Page 1
MOTOROLA CMOS LOGIC DATA
1
MC14538B
The MC14538B is a dual, retriggerable, resettable monostable multivibrator. It may be triggered from either edge of an input pulse, and produces an
accurate output pulse over a wide range of widths, the duration and accuracy
of which are determined by the external timing components, CX and RX.
• Unlimited Rise and Fall Time Allowed on the A Trigger Input
• Pulse Width Range = 10 µs to 10 s
• Latched Trigger Inputs
• Separate Latched Reset Inputs
• 3.0 Vdc to 18 Vdc Operational Limits
• Triggerable from Positive (A Input) or Negative–Going Edge (B–Input)
• Capable of Driving Two Low–power TTL Loads or One Low–power
Schottky TTL Load Over the Rated Temperature Range
• Pin–for–pin Compatible with MC14528B and CD4528B (CD4098)
• Use the MC54/74HC4538A for Pulse Widths Less Than 10 µs with
Supplies Up to 6 V.
MAXIMUM RATINGS* (Voltages Referenced to V
SS
)
Symbol
Parameter
Value
Unit
V
DD
DC Supply Voltage
– 0.5 to + 18.0
V
Vin, V
out
Input or Output Voltage (DC or Transient)
– 0.5 to VDD + 0.5
V
Iin, I
out
Input or Output Current (DC or Transient),
per Pin
± 10
mA
P
D
Power Dissipation, per Package†
500
mW
T
stg
Storage Temperature
– 65 to + 150
_
C
T
L
Lead Temperature (8–Second Soldering)
260
_
C
*Maximum Ratings are those values beyond which damage to the device may occur.
†Temperature Derating:
Plastic “P and D/DW” Packages: – 7.0 mW/_C From 65_C To 125_C
Ceramic “L” Packages: – 12 mW/_C From 100_C To 125_C
ONE–SHOT SELECTION GUIDE
100 ns
MC14528B
MC14536B
MC14538B
MC14541B
MC4538A*
1 µs 10 µs 100 µs 1 ms 10 ms 100 ms 1 s 10 s
*LIMITED OPERATING VOLTAGE (2 – 6 V)
TOTAL OUTPUT PULSE WIDTH RANGE
RECOMMENDED PULSE WIDTH RANGE
23 HR
5 MIN.
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Motorola, Inc. 1995
REV 3
1/94
L SUFFIX
CERAMIC
CASE 620
ORDERING INFORMATION
MC14XXXBCP Plastic
MC14XXXBCL Ceramic
*MC14XXXBDW SOIC
TA = – 55° to 125°C for all packages.
P SUFFIX
PLASTIC
CASE 648
DW SUFFIX
SOIC
CASE 751G
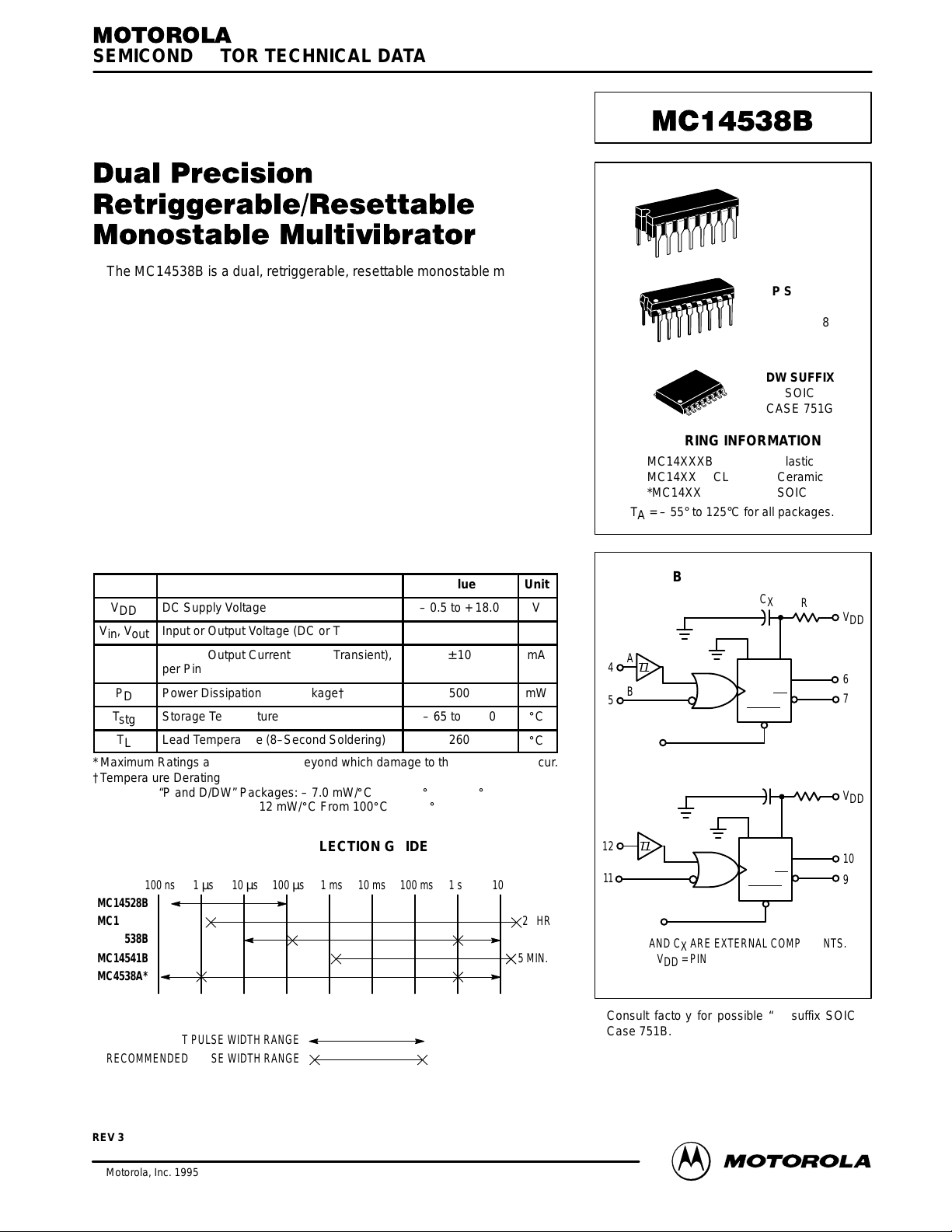
BLOCK DIAGRAM
*Consult factory for possible “D” suffix SOIC
Case 751B.
V
DD
V
DD
6
7
10
9
12
11
5
4
A
B
C
X
R
X
1 2
Q1
Q1
RESET
3
C
X
R
X
15 14
Q2
Q2
RESET
13
A
B
RX AND CX ARE EXTERNAL COMPONENTS.
VDD = PIN 16
VSS = PIN 8, PIN 1, PIN 15
Page 2
MOTOROLA CMOS LOGIC DATAMC14538B
2
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Voltages Referenced to V
SS
)
V
DD
– 55_C 25_C 125_C
Characteristic
Symbol
DD
Vdc
Min Max Min Typ # Max Min Max
Unit
Output Voltage “0” Level
Vin = VDD or 0
V
OL
5.0
10
15
—
—
—
0.05
0.05
0.05
—
—
—
0
0
0
0.05
0.05
0.05
—
—
—
0.05
0.05
0.05
Vdc
“1” Level
Vin = 0 or V
DD
V
OH
5.0
10
15
4.95
9.95
14.95
—
—
—
4.95
9.95
14.95
5.0
10
15
—
—
—
4.95
9.95
14.95
—
—
—
Vdc
Input Voltage “0” Level
(VO = 4.5 or 0.5 Vdc)
(VO = 9.0 or 1.0 Vdc)
(VO = 13.5 or 1.5 Vdc)
V
IL
5.0
10
15
—
—
—
1.5
3.0
4.0
—
—
—
2.25
4.50
6.75
1.5
3.0
4.0
—
—
—
1.5
3.0
4.0
Vdc
“1” Level
(VO = 0.5 or 4.5 Vdc)
(VO = 1.0 or 9.0 Vdc)
(VO = 1.5 or 13.5 Vdc)
V
IH
5.0
10
15
3.5
7.0
11
—
—
—
3.5
7.0
11
2.75
5.50
8.25
—
—
—
3.5
7.0
11
—
—
—
Vdc
Output Drive Current
(VOH = 2.5 Vdc) Source
(VOH = 4.6 Vdc)
(VOH = 9.5 Vdc)
(VOH = 13.5 Vdc)
I
OH
5.0
5.0
10
15
– 3.0
– 0.64
– 1.6
– 4.2
—
—
—
—
– 2.4
– 0.51
– 1.3
– 3.4
– 4.2
– 0.88
– 2.25
– 8.8
—
—
—
—
– 1.7
– 0.36
– 0.9
– 2.4
—
—
—
—
mAdc
(VOL = 0.4 Vdc) Sink
(VOL = 0.5 Vdc)
(VOL = 1.5 Vdc)
I
OL
5.0
10
15
0.64
1.6
4.2
—
—
—
0.51
1.3
3.4
0.88
2.25
8.8
—
—
—
0.36
0.9
2.4
—
—
—
mAdc
Input Current, Pin 2 or 14 I
in
15 — ±0.05 — ±0.00001 ±0.05 — ±0.5 µAdc
Input Current, Other Inputs I
in
15 — ±0.1 — ±0.00001 ±0.1 — ±1.0 µAdc
Input Capacitance, Pin 2 or 14 C
in
— — — — 25 — — — pF
Input Capacitance, Other Inputs
(Vin = 0)
C
in
— — — — 5.0 7.5 — — pF
Quiescent Current
(Per Package)
Q = Low, Q = High
I
DD
5.0
10
15
—
—
—
5.0
10
20
—
—
—
0.005
0.010
0.015
5.0
10
20
—
—
—
150
300
600
µAdc
Quiescent Current, Active State
(Both) (Per Package)
Q = High, Q = Low
I
DD
5.0
10
15
—
—
—
2.0
2.0
2.0
—
—
—
0.04
0.08
0.13
0.20
0.45
0.70
—
—
—
2.0
2.0
2.0
mAdc
**Total Supply Current at an
external load capacitance (CL) and
at external timing network (RX, CX)
I
T
5.0
10
IT = (3.5 x 10–2) RXCXf + 4CXf + 1 x 10–5 CLf
IT = (8.0 x 10–2) RXCXf + 9CXf + 2 x 10–5 CLf
IT = (1.25 x 10–1) RXCXf + 12CXf + 3 x 10–5 CLf
where: IT in µA (one monostable switching only),
where: CX in µF, CL in pF, RX in k ohms, and
where: f in Hz is the input frequency.
µAdc
#Data labelled “Typ” is not to be used for design purposes but is intended as an indication of the IC’s potential performance.
**The formulas given are for the typical characteristics only at 25_C.
This device contains protection circuitry to guard against damage due to high static voltages or electric fields. However,
precautions must be taken to avoid applications of any voltage higher than maximum rated voltages to this high-impedance
circuit. For proper operation, Vin and V
out
should be constrained to the range VSS ≤ (Vin or V
out
) ≤ VDD.
Unused inputs must always be tied to an appropriate logic voltage level (e.g., either VSS or VDD). Unused outputs must
be left open.
Page 3

MOTOROLA CMOS LOGIC DATA
3
MC14538B
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS* (C
L
= 50 pF, TA = 25_C)
V
All Types
Characteristic
Symbol
V
DD
Vdc
Min Typ # Max
Unit
Output Rise Time
t
TLH
= (1.35 ns/pF) CL + 33 ns
t
TLH
= (0.60 ns/pF) CL + 20 ns
t
TLH
= (0.40 ns/pF) CL + 20 ns
t
TLH
5.0
10
15
—
—
—
100
50
40
200
100
80
ns
Output Fall Time
t
THL
= (1.35 ns/pF) CL + 33 ns
t
THL
= (0.60 ns/pF) CL + 20 ns
t
THL
= (0.40 ns/pF) CL + 20 ns
t
THL
5.0
10
15
—
—
—
100
50
40
200
100
80
ns
Propagation Delay Time
A or B to Q or Q
t
PLH
, t
PHL
= (0.90 ns/pF) CL + 255 ns
t
PLH
, t
PHL
= (0.36 ns/pF) CL + 132 ns
t
PLH
, t
PHL
= (0.26 ns/pF) CL + 87 ns
5.0
10
15
—
—
—
300
150
100
600
300
220
ns
Reset to Q or Q
t
PLH
, t
PHL
= (0.90 ns/pF) CL + 205 ns
t
PLH
, t
PHL
= (0.36 ns/pF) CL + 107 ns
t
PLH
, t
PHL
= (0.26 ns/pF) CL + 82 ns
5.0
10
15
—
—
—
250
125
95
500
250
190
ns
Input Rise and Fall Times
Reset
5
10
15
—
—
—
—
—
—
15
5
4
µs
B Input 5
10
15
—
—
—
300
1.2
0.4
1.0
0.1
0.05
ms
A Input 5
10
15
No Limit
—
Input Pulse Width
A, B, or Reset
tWH,
t
WL
5.0
10
15
170
90
80
85
45
40
—
—
—
ns
Retrigger Time t
rr
5.0
10
15
0
0
0
—
—
—
—
—
—
ns
Output Pulse Width — Q or Q
Refer to Figures 8 and 9
CX = 0.002 µF, RX = 100 kΩ
5.0
10
15
198
200
202
210
212
214
230
232
234
µs
CX = 0.1 µF, RX = 100 kΩ 5.0
10
15
9.3
9.4
9.5
9.86
10
10.14
10.5
10.6
10.7
ms
CX = 10 µF, RX = 100 kΩ 5.0
10
15
0.91
0.92
0.93
0.965
0.98
0.99
1.03
1.04
1.06
s
Pulse Width Match between circuits in
the same package.
CX = 0.1 µF, RX = 100 kΩ
100
[(T1 – T2)/T1]
5.0
10
15
—
—
—
± 1.0
± 1.0
± 1.0
± 5.0
± 5.0
± 5.0
%
*The formulas given are for the typical characteristics only at 25_C.
#Data labelled “Typ” is not to be used for design purposes but is intended as an indication of the IC’s potential performance.
OPERATING CONDITIONS
External Timing Resistance R
X
— 5.0 — kΩ
External Timing Capacitance C
X
— 0 — No
Limit†
µF
*The maximum usable resistance RX is a function of the leakage of the capacitor CX, leakage of the MC14538B, and leakage due to board layout
and surface resistance. Susceptibility to externally induced noise signals may occur for RX > 1 MΩ..
†If CX > 15 µF, use discharge protection diode per Fig. 11.
t
,
PLH
t
PHL
tr, t
f
T
Page 4

MOTOROLA CMOS LOGIC DATAMC14538B
4
Figure 1. Logic Diagram
(1/2 of DevIce Shown)
NOTE: Pins 1, 8 and 15 must
be externally grounded
–
+
–
+
V
DD
V
DD
P1
R
X
C
X
21(14)
(15)
4 (12)
5 (11)
3 (13)
A
B
RESET
V
SS
N1
V
ref1
C1 C2
ENABLE
V
ref2
ENABLE
CONTROL
S
RESET LATCH
Q
R
Q
R
RS
RSQ
Q
6 (10)
7 (9)
OUTPUT
LATCH
Figure 2. Power Dissipation Test Circuit and Waveforms
500 pF
V
DD
0.1
µ
F
CERAMIC
R
X
RX′
CX′
V
SS
C
X
V
SS
V
in
CX/R
X
A
B
RESET
A
′
B
′
RESET
′
Q
Q
Q
′
Q
′
V
SS
C
L
C
L
C
L
C
L
20 ns 20 ns
V
DD
0 V
90%
10%
V
in
I
D
INPUT CONNECTIONS
Characteristics Reset A B
t
PLH
, t
PHL
, t
TLH
, t
THL
,
T, tWH, t
WL
V
DD
PG1 V
DD
t
PLH
, t
PHL
, t
TLH
, t
THL
,
T, tWH, t
WL
V
DD
V
SS
PG2
t
PLH(R)
, t
PHL(R)
,
tWH, t
WL
PG3 PG1 PG2
Figure 3. Switching Test Circuit
*Includes capacitance of probes,
wiring, and fixture parasitic.
NOTE: Switching test waveforms
for PG1, PG2, PG3 are shown
In Figure 4.
V
DD
R
X
R
X
′
V
SS
C
X
CX/R
X
A
B
RESET
A
′
B
′
RESET
′
Q
Q
Q
′
Q
′
C
L
C
X
′
C
L
C
L
C
L
V
SS
PULSE
GENERATOR
PULSE
GENERATOR
PULSE
GENERATOR
V
SS
*CL = 50 pF
PG1 =
PG2 =
PG3 =
Page 5

MOTOROLA CMOS LOGIC DATA
5
MC14538B
Figure 4. Switching Test Waveforms
RESET
A
B
t
PLH
Q
Q
50%
t
WH
90%
10%
t
TLH
t
THL
t
WL
t
THL
t
PHL
t
THL
90%
10%
50%
T
50% 50% 50%
90%
10%
t
PLH
t
THL
t
TLH
t
PHL
t
WL
50%
90%
10%
t
PHL
t
PHL
t
TLH
t
THL
t
PLH
50% 50%
90%
10%
50%
50%
50%
t
rr
50% V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
t
TLH
Figure 5. Typical Normalized Distribution
of Units for Output Pulse Width
Figure 6. Typical Pulse Width Variation as
a Function of Supply Voltage V
DD
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
–4 –2 0 2 4
T, OUTPUT PULSE WIDTH (%)
RELATIVE FREQUENCY OF OCCURRENCE
2
1
0
1
2
15141312111098765
VDD, SUPPLY VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
NORMALIZED PULSE WIDTH CHANGE
WITH RESPECT TO VALUE AT V
DD
= 10 V (%)
TA = 25°C
RX = 100 k
Ω
CX = 0.1 µF
0% POINT PULSE WIDTH
VDD = 5.0 V, T = 9.8 ms
VDD = 10 V, T = 10 ms
VDD = 15 V, T = 10.2 ms
RX = 100 k
Ω
CX = 0.1 µF
Figure 7. Typical Total Supply Current
versus Output Duty Cycle
TOTAL SUPPLY CURRENT ( A)
µ
1000
100
10
1.0
0.1
0.001 0.1 1.0 10 100
OUTPUT DUTY CYCLE (%)
RX = 100 kΩ, CL = 50 pF
ONE MONOSTABLE SWITCHING ONLY
VDD = 15 V
10 V
5.0 V
FUNCTION TABLE
Inputs Outputs
Reset A B Q Q
H H
H L
H L Not Triggered
H H Not Triggered
H L, H, H Not Triggered
H L L, H, Not Triggered
L X X L H
X X Not Triggered
Page 6

MOTOROLA CMOS LOGIC DATAMC14538B
6
Figure 8. Typical Error of Pulse Width
Equation versus Temperature
Figure 9. Typical Error of Pulse Width
Equation versus Temperature
–2
–1
0
1
2
–60 –40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
TA, AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (
°
C)
TYPICAL NORMALIZED ERROR
WITH RESPECT TO 25
DD
= 10 V (%)
°
C VALUE AT V
RX = 100 k
Ω
CX = 0.1 µF
VDD = 15 V
VDD = 10 V
VDD = 5 V
–2.0
–1.0
0
1.0
2.0
3.0
–3.0
–60 –40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
TA, AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (
°
C)
RX = 100 k
Ω
CX = .002 µF
VDD = 15 V
VDD = 10 V
VDD = 5.0 V
TYPICAL NORMALIZED ERROR
WITH RESPECT TO 25
DD
= 10 V (%)
°
C VALUE AT V
THEORY OF OPERATION
2
Figure 10. Timing Operation
Positive edge re–trigger (pulse lengthening)Positive edge trigger
1
2
3 4
5
1
3
4
5
RESET
A
B
CX/R
X
Q
V
ref 1
V
ref 1
V
ref 1
V
ref 1
V
ref 2
V
ref 2
V
ref 2
V
ref 2
T T
T
Negative edge trigger
Positive edge trigger
Positive edge re–trigger (pulse lengthening)
TRIGGER OPERATION
The block diagram of the MC14538B is shown in Figure 1,
with circuit operation following.
As shown i n Figure 1 and 1 0, before an input t rigger
occurs, the monostable is in the quiescent state with the Q
output low, and the timing capacitor CX completely charged
to VDD. When the trigger input A goes from VSS to V
DD
(while inputs B and Reset
are held to VDD) a valid trigger is
recognized, which turns on comparator C1 and N–channel
transistor N1 ➀. At the same time the output latch is set. With
transistor N1 on, the capacitor CX rapidly discharges toward
VSS until V
ref1
is reached. A t this p oint the o utput of
comparator C1 changes state and transistor N1 turns off.
Comparator C1 t hen t urns o ff while a t the same time
comparator C2 turns on. With transistor N1 off, the capacitor
CX begins to charge through the timing resistor, RX, toward
VDD. When the voltage across CX equals V
ref 2
, comparator
C2 changes state, causing the output latch to reset (Q goes
low) while at the same time disabling comparator C2 ➁. This
ends at the timing cycle with the monostable in the quiescent
state, waiting for the next trigger.
In the quiescent state, CX is fully charged to VDD causing
the current through resistor RX to be zero. Both comparators
are “off” with total device current due only to reverse junction
leakages. An added feature of the MC14538B is that the output latch is set via the input trigger without regard to the
capacitor voltage. Thus, propagation delay from trigger to Q
is independent of the value of CX, RX, or the duty cycle of the
input waveform.
Page 7

MOTOROLA CMOS LOGIC DATA
7
MC14538B
RETRIGGER OPERATION
The MC14538B is retriggered if a valid trigger occurs ➂ followed by another valid trigger ➃ before the Q output has
returned to the quiescent (zero) state. Any retrigger, after the
timing node voltage at pin 2 or 14 has begun to rise from
V
ref 1
, but has not yet reached V
ref 2
, will cause an increase
in output pulse width T. When a valid retrigger is initiated ➃,
the voltage at CX/RX will a gain drop t o V
ref 1
before
progressing along the RC charging curve toward VDD. The Q
output will remain high until time T, after the last valid retrigger.
RESET OPERATION
The MC14538B may be reset during the generation of the
output pulse. In the reset mode of operation, an input pulse
on Reset
sets the reset latch and causes the capacitor to be
fast charged to VDD by turning on transistor P1 ➄. When the
voltage on the capacitor reaches V
ref 2
, the reset latch will
clear, and will then be ready to accept another pulse. It the
Reset
input is held low, any trigger inputs that occur will be
inhibited and the Q and Q
outputs of the output latch will not
change. Since the Q output is reset when an input low level is
detected on the Reset
input, the output pulse T can be made
significantly shorter than the minimum pulse width specification.
POWER–DOWN CONSIDERATIONS
Large capacitance values can cause problems due to the
large amount of energy stored. When a system containing
the MC14538B is powered down, the capacitor voltage may
discharge from VDD through the standard protection diodes
at pin 2 or 14. Current through the protection diodes should
be limited to 10 mA and therefore the discharge time of the
VDD supply must not be faster than (VDD). (C)/(10 mA). For
example, if VDD = 10 V and CX = 10 µF, the VDD supply
should discharge no faster than (10 V) x (10 µF)/(10 mA) =
10 ms. This is normally not a problem since power supplies
are heavily filtered and cannot discharge at this rate.
When a more rapid decrease of VDD to zero volts occurs,
the MC14538B can sustain damage. To avoid this possibility
use an external clamping diode, DX, connected as shown in
Fig. 11.
Figure 11. Use of a Diode to Limit
Power Down Current Surge
PIN ASSIGNMENT
13
14
15
16
9
10
11
125
4
3
2
1
8
7
6
A
B
RESET
B
CX/RXB
V
SS
V
DD
Q
B
Q
B
B
B
A
A
RESET
A
CX/RXA
V
SS
V
SS
Q
A
Q
A
B
A
V
SS
D
x
V
DD
V
DD
R
x
C
x
Q
Q
RESET
Page 8

MOTOROLA CMOS LOGIC DATAMC14538B
8
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
Figure 12. Retriggerable
Monostables Circuitry
Figure 13. Non–Retriggerable
Monostables Circuitry
C
X
R
X
V
DD
Q
Q
RESET = V
DD
B = V
DD
A
B
RISING–EDGE
TRIGGER
C
X
R
X
V
DD
Q
Q
RESET = V
DD
B
A = V
SS
FALLING–EDGE
TRIGGER
C
X
R
X
V
DD
Q
Q
A
B
RESET = V
DD
C
X
R
X
V
DD
Q
Q
RESET = V
DD
A
B
FALLING–EDGE
TRIGGER
RISING–EDGE
TRIGGER
NC
NC
NC
V
DD
V
DD
A
B
Figure 14. Connection of Unused Sections
Q
Q
C
D
Page 9

MOTOROLA CMOS LOGIC DATA
9
MC14538B
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
P SUFFIX
PLASTIC DIP PACKAGE
CASE 648–08
ISSUE R
NOTES:
1. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ANSI
Y14.5M, 1982.
2. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: INCH.
3. DIMENSION L TO CENTER OF LEADS WHEN
FORMED PARALLEL.
4. DIMENSION B DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD FLASH.
5. ROUNDED CORNERS OPTIONAL.
–A–
B
F
C
S
H
G
D
J
L
M
16 PL
SEATING
1 8
916
K
PLANE
–T–
M
A
M
0.25 (0.010) T
DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
MILLIMETERSINCHES
A 0.740 0.770 18.80 19.55
B 0.250 0.270 6.35 6.85
C 0.145 0.175 3.69 4.44
D 0.015 0.021 0.39 0.53
F 0.040 0.70 1.02 1.77
G 0.100 BSC 2.54 BSC
H 0.050 BSC 1.27 BSC
J 0.008 0.015 0.21 0.38
K 0.110 0.130 2.80 3.30
L 0.295 0.305 7.50 7.74
M 0 10 0 10
S 0.020 0.040 0.51 1.01
____
L SUFFIX
CERAMIC DIP PACKAGE
CASE 620–10
ISSUE V
NOTES:
1. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER
ANSI Y14.5M, 1982.
2. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: INCH.
3. DIMENSION L TO CENTER OF LEAD WHEN
FORMED PARALLEL.
4. DIMENSION F MAY NARROW TO 0.76 (0.030)
WHERE THE LEAD ENTERS THE CERAMIC
BODY.
–A–
–B–
–T–
F
E
G
N
K
C
SEATING
PLANE
16 PLD
S
A
M
0.25 (0.010) T
16 PLJ
S
B
M
0.25 (0.010) T
M
L
DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
MILLIMETERSINCHES
A 0.750 0.785 19.05 19.93
B 0.240 0.295 6.10 7.49
C ––– 0.200 ––– 5.08
D 0.015 0.020 0.39 0.50
E 0.050 BSC 1.27 BSC
F 0.055 0.065 1.40 1.65
G 0.100 BSC 2.54 BSC
H 0.008 0.015 0.21 0.38
K 0.125 0.170 3.18 4.31
L 0.300 BSC 7.62 BSC
M 0 15 0 15
N 0.020 0.040 0.51 1.01
_ _ _ _
16 9
1 8
Page 10

MOTOROLA CMOS LOGIC DATAMC14538B
10
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
DW SUFFIX
PLASTIC SOIC PACKAGE
CASE 751G–02
ISSUE A
DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
INCHESMILLIMETERS
A 10.15 10.45 0.400 0.411
B 7.40 7.60 0.292 0.299
C 2.35 2.65 0.093 0.104
D 0.35 0.49 0.014 0.019
F 0.50 0.90 0.020 0.035
G 1.27 BSC 0.050 BSC
J 0.25 0.32 0.010 0.012
K 0.10 0.25 0.004 0.009
M 0 7 0 7
P 10.05 10.55 0.395 0.415
R 0.25 0.75 0.010 0.029
M
B
M
0.010 (0.25)
NOTES:
1. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ANSI
Y14.5M, 1982.
2. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: MILLIMETER.
3. DIMENSIONS A AND B DO NOT INCLUDE MOLD
PROTRUSION.
4. MAXIMUM MOLD PROTRUSION 0.15 (0.006) PER
SIDE.
5. DIMENSION D DOES NOT INCLUDE DAMBAR
PROTRUSION. ALLOWABLE DAMBAR
PROTRUSION SHALL BE 0.13 (0.005) TOTAL IN
EXCESS OF D DIMENSION AT MAXIMUM
MATERIAL CONDITION.
–A–
–B– P8X
G14X
D16X
SEATING
PLANE
–T–
S
A
M
0.010 (0.25) B
S
T
16 9
81
F
J
R
X 45
_
_ _ _ _
M
C
K
How to reach us:
USA/EUROPE/Locations Not Listed: Motorola Literature Distribution; JAPAN: Nippon Motorola Ltd.; Tatsumi–SPD–JLDC, 6F Seibu–Butsuryu–Center,
P.O. Box 20912; Phoenix, Arizona 85036. 1–800–441–2447 or 602–303–5454 3–14–2 Tatsumi Koto–Ku, Tokyo 135, Japan. 03–81–3521–8315
MFAX: RMFAX0@email.sps.mot.com – TOUCHTONE 602–244–6609 ASIA/PACIFIC: Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.; 8B Tai Ping Industrial Park,
INTERNET: http://Design–NET.com 51 Ting Kok Road, Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong. 852–26629298
Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty , representation or guarantee regarding
the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit,
and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters which may be provided
in Motorola data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters,
including “Typicals” must be validated for each customer application by customer’s technical experts. Motorola does not convey any license under its patent
rights nor the rights of others. Motorola products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant
into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Motorola product could create a
situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized application,
Buyer shall indemnify and hold Motorola and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and
expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or
unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. Motorola and are registered
trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer .
MC14538B/D
*MC14538B/D*
◊
 Loading...
Loading...