Datasheet MCM63Z819TQ11, MCM63Z819TQ11R, MCM63Z819TQ15, MCM63Z819TQ15R, MCM63Z737TQ15 Datasheet (Motorola)
...Page 1
MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Advance Information
128K x 36 and 256K x 18 Bit
Flow–Through ZBT RAM
Synchronous Fast Static RAM
Order this document
by MCM63Z737/D
MCM63Z737
MCM63Z819
The ZBT RAM is a 4M–bit synchronous fast static RAM designed to provide
zero bus turnaround. The ZBT RAM allows 100% use of bus cycles during
back–to–back read/write and write/read cycles. The MCM63Z737 is organized
as 128K words of 36 bits each and the MCM63Z819 is organized as 256K words
of 18 bits each, fabricated with high performance silicon gate CMOS technology .
This device integrates input registers, a 2–bit address counter, and high speed
SRAM onto a single monolithic circuit for reduced parts count in communication
applications. Synchronous design allows precise cycle control with the use of an
external clock (CK). CMOS circuitry reduces the overall power consumption of
the integrated functions for greater reliability .
Addresses (SA), data inputs (DQ), and all control signals except output enable
) and linear burst order (LBO) are clock (CK) controlled through positive–
(G
edge–triggered noninverting registers.
Write cycles are internally self–timed and are initiated by the rising edge of the
clock (CK) input. This feature eliminates complex off–chip write pulse generation
and provides increased timing flexibility for incoming signals.
For read cycles, a flow–through SRAM allows output data to simply flow freely
from the memory array .
• 3.3 V L VTTL and LVCMOS Compatible
• MCM63Z737/MCM63Z819–11 = 11 ns Access/15 ns Cycle (66 MHz)
MCM63Z737/MCM63Z819–15 = 15 ns Access/20 ns Cycle (50 MHz)
• Selectable Burst Sequencing Order (Linear/Interleaved)
• Internally Self–Timed Write Cycle
• Single–Cycle Deselect
• Byte Write Control
• ADV Controlled Burst
• 100–Pin TQFP Package
TQ PACKAGE
TQFP
CASE 983A–01
ZBT and Zero Bus Turnaround are trademarks of Integrated Device Technology, Inc., and the architecture is supported by
Micron Technology, Inc. and Motorola, Inc.
This document contains information on a new product. Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
2/6/98
Motorola, Inc. 1998
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
1
Page 2
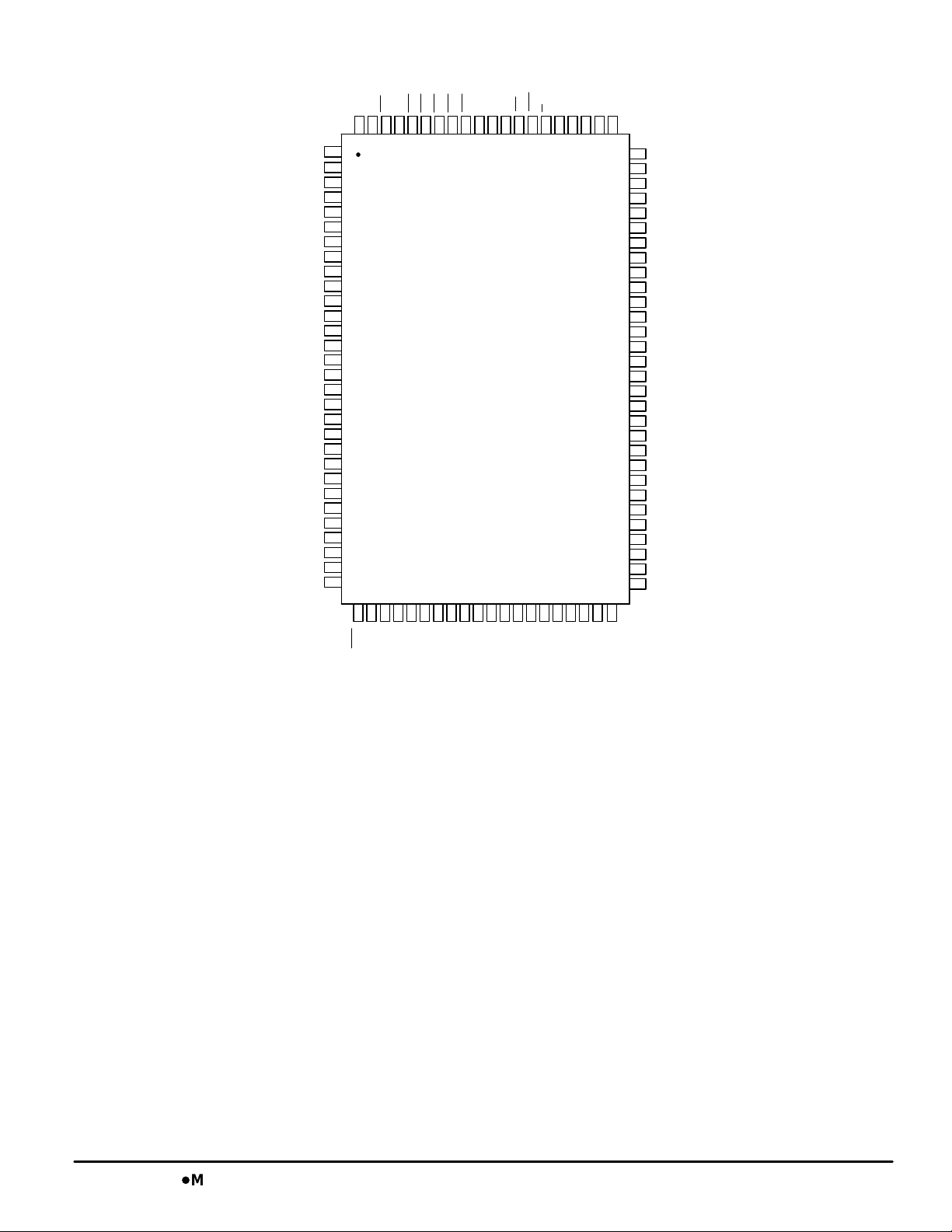
PIN ASSIGNMENT
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
V
V
DQd
V
DDQ
DQd
DQd
DQd
DQd
V
DDQ
DQd
DQd
DQd
DQc
DQc
DQc
V
SS
DQc
DQc
DQc
DQc
V
SS
DQc
DQc
V
SS
DD
DD
V
SS
DQd
V
SS
V
SS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 3233
SASASE1
DD
SE2
SBc
SBa
SBb
SBd
94 93979695 89889291 90 8685871009998 81828384
3738343536 42433940 41 454644
SE3
CK
VSSV
SW
CKE
G
ADV
NC
NC
SA
50494847
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
SA
DQb
DQb
DQb
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQb
DQb
DQb
DQb
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQb
DQb
V
SS
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
DQa
DQa
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQa
DQa
DQa
DQa
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQa
DQa
DQa
SASASA
LBO
SA
NC
SA1
SA0
TOP VIEW
MCM63Z737
NC
V
SS
DD
V
NC
NC
SASASA
SA
SA
SA
SA
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
2
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
Page 3
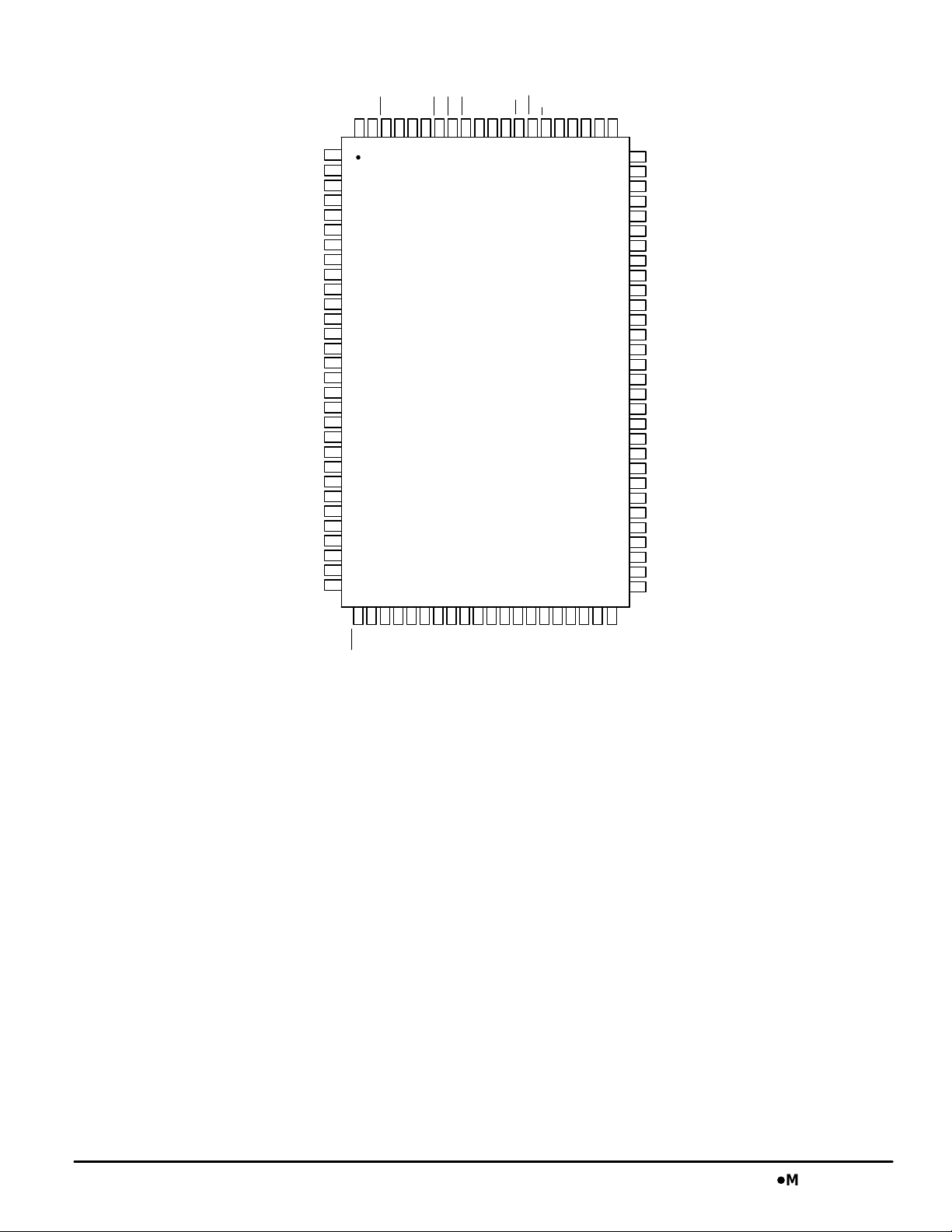
PIN ASSIGNMENT
V
DDQ
DQb
DQb
V
DDQ
DQb
DQb
V
V
DQb
DQb
V
DDQ
DQb
DQb
DQb
V
DDQ
V
V
V
V
V
V
NC
NC
NC
SS
NC
NC
SS
SS
DD
DD
SS
SS
NC
SS
NC
NC
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 3233
SASASE1
DD
SE2
NC
SBa
SBb
NC
94 93979695 89889291 90 8685871009998 81828384
3738343536 42433940 41 454644
SE3
CK
VSSV
SW
CKE
G
ADV
NC
NC
SA
50494847
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
SA
SA
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SS
NC
DQa
DQa
DQa
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQa
DQa
V
SS
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
DQa
DQa
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQa
DQa
NC
NC
V
SS
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
SASASA
LBO
SA
NC
SA1
SA0
TOP VIEW
MCM63Z819
NC
V
SS
DD
V
NC
NC
SASASA
SA
SA
SA
SA
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
3
Page 4
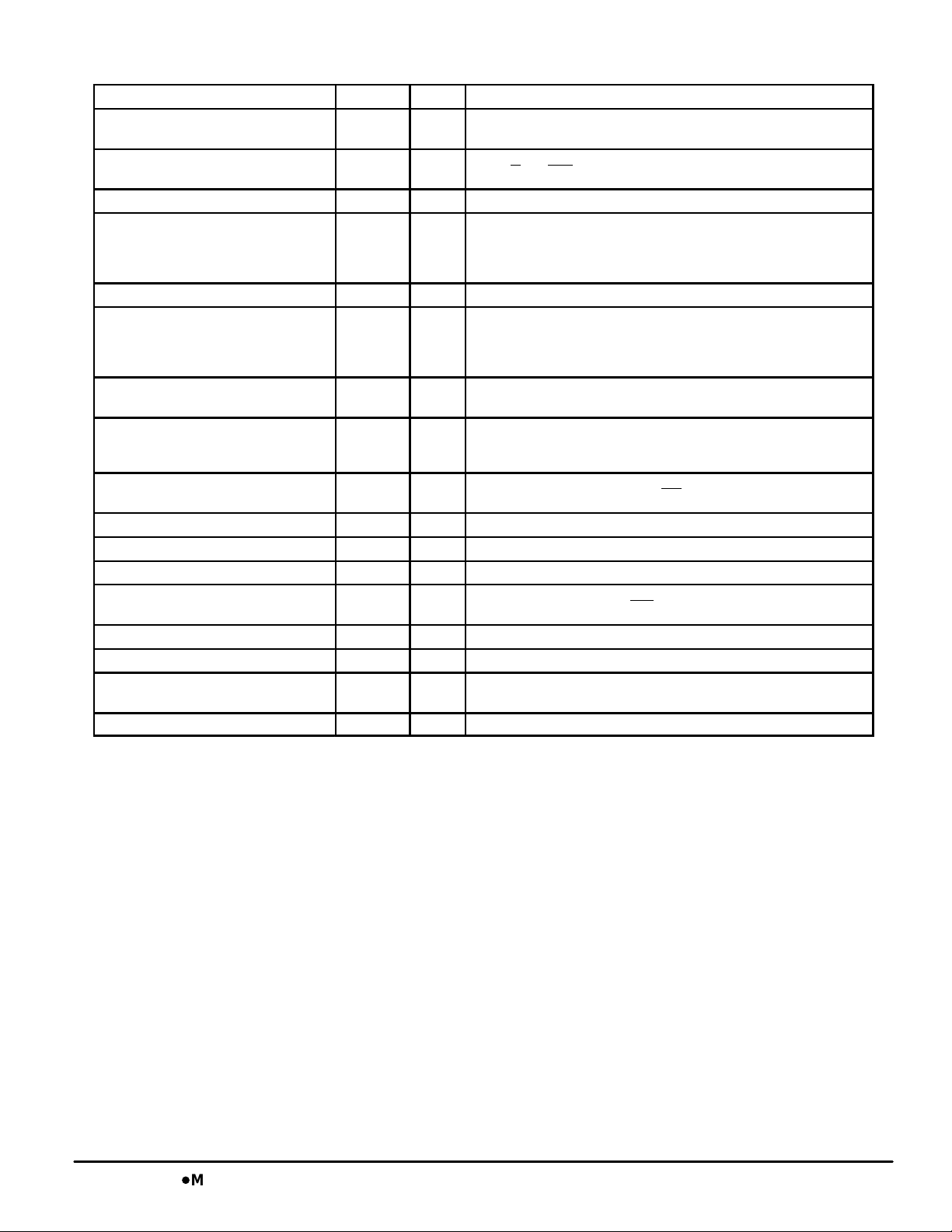
MCM63Z737 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Locations Symbol
85 ADV Input Synchronous Load/Advance: Loads a new address into counter when
89 CK Input Clock: This signal registers the address, data in, and all control signals
87 CKE Input Clock Enable: Disables the CK input when CKE is high.
(a) 51, 52, 53, 56, 57, 58, 59, 62, 63
(b) 68, 69, 72, 73, 74, 75, 78, 79, 80
(c) 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12, 13
(d) 18, 19, 22, 23, 24, 25, 28, 29, 30
86 G Input Asynchronous Output Enable.
31 LBO Input Linear Burst Order Input: This pin must remain in steady state (this
32, 33, 34, 35, 44, 45, 46,
47, 48, 49, 50, 81, 82, 99, 100
36, 37 SA0, SA1 Input Synchronous Burst Address Inputs: The two LSB’s of the address field.
93, 94, 95, 96
(a) (b) (c) (d)
98 SE1 Input Synchronous Chip Enable: Active low to enable chip.
97 SE2 Input Synchronous Chip Enable: Active high for depth expansion.
92 SE3 Input Synchronous Chip Enable: Active low for depth expansion.
88 SW Input Synchronous Write: This signal writes only those bytes that have been
15, 16, 41, 65, 91 V
4, 11, 20, 27, 54, 61, 70, 77 V
5, 10, 14, 17, 21, 26, 40,
55, 60, 64, 66, 67, 71, 76, 90
38, 39, 42, 43, 83, 84 NC — No Connection: There is no connection to the chip.
Type Description
low. RAM uses internally generated burst addresses when high.
except G
DQx I/O Synchronous Data I/O: “x” refers to the byte being read or written
SA Input Synchronous Address Inputs: These inputs are registered and must
SBx Input Synchronous Byte Write Inputs: Enables write to byte “x”
DD
DDQ
V
SS
Supply Core Power Supply.
Supply I/O Power Supply.
Supply Ground.
(byte a, b, c, d).
signal not registered or latched). It must be tied high or low.
Low – linear burst counter.
High – interleaved burst counter.
meet setup and hold times.
These pins must preset the burst address counter values. These inputs
are registered and must meet setup and hold times.
(byte a, b, c, d) in conjunction with SW
selected using the byte write SBx
and LBO.
. Has no effect on read cycles.
pins.
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
4
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
Page 5
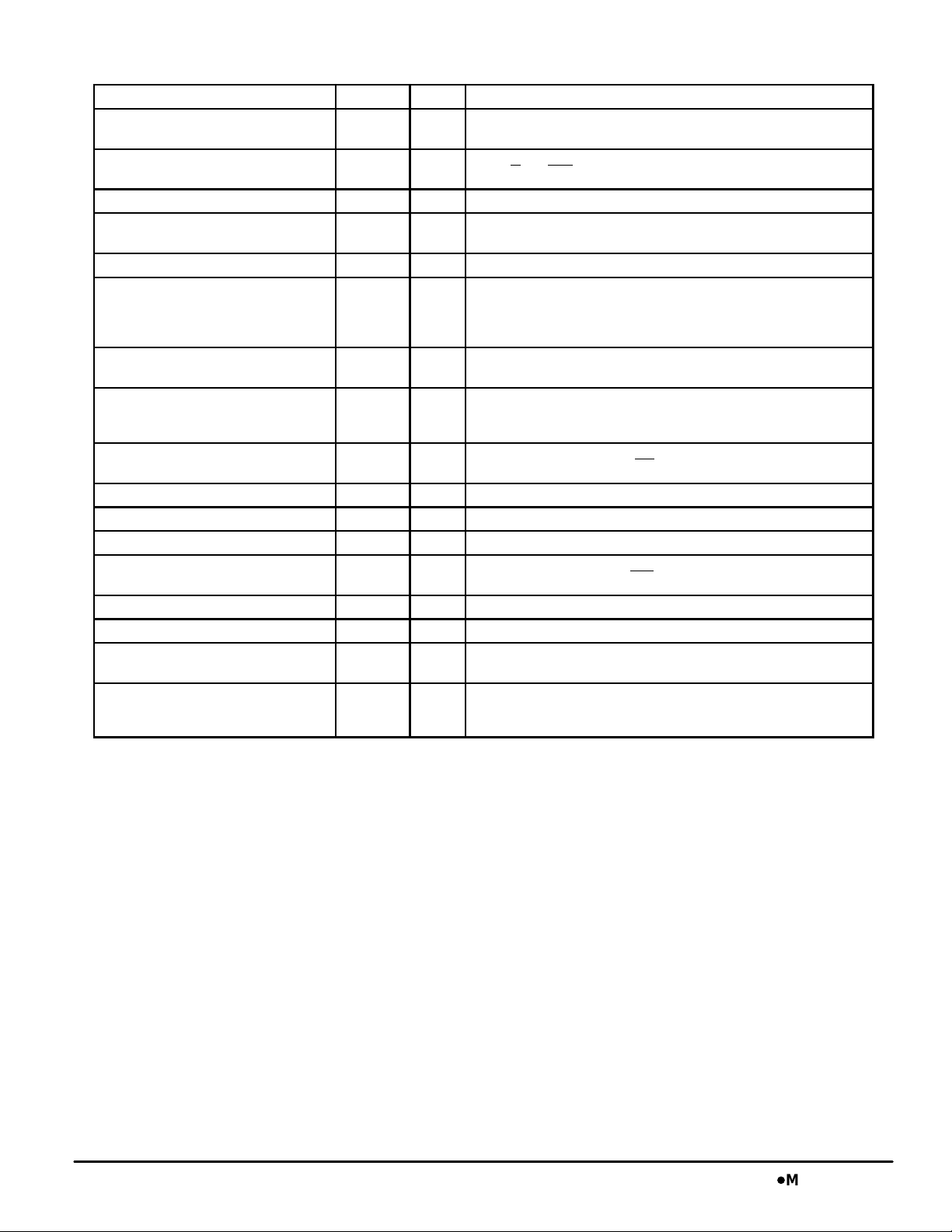
MCM63Z819 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Locations Symbol Type Description
85 ADV Input Synchronous Load/Advance: Loads a new address into counter when
89 CK Input Clock: This signal registers the address, data in, and all control signals
87 CKE Input Clock Enable: Disables the CK input when CKE is high.
(a) 58, 59, 62, 63, 68, 69, 72, 73, 74
(b) 8, 9, 12, 13, 18, 19, 22, 23, 24
86 G Input Asynchronous Output Enable.
31 LBO Input Linear Burst Order Input: This pin must remain in steady state (this
32, 33, 34, 35, 44, 45, 46,
47, 48, 49, 50, 80, 81, 82, 99, 100
36, 37 SA0, SA1 Input Synchronous Burst Address Inputs: The two LSB’s of the address field.
93, 94
(a) (b)
98 SE1 Input Synchronous Chip Enable: Active low to enable chip.
97 SE2 Input Synchronous Chip Enable: Active high for depth expansion.
92 SE3 Input Synchronous Chip Enable: Active low for depth expansion.
88 SW Input Synchronous Write: This signal writes only those bytes that have been
15, 16, 41, 65, 91 V
4, 11, 20, 27, 54, 61, 70, 77 V
5, 10, 14, 17, 21, 26, 40,
55, 60, 64, 66, 67, 71, 76, 90
1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 25, 28, 29, 30, 38,
39, 42, 43, 51, 52, 53, 56, 57,
75, 78, 79, 83, 84, 95, 96
low. RAM uses internally generated burst addresses when high.
except G
DQx I/O Synchronous Data I/O: “x” refers to the byte being read or written
SA Input Synchronous Address Inputs: These inputs are registered and must
SBx Input Synchronous Byte Write Inputs: Enables write to byte “x”
DD
DDQ
V
SS
NC — No Connection: There is no connection to the chip.
Supply Core Power Supply.
Supply I/O Power Supply.
Supply Ground.
(byte a, b).
signal not registered or latched). It must be tied high or low.
Low – linear burst counter.
High – interleaved burst counter.
meet setup and hold times.
These pins must preset the burst address counter values. These inputs
are registered and must meet setup and hold times.
(byte a, b) in conjunction with SW
selected using the byte write SBx
and LBO.
. Has no effect on read cycles.
pins.
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
5
Page 6
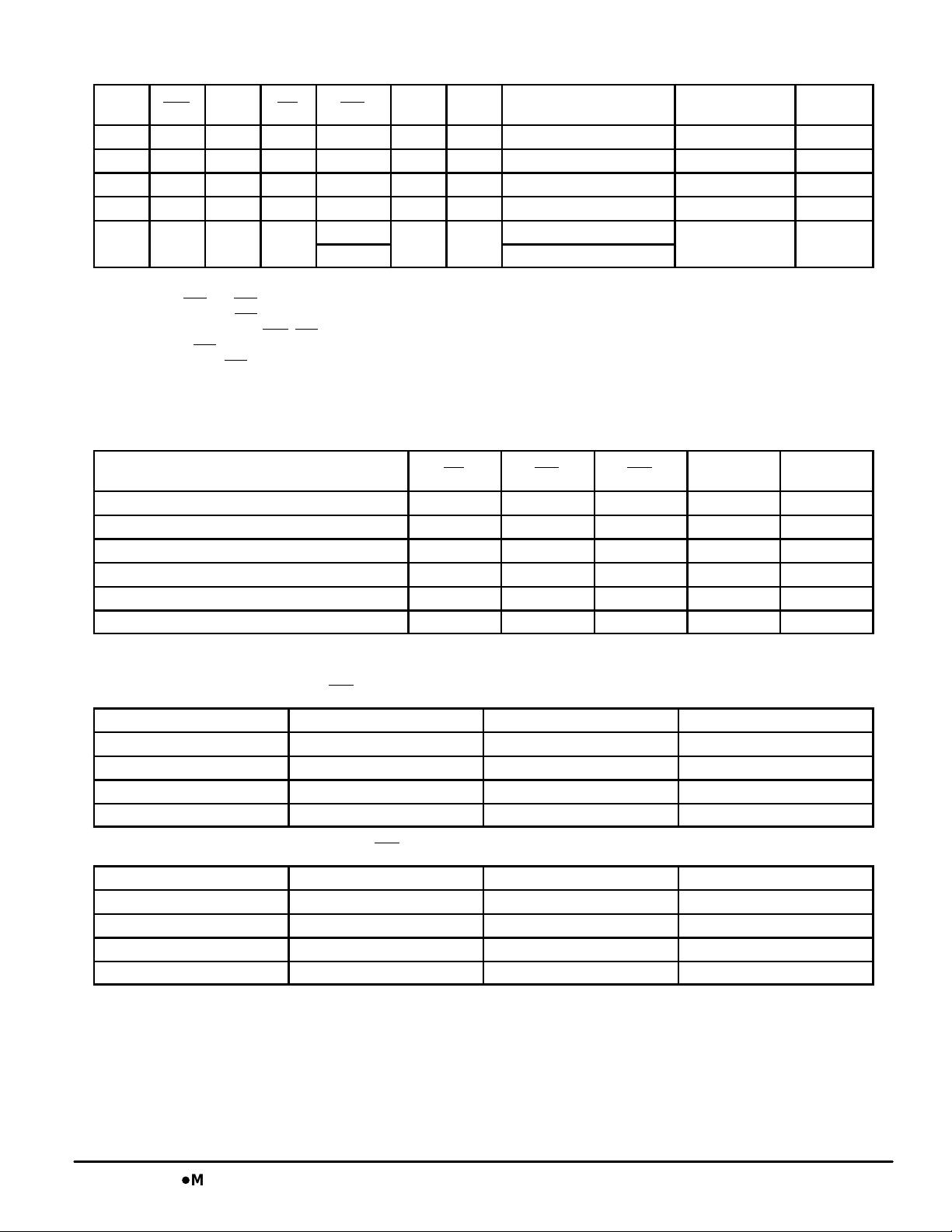
TRUTH TABLE
SA0 –
CK CKE E SW SBx ADV
L–H 1 X X X X X Hold H 1, 2
L–H 0 False X X 0 X Deselect D 1, 2
L–H 0 True 0 V 0 V Load Address, New Write W 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
L–H 0 True 1 X 0 V Load Address, New Read R 1, 2
L–H 0 X X
NOTES:
1. X = don‘t care, 1 = logic high, 0 = logic low, V = valid signal, according to AC Operating Conditions and Characteristics.
2. E = true if SE1
3. Byte write enables, SBx
4. No control inputs except CKE
5. A write with SBx
6. A burst write with SBx
7. ADV controls whether the RAM enters burst mode. If the previous cycle was a write, then ADV = 1 results in a burst write. If the previous
cycle is a read, then ADV = 1 results in a burst read. ADV = 1 will also continue a deselect cycle.
and SE3 = 0, and SE2 = 1.
, are evaluated only as new write addresses are loaded.
, SBx, and ADV are recognized in a clock cycle where ADV is sampled high.
not valid does load addresses.
not valid does increment address.
V (W)
X (R, D) Continue
1 X
SAx
Next Operation
Burst
Input Command
Code
B 1, 2, 4,
Notes
WRITE TRUTH TABLE
SBc
Cycle Type SW SBa SBb
Read H X X X X
Write Byte a L L H H H
Write Byte b L H L H H
Write Byte c (See Note 1) L H H L H
Write Byte d (See Note 1) L H H H L
Write All Bytes L L L L L
NOTE:
1. Valid only for MCM63Z737.
(See Note 1)
SBd
(See Note 1)
6, 7
LINEAR BURST ADDRESS TABLE (LBO = V
1st Address (External) 2nd Address (Internal) 3rd Address (Internal) 4th Address (Internal)
X . . . X00 X . . . X01 X . . . X10 X . . . X11
X . . . X01 X . . . X10 X . . . X11 X . . . X00
X . . . X10 X . . . X11 X . . . X00 X . . . X01
X . . . X11 X . . . X00 X . . . X01 X . . . X10
INTERLEAVED BURST ADDRESS TABLE (LBO = V
1st Address (External) 2nd Address (Internal) 3rd Address (Internal) 4th Address (Internal)
X . . . X00 X . . . X01 X . . . X10 X . . . X11
X . . . X01 X . . . X00 X . . . X11 X . . . X10
X . . . X10 X . . . X11 X . . . X00 X . . . X01
X . . . X11 X . . . X10 X . . . X01 X . . . X00
SS
)
)
DD
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
6
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
Page 7

INPUT
COMMAND
CODE
CK
CKE
INPUT COMMAND CODE AND STATE NAME DEFINITION DIAGRAM
DBW BRBH
DESELECT
CONTINUE
DESELECT
NEW WRITE
BURST
WRITE
NEW READ
BURST
READ
HOLD
FALSEE
SA0 – SAx VALID VALID
ADV
SW
SBX
NOTE: Cycles are named for their control inputs, not for data I/O state.
TRUE TRUE
VALID VALID
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
7
Page 8

B
B
BURST
READ
D
R
W
R
BURST
WRITE
D
W
KEY:
CURRENT
STATE (n)
D
TRANSITION
ƒ
INPUT
COMMAND
CODE
R
STATE (n + 1)
B
NEW
READ
NEXT
W
B
R
DESELECT
D
NOTES:
1. Input command codes (D, W, R, and B) represent control pin inputs
as indicated in the Truth Table.
2. Hold (i.e., CKE
CKE
= 1 blocks clock input and therefore, blocks any state change.
Figure 1. ZBT RAM State Diagram
B
R
W
sampled high) is not shown simply because
NEW
WRITE
D
W
STATE
CK
COMMAND
CODE
DQ
n n + 1 n + 2 n + 3
ƒ
CURRENT
STATE
NEXT
STATE
Figure 2. State Definitions for ZBT RAM State Diagram
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
8
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
Page 9

KEY:
CURRENT
STATE (n)
ƒ
INPUT
COMMAND
CODE
R
B
DATA OUT
(Q VALID)
D
W
B
R
NEXT STATE
n + 1
D
HIGH–Z
W
D
W
HIGH–Z
(DATA IN)
R
NOTES:
1. Input command codes (D, W, R, and B) represent control
pin inputs as indicated in the Truth Table.
2. Hold (i.e., CKE
cause CKE
any state change.
sampled high) is not shown simply be-
= 1 blocks clock input and therefore, blocks
B
STATE
CK
COMMAND
CODE
DQ
Figure 3. Data I/O State Diagram
n n + 1 n + 2 n + 3
ƒ
CURRENT
STATE
NEXT
STATE
Figure 4. State Definitions for ZBT RAM State Diagram
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
9
Page 10

ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (See Note 1)
Rating Symbol Value Unit Notes
Power Supply Voltage V
I/O Supply Voltage V
Input Voltage Relative to VSS for
Any Pin Except V
Input Voltage (Three State I/O) V
Output Current (per I/O) I
Package Power Dissipation P
Temperature Under Bias T
Storage Temperature T
NOTES:
1. Permanent device damage may occur if ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS are
exceeded. Functional operation should be restricted to RECOMMENDED
OPERATING CONDITIONS. Exposure to higher than recommended voltages for
extended periods of time could affect device reliability.
2. This is a steady–state DC parameter that is in effect after the power supply has
achieved its nominal operating level. Power sequencing is not necessary.
3. Power dissipation capability is dependent upon package characteristics and use
environment. See Package Thermal Characteristics.
DD
DD
DDQ
Vin, V
out
bias
stg
out
IT
D
– 0.5 to + 4.6 V
VSS – 0.5 to V
– 0.5 to VDD + 0.5 V 2
VSS – 0.5 to
V
DDQ
– 10 to 85 °C
– 55 to 125 °C
DD
+ 0.5
± 20 mA
1.3 W 3
V 2
V 2
This device contains circuitry to protect the
inputs against damage due to high static voltages or electric fields; however, it is advised
that normal precautions be taken to avoid
application of any voltage higher than maximum rated voltages to this high–impedance
circuit.
PACKAGE THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
Thermal Resistance Symbol Max Unit Notes
Junction to Ambient (@ 200 lfm) Single–Layer Board
Four–Layer Board
Junction to Board (Bottom) R
Junction to Case (Top) R
NOTES:
1. Junction temperature is a function of on–chip power dissipation, package thermal resistance, mounting site (board) temperature, ambient
temperature, air flow, board population, and board thermal resistance.
2. Per SEMI G38–87.
3. Indicates the average thermal resistance between the die and the printed circuit board.
4. Indicates the average thermal resistance between the die and the case top surface via the cold plate method (MIL SPEC–883
Method 1012.1).
R
θJA
θJB
θJC
40
25
17 °C/W 3
9 °C/W 4
°C/W 1, 2
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
10
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
Page 11

DC OPERA TING CONDITIONS AND CHARACTERISTICS
(VDD = 3.3 V ± 5%, TA = 0 to 70°C Unless Otherwise Noted)
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Supply Voltage V
I/O Supply Voltage V
Ambient Temperature T
Input Low Voltage V
Input High Voltage V
Input High Voltage I/O Pins V
*VDD and V
are shorted together on the device and must be supplied with identical voltage levels.
DDQ
V
SS
VSS – 1.0 V
(Voltages Referenced to VSS = 0 V)
V
IH
Figure 5. Undershoot Voltage
DD
* 3.135 3.3 V
DDQ
A
IL
IH
IH2
20% t
3.135 3.3 3.465 V
0 — 70 °C
– 0.3 — 0.8 V
2 — VDD + 0.3 V
2 — V
(MIN)
KHKH
DD
+ 0.3 V
DDQ
V
DC CHARACTERISTICS AND SUPPLY CURRENTS
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Notes
Input Leakage Current (0 V ≤ Vin ≤ VDD) I
Output Leakage Current (0 V ≤ Vin ≤ V
AC Supply Current (Device Selected, All Outputs Open,
Freq = Max) Includes Supply Current for Both VDD and V
Hold Supply Current (Device Selected, Freq = Max,
VDD = Max, V
All Inputs Static at CMOS Levels)
CMOS Standby Supply Current (Device Deselected, Freq = 0,
VDD = Max, V
TTL Standby Supply Current (Device Deselected, Freq = 0,
VDD = Max, V
Output Low Voltage (IOL = 8 mA) V
Output High Voltage (IOH = – 8 mA) V
NOTES:
1. LBO
has an internal pullup and will exhibit leakage currents of ± 5 µA.
2. Reference AC Operating Conditions and Characteristics for Input and Timing.
3. All addresses transition simultaneously low (LSB) then high (MSB).
4. Data states are all zero.
5. Device in deselected mode as defined by the Truth Table.
6. CMOS levels for I/O’s are VIT ≤ VSS + 0.2 V or ≥ V
7. TTL levels for I/O’s are VIT ≤ VIL or ≥ V
= Max, CKE
DDQ
= Max, All Inputs Static at CMOS Levels)
DDQ
= Max, All Inputs Static at TTL Levels)
DDQ
≥ VDD – 0.2 V,
) I
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
. TTL levels for other inputs are Vin ≤ VIL or ≥ VIH.
IH2
– 0.2 V. CMOS levels for other inputs are Vin ≤ VSS + 0.2 V or ≥ VDD – 0.2 V.
lkg(I)
lkg(O)
I
DDA
I
DD1
I
SB2
I
SB3
OL
OH
— — ± 1 µA 1
— — ± 1 µA
— — 300 mA 2, 3, 4
— — 15 mA 6
— — 5 mA 5, 6
— — 25 mA 5, 7
— — 0.4 V
2.4 — — V
CAPACITANCE (f = 1.0 MHz, dV = 3.0 V, T
Parameter
Input Capacitance C
Input/Output Capacitance C
= 0 to 70°C, Periodically Sampled Rather Than 100% Tested)
A
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
in
I/O
— 4 5 pF
— 7 8 pF
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
11
Page 12

AC OPERA TING CONDITIONS AND CHARACTERISTICS
(VDD = 3.3 V ± 5%, TA = 0 to 70°C Unless Otherwise Noted)
Input Timing Measurement Reference Level 1.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input Pulse Levels 0 to 3.0 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input Rise/Fall Time 1 V/ns (20% to 80%). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output Timing Reference Level 1.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output Load See Figure 6 Unless Otherwise Noted. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
R
Under Test TBD. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
θJA
READ/WRITE CYCLE TIMING (See Notes 1 and 2)
MCM63Z737–1 1
MCM63Z819–1 1
66 MHz
Parameter Symbol
Cycle Time t
Clock High Pulse Width t
Clock Low Pulse Width t
Clock Access Time t
Output Enable to Output Valid t
Clock High to Output Active t
Output Hold Time t
Output Enable to Output Active t
Output Disable to Q High–Z t
Clock High to Q High–Z t
Setup Times: Address
Clock Enable
Hold Times: Address
Clock Enable
NOTES:
1. Write is defined as any SBx
2. All read and write cycle timings are referenced from CK or G
3. In order to reduce test correlation issues and to reduce the effects of application specific input edge rate variations on correlation between
data sheet parameters and actual system performance, FSRAM AC parametric specifications are always specified at V
design exercises, it is desirable to evaluate timing using other reference levels. Since the maximum test input edge rate is known and is
given in the AC Test Conditions section of the data sheet as 1 V/ns, one can easily interpolate timing values to other reference levels.
4. This parameter is sampled and not 100% tested.
5. Measured at
± 200 mV from steady state.
and SW low. Chip enable is defined as SE1 low, SE2 high, and SE3 low whenever ADV is low.
ADV
Data In
Write
Chip Enable
ADV
Data In
Write
Chip Enable
KHKH
KHKL
KLKH
KHQV
GLQV
KHQX1
KHQX
GLQX
GHQZ
KHQZ
t
ADKH
t
LVKH
t
DVKH
t
WVKH
t
EVKH
t
CVKH
t
KHAX
t
KHLX
t
KHDX
t
KHWX
t
KHEX
t
KHCX
Min Max Min Max
15 — 20 — ns
6 — 8 — ns 3
6 — 8 — ns 3
— 11 — 15 ns
— 6 — 7 ns
1.5 — 1.5 — ns 4, 5
1.5 — 1.5 — ns 4
0 — 0 — ns 4, 5
— 4.5 — 5 ns 4, 5
1.5 4.5 1.5 5 ns 4, 5
2.5
2.5
2
2.5
2.5
2.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
.
— 2.5
— 0.5
MCM63Z737–15
MCM63Z819–15
50 MHz
2.5
2
2.5
2.5
2.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
Unit Notes
— ns
— ns
DDQ
/2. In some
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
12
OUTPUT
Z0 = 50
Ω
1.5 V
Figure 6. AC Test Load
RL = 50
Ω
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
Page 13

CK
SA0 – SAx
SW
SBx
E
ADV
t
AVKH
t
WVKH
t
WVKH
t
EVKH
t
LVKH
t
KHKH
t
KHKL
t
KLKH
t
KHAX
t
KHWX
t
KHWX
t
KHEX
t
KHLX
t
CKE
DQ
DQ
DQ
G
CVKH
t
KHQX1
t
GLQX
t
GLQV
t
KHQV
t
DVKH
t
KHCX
D
Q
t
GHQZ
Q
t
KHDX
t
KHQX
Q
Figure 7. AC Timing Parameter Definitions
t
KHQZ
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
13
Page 14

READ/WRITE CYCLES WITH HOLD AND DESELECT CYCLES
RHWRDWRD
D
Q(A0) D(B0) Q(C0) D(D0) Q(E0) D(F0) Q(G0) D(H0) Q(I0)
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
14
CK
AB CD E FG HIJ
ADDRESS
RWHRW
CODE
COMMAND
DQ
NOTE: Command code definitions are shown in Truth Table.
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
Page 15

BBBB
R
Q(C0) Q(C1) Q(C2) Q(C3) Q(C0)
Q(B3)
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
READ CYCLES (SINGLE, BURST, AND BURST WRAP–AROUND)
CK
AB C
ADDRESS
RRBBB
CODE
COMMAND
Q(A0) Q(B0) Q(B1) Q(B2)
DQ
NOTE: Command code definitions are shown in Truth Table.
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
15
Page 16

BBBB
D(C0) D(C1) D(C2) D(C3) D(C0)
WRITE CYCLES (SINGLE, BURST, AND BURST WRAP–AROUND)
CK
AB C
ADDRESS
W
WWBBB
CODE
COMMAND
D(B3)
D(B0) D(B1) D(B2)
D(A0)
DQ
NOTE: Command code definitions are shown in Truth Table.
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
16
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
Page 17

Q(D0) Q(E0)
RR
BC D DE
READ, WRITE, READ COHERENCY WITH HOLD, AND DESELECT CYCLES
AB C
CK
ADDRESS
BDWH
R
RWRWB
CODE
COMMAND
Q(C0) Q(C1) D(D0)
D(C1)
Q(A0) D(B0) Q(B0) D(C0)
DQ
NOTE: Command code definitions are shown in Truth Table.
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
17
Page 18

ORDERING INFORMATION
(Order by Full Part Number)
Motorola Memory Prefix
Part Number
Full Part Numbers — MCM63Z737TQ11 MCM63Z737TQ15
MCM 63Z819 XX X X
63Z737
Blank = Trays, R = Tape and Reel
Speed (1 1 = 11 ns, 15 = 15 ns)
Package (TQ = TQFP)
MCM63Z737TQ11R MCM63Z737TQ15R
MCM63Z819TQ11 MCM63Z819TQ15
MCM63Z819TQ11R MCM63Z819TQ15R
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
18
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
Page 19

–A–
4X
A–B0.20 (0.008) H
D
80 51
81
–D–
P ACKAGE DIMENSIONS
TQ PACKAGE
100–PIN TQFP
CASE 983A–01
2X 30 TIPS
C D
A–B0.20 (0.008)
50
E/2
–B–
E1
E1/2
e
e/2
B
B
–X–
X=A, B, OR D
VIEW Y
E
BASE
METAL
PLATING
b1
–H–
–C–
SEATING
PLANE
0.05 (0.002)
100
2X 20 TIPS
A
S
A2
A1
D1/2
C D
S
R1
VIEW AB
31
301
D/2
D1
D
A–B0.20 (0.008)
q
2
q
3
0.10 (0.004)
C
VIEW AB
q
1
0.25 (0.010)
GAGE PLANE
R2
L2
L
q
L1
c
b
0.13 (0.005) D
NOTES:
1. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ANSI
Y14.5M, 1982.
2. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: MILLIMETER.
3. DATUM PLANE –H– IS LOCATED AT BOTTOM OF
LEAD AND IS COINCIDENT WITH THE LEAD
WHERE THE LEAD EXITS THE PLASTIC BODY AT
THE BOTTOM OF THE PARTING LINE.
4. DATUMS –A–, –B– AND –D– TO BE DETERMINED AT
DATUM PLANE –H–.
5. DIMENSIONS D AND E TO BE DETERMINED AT
SEATING PLANE –C–.
6. DIMENSIONS D1 AND E1 DO NOT INCLUDE MOLD
PROTRUSION. ALLOWABLE PROTRUSION IS 0.25
(0.010) PER SIDE. DIMENSIONS D1 AND B1 DO
INCLUDE MOLD MISMATCH AND ARE
DETERMINED AT DATUM PLANE –H–.
7. DIMENSION b DOES NOT INCLUDE DAMBAR
PROTRUSION. DAMBAR PROTRUSION SHALL NOT
CAUSE THE b DIMENSION TO EXCEED 0.45 (0.018).
DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
A ––– 1.60 ––– 0.063
A1 0.05 0.15 0.002 0.006
A2 1.35 1.45 0.053 0.057
b 0.22 0.38 0.009 0.015
b1 0.22 0.33 0.009 0.013
c 0.09 0.20 0.004 0.008
c1 0.09 0.16 0.004 0.006
D 22.00 BSC 0.866 BSC
D1 20.00 BSC 0.787 BSC
E 16.00 BSC 0.630 BSC
E1 14.00 BSC 0.551 BSC
e 0.65 BSC 0.026 BSC
L 0.45 0.75 0.018 0.030
L1 1.00 REF 0.039 REF
L2 0.50 REF
S 0.20 ––– 0.008 –––
R1 0.08 ––– 0.003 –––
R2 0.08 0.20 0.003 0.008
q
q
1
q
2
q
3
M
SECTION B–B
0 7 0 7
_
0 ––– 0 –––
_
11 13 11 13
_
11 13 11 13
_
C
_
_
_
A–B
INCHESMILLIMETERS
0.020 REF
_
_
_
_
c1
S
S
_
_
_
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
19
Page 20

Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty , representation or guarantee regarding
the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and
specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. “T ypical” parameters which may be provided in Motorola
data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters, including “Typicals”
must be validated for each customer application by customer’s technical experts. Motorola does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of
others. Motorola products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other
applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury
or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Motorola
and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees
arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that
Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. Motorola and are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal
Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
How to reach us:
USA/EUROPE/ Locations Not Listed: Motorola Literature Distribution; JAPAN: Nippon Motorola Ltd.: SPD, Strategic Planning Office, 141,
P.O. B o x 5405, Denver , Colorado, 80217. 1-303-675-2140 or 1-800-441-2447 4-32-1 Nishi-Gotanda, Shagawa-ku, Tokyo, Japan. 03-5487-8488
Mfax: RMFAX0@email.sps.mot.com – TOUCHTONE 1-602-244-6609 ASIA/P ACIFIC: Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.; 8B T ai Ping Industrial Park,
Motorola Fax Back System – US & Canada ONLY 1-800-774-1848 51 Ting Kok Road, Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong. 852-26629298
– http://sps.motorola.com/mfax/
HOME PAGE: http://motorola.com/sps/ CUST OMER FOCUS CENTER: 1-800-521-6274
Mfax is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
MCM63Z737DMCM63Z819
20
◊
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM
MCM63Z737/D
 Loading...
Loading...