Page 1

CMOS LSI
No. 5489
Preriminary
Overview
The LC66P5316 is an on-chip OTP PROM version of the
LC6653XX Series CMOS 4-bit single-chip microcontrollers. The LC66P5316 is appropriate for program
development and product evaluation since it provides
identical functionality and pin compatibility with the
LC665316A.
Features and Functions
• On-chip OTP ROM capacity of 16 kilobytes, and an on-
chip RAM capacity of 512 × 4 bits.
• Fully supports the LC66000 Series common instruction
set (128 instructions).
• I/O ports: 42 pins
• A sub-oscillator circuit can be used (option)
This circuit allows power dissipation to be reduced by
operating at lower speeds.
• 8-bit serial interface: two circuits (can be connected in
cascade to form a 16-bit interface)
• Instruction cycle time: 0.95 to 10 µs (at 4.0 to 5.5 V)
• Powerful timer functions and prescalers
— Time limit timer, event counter, pulse width
measurement, and square wave output using a 12-bit
timer.
— Time limit timer, event counter, PWM output, and
square wave output using an 8-bit timer.
— Time base function using a 12-bit prescaler
• Powerful interrupt system with 8 interrupt factors and 8
interrupt vector locations.
— External interrupts: 3 factors/3 vector locations
— Internal interrupts: 5 factors/5 vector locations
• Flexible I/O functions
16-value comparator inputs, 20-mA drive outputs,
inverter circuits, pull-up and open-drain circuits
selectable as options.
• Optional runaway detection function (watchdog timer)
• 8-bit I/O functions
• Power saving functions using halt and hold modes.
• Packages: DIP48S, QIP48E (QFP48E)
• Evaluation LSIs: LC66599 (evaluation chip) +
EVA800/850-TB662YXX2
LC66P5316
Four-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller
with 16 KB of On-Chip OTP PROM
Package Dimensions
unit: mm
3149-DIP48S
[LC66P5316]
2548
15.24
13.8
1
0.48
unit: mm
3156-QFP48E
1.614.0
17.2
3.0max
46.0
1.05 1.78
[LC66P5316]
17.2
14.0
1.0
1.5
36
37
1.5
1.0
1.5
48
112
0.35
0.8
15.6
24
2.53
1.6
1.5
25
24
13
SANYO: QFP48E
5.1max
4.25
3.8
0.51min
SANYO: DIP48S
0.15
0.1
2.70
(STAND OFF)
0.25
SANYO Electric Co.,Ltd. Semiconductor Bussiness Headquarters
TOKYO OFFICE Tokyo Bldg., 1-10, 1 Chome, Ueno, Taito-ku, TOKYO, 110 JAPAN
22897HA (OT) No. 5489-1/28
Page 2
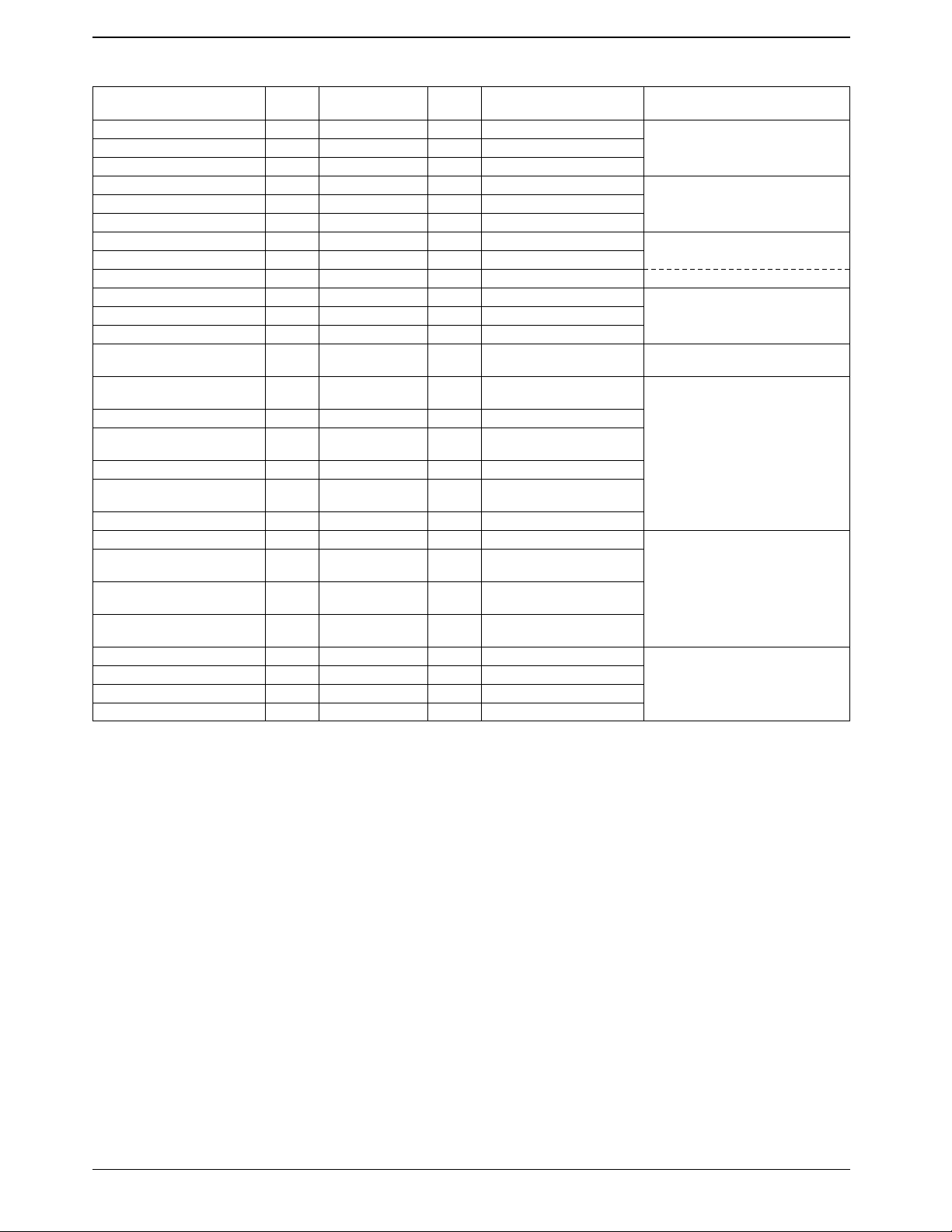
Series Organization
LC66P5316
Type No.
LC66304A/306A/308A 42 4 K/6 K/8 KB 512 W DIP42S QFP48E
LC66404A/406A/408A 42 4 K/6 K/8 KB 512 W DIP42S QFP48E
LC66506B/508B/512B/516B 64 6 K/8 K/12 K/16 KB 512 W DIP64S QFP64A
LC66354A/356A/358A 42 4 K/6 K/8 KB 512 W DIP42S QFP48E
LC66354S/356S/358S 42 4 K/6 K/8 KB 512 W QFP44M
LC66556A/558A/562A/566A 64 6 K/8 K/12 K/16 KB 512 W DIP64S QFP64E
LC66354B/356B/358B 42 4 K/6 K/8 KB 512 W DIP42S QFP48E
LC66556B/558B/562B/566B 64 6 K/8 K/12 K/16 KB 512 W DIP64S QFP64E
LC66354C/356C/358C 42 4 K/6 K/8 KB 512 W DIP42S QFP48E 2.5 to 5.5 V/0.92 µs
LC662104A/06A/08A 30 4 K/6 K/8 KB 384 W DIP30SD MFP30S
LC662304A/06A/08A/12A/16A 42
LC662508A/12A/16A 64 8 K/12 K/16 KB 512 W DIP64S QFP64E
LC665304A/06A/08A/12A/16A 48
LC66E308 42 EPROM 8 KB 512 W
LC66P308 42 OTPROM 8 KB 512 W DIP42S QFP48E
LC66E408 42 EPROM 8 KB 512 W
LC66P408 42 OTPROM 8 KB 512 W DIP42S QFP48E
LC66E516 64 EPROM 16 KB 512 W
LC66P516 64 OTPROM 16 KB 512 W DIP64S QFP64E
LC66E2108* 30 EPROM 8 KB 384 W
LC66E2316 42 EPROM 16 KB 512 W
LC66E2516 64 EPROM 16 KB 512 W
LC66E5316 52/48 EPROM 16 KB 512 W
LC66P2108* 30 OTPROM 8 KB 384 W DIP30SD MFP30S
LC66P2316* 42 OTPROM 16 KB 512 W DIP42S QFP48E
LC66P2516 64 OTPROM 16 KB 512 W DIP64S QFP64E
LC66P5316 48 OTPROM 16 KB 512 W DIP48S QFP48E
Note: * Under development
No. of
pins capacity
ROM capacity
4 K/6 K/8 K/12 K/16 KB
4 K/6 K/8 K/12 K/16 KB
RAM
512 W DIP42S QFP48E
512 W DIP48S QFP48E
DIC42S QFC48
with window with window
DIC42S QFC48
with window with window
DIC64S QFC64
with window with window
DIC42S QFC48
with window with window
DIC64S QFC64
with window with window
DIC52S QFC48
with window with window
Package Features
Normal versions
4.0 to 6.0 V/0.92 µs
Low-voltage versions
2.2 to 5.5 V/3.92 µs
Low-voltage high-speed versions
3.0 to 5.5 V/0.92 µs
On-chip DTMF generator versions
3.0 to 5.5 V/0.95 µs
Dual oscillator support
3.0 to 5.5 V/0.95 µs
Window and OTP evaluation versions
4.5 to 5.5 V/0.92 µs
Window evaluation versions
4.5 to 5.5 V/0.92 µs
OTP
4.0 to 5.5 V/0.95 µs
No. 5489-2/28
Page 3
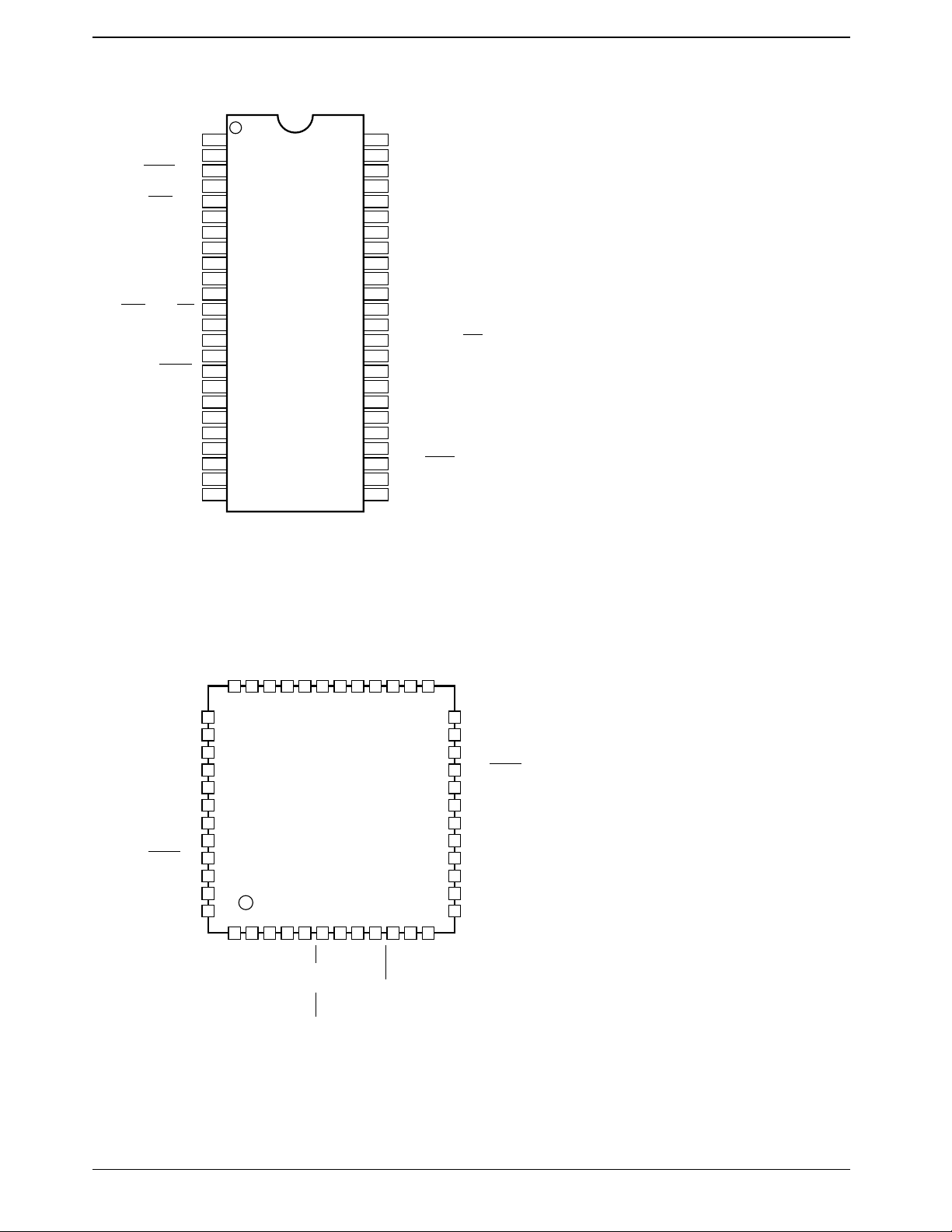
Pin Assignments
LC66P5316
DIP48S
P20/SI0/A0
P21/SO0/A1
P22/SCK0/A2
P23/INT0/A3
P30/INT1/A4
P31/POUT0/A5
P32/POUT1/A6
RES/VPP/OE
TEST/EPMOD
P40/INV0I/A7
P41/INV0O/A8
P42/INV1I/A9
P43/INV1O/A10
V
SS
OSC1
OSC2
V
DD
PE0/XT1
PE1/XT2
P33/HOLD
P50/A11
P51/A12
P52/A13
P53/INT2/TA
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
LC66P5316
QFP48E
P13/D7
48
P12/D6
47
P11/D5
46
P10/D4
45
P03/D3
44
P02/D2
43
P01/D1
42
P00/D0
41
PD3/AN4/INV4O
40
PD2/AN3/INV4I
39
PD1/AN2/INV3O
38
PD0/AN1/INV3I
37
PC3/INV2O/DASEC
36
PC2/INV2I/CE
35
PC1
34
PC0
33
P83
32
P82
31
P81/DS1
30
P80/DS0
29
P63/PIN1
28
P62/SCK1
27
P61/SO1
26
P60/SI1
25
P01/D1
P00/D0
PD3/AN4/INV4O
PD2/AN3/INV4I
PD1/AN2/INV3O
PD0/AN1/INV3I
PC3/INV2O/DASEC
PC2/INV2I/CE
PC1
PC0
P83
P82
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
37P02/D2
38P03/D3 23 P80/DS0
39P10/D4 22 P63/PIN1
40P11/D5 21 P62/SCK1
41P12/D6 20 P61/SO1
42P13/D7 19 P60/SI1
43P20/SI0/A0 18 P53/INT2/TA
44P21/SO0/A1 17 P52/A13
45P22/SCK0/A2 16 P51/A12
46P23/INT0/A3 15 P50/A11
47P30/INT1/A4 14 P43/INV1O/A10
48P31/POUT0/A5 13 P42/INV1I/A9
1
2
P32/POUT1/A6
V
3
SS
LC66P5316
4
OSC1
OSC2
5
6
7
8
9
DD
/OE
V
PP
PE0/XT1
PE1/XT2
RES/V
TEST/EPMOD
10
11
12
P33/HOLD
P40/INV0I/A7
24 P81/DS1
P41/INV0O/A8
Top view
We recommend the use of reflow soldering techniques to solder-mount QFP packages.
Please consult with your Sanyo representative for details on process conditions if the package itself is to be directly
immersed in a dip-soldering bath (dip-soldering techniques).
No. 5489-3/28
Page 4
LC66P5316
Usage Notes
The LC66P5316 was created for program development, product evaluation, and prototype development for products
based on the LC6653XX Series microcontrollers. Keep the following points in mind when using this product.
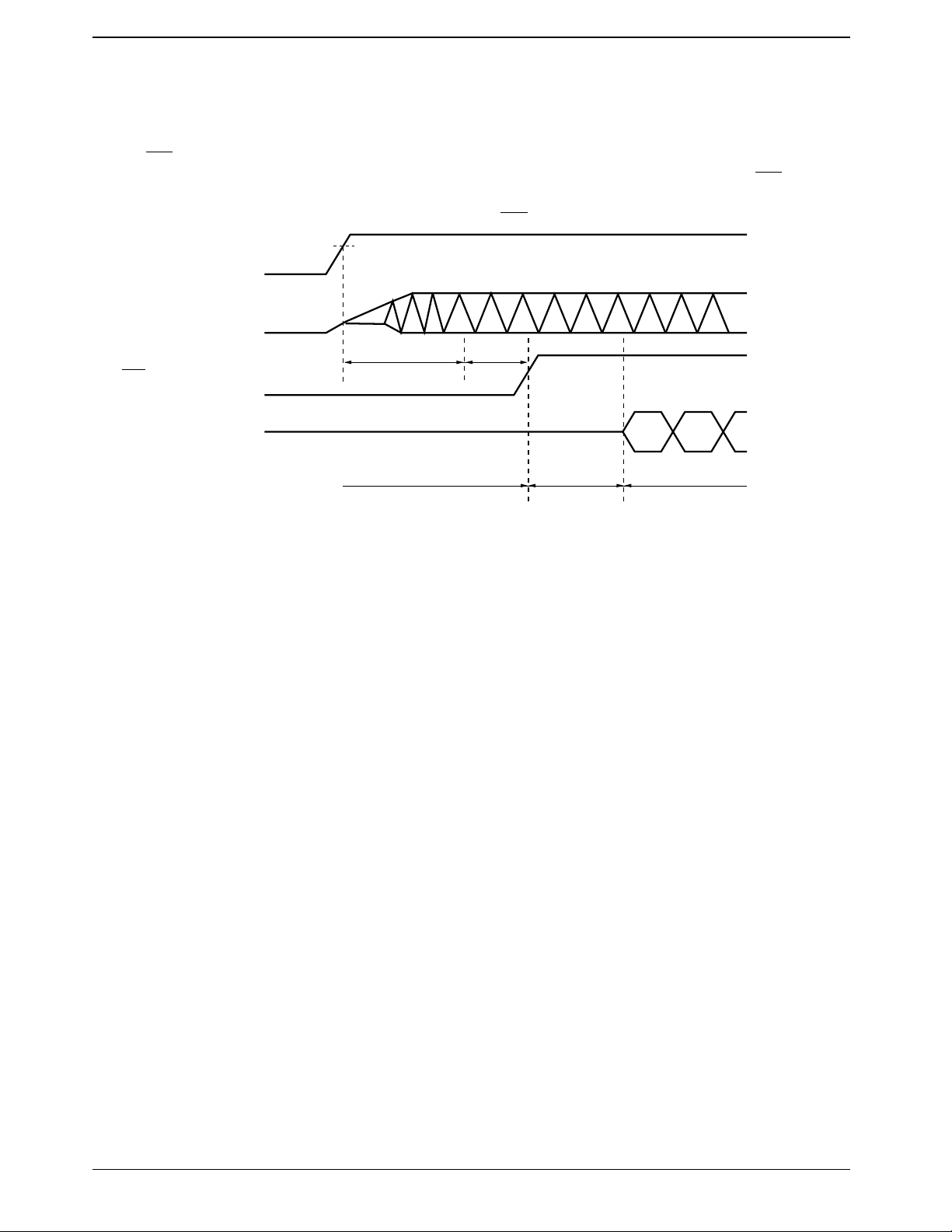
1. After a reset
The RES pin must be held low for an additional 3 instruction cycles after the oscillator stabilization period has
elapsed. Also, the port output circuit types are set up during the 9 instruction cycles immediately after RES is set
high. Only then is the program counter set to 0 and program execution started from that location. (The port output
circuits all revert to the open-drain type during periods when RES is low.)
V
min
V
DD
OSC
RES
DD
At least 10 ms
Oscillator
stabilization
At least 3
instruction
Program execution (PC)
Port output type
Open drain
Option switching
period
9 instruction
cycles
Location 0Location
1
Option specification
2. Notes on LC6653XX evaluation
The high end of the EPROM area (locations 3FF0H to 3FFFH) are the option specification area. Option specification
data must be programmed for and loaded into this area. The Sanyo specified cross assembler for this product is the
program LC66S.EXE. Also, insert JMP instructions so that user programs do not attempt to execute addresses that
exceed the capacity of the mask ROM, and write zeros (00H) to areas (other than 3FF0H to 3FFFH) that exceed the
actual capacity of the mask ROM.
3. Mounting notes
Due to structural considerations, Sanyo is unable to fully test one-time programmable products. Therefore, the user
must apply the screening procedure described on page 20 to these products.
4. Use the following procedure when ordering ROM through the Sanyo PROM writing service. (Note that this is a forfee service.)
• If ordering one-time programmable and mask ROM versions at the same time:
The customer must provide the EPROM for the mask ROM version, the order forms for the mask ROM version,
and the order forms for the one-time programmable version.
• If ordering only the one-time programmable version:
The customer must provide the EPROM and the order forms for the one-time programmable version. The last
section of the EPROM (locations 3FF0H to 3FFFH) is the option specification area, and the option specification
data must be written to this area. The Sanyo specified cross assembler for this product is the program LC66S.EXE.
Also, insert JMP instructions so that user programs do not attempt to execute addresses that exceed the capacity of
the mask ROM, and write zeros (00H) to areas (other than 3FF0H to 3FFFH) that exceed the actual capacity of the
mask ROM.
5. Differences between this product and the mask ROM version:
Carefully read the sections on the following pages that describe these differences.
No. 5489-4/28
Page 5

LC66P5316
Main differences between the LC66E5316, LC66P5316, and LC6653XX Series
Item LC6653XX Series (mask version) LC66E5316 LC66P5316
Differences in the main
characteristics –30 to +70°C +10 to +40°C –30 to +70°C
• Operating temperature range
3.0 to 5.5 V/0.95 to 10 µs 4.5 to 5.5 V/0.95 to 10 µs 4.0 to 5.5 V/0.92 to 10 µs
• Operating supply voltage/operating
frequency (cycle time)
• Input high-level current (RES) Maximum: 1 µA (normal operation and halt mode) (normal operation and halt mode)
• Input low-level current (RES) Maximum: 1 µA Typical: 100 µA Typical: 100 µA
• Current drain
(Operating at 4 MHz)
(Operating at 32 kHz)
(Halt mode at 4 MHz) Typical: 10 nA, maximum: 10 µA* Typical: 10 nA, maximum: 10 µA*
(Halt mode at 32 kHz)
(Hold mode)
Port output types at reset
Package
Note: * Although the microcontroller will remain in hold mode if the RES pin is set low while it is in hold mode, always use the reset start sequence (after
switching HOLD from low to high, switch RES from low to high) when clearing hold mode. Also a current of about 100 µA flows from the RES pin
when it is low. This increases the hold mode current drain by about 100 µA.
(When the main oscillator is (When the main oscillator is (When the main oscillator is
operating) operating) operating)
3.0 to 5.5 V/25 to 127 µs 4.5 to 5.5 V/25 to 127 µs 4.0 to 5.5 V/25 to 127 µs
(When the sub-oscillator is operating) (When the sub-oscillator is operating) (When the sub-oscillator is operating)
Typical: 10 µA Typical: 10 µA
Hold mode: 1 µA maximum Hold mode: 1 µA maximum
Typical: 10 nA, maximum: 10 µA
The output type specified in
the options
• DIP48S • DIC52S window package • DIP48S
• QFP48E • QFC48 window package • QFP48E
Larger than that for the mask versions Larger than that for the mask versions
Open-drain outputs Open-drain outputs
See the data sheets for the individual products for details on other differences.
System Block Diagram
RAM STACK
RES
TEST
OSC1
OSC2
HOLD
XT1
XT2
AN1 to 4
SYSTEM
CONTROL
ADC
PE
PD
PC
(512W)
FLAG
E
D
D
D
SP E A
M
P
P
P
R
X
L
H
PRESCALER
CZ
D
P
Y
ALU
MPX TIMER0 SERIAL I/O 0
MPX
INTERRUPT
CONTROL
MPX
TIMER1
P0 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6
SERIAL I/O 1
P8
OTP ROM
(16KB)
PC
POUT0
SI0
SO0
SCK0
INT0
INT1, INT2
SI1
SO1
SCK1
PIN1, POUT1
INV
xO INVxI
DS1 DS0
PROM
control
(x=0 to 4)
A0 to A13
D0 to D7
CE
DASEC
VPP/OE
EPMOD
TA
No. 5489-5/28
Page 6

Pin Function Overview
LC66P5316
Pin I/O Overview Output driver type Options
P00/D0
P01/D1
P02/D2
P03/D3
P10/D4
P11/D5
P12/D6
P13/D7
P20/SI0/A0
P21/SO0/A1
P22/SCK0/
A2
P23/INT0/A3
I/O ports P00 to P03
• Input or output in 4-bit or 1-bit units
• P00 to P03 support the halt mode
I/O
control function (This function can be
specified in bit units.)
• Used as data pins in EPROM mode
I/O ports P10 to P13
• Input or output in 4-bit or 1-bit units
I/O
• Used as data pins in EPROM mode
I/O ports P20 to P23
• Input or output in 4-bit or 1-bit units
• P20 is also used as the serial input SI0
pin.
• P21 is also used as the serial output
SO0 pin.
• P22 is also used as the serial clock
I/O
SCK0 pin.
• P23 is also used as the INT0 interrupt
request pin, and also as the timer 0
event counting and pulse width
measurement input.
• Used as address pins in EPROM mode
• Pch: Pull-up MOS type
• Nch: Intermediate sink current
type
• Pch: Pull-up MOS type
• Nch: Intermediate sink current
type
• Pch: CMOS type
• Nch: Intermediate sink current
type
• Pull-up MOS or
• Output level on
• Pull-up MOS or
• Output level on
CMOS or Nch OD
output
Nch OD output
reset
Nch OD output
reset
State after a Standby mode
reset operation
Hold mode:
High or low
(option)
High or low
(option)
H
Output off
Halt mode:
Output
retained
Hold mode:
Output off
Halt mode:
Output
retained
Hold mode:
Output off
Hold mode:
Output off
P30/INT1/A4
P31/POUT0/
A5
P32/POUT1/
A6
P33/HOLD
P40/INV0I/
A7
P41/INV0O/
A8
P42/INV1I/
A9
P43/INV1O/
A10
I/O ports P30 to P32
• Input or output in 3-bit or 1-bit units
• P30 is also used as the INT1 interrupt
request.
• P31 is also used for the square wave
output from timer 0.
I/O
• P32 is also used for the square wave
and PWM output from timer 1.
• P31 and P32 also support 3-state
outputs.
• Used as address pins in EPROM mode
Hold mode control input
• Hold mode is set up by the HOLD
instruction when HOLD is low.
• In hold mode, the CPU is restarted by
setting HOLD to the high level.
• This pin can be used as input port P33
I
along with P30 to P32.
• When the P33/HOLD pin is at the low
level, the CPU will not be reset by a
low level on the RES pin. Therefore,
applications must not set P33/HOLD
low when power is first applied.
I/O ports P40 to P43
• Input or output in 4-bit or 1-bit units
• Input or output in 8-bit units when used
in conjunction with P50 to P53.
• Can be used for output of 8-bit ROM
I/O
data when used in conjunction with
P50 to P53.
• Dedicated inverter circuit (option)
• Used as address pins in EPROM mode
• Pch: CMOS type
• Nch: Intermediate sink current
type
• Pch: Pull-up MOS type
• CMOS type when the inverter
circuit option is selected
• Nch: Intermediate sink current
type
CMOS or Nch OD
output
• Pull-up MOS or
Nch OD output
• Output level on
reset
• Inverter circuit
H
• High or
low
(option)
• Inverter
I/O is set
to the
output off
state.
Hold mode:
Output off
Halt mode:
Output
retained
Hold mode:
Port output
off, inverter
output off
Halt mode:
Port output
retained,
inverter
output
continues
Continued on next page.
No. 5489-6/28
Page 7

Continued from preceding page.
LC66P5316
Pin I/O Overview Output driver type Options
I/O ports P50 to P53
• Input or output in 4-bit or 1-bit units
• Input or output in 8-bit units when used
P50/A11
P51/A12
P52/A13
P53/INT2/TA
in conjunction with P40 to P43.
• Can be used for output of 8-bit ROM
I/O
data when used in conjunction with
P40 to P43.
• Pch: Pull-up MOS type
• Nch: Intermediate sink current
type
• Pull-up MOS or
• Output level on
• P53 is also used as the INT2 interrupt
request.
• Used as address pins in EPROM mode
I/O ports P60 to P63
• Input or output in 4-bit or 1-bit units
• P60 is also used as the serial input SI1
P60/SI1
P61/SO1
P62/SCK1
P63/PIN1
pin.
• P61 is also used as the serial output
I/O
SO1 pin.
• P62 is also used as the serial clock
• Pch: CMOS type
• Nch: Intermediate sink current
type
• CMOS or Nch OD
SCK1 pin.
• P63 is also used for the event count
input to timer 1.
P80/DS0
P81/DS1
P82
P83
Dedicated output ports P80 to P83
• Output in 4-bit or 1-bit units
• The contents of the output latch are
O
input using input instructions.
• P80 is a data shaper input (options)
• Pch: CMOS type
• Nch: Intermediate sink current
type
• CMOS or Nch OD
• Output level at
• Data shaper
• P81 is a data shaper output (options)
Nch OD output
reset
output
output
reset
circuit
State after a Standby mode
reset operation
Hold mode:
Output off
High or low
(option)
Halt mode:
Output
retained
Hold mode:
Output off
H
Halt mode:
Output
retained
Hold mode:
Output off
High or low
(option)
Halt mode:
Output
retained
PC0
PC1
PC2/INV2I/
CE
PC3/INV2O/
DASEC
I/O ports PC0 to PC3
• Output in 4-bit or 1-bit units
I/O
• Dedicated inverter circuits (option)
• Used as the control CE and DASEC
pin in EPROM mode.
• Pch: CMOS type
• Nch: Intermediate sink current
type
PD0/AN1/
INV3I
PD1/AN2/
INV3O
PD2/AN3/
INV4I
PD3/AN4/
Dedicated input ports PD0 to PD3
• Can be switched in software to function
I
as 16-value analog inputs.
• Dedicated inverter circuits (option)
• Only when the inverter circuit
option is selected:
• Pch: CMOS type
• Nch: Intermediate sink current
type
INV4O
PE0/XT1
PE1/XT2
OSC1
Dedicated input ports and sub-oscillator
I
connections
I
System clock oscillator connections
When an external clock is used, leave
OSC2
O
OSC2 open and connect the clock signal
to OSC1.
System reset input
• When the P33/HOLD pin is at the high
/
RES/V
OE
TEST/
EPMOD
V
V
PP
DD
SS
level, a low level input to the RES pin
I
will initialize the CPU.
• Used as the V
mode.
/OE pin in EPROM
PP
CPU test pin
This pin must be connected to V
I
during normal operation.
Power supply pins
SS
Note: Pull-up MOS type: The output circuit includes a MOS transistor that pulls the pin up to VDD.
CMOS output: Complementary output.
OD output: Open-drain output.
• CMOS or Nch OD
output
• Inverter circuits
Inverter circuits
Sub-oscillator/port
PE selection
Ceramic oscillator
or external clock
selection
H
Normal
input
Option
selection
Option
selection
Hold mode:
Output off
Halt mode:
Output
retained
Inverter
• Hold mode:
Output off
• Halt mode:
Output
continues
Hold mode:
Oscillator stops
Halt mode:
Oscillator
continues
No. 5489-7/28
Page 8

LC66P5316
User Options
1. Port 0, 1, 4, 5, and 8 output level at reset option
The output levels at reset for I/O ports 0, 1, 4, 5, and 8, in independent 4-bit groups, can be selected from the
following two options.
Option Conditions and notes
1. Output high at reset The four bits of ports 0, 1, 4, 5, or 8 are set in a group
2. Output low at reset The four bits of ports 0, 1, 4, 5, or 8 are set in a group
2. Oscillator circuit options
• Main clock
Option Circuit Conditions and notes
1. External clock
2. Ceramic oscillator
Note: There is no RC oscillator option.
• Sub-clock
Option Circuit Conditions and notes
1. Ports PE0 and PE1
2 Sub-oscillator
(crystal oscillator)
OSC1
Ceramic oscillator
C1
Crystal oscillator
C2
C1
C2
The input has Schmitt characteristics
OSC1
OSC2
DSB
Input data
XT1
XT2
3. Watchdog timer option
A runaway detection function (watchdog timer) can be selected as an option.
4. Port output type options
• The output type of each bit (pin) in ports P0, P1, P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin), P4, P5, P6, and PC can be
Option Circuit Conditions and notes
1. Open-drain output
2. Output with built-in pull-up
resistor
Output data
Input data
DSB
Output data
Input data
DSB
The port P2, P3, P5, and P6 inputs have Schmitt
characteristics.
The port P2, P3, P5, and P6 inputs have Schmitt
characteristics.
The CMOS outputs (ports P2, P3, P6, and PC)
and the pull-up MOS outputs (P0, P1, P4, and
P5) are distinguished by the drive capacity of the
p-channel transistor.
No. 5489-8/28
Page 9

LC66P5316
• One of the following two options can be selected for P8, in bit units.
Option Circuit Conditions and notes
1. Open-drain output
DSB
Output data
Output data
2. Output with built-in pulldown resistor
(CMOS output)
DSB
5. Inverter array circuit option
One of the following options can be selected for each of the following port sets: P40/P41, P42/P43, PC2/PC3,
PD0/PD1, and PD2/PD3. (PDs do not use option 1 because they are dedicated to inputs.)
Option Circuit Conditions and notes
Output data
Input data
DSB
1. Normal port I/O circuit
Output data
Input data
DSB
When the open-drain output type is selected
When the built-in pull-up resistor output type is
selected
The CMOS outputs (PC) and the pull-up MOS
outputs (P4) are distinguished by the drive
capacity of the p-channel transistor.
2. Inverter I/O circuit
Output data
high
Input data
DSB
Output data
If this option is selected, the I/O circuit is disabled
by the DSB signal.
Also note that the open-drain port output type
option and the high level at reset option must be
selected.
high
Input data
DSB
No. 5489-9/28
Page 10

LC66P5316
6. Buffer array circuit option
In addition to normal port output, one of the following two options may also be selected for P80 and P81.
Option Circuit Conditions and notes
1. Normal port output
2. Buffer input (P80) and
buffer output (P81) circuits
P80
P81
P80
DSB
DSB
DSB
Output data
Output data
Output data
low
Output data
low
Output data
low
When the open-drain output type is selected
When the built-in pull-down resistor output type is
selected (CMOS output)
If this option is selected, the I/O circuit is disabled
by the DSB signal.
Also note that the open-drain port output type
option and the high level at reset option must be
selected.
3. Buffer input (P80) and
buffer output (P81) circuits
with built-in zero-cross
detection circuits
P81
If this option is selected, the I/O circuit is disabled
by the DSB signal.
Also note that the open-drain port output type
option and the high level at reset option must be
selected.
Output data
DSB
low
No. 5489-10/28
Page 11

LC66P5316
LC665316 Series Option Data Area and Definitions
ROM area Bit Option specified Option/data relationship
3FF0H
3FF1H
3FF2H
3FF3H
3FF4H
3FF5H
3FF6H
7P5
6P4
5 Sub-oscillator option 0 = port PE, 1 = crystal oscillator
4 Oscillator option 0 = external clock, 1 = ceramic oscillator
3P8
2 P1 Output level at reset 0 = low level, 1 = high level
1P0
0 Watchdog timer option 0 = none, 1 = yes (present)
7 P13
6 P12
5 P11
4 P10
3 P03
2 P02
1 P01
0 P00
7 Unused This bit must be set to 0.
6 P32
5 P31 Output type 0 = OD, 1 = PU
4 P30
3 P23
2 P22
1 P21
0 P20
7 P53
6 P52
5 P51
4 P50
3 P43
2 P42
1 P41
0 P40
7
6
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
5
4
3 P63
2 P62
1 P61
0 P60
7
6
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
5
4
3 P83
2 P82
1 P81
0 P80
7
6
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
5
4
3
2
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
1
0
Output level at reset 0 = high level, 1 = low level
Output type 0 = OD, 1 = PU
Output type 0 = OD, 1 = PU
Output type 0 = OD, 1 = PU
Output type 0 = OD, 1 = PU
Output type 0 = OD, 1 = PU
Output type 0 = OD, 1 = PU
Output type 0 = OD, 1 = PD
Continued on next page.
Page 12

LC66P5316
Continued from preceding page.
ROM area Bit Option specified Option/data relationship
7
6
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
5
3FF7H
3FF8H
3FF9H
3FFAH
3FFBH
3FFCH
3FFDH
4
3 PC3
2 PC2
1 PC1
0 PC0
7 Unused This bit must be set to 1.
6 Buffer output 0 = used, 1 = none
5 Buffer output with zero-cross bias input 0 = used, 1 = none
4 PD3
3 PD1
2 PC3 Inverter output 0 = inverter output, 1 = none
1 P43
0 P41
7
6
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
5
4
3
2
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
1
0
7
6
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
5
4
3
2
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
1
0
7
6
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
5
4
3
2
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
1
0
7
6
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
5
4
3
2
Unused This bit must be set to 0.
1
0
7
6
5
4
Reserved. Must be set to predefined data values.
3
2
1
0
Output type 0 = OD, 1 = PU
This data is generated by the assembler.
If the assembler is not used, set this data to ‘00’.
Continued on next page.
No. 5489-12/28
Page 13

LC66P5316
Continued from preceding page.
ROM area Bit Option specified Option/data relationship
7
6
5
3FFEH
3FFFH
4
Reserved. Must be set to predefined data values.
3
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
Reserved. Must be set to predefined data values.
3
2
1
0
This data is generated by the assembler.
If the assembler is not used, set this data to ‘00’.
This data is generated by the assembler.
If the assembler is not used, set this data to ‘00’.
Usage Notes
1. Option specification
When using a Sanyo cross assembler with the LC66P5316, use the version called “LC66S.EXE” and specify the
actual microcontroller to be evaluated with the CPU pseudoinstruction in the source file. The port options must be
specified in the source file. The cross assembler will create an options code list in the option specification area
(locations 3FF0H to 3FFFH). It is also possible to directly set up data in the option specification area. If this is done,
the options must be specified according to the option code creation table shown on the following page.
2. Writing the EPROM
Use a special-purpose writing conversion board (the W66EP5316D for the DIP package, and the W66EP5316Q for
the QFP package) to allow the EPROM programmers listed below to be used when writing the data created by the
cross assembler to the LC66P5316.
• The EPROM programmers listed below can be used.
Manufacturer Models that can be used
Advantest R4945, R4944A, R4943, or equivalent products
Ando AF9704
AVAL —
Minato Electronics MODEL1890A
• The “27512 (VPP12.5 V) Intel high-speed write” technique must be used to write the EPROM. Set the address
range to location 0 to 3FFFH. The DASEC jumper must be off.
3. Using the data security function
The data security function sets up the microcontroller in advance so that data that was written to the microcontroller
EPROM cannot be read out.
Use the following procedure to enable the LC66P5316 data security function.
• Set the write conversion board DASEC jumper to the on position.
• Write the data to the EPROM once again.
At this time, since this function will operate, the EPROM programmer will issue an error. However, this error does
not indicate that there was a problem in either the programmer or the LSI.
Notes: 1. If the data at all addresses was “FF” at step 2, the data security function will not be activated.
Notes: 2. The data security function will not be activated at step 2 if the “blank → program → verify” operation
sequence is used.
Notes: 3. Always return the jumper to the off position after the data security function has been activated.
No. 5489-13/28
Page 14

Pin 1
Aligned to the top
SW DASEC
LC66P5316
LC66P5316 (DIP) LC66P5316 (QFP)
Cut corner
Pin 1
SW
DASEC
Pin 1
Write board (W66EP5316D) Write board (W66EP5316Q)
Specifications
Absolute Maximum Ratings at Ta = 25°C, VSS= 0 V
Parameter Symbol Conditions Ratings Unit Note
Maximum supply voltage V
Input voltage
Output voltage
Output current per pin
Total pin current
Allowable power dissipation Pd max Ta = –30 to +70°C: DIP48S (QFP48E) 600 (430) mW 5
Operating temperature Topr –30 to +70 °C
Storage temperature Tstg –55 to +125 °C
Note: 1. Applies to pins with open-drain output specifications. For pins with other than open-drain output specifications, the ratings in the pin column for that
pin apply.
2. For the oscillator input and output pins, levels up to the free-running oscillation level are allowed.
3. Sink current (Applies to P8 and PD when either the CMOS output specifications or the inverter array specifications have been selected.)
4. Source current (Applies to all pins except P8 and PD for which the pull-up output specifications, the CMOS output specifications, or the inverter
array specifications have been selected. Applies to PD pins for which the inverter array specifications have been selected.) Contact your Sanyo
representative for the electrical characteristics when the inverter array or buffer array options are specified.
5. We recommend the use of reflow soldering techniques to solder mount QFP packages.
Please consult with your Sanyo representative for details on process conditions if the package itself is to be directly immersed in a solder dip bath
(solder dip or spray techniques).
max V
DD
V
V
Σ I
Σ I
Σ I
Σ I
–I
–I
–I
V
V
OUT
OUT
I
ON
IN
IN
OP
OP
OP
ON
ON
OP
OP
DD
P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin),
1
P61, and P63
2 All other inputs –0.3 to VDD+ 0.3 V 2
P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin),
1
P61, and P63
2 All other inputs –0.3 to VDD+ 0.3 V 2
P0, P1, P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin),
1
P4, P5, P6, P8, PC, PD1, PD3
1 P0, P1, P4, P5 2 mA 4
P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin),
2
P6,P8, and PC
3 P41, P43, PC3, PD1, PD3, P81 10 mA 4
1 P4, P5, P6, P8, PC 75 mA 3
P0, P1, P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin),
2
PD1, PD3
1 P4, P5, P6, P8, PC 25 mA 4
P0, P1, P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin),
2
PD1, PD3
–0.3 to +7.0 V
–0.3 to +7.0 V 1
–0.3 to +7.0 V 1
20 mA 3
4mA 4
75 mA 3
25 mA 4
Page 15

LC66P5316
Allowable Operating Ranges at Ta = –30 to +70°C, VSS= 0 V, VDD= 4.0 to 5.5 V, unless otherwise specified.
Parameter Symbol Conditions min typ max Unit Note
Operating supply voltage V
Memory retention supply voltage V
V
Input high-level voltage VIH2
VIH3
VIL1
Input low-level voltage
V
V
Operating frequency fop
(instruction cycle time) (Tcyc)
[External clock input conditions]
Frequency f
Pulse width t
Rise and fall times t
extH
extR
Note: 1. Applies to pins with open-drain specifications. However, VIH2 applies to the P33/HOLD pin.
When ports P2, P3, and P6 have CMOS output specifications they cannot be used as input pins.
2. PC port pins with CMOS output specifications cannot be used as input pins.
Contact your Sanyo representative for the allowable operating ranges for P4, PC, and PD when the inverter array is used, and for P8 when the
buffer array is used.
3. Applies to pins with open-drain specifications. However, V
P2, P3, and P6 port pins with CMOS output specifications cannot be used as input pins.
V
DD
DD
IH
DD
HVDD: During hold mode 1.8 5.5 V
P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin),
1
P61, and P63: N-channel output transistor off
P33/HOLD, RES, OSC1:
N-channel output transistor off
P0, P1, P4, P5, PC, PD, PE:
N-channel output transistor off
P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin), P6,
RES, and OSC1: N-channel output transistor off
2 P33/HOLD: VDD= 1.8 to 5.5 V V
IL
P0, P1, P4, P5, PC, PD, PE, TEST:
3
IL
N-channel output transistor off
When the main oscillator is operating
When the sub-oscillator is operating
4.0 5.5 V
0.8 V
0.8 V
0.8 V
DD
DD
DD
V
SS
SS
V
SS
+7.0 V 1
V
DD
V
DD
0.2 V
DD
0.2 V
DD
0.2 V
DD
0.4 4.20 MHz
(10) (0.95) (µs)
30 32.768 100 kHz
(133.2) (122) (40) (µs)
OSC1: Defined by Figure 1. Input the clock
signal to OSC1 and leave OSC2 open.
ext
(External clock input must be selected as the
0.4 4.20 MHz
oscillator circuit option.)
OSC1: Defined by Figure 1. Input the clock
signal to OSC1 and leave OSC2 open.
, t
extL
(External clock input must be selected as the
100 ns
oscillator circuit option.)
OSC1: Defined by Figure 1. Input the clock
signal to OSC1 and leave OSC2 open.
, t
extF
(External clock input must be selected as the
30 ns
oscillator circuit option.)
2 applies to the P33/HOLD pin.
IL
V
V2
V
V
V2
No. 5489-15/28
Page 16

LC66P5316
Electrical Characteristics at Ta = –30 to +70°C, VSS= 0 V, VDD= 4.0 to 5.5 V unless otherwise specified.
Parameter Symbol Conditions min typ max Unit Note
IIH1 P61, and P63: VIN= +10.0 V, with the output 5.0 µA 1
I
Input high-level current
I
IIH4 RES: VIN= VDD, operating, halt mode 10 µA 1
I
I
IIL1
I
Input low-level current
IIL3 RES: VIN= V
IIL4 when the sub-oscillator option is selected.): 20 µA 1
Output high-level voltage V
Value of the output pull-up resistor R
V
Output low-level voltage
V
I
OFF
Output off leakage current I
I
OFF
OFF
[Schmitt characteristics]
Hysteresis voltage V
High-level threshold voltage Vt H P2, P3, P5, P6, OSC1 (EXT), RES 0.5 V
Low-level threshold voltage Vt L 0.2 V
[Ceramic oscillator]
Oscillator frequency f
Oscillator stabilization time f
CFS
[Crystal oscillator]
Oscillator frequency f
Oscillator stabilization time f
[Serial clock]
Cycle time
Low-level and high-level
pulse widths
Rise an fall times Output t
Input
Output 2.0 Tcyc
t
CKCY
Input t
Output t
CKH
CKR
[Serial input]
P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin),
Nch transistor off
P0, P1, P4, P5, P6, PC, OSC1, and P33/HOLD
2 (Does not apply to PD, PE, PC2, and PC3): 1.0 µA 1
IH
= VDD, with the output Nch transistor off
V
IN
PD, PC2, PC3, PE0, (When used as a port; does
not apply when the sub-oscillator option is
3
IH
selected.): V
transistor off
5 RES: VIN= VDD, hold mode 1.0 µA 1
IH
PE1 (When used as a port; does not apply when
6
IH
the sub-oscillator option is selected.) : V
Input ports other than PD, PE, PC2, and PC3:
V
= VSS, with the output Nch transistor off
IN
PD, PC2, PC3, PE0: V
2
IL
with the output Nch transistor off
= VDD, with the output Nch
IN
= VSS,
IN
SS
= V
IN
DD
–1.0 µA 2
–1.0 µA 2
100 µA 1
1.0 µA 1
1.0 µA 1
PE1 (When used as a port; does not apply
= V
V
IN
SS
P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin),
P6, P8, and PC: I
1
OH
P2, P3 (except for the P33/HOLD pin),
P6, P8, and PC: I
P0, P1, P4, P5 30 100 150 kΩ 4
PO
P0, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P8, and PC
1
OL
(except for the P33/HOLD pin): I
P0, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P8, and PC
2
OL
(except for the P33/HOLD pin): I
= –1 mA
OH
= –0.1 mA
OH
= 1.6 mA
OL
= 8 mA
OL
V
– 1.0
DD
V
– 0.5
DD
0.4 V 5
1.5 V
1 P2, P3, P61, P63: VIN= +7.0 V 5.0 µA 6
Does not apply to P2, P3, P61, P63, and P8.:
2
V
= V
IN
DD
3 P8: VIN= V
HYS
OSC1, OSC2: Figure 2, 4 MHz 4.0 MHz
CF
SS
–1.0 µA 7
0.1 V
DD
DD
DD
1.0 µA 6
0.8 V
DD
0.5 V
DD
Figure 3, 4 MHz 10.0 ms
XT1, XT2: Figure 2, when the sub-oscillator
XT
option is selected, 32 kHz
Figure 3, when the sub-oscillator option is
XTS
selected, 32 kHz
32.768 kHz
1.0 5.0 s
0.9 µs
SCK0, SCK1: With the timing of Figure 4 and
CKL
the test load of Figure 5.
, t
CKF
0.4 µs
1.0 Tcyc
0.1 µs
V3
V
V
V
Data setup time t
Data hold time t
[Serial output]
Output delay time t
ICK
CKI
CKO
SI0, SI1: With the timing of Figure 4.
0.3 µs
Stipulated with respect to the rising edge (↑) of
SCK0 or SCK1.
0.3 µs
SO0, SO1: With the timing of Figure 5 and
the test load of Figure 5. Stipulated with respect 0.3 µs
to the falling edge (↓) of SCK0 or SCK1.
Continued on next page.
Page 17

LC66P5316
Continued from preceding page.
Parameter Symbol Conditions min typ max Unit Note
[Pulse conditions]
INT0: Figure 6, conditions under which the INT0
INT0 high and low-level t
High and low-level pulse widths
for interrupt inputs other than INT0 the corresponding interrupt can be accepted
PIN1 high and low-level
pulse widths timer 1 event counter input can be accepted
RES high and low-level
pulse widths can be applied.
t
PINH
t
RSH
IOH
t
IIH
interrupt can be accepted, conditions under
, t
IOL
which the timer 0 event counter or pulse width
measurement input can be accepted
INT1, INT2: Figure 6, conditions under which
, t
IIL
PIN1: Figure 6, conditions under which the
, t
PINL
RES: Figure 6, conditions under which reset
, t
RSL
2 Tcyc
2 Tcyc
2 Tcyc
3 Tcyc
Operating current drain I
Halt mode current drain I
Hold mode current drain I
Note: 1. With the output Nch transistor off in shared I/O ports with the open-drain output specifications. These pins cannot be used as input pins if the
CMOS output specifications are selected.When the port option is selected for PE.
2. With the output Nch transistor off in shared I/O ports with the open-drain output specifications. The rating for the pull-up output specification pins is
stipulated in terms of the output pull-up current IPO. These pins cannot be used as input pins if the CMOS output specifications are selected.
3. With the output Nch transistor off for CMOS output specification pins. (Also applies when the Pch open-drain option is selected for P8.)
4. With the output Nch transistor off for pull-up output specification pins.
5. When CMOS output specifications are selected for P8.
6. With the output Nch transistor off for open-drain output specification pins.
7. With the output Pch transistor off for open-drain output specification pins.
8. Reset state
DD OP
DDHALT
DDHOLDVDD
VDD: 4-MHz ceramic oscillator 6.0 12 mA
V
: 4-MHz external clock 6.0 12 mA
DD
V
: 4-MHz ceramic clock 4.0 8 mA
DD
VDD: 32 kHz (main oscillator stopped), 100 500 µA
sub-oscillator: crystal
: VDD= 1.8 to 5.5 V 0.01 10 µA
Comparator Characteristics at Ta = –30 to +70°C, VSS= 0 V
Parameter Symbol Conditions min typ max Unit Note
Absolute precision V
Threshold voltage V
Input voltage V
Conversion time T
Note: 1. Does not include the quantization error.
CECM
THCMVDD
INCM
AN1 to AN4: VDD= 4.0 to 5.5 V ±1/2 ±1 LSB 1
= 4.0 to 5.5 V V
AN1 to AN4: VDD= 4.0 to 5.5 V V
VDD= 4.0 to 5.5 V 30 µs
CCM
SS
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
V
8
External clock
(OSC2)OSC1
OPEN
t
extF
t
extL
t
extR
t
extH
1/fext
Figure 1 External Clock Input Waveform
V
DD
0.8V
0.2V
V
SS
DD
DD
No. 5489-17/28
Page 18

LC66P5316
V
DD
Operating VDD
minimum value
OSC1
OSC2
Rd
Ceramic
C1 C2
oscillator
XT1
XT2
Rd
Crystal
C1 C2
oscillator
OSC
Oscillator
unstable period
t
CFS
Figure 2 Ceramic Oscillator Circuit Figure 3 Oscillator Stabilization Period
Table 1 Guaranteed Ceramic Oscillator Constants External capacitor type
External capacitor type Built-in capacitor type
4 MHz
(Murata Mfg. Co., Ltd.) C2 = 33 pF ± 10% (Murata Mfg. Co., Ltd.) Rd = 220 Ω ± 5%
CSA4.00MG
4 MHz
(Kyocera Corporation) C2 = 33 pF ± 10% (Kyocera Corporation)
KBR4.0MS
C1 = 33 pF ± 10%
Rd = 220 Ω ± 5%
C1 = 33 pF ± 10%
Rd = 0 Ω
4 MHz
CST4.00MG
4 MHz
KBR4.0MES
Table 2 Guaranteed Crystal Oscillator Constants
32 kHz
(Seiko Epson) C2 = 18 pF ± 10%
C-002RX
SCK0
SCK1
0.2V
DD (input)
0.4V
DD (output)
SI0
SI1
SO0
SO1
C1 = 18 pF ± 10%
Rd = 470 kΩ ± 5%
t
CKCY
t
CKR
t
CKL
t
ICKtCKI
t
CK0
VDD-1
0.4V
DD
t
CKH
0.8V
0.2V
DD
DD
t
CKF
0.8V
VDD-1
DD (input)
(output)
TEST
point
R=1kΩ
C=50pF
0V
Stable oscillation
Figure 4 Serial I/O Timing Figure 5 Timing Load
t
I0H
t
I1H
t
PINH
t
RSH
0.8V
DD
0.2V
DD
t
I0L
t
I1L
t
PINL
t
RSL
Figure 6 Input Timing for the INT0, INT1, INT2, PIN1, and RES pins
No. 5489-18/28
Page 19

LC66P5316
Preconditions for mounting one-time programmable microprocessors
Usage Notes
Due to inherent structural considerations, it is impossible to fully test one-time programmable microprocessors before
the PROM has been programmed, i.e. before shipment from the factory. We recommend that users screen products
whose PROM has been written according to the following procedure to improve the reliability of these products.
• Due to the nature of the product, it is not possible to test write operations to all bits in one-time programmable
microprocessors whose PROM has not been written. Therefore it may be impossible to guarantee a 100% yield on
writing to these products. Please understand that no such guarantee may be made.
• Storage of products in the moisture-proof packed (unopened) state
• Store products in moisture-proof packages in an environment in which the temperature is no higher than 30°C and
the relative humidity is no higher than 70%.
• Storage of products after opening the moisture-proof packaging
• After opening products that were packed in moisture-proof packaging, mount (solder) those products as soon as
possible. Store products for no more than 96 hours after opening the moisture-proof packaging in an environment
in which the temperature is no higher than 30°C and the relative humidity is no higher than 70%.
a. Preconditions for mounting products that were programmed by the user b. Preconditions for mounting products that were programmed by Sanyo
DIP/QFP product
Programming and verification
Recommended screening conditions
High-temperature bake (disconnected)
150°C ±5°C, 24 HR
Program data verification
Mounting Mounting
+1HR
–0HR
DIP/QFP product
Sanyo ROM writing service
Sanyo provides a for-fee ROM writing service that includes writing the one-time programmable ROM, printing,
screening, and read-out verification. Contact your Sanyo sales representative for details.
No. 5489-19/28
Page 20

LC66P5316
LC66XXXX Series Instruction Table (by function)
Abbreviations:
AC: Accumulator
E: E register
CF: Carry flag
ZF: Zero flag
HL: Data pointer DPH, DPL
XY: Data pointer DPX, DPY
M: Data memory
M (HL): Data memory pointed to by the DPH, DPL data pointer
M (XY): Data memory pointed to by the DPX, DPY auxiliary data pointer
M2 (HL): Two words of data memory (starting on an even address) pointed to by the DPH, DPL data pointer
SP: Stack pointer
M2 (SP): Two words of data memory pointed to by the stack pointer
M4 (SP): Four words of data memory pointed to by the stack pointer
in: n bits of immediate data
t2: Bit specification
t2 11 10 01 00
3
2
1
Bit 2
2
2
0
2
PCh: Bits 8 to 11 in the PC
PCm: Bits 4 to 7 in the PC
PCl: Bits 0 to 3 in the PC
Fn: User flag, n = 0 to 15
TIMER0: Timer 0
TIMER1: Timer 1
SIO: Serial register
P: Port
P (i4): Port indicated by 4 bits of immediate data
INT: Interrupt enable flag
( ), [ ]: Indicates the contents of a location
←: Transfer direction, result
: Exclusive or
: Logical and
: Logical or
+: Addition
–: Subtraction
—: Taking the one's complement
No. 5489-20/28
Page 21

LC66P5316
Mnemonic Operation Description status Note
Instruction code Affected
D
7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
Number of
cycles
Number of
bytes
bits
[Accumulator manipulation instructions]
CLA Clear AC 1000 0000 1 1
DAA
DAS
Decimal adjust AC 1100 1111
in addition 0010 0110 (Equivalent to ADI 6.)
Decimal adjust AC 1100 1111
in subtraction 0010 1010
22
2 2 (Equivalent to Add 10 to AC. ZF
AC ← 0
(Equivalent to LAI 0.) skip function.
AC ← (AC) + 6
Clear AC to 0. ZF
Add six to AC. ZF
AC ← (AC) + 10
ADI 0AH.)
CLC Clear CF 0001 1110 1 1 CF ←0 Clear CF to 0. CF
STC Set CF 0001 1111 1 1 CF ←1 Set CF to 1. CF
CMA Complement AC 0001 1000 1 1 AC ←(AC)
Take the one’s complement
of AC.
ZF
IA Increment AC 0001 0100 1 1 AC ←(AC) + 1 Increment AC. ZF, CF
DA Decrement AC 0010 0100 1 1 AC ←(AC) – 1 Decrement AC. ZF, CF
← (CF),
AC
RAR
RAL
Rotate AC right
through CF
Rotate AC left
through CF
0001 0000 1 1 ACn ← (ACn + 1), Shift AC (including CF) right. CF
0000 0001 1 1 ACn + 1 ← (ACn), Shift AC (including CF) left. CF, ZF
TAE Transfer AC to E 0100 0101 1 1 E ←(AC)
3
CF ← (AC
← (CF),
AC
0
CF ← (AC
)
0
)
3
Transfer the contents of AC to E.
TEA Transfer E to AC 0100 0110 1 1 AC ←(E) Transfer the contents of E to AC. ZF
XAE Exchange AC with E 0100 0100 1 1 (AC) ↔ (E)
Exchange the contents of
AC and E.
[Memory manipulation instructions]
IM Increment M 0001 0010 1 1
DM Decrement M 0010 0010 1 1
IMDR i8 Increment M direct
DMDR i8 Decrement M direct
1100 0111
I
7I6I5I4I3I2I1I0
1100 0011
I
7I6I5I4I3I2I1I0
2 2 M (i8) ← [M (i8)] + 1 Increment M (i8). ZF, CF
2 2 M (i8) ← [M (i8)] – 1 Decrement M (i8). ZF, CF
SMB t2 Set M data bit 0000 11t1t01 1 [M (HL), t2] ← 1
RMB t2 Reset M data bit 0010 11t
1 1 [M (HL), t2] ← 0
1t0
M (HL) ←
[M (HL)] + 1
M (HL) ←
[M (HL)] – 1
Increment M (HL). ZF, CF
Decrement M (HL). ZF, CF
Set the bit in M (HL) specified
by t0 and t1 to 1.
Clear the bit in M (HL)
specified by t0 and t1 to 0.
ZF
[Arithmetic, logic and comparison instructions]
Add the contents of AC and
AD Add M to AC 0000 0110 1 1
AC ← (AC) + M (HL) as two’s complement
[M (HL)] values and store the result
ZF, CF
in AC.
Add the contents of AC and
ADDR i8 Add M direct to AC
1100 1001
I
7I6I5I4I3I2I1I0
2 2 AC ← (AC) + [M (i8)]
M (i8) as two’s complement
values and store the result
in AC.
ZF, CF
Add the contents of AC,
ADC Add M to AC with CF 0000 0010 1 1
AC ← (AC) + M (HL) and C as two’s
[M (HL)] + (CF) complement values and
ZF, CF
store the result in AC.
Add the contents of AC and
ADI i4
Add immediate data 1100 1111
to AC 0010 I
3I2I1I0
22
AC ← (AC) + the immediate data as two’s
I3, I2, I1, I
0
complement values and store
the result in AC.
ZF
Subtract the contents of AC CF will be zero if
SUBC
Subtract AC from M
with CF (AC) – (CF) complement values and store borrow and one
0001 0111 1 1
AC ← [M (HL)] – and CF from M (HL) as two’s
ZF, CF
the result in AC. otherwise.
ANDA
ORA
And M with AC then AC ← (AC)
store AC
Or M with AC then AC ← (AC)
store AC
0000 0111 1 1
0000 0101 1 1
[M (HL)]
[M (HL)]
Take the logical and of AC
and M (HL) and store the ZF
result in AC.
Take the logical or of AC and
M (HL) and store the result ZF
in AC.
Continued on next page.
Has a vertical
there was a
No. 5489-21/28
Page 22

Continued from preceding page.
LC66P5316
Mnemonic Operation Description status Note
Instruction code Affected
D
7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
Number of
cycles
Number of
bytes
bits
[Arithmetic, logic and comparison instructions]
EXL
ANDM
ORM
Exclusive or M with AC ← (AC)
AC then store AC
And M with AC then M (HL) ← (AC)
store M
Or M with AC then M (HL) ← (AC)
store M
0001 0101 1 1
0000 0011 1 1
0000 0100 1 1
[M (HL)]
[M (HL)]
[M (HL)]
Take the logical exclusive or
of AC and M (HL) and store ZF
the result in AC.
Take the logical and of AC
and M (HL) and store the ZF
result in M (HL).
Take the logical or of AC and
M (HL) and store the result ZF
in M (HL).
Compare the contents of AC
and M (HL) and set or clear CF
and ZF according to the result.
CM Compare AC with M 0001 0110 1 1 [M (HL)] + (AC) + 1 ZF, CF
Magnitude
comparison
CF ZF
[M (HL)] > (AC) 0 0
[M (HL)] = (AC) 1 1
[M (HL)] < (AC) 1 0
Compare the contents of AC
and the immediate data
and set or clear CF
I
3I2I1I0
and ZF according to the result.
CI i4
Compare AC with 1100 1111
immediate data 1010 I
3I2I1I0
22I
3I2I1I0
+ (AC) + 1 ZF, CF
Magnitude
comparison
I
3I2I1I0
I
3I2I1I0
I
3I2I1I0
CF ZF
> AC 0 0
= AC 1 1
< AC 1 0
ZF ← 1 Compare the contents of DP
CLI i4
Compare DP
immediate data 1011 I
with 1100 1111
L
3I2I1I0
22
if (DPL) = I3I2I1I0with the immediate data.
ZF ← 0 Set ZF if identical and clear
) ≠ I3I2I1I0ZF if not.
if (DP
L
ZF ← 1
if (AC, t2) = [M (HL), Compare the corresponding
CMB t2
Compare AC bit with 1100 1111
M data bit 1101 00t
1t0
22
t2] bits specified by t0 and t1 in
ZF← 0 AC and M (HL). Set ZF if
if (AC, t2) ≠ [M (HL), identical and clear ZF if not.
t2]
[Load and store instructions]
LAE
LAI i4
LADR i8
Load AC and E from
M2 (HL) E ← M (HL + 1) into AC, E.
Load AC with
immediate data into AC. skip function
Load AC from M 1100 0001
direct I
0101 1100 1 1
1000 I
7I6I5I4I3I2I1I0
3I2I1I0
1 1 AC ← I3I2I1I
2 2 AC ← [M (i8)]
AC ← M (HL), Load the contents of M2 (HL)
S Store AC to M 0100 0111 1 1 M (HL) ← (AC)
SAE
LA reg
Store AC and E to
M2 (HL) M (HL + 1) ← (E) into M2 (HL).
Load AC from
M (reg)
0101 1110 1 1
0100 10t
0 1 1 AC ← [M (reg)] ZF
0
M (HL) ← (AC) Store the contents of AC, E
Load the immediate data
0
Load the contents of M (i8)
into AC.
Store the contents of AC into
M (HL).
Load the contents of M (reg)
into AC.
The reg is either HL or XY
depending on t
reg T
HL 0
XY 1
L
ZF
ZF
ZF
Has a vertical
ZF
.
0
0
Continued on next page.
No. 5489-22/28
Page 23

Continued from preceding page.
LC66P5316
Mnemonic Operation Description status Note
Instruction code Affected
D
7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
Number of
Number of
bytes
[Load and store instructions]
LA reg, I
LA reg, D
XA reg
Load AC from M (reg)
then increment reg
Load AC from M (reg)
then decrement reg
Exchange AC with
M (reg)
0100 10t
0101 10t
0100 11t
112DPL←(DPL) + 1 contents of either DPLor DPY. ZF result of
0
112DPL←(DPL) – 1 contents of either DPLor DPY. ZF result of
0
0 1 1 (AC) ↔ [M (reg)]
0
Exchange AC with (AC) ↔ [M (reg)]
XA reg, I M (reg) then 0100 11t
increment reg or DP
112DPL←(DPL) + 1
0
Exchange AC with (AC) ↔ [M (reg)]
XA reg, D M (reg) then 0101 11t
decrement reg or DP
XADR i8
LEAI i8
RTBL
Exchange AC with 1100 1000
M direct I
7I6I5I4I3I2I1I0
Load E & AC with 1100 0110
immediate data I
Read table data from
program ROM [ROM (PCh, E, AC)] replacing the lower 8 bits of
7I6I5I4I3I2I1I0
0101 1010 1 2
112DPL←(DPL) – 1
0
2 2 (AC) ↔ [M (i8)]
22
Read table data from
RTBLP program ROM then 0101 1000 1 2
output to P4, 5 lower 8 bits of the PC with
[Data pointer manipulation instructions]
with zero
H
with
L
0110 I
3I2I1I0
11
LDZ i4
Load DP
and DP
immediate data DPL ← I
respectively
LHI i4
LLI i4
LHLI i8
LXYI i8
Load DP
immediate data 0000 I
Load DP
immediate data 0001 I
Load DP
immediate data I
Load DP
immediate data I
with 1100 1111
H
with 1100 1111
L
, DPLwith 1100 0000
H
, DPYwith 1100 0000
X
7I6I5I4I3I2I1I0
7I6I5I4I3I2I1I0
3I2I1I0
3I2I1I0
22DP
22DP
22
22
cycles
bits
Load the contents of M (reg)
into AC. (The reg is either HL ZF is set
AC ← [M (reg)] or XY.) Then increment the according to the
← (DPY) + 1 The relationship between t
or DP
Y
and reg is the same as that DP
for the LA reg instruction.
0
incrementing
or DPY.
L
Load the contents of M (reg)
into AC. (The reg is either HL ZF is set
AC ← [M (reg)] or XY.) Then decrement the according to the
← (DPY) – 1 The relationship between t
or DP
Y
and reg is the same as that DP
for the LA reg instruction.
0
decrementing
or DPY.
L
Exchange the contents of
M (reg) and AC.
The reg is either HL or XY
depending on t
reg T
.
0
0
HL 0
XY 1
Exchange the contents of
← (DPY) + 1
Y
M (reg) and AC. (The reg is
either HL or XY.) Then
increment the contents of
either DP
relationship between t
reg is the same as that for
or DPY. The
L
0
and
ZF result of
ZF is set
according to the
incrementing
DP
or DPY.
L
the XA reg instruction.
Exchange the contents of
← (DPY) – 1
Y
M (reg) and AC. (The reg is
either HL or XY.) Then
decrement the contents of
either DP
relationship between t
reg is the same as that for
or DPY. The
L
0
and
ZF result of
ZF is set
according to the
decrementing
DP
or DPY.
L
the XA reg instruction.
Exchange the contents of AC
and M (i8).
E ← I
7I6I5I4
AC ← I3I2I1I
Load the immediate data i8
into E, AC.
0
Load into E, AC the ROM data
E, AC ← at the location determined by
the PC with E, AC.
Output from ports 4 and 5 the
Port 4, 5 ←
[ROM (PCh, E, AC)]
ROM data at the location
determined by replacing the
E, AC.
← 0 Load zero into DPHand the
DP
H
3I2I1I0
← I3I2I1I
H
←I3I2I1I
L
DPH← I7I6I5I
DPL← I3I2I1I
DPX← I7I6I5I
DPY← I3I2I1I
immediate data i4 into DPL.
Load the immediate data i4
0
into DPH.
Load the immediate data i4
0
into DPL.
Load the immediate data into
4
DLH, DPL.
0
Load the immediate data into
4
DLX, DPY.
0
Continued on next page.
No. 5489-23/28
Page 24

Continued from preceding page.
LC66P5316
Mnemonic Operation Description status Note
Instruction code Affected
D
7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
Number of
cycles
Number of
bytes
[Data pointer manipulation instructions]
IL Increment DP
DL Decrement DP
IY Increment DP
DY Decrement DP
L
L
Y
Y
TAH Transfer AC to DP
THA Transfer DP
XAH
Exchange AC
with DP
to AC
H
H
TAL Transfer AC to DP
TLA Transfer DP
XAL
Exchange AC
with DP
to AC
L
L
TAX Transfer AC to DP
TXA Transfer DP
XAX
Exchange AC
with DP
to AC
X
X
TAY Transfer AC to DP
TYA Transfer DP
XAY
Exchange AC
with DP
to AC
Y
Y
0001 0001 1 1 DPL←(DPL) + 1
0010 0001 1 1 DPL←(DPL) – 1
0001 0011 1 1 DPY←(DPY) + 1
0010 0011 1 1 DPY←(DPY) – 1
1100 1111
H
1111 0000 to DP
1100 1111
1110 0000 to AC.
22DP
←(AC)
H
2 2 AC ← (DPH)
0100 0000 1 1 (AC) ↔ (DPH)
1100 1111
L
1111 0001 to DP
1100 1111
1110 0001 to AC.
22DP
←(AC)
L
2 2 AC ← (DPL)
0100 0001 1 1 (AC) ↔ (DPL)
1100 1111
X
1111 0010 to DP
1100 1111
1110 0010 to AC.
22DP
←(AC)
X
2 2 AC ← (DPX)
0100 0010 1 1 (AC) ↔ (DPX)
1100 1111
Y
1111 0011 to DP
1100 1111
1110 0011 to AC.
22DP
←(AC)
Y
2 2 AC ← (DPY)
0100 0011 1 1 (AC) ↔ (DPY)
Increment the contents
of DP
.
L
Decrement the contents
of DP
.
L
Increment the contents
of DP
.
Y
Decrement the contents
of DP
.
Y
Transfer the contents of AC
.
H
Transfer the contents of DP
Exchange the contents of AC
and DPH.
Transfer the contents of AC
.
L
Transfer the contents of DP
Exchange the contents of AC
and DPL.
Transfer the contents of AC
.
X
Transfer the contents of DP
Exchange the contents of AC
and DPX.
Transfer the contents of AC
.
Y
Transfer the contents of DP
Exchange the contents of AC
and DPY.
[Flag manipulation instructions]
SFB n4 Set flag bit 0111 n
RFB n4 Reset flag bit 0011 n
3n2n1n0
3n2n1n0
1 1 Fn ← 1
1 1 Fn ← 0
Set the flag specified
by n4 to 1.
Reset the flag specified
by n4 to 0.
[Jump and subroutine instructions]
JMP Jump in the current 1110P11P10P9P
addr bank P
7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
8
22
Jump to the address
JPEA stored at E and AC 0010 0111 1 1
in the current page
PC13, 12 ←
PC13, 12
PC11 to 0 ←
P11to P
8
PC13 to 8 ← Jump to the location
PC13 to 8, determined by replacing the
PC7 to 4 ← (E), lower 8 bits of the PC
PC3 to 0 ← (AC) by E, AC.
Jump to the location in the PC12 + (PC12)
same bank specified by the immediately
immediate data P12. following a BANK
PC13 to 11 ← 0,
PC10 to 0 ←
to P0,
CAL
addr P
Call subroutine
0101 0P
7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
10P9P8
22
P
10
M4 (SP) ←
(CF, ZF, PC13 to 0),
Call a subroutine.
SP ← (SP)-4
PC13 to 6,
PC10 ← 0,
CZP Call subroutine in the
addr zero page M4 (SP) ← in bank 0.
1010P
3P2P1P0
12
PC5 to 2 ← P
to P0, Call a subroutine on page 0
3
(CF, ZF, PC12 to 0),
SP ← SP-4
BANK Change bank 0001 1011 1 1
Change the memory bank
and register bank.
bits
ZF
ZF
ZF
ZF
H
ZF
L
ZF
X
ZF
Y
ZF
ZF
Continued on next page.
This becomes
instruction.
No. 5489-24/28
Page 25

Continued from preceding page.
LC66P5316
Mnemonic Operation Description status Note
Instruction code Affected
D
7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
Number of
cycles
Number of
bytes
[Jump and subroutine instructions]
PUSH
reg 1111 1i
POP 1100 1111 SP ←(SP) + 2
reg
RT
RTI
Push reg on M2 (SP)
Pop reg off M2 (SP)
Return from SP ← (SP) + 4
subroutine
Return from interrupt
routine
1100 1111
1i0
1110 1i
1i0
22
0 SP ←(SP) – 2
22
0
0001 1100 1 2
M2 (SP) ← (reg)
reg ← [M2 (SP)]
PC ← [M4 (SP)]
SP ← (SP) + 4 Return from a subroutine or
0001 1101 1 2 PC ←[M4 (SP)] interrupt handling routine. ZF ZF, CF
CF, ZF ← [M4 (SP)] and CF are restored.
[Branch instructions]
PC7 to 0 ← Branch to the location in the
BAt2
addr P
Branch on AC bit
1101 00t
7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
1t0
22
P
7P6P5P4
P3P2P1P
if (AC, t2) = 1 the immediate data t
PC7 to 0 ← Branch to the location in the
BNAt2
addr P
Branch on no AC bit
1001 00t1t
7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
0
22
P
7P6P5P4
P3P2P1P
if (AC, t2) = 0 the immediate data t
PC7 to 0 ← Branch to the location in the
BMt2 1101 01t
addr
Branch on M bit
P7P6P5P4P3P2P1P
1t0
22 P3P2P1P0P0if the bit in M (HL) specified
0
P7P6P5P4same page specified by P7to
if [M (HL),t2] by the immediate data t
= 1 is one.
PC7 to 0 ← Branch to the location in the
BNMt2 1001 01t
addr
Branch on no M bit
P7P6P5P4P3P2P1P
1t0
22 P3P2P1P0P0if the bit in M (HL) specified
0
P7P6P5P4same page specified by P7to
if [M (HL),t2] by the immediate data t
= 0 is zero.
PC7 to 0 ← Branch to the location in the
P
BPt2
addr P
Branch on Port bit
1101 10t
7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
1t0
22 P3P2P1P0P0if the bit in port (DPL)
7P6P5P4
if [P (DPL), t2] specified by the immediate
= 1 data t
PC7 to 0 ← Branch to the location in the
P
BNPt2
addr P
Branch on no Port bit
1001 10t
7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
1t0
22 P3P2P1P0P0if the bit in port (DPL)
7P6P5P4
if [P (DPL), t2] specified by the immediate
= 0 data t
Store the contents of reg in
M2 (SP). Subtract 2 from SP
after the store.
reg i1i
HL 0 0
XY 0 1
AE 1 0
Illegal value 1 1
Add 2 to SP and then load the
contents of M2(SP) into reg.
The relation between i1i0 and
reg is the same as that for the
PUSH reg instruction.
Return from a subroutine or
interrupt handling routine. ZF
and CF are not restored.
same page specified by P7to
P0if the bit in AC specified by
0
same page specified by P7to
P0if the bit in AC specified by
0
same page specified by P7to
is one.
1t0
same page specified by P7to
is zero.
1t0
1t0
1t0
bits
0
is one.
is zero.
1t0
1t0
Internal control
registers can also
be tested by
executing this
instruction
immediately after
a BANK
instruction.
However, this is
limited to
registers that can
be read out.
Internal control
registers can also
be tested by
executing this
instruction
immediately after
a BANK
instruction.
However, this is
limited to
registers that can
be read out.
Continued on next page.
No. 5489-25/28
Page 26

Continued from preceding page.
LC66P5316
Mnemonic Operation Description status Note
Instruction code Affected
D
7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
Number of
cycles
Number of
bytes
[Branch instructions]
BC addr Branch on CF
BNC
addr P
Branch on no CF
BZ addr Branch on ZF
BNZ
addr P
BFn4 1111n
addr
BNFn4 1011n
addr
Branch on no ZF
Branch on flag bit
Branch on no flag bit
1101 1100
P
7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
1001 1100
7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
1101 1101
P
7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
1001 1101
7P6P5P4P3P2P1P0
P7P6P5P4P3P2P1P
P7P6P5P4P3P2P1P
3n2n1n0
0
3n2n1n0
0
22
22
22
22
22
22
PC7 to 0 ←
P
7P6P5P4
P3P2P1P
if (CF) = 1
PC7 to 0 ←
P
7P6P5P4
P3P2P1P
if (CF) = 0
PC7 to 0 ←
P
7P6P5P4
P3P2P1P
if (ZF) = 1
PC7 to 0 ←
P
7P6P5P4
P3P2P1P
if (ZF) = 0
PC7 to 0 ←
P7P6P5P
P
3P2P1P0
if (Fn) = 1
PC7 to 0 ←
P7P6P5P
P
3P2P1P0
if (Fn) = 0
Branch to the location in the
same page specified by P7to
0
P0if CF is one.
Branch to the location in the
same page specified by P7to
0
P0if CF is zero.
Branch to the location in the
same page specified by P7to
0
P0if ZF is one.
Branch to the location in the
same page specified by P7to
0
P0if ZF is zero.
Branch to the location in the
same page specified by P0to
4
P7if the flag (of the 16 user
flags) specified by n
is one.
Branch to the location in the
same page specified by P0to
4
P7if the flag (of the 16 user
flags) specified by n
is zero.
3n2n1n0
3n2n1n0
[I/O instructions]
IP0 Input port 0 to AC 0010 0000 1 1 AC ←(P0)
IP Input port to AC 0010 0110 1 1 AC ←[P (DP
L
IPM Input port to M 0001 1001 1 1 M (HL) ← [P (DP
IPDR i4
IP45
OP Output AC to port 0010 0101 1 1 P (DP
OPM Output M to port 0001 1010 1 1 P (DP
OPDR i4
OP45
Input port to 1100 1111
AC direct 0110 I3I2I1I
Input port 4, 5 to 1100 1111 E ←[P (4)]
E, AC respectively 1101 0100
Output AC to 1100 1111
port direct 0111 I
3I2I1I0
Output E, AC to port 1100 1111 P (4) ← (E)
4, 5 respectively 1101 0101
2 2 AC ← [P (i4)]
0
22
AC ← [P (5)]
2 2 P (i4) ← (AC)
22
P (5) ← (AC)
) ← (AC)
L
) ← [M (HL)]
L
Input the contents of port
0 to AC.
Input the contents of port
)]
P (DP
) to AC.
L
Input the contents of port
)]
L
P (DP
) to M (HL).
L
Input the contents of
P (i4) to AC.
Input the contents of ports
P (4) and P (5) to E and AC
respectively.
Output the contents of AC to
port P (DP
Output the contents of M (HL)
to port P (DP
Output the contents of AC
to P (i4).
Output the contents of E and
AC to ports P (4) and P (5)
respectively.
ZF
ZF
ZF
).
L
).
L
Set to one the bit in port
SPB t2 Set port bit 0000 10t
1 1 [P (DPL), t2] ← 1 P (DPL) specified by the
1t0
immediate data t
1t0
.
Clear to zero the bit in port
RPB t2 Reset port bit 0010 10t1t01 1 [P (DPL), t2] ← 0 P (DPL) specified by the ZF
1t0
.
3
ZF
3
ANDPDR
i4, p4
ORPDR
i4, p4
And port with P (P
immediate data then
output
Or port with P (P
immediate data then
output
1100 0101
I
3I2I1I0P3P2P1P0
1100 0100
I
3I2I1I0P3P2P1P0
2 2 [P (P
I3to I
2 2 [P (P
I3to I
to P0) ←
3
to P0)]
3
0
to P0) ←
3
to P0)]
3
0
immediate data t
Take the logical AND of P (P
) and the immediate data
to P
0
I3I2I1I0and output the result
to P0).
to P (P
3
Take the logical OR of P (P
) and the immediate data ZF
to P
0
I3I2I1I0and output the result
to P0).
to P (P
3
bits
Continued on next page.
No. 5489-26/28
Page 27

Continued from preceding page.
LC66P5316
Mnemonic Operation Description status Note
Instruction code Affected
D
7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
Number of
cycles
Number of
bytes
[Timer control instructions]
WTTM0 Write timer 0 1100 1010 1 2
WTTM1 Write timer 1
1100 1111
1111 0100
2 2 TIMER1 ← (E), (AC) into the timer 1 reload
RTIM0 Read timer 0 1100 1011 1 2
RTIM1 Read timer 1
START0 Start timer 0
START1 Start timer 1
STOP0 Stop timer 0
STOP1 Stop timer 1
1100 1111
1111 0101 timer 1 counter into E, AC.
1100 1111
1110 0110
1100 1111
1110 0111
1100 1111
1111 0110
1100 1111
1111 0111
2 2 E, AC ← (TIMER1)
2 2 Start timer 0 counter Start the timer 0 counter.
2 2 Start timer 1 counter Start the timer 1 counter.
2 2 Stop timer 0 counter Stop the timer 0 counter.
2 2 Stop timer 1 counter Stop the timer 1 counter.
TIMER0 ← [M2 (HL)],
(AC)
M2 (HL),
AC ← (TIMER0)
Write the contents of M2 (HL),
AC into the timer 0 reload
register.
Write the contents of E, AC
register A.
Read out the contents of the
timer 0 counter into M2 (HL),
AC.
Read out the contents of the
[Interrupt control instructions]
MSET
MRESET
Set interrupt master 1100 1101
enable flag 0101 0000 enable flag to one.
Reset interrupt 1100 1101
master enable flag 1001 0000 enable flag to zero.
EIH i4 Enable interrupt high
EIL i4 Enable interrupt low
DIH i4 Disable interrupt high
DIL i4 Disable interrupt low
WTSP Write SP
RSP Read SP
2 2 MSE ← 1
2 2 MSE ← 0
1100 1101
0101 I
3I2I1I0
1100 1101
0100 I
3I2I1I0
1100 1101
1001 I3I2I1I
1100 1101
1000 I3I2I1I
1100 1111
1101 1010 AC to SP.
1100 1111
1101 1011 to E, AC.
2 2 EDIH ← (EDIH) i4
2 2 EDIL ← (EDIL) i4
2 2 EDIH ← (EDIH) i4
0
2 2 EDIL ← (EDIL) i4
0
2 2 SP ← (E), (AC)
2 2 E, AC ← (SP)
Set the interrupt master
Clear the interrupt master
Set the interrupt enable flag
to one.
Set the interrupt enable flag
to one.
Clear the interrupt enable
flag to zero.
Clear the interrupt enable
flag to zero.
Transfer the contents of E,
Transfer the contents of SP
[Standby control instructions]
HALT HALT
HOLD HOLD
1100 1111
1101 1110
1100 1111
1101 1111
2 2 HALT Enter halt mode.
2 2 HOLD Enter hold mode.
[Serial I/O control instructions]
STARTS Start serial I O
WTSIO Write serial I O
RSIO Read serial I O
1100 1111
1110 1110
1100 1111
1110 1111 AC to SIO.
1100 1111
1111 1111 into E, AC.
2 2 START SI O Start SIO operation.
2 2 SIO ← (E), (AC)
2 2 E, AC ← (SIO)
Write the contents of E,
Read out the contents of SIO
[Other instructions]
Consume one machine cycle
NOP No operation 0000 0000 1 1 No operation without performing any
operation.
SB i2 Select bank
1100 1111
1100 00I
1I0
2 2 PC13, PC12 ← I
Specify the memory bank.
1I0
bits
ZF
ZF
No. 5489-27/28
Page 28

LC66P5316
■ No products described or contained herein are intended for use in surgical implants, life-support systems, aerospace
equipment, nuclear power control systems, vehicles, disaster/crime-prevention equipment and the like, the failure of
which may directly or indirectly cause injury, death or property loss.
■ Anyone purchasing any products described or contained herein for an above-mentioned use shall:
➀ Accept full responsibility and indemnify and defend SANYO ELECTRIC CO., LTD., its affiliates, subsidiaries and
distributors and all their officers and employees, jointly and severally, against any and all claims and litigation and all
damages, cost and expenses associated with such use:
➁ Not impose any responsibility for any fault or negligence which may be cited in any such claim or litigation on
SANYO ELECTRIC CO., LTD., its affiliates, subsidiaries and distributors or any of their officers and employees
jointly or severally.
■ Information (including circuit diagrams and circuit parameters) herein is for example only; it is not guaranteed for
volume production. SANYO believes information herein is accurate and reliable, but no guarantees are made or implied
regarding its use or any infringements of intellectual property rights or other rights of third parties.
This catalog provides information as of February, 1997. Specifications and information herein are subject to
change without notice.
No. 5489-28/28
 Loading...
Loading...