Datasheet MIC2524-1BN, MIC2524-1BWM, MIC2524-2BN, MIC2524-2BWM, MIC2527-2BWM Datasheet (MICREL)
...Page 1
MIC2524/2527 Micrel
MIC2524/2527
Quad USB Power Control Switch
Not Recommended for New Designs
Refer to MIC2027
General Description
The MIC2524 and MIC2527 are cost-effective high-side
power switches with four independently controlled channels,
optimized for self-powered and bus-powered Universal Serial Bus (USB) applications. Few external components are
necessary to satisfy USB requirements.
The MIC2524/7 satisfies the following USB requirements:
each switch channel supplies up to 500mA as required by
USB downstream devices; the switch’s low on-resistance
meets USB voltage drop requirements; fault current is limited
to typically 750mA, well below the UL 25VA safety requirements; and a flag output is available to indicate fault conditions to the local USB controller. Soft start eliminates the
momentary voltage drop on the upstream port that may occur
when the switch is enabled in bus-powered applications.
Additional features include thermal shutdown to prevent
catastrophic switch failure from high-current loads,
undervoltage lockout (UVLO) to ensure that the device remains off unless there is a valid input voltage present, and
3.3V and 5V logic compatible enable inputs.
The MIC2524/7 is available in active-high and active-low
versions in 16-pin DIP and SOIC packages.
Features
• Compliant to USB specifications
• UL Recognized Component
• 4 independent switches
• 3V to 5.5V input
• 500mA minimum continuous load current per port
• 140mΩ maximum on-resistance (MIC2524)
• 1.25A maximum short circuit current limit
• Individual open-drain fault flag pins
• 220µA on-state supply current
• 1µA typical off-state supply current
• Output can be forced higher than input (off-state)
• Thermal shutdown
• 2.4V typical undervoltage lockout (UVLO)
• 1ms turn-on (soft-start) and fast turnoff
• Active-high or active-low enable versions
• 16-pin SOIC and DIP packages
Applications
• USB bus-powered hubs
• USB self-powered hubs
• USB monitors
• USB printers
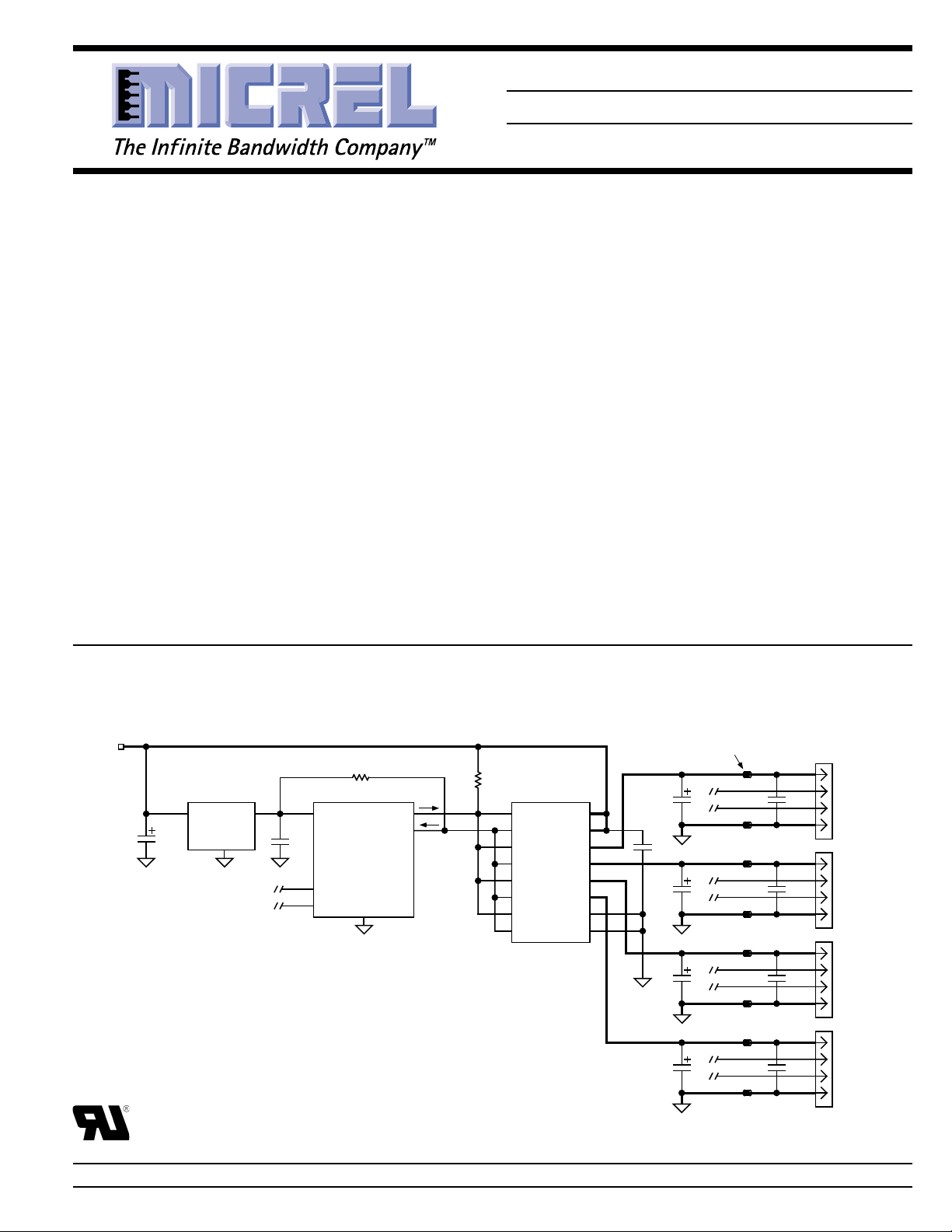
Typical Application
MIC2527
5.1V ± 3%
5V ± 1%
or
MIC2524
5V ±3%
MIC5207-3.3
LDO Regulator
IN OUT
4.7
µF
GND
Bold lines indicate
0.1" wide, 1-oz. copper
high-current traces.
* 33µF, 16V tantalum or 100µF, 10V electrolytic per port
3.3V USB Controller
V+
1µF
OVERCURRENT
D+
D–
10k
GND
ON/OFF
27k
MIC2524
MIC2527
ENA
FLGA IN
ENB OUTA
FLGB
OUTB
ENC
OUTC
OUTDFLGC
END
FLGD GND
GND
Ferrite
Bead
V
BUS
33µF*
IN
0.1
µF
33µF*
33µF*
33µF*
0.01µF
0.01µF
0.01µF
0.01µF
D+
D–
GND
V
BUS
D+
D–
GND
V
BUS
D+
D–
GND
V
BUS
D+
D–
GND
Downstream
USB
Port 1
500mA max.
Downstream
USB
Port 2
500mA max.
Downstream
USB
Port 3
500mA max.
Downstream
USB
Port 4
500mA max.
UL Recognized Component
Micrel, Inc. • 1849 Fortune Drive • San Jose, CA 95131 • USA • tel + 1 (408) 944-0800 • fax + 1 (408) 944-0970 • http://www.micrel.com
June 1999 1 MIC2524/2527
4-Port Self-Powered Hub
Page 2
MIC2524/2527 Micrel
Ordering Information
Part Number On-Resistance Enable Temperature Range Package
MIC2524-1BWM 100mΩ typ. Active High –40°C to +85°C 16-Pin SOIC
MIC2524-1BN 100mΩ typ. Active High –40°C to +85°C 16-pin DIP
MIC2524-2BWM 100mΩ typ. Active Low –40°C to +85°C 16-Pin SOIC
MIC2524-2BN 100mΩ typ. Active Low –40°C to +85°C 16-pin DIP
MIC2527-1BWM 200mΩ typ. Active High –40°C to +85°C 16-Pin SOIC
MIC2527-1BN 200mΩ typ. Active High –40°C to +85°C 16-pin DIP
MIC2527-2BWM 200mΩ typ. Active Low –40°C to +85°C 16-Pin SOIC
MIC2527-2BN 200mΩ typ. Active Low –40°C to +85°C 16-pin DIP
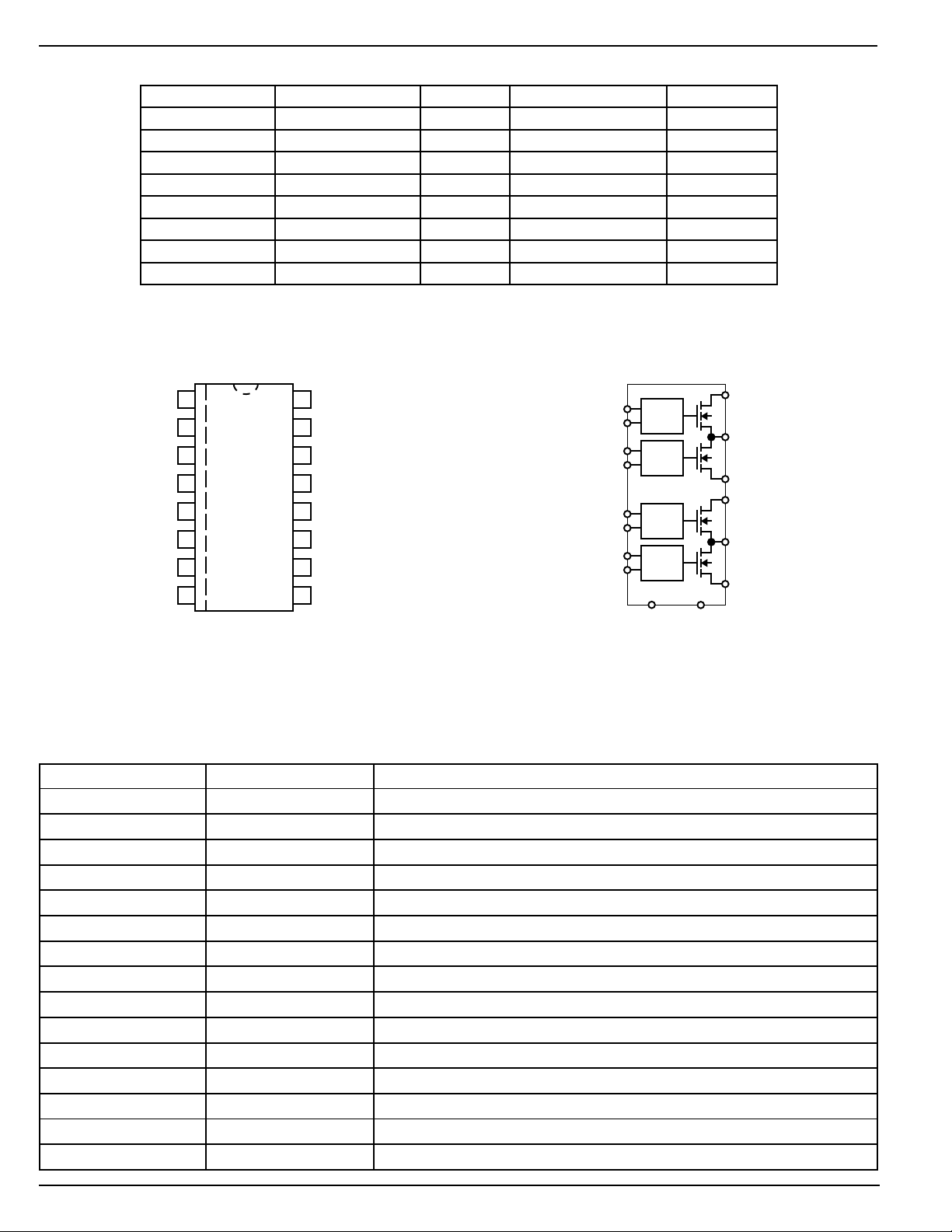
Pin Configuration
FLGA
ENA
OUTA
GND
IN(C/D)
OUTC
ENC
FLGC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
FLGB
ENB
OUTB
IN(A/B)
GND
OUTD
END
FLGD
16-Pin SOIC (WM)
16-Pin DIP (N)
Pin Description
Pin Number Pin Name Pin Function
1 FLGA Flag A: (Output): Channel A open-drain fault flag output.
2 ENA Enable A (Input): Channel A control input.
3 OUTA Output A: Channel A switch output.
4, 12 GND Ground: Supply return. Connect both pins to ground.
5 IN(C/D) Supply Input: Channel C and D switch, logic, and charge-pump supply input.
6 OUTC Output C: Channel C switch output.
7 ENC Enable C (Input): Channel C control input.
8 FLGC Flag C (Output): Channel C open-drain fault flag output.
9 FLGD Flag D (Output): Channel D open-drain fault flag output.
10 END Enable D (Input): Channel D control input.
11 OUTD Output D: Channel D switch output.
13 IN(A/B) Supply Input: Channel A and B switch, logic, and charge-pump supply input.
14 OUTB Output B: Channel B switch output.
15 ENB Enable B (Input): Channel B control input.
16 FLGB Flag B (Output): Channel B open-drain fault flag output.
ENA 2
FLGA 1
ENB 15
FLGB 16
ENC 7
FLGC 8
END 10
FLGD 9
Functional Pinout
LOGIC,
CHARGE
PUMP
LOGIC,
CHARGE
PUMP
LOGIC,
CHARGE
PUMP
LOGIC,
CHARGE
PUMP
3 OUTA
13 IN(A/B)
14 OUTB
6 OUTC
5 IN(C/D)
11 OUTD
124 GND
MIC2524/2527 2 June 1999
Page 3
MIC2524/2527 Micrel
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
Supply Voltage (V
Fault Flag Voltage (V
Fault Flag Current (I
Output Voltage (V
Output Current (I
Control Input (V
) .....................................................+6V
IN
)..............................................+6V
FLG
) ............................................50mA
FLG
) ..................................................+6V
OUT
)...............................Internally Limited
OUT
)......................................... –0.3V to 12V
EN
Operating Ratings (Note 2)
Supply Voltage (V
Ambient Operating Temperature (T
Thermal Resistance
SOIC (θ
).........................................................120°C/W
JA
DIP(θJA).............................................................130°C/W
) ...................................... +3V to +5.5V
IN
) ........ –40°C to +85°C
A
Storage Temperature (TS) ....................... –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering 5 sec.) ....................... 260°C
ESD Rating, Note 3 ......................................................2kV
Electrical Characteristics
VIN = +5V; TA = 25°C; unless noted.
Parameter Condition Min Typ Max Units
Supply Current Note 4, switch off, OUT = open 1.5 10 µA
Note 4, all switches on, OUT = open 220 320 µA
Enable Input Threshold low-to-high transition 2.1 2.4 V
high-to-low transition, Note 4 0.8 1.9 V
Enable Input Current VEN = 0V to 5.5V –1 ±0.01 1 µA
Enable Input Capacitance 1pF
Switch Resistance MIC2524, I
MIC2527, I
Output Turn-On Delay RL = 10Ω each output 0.5 ms
Output Turn-On Rise Time RL = 10Ω each output 1 ms
Output Turnoff Delay RL = 10Ω each output 1 20 µs
Output Turnoff Fall Time RL = 10Ω each output 1 20 µs
Output Leakage Current each output (output disabled) 10 µA
Continuous Load Current each output 0.5 A
Short-Circuit Current Limit each output (enable into load), V
Current-Limit Threshold ramped load applied to enabled output, V
Overtemperature Shutdown TJ increasing 135 °C
Threshold
Error Flag Output Resistance VIN = 5V, IL = 10mA 10 Ω
Error Flag Off Current V
UVLO Threshold VIN = increasing 2.5 V
TJ decreasing 125 °C
VIN = 3.3V, IL = 10mA 15 Ω
= 5V 0.01 1 µA
FLAG
VIN = decreasing 2.3 V
= 500mA, each switch 100 140 mΩ
OUT
= 500mA, each switch 200 300 mΩ
OUT
= 4.0V 0.5 0.75 1.25 A
OUT
≤ 4.0V, Note 5 1.6 2.2 A
OUT
Note 1. Exceeding the absolute maximum rating may damage the device.
Note 2. The device is not guaranteed to function outside its operating rating.
Note 3. Devices are ESD sensitive. Handling precautions recommended. Human body model, 1.5k in series with 100pF.
Note 4. Off is ≤ 0.8V and on is ≥ 2.4V for the MIC252x-1. Off is ≥ 2.4V and on is ≤ 0.8V for the MIC252x-2. The enable input has approximately 200mV
Note 5. See “Functional Characteristics: Current-Limit Response” photo.
of hysteresis. See control threshold charts.
June 1999 3 MIC2524/2527
Page 4
MIC2524/2527 Micrel
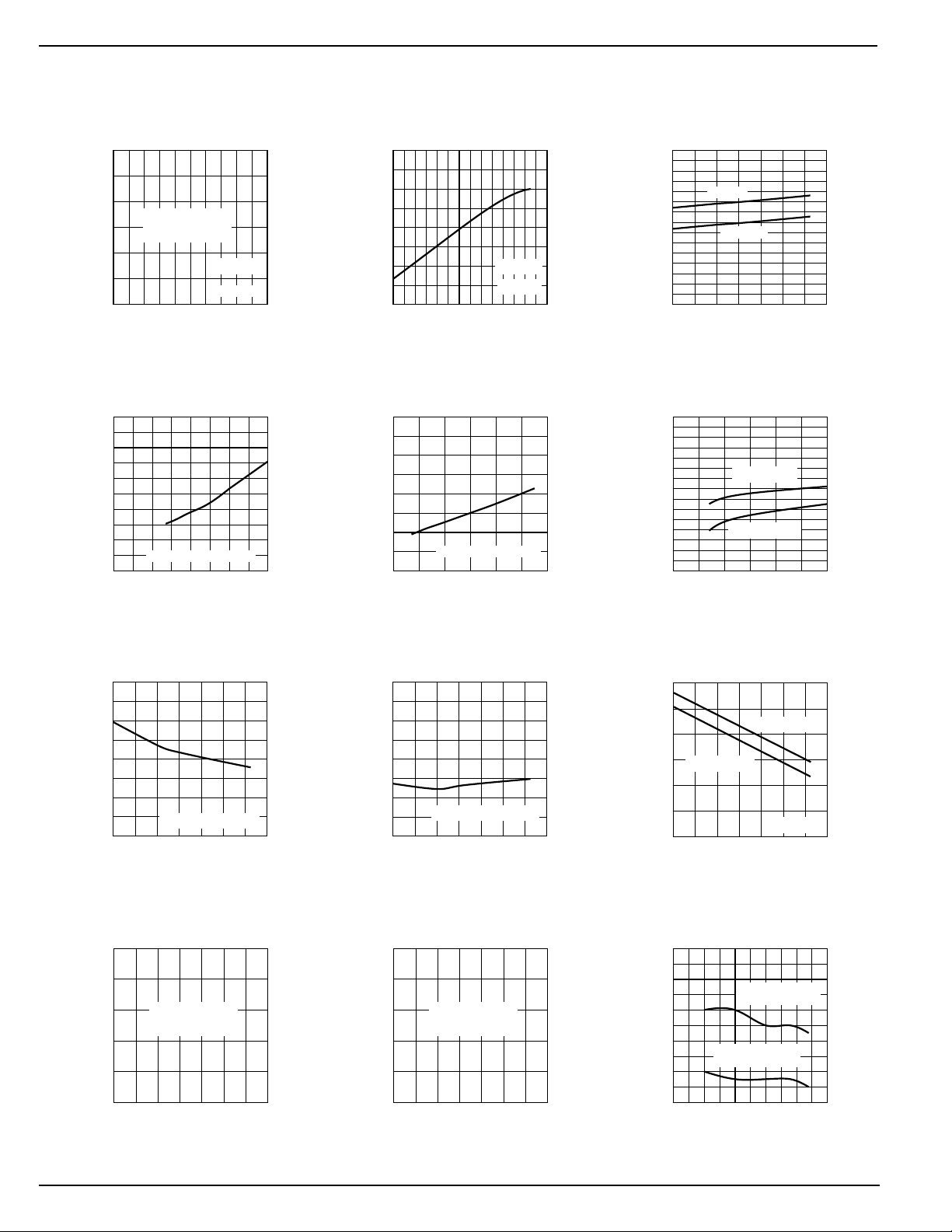
Typical Characteristics
VIN = 5V; TA = 25°C; one switch section; unless noted.
Output On-Resistance
vs. Supply Voltage
110
100
90
OUTPUT RESISTANCE (mΩ)
80
3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5 5.5
Awaiting Full
Characterization
Data
RL = 44Ω
T = 25°C
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
On-State Supply Current
vs. Supply Voltage
500
400
300
200
100
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
ALL SWITCHES ON
0
02468
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
Output On-Resistance
140
120
100
ON-RESISTANCE (mΩ)
vs. Temperature
80
60
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
RL = 44Ω
VIN = 5V
Off-State Supply Current
vs. Supply Voltage
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
0
2345678
ALL SWITCHES OFF
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
UVLO Threshold Voltage
3.0
2.5
2.0
THRESHOLD VOLTAGE (V)
1.5
vs. Temperature
RISING
FALLING
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Control Threshold
vs. Supply Voltage
2.5
2.0
1.5
THRESHOLD VOLTAGE (V)
1.0
2345
V
RISING
CTL
V
FALLING
CTL
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
On-State Supply Current
400
350
300
250
200
150
100
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
vs. Temperature
50
0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100
ALL SWITCHES ON
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Output Rise Time
vs. Temperature
5
4
3
2
TIME (µs)
1
0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100
Awaiting Full
Characterization
Data
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Off-State Supply Current
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
vs. Temperature
ALL SWITCHES OFF
0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Output Fall Time
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
TIME (ms)
0.2
vs. Temperature
Awaiting Full
Characterization
Data
0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Control Threshold
2.5
2.0
1.5
ENABLE VOLTAGE (V)
1.0
vs. Temperature
VEN RISING
VEN FALLING
VIN = 5V
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Current-Limit Threshold
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
CURRENT (A)
1.2
1.0
vs. Temperature
CURRENT LIMIT
THRESHOLD
SHORT CIRCUIT
CURRENT LIMIT
-25 0 25 50 75 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
MIC2524/2527 4 June 1999
Page 5

MIC2524/2527 Micrel
Functional Characteristics
V
V
V
I
V
V
EN
OUT
FLG
OUT
EN
FLG
Input V oltage
Response
EN
V
(5V/div.)
2.6V (UVLO) Threshold
(2V/div.)
V
V
FLG
(5V/div.)
OUT
(2V/div.)
T urn-On, T urnoff
Characteristics
(2V/div.)
= 5.0V
V
(5V/div.)
(200mA/div.)
TIME (100ns/div.)
T urn-On, T urnoff
Characteristics
(5V/div.)
IN
RL = 35Ω
= 15µF
C
L
I
V
OUT
(100mA/div.)
TIME (2.5ms/div.)
Short Circuit Response
(Short Applied to Output)
FLG
(5V/div.)
144mA
V
IN
RL = 35Ω
CL = 10µF
= 5.0V
(5V/div.)
V
I
OUT
OUT
OUT
V
I
OUT
(2V/div.)
1A Short Circuit Current Limit
(1A/div.)
Thermal Shutdown
TIME (500ms/div.)
(2V/div.)
144mA
RL = 35Ω
= 150µF
C
L
(100mA/div.)
TIME (2.5ms/div.)
Short Circuit Response
Enable into Short Circuit
EN
V
(5V/div.)
FLG
V
(5V/div.)
OUT
V
I
OUT
(2V/div.)
1.1A Short Circuit
(1A/div.)
Current-Limiting
TIME (250ms/div.)
Thermal
Shutdown
June 1999 5 MIC2524/2527
Page 6
MIC2524/2527 Micrel
OUT
V
(5V/div.)
FLG
V
(5V/div.)
OUT
I
(1A/div.)
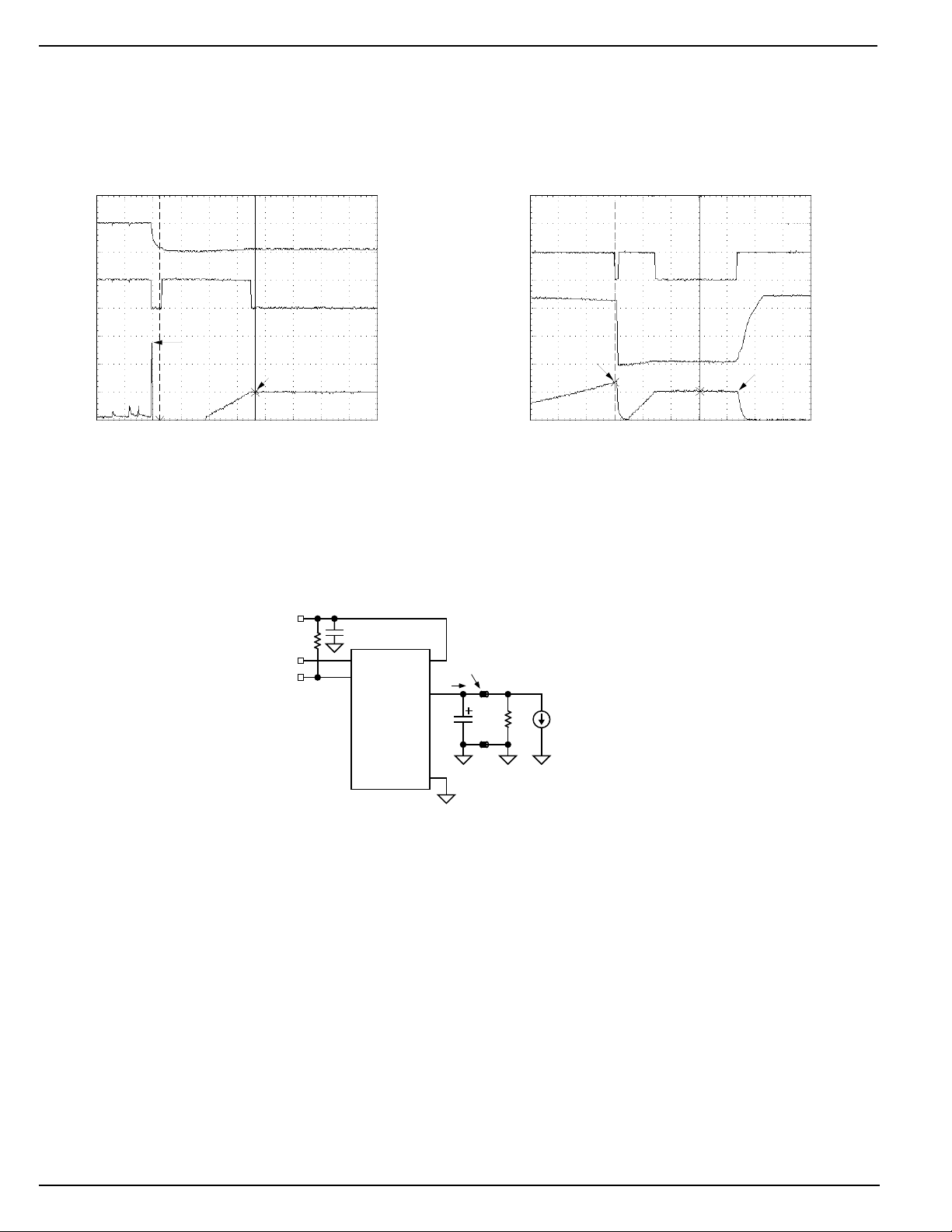
Test Circuit
Short Circuit Transient Response
(Short Applied to Output)
2.76A
1A Current Limit
TIME (500µs/div.)
5V
10k
0.1µF
MIC2524/7
ENA
FLGA NC
ENB OUTA
FLGB
OUTB
ENC
OUTC
OUTDFLGC
END
FLGD
NC
GND
Current-Limit Response
(Ramped Load)
FLG
V
(5V/div.)
OUT
V
(2V/div.)
Current Limit
Threshold
OUT
I
(1A/div.)
TIME (1ms/div.)
(1 output shown)
Ferrite
IN
Bead
I
OUT
I
C
L
R
L
LOAD
(for Current
Limit Response)
1A Current
Limit
Functional Characteristics Test Circuit
MIC2524/2527 6 June 1999
Page 7

MIC2524/2527 Micrel
Block Diagrams
FLGA
OUTA
ENA
CHARGE
PUMP
GATE
CONTROL
CURRENT
LIMIT
ENB
ENC
OSC.
CHARGE
PUMP
CHARGE
PUMP
OSC.
THERMAL
SHUTDOWN
THERMAL
SHUTDOWN
UVLO
UVLO
REFERENCE
GATE
CONTROL
GATE
CONTROL
REFERENCE
1.2V
1.2V
CURRENT
LIMIT
CURRENT
LIMIT
IN (A/B)
OUTB
FLGB
FLGC
OUTC
IN (C/D)
END
MIC2527
CHARGE
PUMP
GND
GATE
CONTROL
CURRENT
LIMIT
OUTD
FLGD
June 1999 7 MIC2524/2527
Page 8

MIC2524/2527 Micrel
Functional Description
The MIC2524/7-1 and MIC2524/7-2 are quad high-side
switches with active-high and active-low enable inputs, respectively. Fault conditions turn off or inhibit turn-on of one or
more of the output transistors, depending upon the type of
fault, and activate the open-drain error flag transistors making them sink current to ground.
Input and Output
IN (input) is the power supply connection to the logic circuitry
and the drain of the output MOSFET. OUTx (output) is the
source of its respective MOSFET. In a typical circuit, current
flows through the switch from IN to OUT toward the load. If
V
is greater than VIN, current will flow from OUT to IN
OUT
since the MOSFET is bidirectional when on.
The output MOSFET and driver circuitry are also designed to
allow the MOSFET source to be externally forced to a higher
voltage than the drain (V
this situation, the MIC2524/7 prevents reverse current flow.
If VIN < 2.5V, UVLO disables both switches.
Thermal Shutdown
Thermal shutdown shuts off the affected output MOSFETs
and signals all fault flags if the die temperature exceeds
135°C. 10°C of hysteresis prevents the switch from turning on
until the die temperature drops to 125°C. Overtemperature
detection functions only when at least one switch is enabled.
Current Limit Induced Thermal Shutdown
Internal circuitry increases the output MOSFET on-resistance until the series combination of the MOSFET on-resistance and the load impedance limit current to typically 850mA.
The increase in power dissipation, in most cases, will cause
the MIC2524/7 to go into thermal shutdown, disabling affected channels. When this is undesirable, thermal shutdown
can be avoided by externally responding to the fault and
disabling the current limited channel before the shutdown
temperature is reached. The delay between the flag indication of a current limit fault and thermal shutdown will vary with
ambient temperature, board layout, and load impedance, but
is typically several hundred milliseconds. The USB controller
must therefore recognize a fault and disable the appropriate
channel within this time. If the fault is not removed or the
switch is not disabled within this time, then the device will
enter into a thermal oscillation of about 2Hz. This does not
cause any damage to the device. Refer to “Functional Characteristics: Thermal Shutdown Response.”
> VIN) when the output is off. In
OUT
Undervoltage Lockout
UVLO (undervoltage lockout) prevents the output MOSFET
from turning on until VIN exceeds approximately 2.5V. In the
undervoltage state, the FLAG will be low. After the switch
turns on, if the voltage drops below approximately 2.3V,
UVLO shuts off the output MOSFET and signals fault flag.
Undervoltage detection functions only when at least one
switch is enabled.
Current Sensing and Limiting
The current-limit threshold is preset internally. The preset
level prevents damage to the output MOSFET and external
load but allows a minimum current of 0.5A through the output
MOSFET of each channel.
The current-limit circuit senses a portion of the output FET
switch current. The current sense resistor shown in the block
diagram is virtual and has no voltage drop. The reaction to an
overcurrent condition varies with three scenarios:
Switch Enabled into Short Circuit
If a switch is powered on or enabled into a heavy load or shortcircuit, the switch immediately goes into a constant-current
mode, reducing the output voltage. The fault flag goes low
until the load is reduced. See the “Functional Characteristics:
Short Circuit Response, Enabled into Short Circuit” photo.
Short Circuit Applied to Output
When a heavy load is applied, a large transient current may
flow until the current limit circuitry will respond. Once this
occurs, the device limits current to less than the short-circuit
current limit specification. See the “Short Circuit Transient
Response, Short Applied to Output” graph.
Current-Limit Response
The MIC2524/7 current-limit profile exhibits a small foldback
effect of approximately 500mA. Once this current-limit threshold is exceeded the device enters constant-current mode.
This constant current is specified as the short circuit current
limit in the “Electrical Characteristics” table. It is important to
note that the MIC2524/7 will deliver load current up to the
current-limit threshold which is typically 1.6A. Refer to “Func-
tional Characteristics: Current-Limit Response” photo for
details.
Fault Flag
FLG is an N-channel, open-drain MOSFET output. The faultflag is active (low) for one or more of the following conditions:
undervoltage (while 2V < VIN < 2.7), current limit, or thermal
shutdown. The flag output MOSFET is capable of sinking a
10mA load to typically 100mV above ground. Multiple FLG
pins may be “wire NORed” to a common pull-up resistor.
MIC2524/2527 8 June 1999
Page 9

MIC2524/2527 Micrel
Applications Information
Supply Filtering
A 0.1µF to 1µF bypass capacitor from IN to GND, located at
the device, is strongly recommended to control supply transients. Without a bypass capacitor, an output short may
cause sufficient ringing on the input (from supply lead inductance) to damage internal control circuitry.
Input or output transients must not exceed the absolute
maximum supply voltage (V
duration.
V
IN
2.7V to 5.5V
0.1µF to 1µF
MIC2524/7
FLGA FLGB
ENA
OUTA OUTB
GND IN
IN GND
OUTC
ENC END
FLGC FLGD
Figure 1. Supply Bypassing
= 7V) even for a short
IN max
ENB
0.1µF to 1µF
OUTD
Transient Overcurrent Filter
When the MIC2524/7 is enabled, large values of capacitance
at the output of the device will cause inrush current to exceed
the short circuit current-limit threshold of the device and
assert the flag. The duration of this time will depend on the
size of the output capacitance. Refer to the “Functional
Characteristics” turn-on and turnoff behaviors for details.
During the capacitance charging time, the device enters into
constant-current mode. As the capacitance is charged, the
current decreases below the short circuit current-limit threshold, and the flag will then be deasserted.
In USB applications, it is required that output bulk capacitance is utilized to support hot-plug events. When the
MIC2524/7 is enabled, the flag may go active for about 1ms
due to inrush current exceeding the current-limit setpoint.
Additionally, during hot-plug events, inrush currents may also
cause the flag to go active for 30µs. Since these conditions
are not valid overcurrent faults, the USB controller must
ignore the flag during these events. To prevent this erroneous
overcurrent reporting, a 1ms RC filter as shown in Figure 2
may be used. Alternatively, a 1ms debounce routine may be
programmed into the USB logic controller, eliminating the
need for the RC filter.
Enable Input
EN must be driven logic high or logic low for a clearly defined
input. Floating the input may cause unpredictable operation.
EN should not be allowed to go negative with respect to GND.
Soft Start
The MIC2524/7 presents a high impedance when off, and
slowly becomes a low impedance as it turns on. This reduces
inrush current and related voltage drop that results from
charging a capacitive load, satisfying the USB voltage droop
requirements.
USB Controller
OVERCURRENT
10k
10k
0.1µF
Figure 2. Transient Filter
FLGA
FLGB
FLGC
FLGD
June 1999 9 MIC2524/2527
Page 10
MIC2524/2527 Micrel
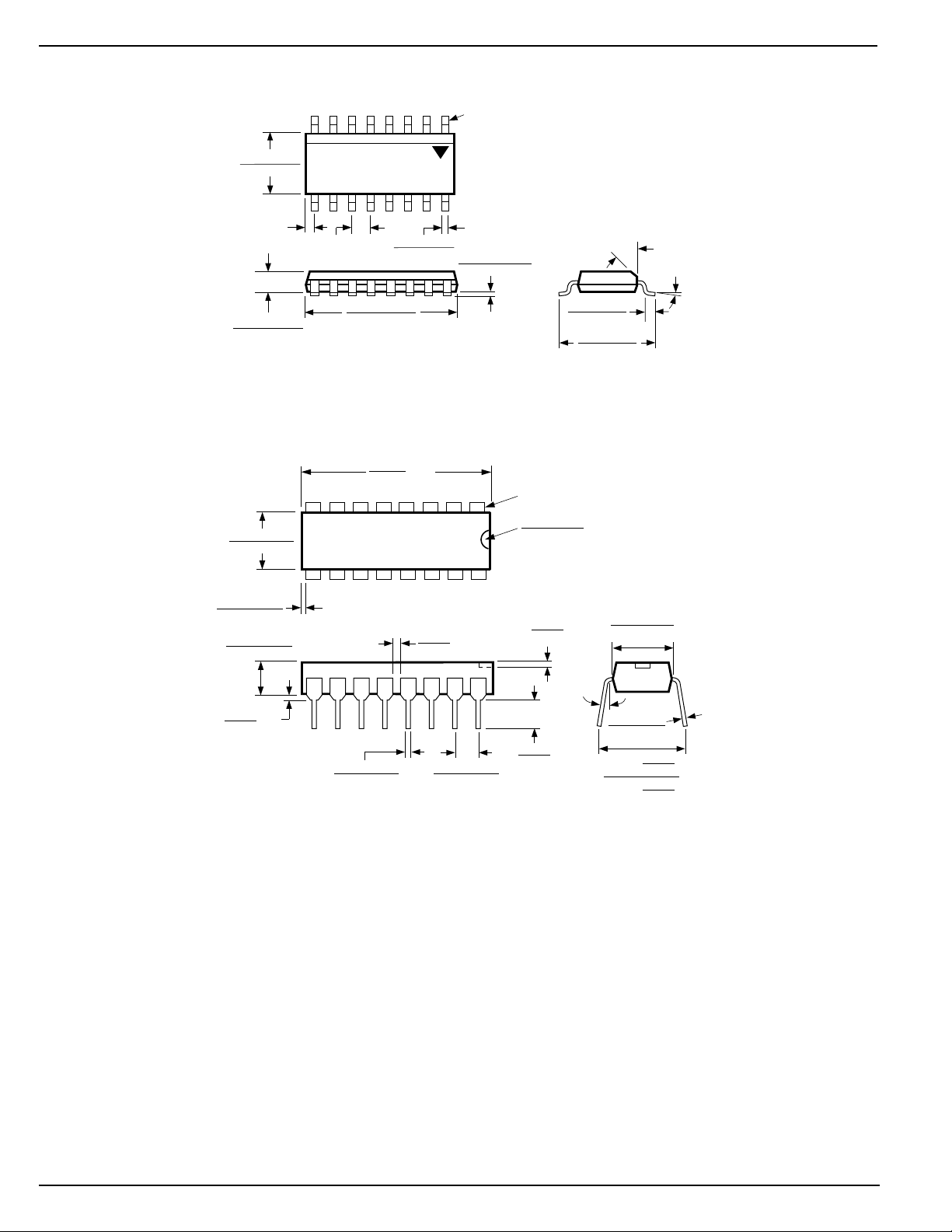
Package Information
PIN 1
0.157 (3.99)
0.150 (3.81)
0.020 (0.51)
REF
0.0648 (1.646)
0.0434 (1.102)
.250±0.005
(6.350±0.127)
0.025±0.015
(0.635±0.381)
0.130±0.005
(3.302±0.127)
0.050 (1.27)
BSC
0.394 (10.00)
0.386 (9.80)
0.020 (0.51)
0.013 (0.33)
16-Pin SOP (M)
0.780
MAX
(19.812)
0.040
(1.016)
0.0098 (0.249)
0.0040 (0.102)
SEATING
PLANE
TYP
DIMENSIONS:
INCHES (MM)
0.050 (1.27)
0.016 (0.40)
PIN 1
0.030-0.110
(0.762-2.794)
0.020
(0.508)
45°
0°–8°
0.244 (6.20)
0.228 (5.79)
RAD
0.290-0.320
(7.336-8.128)
0.020
(0.508)
MIN
0.018±0.003
(0.457±0.076)
16-Pin Plastic DIP (N)
0.100±0.010
(2.540±0.254)
0.125
(3.175)
MIN
0°-10°
0.009-0.015
(0.229-0.381)
+0.025
0.325
–0.015
+0.635
8.255
()
–0.381
MIC2524/2527 10 June 1999
Page 11

MIC2524/2527 Micrel
June 1999 11 MIC2524/2527
Page 12

MIC2524/2527 Micrel
MICREL INC. 1849 FORTUNE DRIVE SAN JOSE, CA 95131 USA
TEL + 1 (408) 944-0800 FAX + 1 (408) 944-0970 WEB http://www.micrel.com
This information is believed to be accurate and reliable, however no responsibility is assumed by Micrel for its use nor for any infringement of patents or
other rights of third parties resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent right of Micrel Inc.
© 1999 Micrel Incorporated
MIC2524/2527 12 June 1999
 Loading...
Loading...