Page 1
IS487/IS488
IS487/IS488
Built-in Amp.Type
OPIC Light Detector
■ Features
1. Compact type
2. Built-in schmidt trigger circuit
3. LSTTL and TTL compatible output
4. Open collector output
5. Low level output under incident light
(IS487
)
High level output under incident light
(IS488
)
6. A wide range of operating supply voltage
(VCC: 4.5 to 17v
)
■ Applications
1. Floppy disk drive Units
2. Copiers, printers, facsimiles
3. VCRs
4. Automatic vending machines
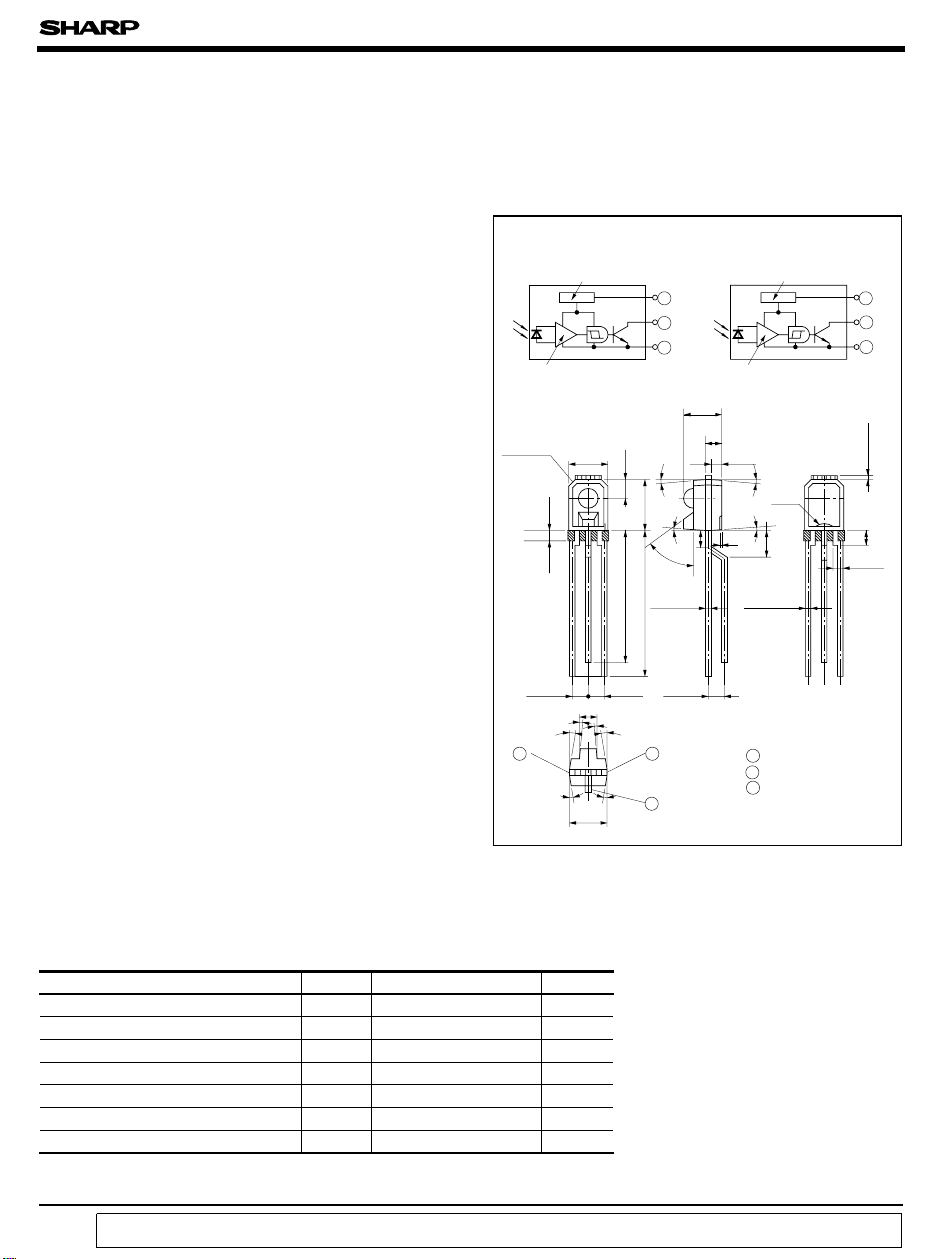
■ Outline Dimensions
Internal connection diagram
IS487
Voltage regulator
3
2
1
Amp.
2-C0.5
1
MAX.
0.8
Rugged resin
1.27
6˚
6˚
6˚
3.0
1.6
2.8
1.0
±
1.27
6˚
6˚
1.5
16.5
6˚
+1.5
0.2
±
18.0
4.0
3- 0.4
-1.0
3
2
4˚
4˚
60˚
(1.27)
+ 0.3
- 0.1
2.95
1.15
1.6
IS488
Voltage regulator
Amp.
0.75
4˚
R0.5
4˚
0.15
2.6
+ 0.3
3- 0.45
- 0.1
1 GND
2 V
O
3 V
CC
(
Unit : mm
MAX.
Gate burr
2- 0.8
)
3
2
1
0.3
1.4
*“ OPIC ” (Optical IC) is a trademark of the SHARP Corporation.
An OPIC consists of a light-detecting element and signal processing circuit integrated onto a single chip.
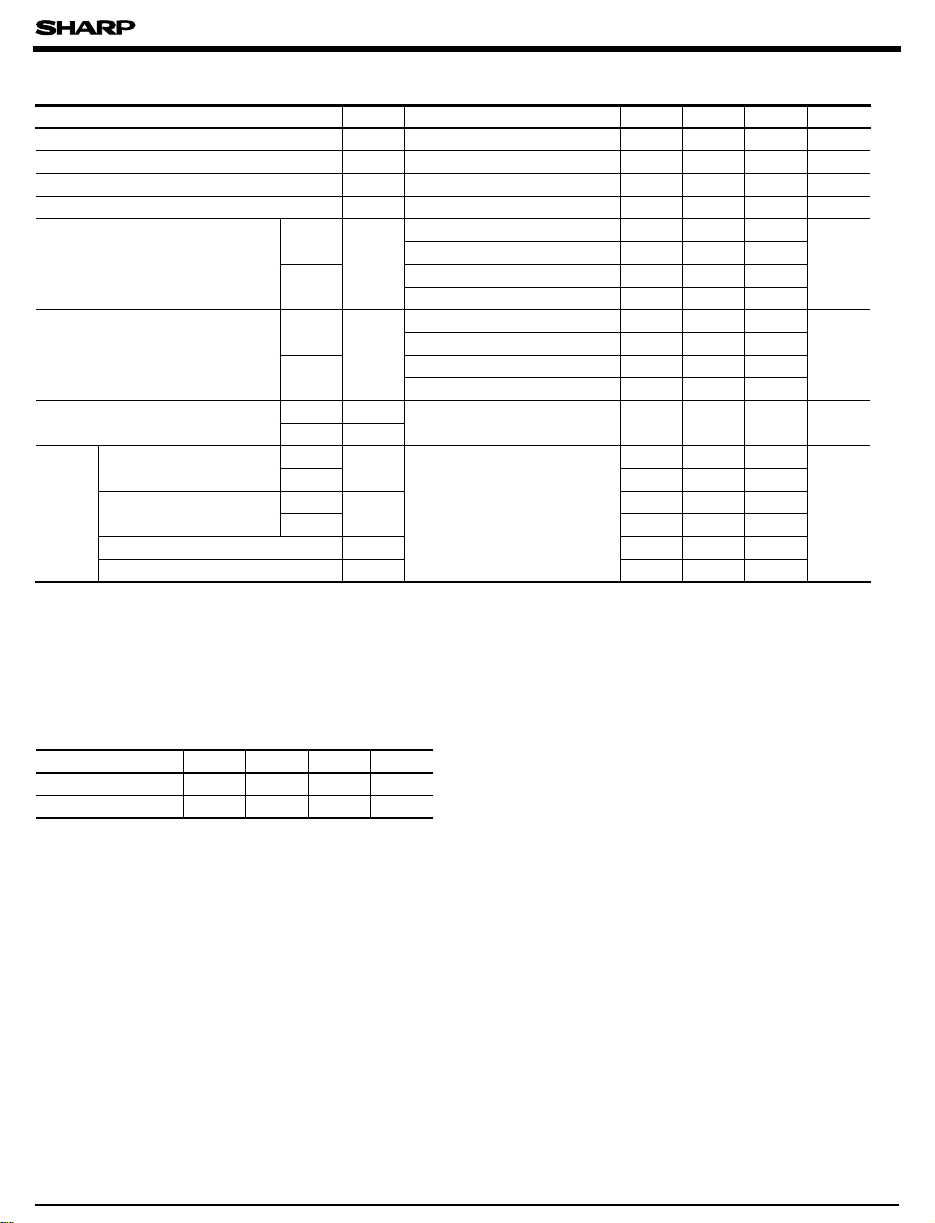
■ Absolute Maximum Ratings
(
Ta= 25˚C
)
Parameter Symbol Rating Unit
Supply voltage V
Output voltage V
Output current I
CC
O
O
- 0.5 to + 35 V
- 0.5 to + 40 V
50 mA
Power dissipation P 175 mW
Operating temperature T
Storage temperature T
*1
Soldering temperature T
*1 For 5 seconds at the position of 1.4mm from the bottom face of resin package
“ In the absence of confirmation by device specification sheets, SHARP takes no responsibility for any defects that occur in equipment using any of SHARP's devices, shown in catalogs,
data books, etc. Contact SHARP in order to obtain the latest version of the device specification sheets before using any SHARP's device.”
opr
stg
sol
-25 to +85 ˚C
- 40 to +100 ˚C
260 ˚C
Page 2
IS487/IS488
■ Electro-optical Characteristics
(
Unless otherwise specified, Ta= 0 to 70˚C, V
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
*2
Low level output voltage V
High level output current I
Low level supply current I
High level supply current I
*4
“ High→Low”
Threshold illuminance
*5
“ Low→High”
Threshold illuminance
*6
Hysteresis
“Low→High”
Propagation time
Response
time
“High→Low”
Propagation time
IS487
IS488
IS487
IS488
IS487
IS488
IS487
IS488 -39
IS487
IS488 -515
Rise time t
Fall time t
*2 Defines E
*3 Defines E
*4 E
represents illuminance by CIE standerd light source A (tungsten lamp) when output changes from high
VHL
to low.
represents illuminance by CIE standerd light source A (tungsten lamp) when output changes from low
*5 E
VLH
to high.
*6 Hysteresis stands for E
(
IS487) and EV=0 (IS488).
= 50lx
V
=0 (IS487) and E
V
VLH/EVHL
(
IS488).
= 50lx
V
(IS487) and E
OL
OH
CCL
CCH
E
VHL
E
VLH
E
VLH/EVHL
E
VHL/EVLH
t
PLH
t
PHL
r
f
VHL/EVLH
IOL= 16mA - 0.15 0.4 V
*3
VCC= 20V, VO= 30V - - 100 µA
*2 - 1.3 3.4 mA
*3 - 0.7 2.2 mA
Ta= 25˚C, RL= 280Ω -1535
= 280Ω --50
R
L
= 25˚C, RL= 280Ω 1.5 10 -
T
a
R
= 280Ω 1--
L
Ta= 25˚C, RL= 280Ω 1.5 10 -
= 280Ω 1--
R
L
= 25˚C, RL= 280Ω -1535
T
a
R
= 280Ω --50
L
Ta= 25˚C, RL= 280Ω 0.50 0.65 0.90 -
Ta= 25˚C
E
= 50lx
V
= 280 Ω
R
L
(IS488).
■ Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter Symbol MIN. MAX. Unit
Supply voltage V
Output current I
In order to stabilize power supply line, connect a by-pass capacitor of 0.01µ
the device.
4.5 17 V
CC
OL
-16mA
or more between VCC and GND near
F
CC
-515
-39
- 0.1 0.5
- 0.05 0.5
)
=5V
lx
lx
µs
Page 3

IS487/IS488
Fig. 1 Low Level Output Current vs.
Ambient Temperature
60
)
50
mA
(
OL
40
Fig. 2 Power Dissipation vs.
Ambient Temperature
300
250
)
mW
200
(
175
30
20
150
100
Power dissipation P
10
Low level output current I
0
-25 -25
0 25 10050 75 85
)
Ambient temperature T
a
(˚C
Fig. 3 Relative Threshold Illuminance vs.
Supply Voltage Ambient Temperature
1.1
T
= 25˚C
a
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
1 E
E
VHL
VLH
(
IS487
(
IS488
)
(
)
2 E
E
VLH
VHL
IS487
(
IS488
)
)
1
50
0
Ambient temperature Ta (˚C
Fig. 4 Low Level Output Voltage vs.
0.6
E
= 50 lx(IS487
V
= 0 (IS488
E
)
0.5
V
(
OL
0.4
0.3
0.2
V
2
0.6
Relative threshold illuminance
0.5
0
(
E
VHL
at V
CC
510 2015
Supply voltage VCC (V
IS487), E
=0
VLH
(
IS488)=1
)
25
0.1
Low level output voltage V
0
-25
Ambiment temperature T
Fig. 5 Supply Current vs.
Ambient Temperature
3.0
857550 100250
)
)
)
I
OL
= 30mA
=
V
CC
5V
16mA
5mA
7550 100250
)
(˚C
a
2.5
)
2.0
mA
(
cc
1.5
1.0
Supply current I
0.5
0
-25
V
= 17V
CC
10V
I
CCL
5V
V
= 17V
CC
10V
I
CCH
5V
0255075100
Ambient temperature T
a
(˚C
)
Page 4

Fig. 6 Propagation Delay Time vs. Fig. 7 Rise Time, Fall Time vs.
Illuminance
12
=5V
V
)
µ s
(
PHL
, t
PLH
CC
11
R
= 280Ω
L
10
T
= 25˚C
a
9
1
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
Propagation delay time t
1
0
0 600
1 t
PLH
t
PHL
100 500300 400200
(
IS487
(
IS488
Illuminance E
)
)
2 t
(
IS487
PHL
(
t
IS488
PLH
(lx
v
2
)
)
)
Test Circuit for Response Time (IS487
)
Load Resistance
0.8
0.7
)
0.6
µ s
(
f
, t
0.5
r
0.4
0.3
0.2
Rise time, fall time t
0.1
0
0.2 0.5 1 2 5 10 20 50
0.1
Load resistance RL (kΩ
Test Circuit for Response Time (IS488
IS487/IS488
Ta= 25˚C
= 5V
V
CC
E
= 50lx
V
t
r
t
f
)
)
Voltage regulater
Input
= tf= 0.01 µ s
t
r
Zo = 50Ω
Input
Output
47Ω
t
PHL
V
= 5V
cc
R
L
Output
Amp
0.01µ F
50%
t
PLH
V
OH
90%
1.5V
10%
t
f
t
r
Input
tr= tf= 0.01 µ s
Zo = 50Ω
Input
Output
47Ω
t
PLH
t
r
Fig. 8 Sensitivity Diagram Fig. 9 Spectral Sensitivity
)
+20˚+10˚
+30˚
+40˚
+50˚
+60˚
+70˚
+80˚
+90˚
100
Ta= 25˚C
90
80
)
70
%
(
60
50
40
30
Relative sensitivity
20
10
0
400 800 1000 1200
600
Wavelength λ (nm
- 30˚
- 40˚
- 50˚
- 60˚
- 70˚
- 80˚
- 90˚
(T
0
-10˚- 20˚
100
80
)
%
(
60
40
Relative radiant intensity
20
0
Angular displacement θ
= 25˚C
a
● Please refer to the chapter “Precautions for Use.”
Voltage regulater
Amp
50%
t
PHL
90%
t
f
V
= 5V
cc
R
L
Output
0.01µ F
V
OH
1.5V
10%
V
OL
)
 Loading...
Loading...