Page 1
MOTOROLA, INC. 1997
MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Order this Data Sheet by MC92053/D
Product Brief
MC92053
Quad FTTC Network Framer
The MC92053 is a peripheral device composed of four parallel bidirectional TC-sublayer functional units with
UTOPIA Level 2 compliant ATM-layer ports.
MC92053 Features
• Implements the DAVIC short-range baseband asymmetrical physical layer standard
• Interfaces to an ATM-layer device using a multi-PHY UTOPIA Level 2 compliant interface
• Provides an 8-bit system interface as a generic slave device
• IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) boundary scan test port
• 3.3 V operation with TTL compatibility on I/O pins
• Extended temperature operation: -40 to 85°C
• Available in 208 Pin Plastic Quad Flat Package
Each of the four framers:
• Provides a bit rate of up to 51.84 Mbit/sec downstream
• Controls the TIme Division Multiple Access (TDMA) among up to 4 user devices
• Supports a bit rate of up to 6.48 Mbit/s upstream, including DAVIC Bit Rates B, C, and D
• Includes serial data link interfaces for upstream and downstream frames
• Performs convolutional interleaving of the downstream payload blocks for the full range of interleaving
depths (M = 1-31) using an external 32K x 16 SRAM shared by all four framers
• Performs Reed-Solomon encoding of the downstream frames and decoding of the upstream frames
• Performs ATM cell TC functions, including HEC-based error detection and correction on the upstream data
• Includes serial data interfaces to Physical Media Devices (PMD).
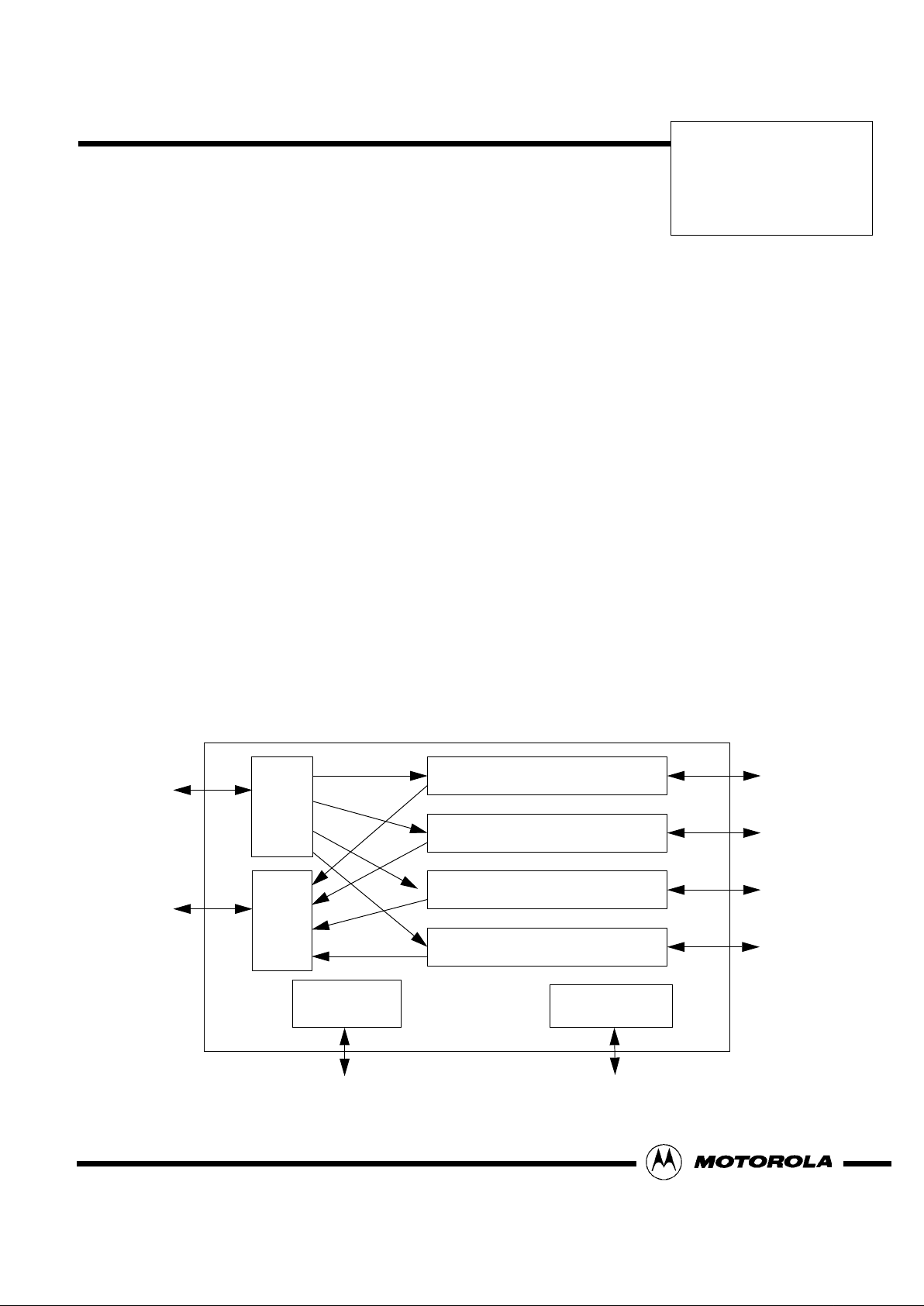
Figure 1. MC92053 Block Diagram
Microprocessor
JTAG Controller
Tx
UTOPIA
I/F
Interface
Rx
UTOPIA
I/F
Framer #1
Framer #2
Framer #3
Framer #0
MC92053
This document contains information on a new product.
Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
Page 2
Motorola MC92053
2
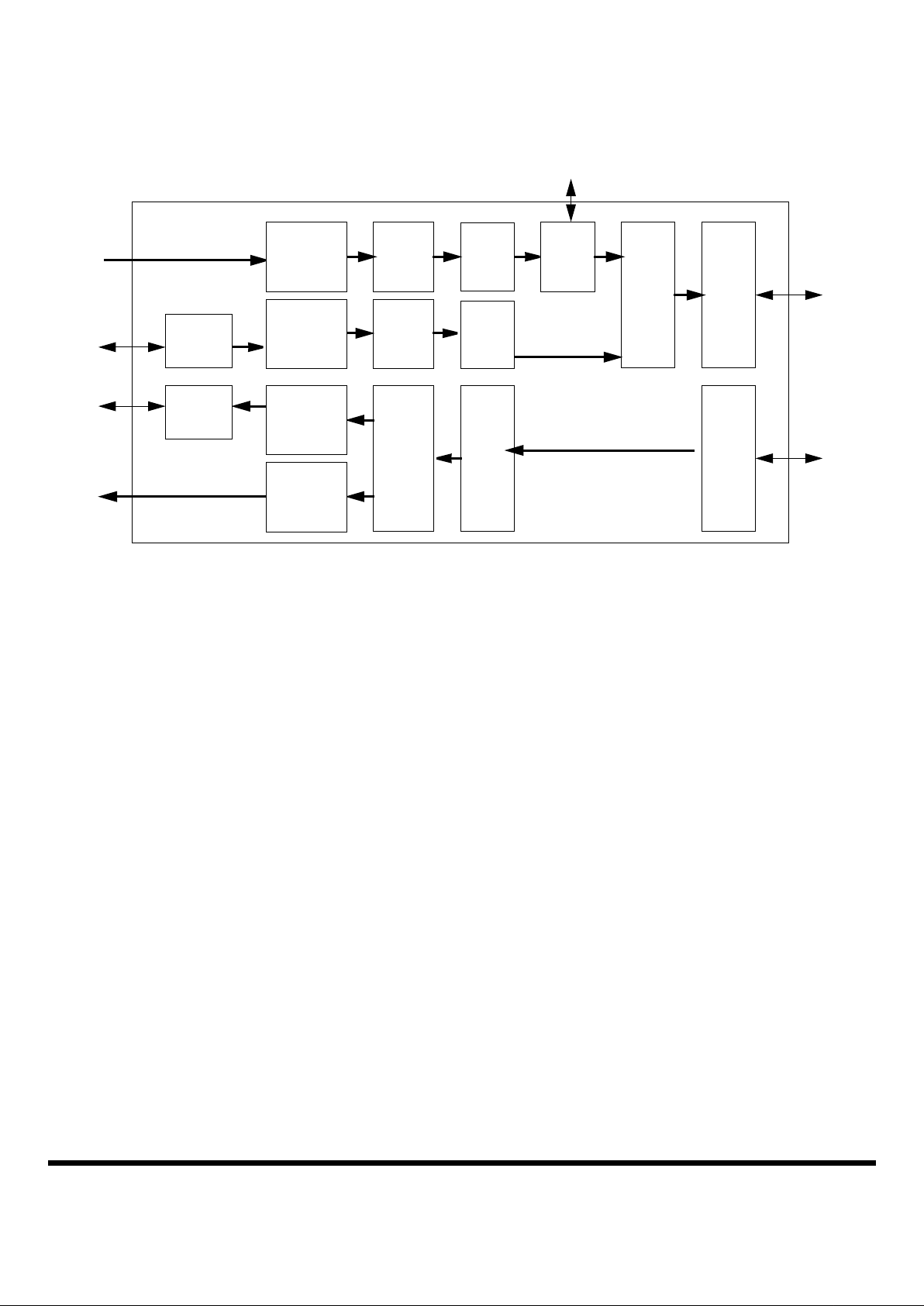
Figure 2. Framer Block Diagram
General Description
The MC92053 implements four copies of the TC sublayer of the DAVIC asymmetrical FTTC PHY specification
for network devices. The MC92053 key functional
blocks are described in the paragraphs which follow.
Tx UTOPIA Interface
The Transmit UTOPIA interface accepts ATM cells from
the ATM layer according to the UTOPIA Level 2 specification. Each cell is stored in one of the four transmit
cell FIFO’s. This block uses TXCLK provided by the
ATM layer. The FIFO’s are used for rate adaptation between TXCLK (the UTOPIA interface clock) and the device clock.
Rx UTOPIA Interface
The receive UTOPIA interface reads ATM cells from the
four receive cell FIFO’s and transfers them to the ATM
layer according to the ATM Forum UTOPIA Level 2
specification. This block uses RXCLK provided by the
ATM layer. The FIFO is used for rate adaptation between RXCLK (the UTOPIA interface clock) and the device clock.
Microprocessor Interface
The microprocessor interface is an 8-bit generic slave
interface. It is used for initializing the internal registers
and reading status registers and counters.
JTAG
The MC92053 provides JTAG boundary scan.
Framers
Each of the four framers performs the TC functions for
a single user. The blocks contained in a framer are
shown in Figure 2 and are described in the paragraphs
which follow.
Tx Cell Functions
The transmit cell functions block reads ATM cells from
a transmit cell FIFO. If there are no cells available when
a downstream frame should be transmitted, the cell
functions block generates an idle cell. It calculates the
HEC value based on the ATM header of each cell and
inserts it in the fifth octet of the cell. This block also randomizes the payload of the ATM cells according to
ITU-T Recommendation I.432.
A count of the cells transferred from the transmit cell
FIFO is maintained.
Data Link Insertion Block
The data link insertion block provides direct serial access to the data link bytes of the downstream frame
headers. The data link stream for the downstream
frames is optionally inserted using an output clock pin
and an input data pin. The device ID to which the data
link stream is destined is programmable.
Framing
Inter-
leaver
Random-
izer
Tx
PMD
I/F
ReedSolomon
Decoder
Deran-
domizer
Rx
PMD
I/F
ReedSolomon
Encoder
Tx Cell
Functions
Data
Link
Insertion
ReedSolomon
Encoder
Random-
izer
Frame
Interpretation
Rx Cell
Functions
Data
Link
Extraction
Header
Frame
Generation
Header
Page 3

MC92053 Motorola
3
Frame Header Generation Block
The frame header generation block generates the 12
header bytes (excluding the two sync bytes) for each
downstream frame. One of the main functions of this
block is to allocate grants to the user devices. A programmable grant allocation mechanism is implemented
to provide a combination of fixed and on-demand allocations in order to support both CBR and ABR connections.
Randomizers
The data is randomized for better transmission performance. The two randomizers are identical. One is used
for 12 header bytes per frame, and the other is used for
the (12 * 58) payload bytes per frame.
Reed-Solomon Encoders
There are two Reed-Solomon encoders. One encoder
adds four parity bytes to the 12 header bytes to produce
a (16,12) RS code. The other encoder adds eight parity
bytes to each block of 58 payload bytes to produce
(66,58) RS codes.
Interleaver
The interleaver block spreads the blocks of payload
data over a large period of time. Transmitting interleaved data allows for better correction of bursts of errors because the deinterleaver at the receiving end
spreads the incorrect data over many blocks so that the
Reed-Solomon decoder can correct the small number
of errors in each block.
The interleaver separates the data byte stream into 33
branches. Each of the branches is delayed by a different amount, and then they are recombined into a single
data stream. The delay of branch k (0 ≤ k ≤ 32) is M * k.
M is the programmable Interleaving Depth Parameter
which is included in the downstream frame header and
ranges from 0 to 31. M=0 effectively disables the interleaver.
The delay of the interleaver/deinterleaver combination
is 1056 * M payload byte periods.
The four interleavers are implemented together since
the downstream frame alignment is synchronized
among the four framers. This requires the same value
of M to be used for all four framers.
An external SRAM must be provided for temporary storage of the data unless interleaving is disabled.
Tx PMD Interface
The Tx PMD interface block constructs the downstream
frames by combining the 2 sync bytes with 1 header
block and 12 payload blocks. It transmits a serial data
stream along with a signal that indicates the symbol
alignment.
Rx PMD Interface
The receive PMD interface consists of a clock signal, a
data signal, and a start-of-frame signal. The clock signal
is only required to be active while valid data is being
transferred. The start-of-frame signal indicates the first
bit of each frame.
Reed-Solomon Decoder
The Reed-Solomon decoder operates on the 65-byte
RS codeword of the upstream frame. It either corrects
up to 4 bytes of the 57 data bytes or declares the frame
to be uncorrectable, in which case the frame is discarded.
Derandomizer
The received data has been randomized on the user
side for better transmission performance. The derandomizer performs the inverse function to restore the
original data. The derandomizer is initialized at the beginning of each frame.
Frame Header Interpretation Block
The frame header interpretation block extracts the useful information from the received frame header. It provides status information to both the frame header
generation block and to the processor.
Data Link Extraction Block
The data link extraction block optionally provides the
data link bytes of the upstream frame headers to a serial
data link controller (e.g., MC68360 QUICC) for further
processing. The received upstream data link bytes are
filtered on the basis of the device ID in the data link address byte according to a programmable filter. The filtered data link stream is extracted using a clock pin and
a data pin.
Rx Cell Functions
The receive cell functions block checks the received
HEC value against the calculated value and corrects
single-bit errors in the header. Any cell with non-correctable errors is discarded. Also, all idle cells are discarded.
The cell functions block transfers entire ATM cells to the
receive cell FIFO. A count of the cells transferred to the
receive cell FIFO is maintained.
Page 4

Motorola MC92053
4
System Functional Description
Downstream Data Flow
In the downstream direction, the MC92053 receives
ATM cells from an ATM-layer device. Each cell is directed to one of the four downstream framers as indicated
by the ATM layer. Each framer adds idle cells, as necessary, to produce a continuous cell stream.
The ATM cell stream is randomized and then divided
into blocks of 58 bytes. The Reed-Solomon encoder
adds eight parity bytes to each block. The block is then
sent to the interleaver.
Frame headers are generated internally. The frame
headers include the control of the TDMA for the upstream direction. A data link byte may also be included.
Each header is randomized, and then the Reed-Solomon encoder adds four parity bytes.
One frame header is combined with twelve payload
blocks from the output of the interleaver to produce an
810-byte frame. Such frames are transmitted continuously through the Tx PMD interface.
Upstream Data Flow
In the upstream direction, the MC92053 receives the
frames recovered by the PMD device. Each frame undergoes error correction by a Reed-Solomon decoder.
The corrected frame is derandomized, and then the
frame header is separated from the ATM cell.
The frame header is processed in accordance with the
definition of the header bytes. The payload is sent to the
cell functions block. Any physical layer cells are discarded, and the remaining cells are transferred to the ATM
layer using a UTOPIA-compliant interface shared by the
four framers.
Other Functions
A microprocessor interface is provided for configuration
control and status monitoring.
A standard IEEE 1149.1 boundary scan test port is provided.
Applications
The primary application of the MC92053 is to provide
TC-sublayer processing functions for a network device,
e.g., an optical network unit (ONU), in an FTTC network. Figure 3 shows the location of the network device
within an FTTC network. Figure 4 shows a generic ONU
architecture using the MC92053.
The MC92053 uses an external memory for convolutional interleaving of the downstream data. If interleaving is not performed, the external memory is not
required.
Figure 3. Typical FTTC Network
Access
Network
optical fiber
ONU
coax / copper pair
Passive
Splitter
Network
Device
User Device
(Set-Top Box /
Adaptor Card / etc.)
Passive
Splitter
MC92052
User Device
(Set-Top Box /
Adaptor Card / etc.)
MC92052
User Device
(Set-Top Box /
Adaptor Card / etc.)
MC92052
User Device
(Set-Top Box /
Adaptor Card / etc.)
MC92052
MC92053
Network
Device
MC92053
Page 5

MC92053 Motorola
5
Figure 4. Generic ONU
MCM6206
SRAM
MCM6306
or
MCM6206
SRAM
MCM6306
or
MCM6206
SRAM
MCM6306
or
optical fiber
ONU
coax / copper pair
PHY
Device
ATM-Layer
Device
ATM-Layer
Device
MC92053
UTOPIA
ATM-Layer
Device
MC92053
µP
µP
PMD
PMD
PMD
PMD
PMD
PMD
PMD
PMD
Level 2
UTOPIA
Level 2
MCM6206
SRAM
MCM6306
or
Switch
Fabric
Table 1. MC92053 Package/Frequency Availability
Package Type Frequency (MHz) Temperature Order Number
208-pin PQFP 0 - 52 -40˚ to 85˚ C MC92053CN
Page 6

MC92053/D
http://www.mot.com/ADC
How to reach us:
USA/EUROPE/Locations Not Listed: Motorola Literature Distribution; JAPAN: Nippon Motorola Ltd.; Tatsumi-SPD-JLDC, 6F Seibu-Butsuryu-Center,
P.O. Box 5405, Denver Colorado 80217. 1-800-441-2447 or 303-675-2140 3-14-2 Tatsumi Koto-Ku, Tokyo 135, Japan. 81-3-3521-8315
MFax
TM
: RMFAX0@email.sps.mot.com -TOUCHTONE (602) 244-6609 ASIA/PACIFIC:Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.; 8B Tai Ping Industrial Park,
INTERNET: http://www.mot-sps.com 51 Ting Kok Road, Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong. 852-26629298
Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the
suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and
specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters which may be provided in Motorola
data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters, including
“Typicals” must be validated for each customer application by customer’s technical experts. Motorola does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the
rights of others. Motorola products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other
applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury
or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold
Motorola and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney
fees arising out of directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that
Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. Motorola and are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal
Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
 Loading...
Loading...