Page 1
SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
M51996A is the primary switching regulator controller which is
especially designed to get the regulated DC voltage from AC power
supply.
This IC can directly drive the MOS-FET with fast rise and fast fall
output pulse and with a large-drive totempole output.
Type M51996A has the functions of not only high frequency OSC
and fast output drive but also current limit with fast response and
high sensibility so the true "fast switching regulator" can be
realized.
The M51996A is equivalent to the M51978 with externally resettable OVP(over voltage protection)circuit.
FEATURES
500kHz operation to MOS FET
Output current...............................................................±1A
Output rise time 60ns,fall time 40ns
Modified totempole output method with small through current
Compact and light-weight power supply
•Small start-up current............................................100µA typ.
•Big difference between "start-up voltage" and "stop voltage"
makes the smoothing capacitor of the power input section small.
Start-up threshold 16V,stop voltage 10V
•Packages with high power dissipation are used to with-stand the
heat generated by the gate-drive current of MOS FET.
14-pin DIP,16-pin SOP 1.5W(at 25°C)
Simplified peripheral circuit with protection circuit and built-in
large-capacity totempole output
•High-speed current limiting circuit using pulse-by-pulse
method(CLM+pin)
•Over-voltage protection circuit with an externally re-settable
latch(OVP)
•Protection circuit for output miss action at low supply
voltage(UVLO)
High-performance and highly functional power supply
•Triangular wave oscillator for easy dead time setting
•SOFT start function by expanding period
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
Vcc
COLLECTOR
VOUT
EMITTER
OVP
F/B
DET
REG SOFT
COLLECTOR
VOUT
EMITTER
HEAT SINK PIN
OVP
F/B
DET
REG
1
2
3
4
Outline 14P4
1
2
3
4
Outline 16P2N-A
Connect the heat sink pin to GND.
14
CLM+
13
GND
12
T-OFF
11
CF
105
96
T-ON
87
Vcc
16
CLM+
15
14
GND
13
HEAT SINK PIN
125
T-OFF
CF
116
107
T-ON
SOFT
98
APPLICATION
Feed forward regulator,fly-back regulator
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Supply voltage range............................................12 to 30V
Operating frequency.................................less than 500kHz
Oscillator frequency setting resistance
•T-ON pin resistance RON...........................10k to 75kΩ
•T-OFF pin resistance ROFF..........................2k to 30kΩ
1
( / 22 )
Page 2
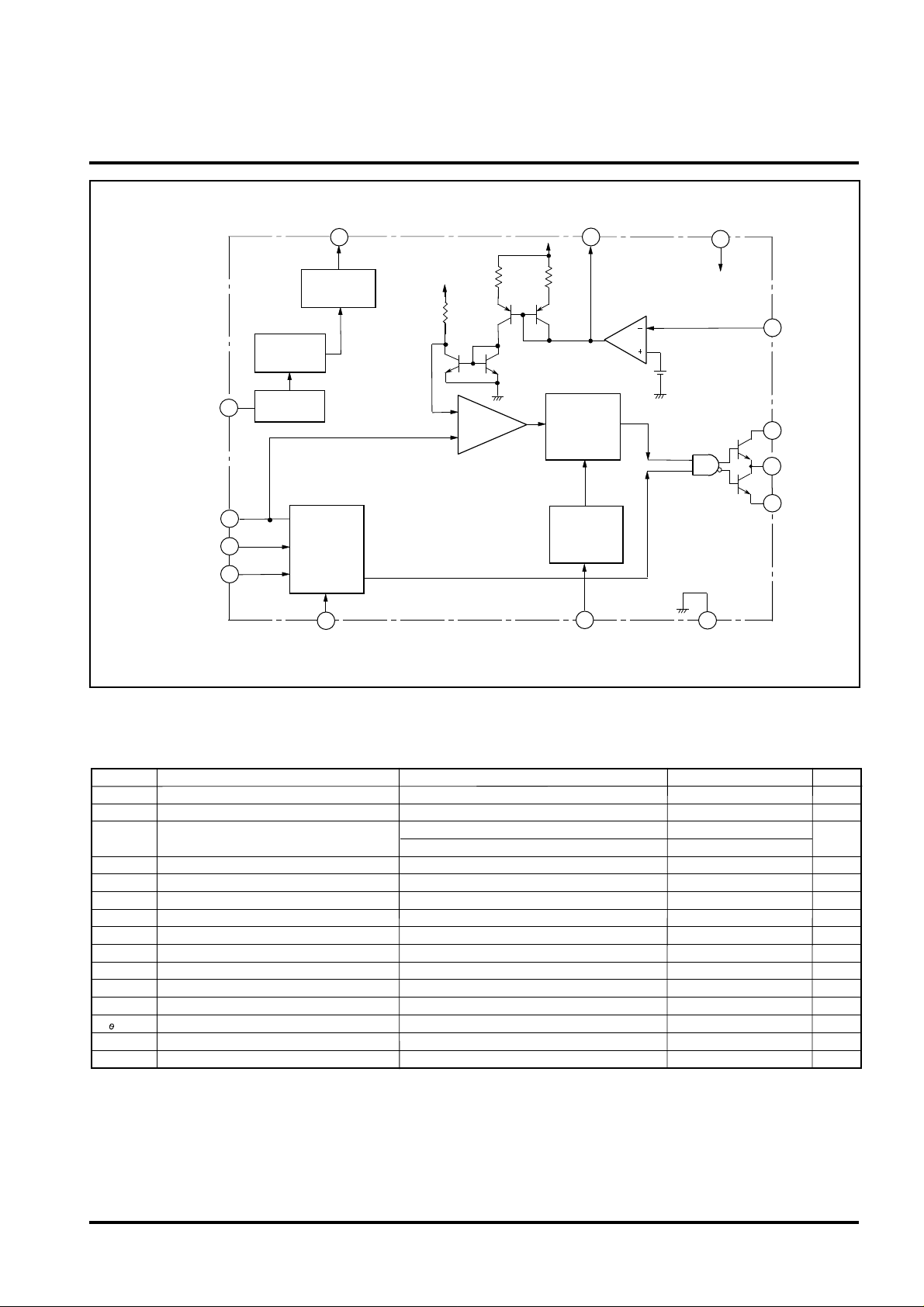
SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
BLOCK DIAGRAM
OP AMP
REG(7.8V)
7.1V
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
F/B
VCC
OVP
CF
T-ON
T-OFF
UNDER
VOLTAGE
LOCK OUT
LATCH
OSCILLATOR
(TRIANGLE)
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
SOFT
5.8V
15.2K
1S
1S
1S
PWM
COMPARATOR
3K
500
6S
PWM
LATCH
CURRENT LIMIT
DETECTION
CLM+
DET
2.5V
COLLECTOR
VOUT
EMITTER
GND
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Symbol Ratings UnitParameter Conditions
VCC Supply voltage
VC
IO
IVREG
VSOFT
VCLM+
VDET
IOVP
IFB
ITON
ITOFF
Pd
K
Topr
Tstg
Note 1."+" sign shows the direction of current flowing into the IC and "-" sign shows the current flowing out from the IC.
2.The low impedance voltage supply should not be applied to the OVP terminal.
Collector voltage
Output current
VREG terminal output current
SOFT terminal voltage
CLM+ terminal voltage
DET terminal voltage
OVP terminal current
F/B terminal current
T-ON terminal input current
T-OFF terminal input current
Power dissipation
Thermal derating
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Peak
Continuous
Ta=25˚C
Ta>25˚C
±0.15
VREG +0.2
-0.3 to +3
-30 to +85
-40 to +125
31
31
±1
-6
6
8
-10
-1
-2
1.5
12
V
V
A
mA
V
V
V
mA
mA
mA
mA
W
mW/˚C
˚C
˚C
( / 22 )
2
Page 3
SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
Oscillating frequency during
SOFT operation
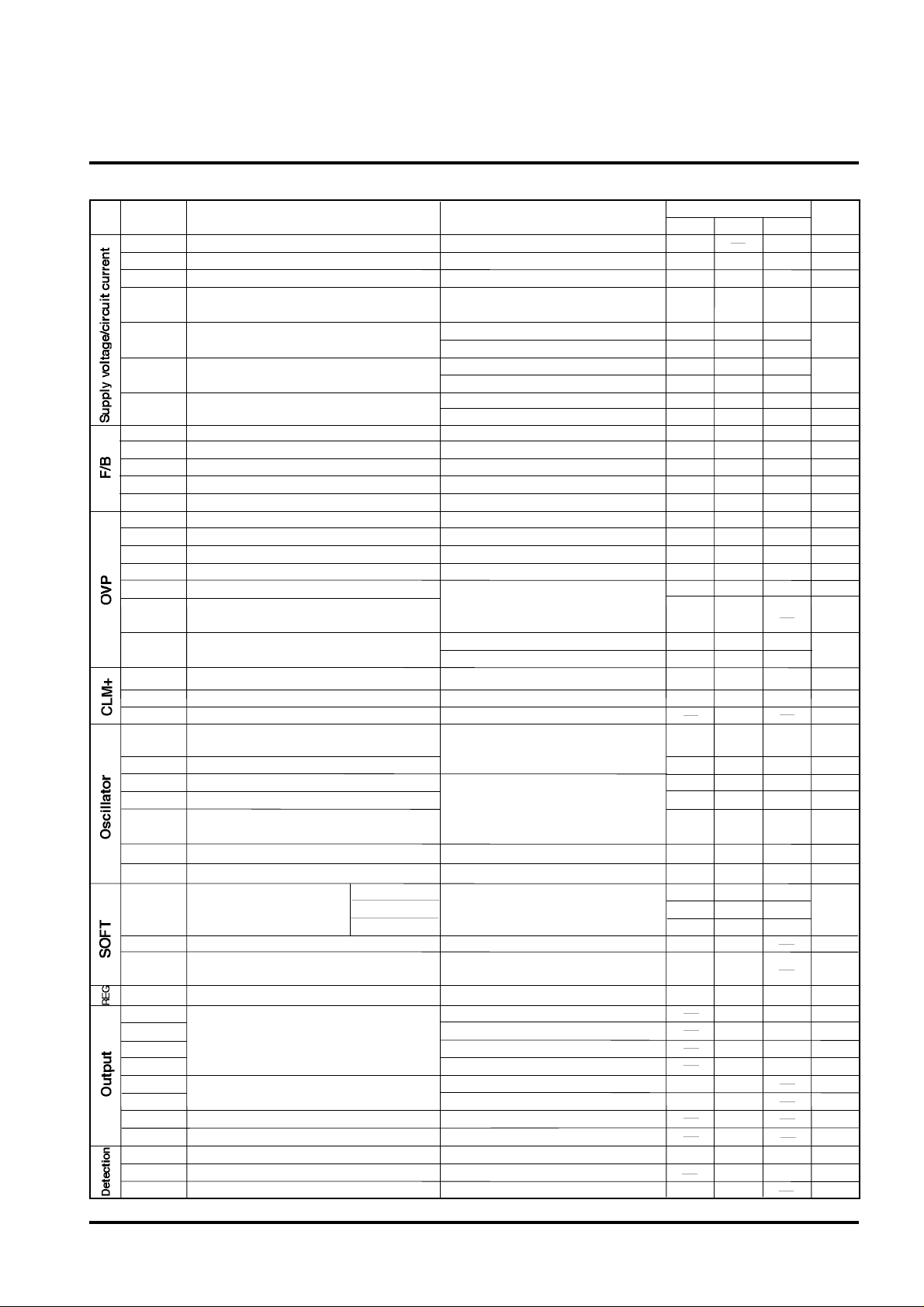
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (VCC=18V, Ta=25°C, unless otherwise noted)
Block
Symbol Test conditions UnitParameter
VCC
VCC(START)
VCC(STOP)
∆Vcc
IccL
IccO
IccOVP
IFBMIND
IFBMAXD
∆IFB
VFB
RFB
VTHOVPH
∆VTHOVP
ITHOVP
IINOVP
VCCOVPC
VCC(STOP)
-VCCOVPC
ITHOVPC
VTHCLM+
IINCLM+
TPDCLM+
fOSC
TDUTY
VOSCH
VOSCL
∆VOSC
VT-ON
VT-OFF
fOSCSOFT
ISOFTIN
ISOFDIS
VREG
VOL1
VOL2
VOL3
VOL4
VOH1
VOH2
TRISE
TFALL
VDET
IINDET
GAVDET
Operating supply voltage range
Operation start up voltage
Operation stop voltage
Vcc(START),Vcc(STOP) difference
Stand-by current
Operating circuit current
Circuit current in OVP state
Current at 0% duty
Current at maximum duty
Current difference between max and 0% duty
F/B terminal voltage
OVP terminal resistance
OVP terminal H threshold voltage
OVP terminal hysteresis voltage
OVP terminal threshold current
OVP terminal input current
OVP reset supply voltage
Difference supply voltage between
operation stop and OVP reset
Current from OVP terminal for
OVP reset
CLM+ terminal threshold voltage
CLM+ terminal current
Delay time from CLM+ to VOUT
Oscillating frequency
Maximum ON duty
Upper limit voltage of oscillation waveform
Lower limit voltage of oscillation waveform
Voltage difference between upper limit and
lower limit of OSC waveform
T-ON terminal voltage
T-OFF terminal voltage
VSOFT=5.5V
VSOFT=2.5V
VSOFT=0.2V
SOFT terminal input current
SOFT terminal discharging current
Regulator output voltage
Output low voltage
Output high voltage
Output voltage rise time
Output voltage fall time
Detection voltage
DET terminal input current
Voltage gain of detection amp
∆Vcc=Vcc(START) -Vcc(STOP)
Vcc=14.5V,Ta=25°C
Vcc=14.5V,-30≤Ta≤85°C
Vcc=15V,f=188kHz
Vcc=30V,f=188kHz
Vcc=25V
Vcc=9.5V
F/B terminal input current
F/B terminal input current
∆IFB=IFBMIND-IFBMAXD
F/B terminal input current=0.95mA
∆VTHOVP=VTHOVPH-VTHOVPL
VOVP=400mV
OVP terminal is open.
(high impedance)
Vcc=30V
Vcc=18V
VCLM+=0V
RON=20kΩ,ROFF=17kΩ
CF=220pF,-5≤Ta≤85°C
RON=20kΩ,ROFF=17kΩ
CF=220pF
RON=20kΩ
ROFF=17kΩ
RON=20kΩ,ROFF=17kΩ
CF=220pF
VSOFT=1V
Discharge current of SOFT terminal at
Vcc less than Vcc(STOP)
Vcc=18V,Io=10mA
Vcc=18V,Io=100mA
Vcc=5V,Io=1mA
Vcc=5V,Io=100mA
Vcc=18V,Io=-10mA
Vcc=18V,Io=-100mA
VDET=2.5V
M51996AP/FP
Limits
Min. Typ. Max.
Vcc(STOP)
15.2
-2.1
-0.9
-1.35 -0.99 -0.70
420
-480
-210
-280
170 188 207
47 50 53
3.97 4.37 4.77
1.76 1.96 2.16
2.11
170
111
19.0
-0.5
16.0
15.5
16.2 17.2
5.0
65
50
7.3
1.3
140 320
4.9
540
80
80 150
7.5
0.55
180
3.8
2.9
6.8
2.4 2.5 2.6
30
8
1
6.3 7.6
100
100
11
12
2.0
210
-1.5
-0.6
5.9
600
750
150 250
9.0 10.0
1.20
-320 -213
-140 -93
200
-200
100
2.41 2.71
4.5
3.5
188 207
131 151
23.3
-0.1
3.3
7.8
0.04
0.7
0.85
1.3
16.7
16.5
60
40
1.0
40
30
150
200
17
19
3.0
-1.0
-0.4
7.1
780
960
30
250
220
-140
5.4
4.2
27.0
8.8
0.4
1.4
1.0
2.0
3.0
V
V
V9.0 9.9 10.9
V
µA
mA
mA
µA
mA
mA
mA
V
Ω
mV
mV
µA
µA
V
V
µA
mV
µA
ns
kHz
%
V
V
V
V
V
kHz
µA
mA
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
ns
ns
V
µA
dB
( / 22 )
3
Page 4
SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
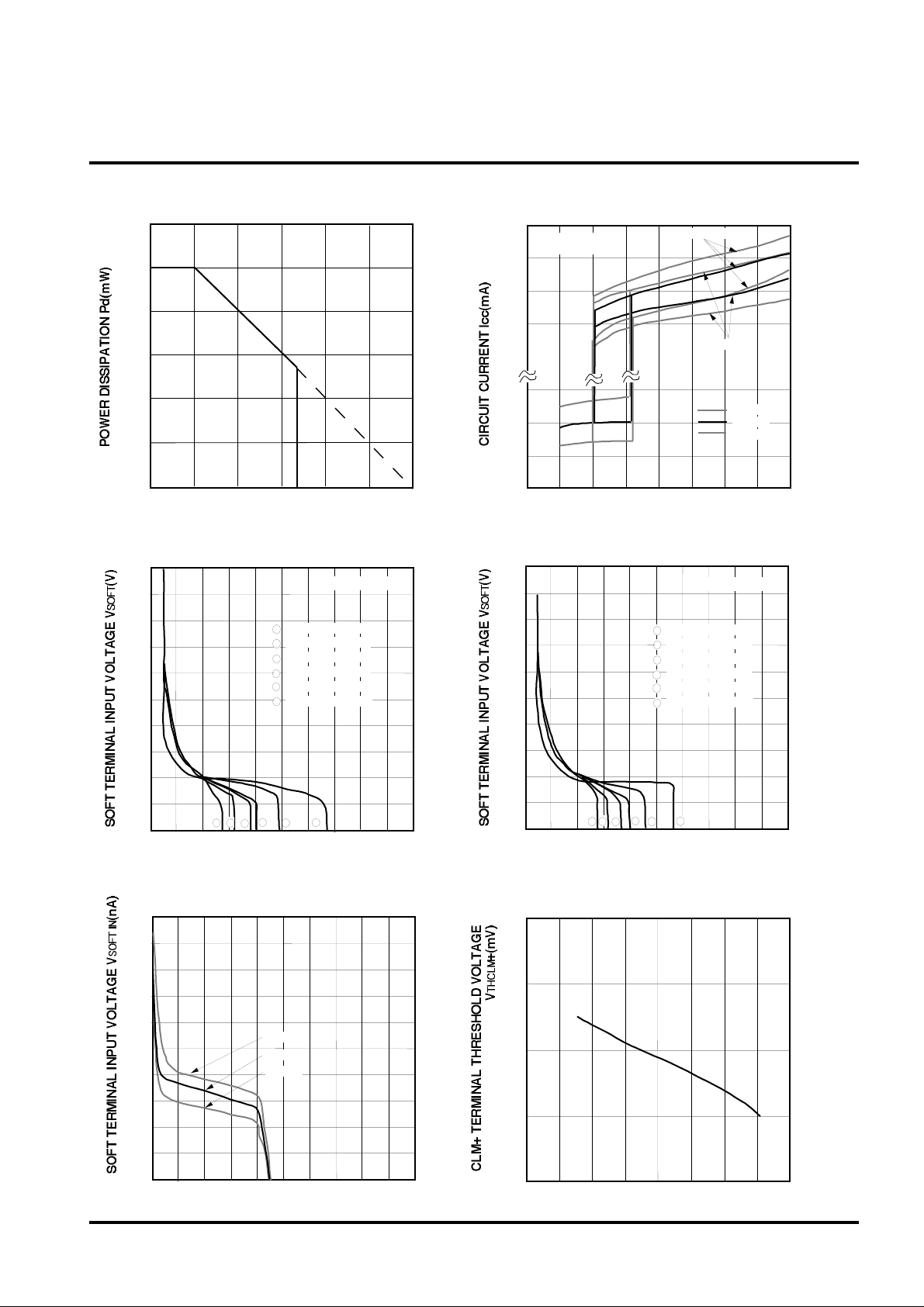
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
ROFF=20kΩ
Ta=-30°C
Ta=25°C
Ta=85°C
fOSC=500kHz
fOSC=100kHz
12345
6
RON=15k,ROFF=27k
RON=18k,ROFF=24k
RON=22k,ROFF=22k
RON=24k,ROFF=20k
RON=22k,ROFF=12k
RON=36k,ROFF=6.2k
12345
6
12345
6
RON=15k,ROFF=27k
RON=18k,ROFF=24k
RON=22k,ROFF=22k
RON=24k,ROFF=20k
RON=22k,ROFF=12k
RON=36k,ROFF=6.2k
12345
6
Ta=-30°C
Ta=25°C
Ta=85°C
THERMAL DERATING
1800
1500
1200
900
(MAXIMUM RATING)
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
CIRCUIT CURRENT VS.SUPPLY VOLTAGE
16m
14m
12m
10m
(NORMAL OPERATION)
RON=18kΩ
600
300
0
0 25 50 75
85
100
125 150
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
SOFT TERMINAL INPUT VOLTAGE VS.
5.0
4.5
EXPANSION RATE OF PERIOD
(fOSC=100kHz)
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
EXPANSION RATE OF PERIOD(TIMES)
150m
100µ
50µ
10
0 20 30 40
5
15 25 35
SUPPLY VOLTAGE Vcc(V)
SOFT TERMINAL INPUT VOLTAGE VS.
5.0
4.5
EXPANSION RATE OF PERIOD
(fOSC=500kHz)
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
EXPANSION RATE OF PERIOD(TIMES)
SOFT TERMINAL INPUT VOLTAGE VS.
-100
INPUT VOLTAGE
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0
2 3 4 5 6 7
1
SOFT TERMINAL INPUT VOLTAGE VSOFT(V)
CLM+ TERMINAL THRESHOLD VOLTAGE
VS. AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
205
200
195
10
9
8
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
-60
100
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
( / 22 )4
Page 5
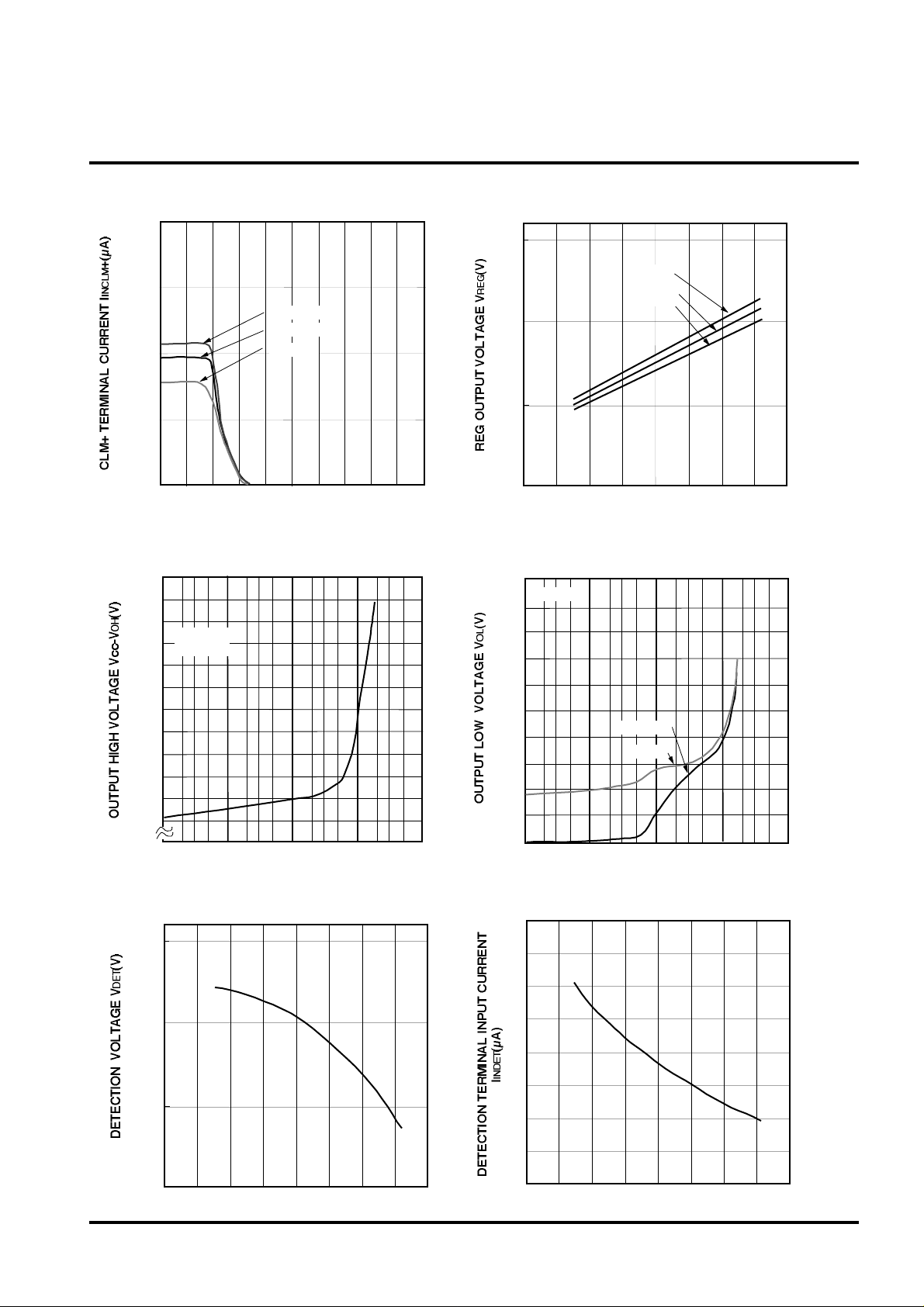
SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
-3-2-101-3-2-10123523523523523523523523
5
M51996AP/FP
-400
-300
-200
-100
4.5
4.2
3.9
3.6
3.3
3.0
2.7
2.4
2.1
1.8
1.5
1.2
2.55
CLM+ TERMINAL CURRENT
VS. CLM+ TERMINAL VOLTAGE
Ta=-30°C
Ta=25°C
Ta=85°C
0
0
Vcc=18V
Ta=25°C
10
0.1 0.2
0.3
0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9
CLM+ TERMINAL VOLTAGE VCLM+(V)
OUTPUT HIGH VOLTAGE VS.
SOURCE CURRENT
10
SOURCE CURRENT IOH(A)
DETECTION VOLTAGE
VS. AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
10
1.0
10 10
REG OUTPUT VOLTAGE
VS. AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
8.5
Rc=∞
Rc=3.6k
Rc=1.5k
8.0
7.5
7.0
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE
5.0
Ta=25°C
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
10
DETECTION TERMINAL INPUT CURRENT
1.4
1.3
VS. SINK CURRENT
Vcc=18V
Vcc=5V
10 10
SINK CURRENT IOL(A)
VS. AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
10
100
10
1.2
2.50
2.45
2.40
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
-60
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
100
( / 22 )
5
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
-60
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
100
Page 6
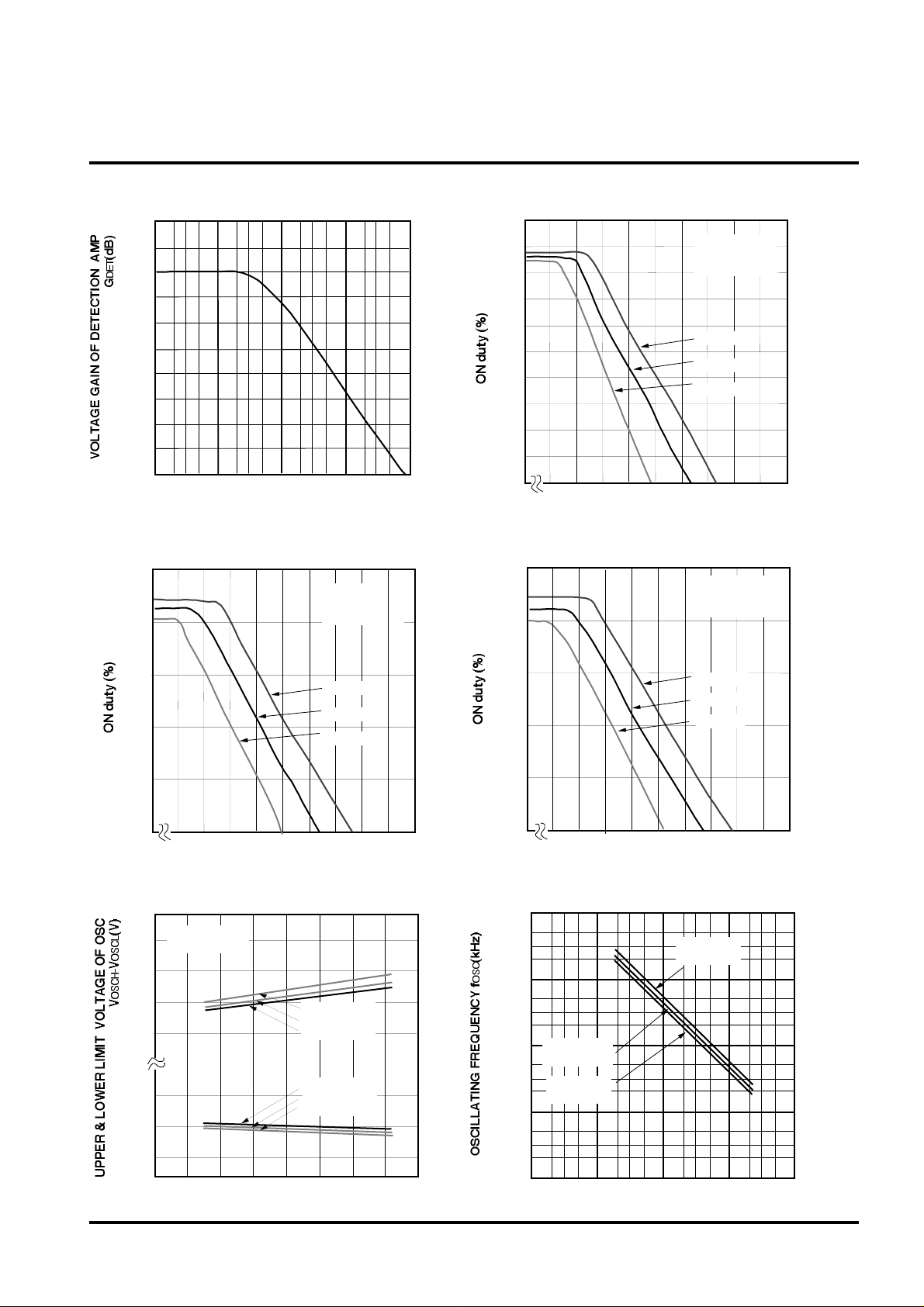
SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
2103104105106235235235235
012340123
4
23523523523523523523523
5
M51996AP/FP
VOLTAGE GAIN OF DETECTION AMP
VS. FREQUENCY
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
10
FREQUENCY f(Hz)
ON duty
VS. F/B TERMINAL INPUT CURRENT
50
40
(fOSC=200kHz)
RON=18kΩ
ROFF=20kΩ
VS. F/B TERMINAL INPUT CURRENT
ON duty
50
45
40
(fOSC=100kHz)
RON=18kΩ
ROFF=20kΩ
35
30
Ta=-30°C
25
20
Ta=25°C
Ta=85°C
15
10
5
0
0 0.4 1.0 2.0
0.6 0.8 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.2
F/B TERMINAL INPUT CURRENT IF/B (mA)
ON duty VS.
F/B TERMINAL INPUT CURRENT
50
(fOSC=500kHz)
RON=18kΩ
40
ROFF=20kΩ
30
Ta=-30°C
20
Ta=25°C
Ta=85°C
10
0
0 0.4 1.0 2.0
0.6 0.8 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.2
F/B TERMINAL INPUT CURRENT IF/B (mA)
UPPER & LOWER LIMIT VOLTAGE OF OSC
VS. AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
RON=18kΩ
5.2
ROFF=20kΩ
4.8
4.4
4.0
2.2
fOSC=500kHz
fOSC=200kHz
fOSC=100kHz
fOSC=100kHz
fOSC=200kHz
fOSC=500kHz
2.0
30
20
10
0
0.4
0
0.6 0.8 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.2
1.0
F/B TERMINAL INPUT CURRENT IF/B(mA)
OSCILLATING FREQUENCY VS. CF
TERMINAL CAPACITANCE
10
RON=22kΩ
ROFF=12kΩ
10
RON=36kΩ
10
ROFF=6.2kΩ
RON=24kΩ
ROFF=20kΩ
10
Ta=-30°C
Ta=25°C
Ta=85°C
2.0
1.8
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
-60
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
100
10
10 10
10
10
CF TERMINAL CAPACITANCE(pF)
10
( / 22 )6
Page 7
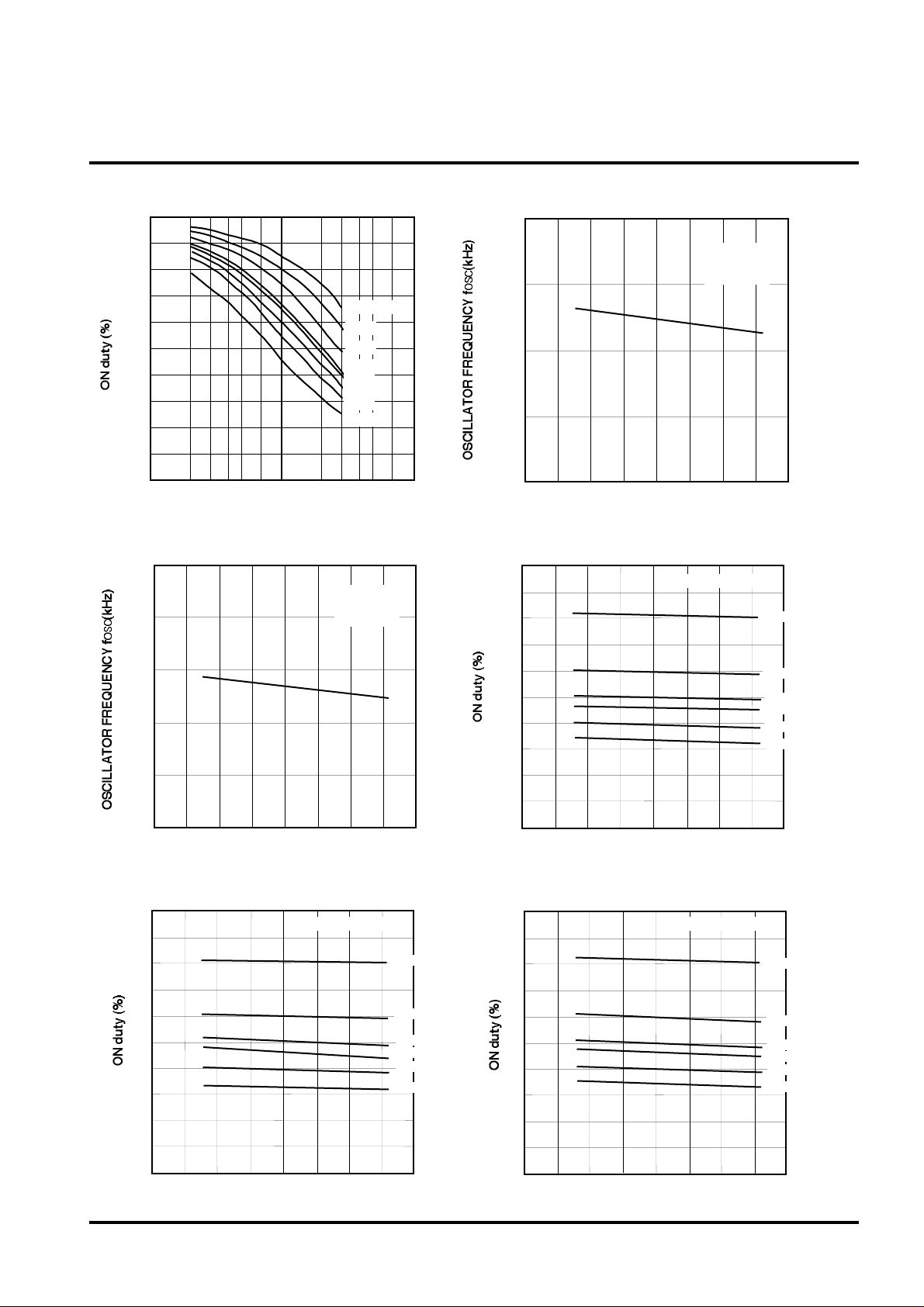
SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
33557
7
RON=36k,ROFF=6.2k
RON=22k,ROFF=12k
RON=24k,ROFF=20k
RON=22k,ROFF=22k
RON=18k,ROFF=24k
RON=15k,ROFF=27k
RON=36k,ROFF=6.2k
RON=22k,ROFF=12k
RON=24k,ROFF=20k
RON=22k,ROFF=22k
RON=18k,ROFF=24k
RON=15k,ROFF=27k
RON=36k,ROFF=6.2k
RON=22k,ROFF=12k
RON=24k,ROFF=20k
RON=22k,ROFF=22k
RON=18k,ROFF=24k
RON=15k,ROFF=27k
012
M51996AP/FP
100
ON duty VS. ROFF
90
80
70
RON=75kΩ
60
50
40
30
20
51kΩ
36kΩ
24kΩ
22kΩ
18kΩ
15kΩ
10kΩ
10
0
10 10 10
ROFF(kΩ)
OSCILLATOR FREQUENCY VS.
700
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
RON=24kΩ
600
ROFF=20kΩ
CF=47pF
500
400
300
200
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
-60
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
100
OSCILLATOR FREQUENCY VS.
120
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
110
100
90
80
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
-60
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
ON duty VS. AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
-60
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
RON=24kΩ
ROFF=20kΩ
CF=330pF
100
(fOSC=100kHz)
100
ON duty VS. AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
-60
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
(fOSC=200kHz)
100
ON duty VS. AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
-60
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
( / 22 )
7
(fOSC=500kHz)
100
Page 8

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
threshold voltage
(VTHOVPL)
M51996AP/FP
OVP TERMINAL INPUT VOLTAGE VS.
1m
100µ
10µ
1µ
0.2
OVP TERMINAL INPUT VOLTAGE VOVP(V)
CIRCUIT CURRENT VS.SUPPLY VOLTAGE
8.0
OVP RESET POINT
8.87V(-30°C)
7.0
8.94V(25°C)
9.23V(85°C)
6.0
INPUT CURRENT
Ta=85°C
Ta=25°C
Ta=-30°C
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
(OVP OPERATION)
OVP TERMINAL THRESHOLD VOLTAGE
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
800
700
600
VS.AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
Vcc=18V
H threshold voltage
L
-40 -20 0 20 40 60
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE Ta(°C)
CURRENT FROM OVP TERMINAL FOR
OVP RESET VS.SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(VTHOVPH)
80 100
5.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
1.0
0
0
OUTPUT THRUGH CURRENT WAVEFORM
AT RISING EDGE OF OUTPUT PULSE
10.0 20.0 30.0
SUPPLY VOLTAGE Vcc(V)
Ta=-30°C
Ta=25°C
Ta=85°C
40.0
500
400
300
200
100
0
5
0
AT FALLING EDGE OF OUTPUT PULSE
10 20 30
SUPPLY VOLTAGE Vcc(V)
Ta=-30°C
Ta=25°C
Ta=85°C
15 25 35
40
Horizontal-axis : 20ns/div
Vertical-axis : 50mA/div
Horizontal-axis : 20ns/div
Vertical-axis : 5mA/div
( / 22 )
8
Page 9

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
DC OUTPUT
OVP
INPUT
PREVENTION CIRCUIT
Vcc
COLLECTOR
CLM+
EMITTER
GND
DET
VOUT
T-OFFCFT-ON
F/B
OVP
SOFT
R1
ROFFCFRON
CVccR2CFIN
FEEDBACK
(TL431)
DC OUTPUT
INPUT
PREVENTION CIRCUIT
Vcc
COLLECTOR
CLM+
EMITTER
GND
DET
VOUT
T-OFFCFT-ON
SOFT
R1
ROFFCFRON
CVcc
CFIN
F/B
DET
Type M51996AP and M51996AFP are especially designed for
off-line primary PWM control IC of switching mode power supply
to get DC voltage from AC power supply.
Using this IC,smart SMPS can be realized with reasonable
cost and compact size as the number of external electric
RUSH CURRENT
REG
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
parts can be reduced and also parts can be replaced by
reasonable one.
In the following circuit diagram,MOS-FIT is used for output
transistor,however bipolar transistor can be replaced with no
problem.
AC
M51996AP/FP
Fig.1 Application example for feed forward regulator
RUSH CURRENT
AC
REG
M51996AP/FP
Fig.2 Application example for fly-back regulator
( / 22 )
9
Page 10

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
(1)Oscillator operation when SOFT circuit does
not operate
from the constant voltage source
of 5.8V.CF is charged up by the same amplitude as RON
current,when internal switch SW1,SW2 is switched to "charging
side".The rise rate of CF terminal is given as
(STOP)
current by the function of Q2,Q3 and Q4
when SW1,SW2 are switched to "discharge side".
SW2Q2Q1
Q4
1/16
SIGNAL
DISCHARGING
CHARGING
SW1
T-ON
T-OFFCFRON
ROFF
CF
Vz 4.2V
~
operation of intermittent action and OSC.control
circuit)
VOH
VOL
VOSCH
VOSCL
4.4V
2.0V
~
Q3
M51996AP/FP
Start-up circuit section
The start-up current is such low current level as typical 100µ
A,as shown in Fig.3,when the Vcc voltage is increased
from low level to start-up voltage Vcc(START).
In this voltage range,only a few parts in this IC,which has the
function to make the output voltage low level,is alive and
Icc current is used to keep output low level.The large voltage
difference between Vcc(START) and Vcc(STOP) makes start-up
easy,because it takes rather long duration from Vcc(START) to
Vcc(STOP).
Icco
~
11mA
IccL
~
100µA
Vcc
~
9.9V
Vcc
(START)
~
16.2V
SUPPLY VOLTAGE Vcc(V)
Fig.3 Circuit current vs.supply voltage
Oscillator section
The oscillation waveform is the triangle one.The ON-duration
of output pulse depends on the rising duration of the triangle
waveform and dead-time is decided by the falling duration.
The rising duration is determined by the product of external
resistor RON and capacitor CF and the falling duration is mainly
determined by the product of resistor ROFF and capacitor CF.
VOSCL
~
2.0V
~
where VOSCH 4.4V
CF is discharged by the summed-up of ROFF current and one
sixteenth (1/16) of RON
5.8V
FROM
VF SIGNAL
SWITCHED BY
CHARGING AND
DISCHARGING
M51996A
Fig.4 Schematic diagram of charging and discharging
control circuit for OSC.capacitor CF
~
Fig.4 shows the equivalent charging and discharging circuit
diagram of oscillator.
The current flows through RON
VT - ON
~
RON X CF
where VT - ON
(V/s)
................................................(1)
~
4.5V
The maximum on duration is approximately given as
(VOSCH-VOSCL) X RON X CF
~
VT - ON
(s)
........................(2)
Fig.5 OSC.waveform at normal condition (no-
So fall rate of CF terminal is given as
~
VT - OFF
ROFF X CF
VT - ON
+
16 X RON X CF
(V/s)
.....................(3)
The minimum off duration approximately is given as
(VOSCH-VOSCL) X CF
~
VT-OFF
ROFF
where VT - OFF
VT-ON
+
16 X RON
~
3.5V
(s)
.....................................(4)
The cycle time of oscillation is given by the summation of
Equations 2 and 4.
The frequency including the dead-time is not influenced by the
temperature because of the built-in temperature compensating
circuit.
10
( / 22 )
Page 11

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
Output transistor is protected from rush current by CLM function
at the start time of power on.SOFT terminal is used to improve
the rising response of the output voltage of power
supply(prevention of overshooting).
The ON duration of output is kept constant,and the OFF
duration is extended as the SOFT terminal voltage becomes
lower by the soft start circuit of this IC.
The maximum value of extension is set internally at
approximately sixteen times of the maximum ON duartion.
The features of this method are as follows:
1 It is ideal for primary control as IC driving current is supplied
from the third widing of the main transformer at the start-up
because constant ON duration is obtained from start-up.
2 It is possible to get a wide dynamic range for ON/OFF ratio
by pulse-by-pulse current limit circuit.
3 The response characteristics at power-on is not affected by
input voltage as the pulse-by-pulse limit current value is not
affected by the input voltage.
Fig.6 shows the circuit diagram of the soft start.If SOFT terminal
voltage is low,T-OFF terminal voltage bocomes low and VT-OFF
in equations (3) and (4) become low.
VOH
VOL
VOSCH
VOSCL
4.4V
2.0V
~
VOH
VOL
VOSCH
VOSCL
coincides with the rising duration of CF terminal waveform,when
the no output current flows from F/B terminal.
When the F/B terminal has finite impedance and current flows
out from F/B terminal,"A" point potential shown in Fig.9 depends
on this current.So the "A" point potential is close to GND level
when the flow-out current becomes large.
"A" point potential is compared with the CF terminal oscillator
waveform and PWM comparator,and the latch circuit is set
when the potential of oscillator waveform is higher than "A"
point potential.
The latch circuit is reset during the dead-time of oscillation
(falling duration of oscillation current).So the "B" point potential
or output waveform of latch circuit is the one shown in Fig.10.
The final output waveform or "C" point potential is got by
combining the "B" point signal and dead-time signal
logically.(please refer to Fig.10)
CSOFT
Vz 4.2V
~
DISCHARGING TRANSISTOR*
IC's INTERNAL CIRCUIT
*Active when operation stops.
GND
TERMINAL
TERMINAL
RSOFT
TERMINAL
TERMINAL
TERMINAL
M51996AP/FP
(2)Oscillator operation when the SOFT(soft
start) circuit is operating.
TO REG
SOFT
TO REG
START FROM 0V
0
THE FIRST
OUTPUT PULSE
NO OUTPUT
PULSE
0
t
Fig.8 Relationship between oscillator waveform and
output waveform at start-up
Fig.7 shows the relationship between oscillator waveform and
output pulse.
If the SOFT terminal voltage is VSOFT,the rise rate of CF
terminal given as
VT - ON
~
RON • CF
(V/S)
..............................................................(5)
Fig.6 Circuit diagram of SOFT terminal section and T OFF terminal section
~
Fig.7 Oscillator waveform when the SOFT circuit is
operating
T-OFF
The fall rate of oscillation waveform is given as
VSOFT - VBE
~
RON • CF
+
16 • RON • CF
where
VSOFT;SOFT terminal applied voltage
VBE ~ 0.65V
If VSOFT - VBE < 0, VSOFT - VBE = 0
If VSOFT - VBE > VT - OFF (~3.5V), VSOFT - VBE =VT - OFF
PWM comparator, PWM latch and current limit
latch section
Fig.9 shows the scematic diagram of PWM comparator and
PWM latch section. The on-duration of output waveform
t
t
( / 22 )
11
VT - ON
.............................(6)
(V/S)
Page 12

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
F/B
OSCTOOUTPUT
POINT C
POINT B
CURRENT
COMP
POINT A
5.8V
6S1S7.1V~WAVEFORM AT POINT A
OSC WAVEFORM
POINT A
POINT B
POINT C
VTHCLM 200mV
~
continue until next cycle.Fig.11 shows the timing relation among
them.
If the current limiting circuit is set,no waveform is generated at
output terminal, however this state is reset during the
succeeding dead-time.
So this current limiting circuit is able to have the function in
every cycle,and is named "pulse-by-pulse current limit".
There happen some noise voltage on RCLM during the switching
of power transistor due to the snubber circuit and stray
capacitor of the transformer windings.
VOUT
CLM+
GND
RNF
CNF
RCLM
*2
*1
POINT D
D
M51996
WAVEFORM
OF O.S.C. &
-
LATCH
+
PWM
CF
CLM+
*1 Resistor to determine current limit sensitivety
*2 High level during dead time
Fig.9 PWM comparator PWM latch and
current limit latch section
FROM
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
OSC WAVEFORM
OF CF TERMINAL
WAVEFORM OF
CLM+ TERMINAL
CURRENT LIMIT
SIGNAL TO SET
LATCH
WAVEFORM OF
VOUT TERMINAL
Fig.11 Operating waveform of current limiting circuit
To eliminate the abnormal operation by the noise voltage,the
low pass filter,which consists of RNF and CNF is used as shown
in Fig.12.
It is recommended to use 10 to 100Ω for RNF because such
range of RNF is not influenced by the flow-out current of some
200µA from CLM+ terminal and CNF is designed to have the
enough value to absorb the noise voltage.
Fig.10 Waveforms of PWM comparator input point A,
latch circuit points B and C
Current limiting section
When the current-limit signal is applied before the crossing
instant of "A" pint potential and CF terminal voltage shown in
Fig.9,this signal makes the output "off" and the off state will
M51996
POINT
Fig.12 Connection diagram of current limit circuit
Voltage detector circuit(DET) section
The DET terminal can be used to control the output voltage
which is determined by the winding ratio of fly back transformer
in fly-back system or in case of common ground circuit of
primary and secondary in feed forward system.
The circuit diagram is quite similar to that of shunt regulator
type 431 as shown in Fig.13.As well known from Fig.13 and
Fig.14,the output of OP AMP has the current-sink ability,when
the DET terminal voltage is higher than 2.5V
( / 22 )
12
Page 13

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
Fig.13 Voltage detector circuit section(DET)
AMP
2.5V
DET
F/B
500Ω3k6S1S7.1V
7.1V
DET
F/B3k500Ω1S6S
10S
1.2k
10.8k
10.8k
5.4k
It is necessary that OVP state holds by circuit current from R1 in
the application example,so this IC has the characteristic of
small Icc at the OVP reset supply voltage(~stand-by current +
20µA)
On the other hand,the circuit current is large in the higher
supply voltage,so the supply voltage of this IC doesn't become
so high by the voltage drop across R1.
This characteristic is shown in Fig.16.
The OVP terminal input current in the voltage lower than the
OVP threshold voltage is based on I2 and the input current in
the voltage higher than the OVP threshold voltage is the sum of
the current flowing to the base of Q3 and the current flowing
from the collector of Q2 to the base.
For holding in the latch state,it is necessary that the OVP
terminal voltage is kept in the voltage higher than VBE of Q3.
So if the capacitor is connected between the OVP terminal and
GND,even though Q2 turns on in a moment by the surge
voltage,etc,this latch action does not hold if the OVP terminal
voltage does not become higher than VBE of Q3 by charging
this capacitor.
For resetting OVP state,it is necessary to make the OVP
terminal voltage lower than the OVP L threshold voltage or
make Vcc lower than the OVP reset supply voltage.
As the OVP reset voltage is settled on the rather high voltage of
9.0V,SMPS can be reset in rather short time from the switch-off
of the AC power source if the smoothing capacitor is not so
large value.
I1=0 when OVP operates
but it becomes high impedance state when lower than
2.5V DET terminal and F/B terminal have inverting
phase characteristics each other,so it is recommended
to connect the resistor and capacitor in series between
them for phase compensation.It is very important one
can not connect by resistor directly as there is the
voltage difference between them and the capacitor has
the DC stopper function.
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
It is necessary to input the sufficient larger current(800µA to
8mA)than I2 for triggering the OVP operation.
The reason to decrease I2 is that it is necessary that Icc at the
OVP rest supply voltage is small.
-
OP
+
Fig.14 Schmatic diagram of voltage detector circuit section(DET)
OVP circuit(over voltage protection circuit)section
OVP circuit is basically positive feedback circuit constructed
by Q2,Q3 as shown in Fig.15.
Q2,Q3 turn on and the circuit operation of IC stops,when the
input signal is applied to OVP terminal.(threshold voltage ~
750mV)
The current value of I2 is about 150µA when the OVP does
not operates but it decreases to about 2µA when OVP
operates.
Vcc
7.8V
8k
12k
OVP
GND
I2
Fig.15 Detail diagram of OVP circuit
( / 22 )
13
100µA
I1
Q1
Q2
400
Q3
2.5k
Page 14

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
,and the high gate
drive voltage causes high gate dissipation,on the other hand,too
low gate drive voltage does not make the MOS-FET fully onstate or the saturation state.
GND
VccR1VF
CVcc
MAIN TRANSFORMER
SMOOTHING CAPACITOR
and Cvcc is in the range of 10 to 47µF.The product of
R1 by Cvcc causes the time delay of operation,so the response
time will be long if the product is too much large.
Design of start-up circuit and the power supply
of IC
GND
VccR1VF
CVcc
OF TRANSFORMER
SMOOTHING CAPACITOR
NPNBVIN
R2
M51996AP/FP
8
OVP RESET POINT
8.87V(-30°C)
7
8.94V(25°C)
9.23V(85°C)
6
5
4
Ta=-30°C
Ta=25°C
Ta=85°C
3
2
1
0
0
10
20
30 40
SUPPLY VOLTAGE Vcc(V)
Fig.16 CIRCUIT CURRENT VS. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(OVP OPERATION)
Output section
It is required that the output circuit have the high sink and
source abilities for MOS-FET drive.It is well known that the
"totempole circuit has high sink and source ability.However,it
has the demerit of high through current.
For example,the through current may reach such the high
current level of 1A,if type M51996A has the "conventional"
totempole circuit.For the high frequency application such as
higher than 100kHz,this through current is very important factor
and will cause not only the large Icc current and the inevitable
heat-up of IC but also the noise voltage.
This IC uses the improved totempole circuit,so without
deteriorating the characteristic of operating speed,its through
current is approximately 100mA.
APPLICATION NOTE OF TYPE M51996AP/FP
RECTIFIED DC
VOLTAGE FROM
THIRD WINDING OR
BIAS WINDING
M51996A
Fig.24 Start-up circuit diagram when it is not
necessary to set the start and stop input voltage
Just after the start-up,the Icc current is supplied from
Cvcc,however,under the steady state condition ,IC will be
supplied from the third winding or bias winding of
transformer,the winding ratio of the third winding must be
designed so that the induced voltage may be higher than the
operation-stop voltage Vcc(STOP).
The Vcc voltage is recommended to be 12V to 17V as the
normal and optimum gate voltage is 10 to 15V and the output
voltage(VOH) of type M51996AP/FP is about(Vcc-2V).
It is not necessary that the induced voltage is settled higher
than the operation start-up voltage Vcc(START)
(2)The start-up circuit when it is not necessary to set the
start and stop input voltage
It is recommend to use the third winding of "forward winding"
or "positive polarity" as shown in Fig.18,when the DC source
voltages at both the IC operation start and stop must be
settled at the specified values.
The input voltage(VIN(START)),at which the IC operation
starts,is decided by R1 and R2 utilizing the low start-up
(1)The start-up circuit when it is not necessary to set the
start and stop input voltage
Fig.17 shows one of the example circuit diagram of the start-up
circuit which is used when it is not necessary to set the start
and stop voltage.
It is recommended that the current more than 300µA flows
through R1 in order to overcome the operation start-up current
Icc(START)
RECTIFIED DC
VOLTAGE FROM
M51996A
Fig.18 Start-up circuit diagram when it is not
necessary to set the start and stop input voltage
( / 22 )
14
PRIMARY WINDING
THIRD WINDING OF
TRANSFORMER
Page 15

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
current characteristics of type M51996AP/FP.
GND
Vcc
COLLECTOR
EMITTER
CVcc
To design the conductor-pattern on PC board,following cautions
must be considered as shown in Fig.19.
(a)To separate the emitter line of type M51996A from the GND
line of the IC
(b)The locate the CVCC as near as possible to type M51996A
and connect directly
(c)To separate the collector line of type M51996A from the Vcc
line of the IC
(d)To connect the ground terminals of peripheral parts of ICs to
GND of type M51996A as short as possible
OUTPUT
CVcc1
CVcc2
GND
Vcc
R1
The input voltage(VIN(STOP)),at which the IC operation stops,is
decided by the ratio of third winding of transformer.
The VIN(START) and VIN(STOP) are given by following equations.
VIN(START) R1 • ICCL + ( + 1) • Vcc(START)
VIN(STOP) (Vcc(STOP)-VF) •
~
~
R1
R2
NP
NB
1
+
2
V'IN RIP(P-P)
...............(7)
............(8)
where
ICCL is the operation start-up current of IC
Vcc(START) is the operation start-up voltage of IC
Vcc(STOP) is the operation stop voltage of IC
VF is the forward voltage of rectifier diode
V'IN(P-P) is the peak to peak ripple voltage of
NB
Vcc terminal
~
V'IN RIP(P-P)
NP
It is required that the VIN(START) must be higher than VIN(STOP).
When the third winding is the "fly back winding" or "reverse
polarity",the VIN(START) can be fixed,however,VIN(STOP) can not
be settled by this system,so the auxiliary circuit is required.
(3)Notice to the Vcc,Vcc line and GND line
To avoid the abnormal IC operation,it is recommended to
design the Vcc is not vary abruptly and has few spike
voltage,which is induced from the stray capacity between the
winding of main transformer.
To reduce the spike voltage,the Cvcc,which is connected
between Vcc and ground,must have the good high frequency
characteristics.
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
MAIN
TRANSFORMER
THIRD
WINDING
M51996A
RCLM
Fig.19 How to design the conductor-pattern of type
M51996A on PC board(schematic example)
(4)Power supply circuit for easy start-up
When IC start to operate,the voltage of the CVCC begins to
decrease till the CVCC becomes to be charged from the third
winding of main-transformer as the Icc of the IC increases
abruptly.In case shown in Fig.17 and 18,some "unstable startup" or "fall to start-up" may happen, as the charging interval of
CVCC is very short duration;that is the charging does occur only
the duration while the induced winding voltage is higher than
the CVCC voltage,if the induced winding voltage is nearly equal
to the "operation-stop voltage" of type M51996A.
It is recommended to use the 10 to 47µF for CVCC1,and about 5
times capacity bigger than CVCC1 for CVCC2.
M51996A
Fig.20 DC source circuit for stable start-up
( / 22 )
15
MAIN
TRANSFORMER
THIRD
WINDING
Page 16

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
OVP circuit
OVP
GND
Vcc
CVcc
GND
Vcc
forcedly and
to make the Vcc low value;This makes the OVP-reset time fast.
R1R2GND
Vcc
TRANSFORMER
CFIN
Cvcc
THIS PART SHOULD BE SHORT
470Ω
OVP
Of course you can make use of the transistor or photo-transistor
instead of SW.
SW
ON/OFF
REG
5.1k
(1)To avoid the miss operation of OVP
It is recommended to connect the capacitor between OVP
terminal and GND for avoiding the miss operation by the spike
noise.
The OVP terminal is connected with the sink current source
(~150µA) in IC when OVP does not operate,for absorbing the
leak current of the photo coupler in the application.
So the resistance between the OVP terminal and GND for leakcut is not necessary.
If the resistance is connected,the supply current at the OVP
reset supply voltage becomes large.
As the result,the OVP reset supply voltage may become higher
than the operation stop voltage.
In that case,the OVP action is reset when the OVP is triggered
at the supply voltage a little high than the operation stop
voltage.
So it should be avoided absolutely to connect the resistance
between the OVP terminal and GND.
To REG or Vcc
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
~
THE TIME CONSTANT OF
Fig.22 Example circuit diagram to make the
OVP-reset-time fast
TO MAIN
M51996A
5.6k
M51996A
PHOTO COUPLER
Fig.21 Peripheral circuit of OVP terminal
(2)Application circuit to make the OVP-reset time fast
The reset time may becomes problem when the discharge time
constant of CFIN • (R1+R2) is long. Under such the circuit
condition,it is recommended to discharge the CVCC
(3)OVP setting method using the induced third winding
voltage on fly back system
For the over voltage protection (OVP),the induced fly back type
third winding voltage can be utilized,as the induced third
winding voltage depends on the output voltage.Fig.23 shows
one of the example circuit diagram.
MAIN
TRANSFORMER
THIRD
WINDING
M51996A
FIG.23 OVP setting method using the induced
third winding voltage on fly back system
(4)Method to control for ON/OFF using the OVP terminal
You can reset OVP to lower the OVP terminal voltage lower
than VTHOVPL.
So you can control for ON/OFF using this nature.
The application is shown in Fig.24.
The circuit turns off by SW OFF and turns on by SW ON in this
application.
M51996A
FIG.24 Method to control for ON/OFF using the
OVP terminal
( / 22 )
16
Page 17

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
Current limiting circuit
GND
Vcc
R1
Cvcc
CAPACITOR
CFIN
COLLECTOR
CLM+
VOUT
EMITTER
CNF
RCLM
I1I2RCLM
CLM
IP1
IP2I1I2
OUTPUT CURRENT
(1)Peripheral circuit of CLM+ terminal
Fig.25 shows the example circuit diagrams around the CLM+
terminal.It is required to connect the low pass filter,in order to
reduce the spike current component,as the main current or
drain current contains the spike current especially during the
turn-on duration of MOS-FIT.
1,000pF to 22,000pF is recommended for CNF and the RNF1
and RNF2 have the functions both to adjust the "currentdetecting-sensitivity" and to consist the low pass filter.
INPUT
SMOOTHING
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
(a) Feed forward system
M51996A
RNF1
RNF2
Fig.25 Peripheral circuit diagram of CLM+ terminal
To design the RNF1 and RNF2,it is required to consider the
influence of CLM+ terminal source current(IINCLM+),
which value is in the range of 90 to 270µA.
In order to be not influenced from these resistor paralleled value
of RNF1 and RNF2,(RNF1/RNF2)is recommended to be less than
100Ω.
The RCLM should be the non-inductive resistor.
(2)Over current limiting curve
(a)In case of feed forward system
Fig.26 shows the primary and secondary current wave-forms
under the current limiting operation.
At the typical application of pulse by pulse primary current
detecting circuit,the secondary current depends on the primary
current.As the peak value of secondary current is limited to
specified value,the characteristics curve of output voltage
versus output current become to the one as shown in Fig.27.
(b) Primary and secondary current
Fig.26 Primary and secondary current waveforms
under the current limiting operation
condition on feed forward system
Fig.27 Over current limiting curve on feed forward
system
The demerit of the pulse by pulse current limiting system is that
the output pulse width can not reduce to less than some value
because of the delay time of low pass filter connected to the
CLM+ terminal and propagation delay time TPDCLM from CLM+
terminal to output terminal of type M51996A.The typical
TPDCLM+ is 100ns.
As the frequency becomes higher,the delay time must be
shorter.And as the secondary output voltage becomes
higher,the dynamic range of on-duty must be wider;it means
that it is required to make the on-duration much more narrower.
So this system has the demerit at the higher oscillating
frequency and higher output voltage applications.
To prevent that the SOFT terminal is used to lower the
frequency when the curve starts to become vertical.
( / 22 )
17
Page 18

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
VOUT
VOUT
VOUT
CVcc
Vcc
R3
SOFT
COLLECTOR
R1R2F/B
REG
REG
F/B
5003K1S
6S
M51996A
Under the condition in which I2 in Fig.26 does not become 0,the
output voltage is proportional to the product of the input voltage
VIN(primary side voltage of the main transformer) and on duty.If
the bias winding is positive,Vcc is approximately proportional to
VIN.The existance of feed back current of the photo-coupler is
known by measuring the F/B terminal voltage which becomes
less than 2VBE in the internal circuit of REG terminal and F/B
terminal if the output current flows from the F/B terminal.
Fig.29 shows an application example.
Q1 is turned on when normal output voltage is controlled at a
certain value.The SOFT terminal is clampedto a high-level
voltage.If the output voltage decreases and the curve starts to
drop,no feed back current flows,Q1 is turned off and the SOFT
terminal responds to the smoothed output voltage.
It is recommended to use an R1 and R2 of 10kΩ~30kΩ.An R3
of 20 to 100kΩ and C of 1000pF to 8200pF should be used.
To change the knee point of frequency drop,use the circuit in
Fig.30.
To have a normal SOFT start function in the circuit in Fig.29,use
the circuit in Fig.31.It is recommended to use an R4 of 10kΩ.
Q1D1VOUT
THE MAIN TRANSFORMER
C
TO OUTPUT TRANSISTOR
SOFT
SOFT
SOFT
CVcc
Vcc
R3
SOFT
R1R2F/B
REG
Q1D1VOUT
THE MAIN TRANSFORMER
C
TO OUTPUT TRANSISTOR
RSOFT
CSOFTQ2R4D2D2
Fig.28 Relationship between REG terminal and
F/B terminal
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
BIAS WINDING OF
M51996A
If the curve becomes vertical because of an excess current, the
output voltage is lowered and no feedback current flows from
feedback photo-coupler;the PWM comparator operates to
enlarge the duty sufficiently,but the signal from the CLM+
section operates to make the pulse width narrower.
PHOTO-COUPLER
FOR FEED BACK SIGNAL
Fig.29 Current to lower frequency during over current
TO MAKE THE KNEE POINT HIGH
TO MAKE THE KNEE POINT LOW
Fig.30 Method to control the knee point of
frequency drop
BIAS WINDING OF
COLLECTOR
M51996A
PHOTO-COUPLER
FOR FEED BACK SIGNAL
Fig.31 Circuit to use frequency drop during the over
current and normal soft start
( / 22 )
18
Page 19

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
type M51996A when the polarity of the third winding is negative
and the system is fly back.So the operation of type M51996A
will stop when the Vcc becomes lower than "Operation-stop
voltage" of M51996A when the DC output voltage of SMPS
decreases under specified value at over load condition.
However,the M51996A will non-operate and operate
intermittently,as the Vcc voltage rises in accordance with the
decrease of Icc current.
The fly back system has the constant output power
characteristics as shown in Fig.32 when the peak primary
current and the operating frequency are constant.
Toavoid anincrease of the output current,the frequency is
lowered when the DC output voltage of SMPS starts to drop
using the SOFT terminal.Vcc is divided and is input to the SOFT
terminal as shown in Fig.33,because the voltage in proportional
to the output voltage is obtained from the bias winding.In this
application example,the current flowing to R3 added to the startup current.So please use high resistance or 100kΩ to 200kΩ for
R3.
The start-up current is not affected by R3 if R3 is connected to
Cvcc2 in the circuit shown in Fig.20.
DC OUTPUT CURRENT
VOLTAGE"
CVcc
Vcc
R3R4SOFT
COLLECTOR
)
(It means that the terminal is "Output low state" and please refer
characteristics of output low voltage versus sink current.)
This characteristics has the merit not to damage the MOS-FIT
at the stop of operation when the Vcc voltage decreases lower
than the voltage of Vcc(STOP),as the gate charge of MOSFIT,which shows the capacitive load characteristics to the
output terminal,is drawn out rapidly.
The output terminal has the draw-out ability above the Vcc
voltage of 2V,however,lower than the 2V,it loses the ability and
the output terminal potential may rise due to the leakage
current.
In this case, it is recommended to connect the resistor of 100kΩ
between gate and source of MOS-FIT as shown in Fig.34.
RCLM
VOUT
100kΩ
charge makes the gate power dissipation.The relation between
gate drive current ID and total gate charge QGSH is shown by
following equation;
R1R2F/B
REG
To photo-coupler for feed back signal
M51996AP/FP
(b)In case of fly back system
The DC output voltage of SMPS depends on the Vcc voltage of
POINT THAT Vcc VOLTAGE
OR THIRD WINDING
VOLTAGE DECREASES
UNDER "OPERATION-STOP
Output circuit
(1)The output terminal characteristics at the Vcc voltage
lower than the "Operation-stop" voltage
TO MAIN
TRANSFORMER
M51996A
Fig.34 Circuit diagram to prevent the MOS-FIT gate
potential rising
The output terminal has the current sink ability even though the
Vcc voltage lower than the "Operation-stop" voltage or Vcc(STOP
Fig.32 Over current limitting curve on fly back system
M51996A
Fig.33 Current to lower the frequency during the
over current in the fly back system
(2)MOS-FIT gate drive power dissipation
Fig.35 shows the relation between the applied gate voltage
and the stored gate charge.
In the region 1 ,the charge is mainly stored at CGS as the
depletion is spread and CGD is small owing to the off-state of
MOS-FIT and the high drain voltage.
In the region 2 ,the CGD is multiplied by the "mirror effect" as
the characteristics of MOS-FIT transfers from off-state to onstate.
In the region 3 ,both the CGD and CGS affect to the
characteristics as the MOS-FIT is on-state and the drain
voltage is low.
The charging and discharging current caused by this gate
ID=QGSH • fOSC
.....................................(11)
Where
fOSC is switching frequency
( / 22 )
19
Page 20

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
MOS-FIT,the power dissipation caused by the gate current can
not be neglected.
In this case,following action will be considered to avoid heat
up of type M51996A.
123
VDS=80V
VDS=200V
VDS=320V
DRAIN
GATE
SOURCE
CGS
CGD
CDS
VGS
VD
VOUT
C1CF/B
DETC4R2BR1R3C2
VOLTAGE
1
2
1
2
Please take notice that the current flows through the R1 and R2
are superposed to Icc(START).Not to superpose,R1 is connected
to Cvcc2 as shown in Fig.20.
GAVDET
(DC VOLTAGE GAIN)
G112
Log
ID
M51996AP/FP
As the gate drive current may reach up to several tenths
milliamperes at 500kHz operation,depending on the size of
20
15
10
5
ID=4A
0
0 4
8 12 16
20
TOTAL STORED GATE CHARGE(nC)
Fig.35 The relation between applied gate-source
voltage and stored gate charge
DETECTING
M51996A
Fig.37 How to use the DET circuit for the voltage
detector
Fig.38 shows the gain-frequency characteristics between point
B and point C shown in Fig.37.
The G1, and are given by following equations;
R3
G1=
=
=
.............................................(10)
R1/R2
1
C2 • R3
C1 • C2 • R3
............................................(11)
C1 + C2
....................................(12)
At the start of the operation,there happen to be no output pulse
due to F/B terminal current through C1 and C2,as the potential
of F/B terminal rises sharply just after the start of the operation.
Not to lack the output pulse,is recommended to connect the
capacitor C4 as shown by broken line.
(1) To attach the heat sink to type M51996A
(2) To use the printed circuit board with the good
thermal conductivity
(3) To use the buffer circuit shown next section
(3)Output buffer circuit
It is recommended to use the output buffer circuit as shown in
Fig.36,when type M51996A drives the large capacitive load or
bipolar transistor.
M51996A
Fig.36 Output buffer circuit diagram
DET
Fig.37 shows how to use the DET circuit for the voltage detector
and error amplifier.
For the phase shift compensation,it is recommended to
connected the CR network between det terminal and F/B
terminal.
Fig.38 Gain-frequency characteristics between
point B and C shown in Fig.37
How to get the narrow pulse width during the
start of operation
Fig.39 shows how to get the narrow pulse width during the start
of the operation.If the pulse train of forcedly narrowed pulsewidth continues too long,the misstart of operation may
happen,so it is recommended to make the output pulse width
narrow only for a few pulse at the start of operation.0.1µF is
recommended for the C.
( / 22 )
20
Page 21

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
M51996A
F/B
COUPLER
100Ω
C
ROFFCFRON
T-ONCFT-OFF0V0V
PULSE
SYNCHRONOUS PULSE
GND
EMITTER
VOUT
COLLECTOR
Vcc
TRANSISTOR
GND
EMITTER
VOUT
COLLECTOR
Vcc
Vcc
-Vss
(-2V to -5V)
TO PHOTO
Fig.39 How to get the narrow pulse width
during the start of operation
How to synchronize with external circuit
Type M51996A has no function to synchronize with external
circuit,however,there is some application circuit for
synchronization as shown in Fig.40.
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
Driver circuit for bipolar transistor
When the bipolar transistor is used instead of MOS-FIT,the
base current of bipolar transistor must be sinked by the
negative base voltage source for the switching-off duration,in
order to make the switching speed of bipolar transistor fast one.
In this case,over current can not be detected by detecting
resistor in series to bipolar transistor,so it is recommended to
use the CT(current transformer).
For the low current rating transistor,type M51996A can drive it
directly as shown in Fig.42.
M51996A
MINIMUM PULSE
WIDTH OF
SYNCHRONOUS
Q1
SYNCHRONOUS
PULSE
MAXIMUM PULSE WIDTH OF
M51996A
BIPOLAR
Fig.42 Driver circuit diagram (2) for bipolar transistor
Fig.40 How to synchronize with external circuit
M51996A
Fig.41 Driver circuit diagram (1) for bipolar transistor
( / 22 )
21
Page 22

SWITCHING REGULATOR CONTROL
of IC package is 15°C or less,when the IC junction temperature is
measured by temperature dependency of forward voltage of pin
junction,and IC package temperature is measured by "thermoviewer",and also the IC is mounted on the "phenol-base" PC
board in normal atmosphere.
So it is concluded that the maximum case temperature(surface
temperature of IC) rating is 120°C with adequate margin.
Attention for heat generation
The maximum ambient temperature of type M51996A is
+85°C,however,the ambient temperature in vicinity of the IC is
not uniform and varies place by place,as the amount of power
dissipation is fearfully large and the power dissipation is
generated locally in the switching regulator.
So it is one of the good idea to check the IC package
temperature.
The temperature difference between IC junction and the surface
MITSUBISHI (Dig./Ana. INTERFACE)
M51996AP/FP
( / 22 )
22
 Loading...
Loading...