Page 1

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
1
MOTOROLA
INTRODUCTION
The MC145192EVK and MC145202EVK are two versions of one board with a few component changes.
They allow users to exercise features of both devices and to build PLLs which meet individual performance requirements. The control program works with any board and can be used with other Motorola
PLL devices (MC145190, MC145191, MC145200, MC145201, MC145220*). It will select frequency defaults that apply to each. All board functions are controlled through the printer port of an IBM PC. Up to
three different EVKs may be controlled at the same time from one printer port. The functional block diagram is given in Figure 1.
This manual is divided into two sections. Section 1 describes the hardware and Section 2 covers the
software control program.
VCO
733–751 MHz
MC145192
MC145202
PLL
Control Voltage
External Reference Input
TCXO Reference
RF Output
Frequency
Control Data
Out A, Out B
Lock Detect
Loop Filter
2nd Harmonic
Filter, Amplifier
74HCT241, 74LS126
Buffer Logic
Logic Control Switches
Parallel Port Connector
Isolation Resistor
PD
out
Current
F
in
Figure 1. Evaluation Kit Block Diagram
* The MC145220 is not available with Rev. 2.5 software.
All brand names and product names appearing in this document are registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective holders.
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Motorola, Inc. 1996
REV 1
3/96
Page 2

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
2
SECTION 1 – HARDWARE
FEATURES
1. The EVK is a complete working synthesizer, including VCO.
2. Control program is written in Turbo Pascal.
3. Board is controlled by an IBM PC–compatible computer through the printer port.
4. Up to three boards can be operated independently through one printer port.
5. A prototype area and mounting holes are provided for VCOs, mixers, and amplifiers.
6. External reference input can be used.
7. Five element loop filter is included.
8. Frequency range of operation, step size and reference frequency can be changed in the control
program.
9. Lock Detect, Out A, and Out B on any single board are accessible through the printer port.
CONTENTS OF EVALUATION KIT
1. Assembled evaluation board.
2. Nine–foot flat cable with four DB–25 male connectors.
3. MC145192/202 EVK manual.
4. 3.5″ PC–compatible disk containing compiled program.
5. PLL device data sheets.
GETTING STARTED
To perform basic functions, do the following:
1. Plug in 12 volts at J6, observing the polarity marked on the board.
2. Short circuit section 1 of the DIP switch (S1) and open circuit all other sections.
3. Connect the supplied flat cable between the computer printer port and the DB–25 connector on
the board (J5).
4. Type PLL at the DOS prompt. Then press enter.
5. Type the number that corresponds with the type of board given in the on–screen menu. Then
press Q.
You should now see the main menu displayed. There should be a signal present at J8 on the current
output frequency given in the main menu. If the signal is not on the correct frequency , check to see if your
printer card address is $278 (hexadecimal 278). If not, then select the P menu item and enter the correct
address. After returning to the main menu, select the I menu item to send data to the board. You should
now be on frequency.
MODIFICATIONS
The user may modify the hardware, such as utilizing a different VCO, by using the prototyping area of the
board. After such modifications are made, the default values in the software may need to be changed.
This is facilitated from screen #2 ‘Select from the available options’ screen.
Note that the on–board voltage regulators allow for maximum control voltage range of 0.5 to 4.5 V.
Page 3

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
3
MOTOROLA
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE
Common to both kits, unless noted. Typical performance applies only to the configuration as shipped.
The MC145192EVK is shipped with VCC = 3 V and VPD = 5 V. The MC145202EVK is shipped with
VCC = 5 V and VPD = 5 V.
Supply Voltage (J6) 11.5 – 12.5 V
Supply Current (J6) (Note 1) 120 mA
Available Current (Note 2)
60 mA
Frequency Range (’192) (Note 3) 733 – 743 MHz
Frequency Range (’202) (Note 3) 1466 – 1486 MHz
Reference Frequency 14.4 MHz
Temperature Stability (– 30°C to + 85°C) < ± 2 ppm
TCXO Aging < ± 1 ppm / year
Step Size (’192) 100 kHz
Step Size (’202) 200 kHz
Power Output 4.5 – 7.5 dBm
2nd Harmonic Level (’192) < – 18 dB
Fundamental Level (’202) < – 23 dB
3rd Harmonic Level < – 18 dB
Frequency Accuracy (’192) ± 1.5 kHz
Frequency Accuracy (’202) ± 3.0 kHz
Reference Sidebands – 70 dB
Phase Noise (100 Hz, ’192) – 70 dBc/Hz
Phase Noise (100 Hz, ’202) – 69 dBc/Hz
Phase Noise (10 kHz, ’192) (Note 4) – 86 dBc/Hz
Phase Noise (10 kHz, ’202) (Note 4) – 90 dBc/Hz
Switching Time (Note 5) 2.6 ms
NOTES:
1. Supply current is current the board requires without user modifications.
2. Available current is the sum of currents available to the user (in the prototype area) from the 5 V and 8.5 V supply. The 12 V supply is not
regulated. Current at 12 V is limited by the external power supply . If the on–board VCO and amplifier are disconnected from the power bus,
more current can be drawn in the prototype area. The current flowing into U3 (the 8.5 V regulator) should not exceed 180 mA. This will limit
temperature rise in U3.
3. Frequency ranges require use of the 5 V default charge pump supply voltage.
4. 10 kHz phase noise is limited by the PLL device noise. For low noise designs, the loop bandwidth is made more narrow and the VCO is relied
upon to provide the 10 kHz phase noise. This can be seen on the EVKs since the VCO has much lower noise.
5. 10 MHz step, within ± 1 kHz of final frequency (’192).
20 MHz step, within ± 2 kHz of final frequency (’202).
Page 4

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
4
SUPPORT MATERIAL
To provide further information, the following documents are included:
1. Schematic diagram of ’192/202EVK.
2. Separate Bill of Materials for each board.
3. Parts layout diagram.
4. Mechanical drawing of board.
5. MC145192 and MC145202 data sheets.
6. Printer port diagram.
7. Typical signal plots for each type of EVK.
PRODUCTION TEST
After assembly is complete, the following alignment and test is performed on ’192EVK (or ’202EVK):
1. The control program is started in single board ’190EVK (’200EVK) mode.
2. L menu item is selected.
3. Power is applied to the board. DIP switch section 1 is closed circuit with all others being open
circuit.
4. After attaching computer cable, menu item I is selected.
5. Trim resistor VR1 is adjusted to obtain an output frequency at J8 of 740.999 – 741.001 MHz
(1481.998 – 1482.002 MHz).
6. Voltage at the control voltage test point is measured. It must be 2.5 – 3.1 V.
7. When testing more than 1 board, steps 3 – 6 are repeated.
If in step 5 it isn’t possible to obtain a signal on frequency, menu item P should be selected and the correct printer port address entered. Menu item I would then be selected to reload the data.
BOARD OPERATION
A computer is connected to the DB–25 connector J5. Data is output from the printer port. The printer card
is in slot 0 using the default address in the control program. Data is sent to the PLL device (U1) through
the DIP switch (S1), and 74HCT241 buffer (U5). D2, D3, D4, R19, R20, and R21 are in the data path
between the 74HCT241 and PLL devices. This limits the high level output voltage of the buffer. Voltage
on the PLL device inputs must not be greater than 0.5 V above VCC. A ’192/202 PLL has three output
lines which are routed through a 74LS126 line driver (U2) to the computer.
U5, the 74HCT241, provides isolation, logic translation and a turn–on delay for PLL input lines. Logic
translation is needed from the TTL levels on the printer port to the CMOS levels on the ’192/202 inputs.
Turn–on delay is used to ensure the power–on reset functions properly. The enable line to the PLL must
be held low during power–up.
A 12 V power supply should be used to power the board at J6 (Augat 2SV–02 connector). The 2SV–02
will accept 18–24 AWG bare copper power leads. No tools are needed for connection. If power is properly connected, LED D2 will be lit.
Power passes from J6 to U3 (LM317 regulator) configured as an 8.5 V regulator. Both boards use 8.5 V
to power the VCO and RF amplifier. Regulators U4 and U7 use the 8.5 V supply to produce 3 V and 5 V.
The ’192 always uses 3 V to power logic and 5 V to power the charge pump, while the ’202 can have
either power both the logic and charge pump. J3 and J4 are jumpers which select voltages for the logic
and charge pump supplies. U4 and U7 are cascaded with U3 to equalize their individual voltage drops.
The PLL loop is composed of the PLL device (U1), 733 – 743 MHz VCO (M1), passive loop filter (R11,
R12, C4, C5, C6) and second harmonic filter amplifier (U6). A passive loop filter was used to keep the
Page 5

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
5
MOTOROLA
design simple, reduce noise, and reduce the quantity of traces susceptible to stray pickup. About 56 dB
rejection of fundamental and 23 dB gain is provided by the harmonic filter amplifier. This allows the ’202
to lock at 1466 – 1486 MHz.
A single VCO model is used for both boards. It is an internal Motorola part which is not sold for other
applications. The ’192 operates at half the output frequency and step size of the ’202. This allows the
same loop filter components to be used. RF is fed to the PLL chip Fin input through voltage dividers R14
and R10. These two resistors terminate the PLL chip RF input with 50 ohms and provide isolation.
Both boards use a phase detector current of 2 mA. J1 and J2 are removable jumpers and cut traces.
They are used as connection points for a current measurement of VPD or VCC. A potentiometer VR1 is
used to set M2 (14.4 MHz TCXO) on frequency.
COMPONENTS UNIQUE TO EACH EVK
Components that are not the same on all EVKs are given in the following table:
’192EVK
’202EVK
U1
MC145192
MC145202
R2
18 kΩ
3.9 kΩ
R8
0 Ω
Not Used
C22
Not Used
1.0 pF
J3
3 V
5 V
EXTERNAL REFERENCE INPUT
As shipped, all boards are configured for a 14.4 MHz TCXO (supplied). To use an external reference,
disconnect J13 and connect J9. Use a reference signal at J10 which complies with data sheet requirements. Then modify the reference frequency in the program main menu to reflect the changes made ( [F]
menu item ).
DATA TRANSFER FROM COMPUTER TO EVK
To control the serial input EVK with the parallel printer port, a conversion is done. Printer cards are designed to output eight bits through eight lines. A bit mask is used to obtain the bit combination for the
three required output lines (Data, Clock, Load). As bytes are sent to the printer card in sequence, it appears to be a serial transfer. The printer port is used because data transfer using the serial port is much
slower. A standard IBM PC can support a parallel port data rate of 4.77 MHz.
IBM PCs and compatibles can accept up to three printer port cards. These ports are called LPT1, LPT2,
and LPT3. Each printer card has jumpers or DIP switches on it to set a unique address. Two sets of
addresses are in common use. One set applies to IBM PC XT, AT, and clones. The other is for the PS 2
line. To load data into the EVK, the correct address must be selected. The program default is $278, which
is LPT1 in a clone. If $278 is not the address in use, it must be modified by entering the O menu item in
the main menu. All allowed addresses given in hexadecimal are as follows:
Label
IBM PC and Clones PS 2
LPT1 278 3BC
LPT2 378 378
LPT3 3BC 278
Page 6
MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
6
Up to three EVK boards can operate independently from one printer port. All lines on the printer port are
connected to every EVK. Even with three boards operating, only three output lines (Clock, Data and
Load) from the printer card are used. If two boards are controlled together, data for the second board is
received from the Output A of the first. Output A is a configurable output on ’192/202 devices, which in
this case is used to shift data through chip 1 into chip 2. Output A and Data are connected using a printer
port input line. This was done to avoid connecting extra wires. Fortunately not all port input lines are
needed for computer input. Load and Clock are common to both boards.
A three–board cascade is handled similarly to a two–board cascade. Out A on the first board is fed to
Data on the second. Out A on the second connects to Data on the third. Instructing the program on the
quantity of boards connected together allows it to modify the number of bits sent.
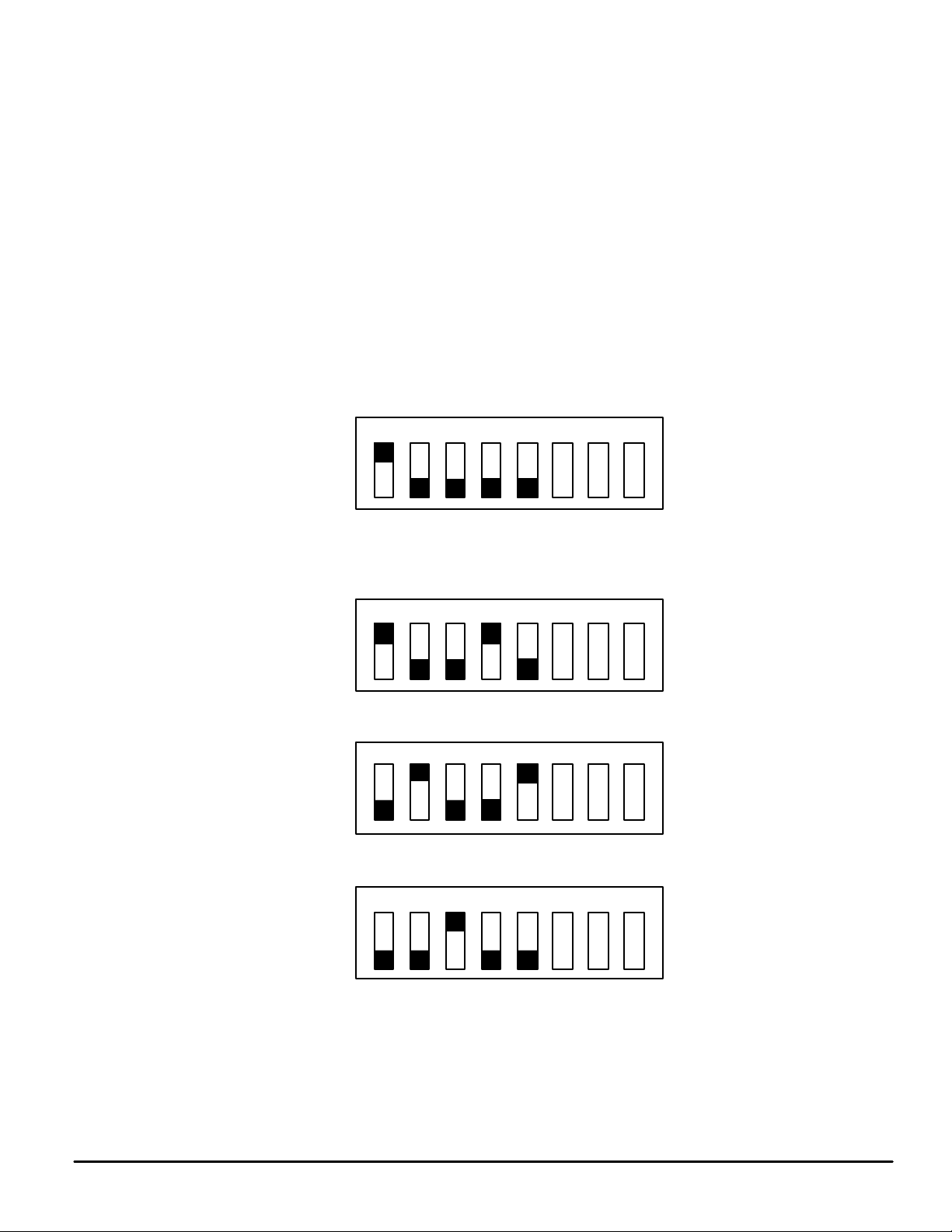
All boards have a DIP switch S1 which gives each a unique address. The configuration menu is used to
tell the program what type of board is connected at a board address. Switch positions for all possible
addresses are given in Figure 2.
Single Board Operation
Two– or Three–Board Cascade
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Closed
Open
Board A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Closed
Open
Board B
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Closed
Open
Board C
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Closed
Open
Figure 2. Switch Positions
Page 7

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
7
MOTOROLA
In Figure 2, DIP switch sections 6, 7, and 8 allow the computer to read Out A, Out B or Lock Detect from
the PLL device. Each of the inputs can only be read on one board at a time, but each item could be read
on a different board. In a three–board cascade, Out A could be read from the first board, Out B from the
second, and Lock Detect from the third. There is no way to determine in software the board address of a
particular input. The control program does not make use of these inputs. Pin assignment on the printer
port connector is:
Label
Pin Number
Out A 12
Out B 13
Lock Detect 15
PRINTER PORT CONFIGURATION
Printer port outputs on an IBM PC or clone use TTL–LS logic levels. Inputs are one TTL–LS load. Signal
lines can be used for any purpose. The standard names, direction of data flow, true and inverted data are
shown in Figure 3.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 – 25
Printer
IBM Printer
Port
Pin Number
– Strobe
+ Data Bit 0
+ Data Bit 1
+ Data Bit 3
+ Data Bit 4
+ Data Bit 2
+ Data Bit 5
+ Data Bit 6
+ Data Bit 7
– Acknowledge
+ Busy
+ P. End (out of paper)
+ Select
– Auto Feed
– Error
– Initialize Printer
– Select Input
Ground
Signal Name
Figure 3. Printer Port Data Lines
Page 8

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
8
Pin numbers for the port connector are shown in Figure 4.
1
13
14
25
(front view)
Figure 4. DB–25 Male Connector
Page 9

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
9
MOTOROLA
SECTION 2 – SOFTWARE
INTRODUCTION
The MC145xxx PLL software is provided to demonstrate the capabilities of the MC145xxx family of PLLs.
The family includes the following devices:
Table 1.
Board Type
Board Description
MC145190
MC145191
MC145192
Low voltage version of the ’191
MC145200
MC145201
MC145202
Low voltage version of the ’201
MC145220 in Single Loop Mode*
MC145220 in Dual Loop Mode*
* The ’220 is not available in Rev. 2.5 software.
Most of these ICs are provided on an evaluation circuit board to allow the easy demonstration of the PLL
capabilities.
PURPOSE
The user guide for the MC145xxx PLL software familiarizes the user with the use and capabilities of the
program referred from here on as PLL Version 3.0. The guide covers the user interface and a summary
of the commands that are available.
The user should read the data sheet of the PLL frequency synthesizer of interest before using the software.
DESCRIPTION
The PLL software:
• is a Pascal program developed with Borland Turbo Pascal v7.0.
• runs under MS–DOS.
• is a character–based, menu–driven program.
USER COMMENTS
Comments on this program may be faxed to MDAD Development Tools Group at (512) 933–8570.
Page 10

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
10
USER INTERFACE
The user interface consists of numerous character–based, menu–driven screens which are displayed
below. Each screen is shown, along with a description of its purpose.
CONVENTIONS
Some of the PLL screens are necessarily “busy”. Because of this, the program follows several conventions to help the user quickly absorb the screen information. These conventions are briefly described on
a help screen that is available throughout the program. Type the help command, [?], at any time to view
the help screen.
The conventions are as follows:
1. Command keys are surrounded by [ ]s. Type the letter between the [ ]s to execute the command.
[ ]s are followed by a description of the command.
2. [–] indicates a command not available to the user. Commands become available when they are
applicable to the currently targeted board.
3. [ ]s followed by an ! indicate the command will execute immediately. Otherwise a submenu is
displayed from which further choices may be made.
4. If no changes are desired to an input field, leave the field blank. The previous value will then be
used for that field. Type the TAB key to move to the next input field, or shift–TAB to move to the
prior input field. Type RETURN to store the new input values while remaining on the same screen.
Type Q to store the new values and return to the prior screen.
5. All numbers are entered as decimal values unless otherwise noted. A $ followed by a value indi–
cates the value is in hexadecimal format. The output port address is in hexadecimal format.
6. The second line from the top of screen (screen title) states the purpose of the screen.
7. Screen information that can be changed by the user is displayed in bold or reverse video.
8. Commands are case independent. X is the same as x.
9. Frequencies are entered as two numbers, and displayed as one. The two input numbers repre–
sent the desired frequency in MHz, and in kHz. These input values are added together to obtain
the final frequency. Leave either input field blank to retain the prior value for that portion of fre–
quency.
Page 11

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
11
MOTOROLA
SCREENS
Screen #1 ‘Define boards to program’
The first screen the user sees when the program begins has a screen title of ‘Define boards to program’.
This screen is used to define which boards are connected to the LPT1 printer port of the computer. Refer
to the hardware setup section to determine how to cascade the evaluation boards.
This screen is also available from the main menu (screen #2). The user may return to this screen to
change the boards that are connected to the computer.
The screen is divided into two sections. The upper section shows the current board type settings while
the lower section allows the user to define a board’s type and position in the cascade connection.
Notice the section labeled ‘Available Boards:’ shows three labels, one for each board that may be cascaded. When the program first starts up it shows ‘N/A’ (not applicable) after each label. The user must
enter the boards contiguously. Initially the program requests for the user to enter board A’s type. This is
signified by
A
(in the screen below) being set to A. The user can the select the board type for board A by
typing the corresponding command.
Once board A’s type is selected,
A
automatically increments to B and the process may be repeated.
Once all boards have been correctly defined, the user may select [Q] which sends default data to the
boards and continues to the next screen. NOTE: Before selecting [Q], the user should insure that the
DIP switch settings shown in Figure 2 are correct.
If a board is incorrectly identified, select the board that is not correctly defined by typing the corresponding board letter ([A], [B], or [C]). The user may then reselect the board’s type. Once the board has been
identified, the user may select the letter ([A], [B], or [C]) of the board followed by [S] to change hardware–
dependent variables for that board. See screen #1b.
[X] can be selected to exit the program completely. [?] can be selected to view the help screen.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Define boards to program
Available Boards:
Brd [A]!: N/A Brd [B]!: N/A Brd [C]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Board
A
is:
[–]! no board [4]! MC145200
[1]! MC145190 [5]! MC145201
[2]! MC145191 [6]! MC145202
[3]! MC145192
[–] Boards defined, Continue
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 12

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
12
Screen #1a Help Screen
Screen #1a is the help screen for the program. This screen is available from any point throughout the
program. A short list of the interface conventions are presented on this screen.
[X] can be selected to exit the program completely. [Q] can be selected to exit the help screen.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
1) Command keys are surrounded by []’s. Type the letter between the []’s to execute
the command. []’s are followed by a description of the command.
2) [–] indicates a command not available to the user.
3) []’s followed by an ! indicate the command will execute immediately. Otherwise a
sub menu will be displayed.
4) If no changes are desired to an input field, type the TAB key to move to the next
input field. The previous value will be used for that field.
5) All numbers are entered as decimal values unless otherwise noted. A $ followed by a
value indicates the value is in hexadecimal format.
6) The second line from the top of screen (screen title) states the purpose of the
screen.
7) Screen information that can be changed by the user is displayed in bold or reverse
video.
8) Commands are case independent. X is the same as x.
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [Q]! Quit help screen.
Page 13

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
13
MOTOROLA
Screen #2 ‘Select from the available options’
Screen #2 is the main screen of the program. This is where the user enters commands to demonstrate
the capabilities of the various boards connected to the computer. The title of the screen is ‘Select from
the available options’.
This screen is broken down into three sections:
Section #1, ‘Available Boards’
This section displays the board types that are connected to the computer. It also designates which
board is the currently selected ‘target’ board. This is the board that will receive the commands from
section #2. This section also provides the ability to change the targeted board. Type the target
board command ([A], [B], or [C]) to target that particular board.
Section #2, ‘MC145xxx Commands’
This section is further divided into three subsections. Each subsection contains commands that can
be sent to the ‘target’ board to demonstrate its capabilities. Each of these commands is described in
full in the Command Summary.
The first subsection, ‘MC145xxx Frequency Commands’, contains commands that are
used to modify the PLL frequency in some way . These commands are available for all possible target board types.
In the top line of this section, ‘Current Output Frequency is
746 MHz’
designates what the
frequency is for the currently targeted board. This value is dynamic.
On the lines below this,
741 MHz
is the current setting for the default low frequency.
746 MHz
is the current setting for the default medium frequency.
751 MHz is
the current
setting for the default high frequency.
The second subsection, ‘MC145xxx Additional Commands’, contains commands that
are used to further modify the currently targeted board. These commands also work with all
of the MC145xxx board types.
The third subsection, ‘MC145220 EVK – Single Specific Commands’, are only displayed when the MC145220EVK in single loop mode is the currently targeted board. This
section shows commands that are specific to this board. This is required since this board
contains the equivalent of two PLLs.
The command letter for ‘Set target PLL on board’ is [T]!. In single loop mode, the user may
toggle between PLL and PLL’ on the MC145220EVK by using this command. Feedback is
given to the user as to whether PLL or PLL’ will be accessed. See near the top of the screen
on the line titled “Available Boards - Current target board is: ...”
Section #3, ‘Initialization/System Setup Commands’
This section contains commands that are used to initialize all boards connected to the computer or
to set up the computer.
Page 14

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
14
Screen #2 ‘Select from the available options’ (continued)
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Select from the available options
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
MC145xxx Frequency Commands – Current Output Frequency is
746 MHz
[L]! Set to low freq
741 MHz
[W] Change default low freq.
[M]! Set to med. freq
746 MHz
[Y] Change default med. freq.
[H]! Set to high freq.
751 MHz
[Z] Change default high freq.
[U]! Step frequency up by step size [O] Set PLL output frequency
[D]! Step frequency down by step size [F] Set REFin freq. & channel spacing
MC145xxx Additional Commands
[E] Set function of output A [N] Change C Register
[R] Set crystal/reference mode – Current mode is Ref. mode, REFout low
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Initialization/System Setup Commands:
[P] Set output port address – Current address is $278
[G] Change board definitions
[I] Initialize board(s), Write all registers
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 15
MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
15
MOTOROLA
Screen #3 After [O] Command Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[O] Set PLL output frequency’
command. The user is prompted to enter the new frequency.
The current output frequency is automatically retained if the user hits return or [Q] without entering a
value.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Set PLL output frequency
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Input new frequency in integer values of MHz and kHz.
Original program default PLL output frequency is 746 MHz
Current PLL output frequency is 746 MHz
Current frequency range is 741 MHz to 751 MHz
Frequencies outside this range will be accepted.
New PLL frequency: 746 MHz + 000 kHz
[TAB] to move to next field
[Q] to return to main menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 16

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
16
Screen #4 After [F] Command Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[F] Set REFin freq. and channel
spacing’ command. The user is prompted to enter the new REFin frequency and channel spacing values,
or leave the fields blank to retain the prior settings.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Set REFin frequency and channel spacing
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Input new REFin frequency in integer values of MHz and kHz.
Original program default REFin frequency is 14.4 MHz
Current REFin frequency is 14.4 MHz
New REFin frequency: 14 MHz + 400 kHz
Input new channel spacing in integer values of MHz, kHz, and Hz.
Original program default channel spacing is 100 kHz
Current channel spacing is 100 kHz
New channel spacing: 0 MHz + 100 kHz + 000 Hz
[TAB] to move to next field
[Q] to return to main menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 17

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
17
MOTOROLA
Screen #5 After [W, Y or Z] Command Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[W] Change default low freq.’ command. The user is prompted to enter the new default low frequency value.
Entering a new value does not change the current output frequency of the target board. Changing the low
frequency simply adjusts the low frequency setting available from the main menu. The ‘[L]! Set to low
freq.’ command changes the current output frequency.
The screen is similar for the Y and Z commands except that the prompts specify medium or high frequency, respectively.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Set default low frequency
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Input new default low frequency in integer values of MHz and kHz.
Original program default low frequency is 741 MHz
Current low frequency is 741 MHz
New default low frequency: 741 MHz + 000 kHz
[TAB] to move to next field
[Q] to return to main menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 18

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
18
Screen #6 After [E] Command Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[E] Set function of output A’ command. The user is provided a submenu to select from.
The current setting for the function of Output A is displayed as Port, Data Out, fv or fr. The user may
choose from the listed commands to adjust this setting.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Set function of Output A
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Set Output A function – Currently: Data Out
[0]! Port
[1]! Data Out
[2]! fv
[3]! fr
[Q] to return to main menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 19

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
19
MOTOROLA
Screen #7 After [N] Command Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[N] Change C register and Prescale’ command. The user is provided a submenu to select from. Each submenu option also shows a
submenu.
If [Q] command is selected, the user is returned to the main menu. See screen #2.
If [0] command is selected, the user is presented with screen #8.
If [1] command is selected, the user is presented with screen #9.
If [2] command is selected, the user is presented with screen #10.
If [3] command is selected, the user is presented with screen #11.
If [4] command is selected, the user is presented with screen #12.
If [5] command is selected, the user is presented with screen #13.
If [6] command is selected, the user is presented with screen #14.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Change C Register
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Change C register:
[0] Output A – (Output A set to Port)
[1] Output B – (Out B)
[2] PDout Current – (PDout)
[3] Phase Detector Select – (PDA/B)
[4] Lock Detect Enable – (LDE)
[5] Phase Detector Polarity – (POL)
[6] Standby – (STBY)
Prescale:
[7] Prescale
[Q] to return to main menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 20

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
20
Screen #8 After [N] & [0] Commands Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[N] Change C Register’ and then
the ‘[0] Change output A’ command. The user is provided a submenu to select from. This submenu contains commands to toggle the Output A settings.
The current setting for Output A is displayed as Output High or Output Low. The user may choose from
the listed commands to toggle this setting.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Change C Register, Output A
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Change C Register, Output A state – Currently: Output High
[0]! Set to 0 (low)
[1]! Set to 1 (high)
[Q] to return to previous menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 21

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
21
MOTOROLA
Screen #9 After [N] & [1] Commands Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[N] Change C Register’ and then
the ‘[1] Change output B’ command. The user is provided a submenu to select from. This submenu contains commands to toggle the Output B settings.
The current setting for Output B is displayed as Output High or Output Low. The user may choose from
the listed commands to toggle this setting.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Change C Register, Output B
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Change C Register, Output B State – Currently: Output High
[0]! Set to 0 (low)
[1]! Set to 1 (high)
[Q] to return to previous menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 22

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
22
Screen #10 After [N] & [2] Commands Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[N] Change C Register’ and then
the ‘[2] Change PD
out
Current’ command. The user is provided a submenu to select from. This submenu
contains commands to change the PD
out
current settings.
The screen is slightly different depending on whether Output A is defined as a port or not. See command
[E] from the main menu.
Output A is configured as a port.
The current PD
out
setting is displayed as ‘70%’, ‘80%’, ‘90%’, or ‘100%’.
The user can select the [0], [1], [2], and [3] menu options to change the percent of PD
out
current.
If the [Q] command is selected, then the user is returned to the main menu. See screen #2.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Change C Register, PDout Current
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
When Output A is set to Port, Current range is 70 – 100%.
When Output A is NOT set to Port, Current range depends upon PDout Current Step Size.
When PDout Current Step Size is set to 10%, current range is 70 – 100%.
When PDout Current Step Size is set to 25%, current range is 25 – 100%.
Output A is currently defined as Port.
Change C Register, PDout Current – Currently: 100%
[0]! 70%
[1]! 80%
[2]! 90%
[3]! 100%
[Q] to return to previous menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 23

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
23
MOTOROLA
Screen #10a After [N] & [2] Commands Selected
Output A is NOT configured as a port.
The current PD
out
setting is displayed as ‘25%’, ‘50%’, ‘75%’, or ‘100%’, depending on current PD
out
setting.
The user can select the [0], [1], [2], and [3] menu options to change the percent of PD
out
current.
If the [Q] command is selected, then the user is returned to the main menu. See screen #2.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Change C Register, PDout Current
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
When Output A is set to Port, Current range is 70 – 100%.
When Output A is NOT set to Port, Current range depends upon PDout Current Step Size.
When PDout Current Step Size is set to 10%, current range is 70 – 100%.
When PDout Current Step Size is set to 25%, current range is 25 – 100%.
Output A is currently NOT defined as Port.
PDout Current Step Size is currently 25%
Change C Register, PDout Current – Currently: 100%
[0]! 25%
[1]! 50%
[2]! 75%
[3]! 100%
[Q] to return to previous menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 24

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
24
Screen #11 After [N] & [3] Commands Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[N] Change C Register’ and then
the ‘[3] Change Phase Detector Select’ command. The user is provided a submenu to select from. This
submenu contains commands to toggle the phase detector setting.
The current phase detector setting is displayed as ‘phi R & phi V’ or ‘PD
out
’, depending on the setting.
The user can select the [0] and [1] menu options to toggle the phase detector select setting.
If the [Q] command is selected, then the user is returned to the main menu. See screen #2.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Change C Register, Phase Detector Select
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Change C Register, Phase Detector Select – Currently: PDout
[0]! phi R & phi V
[1]! PDout
[Q] to return to previous menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 25

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
25
MOTOROLA
Screen #12 After [N] & [4] Commands Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[N] Change C Register’ and then
the ‘[4] Change Lock Detect Enable’ command. The user is provided a submenu to select from. This
submenu contains commands to toggle the lock detect enable setting.
The current setting for the lock detect is displayed as ‘Output low’ or ‘Enable output’, depending on the
setting.
The user can select the [0] and [1] menu options to toggle the lock detect enable setting.
If [Q] command selected then the user is returned to the main menu. See screen #2.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Change C Register, Lock Detect Enable
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Change C Register, Lock Detect Enable – Currently: Enable output
[0]! Output low
[1]! Enable output
[Q] to return to previous menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 26

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
26
Screen #13 After [N] & [5] Commands Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[N] Change C Register’ and then
the ‘[5] Change polarity of phase detector’ command. The user is provided a submenu to select from.
This submenu contains commands to toggle the polarity setting.
The current setting of the polarity is displayed as ‘Non–invert PD
out
, do not interchange phi R & phi V’ or
‘Invert PD
out
, interchange phi R & phi V’, depending on the polarity setting.
The user can select the [0] and [1] menu options to toggle the polarity setting.
If the [Q] command is selected, then the user is returned to the main menu. See screen #2.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Change C Register, Polarity
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Change C Register, Polarity – Currently: Non–invert PDout
[0]! Non–invert PDout, do not interchange phi R & phi V
[1]! Invert PDout, interchange phi R & phi V
[Q] to return to previous menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 27

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
27
MOTOROLA
Screen #14 After [N] & [6] Commands Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[N] Change C Register’ and then
the ‘[6] Change standby’ command. The user is provided a submenu to select from. This submenu contains commands to toggle the standby state setting.
The standby state setting is displayed as ‘Normal operation’ or ‘Standby’, depending on the current setting.
The user can select the [0] and [1] menu options to toggle the standby state setting.
If the [Q] command is selected, then the user is returned to the main menu. See screen #2.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Change C Register, Standby
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Change C Register, Standby – Currently: Normal Operation
[0]! Normal operation
[1]! Stand by
[Q] to return to previous menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 28

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
28
Screen #14a After [N] & [7] Commands Selected
This screen displays the current prescale ratio. However, the value may not be modified.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Change C Register, Prescale
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Evaulation program does not allow Prescale to be changed on this board.
Current Prescale Ratio is 64/65
[Q] to return to previous menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 29

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
29
MOTOROLA
Screen #15 After [P] Command Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[P] Set output port address’ command. The user is prompted to enter the new output port address in hexadecimal. This should be the port
address of the LPT1 printer port for the user’s computer.
The original program default port address and the current setting are displayed.
Enter the new output port address in hexadecimal format.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Set output port address
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Input new output port address in hexadecimal.
Original program default port address is $278
Current port address is $278
New output port address: $278
[Q] to return to main menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 30

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
30
Screen #16 After [R] Command Selected
This is the resulting screen that is displayed after the user selects the ‘[R] Set crystal/reference mode’
command. The user is provided a submenu to select from. This submenu contains commands to change
the crystal/reference mode.
The current reference mode is displayed as ‘Crystal mode, Shutdown’; ‘Crystal mode, Active’; ‘Reference mode, REFin enabled, REF
out
low’; ‘Reference mode, REF
out
= REFin’; ‘Reference mode, REF
out
=
REFin/2’; ‘Reference mode, REF
out
= REFin/4’; ‘Reference mode, REF
out
= REFin/8’; or ‘Reference
mode, REF
out
= REFin/16’, depending on the current setting.
The user can select the [0] to [7] menu options to change the crystal/reference mode setting.
If the [Q] command is selected, then the user is returned to the main menu. See screen #2.
Welcome to MC145xxx EVK Demonstration Program, rev 2.5
Set crystal or reference mode
Available Boards – Current target board is: A, MC145190
Brd [A]!: MC145190 Brd [–]!: N/A Brd [–]!: N/A
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Set crystal or reference mode – Currently: Ref. mode, REFout low
[0]! Crystal mode, Shutdown
[1]! Crystal mode, Active
[2]! Reference mode, REFin enabled, REFout low
[3]! Reference mode, REFout = REFin
[4]! Reference mode, REFout = REFin/2
[5]! Reference mode, REFout = REFin/4
[6]! Reference mode, REFout = REFin/8
[7]! Reference mode, REFout = REFin/16
[Q] to return to previous menu
[X]! Terminate demonstration program. [?]! View help screen.
Page 31

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
31
MOTOROLA
COMMAND SUMMARY
NOTE: MC145220 selections are not implemented in rev. 2.5.
[A]! Set board A as target
This command sets the target board to the board shown as A. This means that the commands that follow
will affect board A only. The user is informed of, and may modify, the target board in any screen of the
program except the help screen.
This is strictly an internal program command and has no effect on the MC145xxx EVKs connected to the
computer.
[B]! Set board B as target
This command sets the target board to the board shown as B. This means that the commands that follow
will affect board B only. The user is informed of, and may modify, the target board in any screen of the
program except the help screen.
This is strictly an internal program command and has no effect on the MC145xxx EVKs connected to the
computer.
[C]! Set board C as target
This command sets the target board to the board shown as C. This means that the commands that follow
will affect board C only. The user is informed of, and may modify, the target board in any screen of the
program except the help screen.
This is strictly an internal program command and has no effect on the MC145xxx EVKs connected to the
computer.
[L]! Set to low freq.
This command is used to set the frequency of the currently selected board to the currently defined low
value. This value can be changed via the [W] command.
This is accomplished by correctly adjusting the A register for the targeted board.
If the current EVK is the MC145220 and the board is in DUAL mode, then the currently targeted PLL on
the board is set to the specified low frequency. Otherwise, if the board is in SINGLE mode, both on–
board PLLs are set to the new frequency.
[M]! Set to medium freq.
This command is used just as the [L]! command except that the defined medium frequency value is used.
This default value can be changed by selecting command [N]. Reference [L]! command for further details.
[H]! Set to high freq.
This command is used just like the [L]! command except that the defined high frequency value is used.
This default value can be changed by selecting command [W]. Reference [L]! command for further details.
Page 32

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
32
[W] Change default low frequency
This command prompts the user (screen #5) to input a decimal value in MHz for the default low frequency. The program default low value is displayed along with the current value. The user may leave the low
frequency value as is by entering return without a value. The program low default value is dependent on
the targeted board type (see Table 2).
This value is not sent to the board immediately . It is the value that is sent to the board when the [L] command is executed.
Table 2.
Board Type
Program Default Low Frequency
MC145190
741 MHz
MC145191
733 MHz
MC145192
733 MHz
MC145200
1482 MHz
MC145201
1466 MHz
MC145202
1466 MHz
MC145220 in Single Loop Mode
733 MHz (PLL)
790 MHz (PLL’)
MC145220 in Dual Loop Mode
45 MHz
[Y] Change default medium frequency
This command prompts the user (screen #5) to input a decimal value in MHz for the default medium
frequency. The program default medium value is displayed along with the current value. The user may
leave the medium frequency value as is by entering return without a value. The program medium default
value is dependent on the targeted board type (see Table 3).
This value is not sent to the board at this time. It is the value that is sent to the board when the [M] command is executed.
Table 3.
Board Type
Program Default Medium Frequency
MC145190
746 MHz
MC145191
738 MHz
MC145192
738 MHz
MC145200
1492 MHz
MC145201
1476 MHz
MC145202
1476 MHz
MC145220 in Single Loop Mode
738 MHz (PLL)
805 MHz (PLL’)
MC145220 in Dual Loop Mode
60 MHz
Page 33

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
33
MOTOROLA
[Z] Change default high frequency
This command prompts the user (screen #5) to input a decimal value in MHz for the default high frequency. The program default high value is displayed along with the current value. The user may leave the high
frequency value as is by entering return without a value. The program high default value is dependent on
the targeted board type (see Table 4).
This value is not sent to the board immediately . It is the value that is sent to the board when the [L] command is executed.
Table 4.
Board Type
Program Default High Frequency
MC145190
751 MHz
MC145191
743 MHz
MC145192
743 MHz
MC145200
1502 MHz
MC145201
1486 MHz
MC145202
1486 MHz
MC145220 in Single Loop Mode
738 MHz (PLL)
820 MHz (PLL’)
MC145220 in Dual Loop Mode
75 MHz
[U]! Step frequency up by step size
This command increments the NCOUNTER and ACOUNTER fields of the A register for the currently
targeted board. This steps up the PLL’s frequency by the current step size for the board.
If the currently selected board is an MC145220 in DUAL mode, then the currently targeted PLL on the
board is “stepped”. If the MC145220 is in SINGLE mode, then both PLLs on the board are “stepped”.
[D]! Step frequency down by step size
This command decrements the NCOUNTER and ACOUNTER fields of the A register for the currently
targeted board. This is the effect of stepping down the PLL’s frequency by the current step size for the
board.
If the currently selected board is an MC145220 in DUAL mode, then the currently targeted PLL on the
board is “stepped”. If the MC145220 is in SINGLE mode, then both PLLs on the board are “stepped”.
[O] Set PLL output frequency
This command prompts the user (screen #3) to input a decimal value in MHz and kHz to set the targeted
board frequency. The program default PLL output frequency is displayed along with the current value.
The user may leave the output frequency value as is by entering return without entering a value. The
program validates the entered frequency by checking to ensure that the value is a multiple of the board’s
current step size and that the entered frequency / frequency step size is ≥ 4032. The program accepts
total divide values < 4032 if N ≥ A. (Total divide must be ≤ 262,143 for all PLLs.)
N*P+A = total divide (p = prescale = 64 for ’191).
A further check is made to ensure that the entered frequency is within the capability of the currently tar-
geted demonstration board (see Table 5). Frequencies outside the range are allowed for users who use
their own VCO.
Page 34

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
34
Table 5.
Board Type
Minimum Frequency
Maximum Frequency
MC145190
741 MHz
751 MHz
MC145191
733 MHz
743 MHz
MC145192
733 MHz
738 MHz
MC145200
1482 MHz
1502 MHz
MC145201
1466 MHz
1486 MHz
MC145202
1466 MHz
1486 MHz
MC145220 in Single Loop Mode
733 MHz (PLL)
790 MHz (PLL’)
743 MHz (PLL)
820 MHz (PLL’)
MC145220 in Dual Loop Mode
45 MHz
75 MHz
Once validated, the NCOUNTER and ACOUNTER fields of the A register are appropriately modified to
set the PLL frequency for the targeted board to the specified value.
If the currently targeted board is an MC145220 in DUAL mode, then the currently targeted PLL on the
board will have its frequency set. If the MC145220 is in single mode, then both PLLs on the board will
have their frequencies set.
[F] Set REFin frequency and channel spacing
This command prompts the user (screen #4) to input two values. First, a decimal value, in the form of
XX MHz + XXX kHz, to set the reference frequency of the targeted board. The program default frequency
is displayed along with the current value. The user may leave the reference frequency value as is by
entering return. A second input, in the form of XX MHz + XXX kHz, sets the channel spacing (step size)
of the targeted board. The program default step size is displayed along with the current value. The user
may leave the step size as is by entering return.
The inputs are validated by checking that the step size remains ≤ 2 MHz (≤ 1 MHz for the ’220) for all
boards. The entered frequency is validated to ensure that the new reference frequency / new step size is
< 8191 and is an even multiple of the new channel spacing.
Finally, the RCOUNTER of the R register is set with the value of (new reference frequency / new channel
spacing) and R register is written to the targeted board. Then the ACOUNTER and NCOUNTER are reset to the previous frequency using the new channel spacing (previous frequency / new channel spacing)
and the A register is written out.
Page 35

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
35
MOTOROLA
Table 6.
Board Type
Default Reference Frequency
Default Step Size
MC145190
14.4 MHz
100 kHz
MC145191
14.4 MHz
100 kHz
MC145192
14.4 MHz
100 kHz
MC145200
14.4 MHz
200 kHz
MC145201
14.4 MHz
200 kHz
MC145202
14.4 MHz
200 kHz
MC145220 in Single Loop Mode
10.01 MHz
10 kHz
MC145220 in Dual Loop Mode
10.01 MHz
10 Hz (10.01 kHz (PLL),
10 kHz (PLL’))
[E] Set function of output A
This command displays a submenu (screen #6) with the next four options displayed if the currently targeted board is the last board in the cascade. The user may only change the Output A configuration on
the last board in line. The user can select one of the following options to configure the Output A:
[0]! Port
Bits A23 and A22 (A22, A21 on ’220) are set to 00 binary while the remaining bits of register A are
preserved and the A register is written to the targeted board. Enable the [C][A] command.
[1]! Data Out
Bits A23 and A22 (A22, A21 on ’220) are set to 01 binary while the remaining bits of register A are
preserved and the A register is written to the targeted board. Disable the [C][A] command.
[2]! fv
Bits A23 and A
22
(A
22
, A21 on ’220) are set to 10 binary while the remaining bits of register A are
preserved and the A register is written to the targeted board. Disable the [C][A] command.
[3]! fr
Bits A23 and A22 (A22, A21 on ’220) are set to 1 1 binary while the remaining bits of register A are
preserved and the A register is written to the targeted board. Disable the [C][A] command.
[N] Change C Register
This command displays a submenu (screen #7) with the next seven options displayed. This is where the
user can modify the C register settings.
[0] Change output A – (Port)
This is only available with Output A configured as a port for the currently targeted board. See [A][0]!
command.
[0]! Reset output A to 0
This resets the PORT field of register C (C
1) to 0 and then writes register C to the currently
targeted board.
Page 36

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
36
[1]! Set output A to 1
This sets the PORT field of register C (C
1) to 1 and then writes register C to the currently
targeted board.
[1] Change output B (Out B) (not available on ’220)
Selects the logic state of output B.
[0]! Reset output B to 0
This resets the OUTB bit of register C (C0) to 0 and then writes register C to the currently
targeted board.
[1]! Set output B to 1
This sets the OUTB bit of register C (C0) to 1 and then writes register C to the currently targeted board.
[2] Change PD
out
current with Output A defined as port (not available on ’220)
If A23, A22 are both 0 then the currently targeted board is set up as a port and the following sub–
menu options are provided:
[0]! 70%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C3 and C2) is set to 00 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[1]! 80%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C3 and C2) is set to 01 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[2]! 90%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C3 and C2) is set to 10 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[3]! 100%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C3 and C2) is set to 1 1 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[2] Change PD
out
current with Output A NOT defined as port (not available on ’220)
[0]! 25%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C3 and C2) is set to 00 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[1]! 50%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C3 and C2) is set to 01 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[2]! 75%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C3 and C2) is set to 10 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
Page 37

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
37
MOTOROLA
[3]! 100%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C3 and C2) is set to 1 1 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[2] Change PD
out
current (only available on ’220)
[0]! 5%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C5 and C4) is set to 00 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[1]! 50%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C5 and C4) is set to 01 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[2]! 80%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C5 and C4) is set to 10 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[3]! 100%
The PD
out
field of register C (bits C5 and C4) is set to 1 1 binary while the remaining bits of
register C are preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[3] Change phase detector select (not available on ’220)
This command displays a submenu (screen #11) with the following options. It gives the user the
ability to select which phase detector is selected.
[0]! phi R & phi V
Bit C6 of register C is reset to 0 while the remaining bits are preserved and the C register is
written to the targeted board.
[1]! PD
out
Bit C6 of register C is set to 1 while the remaining bits are preserved and the C register is
written to the targeted board.
[3] Change phase detector (only available on ’220)
This command displays a submenu (screen #11) with the following options. It gives the user the
ability to select which phase detector is selected.
[0]! phi R & phi V
Bit C2 of register C is set to 1 while the remaining bits are preserved and the C register is
written to the targeted board.
[1]! PDout
Bit C2 of register C is reset to 0 while the remaining bits are preserved and the C register is
written to the targeted board.
Page 38

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
38
[4] Change lock detect enable (not available on ’220)
This command displays a submenu (screen #12) with the following options. It gives the user the
ability to change the lock detect setting.
[0]! Output low
Bit C5 of the C register is reset to 0 while the remaining bits are preserved and the C register
is written to the targeted board.
[1]! Enable output
Bit C5 of the C register is set to 1 while the remaining bits are preserved and the C register is
written to the targeted board.
[5] Change polarity
This command displays a submenu (screen #13) with the following options. It gives the user the
ability to change the output polarity of the phase detector.
[0]! Non–invert PD
out
Bit C7 (C0 for ’220) of the C register is reset to 0 while the remaining bits are preserved and
the C register is written to the targeted board.
[1]! Invert PD
out
Bit C7 (C0 for ’220) of the C register is set to 1 while the remaining bits are preserved and the
C register is written to the targeted board.
[6] Change standby (not available on ’220)
This command displays a submenu (screen #14) with the following commands available to set the
STBY (standby) field of the C register:
[0]! Normal operation
The STBY field of register C (bit C4) is reset to 0 while the remaining bits of register C are
preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[1]! Stand by
The STBY field of register C (bit C4) is set to 1 while the remaining bits of register C are
preserved and the C register is written to the targeted board.
[7] Change prescale (only available on ’220)
This command displays a submenu (screen #14a) with the following commands available to set the
prescale:
[0]! Prescale 32/33
The prescale is set to 32/33 while the remaining bits of the C register are preserved and the
C register is written to the targeted board.
[1]! Prescale 64/65
The prescale is set to 64/65 while the remaining bits of the C register are preserved and the
C register is written to the targeted board.
Page 39

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
39
MOTOROLA
[R] Set crystal/reference mode
This command displays a submenu (screen #16) with the following commands:
[0]! Crystal mode, shutdown
Bits R15, R14, and R13 of register R are reset to 000 binary while the remaining bits are preserved
and the R register is written to the targeted board.
[1]! Crystal mode, active
Bits R15, R14, and R13 of register R are set to 001 binary while the remaining bits are preserved and
the R register is written to the targeted board.
[2]! Reference mode, REFin enabled, REF
out
low
Bits R15, R14, and R13 of register R are set to 010 binary while the remaining bits are preserved and
the R register is written to the targeted board.
[3]! Reference mode, REF
out
= REF
in
Bits R15, R14, and R13 of register R are set to 01 1 binary while the remaining bits are preserved and
the R register is written to the targeted board.
[4]! Reference mode, REF
out
= REFin/2
Bits R15, R14, and R13 of register R are set to 100 binary while the remaining bits are preserved and
the R register is written to the targeted board.
[5]! Reference mode, REF
out
= REFin/4
Bits R15, R14, and R13 of register R are set to 101 binary while the remaining bits are preserved and
the R register is written to the targeted board.
[6]! Reference mode, REF
out
= REFin/8
Bits R15, R14, and R13 of register R are set to 1 10 binary while the remaining bits are preserved and
the R register is written to the targeted board.
[7]! Reference mode, REF
out
= REFin/16
Bits R15, R14, and R13 of register R are set to 1 11 binary while the remaining bits are preserved and
the R register is written to the targeted board.
[T]! Set target PLL on board
This command is only available when the targeted board is a MC145220EVK, and that board is in single
loop mode (see [B]! command). The MC145220EVK contains two PLLs, which are designated PLL and
PLL’. This command is a toggle function which directs the program to “steer” subsequent commands to
either PLL or PLL’ on the targeted MC145220EVK.
[P] Set output port address
This command prompts the user (screen #13) to input a hexadecimal address of the printer port on their
computer. This address is where the EVK boards are connected. The entered address is displayed on
screen #2 next to the [P] command prompt.
[G] Change board definitions
This command returns the user to the board definition screen. The user may then define a different cascade of boards.
Page 40

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
40
[I]! Initialize board(s), write all registers
This command writes out all of the registers for all of the boards that are currently attached to the computer. The current settings are used for the registers.
This correctly writes out the C, R, and A registers for each EVK board connected to the bus. In the case
of MC145220EVKs, they are set to SINGLE (RESET/DEFAULT) mode and then have both PLL and PLL’
registers written.
[X]! Terminate demonstration program
This command causes the program to terminate and returns the user to DOS.
[?]! View help screen
This command displays the help screen (screen #1a).
Page 41

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
41
MOTOROLA
APPENDIX
MC145192/202 EVK PLL and BUS Interface Rev. 2
Page 42

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
42
MC145192/202 EVK Power Supply Rev. 2
NOTES:
1. Default unit for capacitance is pF.
2. Default unit for resistance is ohms.
3. Board material is 1/16” thick G10.
4. Test points are 0.04” diameter plated through holes.
5. U1, R2, R8, C22, J3, and J4 are different on each type of EVK.
See the manual section titled “Components Unique to Each EVK”.
Page 43

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
43
MOTOROLA
Drill Layer with Silkscreen (Top View)
Dimensions are in Inches
Page 44

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
44
Silkscreen Layer (Top View)
Page 45

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
45
MOTOROLA
MC145192EVK Signal Plot
RL 10.0 dBm 10 dB/Div.
CENTER 738 MHz SPAN 250.0 kHz
RBW 1.0 kHz VBW 1.0 kHz
∆MKR
100.4 kHz
–77.00 dB
D
MC145202EVK Signal Plot
RL 10.0 dBm 10 dB/Div.
CENTER 1.476 GHz SPAN 500.0 kHz
RBW 3.0 kHz VBW 3.0 kHz
∆MKR
200.0 kHz
–79.66 dB
D
Page 46

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
46
Bill of Materials — MC145192 PLL Evaluation Board Rev. 2
Part Type Package Manufacturer Value Quantity References
2SV–02 Pwr Connect Special Augat 1 J6
50–651–0000–31 SMA Female Special ITT Sealectro 2 J8, J10
51R05279V17 VCO, MS Spec Special Motorola 1 M1
76SB08S DIP Switch 16 Pin Grayhill 1 S1
617Y–025SAJ120 DB–25 Female Special Amphenol 1 J5
3266W1–103 Trim Pot. Special Bourns 10 k 1 VR1
Capacitor 5%, X7R 0805 0.022 µF 1 C4
Capacitor Ceramic 0805 0.1 µF 9 C1, C2, C8, C9, C12,
C14, C16, C23, C26
Capacitor AccuF, ± .1, 50 V 0805 AVX 0.5 1 C15
Capacitor AccuF, ± .1, 50 V 0805 AVX 1.5 1 C25
Capacitor AccuF, ± .1, 50 V 0805 AVX 1.8 2 C13, C18
Capacitor AccuF, ± .1, 50 V 0805 AVX 6.2 2 C19, C21
Capacitor AccuF, ± .1, 50 V 0805 AVX 8.2 1 C20
Capacitor 5% NPO 0805 82 1 C6
Capacitor 5% NPO 0805 100 2 C3, C7
Capacitor 5% NPO 0805 3900 1 C5
HLMP–6001–011 LED Special HP 1 D1
HSMS–8101 Diode SOT–23 HP 3 D2, D3, D4
INA–10386 MMIC Amp Special HP 1 U6
Jumper 2 x 1 Header 0.1″ Grid 2 J1, J2
KXN1142AA SP01 Saber TCXO Special Motorola 14.4 MHz 1 M2
LM317MDT Regulator Special Motorola 3 U3, U4, U7
MC74HCT241ADW Octal Buffer SO–20 Motorola 1 U5
MC145192F PLL IC SOG Motorola 1 U1
Resistor 5% CF 0805 0 1 R8
Resistor 5% CF 0805 1 k 4 R1, R5, R7, R18
Resistor 5% CF 0805 1.8 k 1 R3
Resistor 5% CF 0805 3.9 k 3 R19, R20, R21
Resistor 5% CF 0805 13 k 1 R11
Resistor 5% CF 0805 18 k 1 R2
Resistor 5% CF 0805 Kamaya 51 1 R10
Resistor 5% CF 0805 100 k 2 R9, R12
Resistor 5% CF 0805 Kamaya 120 1 R6
Resistor 5% CF 0805 Kamaya 180 1 R14
Resistor 5% CF 0805 300 3 R4, R15, R17
Resistor 5% CF 0805 430 1 R13
Resistor 5% CF 0805 910 1 R16
SN74LS126D Quad Buffer SO–14 Motorola 1 U2
TDC–336K010NSF Tant. Cap Special Mallory 33 µF, 10 V 2 C10, C11
Wire Jumper 0.6″, 24 AWG 1 J13
Wire Jumper, 2–Way 0.6″, 24 AWG 2 J3, J4
SJ5027SPBL Rubber Bumpers 3M 5
NOTE:J3 is connected to 3 V; J4 to 5 V. The rubber bumpers must be glued on bottom side of board in the four corners and in the center.
Page 47

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
47
MOTOROLA
Bill of Materials — MC145202 PLL Evaluation Board Rev. 2
Part Type Package Manufacturer Value Quantity References
2SV–02 Pwr Connect Special Augat 1 J6
50–651–0000–31 SMA Female Special ITT Sealectro 2 J8, J10
51R05279V17 VCO, MS Spec Special Motorola 1 M1
76SB08S DIP Switch 16 Pin Grayhill 1 S1
617Y–025SAJ120 DB–25 Female Special Amphenol 1 J5
3266W1–103 Trim Pot. Special Bourns 10 k 1 VR1
Capacitor 5%, X7R 0805 0.022 µF 1 C4
Capacitor Ceramic 0805 0.1 µF 9 C1, C2, C8, C9, C12,
C14, C16, C23, C26
Capacitor AccuF, ± .1, 50 V 0805 AVX .05 1 C15
Capacitor AccuF, ± .1, 50 V 0805 AVX 1.0 1 C22
Capacitor AccuF, ± .1, 50 V 0805 AVX 1.5 1 C25
Capacitor AccuF, ± .1, 50 V 0805 AVX 1.8 2 C13, C18
Capacitor AccuF, ± .1, 50 V 0805 AVX 6.2 2 C19, C21
Capacitor AccuF, ± .1, 50 V 0805 AVX 8.2 1 C20
Capacitor 5% NPO 0805 82 1 C6
Capacitor 5% NPO 0805 100 2 C3, C7
Capacitor 5% NPO 0805 3900 1 C5
HLMP–6001–011 LED Special HP 1 D1
HSMS–8108 Diode SOT–23 HP 3 D2, D3, D4
INA–10386 MMIC Amp Special HP 1 U6
Jumper 2 x 1 Header 0.1″ Grid 2 J1, J2
KXN1142AA SP01 Saber TCXO Special Motorola 14.4 MHz 1 M2
LM317MDT Regulator Special Motorola 3 U3, U4, U7
MC74HCT241ADW Octal Buffer SO–20 Motorola 1 U5
MC145202F PLL IC SOG Motorola 1 U1
Resistor 5% CF 0805 1 k 4 R1, R5, R7, R18
Resistor 5% CF 0805 1.8 k 1 R3
Resistor 5% CF 0805 3.9 k 4 R2, R19, R20, R21
Resistor 5% CF 0805 13 k 1 R11
Resistor 5% CF 0805 Kamaya 51 1 R10
Resistor 5% CF 0805 100 k 2 R9, R12
Resistor 5% CF 0805 Kamaya 120 1 R6
Resistor 5% CF 0805 Kamaya 180 1 R14
Resistor 5% CF 0805 300 3 R4, R15, R17
Resistor 5% CF 0805 430 1 R13
Resistor 5% CF 0805 910 1 R16
SN74LS126D Quad Buffer SO–14 Motorola 1 U2
TDC–336K010NSF Tant. Cap Special Mallory 33 µF, 10 V 2 C10, C11
Wire Jumper 0.6″, 24 AWG 1 J13
Wire Jumper, 2–Way 0.6″, 24 AWG 2 J3, J4
SJ5027SPBL Rubber Bumpers 3M 5
NOTE:J3 and J4 are connected to 5 V. The rubber bumpers must be glued on bottom side of board in the four corners and in the center.
Page 48

MC145192EVK • MC145202EVK
MOTOROLA
48
How to reach us:
USA/EUROPE: Motorola Literature Distribution; JAPAN: Nippon Motorola Ltd.; Tatsumi–SPD–JLDC, Toshikatsu Otsuki,
P.O. Box 20912; Phoenix, Arizona 85036. 1–800–441–2447 6F Seibu–Butsuryu–Center, 3–14–2 Tatsumi Koto–Ku, Tokyo 135, Japan. 03–3521–8315
MFAX: RMFAX0@email.sps.mot.com – TOUCHTONE (602) 244–6609 HONG KONG: Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.; 8B Tai Ping Industrial Park,
INTERNET: http://Design–NET.com 51 Ting Kok Road, Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong. 852–26629298
Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty , representation or guarantee regarding
the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit,
and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. “T ypical” parameters can and do vary in different
applications. All operating parameters, including “T ypicals” must be validated for each customer application by customer’s technical experts. Motorola does
not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Motorola products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in
systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of
the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such
unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Motorola and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless
against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death
associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
Motorola and are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
◊
 Loading...
Loading...