Page 1
LM4864
300 mW Audio Power Amplifier with Shutdown Mode
General Description
The LM4864 is a bridged audio power amplifier capable of
delivering 300 mW of continuous average power into an 8Ω
load with 1%(THD) from a 5V power supply.
Boomer
®
audio power amplifiers were designed specifically
to provide high quality output power from a low supply voltage while requiring a minimal amount of external components. Since the LM4864 does not require output coupling
capacitors, bootstrap capacitors or snubber networks, it is
optimally suited for low-power portable applications.
The LM4864 features an externally controlled, low power
consumption shutdown mode, and thermal shutdownprotection.
The closed loop response of the unity-gain stable LM4864,
can be configured by external gain-setting resistors. The device is available in multiple package types to suit various applications.
Key Specifications
n THD at 1 kHz at 300 mW continuous
average output power into 8Ω 1.0%(max)
n THD at 1 kHz at 300 mW continuous
average output power into 16Ω 1.0%(max)
n Shutdown current 0.7 µA (typ)
Features
n MSOP, SOP, and DIP packaging
n No output coupling capacitors, bootstrap capacitors, or
snubber circuits are necessary
n Thermal shutdown protection circuitry
n Unity-gain stable
n External gain configuration capability
Applications
n Cellular Phones
n Personal Computers
n General Purpose Audio
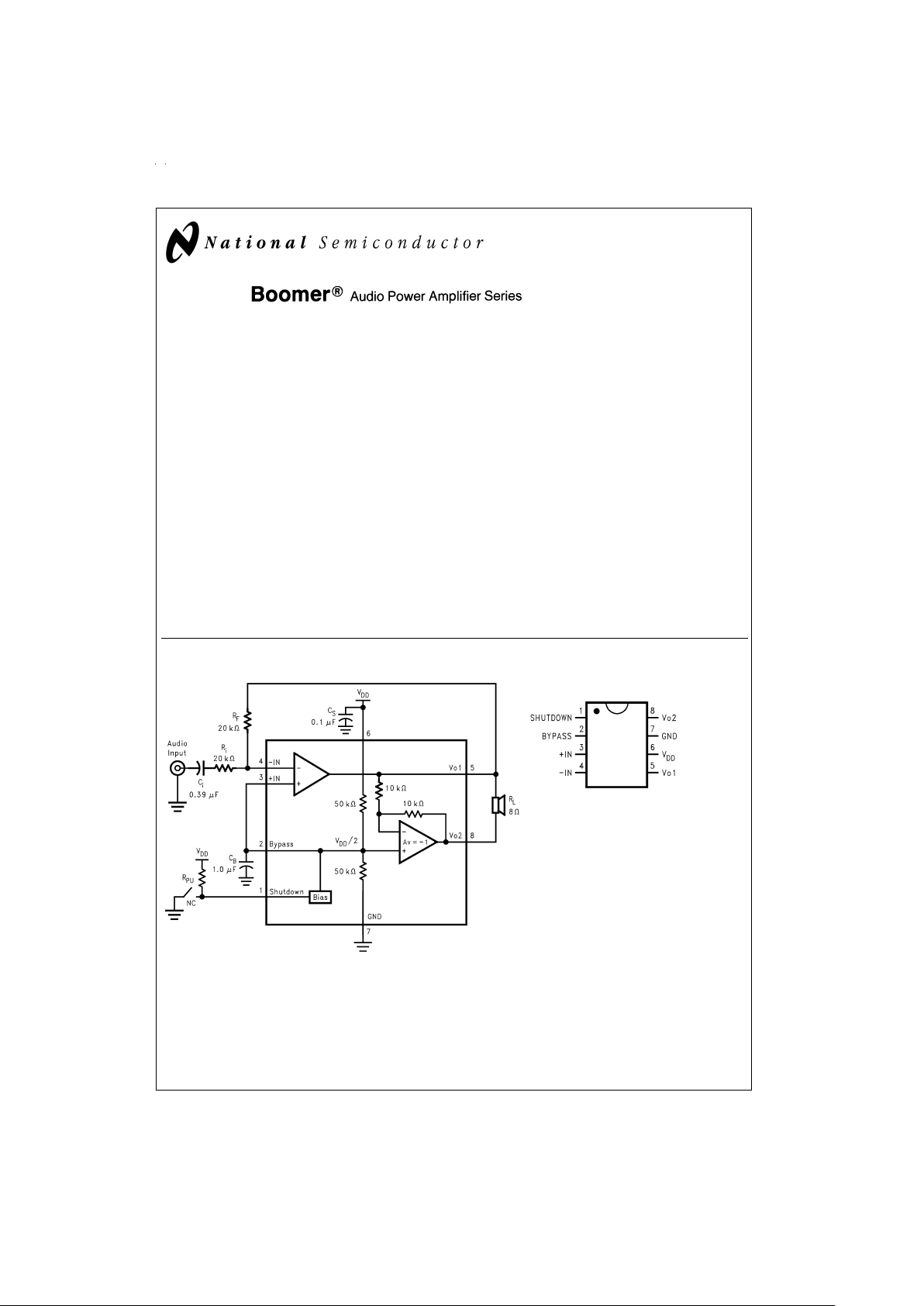
Typical Application Connection Diagram
Boomer®is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
DS012607-1
FIGURE 1. Typical Audio Amplifier Application Circuit
MSOP, SOP, and DIP Package
DS012607-2
Top View
Order Number LM4864MM,
LM4864M or LM4864N
See NS Package Number MUA08A,
M08A or N08E
September 1999
LM4864 300 mW Audio Power Amplifier with Shutdown Mode
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS012607 www.national.com
Page 2
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 2)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage 6.0V
Storage Temperature −65˚C to +150˚C
Input Voltage −0.3V to V
DD
+ 0.3V
Power Dissipation (Note 3) Internally limited
ESD Susceptibility (Note 4) 3500V
ESD Susceptibility (Note 5) 250V
Junction Temperature 150˚C
Soldering Information
Small Outline Package
Vapor Phase (60 sec.) 215˚C
Infrared (15 sec.) 220˚C
See AN-450 “Surface Mounting and their Effects on
Product Reliability” for other methods of soldering surface
mount devices.
Thermal Resistance
θ
JC
(MSOP) 56˚ C/W
θ
JA
(MSOP) 210˚C/W
θ
JC
(SOP) 35˚C/W
θ
JA
(SOP) 170˚C/W
θ
JC
(DIP) 37˚C/W
θ
JA
(DIP) 107˚C/W
Operating Ratings
Temperature Range
T
MIN
≤ TA≤ T
MAX
−40˚C ≤ TA≤ +85˚C
Supply Voltage 2.7V ≤ V
DD
≤ 5.5V
Electrical Characteristics(Note 1) (Note 2)
The following specifications apply for V
DD
=
5V, for all available packages, unless otherwise specified. Limits apply for T
A
=
25˚C
Symbol Parameter Conditions
LM4864
Units
(Limits)
Typical
(Note 6)
Limit
(Note 7)
I
DD
Quiescent Power Supply Current V
IN
=
0V, I
O
=
0A (Note 8) 3.6 6.0 mA (max)
I
SD
Shutdown Current V
PIN1
=
V
DD
0.7 5 µA (max)
V
OS
Output Offset Voltage V
IN
=
0V 5 50 mV (max)
P
O
Output Power THD=1%(max); f=1 kHz; R
L
=
8Ω;
LM4864MM (Note 9)
300 mW (min)
THD=1%(max); f=1 kHz; R
L
=
8Ω;
LM4864M and LM4864N
675 300 mW (min)
THD+N=1%;f=1 kHz; R
L
=
16Ω;
LM4864MM, LM4864M and LM4864N
550 mW
THD+N Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise P
O
=
300 mWrms; A
VD
=
2; R
L
=
8Ω;
20 Hz ≤ f ≤ 20 kHz
0.7
%
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio V
DD
=
4.9V–5.1V 50 dB
Electrical Characteristics(Note 1) (Note 2)
The following specifications apply for V
DD
=
3V, for all available packages, unless otherwise specified. Limits apply for T
A
=
25˚C
Symbol Parameter Conditions
LM4864
Units
(Limits)
Typical
(Note 6)
Limit
(Note 7)
I
DD
Quiescent Power Supply Current V
IN
=
0V, I
O
=
0A (Note 8) 1.0 3.0 mA (max)
I
SD
Shutdown Current V
PIN1
=
V
DD
0.3 2.0 µA (max)
V
OS
Output Offset Voltage V
IN
=
0V 5 mV
P
O
Output Power THD=1%(max); f=1 kHz; R
L
=
8Ω 200 mW
THD=1%(max); f=1 kHz; R
L
=
16Ω 175 mW
THD+N Total Harmonic Distortion+Noise P
O
=
100 mWrms; A
VD
=
2; R
L
=
8Ω;
20 Hz ≤ f ≤ 20 kHz, BW
<
80 kHz
1.5
%
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio V
DD
=
2.9V–3.1V 50 dB
Note 1: All voltages are measured with respect to the ground pin, unless otherwise specified.
Note 2: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is func-
tional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. Electrical Characteristics state DC and AC electrical specifications under particular test conditions which guarantee specific performance limits. This assumes that the device is within the Operating Ratings. Specifications are not guaranteed for parameters where no limit is
given, however, the typical value is a good indication of device performance.
www.national.com 2
Page 3
Electrical Characteristics(Note 1) (Note 2) (Continued)
Note 3: The maximum power dissipation must be derated at elevated temperatures and is dictated by T
JMAX
, θJA, and the ambient temperature TA. The maximum
allowable power dissipation is P
DMAX
=
(T
JMAX−TA
)/θJAor the number given in the Absolute Maximum Ratings, whichever is lower. For the LM4864, T
JMAX
=
150˚C.
The typical junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, when board mounted, is 230˚C/W for package number MUA08A, 170˚C/W for package number M08A and is
107˚C/W for package number N08E.
Note 4: Human body model, 100 pF discharged through a 1.5 kΩ resistor.
Note 5: Machine Model, 220 pF–240 pF discharged through all pins.
Note 6: Typicals are measured at 25˚C and represent the parametric norm.
Note 7: Limits are guaranteed to National’s AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
Note 8: The quiescent power supply current depends on the offset voltage when a practical load is connected to the amplifier.
Note 9: The MUA08BA package is thermally limited to 595 mW of power dissipation at room temperature. Refering to the Power Dissipation vs Output Power graph
in the Typical Performance Characteristics section, the power dissipation limitation for the package occurs at 300 mW of output power. This package limitation is
based on 25˚C ambient temperature and θ
JA
= 210˚C. For higher output power possibilities refer to the Power Dissipation Section.
www.national.com3
Page 4

External Components Description
(Figure 1)
Components Functional Description
1. R
i
Inverting input resistance which sets the closed-loop gain in conjunction with RF. This resistor also forms a
high pass filter with C
i
at f
c
=
1/(2π R
iCI
).
2. C
i
Input coupling capacitor which blocks the DC voltage at the amplifier’s input terminals. Also creates a
highpass filter with R
i
at f
c
=
1/(2π R
iCi
). Refer to the section, Proper Selection of External
Components, for an explanation of how to determine the value of C
i
.
3. R
F
Feedback resistance which sets the closed-loop gain in conjunction with Ri.
4. C
S
Supply bypass capacitor which provides power supply filtering. Refer to the Power Supply Bypassing
section for information concerning proper placement and selection of the supply bypass capacitor.
5. C
B
Bypass pin capacitor which provides half-supply filtering. Refer to the Proper Selection of External
Components for information concerning proper placement and selection of C
B
.
Typical Performance Characteristics
THD+N vs Frequency
DS012607-3
THD+N vs Frequency
DS012607-4
THD+N vs Frequency
DS012607-5
THD+N vs Frequency
DS012607-6
THD+N vs Frequency
DS012607-7
THD+N vs Frequency
DS012607-8
www.national.com 4
Page 5

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
THD+N vs Output Power
DS012607-9
THD+N vs Output Power
DS012607-10
THD+N vs Output Power
DS012607-11
THD+N vs Output Power
DS012607-12
THD+N vs Output Power
DS012607-13
THD+N vs Output Power
DS012607-14
Output Power vs
Supply Voltage
DS012607-15
Output Power vs
Supply Voltage
DS012607-16
Output Power vs
Supply Voltage
DS012607-17
www.national.com5
Page 6

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Output Power vs
Load Resistance
DS012607-18
Power Dissipation vs
Output Power
DS012607-19
Power Derating Curve
DS012607-20
Dropout Voltage vs
Supply Voltage
DS012607-21
Noise Floor
DS012607-22
Frequency Response vs
Input Capacitor Size
DS012607-23
Power Supply
Rejection Ratio
DS012607-24
Open Loop
Frequency Response
DS012607-25
Supply Current vs
Supply Voltage
DS012607-26
www.national.com 6
Page 7

Application Information
BRIDGE CONFIGURATION EXPLANATION
As shown in
Figure 1
, the LM4864 has two operational amplifiers internally, allowing for a few different amplifier configurations. The first amplifier’s gain is externally configurable, while the second amplifier is internally fixed in a
unity-gain, inverting configuration. The closed-loop gain of
the first amplifier is set by selecting the ratio of R
F
to Riwhile
the second amplifier’s gain is fixed by the two internal 10 kΩ
resistors.
Figure 1
shows that the output of amplifier one
serves as the input to amplifier two which results in both amplifiers producing signals identical in magnitude, but out of
phase 180˚. Consequently, the differential gain for the IC is
A
VD
=
2
*
(RF/Ri)
By driving the load differentially through outputs V
o1
and Vo2,
an amplifier configuration commonly referred to as “bridged
mode” is established. Bridged mode operation is different
from the classical single-ended amplifier configuration where
one side of its load is connected to ground.
A bridge amplifier design has a few distinct advantages over
the single-ended configuration, as it provides differential
drive to the load, thus doubling output swing for a specified
supply voltage. Four times the output power is possible as
compared to a single-ended amplifier under the same conditions. This increase in attainable output power assumes that
the amplifier is not current limited or clipped. In order to
choose an amplifier’s closed-loop gain without causing excessive clipping, please refer to the Audio Power Amplifier
Design section.
A bridge configuration, such as the one used in LM4864,
also creates a second advantage over single-ended amplifiers. Since the differential outputs, V
o1
and Vo2, are biased at
half-supply, no net DC voltage exists across the load. This
eliminates the need for an output coupling capacitor which is
required in a single supply,single-ended amplifier configuration. If an output coupling capacitor is not used in a
single-ended configuration, the half-supply bias across the
load would result in both increased internal lC power dissipation as well as permanent loudspeaker damage.
POWER DISSIPATION
Power dissipation is a major concern when designing a successful amplifier, whether the amplifier is bridged or
single-ended. Equation 1 states the maximum power dissipation point for a bridge amplifier operating at a given supply
voltage and driving a specified output load.
P
DMAX
=
(V
DD
)2/(2π2RL) Single-Ended (1)
However, a direct consequence of the increased power delivered to the load by a bridge amplifier is an increase in internal power dissipation point for a bridge amplifier operating
at the same conditions.
P
DMAX
=
4(V
DD
)2/(π2RL) Bridge Mode (2)
Since the LM4864 has two operational amplifiers in one
package, the maximum internal power dissipation is 4 times
that of a single-ended amplifier. Even with this substantial increase in power dissipation, the LM4864 does not require
heatsinking. From Equation 1, assuming a 5V power supply
and an 8Ω load, the maximum power dissipation point is
625 mW. The maximum power dissipation point obtained
from Equation 2 must not be greater than the power dissipation that results from Equation 3:
P
DMAX
=
(T
JMAX−TA
)/θ
JA
(3)
For package MUA08A, θ
JA
=
210˚C/W, for package M08A,
θ
JA
=
170˚C/W and for package N08E, θ
JA
=
107˚C/W.
T
JMAX
=
150˚C for the LM4864. Depending on the ambient
temperature, T
A
, of the system surroundings, Equation 3 can
be used to find the maximum internal power dissipation supported by the IC packaging. If the result of Equation 2 is
greater than that of Equation 3, then either the supply voltage must be decreased, the load impedance increased, the
ambient temperature reduced, or the θ
JA
reduced with heat-
sinking. In many cases larger traces near the output, V
DD
,
and Gnd pins can be used to lower the θ
JA
. The larger areas
of copper provide a form of heatsinking allowing a higher
power dissipation. For the typical application of a 5V power
supply, with an 8Ω load, the maximum ambient temperature
possible without violating the maximum junction temperature
is approximately 44˚C provided that device operation is
around the maximum power dissipation point and assuming
surface mount packaging. Internal power dissipation is a
function of output power. If typical operation is not around the
maximum power dissipation point, the ambient temperature
can be increased. Refer to the Typical Performance Char-
acteristics curves for power dissipation information for
lower output powers.
POWER SUPPLY BYPASSING
As with any power amplifier, proper supply bypassing is critical for low noise performance and high power supply rejection. The capacitor location on both the bypass and power
supply pins should be as close to the device as possible. The
effect of a larger half supply bypass capacitor is improved
PSRR due to increased half-supply stability. Typical applications employ a 5V regulator with 10 µF and a 0.1 µF bypass
capacitors which aid in supply stability, but do not eliminate
the need for bypassing the supply nodes of the LM4864. The
selection of bypass capacitors, especially C
B
, is thus dependent upon desired PSRR requirements, click and pop performance as explained in the section, Proper Selection of Ex-
ternal Components, system cost, and size constraints.
SHUTDOWN FUNCTION
In order to reduce power consumption while not in use, the
LM4864 contains a shutdown pin to externally turn off the
amplifier’s bias circuitry.This shutdown feature turns the amplifier off when a logic high is placed on the shutdown pin.
The trigger point between a logic low and logic high level is
typically half supply. It is best to switch between ground and
supply to provide maximum device performance. By switching the shutdown pin to V
DD
, the LM4864 supply current
draw will be minimized in idle mode. While the device will be
disabled with shutdown pin voltages less than V
DD
, the idle
current may be greater than the typical value of 0.7 µA. In either case, the shutdown pin should be tied to a definite voltage to avoid unwanted state changes.
In many applications, a microcontroller or microprocessor
output is used to control the shutdown circuitry which provides a quick, smooth transition into shutdown. Another solution is to use a single-pole, single-throw switch in conjunction
with an external pull-up resistor. When the switch is closed,
the shutdown pin is connected to ground and enables the
amplifier. If the switch is open, then the external pull-up resistor will disable the LM4864. This scheme guarantees that
the shutdown pin will not float, thus preventing unwanted
state changes.
www.national.com7
Page 8

Application Information (Continued)
PROPER SELECTION OF EXTERNAL COMPONENTS
Proper selection of external components in applications using integrated power amplifiers is critical to optimize device
and system performance. While the LM4864 is tolerant to a
variety of external component combinations, consideration
to component values must be used to maximize overall system quality.
The LM4864 is unity-gain stable, giving a designer maximum
system flexibility. The LM4864 should be used in low gain
configurations to minimize THD+N values, and maximize the
signal to noise ratio. Low gain configurations require large input signals to obtain a given output power. Input signals
equal to or greater than 1 Vrms are available from sources
such as audio codecs. Please refer to the section, Audio
Power Amplifier Design, for a more complete explanation
of proper gain selection.
Besides gain, one of the major considerations is the
closed-loop bandwidth of the amplifier.Toa large extent, the
bandwidth is dictated by the choice of external components
shown in
Figure 1
. The input coupling capacitor, Ci, forms a
first order high pass filter which limits low frequency response. This value should be chosen based on needed frequency response for a few distinct reasons.
Selection of Input Capacitor Size
Large input capacitors are both expensive and space hungry
for portable designs. Clearly, a certain sized capacitor is
needed to couple in low frequencies without severe attenuation. But in many cases the speakers used in portable systems, whether internal or external, have little ability to reproduce signals below 150 Hz. In this case using a large input
capacitor may not increase system performance.
In addition to system cost and size, click and pop performance is effected by the size of the input coupling capacitor,
C
i
. A larger input coupling capacitor requires more charge to
reach its quiescent DC voltage (nominally
1
⁄2VDD). This
charge comes from the output via the feedback and is apt to
create pops upon device enable. Thus, by minimizing the capacitor size based on necessary low frequency response,
turn-on pops can be minimized.
Besides minimizing the input capacitor size, careful consideration should be paid to the bypass capacitor value. Bypass
capacitor, C
B
, is the most critical component to minimize
turn-on pops since it determines how fast the LM4864 turns
on. The slower the LM4864’s outputs ramp to their quiescent
DC voltage (nominally
1
⁄2VDD), the smaller the turn-on pop.
Choosing C
B
equal to 1.0 µF along with a small value of C
i
(in the range of 0.1 µF to 0.39 µF), should produce a clickless and popless shutdown function. While the device will
function properly, (no oscillations or motorboating), with C
B
equal to 0.1 µF, the device will be much more susceptible to
turn-on clicks and pops. Thus, a value of C
B
equal to 1.0 µF
or larger is recommended in all but the most cost sensitive
designs.
AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER DESIGN
Design a 300 mW/8Ω Audio Amplifier
Given:
Power Output 300 mWrms
Load Impedance 8Ω
Input Level 1 Vrms
Input Impedance 20 kΩ
Bandwidth 100 Hz–20 kHz
±
0.25 dB
A designer must first determine the minimum supply rail to
obtain the specified output power. By extrapolating from the
Output Power vs Supply Voltage graphs in the Typical Per-
formance Characteristics section, the supply rail can be
easily found. A second way to determine the minimum supply rail is to calculate the required V
opeak
using Equation 4
and add the dropout voltage. Using this method, the minimum supply voltage would be (V
opeak
+(2*VOD)), where
V
OD
is extrapolated from the Dropout Voltage vs Supply Voltage curve in the Typical Performance Characteristics section.
(4)
Using the Output Power vs Supply Voltage graph for an 8Ω
load, the minimum supply rail is 3.5V. But since 5V is a standard supply voltage in most applications, it is chosen for the
supply rail. Extra supply voltage creates headroom that allows the LM4864 to reproduce peaks in excess of 500 mW
without producing audible distortion. At this time, the designer must make sure that the power supply choice along
with the output impedance does not violate the conditions
explained in the Power Dissipation section.
Once the power dissipation equations have been addressed,
the required differential gain can be determined from Equation 5.
(5)
R
F/Ri
=
A
VD
/2 (6)
From Equation 5, the minimum A
VD
is 1.55; use A
VD
=
2.
Since the desired input impedance was 20 kΩ, and with a
A
VD
of 2, a ratio of 1:1 of RFto Riresults in an allocation of
R
i
=
R
F
=
20 kΩ. The final design step is to address the
bandwidth requirements which must be stated as a pair of
−3 dB frequency points. Five times away from a pole gives
0.17 dB down from passband response which is better than
the required
±
0.25 dB specified.
f
L
=
100 Hz/5=20 Hz
f
H
=
20 kHz x 5=100 kHz
As stated in the External Components section, R
i
in con-
junction with C
i
create a highpass filter.
Ci≥ 1/(2π*20 kΩ*20 Hz)=0.397 µF; use 0.39 µF
The high frequency pole is determined by the product of the
desired high frequency pole, f
H
, and the differential gain,
A
VD
. With a A
VD
=
2 and f
H
=
100 kHz, the resulting GBWP
=
100 kHz which is much smaller than the LM4864 GBWP of
18 MHz. This figure displays that if a designer has a need to
design an amplifier with a higher differential gain, the
LM4864 can still be used without running into bandwidth
problems.
www.national.com 8
Page 9

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
8-Lead (0.150" Wide) Molded Small Outline Package, JEDEC
Order Number LM4864M
NS Package Number M08A
8-Lead (0.300" Wide) Molded Dual-In-Line Package
Order Number LM4864N
NS Package Number N08E
www.national.com9
Page 10

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued)
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and
whose failure to perform when properly used in
accordance with instructions for use provided in the
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury to the user.
2. A critical component is any component of a life
support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of
the life support device or system, or to affect its
safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
Fax: 1-800-737-7018
Email: support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 85
English Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 78 32
Français Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 93 58
Italiano Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-534 16 80
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: sea.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
www.national.com
8-Lead (0.118" Wide) Molded Mini Small Outline Package
Order Number LM4864MM
NS Package Number MUA08A
LM4864 300 mW Audio Power Amplifier with Shutdown Mode
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
 Loading...
Loading...