Page 1
October 2007
LM3103
SIMPLE SWITCHER® Synchronous 1MHz 0.75A
Step-Down Voltage Regulator
General Description
The LM3103 Synchronously Rectified Buck Converter features all required functions to implement a highly efficient and
cost effective buck regulator. It is capable of supplying 0.75A
to loads with an output voltage as low as 0.6V. Dual N-Channel synchronous MOSFET switches allow a low component
count, thus reducing complexity and minimizing board size.
Different from most other COT regulators, the LM3103 does
not rely on output capacitor ESR for stability, and is designed
to work exceptionally well with ceramic and other very low
ESR output capacitors. It requires no loop compensation, results in a fast load transient response and simple circuit
implementation. The operating frequency remains nearly constant with line variations due to the inverse relationship between the input voltage and the on-time. The operating
frequency can be externally programmed up to 1 MHz. Protection features include VCC under-voltage lock-out, output
over-voltage protection, thermal shutdown, and gate drive
under-voltage lock-out. The LM3103 is available in the thermally enhanced eTSSOP-16 package.
Key Specifications
■
Input voltage range 4.5V-42V
■
0.75A output current
■
0.6V, ±2% reference
■
Integrated dual N-Channel main and synchronous
MOSFETs
■
Thermally enhanced eTSSOP-16 package
Features
■
Low component count and small solution size
■
Stable with ceramic and other low ESR capacitors
■
No loop compensation required
■
High efficiency at a light load by DCM operation
■
Pre-bias startup
■
Ultra-fast transient response
■
Programmable soft-start
■
Programmable switching frequency up to 1 MHz
■
Valley current limit
■
Thermal shutdown
■
Output over-voltage protection
■
Precision internal reference for an adjustable output
voltage down to 0.6V
Typical Applications
■
5VDC, 12VDC, 24VDC, 12VAC, and 24VAC systems
■
Embedded Systems
■
Industrial Control
■
Automotive Telematics and Body Electronics
■
Point of Load Regulators
■
Storage Systems
■
Broadband Infrastructure
■
Direct Conversion from 2/3/4 Cell Lithium Batteries
Systems
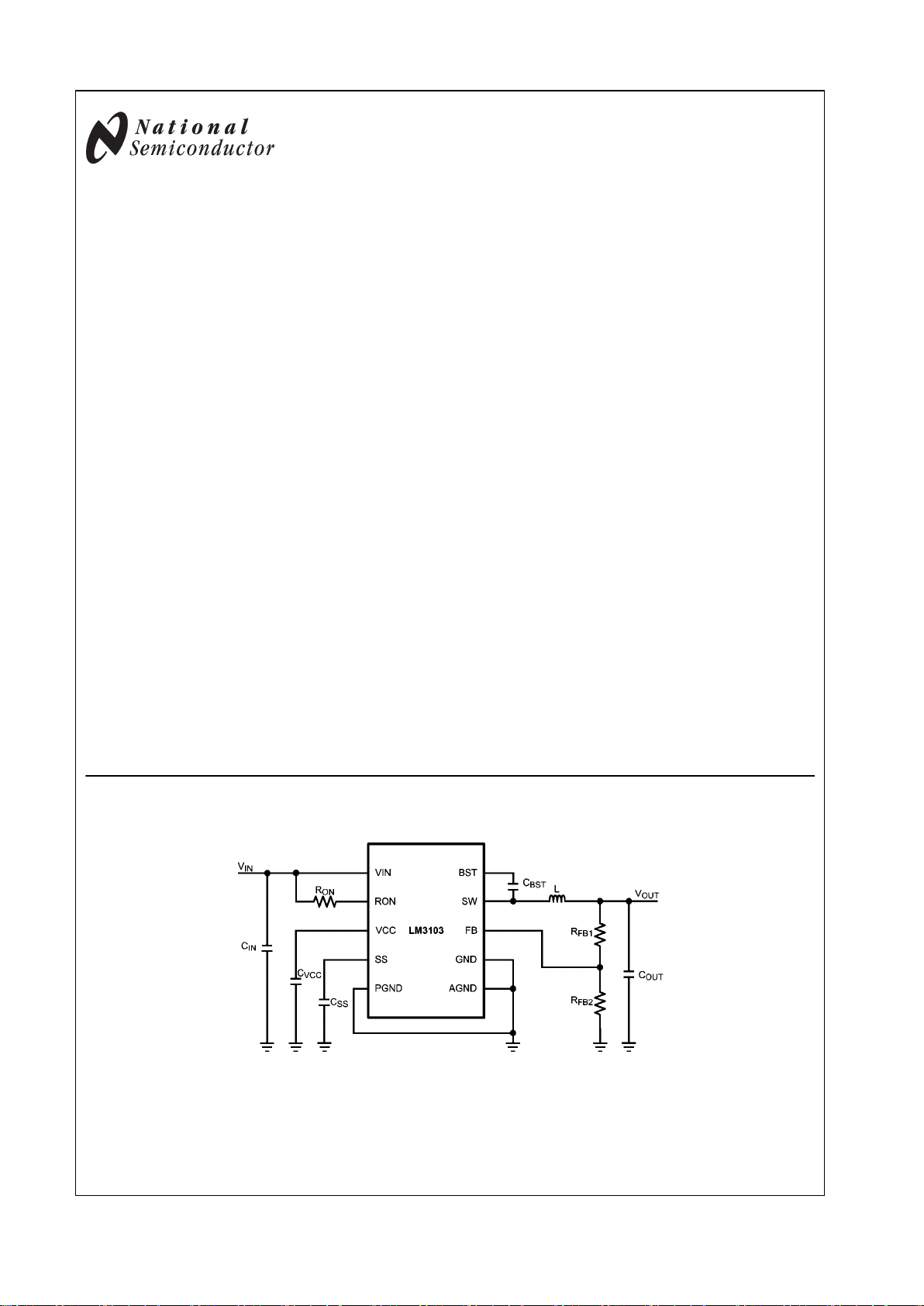
Typical Application
30029701
SIMPLE SWITCHER® is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation
© 2007 National Semiconductor Corporation 300297 www.national.com
LM3103 SIMPLE SWITCHER® Synchronous 1MHz 0.75A Step-Down Voltage Regulator
Page 2
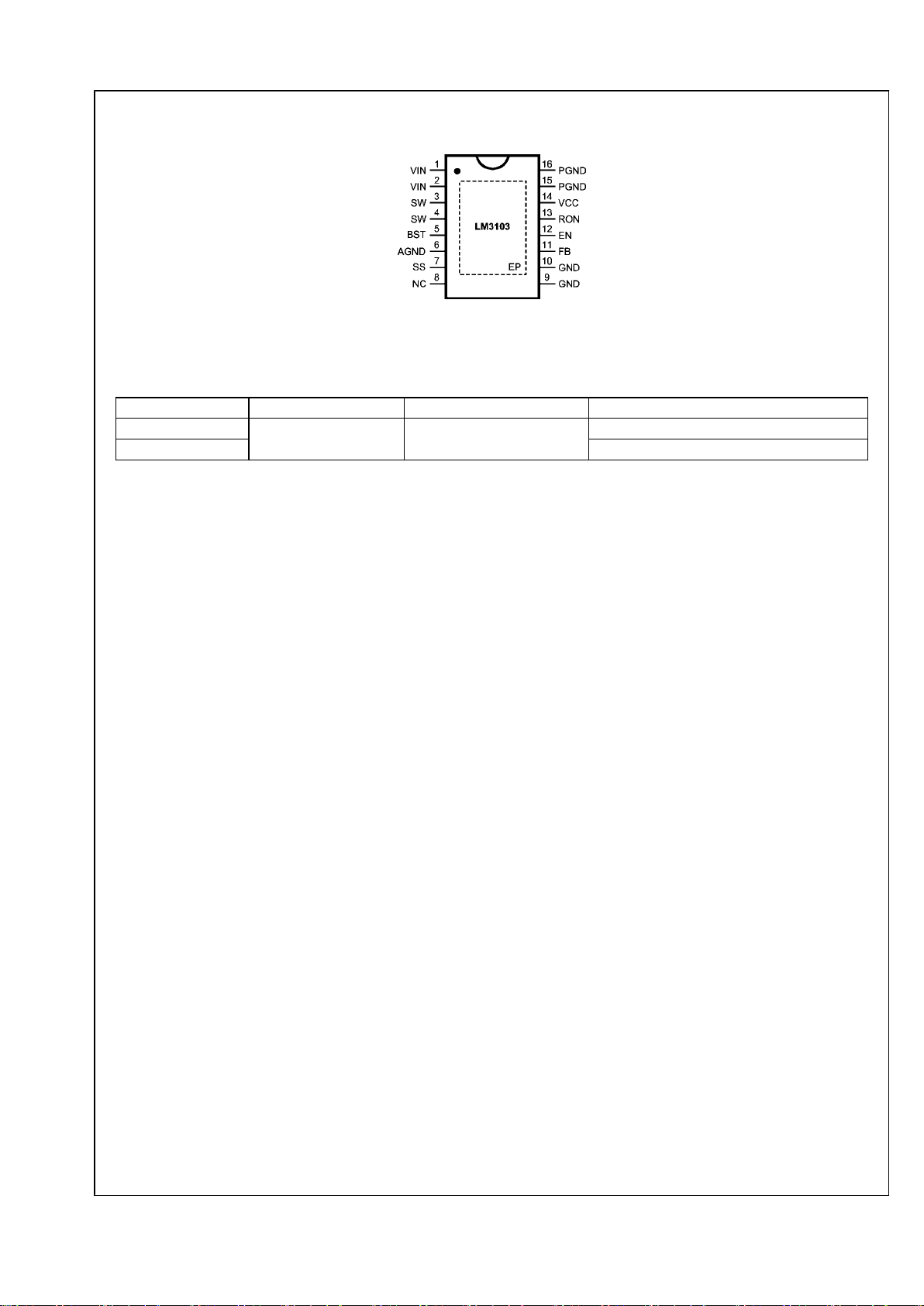
Connection Diagram
30029702
16-Lead Plastic eTSSOP
NS Package Number MXA16A
Ordering Information
Order Number Package Type NSC Package Drawing Supplied As
LM3103MH Exposed Pad TSSOP-16 MXA16A 92 units per Anti-Static Tube
LM3103MHX 2500 Units on Tape and Reel
www.national.com 2
LM3103
Page 3

Pin Descriptions
Pin Name Description Application Information
1, 2 VIN Input supply voltage Supply pin to the device. Nominal input range is 4.5V to 42V.
3, 4 SW Switch Node Internally connected to the source of the main MOSFET and the drain of the
synchronous MOSFET. Connect to the output inductor.
5 BST Connection for
bootstrap capacitor
Connect a 33 nF capacitor from the SW pin to this pin. This capacitor is charged through
an internal diode during the main MOSFET off-time.
6 AGND Analog Ground Ground for all internal circuitry other than the PGND pin.
7 SS Soft-start A 70 µA internal current source charges an external capacitor of larger than 22 nF to
provide the soft-start function.
8 NC No Connection This pin should be left unconnected.
9, 10 GND Ground Must be connected to the AGND pin for normal operation. The GND and AGND pins
are not internally connected.
11 FB Feedback Internally connected to the regulation and over-voltage comparators. The regulation
setting is 0.6V at this pin. Connect to feedback resistors.
12 EN Enable pin Internal pull-up. Connect to a voltage higher than 1.6V to enable the device.
13 RON On-time Control An external resistor from the VIN pin to this pin sets the main MOSFET on-time.
14 VCC Startup regulator
Output
Nominally regulated to 6V. Connect a capacitor of larger than 1 µF between the VCC
and AGND pins for stable operation.
15, 16 PGND Power Ground Synchronous MOSFET source connection. Tie to a ground plane.
DAP EP Exposed Pad Thermal connection pad. Connect to the ground plane.
3 www.national.com
LM3103
Page 4
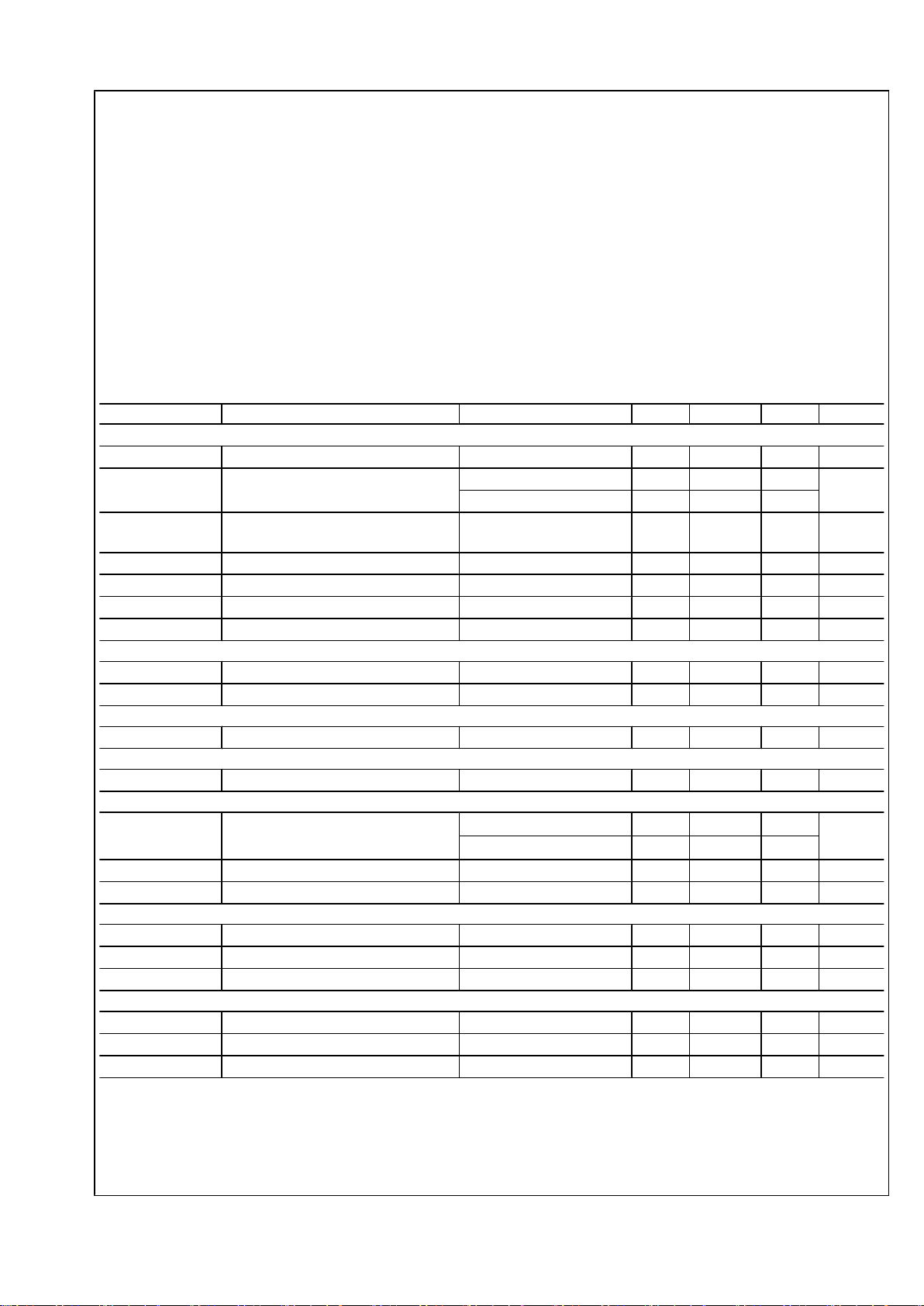
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
VIN, RON to AGND -0.3V to 43.5V
SW to AGND -0.3V to 43.5V
SW to AGND (Transient) -2V (< 100ns)
VIN to SW -0.3V to 43.5V
BST to SW -0.3V to 7V
VCC to AGND -0.3V to 7V
FB to AGND -0.3V to 5V
All Other Inputs to AGND -0.3V to 7V
ESD Rating (Note 2)
Human Body Model ±2kV
Storage Temperature Range -65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature (TJ) 150°C
Operating Ratings (Note 1)
Supply Voltage Range (VIN) 4.5V to 42V
Junction Temperature Range (TJ)
−40°C to +125°C
Thermal Resistance (θJA) (Note 3)
35°C/W
Electrical Characteristics Specifications with standard type are for T
J
= 25°C only; limits in boldface type apply
over the full Operating Junction Temperature (TJ) range. Minimum and Maximum limits are guaranteed through test, design, or
statistical correlation. Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm at TJ = 25°C, and are provided for reference
purposes only. Unless otherwise stated the following conditions apply: VIN = 18V, V
OUT
= 3.3V.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Start-Up Regulator, V
CC
V
CC
VCC output voltage C
VCC
= 1 µF, no load 5.6 6.0 6.2 V
VIN - V
CC
V
IN
- VCC dropout voltage (Note 4) ICC = 2mA 55 150 mV
ICC = 10mA 235 500
V
CC-UVLO
VCC under-voltage lockout threshold
(UVLO)
VIN increasing 3.5 3.7 4.1 V
V
CC-UVLO-HYS
VCC UVLO hysteresis VIN decreasing 275 mV
I
IN
IIN operating current No switching, VFB = 1V 1.0 1.25 mA
I
IN-SD
IIN operating current, Device shutdown VEN = 0V 20 40 µA
I
VCC
VCC current limit VCC = 0V 20 33 42 mA
Switching Characteristics
R
DS-UP-ON
Main MOSFET R
DS(on)
0.370 0.7
Ω
R
DS- DN-ON
Syn. MOSFET R
DS(on)
0.220 0.4
Ω
Soft-start
I
SS
SS pin source current VSS = 0V 45 70 95 µA
Current Limit
I
CL
Syn. MOSFET current limit threshold 0.9 A
ON/OFF Timer
t
on
ON timer pulse width
VIN = 10V, RON = 33 kΩ
0.350 µs
VIN = 18V, RON = 33 kΩ
0.170
t
on-MIN
ON timer minimum pulse width 100 ns
t
off
OFF timer pulse width 240 ns
Enable Input
V
EN
EN Pin input threshold VEN rising 1.6 1.85 V
V
EN-HYS
Enable threshold hysteresis VEN falling 230 mV
I
EN
Enable Pull-up Current VEN = 0V 1 µA
Regulation and Over-Voltage Comparator
V
FB
In-regulation feedback voltage TJ = −40°C to +125°C 0.588 0.6 0.612 V
V
FB-OV
Feedback over-voltage threshold 0.655 0.680 0.705 V
I
FB
1 nA
www.national.com 4
LM3103
Page 5
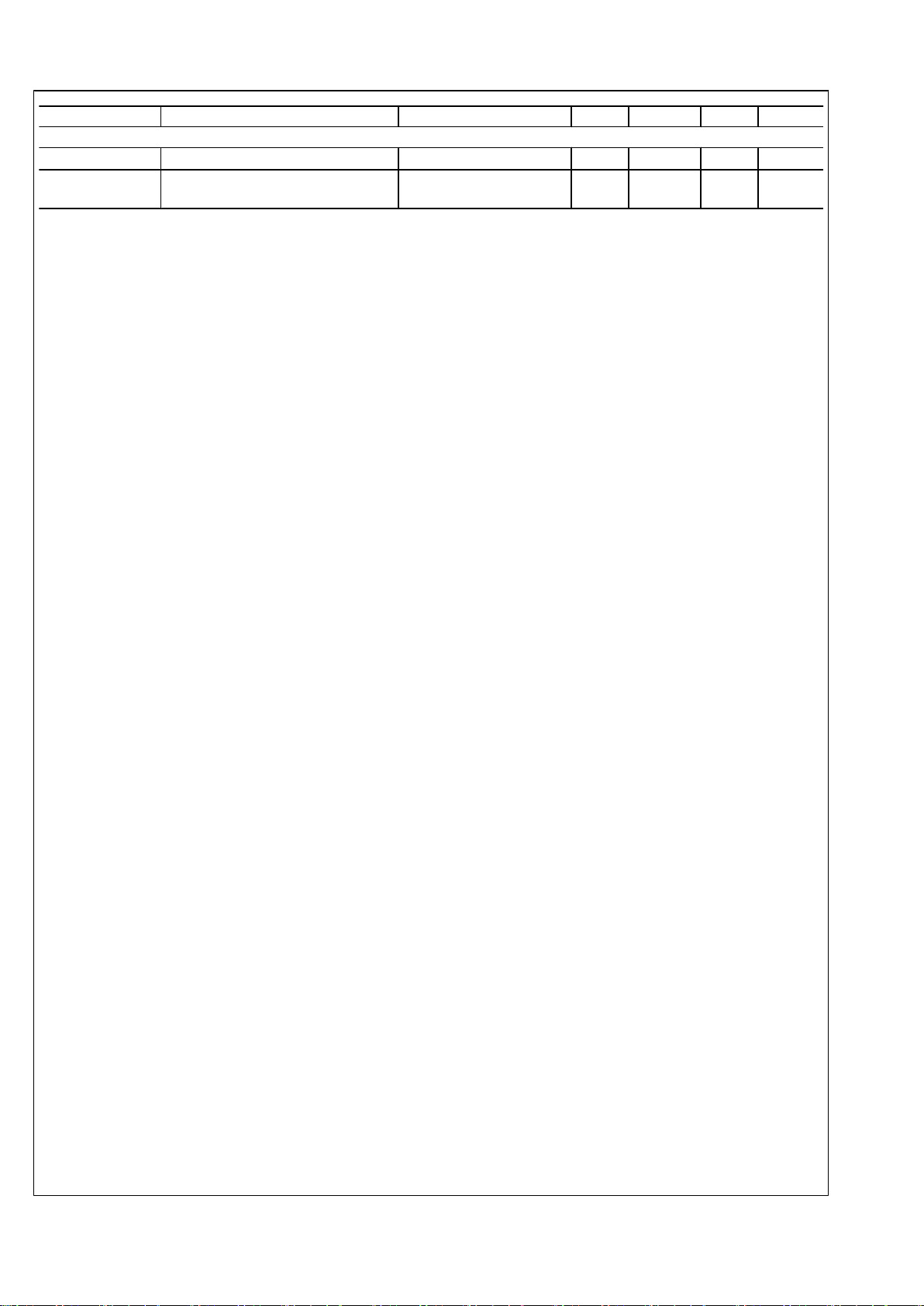
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Thermal Shutdown
T
SD
Thermal shutdown temperature TJ rising 165 °C
T
SD-HYS
Thermal shutdown temperature
hysteresis
TJ falling 20 °C
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings are limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings are conditions under which operation of the
device is intended to be functional. For guaranteed specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics.
Note 2: The human body model is a 100pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5kΩ resistor into each pin.
Note 3: θJA measurements were performed in general accordance with JEDEC Standards JESD51-1 to JESD51-11.
Note 4: VCC provides self bias for the internal gate drive and control circuits. Device thermal limitations limit external loading.
5 www.national.com
LM3103
Page 6

Typical Performance Characteristics
All curves are taken at VIN = 18V with the configuration in the typical application circuit for V
OUT
= 3.3V shown in this datasheet.
TA = 25°C, unless otherwise specified.
Quiescent Current, IIN vs V
IN
30029703
VCC vs I
CC
30029704
VCC vs V
IN
30029705
ton vs V
IN
30029706
Switching Frequency, fSW vs V
IN
30029707
VFB vs Temperature
30029708
www.national.com 6
LM3103
Page 7

R
DS(on)
vs Temperature
30029709
Efficiency vs Load Current
(V
OUT
= 3.3V)
30029710
V
OUT
Regulation vs Load Current
(V
OUT
= 3.3V)
30029711
Efficiency vs Load Current
(V
OUT
= 0.6V)
30029712
V
OUT
Regulation vs Load Current
(V
OUT
= 0.6V)
30029713
Power Up
(V
OUT
= 3.3V, 0.75A Loaded)
30029714
7 www.national.com
LM3103
Page 8

Enable Transient
(V
OUT
= 3.3V, 0.75A Loaded)
30029715
Shutdown Transient
(V
OUT
= 3.3V, 0.75A Loaded)
30029716
Continuous Mode Operation
(V
OUT
= 3.3V, 2.5A Loaded)
30029717
Discontinuous Mode Operation
(V
OUT
= 3.3V, 0.02A Loaded)
30029718
DCM to CCM Transition
(V
OUT
= 3.3V, 0.01A - 0.75A Load)
30029719
Load Transient
(V
OUT
= 3.3V, 0.075A - 0.75A Load, Current slew-rate: 2.5A/µs)
30029720
www.national.com 8
LM3103
Page 9

Simplified Functional Block Diagram
30029721
9 www.national.com
LM3103
Page 10

Functional Description
The LM3103 Step Down Switching Regulator features all required functions to implement a cost effective, efficient buck
power converter which is capable of supplying 0.75A to loads.
It contains dual N-Channel main and synchronous MOSFETs. The Constant ON-Time (COT) regulation scheme requires no loop compensation, results in a fast load transient
response and simple circuit implementation. The regulator
can function properly even with an all ceramic output capacitor network, and does not rely on the output capacitor’s ESR
for stability. The operating frequency remains constant with
line variations due to the inverse relationship between the input voltage and the on-time. The valley current limit detection
circuit, with a limit set internally at 0.9A, inhibits the main
MOSFET until the inductor current level subsides.
The LM3103 can be applied in numerous applications and
can operate efficiently for inputs as high as 42V. Protection
features include VCC under-voltage lockout, output over-voltage protection, thermal shutdown, gate drive under-voltage
lock-out. The LM3103 is available in the thermally enhanced
eTSSOP-16 package.
COT Control Circuit Overview
COT control is based on a comparator and a one-shot ontimer, with the output voltage feedback (feeding to the FB pin)
compared with a 0.6V internal reference. If the voltage of the
FB pin is below the reference, the main MOSFET is turned on
for a fixed on-time determined by a programming resistor
RON and the input voltage VIN, upon which the on-time varies
inversely. Following the on-time, the main MOSFET remains
off for a minimum of 240 ns. Then, if the voltage of the FB pin
is below the reference, the main MOSFET is turned on again
for another on-time period. The switching will continue to
achieve regulation.
The regulator will operate in the discontinuous conduction
mode (DCM) at a light load, and the continuous conduction
mode (CCM) with a heavy load. In the DCM, the current
through the inductor starts at zero and ramps up to a peak
during the on-time, and then ramps back to zero before the
end of the off-time. It remains zero and the load current is
supplied entirely by the output capacitor. The next on-time
period starts when the voltage at the FB pin falls below the
internal reference. The operating frequency in the DCM is
lower and varies larger with the load current as compared with
the CCM. Conversion efficiency is maintained since conduction loss and switching loss are reduced with the reduction in
the load and the switching frequency respectively. The operating frequency in the DCM can be calculated approximately
as follows:
(1)
In the continuous conduction mode (CCM), the current flows
through the inductor in the entire switching cycle, and never
reaches zero during the off-time. The operating frequency remains relatively constant with load and line variations. The
CCM operating frequency can be calculated approximately as
follows:
(2)
The output voltage is set by two external resistors R
FB1
and
R
FB2
. The regulated output voltage is
V
OUT
= 0.6V x (R
FB1
+ R
FB2
)/R
FB2
(3)
Startup Regulator (VCC)
A startup regulator is integrated within the LM3103. The input
pin VIN can be connected directly to a line voltage up to 42V.
The VCC output regulates at 6V, and is current limited to 30
mA. Upon power up, the regulator sources current into an external capacitor C
VCC
, which is connected to the VCC pin. For
stability, C
VCC
must be at least 1 µF. When the voltage on the
VCC pin is higher than the under-voltage lock-out (UVLO)
threshold of 3.7V, the main MOSFET is enabled and the SS
pin is released to allow the soft-start capacitor CSS to charge.
The minimum input voltage is determined by the dropout voltage of the regulator and the VCC UVLO falling threshold
(≊3.4V). If VIN is less than ≊4.0V, the regulator shuts off and
VCC goes to zero.
Regulation Comparator
The feedback voltage at the FB pin is compared to a 0.6V
internal reference. In normal operation (the output voltage is
regulated), an on-time period is initiated when the voltage at
the FB pin falls below 0.6V. The main MOSFET stays on for
the programmed on-time, causing the output voltage to rise
and consequently the voltage of the FB pin to rise above 0.6V.
After the on-time period, the main MOSFET stays off until the
voltage of the FB pin falls below 0.6V again. Bias current at
the FB pin is nominally 1 nA.
Zero Coil Current Detect
The current of the synchronous MOSFET is monitored by a
zero coil current detection circuit which inhibits the synchronous MOSFET when its current reaches zero until the
next on-time. This circuit enables the DCM operation, which
improves the efficiency at a light load.
Over-Voltage Comparator
The voltage at the FB pin is compared to a 0.68V internal
reference. If it rises above 0.68V, the on-time is immediately
terminated. This condition is known as over-voltage protection (OVP). It can occur if the input voltage or the output load
changes suddenly. Once the OVP is activated, the main
MOSFET remains off until the voltage at the FB pin falls below
0.6V. The synchronous MOSFET will stay on to discharge the
inductor until the inductor current reduces to zero and then
switch off.
ON-Time Timer, Shutdown
The on-time of the LM3103 main MOSFET is determined by
the resistor RON and the input voltage VIN. It is calculated as
follows:
(4)
The inverse relationship of ton and VIN gives a nearly constant
frequency as VIN is varied. RON should be selected such that
the on-time at maximum VIN is greater than 100 ns. The ontimer has a limiter to ensure a minimum of 100 ns for ton. This
limits the maximum operating frequency, which is governed
by the following equation:
www.national.com 10
LM3103
Page 11

(5)
The LM3103 can be remotely shut down by pulling the voltage
of the EN pin below 1.6V. In this shutdown mode, the SS pin
is internally grounded, the on-timer is disabled, and bias currents are reduced. Releasing the EN pin allows normal operation to resume because the EN pin is internally pulled up.
30029726
FIGURE 1. Shutdown Implementation
Current Limit
Current limit detection is carried out during the off-time by
monitoring the re-circulating current through the synchronous
MOSFET. Referring to the Functional Block Diagram, when
the main MOSFET is turned off, the inductor current flows
through the load, the PGND pin and the internal synchronous
MOSFET. If this current exceeds 0.9A, the current limit comparator toggles, and as a result the start of the next on-time
period is disabled. The next switching cycle starts when the
re-circulating current falls back below 0.9A (and the voltage
at the FB pin is below 0.6V). The inductor current is monitored
during the on-time of the synchronous MOSFET. As long as
the inductor current exceeds 0.9A, the main MOSFET will remain inhibited to achieve current limit. The operating frequency is lower during current limit owing to a longer off-time.
Figure 2 illustrates an inductor current waveform. On average, the output current I
OUT
is the same as the inductor
current IL, which is the average of the rippled inductor current.
In case of current limit (the current limit portion of Figure 2),
the next on-time will not initiate until that the current drops
below 0.9A (assume the voltage at the FB pin is lower than
0.6V). During each on-time the current ramps up an amount
equal to:
(6)
During current limit, the LM3103 operates in a constant current mode with an average output current I
OUT(CL)
equal to
0.9A + ILR / 2.
30029728
FIGURE 2. Inductor Current - Current Limit Operation
11 www.national.com
LM3103
Page 12

N-Channel MOSFET and Driver
The LM3103 integrates an N-Channel main MOSFET and an
associated floating high voltage main MOSFET gate driver.
The gate drive circuit works in conjunction with an external
bootstrap capacitor C
BST
and an internal high voltage diode.
C
BST
connected between the BST and SW pins powers the
main MOSFET gate driver during the main MOSFET on-time.
During each off-time, the voltage of the SW pin falls to approximately -1V, and C
BST
charges from VCC through the
internal diode. The minimum off-time of 240 ns provides
enough time for charging C
BST
in each cycle.
Soft-Start
The soft-start feature allows the converter to gradually reach
a steady state operating point, thereby reducing startup
stresses and current surges. Upon turn-on, after VCC reaches
the under-voltage threshold and a 180 µs fixed delay, a 70 µA
internal current source charges an external capacitor C
SS
connecting to the SS pin. The ramping voltage at the SS pin
(and the non-inverting input of the regulation comparator as
well) ramps up the output voltage V
OUT
in a controlled manner. An internal switch grounds the SS pin if any of the
following three cases happen: (i) VCC is below the under-voltage lockout threshold; (ii) a thermal shutdown occurs; or (iii)
the EN pin is grounded. Alternatively, the output voltage can
be shut off by connecting the SS pin to the ground using an
external switch. Releasing the switch allows the voltage of the
SS pin to ramp up and the output voltage to return to normal.
The shutdown configuration is shown in Figure 3.
30029729
FIGURE 3. Alternate Shutdown Implementation
Thermal Protection
The junction temperature of the LM3103 should not exceed
the maximum limit. Thermal protection is implemented by an
internal Thermal Shutdown circuit, which activates (typically)
at 165°C to make the controller enter a low power reset state
by disabling the main MOSFET, disabling the on-timer, and
grounding the SS pin. Thermal protection helps prevent
catastrophic failures from accidental device overheating.
When the junction temperature falls back below 145°C (typical hysteresis = 20°C), the SS pin is released and normal
operation resumes.
Applications Information
EXTERNAL COMPONENTS
The following guidelines can be used to select external components.
R
FB1
and R
FB2
: These resistors should be chosen from stan-
dard values in the range of 1.0 kΩ to 10 kΩ, satisfying the
following ratio:
R
FB1/RFB2
= (V
OUT
/0.6V) - 1 (7)
For V
OUT
= 0.6V, the FB pin can be connected to the output
directly with a pre-load resistor drawing more than 20 µA. This
is because the converter operation needs a minimum inductor
current ripple to maintain good regulation when no load is
connected.
RON: Equation (2) can be used to select RON if a desired op-
erating frequency is selected. But the minimum value of
RON is determined by the minimum on-time. It can be calculated as follows:
(8)
If RON calculated from (2) is smaller than the minimum value
determined in (8), a lower frequency should be selected to recalculate RON by (2). Alternatively, V
IN(MAX)
can also be limited
in order to keep the frequency unchanged. The relationship
of V
IN(MAX)
and RON is shown in Figure 4.
On the other hand, the minimum off-time of 240 ns can limit
the maximum duty ratio. This may be significant at low VIN. A
larger RON should be selected in any application requiring a
large duty ratio.
30029738
FIGURE 4. Maximum VIN for selected R
ON
L: The main parameter affected by the inductor is the ampli-
tude of the inductor current ripple (ILR), which is recommended to be greater than 0.3A. Once ILR is selected, L can be
determined by:
(9)
where VIN is the input voltage and fSW is determined from (2).
www.national.com 12
LM3103
Page 13

If the output current I
OUT
is known, by assuming that I
OUT
=
IL, the peak and valley of ILR can be determined. Beware that
the peak of ILR should not be larger than the saturation current
of the inductor and the current rating of the main and synchronous MOSFETs. Also, the valley of ILR must be positive
if CCM operation is required.
30029732
FIGURE 5. Inductor selection for V
OUT
= 3.3V
30029733
FIGURE 6. Inductor selection for V
OUT
= 0.6V
Figures 5 and 6 show curves on inductor selection for various
V
OUT
and RON. According to (8), VIN is limited for small RON.
Some curves are therefore limited as shown in the figures.
C
VCC
: The capacitor on the VCC output provides not only noise
filtering and stability, but also prevents false triggering of the
VCC UVLO at the main MOSFET on/off transitions. C
VCC
should be no smaller than 1 µF for stability, and should be a
good quality, low ESR, ceramic capacitor.
C
OUT
and C
OUT3
: C
OUT
should generally be no smaller than
10 µF. Experimentation is usually necessary to determine the
minimum value for C
OUT
, as the nature of the load may require
a larger value. A load which creates significant transients requires a larger C
OUT
than a fixed load.
C
OUT3
is a small value ceramic capacitor located close to the
LM3103 to further suppress high frequency noise at V
OUT
. A
47 nF capacitor is recommended.
CIN and C
IN3
: The function of CIN is to supply most of the main
MOSFET current during the on-time, and limit the voltage ripple at the VIN pin, assuming that the voltage source connecting to the VIN pin has finite output impedance. If the voltage
source’s dynamic impedance is high (effectively a current
source), CIN supplies the difference between the instantaneous input current and the average input current.
At the maximum load current, when the main MOSFET turns
on, the current to the VIN pin suddenly increases from zero
to the valley of the inductor’s ripple current and ramps up to
the peak value. It then drops to zero at turn-off. The average
current during the on-time is the load current. For a worst case
calculation, CIN must be capable of supplying this average
load current during the maximum on-time. CIN is calculated
from:
(10)
where I
OUT
is the load current, ton is the maximum on-time,
and ΔVIN is the allowable ripple voltage at VIN.
C
IN3
’s purpose is to help avoid transients and ringing due to
long lead inductance at the VIN pin. A low ESR 0.1 µF ceramic
chip capacitor located close to the LM3103 is recommended.
C
BST
: A 33 nF high quality ceramic capacitor with low ESR is
recommended for C
BST
since it supplies a surge current to
charge the main MOSFET gate driver at each turn-on. Low
ESR also helps ensure a complete recharge during each offtime.
CSS: The capacitor at the SS pin determines the soft-start
time, i.e. the time for the reference voltage at the regulation
comparator and therefore, the output voltage to reach their
final value. The time is determined from the following equation:
(11)
CFB: If the output voltage is higher than 1.6V, CFB is needed
in the Discontinuous Conduction Mode to reduce the output
ripple. The recommended value for CFB is 10 nF.
PC BOARD LAYOUT
The LM3103 regulation, over-voltage, and current limit comparators are very fast so they will respond to short duration
noise pulses. Layout is therefore critical for optimum performance. It must be as neat and compact as possible, and all
external components must be as close to their associated
pins of the LM3103 as possible. Refer to the functional block
diagram. The loop formed by CIN, the main and synchronous
MOSFET internal to the LM3103, and the PGND pin should
be as small as possible. The connection from the PGND pin
to CIN should be as short and direct as possible. Vias should
be added to connect the ground of CIN to a ground plane,
located as close to the capacitor as possible. The bootstrap
capacitor C
BST
should be connected as close to the SW and
BST pins as possible, and the connecting traces should be
thick. The feedback resistors and capacitor R
FB1
, R
FB2
, and
CFB should be close to the FB pin. A long trace running from
V
OUT
to R
FB1
is generally acceptable since this is a low
impedance node. Ground R
FB2
directly to the AGND pin (pin
7). The output capacitor C
OUT
should be connected close to
the load and tied directly to the ground plane. The inductor L
should be connected close to the SW pin with as short a trace
as possible to reduce the potential for EMI (electromagnetic
interference) generation. If it is expected that the internal dis-
13 www.national.com
LM3103
Page 14

sipation of the LM3103 will produce excessive junction temperature during normal operation, making good use of the PC
board’s ground plane can help considerably to dissipate heat.
The exposed pad on the bottom of the LM3103 IC package
can be soldered to the ground plane, which should extend out
from beneath the LM3103 to help dissipate heat. The exposed
pad is internally connected to the LM3103 IC substrate. Ad-
ditionally the use of thick traces, where possible, can help
conduct heat away from the LM3103. Using numerous vias to
connect the die attached pad to the ground plane is a good
practice. Judicious positioning of the PC board within the end
product, along with the use of any available air flow (forced or
natural convection) can help reduce the junction temperature.
30029736
Typical Application Schematic for V
OUT
= 3.3V
30029737
Typical Application Schematic for V
OUT
= 0.6V
www.national.com 14
LM3103
Page 15

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
16-Lead Plastic eTSSOP Package
NS Package Number MXA16A
15 www.national.com
LM3103
Page 16

Notes
LM3103 SIMPLE SWITCHER® Synchronous 1MHz 0.75A Step-Down Voltage Regulator
THE CONTENTS OF THIS DOCUMENT ARE PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION
(“NATIONAL”) PRODUCTS. NATIONAL MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES WITH RESPECT TO THE ACCURACY
OR COMPLETENESS OF THE CONTENTS OF THIS PUBLICATION AND RESERVES THE RIGHT TO MAKE CHANGES TO
SPECIFICATIONS AND PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS AT ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE. NO LICENSE, WHETHER EXPRESS,
IMPLIED, ARISING BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS
DOCUMENT.
TESTING AND OTHER QUALITY CONTROLS ARE USED TO THE EXTENT NATIONAL DEEMS NECESSARY TO SUPPORT
NATIONAL’S PRODUCT WARRANTY. EXCEPT WHERE MANDATED BY GOVERNMENT REQUIREMENTS, TESTING OF ALL
PARAMETERS OF EACH PRODUCT IS NOT NECESSARILY PERFORMED. NATIONAL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY FOR
APPLICATIONS ASSISTANCE OR BUYER PRODUCT DESIGN. BUYERS ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR THEIR PRODUCTS AND
APPLICATIONS USING NATIONAL COMPONENTS. PRIOR TO USING OR DISTRIBUTING ANY PRODUCTS THAT INCLUDE
NATIONAL COMPONENTS, BUYERS SHOULD PROVIDE ADEQUATE DESIGN, TESTING AND OPERATING SAFEGUARDS.
EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN NATIONAL’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, NATIONAL ASSUMES NO
LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND NATIONAL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY RELATING TO THE SALE
AND/OR USE OF NATIONAL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
RIGHT.
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR
SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS PRIOR WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
Life support devices or systems are devices which (a) are intended for surgical implant into the body, or (b) support or sustain life and
whose failure to perform when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling can be reasonably expected
to result in a significant injury to the user. A critical component is any component in a life support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor and the National Semiconductor logo are registered trademarks of National Semiconductor Corporation. All other
brand or product names may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Copyright© 2007 National Semiconductor Corporation
For the most current product information visit us at www.national.com
National Semiconductor
Americas Customer
Support Center
Email:
new.feedback@nsc.com
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
National Semiconductor Europe
Customer Support Center
Fax: +49 (0) 180-530-85-86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 69 9508 6208
English Tel: +49 (0) 870 24 0 2171
Français Tel: +33 (0) 1 41 91 8790
National Semiconductor Asia
Pacific Customer Support Center
Email: ap.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor Japan
Customer Support Center
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
Email: jpn.feedback@nsc.com
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
www.national.com
 Loading...
Loading...