Page 1

KB9223 / KB9223-L
OVERVIEW
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
The KB9223 is a 1-chip BICMOS integrated circuit to perform the function of RF amp and servo signal processor for
compact disc player applications.It consist of blocks for RF
signal processing ,focus, tracking, sled and spindle
servo.Also this IC has adjustment free function and embedded opamp for audio post filter.
FEATURES
• RF amplifier & RF equalizer
• Focus error amplifier & servo control
• Tracking error amplifier & servo control
• Mirror & defect detector circuit
• Focus OK detector circuit
• APC(Auto Laser Power Control) circuit for constant laser
power
• FE bias & focus servo offset adjustment free
• EF balance & tracking error gain adjustment free
• Embedded audio post filter
• The circuit for Interruption countermeasure
• Double speed play available
• Operating voltage range
KB9223 : 5V
80-QFP-1420C
ORDERING INFORMATION
Device Package Tempe. Range
KB9223
KB9223-L
APPLICATIONS
• CD Player
• Video-CD
RELATED PRODUCT
• KS9286 Data Processor
• KS9284 Data Processor
• KA9258D/KA9259D Motor Driver
80-QFP-1420C -20°C ~ +70°C
KB9223-L : 3.4V
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
1
Page 2
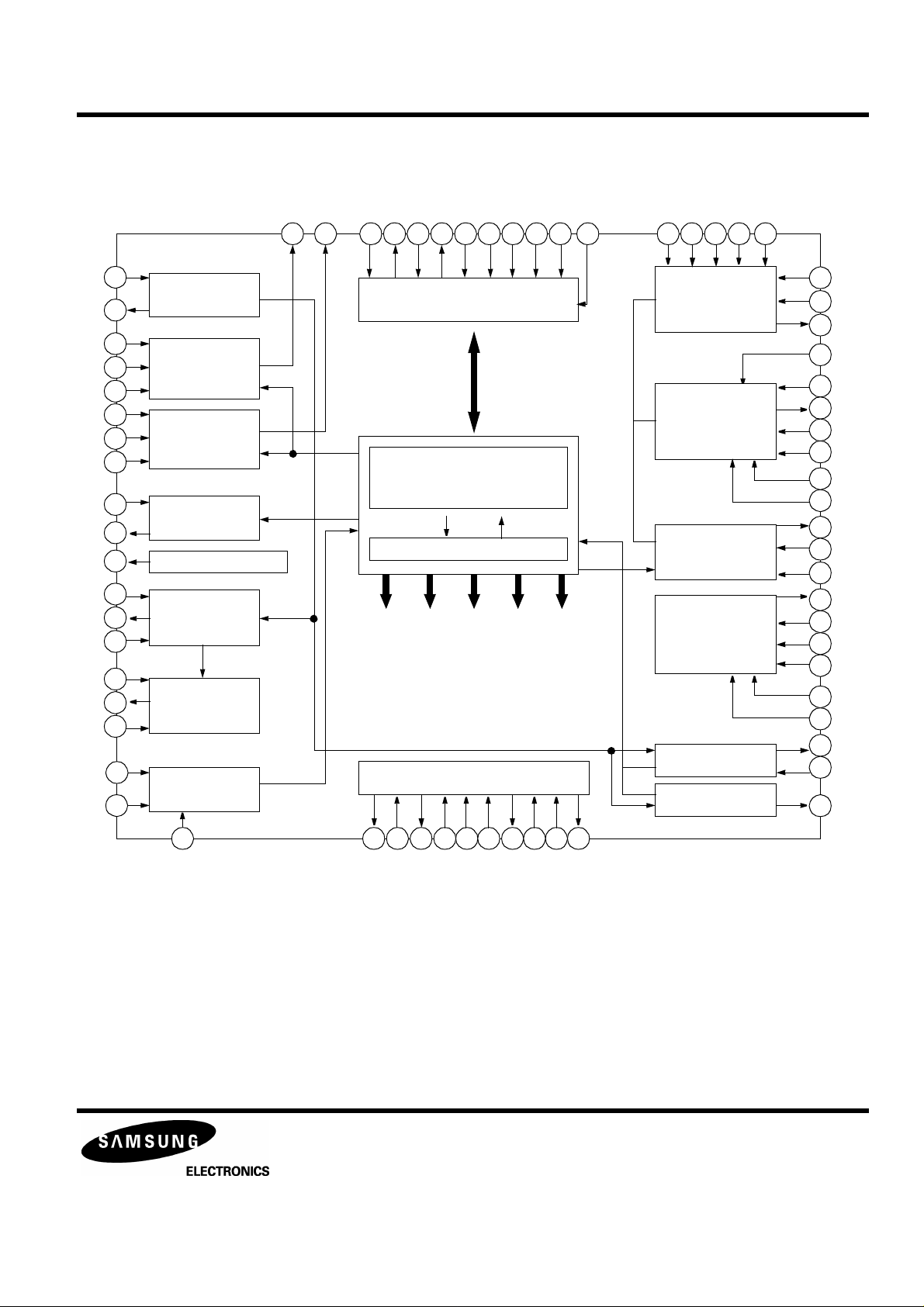
KB9223 / KB9223-L
BLOCK DIAGRAM
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
RF-
RFO
PD1
PD2
FEBIAS
EQC
EQO
IRF
ASY
EFM
RFI
DCB
DCC2
FE1
TE1
WDCH
TRCNT
LOCK
ISTAT
59
54 22 30 29 31 38 37 36 35 51 52 58 26 28 27
73
RF Amp
74
65
Focus Error Amp
66
FE-BIAS Adjustment
63
67
F
E
EI
68
79
Tracking Error Amp
E/F Balance & Gain
Control
Micom Data
Interface Logic
MICOM TO SERVO CONTROL
MLT
RESET
MDATA
MCK
TZC
ATSC
FE2
FLB
Focus Phase
Compensation
& Offset cancel circuit
Tracking Phase
Compensation Block
& Jump Pulse GEN.
AUTO SEQUENCER
PD
69
LD
70
VR
71
78
76
75
32
33
77
APC Amp
Center Voltage Amp.
RF Level AGC
&
Equalizer
EFM
Comparator
LDON
ADJUSTMENT-FREE CONTROL
TM1~
TM6
BAL1~
BAL5
FS1~
FS4
PS1~
PS4
GA1~
GA5
Sled Servo Amplifier
& Sled Kick GEN.
Spindle Servo LPF
( Double Speed )
Mirror Detection
2
Defect Detection
Circuit
4
Built-in Post Filter Amp ( L&R )
Circuit
FOK Detection
Circuit
FS3
FGD
FRSH
3
FDFCT
60
47
FE-
FEO
48
TDFCT
57
49
TE-
TEO
50
TE2
53
LPFT
55
TG2
62
TGU
61
SLO
43
SL-
44
SL+
42
46
SPDLO
SPDL-
45
SMDP
23
SMON
24
SMEF
25
FSET
6
MIRROR
39
MCP
1
FOK
40
5 15 16 13 14 19 17 12 11 9 10
RRC
GC1I
DCC1
GC1O
CH1I
CH1O
MUTEI
CH2I
GC2I
CH2O
Figure 1. Block diagram
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
GC2O
2
Page 3
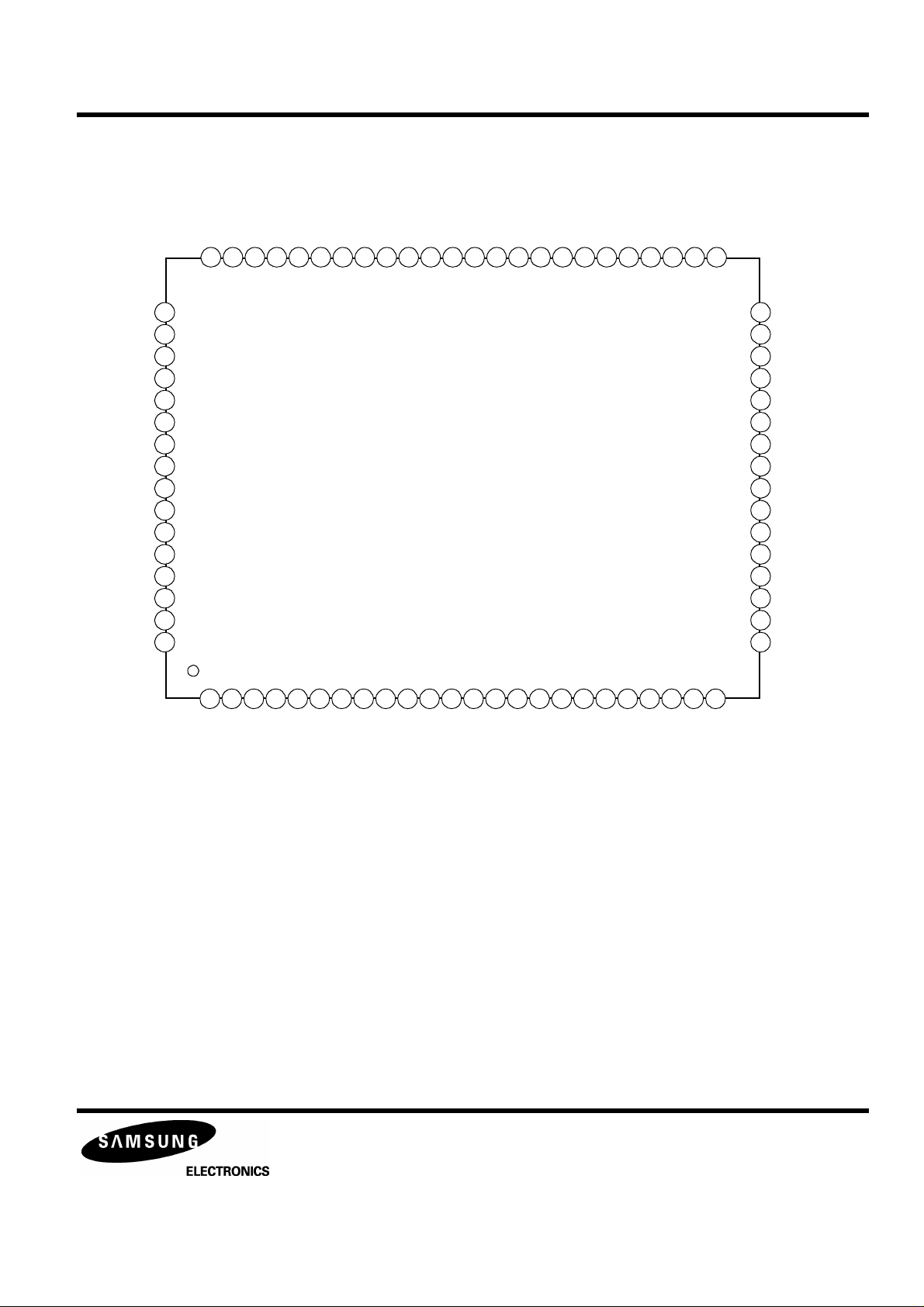
KB9223 / KB9223-L
PIN CONFIGURATION
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54
TG2
DVEE
65
PD1
66
PD2
67
F
68
E
69
PD
70
LD
71
VR
72
VCC
73
RF-
74
RFO
75
IRF
76
EQO
77
RFI
78
EQC
79
EI
80
GND
FEBIAS
MCP
DCB
FRSH
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
FE1
TGU
FDFCT
DCC2
DCC1
FSET
53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41
TE-
FE2
TDFCT
TE1
TE2
TZC
LPFT
DVDD
TEO
ATSC
FE-
FEO
KB9223
VDDA
VCCP
GC2I
10 11
CH2O
CH1O
CH1I
GC1O
GC1I
RRC
VSSP
GC2O
CH2I
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
MUTEI
SL-
SL+
SLO
SPDL-
SPDLO
ISET
VREG
WDCK
MIRROR
RESET
MDATA
VSSA
ISTAT
TRCNT
LOCK
SMEF
SMDP
SMON
SSTOP
FOK
MLT
MCK
EFM
ASY
FGD
FS3
FLB
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
Figure 2. Pin configuration
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
3
Page 4
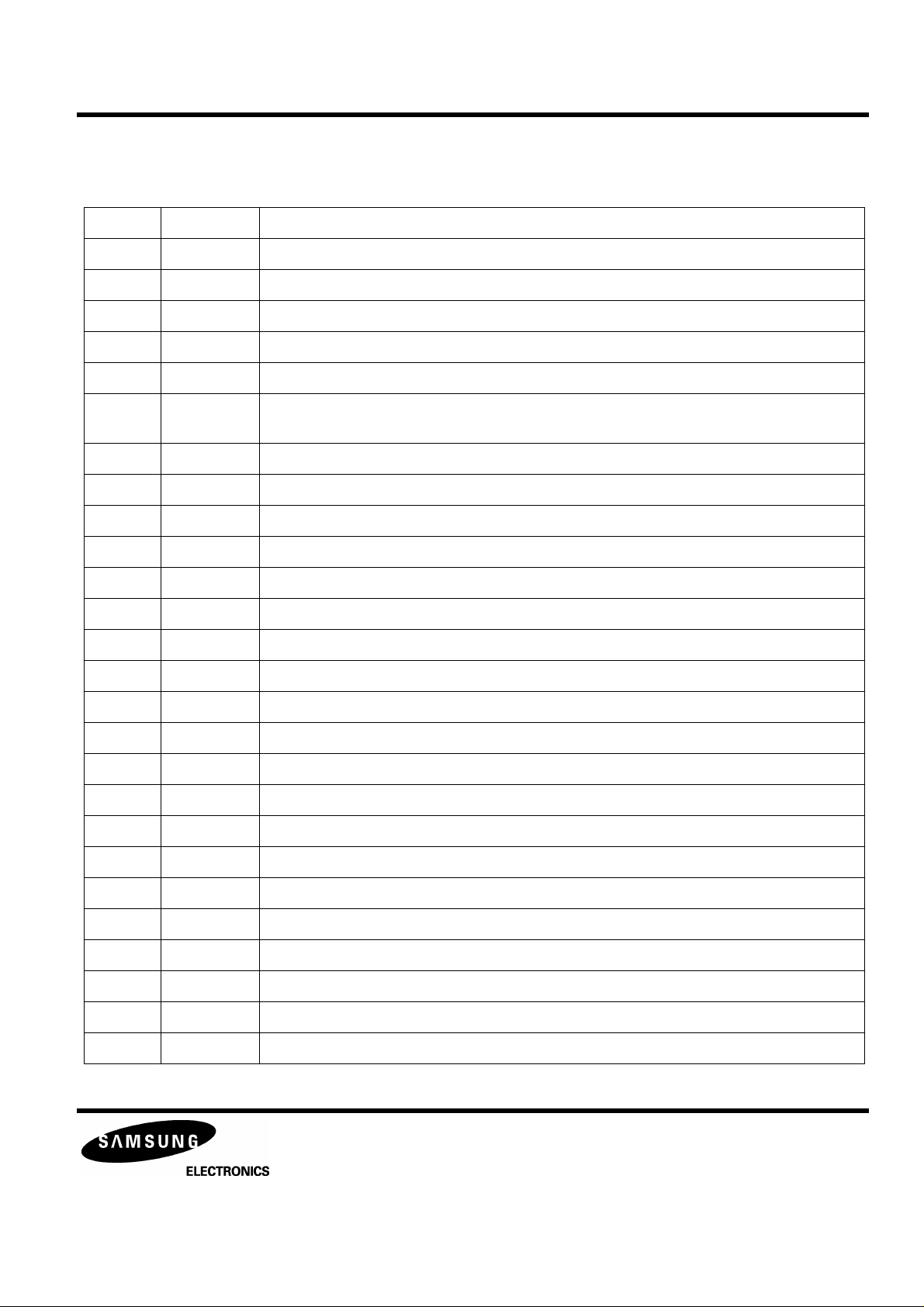
KB9223 / KB9223-L
PIN DESCRIPTION
Table 1. PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin No. Symbol Description
1 MCP Capacitor connection pin for mirror hold
2 DCB Capacitor connection pin for defect Bottom hold
3 FRSH Capacitor connection pin for time constant to generate focus search waveform
4 DCC2 The input pin through capacitor of defect bottom hold output
5 DCC1 The output pin of defect bottom hold
6 FSET The peak frequency setting pin for focus,tracking servo and cut off frequency of CLV
LPF
7 VDDA Analog VCC for servo part
8 VCCP VCC for post filter
9 GC2I Amplifier negative input pin for gain and low pass filtering of DAC output CH2
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
PRELIMINARY
10 GC2O Amplifier output pin for gain and low pass filtering of DAC output CH2
11 CH2I The input pin for post filter channel2
12 CH2O The output pin for post filter channel2
13 CH1O The output pin for post filter channel1
14 CH1I The input pin for post filter channel1
15 GC1O Amplifier output pin for gain and low pass filtering of DAC output CH1
16 GC1I Amplifier negative input pin for gain and low pass filtering of DAC output CH1
17 RRC The pin for noise reduction of post filter bias
18 VSSP VSS for post filter
19 MUTEI The input pin for post filter muting control
20 ISET The input pin for current setting of focus search,track jump and sled kick voltage
21 VREG The output pin of regulator
22 WDCK The clock input pin for auto sequence
23 SMDP The input pin of CLV control output pin SMDP of DSP
24 SMON The input pin for spindle servo ON through SMON of DSP
25 SMEF The input pin of provide for an external LPF time constant
26 FLB Capacitor connection pin to perform rising low bandwidth of focus loop
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
4
Page 5
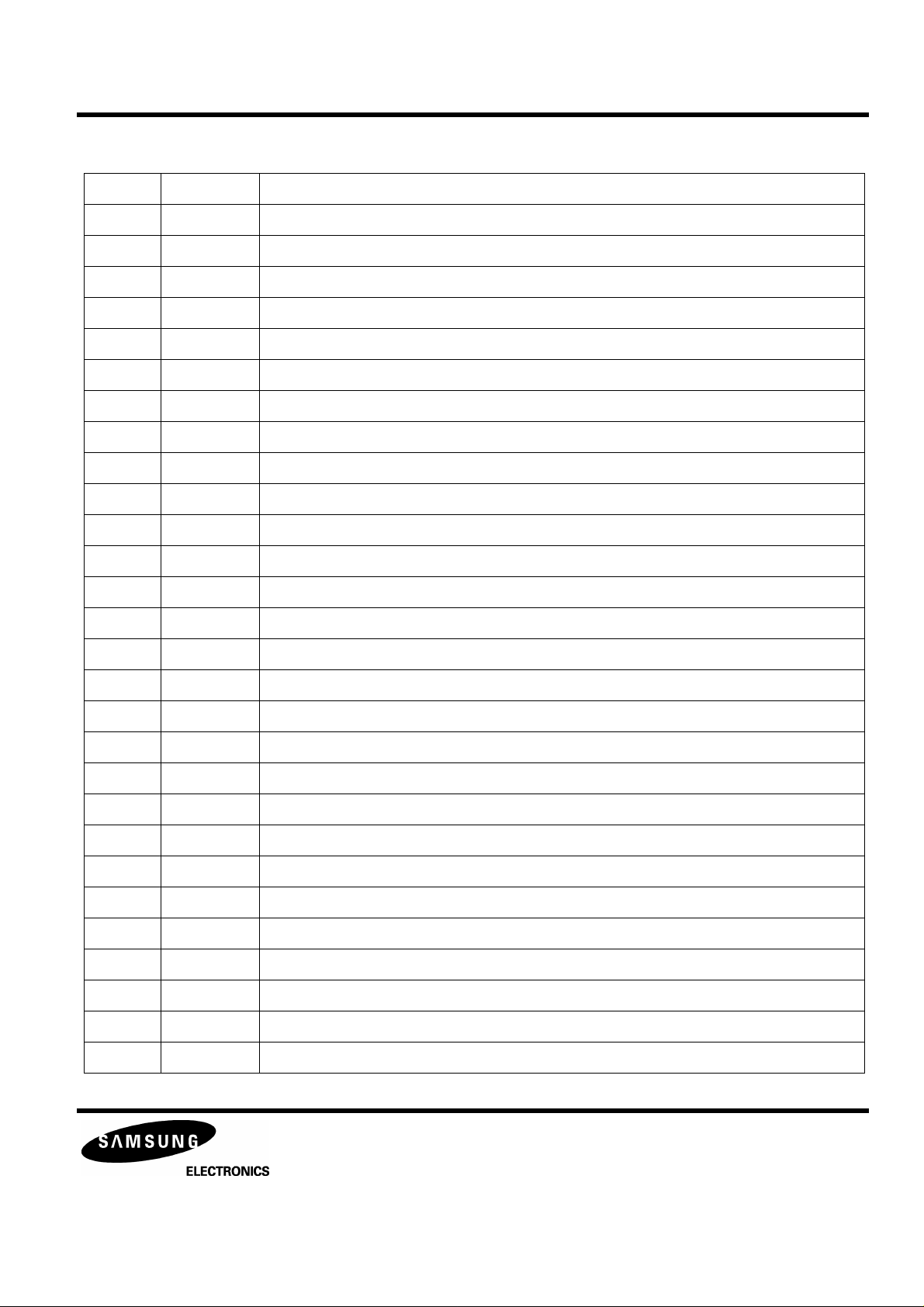
KB9223 / KB9223-L
Table 1. PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Pin No. Symbol Description
27 FS3 The pin for high frequency gain change of focus loop with internal FS3 switch
28 FGD Reducing high frequency gain with capacitor between FS3 pin
29 LOCK Sled runaway prevention pin
30 TRCNT Track count output pin
31 ISTAT Internal status output pin
32 ASY The input pin for asymmetry control
33 EFM EFM comparator output pin
34 VSSA Analog VSS for servo part
35 MCK Micom clock input pin
36 MDATA Micom data input pin
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
PRELIMINARY
37 MLT Micom data latch input pin
38 RESET Reset input pin
39 MIRROR The mirror output for test
40 FOK The output pin of focus OK comparator
61 TGU The capacitor connection pin for high frequency tracking gain switch
62 TG2 The pin for high frequency gain change of tracking servo loop with internal TG2 switch
63 FEBIAS Focus error bias voltage control pin
64 DVEE The DVEE pin for logic circuit
65 PD1 The negative input pin of RF I/V amplifier1(A+C signal)
66 PD2 The negative input pin of RF I/V amplifier2(B+D signal)
67 F The negative input pin of F I/V amplifier (F signal)
68 E The negative input pin of E I/V amplifier(E signal)
69 PD The input pin for APC
70 LD The output pin for APC
71 VR The output pin of (AVEE+AVCC)/2 voltage
72 VCC VCC for RF part
73 RF- RF summing amplifier inverting input pin
74 RFO RF summing amplifier output pin
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
5
Page 6
KB9223 / KB9223-L
Table 1. PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Pin No. Symbol Description
75 IRF The input pin for AGC
76 EQO The output pin for AGC
77 RFI Tne input pin for EFM comparision
78 EQC The capacitor connection pin for AGC
79 EI Feedback input pin of E I/V amplifier for EF Balance control
80 GND GND for RF part
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
PRELIMINARY
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
6
Page 7
KB9223 / KB9223-L
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
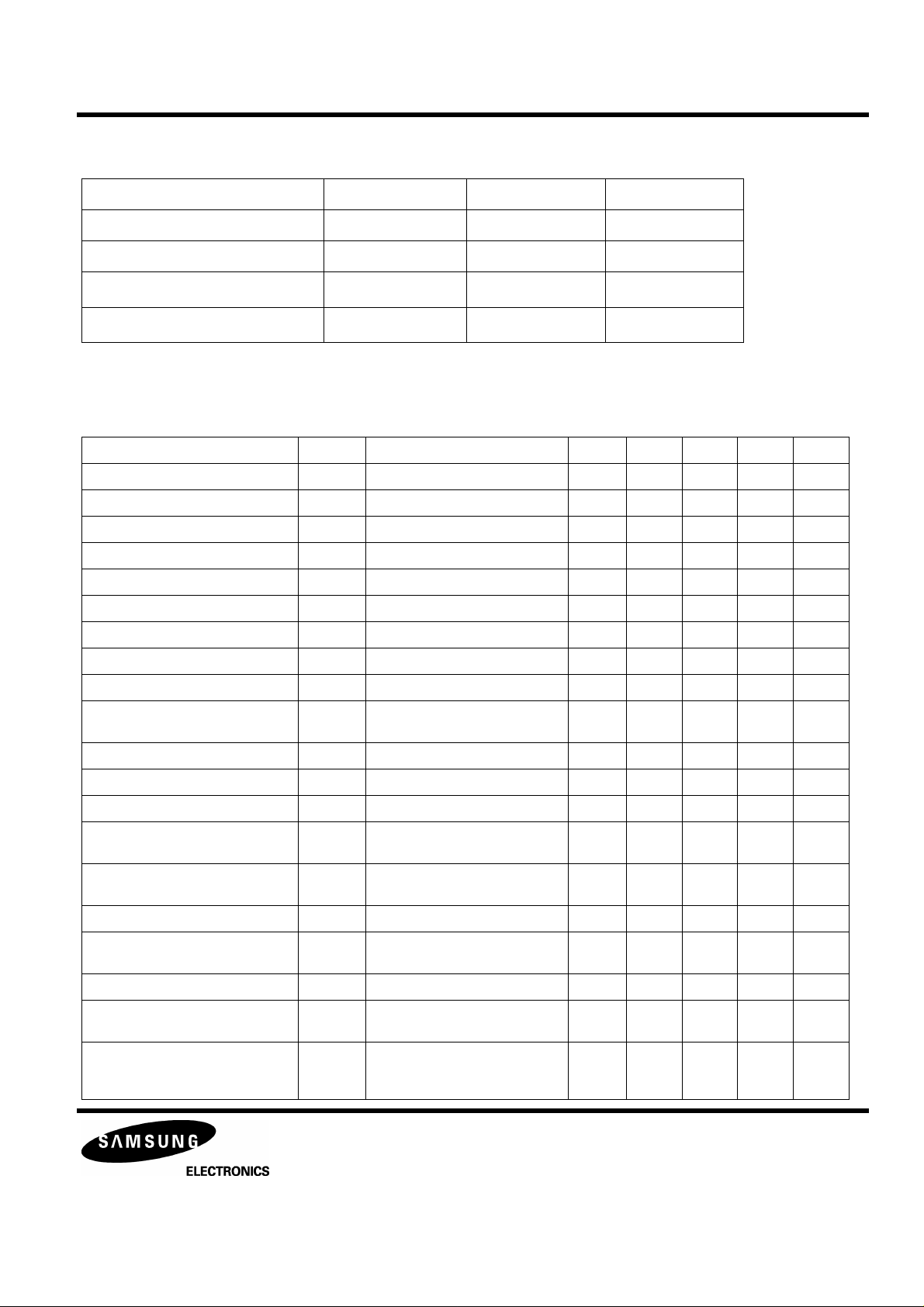
Table 2. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Characteristic Symbol Value Unit
Supply Voltage Vmax 6 V
Power Dissipation PD 200 mW
PRELIMINARY
Operating Temperature
Storage temperature
T
T
OPR
STG
-20 ~ +70
-55 ~ +150
o
C
o
C
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Table 3. Electrical Characteristics
(Ta=25°C, VDD = DVDD = VCC = +5V, VSS = DVSS = GND = VSSP = 0V )
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Output Min Typ Max Unit
Supply Current High ICCHI VCC=6V,No load - 20 40 60 mA
Supply Current Typ ICCTY VCC=5V,No Load - 12 30 48 mA
Supply Current Low ICCLO VCC=3.4V,No Load - 10 25 40 mA
RF Amp Offset Voltage Vrfo input open pin 74 -80 0 +80 mV
RF Amp Voltage Gain Grf SG3 f=10KHz,40mVp-p,sine pin 74 25.1 28.1 31.1 dB
RF THD Grfmd SG3 f=1KHz,40mVp-p,sine pin 74 - - 5 %
RF Amp Max. Output Voltage Vrfpp1 SG3 DC 2.7V pin 74 3.8 - - V
RF Amp Min. Output Voltage Vrfpp2 SG3 DC 2.3V pin 74 - - 1.2 V
Focus Error Amp Offset Voltage Vfeo1 input open pin 59 -450 -250 -50 mV
Focus Error Amp Auto Offset
Voltage
Vfeo2 WDCH=88.2KHz Pulse ,$841 pin 59 -35 0 35 mV
Focus Error Amp PD1 Voltage Gain Gfe1 SG3 f=10KHz,32mVp-p,sine pin 59 27 30 33 dB
Focus Error Amp PD2 Voltage Gain Gfe2 SG3 f=10KHz,32mVp-p,sine pin 59 27 30 33 dB
Focus Error Amp Voltage Difference Gfe∆ ∆Gfe1-∆Gfe1 pin 59 -3 0 +3 dB
Focus Error Amp Max. Output
Voltage
Focus Error Amp Min. Output Volt-
age
AGC Max Gain Gagc SG4 f=500KHz,20mVp-p,sine pin 76 16 19 22 dB
AGC EQ Gain Geq Gain Difference of Gagc at
AGC Gain2 Gagc2 SG4 f=500KHz,0.5Vp-p,sine pin 76 3.5 6 9 dB
AGC Cpmpress Ratio Cagc Gain Difference of Gagc2 at
AGC Frequency Fagc Gain Difference
Gfepp1 SG3 DC 2.7V pin 59 4.4 - - V
Gfepp2 SG3 DC2.3V pin 59 - - 0.6 V
pin 76 0 1 2 dB
f=1.5MHz
pin 76 0 2.5 5 dB
0.1Vp-p
pin 76 -1.5 0 2.5 dB
SG4 f=1.5MHz,0.1Vp-p,sine
and f=500KHz,0.1Vp-p,sine
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
7
Page 8
PRELIMINARY
KB9223 / KB9223-L
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
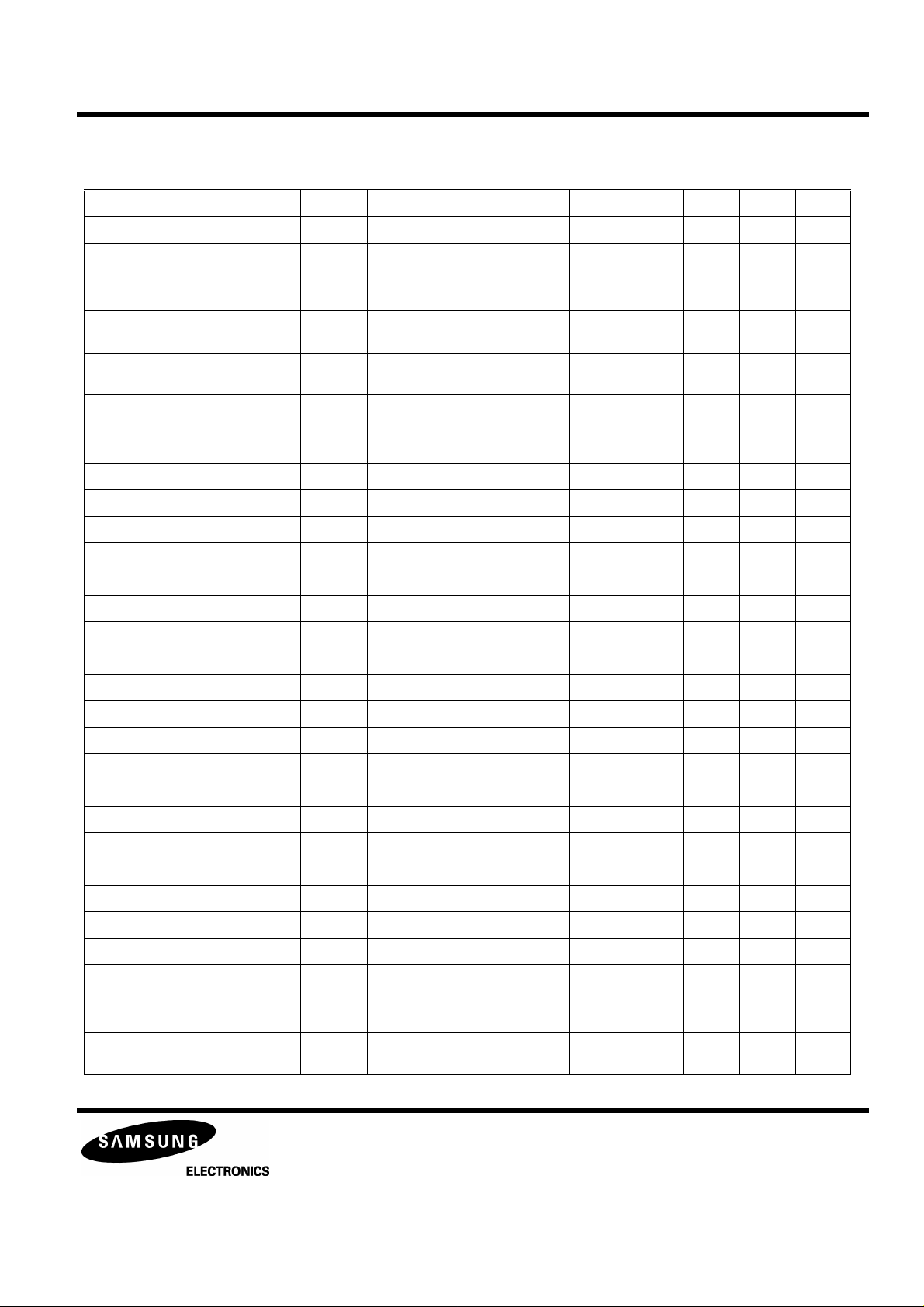
Table 3. Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(Ta=25°C, VDD = DVDD = VCC = +5V, VSS = DVSS = GND = VSSP = 0V )
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Output Min Typ Max Unit
Tracking Error Offset Voltage Vteo $800,$820,input open pin 54 -50 0 +50 mV
Tracking Error Amp Voltage Gain F Gtef $800,$820
SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine
Tracking Error AmpVoltage Gain E Gtee SG3 0.3Vp-p,40KHz,sine pin 54 -0.75 2.25 5.25 dB
Tracking Error Amp
Voltage Gain Difference
Tracking Error Amp
Maximum Output Voltage H
Tracking Error Amp
Minimum Output Voltage L
Tracking Error Amp Gain up F Tguf $830 SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine pin 54 8.0 11.0 14.0 dB
Tracking Error Amp Gain up E Tgue $830 SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine pin 54 5.3 8.3 11.3 dB
Tracking Gain Normal Fgfn SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine,$820 pin 54 2.1 5.1 8.1 dB
Tracking F Gain 1 Fgf1 SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine,$821 pin 54 0.1 3.1 6.1 dB
Tracking F Gain 2 Fgf2 SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine,$822 pin 54 -1.7 1.3 4.3 dB
Tracking F Gain 3 Fgf3 SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine,$824 pin 54 -5.0 -2.0 1.0 dB
Tracking F Gain 4 Fgf4 SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine,$824 pin 54 -9.2 -6.2 -3.2 dB
Tracking E Balance Normal Tben SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine,$800 pin 54 -0.27 2.27 5.27 dB
Tracking E Balance 1 Tbe1 SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine,$801 pin 54 -0.51 2.51 5.51 dB
Tracking E Balance 2 Tbe2 SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine,$802 pin 54 -0.74 2.74 5.74 dB
Tracking E Balance 3 Tbe3 SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine,$804 pin 54 0.17 3.17 6.17 dB
Gte∆ Gtef-Gtee pin 54 -0.25 2.75 5.75 dB
Vtepp1 DG3 DC 4.5V pin 54 3.5 - - V
Vtepp2 SG3 DC 0.5V pin 54 - - 1.5 V
pin 54 2.1 5.1 8.1 dB
Tracking E Balance 4 Tbe4 SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine,$808 pin 54 1.03 4.03 7.03 dB
Tracking E Balance 5 Tbe5 SG3 0.3Vp-p,10KHz,sine,$810 pin 54 2.63 5.63 8.63 dB
FGFN-FGF1 ∆FG1 - - 0 1.5 3 dB
FGFN-FGF2 ∆FG2 - - 0.5 2.0 3.5 dB
FGFN-FGF3 ∆FG3 - - 2.0 3.25 4.5 dB
FGFN-FGF4 ∆FG4 - - 3.0 4.25 5.5 dB
TBE5 - TBE4 ∆TB1 - - 0.6 1.6 2.6 dB
TBE4 - TBE3 ∆TB2 - - -0.14 0.86 1.86 dB
TBE3 - TBE2 ∆TB3 - - -0.57 0.43 1.43 dB
TBE2 - TBE1 ∆TB4 - - -0.77 0.23 1.23 dB
APC PSUB Voltage 1 Vapc1 LDON,$853,PN=open,
SG4 GND+85mV
APC PSUB Voltage 2 Vapc2 LDON,$853,PN=open,
SG4 GND+185mV
pin 70 - - 1.2 V
pin 70 3.8 - - V
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
8
Page 9
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
KB9223 / KB9223-L
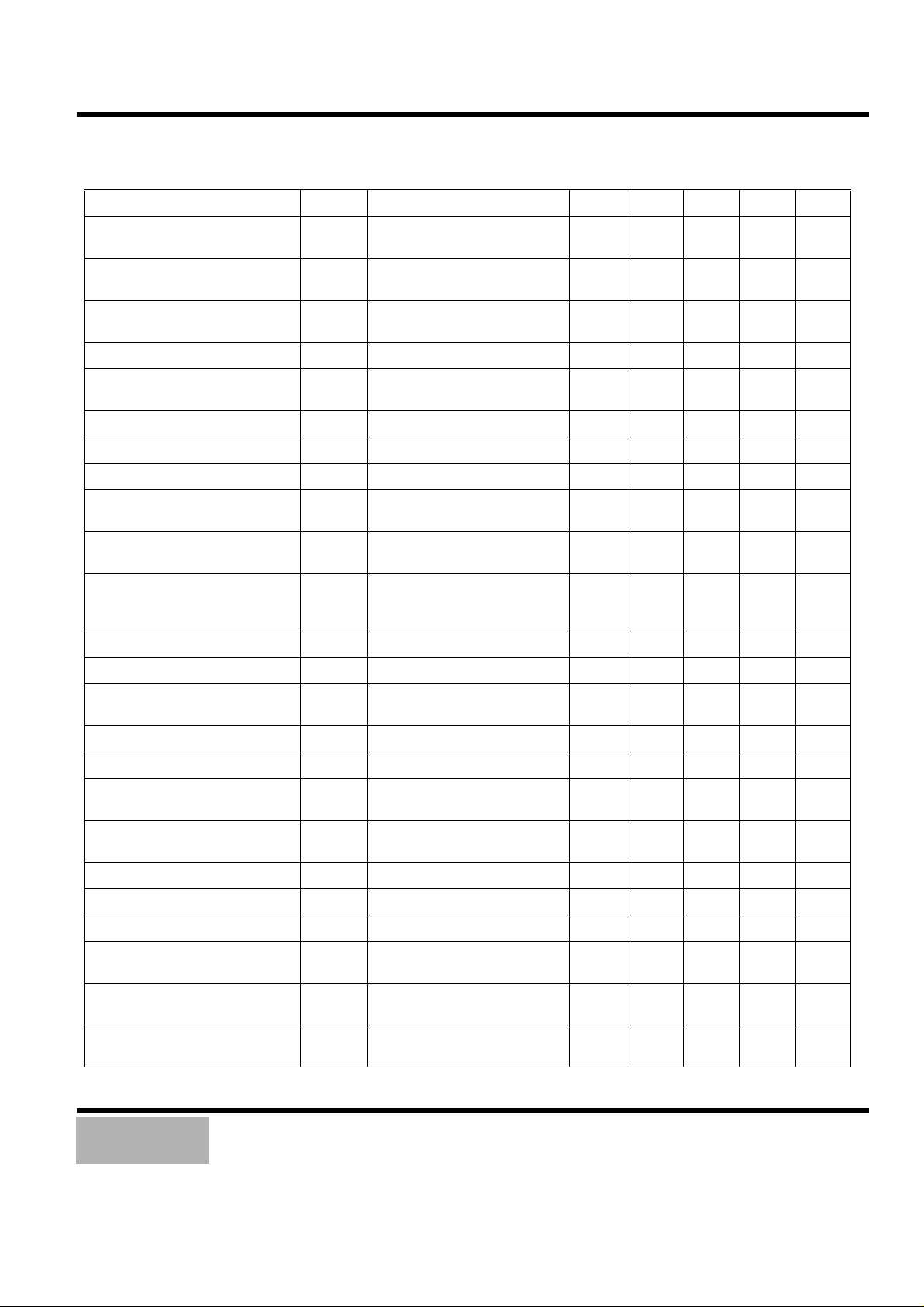
Table 3. Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(Ta=25°C, VDD = DVDD = VCC = +5V, VSS = DVSS = GND = VSSP = 0V )
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Output Min Typ Max Unit
APC NSUB Voltage 1 Vapc3 LDON,$857,PN=2.5V,
SG4 GND+95mV
pin 70 3.8 - - V
APC NSUB Voltage 2 Vapc4 LDON,$857,PN=2.5V,
SG4 GND+165mV
APC LD Off Voltage 1 Vapc5 LDOFF,$85C,PN=open,SG4
2.5V
APC LD Off Voltage 2 Vapc6 LDOFF,$858,PN=2.5V.SG4 2.5V pin 70 - - 1.0 V
APC Maximum Output Current H Vapc7 LDON,$854,PN=open, SG4 GND
APC Minimum Output Current L Vapc8 LDON,$854,SG4 GND + 85mV pin 70 - - 2.5 V
Mirror Maximum Output Voltage H Vmirh SG4 2.1V+0.8Vp-p,1KHz,sine pin 39 4.3 - - V
Mirror Minimum Output Voltage L Vmirl SG4 2.1V+0.8Vp-p,1KHz,sine pin 39 - - 0.7 V
Mirror Minimum Operating
Frequency
Mirror Maximum Operating
Frequency
Mirror AM Frequency Characteristic Fmir SG4 2.1V+0.8Vp-p
Mirror Minimum Input Voltage Vmir SG4 2.1V+0.2Vp-p,10KHz,sine pin 39 - 0.1 0.2 V
Mirror Maximum Input Voltage Vmih SG4 2.1V+1.8Vp-p,10KHz,sine pin 39 1.8 - - V
FOK Threshold Voltage Vfokt SG4 2.25V~2.0V,DCsweep,
Fmirh SG4 2.1V+0.8Vp-p,900Hz,sine pin 39 - 550 900 Hz
Fmirb SG4 2.1V+0.8Vp-p,30KHz,sine pin 39 30 75 - KHz
+ 185mV
600Hz,fc=500KHz
55% modulation
10mV step
pin 70 - - 1.2 V
pin 70 4.0 - - V
pin 70 2.5 - - V
pin 39 - 400 600 Hz
pin 40 -420 -360 -300 mV
FOK Output Voltage H Vfokh SG4 DC 1.5V pin 40 4.3 - - V
FOK Output Voltage L Vfokl SG4 DC 2.5V pin 40 - - 0.7 V
Defect Output Voltage H Vdfcth $863,SG3 2.520V+0.04Vp-p,
f=1Khz,sine
Output Voltage L Vdfcth $863,SG3 2.520V+0.04Vp-p,
f=1Khz,sine
Focus Loop Mute Fmute SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,1KHz,sine pin 48 -100 0 100 mV
Tracking Loop Mute Tmute SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,1KHz,sine pin 50 -100 0 120 mV
Interruption Imute SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,1KHz,sine pin 50 -100 0 120 mV
Defect Bottom Voltage Fdfct1 SG3 2.520 V+0.04Vp-p,
1KHz,sine
Defect Max Freq. Voltage Fdfct2 SG3 2.520V+0.04Vp-p,
2KHz,sine
Defect Minimum Input Voltage Vdfct1 SG 3 2.510V+0.020Vp-p,
1KHz,sine
pin 41 4.3 - - V
pin 41 - - 0.7 V
pin 41 - 670 1000 Hz
pin 41 2.0 4.7 - KHz
pin 41 - 0.3 0.5 V
M/M-97-P006
ELECTRONICS
1997. 10 .17
14
Page 10
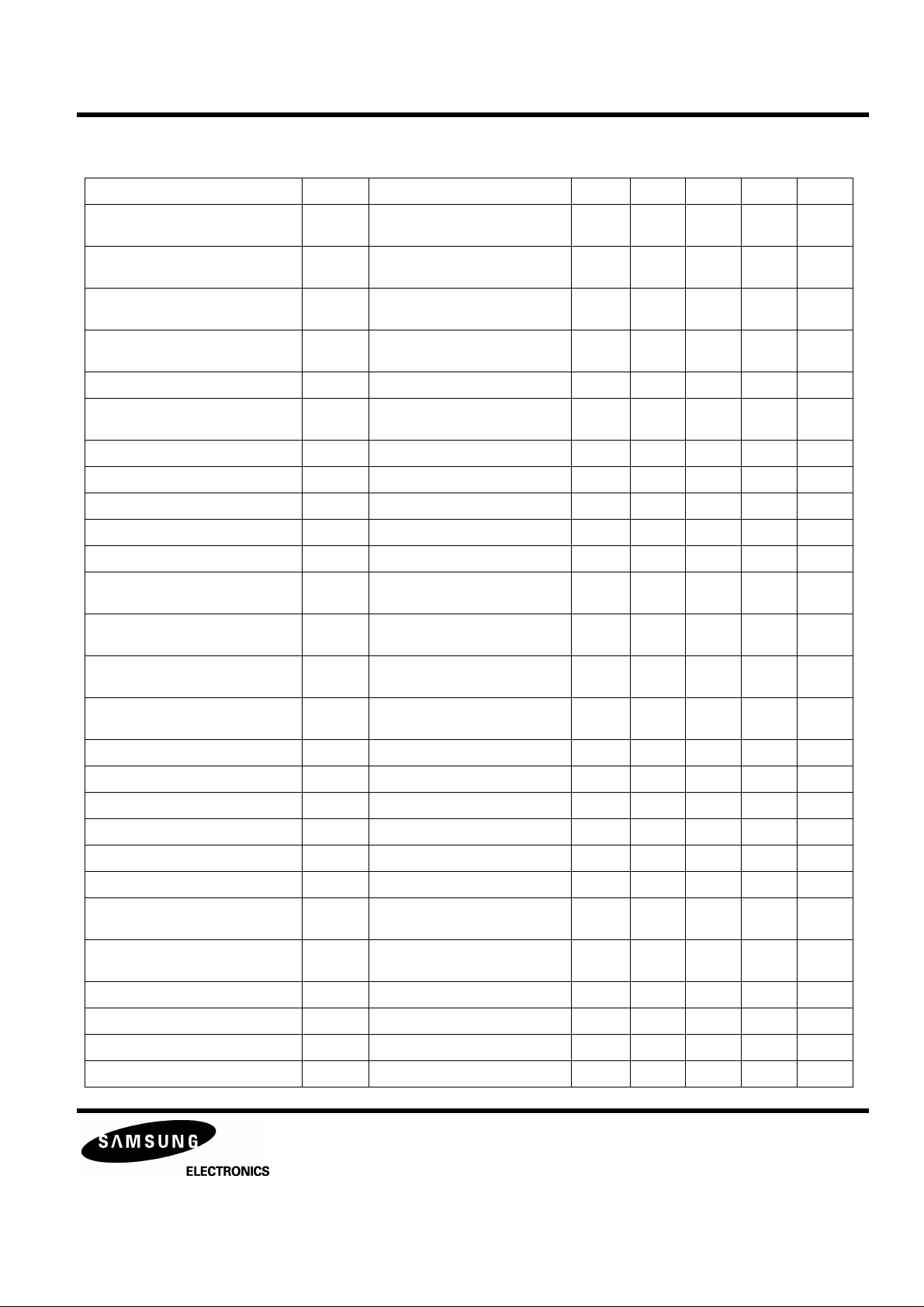
PRELIMINARY
KB9223 / KB9223-L
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
Table 3. Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(Ta=25°C, VDD = DVDD = VCC = +5V, VSS = DVSS = GND = VSSP = 0V )
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Output Min Typ Max Unit
Defect Maximum Input Voltage Vdfct2 SG32.535V+0.070Vp-p,
EFM Duty Voltage 1 Defm1 SG4 2.5V+0.75Vp-p,
EFM Duty Voltage 2 Defm2 SG42.75V+0.75Vp-p,
EFM Minimum input Voltage Vefm1 SG4 2.5V+0.12Vp-p,
EFM Maximum input Voltage Vefm2 SG4 2.5V+1.8Vp-p,750KHz,sine pin 33 1.8 - - V
EFM Maximum Operating
Frequency
FZC Threshold Voltage Vfzc DC 2.5V+38mV,100mV pin 31 39 69 100 mV
ATSC Threshold Voltage 1 Vatsc1 $10,SG2 DC 2.5V-6mV,-45mV pin 31 -67 -32 -7 mV
ATSC Threshold Voltage 2 Vatsc2 SG2 DC 2.5V+6mV,+45mV pin 33 7 32 67 mV
TZC Threshold Voltage Vtzc $20,SG2 DC 2.5V-20mV,+20mV pin 31 -30 0 30 mV
SSTOP Threshold Voltage Vsstop $30,SG2 DC 2.5V-71mV,-30mV pin 31 -100 -50 -30 mV
Tracking gain window voltage
Tracking gain window range
Tracking balance window voltage
Fefm SG4 2.5V+0.75Vp-p,4MHz pin 33 4 - - MHz
VtGW $840+$830 SG2 2.5V 2.9V 5mV
VTGW2 $848+$830 SG2 2.5V 5mV DC
VTBW $844+$810 SG2 2.555V ~
1KHz,sine
750KHz,sine
750KHz,sine
750KHz,sine
DC
sweep
2.475V 5mV DC sweep
pin 41 1.8 - - V
pin 32 -50 0 50 mV
pin 32 0 50 100 mV
pin 33 - - 0.12 V
pin 30 200 250 300 mV
pin 30 100 150 200 mV
pin 31 -25 15 55 mV
Tracking balance window range
Vreg Threshold Voltage Vreg - pin 21 3.2 3.4 3.6 V
Center Voltage VCVO 2.5V Reference pin 71 -100 0 100 mV
VREF Current Drive Voltage 1 VCVO1 2.5V Reference pin 71 -100 0 100 mV
VREF Current Drive Voltage 2 VCVO2 2.5V Reference pin 71 -100 0 100 mV
Post CH1 Freq. Characteristic Fpos1 SG1 2.5V+1Vp-p,40KHz,sine pin 13 -4.5 -3.0 -1.5 dB
Post CH2 Freq. Characteristic Fpos2 SG1 2.5V+1Vp-p,40KHz,sine pin 12 -4.5 -3.0 -1.5 dB
Post CH1 Mute Mute1 Mute=5V
Post CH2 Mute Mute2 Mute=5V
Focus Loop DC Gain Gf $08,SG2 DC 2.6V,2.4V average pin 48 19.0 21.5 24.0 dB
Focus Off Offset Vosf1 $00 pin 48 -100 0 100 mV
Focus On Offset Vofs2 $08,DC 2.5V pn 48 0 250 500 mV
Focus Auto Offset Vaof $842,WDCK,after100ms pin 48 -65 0 65 mV
VTBW2 $844+$810 SG2 2.555V ~
2.470V 5mV DC sweep
SG1 2.5V+1Vp-p,1KHz,sine
SG1 2.5V+1Vp-p,1KHz,sine
pin 31 -25 15 55 mV
pin13 - - -35 dB
pin 12 - - -35 dB
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
10
Page 11
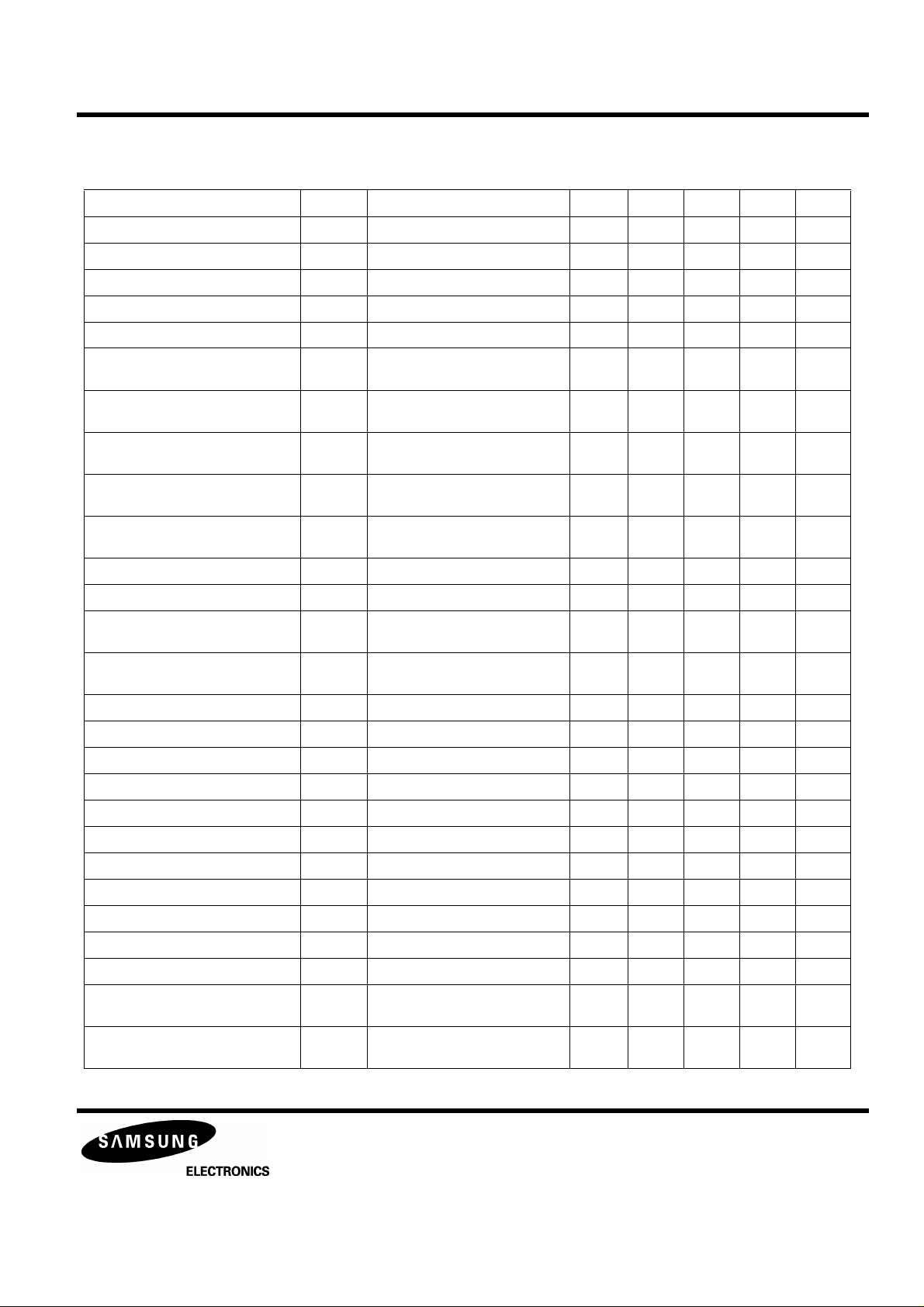
PRELIMINARY
KB9223 / KB9223-L
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
Table 3. Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(Ta=25°C, VDD = DVDD = VCC = +5V, VSS = DVSS = GND = VSSP = 0V )
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Output Min Typ Max Unit
Focus Output Voltage H Vfoh1 $08,DC 3.0V pin 48 4.40 - - V
Focus Output Voltage L Vfol1 $08,DC 2.0V pin 48 - - 0.60 V
Focus Output Drive Voltage H Vfoh2 $08,DC 3.0V pin 48 3.68 - - V
Focus Output Drive Voltage L Vfol2 $08,DC 2.0V pin 48 - - 1.32 V
Focus Oscillation Voltage Vosc $08,DC2.5V pin 48 0 100 200 mV
Focus Feed Through Gff Gain Difference at Servo on
and off
Focus AC Gain 1 Gfa1 $08,
SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,1.2KHz,sine
Focus AC Phase 1 Pfa1 $08,
SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,1.2KHz,sine
Focus AC Gain 2 Gfa2 $08,
SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,2.7KHz,sine
Focus AC Phase 2 Pfa2 $08,
SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,2.7KHz,sine
Focus Search Voltage1 Vfs1 $30+$02 pin 48 -0.64 -0.50 -0.36 V
Focus Search Voltage2 Vfs2 $30+$03 pin 48 0.36 0.50 0.64 V
Focus Loop Total Gain Gftg Focus PD gain + Focus loop DC
gain
Tracking DC Gain Gto $25
SG2 DC 2.3V,2.7V average gain
Tracking Off Offset Vost1 $20 pin 50 -100 0 100 mV
Tracking On Offset Vost2 SG2 DC 2.5V,$25 pin 50 -100 0 120 mV
Tracking Oscillation Voltage Vosa1 $25,SG2 DC2.5V pin 50 0 100 200 mV
Tracking gain boost for ATSC Gatsc 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,1KHz,sine pin 50 17.5 20.5 23.5 dB
pin 48 - - -35 dB
pin 48 19.0 23.0 27.0 dB
pin 48 40 65 90 deg
pin 48 14.0 18.5 23.0 dB
pin 48 40 65 90 deg
pin 48 49.5 51.5 53.5 dB
pin 50 13.5 15.5 17.5 dB
Tracking gain boost on LOCK (L) Glock 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,1KHz,sine pin 50 17.5 20.5 23.5 dB
Tracking Output Voltage H Vth1 $25,SG2 DC 1.0V pin 50 4.48 - - V
Tracking Output Voltage L Vtl1 $25SG2 ,DC 4.0V pin 50 - - 0.52 V
Tracking Output Drive Voltage H Vth2 $25,SG2 DC2.0V pin 50 3.68 - - V
Tracking Output Drive Voltage L Vtl2 $25, SG2 DC3.0V pin 50 - - 1.32 V
Tracking Jump Voltage 1 Vtj1 $2C pin 50 -0.64 -0.5 -0.36 V
Tracking Jump Voltage 2 Vtj2 $28 pin 50 0.36 0.5 0.64 V
Tracking Feed Through Gtf Gain Difference at Tracking servo
on and off
Tracking AC Gain 1 Gta1 $10,$25,SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,
1.2KHz,sine
pin 50 - - -39 dB
pin 50 9.0 12.5 16.0 dB
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
11
Page 12

PRELIMINARY
KB9223 / KB9223-L
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
Table 3. Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(Ta=25°C, VDD = DVDD = VCC = +5V, VSS = DVSS = GND = VSSP = 0V )
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Output Min Typ Max Unit
Tracking AC Phase 1 Pta1 $10,$25,SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,
1.2KHz,sine
pin 50 -140 -115 -90 deg
Tracking AC Gain 2 Gta2 $10,$25,SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,
2.7KHz,sine
Tracking AC Phase 2 Pta2 $10,$25,SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,
2.7KHz,sine
Tracking Loop Gain Gtrt tracking Amp F gain+ servo DC
gain
Sled DC Gain Gsl SG2 DC 2.6V,2.4V pin 43 20.5 22.5 24.5 dB
Sled Feed Through Gslf Gain Difference at sled servo
on and off
SG2 2.5V+0.1Vp-p,1.2KHz,sine
Sled Output Voltage H Vslh1 $25,SG2 DC 2.9V pin 43 4.48 - - V
Sled Output Voltage L Vsll1 $25,SG2 DC 2.1V pin 43 - - 0.52 V
Sled Output Drive Voltage H Vslh2 $25,SG2 DC 2.9V pin 43 3.68 - - V
Sled Output Drive Voltage L Vsll2 $25,SG2 DC 2.1V pin 43 - - 1.32 V
Sled Forward Kick Voltage Vsk1 $22 pin 43 0.38 0.60 0.75 V
Sled Reverse Kick Voltage Vsk2 $23 pin 43 -0.75 -0.6 -0.38 V
Spindle Normal Speed Gain Gsp $F0
SG1 DC 2.6V,2.4V, average gain
Spindle Double Speed Gain Gsp2 $F3
SG1 DC 2.6V,2.4V, average gain
Spindle Output Voltage H Gsph1 $F0, SG1 DC 3.5V pin 46 4.48 - - V
pin 50 17.5 21.5 25.5 dB
pin 50 -195 -150 -100 deg
- 18.5 20.5 22.5 dB
pin 43 - - -34 dB
pin 46 14.0 16.5 19.0 dB
pin 46 19.0 23.0 27.0 dB
Spindle Output Voltage L Gspl1 $F0, SG1 DC 1.5V pin 46 - - 0.52 V
Spindle Output Drive Voltage H Gsph2 $F0,SG1 DC 3.5V pin 46 3.68 - - V
Spindle Output Drive Voltage L Gspl2 $F0,SG1 DC 1.5V pin 46 - - 1.32 V
Spindle AC Gain Gspa $F0,SG1 2.5V+0.2Vp-p,
2KHz,sine
Spindle AC Phase Pspa $F0,SG1 2.5V+0.2Vp-p,
2KHz,sine
pin 46 -7.0 -3.5 0 dB
pin 46 -120 -90 -60 deg
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
12
Page 13

PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
KB9223 / KB9223-L
Table 3. Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(Ta=25°C, VDD = DVDD = VCC = +5V, VSS = DVSS = GND = VSSP = 0V )
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Output Min Typ Max Unit
FOCUS output voltage H Vfh1l
FOCUS output voltage L Vfl1l pin 48 - - 0.68 V
FOCUS SEARCH voltage 1 Vfs1l pin 48 -0.64 -0.50 -0.36 V
FOCUS SEARCH voltage 2 Vfs2l pin 48 0.36 0.50 0.64 V
TRACKING on OFFSET Vost21 pin 50 -100 0 +120 mV
TRACKING output voltage H Vth1l pin 50 2.88 - - V
TRACKING output voltage L Vtl1l pin 50 - - 0.68 V
TRACKING jump voltage 1 Vtj1l pin 50 -0.64 -0.50 -0.36 V
TRACKING jump voltage 2 Vtj2l pin 50 0.36 0.50 0.64 V
SLED output voltage H Vslh1l pin 43 2.88 - - V
SLED output voltage L Vsll1l pin 43 - - 0.68 V
SLED forward kick voltage Vsk1l pin 43 0.38 0.60 0.75 V
SLED reverse kick voltage Vsk2l pin 43 -0.75 -0.60 -0.38 V
pin 48 2.88 - - V
SPINDLE output voltage H Vsph1l pin 46 2.88 - - V
SPINDLE output voltage L Vspl1l pin 46 - - 0.68 V
RF amp OFFSET voltage Vrfol pin 74 -80 0 +80 mV
Tracking error offset Vteol pin 54 -50 0 +50 mV
RF amp output voltage H Vrfpp1l pin 74 2.8 - - V
RF amp output voltage L Vrfpp2l pin 74 - - 0.6 V
FOCUS error output voltage H Vfepp1l pin 59 2.8 - - V
FOCUS error output voltage L Vfepp2l pin 59 - - 0.6 V
Tracking error output voltage Vtepp1l pin 54 2.2 - - V
Tracking error output voltage Vtepp2l pin 54 - - 1.2 V
APC output voltage 1L Vapc1l pin 70 - - 1.2 V
APC output voltage 2L Vapc2l pin 70 2.5 - - V
APC output voltage 3L Vapc3l pin 70 2.5 - - V
APC output voltage 4L Vapc4l pin 70 - - 1.2 V
APC output voltage 5L Vapc5l pin 70 - - 1.1 V
APC output voltage 6L Vapc6l pin 70 2.7 - - V
FOK threshold voltage Vfoktl pin 40 -420 -360 -300 V
Post Filter Output Voltage max. 1 Vpom1 SG1 2.5V+3.2Vp-p,1KHz,
VDD, DVDD, VCC = +3.4V
Low Voltage Test for Servo Part
& RF part
: the test method is the same as
5V test
pin 13 1.1 1.3 - Vrms
within THD 1%
ELECTRONICS
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10 .17
14
Page 14

PRELIMINARY
KB9223 / KB9223-L
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
Table 3. Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(Ta=25°C, VDD = DVDD = VCC = +5V, VSS = DVSS = GND = VSSP = 0V )
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Output Min Typ Max Unit
Post Filter Output Voltage max. 2 Vpom2 SG1 2.5V+3.2Vp-p,1KHz,
within THD 1%
Total Harmonic Distoration 1 THD11 SG1 f=100Hz,0dBm pin 13 - 0.01 0.05 %
Total Harmonic Distoration 1 THD12 SG1 f=1KHz,0dBm pin 13 - 0.01 0.05 %
Total Harmonic Distoration 1 THD13 SG1 f=10KHz,0dBm pin 13 - 0.05 0.1 %
Total Harmonic Distoration 1 THD14 SG1 f=16KHz,0dBm pin 13 - 0.1 0.2 %
Total Harmonic Distoration 1 THD15 SG1 f=20KHz,0dBm pin 13 - 0.1 0.2 %
Total Harmonic Distoration 2 THD21 SG1 f=100Hz,0dBm Pin 12 - 0.01 0.05 %
Total Harmonic Distoration 2 THD22 SG1 f=1KHz,0dBm Pin 12 - 0.01 0.05 %
Total Harmonic Distoration 2 THD23 SG1 f=10KHz,0dBm Pin 12 - 0.05 0.1 %
Total Harmonic Distoration 2 THD24 SG1 f=16KHz,0dBm Pin 12 - 0.1 0.2 %
Total Harmonic Distoration 2 THD25 SG1 f=20KHz,0dBm Pin 12 - 0.1 0.2 %
pin 12 1.1 1.3 - Vrms
Frequency Characteristics 1 fv11 SG1 f=100Hz,0dBm pin 13 -0.1 0 0.1 dB
Frequency Characteristics 1 fv12 SG1 f=1KHz,0dBm pin 13 -0.25 0 +0.25 dB
Frequency Characteristics 1 fv13 SG1 f=10KHz,0dBm pin 13 -0.5 0 0.5 dB
Frequency Characteristics 1 fv14 SG1 f=16KHz,0dBm pin 13 -1.0 0 1.0 dB
Frequency Characteristics 1 fv15 SG1 f=20KHz,0dBm pin 13 -1.5 0 1.5 dB
Frequency Characteristics 2 fv21 SG1 f=100Hz,0dBm Pin 12 -0.1 0 0.1 dB
Frequency Characteristics 2 fv22 SG1 f=1KHz,0dBm Pin 12 -0.25 0 +0.25 dB
Frequency Characteristics 2 fv23 SG1 f=10KHz,0dBm Pin 12 -0.5 0 0.5 dB
Frequency Characteristics 2 fv24 SG1 f=16KHz,0dBm Pin 12 -1.0 0 1.0 dB
Frequency Characteristics 2 fv25 SG1 f=20KHz,0dBm Pin 12 -1.5 0 1.5 dB
Crosstalk 1 CT11 SG1 100Hz,0dBm,ratio on Ch2 pin 13 70 80 - dB
Crosstalk 1 CT12 SG1 1KHz,0dBm,ratio on Ch2 pin 13 65 75 - dB
Crosstalk 1 CT13 SG1 10KHz,0dBm,ratio on Ch2 pin 13 60 65 - dB
Crosstalk 2 CT21 SG1 100Hz,0dBm,ratio on Ch1 pin 12 70 80 - dB
Crosstalk 2 CT22 SG1 1KHz,0dBm,ratio on Ch1 pin 12 65 75 - dB
Crosstalk 2 CT23 SG1 10KHz,0dBm,ratio on Ch1 pin 12 60 65 - dB
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Output Min Typ Max Unit
Signal to Noise Ratio 1 S/N 1 DC 2.5V 0dbm,ratio on Noise pin 13 73 80 - dB
Signal to Noise Ratio 2 S/N 2 DC 2.5V 0dbm,ratio on Noise pin 12 73 80 - dB
Channel Balance CB Gain Difference Ch1 and Ch2 - -0.1 0 +0.1 dB
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
14
Page 15

PRELIMINARY
KB9223 / KB9223-L
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
Table 3. Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
(Ta=25°C, VDD = DVDD = VCC = +5V, VSS = DVSS = GND = VSSP = 0V )
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Output Min Typ Max Unit
Post filter output voltage mix.1L Vpom1L
Post filter output voltage mix. 2L Vpom2L pin 12 0.5 0.55 - Vrms
Total harmonic distortion 1L THD11L pin 13 - 0.01 0.05 %
Total harmonic distortion 1L THD12L pin 13 - 0.01 0.05 %
Total harmonic distortion 1L THD13L pin 13 - 0.05 0.1 %
Total harmonic distortion 1L THD14L pin 13 - 0.1 0.2 %
Total harmonic distortion 1L THD15L pin 13 - 0.1 0.2 %
Total harmonic distortion 2L THD21L pin 12 - 0.01 0.05 %
Total harmonic distortion 2L THD22L pin 12 - 0.01 0.05 %
Total harmonic distortion 2L THD23L pin 12 - 0.05 0.1 %
Total harmonic distortion 2L THD24L pin 12 - 0.1 0.2 %
Total harmonic distortion 2L THD25L pin 12 - 0.1 0.2 %
Frequency Characteristics 1L fv11L pin 13 -0.1 0 0.1 dB
pin 13 0.5 0.55 - Vrms
Frequency Characteristics 1L fv12L pin 13 -0.25 0 +0.25 dB
Frequency Characteristics 1L fv13L pin 13 -0.5 0 0.5 dB
Frequency Characteristics 1L fv14L pin 13 -1.0 0 1.0 dB
Frequency Characteristics 1L fv15L pin 13 -1.5 0 1.5 dB
Frequency Characteristics 2L fv21L pin 12 -0.1 0 0.1 dB
Frequency Characteristics 2L fv22L pin 12 -0.25 0 +0.25 dB
Frequency Characteristics 2L fv23L pin 12 -0.5 0 0.5 dB
Frequency Characteristics 2L fv24L pin 12 -1.0 0 1.0 dB
Frequency Characteristics 2L fv25L pin 12 -1.5 0 1.5 dB
Cross talk 1L CT11L pin 13 67 80 - dB
Cross talk 1L CT12L pin 13 62 75 - dB
Cross talk 1L CT13L pin 13 57 65 - dB
Cross talk 2L CT21L pin 12 67 80 - dB
Cross talk 2L CT22L pin 12 62 75 - dB
Cross talk 2L CT23L pin 12 57 65 - dB
Signal to noise ratio 1L S/N1L pin 13 67 80 - dB
Signal to noise ratio 2L S/N2L pin 12 67 80 - dB
Channel balance L CBL - -0.1 0 +0.1 dB
VDD, DVDD, VCC
VCCP= +3.4V
Low voltage test for post filter.
The test method is the same as
5V test except for input signal
: SG1 1.7V + 1.55Vp-p
Note1) The notation $ means hexa decimal of micom command
Note2) Low voltage test items only refer to KB9223-L
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
15
Page 16

KB9223 / KB9223-L
TEST CIRCUIT
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
SWP1
SG1
SWP2
SG-D1
3K
SW35
69
MDATA
36
SW34
686766
MLT
373839
VECTOR_ TEST_IN
SG3
DC
AC
390K
390K
10K
10K
SW30
SW31
SW32
SW33
65
PD1
64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54
DVEE
FEBIAS
96K
SW29
TG2
TGU
FDFCT
TDFCT
FE1
FE2
SW28
SW27
VERTOR_TEST_IN
SW26
SW25
0.01UF
0.01UF
+
ACDCSG2
+
DVDD
LPFT
TE1
TE2
TZC
ATSC
TEO
TE-
FEO
FE-
SPDLO
SPDL-
SL-
SLO
MIRROR
FOK
SSTOP
SL+
RESET
40
VECTOR_ TEST_IN
VECTOR_ TEST_IN
VECTOR_ TEST_IN
VECTOR_ TEST_IN
53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41
SW24
SW23
VERTOR_TEST_IN
VERTOR_TEST_IN
SW22
SW21
100K
200K
100K
SW18SW20
200K
100K
5K
60K
SW14
SW13
VECTOR_TEST_IN
SG-_D11
SG-_D10
13K
0.25K
13K
0.25K
13K
0.25K
13K
0.25K
1 2
SW17SW19
1 2
SW16
1 2
1 2
SW15
SG_D12
DC
SG4
AC
+
1uF
SW42
SW41
80
787776
79
GND
EQC
EI
3300PF
SW4
0.01PF
510K
27K
4.7UF
+
SW1
5.6K
0.001UF
5.6K
3.3UF
+ +
10K
3.3UF
5.6K
10K
5.6K
AC
DC
SW2
4.7UF
27K
+
4.7UF
1000PF
3300PF
5.6K
5.6K
+
4.7UF
10PF
10PF
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
MCP
DCB
+
FRSH
DCC2
DCC1
FSET
VDDA
VCCP
GC2I
27K
10 11
GC2O
CH2I
330PF 330PF
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
CH2O
CH1O
CH1I
GC1O
27K
GC1I
RRC
0.01UF
SW39
SW40
75
RFI
EQO
IRF
SW-VC
+
33UF
0.5K
2PF
22K
74
RFO
0.5K
3K
SW37
SW38
SW36
73
72
71
70
RF-
VCC
VR
LDPDEFPD2
KB9223
VSSP
0.1UF
+
SW5
VECTOR_TEST_IN
SW6
SW7
SW3
240K
MUTEI
ISET
VREG
WDCK
SMDP
SMON
TRCNT
SMEF
25
1000PF
FLB
26
FGD
FS3
272829
SW9
SW8
VECTOR_ TEST_IN
ISTAT
LOCK
30
313233
VECTOR_TEST_OUT
VECTOR_T EST_OUT
SW10
VSSA
MCK
EFM
ASY
34
35
VECTOR_ TEST_IN
SW11
11K
0.01UF
+
VCC(5V)
VC(2.5V)
GND(0V)
SG-D2
Figure 3. Test Circuit
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
SG-D3
SG-D4
SG-D5
SG-D6
SG-D7
SG-D8
16
Page 17

KB9223 / KB9223-L
FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
1.RF Amp Block
1.1 RF Amplifier
The optical currents inputted through pins PD1(A+C) and PD2(B+D) are converted into voltages through
I-V amp, and they are added to RF summing amp. The voltage, converted from the photo diode
(A+B+C+D) signal, is outputted through RFO(pin74) and the eye pattern can be checked at this pin.
PD1
PD2
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
58K
65
66
VC
VC
-
+
58K
-
+
VA
I-V amp(1)
VB
I-V amp(2)
10K
10K
-
+
VC
RFO
74
RF summing amp
RF-
73
Figure 4. RF amp circuit
1.2 Focus Error Amp
The output of the focus error amp is the difference between I-V amp(1) output VA and
RF I-V amp(2) output VB. The focus error bias voltage applied to the (+) of focus error amp can be
changed by output voltage of D/A converter as shown in diagram, so that the offset of focus error amp
can be adjusted automatically by controlling 5 bits counter switches. Focus error bias can be adjusted
from the range of +100mV ~ -100mV by connecting the resistor on pin 63 (FEBIAS).
164K
32K
32K
3K
-
+
160K
4K
-
+
-
fcmpo
+
fe-stopb
fe-stopb
vcFEBIAS
FE1
59
FEBIAS
sev-stopb
63
sev-stop
<5 Bit Counter>
X1 X2 X4 X8 X16
VB >
VA >
SW1
Figure 5. Focus error amp circuit
note1> VA and VB refer to output signal of PD1 and PD2 I/V amp.
note2> sev-stopb,sev-stop,fe-stopb and fcmpo are internal signals
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
17
Page 18

KB9223 / KB9223-L
1.3 Tracking Error Amp
The optical currents detected from the side photo diode (E and F) pf pick-up are inputted to the E and F
pin and converted into voltage signals by E I-V and F I-V amp. The output of tracking error amp
generates the difference between E I-V AMP and F I-V AMP voltage output.
The E-F balance can be adjusted by modifying the gain of E I-V AMP, and the tracking gain
can be adjusted automatically by controlling the peak voltage at pin TE2 by micom program.
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
TE2
TE1 LPFT
54
55
53
PRELIMINARY
F
67
68
E
EI
79
I-V AMP
I-V AMP
75K
220K
BAL < 4 : 0 >
110K
27K
56K
GAIN_UP/DOWN
-
+
13K
13K
GAIN < 3 : 0 >
-
16K
3.3K
7.5K
1.5K
Balance
Window Comp
Gain
Window Comp
To ISTAT
To ISTAT
To TRCNT
Figure 6. Tracking error amp circuit
1.4 Focus OK Circuit
The FOK is the output. The focus OK circuit generates a timing window to enable focus servo operation
from focus search status. When the difference of the RFO (pin74)signal and DC coupled signal
IRF(pin75) are above the predefined voltage the Focus OK circuit output (pin40) becomes active(High
output). The predefined voltage is -0.39V
RFO
IRF
40K
40K
74
75
40K
-
+
57K
90K
VC+0.625V
-
+
FOK
40
Figure 7. Focus OK circuit
M/M-97-P006
18
1997. 10. 17
Page 19

KB9223 / KB9223-L
1.5 Mirror Circuit
IRF signal is amplified by the mirror amp, and the peak and bottom component of amplified signal are
detected by peak and bottom hold circuit. The peak hold circuit covers traverse signal of up to 100KHz
component and bottom hold circuit capable of covering the envelope frequency of disc rotation. The time
constant for the mirror hold must be sufficiently larger than that of the traverse signal.
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
IRF
38K
17K
75
19K
-
+
Peak and
Bottom
Hold
-
+
2.5K
96K
+
17K
+
-
1.5K
1
39
MCP
MIRROR
-
Figure 8. Mirror Circuit
1.6 EFM Comparator
The EFM comparator converts a RF signal into a binary signal.
Beacuse the asymmetry generated due to variations in disc manufacturing can not be eliminated by the
AC coupling alone, this circuit uses to control reference voltage of EFM comparator for eliminating
asymmetry.
RFI
40K
77
+
-
100K
100K
+
20K
-
19K
Figure 9. EFM Comparator & asymmetry circuit
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
85K
1
EFM
+
39
ASY
-
19
Page 20

KB9223 / KB9223-L
1.7 Defect Circuit
The RFO signal bottom, after being inverted, is held with two time constants of long and short.
The short time-constant bottom hold is done for a disc mirror defect more than 0.1msec, the long timeconstant bottom hold is done with the mirror level prior to the defect. By differentiating this with a
capacitor coupling and shifting the level, both signals are compared to generate the mirror defect
detection signal.
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
75K
37.5K
75
RFO
VC+0.6254V 43K
28K
75K
-
+
BOTTOM
HOLD
2
DCB
DCC1
5
BOTTOM
HOLD
DCC2
4
-
DFCT
+
SSTOP/DFCT
41
Figure 10. Defect Circuit
1.8 APC (Auto Power Control) Circuit
The laser diode has large negative temperature characteristic in its optical output when driven with a
constant current on laser diode. Therefore, the output on processing monitor photo diode, must be a
controlled current for getting regular output power, thus the APC (Auto Power Control) circuit is
composed.
PD
69
1.25V
43.5K
+
-
150K
5.5K
(From micom command)
LDON
Figure 11. APC Circuit
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
PN (From micom command)
150K
+
-
150K
300K
0.75K
LD
70
20
Page 21

KB9223 / KB9223-L
1.9 AGC Stability Circuit
The AGC block is the function used to maintain the constant level of RF peak to peak voltage. After the
operation of RF envelop detection and comparing with reference voltage, RFO level is kept stable in 1Vpp, and inputted to EFM Slice.
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
IRF
75
VCA EQUALIZE
78
EQC
76
EQO
Figure 12. AGC block
1.10 Post Filter
The adjustment of audio output gain and the integration of possible de-emphasis output are executed by
this circuit. This block has amps of 2 channel for gain and filter setting and mute pin for audio signal
muting.
25K
25K
VCC
CH2I
GC2I
-
+
GC1I
CH1I
-
+
-
+
+
12
CH2O
GC2O
10
GC1O
15
-
+
-
CH1O
13
Figure 13. Post Filter circuit
1.11 Center Voltage Generation Circuit
The center voltage is generated by voltage
divide using resistor .
Figure 14.
Center Voltage
Generation Circuit
19
MUTEI
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
VCC
30K
30K
-
+
71
VR
21
Page 22

KB9223 / KB9223-L
2.Servo Block
2.1 Focus Servo Block
When defect is "H"(the defect signal is detected), the focus servo loop is muting in case of focus phase
compensation. At this time, the focus error signal is outputted through the low pass filter formed by
connecting a capacitor(0.1uF) and a built-in 470KΩ resistor to the FDFCT pin(pin 60). Accordingly, the
focus error output is held at the error value just before defect error during defect occurring. The peak
frequency of focus loop phase compensation is at about 1.2KHz when the resistor connected to FSET
pin(pin 6) is 510KΩ, and it is inversely proportional to the resistor connected to the FSET pin. While the
focus search is operating, the FS4 switch is on and then the focus error signal is isolated, accordingly the
focus search signal is outputted by FEO pin(pin 48). When the FS2 switch is on(focus on), the focus
servo loop is on and the focus error signal from FE2 pin(pin 58) is outputted through the focus servo loop.
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
FE2
FDFCT
FGD
FS3
3.6K
60K
-
FZCI
+
X3
X2
20K
FS4B
FS3
48K
470K
Focus Phase
Compensation
130K
40K
26
FLB FRCH
58
60
28
27
470K
46K
DFCTI
580K
92K
FS2B
6
X4
40K
10K
50K
FSET
X1
-
+
-
+
3
3.6K
FS1
VC
FSCMPO
-
+
-
+
PS
4 3
X1
0 0
X2
0 1
X3
1 0
X4
1 1
FEO
48
FE-
47
Figure 15. Focus servo block
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
22
Page 23

KB9223 / KB9223-L
2.2 Tracking Servo Block
During detection of defect, the tracking error signal is outputted through the tracking servo loop after
passing the low pass filter formed by connecting a capacitor(0.1uF) and a built-in 470KΩ resistor to the
TDFCT pin(pin57) in case of tracking phase compensation. The value of tracking gain up/down can be
controlled by TGU and TG2 pin. The peak frequency of tracking loop phase compensation, the dynamic
range and offset of opamp can be adjusted by changing the value of resistor connected to FSET pin
same as focus loop. In case of unstable status of actuator after jumping, the ON/OFF of tracking loop is
controlled by TM7 switch of break circuit.
After 10-track jumping, servo circuit gets out of the liner range and actuator's tracking becomes
occasionally unstable. Hence unnecessary jumping with many tracking error should be prevented.
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
TE2
TDFCT
TGU
TG2
TM4
53
470K
57
61
62
470K
DFCTI
20K
TG2
680K
TG1
TM1
110K
82K
10K
TG1
TRACKING
PHASE
COMPENSATION
680K
TM3
66PF
10K
90K
TM7
6
FSET
-
+
TE-
49
TEO
50
Figure 16. Tracking servo block
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
23
Page 24

KB9223 / KB9223-L
2.3 Sled Servo Block
The moving of pick-up is controlled by tracking servo output through a low pass filter.
The sled kick voltage is outputted for track jump operation.
TM6
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
SLO
43
X 1
X 2
X 3
X 4
TM7
PS
4 3
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
-
+
TM2
SL-
44
SL+
42
Figure 17. Sled servo block
2.4 Spindle Servo Block
The 20KΩ resistor and 0.33uF capacitor form the 200Hz low pass filter, and the carrier component of
spindle servo error signals is eliminated. In CLV-S mode, SMEF becomes "L" and pin 25 low pass filter fc
lowers, strengthening the filter further. The characteristics of high frequency phase compensation in
focus tracking servo and the characteristics of cut off frequency in CLV low pass filter are tested by FSET
pin.
SMON
SMDP
24
23
15K 220K
15K
20K
22K
22K
220K
220K
220K
25
SMEF
-
+
100K
6
FSET
Figure 18. Spindle servo block
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
50K
Double
speed
+
-
SPDLO
46
45
SPDL-
24
Page 25

KB9223 / KB9223-L
3.Digital Block
3.1 Description
Digital block is transferred serial data by micom and 8-bit serial data is converted to parallel data by
serial to parallel register. This data is decoded by latch signal. The status output of focus servo,tracking servo,and sled servo system,etc is determined by each data. The auto-sequence function process
2~4 micom command by one auto-sequence command.
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
MDATA
MCK
MLT
D0 D1 D2
twck
twck
D3
D4
tsu
D5
D6 D7
tsn
td
twl
Figure 19. CPU serial interface timing chart
Table 4. CPU serial interface timing characteristics
Item Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Clock Frequency fck - - 1 MHz
Clock Pulse Width fwck 500 - - ns
Hold Time tsu 500 - - ns
Setup Time tn 500 - - ns
Delay Time td 500 - - ns
Latch Pulse Width twl 1000 - - ns
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
25
Page 26

KB9223 / KB9223-L
3.2 Micom Command Set
Table 5. Servo control command set
Item Hexa Address Data ISTA
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
TOUT
Focus Con-
trol
Tracking
Control
Tracking
Mode
Select $3X 0 0 1 1 PS4
Auto
Sequence
R
Blind/
A
over-
M
flow
Break 0.36ms 0.18ms 0.09ms 0.045ms
S
E
Kick $6X 0 1 1 0 11.6ms 5.80ms 0.09ms 0.045ms
T
2N
jump
move
(M)
$0X 0 0 0 0 FS4
Focus On
$1X 0 0 0 1 Anti Shock Brake On TG2
$2X 0 0 1 0 Tracking Mode Sled Mode TZC
Focus
Search+2
$4X 0 1 0 0 AS3 AS2 AS1 AS0 /
0.18ms 0.09ms 0.045ms 0.022ms
$5X 0 1 0 1
64 32 16 8
$7X 0 1 1 1
128 64 32 16
FS3
Gain Down
PS3
Focus
Search+2
FS2
Search On
Gain Set
PS2
Sled Kick+2
FS1
Search Up
TG1
Gain Set
PS1
Sled Kick+1
FZC
A.S
STOP
BUSY
Hi-Z
Auto Adj. $8XX 1 0 0 0 Offset,Balance,Gain,APC Control -
Speed $FX 1 1 1 1 $F0:Normal Speed, $F3:Double Speed -
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
26
Page 27

KB9223 / KB9223-L
3.2.1 Focus Control($0X)
This command consists of 8 bits data and expressed by two hexa $0X.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 ISTAT
0 0 0 0 FS4 FS3 FS2 FS1 FZC
-Focus Search Operation(FS2,FS1)
$02:FS2 switch become off and the value of servo output pin is as below.
(10uA-5uA)*50k*(feedback Resistor/50k)
$03:If FS1 switch is 1, the current supply is cut off and the discharge is performed.
The waveform is as below and the time constant is determined by internal resistor 50K
and external capacitor.
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
FS4,FS3,FS2,FS1:internal switch for focus control
0V
Figure 20. Waveform at pin 3 when FS1 is switched from 0 to 1
The waveform of servo output pin according to FS1 and FS2 switches is as below.
$00 02 03 02 03 02 03 00
Figure 21. Focus search waveform at pin 48 by $02 and $03
FS4 is switch for on/off control of focus servo loop
$00:Focus servo off
$08:Focus servo on
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
27
Page 28

KB9223 / KB9223-L
3.2.2 Tracking Control($1X)
This command is used for tracking loop gain control, break circuit and anti-shock on/off control.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 ISTAT
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
0 0 0 1 Anti
shock
on/off
TG2 and TG1 are internal switch for tracking gain set.
3.2.3 Tracking mode($2X)
This command is used for tracking and sled servo on/off and jump for searching track.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 ISTA
0 0 1 0 Tracking control Sled control TZC
<Tracking control & Sled control>
D3 D2 Tracking mode D1 D0 Sled mode
0 0 Tracking servo off 0 0 Sled servo off
0 1 servo on 0 1 servo on
1 0 Forward jump 1 0 Forward kick
1 1 Reverse jump 1 1 Reverse kick
Break
circuit
on/off
TG2 TG1 Anti
shock
T
3.2.4 Peak value set($3X)
This command is used for the peak value setting of focus search and sled kick .
D0,D1:Sled kick
D2,D3:Focus search peak value
3.2.5 Auto Sequencer command($4X)
This command is used for reducing control time and replacing several command by one auto- sequence
command.
•Auto sequencer mode is performed from the first falling edge of WDCK clock after the falling of
the latch pulse.
•Auto sequencer does not carry out tracking gain up,brake,anti-shock and focus gain down.
•Micom checks ISTAT pin(/BUSY) and sends to $40 command to reset preceding auto
sequencer status
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
28
Page 29

KB9223 / KB9223-L
Table 6. Auto sequence command
Cancel $40 0 0 0 0 Reset
Auto focus $47 0 1 1 1 -
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
Hexa AS3 AS2 AS1 AS0 Remark
1 Track jump $48
$49
10 Track
jump
2N track jump $4C
M track move $4E
3.2.6 RAM Set($5X~$7X)
The value of RAM set is somewhat different to the actual count and the initial value is like below
Table 7. RAM set table
Item Initial value actual count value
Blind $55 Set value +4~5 WDCK clock
overflow, Brake Set value +3 WDCK clock
Kick $67 Set value +5 WDCK clock
2N ,M Track jump $7E Set value +3 WDCK clock
$4A
$4B
$4D
$4F
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
Forward
Reverse
Forward
Reverse
Forward
Reverse
Forward
Reverse
4.Auto Adjustment Command
This command is used for auto control of offset,balance,gain adjustment and reference voltage setting. .
This command is also in control of on/off and sub type of laser diode and test or set mode.
4.1 Tracking balance ($800~$81F)
Item Hexa Data(5bits) initial value ISTAT(pin31) TRCNT(pin30)
Tracking balance $800~$81F D4~D0 $81F BAL TRCNT
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
29
Page 30

KB9223 / KB9223-L
4.2 Tracking gain ($820~$83F)
Item Hexa Data(5bits) initial value ISTAT(pin31) TRCNT(pin30)
Tracking gain $820~$83F D4~D0 $820 GAIN TGL
4.3 Tracking balance & gain window level setting
Item Hexa D3 D2 D1 D0 initial value
window level setting $84X gain balance 0 0 $840
•The tracking balance and gain window level is set by D2,D3 data and the value has two
kinds of window levels set
4.3.1 Tracking balance window level
D2 data 0 1
Tracking balance window level -10~+15mV -20~+20mV
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
PRELIMINARY
4.3.2 Tracking gain window level
D3 data 0 1
Tracking gain window level 250~400mV 150~300mV
4.4 Focus loop offset adjustment start command($841,$842)
This command is used for adjusting focus error bias and removing focus servo offset.
This command is executed during laser diode off.
Hexa command meaning
$841 Focus error bias adjustment start command
$842 Focus servo offset cancel adjustment start command
4.5 APC circuit operation and Interruption on/off setting condition($85X)
This command is used for setting of laser diode on/off ,sub type(P_sub or N_sub) of laser diode and
interruption countermeasure circuit on/off.
Item Hexa D3 D2 D1 D0 initial value
APC &
Interruption on/off
condition
$85X
LD on/off
0 : On
1 : Off
Sub-type
0:N_sub
1:P_sub
Interruption ON/OFF
and time setting
$858
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
30
Page 31

KB9223 / KB9223-L
4.5.1 Time setting for Interruption countermeasure circuit on/off
D1 D0 Meaning
0 0 Countermeasure circuit on for all mirror signal
0 1 Countermeasure circuit on up to 20KHz mirror signal
1 0 Countermeasure circuit off
1 1 Countermeasure circuit on up to 10KHz mirror signal
4.6 Focus servo offset reset command and set mode command (86X)
This command is used for set and release before focus servo loop offset adjustment and
mode change.
Item Hexa D3 D2 D1 D0
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
Set mode
&
focus servo offset
reset command
(note1) The set mode command is sent by micom right after tracking gain is tuned.
(note2) The ISTAT pin is outputted the internal status of $00 ~ $7X command.
4.7 Direct command(DIRC) and focus bias reset command($87X)
This command is used for direct 1 track jump on/off setting and focus bias adjustment set and
release
Item Hexa D3 D2 D1 D0
DIRC
&
focus bias reset
$86X 0:offset
release
1:offset
reset
$87X 0:DIRC On
1:DIRC Off
option
(Pin41 output)
0:Defect
1:SSTOP
0:reset
1:reset
release
1 1
X X
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
31
Page 32

KB9223 / KB9223-L
5.The Example of Adjustment Free Algorithm
5.1 Focus Error Bias & Servo Offset Cancel Adjustment
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
Focus_RF_Offset Adjustment
[Command:841]
5bit Counter
17mV/Bit
Tuning range : + 260mV
4bit Counter
40mV/Bit
tuning range : + 280mV
Increment Count
no
[RF CNT value Latch]
Focus_Servo_Offset Adjust-
Increment Count
no
ISTAT
Check
L--> H
yes
Finish
ment [Command:842]
ISTAT
Check
L--> H
yes
Finish
[Servo value Latch]
Time
Max 100msec
Time
Max 100msec
Figure 22. Focus error bias & servo offset cancel adjustment flow chart
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
32
Page 33

KB9223 / KB9223-L
5.2 Tracking Balance Adjustment
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
YES
Figure 23. Tracking balance adjustment flow chart
5.3 Tracking Gain Adjustment
Balance adjustment Range window
setting + 20mv, + 15mv setting
ISTAT
Check
L--> H
NO
ISTAT
Check
L--> H
NO
Finish
[RF CNT value Latch
YES
$844
Micom Balance
5Bit adjustment
Command Up
$800 ~ $81F
Gain adjustment range
setting Command
ISTAT
Check
L--> H
YES
Gain adjustment finish
TOC READ
NO
$848
5 Bit Gain adjust-
ment Command
$820 ~ $83F
Figure 24. Tracking gain adjustment flow chart
M/M-97-P006
1997. 10. 17
33
Page 34

KB9223 / KB9223-L
APPLICATION CIRCUIT
152p
103p
4.7uF
+
VCC
VCC(POST)
from DAC CH2
CH1 out
CH2 out
from DAC CH1
from MICOM
from DSP
from DSP(SMDP)
from DSP(SMON)
103p
+
4.7uF
152p
152p
4.7uF
+
GND (POST)
510K
27K
27K
27K
5.6K
5.6K
5.6K
+ +
5.6K
5.6K
5.6K
27K
4.7uF
333p
+
180K
PRELIMINARY
RF AMP & SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR
to pick-up
VCC
22K
+
102
100uF
from pick-up
+
33uF
1uF
+
472p
103p
+
33uF
4pF
F
E
B
C
D
22K
80
78
777675
79
GND
EQC
RFI
EI
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
MCP
DCB
FRSH
DCC2
DCC1
FSET
VDDA
VCCP
150p
GC2I
10 11
GC2O
CH2I
331p
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
CH2O
CH1O
331p
CH1I
GC1O
150p
GC1I
RRC
VSSP
MUTEI
ISET
VREG
WDCK
SMDP
SMEF
SMON
FGD
FLB
FS3
74
73
72
71
70
696867
EQO
IRF
RFO
RF-
VCCVRLDPDEFPD2
66
65
PD1
DVEE
FEBIAS
TG2
TGU
FDFCT
FE1
FE2
TDFCT
DVDD
LPFT
KB9223
TE1
TE2
TZC
ATSC
TEO
TE-
FEO
FE-
SPDLO
SPDL-
SL-
SLO
MIRROR
FOK
SSTOP
SL+
TRCNT
ISTAT
LOCK
EFM
ASY
MDATA
VSSA
MCK
RESET
MLT
VC
GND
VCC
1K
VCC
3.3uF
+
A
GND
64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54
104p
104p
10K
10K
222p
104p
VCC
100K
102p
222p
333p
100K
0.47uF
47K
103p
+
15K
103p
150K
104p
to KA9258D
39K
to KA9258D
391p
to KA9258D
120K
10uF
+
47K
683p
to KA9258D
1K
53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41
120K
56K
from DSP(SMSD)
from DSP(SMEF)
8.2K
25
27
282930
26
1M
0.47uF
104p
+
104p
333p
from DSP
32
33
34
35
31
0.47uF 103p
+
100K
12K
to MOCOM
to MOCOM
to DSP
373839
36
from MOCOM
from MOCOM
from MOCOM
40
from deck
from MOCOM
to MOCOM
Figure 25. Application circuit
M/M-97-P006
34
1997. 10. 17
 Loading...
Loading...