Page 1
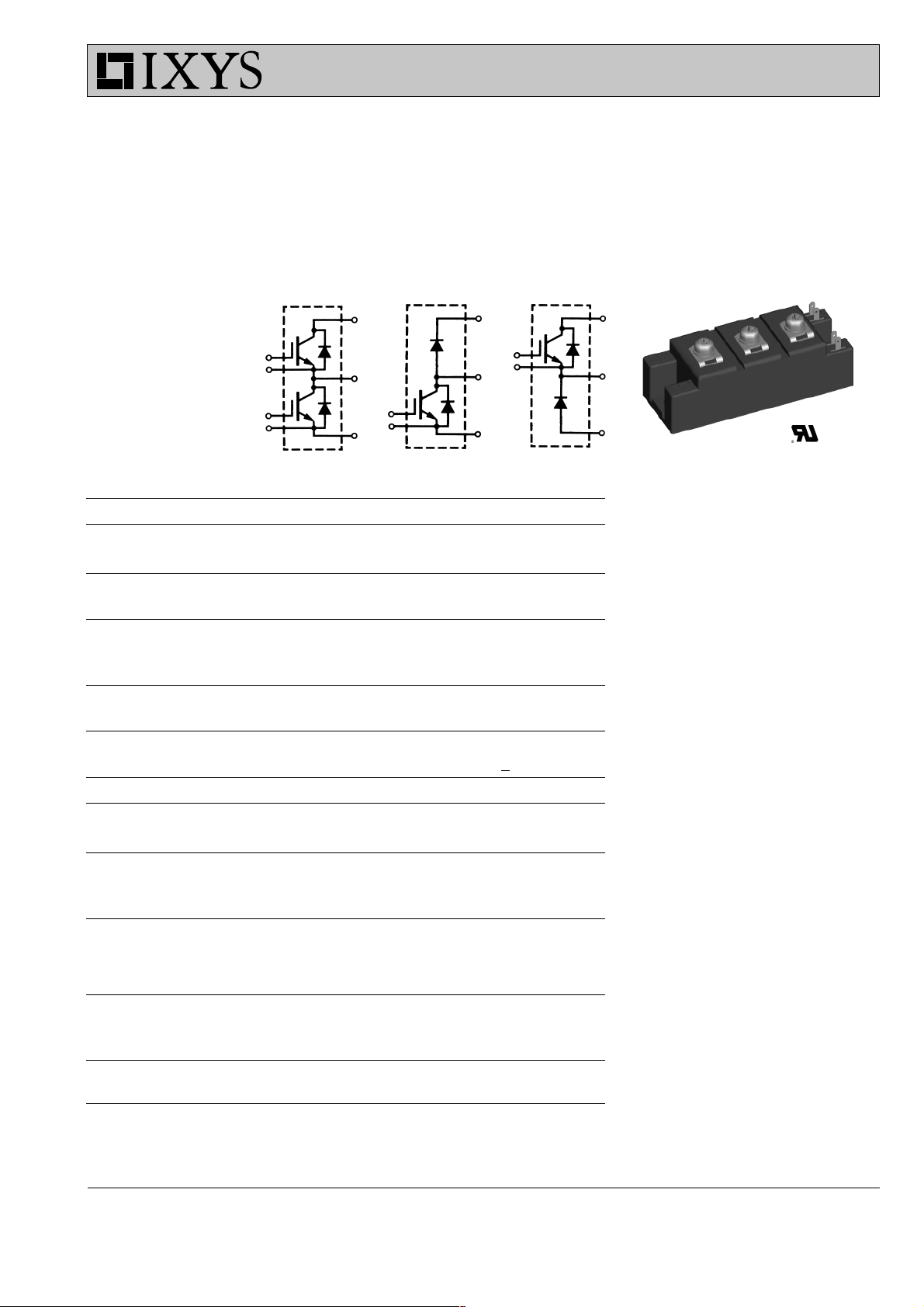
MII 100-12 A3 MID 100-12 A3
MDI 100-12 A3
IGBT Modules
Short Circuit SOA Capability
Square RBSOA
MII
1
7
6
4
5
3
2
Symbol Conditions Maximum Ratings
V
CES
V
CGR
V
GES
V
GEM
I
C25
I
C80
I
CM
t
SC
TJ= 25°C to 150°C 1200 V
TJ= 25°C to 150°C; RGE = 20 kW 1200 V
Continuous ±20 V
Transient ±30 V
TC= 25°C 135 A
TC= 80°C90A
TC= 80°C, tp = 1 ms 180 A
VGE = ±15 V, VCE = V
, TJ = 125°C10ms
CES
(SCSOA) RG= 15 W, non repetitive
RBSOA V
= ±15 V, TJ = 125°C, RG = 15 W ICM = 150 A
GE
Clamped inductive load, L = 100 mHV
P
tot
T
J
T
stg
V
ISOL
M
d
TC= 25°C 560 W
50/60 Hz, RMS t = 1 min 4000 V~
£ 1 mA t = 1 s 4800 V~
I
ISOL
Insulating material: Al2O
3
Mounting torque (module) 2.25-2.75 Nm
(teminals) 2.5-3.7 Nm
d
S
d
A
Creepage distance on surface 12.7 mm
Strike distance through air 9.6 mm
a Max. allowable acceleration 50 m/s
Weight Typical 130 g
MID
1
3
4
5
2
< V
CEK
MDI
7
6
CES
150 °C
-40 ... +150 °C
20-25 lb.in.
22-33 lb.in.
4.6 oz.
I
C25
V
CES
V
CE(sat) typ.
1
3
2
= 135 A
= 1200 V
= 2.2 V
3
1
2
Features
●
NPT IGBT technology
●
low saturation voltage
●
low switching losses
●
switching frequency up to 30 kHz
●
square RBSOA, no latch up
●
high short circuit capability
●
positive temperature coefficient for
easy parallelling
●
MOS input, voltage controlled
●
ultra fast free wheeling diodes
●
package with DCB ceramic base plate
●
isolation voltage 4800 V
●
UL registered E72873
Advantages
●
space and weight savings
●
reduced protection circuits
Typical Applications
●
AC and DC motor control
●
AC servo and robot drives
●
power supplies
●
welding inverters
2
4
5
E 72873
6
7
Data according to a single IGBT/FRED unless otherwise stated.
© 2000 IXYS All rights reserved
030
1 - 4
Page 2
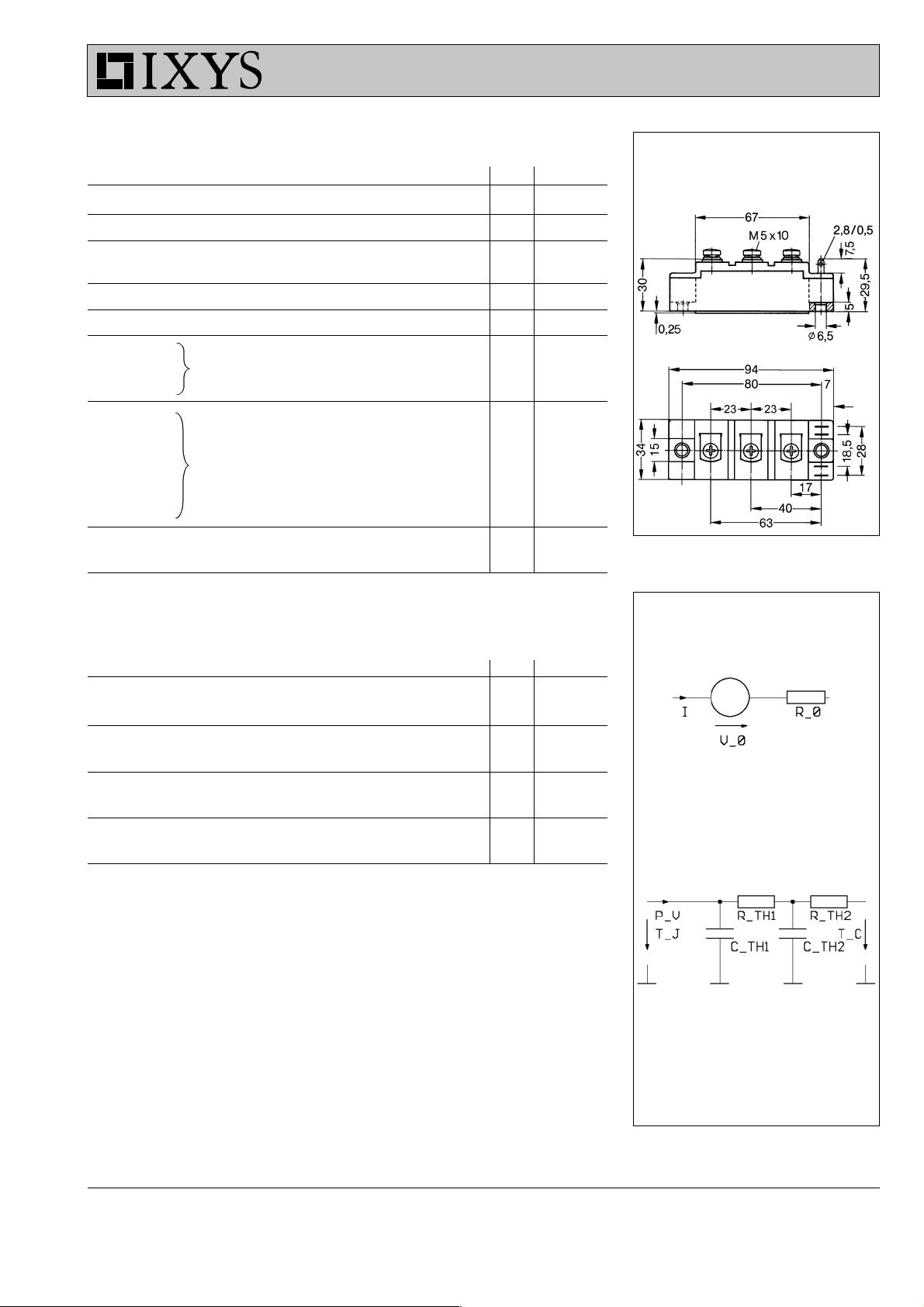
MII 100-12 A3 MID 100-12 A3
MDI 100-12 A3
Symbol Conditions Characteristic Values
(TJ = 25°C, unless otherwise specified)
min. typ. max.
V
(BR)CES
V
GE(th)
I
CES
VGE = 0 V 1200 V
IC = 3 mA, VCE = V
VCE= V
CES
GE
TJ = 25°C5mA
4.5 6.5 V
TJ = 125°C 7.5 mA
I
GES
V
C
C
C
t
d(on)
t
r
t
d(off)
t
f
E
E
R
R
CE(sat)
ies
oes
res
on
off
thJC
thJS
VCE= 0 V, VGE = ±20 V ±300 nA
IC = 75 A, VGE = 15 V 2.2 2.7 V
5.5 nF
VCE = 25 V, VGE = 0 V, f = 1 MHz 0.75 nF
0.33 nF
100 ns
Inductive load, T
= 75 A, VGE = ±15 V
I
C
= 125°C
J
VCE = 600 V, RG = 15 W
50 ns
650 ns
50 ns
12.1 mJ
10.5 mJ
0.22 K/W
with heatsink compound 0.44 K/W
Dimensions in mm (1 mm = 0.0394")
Reverse Diode (FRED) Characteristic Values
= 25°C, unless otherwise specified)
(T
J
min. typ. max.
V
F
IF = 75 A, VGE = 0 V, 2.2 2.5 V
IF = 75 A, VGE = 0 V, TJ = 125°C 1.7 1.8 V
I
F
TC = 25°C 150 A
TC = 80°C95A
I
RM
t
rr
R
thJC
R
thJS
IF = 75 A, VGE = 0 V, -diF/dt = 600 A/ms62A
TJ = 125°C, VR = 600 V 200 ns
0.45 K/W
with heatsink compound 0.9 K/W
Equivalent Circuits for Simulation
Conduction
IGBT (typ. at VGE = 15 V; TJ = 125°C)
V0 = 1.5 V; R0 = 13.6 mW
Free Wheeling Diode (typ. at TJ = 125°C)
Thermal Response
IGBT (typ.)
V0 = 1.3 V; R0 = 6.5 mW
C
= 0.20 J/K; R
th1
C
= 0.47 J/K; R
th2
= 0.218 K/W
th1
= 0.005 K/W
th2
© 2000 IXYS All rights reserved
Free Wheeling Diode (typ.)
C
= 0.14 J/K; R
th1
C
= 0.26 J/K; R
th2
= 0.443 K/W
th1
= 0.009 K/W
th2
2 - 4
Page 3

MII 100-12 A3 MID 100-12 A3
MDI 100-12 A3
175
TJ = 25°C
A
150
I
C
125
100
75
50
25
0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
VGE=17V
15V
13V
11V
9V
V
V
CE
175
T
= 125°C
J
A
150
I
125
C
100
75
50
25
0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5
Fig. 1 Typ. output characteristics Fig. 2 Typ. output characteristics
150
VCE = 20V
= 25°C
T
J
125
A
I
C
100
75
300
A
250
I
F
200
150
= 125°C
T
J
VGE=17V
15V
13V
11V
9V
V
V
CE
TJ = 25°C
50
25
0
567891011
V
GE
V
100
50
0
01234
Fig. 3 Typ. transfer characteristics Fig. 4 Typ. forward characteristics of
free wheeling diode
20
VCE = 600V
V
= 75A
I
C
15
V
GE
10
5
0
0 100 200 300 400
Q
nC
G
120
A
t
I
RM
rr
80
40
I
RM
0
0 200 400 600 800 1000
Fig. 5 Typ. turn on gate charge Fig. 6 Typ. turn off characteristics of
free wheeling diode
V
F
TJ = 125°C
= 600V
V
R
I
= 75A
F
A/ms
-di/dt
V
100-12
300
ns
200
100
0
t
rr
© 2000 IXYS All rights reserved
3 - 4
Page 4

MII 100-12 A3 MID 100-12 A3
MDI 100-12 A3
E
t
t
on
d(on)
r
W
160
ns
120
t
80
40
0
A
20
mJ
15
E
off
10
5
0
0 50 100 150
I
C
VCE = 600V
V
= ±15V
GE
R
= 15
G
TJ = 125°C
40
mJ
30
E
on
20
VCE = 600V
= ±15V
10
V
GE
= 15
R
G
TJ = 125°C
0
0 50 100 150
I
C
t
E
d(off)
t
f
800
off
ns
600
t
400
W
200
0
A
Fig. 7 Typ. turn on energy and switching Fig. 8 Typ. turn off energy and switching
times versus collector current times versus collector current
t
d(off)
E
2000
ns
1600
t
1200
off
800
25
V
= 600V
CE
mJ
V
= ±15V
GE
20
= 75A
I
E
on
C
= 125°C
T
J
15
10
t
E
t
d(on)
on
r
200
ns
160
t
120
80
25
V
= 600V
CE
mJ
20
E
off
= ±15V
V
GE
I
= 75A
C
= 125°C
T
J
15
10
5
0
0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56
R
G
40
0
W
5
0
0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56
R
G
400
t
f
0
W
Fig. 9 Typ. turn on energy and switching Fig.10 Typ. turn off energy and switching
times versus gate resistor times versus gate resistor
200
A
160
I
CM
120
RG = 15
W
= 125°C
T
80
J
< V
V
CEK
CES
40
0
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200
V
V
CE
1
K/W
0.1
Z
thJC
0.01
diode
IGBT
0.001
0.0001
single pulse
0.00001
0.00001 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1
t
100-12
s
Fig. 11 Reverse biased safe operating area Fig. 12 Typ. transient thermal impedance
RBSOA
© 2000 IXYS All rights reserved
4 - 4
 Loading...
Loading...