Page 1
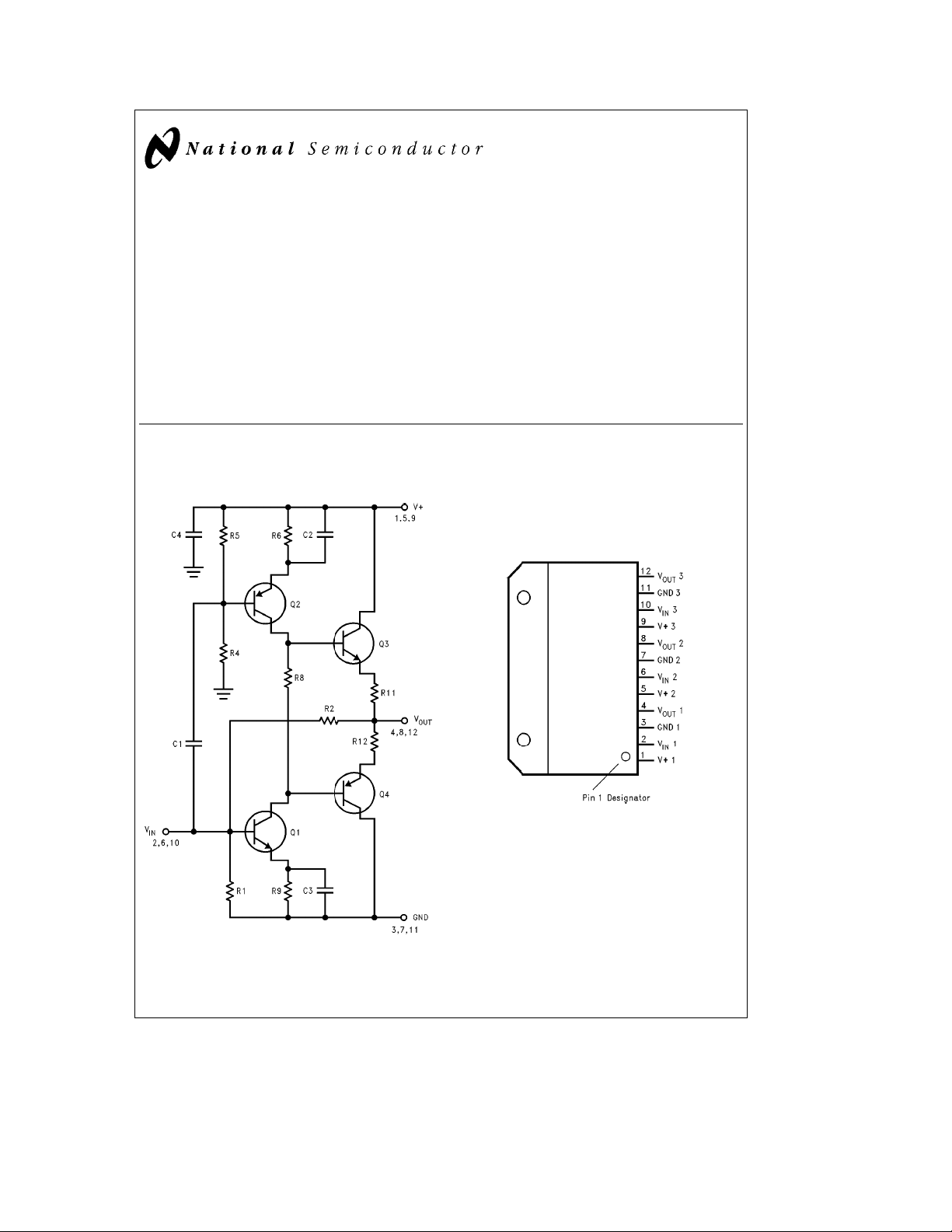
LM2427
Triple 80 MHz CRT Driver
LM2427 Triple 80 MHz CRT Driver
April 1995
General Description
The LM2427 is a high performance triple CRT driver for
simplifying color monitor designs. The device contains three
large signal transimpedance amplifiers, and provides direct
cathode drive capability. A plastic power package and pinto-pin compatibility make the LM2427 ideal for new designs
or as a low cost replacement for designs using the LH2426
or CR5527.
Schematic and Connection Diagrams
(One Section)
Features
Y
Low-cost plastic power package
Y
Typical rise/fall times of 3.5 ns
Y
80 MHz video bandwidth at 50 VPPwith 8 pF load
Y
Operation from 80V power supply
Applications
Y
CRT driver for color monitors
Y
Drives CRT cathode directly
Y
Pin-to-pin compatible with the LH2426 and CR5527
CRT drivers
Top View
Order Number LM2427T
See NS Package Number MKT-TA12A
TL/H/11967– 1
C
1995 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M115/Printed in U. S. A.
TL/H/11967
TL/H/11967– 2
Page 2
Absolute Maximum Ratings
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales
Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage, V
Safe Operating Power Consumption 14W
aa
85V
CASE
b
25§Ctoa100§C
b
20§Ctoa90§C
Storage Temperature Range, T
Operating Temperature Range, T
STG
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec.) 300§C
ESD Tolerance TBD
Electrical Characteristics V
offset. See
Figure 1.
T
e
25§C unless otherwise noted.
CASE
ae
80V, R
e
430X,C1e47 pF, C
G
Symbol Parameter Conditions
I
CC
V
INDC
V
OUTDC
t
R
t
F
A
V
LE Linearity Error V
DA
V
Note 1: Input signal: tr,t
Note 2: Linearity error is defined as: The variation in small signal gain from
Note 3: Calculated value from voltage gain test on each channel.
Supply Current (per Amplifier) No Input or Output Load 24 30 mA
Input Offset Voltage 1.4 1.6 1.8 V
Output Offset Voltage 34 40 46 V
Rise Time 10% to 90% (Note 1) 3.5 ns
Fall Time 90% to 10% (Note 1) 3.5 ns
Voltage Gain
froma10V toa70V (Note 2) 5 %
OUT
Gain Matching (Note 3) 0.2 dB
k
f
1.5 ns, f
e
1 MHz.
in
a
20V toa70V output with a 100 mVAC, 1 MHz, input signal.
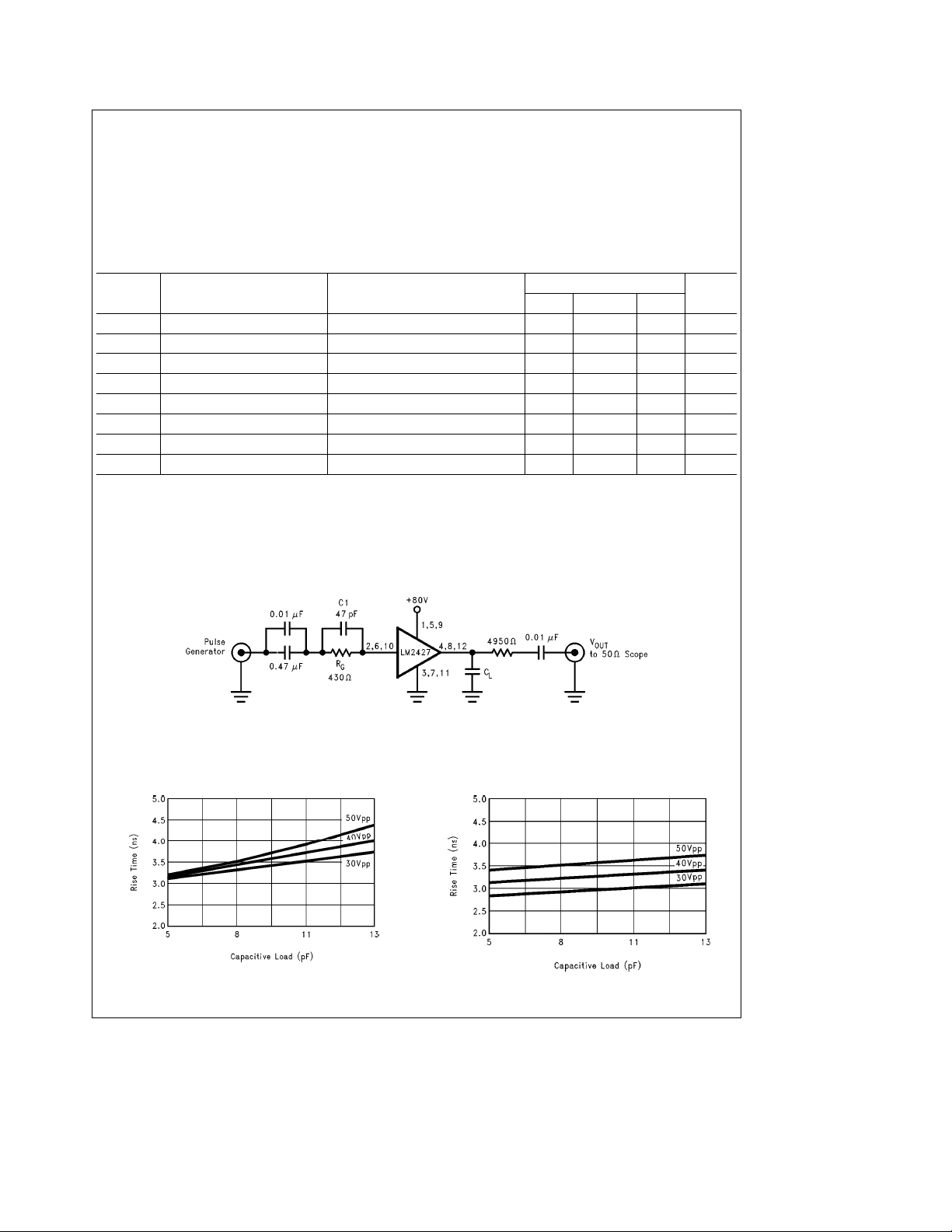
Typical Performance Characteristics
Typical Test Circuit (One Section)
e
8 pF, 50 VPPoutput swing with 40V DC
L
LM2427
Min Typical Max
b
b
11
b
13
14 V/V
Units
Note: CL, total load capacltance, includes all parasitic capacitances.
FIGURE 1. Test Circuit (One Section)
This test circuit is used for both characteristic plots.
Typical Rise Time vs Capacitive Loading
TL/H/11967– 10
TL/H/11967– 3
Typical Fall Time vs Capacitive Loading
TL/H/11967– 5
2
Page 3

Test Circuit
Figure 1
shows a typical test circuit for evaluation of the
LM2427. This circuit is designed to allow testing of the
LM2427 in a 50X environment, such as a pulse generator,
oscilloscope or network analyzer. The 4950X resistor in series with the output of the LM2427 forms a 100:1 voltage
divider when connected to a 50X-input oscilloscope or network analyzer. To calibrate pulse generator, set to 2.4 V
into 50X.
THEORY OF OPERATlON
The LM2427 is a triple channel transimpedance amplifier for
CRT’s, suitable for SVGA, XGA, IBM and Macintosh display
resolution monitors. The LM2427 is pin-to-pin compatible
with the LH2426 and CR5527 CRT drivers. The device is
packaged in the industry standard 12-lead SIP TO-220
molded plastic power package. The heat sink is electrically
isolated and may be grounded for ease of manufacturing
and RFI/EMI shielding.
Applying an input current to the LM2427 will result in an
output voltage. An input current of about
vide a full output swing of
input converts the device into a voltage amplifier; with a
resistor value of 430X the voltage gain becomes
The LM2427 is a two stage amplifier configured in a pushpull configuration (see schematic on front page). Q2 is biased by resistors R4 and R5, Q1 gets its bias through a
5700X feedback resistor and the input biasing current. The
bases of Q1 and Q2 are capacitively coupled and, therefore,
Q2 will be actively driven.
The emitter resistors of Q1 and Q2 are bypassed with small
capacitors. This increases the gain of the stage for high
frequencies and increases the bandwidth of the amplifier.
Emitter followers Q3 and Q4 isolate the input stage from the
output capacitance load, and minimizes the circuit sensitivity
to load capacitance.
The power supply pin is intemally bypassed. If low frequencies are present in the power supply line, an electrolytic
capacitor is recommended.
g
25V. A resistor in series with the
g
4.5 mA will pro-
b
13.
Bypassing the resistor with a capacitor of about 47 pF will
restore the rise and fall times but will result in some overshoot.
(Figure 2b)
Adding a resistor in series with the 47 pF capacitor will reduce the overshoot but also increases the rise and fall
times.
(Figure 2c)
The addition of a second capacitor offers a compromise
PP
between the above networks by improving the rise and fall
times at the expense of some overshoot.
Suggested values for the resistors and capacitors are
shown, however, optimum values may differ depending
upon the stray inductances and capacitances present in different board layouts.
(Figure 2d)
Application Hints
The LM2427 is designed as a triple power amplifier for delivering red, green, and blue video signals to a cathode ray
tube (CRT). It can provide a 50V output swing and energize
a 12 ns pixel at a CRT cathode with 8 pF of capacitance.
As with any CRT driver, when designing a video amplifier
board with the LM2427, careful attention should be paid at
reducing stray capacitance along the entire video signal
path. This is especially important in the path between the
output of the CRT driver and the cathodes, because any
additional capacitance load will increase rise and fall times
and will result in reduced picture quality.
INPUT NETWORKS
The voltage gain and the response of the amplifiers can be
set by adding an R-C network to the input.
A 430X resistor in series with the input will set the voltage
b
gain to
the system (see
13, but this will increase the rise and fall times of
Figure 2a
).
FIGURE 2. Influence of Input Networks
TL/H/11967– 6
on Switching Performance
3
Page 4

Application Hints (Continued)
TILT AND OVERSHOOT COMPENSATlON
When a low frequency square is displayed on a monitor
screen, some tilt may appear on the video signal due to the
large power and thermal dissipation changes in the input
transistors. This problem is illustrated in
Figure 3.
PROTECTlNG AMPLIFIER OUTPUT
FROM TUBE ARCING
During normal CRT operation, internal arcing may occasionally occur. Spark gap protectors will limit the maximum voltage, but to a value that is much higher than allowable on the
LM2427. This fast, high voltage, high energy pulse can damage the LM2427 output stage. The addition of two current
limiting resistors of 50X to 100X total, and clamping diodes
D1 and D2, will provide protection but will slow down the
response. The diodes should have a fast transient response, high peak current rating, low series impedance and
low shunt capacitance. FDH400 or equivalent diodes are
recommended. Adding a series peaking inductor of 100 nH
to 150 nH will restore the bandwidth and provide additional
protection. (See
Figure 5
)
The value of the inductor can be calculated from:
R
2.4
2
a
R2)
1
C
L
a
(R
O
e
Lp
where CLis the total load and ROis the intrinsic high frequency output resistance of the amplifier, generally 160X.
FIGURE 3. Tilt on a Low Frequency
TL/H/11967– 7
Signal and Its Effects
The tilt can be compensated by adding an external RC feedback network as shown in
Figure 4.
The RC feedback helps
by reducing the gain of the amplifier during the edge transition for a duration corresponding to
C should be selected so that the gain is reduced (DV
for the duration of the tilt (
u).
u. The values of R and
e
TL/H/11967– 8
FIGURE 4. RC Feedback Network for Tilt Compensation
To find the value of resistor R, the following formula can be
used:
(100bx%)
e
R
x%
R
F
where x% is the percentage value of DV to the peak-topeak output swing (V
The value of capacitor C is determined by:
). RFis internally fixed to 5700X.
PP
e
C
u/R
where u is the duration of the tilt.
For optimum results in a specific application, the values for
R and C may need to be tested and adjusted in the given
application board.
FIGURE 5. One Section of the LM2427
with Tilt Compensation, Arc Protection
0)
and Peaking Inductance L
in the Output
P
SHORT CIRCUIT PROTECTION
WARNING!
To provide maximum output speed, the LM2427 does not
have short circuit protection. Shorting the output can destroy the device.
SUPPLY BYPASSlNG
Although the LM2427 has internal supply bypassing, some
values of supply line inductance can cause ringing in the
supply lines. If this occurs, an additional bypass capacitor or
a low-pass filter should be placed as close as possible to
the supply (V
a
) pins of the LM2427.
CAPACITlVE LOADS
The LM2427 is designed to drive capacitive loads, however,
the very high output slew rate of about 13,700 V/ms can
result in charging currents of over 200 mA into a 20 pF load.
These very high currents can damage the output transistors.
HEAT SlNKlNG
Power consumption by the LM2427 will depend on the supply voltage used, the output loading, the peak-to-peak output swing and the operating frequency. Since the LM2427
will dissipate up to 14W, an external heatsink is always required. The maximum allowed case temperature is 90
calculate maximum heatsink thermal resistance, use the following formula:
(90§CbMax Ambient)
e
R
th
14
.
TL/H/11967– 9
C. To
§
4
Page 5

PC BOARD LAYOUT CONSIDERATIONS
Input pins 2, 6 and 10 are amplifier summing junctions. All
connections to these points should be as short as possible
and should be separated from other signals. The components connected to these pins should be located close to
the LM2427, and the total conductor length connected to
these points should be no more than one inch.
For optimum performance, an adequate ground plane, isolation between channels, good supply bypassing and minimizing unwanted feedback are necessary. Also, the length of
the signal traces from the preamplifier to the LM2427 and
from the LM2427 to the CRT cathode should be as short as
possible. The following references are recommended:
Ott, Henry W.,
Systems’’,
‘‘Guide to CRT Video Design’’,
plication Note 861.
‘‘Noise Reduction Techniques in Electronic
John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1976.
National Semiconductor Ap-
5
Page 6

Physical Dimensions inches
[
millimeters
]
LM2427 Triple 80 MHz CRT Driver
Note 1: Unless otherwise specified. Standard Lead Finish: 200 microinches/5.08 micrometers minimum. Lead/Tin (Solder) on Olin 194 or equivalent.
Note 2: No JEDEC Registration as of 09-01-93.
Order Number LM2427T
NS Package Number MKT-TA12A
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT OF NATIONAL
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or 2. A critical component is any component of a life
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant support device or system whose failure to perform can
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and whose be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life
failure to perform, when properly used in accordance support device or system, or to affect its safety or
with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can effectiveness.
be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury
to the user.
National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor
Corporation Europe Hong Kong Ltd. Japan Ltd.
1111 West Bardin Road Fax: (
Arlington, TX 76017 Email: cnjwge@tevm2.nsc.com Ocean Centre, 5 Canton Rd. Fax: 81-043-299-2408
Tel: 1(800) 272-9959 Deutsch Tel: (
Fax: 1(800) 737-7018 English Tel: (
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
Fran3ais Tel: (
Italiano Tel: (
a
49) 0-180-530 85 86 13th Floor, Straight Block, Tel: 81-043-299-2309
a
49) 0-180-530 85 85 Tsimshatsui, Kowloon
a
49) 0-180-532 78 32 Hong Kong
a
49) 0-180-532 93 58 Tel: (852) 2737-1600
a
49) 0-180-534 16 80 Fax: (852) 2736-9960
 Loading...
Loading...