Page 1

查询ISL4221供应商
®
ISL4221E, ISL4223E
Data Sheet August 2004
QFN Packaged, +/-15kV ESD Protected,
+2.7V to +5.5V, 150Nanoamp, 250kBps,
RS-232 Transmitters/Receivers
The Intersil ISL422XE devices are 2.7V to 5.5V powered
RS-232 transmitters/receivers which meet ElA/TIA-232 and
V.28/V.24 speci fications, even at V
they provide
±15kV ESD protection (IEC61000-4-2 Air Gap,
and Human Body Model) on transmitter outputs and receiver
inputs (RS-232 pins). Targeted applications are PDAs,
Palmtops, and hand-held products where the low
operational, and even lower standby, power consumption is
critical. Efficient on-chip charge pumps, coupled with manual
and automatic powerdown functions, reduce the standby
supply current to a 150nA trickle. Tiny 5mm x 5mm Quad
Flat No-Lead (QFN) packaging and the use of small, low
value capacitors ensure board space savings as well. Data
rates greater than 250kBps are guaranteed at worst case
load conditions.
The ISL4221E is a 1 driver, 1 receiver device and the
ISL4223E is a 2 driver, 2 receiver device that, coupled with
the 5x5 QFN package, provide the industry’s smallest,
lowest power serial port suitable for PDAs, and hand-held
applications. The 5x5 QFN requires 40% less board area
than a 20 lead TSSOP, and is nearly 20% thinner.
The ISL422XE features an automatic powerdown function
that powers down the on-chip power-supply and driver
circuits. This occurs when an attached peripheral device is
shut off or the RS-232 cable is removed, conserving system
power automatically without changes to the hardware or
operating system. It powers up again when a valid RS-232
voltage is applied to any receiver input.
Table 1 summarizes the features of the ISL422XE, while
Application Note AN9863 summarizes the features of each
device comprising the 3V RS-232 family.
= 3.0V. Additionally,
CC
FN6045.1
Features
• Available in Near Chip Scale QFN (5mmx5mm) Package
which is 40% Smaller than a 20 Lead TSSOP
• ESD Protection for RS-232 I/O Pins to
±15kV (IEC61000)
• Meets EIA/TIA-232 and V.28/V.24 Specifications at 3V
• RS-232 Compatible with VCC = 2.7V
• On-Chip Voltage Converters Require Only Four External
0.1µF Capacitors
• Manual and Automatic Powerdown Features
• Receiver Hysteresis For Improved Noise Immunity
• Guaranteed Minimum Data Rate . . . . . . . . . . . . 250kBps
• Wide Power Supply Range. . . . . . . Single +2.7V to +5.5V
• Low Supply Current in Powerdown State. . . . . . . . .150nA
• Pb-free Available as an Option
Applications
• Any Space Constrained System Requiring RS-232 Ports
- Battery Powered, and Portable Equipment
- Hand-Held Products (GPS Receivers, Bar Code
Scanners, etc.)
- PDAs and Palmtops, Data Cables
- Cellular/Mobile Phones, Digital Cameras
Related Literature
• Technical Brief TB363 “Guidelines for Handling and
Processing Moisture Sensitive Surface Mount Devices
• ”Technical Brief TB379 “Thermal Characterization of
Packages f or ICs”
• Technical Brief TB389 “PCB Land Pattern Design and
Surface Mount Guidelines for QFN Packages”
TABLE 1. SUMMARY OF FEATURES
PART
NUMBER
ISL4221E 1 1 YES 250 YES YES YES
ISL4223E 2 2 YES 250 YES YES YES
NO. OF
Tx.
NO. OF
Rx.
1
QFN PKG.
AVAILABLE?
DATA RATE
(kBps)
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
1-888-INTERSIL or 321-724-7143
Rx. ENABLE
FUNCTION?
All other trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
MANUAL
POWERDOWN?
| Intersil (and design) is a registered trademark of Intersil Americas Inc.
Copyright © Intersil Americas Inc. 2004. All Rights Reserved
AUTOMATIC POWERDOWN
FUNCTION?
Page 2
ISL4221E, ISL4223E
Ordering Information
PART NO. TEMP. RANGE (°C) PACKAGE PKG. DWG. #
ISL4221EIR -40 to 85 16 Ld QFN L16.5x5
ISL4221EIR-T -40 to 85 16 Ld QFN
L16.5x5
Tape & Reel
ISL4221EIRZ-T
(Note)
-40 to 85 16 Ld QFN
Tape & Reel
L16.5x5
(Pb-free)
ISL4223EIR -40 to 85 20 Ld QFN L20.5x5
ISL4223EIRZ
(Note)
-40 to 85 20 Ld QFN
(Pb-free)
L20.5x5
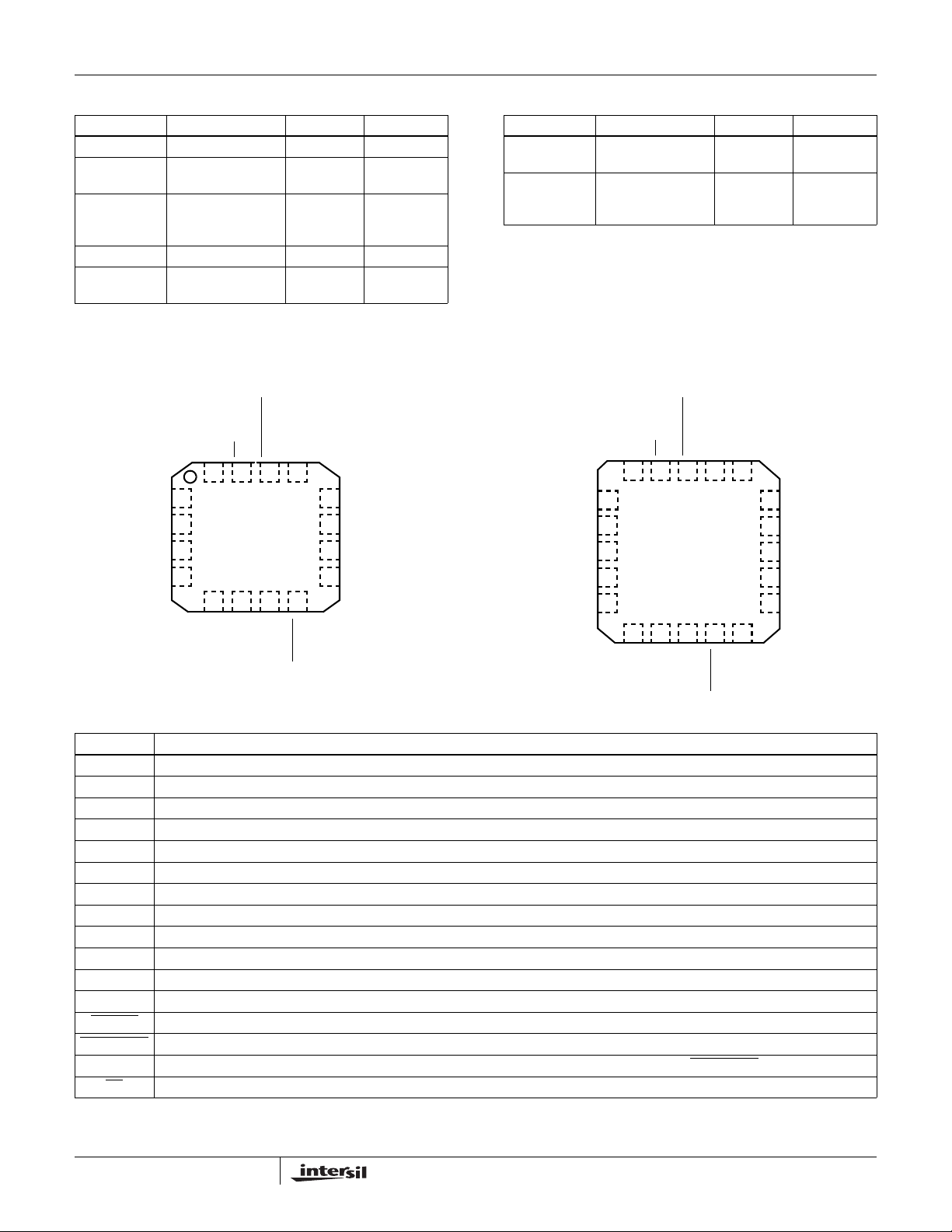
Pinouts
ISL4221E (QFN)
TOP VIEW
FORCEOFF
OUT
R1
V
CC
INVALID
12
GND
11
T1
FORCEON
10
T1
9
OUT
IN
V+
C1-
C2+
C2-
C1+
16 14 13
1
2
3
4
V-
EN
15
6578
IN
R1
Ordering Information (Continued)
PART NO. TEMP. RANGE (°C) PACKAGE PKG. DW G . #
ISL4223EIR-T -40 to 85 20 Ld QFN
Tape & Reel
ISL4223EIRZ-T
(Note)
-40 to 85 20 Ld QFN
Tape & Reel
(Pb-free)
NOTE: Intersil Pb-free products employ special Pb-free material
sets; molding compounds/die attach materials and 100% matte tin
plate termination finish, which is compatible with both SnPb and
Pb-free soldering operations. Intersil Pb-free products are MSL
classified at Pb-free peak reflow temperatures that meet or exceed
the Pb-free requirements of IPC/JEDEC J Std-020B.
ISL4223E (QFN)
TOP VIEW
C1+
EN
FORCEOFF
VCCGND
20 19 18 17 16
V+
1
C1-
2
C2+
3
C2-
4
5
V-
789106
IN
OUT
T2
R2
R2
OUT
T2
INVALID
IN
T1
15
R1
14
13
R1
FORCEON
12
T1
11
L20.5x5
L20.5x5
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
Pin Descriptions
PIN FUNCTION
V
CC
V+ Internally generated positive transmitter supply (+5.5V).
V- Internally generated negative transmitter supply (-5.5V).
GND Ground connection.
C1+ External capacitor (voltage doubler) is connected to this lead.
C1- External capacitor (voltage doubler) is connected to this lead.
C2+ External capacitor (voltage inverter) is connected to this lead.
C2- External capacitor (voltage inverter) is connected to this lead.
T
T
OUT
R
R
OUT
INVALID
FORCEOFF
FORCEON Active high input to override automatic powerdown circuitry thereby keeping transmitters active. (FORCEOFF
EN
System power supply input (2.7V to 5.5V).
TTL/CMOS compatible transmitter Inputs.
IN
±15kV ESD Protected, RS-232 level (nominally ±5.5V) transmitter outputs.
±15kV ESD Protected, RS-232 compatible receiver inputs.
IN
TTL/CMOS level receiver outputs.
Active low output that indicates if no valid RS-232 levels are present on any receiver input.
Active low to shut down transmitters and on-chip power supply. This overrides any automatic circuitry and FORCEON (see Table 2).
Active low receiver enable control.
2
must be high).
Page 3
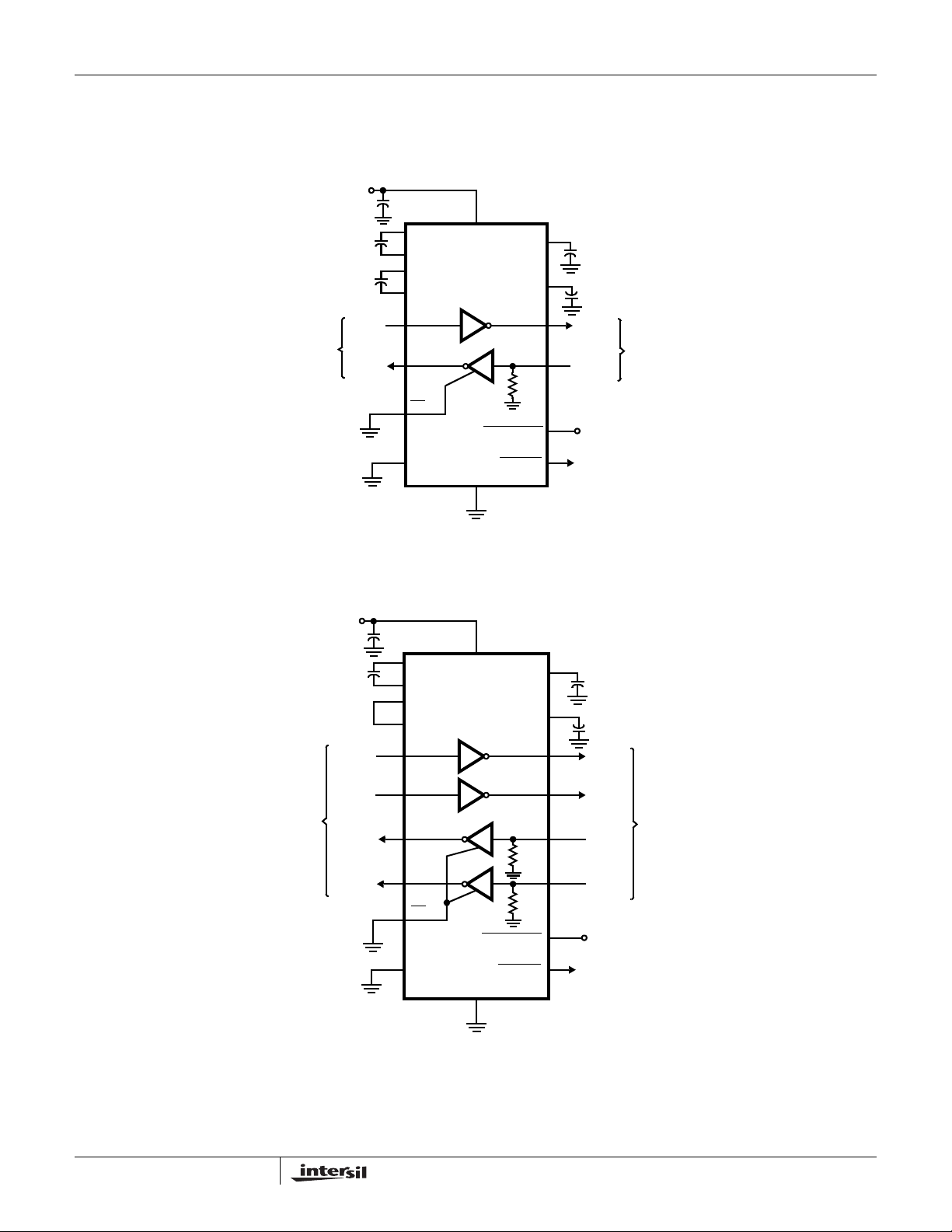
Typical Operating Circuits
ISL4221E, ISL4223E
ISL4221E
TTL/CMOS
LOGIC
LEVELS
TTL/CMOS
LOGIC LEVELS
+3.3V
+3.3V
0.1µF
0.1µF
R1
R2
C
0.1µF
C
0.1µF
R1
C
1
C
2
T1
T2
OUT
OUT
1
2
T1
OUT
IN
IN
IN
+
16
+
+
15
10
+
20
+
+
11
10
13
19
12
0.1µF
C1+
2
C1-
3
C2+
4
C2-
9
EN
FORCEON
0.1µF
C1+
2
C1-
3
C2+
4
C2-
EN
FORCEON
13
V
CC
T
1
R
1
FORCEOFF
GND
12
ISL4223E
17
V
CC
T
1
T
2
R
1
R
2
FORCEOFF
GND
16
5kΩ
INVALID
5kΩ
5kΩ
INVALID
V+
V-
V+
V-
1
C
3
+
0.1µF
5
C
4
0.1µF
+
11
T1
OUT
67
R1
IN
14
V
CC
8
TO POWER
CONTROL LOGIC
1
C
3
+
0.1µF
5
C
4
0.1µF
+
15
T1
OUT
6
T2
OUT
14
R1
78
R2
18
V
CC
9
TO POWER
CONTROL LOGIC
IN
IN
RS-232
LEVELS
RS-232
LEVELS
3
Page 4
ISL4221E, ISL4223E
Absolute Maximum Ratings Thermal Information
VCC to Ground. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3V to 6V
V+ to Ground . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3V to 7V
V- to Ground. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +0.3V to -7V
V+ to V- . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14V
Input Voltages
T
, FORCEOFF, FORCEON, EN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3V to 6V
IN
R
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±25V
IN
Output Voltages
T
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±13.2V
OUT
R
, INVALID. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3V to VCC +0.3V
OUT
Short Circuit Duration
T
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Continuous
OUT
ESD Rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Specification Table
CAUTION: Stresses above those listed in “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress only rating and operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
NOTE:
is measured in free air with the component mounted on a high effective thermal conductivity test board with “direct attach” features. See
1. θ
JA
Tech Brief TB379, and Tech Brief TB389.
Thermal Resistance (Typical, Note 1)
θ
JA
(oC/W)
16 Ld QFN Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
20 Ld QFN Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Moisture Sensitivity (see Technical Brief TB363)
QFN Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Level 1
Maximum Junction Temperature (Plastic Package) . . . . . . . 150
Maximum Storage Temperature Range. . . . . . . . . . -65
o
C to 150oC
Maximum Lead Temperature (Soldering 10s) . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
Operating Conditions
Temperature Range
ISL422XEIR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -40
o
C to 85oC
o
o
C
C
Electrical Specifications Test Conditions: V
Typicals are at T
= 3V to 5.5V, C1 - C4 = 0.1µF; Unless Otherwise Specified.
CC
= 25oC
A
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Supply Current, Automatic
Powerdown
Supply Current, Powerdown FORCEOFF
Supply Current,
Automatic Powerdown Disabled
Open, FORCEON = GND, FORCEOFF = V
All R
IN
= GND 25 - 0.15 1 µA
All Outputs Unloaded,
FORCEON = FORCEOFF
= V
LOGIC AND TRANSMITTER INPUTS AND RECEIVER OUTPUTS
Input Logic Threshold Low T
Input Logic Threshold High T
Input Leakage Current T
Output Leakage Current EN
Output Voltage Low I
Output Voltage High I
, FORCEON, FORCEOFF, EN Full - - 0.8 V
IN
, FORCEON, FORCEOFF, ENVCC = 3.3V Full 2.0 - - V
IN
, FORCEON, FORCEOFF, EN Full - ±0.01 ±1.0 µA
IN
= V
CC
= 1.6mA Full - - 0.4 V
OUT
= -1.0mA Full V
OUT
AUTOMATIC POWERDOWN (FORCEON = GND, FORCEOFF
Receiver Input Thresholds to
ISL422XE Powers Up (See Figure 6) Full -2.7 - 2.7 V
Enable Transmitters
Receiver Input Thresholds to
ISL422XE Powers Down (See Figure 6) Full -0.3 - 0.3 V
Disable Transmitters
INVALID
INVALID
Output Voltage Low I
Output Voltage High I
= 1.6mA Full - - 0.4 V
OUT
= -1.0mA Full VCC-0.6 - - V
OUT
Receiver Threshold to Transmitters
Enabled Delay (t
WU
)
Receiver Positive or Negative
Threshold to INVALID
(t
)
INVH
High Delay
Receiver Positive or Negative
Threshold to INVALID
(t
)
INVL
Low Delay
TEMP
o
C) MIN TYP MAX UNITS
(
CC
25 - 0.15 1 µA
VCC = 3.15V 25 - 0.3 1.0 mA
CC
= 5.0V Full 2.4 - - V
V
CC
Full - ±0.05 ±10 µA
CC
-0.6 V
-0.1 - V
CC
= VCC)
25 - 100 - µs
25 - 1 - µs
25 - 30 - µs
4
Page 5

ISL4221E, ISL4223E
Electrical Specifications Test Conditions: V
Typicals are at T
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS
RECEIVER INPUTS
Input Voltage Range 25 -25 - 25 V
Input Threshold Low V
Input Threshold High V
Input Hysteresis 25 - 0.5 - V
Input Resistance 25 3 5 7 kΩ
TRANSMITTER OUTPUTS
Output Voltage Swing All Transmitter Outputs Loaded with 3kΩ to Ground Full ±5.0 ±5.4 - V
Output Resistance V
Output Short-Circuit Current Full - ±35 ±60 mA
Output Leakage Current V
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Maximum Data Rate R
Receiver Propagation Delay Receiver Input to Receiver
Receiver Output Enable Time Normal Operation 25 - 200 - ns
Receiver Output Disable Time Normal Operation 25 - 200 - ns
Transmitter Skew t
Receiver Skew t
Transition Region Slew Rate V
ESD PERFORMANCE
RS-232 Pins (T
All Other Pins Human Body Model 25 - ±2-kV
NOTE:
2. Transmitter skew is measured at the transmitter zero crossing points.
, RIN) Human Body Model 25 - ±15 - kV
OUT
= 3.3V 25 0.6 1.2 - V
CC
V
= 5.0V 25 0.8 1.5 - V
CC
= 3.3V 25 - 1.5 2.4 V
CC
= 5.0V 25 - 1.8 2.4 V
V
CC
= V+ = V- = 0V, Transmitter Output = ±2V Full 300 10M - Ω
CC
= ±12V, VCC = 0V or 3V to 5.5V,
OUT
Automatic Powerdown or FORCEOFF
= 3kΩ, CL = 1000pF, One Transmitter Switching Full 250 500 - kBps
L
Output, C
PHL
PHL
CC
Measured From 3V to -3V
or -3V to 3V
IEC61000-4-2 Contact Discharge 25 - ±8-kV
IEC61000-4-2 Air Gap Discharge 25 - ±15 - kV
= 150pF
L
- t
PLH
- t
PLH
= 3.3V, RL = 3kΩ to 7kΩ,
= 3V to 5.5V, C1 - C4 = 0.1µF; Unless Otherwise Specified.
CC
= 25oC (Continued)
A
TEMP
o
C) MIN TYP MAX UNITS
(
Full - - ±25 µA
= GND
t
PHL
t
PLH
(Note 2) 25 - 100 - ns
C
= 150pF to 2500pF 25 4 - 30 V/µs
L
= 150pF to 1000pF 25 6 - 30 V/µs
C
L
25 - 0.15 - µs
25 - 0.15 - µs
25 - 50 - ns
Detailed Description
The ISL422XE operate from a single +2.7V to +5.5V supply,
guarantee a 250kBps minimum data rate, require only four
small external 0.1µF capacitors, feature low power
consumption, and meet all ElA RS-232C and V.28
specifications even with V
into three sections: The charge pump, the transmitters, and
the receivers.
= 3.0V. The circuit is divided
CC
5
Charge-Pump
Intersil’s new ISL422XE devices utilize regulated on-chip
dual charge pumps as voltage doublers, and voltage
inverters to generate ±5.5V transmitter supplies from a V
supply as low as 3.0V. This a llows them to maintain RS-232
compliant output levels over the ±10% tolerance range of
3.3V powered systems. The efficient on-chip power supplies
require only four small, external 0.1µF capacitors for the
voltage doubler and inverter functions. The charge pumps
operate discontinuously (i.e., they turn off as soon as the V+
CC
Page 6

ISL4221E, ISL4223E
and V- supplies are pumped up to the nominal values),
resulting in significant power savings.
Transmitters
The transmitters are proprietary, low dropout, inverting
drivers that translate TTL/CMOS inputs to EIA/TIA-232
output levels. Coupled with the on-chip ±5.5V supplies, these
transmitters deliver true RS-232 levels over a wide range of
single supply system voltages.
All transmitter outputs disable and assume a high
impedance state when the device enters the powerdown
mode (see Table 2). These outputs may be driven to ±12V
when disabled.
The devices guarantee a 250kBps data rate for full load
conditions (3kΩ and 1000pF), V
≥ 3.0V, with one
CC
transmitter operating at full speed. Under more typical
conditions of V
≥ 3.3V, RL = 3kΩ, and CL = 250pF, one
CC
transmitter easily operates at 900kBps.
Transmitter inputs float if left unconnected, and may cause
I
increases. Connect unused inputs to GND for the best
CC
performance.
Receivers
All the ISL422XE devices contain standard inverting
receivers that three-state via the EN
receivers convert RS-232 signals to CMOS output levels and
accept inputs up to ±25V while presenting the required 3kΩ
to 7kΩ input impedance (see Figure 1) even if the power is
off (V
= 0V). The receivers’ Schmitt trigger input stage
CC
uses hysteresis to increase noise immunity and decrease
errors due to slow input signal transitions.
V
CC
R
XIN
-25V ≤ V
FIGURE 1. INVERTING RECEIVER CONNECTIONS
RIN
≤ +25V
GND
5kΩ
control line. All the
R
XOUT
GND ≤ V
ROUT
≤ V
CC
11mA current required by comparable 5V RS-232 devices,
allowing users to reduce system power simply by switching
to this new family.
Po werdown Functionality
The already low current requirement drops significantly
when the device enters powerdown mode. In powerdown,
supply current drops to 150nA, because the on-chip charge
pump turns off (V+ collapses to V
and the transmitter outputs three-state. Receiver outputs are
unaffected by powerdown; refer to Table 2 for details. This
micro-power mode makes the ISL422XE ideal for battery
powered and portable applications.
V
CC
V
CC
V
OUT = VCC
Rx
POWERED
DOWN
UART
Tx
GND
FIGURE 2. POWER DRAIN THROUGH PO WERED DO WN
PERIPHERAL
TO
WAKE-UP
LOGIC
V
CC
SHDN
TRANSITION
DETECTOR
V
CC
, V - collapses to GND),
CC
V
CURRENT
FLOW
OLD
= GND
RS-232 CHIP
ISL422XE
INVALID
CC
Receivers driving a powered down UART must be disabled
to prevent current flow through, and possible damage to, the
UART’s protection diodes (see Figures 2 and 3). This can be
accomplished on the ISL422XE by driving the EN
input high
whenev e r th e UART powers down. Fig u re 3 a lso s hows that
the INVALID
output can be used to determine when the
UART should be powered down. When the RS-232 cable is
disconnected, INVALID
switches low indicating that the
UART is no longer needed. Reconnecting the cable drives
INVALID
back high, indicating that the UART should be
powered up.
Low Power Operation
These 3V devices require a nominal supply current of
0.3mA, even at V
powerdown mode). This is considerably less than the 5mA to
= 5.5V, during normal operation (not in
CC
6
R
POWERED
DOWN
UART
FIGURE 3. DISABLED RECEIVERS PREVENT POWER DRAIN
T
V
X
X
OUT =
EN
R
= V
HI-Z
OUT
T
IN
CC
R
T
IN
OUT
Software Controlled (Manual) Powerdown
The ISL422XE family provides pins that allow the user to
force the IC into the low power , standby state.
The ISL422XE utilize a two pin approach where the
FORCEON and FORCEOFF
inputs determine the IC’s
Page 7

ISL4221E, ISL4223E
TABLE 2. POWERDOWN AND ENABLE LOGIC TRUTH TABLE
RS-232 SIGNAL
PRESENT AT
RECEIVER INPUT?
NO H H L Active Active L Normal Operation
NO H H H Active High-Z L
YES H L L Active Active H Normal Operation
YES H L H Active High-Z H
NO H L L High-Z Active L Powerdown Due to Auto Powerdown
NO H L H High-Z High-Z L
YES L X L High-Z Active H Manual Powerdown
YES L X H High-Z High-Z H Manual Powerdown w/ Rcvr. Disabled
NO L X L High-Z Active L Manual Powerdown
NO L X H High-Z High-Z L Manual Powerdown w/Rcvr. Disabled
mode. For always enabled operation, FORCEON and
FORCEOFF
are both strapped high. To switch between
active and powerdown modes, under logic or software
control, only the FORCEOFF
FORCEON state isn’t critical, as FORCEOFF
over FORCEON. Ne vertheless, if strictly manual control over
powerdown is desired, the user must strap FORCEON high
to disable the automatic po werdown circuitry.
Connecting FORCEOFF
the automatic powerdown feature, enabli ng them to function
as a manual SHUTDOWN
PWR
MGT
LOGIC
CPU
FORCEOFF
INPUT
FORCEON
INPUTENINPUT
input need be driven. The
dominates
and FORCEON together disables
input (see Figure 4).
FORCEOFF
FORCEON
INVALID
ISL422XE
I/O
UART
TRANSMITTER
OUTPUTS
RECEIVER
OUTPUTS
POWER
MANAGEMENT
FIGURE 5. CIRCUIT TO PREVENT AUT O PO WERDO WN FOR
INVALID
OUTPUT MODE OF OPERATION
(Auto Powerdown Disabled)
(Auto Powerdown Enabled)
Logic
MASTER POWERDO WN LINE
UNIT
FORCEOFF
100ms AFTER FORCED POWERUP
0.1µF
ISL422XE
1MΩ
FORCEON
Automatic Powerdown
Even greater power savings is available by using the
automatic powerdown function. When no valid RS-232
voltages (see Figure 6) are sensed on any receiver input for
30µs, the charge pump and transmitters powerdown, thereby
reducing supply current to 10nA. Invalid receiver lev els occur
whenever the driving peripheral’s outputs are shut off
(powered down) or when the RS-232 interface cable is
disconnected. The ISL422XE powers back up whenever it
detects a valid RS-232 voltage level on any receiver input.
This automatic powerdown feature provides additional
system power savings without changes to the e xisting
operating system.
FIGURE 4. CONNECTIONS FOR MANUAL POWERDO WN
WHEN NO VALID RECEIVER SIGNALS ARE
PRESENT
The time to recover from automatic powerdown mode is
typically 100µs.
7
Automatic powerdown operates when the FORCEON input
is low, and the FORCEOFF
input is high. Tying FORCEON
high disables automatic powerdown, but manual powerdo wn
is always av ailable via the overriding FORCEOFF
input.
Table 2 summarizes the automatic powerdown functionality.
Some applications may need more time to wake up from
shutdown. If automatic powerdown is being utilized, the RS232 device will reenter powerdown if valid receiver levels
aren’t reestablished within 30µs of the ISL422XE powering
up. Figure 5 illustrates a circuit that keeps the ISL422XE
Page 8

ISL4221E, ISL4223E
from initiating automatic powerdown for 100ms after
powering up. This gives the slow-to-wake peripheral circuit
time to reestablish valid RS-232 output levels.
The time to recover from automatic powerdown mode is
typically 100µs.
INVALID Output
The INVALID output always indicates whether or not a valid
RS-232 signal (see Figure 6) is present at any of the receiver
inputs (see Table 2), giving the user an easy way to
determine when the interface block should power down.
Invalid receiver levels occur whenever the driving
peripheral’s outputs are shut off (powered down) or when the
RS-232 interface cable is disconnected. In the case of a
disconnected interface cable where all the receiver inputs
are floating (but pulled to GND by the internal receiver pull
down resistors), the INVALID
and drives the output low. The power management logic
then uses this indicator to power down the interface block.
Reconnecting the cable restores valid lev els at the receiv er
inputs, INVALID
switches high, and the power management
logic wakes up the interface block. INVALID
used to indicate the DTR or RING INDICATOR signal, as
long as the other receiver inputs are floating, or driven to
GND (as in the case of a powered down driver).
2.7V
0.3V
-0.3V
-2.7V
FIGURE 6. DEFINITION OF VALID RS-232 RECEIVER LEVELS
VALID RS-232 LEVE L - IS L422XE IS ACTIVE
INDETERMINATE - POWERDOWN MAY OR
INVALID LEVEL - POWERDOWN OCCURS AFTER 30µs
INDETERMINATE - POWERDOWN MAY OR
VALID RS-232 LE VEL - ISL422XE IS ACTIVE
logic detects the invalid levels
can also be
MAY NOT OCCUR
MAY NOT OCCUR
circuitry. When automatic powerdown is utilized, INVALID
=
0 indicates that the ISL422XE is in powerdown mode.
RECEIVER
INPUTS
TRANSMITTER
OUTPUTS
V
INVALID
OUTPUT
FIGURE 7. AUTOMA TIC PO WERDO WN AND INV ALID TIMING
CC
0
AUTOPWDN
V+
V
CC
0
V-
DIAGRAMS
t
INVL
t
INVH
INVALID
}
REGION
PWR UP
Capacitor Selection
The charge pumps require 0.1µF, or greater, capacitors for
proper operation. Increasing the capacitor values (by a factor
of 2) reduces ripple on the transmitter outputs and slightly
reduces power consumption.
When using minimum required capacitor values, make sure
that capacitor values do not degrade excessively with
temperature. If in doubt, use capacitors with a larger nominal
value. The capacitor’s equivalent series resistance (ESR)
usually rises at low temperatures and it influences the
amount of ripple on V+ and V-
.
Po wer Supply Decoupling
In most circumstances a 0.1µF bypass capacitor is
adequate. In applications that are particularly sensitive to
power supply noise, decouple V
capacitor of the same value as the charge-pump capacitor C
Connect the bypass capacitor as close as possible to the IC.
to ground with a
CC
1
.
INVALID
switches low after invalid levels have persisted on
all of the receiver inputs for more than 30µs (see Figure 7).
INVALID
RS-232 level on a receiver input. INVALID
switches back high 1µs after detecting a valid
operates in all
modes (forced or automatic powerdown, or forced on), so it
is also useful for systems employing manual powerdown
8
Transmitter Outputs when Exiting
Powerdown
Figure 8 shows the response of two transmitter outputs
when exiting powerdown mode. As they activate, the two
transmitter outputs properly go to opposite RS-232 levels,
with no glitching, ringing, nor undesirable transients. Each
transmitter is loaded with 3kΩ in parallel with 2500pF.
Page 9

ISL4221E, ISL4223E
Note that the transmitters enable only when the magnitude
of the supplies exceed approximately 3V.
5V/DIV.
2V/DIV.
FIGURE 8. TRANSMITTER OUTPUTS WHEN EXITING
FORCEOFF
T1
T2
VCC = +3.3V
C1 - C4 = 0.1µF
TIME (20µs/DIV.)
POWERDOWN
5V/DIV.
T1
T1
OUT
R1
OUT
5V/DIV.
IN
VCC = +3.3V
C1 - C4 = 0.1µF
5µs/DIV.
FIGURE 10. LOOPBACK TEST AT 120kBps
Operation Down to 2.7V
ISL422XE transmitter outputs meet RS-562 levels (±3.7V), at
the full data rate, with V
as low as 2.7V. RS-562 levels
CC
typically ensure inter operability with RS-232 devices.
High Data Rates
The ISL422XE maintain the RS-232 ±5V minimum
transmitter output voltages even at high data rates. Figure 9
details a transmitter loopback test circuit, and Figure 10
illustrates the loopback test result at 120kBps. For this test,
all transmitters were simultaneously driving RS-232 loads in
parallel with 1000pF, at 120kBps. Figure 11 shows the
loopback results for a single transmitter driving 1000pF and
an RS-232 load at 250kBps. The static transmitters were
also loaded with an RS-232 receiver.
V
CC
0.1µF
+
C
1
+
C
2
V
CC
FIGURE 9. TRANSMITTER LOOPBACK TEST CIRCUIT
+
C1+
C1-
ISL422XE
C2+
C2-
T
IN
R
OUT
FORCEON
FORCEOFF
V
CC
T
OUT
5k
V+
V-
R
IN
+
C
3
C
4
+
1000pF
T1
IN
T1
OUT
R1
OUT
VCC = +3.3V
C1 - C4 = 0.1µF
2µs/DIV.
FIGURE 11. LOOPBACK TEST AT 250kBps
Interconnection with 3V and 5V Logic
The ISL422XE directly interface with 5V CMOS and TTL
logic families. Nevertheless, with the ISL422XE at 3.3V, and
the logic supply at 5V, AC, HC, and CD4000 outputs can
drive ISL422XE inputs, but ISL422XE outputs do not reach
the minimum V
more information.
T ABLE 3. LOGIC F AMILY COMP ATIBILITY WITH VARIOUS
SYSTEM
POWER-SUPPLY
VOLTAGE
(V)
3.3 3.3 Compatible with all CMOS
5 5 Compatible with all TTL and
5 3.3 Compatible with ACT and HCT
for these logic families. See Table 3 for
IH
SUPPLY VOLTAGES
V
CC
SUPPLY
VOLTAGE
(V) COMPATIBILITY
families.
CMOS logic families.
CMOS, and with TTL. ISL422XE
outputs are incompatible with AC,
HC, and CD4000 CMOS inputs.
9
Page 10

ISL4221E, ISL4223E
±15kV ESD Protection
All pins on ISL422XE devices include ESD protection
structures, but the RS-232 pins (transmitter outputs and
receiver inputs) incorporate advanced structures which allow
them to survive ESD events up to ±15kV. The RS-232 pins
are particularly vulnerable to ESD damage because they
typically connect to an exposed port on the exterior of the
finished product. Simply touching the por t pi ns, or
connecting a cable, can cause an ESD event that might
destroy unprotected ICs. These new ESD structures protect
the device whether or not it is powered up, protect without
allowing any latchup mechanism to activate, and don’t
interfere with RS-232 signals as large as ±25V.
Human Body Model (HBM) Testing
As the name implies, this test method emulates the ESD
event delivered to an IC during human handling. The tester
delivers the charge through a 1.5kΩ current limiting resistor,
making the test less severe than the IEC61000 test which
utilizes a 330Ω limiting resistor. The HBM method
determines an ICs ability to withstand the ESD transients
typically present during handling and manufacturing. Due to
the random nature of these events, each pin is tested with
respect to all other pins. The RS-232 pins on “E” family
devices can withstand HBM ESD events to ±15kV.
IEC61000-4-2 Testing
The IEC61000 test method applies to finished equipment,
rather than to an individual IC. Therefore, the pins most likely
to suffer an ESD event are those that are exposed to the
outside world (the RS-232 pins in this case), and the IC is
tested in its typical application configuration (power applied)
rather than testing each pin-to-pin combination. The lower
current limiting resistor coupled with the larger charge
storage capacitor yields a test that is much more severe than
the HBM test. The extra ESD protection built into this
device’s RS-232 pins allows the design of equipment
meeting level 4 criteria without the need for additional board
level protection on the RS-232 port.
AIR-GAP DISCHARGE TEST METHOD
For this test method, a charged probe tip moves toward the
IC pin until the voltage arcs to it. The current waveform
delivered to the IC pin depends on approach speed,
humidity, temperature, etc., so it is difficult to obtain
repeatable results. The “E” device RS-232 pins withstand
±15kV air-gap discharges.
CONTACT DISCHARGE TEST METHOD
During the contact discharge test, the probe contacts the
tested pin before the probe tip is energized, thereby
eliminating the variables associated with the air-gap
discharge. The result is a more repeatable and predictable
test, but equipment limits prevent testing de vices at voltages
higher than ±8kV. All “E” family devices survive ±8kV contact
discharges on the RS-232 pins.
10
Page 11

ISL4221E, ISL4223E
Typical Performance Curves V
6
4
2
1 TRANSMITTER AT 250kBps
OTHER TRANSMITTERS AT 30kBps
0
-2
-4
TRANSMITTER OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
-6
1000 2000 3000 4000 50000
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
= 3.3V, TA = 25oC
CC
V
OUT
V
OUT
FIGURE 12. TRANSMITTER OUTPUT VOL TAGE vs LOAD
CAPACITANCE
45
ISL4221E
40
35
30
25
20
15
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
10
5
0
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
250kBps
120kBps
20kBps
FIGURE 14. SUPPL Y CURRENT vs LOAD CAPACIT ANCE
WHEN TRANSMITTING DATA
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
0.5
NO LOAD
ALL OUTPUTS STATIC
25
+
20
15
-SLEW
SLEW RATE (V/µs)
-
10
5
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000
+SLEW
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
FIGURE 13. SLEW RATE vs LOAD CAPACITANCE
45
ISL4223E
40
35
30
25
20
15
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
10
5
0
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
250kBps
120kBps
20kBps
FIGURE 15. SUPPLY CURRENT vs LOAD CAPACITANCE
WHEN TRANSMITTING DATA
Die Characteristics
SUBSTRATE POTENTIAL (POWERED UP):
GND
TRANSISTOR COUNT:
ISL4221E: 286
ISL4223E: 357
PROCESS:
Si Gate CMOS
0
2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
FIGURE 16. SUPPLY CURRENT vs SUPPLY VOLTAGE
11
Page 12

ISL4221E, ISL4223E
Quad Flat No-Lead Plastic Package (QFN)
Micro Lead Frame Plastic Package (MLFP)
L16.5x5
16 LEAD QUAD FLAT NO-LEAD PLASTIC PACKAGE
(COMPLIANT TO JEDEC MO-220VHHB ISSUE C)
MILLIMETERS
SYMBOL
A 0.80 0.90 1.00 A1 - - 0.05 A2 - - 1.00 9
A3 0.20 REF 9
b 0.28 0.33 0.40 5, 8
D 5.00 BSC D1 4.75 BSC 9
D2 2.55 2.70 2.85 7, 8
E 5.00 BSC E1 4.75 BSC 9
E2 2.55 2.70 2.85 7, 8
e 0.80 BSC -
k0.25 - - -
L 0.35 0.60 0.75 8
L1 - - 0.15 10
N162
Nd 4 3
Ne 4 4 3
P- -0.609
θ --129
NOTES:
1. Dimensioning and tolerancing conform to ASME Y14.5-1994.
2. N is the number of terminals.
3. Nd and Ne refer to the number of terminals on each D and E.
4. All dimensions are in millimeters. Angles are in degrees.
5. Dimension b applies to the metallized terminal and is measured
between 0.15mm and 0.30mm from the terminal tip.
6. The configuration of the pin #1 identifier is optional, but must be
located within the zone indicated. The pin #1 identifier may be
either a mold or mark feature.
7. Dimensions D2 and E2 are for the exposed pads which provide
improved electrical and thermal performance.
8. Nominal dimensions are provided to assist with PCB Land Pattern
Design efforts, see Intersil Technical Brief TB389.
9. Features and dimensions A2, A3, D1, E1, P & θ are present when
Anvil singulation method is used and not present for saw
singulation.
10. Depending on the method of lead termination at the edge of the
package, a maximum 0.15mm pull back (L1) maybe present. L
minus L1 to be equal to or greater than 0.3mm.
NOTESMIN NOMINAL MAX
Rev. 2 10/02
12
Page 13

ISL4221E, ISL4223E
Quad Flat No-Lead Plastic Package (QFN)
Micro Lead Frame Plastic Package (MLFP)
L20.5x5
20 LEAD QUAD FLAT NO-LEAD PLASTIC PACKAGE
(COMPLIANT TO JEDEC MO-220VHHC ISSUE C)
MILLIMETERS
SYMBOL
A 0.80 0.90 1.00 A1 - - 0.05 A2 - - 1.00 9
A3 0.20 REF 9
b 0.23 0.28 0.38 5, 8
D 5.00 BSC D1 4.75 BSC 9
D2 2.95 3.10 3.25 7, 8
E 5.00 BSC E1 4.75 BSC 9
E2 2.95 3.10 3.25 7, 8
e 0.65 BSC -
k0.25 - - -
L 0.35 0.60 0.75 8
L1 - - 0.15 10
N202
Nd 5 3
Ne 5 3
P- -0.609
θ --129
NOTES:
1. Dimensioning and tolerancing conform to ASME Y14.5-1994.
2. N is the number of terminals.
3. Nd and Ne refer to the number of terminals on each D and E.
4. All dimensions are in millimeters. Angles are in degrees.
5. Dimension b applies to the metallized terminal and is measured
between 0.15mm and 0.30mm from the terminal tip.
6. The configuration of the pin #1 identifier is optional, but must be
located within the zone indicated. The pin #1 identifier may be
either a mold or mark feature.
7. Dimensions D2 and E2 are for the exposed pads which provide
improved electrical and thermal performance.
8. Nominal dimensions are provided to assist with PCB Land Pattern
Design efforts, see Intersil Technical Brief TB389.
9. Features and dimensions A2, A3, D1, E1, P & θ are present when
Anvil singulation method is used and not present for saw
singulation.
10. Depending on the method of lead termination at the edge of the
package, a maximum 0.15mm pull back (L1) maybe present. L
minus L1 to be equal to or greater than 0.3mm.
NOTESMIN NOMINAL MAX
Rev. 3 10/02
All Intersil U.S. products are manufactured, assembled and tested utilizing ISO9000 quality systems.
Intersil Corporation’s quality certifications can be viewed at www.intersil.com/design/quality
Intersil products are sold by description only. Intersil Corporation reserves the right to make changes in circuit design, software and/or specifications at any time without
notice. Accordingly, the reader is cautioned to verify that data sheets are current before placing orders. Information furnished by Intersil is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Intersil or its subsidiaries for its use; nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result
from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Intersil or its subsidiaries.
For information regarding Intersil Corporation and its products, see www.intersil.com
13
 Loading...
Loading...