Page 1
LM148/LM248/LM348
Quad 741 Op Amps
LM149
LM148/LM149 Series Quad 741 Op Amp
December 2000
Wide Band Decompensated (A
General Description
The LM148 series is a true quad 741. It consists of four
independent, high gain, internally compensated, low power
operational amplifiers which have been designed to provide
functional characteristics identical to those of the familiar
741 operational amplifier. In addition the total supply current
for all four amplifiers is comparable to thesupplycurrentofa
single 741 type op amp. Other features include input offset
currents and input bias current which are much less than
those of a standard 741. Also, excellent isolation between
amplifiers has been achieved by independently biasing each
amplifier and using layout techniques which minimize
thermal coupling. The LM149 series has the same features
as the LM148 plus a gain bandwidth product of 4 MHz at a
gain of 5 or greater.
The LM148 canbeused anywhere multiple 741 or 1558 type
amplifiers are being used and in applications where amplifier
matching or high packing density is required. For lower
power refer to LF444.
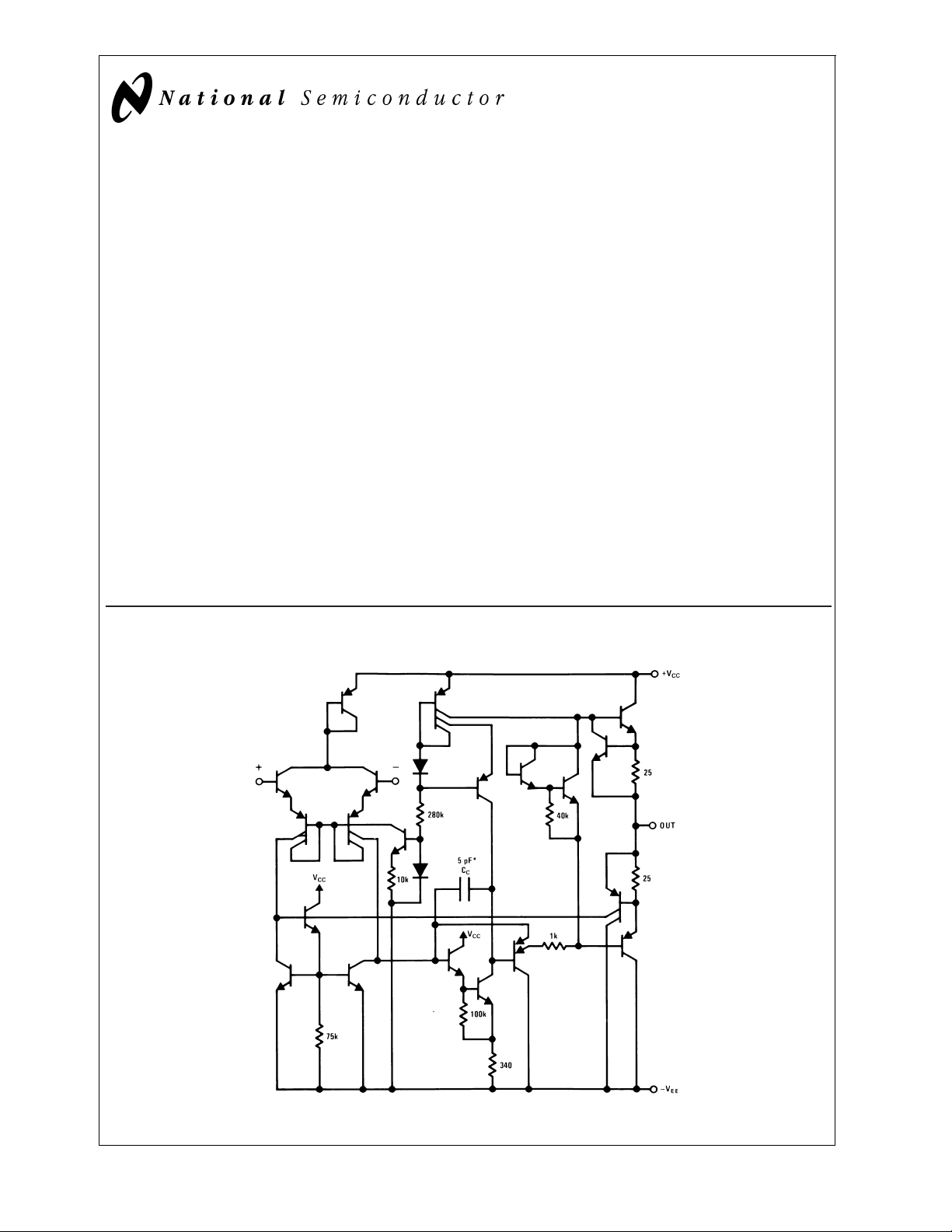
Schematic Diagram
V (MIN)
=5)
Features
n 741 op amp operating characteristics
n Class AB output stage—no crossover distortion
n Pin compatible with the LM124
n Overload protection for inputs and outputs
n Low supply current drain: 0.6 mA/Amplifier
n Low input offset voltage: 1 mV
n Low input offset current: 4 nA
n Low input bias current 30 nA
n High degree of isolation between amplifiers: 120 dB
n Gain bandwidth product
n LM148 (unity gain): 1.0 MHz
n LM149 (A
≥ 5): 4 MHz
V
DS007786-1
* 1 pF in the LM149
© 2001 National Semiconductor Corporation DS007786 www.national.com
Page 2
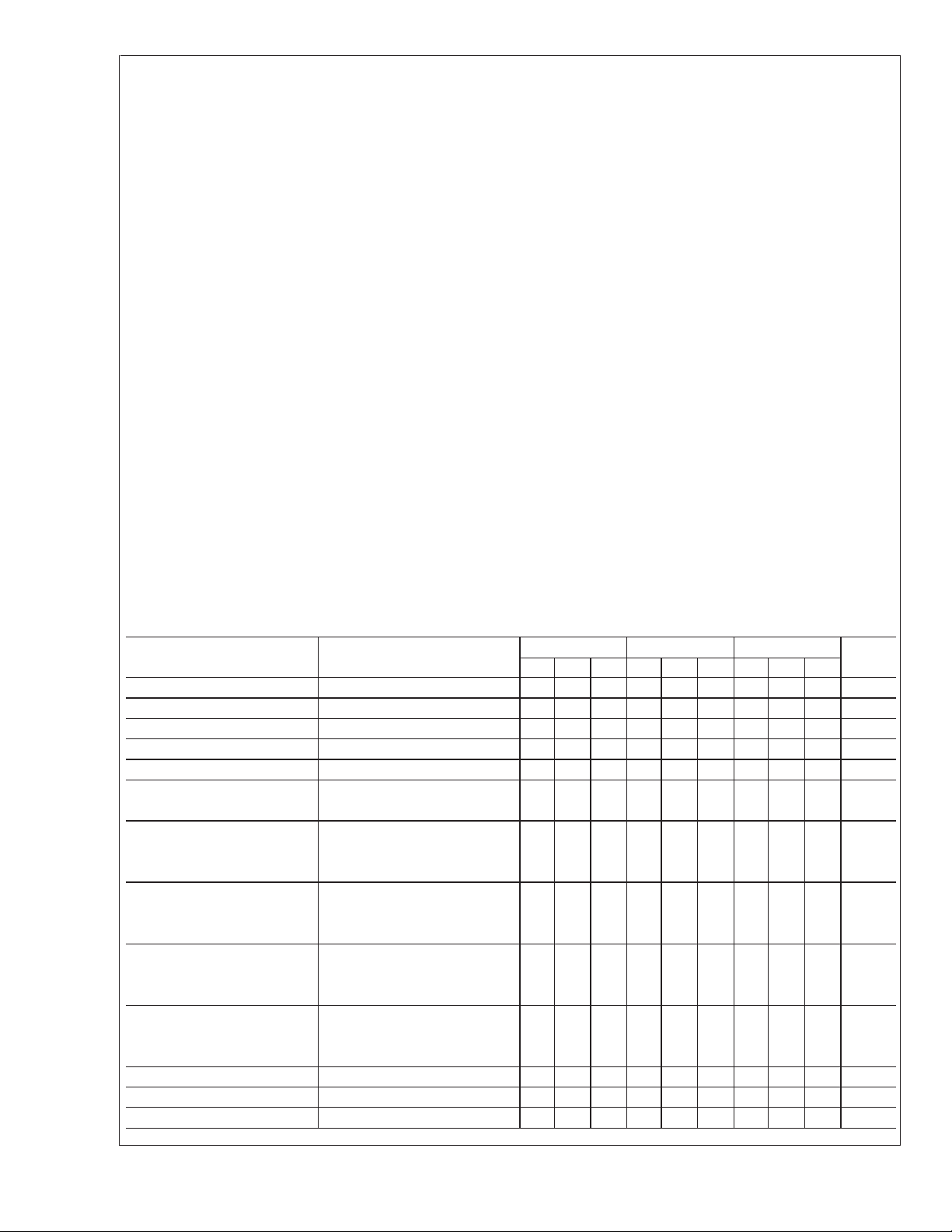
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 4)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the National Semiconductor Sales
Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
LM148/LM149 LM248 LM348
Supply Voltage
Differential Input Voltage
±
±
22V
44V
Output Short Circuit Duration (Note 1) Continuous Continuous Continuous
Power Dissipation (P
Thermal Resistance (θ
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
Molded DIP (N) P
Cavity DIP (J) P
Maximum Junction Temperature (T
Operating Temperature Range −55˚C ≤ T
d
d
θ
jA
d
θ
JA
at 25˚C) and
), (Note 2)
jA
— — 750 mW
— — 100˚C/W
1100 mW 800 mW 700 mW
110˚C/W 110˚C/W 110˚C/W
) 150˚C 110˚C 100˚C
jMAX
≤ +125˚C −25˚C ≤ TA≤ +85˚C 0˚C ≤ TA≤ +70˚C
A
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to +150˚C −65˚C to +150˚C −65˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec.) Ceramic 300˚C 300˚C 300˚C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec.) Plastic 260˚C
Soldering Information
Dual-In-Line Package
Soldering (10 seconds) 260˚C 260˚C 260˚C
Small Outline Package
Vapor Phase (60 seconds) 215˚C 215˚C 215˚C
Infrared (15 seconds) 220˚C 220˚C 220˚C
See AN-450 “Surface Mounting Methods and Their Effect on Product Reliability” for other methods of soldering surface mount
devices.
ESD tolerance (Note 5) 500V 500V 500V
±
±
18V
36V
±
±
18V
36V
Electrical Characteristics
(Note 3)
Parameter Conditions LM148/LM149 LM248 LM348 Units
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
Input Offset Voltage T
Input Offset Current T
Input Bias Current T
Input Resistance T
Supply Current All Amplifiers T
Large Signal Voltage Gain T
Amplifier to Amplifier T
Coupling (Input Referred) See Crosstalk −120 −120 −120 dB
Small Signal Bandwidth LM148 Series 1.0 1.0 1.0 MHz
Phase Margin LM148 Series (A
Slew Rate LM148 Series (A
Output Short Circuit Current T
Input Offset Voltage R
Input Offset Current 75 125 100 nA
= 25˚C, RS≤ 10 kΩ 1.0 5.0 1.0 6.0 1.0 6.0 mV
A
= 25˚C 4 25 4 50 4 50 nA
A
= 25˚C 30 100 30 200 30 200 nA
A
= 25˚C 0.8 2.5 0.8 2.5 0.8 2.5 MΩ
A
= 25˚C, VS=±15V 2.4 3.6 2.4 4.5 2.4 4.5 mA
A
= 25˚C, VS=±15V 50 160 25 160 25 160 V/mV
A
V
=±10V, RL≥ 2kΩ
OUT
= 25˚C, f = 1 Hz to 20 kHz
A
Test Circuit
T
= 25˚C
A
LM149 Series 4.0 4.0 4.0 MHz
= 1) 60 60 60 degrees
V
T
= 25˚C
A
LM149 Series (A
T
= 25˚C
A
LM149 Series (A
= 25˚C 25 25 25 mA
A
≤ 10 kΩ 6.0 7.5 7.5 mV
S
= 5) 60 60 60 degrees
V
= 1) 0.5 0.5 0.5 V/µs
V
= 5) 2.0 2.0 2.0 V/µs
V
www.national.com 2
Page 3
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(Note 3)
Parameter Conditions LM148/LM149 LM248 LM348 Units
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
Input Bias Current 325 500 400 nA
Large Signal Voltage Gain V
Output Voltage Swing V
Input Voltage Range V
Common-Mode Rejection R
=±15V, V
S
>
R
2kΩ
L
=±15V, RL=10kΩ
S
R
=2kΩ
L
=±15V
S
≤ 10 kΩ 70 90 70 90 70 90 dB
S
=±10V, 25 15 15 V/mV
OUT
±12±
±10±
±
12
13
12
±12±
±10±
±
12
13
12
±12±
13 V
±10±
12 V
±
12 V
Ratio
Supply Voltage Rejection R
Note 1: Any of the amplifier outputs can be shorted to ground indefinitely; however, more than one should not be simultaneously shorted as the maximum junction
temperature will be exceeded.
Note 2: The maximum power dissipation for these devices must be derated at elevated temperatures and is dicated by T
. The maximum available power dissipation at any temperature is Pd=(T
T
A
Note 3: These specifications apply for V
Note 4: Refer to RETS 148X for LM148 military specifications and refer to RETS 149X for LM149 military specifications.
Note 5: Human body model, 1.5 kΩ in series with 100 pF.
≤ 10 kΩ,±5V ≤ VS≤±15V 77 96 77 96 77 96 dB
S
, θjA, and the ambient temperature,
)/θjAor the 25˚C P
=±15V and over the absolute maximum operating temperature range (TL≤ TA≤ TH) unless otherwise noted.
S
jMAX−TA
, whichever is less.
dMAX
jMAX
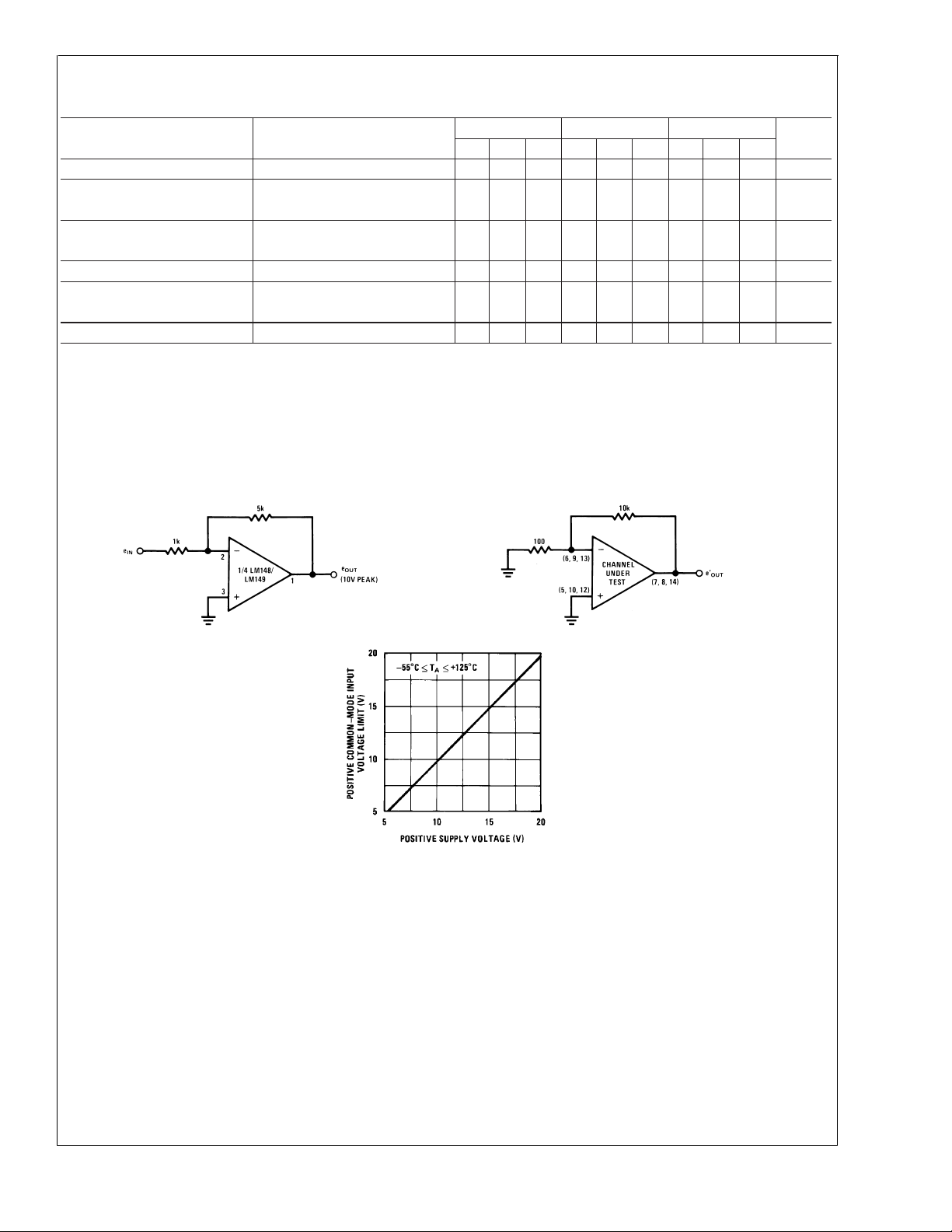
Cross Talk Test Circuit
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
DS007786-6
VS=±15V
Application Hints
The LM148 series are quad low power 741 op amps. In the
proliferation of quad op amps, these are the first to offer the
convenience of familiar, easy to use operating
characteristics of the 741 op amp. In those applications
where 741 op amps have been employed, the LM148 series
op amps can be employed directly with no change in circuit
performance.
DS007786-7
DS007786-43
The LM149 series has the same characteristics as the
LM148 except it has been decompensated to provide a
wider bandwidth. As a result the part requires a minimum
gain of 5.
www.national.com3
Page 4
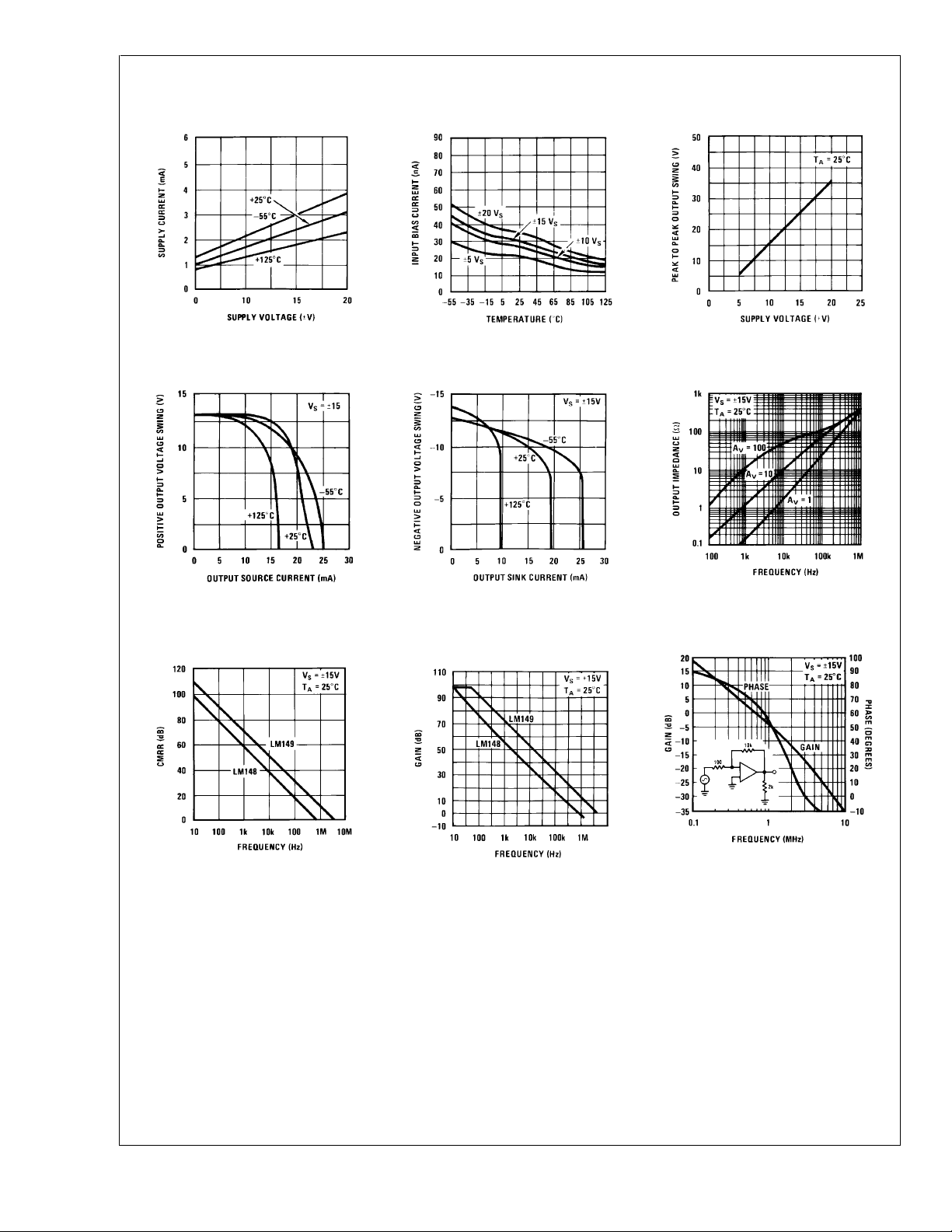
Typical Performance Characteristics
Supply Current
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
DS007786-23
Positive Current Limit
Input Bias Current
Negative Current Limit
DS007786-24
Voltage Swing
DS007786-25
Output Impedance
Common-Mode Rejection
Ratio
DS007786-26
DS007786-29
Open Loop Frequency
Response
DS007786-27
DS007786-30
DS007786-28
Bode Plot LM148
DS007786-31
www.national.com 4
Page 5
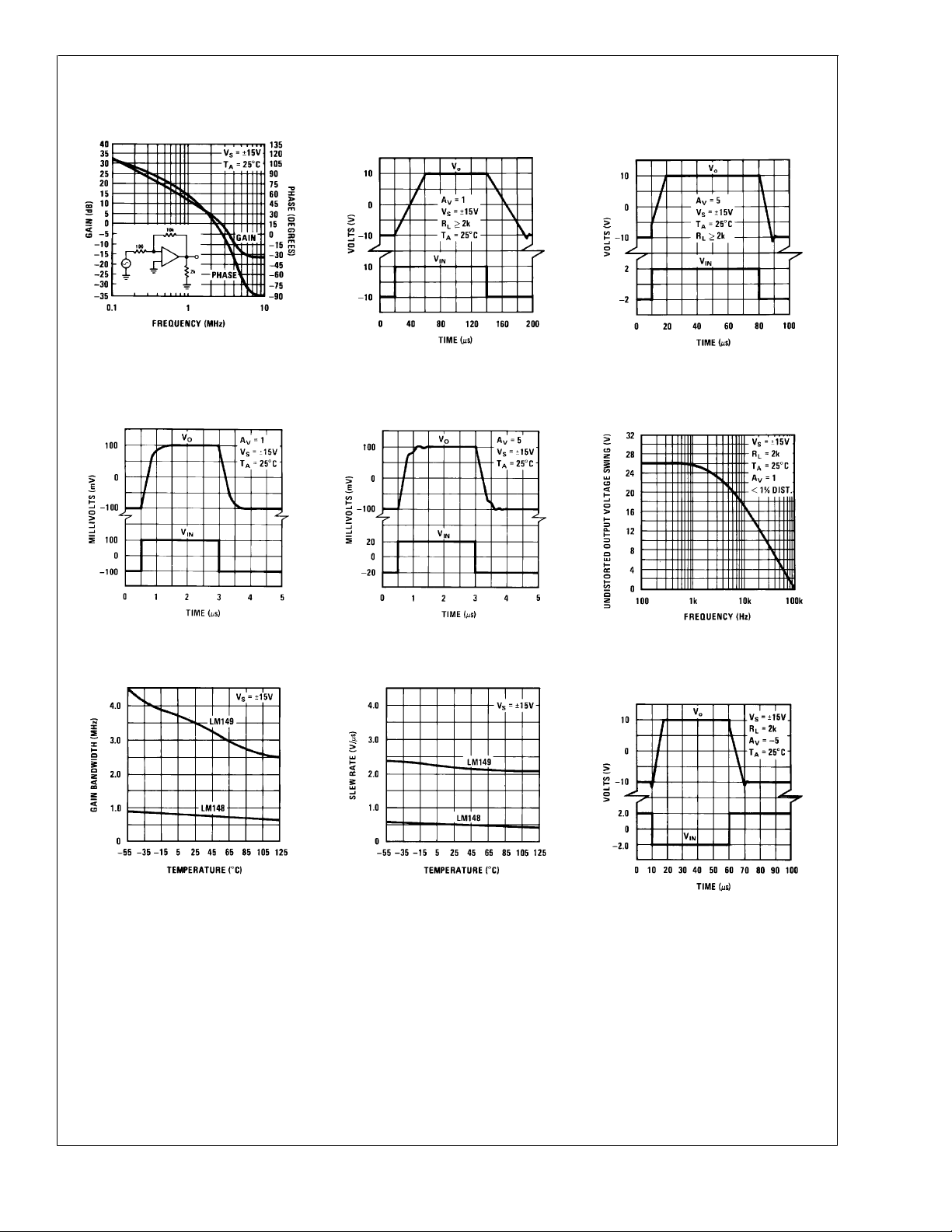
Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
Bode Plot LM149
Small Signal Pulse
Response (LM148)
DS007786-32
Large Signal Pulse
Response (LM148)
Small Signal Pulse
Response (LM149)
DS007786-33
Large Signal Pulse
Response (LM149)
DS007786-34
Undistorted Output
Voltage Swing
Gain Bandwidth
DS007786-35
DS007786-38
Slew Rate
DS007786-36
DS007786-39
DS007786-37
Inverting Large Signal Pulse
Response (LM149)
DS007786-40
www.national.com5
Page 6
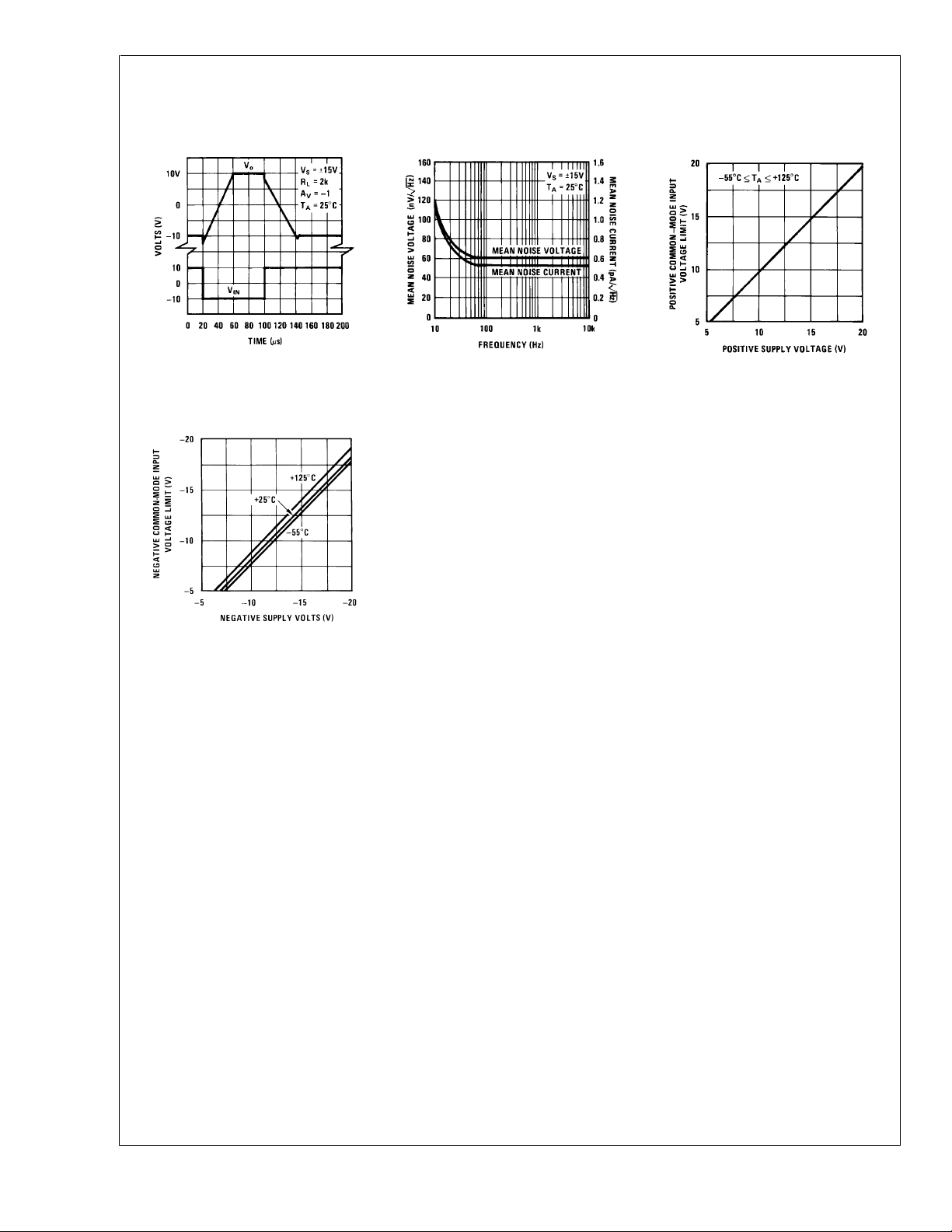
Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Inverting Large Signal Pulse
Response (LM148)
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
DS007786-41
Negative Common-Mode Input
Voltage Limit
Input Noise Voltage and
Noise Current
DS007786-42
Positive Common-Mode
Input Voltage Limit
DS007786-43
DS007786-5
Application Hints
The LM148 series are quad low power 741 op amps. In the
proliferation of quad op amps, these are the first to offer the
convenience of familiar, easy to use operating
characteristics of the 741 op amp. In those applications
where 741 op amps have been employed, the LM148 series
op amps can be employed directly with no change in circuit
performance.
The LM149 series has the same characteristics as the
LM148 except it has been decompensated to provide a
wider bandwidth. As a result the part requires a minimum
gain of 5.
The package pin-outs are such that the inverting input of
each amplifier is adjacent to its output. In addition, the
amplifier outputs are located in the corners of the package
which simplifies PC board layout and minimizes package
related capacitive coupling between amplifiers.
The input characteristics of these amplifiers allow differential
input voltages which can exceed the supply voltages. In
addition, if either of the input voltages is within the operating
common-mode range, the phase of the output remains
correct. If the negative limit of the operating common-mode
range is exceeded at both inputs, the output voltage will be
positive. For input voltages which greatly exceed the
maximum supply voltages, either differentially or
common-mode, resistors should be placed in series with the
inputs to limit the current.
Like the LM741, these amplifiers can easily drive a 100 pF
capacitive load throughout the entire dynamic output voltage
and current range. However, if very large capacitive loads
must be driven by a non-inverting unity gain amplifier, a
resistor should be placed between the output (and feedback
connection) and the capacitance to reduce the phase shift
resulting from the capacitive loading.
The output current of each amplifier in the package is limited.
Short circuits from an output to either ground or the power
supplies will not destroy the unit. However, if multiple output
shorts occur simultaneously, the time duration should be
short to prevent the unit from being destroyed as a result of
excessive power dissipation in the IC chip.
www.national.com 6
Page 7

Application Hints (Continued)
As with most amplifiers, care should be taken lead dress,
component placement and supply decoupling in order to
ensure stability. For example, resistors from the output to an
input should be placed with the body close to the input to
minimize “pickup” and maximize the frequency of the
feedback pole which capacitance from the input to ground
creates.
A feedback pole is created when the feedback around any
amplifier is resistive. The parallel resistance and capacitance
Typical Applications—LM148
One Decade Low Distortion Sinewave Generator
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
from the input of the device (usually the inverting input) to AC
ground set the frequency of the pole. In many instances the
frequency of this pole is much greater than the expected 3
dB frequency of the closed loop gain and consequently there
is negligible effect on stability margin. However, if the
feedback pole is less than approximately six times the
expected 3 dB frequency a lead capacitor should be placed
from the output to the input of the op amp. The value of the
added capacitor should be such that the RC time constant of
this capacitor and the resistance it parallels is greater than or
equal to the original feedback pole time constant.
DS007786-8
f
= 5 kHz, THD ≤ 0.03%
MAX
R1 = 100k pot. C1 = 0.0047 µF, C2 = 0.01 µF, C3 = 0.1 µF, R2 = R6 = R7 = 1M,
R3 = 5.1k, R4 = 12Ω, R5 = 240Ω, Q = NS5102, D1 = 1N914, D2 = 3.6V avalanche
diode (ex. LM103), V
A simpler version with some distortion degradation at high frequencies can be made by using A1 as a simple inverting amplifier, and by putting back to back
zeners in the feedback loop of A3.
=±15V
S
www.national.com7
Page 8

Typical Applications—LM148 (Continued)
Low Cost Instrumentation Amplifier
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
VS=±15V
R = R2, trim R2 to boost CMRR
DS007786-9
Adjust R for minimum drift
D3 low leakage diode
D1 added to improve speed
=±15V
V
S
Low Drift Peak Detector with Bias Current Compensation
DS007786-10
www.national.com 8
Page 9

Typical Applications—LM148 (Continued)
Universal State-Variable Filter
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
Tune Q through R0,
For predictable results: f
Use Band Pass output to tune for Q
Q ≤ 4x10
O
DS007786-11
4
www.national.com9
Page 10

Typical Applications—LM148 (Continued)
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
A 1 kHz 4 Pole Butterworth
Use general equations, and tune each section separately
Q
1stSECTION
The response should have 0 dB peaking
= 0.541, Q
2ndSECTION
= 1.306
DS007786-12
A 3 Amplifier Bi-Quad Notch Filter
DS007786-13
Ex: f
Better noise performance than the state-space approach.
= 3 kHz, Q = 5, R1 = 270k, R2 = R3 = 20k, R4 = 27k, R5 = 20k, R6 = R8 = 10k, R7 = 100k, C1 = C2 = 0.001 µF
NOTCH
www.national.com 10
Page 11

Typical Applications—LM148 (Continued)
A 4th Order 1 kHz Elliptic Filter (4 Poles, 4 Zeros)
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
R1C1 = R2C2 = t
R'1C'1 = R'2C'2 = t'
= 1 kHz, fS= 2 kHz, fp= 0.543, fZ= 2.14, Q = 0.841, f'P= 0.987, f'Z= 4.92, Q' = 4.403, normalized to ripple BW
f
C
Use the BP outputs to tune Q, Q', tune the 2 sections separately
R1 = R2 = 92.6k, R3 = R4 = R5 = 100k, R6 = 10k, R0 = 107.8k, R
R'1 = R'2 = 50.9k, R'4 = R'5 = 100k, R'6 = 10k, R'0 = 5.78k, R'
= 100k, RH= 155.1k,
L
= 100k, R'H= 248.12k, R'f = 100k. All capacitors are 0.001 µF.
L
Lowpass Response
DS007786-15
DS007786-14
www.national.com11
Page 12

Typical Applications—LM149
Minimum Gain to Insure LM149 Stability
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
The LM149 as a Unity Gain Inverter
DS007786-16
Non-inverting-Integrator Bandpass Filter
DS007786-17
For stability purposes: R7 = R6/4, 10R6 = R5, CC= 10C
f
O(MAX),QMAX
Better Q sensitivity with respect to open loop gain variations than the state variable filter.
R7, C
= 20 kHz, 10
added for compensation
C
www.national.com 12
DS007786-18
Page 13

Typical Applications—LM149 (Continued)
Active Tone Control with Full Output Swing (No Slew Limiting at 20 kHz)
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
VS=±15V, V
= 20 kHz, THD ≤ 1%
f
MAX
Duplicate the above circuit for stereo
Max Bass Gain . (R1 + R2)/R1
Max Treble Gain . (R1 + 2R7)/R5
as shown: f
. 11 kHz, fHB. 1.1 Hz
f
H
. 32 Hz, fLB. 320 Hz
L
OUT(MAX)
= 9.1 V
RMS
DS007786-19
,
www.national.com13
Page 14

Typical Applications—LM149 (Continued)
Triangular Squarewave Generator
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
DS007786-20
Use LM125 for±15V supply
The circuit can be used as a low frequency V/F for process control.
Q1, Q3: KE4393, Q2, Q4: P1087E, D1–D4 = 1N914
www.national.com 14
Page 15

Typical Simulation
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
LM148, LM149, LM741 Macromodel for Computer Simulation
For more details, see IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, Vol. SC-9, No. 6, December 1974
Note 6:
Note 7:o2= 144*C2 = 6 pF for LM149
= 112IS=8x10
o1
−16
DS007786-21
DS007786-22
www.national.com15
Page 16

Connection Diagram
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
Order Number LM148J, LM148J/883, LM149J/883, LM248J, LM348M, or LM348N
DS007786-2
Top View
See NS Package Number J14A, M14A or N14A
LM148J is available per JM38510/11001
www.national.com 16
Page 17

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
Ceramic Dual-In-Line Package (J)
Order Number LM148J, LM148J/883, LM149J/883, LM248J
NS Package Number J14A
LM148/LM149/LM248/LM348
S.O. Package (M)
Order Number LM348M or LM348MX
NS Package Number M14A
www.national.com17
Page 18

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued)
LM148/LM149 Series Quad 741 Op Amp
Molded Dual-In-Line Package (N)
Order Number LM348N
NS Package Number N14A
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and
whose failure to perform when properly used in
accordance with instructions for use provided in the
2. A critical component is any component of a life
support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of
the life support device or system, or to affect its
safety or effectiveness.
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury to the user.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
Fax: 1-800-737-7018
Email: support@nsc.com
www.national.com
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 180-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 69 9508 6208
English Tel: +44 (0) 870 24 0 2171
Français Tel: +33 (0) 1 41 91 8790
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: ap.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
 Loading...
Loading...