Page 1

TL/F/11417
LV8572A Real Time Clock (RTC)
PRELIMINARY
December 1993
LV8572A Low Voltage Real Time Clock (RTC)
General Description
The LV8572A is intended for use in microprocessor based
systems where information is required for multi-tasking, data
logging or general time of day/date information. This device
is implemented in low voltage silicon gate microCMOS technology to provide low standby power in battery back-up environments. The circuit’s architecture is such that it looks
like a contiguous block of memory or I/O ports. The address
space is organized as 2 software selectable pages of 32
bytes. This includes the Control Registers, the Clock Counters, the Alarm Compare RAM, and the Time Save RAM.
Any of the RAM locations that are not being used for their
intended purpose may be used as general purpose CMOS
RAM.
Time and date are maintained from 1/100 of a second to
year and leap year in a BCD format, 12 or 24 hour modes.
Day of week, day of month and day of year counters are
provided. Time is controlled by an on-chip crystal oscillator
requiring only the addition of the crystal and two capacitors.
The choice of crystal frequency is program selectable.
Power failure logic and control functions have been integrated on chip. This logic is used by the RTC to issue a power
fail interrupt, and lock out the mp interface. The time power
fails may be logged into RAM automatically when V
BB
l
VCC. Additionally, two supply pins are provided. When
V
BB
l
VCC, internal circuitry will automatically switch from
the main supply to the battery supply. Status bits are provided to indicate initial application of battery power, system
power, and low battery detect. (Continued)
Features
Y
3.3Vg10% supply
Y
Full function real time clock/calendar
Ð 12/24 hour mode timekeeping
Ð Day of week and day of years counters
Ð Four selectable oscillator frequencies
Ð Parallel resonant oscillator
Y
Power fail features
Ð Internal power supply switch to external battery
Ð Power Supply Bus glitch protection
Ð Automatic log of time into RAM at power failure
Y
On-chip interrupt structure
Ð Periodic, alarm, and power fail interrupts
Y
Up to 44 bytes of CMOS RAM
Block Diagram
TL/F/11417– 1
FIGURE 1
TRI-STATEÉis a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
C
1995 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M105/Printed in U. S. A.
Page 2
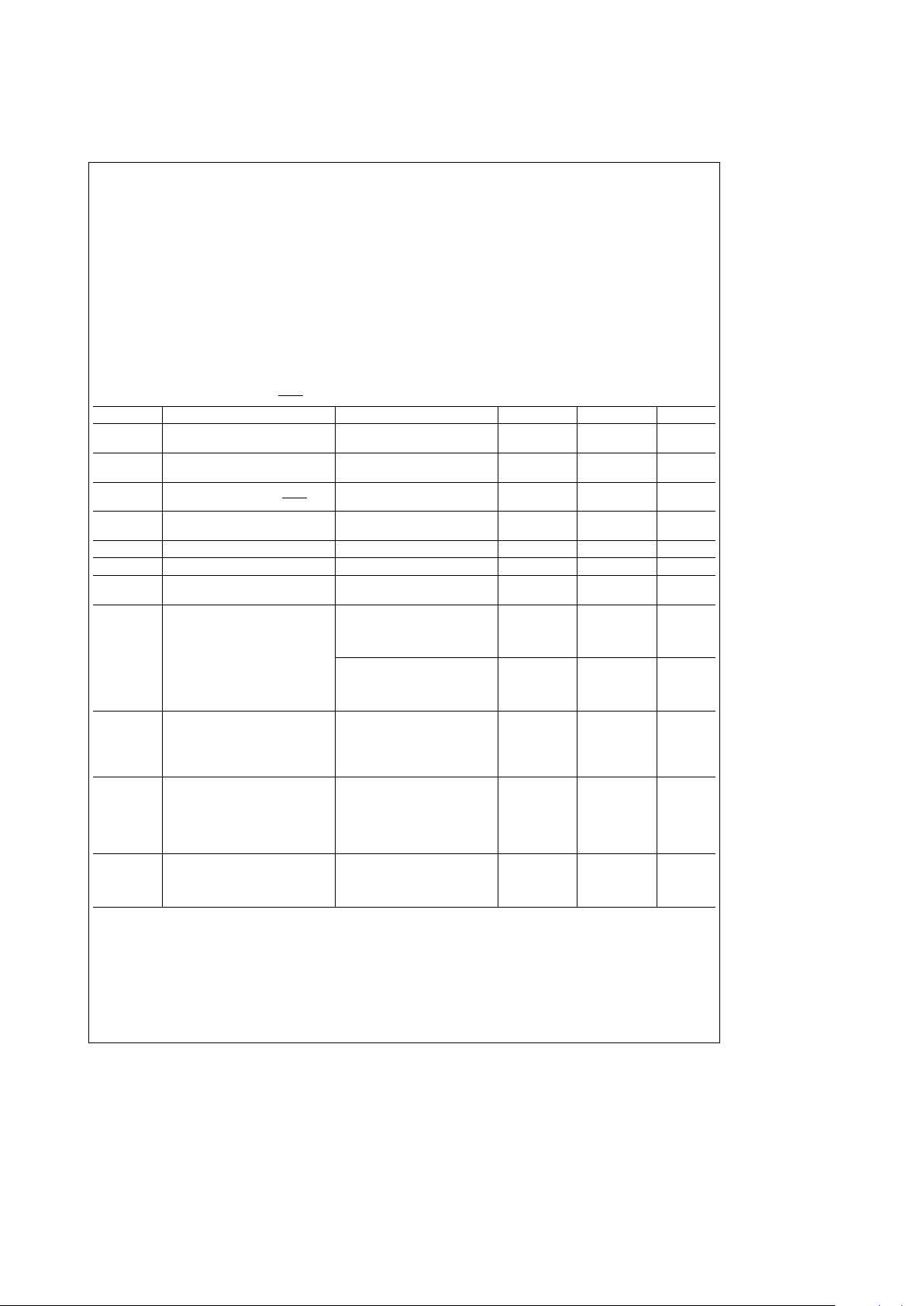
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Notes1&2)
Specifications for the 883 version of this product are
listed separately.
Supply Voltage (V
CC
)
b
0.5V toa7.0V
DC Input Voltage (V
IN
)
b
0.5V to V
CC
a
0.5V
DC Output Voltage (V
OUT
)
b
0.5V to V
CC
a
0.5V
Storage Temperature Range
b
65§Ctoa150§C
Power Dissipation (PD) 500 mW
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec.) 260
§
C
Operation Conditions
Min Max Unit
Supply Voltage (V
CC
) (Note 3) 3.0 3.6 V
Supply Voltage (VBB) (Note 3) 2.2 V
CC
b
0.4 V
DC Input or Output Voltage
0.0 V
CC
V
(V
IN,VOUT
)
Operation Temperature (T
A
)
b40a
85§C
Electr-Static Discharge Rating 1 kV
Typical Values
i
JA
DIP Board 61§C/W
Socket 67
§
C/W
i
JA
PLCC Board 80§C/W
Socket 88
§
C/W
DC Electrical Characteristics
V
CC
e
3.3Vg10%, V
BB
e
2.5V, V
PFAIL
l
VIH,C
L
e
100 pF (unless otherwise specified)
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Units
V
IH
High Level Input Voltage Any Inputs Except OSC IN, 2.0 V
CC
a
0.3 V
(Note 4) OSC IN with External Clock V
BB
b
0.2 V
V
IL
Low Level Input Voltage All Inputs Except OSC IN
b
0.3 0.8 V
OSC IN with External Clock
b
0.3 0.2 V
V
OH
High Level Output Voltage I
OUT
eb
20 mAV
CC
b
0,2 V
(Excluding OSC OUT, INTR
)I
OUT
eb
2.0 mA 2.4 V
V
OL
Low Level Output Voltage I
OUT
e
20 mA 0.2 V
(Excluding OSC OUT) I
OUT
e
2.0 mA 0.3 V
I
IN
Input Current (Except OSC IN) V
IN
e
VCCor GND
g
0.7 mA
I
OZ
Output TRI-STATEÉCurrent V
OUT
e
VCCor GND
g
1 mA
I
LKG
Output High Leakage Current V
OUT
e
VCCor GND
g
1 mA
MFO, INTR Pins Outputs Open Drain
I
CC
Quiescent Supply Current F
OSC
e
32.768 kHz
(Note 7) V
IN
e
VCCor GND (Note 5) 220 mA
V
IN
e
VCCor GND (Note 6) 700 mA
V
IN
e
VIHor VIL(Note 6) 5 mA
F
OSC
e
4.194304 MHz or
4.9152 MHz
V
IN
e
VCCor GND (Note 6) 4 mA
V
IN
e
VIHor VIL(Note 6) 6 mA
I
CC
Quiescent Supply Current V
BB
e
GND
(Single Supply Mode) V
IN
e
VCCor GND
(Note 7) F
OSC
e
32.768 kHz 30 mA
F
OSC
e
4.9152 MHz or 3 mA
4.194304 MHz
I
BB
Standby Mode Battery V
CC
e
GND
Supply Current OSC OUT
e
open circuit,
(Note 7) other pins
e
GND
F
OSC
e
32.768 kHzmA8mA
F
OSC
e
4.9152 MHz or 400 mA
4.194304 MHz
I
BLK
Battery Leakage 2.2VsV
BB
s
2.6V
other pins at GND
V
CC
e
GND, V
BB
e
2.6V 0.8 m A
V
CC
e
3.6V, V
BB
e
2.2V
b
0.8 mA
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings are those values beyond which damage to the device may occur.
Note 2: Unless otherwise specified all voltages are referenced to ground.
Note 3: For F
OSC
e
4.194304 or 4.9152 MHz, VBBminimume2.8V. In battery backed mode, V
BB
s
V
CC
b
0.4V.
Single Supply Mode: Data retention voltage is 2.2V min.
In single Supply Mode (Power connected to V
CC
pin) 3.0VsV
CC
s
3.6.
Note 4: This parameter (V
IH
) is not tested on all pins at the same time.
Note 5: This specification tests I
CC
with all power fail circuitry disabled, by setting D7 of Interrupt Control Register 1 to 0.
Note 6: This specification tests I
CC
with all power fail circuitry enabled, by setting D7 of Interrupt Control Register 1 to 1.
Note 7: OSC IN is driven by a signal generator. Contents of the Test Register
e
00(H) and the MFO pin is not configured as buffered oscillator out.
2
Page 3
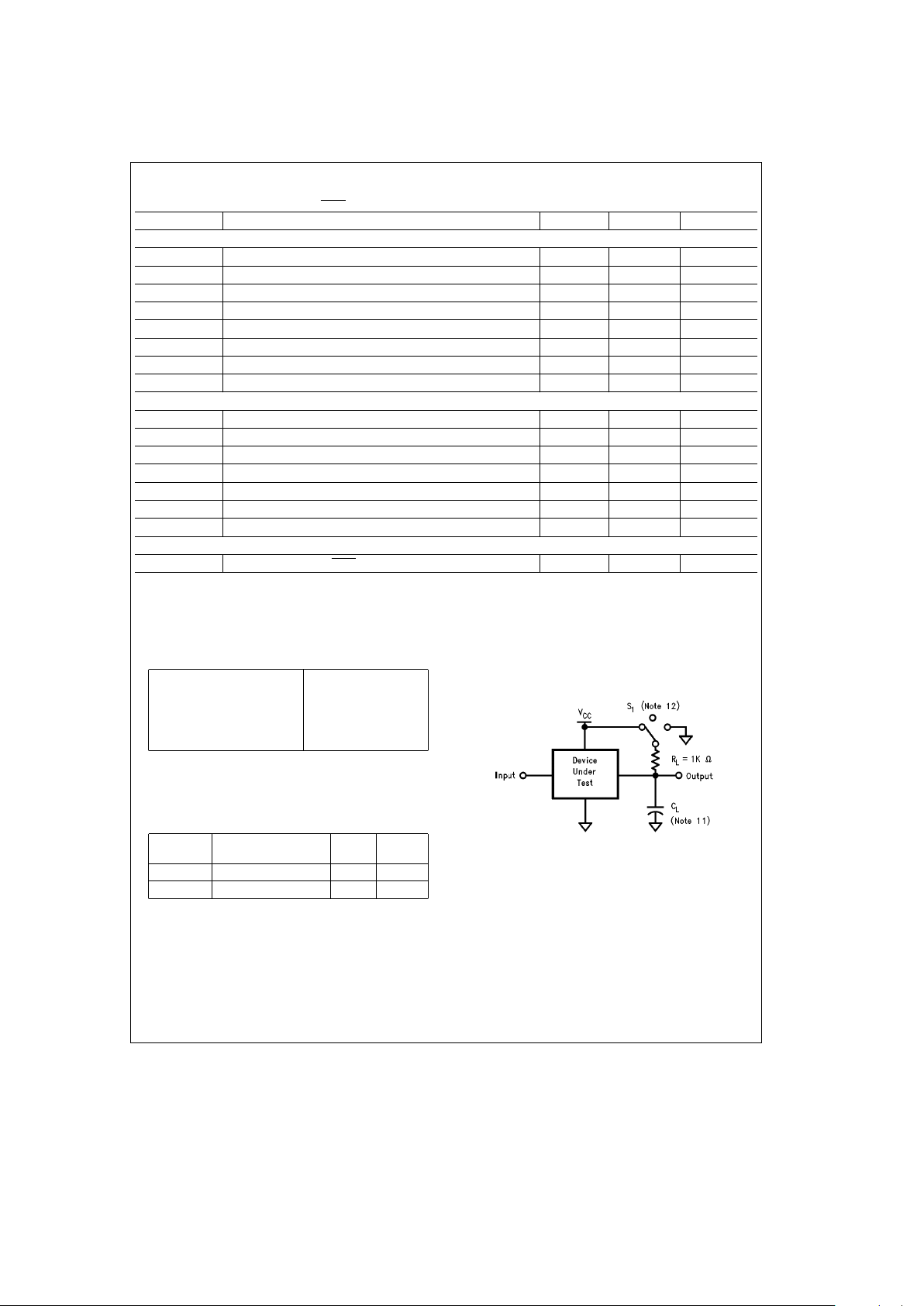
AC Electrical Characteristics
V
CC
e
3.3Vg10%, V
BB
e
2.5V, V
PFAIL
l
VIH,C
L
e
100 pF (unless otherwise specified)
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units
READ TIMING
t
AR
Address Valid Prior to Read Strobe 10 ns
t
RW
Read Strobe Width (Note 8) 100 ns
t
CD
Chip Select to Data Valid Time 100 ns
t
RAH
Address Hold after Read (Note 9) 2 ns
t
RD
Read Strobe to Valid Data 90 ns
t
DZ
Read or Chip Select to TRI-STATE 80 ns
t
RCH
Chip Select Hold after Read Strobe (Note 9) 0 ns
t
DS
Minimum Inactive Time between Read or Write Accesses 70 ns
WRITE TIMING
t
AW
Address Valid before Write Strobe 10 ns
t
WAH
Address Hold after Write Strobe (Note 9) 2 ns
t
CW
Chip Select to End of Write Strobe 110 ns
t
WW
Write Strobe Width (Note 10) 100 ns
t
DW
Data Valid to End of Write Strobe 70 ns
t
WDH
Data Hold after Write Strobe (Note 9) 2 ns
t
WCH
Chip Select Hold after Write Strobe (Note 9) 0 ns
INTERRUPT TIMING
t
ROLL
Clock Rollover to INTR Out is Typically 20 ms
Note 8: Read Strobe width as used in the read timing table is defined as the period when both chip select and read inputs are low. Hence read commences when
both signals are low and terminates when either signal returns high.
Note 9: Hold time is guaranteed by design but not production tested. This limit is not used to calculate outgoing quality levels.
Note 10: Write Strobe width as used in the write timing table is defined as the period when both chip select and write inputs are low. Hence write commences when
both signals are low and terminates when either signal returns high.
AC Test Conditions
Input Pulse Levels GND to 3.0V
Input Rise and Fall Times 6 ns (10% –90%)
Input and Output
1.3V
Reference Levels
TRI-STATE Reference Active High
a
0.5V
Levels (Note 12) Active Low
b
0.5V
Note 11: C
L
e
100 pF, includes jig and scope capacitance.
Note 12: S1
e
VCCfor active low to high impedance measurements.
S1
e
GND for active high to high impedance measurements.
S1
e
open for all other timing measurements.
Capacitance (T
A
e
25§C, fe1 MHz)
Symbol
Parameter
Typ Units
(Note 13)
C
IN
Input Capacitance 5 pF
C
OUT
Output Capacitance 7 pF
Note 13: This parameter is not 100% tested.
Note 14: Output rise and fall times 25 ns max (10%– 90%) with 100 pF load.
TL/F/11417– 2
3
Page 4
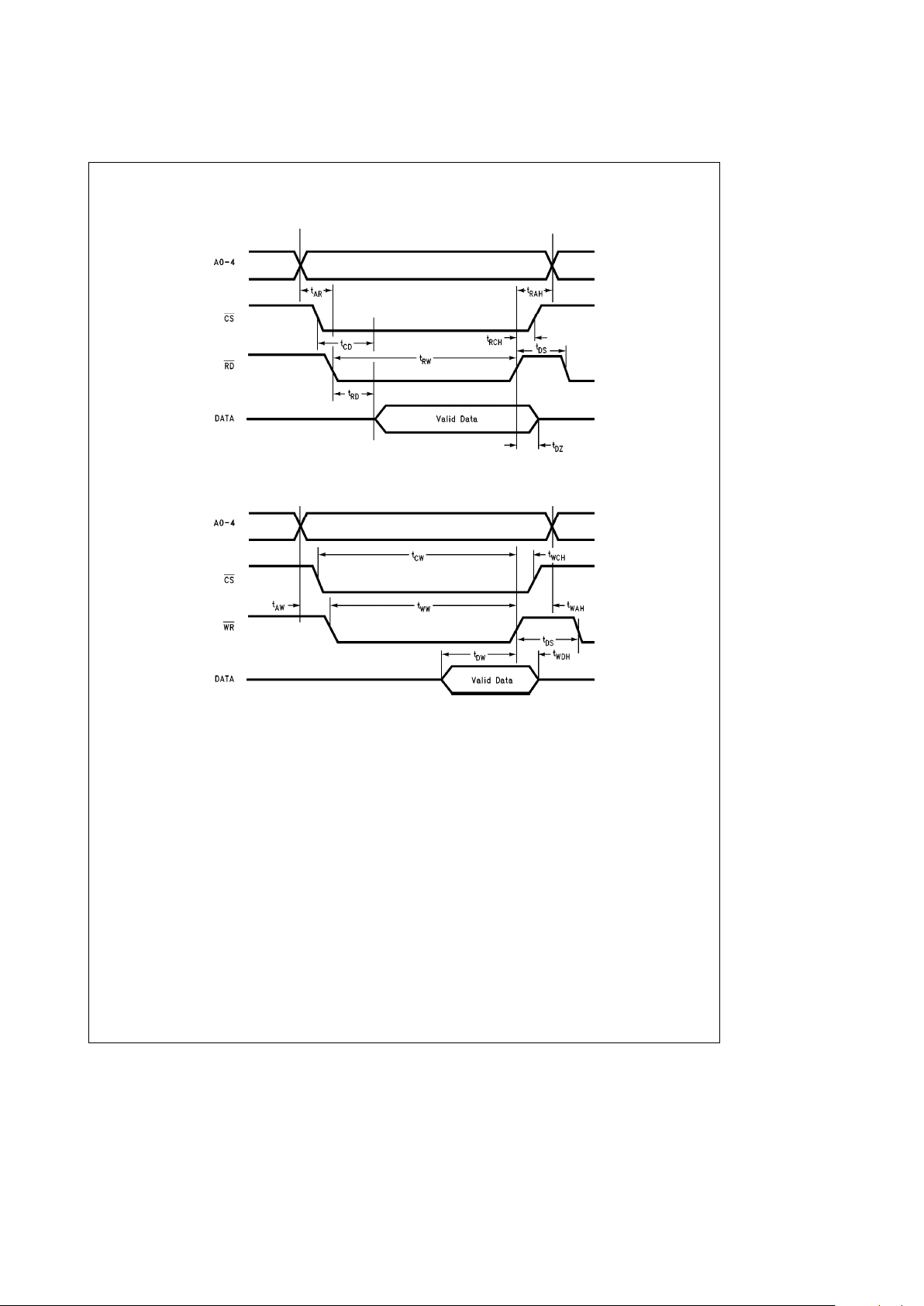
Timing Waveforms
Read Timing Diagram
TL/F/11417– 3
Write Timing Diagram
TL/F/11417– 4
4
Page 5
General Description (Continued)
The LV8572A’s interrupt structure provides three basic
types of interrupts: Periodic, Alarm/Compare, and Power
Fail. Interrupt mask and status registers enable the masking
and easy determination of each interrupt.
Pin Description
CS,RD,WR(Inputs): These pins interface to mP control
lines. The CS
pin is an active low enable for the read and
write operations. Read and Write pins are also active low
and enable reading or writing to the RTC. All three pins are
disabled when power failure is detected. However, if a read
or write is in progress at this time, it will be allowed to complete its cycle.
A0–A4 (Inputs): These 5 pins are for register selection.
They individually control which location is to be accessed.
These inputs are disabled when power failure is detected.
OSC IN (Input): OSC OUT (Output): These two pins are
used to connect the crystal to the internal parallel resonant
oscillator. The oscillator is always running when power is
applied to V
BB
and VCC, and the correct crystal select bits in
the Real Time Mode Register have been set.
MFO (Output): The multi-function output can be used as a
second interrupt output for interrupting the mP. This pin can
also provide an output for the oscillator. The MFO output is
configured as push-pull, active high for normal or single
power supply operation and as an open drain during standby mode (V
BB
l
VCC). If in battery backed mode and a pullup resistor is attached, it should be connected to a voltage
no greater than V
BB
.
INTR (Output): The interrupt output is used to interrupt the
processor when a timing event or power fail has occurred
and the respective interrupt has been enabled. The INTR
output is permanently configured active low, open drain. If in
battery backed mode and a pull-up resistor is attached, it
should be connected to a voltage no greater than V
BB
.
D0–D7 (Input/Output): These 8 bidirectional pins connect
to the host mP’s data bus and are used to read from and
write to the RTC. When the PFAIL
pin goes low and a write
is not in progress, these pins are at TRI-STATE.
PFAIL
(Input): In battery backed mode, this pin can have a
digital signal applied to it via some external power detection
logic. When PFAIL
e
logic 0 the RTC goes into a lockout
mode, in a minimum of 30 ms or a maximum of 63 ms unless
lockout delay is programmed. In the single power supply
mode, this pin is not useable as an input and should be tied
to V
CC
. Refer to section on Power Fail Functional Descrip-
tion.
V
BB
(Battery Power Pin): This pin is connected to a back-
up power supply. This power supply is switched to the internal circuitry when the V
CC
becomes lower than VBB. Utilizing this pin eliminates the need for external logic to switch in
and out the back-up power supply. If this feature is not to be
used then this pin must be tied to ground, the RTC programmed for single power supply only, and power applied to
the V
CC
pin.
V
CC
: This is the main system power pin.
GND: This is the common ground power pin for both V
BB
and VCC.
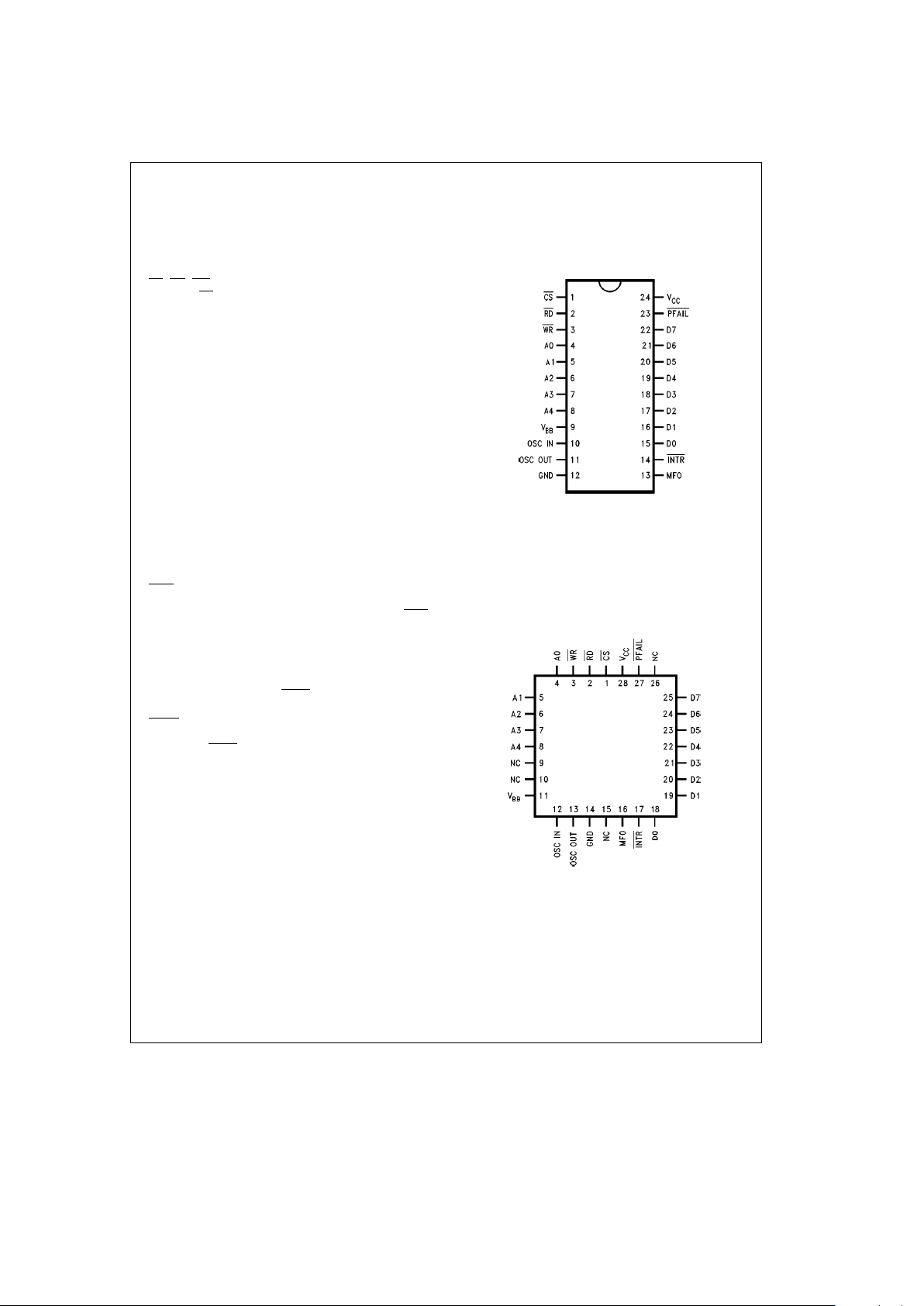
Connection Diagrams
In-Line Packages
TL/F/11417– 5
Top View
DIP: Order Number LV8572AN
See NS Package Number N24C
SOIC: Order Number LV8572AM
See NS Package Number M24B
Plastic Chip Carrier
TL/F/11417– 6
Top View
Order Number LV8572AV
See NS Package Number V28A
5
Page 6
Functional Description
The LV8572A contains a fast access real time clock, interrupt control logic, power fail detect logic, and CMOS RAM.
All functions of the RTC are controlled by a set of seven
registers. A simplified block diagram that shows the major
functional blocks is given in
Figure 1
.
The blocks are described in the following sections:
1. Real Time Clock
2. Oscillator Prescaler
3. Interrupt Logic
4. Power Failure Logic
5. Additional Supply Management
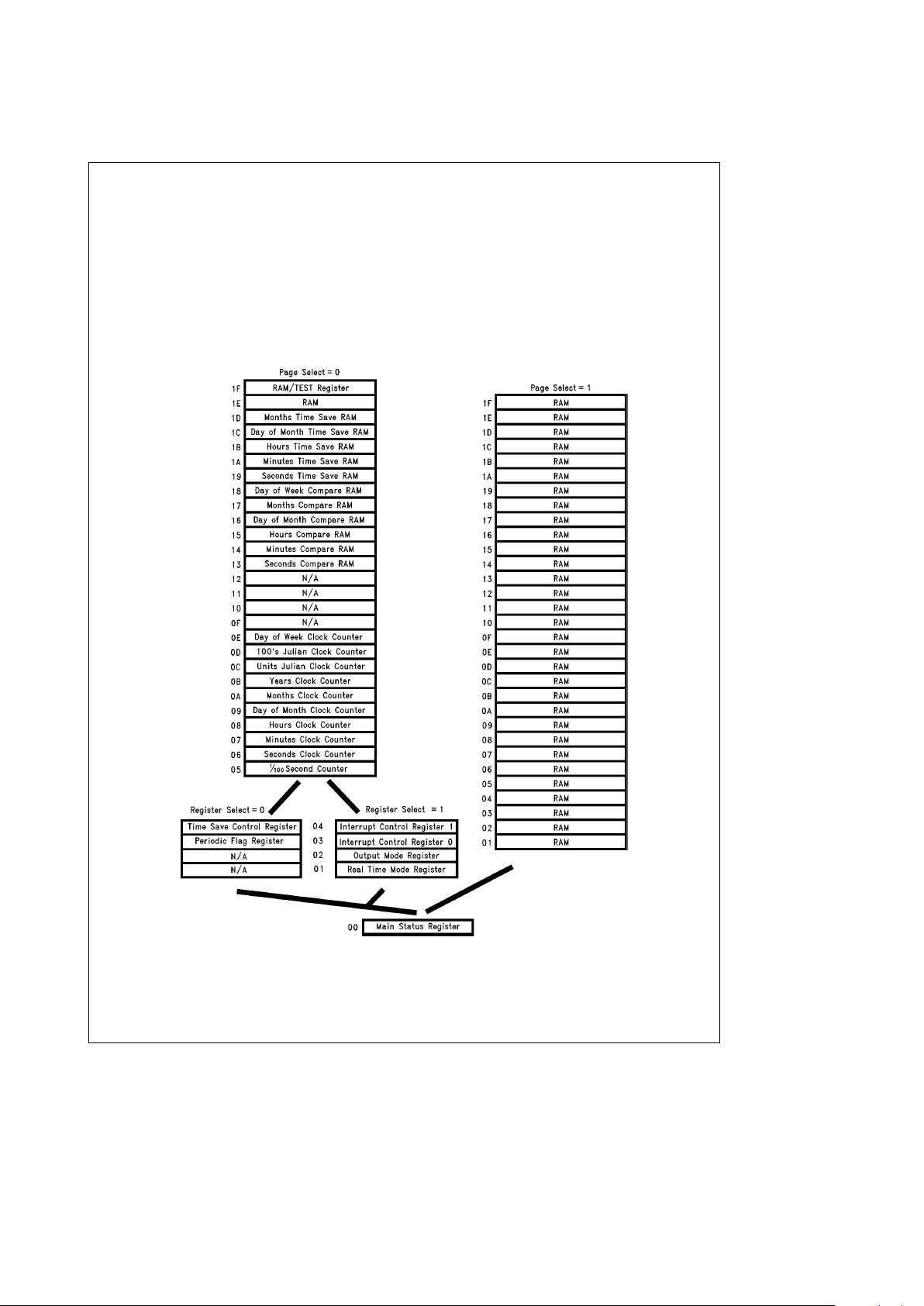
The memory map of the RTC is shown in the memory addressing table. The memory map consists of two 31 byte
pages with a main status register that is common to both
pages. A control bit in the Main Status Register is used to
select either page.
Figure 2
shows the basic concept.
Page 0 contains all the clock timer functions, while page 1
has scratch pad RAM. The control registers are split into
two separate blocks to allow page 1 to be used entirely as
scratch pad RAM. Again a control bit in the Main Status
Register is used to select either control register block.
TL/F/11417– 7
FIGURE 2. LV8572A Internal Memory Map
6
Page 7

Functional Description (Continued)
INITIAL POWER-ON of BOTH V
BB
and V
CC
VBBand VCCmay be applied in any sequence. In order for
the power fail circuitry to function correctly, whenever power
is off, the V
CC
pin must see a path to ground through a
maximum of 1 MX. The user should be aware that the control registers will contain random data. The first task to be
carried out in an initialization routine is to start the oscillator
by writing to the crystal select bits in the Real Time Mode
Register. If the LV8572A is configured for single supply
mode, an extra 50 mA may be consumed until the crystal
select bits are programmed. The user should also ensure
that the RTC is not in test mode (see register descriptions).
REAL TIME CLOCK FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
As shown in
Figure 2
, the clock has 10 bytes of counters,
which count from 1/100 of a second to years. Each counter
counts in BCD and is synchronously clocked. The count sequence of the individual byte counters within the clock is
shown later in Table VII. Note that the day of week, day of
month, day of year, and month counters all roll over to 1.
The hours counter in 12 hour mode rolls over to 1 and the
AM/PM bit toggles when the hours rolls over to 12
(AM
e
0, PMe1). The AM/PM bit is bit D7 in the hours
counter.
All other counters roll over to 0. Also note that the day of
year counter is 12 bits long and occupies two addresses.
Upon initial application of power the counters will contain
random information.
READING THE CLOCK: VALIDATED READ
Since clocking of the counter occurs asynchronously to
reading of the counter, it is possible to read the counter
while it is being incremented (rollover). This may result in an
incorrect time reading. Thus to ensure a correct reading of
the entire contents of the clock (or that part of interest), it
must be read without a clock rollover occurring. In general
this can be done by checking a rollover bit. On this chip the
periodic interrupt status bits can serve this function. The
following program steps can be used to accomplish this.
1. Initialize program for reading clock.
2. Dummy read of periodic status bit to clear it.
3. Read counter bytes and store.
4. Read rollover bit, and test it.
5. If rollover occured go to 3.
6. If no rollover, done.
To detect the rollover, individual periodic status bits can be
polled. The periodic bit chosen should be equal to the highest frequency counter register to be read. That is if only
SECONDS through HOURS counters are read, then the
SECONDS periodic bit should be used.
READING THE CLOCK: INTERRUPT DRIVEN
Enabling the periodic interrupt mask bits cause interrupts
just as the clock rolls over. Enabling the desired update rate
and providing an interrupt service routine that executes in
less than 10 ms enables clock reading without checking for
a rollover.
READING THE CLOCK: LATCHED READ
Another method to read the clock that does not require
checking the rollover bit is to write a one into the Time
Save Enable bit (D7) of the Time Save Control Register, and
then to write a zero. Writing a one into this bit will enable the
clock contents to be duplicated in the Time Save RAM.
Changing the bit from a one to a zero will freeze and store
the contents of the clock in Time Save RAM. The time then
can be read without concern for clock rollover, since internal logic takes care of synchronization of the clock. Because only the bits used by the clock counters will be
latched, the Time Save RAM should be cleared prior to use
to ensure that random data stored in the unused bits do not
confuse the host microprocessor. This bit can also provide
time save at power failure, see the Additional Supply Management Functions section. With the Time Save Enable bit
at a logical 0, the Time Save RAM may be used as RAM if
the latched read function is not necessary.
INITIALIZING AND WRITING TO THE
CALENDAR-CLOCK
Upon initial application of power to the RTC or when making
time corrections, the time must be written into the clock. To
correctly write the time to the counters, the clock would
normally be stopped by writing the Start/Stop
bit in the Real
Time Mode Register to a zero. This stops the clock from
counting and disables the carry circuitry. When initializing
the clock’s Real Time Mode Register, it is recommended
that first the various mode bits be written while maintaining
the Start/Stop
bit reset, and then writing to the register a
second time with the Start/Stop
bit set.
The above method is useful when the entire clock is being
corrected. If one location is being updated the clock need
not be stopped since this will reset the prescaler, and time
will be lost. An ideal example of this is correcting the hours
for daylight savings time. To write to the clock ‘‘on the fly’’
the best method is to wait for the 1/100 of a second periodic interrupt. Then wait an additional 16 ms, and then write
the data to the clock.
PRESCALER/OSCILLATOR FUNCTIONAL
DESCRIPTION
Feeding the counter chain is a programmable prescaler
which divides the crystal oscillator frequency to 32 kHz and
further to 100 Hz for the counter chain (see
Figure 3
). The
crystal frequency that can be selected are: 32 kHz, 32.768
kHz, 4.9152 MHz, and 4.194304 MHz.
TL/F/11417– 8
FIGURE 3. Programmable Clock Prescaler Block
7
Page 8

Functional Description (Continued)
The oscillator is programmed via the Real Time Mode Register to operate at various frequencies. The crystal oscillator
is designed to offer optimum performance at each frequency. Thus, at 32.768 kHz the oscillator is configured as a low
frequency and low power oscillator. At the higher frequencies the oscillator inverter is reconfigured. In addition to the
inverter, the oscillator feedback bias resistor is included on
chip, as shown in
Figure 4
. The oscillator input may be driven from an external source if desired. Refer to test mode
application note for details. The oscillator stability is enhanced through the use of an on chip regulated power supply.
The typical range of trimmer capacitor (as shown in Oscillator Circuit Diagram
Figure 4
, and in the typical application) at
the oscillator input pin is suggested only to allow accurate
tuning of the oscillator. This range is based on a typical
printed circuit board layout and may have to be changed
depending on the parasitic capacitance of the printed circuit
board or fixture being used. In all cases, the load capaci-
tance specified by the crystal manufacturer (nominal value
11 pF for the 32.768 crystal) is what determines proper oscillation. This load capcitance is the series combination of
capacitance on each side of the crystal (with respect to
ground).
TL/F/11417– 9
FIGURE 4. Oscillator Circuit Diagram
R
OUT
XTAL C
o
C
t
(Switched
Internally)
32/32.768 kHz 47 pF 2 pF–22 pF 150 kX to 350 kX
4.194304 MHz 68 pF 0 pF –80 pF 500X to 900X
4.9152 MHz 68 pF 29 pF – 49 pF 500X to 900X
INTERRUPT LOGIC FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The RTC has the ability to coordinate processor timing activities. To enhance this, an interrupt structure has been implemented which enables several types of events to cause
interrupts. Interrupts are controlled via two Control Registers in block 1 and two Status Registers in block 0. (See
Register Description for notes on paging and also
Figure 5
and Table I.)
The interrupts are enabled by writing a one to the appropriate bits in Interrupt Control Register 0 and/or 1.
TABLE I. Registers that are
Applicable to Interrupt Control
Register Name
Register Page
Address
Select Select
Main Status Register X X 00H
Periodic Flag Register 0 0 03H
Interrupt Control
1 0 03H
Register 0
Interrupt Control
1 0 04H
Register 1
Output Mode
1 0 02H
Register
The Interrupt Status Flag D0, in the Main Status Register,
indicates the state of INTR and MFO outputs. It is set when
either output becomes active and is cleared when all RTC
interrupts have been cleared and no further interrupts are
pending (i.e., both INTR and MFO are returned to their inactive state). This flag enables the RTC to be rapidly polled by
the mP to determine the source of an interrupt in a wiredÐ
OR interrupt system. (The Interrupt Status Flag provides a
true reflection of all conditions routed to the external pins.)
Status for the interrupts are provided by the Main Status
Register and the Periodic Flag Register. Bits D1 – D5 of the
Main Status Register are the main interrupt bits.
These register bits will be set when their associated timing
events occur. Enabled Alarm comparisons that occur will
set its Main Status Register bit to a one. However, an external interrupt will only be generated if the Alarm interrupt
enable bit is set (see
Figure 5
).
Disabling the periodic interrupts will mask the Main Status
Register periodic bit, but not the Periodic Flag Register bits.
The Power Fail Interrupt bit is set when the interrupt is enabled and a power fail event has occurred, and is not reset
until the power is restored. If all interrupt enable bits are 0
no interrupt will be asserted. However, status still can be
read from the Main Status Register in a polled fashion (see
Figure 5
).
To clear a flag in bits D2 and D3 of the Main Status Register
a 1 must be written back into the bit location that is to be
cleared. For the Periodic Flag Register reading the status
will reset all the periodic flags.
8
Page 9

Functional Description (Continued)
Interrupts Fall Into Three Categories:
1. The Alarm Compare Interrupt: Issued when the value in
the time compared RAM equals the counter.
2. The Periodic Interrupts: These are issued at every increment of the specific clock counter signal. Thus, an interrupt is issued every minute, second, etc. Each of these
interrupts occurs at the roll-over of the specific counter.
3. The Power Fail Interrupt: Issued upon recognition of a
power fail condition by the internal sensing logic. The
power failed condition is determined by the signal on the
PFAIL
pin. The internal power fail signal is gated with the
chip select signal to ensure that the power fail interrupt
does not lock the chip out during a read or write.
ALARM COMPARE INTERRUPT DESCRIPTON
The alarm/time comparison interrupt is a special interrupt
similar to an alarm clock wake up buzzer. This interrupt is
generated when the clock time is equal to a value programmed into the alarm compare registers. Up to six bytes
can be enabled to perform alarm time comparisons on the
counter chain. These six bytes, or some subset thereof,
would be loaded with the future time at which the interrupt
will occur. Next, the appropriate bits in the Interrupt Control
Register 1 are enabled or disabled (refer to detailed description of Interrupt Control Register 1). The RTC then compares these bytes with the clock time. When all the enabled
compare registers equal the clock time an alarm interrupt is
issued, but only if the alarm compare interrupt is enabled
can the interrupt be generated externally. Each alarm compare bit in the Control Register will enable a specific byte for
comparison to the clock. Disabling a compare byte is the
same as setting its associated counter comparator to an
‘‘always equal’’ state. For example, to generate an interrupt
at 3:15 AM of every day, load the hours compare with 0 3
(BCD), the minutes compare with 1 5 (BCD) and the faster
counters with 0 0 (BCD), and then disable all other compare
registers. So every day when the time rolls over from
3:14:59.99, an interrupt is issued. This bit may be reset by
writing a one to bit D3 in the Main Status Register at any
time after the alarm has been generated.
If time comparison for an individual byte counter is disabled,
that corresponding RAM location can then be used as general purpose storage.
PERIODIC INTERRUPTS DESCRIPTION
The Periodic Flag Register contains six flags which are set
by real-time generated ‘‘ticks’’ at various time intervals, see
Figure 5
. These flags constantly sense the periodic signals
and may be used whether or not interrupts are enabled.
These flags are cleared by any read or write operation performed on this register.
To generate periodic interrupts at the desired rate, the associated Periodic Interrupt Enable bit in Interrupt Control Register 0 must be set. Any combination of periodic interrupts
may be enabled to operate simultaneously. Enabled periodic interrupts will now affect the Periodic Interrupt Flag in the
Main Status Register.
When a periodic event occurs, the Periodic Interrupt Flag in
the Main Status Register is set, causing an interrupt to be
generated. The mP clears both flag and interrupt by writing a
‘‘1’’ to the Periodic Interrupt Flag. The individual flags in the
periodic Interrupt Flag Register do not require clearing to
cancel the interrupt.
If all periodic interrupts are disabled and a periodic interrupt
is left pending (i.e., the Periodic Interrupt Flag is still set), the
Periodic Interrupt Flag will still be required to be cleared to
cancel the pending interrupt.
POWER FAIL INTERRUPTS DESCRIPTION
The Power Fail Status Flag in the Main Status Register
monitors the state of the internal power fail signal. This flag
may be interrogated by the mP, but it cannot be cleared; it is
cleared automatically by the RTC when system power is
restored. To generate an interrupt when the power fails, the
Power Fail Interrupt Enable bit in Interrupt Control Register
1 is set. Although this interrupt may not be cleared, it may
be masked by clearing the Power Fail Interrupt Enable bit.
POWER FAILURE CIRCUITRY FUNCTIONAL
DESCRIPTION
Since the clock must be operated from a battery when the
main system supply has been turned off, the LV8572A provides circuitry to simplify design in battery backed systems.
This switches over to the back up supply, and isolates itself
from the host system.
Figure 6
shows a simplified block
diagram of this circuitry, which consists of three major sections; 1) power loss logic: 2) battery switch over logic: and 3)
isolation logic.
Detection of power loss occurs when PFAIL
is low. Debounce logic provides a 30 ms–63 ms debounce time, which
will prevent noise on the PFAIL
pin from being interpreted
as a system failure. After 30 ms–63 ms the debounce logic
times out and a signal is generated indicating that system
power is marginal and is failing. The Power Fail Interrupt will
then be generated.
9
Page 10

Functional Description (Continued)
TL/F/11417– 10
FIGURE 5. Interrupt Control Logic Overview
10
Page 11

Functional Description (Continued)
TL/F/11417– 11
FIGURE 6. System-Battery Switchover (Upper Left), Power Fail
and Lock-Out Circuits (Lower Right)
If chip select is low when a power failure is detected, a
safety circuit will ensure that if a read or write is held active
continuously for greater than 30 ms after the power fail signal is asserted, the lock-out will be forced. If a lock-out delay
is enabled, the LV8572A will remain active for 480 ms after
power fail is detected. This will enable the mP to perform
last minute bookkeeping before total system collapse.
When the host CPU is finished accessing the RTC it may
force the bus lock-out before 480 ms has elapsed by resetting the delay enable bit.
The battery switch over circuitry is completely independent
of the PFAIL
pin. A separate circuit compares VCCto the
V
BB
voltage. As the main supply fails, the RTC will continue
to operate from the V
CC
pin until VCCfalls below the V
BB
voltage. At this time, the battery supply is switched in, VCCis
disconnected, and the device is now in the standby mode. If
indeterminate operation of the battery switch over circuit is
to be avoided, then the voltage at the V
CC
pin must not be
allowed to equal the voltage at the V
BB
pin.
After the generation of a lock-out signal, and eventual
switch in of the battery supply, the pins of the RTC will be
configured as shown in Table II. Outputs that have a pull-up
resistor should be connected to a voltage no greater than
V
BB
.
TABLE II. Pin Isolation during a Power Failure
Pin
PFAIL
e
Standby Mode
Logic 0 V
BB
l
V
CC
CS,RD,WR Locked Out Locked Out
A0–A4 Locked Out Locked Out
D0–D7 Locked Out Locked Out
Oscillator Not Isolated Not Isolated
PFAIL
Not Isolated Not Isolated
INTR, MFO Not Isolated Open Drain
The Interrupt Power Fail Operation bit in the Real-Time
Mode Register determine whether or not the interrupts will
continue to function after a power fail event.
As power returns to the system, the battery switch over circuit will switch back to V
CC
power as soon as it becomes
greater than the battery voltage. The chip will remain in the
locked out state as long as PFAIL
e
0. When PFAILe1
11
Page 12

Functional Description (Continued)
the chip is unlocked, but only after another 30 ms min
x
63 ms max debounce time. The system designer must ensure that his system is stable when power has returned.
The power fail circuitry contains active linear circuitry that
draws supply current from V
CC
. In some cases this may be
undesirable, so this circuit can be disabled by masking the
power fail interrupt. The power fail input can perform all
lock-out functions previously mentioned, except that no external interrupt will be issued. Note that the linear power fail
circuitry is switched off automatically when using V
BB
in
standby mode.
LOW BATTERY, INITIAL POWER ON DETECT, AND
POWER FAIL TIME SAVE
There are three other functions provided on the LV8572A to
ease power supply control. These are an initial Power On
detect circuit, which also can be used as a time keeping
failure detect, a low battery detect circuit, and a time save
on power failure.
On initial power up the Oscillator Fail Flag will be set to a
one and the real time clock start bit reset to a zero. This
indicates that an oscillator fail event has occurred, and time
keeping has failed.
The Oscillator Fail flag will not be reset until the real-time
clock is started. This allows the system to discriminate between an initial power-up and recovery from a power failure.
If the battery backed mode is selected, then bit D6 of the
Periodic Flag Register must be written low. This will not affect the contents of the Oscillator Fail Flag.
Another status bit is the low battery detect. This bit is set
only when the clock is operating under the V
CC
pin, and
when the battery voltage is determined to be less than 2.1V
(typical). When the power fail interrupt enable bit is low, it
disables the power fail circuit and will also shut off the low
battery voltage detection circuit as well.
To relieve CPU overhead for saving time upon power failure,
the Time Save Enable bit is provided to do this automatically. (See also Reading the Clock: Latched Read.) The Time
Save Enable bit, when set, causes the Time Save RAM to
follow the contents of the clock. This bit can be reset by
software, but if set before a power failure occurs, it will automatically be reset when the clock switches to the battery
supply (not when a power failure is detected by the PFAIL
pin). Thus, writing a one to the Time Save bit enables both a
software write or power fail write.
SINGLE POWER SUPPLY APPLICATIONS
The LV8572A can be used in a single power supply application. To achieve this, the V
BB
pin must be connected to
ground, and the power connected to V
CC
and PFAIL pins.
The Oscillator Failed/Single Supply bit in the Periodic Flag
Register should be set to a logic 1, which will disable the
oscillator battery reference circuit. The power fail interrupt
should also be disabled. This will turn off the linear power
fail detection circuits, and will eliminate any quiescent power
drawn through these circuits. Until the crystal select bits are
initialized, the LV8572A may consume about 50 mA due to
arbitrary oscillator selection at power on.
(This extra 50 mA is not consumed if the battery backed
mode is selected).
DETAILED REGISTER DESCRIPTION
There are 5 external address bits: Thus, the host microprocessor has access to 28 locations at one time. An internal
switching scheme provides a total of 61 locations.
This complete address space is organized into two pages.
Page 0 contains two blocks of control registers, timers, real
time clock counters, and special purpose RAM, while page
1 contains general purpose RAM. Using two blocks enables
the 9 control registers to be mapped into 5 locations. The
only register that does not get switched is the Main Status
Register. It contains the page select bit and the register
select bit as well as status information.
A memory map is shown in
Figure 2
and register addressing
in Table III. They show the name, address and page locations for the LV8572A.
TABLE III. Register/Counter/RAM
Addressing for LV8572A
A0-4
PS RS
Description
(Note 1) (Note 2)
CONTROL REGISTERS
00 X X Main Status Register
03 0 0 Periodic Flag Register
04 0 0 Time Save Control Register
01 0 1 Real Time Mode Register
02 0 1 Output Mode Register
03 0 1 Interrupt Control Register 0
04 0 1 Interrupt Control Register 1
COUNTERS (CLOCK CALENDAR)
05 0 X 1/100, 1/10 Seconds (0 –99)
06 0 X Seconds (0–59)
07 0 X Minutes (0 –59)
08 0 X Hours (1– 12, 0– 23)
09 0 X Days of
Month (1 – 28/29/30/31)
0A 0 X Months (1– 12)
0B 0 X Years (0– 99)
0C 0 X Julian Date (LSB) (1– 99)
0D 0 X Julian Date (0 –3)
0E 0 X Day of Week (1 –7)
TIME COMPARE RAM
13 0 X Sec Compare RAM (0 –59)
14 0 X Min Compare RAM (0– 59)
15 0 X Hours Compare
RAM (1 –12, 0 –23)
16 0 X DOM Compare
RAM (1– 28/29/30/31)
17 0 X Months Compare
RAM (1 –12)
18 0 X DOW Compare RAM (1 –7)
TIME SAVE RAM
19 0 X Seconds Time Save RAM
1A 0 X Minutes Time Save RAM
1B 0 X Hours Time Save RAM
1C 0 X Day of Month Time Save RAM
1D 0 X Months Time Save RAM
1E 0 1 RAM
1F 0 X RAM/Test Mode Register
01– 1F 1 X 2nd Page General Purpose RAM
1 PSÐPage Select (Bit D7 of Main Status Register)
2 RSÐRegister Select (Bit D6 of Main Status Register)
12
Page 13

Functional Description (Continued)
MAIN STATUS REGISTER
TL/F/11417– 12
The Main Status Register is always located at address 0
regardless of the register block or the page selected.
D0: This read only bit is a general interrupt status bit that is
taken directly from the interrupt pins. The bit is a one when
an interrupt is pending on either the INTR pin or the MFO
pin (when configured as an interrupt). This is unlike D3
which can be set by an internal event but may not cause an
interrupt. This bit is reset when the interrupt status bits in the
Main Status Register are cleared.
D1–D3: These three bits of the Main Status Register are the
main interrupt status bits. Any bit may be a one when any of
the interrupts are pending. Once an interrupt is asserted the
mP will read this register to determine the cause. These
interrupt status bits are not reset when read. Except for D1,
to reset an interrupt a one is written back to the corresponding bit that is being tested. D1 is reset whenever the PFAIL
pinelogic 1. This prevents loss of interrupt status when
reading the register in a polled mode. D1 and D3 are set
regardless of whether these interrupts are masked or not by
bits D6 and D7 of Interrupt Control Registers 0 and 1.
D4–D5: General purpose RAM bits.
D6 and D7: These bits are Read/Write bits that control
which register block or RAM page is to be selected. Bit D6
controls the register block to be accessed (see memory
map). The memory map of the clock is further divided into
two memory pages. One page is the registers, clock and
timers, and the second page contains 31 bytes of general
purpose RAM. The page selection is determined by bit D7.
PERIODIC FLAG REGISTER
TL/F/11417– 13
The Periodic Flag Register has the same bit for bit correspondence as Interrupt Control Register 0 except for D6
and D7. For normal operation (i.e., not a single supply application) this register must be written to on initial power up or
after an oscillator fail event. D0– D5 are read only bits, D6
and D7 are read/write.
D0–D5: These bits are set by the real time rollover events:
(Time Change
e
1). The bits are reset when the register is
read and can be used as selective data change flags.
D6: This bit performs a dual function. When this bit is read, a
one indicates that an oscillator failure has occurred and the
time information may have been lost. Some of the ways an
oscillator failure might be caused are: failure of the crystal,
shorting OSC IN or OSC OUT to GND or V
CC
, removal of
crystal, removal of battery when in the battery backed mode
(when a ‘‘0’’ is written to D6), lowering the voltage at the
V
BB
pin to a value less than 2.2V when in the battery
backed mode. Bit D6 is automatically set to 1 on initial power-up or an oscillator fail event. The oscillator fail flag is
reset by writing a one to the clock start/stop bit in the Real
Time Mode Register, with the crystal oscillating.
When D6 is written to, it defines whether the TCP is being
used in battery backed (normal) or in a single supply mode
application. When set to a one this bit configures the TCP
for single power supply applications. This bit is automatically
set on initial power-up or an oscillator fail event. When set,
D6 disables the oscillator reference circuit. The result is that
the oscillator is referenced to V
CC
. When a zero is written to
D6 the oscillator reference is enabled, thus the oscillator is
referenced to V
BB
. This allows operation in standard battery
standby applications.
At initial power on, if the LV8572A is going to be programmed for battery backed mode, the V
BB
pin should be
connected to a potential in the range of 2.2V to V
CC
b
0.4V.
For single supply mode operation, the V
BB
pin should be
connected to GND and the PFAIL
pin connected to VCC.
D7: Writing a one to this bit enables the test mode register
at location 1F (see Table III). This bit should be forced to
zero during initialization for normal operation. If the test
mode has been entered, clear the test mode register before
leaving test mode. (See separate test mode application
note for further details.)
TIME SAVE CONTROL REGISTER
TL/F/11417– 14
D0–D4: General purpose RAM bits.
13
Page 14

Functional Description (Continued)
D5: The Delay Enable bit is used when a power fail occurs.
If this bit is set, a 480 ms delay is generated internally before
the mP interface is locked out. This will enable the mPto
access the registers for up to 480 ms after it receives a
power fail interrupt. After a power failure is detected but
prior to the 480 ms delay timing out, the host mP may force
immediate lock out by resetting the Delay Enable bit. Note if
this bit is a 0 when power fails then after a delay of 30 ms
min/63 ms max the mP cannot read the chip.
D6: This read only bit is set and reset by the voltage at the
V
BB
pin. It can be used by the mP to determine whether the
battery voltage at the V
BB
pin is getting too low. A compara-
tor monitors the battery and when the voltage is lower than
2.1V (typical) this bit is set. The power fail interrupt must be
enabled to check for a low battery voltage.
D7: Time Save Enable bit controls the loading of real-timeclock data into the Time Save RAM. When a one is written
to this bit the Time Save RAM will follow the corresponding
clock registers, and when a zero is written to this bit the time
in the Time Save RAM is frozen. This eliminates any synchronization problems when reading the clock, thus negating the need to check for a counter rollover during a read
cycle.
This bit must be set to a one prior to power failing to enable
the Time Save feature. When the power fails this bit is automatically reset and the time is saved in the Time Save RAM.
REAL TIME MODE REGISTER
TL/F/11417– 15
D0–D1: These are the leap year counter bits. These bits are
written to set the number of years from the previous leap
year. The leap year counter increments on December 31st
and it internally enables the February 29th counter state.
This method of setting the leap year allows leap year to
occur whenever the user wishes to, thus providing flexibility
in implementing Japanese leap year function.
LY1 LY0
Leap Year
Counter
0 0 Leap Year Current Year
0 1 Leap Year Last Year
1 0 Leap Year 2 Years Ago
1 1 Leap Year 3 Years Ago
D2: The count mode for the hours counter can be set to
either 24 hour mode or 12 hour mode with AM/PM indicator.
A one will place the clock in 12 hour mode.
D3: This bit is the master Start/Stop
bit for the clock. When
a one is written to this bit the real time counter’s prescaler
and counter chain are enabled. When this bit is reset to zero
the contents of the real time counter is stopped and the
prescaler is cleared. When the RTC is initially powered up
this bit will be held at a logic 0 until the oscillator starts
functioning correctly after which this bit may be modified. If
an oscillator fail event occurs, this bit will be reset to logic 0.
D4: This bit controls the operation of the interrupt output in
standby mode. If set to a one it allows Alarm, Periodic, and
Power Fail interrupts to be functional in standby mode. Note
that the MFO pin is configured as open drain in standby
mode.
If bit D4 is set to a zero then interrupt control register and
the periodic interrupt flag will be reset when the RTC enters
the standby mode (V
BB
l
VCC). They will have to be re-
configured when system (V
CC
) power is restored.
D5: General purpose RAM.
D6 and D7: These two bits select the crystal clock frequen-
cy as per the following table:
XT1 XT0
Crystal
Frequency
0 0 32.768 kHz
0 1 4.194304 MHz
1 0 4.9152 MHz
1 1 32.000 kHz
All bits are Read/Write, and any mode written into this register can be determined by reading the register. On initial
power up these bits are random.
OUTPUT MODE REGISTER
TL/F/11417– 16
D0–D6: General Purpose RAM
14
Page 15

Functional Description (Continued)
D7: This bit is used to program the signal appearing at the
MFO output, as follows:
D7 MFO Output Signal
0 Power Fail Interrupt
1 Buffered Crystal Oscillator
INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTER 0
TL/F/11417– 17
D0–D5: These bits are used to enable one of the selected
periodic interrupts by writing a one into the appropriate bit.
These interrupts are issued at the rollover of the clock. For
example, the minutes interrupt will be issued whenever the
minutes counter increments. In all likelihood the interrupt
will be enabled asynchronously with the real time change.
Therefore, the very first interrupt will occur in less than the
periodic time chosen, but after the first interrupt all subsequent interrupts will be spaced correctly. These interrupts
are useful when minute, second, real time reading, or task
switching is required. When all six bits are written to a 0 this
disables periodic interrupts from the Main Status Register
and the interrupt pin.
D6 and D7: General Purpose RAM.
INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTER 1
TL/F/11417– 18
D0–D5: Each of these bits are enable bits which will enable
a comparison between an individual clock counter and its
associated compare RAM. If any bit is a zero then that
clock-RAM comparator is set to the ‘‘always equal’’ state
and the associated TIME COMPARE RAM byte can be used
as general purpose RAM. However, to ensure that an alarm
interrupt is not generated at bit D3 of the Main Status Register, all bits must be written to a logic zero.
D6: In order to generate an external alarm compare interrupt to the mP from bit D3 of the Main Status Register, this
bit must be written to a logic 1. If battery backed mode is
selected then this bit is controlled by D4 of the Real Time
Mode Register.
D7: The MSB of this register is the enable bit for the Power
Fail Interrupt. When this bit is set to a one an interrupt will
be generated to the mP when V
BB
l
VCC. If battery backed
mode is selected then this bit is controlled by D4 of the Real
Time Mode Register.
This bit also enables the low battery detection analog circuitry.
15
Page 16

Control and Status Register Address Bit Map
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
1. Reset by
Main Status Register PS
e
XRSeX ADDRESSe00H
writing
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
1
R/W
1
R
2
R
3
1 to bit.
Page Register
RAM RAM
Alarm Periodic Power Fail Interrupt
2. Set/reset by
Select Select Interrupt Interrupt Interrupt Status
voltage at
PFAIL pin.
3. Reset when
all pending
interrupts
are removed.
Periodic Flag Register PS
e
0RS
e
0 Addresse03H
4. Read Osc fail
R/W R/W
4
R
5
R
5
R
5
R
5
R
5
R
5
Write 0 Batt-
Test Osc. Fail/ 1 ms 10 ms 100 ms Seconds 10 Second Minute
Backed Mode
Mode Single Supply Flag Flag Flag Flag Flag Flag
Write 1 Single
Supply Mode
5. Reset by
positive edge
of read.
Time Save Control Register PS
e
0RS
e
0 Addresse04H
R/W R
6
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Time Save Low Battery
Power Fail 6. Set and reset
by V
BB
Enable Flag
Delay RAM RAM RAM RAM RAM
voltage.
Enable
Real Time Mode Register PSe0RS
e
1 Addresse01H
Crystal Crystal
RAM
Interrupt EN Clock 12/24 Hr. Leap Year Leap Year
All Bits R/W
Freq. XT1 Freq. XT0 on Back-Up Start/Stop
Mode MSB LSB
Output Mode Register PSe0RS
e
1 Addresse02H
MFO as
RAM RAM RAM RAM RAM RAM RAM All Bits R/W
Crystal
Interrupt Control Register 0 PSe0RS
e
1 Addresse03H
1 ms 10 ms 100 ms Seconds 10 Second Minute
RAM RAM Interrupt Interrupt Interrupt Interrupt Interrupt Interrupt All Bits R/W
Enable Enable Enable Enable Enable Enable
Interrupt Control Register 1 PSe0RS
e
1 Addresse04H
Power Fail Alarm DOW Month DOM Hours Minute Second
Interrupt Interrupt Interrupt Interrupt Interrupt Interrupt Interrupt Interrupt All Bits R/W
Enable Enable Enable Enable Enable Enable Enable Enable
16
Page 17

Application Hints
Suggested Initialization Procedure for LV8572A in Battery
Backed Applications that use the V
BB
Pin.
1. Enter the test mode by writinga1tobitD7inthePeriodic Flag Register.
2. Write zero to the RAM/TEST mode Register located in
page 0, address HEX 1F.
3. Leave the test mode by writinga0tobitD7inthePeriodic Flag Register. Steps 1,2,3 guarantee that if the test
mode had been entered during power on (due to random pulses from the system), all test mode conditions
are cleared. Most important is that the OSC Fail Disable
bit is cleared. Refer to AN-589 for more information on
test mode operation.
4. After power on (V
CC
and VBBpowered), select the correct crystal frequency bits (D7, D6 in the Real Time
Mode Register) as shown in Table IV.
TABLE IV
Frequency D7 D6
32.768 kHz 0 0
4.194304 MHz 0 1
4.9152 MHz 1 0
32.0 kHz 1 1
5. Enter a software loop that does the following:
Set a 3 second(approx) software counter. The crystal
oscillator may take 1 second to start.
5.1 Writea1tobitD3intheReal Time Mode Register (try
to start the clock). Make sure the crystal select bits re-
main the same as in step 1. Under normal operation, this
bit can be set only if the oscillator is running. During the
software loop, RAM, real time counters, output configuration, interrupt control and timer functions may be initialized.
6. Test bit D6 in the Periodic Flag Register:
IFa1,go to 5.1. If this bit remains a 1 after 3 seconds,
then abort and check hardware. The crystal may be defective or not installed. There may be a short at OSC IN
or OSC OUT to V
CC
or GND, or to some impedance that
is less than 10 MX.
IFa0,then the oscillator is running, go to step 7.
7. Writea0tobitD6inthePeriodic Flag Register. This
action puts the clock chip in the battery backed mode.
This mode can be entered only if the OSC fail flag (bit
D6 of the Periodic Flag Register) is a 0. Reminder, Bit
D6 is a dual function bit. When read, D6 returns oscillator status. When written, D6 causes either the Battery
Backed Mode, or the Single Supply Mode of operation.
The only method to ensure the chip is in the battery
backed mode is to measure the waveform at the OSC
OUT pin. If the battery backed mode was selected successfully, then the peak to peak waveform at OSC OUT
is referenced to the battery voltage. If not in battery
backed mode, the waveform is referenced to V
CC
. The
measurement should be made with a high impedance
low capacitance probe (10 MX, 10 pF oscilloscope
probe or better). Typical peak to peak swings are within
0.6V of V
CC
and ground respectively.
8. Writea1tobitD7ofInterrupt Control Register 1. This
action enables the PFAIL pin and associated circuitry.
9. Initialize the rest of the chip as needed.
Typical Application
TL/F/11417– 19
*These components may be necessary to meet UL requirements
for lithium batteries. Consult battery manufacturer.
17
Page 18

Typical Performance Characteristics
Operating Current vs
Supply Voltage
(Single Supply Mode
F
OSC
e
32.768 kHz)
TL/F/11417– 20
Operating Current vs
Supply Voltage
(Battery Backed Mode
F
OSC
e
32.768 kHz,
V
BB
e
2.5V)
TL/F/11417– 21
Standby Current vs Power
Supply Voltage
(F
OSC
e
32.768 kHz)
TL/F/11417– 22
Standby Current vs Power
Supply Voltage
F
OSC
e
4.194304 MHz
TL/F/11417– 23
18
Page 19

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters)
Molded Small Outline Package (M)
Order Number LV8572AM
NS Package Number M24B
Molded Dual-In-Line Package (N)
Order Number LV8572AN
NS Package Number N24C
19
Page 20

LV8572A Real Time Clock (RTC)
Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) (Continued)
Plastic Chip Carrier Package (V)
Order Number LV8572AV
NS Package Number V28A
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT OF NATIONAL
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or 2. A critical component is any component of a life
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant support device or system whose failure to perform can
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and whose be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life
failure to perform, when properly used in accordance support device or system, or to affect its safety or
with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can effectiveness.
be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury
to the user.
National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor
Corporation Europe Hong Kong Ltd. Japan Ltd.
1111 West Bardin Road Fax: (
a
49) 0-180-530 85 86 13th Floor, Straight Block, Tel: 81-043-299-2309
Arlington, TX 76017 Email: cnjwge@tevm2.nsc.com Ocean Centre, 5 Canton Rd. Fax: 81-043-299-2408
Tel: 1(800) 272-9959 Deutsch Tel: (
a
49) 0-180-530 85 85 Tsimshatsui, Kowloon
Fax: 1(800) 737-7018 English Tel: (
a
49) 0-180-532 78 32 Hong Kong
Fran3ais Tel: (
a
49) 0-180-532 93 58 Tel: (852) 2737-1600
Italiano Tel: (
a
49) 0-180-534 16 80 Fax: (852) 2736-9960
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
 Loading...
Loading...