Datasheet LP3966ET-ADJ, LP3966ET-5.0, LP3966ET-3.3, LP3966ET-1.8, LP3966ESX-ADJ Datasheet (NSC)
...Page 1
LP3963/LP3966
3A Fast Ultra Low Dropout Linear Regulators
LP3963/LP3966 3A Fast Ultra Low Dropout Linear Regulators
April 2000
General Description
The LP3963/LP3966 series of fast ultra low-dropout linear
regulators operate from a +2.5V to +7.0V input supply.Wide
range of preset output voltage options are available. These
ultra low dropout linear regulators respond very fast to step
changes in load which makes them suitable for low voltage
microprocessor applications. The LP3963/LP3966 are developed on a CMOS process which allows low quiescent
current operation independent of output load current.This
CMOS process also allows the LP3963/LP3966 to operate
under extremely low dropout conditions.
Dropout Voltage: Ultra low dropout voltage; typically 80mV
at 300mA load current and 800mV at 3A load current.
Ground Pin Current: Typically 6mA at 3A load current.
Shutdown Mode: Typically 15µA quiescent current when
the shutdown pin is pulled low.
Error Flag: Error flag goes low when the output voltage
drops 10% below nominal value (for LP3963).
SENSE: Sense pin improves regulation at remote loads.
(For LP3966)
Precision Output Voltage: Multiple output voltage options
are available ranging from 1.2V to 5.0V and adjustable, with
a guaranteed accuracy of
±
3.0% over all conditions ( varying line, load, and tempera-
ture).
±
1.5% at room temperature, and
Features
n Ultra low dropout voltage
n Low ground pin current
n Load regulation of 0.06%
n 15µA quiescent current in shutdown mode
n Guaranteed output current of 3A DC
n Available in TO-263 and TO-220 packages
n Output voltage accuracy
n Error flag indicates output status (LP3963)
n Sense option improves better load regulation (LP3966)
n Extremely low output capacitor requirements
n Overtemperature/overcurrent protection
n −40˚C to +125˚C junction temperature range
±
1.5%
Applications
n Microprocessor power supplies
n GTL, GTL+, BTL, and SSTL bus terminators
n Power supplies for DSPs
n SCSI terminator
n Post regulators
n High efficiency linear regulators
n Battery chargers
n Other battery powered applications
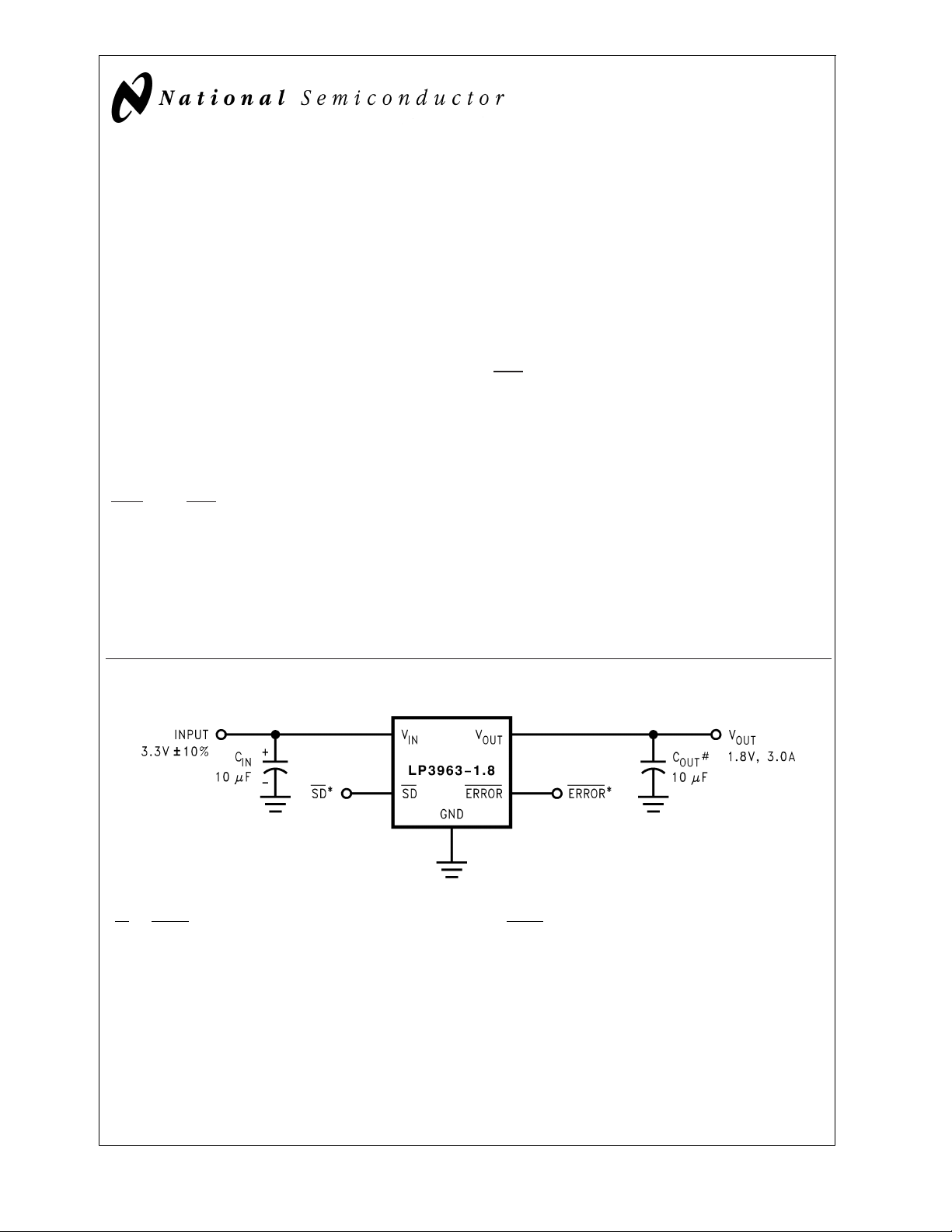
Typical Application Circuits
DS101267-1
#
Minimum output capacitance is 10 µF to ensure stability over full load current range. More capacitance provides superior dynamic performance and additional
stability margin.
*SD and ERROR pins must be pulled high through a 10kΩ pull-up resistor. Connect the ERROR pin to ground if this function is not used. See applications section for more information.
© 2000 National Semiconductor Corporation DS101267 www.national.com
Page 2
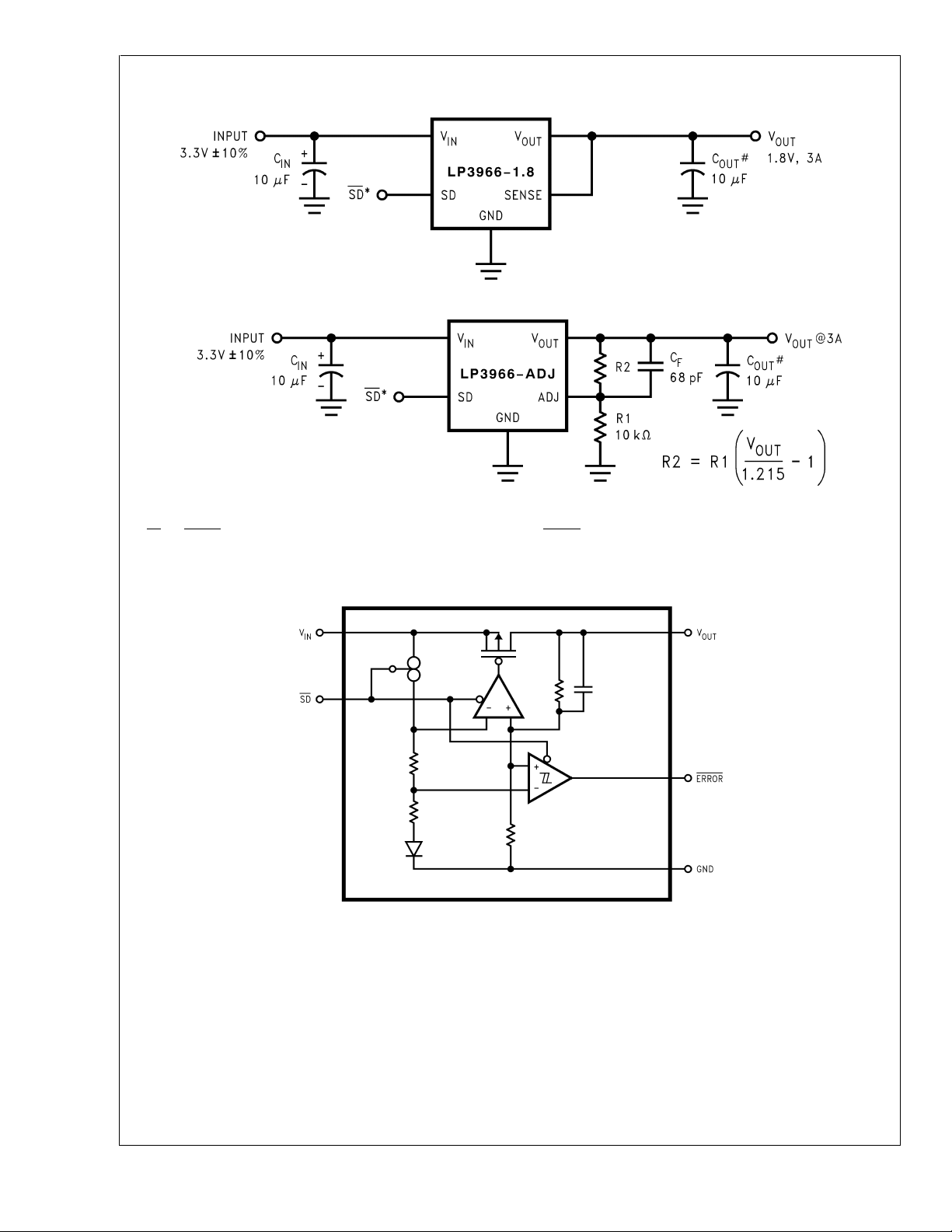
Typical Application Circuits (Continued)
LP3963/LP3966
DS101267-34
#
Minimum output capacitance is 10 µF to ensure stability over full load current range. More capacitance provides superior dynamic performance and additional stability margin.
*SD and ERROR pins must be pulled high through a 10kΩ pull-up resistor. Connect the ERROR pin to ground if this function is not used. See applications section
for more information.
Block Diagram LP3963
DS101267-3
www.national.com 2
Page 3
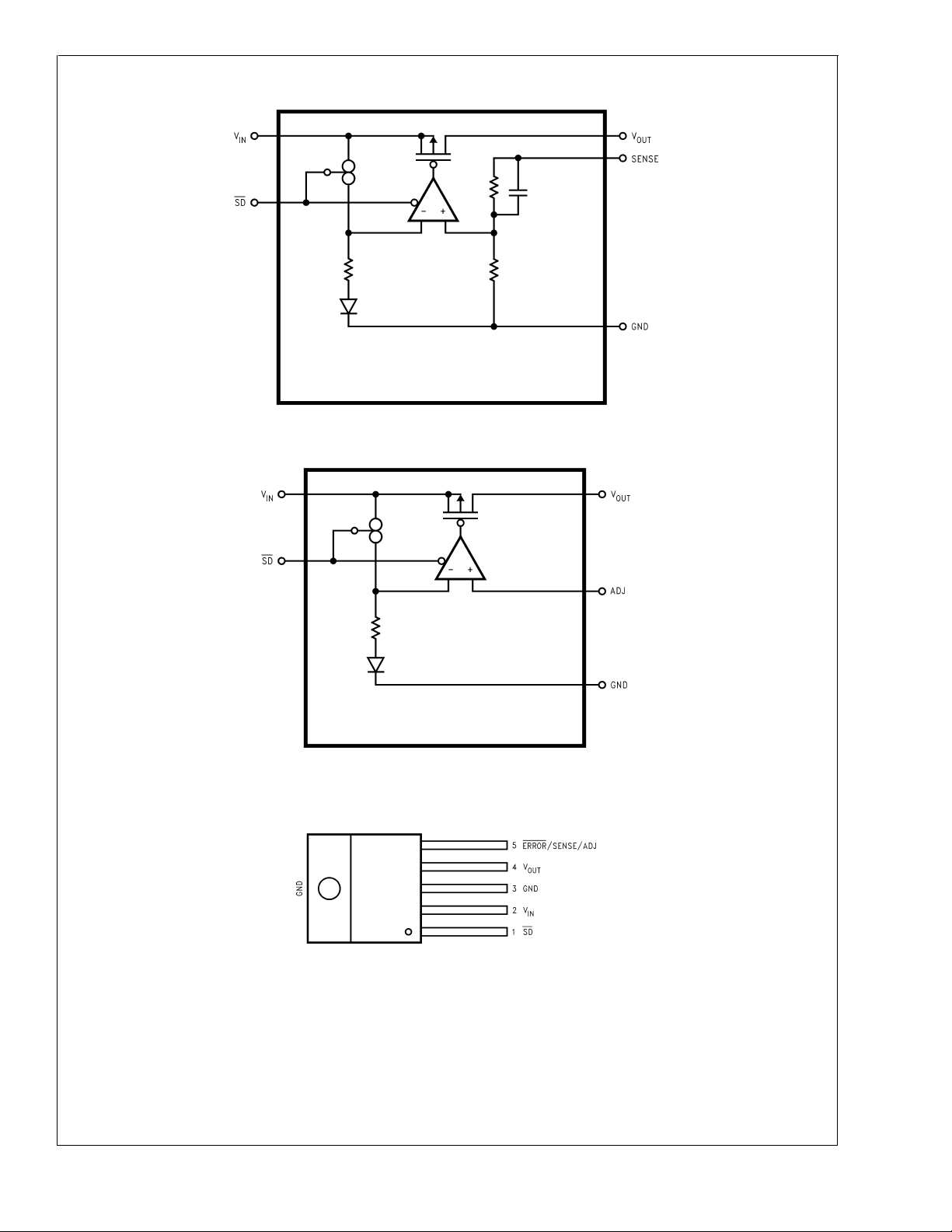
Block Diagram LP3966
Block Diagram LP3966-ADJ
LP3963/LP3966
DS101267-29
Connection Diagrams
DS101267-35
DS101267-5
Top View
TO220-5 Package
Bent, Staggered Leads
www.national.com3
Page 4
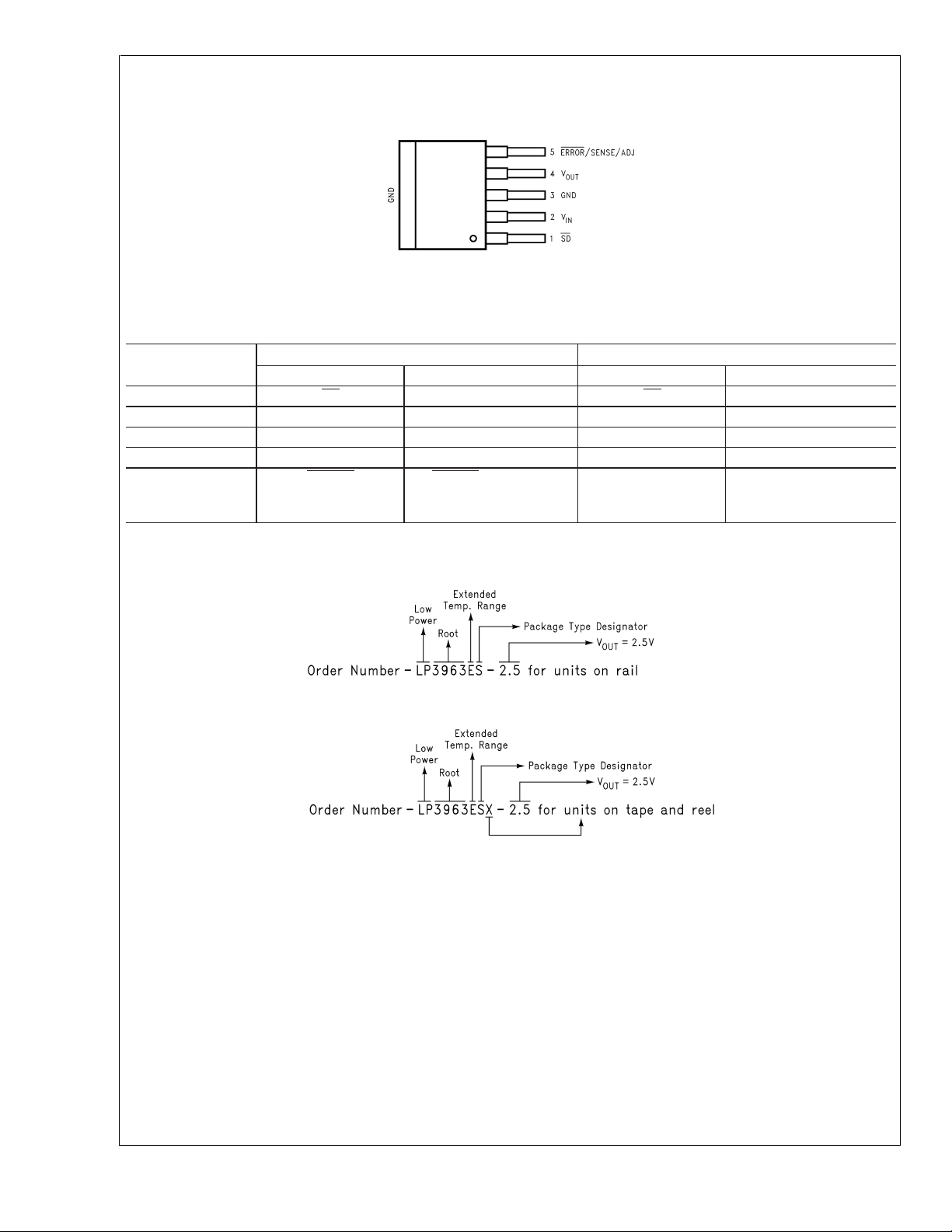
Connection Diagrams (Continued)
LP3963/LP3966
Top View
TO263-5 Package
Pin Description for TO220-5 and TO263-5 Packages
DS101267-6
#
Pin
Name Function Name Function
1SD
2V
IN
LP3963 LP3966
Shutdown SD Shutdown
Input Supply V
IN
3 GND Ground GND Ground
4V
OUT
5 ERROR
Output Voltage V
OUT
ERROR Flag SENSE/ADJ Remote Sense
Ordering Information
Input Supply
Output Voltage
Pin/Output Adjust
Pin
Package Type Designator is ″T″ for TO220 package, and ″S″ for TO263 package.
www.national.com 4
DS101267-31
Page 5
Ordering Information (Continued)
TABLE 1. Package Marking and Ordering Information
LP3963/LP3966
Output
Voltage
5.0 LP3963ES-5.0 3A, Error Flag
5.0 LP3963ESX-5.0 3A, Error Flag
3.3 LP3963ES-3.3 3A, Error Flag
3.3 LP3963ESX-3.3 3A, Error Flag
2.5 LP3963ES-2.5 3A, Error Flag
2.5 LP3963ESX-2.5 3A, Error Flag
1.8 LP3963ES-1.8 3A, Error Flag
1.8 LP3963ESX-1.8 3A, Error Flag
5.0 LP3966ES-5.0 3A, SENSE TO263-5 LP3966ES-5.0 Rail
5.0 LP3966ESX-5.0 3A, SENSE TO263-5 LP3966ESX-5.0 Tape and Reel
3.3 LP3966ES-3.3 3A, SENSE TO263-5 LP3966ES-3.3 Rail
3.3 LP3966ESX-3.3 3A, SENSE TO263-5 LP3966ES-3.3 Tape and Reel
2.5 LP3966ES-2.5 3A, SENSE TO263-5 LP3966ES-2.5 Rail
2.5 LP3966ESX-2.5 3A, SENSE TO263-5 LP3966ES-2.5 Tape and Reel
1.8 LP3966ES-1.8 3A, SENSE TO263-5 LP3966ES-1.8 Rail
1.8 LP3966ESX-1.8 3A, SENSE TO263-5 LP3966ES-1.8 Tape and Reel
ADJ LP3966ES-ADJ 3A, ADJ TO263-5 LP3966ES-ADJ Rail
ADJ LP3966ESX-ADJ 3A, ADJ TO263-5 LP3966ES-ADJ Tape and Reel
5.0 LP3963ET-5.0 3A, Error Flag
3.3 LP3963ET-3.3 3A, Error Flag
2.5 LP3963ET-2.5 3A, Error Flag
1.8 LP3963ET-1.8 3A, Error Flag
5.0 LP3966ET-5.0 3A, SENSE TO220-5 LP3966ET-5.0 Rail
3.3 LP3966ET-3.3 3A, SENSE TO220-5 LP3966ET-3.3 Rail
2.5 LP3966ET-2.5 3A, SENSE TO220-5 LP3966ET-2.5 Rail
1.8 LP3966ET-1.8 3A, SENSE TO220-5 LP3966ET-1.8 Rail
ADJ LP3966ET-ADJ 3A, ADJ TO220-5 LP3966ET-ADJ Rail
Order Number Description
(Current, Option)
Package
Type
TO263-5 LP3963ES-5.0 Rail
TO263-5 LP3963ESX-5.0 Tape and Reel
TO263-5 LP3963ES-3.3 Rail
TO263-5 LP3963ES-3.3 Tape and Reel
TO263-5 LP3963ES-2.5 Rail
TO263-5 LP3963ES-2.5 Tape and Reel
TO263-5 LP3963ES-1.8 Rail
TO263-5 LP3963ES-1.8 Tape and Reel
TO220-5 LP3963ET-5.0 Rail
TO220-5 LP3963ET-3.3 Rail
TO220-5 LP3963ET-2.5 Rail
TO220-5 LP3963ET-1.8 Rail
Package Marking Supplied As:
www.national.com5
Page 6

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
(Survival) Short Circuit Protected
I
OUT
Maximum Voltage for ERROR Pin
Maximum Voltage for SENSE Pin V
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to +150˚C
LP3963/LP3966
Lead Temperature
(Soldering, 5 sec.) 260˚C
ESD Rating (Note 3) 2 kV
Power Dissipation (Note 2) Internally Limited
Input Supply Voltage (Survival) −0.3V to +7.5V
Shutdown Input Voltage (Survival) −0.3V to V
+0.3V
IN
Operating Ratings
Input Supply Voltage (Operating) 2.5V to 7.0V
Shutdown Input Voltage
(Operating) −0.3V to V
Maximum Operating Current
(DC) 3A
Operating Junction Temp. Range −40˚C to +125˚C
Output Voltage (Survival), (Note
6), (Note 7) −0.3V to +7.5V
Electrical Characteristics
LP3963/LP3966
Limits in standard typeface are for TJ= 25˚C, and limits in boldface type apply over the full operating temperature
range. Unless otherwise specified: VIN=V
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ(Note
Output Voltage
V
O
Tolerance
(Note 8)
∆V
OL
Output Voltage Line
Regulation (Note 8)
∆V
/
O
∆I
OUT
Output Voltage Load
Regulation
(Note 8)
V
-
IN
V
OUT
Dropout Voltage
(Note 10)
Ground Pin Current In
I
GND
Normal Operation
Mode
I
GND
Ground Pin Current In
Shutdown Mode
(Note 11)
I
O(PK)
Peak Output Current (Note 2) 4.5 4
SHORT CIRCUIT PROTECTION
I
SC
Short Circuit Current 5.5 A
OVER TEMPERATURE PROTECTION
Tsh(t) Shutdown Threshold 165 ˚C
Tsh(h) Thermal Shutdown
Hysteresis
SHUTDOWN INPUT
V
SDT
T
dOFF
T
dON
I
SD
V
T
V
TH
Shutdown Threshold
Turn-off delay IL=3A 20 µs
Turn-on delay IL=3A 25 µs
SD Input Current VSD=V
Threshold (Note 9) 10 516%
Threshold Hysteresis (Note 9) 5 28%
+ 1.5V, IL= 10 mA, C
O(NOM)
=10µF, VSD=VIN-0.3V.
OUT
LP3963/6 (Note 5) Units
V
OUT
7.0V
10 mA
V
OUT
7.0V,
10 mA
+1.5V<V
<
<
I
L
+1.5V<V
<
<
I
L
4)
<
IN
0
3A
<
IN
0.02
0.06
3A 0.06
Min Max
-1.5
-3.0
0.01
I
= 300 mA 80 100
L
= 3A 800 1000
I
L
= 300 mA 5 9
I
L
=3A 6 14
I
L
≤ 0.2V 15 25
V
SD
3.5
10 ˚C
Output = High V
IN
VIN–0.3
Output = Low 0 0.2
IN
1nA
+1.5
+3.0
120
1200
10
15
75
VIN+0.3V
+0.3V
OUT
+0.3V
IN
%
%
%
mV
mA
µA
A
V
www.national.com 6
Page 7

Electrical Characteristics
LP3963/LP3966
Limits in standard typeface are for TJ= 25˚C, and limits in boldface type apply over the full operating temperature
range. Unless otherwise specified: VIN=V
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ(Note
SHUTDOWN INPUT
V
EF(Sat)
Td Flag Reset Delay 1 µs
I
lk
I
max
AC PARAMETERS
PSRR Ripple Rejection
ρ
n(l/f
e
n
Note 1: Absolute maximum ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating ratings indicate conditions for which the device is intended to be functional, but does notguaranteespecificperformancelimits.Forguaranteedspecificationsandtestconditions,see Electrical Charateristics.The guaranteed specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. Some performance characteristics may degrade when the device is not operated under the listed test
conditions.
Note 2: At elevated temperatures, devices must be derated based on package thermal resistance. The devices in TO220 package must be derated at θ
(with 0.5in
0.5in
Note 3: The human body model is a 100pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5kΩ resistor into each pin.
Note 4: Typical numbers are at 25˚C and represent the most likely parametric norm.
Note 5: Limits are 100% production tested at 25˚C. Limits over the operating temperature range are guaranteed through correlation using Statistical Quality Control
(SQC) methods. The limits are used to calculate National’s Average Outgoing Quality Level (AOQL).
Note 6: If used in a dual-supply system where the regulator load is returned to a negative supply, the LP396X output must be diode-clamped to ground.
Note 7: The output PMOS structure contains a diode between the V
if the voltage at the output terminal is forced to be higher than the voltage at the input terminal. This diode can typically withstand 200mA of DC current and 1Amp
of peak current.
Note 8: Output voltage line regulation is defined as the change in output voltage from the nominal value due to change in the input line voltage. Output voltage load
regulation is defined as the change in output voltage from the nominal value due to change in load current. The line and load regulation specification contains only
the typical number. However, the limits for line and load regulation are included in the output voltage tolerance specification.
Note 9: Error Flag threshold and hysteresis are specified as percentage of regulated output voltage.
Note 10: Dropout voltage is defined as the minimum input to output differential voltage at which the output drops 2% below the nominal value. Dropout voltage speci-
fication applies only to output voltages of 2.5V and above. For output voltages below 2.5V, the drop-out voltage is nothing but the input to output differential, since
the minimum input voltage is 2.5V.
Note 11: This specification has been tested for −40˚C ≤ T
2
2
, 1oz. copper area), junction-to-ambient.
Error Flag Saturation I
Error Flag Pin Leakage
Current
Error Flag Pin Sink
Current
Output Noise Density f = 120Hz 0.8 µV
Output Noise Voltage
(rms)
, 1oz. copper area), junction-to-ambient (with no heat sink). The devices in the TO263 surface-mount package must be derated at θjA= 60˚C/W (with
(Continued)
+ 1.5V, IL= 10 mA, C
O(NOM)
=10µF, VSD=VIN-0.3V.
OUT
LP3963/6 (Note 5) Units
4)
= 100µA 0.02 0.1 V
sink
Min Max
1nA
V
= 0.5V 1mA
Error
V
IN=VOUT
C
OUT
V
OUT
V
IN=VOUT
C
OUT
V
OUT
+ 1.5V
= 100uF
= 3.3V
+ 0.3V
= 100uF
= 3.3V
60
40
BW = 10Hz – 100kHz 150
BW = 300Hz – 300kHz 100
and V
IN
≤ 85˚C since the temperature rise of the device is negligible under shutdown conditions.
J
terminals. This diode is normally reverse biased. This diode will get forward biased
OUT
(rms)
= 50˚C/W
jA
dB
µV
LP3963/LP3966
www.national.com7
Page 8

Typical Performance Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, V
2.5V, C
OUT
= 10µF, I
= 10mA, CIN= 10µF, VSD=VIN, and TA= 25˚C.
OUT
IN=VO(NOM)
+ 1.5V, V
OUT
=
Drop-Out Voltage Vs Temperature for Different Load
Currents
LP3963/LP3966
Ground Pin Current Vs Input Voltage (VSD=VIN)
DS101267-9
Drop-Out Voltage Vs Temperature for Different Output
Voltages (I
OUT
= 800mA)
DS101267-10
Ground Pin Current Vs Input Voltage (VSD=100mV)
DS101267-11
Ground Current Vs Temperature (VSD=VIN)
DS101267-18
DS101267-15
Ground Current Vs Temperature (VSD=0V
DS101267-12
www.national.com 8
Page 9

LP3963/LP3966
Typical Performance Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, V
2.5V, C
Ground Pin Current Vs Shutdown Pin Voltage
Output Noise Density, V
OUT
= 10µF, I
= 10mA, CIN= 10µF, VSD=VIN, and TA= 25˚C. (Continued)
OUT
Input Voltage Vs Output Voltage
DS101267-16
OUT
= 2.5V
Output Noise Density, V
OUT
IN=VO(NOM)
=5V
+ 1.5V, V
DS101267-17
OUT
=
DS101267-13
DS101267-14
www.national.com9
Page 10

Applications Information
Input Capacitor Selection
The LP3963 and LP3966 require a minimum input capacitance of 10µF between the input and ground pins to prevent
LP3963/LP3966
any impedance interactions with the supply. This capacitor
should be located very close to the V
can be of any type such as ceramic, tantalum, or low ESR
aluminium. Any good quality capacitor which has good tolerance over temperature and frequency is recommended.
Output Capacitor Selection
The LP3963 and LP3966 require a minimum of 10µF capacitance between the output and ground pins for proper operation. LP3963 and LP3966 work best with Tantalum or Electrolytic capacitor. The output capacitor should have a good
tolerance over temperature, voltage, and frequency. Larger
capacitance provides better improved load dynamics and
noise performance. The output capacitor should be connected very close to the Vout pin.
Output Adjustment
An adjustable output device has output voltage range of
1.215V to 5.1V. To obtain a desired output voltage, the following equation can be used with R1 always a 10kΩ resistor.
For output stability, CFmust be between 68pF and 100pF.
Output Noise
Noise is specified in two waysSpot Noise or Output noise density is the RMS sum of all
noise sources, measured at the regulator output, at a specific frequency (measured with a 1Hz bandwidth). This type
of noise is usually plotted on a curve as a function of frequency.
Total output Noise or Broad-band noise is the RMS sum
of spot noise over a specified bandwidth, usually several decades of frequencies.
Attention should be paid to the units of measurement. Spot
noise is measured in units µV/
noise is measured in µV(rms).
The primary source of noise in low-dropout regulators is the
internal reference. In CMOS regulators, noise has a low fre-
√
Hz or nV/√Hz and total output
pin. This capacitor
IN
quency component and a high frequency component, which
depend strongly on the silicon area and quiescent current.
Noise can be reduced in two ways: by increasing the transistor area or by increasing the current drawn by the internal
reference. Increasing the area will decrease the chance of
fitting the die into a smaller package. Increasing the current
drawn by the internal reference increases the total supply
current (ground pin current). Using an optimized trade-off of
ground pin current and die size, LP3963/LP3966 achieves
low noise performance and low quiescent current operation.
The total output noise specification for LP3963/LP3966 is
presented in the Electrical Characteristics table. The Output
noise density at different frequencies is represented by a
curve under typical performance characteristics.
Short-Circuit Protection
The LP3963and LP3966 is short circuit protected and in the
event of a peak over-current condition, the short-circuit control loop will rapidly drive the output PMOS pass element off.
Once the power pass element shuts down, the control loop
will rapidly cycle the output on and off until the average
power dissipation causes the thermal shutdown circuit to respond to servo the on/off cycling to a lower frequency.
Please refer to the section on thermal information for power
dissipation calculations.
Error Flag Operation
The LP3963/LP3966 produces a logic low signal at the Error
Flag pin when the output drops out of regulation due to low
input voltage, current limiting, or thermal limiting. This flag
has a built in hysteresis. The timing diagram in
shows the relationship between the ERROR and the output
voltage. In this example, the input voltage is changed to
demonstrate the functionality of the Error Flag.
The internal Error flag comparator has an open drain output
stage. Hence, the ERROR pin should be pulled high through
a pull up resistor. Although the ERROR pin can sink current
of 1mA, this current is energy drain from the input supply.
Hence, the value of the pull up resistor should be in the
range of 10kΩ to 1MΩ. The ERROR pin must be con-
nected to ground if this function is not used. It should
also be noted that when the shutdown pin is pulled low, the
ERROR pin is forced to be invalid for reasons of saving
power in shutdown mode.
Figure 1
www.national.com 10
Page 11

Applications Information (Continued)
FIGURE 1. Error Flag Operation
Sense Pin
In applications where the regulator output is not very close to
the load, LP3966 can provide better remote load regulation
using the SENSE pin.
SENSE option. LP3963 regulates the voltage at the output
pin. Hence, the voltage at the remote load will be the regulator output voltage minus the drop across the trace resis-
Figure 2
depicts the advantage of the
DS101267-7
tance. For example, in the case of a 3.3V output, if the trace
resistance is 100mΩ, the voltage at the remote load will be
3V with 3A of load current, I
. The LP3966 regulates the
LOAD
voltage at the sense pin. Connecting the sense pin to the remote load will provide regulation at the remote load, as
shown in
sense pin must be connected to the V
Figure 2
. If the sense option pin is not required, the
pin.
OUT
LP3963/LP3966
FIGURE 2. Improving remote load regulation using LP3966
DS101267-8
www.national.com11
Page 12

Applications Information (Continued)
Shutdown Operation
A CMOS Logic level signal at the shutdown ( SD) pin will
turn-off the regulator. Pin SD must be actively terminated
through a 10kΩ pull-up resistor for a proper operation. If this
LP3963/LP3966
pin is driven from a source that actively pulls high and low
(such as a CMOS rail to rail comparator), the pull-up resistor
is not required. This pin must be tied to Vin if not used.
Dropout Voltage
The dropout voltage of a regulator is defined as the minimum
input-to-output differential required to stay within 2% of the
output voltage. The LP3963/LP3966 use an internal MOSFET with an Rds(on) of 240mΩ (typically). For CMOS LDOs,
the dropout voltage is the product of the load current and the
Rds(on) of the internal MOSFET.
Reverse Current Path
The internal MOSFET in LP3963and LP3966 has an inherent parasitic diode. During normal operation, the input voltage is higher than the output voltage and the parasitic diode
is reverse biased. However, if the output is pulled above the
input in an application, then current flows from the output to
the input as the parasitic diode gets forward biased. The output can be pulled above the input as long as the current in
the parasitic diode is limited to 200mA continuous and 1A
peak.
θ
HA≤θJA
In this equation, θ
tion to the surface of the heat sink and θ
sistance from the junction to the surface of the case. θ
about 3˚C/W for a TO220 package. The value for θ
pends on method of attachment, insulator, etc. θ
− θCH− θJC.
CH
is the thermal resistance from the junc-
is the thermal re-
JC
JC
de-
CH
varies
CH
between 1.5˚C/W to 2.5˚C/W. If the exact value is unknown,
2˚C/W can be assumed.
Heatsinking TO-263 Package
The TO-263 package uses the copper plane on the PCB as
a heatsink. The tab of these packages are soldered to the
copper plane for heat sinking.
θ
of TO-263 package for different copper area sizes, using
JA
Figure 3
shows a curve for the
a typical PCB with 1 ounce copper and no solder mask over
the copper area for heat sinking.
is
Maximum Output Current Capability
LP3963 and LP3966 can deliver a continuous current of 3A
over the full operating temperature range. A heatsink may be
required depending on the maximum power dissipation and
maximum ambient temperature of the application. Under all
possible conditions, the junction temperature must be within
the range specified under operating conditions. The total
power dissipation of the device is given by:
P
=(VIN−V
D
where I
OUT)IOUT
is the operating ground current of the device
GND
+(VIN)I
GND
(specified under Electrical Characteristics).
The maximum allowable temperature rise (T
on the maximum ambient temperature (T
Rmax
) of the appli-
Amax
) depends
cation, and the maximum allowable junction temperature(T
):
max
T
Rmax=TJmax−TAmax
The maximum allowable value for junction to ambient Thermal Resistance, θ
θ
JA=TRmax/PD
, can be calculated using the formula:
JA
LP3963 and LP3966 are available in TO-220 and TO-263
packages. The thermal resistance depends on amount of
copper area or heat sink, and on air flow. If the maximum allowable value of θ
calculated above is ≥ 60 ˚C/W for TO-
JA
220 package and ≥ 60 ˚C/W for TO-263 package no heatsink
is needed since the package can dissipate enough heat to
satisfy these requirements. If the value for allowable θ
falls
JA
below these limits, a heat sink is required.
DS101267-32
FIGURE 3. θJAvs Copper(1 Ounce) Area for TO-263
package
As shown in the figure, increasing the copper area beyond 1
square inch produces very little improvement. The minimum
value for θ
for the TO-263 packag mounted to a PCB is
JA
32˚C/W.
Figure 4
shows the maximum allowable power dissipation
for TO-263 packages for different ambient temperatures, as-
-
J
suming θ
ture is 125˚C.
is 35˚C/W and the maximum junction tempera-
JA
Heatsinking TO-220 Package
The thermal resistance of a TO220 package can be reduced
by attaching it to a heat sink or a copper plane on a PC
board. If a copper plane is to be used, the values of θ
will
JA
be same as shown in next section for TO263 package.
The heatsink to be used in the application should have a
heatsink to ambient thermal resistance,
www.national.com 12
DS101267-33
FIGURE 4. Maximum power dissipation vs ambient
temperature for TO-263 package
Page 13

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
LP3963/LP3966
TO220 5-lead, Molded, Stagger Bend Package (TO220-5)
NS Package Number T05D
For Order Numbers, refer to the “Ordering Information” section of this document.
www.national.com13
Page 14

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued)
TO263 5-Lead, Molded, Surface Mount Package (TO263-5)
NS Package Number TS5B
For Order Numbers, refer to the “Ordering Information” section of this document.
LP3963/LP3966 3A Fast Ultra Low Dropout Linear Regulators
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and
whose failure to perform when properly used in
accordance with instructions for use provided in the
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury to the user.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
Fax: 1-800-737-7018
Email: support@nsc.com
www.national.com
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 180-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 69 9508 6208
English Tel: +44 (0) 870 24 0 2171
Français Tel: +33 (0) 1 41 91 8790
2. A critical component is any component of a life
support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of
the life support device or system, or to affect its
safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: ap.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
 Loading...
Loading...