Page 1
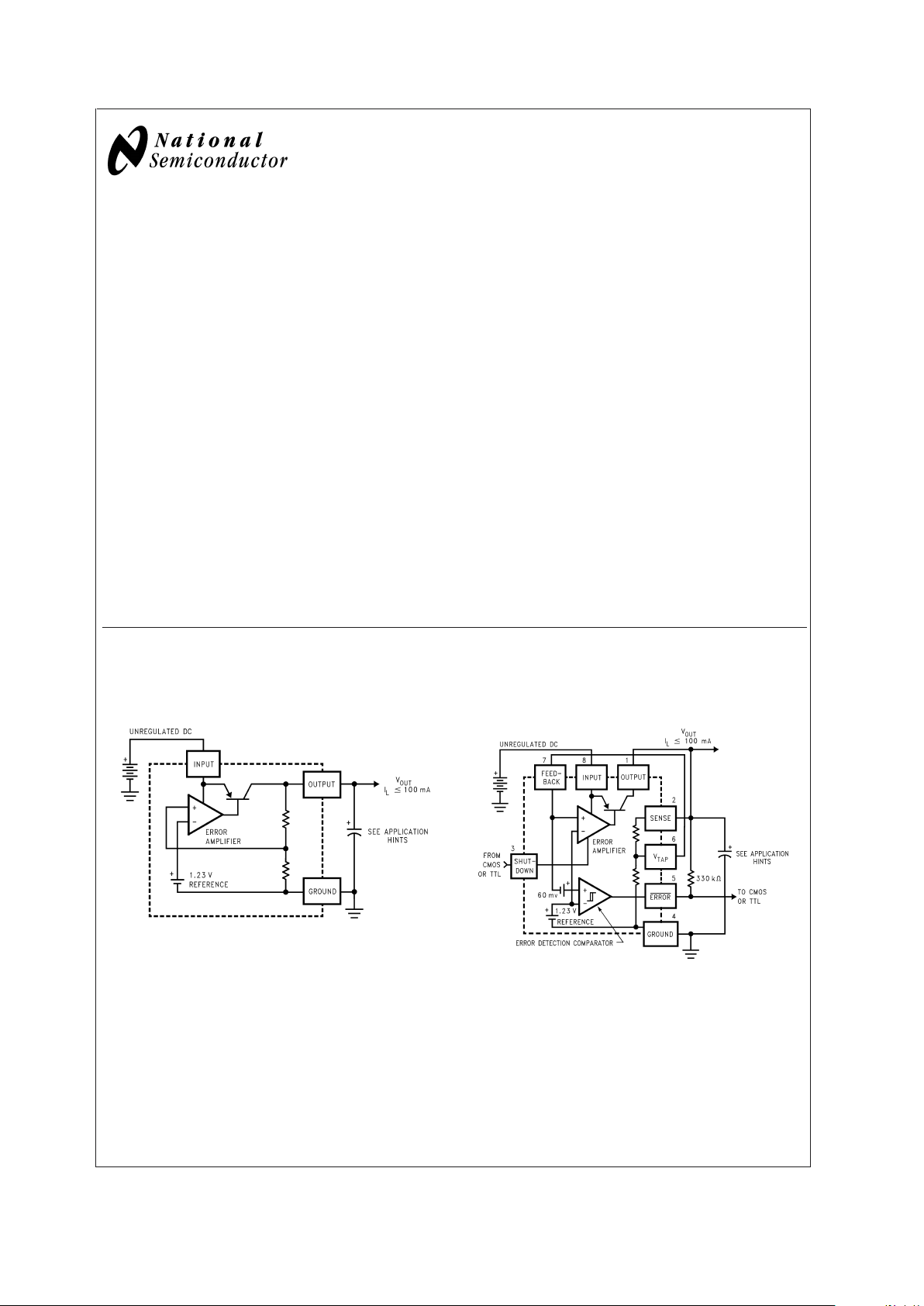
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
Adjustable Micropower Voltage Regulators
General Description
The LP4950C and LP4951C are micropower voltage regulators with very low quiescent current (75µA typ.) and very
low dropout voltage (typ. 40mV at light loads and 380mV at
100mA). They are ideally suited for use in battery-powered
systems. Furthermore, the quiescent current of the
LP4950C/LP4951C increases only slightly in dropout, prolonging battery life.
The LP4950C in the popular 3-pin TO-92 package is pin
compatible with older 5V regulators. The 8-lead LP4951C is
available in a plastic surface mount package and offers
additional system functions.
One such feature is an error flag output which warns of a low
output voltage, often due to falling batteries on the input. It
may be used for a power-on reset. A second feature is the
logic-compatible shutdown input which enables the regulator
to be switched on and off. Also, the part may be pin-strapped
for a 5V output or programmed from 1.24V to 29V with an
external pair of resistors.
Careful design of the LP4950C/LP4951C has minimized all
contributions to the error budget. This includes a tight initial
tolerance (.5% typ.), extremely good load and line regulation
(.05% typ.) and a very low output voltage temperature coefficient, making the part useful as a low-power voltage reference.
Features
n High accuracy 5V guaranteed 100mA output
n Extremely low quiescent current
n Low dropout voltage
n Extremely tight load and line regulation
n Very low temperature coefficient
n Use as Regulator or Reference
n Needs only 1µF for stability
n Current and Thermal Limiting
LP4951C versions only
n Error flag warns of output dropout
n Logic-controlled electronic shutdown
n Output programmable from 1.24 to 29V
Block Diagram and Typical
Applications
LP4950C LP4951C
20052825
20052801
September 2002
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C Adjustable Micropower Voltage Regulators
© 2002 National Semiconductor Corporation DS200528 www.national.com
Page 2
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Input Supply Voltage −0.3 to +30V
SHUTDOWN Input Voltage,
Error Comparator Output
Voltage, (Note 9)
−0.3 to +30V
FEEDBACK Input Voltage −1.5 to +30V
(Note 9) (Note 10)
Power Dissipation Internally Limited
Junction Temperature (T
J
) +150˚C
Ambient Storage Temperature −65˚ to +150˚C
Soldering Dwell Time, Temperature
Wave
Infrared
Vapor Phase
4 seconds, 260˚C
10 seconds, 240˚C
75 seconds, 219˚C
ESD TBD
Operating Ratings (Note 1)
Maximum Input Supply Voltage 30V
Junction Temperature Range
(Note 8)
LP4950C, LP4951C −40˚C to 125˚C
Electrical Characteristics (Note 2)
Parameter
Conditions
(Note 2)
LP4950CZ
Units
LP4951CM
Tested Design
Typ Limit Limit
(Note 3) (Note 4)
Output Voltage T
J
= 25˚C 5.0 5.1 V max
4.9 V min
−25˚C ≤ T
J
≤ 85˚C 5.15 V max
4.85 V min
Full Operating 5.2 V max
Temperature Range 4.8 V min
Output Voltage 100 µA ≤ I
L
≤ 100 mA 5.24 V max
T
J
≤ T
JMAX
4.76 V min
Output Voltage
Temperature Coefficient
(Note 12) 150 ppm/˚C
Line Regulation
(Note 14)
6V ≤ V
IN
≤ 30V (Note 15) 0.04 0.2 % max
0.4 % max
Load Regulation
(Note 14)
100µA ≤ I
L
≤ 100mA 0.1 0.2 % max
0.3 % max
Dropout Voltage
(Note 5)
I
L
= 100µA 50 80 mV max
150 mV max
I
L
= 100mA 380 450 mV max
600 mV max
Ground Current I
L
= 100µA 75 150 µA max
170 µA max
I
L
= 100mA 8 15 mA max
19 mA max
Dropout Ground Current V
IN
= 4.5V 110 200 µA max
I
L
= 100µA 230 µA max
Current Limit V
OUT
= 0 160 200 mA max
220 mA max
Thermal Regulation (Note 13) 0.05 0.2 %/W max
Output Noise, C
L
= 1µF 430 µV rms
10 Hz to 100 kHz C
L
= 200µF 160 µV rms
C
L
= 3.3µF (Bypass = 0.01µF
Pins 7 to 1 (LP4951C)
100 µV rms
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com 2
Page 3
Electrical Characteristics
LP4951C
Parameter Conditions (Note 2) Typ Tested
Limit (Note
3)
Desgin
Limit (Note
4)
Units
8-PIN VERSIONS ONLY
Reference Voltage 1.235 1.285 V max
1.295 V max
1.185 V min
1.165 Vmin
Reference Voltage (Note 7) 1.335 V max
1.135 V min
Feedback Pin Bias
Current
20 40 nA max
60 nA max
Reference Voltage
Temperature Coefficient
(Note 12) 50 ppm/˚C
Feedback Pin Bias
Current Temperature
Coefficient
0.1 nA/˚C
Error Comparator
Output Leakage Current VOH = 30V 0.01 1 µA max
2 µA max
Output Low Voltage V
IN
= 4.5V
I
OL
= 400µA
150 250 mV max
400 mV max
Upper Threshold Voltage (Note 4) 60 40 mV min
25 mV min
Lower Threshold Voltage (Note 6) 75 95 mV max
140 mV max
Hysteresis (Note 6) 15 mV
Shutdown Input
Input Logic Voltage 1.3 V
Low (Regulator ON) 0.7 V max
High (Regulator OFF) 2.0 V min
Shutdown Pin Input
Current
V
SHUTDOWN
= 2.4V 30 50 µA max
100 µA max
V
SHUTDOWN
= 30V 450 600 µA max
750 µA max
Regulator Output Current
in Shutdown
(Note 11) 3 10 µA max
20 µA max
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings are limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings are conditions under which operation of the device
is guaranteed. Operating Ratings do not imply guaranteed performance limits. For guaranteed performance limits and associated test conditions, see the Electrical
Characteristics tables.
Note 2: Unless otherwise specified all limits guaranteed for V
IN
=6V,IL= 100µA and CL= 1µF. Limits appearing in boldface type apply over the entire junction
temperature range for operation. Limits appearing in normal type apply for T
A=TJ
= 25˚C. Additional conditions for the 8-pin versions are FEEDBACK tied to V
TAP
,
OUTPUT tied to SENSE (V
OUT
= 5V), and V
SHUTDOWN
≤ 0.8V.
Note 3: Guaranteed and 100% production tested.
Note 4: Guaranteed but not 100% production tested. These limits are not used to calculate outgoing AQL levels.
Note 5: Dropout Voltage is defined as the input to output differential at which the output voltage drops 100 mV below its nominal value measured at 1V differential.
At very low values of programmed output voltage, the minimum input supply voltage of 2V (2.3V over temperature) must be taken into account.
Note 6: Comparator thresholds are expressed in terms of a voltage differential at the Feedback terminal below the nominal reference voltage measured at V
IN
=
6V. To express these thresholds in terms of output voltage change, multiply by the error amplifier gain = V
OUT/VREF
= (R1 + R2)/R2.For example, at a programmed
output voltage of 5V, the Error output is guaranteed to go low when the output drops by 95 mV x 5V/1.235V = 384 mV.Thresholds remain constant as a percent of
V
OUT
as V
OUT
is varied, with the dropout warning occurring at typically 5% below nominal, 7.5% guaranteed.
Note 7: V
REF
≤ V
OUT
≤ (VIN− 1V), 2.3V ≤ VIN≤ 30V, 100µA ≤ IL≤ 100mA, TJ≤ T
JMAX
.
Note 8: The junction-to-ambient thermal resistances are as follows: 180˚C/W and 160˚C/W for the TO-92 package with 0.40 inch and 0.25 inch leads to the printed
circuit board (PCB) respectively, 160˚C/W for the molded plastic SOP (M). The above thermal resistances for the M package apply when the package is soldered
directly to the PCB.
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com3
Page 4
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Note 9: May exceed input supply voltage.
Note 10: When used in dual-supply systems where the output terminal sees loads returned to a negative supply, the output voltage should be diode-clamped to
ground.
Note 11: V
SHUTDOWN
≥ 2V, VIN≤ 30V, V
OUT
= 0, Feedback pin tied to V
TAP
.
Note 12: Output or reference voltage temperature coefficient is defined as the worst case voltage change divided by the total temperature range.
Note 13: Thermal regulation is defined as the change in output voltage at a time T after a change in power dissipation is applied, excluding load or line regulation
effects. Specifications are for a 50 mA load pulse at V
IN
= 30V (1.25W pulse) for T = 10ms.
Note 14: Regulation is measured at constant junction temperature, using pulse testing with a low duty cycle. Changes in output voltage due to heating effects are
covered under the specification for thermal regulation.
Note 15: Line regulation for the LP4951C is tested at 150˚C for I
L
= 1 mA. For IL= 100µA and TJ= 125˚C, line regulation is guaranteed by design to 0.2%. See
Typical Performance Characteristics for line regulation versus temperature and load current.
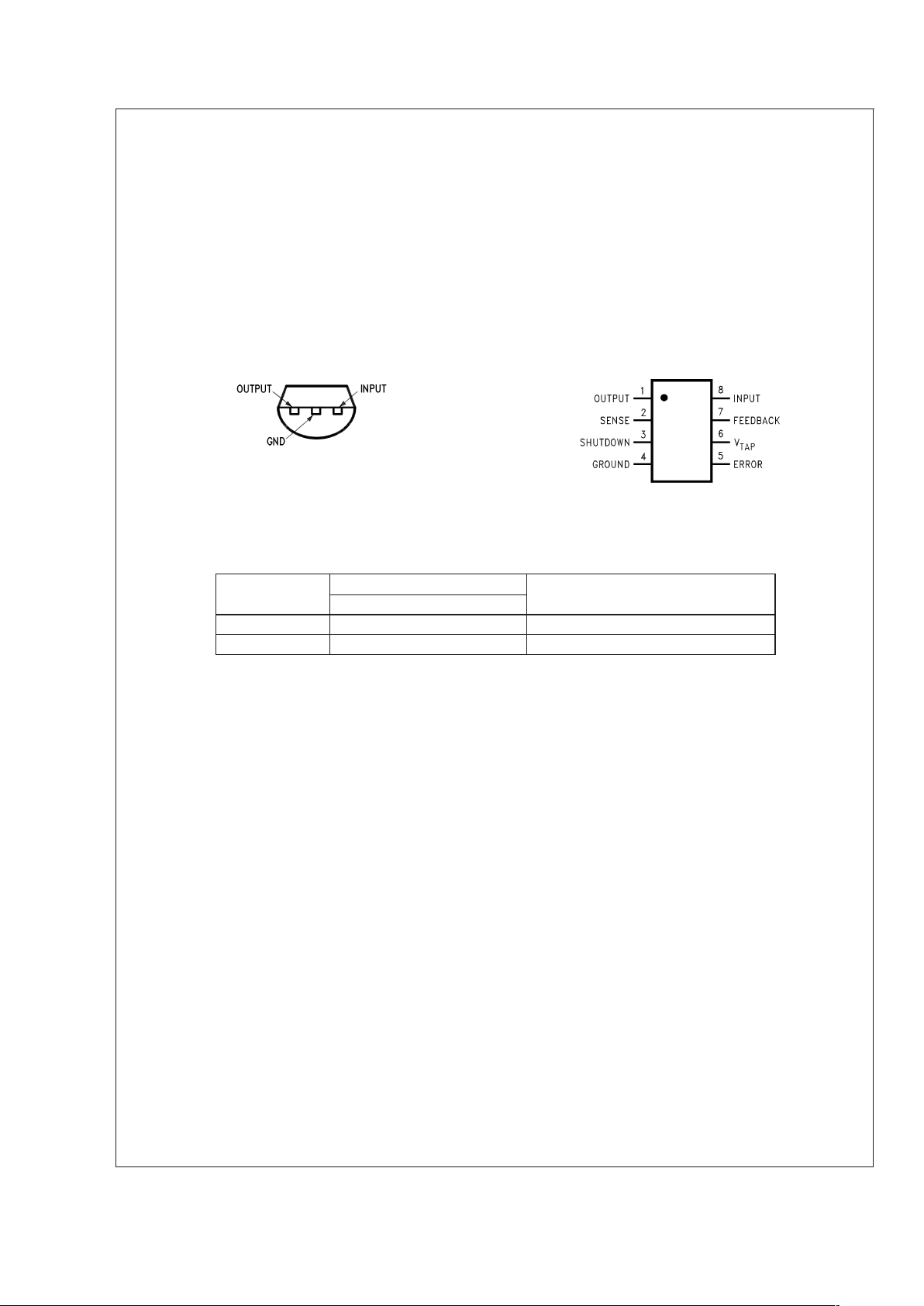
Connection Diagrams
TO-92 Plastic Package (Z) Surface-Mount Package (M)
20052802
Bottom View
20052826
Top View
Ordering Information
Package Output Voltage Temperature
5.0V
TO-92 (Z) LP4950CZ-5.0 −40˚C
<
T
J
<
125˚C
M (M08A) LP4951CM −40˚C
<
T
J
<
125˚C
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com 4
Page 5
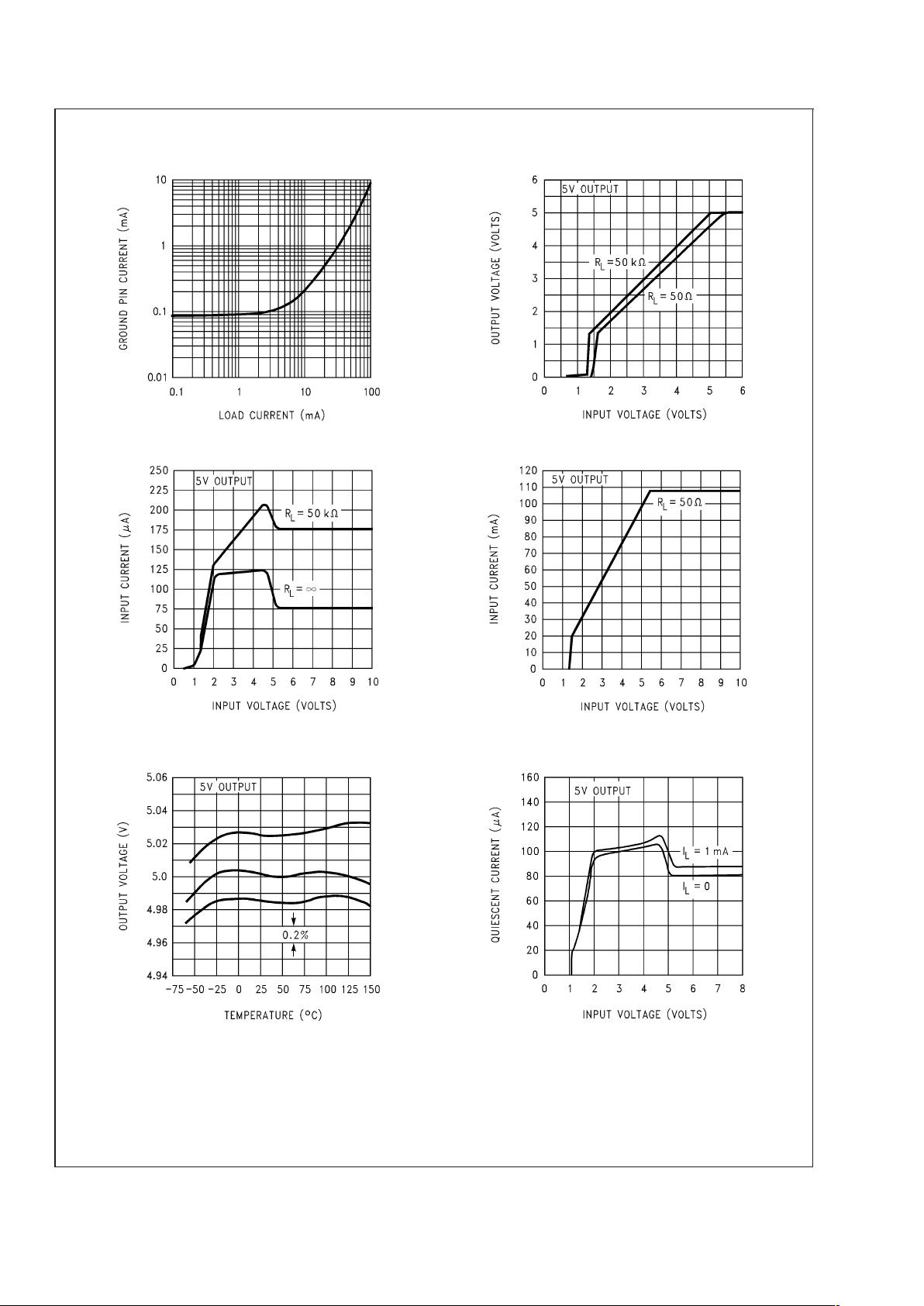
Typical Performance Characteristics
Quiescent Current Dropout Characteristics
20052827
20052828
Input Current Input Current
20052829
20052830
Output Voltage vs. Temperature of 3
Representative Units Quiescent Current
20052831
20052832
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com5
Page 6

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Quiescent Current Quiescent Current
20052833 20052834
Quiescent Current Short Circuit Current
20052835
20052836
Dropout Voltage Dropout Voltage
20052837
20052838
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com 6
Page 7

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
LP4951C Minimum Operating Voltage LP4951C Feedback Bias Current
20052839 20052840
LP4951C Feedback Pin Current LP4951C Error Comparator Output
20052841
20052842
LP4951C Comparator Sink Current Line Transient Response
20052843
20052844
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com7
Page 8

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Load Transient Response Load Transient Response
20052845 20052846
LP4951C Enable Transient Output Impedance
20052847
20052848
Ripple Rejection Ripple Rejection
20052849 20052850
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com 8
Page 9

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Ripple Rejection Output Noise
20052851 20052852
LP4951C Divider Resistance Shutdown Threshold Voltage
20052853
20052854
Line Regulation LP4951C Maximum Rated Output Current
20052855
20052857
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com9
Page 10

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Thermal Response
20052858
Application Hints
EXTERNAL CAPACITORS
A 1.0µF (or greater) capacitor is required between the output
and ground for stability at output voltages of 5V or more. At
lower output voltages, more capacitance is required. Without
this capacitor the part will oscillate. Most types of tantalum or
aluminum electrolytics work fine here; even film types work
but are not recommended for reasons of cost. Many aluminum electrolytics have electrolytes that freeze at about
−30˚C, so solid tantalums are recommended for operation
below −25˚C. The important parameters of the capacitor are
an ESR of about 5 Ω or less and a resonant frequency above
500 kHz. The value of this capacitor may be increased
without limit.
At lower values of output current, less output capacitance is
required for stability. The capacitor can be reduced to
0.33 µF for currents below 10 mA or 0.1 µF for currents
below 1 mA. Using the 8-pin version at voltages below 5V
runs the error amplifier at lower gains so that more output
capacitance is needed. For the worst-case situation of a
100 mA load at 1.23V output (Output shorted to Feedback) a
3.3 µF (or greater) capacitor should be used.
Unlike many other regulators, the LP4950C will remain
stable and in regulation with no load in addition to the
internal voltage divider. This is especially important in CMOS
RAM keep-alive applications. When setting the output voltage of the LP4951C version with external resistors, a minimum load of 1µA is recommended.
A 0.1µF capacitor should be placed from the LP4950C/
LP4951C input to ground if there is more than 10 inches of
wire between the input and the AC filter capacitor or if a
battery is used as the input.
Stray capacitance to the LP4951C Feedback terminal (pin 7)
can cause instability. This may especially be a problem when
using high value external resistors to set the output voltage.
Adding a 100pF capacitor between Output and Feedback
and increasing the output capacitor to at least 3.3µF will fix
this problem.
ERROR DETECTION COMPARATOR OUTPUT
The comparator produces a logic low output whenever the
LP4951C output falls out of regulation by more than approximately 5%. This figure is the comparator’s built-in offset of
about 60 mV divided by the 1.235 reference voltage. (Refer
to the block diagram in the front of the datasheet.) This trip
level remains “5% below normal” regardless of the programmed output voltage of the 4951C. For example, the
error flag trip level is typically 4.75V for a 5V output or 11.4V
for a 12V output. The out of regulation condition may be due
either to low input voltage, current limiting, or thermal limiting.
Figure 1 below gives a timing diagram depicting the ERROR
signal and the regulated output voltage as the LP4951C
input is ramped up and down. The ERROR signal becomes
valid (low) at about 1.3V input. It goes high at about 5V input
(the input voltage at which V
OUT
= 4.75V). Since the
LP4951C’s dropout voltage is load-dependent (see curve in
typical performance characteristics), the input voltage trip
point (about 5V) will vary with the load current. The output
voltage trip point (approx. 4.75V) does not vary with load.
The error comparator has an open-collector output which
requires an external pullup resistor. This resistor may be
returned to the output or some other supply voltage depending on system requirements. In determining a value for this
resistor, note that while the output is rated to sink 400µA, this
sink current adds to battery drain in a low battery condition.
Suggested values range from 100k to 1 MΩ. The resistor is
not required if this output is unused.
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com 10
Page 11

Application Hints (Continued)
PROGRAMMING THE OUTPUT VOLTAGE (LP4951C)
The LP4951C may be pin-strapped for 5V using its internal
voltage divider by tying the pin 1 (output) to pin 2 (sense)
pins together, and also tying the pin 7 (feedback) and pin 6
(V
TAP
) pins together. Alternatively, it may be programmed for
any output voltage between its 1.235V reference and its 30V
maximum rating. As seen in Figure 2, an external pair of
resistors is required.
The complete equation for the output voltage is
where V
REF
is the nominal 1.235 reference voltage and IFBis
the feedback pin bias current, nominally −20 nA. The minimum recommended load current of 1µA forces an upper limit
of 1.2 MΩ on the value of R
2
, if the regulator must work with
no load (a condition often found in CMOS in standby). I
FB
will
produce a 2% typical error in V
OUT
which may be eliminated
at room temperature by trimming R
1
. For better accuracy,
choosing R
2
= 100k reduces this error to 0.17% while increasing the resistor program current to 12µA. Since the
LP4951C typically draws 60µA at no load with Pin 2 opencircuited, this is a small price to pay.
REDUCING OUTPUT NOISE
In reference applications it may be advantageous to reduce
the AC noise present at the output. One method is to reduce
the regulator bandwidth by increasing the size of the output
capacitor. This is the only way noise can be reduced on the
3 lead LP4950C but is relatively inefficient, as increasing the
capacitor from 1µF to 220µF only decreases the noise from
430µV to 160µV rms for a 100kHz bandwidth at 5V output.
Noise can be reduced fourfold by a bypass capacitor across
R
1
, since it reduces the high frequency gain from 4 to unity.
Pick
or about 0.01µF. When doing this, the output capacitor must
be increased to 3.3µF to maintain stability. These changes
reduce the output noise from 430µV to 100µV rms for a
100kHz bandwidth at 5V output. With the bypass capacitor
added, noise no longer scales with output voltage so that
improvements are more dramatic at higher output voltages.
20052820
*
When VIN≤ 1.3V, the error flag pin becomes a high impedance, and the
error flag voltage rises to its pull-up voltage. Using V
OUT
as the pull-up
voltage (see Figure 2), rather than an external 5V source, will keep the
error flag voltage under 1.2V (typ.) in this condition. The user may wish to
divide down the error flag voltage using equal-value resistors (10 kΩ
suggested), to ensure a low-level logic signal during any fault condition,
while still allowing a valid high logic level during normal operation.
FIGURE 1. ERROR Output Timing
20052807
*
See Application Hints
**
Drive with TTL-high to shut down. Ground or leave open if shutdown
feature is not to be used.
Note: Pins 2 and 6 are left open.
FIGURE 2. Adjustable Regulator (LP4951C)
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com11
Page 12

Schematic Diagram
20052823
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com 12
Page 13

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters)
unless otherwise noted
Surface Mount Package (M)
NS Package Number M08A
Molded TO-92 Package (Z)
NS Package Number Z03A
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C
www.national.com13
Page 14

Notes
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and
whose failure to perform when properly used in
accordance with instructions for use provided in the
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury to the user.
2. A critical component is any component of a life
support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of
the life support device or system, or to affect its
safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Email: support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 180-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 69 9508 6208
English Tel: +44 (0) 870 24 0 2171
Français Tel: +33 (0) 1 41 91 8790
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: ap.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
www.national.com
LP4950C-5V and LP4951C Adjustable Micropower Voltage Regulators
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
 Loading...
Loading...