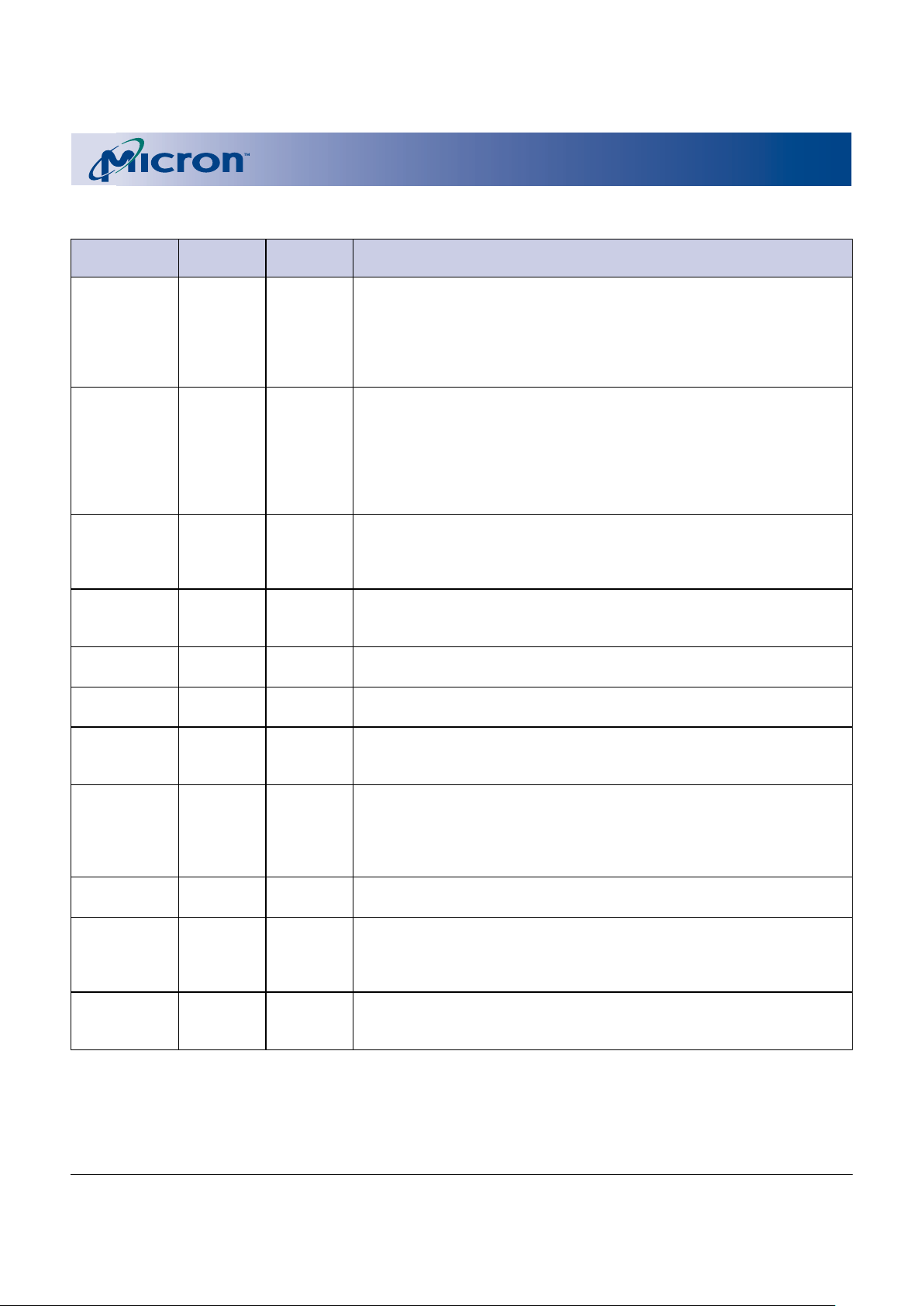
7
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
BALL DESCRIPTIONS
58-BALL FBGA
NUMBERS SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
E8, D8, C8, B8, A0–A20 Input Address Inputs: Inputs for the addresses during READ and WRITE
A8, B7, A7, C7, operations. Addresses are internally latched during READ and WRITE
A2, B2, C2, A1, cycles.
B1, C1, D2, D1,
D4, B6, A6, C6,
B3
B4 CLK Input Clock: Synchronizes the Flash memory to the system operating frequency
during synchronous burst mode READ operations. When configured for
synchronous burst mode READs, address is latched on the first rising (or
falling, depending upon the read configuration register setting) CLK edge
when ADV# is active or upon a rising ADV# edge, whichever occurs first.
CLK is ignored during asynchronous access READ and WRITE operations
and during READ PAGE ACCESS operations.
1
C4 ADV# Input Address Valid: Indicates that a valid address is present on the address
inputs. Addresses are latched on the rising edge of ADV# during READ
and WRITE operations. ADV# may be tied active during asynchronous
READ and WRITE operations.
1
A5 V
PP
Input Program/Erase Enable: [0.9V–1.95V or 11.4V–12.6V] Operates as input at
logic levels to control complete device protection. Provides factory
programming compatibility when driven to 11.4V–12.6V.
E7 CE# Input Chip Enable: Activates the device when LOW. When CE# is HIGH, the
device is disabled and goes into standby power mode.
F8 OE# Input Output Enable: Enables the output buffers when LOW. When OE# is
HIGH, the output buffers are disabled.
C5 WE# Input Write Enable: Determines if a given cycle is a WRITE cycle. If WE# is LOW,
the cycle is either a WRITE to the command state machine (CSM) or to the
memory array.
B5 RST# Input Reset: When RST# is a logic LOW, the device is in reset mode, which drives
the outputs to High-Z and resets the write state machine. When RST# is at
logic HIGH, the device is in standard operation. When RST# transitions
from logic LOW to logic HIGH, the device resets all blocks to locked and
defaults to the read array mode.
D6 WP# Input Write Protect: Controls the lock down function of the flexible locking
feature.
F7, E6, E5, G5, DQ0–DQ15 Input/ Data Inputs/Outputs: Inputs array data on the second CE# and WE#
E4, G3, E3, G1, Output cycle during PROGRAM command. Inputs commands to the command
G7, F6, F5, F4, user interface when CE# and WE# are active. DQ0–DQ15 output data
D5, F3, F2, E2 when CE# and OE# are active.
D3 WAIT# Output Wait: Provides data valid feedback during continuous burst read access.
The signal is gated by OE# and CE#. This signal is always kept at a valid
logic level.
NOTE: 1. The CLK and ADV# inputs can be tied to VSS if the device is always operating in asynchronous or page mode. The
WAIT# signal can be ignored when operating in asynchronous or page mode, as it is always held at logic “1” or “0,”
depending on the RCR8 setting (see Table 8).
(continued on next page)
Page 8
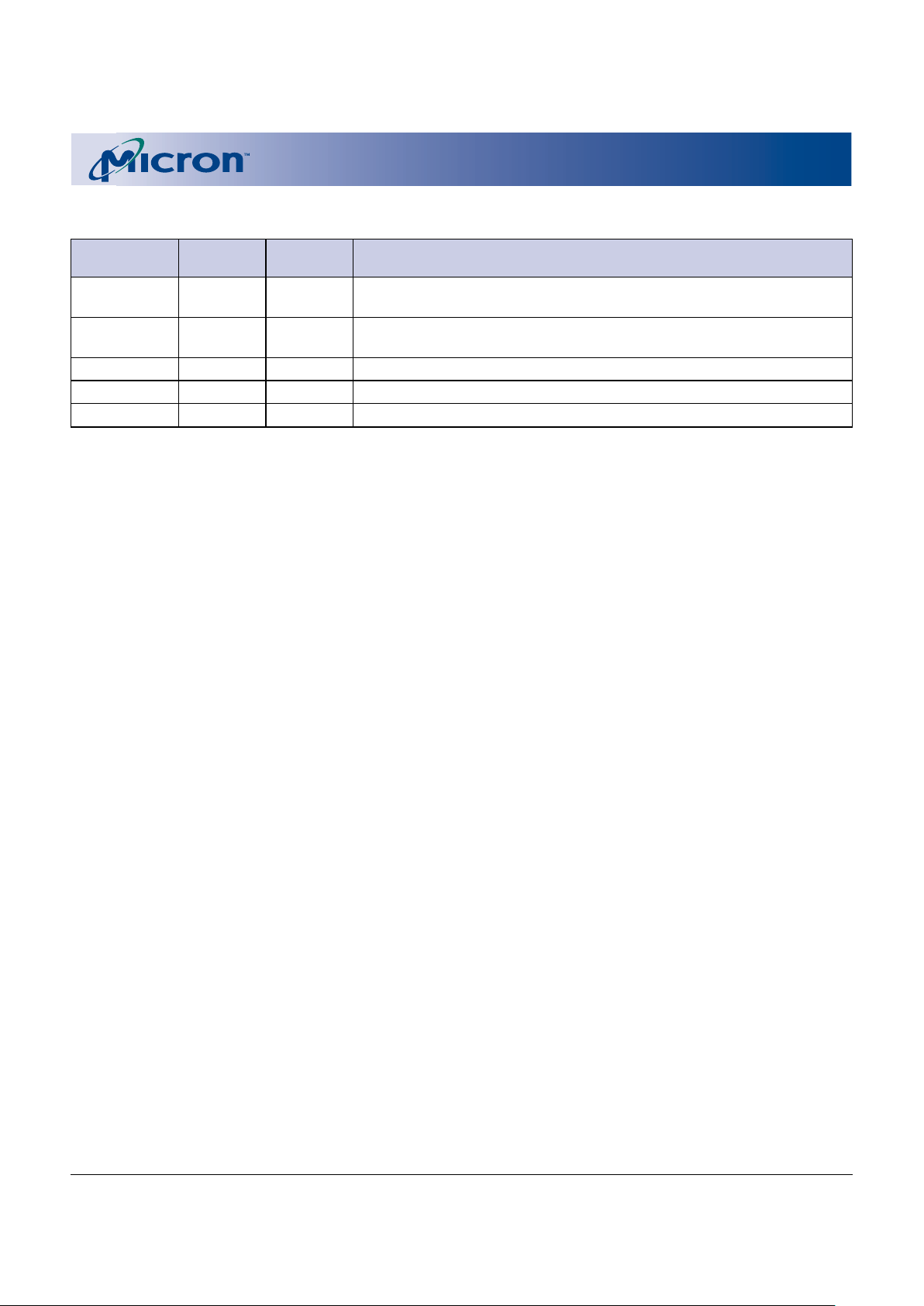
8
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
BALL DESCRIPTIONS (continued)
58-BALL FBGA
NUMBERS SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
A4, G4 V
CC
Supply Device Power Supply: [1.70V–1.90V (MT28F322D18) or 1.80V–2.20V
(MT28F322D20)] Supplies power for device operation.
E1, G6 V
CC
Q Supply I/O Power Supply: [1.70V–1.90V (MT28F322D18) or 1.80V–2.25V
(MT28F322D20)] Supplies power for input/output buffers.
G2, G8 VSSQ Supply I/O Ground. Do not float any ground ball.
A3, F1 V
SS
Supply Do not float any ground ball.
C3, D7 – – Contact ball is not physically present.
Page 9
9
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
COMMAND STATE MACHINE (CSM)
Commands are issued to the command state machine (CSM) using standard microprocessor write timings. The CSM acts as an interface between external
microprocessors and the internal write state machine
(WSM). The available commands are listed in Table 3,
their definitions are given in Table 4, and their descriptions in Table 5. Program and erase algorithms are
automated by an on-chip WSM. (For more specific
information about the CSM transition states, see Micron
technical note TN-28-33, “Command State Machine Description and Command Definition.”
Once a valid PROGRAM/ERASE command is entered,
the WSM executes the appropriate algorithm, which generates the necessary timing signals to control the device
internally to accomplish the requested operation. A command is valid only if the exact sequence of WRITEs is
completed. After the WSM completes its task, the WSM
status bit (SR7) (see Table 7) is set to a logic HIGH level (1),
allowing the CSM to respond to the full command set
again.
OPERATIONS
Device operations are selected by entering a standard
JEDEC 8-bit command code with conventional microprocessor timings into an on-chip CSM through I/Os
DQ0–DQ7. The number of bus cycles required to activate
a command is typically one or two. The first operation is
always a WRITE. Control signals CE#, ADV#, and WE#
must be at a logic LOW level (VIL), and OE# and RST#
must be at logic HIGH (VIH). The second operation, when
needed, can be a WRITE or a READ depending upon the
command. During a READ operation, control signals
CE#, ADV#, and OE# must be at a logic LOW level (VIL),
and WE# and RST# must be at logic HIGH (VIH).
Table 6 illustrates the bus operations for all the modes:
write, read, reset, standby, and output disable.
When the device is powered up, internal reset circuitry initializes the chip to a read array mode of operation. Changing the mode of operation requires that a
command code be entered into the CSM. For each one of
the two memory partitions, an on-chip status register is
available. These two registers allow the progress of the
various operations that can take place on a memory bank
to be monitored. One of the two status registers is interrogated by entering a READ STATUS REGISTER command onto the CSM (cycle 1), specifying an address within
the memory partition boundary, and reading the register
data on I/Os DQ0–DQ7 (cycle 2). Status register bits SR0SR7 correspond to DQ0–DQ7 (see Table 7).
COMMAND DEFINITION
Once a specific command code has been entered, the
WSM executes an internal algorithm, generating the necessary timing signals to program, erase, and verify data.
See Table 4 for the CSM command definitions and data
for each of the bus cycles.
STATUS REGISTER
The status register allows the user to determine
whether the state of a PROGRAM/ERASE operation is
pending or complete. The status register is monitored by
toggling OE# and CE# and reading the resulting status
code on I/Os DQ0–DQ7. The high-order I/Os (DQ8–DQ15)
Table 3
Command State Machine Codes For Device Mode Selection
COMMAND DQ0–DQ7 CODE ON DEVICE MODE
40h/10h Program setup/alternate program setup
20h Block erase setup
50h Clear status register
60h Protection configuration setup
60h Set read configuration register
70h Read status register
90h Read protection configuration register
98h Read query
B0h Program/erase suspend
C0h Protection register program/lock
D0h Program/erase resume – erase confirm
FFh Read array
Page 10
10
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
Table 4
Command Definitions
FIRST BUS CYCLE SECOND BUS CYCLE
COMMAND OPERATION ADDRESS1DATA OPERATION ADDRESS1DATA
1
READ ARRAY WRITE WA FFh
READ PROTECTION CONFIGURATION REGISTER WRITE IA 90h READ IA ID
READ STATUS REGISTER WRITE BA 70h READ X SRD
CLEAR STATUS REGISTER WRITE BA 50h
READ QUERY WRITE QA 98h READ QA QD
BLOCK ERASE SETUP WRITE BA 20h WRITE BA D0h
PROGRAM SETUP/ALTERNATE PROGRAM SETUP WRITE WA 40h/10h WRITE WA WD
PROGRAM/ERASE SUSPEND WRITE BA B0h
PROGRAM/ERASE RESUME – ERASE CONFIRM WRITE BA D0h
LOCK BLOCK WRITE BA 60h WRITE BA 01h
UNLOCK BLOCK WRITE BA 60h WRITE BA D0h
LOCK DOWN BLOCK WRITE BA 60h WRITE BA 2Fh
PROTECTION REGISTER PROGRAM WRITE PA C0h WRITE PA PD
PROTECTION REGISTER LOCK WRITE LPA C0h WRITE LPA FFFDh
SET READ CONFIGURATION REGISTER WRITE RCD 60h WRITE RCD 03h
are set to 00h internally, so only the low-order I/Os
(DQ0–DQ7) need to be interpreted. Address lines select
the status register pertinent to the selected memory
partition.
Register data is updated and latched on the falling
edge of ADV# or rising (falling) CLK when ADV# is LOW
during synchronous burst mode or on the falling edge of
OE# or CE#, whichever occurs last. Latching the data
prevents errors from occurring if the register input
changes during a status register monitoring.
The status register provides the internal state of the
WSM to the external microprocessor. During periods
when the WSM is active, the status register can be polled
to determine the WSM status. Table 7 defines the status
register bits.
After monitoring the status register during a PROGRAM/ERASE operation, the data appearing on
DQ0–DQ7 remains as status register data until a new
command is issued to the CSM. To return the device to
other modes of operation, a new command must be
issued to the CSM.
COMMAND STATE MACHINE
OPERATIONS
The CSM decodes instructions for read array, read
protection configuration register, read query, read status
register, clear status register, program, erase, erase suspend, erase resume, program suspend, program resume,
lock block, unlock block and lock down block, chip protection program, and set read configuration register. The
8-bit command code is input to the device on DQ0–DQ7
(see Table 3 for CSM codes and Table 4 for command
definitions). During a PROGRAM or ERASE cycle, the
CSM informs the WSM that a PROGRAM or ERASE cycle
has been requested.
During a PROGRAM cycle, the WSM controls the program sequences and the CSM responds to a PROGRAM
SUSPEND command only.
NOTE: 1. BA: Address within the block
IA: Identification code address
ID: Identification code data
LPA: Lock protection register address
PA: Protection register address
PD: Data to be written at the location PA
QA: Query code address
QD: Query code data
RCD: Data to be written in the read configuration register
SRD: Data read from the status register
WA: Word address of memory location to be written, or read
WD: Data to be written at the location WA
X: “Don’t Care”
Page 11
11
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
Table 5
Command Descriptions
CODE DEVICE MODE BUS CYCLE DESCRIPTION
10h Alt. Program Setup First Operates the same as PROGRAM SETUP command
20h Erase Setup First Prepares the CSM for the ERASE CONFIRM command. If the next
command is not an ERASE CONFIRM command, the command will be
ignored, and the bank will go to read status mode and wait for
another command.
40h Program Setup First A two-cycle command: The first cycle prepares for a PROGRAM
operation, and the second cycle latches addresses and data and
initiates the WSM to execute the program algorithm. The flash outputs
status register data on the rising edge of ADV#, or on the rising clock
edge when ADV# is LOW during synchronous burst mode, or on the
falling edge of OE# or CE#, whichever occurs first.
50h Clear Status First The WSM can set the block lock status (SR1), VPP status (SR3), program
Register status (SR4), and erase status (SR5) bits in the status register to “1,” but
it cannot clear them to “0.” Issuing this command clears those bits to
“0.”
60h Protection First Prepares the CSM for changes to the block locking status. If the next
Configuration command is not BLOCK UNLOCK, BLOCK LOCK or BLOCK LOCK DOWN
Setup the command will be ignored, and the device will go to read status
mode.
Set Read First Puts the device into the set read configuration mode so that it will
Configuration be possible to set the option bits related to burst read mode.
Register
70h Read Status First This command places the device into a read status register mode.
Register Reading the device will output the contents of the status register for
the addressed bank. The device will automatically enter this mode for
the addressed bank after a PROGRAM or ERASE operation has been
initiated.
90h Read Protection First Puts the device into the read protection configuration mode so that
Configuration reading the device will output the manufacturer/device codes, block
lock status, protection register, or protection register lock status.
98h Read Query First Puts the device into the read query mode so that reading the device
will output common flash interface information.
B0h Program/Erase First Issuing this command will suspend the currently executing PROGRAM/
Suspend ERASE operation. The status register will indicate when the
operation has been successfully suspended by setting either the
program suspend (SR2) or erase suspend (SR6), and the WSM status bit
(SR7) to a “1” (ready). The WSM will continue to idle in the suspend
state, regardless of the state of all input control signals except RST#,
which will immediately shut down the WSM and the remainder of the
chip if RST# is driven to VIL.
C0h Program Device First Writes a specific code into the device protection register.
Protection Register
Lock Device First Locks the device protection register; data can no longer be changed.
Protection Register
(continued on next page)
Page 12
12
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
Table 5
Command Descriptions (continued)
CODE DEVICE MODE BUS CYCLE DESCRIPTION
D0h Erase Confirm Second If the previous command was an ERASE SETUP command, then the
CSM will close the address and data latches, and it will begin erasing
the block indicated on the address pins. During programming/erase,
the device will respond only to the READ STATUS REGISTER, PROGRAM
SUSPEND, or ERASE SUSPEND commands. It will output status register
data on the rising edge of ADV#, or on the rising clock edge when
ADV# is LOW during synchronous burst mode, or on the falling edge
of OE# or CE#, whichever occurs last.
Program/Erase First If a PROGRAM or ERASE operation was previously suspended, this
Resume command will resume the operation.
FFh Read Array First During read array mode, array data will be output on the data bus.
01h Lock Block Second If the previous command was PROTECTION CONFIGURATION SETUP,
the CSM will latch the address and lock the block indicated on the
address bus.
03h Read Configuration Second If the previous command was SET READ CONFIGURATION REGISTER,
Register Data the configuration bits presented on the address bus will be stored into
the read configuration register.
2Fh Lock Down Second If the previous command was PROTECTION CONFIGURATION SETUP,
the CSM will latch the address and lock down the block indicated on
the address bus.
D0h Unlock Block Second If the previous command was PROTECTION CONFIGURATION SETUP,
the CSM will latch the address and unlock the block indicated on the
address bus. If the block had been previously set to lock down, this
operation will have no effect.
00h Invalid/Reserved Unassigned command that should not be used.
Page 13

13
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
ister, the protection register, and PR lock status. Two bus
cycles are required for this operation: the chip identification data is read by entering the command code 90h on
DQ0–DQ7 to the bank containing address 00h and the
identification code address on the address lines. Control
signals CE#, ADV#, and OE# must be at a logic LOW level
(VIL), and WE# and RST# must be at a logic HIGH level
(VIH) to read data from the protection configuration register. Data is available on DQ0–DQ15. After data is read
from the protection configuration register, the READ
ARRAY command, FFh, must be issued to the bank containing address 00h prior to issuing other commands. See
Table 12 for further details.
READ QUERY
The read query mode outputs common flash interface
(CFI) data when the device is read (see Table 16). Two bus
cycles are required for this operation. It is possible to
access the query by writing the read query command
code 98h on DQ0–DQ7 to the bank containing address
0h. Control signals CE#, ADV#, and OE# must be at a logic
LOW level (VIL) and WE# and RST# must be at a logic
HIGH level (VIH) to read data from the query. The CFI data
structure contains information such as block size, density, command set, and electrical specifications. To return to read array mode, write the read array command
code FFh on DQ0–DQ7.
READ STATUS REGISTER
The status register is read by entering the command
code 70h on DQ0–DQ7. Two bus cycles are required for
this operation: one to enter the command code and a
second to read the status register. The address for both
cycles must be in the same partition. In a READ cycle, the
address is latched on the rising edge of the ADV# signal.
Register data is updated and latched on the falling edge of
ADV# or rising (falling) CLK when ADV# is LOW during
burst mode, or on the falling edge of OE# or CE#, whichever occurs last.
During an ERASE cycle, the CSM responds to an ERASE
SUSPEND command only. When the WSM has completed its task, the WSM status bit (SR7) is set to a logic
HIGH level and the CSM responds to the full command
set. The CSM stays in the current command state until
the microprocessor issues another command.
The WSM successfully initiates an ERASE or PROGRAM operation only when VPP is within its correct voltage range.
CLEAR STATUS REGISTER
The internal circuitry can set, but not clear, the block
lock status bit (SR1), the VPP status bit (SR3), the program
status bit (SR4), and the erase status bit (SR5) of the status
register. The CLEAR STATUS REGISTER command (50h)
allows the external microprocessor to clear these status
bits and synchronize to the internal operations. When
the status bits are cleared, the device returns to the read
array mode.
READ OPERATIONS
The following READ operations are available: READ
ARRAY, READ PROTECTION CONFIGURATION REGISTER, READ QUERY and READ STATUS REGISTER.
READ ARRAY
The array is read by entering the command code FFh
on DQ0–DQ7. Control signals CE#, ADV#, and OE# must
be at a logic LOW level (VIL) and WE# and RST# must be
at a logic HIGH level (VIH) to read data from the array.
Data is available on DQ0–DQ15. Any valid address within
any of the blocks selects that address and allows data to
be read from that address. Upon initial power-up or
device reset, the device defaults to the read array mode.
READ PROTECTION CONFIGURATION DATA
The read protection configuration mode outputs five
types of information: the manufacturer/device identifier, the block locking status, the read configuration reg-
Page 14
14
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
STATUS
BIT # STATUS REGISTER BIT DESCRIPTION
SR7 WRITE STATE MACHINE STATUS (WSMS) Check write state machine bit first to determine word
1 = Ready program or block erase completion, before checking program
0 = Busy or erase status bits.
SR6 ERASE SUSPEND STATUS (ESS) When ERASE SUSPEND is issued, WSM halts execution and
1 = BLOCK ERASE Suspended sets both WSMS and ESS bits to “1.” ESS bit remains set to “1”
0 = BLOCK ERASE in until an ERASE RESUME command is issued.
Progress/Completed
SR5 ERASE STATUS (ES) When this bit is set to “1,” WSM has applied the maximum
1 = Error in Block Erasure number of erase pulses to the block and is still unable to
0 = Successful BLOCK ERASE verify successful block erasure.
SR4 PROGRAM STATUS (PS) When this bit is set to “1,” WSM has attempted but failed to
1 = Error in PROGRAM program a word.
0 = Successful PROGRAM
SR3 VPP STATUS (VPPS) The VPP status bit does not provide continuous indication of
1 = VPP Low Detect, Operation the VPP level. The WSM interrogates the VPP level only after
Abort the program or erase command sequences have been entered
0 = VPP = OK and informs the system if VPP < 0.9V. The VPP level is also
checked before the PROGRAM/ERASE is verified by the WSM.
SR2 PROGRAM SUSPEND STATUS (PSS) When PROGRAM SUSPEND is issued, WSM halts execution and
1 = PROGRAM Suspended sets both WSMS and PSS bits to “1.” PSS bit remains set to “1”
0 = PROGRAM in Progress/Completed until a PROGRAM RESUME command is issued.
SR1 BLOCK LOCK STATUS (BLS) If a PROGRAM or ERASE operation is attempted to one of the
1 = PROGRAM/ERASE Attempted on a locked blocks, this is set by the WSM. The operation specified
Locked Block; Operation Aborted is aborted and the device is returned to read status mode.
0 = No Operation to Locked Blocks
SR0 RESERVED FOR FUTURE ENHANCEMENT This bit is reserved for future use.
Table 7
Status Register Bit Definitions
WSMS ESS ES PS VPPS PSS BLS R
76543210
Table 6
Bus Operations
MODE RST# CE# ADV# OE# WE# ADDRESS DQ0–DQ15
Read (array, status registers, V
IH VIL VIL VIL VIH XDOUT
device identification register, or
query)
Standby VIH VIH XXXXHigh-Z
Output disable VIH VIH XXXXHigh-Z
Reset VIL XXXXXHigh-Z
Write VIH VIL VIL VIH VIL XDIN
Page 15

15
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
PROGRAMMING OPERATIONS
There are two CSM commands for programming:
PROGRAM SETUP and ALTERNATE PROGRAM SETUP
(see Table 3).
After the desired command code is entered (10h or
40h command code on DQ0–DQ7), the WSM takes over
and correctly sequences the device to complete the PROGRAM operation. Monitoring of the WRITE operation is
possible through the status register (see the Status Register section). During this time, the CSM responds only to
a PROGRAM SUSPEND command until the PROGRAM
operation has been completed, after which all commands
to the CSM become valid again. The PROGRAM operation can be suspended by issuing a PROGRAM SUSPEND
command (B0h). Once the WSM has reached the suspend state, it allows the CSM to respond only to READ
ARRAY, READ STATUS REGISTER, READ PROTECTION
CONFIGURATION, READ QUERY, PROGRAM SETUP, or
PROGRAM RESUME. During the PROGRAM SUSPEND
operation, array data should be read from an address
other than the one being programmed. To resume the
PROGRAM operation, a PROGRAM RESUME command
(D0h) must be issued to cause the CSM to clear the
suspend state previously set (see Figure 4 for programming operation and Figure 5 for program suspend and
program resume).
Taking RST# to VIL during programming aborts the
PROGRAM operation. During programming, VPP must
remain in the appropriate VPP voltage range as shown in
the recommended operating conditions table.
ERASE OPERATIONS
An ERASE operation must be used to initialize all bits
in an array block to “1s.” After BLOCK ERASE CONFIRM
is issued, the CSM responds only to an ERASE SUSPEND
command until the WSM completes its task.
Block erasure inside the memory array sets all bits
within the address block to logic 1s. Erase is accomplished only by blocks; data at single address locations
within the array cannot be erased individually. The block
to be erased is selected by using any valid address within
that block. Block erasure is initiated by a command sequence to the CSM: BLOCK ERASE SETUP (20h) followed
by BLOCK ERASE CONFIRM (D0h) (see Figure 6). A twocommand erase sequence protects against accidental
erasure of memory contents.
When the BLOCK ERASE CONFIRM command is complete, the WSM automatically executes a sequence of
events to complete the block erasure. During this sequence, the block is programmed with logic 0s, data is
verified, all bits in the block are erased to logic 1 state, and
finally verification is performed to ensure that all bits are
correctly erased. The ERASE operation may be monitored through the status register (see the Status Register
section).
During the execution of an ERASE operation, the
ERASE SUSPEND command (B0h) can be entered to direct the WSM to suspend the ERASE operation. Once the
WSM has reached the suspend state, it allows the CSM to
respond only to the READ ARRAY, READ STATUS REGISTER, READ QUERY, READ CHIP PROTECTION CONFIGURATION, PROGRAM SETUP, PROGRAM RESUME,
ERASE RESUME and LOCK SETUP (see the Block Locking
section). During the ERASE SUSPEND operation, array
data must be read from a block other than the one being
erased. To resume the ERASE operation, an ERASE RESUME command (D0h) must be issued to cause the CSM
to clear the suspend state previously set (see Figure 7). It
is also possible to suspend an ERASE in any bank and
initiate a WRITE to another block in the same bank. After
the completion of a WRITE, an ERASE can be resumed by
writing an ERASE RESUME command.
Page 16

16
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
YES
NO
Full Status Register
Check (optional)
NO
YES
PROGRAM
SUSPEND?
SR7 = 1?
Issue PROGRAM SETUP
Command and
Word Address
Start
Word Program Passed
VPP Range Error
Word Program Failed
FULL STATUS REGISTER CHECK FLOW
Read Status Register
Bits
Issue Word Address
and Word Data
PROGRAM
SUSPEND Loop
1
YES
NO
SR1 = 0?
YES
NO
SR3 = 0?
YES
NO
SR4 = 0?
Word Program
Completed
Read Status Register
Bits
PROGRAM Attempted
on a Locked Block
Figure 4
Automated Word Programming
Flowchart
NOTE: 1. Full status register check can be done after each word or after a sequence of words.
2. SR3 must be cleared before attempting additional PROGRAM/ERASE operations.
3. SR4 is cleared only by the CLEAR STATUS REGISTER command, but it does not prevent additional program operation
attempts.
BUS
OPERATION COMMAND COMMENTS
WRITE WRITE Data = 40h or 10h
PROGRAM Addr = Address of word to be
SETUP programmed
WRITE WRITE Data = Word to be
DATA programmed
Addr = Address of word to be
programmed
READ Status register data
Toggle OE# or CE# to
update status register.
Standby Check SR7
1 = Ready, 0 = Busy
Repeat for subsequent words.
Write FFh after the last word programming operation
to reset the device to read array mode.
BUS
OPERATION COMMAND COMMENTS
Standby Check SR1
1 = Detect locked block
Standby Check SR3
2
1 = Detect VPP LOW
Standby Check SR4
3
1 = Word program error
Page 17

17
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
Issue READ ARRAY
Command
PROGRAM
Complete
Finished
Reading
?
Issue PROGRAM
RESUME Command
YES
YES
NO
NO
SR2 = 1?
Start
PROGRAM Resumed
Read Status Register
Bits
Issue PROGRAM
SUSPEND Command
YES
NO
SR7 = 1?
Figure 5
PROGRAM SUSPEND/
PROGRAM RESUME Flowchart
BUS
OPERATION COMMAND COMMENTS
WRITE PROGRAM Data = B0h
SUSPEND
READ Status register data
Toggle OE# or CE# to update
status register.
Standby Check SR7
1 = Ready
Standby Check SR2
1 = Suspended
WRITE READ Data = FFh
ARRAY
READ Read data from block other
than that being programmed
WRITE PROGRAM Data = D0h
RESUME
Page 18

18
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
YES
NO
Full Status Register
Check (optional)
NO
YES
ERASE
SUSPEND?
SR 7 = 1?
Start
BLOCK ERASE Passed
VPP Range Error
BLOCK ERASE Failed
FULL STATUS REGISTER CHECK FLOW
Read Status Register
Bits
ERASE
SUSPEND Loop
1
YES
NO
SR1 = 0?
YES
NO
YES
NO
BLOCK ERASE
Completed
Read Status Register
Bits
ERASE Attempted
on a Locked Block
SR3 = 0?
SR5 = 0?
Issue ERASE SETUP
Command and
Block Address
Issue BLOCK ERASE
CONFIRM Command
and Block Address
Figure 6
BLOCK ERASE Flowchart
NOTE: 1. Full status register check can be done after each block or after a sequence of blocks.
2. SR3 must be cleared before attempting additional PROGRAM/ERASE operations.
3. SR5 is cleared only by the CLEAR STATUS REGISTER command in cases where multiple blocks are erased before full
status is checked.
BUS
OPERATION COMMAND COMMENTS
WRITE WRITE Data = 20h
ERASE Block Addr = Address
SETUP within block to be erased
WRITE ERASE Data = D0h
Block Addr = Address
within block to be erased
READ Status register data
Toggle OE# or CE# to
update status register.
Standby Check SR7
1 = Ready, 0 = Busy
Repeat for subsequent blocks.
Write FFh after the last BLOCK ERASE operation to
reset the device to read array mode.
BUS
OPERATION COMMAND COMMENTS
Standby Check SR1
1 = Detect locked block
Standby Check SR3
2
1 = Detect VPP block
Standby Check SR5
3
1 = BLOCK ERASE error
Page 19

19
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
READ
PROGRAM
Issue READ ARRAY
Command
PROGRAM
Loop
ERASE
Complete
READ or
PROGRAM?
YES
NO
Issue ERASE
RESUME Command
READ or
PROGRAM
Complete?
YES
NO
SR6 = 1?
Start
ERASE Continued
Read Status Register
Bits
Issue ERASE
SUSPEND Command
2
(Note 1)
YES
NO
SR7 = 1?
Figure 7
ERASE SUSPEND/ERASE RESUME
Flowchart
NOTE: 1. See Word Programming Flowchart for complete programming procedure.
2. See BLOCK ERASE Flowchart for complete erasure procedure.
BUS
OPERATION COMMAND COMMENTS
WRITE ERASE Data = B0h
SUSPEND
READ Status register data
Toggle OE# or CE# to
update status register.
Standby Check SR7
1 = Ready
Standby Check SR6
1 = Suspended
WRITE READ Data = FFh
ARRAY
READ Read data from block
other than that being
erased.
WRITE ERASE Data = D0h
RESUME
Page 20

20
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
Figure 8
READ-While-WRITE Concurrency
Bank a
1 - Erasing/writing to bank a
2 - Erasing in bank a can be
suspended, and a WRITE to
another block in bank a
can be initiated.
3 - After the WRITE in that block
is complete, an ERASE can
be resumed by writing an
ERASE RESUME command.
1 - Reading bank a
Bank b
1 - Reading from bank b
1 - Erasing/writing to bank b
2 - Erasing in bank b can be
suspended, and a WRITE to
another block in bank b
can be initiated.
3 - After the WRITE in that block
is complete, an ERASE can
be resumed by writing an
ERASE RESUME command.
READ-WHILE-WRITE/ERASE
CONCURRENCY
It is possible for the device to read from one bank
while erasing/writing to another bank. Once a bank enters the WRITE/ERASE operation, the other bank automatically enters read array mode. For example, during a
READ CONCURRENCY operation, if a PROGRAM/ERASE
command is issued in bank a, then bank a changes to the
read status mode and bank b defaults to the read array
mode. The device will read from bank b if the latched
address resides in bank b (see Figure 8). Similarly, if a
PROGRAM/ERASE command is issued in bank b, then
bank b changes to read status mode and bank a defaults
to read array mode. When returning to bank a, the device
will read PROGRAM/ERASE status if the latched address
resides in bank a. A correct bank address must be
specified to read status register after returning from concurrent read in the other bank.
When reading the CFI or the chip protection register,
concurrent operation is not allowed on the top boot
device. Concurrent READ of the CFI or the chip protection register is only allowed when a PROGRAM or ERASE
operation is performed on bank b on the bottom boot
device. For a bottom boot device, reading of the CFI table
or the chip protection register is only allowed if bank b is
in read array mode. For a top boot device, reading of the
CFI table or the chip protection register is only allowed if
bank a is in read array mode.
READ CONFIGURATION REGISTER (RCR)
MODE
The SET READ CONFIGURATION REGISTER command is a WRITE operation to the read configuration
register (RCR). It is a two-cycle command sequence. Read
configuration setup is written, followed by a second write
that specifies the data to be written to the read configuration register. The data is placed on the address bus
A0–A15, and it is latched on the rising edge of ADV#, CE#,
or WE#, whichever occurs first. The read configuration
provides the read mode (burst, synchronous, or asynchronous), burst order, latency counter, and burst length.
After executing this command, the device returns to read
array mode.
READ CONFIGURATION
The device supports three read configurations: asynchronous, synchronous burst mode, and page mode. The
bit RCR15 (see Table 9) in the read configuration register
sets the read configuration. Asynchronous random mode
is the default read mode.
At power-up, the RCR is set to BBCFh.
Status registers and the device identification register
support asynchronous and single synchronous READ
operations only.
Page 21

21
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
BIT # DESCRIPTION FUNCTION
15 Read Mode (RM) 0 = Synchronous Burst Access Mode
1 = Asynchronous/Page Access Mode (Default)
14 Reserved Default = 0
13-11 Latency Counter (LC) Sets the number of clock cycles before valid data out:
000 = Code 0 - reserved
001 = Code 1 - reserved
010 = Code 2
011 = Code 3
100 = Code 4
101 = Code 5 - reserved
110 = Code 6 - reserved
111 = Code 7 - reserved (Default)
10 Reserved Default = 0
9 Hold Data Out (HDO) Sets the data output configuration:
0 = Hold data for one clock
1 = Hold data for two clocks (Default)
8 Wait Configuration (WC) Controls the behavior of the WAIT# output signal:
0 = WAIT# asserted during delay
1 = WAIT# asserted one data cycle before delay (Default)
7 Burst Sequence (BS) Specifies the order in which data is addressed in synchronous burst
mode:
0 = Interleaved
1 = Linear (Default)
6 Clock Configuration (CC) Defines the clock edge on which the BURST operation starts and
data is referenced:
0 = Falling edge
1 = Rising edge (Default)
5-4 Reserved Default = 0
3 Burst Wrap (BW) 0 = Burst wraps within the burst length
1 = Burst no wrap (Default)
2-0 Burst Length (BL) Sets the number of words the device will output in burst mode:
001 = 4 words
010 = 8 words
111 = Continuous burst (Default)
Table 8
Read Configuration Register
RM R LC2 LC1 LC0 R HDO WC
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
BS CC R R BW BL2 BL1 BL0
76543210
Page 22

22
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
LATENCY COUNTER
The latency counter provides the number of clocks
that must elapse after ADV# is set active before data will
be available. This value depends on the input clock fre-
Burst CPU/
Wait State Logic
DQ0–DQ15
WAIT#
MT28F322D18
MT28F322D18
DQ0–DQ15
WAIT#
READY #
DATA
.
.
Bus data
Wired OR
Figure 11
Wired OR WAIT# Configuration
Figure 9
Latency Counter
CLK
DQ0–DQ15
Hold
Data
1 CLK
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
DQ0–DQ15
Hold
Data
2 CLK
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
A0–A20
V
IH
V
IL
ADV#
V
IH
V
IL
DQ0–DQ15
CLK
V
IH
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL
Code 2
Code 3
Code 4
DQ0–DQ15
V
OH
V
OL
DQ0–DQ15
V
OH
V
OL
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
ADDRESS
UNDEFINED
Figure 10
Hold Data Output Configuration
quency. See Table 9 for the specific input clock frequency
configuration code. See Figure 9 also.
Table 9
Clock Frequency vs. First Access Latency
MAX LATENCY CLK CYCLES SYNC
FREQUENCY PERIOD CONFIGURATION FOR FIRST ACCESS
(MHz) (ns) COUNTER DATA TIME (ns)
-705
20 50 2 3 150
30 33 3 4 132
54
1
18.5 4 5 92.5
-804
20 50 2 3 150
30 33 3 4 132
40 25 4 5 125
NOTE: 1. Maximum frequency for the MT28F322D18FH-705 device is 52 MHz.
Page 23

23
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
HOLD DATA OUTPUT CONFIGURATION
The hold data output configuration specifies for how
many clocks data will be held valid. (See Figure 10.)
WAIT# CONFIGURATION
The wait configuration bit, RCR8, sets the behavior of
the WAIT# output signal. The WAIT# signal can be active
during an output delay or one data cycle before delay
when continuous burst length is enabled. WAIT# = 1
indicates valid data when RCR8 = 0. WAIT# = 0 indicates
invalid data when RCR8 = 0. The setting of wait before or
wait during RCR8 will depend on the system and CPU
characteristic. If RCR3 = 1 (no wrap mode), then WAIT#
can also be enabled in a four- or eight-word burst if the
no-wrap burst crosses the first eight-word boundary.
A Flash controller (CPU) is able to use this output
signal to drive banks of the devices. An internal 1MΩ
pull-up resistor holds WAIT# = 1 and allows wired OR’ing
multiple bank configurations, as shown in Figure 11.
BURST SEQUENCE
The burst sequence specifies the address order of the
data in synchronous burst mode. It can be programmed
as either linear or interleaved burst order. Continuous
burst length only supports linear burst order. See Table
10 for more details.
Table 10
Sequence and Burst Length
STARTING NO 4-WORD 8-WORD CONTINUOUS
ADDRESS WRAP WRAP BURST LENGTH BURST LENGTH BURST
.
(DEC) RCR3 RCR3 LINEAR INTERLEAVED LINEAR INTERLEAVED LINEAR
0 0 0-1-2-3 0-1-2-3 0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7 0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7 0-1-2-3-4-5-6-…
1 0 1-2-3-0 1-0-3-2 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-0 1-0-3-2-5-4-7-6 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-…
2 0 2-3-0-1 2-3-0-1 2-3-4-5-6-7-0-1 2-3-0-1-6-7-4-5 2-3-4-5-6-7-8-…
3 0 3-0-1-2 3-2-1-0 3-4-5-6-7-0-1-2 3-2-1-0-7-6-5-4 3-4-5-6-7-8-9-…
4 0 4-5-6-7-0-1-2-3 4-5-6-7-0-1-2-3 4-5-6-7-8-9-10-…
5 0 5-6-7-0-1-2-3-4 5-4-7-6-1-0-3-2 5-6-7-8-9-10-11-…
6 0 6-7-0-1-2-3-4-5 6-7-4-5-2-3-0-1 6-7-8-9-10-11-12-…
7 0 7-0-1-2-3-4-5-6 7-6-5-4-3-2-1-0 6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-…
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14 0 14-15-16-17-18-19-20-..
15 0 15-16-17-18-19-20-21-..
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
0 1 0-1-2-3 NA 0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7 NA 0-1-2-3-4-5-6-…
1 1 1-2-3-4 NA 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8 NA 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-…
2 1 2-3-4-5 NA 2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9 NA 2-3-4-5-6-7-8-…
3 1 3-4-5-6 NA 3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10 NA 3-4-5-6-7-8-9-…
4 1 4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11 NA 4-5-6-7-8-9-10-…
51
5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12
NA 5-6-7-8-9-10-11…
61
6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13
NA 6-7-8-9-10-11-12…
71…
7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14
NA 7-8-9-10-11-12-13…
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
14 1 ... 14-15-16-17-18-19-20-…
15 1 15-16-17-18-19-20-21-…
Page 24

24
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
CLOCK CONFIGURATION
The clock configuration configures the starting burst
cycle, output data, and WAIT# signal to be asserted on the
rising or falling edge of the clock.
BURST WRAP
The burst wrap option, RCR3, signals if a four- or an
eight-word linear burst access wraps within the burst
length or whether it crosses the eight-word boundary. In
wrap mode (RCR3 = 0) the four- or eight-word access will
wrap within the four or eight words, respectively. In nowrap mode (RCR3 = 1), the device operates similarly to a
continuous burst. For example, in a four-word burst, nowrap mode, the possible linear burst sequences that do
not assert WAIT# are:
0-1-2-3 8-9-10-11
1-2-3-4 9-10-11-12
2-3-4-5 10-11-12-13
3-4-5-6 11-12-13-14
4-5-6-7 12-13-14-15
The worst-case delay is seen at the end of the eightword boundary: 7-8-9-10 and 15-16-17-18. In a fourword burst, wrap mode, no WAIT# is asserted, and the
possible wrap sequences are:
0-1-2-3 5-6-7-4
1-2-3-0 6-7-4-5
2-3-0-1 7-4-5-6
3-0-1-2 8-9-10-11
4-5-6-7 9-10-11-8 etc.
When the continuous burst option is selected, the internal address wraps to 000000h if the device is read past the
last address.
BURST LENGTH
The burst length defines the number of words the
device outputs. The device supports a burst length of four
or eight words. The device can also be set in continuous
burst mode. In this mode the device linearly outputs data
until the internal burst counter reaches the end of the
burstable address space. RCR2 sets the burst length.
CONTINUOUS BURST LENGTH
During continuous burst mode operation, the Flash
memory may have an output delay when the burst sequence crosses the first eight-word boundary. Also, in
four- or eight-word bursts with the burst wrap set to no
wrap (RCR3 = 1), the Flash memory may have an output
delay when the burst sequence crosses the first eightword boundary. The starting address dictates whether or
not a delay occurs. If the starting address is aligned with
an eight-word boundary, the delay is not seen. For a fourword burst, if the starting address is aligned with a fourword boundary, a delay is not seen. If the starting address
is at the end of an eight-word boundary, the output delay
is the maximum delay, equal to the latency counter
setting.
The delay happens only once during a continuous
burst access. If the burst never crosses an eight-word
boundary, the WAIT# is not asserted. The WAIT# informs
the system if this output delay occurs.
WAIT# SIGNAL IN BURST MODE
In the continuous burst mode or in the four- or eightword burst mode with no wrap (RCR3 = 1), the output
WAIT# informs the system when data is valid. When
WAIT# is asserted during delay (RCR8 = 0), WAIT# = 1
indicates valid data, and WAIT# = 0 indicates invalid
data. If RCR8 = 0, WAIT# is asserted on the same cycle on
which the delay occurs. If RCR8 = 1, WAIT# is asserted one
cycle before the delay occurs.
BLOCK LOCKING
The Flash devices provide a flexible locking scheme
that allows each block to be individually locked or unlocked with no latency.
The devices offer two-level protection for the blocks.
The first level allows software-only control of block locking (for data, which needs to be changed frequently),
while the second level requires hardware interaction before locking can be changed (code which does not require
frequent updates).
Control signals WP#, DQ1, and DQ0 define the state
of a block; for example, state [001] means WP# = 0, DQ1 =
0 and DQ0 = 1.
Table 11 defines all of the possible locking states.
NOTE: All blocks are software-locked upon comple-
tion of a power-up sequence.
LOCKED STATE
After a power-up sequence completion, or after a
reset sequence, all blocks are locked (states [001] or [101]).
This means full protection from alteration. Any PROGRAM or ERASE operations attempted on a locked block
will return an error on bit SR1 of the status register. The
status of a locked block can be changed to unlocked or
lock down using the appropriate software commands.
Writing the lock command sequence, 60h followed by
01h, can lock an unlocked block.
UNLOCKED STATE
Unlocked blocks (states [000], [100], [110]) can be
programmed or erased. All unlocked blocks return to the
locked state when the device is reset or powered down.
An unlocked block can be locked or locked down using
the appropriate software command sequence, 60h followed by D0h (see Table 4).
Page 25

25
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
LOCKED DOWN STATE
Blocks that are locked down (state [011]) are protected from PROGRAM and ERASE operations, but their
protection status cannot be changed using software commands alone. A locked or unlocked block can be locked
down by writing the lock down command sequence, 60h
followed by 2Fh. Locked down blocks revert to the locked
state when the device is reset or powered down.
The LOCK DOWN function is dependent on the WP#
input. When WP# = 0, blocks in lock down [011] are
protected from program, erase, and lock status changes.
When WP# = 1, the lock down function is disabled ([111]),
and locked down blocks can be individually unlocked by
a software command to the [110] state, where they can be
erased and programmed. These blocks can then be
relocked [111] and unlocked [110] as desired while WP#
remains HIGH. When WP# goes LOW, blocks that were
previously locked down return to the locked down state
[011] regardless of any changes made while WP# was
HIGH. Device reset or power-down resets all locks, including those in lock down, to locked state (see Table 12).
READING A BLOCK’S LOCK STATUS
The lock status of every block can be read in the read
device identification mode. To enter this mode, write 90h
to the bank containing address 00h. Subsequent READs
at block address +00002 will output the lock status of that
block. The lowest two outputs, DQ0 and DQ1, represent
the lock status. DQ0 indicates the block lock/unlock status and is set by the LOCK command and cleared by the
UNLOCK command. It is also automatically set when
entering lock down. DQ1 indicates lock down status and
is set by the LOCK DOWN command. It can only be
cleared by reset or power-down, not by software. Table
11 shows the locking state transition scheme. The READ
ARRAY command, FFh, must be issued to the bank containing address 00h prior to issuing other commands.
LOCKING OPERATIONS DURING ERASE SUSPEND
Changes to block lock status can be performed during
an ERASE SUSPEND by using the standard locking command sequences to unlock, lock, or lock down. This is
useful in the case when another block needs to be updated while an ERASE operation is in progress.
To change block locking during an ERASE operation,
first write the ERASE SUSPEND command (B0h), then
check the status register until it indicates that the ERASE
operation has been suspended. Next, write the desired
lock command sequence to block lock, and the lock status will be changed. After completing any desired LOCK,
READ, or PROGRAM operations, resume the ERASE operation with the ERASE RESUME command (D0h).
If a block is locked or locked down during an
ERASE SUSPEND operation on the same block, the locking status bits will be changed immediately. Then, when
the ERASE is resumed, the ERASE operation will complete.
A locking operation cannot be performed during a
PROGRAM SUSPEND.
Table 11
Block Locking State Transition
ERASE/PROG LOCK
WP# DQ1 DQ0 NAME ALLOWED LOCK UNLOCK DOWN
0 0 0 Unlocked Yes To [001] No Change To [011]
0 0 1 Locked (Default) No No Change To [000] To [011]
0 1 1 Lock Down No No Change No Change No Change
1 0 0 Unlocked Yes To [101] No Change To [111]
1 0 1 Locked No No Change To [100] To [111]
1 1 0 Lock Down Yes To [111] No Change To [111]
Disabled
1 1 1 Lock Down No No Change To [110] No Change
Disabled
Page 26

26
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
ITEM ADDRESS
2
DATA
Manufacturer Code (x16) 00000h 002Ch
Device Code 00001h
·
Top boot configuration 44B4h
·
Bottom boot configuration 44B5h
Block Lock Configuration XX002h Lock
·
Block is unlocked DQ0 = 0
·
Block is locked DQ0 = 1
·
Block is locked down DQ1 = 1
Read Configuration Register 00005h RCR
Chip Protection Register Lock 80h PR Lock
Chip Protection Register 1 81h–84h Factory Data
Chip Protection Register 2 85h–88h User Data
NOTE: 1. Other locations within the configuration address space are reserved by
Micron for future use.
2. “XX” specifies the block address of lock configuration.
CHIP PROTECTION REGISTER
A 128-bit chip protection register can be used to fulfill
the security considerations in the system (preventing the
device substitution).
The 128-bit security area is divided into two 64-bit
segments. The first 64 bits are programmed at the manufacturing site with a unique 64-bit unchangeable number. The other segment is left blank for customers to
program as desired. (See Figure 12).
READING THE CHIP PROTECTION REGISTER
The chip protection register is read in the device identification mode. To enter this mode, load the 90h command to the bank containing address 00h. Once in this
mode, READ cycles from addresses shown in Table 12
retrieve the specified information. To return to the read
array mode, write the READ ARRAY command (FFh). The
READ ARRAY command, FFh, must be issued to the bank
containing address 00h prior to issuing other commands.
PROGRAMMING THE CHIP PROTECTION REGISTER
The first 64 bits (PR1) of the protection register (addresses 81h–84h) are programmed with a unique identifier at the factory. DQ0 of the PR lock register (address
80h) is programmed to a “0” state, locking the first 64 bits
and preventing any further programming.
The second 64 bits (PR2) is a user area (addresses 85h–
88h), where the user can program any information into
this area as long as DQ1 of the PR lock register remains
unprogrammed. After DQ1 of the PR lock register is
programmed, no further programming is allowed on PR2.
The programming sequence is similar to array programming except that the PROTECTION REGISTER PROGRAMMING SETUP command (C0h) is issued instead of
an ARRAY PROGRAMMING SETUP command (40h), followed by the data to be programmed at addresses 85h–
88h.
To program the PR lock bit for PR2 (to prevent further
programming), use the above sequence on address 80h,
with data of FFFDh (DQ1 = 0).
Table 12
Chip Configuration Addressing
1
Figure 12
Protection Register Memory Map
4 Words
Factory-Programmed
4 Words
User-Programmed
PR Lock 0
88h
85h
84h
81h
80h
Page 27

27
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
ASYNCHRONOUS READ MODE
The asynchronous read mode is the default read configuration state. To use the device in an asynchronousonly application, ADV# and CLK must be tied to VSS and
WAIT# should be floated.
Toggling the address lines from A0 to A20, the access
is purely random (tAA).
The ADV# signal needs to be toggled to latch the
address, the CE# signal needs to go LOW, and the OE#
signal needs to go LOW. In this case the data is placed on
the data bus and the processor is ready to receive the
data.
SYNCHRONOUS BURST READ MODE
The burst read mode is used to achieve a faster data
rate than is possible with asynchronous read mode. The
rising edge of the clock CLK is used to latch the address
with CE# and ADV# LOW (see timing diagram: Single
Synchronous READ Operation). The burst read configuration is set in the read configuration register, where
frequency, data output, WAIT# signal, burst sequence,
clock, and burst length are configured setting the related
bits.
All blocks in both banks are burstable.
The BURST READ works across the bank boundary in
the following way:
1. In READ operation there is no bank boundary as far as
burst access is concerned. If, for example, burst starts
in bank a, the application can keep clocking until
bank boundary is reached and then read from bank b.
If the application keeps clocking beyond bank b last
location, then the internal counter restarts from bank
a first address. (See Figure 13.)
Bank a start address
bank boundary
Bank a
Bank b
0 00000h
Bank a end address 0 7FFFFh
Bank b start address 0 80000h
Bank b end address 1 FFFFFh
Figure 13
Bank Boundary Wrapping
(Bottom Boot Example)
2. If one bank is in program or erase mode and the
application starts burst access in that bank, then the
status register data is returned. The internal address
counter is incremented at every clock pulse.
3. If burst is started in one bank and the bank boundary
is crossed, and the other bank is in program or erase
mode, then the status register data is returned as the
first location of the bank. If the application keeps
clocking, the internal address counter gets
incremented at every clock cycle. If bank end is
crossed, then data from the other bank is returned as
shown in Figure 13.
Page 28

28
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
ASYNCHRONOUS PAGE READ MODE
After power-up or reset, the device operates in page
mode over the whole memory array. The page size can be
customized at the factory to four or eight words as required; but if no specification is made, the normal size is
eight words. The initial portion of the page mode cycle is
the same as the asynchronous access cycle. Holding CE#
LOW and toggling addresses A0–A2 allows random access of other words in the page.
VPP/VCC PROGRAM AND ERASE
VOLTAGES
The Flash devices provide in-system programming
and erase with VPP in the 0.9V–2.2V range (VPP1). The 12V
VPP (VPP2) mode programming is offered for compatibility with existing programming equipment.
The device can withstand 100,000 WRITE/ERASE operations when VPP = VPP1 or 100 WRITE/ERASE operations
and 10 cumulative hours when VPP = VPP2.
In addition to the flexible block locking, the VPP
programming voltage can be held LOW for absolute hardware write protection of all blocks in the Flash device.
When VPP is below VPPLK, any PROGRAM or ERASE operation will result in an error, prompting the corresponding
status register bit (SR3) to be set.
During WRITE and ERASE operations, the WSM monitors the VPP voltage level. WRITE/ERASE operations are
allowed only when VPP is within the ranges specified in
Table 13.
When VCC is below VLKO or VPP is below VPPLK, any
WRITE/ERASE operation will be prevented.
STANDBY MODE
ICC supply current is reduced by applying a logic HIGH
level on CE# and RST# to enter the standby mode. In the
standby mode, the outputs are High-Z. Applying a CMOS
logic HIGH level on CE# and RST# reduces the current to
ICC4 (MAX). If the device is deselected during an ERASE
operation or during programming, the device continues
to draw current until the operation is complete.
AUTOMATIC POWER SAVE MODE (APS)
Substantial power savings are realized during periods
when the array is not being read and the device is in the
active mode. During this time the device switches to the
automatic power save mode. When the device switches
to this mode, I
CC is reduced to a level comparable to ICC4.
Further power savings can be realized by applying a logic
HIGH level to CE# to place the device in standby mode.
The low level of power is maintained until another operation is initiated. In this mode, the I/Os retain the data
from the last memory address read until a new address is
read. This mode is entered automatically if no address or
control signals toggle.
DEVICE RESET
To correctly reset the Flash devices, the RST# signal
must be asserted (RST# = VIL) for a minimum of tRP. After
reset, the devices can be accessed for a READ operation
with a delayed access time of tRWH from the rising edge
of RST#. The circuitry used for generating the RST# signal
needs to be common with the rest of the system reset to
ensure that correct system initialization occurs. Please
refer to the timing diagram for further details.
POWER-UP SEQUENCE
The following power-up sequence is recommended
to properly initialize internal chip operations:
• At power-up, RST# should be kept at VIL for 2µs after
VCC reaches VCC (MIN).
•VCCQ should not come up before VCC.
•VPP should be kept at VIL to maximize data integrity.
When the power-up sequence is completed, RST#
should be brought to VIH. To ensure a proper power-up,
the rise time of RST (10%–90%) should be < 10µs.
Table 13
VPP Range (V)
MIN MAX
In System (VPP1) 0.9 2.25
In Factory (VPP2) 11.4 12.6
Page 29

29
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN MAX UNITS NOTES
Operating temperature
t
A -40 +85
o
C
VCC supply voltage (MT28F322D20) VCC 1.80 2.20 V
VCC supply voltage (MT28F322D18) VCC 1.70 1.90 V
I/O supply voltage (MT28F322D20) VCCQ 1.80 2.25 V
I/O supply voltage (MT28F322D18) VCCQ 1.70 1.90 V
VPP voltage VPP1 0.9 2.25 V
VPP in-factory programming voltage VPP2 11.4 12.6 V
Block erase cycling (VPP = VPP1) – 100,000 Cycles
Block erase cycling (VPP = VPP2) – 100 Cycles 1
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Voltage to Any Ball Except VCC and VPP
with Respect to VSS ........................ -0.5V to +2.45V
VPP Voltage (for BLOCK ERASE and PROGRAM
with Respect to V
SS) .................... -0.5V to +13.5V**
V
CC and VCCQ Supply Voltage
with Respect to VSS ........................ -0.3V to +2.45V
Output Short Circuit Current ................................ 100mA
Operating Temperature Range ................ -40oC to +85oC
Storage Temperature Range .................. -55oC to +125oC
Soldering Cycle ............................................. 260
o
C for 10s
*Stresses greater than those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation
of the device at these or any other conditions above those
indicated in the operational sections of this specification
is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect reliability.
**Maximum DC voltage on V
PP may overshoot to +13.5V
for periods < 20ns.
Figure 15
Output Load Circuit
I/O
14.5K
30pF
V
CC
V
SS
14.5K
OutputTest PointsInput
V
CC
V
SS
AC test inputs are driven at VCC for a logic 1 and VSS for a logic 0. Input timing begins at VCC/2, and output timing ends
at V
CCQ/2. Input rise and fall times (10% to 90%) < 5ns.
VCCQ/2VCC/2
Figure 14
AC Input/Output Reference Waveform
NOTE: 1. VPP = VPP2 is a maximum of 10 cumulative hours.
Page 30

30
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
DC CHARACTERISTICS
1
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN MAX UNITS NOTES
Input Low Voltage VIL 0 0.4 V 2
Input High Voltage VIH VCCQ - 0.4V VCCQV2
Output Low Voltage VOL – 0.10 V
IOL = 100µA
Output High Voltage VOH VCCQ - 0.1V – V
IOH = -100µA
VPP Lockout Voltage VPPLK – 0.4 V
VPP During PROGRAM/ERASE Operations VPP1 0.9 2.2 V
VPP2 11.4 12.6 V
VCC Program/Erase Lock Voltage VLKO 1–V
Input Leakage Current IL –1µA
Output Leakage Current IOZ –1µA
VCC Asynchronous Random Read, 70ns cycle ICC1 – 15 mA 3, 4
VCC Page Mode Read Current, 70ns/30ns cycle ICC2 – 5 mA 3, 4
VCC Burst Mode Read Current , 18.5ns cycle ICC3 –10mA4
VCC Standby Current ICC4 –50µA
VCC Program Current ICC5 –55mA
VCC Erase Current ICC6 –65mA
VCC Erase Suspend Current ICC7 –50µA5
VCC Program Suspend Current ICC8 –50µA5
Read-While-Write Current ICC9 –80mA
VPP Current IPP1
(Read, Standby, Erase Suspend, Program Suspend)
VPP ≤ VCC –1µA
VPP ≥ VCC – 200 µA
NOTE: 1. All currents are in RMS unless otherwise noted.
2. VIL may decrease to -0.4V and VIH may increase to VCCQ + 0.3V for durations not to exceed 20ns.
3. APS mode reduces ICC to approximately ICC4 levels.
4. Test conditions: Vcc = VCC (MAX), CE# = VIL, OE# = VIH. All other inputs = VIH or VIL.
5. ICC7 and ICC8 values are valid when the device is deselected. Any READ operation performed while in suspend mode
will have an additional current draw of suspend current (ICC7 or ICC8).
CAPACITANCE
(TA = +25ºC; f = 1 MHz)
PARAMETER/CONDITION SYMBOL TYP MAX UNITS
Input Capacitance C 7 12 pF
Output Capacitance COUT 912pF
Page 31

31
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
ASYNCHRONOUS READ CYCLE TIMING REQUIREMENTS
1
MT28F322D20 (V
CC = 1.80V–2.25V) and MT28F322D18 (VCC = 1.70V–1.90V)
-70 -80
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
Address setup to ADV# HIGH
t
AVS 10 10 ns
CE# LOW to ADV# HIGH
t
CVS 10 10 ns
READ cycle time
t
RC 70 80 ns
Address to output delay
t
AA 70 80 ns
CE# LOW to output delay
t
ACE 70 80 ns
ADV# LOW to output delay
t
AADV 70 80 ns
ADV# pulse width LOW
t
VP 10 10 ns
ADV# pulse width HIGH
t
VPH 10 10 ns
Address hold from ADV# HIGH
t
AVH 3 3 ns
Page address access
t
APA 30 30 ns
OE# LOW to output delay
t
AOE 25 30 ns
RST# HIGH to output delay
t
RWH 200 200 ns
CE# or OE# HIGH to output High-Z
t
OD 15 25 ns
Output hold from address, CE# or OE# change
t
OH 0 0 ns
NOTE: 1. See Figures 15 and 16 for timing requirements and load configuration.
Page 32

32
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
BURST READ CYCLE TIMING REQUIREMENTS
1
(MT28F322D20)
-705 -804
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
CLK period
t
CLK 18.5 25 ns
CLK HIGH (LOW) time
t
KP 5 7.5 ns
CLK fall (rise) time
t
KHKL 3 5 ns
Address valid setup to CLK
t
AKS 7 7 ns
ADV# LOW setup to CLK
t
VKS 7 7 ns
CE# LOW setup to CLK
t
CKS 9 13 ns
CLK to output delay
t
ACLK 15 20 ns
Output hold from CLK
t
KOH 3.5 5 ns
Address hold from CLK
t
AKH 10 10 ns
CLK to WAIT# delay
t
KHTL 15 20 ns
CE# HIGH between subsequent synchronous READs
t
CBPH 20 20 ns
NOTE: 1. See Figures 15 and 16 for timing requirements and load configuration.
BURST READ CYCLE TIMING REQUIREMENTS
1
(MT28F322D18)
-705 -804
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
CLK period
t
CLK 19.2 25 ns
CLK HIGH (LOW) time
t
KP 5 7.5 ns
CLK fall (rise) time
t
KHKL 3 5 ns
Address valid setup to CLK
t
AKS 7 7 ns
ADV# LOW setup to CLK
t
VKS 7 7 ns
CE# LOW setup to CLK
t
CKS 9 13 ns
CLK to output delay
t
ACLK 17 20 ns
Output hold from CLK
t
KOH 3.5 5 ns
Address hold from CLK
t
AKH 10 10 ns
CLK to WAIT# delay
t
KHTL 15 20 ns
CE# HIGH between subsequent synchronous READs
t
CBPH 20 20 ns
Page 33

33
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
WRITE CYCLE TIMING REQUIREMENTS
-70/-80
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN MAX UNITS
HIGH recovery to WE# going LOW
t
RS 150 ns
CE# setup to WE# going LOW
t
CS 0 ns
Write pulse width
t
WP 50 ns
ADV# pulse width
t
VP 10 ns
Data setup to WE# going HIGH
t
DS 50 ns
Address setup to WE# going HIGH
t
AS 50 ns
ADV# setup to WE# going HIGH
t
VS 50 ns
Address setup to ADV# going HIGH
t
AVS 10 ns
CE# hold from WE# HIGH
t
CH 0 ns
Data hold from WE# HIGH
t
DH 0 ns
Address hold from WE# HIGH
t
AH 1.5 ns
Address hold from ADV# going HIGH
t
AVH 3 ns
Write pulse width HIGH
t
WPH 30 ns
RST# pulse width
t
RP 100 ns
WP# setup to WE# going HIGH
t
RHS 0 ns
VPP setup to WE# going HIGH
t
VPS 200 ns
Write recovery before READ
t
WOS 50 ns
WP# hold from valid SRD
t
RHH 0 ns
VPP hold from valid SRD
t
VPPH 0 ns
WE# HIGH to data valid
t
WB
t
AA + 50 ns
ERASE AND PROGRAM TIMING REQUIREMENTS
-70/-80
PARAMETER TYP MAX UNITS
4KW block program time 40 800 ms
32KW block program time 320 6,400 ms
Word program time 8 10,000 µs
4KW block erase time 0.3 6 s
32KW block erase time 0.5 6 s
Program suspend latency 510µs
Erase suspend latency 520µs
Chip programming time (APA) 20 s
Page 34

34
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
SINGLE ASYNCHRONOUS READ OPERATION
VALID ADDRESS
UNDEFINED
t
OD
t
AA
t
ACE
t
OH
A0–A20
OE#
CE#
WE#
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
t
RC
WAIT#
V
OH
V
OL
t
RWH
ADV#
V
IH
V
IL
DQ0–DQ15
RST#
V
OH
V
OL
VALID OUTPUT
High-Z
t
AOE
READ TIMING PARAMETERS
MT28F322D20 (VCC = 1.80V–2.25V)
MT28F322D18 (VCC = 1.70V–1.90V)
-70 -80
SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
t
AA 70 80 ns
t
ACE 70 80 ns
t
AOE 25 30 ns
t
RC 70 80 ns
-70 -80
SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
t
RWH 200 200 ns
t
OD 15 25 ns
t
OH 0 0 ns
Page 35

35
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
ASYNCHRONOUS PAGE MODE READ OPERATION
VALID ADDRESS
VALID
ADDRESS
VALID
ADDRESS
VALID
ADDRESS
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
UNDEFINED
t
OD
t
AA
t
ACE
t
OH
t
APA
t
AOE
A0–A2
OE#
CE#
WE#
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
VALID ADDRESS
A3–A20
V
IH
V
IL
WAIT#
V
OH
V
OL
t
RWH
ADV#
V
IH
V
IL
DQ0–DQ15
RST#
V
OH
V
OL
High-Z
t
RC
READ TIMING PARAMETERS
MT28F322D20 (VCC = 1.80V–2.25V)
MT28F322D18 (VCC = 1.70V–1.90V)
-70 -80
SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
t
AA 70 80 ns
t
ACE 70 80 ns
t
APA 30 30 ns
t
AOE 25 30 ns
-70 -80
SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
t
RC 70 80 ns
t
RWH 200 200 ns
t
OD 15 25 ns
t
OH 0 0 ns
Page 36

36
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
SINGLE SYNCHRONOUS READ OPERATION
A0–A20
V
IH
V
IL
ADV#
V
IH
V
IL
CE#
V
IH
V
IL
OE#
V
IH
V
IL
WE#
V
IH
V
IL
WAIT#
DQ0–DQ15
V
OH
V
OL
CLK
V
IH
V
IL
UNDEFINED
V
OH
V
OL
t
AKS
t
VP
t
AOE
t
VKS
t
AKH
t
AA
t
AADV
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
ADDRESS
High-Z
t
VPH
t
AVH
t
KOH
t
OH
t
ACLK
t
OD
t
CVS
t
CKS
t
ACE
READ TIMING PARAMETERS
MT28F322D20 (VCC = 1.80V–2.25V)
-705 -804
SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
t
AKS 7 7 ns
t
VKS 7 7 ns
t
CKS 9 13 ns
t
ACLK 15 20 ns
t
KOH 3 5 ns
t
AKH 10 10 ns
t
CVS 10 10 ns
t
AA 70 80 ns
t
ACE 70 80 ns
t
AADV 70 80 ns
t
VP 10 10 ns
t
VPH 10 10 ns
t
AVH 3 3 ns
t
AOE 25 30 ns
t
OD 15 25 ns
t
OH 0 0 ns
READ TIMING PARAMETERS
MT28F322D18 (VCC = 1.70V–1.90V)
-705 -804
SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
t
AKS 7 7 ns
t
VKS 7 7 ns
t
CKS 9 13 ns
t
ACLK 17 20 ns
t
KOH 3 5 ns
t
AKH 10 10 ns
t
CVS 10 10 ns
t
AA 70 80 ns
t
ACE 70 80 ns
t
AADV 70 80 ns
t
VP 10 10 ns
t
VPH 10 10 ns
t
AVH 3 3 ns
t
AOE 25 30 ns
t
OD 15 25 ns
t
OH 0 0 ns
Page 37

37
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
4-WORD SYNCHRONOUS BURST OPERATION
A0–A20
V
IH
V
IL
ADV#
V
IH
V
IL
CE#
V
IH
V
IL
OE#
V
IH
V
IL
WE#
V
IH
V
IL
WAIT#
DQ0–DQ15
V
OH
V
OL
CLK
V
IH
V
IL
UNDEFINED
V
OH
V
OL
t
AKS
t
VP
t
AOE
t
VKS
t
AKH
t
AA
t
AADV
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
ADDRESS
High-Z
t
VPH
t
AVH
t
OH
t
KOH
t
ACLK
t
CVS
t
CKS
t
ACE
t
OD
READ TIMING PARAMETERS
MT28F322D20 (VCC = 1.80V–2.25V)
-705 -804
SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
t
AKS 7 7 ns
t
VKS 7 7 ns
t
CKS 9 13 ns
t
ACLK 15 20 ns
t
KOH 3 5 ns
t
AKH 10 10 ns
t
CVS 10 10 ns
t
AA 70 80 ns
t
ACE 70 80 ns
t
AADV 70 80 ns
t
VP 10 10 ns
t
VPH 10 10 ns
t
AVH 3 3 ns
t
AOE 25 30 ns
t
OD 15 25 ns
t
OH 0 0 ns
READ TIMING PARAMETERS
MT28F322D18 (VCC = 1.70V–1.90V)
-705 -804
SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
t
AKS 7 7 ns
t
VKS 7 7 ns
t
CKS 9 13 ns
t
ACLK 17 20 ns
t
KOH 3 5 ns
t
AKH 10 10 ns
t
CVS 10 10 ns
t
AA 70 80 ns
t
ACE 70 80 ns
t
AADV 70 80 ns
t
VP 10 10 ns
t
VPH 10 10 ns
t
AVH 3 3 ns
t
AOE 25 30 ns
t
OD 15 25 ns
t
OH 0 0 ns
Page 38

38
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
CONTINUOUS BURST READ
SHOWING AN OUTPUT DELAY WITH RCR8 = 0(1)
A0–A20
V
IH
V
IL
ADV#
V
IH
V
IL
CE#
V
IH
V
IL
OE#
V
IH
V
IL
WE#
V
IH
V
IL
WAIT#
DQ0–DQ15
V
OH
V
OL
CLK
V
IH
V
IL
UNDEFINED
V
OH
V
OL
t
ACLK
t
KOH
t
KHTL
t
KHTL
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
VALID
OUTPUT
INVALID
OUTPUT
t
CLK
t
KP
t
KHKL
NOTE: 1.tCLK = 19.2ns (MIN) for the MT28F322D18 device.
2.tACLK = 17ns (MAX) for the MT28F322D18 device.
READ TIMING PARAMETERS
MT28F322D20 (VCC = 1.80V–2.25V)
-705 -804
SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
t
CLK 18.5 25 ns
t
KP 5 7.5 ns
t
KHKL 3 5 ns
t
ACLK 15 20 ns
t
KOH 3.5 5 ns
t
KHTL 15 20 ns
READ TIMING PARAMETERS
MT28F322D18 (VCC = 1.70V–1.90V)
-705 -804
SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
t
CLK 19.2 25 ns
t
KP 5 7.5 ns
t
KHKL 3 5 ns
t
ACLK 17 20 ns
t
KOH 3.5 5 ns
t
KHTL 15 20 ns
Page 39

39
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
TWO-CYCLE PROGRAMMING/ERASE OPERATION
VALID ADDRESS VALID ADDRESS VALID ADDRESS
UNDEFINED
t
CH
t
CH
t
RHS
t
DS
t
AVS
t
AVH
A0–A20
OE#
CE#
WE#
V
PP
RST#
WP#
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IPPLK
V
IL
V
IPPH
t
AS
t
AH
t
WPH
t
WP
t
RS
CMD
t
VPH
t
WOS
ADV#
V
IH
V
IL
t
VP
t
VS
t
CS
t
WB
CMD/
DATA
CMD/
DATA
DQ0–DQ15
V
IH
V
IL
t
RHH
t
VPS
t
VPPH
STATUS
High-Z
-70/-80
SYMBOL MIN MAX UNITS
WRITE TIMING PARAMETERS
-70/-80
SYMBOL MIN MAX UNITS
t
RS 150 ns
t
CS 0 ns
t
WP 70 ns
t
VP 10 ns
t
DS 70 ns
t
AS 70 ns
t
VS 70 ns
t
AVS 10 ns
t
CH 0 ns
t
DH 0 ns
t
AH 1.5 ns
t
AVH 3 ns
t
WPH 30 ns
t
VPH 10 ns
t
RHS 0 ns
t
VPS 200 ns
t
WOS 50 ns
t
RHH 0 ns
t
VPPH 0 ns
t
WB
t
AA + 50 ns
Page 40

40
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
RESET OPERATION
READ AND WRITE TIMING PARAMETERS
-70/-80 -70/-80
1.80V–2.25V 1.70V–1.90V
SYMBOL MIN MAX MIN MAX UNITS
t
RWH 200 200 ns
t
RP 100 100 ns
OE#
DQ0–DQ15
V
IH
V
IL
RST#
V
IH
V
IL
CE#
V
IH
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL
t
RWH
t
RP
Page 41

41
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
Table 15
CFI
OFFSET DATA DESCRIPTION
00 2Ch Manufacturer code
01 B4h Top boot block device code
B5h Bottom boot block device code
02 – 0F reserved Reserved
10, 11 0051, 0052 “QR”
12 0059 “Y”
13, 14 0003, 0000 Primary OEM command set
15, 16 0039, 0000 Address for primary extended table
17, 18 0000, 0000 Alternate OEM command set
19, 1A 0000, 0000 Address for OEM extended table
1B 0017 VCC MIN for Erase/Write; Bit7–Bit4 Volts in BCD; Bit3–Bit0 100mV in BCD
1C 0022 VCC MAX for Erase/Write; Bit7–Bit4 Volts in BCD; Bit3–Bit0 100mV in BCD
1D 00B4 VPP MIN for Erase/Write; Bit7–Bit4 Volts in Hex; Bit3–Bit0 100mV in BCD
1E 00C6 VPP MAX for Erase/Write; Bit7–Bit4 Volts in Hex; Bit3–Bit0 100mV in BCD
1F 0003 Typical timeout for single byte/word program, 2n µs, 0000 = not supported
20 0000 Typical timeout for maximum size multiple byte/word program, 2n µs, 0000 = not
supported
21 0009 Typical timeout for individual block erase, 2n ms, 0000 = not supported
22 0000 Typical timeout for full chip erase, 2n ms, 0000 = not supported
23 000C Maximum timeout for single byte/word program, 2n µs, 0000 = not supported
24 0000 Maximum timeout for maximum size multiple byte/word program, 2n µs, 0000 = not
supported
25 0003 Maximum timeout for individual block erase, 2n ms, 0000 = not supported
26 0000 Maximum timeout for full chip erase, 2n ms, 0000 = not supported
27 0016 Device size, 2n bytes
28 0001 Bus Interface x16 = 1
29 0000 Flash device interface description 0000 = async
2A, 2B 0000, 0000 Maximum number of bytes in multi-byte program or page, 2
n
2C 0003 Number of erase block regions within device (4K words and 32K words)
2D, 2E 002F, 0000 Top boot block device erase block region information 1, 8 blocks …
0007, 0000 Bottom boot block device erase block region information 1, 8 blocks …
2F, 30 0000, 0001 Top boot block device …..of 8KB
0020, 0000 Bottom boot block device …..of 8KB
31, 32 000E, 0000 Top boot block 15 blocks of ….
000E, 0000 Bottom boot block 15 blocks of ….
33, 34 0000, 0001 ……64KB
35, 36 0007, 0000 Top boot block device …..48 blocks of
002F, 0000 Bottom boot block device …..48 blocks of
(continued on next page)
Page 42

42
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
Table 15
CFI (continued)
OFFSET DATA DESCRIPTION
37, 38 0020, 0000 Top boot block device ……64KB
0000, 0001 Bottom boot block device ……64KB
39, 3A 0050, 0052 “PR”
3B 0049 “I”
3C 0030 Major version number, ASCII
3D 0031 Minor version number, ASCII
3E 00E6 Optional Feature and Command Support
3F 0003 Bit 0 Chip erase supported no = 0
40 0000 Bit 1 Suspend erase supported = yes = 1
41 0000 Bit 2 Suspend program supported = yes = 1
Bit 3 Chip lock/unlock supported = no = 0
Bit 4 Queued erase supported = no = 0
Bit 5 Instant individual block locking supported = yes = 1
Bit 6 Protection bits supported = yes = 1
Bit 7 Page mode read supported = yes = 1
Bit 8 Synchronous read supported = no = 0
Bit 9 Simultaneous operation supported = yes = 1
42 0001 Program supported after erase suspend = yes
43, 44 0003, 0000 Bit 0 block lock status active = yes; Bit 1 block lock down active = yes
45 0018 VCC supply optimum, 00 = not supported, Bit7–Bit4 Volts in BCD; Bit3–Bit0 100mV in BCD
46 00C0 VPP supply optimum, 00 = not supported, Bit7–Bit4 Volts in BCD; Bit3–Bit0 100mV in BCD
47 0001 Number of protection register fields in JEDEC ID space
48, 49 0080, 0000 Lock bytes LOW address, lock bytes HIGH address
4A, 4B 0003, 0003 2n factory programmed bytes, 2n user programmable bytes
4C 0003 Background Operation
0000 = Not used
0001 = 4% block split
0002 = 12% block split
0003 = 25% block split
0004 = 50% block split
4D 0072 Burst Mode Type
0000 = No burst mode
00x1 = 4 words MAX
00x2 = 8 words MAX
00x3 = 16 words MAX
001x = Linear burst, and/or
002x = Interleaved burst, and/or
004x = Continuous burst
4E 0002 Page Mode Type
0000 = No page mode
0001 = 4-word page
0002 = 8-word page
0003 = 16-word page
0004 = 32-word page
4F 0000 Not used
Page 43

43
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
NOTE: 1. All dimensions in millimeters.
2. Package width and length do not include mold protrusion; allowable mold protrusion is 0.25mm per side.
58-BALL FBGA
0.80 ±0.075
.10
C
C
SOLDER BALL MATERIAL: EUTECTIC 63% Sn, 37% Pb or
62% Sn, 36% Pb, 2% Ag
SOLDER BALL PAD: Ø .27mm
BALL #1 ID
ENCAPSULATION MATERIAL: EPOXY NOVOLAC
SUBSTRATE: PLASTIC LAMINATE
0.75
TYP
12.00 ± .10
4.50
1.50 (4X)
SUPPORT BALLS
(4X)
2.25 ±0.05
6.00 ±0.05
BALL #1 ID
0.75
TYP
3.50 ±0.052.625 ±0.05
5.25
7.00 ±0.10
0.35 TYP58X
Ø
1.20 MAX
SEATING PLANE
BALL A8
SOLDER BALL DIAMETER
REFERS TO POST REFLOW
CONDITION. THE
PRE-REFLOW DIAMETER
IS Ø 0.33
C
L
C
L
BALL A1
8000 S. Federal Way, P.O. Box 6, Boise, ID 83707-0006, Tel: 208-368-3900
E-mail: prodmktg@micron.com, Internet: http://www.micron.com, Customer Comment Line: 800-932-4992
Micron and the M logo are registered trademarks and the Micron logo is a trademark of Micron Technology, Inc.
DATA SHEET DESIGNATION
No Mark: This data sheet contains minimum and maximum limits specified over the complete power supply and
temperature range for production devices. Although considered final, these specifications are subject
to change, as further product development and data characterization sometimes occur.
Page 44

44
2 Meg x 16 Async/Page/Burst Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F322D20FH_4.p65 – Rev. 4, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2 MEG x 16
ASYNC/PAGE/BURST FLASH MEMORY
REVISION HISTORY
Rev. 4 .................................................................................................................................................................................... 7/02
• Removed PRELIMINARY DESIGNATION
• Updated Status Register section
• Updated command descriptions
• Updated Read-While-Write/EraseConcurrency section
• Updated timing diagrams
• Changed interpage read access voltage from 1.70V to 1.80V
• Changed intrapage read access voltage from 1.90V to 2.20V
Rev. 3, PRELIMINARY ........................................................................................................................................................ 3/02
• Added Note 4 to DC Characteristics table
Rev. 2, PRELIMINARY ........................................................................................................................................................ 1/02
• Added -70 and -80 speed grades for the MT28F322D18
• Removed -90 speed grade
• Updated DC Characteristics Table
• Updated CFI Table
• Updated tAH and tRWH specifications
• Changed data sheet from Advance to Preliminary
Original document, Rev. 1, ADVANCE ............................................................................................................................ 7/01
 Loading...
Loading...