Datasheet MAX6330SUR-T, MAX6330TUR-T, MAX6330LUR-T, MAX6331LUR-T, MAX6331SUR-T Datasheet (Maxim)
...Page 1
For free samples & the latest literature: http://www.maxim-ic.com, or phone 1-800-998-8800.
For small orders, phone 408-737-7600 ext. 3468.
________________General Description
The MAX6330/MAX6331 combine a precision shunt
regulator with a power-on reset function in a single
SOT23-3 package. They offer a low-cost method of
operating small microprocessor (µP)-based systems
from high-voltage sources, while simultaneously protecting µPs from power-up, power-down, and brownout
conditions.
Both active-low (MAX6330) and active-high (MAX6331)
push/pull output versions are available. The output
voltage has ±1.5% tolerance. The MAX6330/MAX6331
operate over a wide shunt current range from 100µA to
50mA, and offer very good transient immunity.
A 3-pin SOT23 package allows for a significant reduction in board space and improves reliability compared
to multiple-IC/discrete solutions. These devices have a
minimum order increment of 2,500 pieces.
________________________Applications
Controllers
Household Appliances
Intelligent Instruments
Critical µP and µC Power Monitoring
Portable/Size-Sensitive Equipment
Automotive
____________________________Features
♦ 100µA to 50mA Shunt Current Range
♦ Low Cost
♦ 3-Pin SOT23 Package
♦ ±1.5% Tolerance on Output Voltage
♦ Three Shunt Voltages Available: 5V, 3.3V, 3.0V
♦ Precision Power-On Reset Threshold:
1.5% Tolerance Available with Either
RESET (MAX6331) or
RESET (MAX6330)
Outputs
♦ 140ms Reset Timeout Period—No External
Components Required
MAX6330/MAX6331
Precision Shunt Regulators with Reset
in SOT23-3
________________________________________________________________
Maxim Integrated Products
1
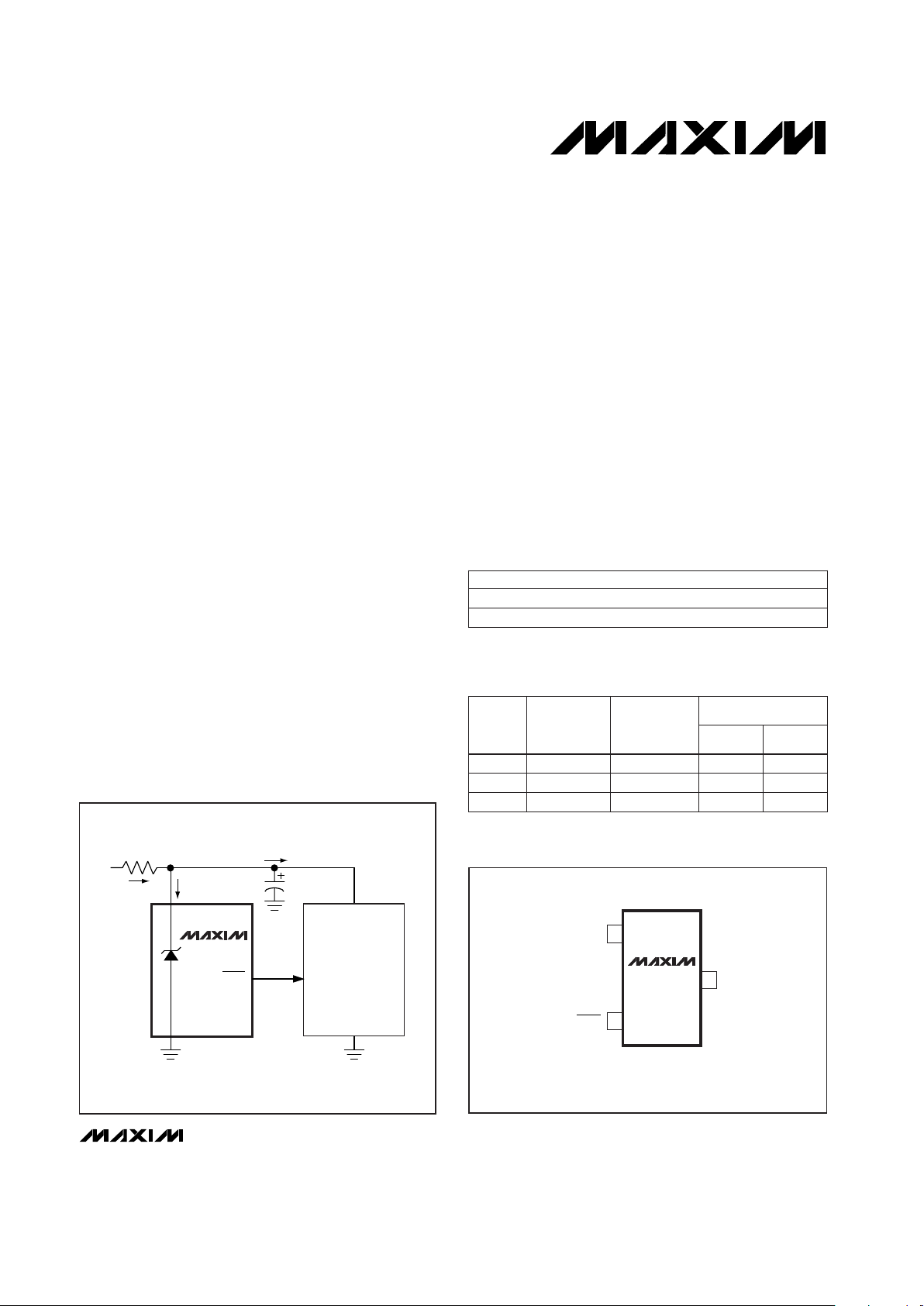
TOP VIEW
RESET
(RESET)
1
GND
( ) ARE FOR THE MAX6331
SHUNT
MAX6330
MAX6331
SOT23-3
2
3
___________________Pin Configuration
____________Typical Operating Circuit
MAX6330
MAX6331
SHUNT
V
SHUNT
I
SHUNT
I
LOAD
V
IN
RESET
(RESET)
RESET
INPUT
GND
V
CC
CL
0.1µF*
GND
µP
*SEE THE SECTION
CHOOSING THE BYPASS CAPACITOR (CL)
I
IN
R
S
19-1348; Rev 0; 4/98
PART*
MAX6330_UR-T
MAX6331_UR-T
-40°C to +85°C
-40°C to +85°C
TEMP. RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
3 SOT23-3
3 SOT23-3
_______________Ordering Information
*Insert the desired suffix letter (from the table below) into the
blank to complete the part number. These devices have a minimum order increment of 2,500 pieces.
SUFFIX
L
T 3.06
4.63
RESET
THRESHOLD
(V)
EKAA
EMAA3.3
5.0
SHUNT
REGULATOR
VOLTAGE (V)
SOT
TOP MARK
ELAA
ENAA
S 3.02.78 EDAA EPAA
MAX6330 MAX6331
Page 2
MAX6330/MAX6331
Precision Shunt Regulators with Reset
in SOT23-3
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
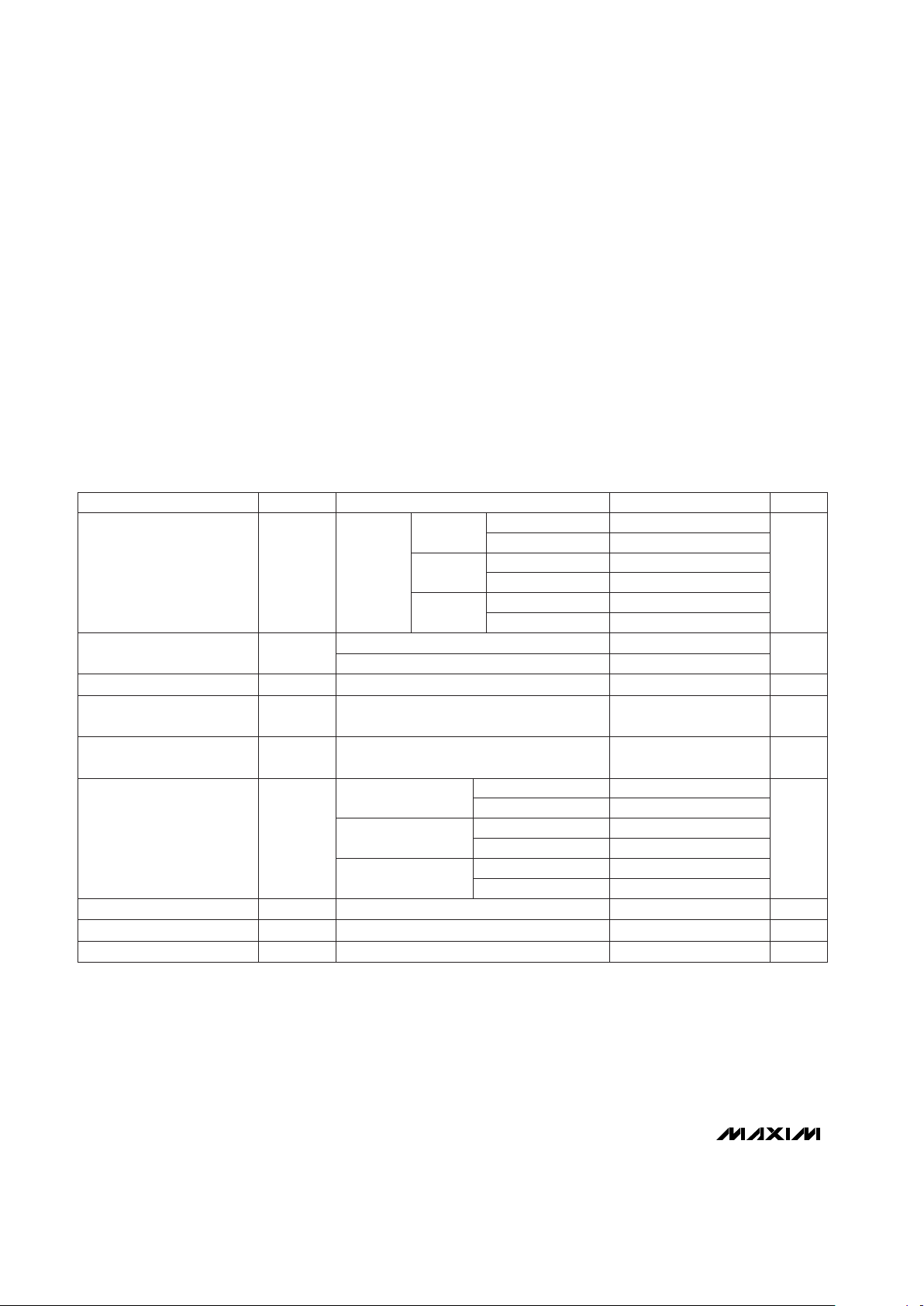
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(I
SHUNT
= 1mA, CL= 0.1µF, TA= -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Terminal Voltage (with respect to GND),
All Pins Except SHUNT....................-0.3V to (V
SHUNT
+ 0.3V)
Input Current (I
SHUNT
)........................................................60mA
Output Current (RESET/
RESET)..........................................20mA
Short-Circuit Duration.................................................Continuous
Continuous Power Dissipation
SOT23-3 (derate 4mW/°C above +70°C)....................320mW
Operating Temperature Range ...........................-40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range.............................-65°C to +160°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10sec).............................+300°C
MAX633_L
TA= 0°C to +70°C
TA= -40°C to +85°C
100mV overdrive, CL= 15pF
CONDITIONS
ms100 140 200Reset Pulse Width
µs20V
SHUNT
to Reset Delay
3.25 3.3 3.35
4.85 5.15
V
4.93 5.0 5.07
V
SHUNT
Regulation Voltage
(Note 1)
ppm/°C40Reset Threshold Tempco
V
4.56 4.63 4.69
V
TH
Reset Threshold Voltage
mA50I
SHUNT(max)
Maximum Shunt Current
(Note 3)
µA100 60I
SHUNT(min)
Minimum Shunt Current
(Note 2)
V
1.0
Minimum V
SHUNT
for which
RESET is Valid (MAX6330)
1.2
ppm/°C40V
SHUNT
Tempco
UNITSMIN TYP MAXSYMBOLPARAMETER
V
SHUNT
2.91 3.09
2.96 3.0 3.04
3.20 3.40
TA= -40°C to +85°C
TA= +25°C
TA= +25°C
TA= -40°C to +85°C
TA= +25°C
TA= -40°C to +85°C
TA= +25°C
TA= -40°C to +85°C
I
SHUNT
=
0.1mA to
50mA
4.50 4.75
2.97 3.15
MAX633_T
TA= +25°C
TA= -40°C to +85°C
3.01 3.06 3.11
2.70 2.86
MAX633_S
TA= +25°C
TA= -40°C to +85°C
2.74 2.78 2.82
MAX633_L
MAX633_T
MAX633_S
Page 3
MAX6330/MAX6331
Precision Shunt Regulators with Reset
in SOT23-3
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
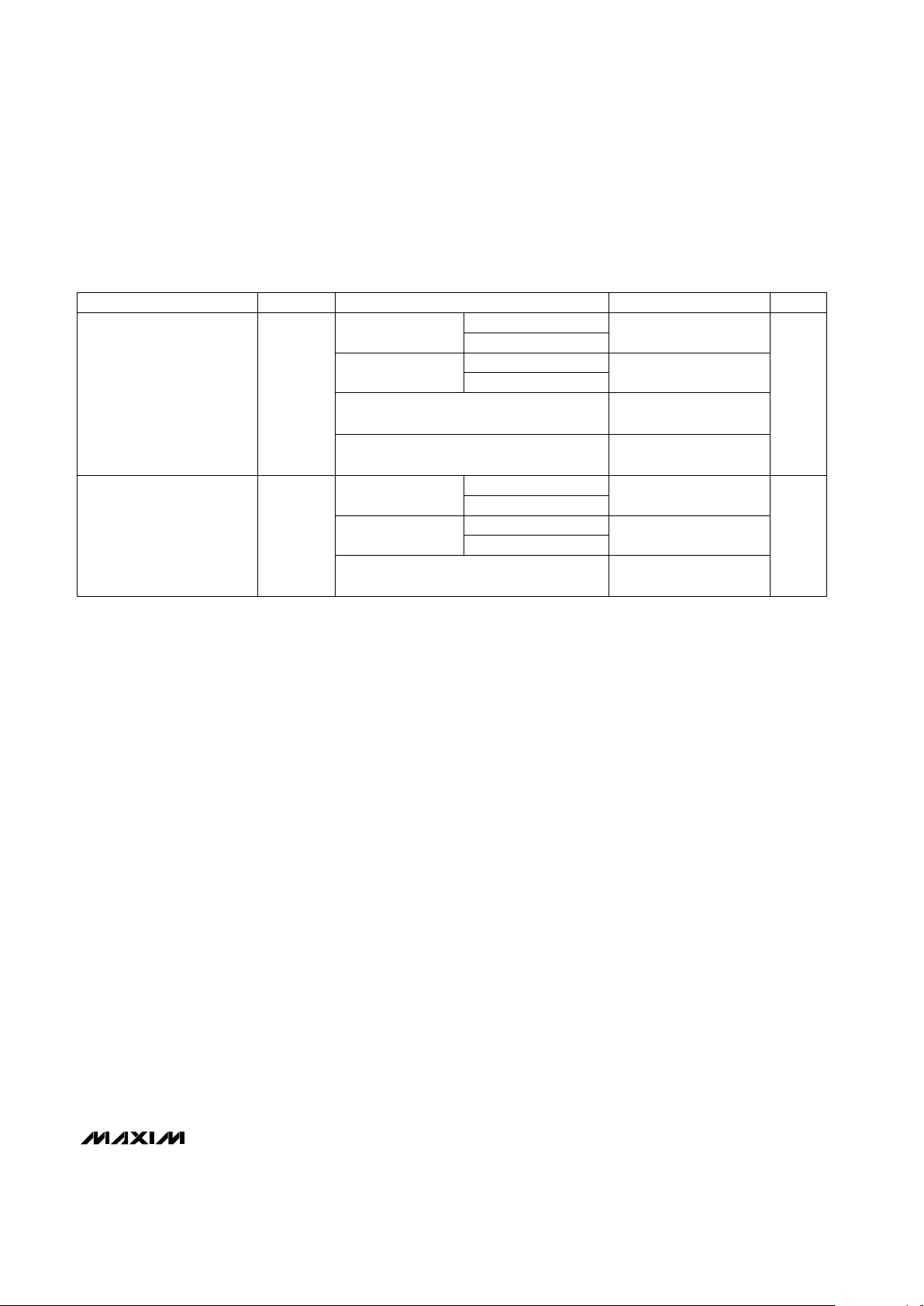
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(I
SHUNT
= 1mA, CL= 0.1µF, TA= -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
Note 1: It is recommended that the regulation voltage be measured using a 4-wire force-sense technique when operating at high
shunt currents. For operating at elevated temperatures, the device must be derated based on a +150°C maximum allowed
junction temperature and a maximum thermal resistance of 0.25°C/mW junction to ambient when soldered on a printed circuit board. The T
A
= +25°C specification over load is measured using a pulse test at 50mA with less than 5ms on time.
Note 2: Minimum shunt current required for regulated V
SHUNT
.
Note 3: Maximum shunt current required for regulated V
SHUNT
.
Note 4: In a typical application where SHUNT serves as the system voltage regulator, note that both I
SOURCE
for VOHand I
SINK
for
V
OL
come from V
SHUNT
(see the
Typical Operating Circuit
).
CONDITIONS UNITSMIN TYP MAXSYMBOLPARAMETER
I
SINK
= 1.2mA
MAX6330T/S, V
TH
(min)
I
SINK
= 3.2mA
MAX6330, V
SHUNT
= 1V, I
SINK
= 50µA,
TA= 0°C to +70°C
0.3
MAX6330L, V
TH
(min)
0.3
MAX6331L, V
TH
(max)
MAX6331T/S, V
TH
(max)
0.4
V
OL
RESET/RESET Output
Voltage Low (Note 4)
MAX6330, V
SHUNT
= 1.2V, I
SINK
= 50µA,
TA= -40°C to +85°C
0.3
V
I
SOURCE
= 500µA
MAX6331T/S, V
TH
(min)
I
SOURCE
= 800µA
MAX6331, 1.8V < V
SHUNT
< V
TH(min)
,
I
SOURCE
= 150µA
0.8 x V
SHUNT
MAX6331L, V
TH
(min)
0.8 x V
SHUNT
MAX6330L, V
TH
(max)
MAX6330T/S, V
TH
(max)
0.8 x V
SHUNT
V
OH
RESET/RESET Output
Voltage High (Note 4)
V
Page 4

MAX6330/MAX6331
Precision Shunt Regulators with Reset
in SOT23-3
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
0.990
0.995
1.000
1.005
0.01 10.1 10 50
NORMALIZED SHUNT VOLTAGE
vs. SHUNT CURRENT
MAX6330 TOC01
SHUNT CURRENT (mA)
NORMALIZED SHUNT VOLTAGE
TA = +85°C
TA = -40°C
TA = +25°C
0.990
0.995
1.000
1.005
-40 0-20 20 40 60 80
NORMALIZED SHUNT VOLTAGE
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX6330 TOC02
TEMPERATURE (°C)
NORMALIZED SHUNT VOLTAGE
I
SHUNT
= 50mA
I
SHUNT
= 25mA
I
SHUNT
= 1mA
100
110
120
130
150
140
160
-40 0-20 20 40 60 80
POWER-UP RESET TIMEOUT
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX6330 TOC03
TEMPERATURE (°C)
POWER-UP RESET TIMEOUT (ms)
0.990
0.995
1.005
1.000
1.010
-40 0-20 20 40 60 80
NORMALIZED RESET THRESHOLD
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX6330 TOC04
TEMPERATURE (°C)
NORMALIZED RESET THRESHOLD
VIN
50V/div
V
SHUNT
2V/div
0
START-UP TRANSIENT
MAX6330 TOC07
RS = 15kΩ
0
0.0047 10.10.01
SHUNT VOLTAGE OVERSHOOT
vs. BYPASS CAPACITANCE (C
L
)
15
5
35
25
40
20
10
30
MAX6330 TOC5
LOAD CAPACITANCE (µF)
SHUNT VOLTAGE OVERSHOOT (mV)
I
SHUNT
= 5mA TO 50mA
I
SHUNT
= 0.1mA TO 5mA
I
SHUNT
= 1mA TO 1mA
50
1
0.001 10.10.01
STABILITY BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
10
20
30
40
MAX6330 TOC06
LOAD CAPACITANCE (µF)
SHUNT CURRENT (mA)
UNSTABLE REGION
RECOMMENDED
CAPACITOR
OPERATING
REGION
RECOMMENDED
CAPACITANCE
RECOMMENDED
CAPACITOR
__________________________________________Typical Operating Characteristics
(Typical Operating Circuit, CL= 0.1µF, I
LOAD
= 0mA, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
Page 5

MAX6330/MAX6331
Precision Shunt Regulators with Reset
in SOT23-3
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
______________________________________________________________Pin Description
PIN
FUNCTION
1 1 Ground
2 —
Inverting Reset Output. RESET remains low while V
SHUNT
is below the reset threshold and
for 140ms after V
SHUNT
rises above the threshold.
—
2
Noninverting Reset Output. RESET remains high while V
SHUNT
is below the reset threshold
and for 140ms after V
SHUNT
rises above the threshold.
3 3 Regulated Shunt Voltage (+5V, +3.3V, or +3.0V)
NAME
GND
RESET
RESET
SHUNT
MAX6331MAX6330
_______________Detailed Description
Reset Output
A microprocessor’s (µP’s) reset input starts the µP in a
known state. The MAX6330/MAX6331 µP supervisory
circuits assert reset to prevent code-execution errors
during power-up, power-down, or brownout conditions.
RESET is guaranteed to be a logic low for V
SHUNT
>
1V. Once V
SHUNT
exceeds the reset threshold, an
internal timer keeps RESET low for the reset timeout
period; after this interval, RESET goes high.
If a brownout condition occurs (V
SHUNT
dips below the
reset threshold), RESET goes low. When V
SHUNT
falls
below the reset threshold, the internal timer resets to
zero and RESET goes low. The internal timer starts after
V
SHUNT
returns above the reset threshold, and RESET
then remains low for the reset timeout period.
The MAX6331 has an active-high RESET output that is
the inverse of the MAX6330’s RESET output.
Shunt Regulator
The shunt regulator consists of a pass device and a
controlling circuit, as illustrated in Figure 1. The pass
device allows the regulator to sink current while regulating the desired output voltage within a ±1.5% tolerance. The shunt current range (I
SHUNT
) is 100µA to
50mA.
The pass transistor in the MAX6330/MAX6331 main-
tains a constant output voltage (V
SHUNT
) by sinking the
necessary amount of shunt current. When I
LOAD
(see
Typical Operating Circuit
) is at a maximum, the shunt
current is at a minimum, and vice versa:
IIN= I
SHUNT
+ I
LOAD
= (VIN- V
SHUNT
) / R
S
Consider the following information when choosing the
external resistor RS:
1) The input voltage range, (V
IN)
2) The regulated voltage, (V
SHUNT
)
3) The output current range, (I
LOAD)
Choose RSas follows:
(V
IN(max)
- V
SHUNT (min)
) / (50mA + I
LOAD(min)
) ≤ RS≤
(V
IN(min)
- V
SHUNT (max)
) / (100µA + I
LOAD(max)
)
Choose the largest nominal resistor value for RSthat
gives the lowest current consumption. Provide a safety
margin to incorporate the worst-case tolerance of the
MAX6330
MAX6331
V
IN
RSV
SHUNT
I
LOAD
I
SHUNT
I
IN
C
L
SHUNT
RESET
GENERATOR
140ms
TIMEOUT
RESET
(RESET)
1.2V
GND
( ) ARE FOR MAX6331
Figure 1. Functional Diagram
Page 6

MAX6330/MAX6331
Precision Shunt Regulators with Reset
in SOT23-3
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
resistor used. Ensure that the resistor’s power rating is
adequate, using the following general power equation:
PR= IIN(V
IN(max)
- V
SHUNT
)
= I
2
INRS
= (V
IN(max)
- V
SHUNT
)2/ R
S
_____________Applications Information
Negative-Going V
SHUNT
Transients
In addition to issuing a reset to the µP during power-up,
power-down, and brownout conditions, the MAX6330/
MAX6331 are relatively immune to short-duration negative-going V
SHUNT
transients (glitches). Additional
bypass filter capacitance mounted close to the SHUNT
pin provides additional transient immunity.
Choosing the Bypass Capacitor, C
L
The bypass capacitor (CL) on the SHUNT pin can significantly affect the device’s load-transient response, so
choose it carefully. When a load transient occurs, the
current for this load is diverted from the shunt regulator.
The maximum load current that can be diverted from
the regulator is:
I
LOAD
(diverted from regulator)
= I
SHUNT(max)
- I
SHUNT(min)
= 50mA - 100µA
= 49.9mA
The shunt regulator has a finite response to this transient. The instantaneous requirements of the load
change are met by the charge on CL, resulting in overshoot/undershoot on V
SHUNT
. The magnitude of this
overshoot/undershoot increases with I
SHUNT
and
decreases with CL. When V
SHUNT
undershoots, the
shunt current decreases to where it will only draw quiescent current (IQ), and the shunt element turns off. At
this point, V
SHUNT
will slew toward VINat the following
rate:
∆V
SHUNT
/ ∆t = (IIN- I
LOAD
- 60µA) / C
L
As V
SHUNT
rises, it will turn on the shunt regulator when
it can sink 100µA of current. A finite response time for
the shunt regulator to start up will result in a brief overshoot of V
SHUNT
before it settles into its regulation volt-
age. Therefore, I
LOAD
should always be 100µA or more
below IIN, or V
SHUNT
will not recover to its regulation
point. To prevent this condition, be sure to select the
correct series-resistor RSvalue (see the
Shunt
Regulator
section).
Figures 2, 3, and 4 show load-transient responses for
different choices of bypass capacitors on V
SHUNT
.
These photos clearly illustrate the benefits and drawbacks of the capacitor options. A smaller bypass
I
LOAD
2mA/div
V
SHUNT
20mV/div
0
0
MAX6330 FIG 02
IIN = 2mA, I
LOAD
= 0 to 1.9mA
V
SHUNT
IS AC COUPLED
Figure 2. Load-Transient Response with CL= 0.22µF
I
LOAD
2mA/div
V
SHUNT
20mV/div
0
0
MAX6330 FIG 03
IIN = 2mA, I
LOAD
= 0 to 1.9mA,
V
SHUNT
IS AC COUPLED
Figure 3. Load-Transient Response with CL= 0.033µF
I
LOAD
2mA/div
V
SHUNT
20mV/div
0
0
MAX6330 FIG 04
IIN = 2mA, I
LOAD
= 0 to 1.9mA
V
SHUNT
IS AC COUPLED
Figure 4. Load-Transient Response with CL= 0.0047µF
Page 7

MAX6330/MAX6331
Precision Shunt Regulators with Reset
in SOT23-3
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
capacitor allows a sharper drop in V
SHUNT
when the
load transient occurs, and will suffer from a steeper
overshoot when the device re-enters regulation. On the
other hand, the increased compensation on a larger
bypass capacitor will lead to a longer recovery time to
regulation. The
Typical Operating Characteristics
graph
Overshoot vs. Bypass Capacitance (CL) illustrates this
trade-off.
If the compensation of the bypass capacitor chosen is
insufficient, the output (V
SHUNT
) can oscillate. Before
choosing a bypass capacitor for the desired shunt current, observe the stability boundary conditions indicated
in the
Typical Operating Characteristics
. The minimum
output capacitance is 0.03µF to ensure stability over the
full load-current range.
Adding Hysteresis
In certain circumstances, the MAX6330 can be trapped
in a state that forces it to enter into and exit from a reset
condition indefinitely. This usually occurs in systems
where V
SHUNT
is just below the device’s trip threshold
and the system draws less quiescent current under reset
conditions than when operating out of reset. The difference in supply current when the device is in or out of
reset can translate to a significant change in the voltage
drop across RS, which the MAX6330’s built-in hysteresis
may not overcome. A 100kΩ pull-up resistor will overcome this condition and add hysteresis (Figure 5).
Note that adding this pull-up resistor to the MAX6330 will
render RESET invalid with V
SHUNT
< 1V, since this output
loses sinking capability at this point, and the pull-up resistor would invalidate the signal. This does not present a
problem in most applications, since most µPs and other
circuitry are inoperative when V
SHUNT
is below 1V.
Interfacing to µPs with
Bidirectional Reset Pins
Microprocessors with bidirectional reset pins (such as
the Motorola 68HC11 series) can contend with
MAX6330’s reset output. If, for example, the MAX6330’s
RESET output is asserted high and the µP wants to pull
it low, indeterminate logic levels may result. To correct
this, connect a 4.7kΩ resistor between the RESET output and the µP reset I/O (Figure 6). Buffer the RESET
output to other system components. Also, RSmust be
sized to compensate for additional current drawn by
the µP during the fault condition.
Shunt Current Effects
on V
SHUNT
and V
TH
When sinking large shunt currents, power dissipation
heats the die to temperatures greater than ambient.
This may cause the V
SHUNT
and VTHtolerances to
approach ±3% at high ambient temperatures and high
shunt currents. Limit the die temperature to less than
+150°C using ΘJA= 0.25°C/mW.
MAX6330
SHUNT
V
IN
RESET
RESET
INPUT
R
HYST
100k
C
L
R
S
GND
V
CC
GND
µP
Figure 5. Adding Hysteresis to the MAX6330
MAX6330
MAX6331
SHUNT
V
IN
RESET
(RESET)
TO OTHER SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
C
L
4.7k
RSV
SHUNT
GND
V
CC
GND
µP
( ) ARE FOR MAX6331
Figure 6. Interfacing to µPs with Bidirectional Reset I/O
___________________Chip Information
TRANSISTOR COUNT: 283
Page 8

MAX6330/MAX6331
Precision Shunt Regulators with Reset
in SOT23-3
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
8
_____________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600
© 1998 Maxim Integrated Products Printed USA is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products.
SOTPO3L.EPS
Package Information
 Loading...
Loading...