Page 1
________________General Description
The MAX6315 low-power CMOS microprocessor (µP)
supervisory circuit is designed to monitor power supplies in µP and digital systems. It provides excellent circuit reliability and low cost by eliminating external
components and adjustments. The MAX6315 also provides a debounced manual reset input.
This device performs a single function: it asserts a reset
signal whenever the VCCsupply voltage falls below a
preset threshold or whenever manual reset is asserted.
Reset remains asserted for an internally programmed
interval (reset timeout period) after V
CC
has risen above
the reset threshold or manual reset is deasserted. The
MAX6315’s open-drain RESET output can be pulled up
to a voltage higher than VCC.
The MAX6315 comes with factory-trimmed reset threshold voltages in 100mV increments from 2.5V to 5V.
Preset timeout periods of 1ms, 20ms, 140ms, and
1120ms (minimum) are also available. The device
comes in a SOT143 package.
For microcontrollers (µCs) and µPs with bidirectional
reset pins, see the MAX6314 data sheet.
________________________Applications
Computers
Controllers
Intelligent Instruments
Critical µP and µC Power Monitoring
Portable/Battery-Powered Equipment
____________________________Features
♦ Small SOT143 Package
♦ Open-Drain RESET Output Can Exceed V
CC
♦ Precision, Factory-Set VCCReset Thresholds:
100mV Increments from 2.5V to 5V
♦ ±1.8% Reset Threshold Accuracy at TA= +25°C
♦ ±2.5% Reset Threshold Accuracy Over Temp.
♦ Four Reset Timeout Periods Available:
1ms, 20ms, 140ms, or 1120ms (minimum)
♦ Immune to Short VCCTransients
♦ 5µA Supply Current
♦ Pin-Compatible with MAX811
MAX6315
Open-Drain SOT µP Reset Circuit
________________________________________________________________
Maxim Integrated Products
1
1
2
4
3
V
CC
MRRESET
GND
MAX6315
SOT143
TOP VIEW
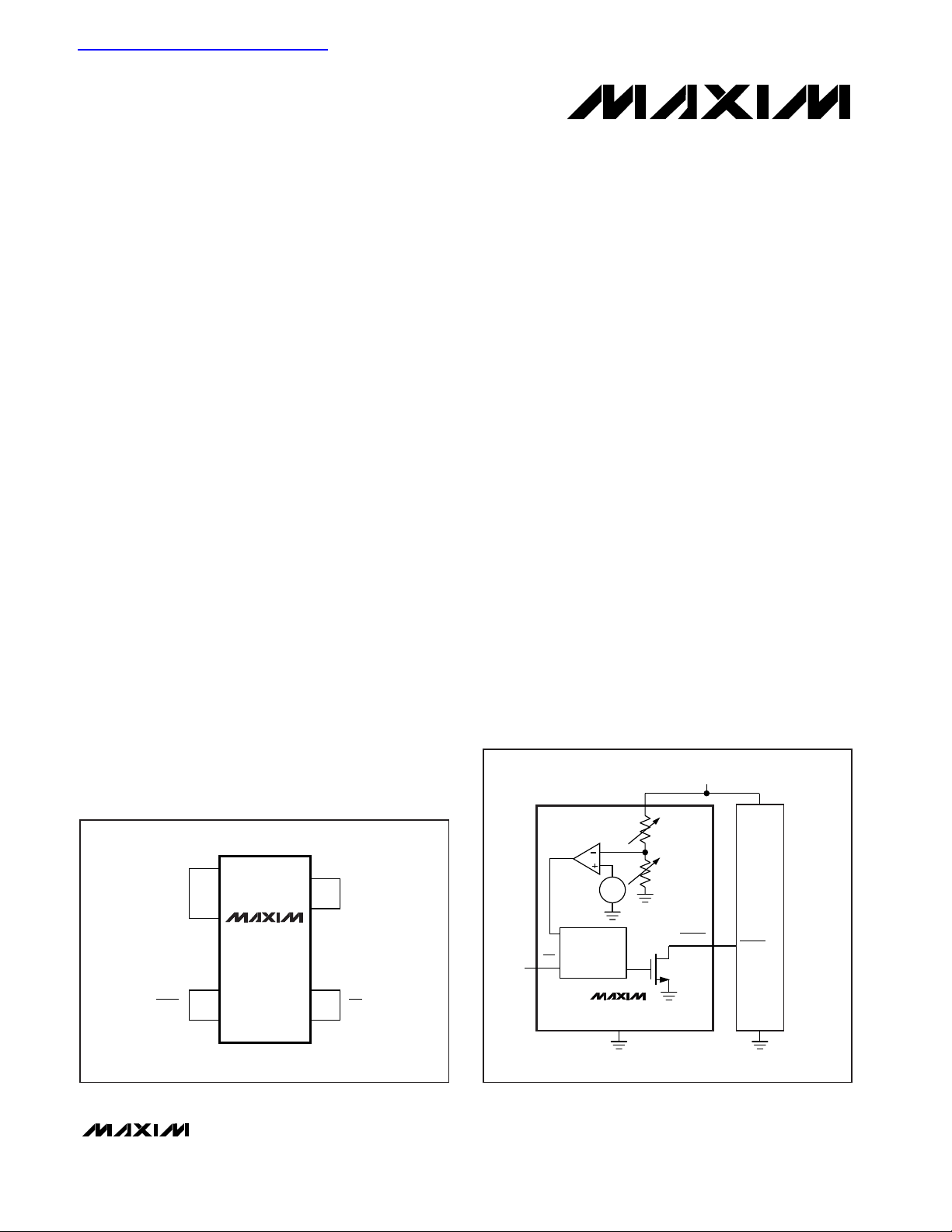
__________________Pin Configuration
MAX6315
V
CC
V
CC
GND
RESET
µP
RESET
MR
LASERTRIMMED
RESISTORS
RESET
CIRCUITRY
__________Typical Operating Circuit
19-2000; Rev 1; 1/99
Ordering and Marking Information appear at end of
data sheet.
For free samples & the latest literature: http://www.maxim-ic.com, or phone 1-800-998-8800.
For small orders, phone 1-800-835-8769.
查询MAX6315US25D1-T供应商
Page 2
MAX6315
Open-Drain SOT µP Reset Circuit
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VCC= +2.5V to +5.5V, TA= -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Note 1: The MAX6315 monitors VCCthrough an internal factory-trimmed voltage divider that programs the nominal reset threshold.
Factory-trimmed reset thresholds are available in 100mV increments from 2.5V to 5V (see
Ordering and Marking
Information
).
V
CC
........................................................................-0.3V to +6.0V
RESET....................................................................-0.3V to +6.0V
All Other Pins..............................................-0.3V to (V
CC
+ 0.3V)
Input Current (V
CC
).............................................................20mA
Output Current (RESET)......................................................20mA
Rate of Rise (V
CC
)...........................................................100V/µs
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +70°C)
SOT143 (derate 4mW/°C above +70°C)........................320mW
Operating Temperature Range ...........................-40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range.............................-65°C to +160°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10sec).............................+300°C
MAX6315US_ _D3-T
MAX6315US_ _D2-T
MAX6315US_ _D4-T
TA= +25°C
VCC> 1.2V, I
SINK
= 0.5mA
VCC= 5.5V, no load
410
TA= -40°C to +85°C
VTH- 2.5% VTH+ 2.5%
1120 1570 2240
140 200 280
20 28 40
VCC> VTH, RESET deasserted
VTH> 4.0V
VCC= falling at 1mV/µs
MAX6315US_ _D1-T
VCC> 4.25V, I
SINK
= 3.2mA
CONDITIONS
VCC> 2.5V, I
SINK
= 1.2mA
VCC> 1.0V, I
SINK
= 80µA
0.3 x V
CC
2.4
0.7 x V
CC
0.3
0.3
V
µA1
RESET Output Leakage Current
V
0.4
V
OL
RESET Output Voltage
kΩ32 63 100
MR Pull-Up Resistance
VTH- 1.8% V
TH
VTH+ 1.8%
V
TH
Reset Threshold (Note 1)
µA
512
I
CC
V1.0 5.5V
CC
Operating Voltage Range
VCCSupply Current
ns500
MR to Reset Delay
ns100
MR Glitch Rejection
µs1
MR Minimum Input Pulse
V
0.8
V
IL
MR Input Threshold
ppm/°C60∆VTH/°CReset Threshold Tempco
µs35VCCto Reset Delay
ms
1 1.4 2
t
RP
Reset Timeout Period
UNITSMIN TYP MAXSYMBOLPARAMETER
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
VCC= 3.6V, no load
TA= -40°C to +85°C
VTH< 4.0V
MANUAL RESET INPUT
Page 3
MAX6315
Open-Drain SOT µP Reset Circuit
_______________________________________________________________________________________
3
6
0
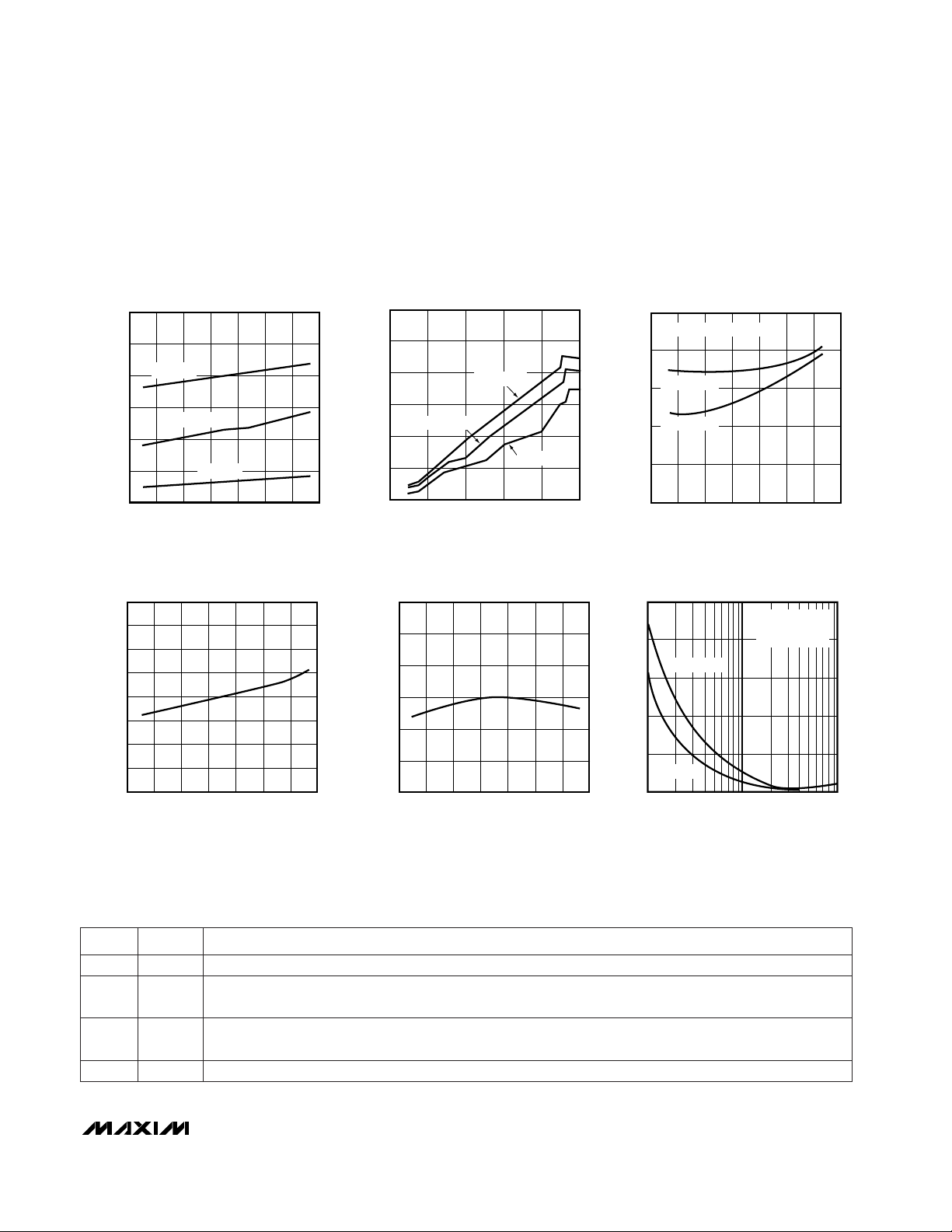
-50 -30 30 90
SUPPLY CURRENT vs. TEMPERATURE
2
1
5
MAX6315-01
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
-10 10 50
3
4
70
VCC = 5V
VCC = 3V
VCC = 1V
6
0
0
1
35
SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
2
1
5
MAX6315-02
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
2
3
4
4
TA = -40°C
TA = +25°C
TA = +85°C
50
0
-50 -30 10 90
POWER-DOWN RESET DELAY
vs. TEMPERATURE
10
40
MAX6315-03
TEMPERATURE (°C)
POWER-DOWN RESET DELAY (µs)
-10
20
30
30 50 70
VCC FALLING AT 1mV/µs
VTH = 4.63V
VTH = 3.00V
1.04
0.96
-50 -30 10 90
NORMALIZED RESET TIMEOUT PERIOD
vs. TEMPERATURE (V
CC
RISING)
0.97
0.98
1.02
1.00
1.03
MAX6315-04
TEMPERATURE (°C)
NORMALIZED RESET TIMEOUT PERIOD
-10
0.99
1.01
30 50 70
1.006
0.994
-50 -30 10 90
NORMALIZED RESET THRESHOLD
vs. TEMPERATURE (V
CC
FALLING)
0.996
0.998
1.004
1.000
MAX6315-05
TEMPERATURE (°C)
NORMALIZED RESET THRESHOLD
-10
1.002
30 50 70
100
0
10 100 1000
MAXIMUM TRANSIENT DURATION
vs. RESET COMPARATOR OVERDRIVE
20
MAX6315-06
RESET COMP. OVERDRIVE, VTH - VCC (mV)
MAXIMUM TRANSIENT DURATION (µs)
40
60
80
TA = +25°C
RESET OCCURS
ABOVE CURVE
VTH = 4.63V
VT = 3.00V
__________________________________________Typical Operating Characteristics
(TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
______________________________________________________________Pin Description
NAME FUNCTION
1 GND Ground
2
RESET
Active-Low Open-Drain Output. Connect to an external pull-up resistor. Can be pulled up to a voltage
higher than VCC, but less than 6V.
PIN
3
MR
Manual Reset Input. A logic low on MR asserts reset. Reset remains asserted as long as MR is low, and
for the reset timeout period (t
RP
) after the reset conditions are terminated. Connect to VCCif not used.
4 V
CC
Supply Voltage and Reset Threshold Monitor Input
Page 4

_______________Detailed Description
Reset Output
A microprocessor’s (µP’s) reset input starts the µP in a
known state. The MAX6315 asserts reset to prevent
code-execution errors during power-up, power-down,
or brownout conditions. RESET is guaranteed to be a
logic low for VCC> 1V (see
Electrical Characteristics
).
Once VCCexceeds the reset threshold, the internal
timer keeps reset asserted for the reset timeout period
(tRP); after this interval RESET goes high. If a brownout
condition occurs (monitored voltage dips below its programmed reset threshold), RESET goes low. Any time
VCCdips below the reset threshold, the internal timer
resets to zero and RESET goes low. The internal timer
starts when VCCreturns above the reset threshold, and
RESET remains low for the reset timeout period.
The MAX6315’s RESET output structure is a simple
open-drain N-channel MOSFET switch. Connect a pullup resistor to any supply in the 0V to +6V range. Select
a resistor value large enough to register a logic low
when RESET is asserted (see
Electrical Characteristics
),
and small enough to register a logic high while supplying all input current and leakage paths connected to the
RESET line. A 10kΩ pull-up is sufficient in most applica-
tions.
Often, the pull-up connected to the MAX6315’s RESET
output will connect to the supply voltage monitored at
the IC’s VCCpin. However, some systems may use the
open-drain output to level-shift from the monitored supply to reset circuitry powered by some other supply
(Figure 1). This is one useful feature of an open-drain
output. Keep in mind that as the MAX6315’s V
CC
decreases below 1V, so does the IC’s ability to sink
current at RESET. Finally, with any pull-up, RESET will
be pulled high as VCCdecays toward 0V. The voltage
where this occurs depends on the pull-up resistor value
and the voltage to which it connects (see
Electrical
Characteristics
).
Manual-Reset Input
Many µP-based products require manual-reset capability, allowing the operator, a test technician, or external
logic circuitry to initiate a reset. A logic low on MR
asserts reset. Reset remains asserted while MR is low,
and for the reset active timeout period after MR returns
high.
MR has an internal 63kΩ pull-up resistor, so it can be
left open if not used. Connect a normally open momentary switch from MR to GND to create a manual reset
function; external debounce circuitry is not required.
If MR is driven from long cables or if the device is used
in a noisy environment, connecting a 0.1µF capacitor
from MR to ground provides additional noise immunity.
__________Applications Information
Negative-Going VCCTransients
In addition to issuing a reset to the µP during power-up,
power-down, and brownout conditions, these devices
are relatively immune to short-duration negative-going
transients (glitches). The
Typical Operating Character-
istics
show the Maximum Transient Duration vs. Reset
Threshold Overdrive, for which reset pulses are not
generated. The graph was produced using negativegoing pulses, starting at V
RST
max and ending below
the programmed reset threshold by the magnitude indicated (reset threshold overdrive). The graph shows the
maximum pulse width that a negative-going VCCtransient may typically have without causing a reset pulse
to be issued. As the transient amplitude increases (i.e.,
goes farther below the reset threshold), the maximum
allowable pulse width decreases. A 0.1µF bypass
capacitor mounted close to VCCprovides additional
transient immunity.
MAX6315
Open-Drain SOT µP Reset Circuit
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Figure 1. MAX6315 Open-Drain RESET Output Allows Use
with Multiple Supplies
MAX6315
V
CC
GND
RESETMR
5V SYSTEM
+5.0V+3.3V
10k
Page 5

MAX6315
Open-Drain SOT µP Reset Circuit
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
________________________________________________________Ordering Information
PART
†
NOMINAL
VTH(V)
MIN t
RP
(ms)
SOT TOP
MARK
††
MAX6315US50D1-T 5.00 1 FX_ _
MAX6315US45D1-T 4.50 1 GC_ _
MAX6315US44D1-T
†††
4.39 1 GD_ _
MAX6315US43D1-T 4.30 1 GE_ _
MAX6315US42D1-T 4.20 1 GF_ _
MAX6315US41D1-T 4.10 1 GG_ _
MAX6315US40D1-T 4.00 1 GH_ _
MAX6315US39D1-T 3.90 1 GI_ _
MAX6315US38D1-T 3.80 1 GJ_ _
MAX6315US37D1-T 3.70 1 GK_ _
MAX6315US36D1-T 3.60 1 GL_ _
MAX6315US35D1-T 3.50 1 GM_ _
MAX6315US34D1-T 3.40 1 GN_ _
MAX6315US33D1-T 3.30 1 GO_ _
MAX6315US32D1-T 3.20 1 GP_ _
MAX6315US31D1-T 3.08 1 GQ_ _
MAX6315US30D1-T 3.00 1 GR_ _
MAX6315US29D1-T 2.93 1 GS_ _
†
The MAX6315 is available in a SOT143 package, -40°C to +85°C temperature range.
††
The first two letters in the package top mark identify the part, while the remaining two letters are the lot tracking code.
†††
Sample stocks generally held on the bolded products; also, the bolded products have 2,500 piece minimum-order quantities.
Non-bolded products have 10,000 piece minimum-order quantities. Contact factory for details.
Note:
All devices available in tape-and-reel only. Contact factory for availability.
PART
†
MAX6315US37D2-T 3.70 20 HK_ _
MAX6315US36D2-T 3.60
NOMINAL
VTH(V)
MIN t
RP
(ms)
20 HL_ _
SOT TOP
MARK
††
MAX6315US50D2-T 5.00 20 GX_ _
MAX6315US49D2-T 4.90 20 GY_ _
MAX6315US48D2-T 4.80 20 GZ_ _
MAX6315US47D2-T 4.70 20 HA_ _
MAX6315US46D2-T 4.63 20 HB_ _
MAX6315US45D2-T 4.50 20 HC_ _
MAX6315US44D2-T
†††
4.39 20 HD_ _
MAX6315US43D2-T 4.30 20 HE_ _
MAX6315US42D2-T 4.20 20 HF_ _
MAX6315US41D2-T 4.10 20 HG_ _
MAX6315US40D2-T 4.00 20 HH_ _
MAX6315US39D2-T 3.90 20 HI_ _
MAX6315US38D2-T 3.80 20 HJ_ _
MAX6315US34D2-T 3.40 20 HN_ _
MAX6315US33D2-T 3.30 20 HO_ _
MAX6315US35D2-T 3.50 20 HM_ _
MAX6315US47D1-T 4.70 1 GA_ _
MAX6315US48D1-T 4.80 1 FZ_ _
MAX6315US46D1-T 4.63 1 GB_ _
MAX6315US49D1-T 4.90 1 FY_ _
MAX6315US26D1-T
†††
2.63 1 GV_ _
MAX6315US27D1-T 2.70 1 GU_ _
MAX6315US28D1-T 2.80 1 GT_ _
MAX6315US25D1-T 2.50 1 GW_ _
MAX6315US29D2-T 2.93 20 HS_ _
MAX6315US28D2-T 2.80 20 HT_ _
MAX6315US26D2-T
†††
2.63 20 HV_ _
MAX6315US25D2-T 2.50 20 HW_ _
MAX6315US27D2-T 2.70 20 HU_ _
MAX6315US32D2-T 4.20 20 HP_ _
MAX6315US31D2-T 3.08 20 HQ_ _
MAX6315US30D2-T 3.00 20 HR_ _
Page 6

MAX6315
Open-Drain SOT µP Reset Circuit
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________Ordering Information (continued)
PART
†
NOMINAL
VTH(V)
MIN t
RP
(ms)
SOT TOP
MARK
††
MAX6315US50D3-T 5.00 140 HX_ _
MAX6315US49D3-T 4.90 140 HY_ _
MAX6315US48D3-T 4.80 140 HZ_ _
MAX6315US47D3-T 4.70 140 IA_ _
MAX6315US46D3-T
†††
4.63 140 IB_ _
MAX6315US45D3-T 4.50 140 IC_ _
MAX6315US44D3-T
†††
4.39 140 ID_ _
MAX6315US43D3-T 4.30 140 IE_ _
MAX6315US42D3-T 4.20 140 IF_ _
MAX6315US41D3-T 4.10 140 IG_ _
MAX6315US40D3-T 4.00 140 IH_ _
MAX6315US39D3-T 3.90 140 II_ _
MAX6315US38D3-T 3.80 140 IJ_ _
MAX6315US37D3-T 3.70 140 IK_ _
MAX6315US36D3-T 3.60 140 IL_ _
MAX6315US35D3-T 3.50 140 IM_ _
MAX6315US34D3-T 3.40 140 IN_ _
MAX6315US33D3-T 3.30 140 IO_ _
MAX6315US32D3-T 3.20 140 IP_ _
MAX6315US31D3-T
†††
3.08 140 IQ_ _
MAX6315US30D3-T 3.00 140 IR_ _
MAX6315US29D3-T
†††
2.93 140 IS_ _
JW_ _11202.50MAX6315US25D4-T
JV_ _11202.63
MAX6315US26D4-T
†††
JU_ _11202.70MAX6315US27D4-T
JT_ _11202.80MAX6315US28D4-T
JS_ _11202.93MAX6315US29D4-T
JR_ _11203.00MAX6315US30D4-T
JQ_ _11203.08MAX6315US31D4-T
JP_ _11203.20MAX6315US32D4-T
JO_ _11203.30MAX6315US33D4-T
JN_ _11203.40MAX6315US34D4-T
JM_ _11203.50MAX6315US35D4-T
JL_ _11203.60MAX6315US36D4-T
JK_ _11203.70MAX6315US37D4-T
JJ_ _11203.80MAX6315US38D4-T
JI_ _11203.90MAX6315US39D4-T
JH_ _11204.00MAX6315US40D4-T
JG_ _11204.10MAX6315US41D4-T
JF_ _11204.20MAX6315US42D4-T
JE_ _11204.30MAX6315US43D4-T
JD_ _11204.39
MAX6315US44D4-T
†††
JC_ _11204.50MAX6315US45D4-T
JB_ _11204.63MAX6315US46D4-T
SOT TOP
MARK
††
MIN t
RP
(ms)
NOMINAL
VTH(V)
PART
†
†
The MAX6315 is available in a SOT143 package, -40°C to +85°C temperature range.
††
The first two letters in the package top mark identify the part, while the remaining two letters are the lot tracking code.
†††
Sample stocks generally held on the bolded products; also, the bolded products have 2,500 piece minimum-order quantities.
Non-bolded products have 10,000 piece minimum-order quantities. Contact factory for details.
Note:
All devices available in tape-and-reel only. Contact factory for availability.
JA_ _11204.70MAX6315US47D4-T
IX_ _
IY_ _
IZ_ _1120
1120
11205.00
4.90
4.80MAX6315US48D4-T
MAX6315US49D4-T
MAX6315US50D4-T
MAX6315US28D3-T 2.80 140 IT_ _
MAX6315US27D3-T 2.70 140 IU_ _
MAX6315US26D3-T
†††
2.63 140 IV_ _
MAX6315US25D3-T 2.50 140 IW_ _
Page 7

MAX6315
Open-Drain SOT µP Reset Circuit
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
___________________Chip Information
TRANSISTOR COUNT: 519
________________________________________________________Package Information
SOT1434.EPS
Page 8

MAX6315
Open-Drain SOT µP Reset Circuit
NOTES
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
8
_____________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600
© 1999 Maxim Integrated Products Printed USA is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products.
 Loading...
Loading...