Page 1
Overview
The LC895195 is a CD-ROM decoder LSI that includes
both an on-chip IDE interface that was developed jointly
with Western Digital and an on-chip subcode ECC
function.
Features
• ATA-PI (IDE) interface
• Supports 16× playback (with IORDY) - Using ×16 70 ns
DRAMs
• 16.6 MB/s transfer rate: Using ×16 70 ns DRAMs
• 8.33 MB/s transfer rate: Using ×8 70 ns DRAMs
• Supports the use of from 1 M to 32 M of buffer RAM.
(DRAM)
• Allows the user to arbitrarily set the CD main channel,
C2 flag and subcode areas in buffer RAM.
• Batch transfer function (function for transferring the CD
main channel, C2 flag and subcode data in one
operation)
• Multi-transfer function (function for sending multiple
blocks in one operation)
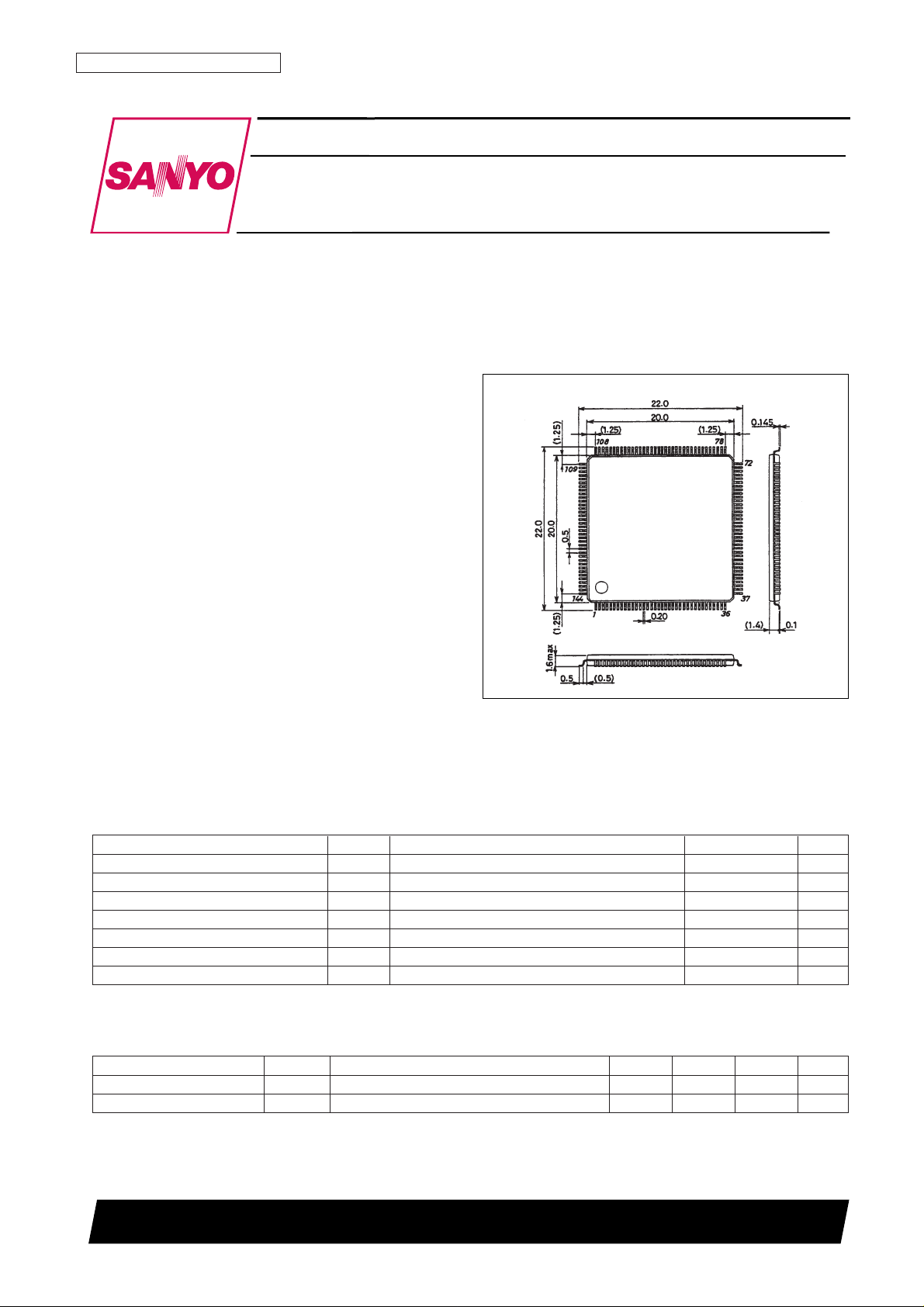
Package Dimensions
unit: mm
3214-SQFP144
CMOS LSI
Ordering number : EN* 5192B
N3097HA (OT)/22896HA (OT) No. 5192-1/8
Preliminary
SANYO: SQFP144
[LC895195]
SANYO Electric Co.,Ltd. Semiconductor Bussiness Headquarters
TOKYO OFFICE Tokyo Bldg., 1-10, 1 Chome, Ueno, Taito-ku, TOKYO, 110 JAPAN
ATA-PI (IDE) CD-ROM Decoder LSI
LC895195
Specifications
Absolute Maximum Ratings at VSS= 0 V
Note: * Per cell for basic I/O cells
Allowable Operating Ranges at Ta = –30 to +75°C, VSS= 0 V
Parameter Symbol Conditions Ratings Unit
Maximum supply voltage V
DD
max Ta = 25°C –0.3 to +7.0 V
I/O voltages V
I
, VOmax Ta = 25°C –0.3 to VDD+ 0.3 V
Allowable power dissipation Pd max Ta ≤ 70°C 550 mW
Operating temperature Topr –30 to +75 °C
Storage temperature Tstg –55 to +125 °C
Soldering heat resistances (pins only) 10 seconds 235 °C
I/O current I
I
, IOmax ±20* mA
Parameter Symbol Conditions min typ max Unit
Supply voltage V
DD
4.5 5.0 5.5 V
Input voltage range V
IN
0V
DD
V
Page 2
No. 5192-2/8
LC895195
DC Characteristics at VSS= 0 V, VDD= 4.5 to 5.5 V, Ta = –30 to +75°C
Note: * The entries in the “Applicable Pins” column specify the following pin sets.
[Input]
1: CSCTRL, SUA0 to SUA6, TEST0 to TEST4
2: SBSO, SCOR, WFCK, ZCS, ZDIOR, ZDIOW, ZDMACK, ZHRST, ZRESET, ZRD, ZWR, BCK, C2PO, LRCK, SDATA, DA0 to DA2, ZCS1FX,
ZCS3FX
[Output]
3: MCK, MCK2
4: ZRSTCPU, ZRSTIC, ZINT1
5: ZINT, ZSWAIT
6: DMARQ, HINTRQ
7: RA0 to RA9, ZCAS0, ZCAS1, ZLWE, ZOE, ZRAS0, ZRAS1, ZUWE, EXCK
8: IORDY, ZIOCS16
[I/O]
9: D0 to D7, IO0 to IO15
10: DD0 to DD15, ZDASP, ZPDIAG
Note: XTAL, XTALCK
The above pins are not included in the DC characteristics.
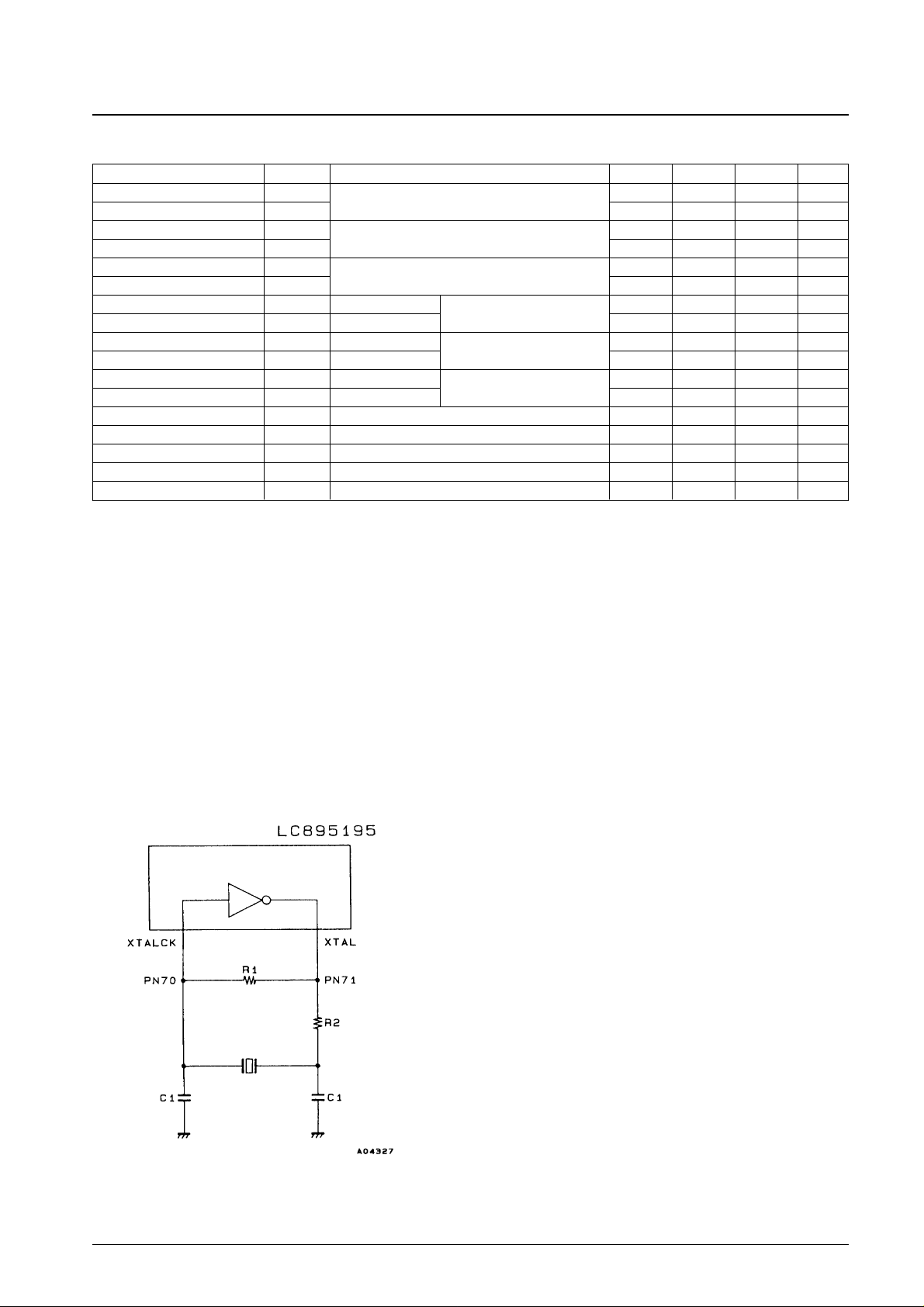
Sample Recommended Oscillator Circuit
R1 = 120 kΩ
R2 = 47 kΩ
C1 = 30 pF
For a crystal oscillator frequency of 16.9344 MHz.
Alternatively:
R1 = 3.3 kΩ
R2 = None
C1 = 5 pF
For a crystal oscillator frequency of 33.8688 MHz.
For an oscillator frequency of 33.8688, the third harmonic is used. This means that
precise component values will be influenced by the printed circuit board. Consult
the manufacturer of the crystal to determine the circuit constants for this frequency.
Parameter Symbol Applicable Pins* (See below) min typ max Unit
Input high level voltage V
IH
1
TTL compatible: (1)
2.2 V
Input low level voltage V
IL
1 0.8 V
Input high level voltage V
IH
2
TTL compatible, with pull-up resistor: (9)
2.2 V
Input low level voltage V
IL
2 0.8 V
Input high level voltage V
IH
3
TTL compatible, Schmitt: (2), and (10)
2.2 V
Input low level voltage V
IL
3 0.8 V
Output high level voltage V
OH
1 IOH= –2 mA
(5), (7), and (9)
VDD– 2.1 V
Output low level voltage V
OL
1 IOL= 2 mA 0.4 V
Output high level voltage V
OH
2 IOH= –8 mA
(3)
VDD– 2.1 V
Output low level voltage V
OL
2 IOL= 8 mA 0.4 V
Output high level voltage V
OH
3 IOH= –4 mA
(6), and (10)
VDD– 2.1 V
Output low level voltage V
OL
3 IOL= 24 mA 0.4 V
Output high level voltage V
OL
5 IOL= 24 mA: (8) 0.4 V
Output high level voltage V
OL
4 IOL= 2 mA: (4) 0.4 V
Input leakage current I
IL
VI= VSS, VDD: (1), (2),and (10) –10 +10 µA
Output leakage current I
OZ
For high-impedance outputs: (6), and (10) –10 +10 µA
Pull-up resistance R
UP
(9) 40 80 160 kΩ
Page 3

No. 5192-3/8
LC895195
Pin Functions
Type: I: Input pin, O: Output pin, B: Bidirectional pin, P: Power supply pin, NC: No connection pin
Note: 1. NC (no connection) pins must be left open.
2. Pin names (signal names) that begin with a Z have negative (inverted) logic.
3. V
SS0
is the logic system ground and V
SS1
is the IDE interface driver ground.
Pin No. Symbol Type Function
1 V
SS0
P
2 ZRAS0 O Buffer DRAM RAS signal output 0 (This pin is used normally.)
3 ZRAS1 O Buffer DRAM RAS signal output 1
4 V
SS0
P
5 ZCAS0 O Buffer DRAM CAS signal output 0 (This pin is used normally.)
6 ZCAS1 O Buffer DRAM CAS signal output 1
7 V
SS0
P
8 ZOE O Buffer RAM output enable
9 ZUWE O Buffer RAM upper write enable
10 ZLWE O Buffer RAM lower write enable
11 RA0 O
12 RA1 O
13 RA2 O
14 RA3 O RA0 to RA6 are the data buffer DRAM address signal output.
15 RA4 O
16 RA5 O
17 RA6 O
18 V
DD
P
19 V
SS0
P
20 RA7 O
21 RA8 O RA7 to RA9 are the data buffer DRAM address signal output.
22 RA9 O
23 V
SS0
P
24 TEST0 NC
25 NC
26 TEST1 NC
27 TEST2 NC
28 TEST3 NC
29 NC
30 IO0 B
31 IO1 B
Data buffer DRAM data I/O
32 IO2 B
These pins have built-in pull-up resistors.
33 IO3 B
34 IO4 B
35 IO5 B
36 V
SS0
P
37 V
DD
P
38 IO6 B
39 IO7 B
40 IO8 B
41 IO9 B Data buffer DRAM data I/O
42 IO10 B These pins have built-in pull-up resistors.
43 IO11 B
44 IO12 B
45 IO13 B
46 IO14 B
47 IO15 B
48 EXCK O SUB-CODE I/O
49 WFCK I
50 SBSO I
Page 4

No. 5192-4/8
LC895195
Continued from preceding page.
Type: I: Input pin, O: Output pin, B: Bidirectional pin, P: Power supply pin, NC: No connection pin
Note: 1. NC (no connection) pins must be left open.
2. Pin names (signal names) that begin with a Z have negative (inverted) logic.
3. V
SS0
is the logic system ground and V
SS1
is the IDE interface driver ground.
Pin No. Symbol Type Function
51 SCOR I SUB-CODE input pin
52 V
SS0
P
53 V
SS0
P
54 TEST4 I Test input. This must be tied low.
55 V
SS0
P
56 V
SS0
P
57 ZINT1 O Interrupt request signal output to the microcontroller from the IDE block.
58 V
SS0
P
59 V
SS0
P
60 V
SS0
P
61 NC
62 NC
63 V
SS0
P
64 SDATA I
65 BCK I
CD-DSP interface
66 LRCK I
67 C2PO I
68 MCK2 O XTALCK 1/1, 1/2, 1/512, and stop output
69 V
SS0
P
70 XTALCK I Xtal oscillator input
71 XTAL O Xtal oscillator output
72 V
SS0
P
73 V
DD
P
74 MCK O XTALCK 1/1, 1/2, and stop output
75 V
SS0
P
76 ZRSTIC I Reset signal to drive reset IC
77 CSCTRL I Selects active high or active low for the microcontroller CS line.
78 ZRESET I LSI reset
79 ZRD I Microcontroller data read signal input
80 ZWR I Microcontroller data write signal input
81 ZCS I Input for the register chip select signal from the microcontroller
82 V
SS0
P
83 SUA0 I
84 SUA1 I
85 SUA2 I
86 SUA3 I Microcontroller register select signals
87 SUA4 I
88 SUA5 I
89 SUA6 I
90 V
DD
P
91 V
SS0
P
92 D0 B
93 D1 B
94 D2 B
Microcontroller data signals
95 D3 B
96 D4 B
These pins have built-in pull-up resistors.
97 D5 B
98 D6 B
99 D7 B
100 ZINT O Interrupt request signal output to the microcontroller
Continued on next page.
Page 5

No. 5192-5/8
LC895195
Continued from preceding page.
Type: I: Input pin, O: Output pin, B: Bidirectional pin, P: Power supply pin, NC: No connection pin
Note: 1. NC (no connection) pins must be left open.
2. Pin names (signal names) that begin with a Z have negative (inverted) logic.
3. V
SS0
is the logic system ground and V
SS1
is the IDE interface driver ground.
Pin No. Symbol Type Function
101 ZRSTCPU O
102 ZWAIT O
103 ZHRST I
104 ZDASP B
ATAPI control signals
105 ZCS3FX I
106 ZCS1FX I
107 DA2 I
108 V
SS0
P
109 V
DD
P
110 DA0 I
111 ZPDIAG B
112 DA1 I ATAPI control signals
113 ZIOCS16 O
114 HINTRQ O
115 ZDMACK I
116 V
SS1
P
117 IORDY O
118 ZDIOR I
ATAPI control signals
119 ZDIOW I
120 DMARQ O
121 DD15 B ATAPI data bus
122 V
SS1
P
123 DD0 B
124 DD14 B
125 DD1 B ATAPI data bus
126 DD13 B
127 V
SS1
P
128 V
DD
P
129 DD2 B
130 DD12 B ATAPI data bus
131 DD3 B
132 V
SS1
P
133 DD11 B
134 DD4 B ATAPI data bus
135 DD10 B
136 V
SS1
P
137 V
DD
P
138 DD5 B
139 DD9 B ATAPI data bus
140 DD6 B
141 V
SS1
P
142 DD8 B
ATAPI data bus
143 DD7 B
144 V
DD
P
Page 6

No. 5192-6/8
LC895195
Pin Functions
1. ATA-PI Pins
• ZCS1FX (input)
Chip select signal for selecting the command block register.
• ZCS3FX (input)
Chip select signal for selecting the control block register.
• DA0 to DA2 (input)
Address for accessing the ATAPI registers.
• ZDASP (I/O)
Drive 1 is output and drive 0 is input.
Signal used to indicate to drive 0 that drive 1 exists.
An external pull-up resistor must be connected to this pin.
• DD0 to DD15 (I/O)
16-bit data bus. Can be used for either 8-bit or 16-bit data transfers.
• ZDIOR (input)
Read strobe signal from the host.
• ZDIOW (input)
Write strobe signal from the host.
• ZDMACK (input)
Acknowledge signal from the host in response to the drive DMARQ request signal during DMA transfers.
The pin circuit does not include a pull-up resistor.
• DMARQ (output)
Drive request signal during DMA transfers
• HINTRQ (output)
Drive interrupt signal to the host
• ZIOCS16 (output)
Signal asserted by the drive when the drive supports 16-bit transfers.
This signal is not asserted during DMA transfers.
• IORDY (output)
Signal that indicates that the drive has completed response preparations during data transfers.
This signal is low when the drive is not ready.
• ZPDIAG (I/O)
Signal asserted by drive 1 to inform drive 0 that diagnostics have completed.
An external pull-up resistor must be connected to this pin.
• ZHRST (input)
Reset signal from the host.
The pin circuit does not include a pull-up resistor.
2. MC (microcontroller) Interface Pins
• ZCS (input)
Microcontroller chip select signal
• CSCTRL (input)
Microcontroller chip select logic selection signal
High - ZCS functions as an active low signal.
Low - ZCS functions as an active high signal.
• ZRD, ZWR, SUA0 to SUA6 (input)
Microcontroller interface control signals.
The SUA0 to SUA6 pins are address lines.
Page 7

No. 5192-7/8
LC895195
• ZSWAIT (output)
When the microcontroller is accessing RAM, the sub-CPU must wait if this pin is low.
• D7 to D0 (I/O)
Microcontroller data bus. Pull-up resistors are built in.
• ZINT (output)
Interrupt request signal output to the microcontroller. A pull-up resistor is built in.
• ZINT1 (output)
Interrupt request signal output from the IDE block to the microcontroller. An external pull-up resistor must be
connected to this pin.
3. Buffer RAM Pins
• IO0 to IO15 (I/O)
Buffer DRAM data bus. A pull-up resistor is built in.
• RA0 to RA9 (output)
Buffer RAM address lines.
• ZRAS0, ZRAS1 (output)
Buffer DRAM RAS outputs. Normally, ZRAS0 is used, but if two 1-Mb (64k × 16 bits) chips are used, then both
ZRAS0 and ZRAS1 are used, one for each of the chips.
• ZCAS0, ZCAS1 (output)
Buffer DRAM CAS outputs. Normally, ZCAS0 is used, but if two 1-Mb (64k × 16 bits) chips are used, then both
ZCAS0 and ZCAS1 are used, one for each of the chips. When using a two-CAS type DRAM, connect ZCAS0 to
UCAS, and ZCAS1 to LCAS.
• ZOE (output)
Buffer DRAM read output signal.
• ZUWE, ZLWE (output)
Buffer DRAM write output signals. Connected the corresponding DRAM pins.
4. Subcode Interface Pins
• EXCK, WFCK, SBSO, SCOR (input or output)
These are the subcode interface connections. The LC895195 acquires subcode data by connection with the CDDSP and sends that data to the host.
5. CD-DSP Data Pins
• BCK, SDATA, LRCK, C2PO (input)
The LC895195 reads in the CD-ROM data by connecting to the CD-DSP.
The C2PO pin is used for the C2 flags.
6. Other Pins
• ZRESET (input)
This is the LC895195 reset pin. The LC895195 is reset by a low level on this pin.
This pin must be held low for at least 1 µs when power is first applied.
• XTALCK, XTAL
These pins can drive a 16.9344-MHz or 33.8688-MHz oscillator.
Alternatively, an external clock can be input to the XTALCK pin.
• MCK (output)
This pin outputs either the XTALCK frequency or that frequency divided by 2. This output can be turned off.
• MCK2 (output)
This pin outputs either the XTALCK frequency or that frequency divided by 512. This output can be turned off.
• ZRSTIC (output)
This pin can be set to output a low level either by writing to the microcontroller write register R46 bit 7
(ZSYSRTS) or by setting the ZHRST pin (pin 103) low. This pin goes to the high-impedance state when both
ZSYSRST and ZHRST are high.
Since this pin has an open-drain circuit, an external pull-up resistor must be used.
Page 8

No. 5192-8/8
LC895195
This catalog provides information as of November, 1997. Specifications and information herein are subject to
change without notice.
■
No products described or contained herein are intended for use in surgical implants, life-support systems, aerospace
equipment, nuclear power control systems, vehicles, disaster/crime-prevention equipment and the like, the failure of
which may directly or indirectly cause injury, death or property loss.
■ Anyone purchasing any products described or contained herein for an above-mentioned use shall:
➀ Accept full responsibility and indemnify and defend SANYO ELECTRIC CO., LTD., its affiliates, subsidiaries and
distributors and all their officers and employees, jointly and severally, against any and all claims and litigation and all
damages, cost and expenses associated with such use:
➁ Not impose any responsibility for any fault or negligence which may be cited in any such claim or litigation on
SANYO ELECTRIC CO., LTD., its affiliates, subsidiaries and distributors or any of their officers and employees
jointly or severally.
■ Information (including circuit diagrams and circuit parameters) herein is for example only; it is not guaranteed for
volume production. SANYO believes information herein is accurate and reliable, but no guarantees are made or implied
regarding its us
e or any infringements of intellectual property rights or other rights of third parties.
• ZRSTCPU (output)
When an ATAPI soft reset command (08h) has been received, this pin generates a low-going pulse with a duration
of about 1 ms (when the XTALCK frequency is 34 MHz). (This pulse will have a duration of about 2 ms when the
XTALCK frequency is 16 MHz.)
At this time a microcontroller interrupt will be generated. When the ZRESET pin (pin 78) becomes active (low),
the ZRESET signal will be output without change to the ZRSTCPU pin.
Since this pin has an open-drain circuit, an external pull-up resistor must be used.
 Loading...
Loading...