Datasheet IDT74FST16163213PV, IDT74FST16163213PF, IDT74FST16163213PA Datasheet (Integrated Device Technology)
Page 1
Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
The IDT logo is a registered trademark of Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
FEATURES:
• Bus switches provide zero delay paths
• Extended commercial range of –40°C to +85°C
• Low switch on-resistance:
FST163xxx – 4Ω
• TTL-compatible input and output levels
• ESD > 2000V per MIL-STD-883, Method 3015;
> 200V using machine model (C = 200pF, R = 0)
• Available in SSOP, TSSOP and TVSOP
COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE FEBRUARY 1997
1997 Integrated Device Technology, Inc. DSC-3684/-
1
IDT74FST163213
PRODUCT PREVIEW
24-BIT BUS EXCHANGE
SWITCH
or source capability. Thus they generate little or no noise of
their own while providing a low resistance path for an external
driver. These devices connect input and output ports through
an n-channel FET. When ther gate-to-source junction of this
FET is adequately forward-biased the device conducts and
the resistance between input and output ports is small. Without adequate bias on the gate-to-source junction of the FET,
the FET is turned off, therefore with no VCC applied, the device
has hot insertion capability.
The low on-resistance and simplicity of the connection
between input and output ports reduces the delay in this path
to close to zero.
The FST163213 provides four 12-bit TTL-compatible ports
that support 2 way bus exchange. The S0-2 pins control the
bus exchange and switch enable functions.
DESCRIPTION:
The FST163213 belongs to IDT's family of Bus switches.
Bus switch devices perform the function of connecting or
isolating two ports without providing any inherent current sink
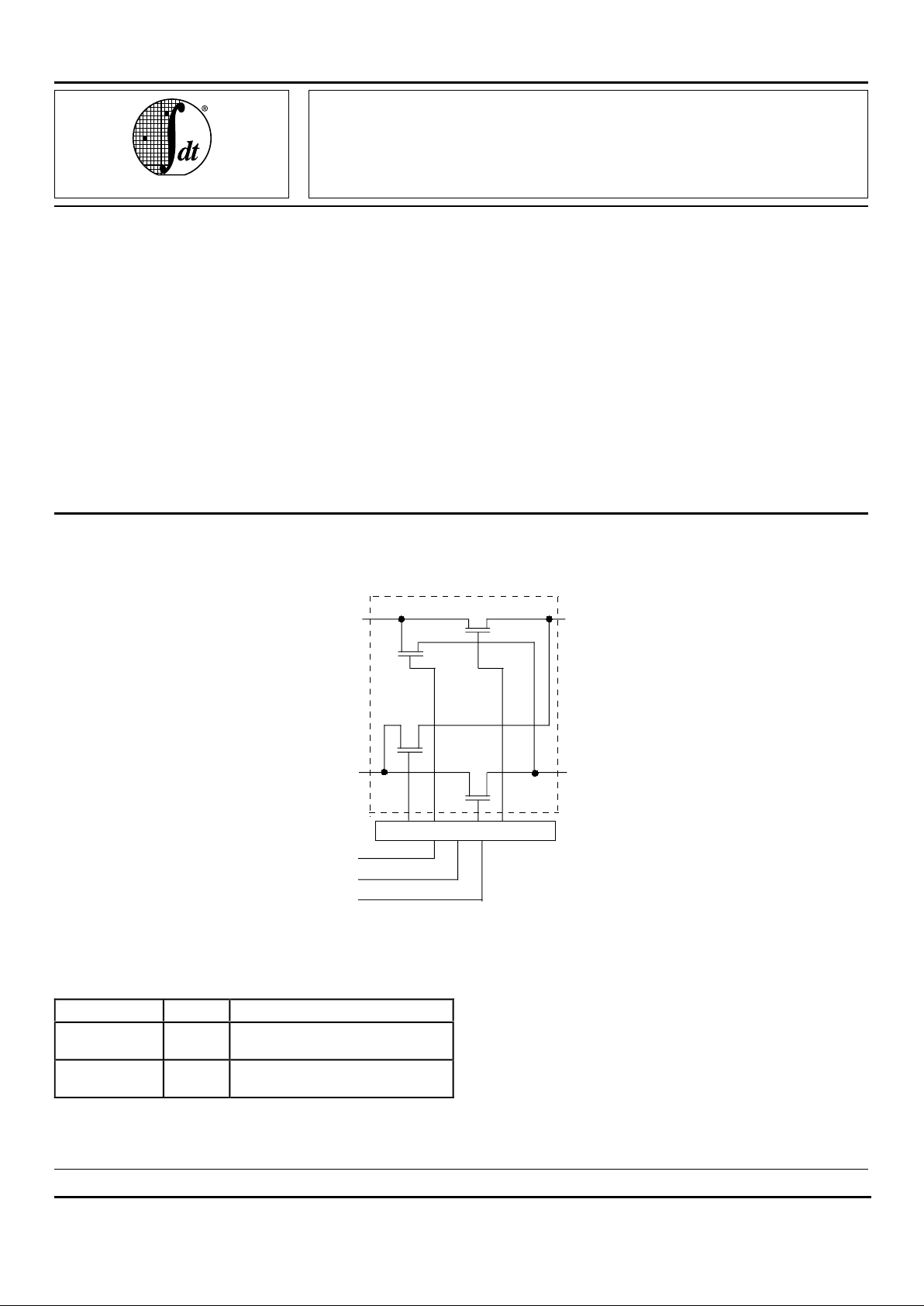
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
1A1
S
0
S
1
1
B
1
1 of 12 Channels
Flow Control
1B2
1
A
2
S
2
3684 drw 01
Pin Names I/O Description
A1, A2
B1, B2
I/O Buses A1, A2, B1, B2
S0-2 I Control Pins for Mux and Switch
Enable Functions
PIN DESCRIPTION
3684 tbl 01
Page 2
2
IDT74FST163213
24-BIT BUS EXCHANGE SWITCH COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
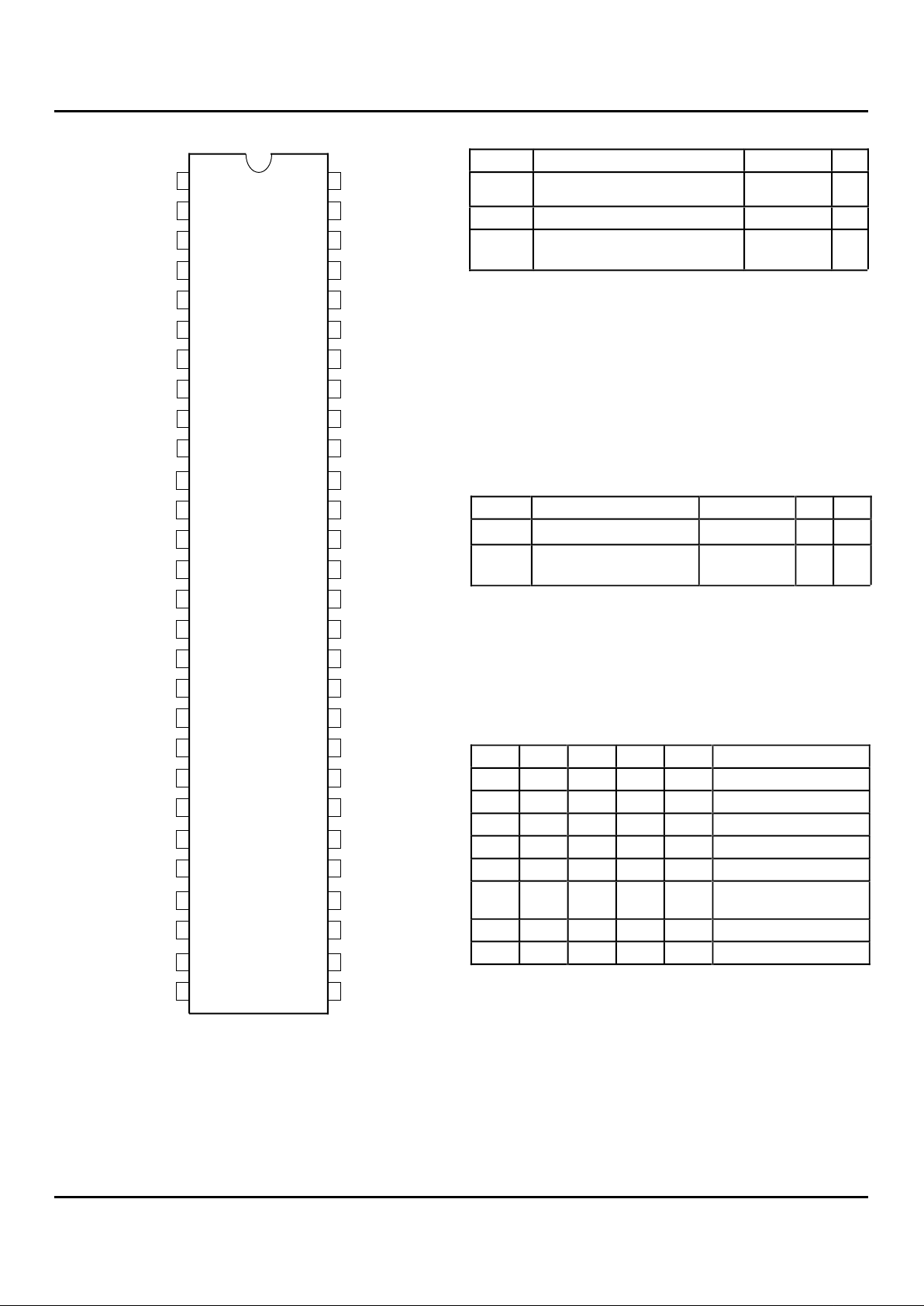
PIN CONFIGURATION
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(1)
Symbol Description Max. Unit
VTERM
(2)
Terminal Voltage with Respect
to GND
–0.5 to +7.0 V
TSTG Storage Temperature –65 to +150 °C
IOUT Maximum Continuous Channel
Current
128 mA
3684 lnk 02
NOTES:
1. Stresses greater than those listed under ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating
only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating condiitions for
extended periods may affect reliability.
2. VCC, Control and Switch terminals.
CAPACITANCE
(1)
Symbol Parameter Conditions
(2)
Typ. Unit
CIN Control Input Capacitance 4 pF
CI/O
Switch Input/Output
Capacitance
Switch Off
pF
NOTES:
1. Capacitance is characterized but not tested
2. TA = 25°C, f = 1MHz, VIN = 0V, VOUT = 0V
3684 lnk 03
SSOP/
TSSOP/TVSOP
TOP VIEW
5
6
7
8
9
10
1
2
3
4
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
4A2
1
A1
1
A2
2
A1
2
A2
3
A1
3
A2
GND
4A1
1
B1
1
B2
2
B1
2
B2
3
B1
3
B2
4
B1
S1
S2
5A1
11
12
55
56
5A2
4
B2
5
B1
17
18
19
20
21
22
13
14
15
16
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
9A2
6
A2
7
A1
7
A2
6
A1
VCC
8
A1
GND
8A2
9
A1
6
B2
7
B1
7
B2
8
B1
GND
8B2
9
B1
9
B2
5
B2
6
B1
SO56-1
SO56-2
SO56-3
10A1
23
24
43
44
10A2
10
B1
10
B2
25
26
32
31
30
29
11A2
11
A111B1
11
B2
12A1
27
28
12A2
12
B1
12
B2
S0
GND
3684 drw 02
FUNCTION TABLE
S
2
S
1
S
0
A
1
A
2
Function
L L L Z Z Disconnect
LLHB
1
ZA
1
to B
1
LHLB
2
ZA
1
to B
2
LHHZB
1
A
2
to B
1
HLLZB
2
A
2
to B
2
HLHA
2
&
B
2
ZA
1
to A2 and B
2
HHLB
1
B
2
A1 to B1, A2 to B
2
HHHB
2
B
1
A1 to B2, A2 to B
1
3684 tbl 04
Page 3

DT74FST163213
24-BIT BUS EXCHANGE SWITCH COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
3
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS OVER OPERATING RANGE
Following Conditions Apply Unless Otherwise Specified:
Commercial: TA = –40°C to +85°C, VCC = 5.0V ±10%
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions
(1)
Min. Typ.
(2)
Max. Unit
VIH Input HIGH Voltage Guaranteed Logic HIGH for Control Inputs 2.0 — — V
VIL Input LOW Voltage Guaranteed Logic LOW for Control Inputs — — 0.8 V
II H Input HIGH Current VCC = Max. VI = VCC ——±1µA
II L Input LOW Voltage VI = GND — — ±1
IOZH High Impedance Output Current VCC = Max. VO = VCC ——±1µA
IOZL (3-State Output pins) VO = GND — — ±1
IOS Short Circuit Current VCC = Max., VO = GND
(3)
— 300 — mA
VIK Clamp Diode Voltage VCC = Min., IIN = –18mA — –0.7 –1.2 V
RON Switch On Resistance
(4)
VCC = Min. VIN = 0.0V — 4 7 Ω
ION = 64mA
VCC = Min. VIN = 0.0V — 4 7 Ω
ION = 30mA
VCC = Min. VIN = 2.4V — 10 15 Ω
ION = 15mA
IOFF Input/Output Power Off Leakage VCC = 0V, VIN or VO ≤ 4.5V — — ±1 µA
ICC Quiescent Power Supply Current VCC = Max., VIN = GND or VCC — 0.1 3 µA
3684 tbl 05
NOTES:
1. For conditions shown as Max. or Min. use appropriate value specified under Electrical Characteristics for the applicable device type.
2. Typical values are at VCC = 5.0V, +25°C ambient.
3. Not more than one output should be testes at one time. Duration of the test should not exceed one second.
4. Measured by voltage drop between ports at indicated current through the switch.
Page 4

4
IDT74FST163213
24-BIT BUS EXCHANGE SWITCH COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
POWER SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS
3684 tbl 06
NOTES:
1. For conditions shown as Max. or Min., use appropriate value specified under Electrical Characteristics for the applicable device type.
2. Typical values are at VCC = 5.0V, +25°C ambient.
3. Per TTL driven input (VIN = 3.4V). All other inputs at VCC or GND.
4. This parameter is not directly testable, but is derived for use in Total Power Supply Calculations.
5. Values for these conditions are examples of the ICC formula. These limits are guaranteed but not tested.
6. IC = IQUIESCENT + IINPUTS + IDYNAMIC
IC = ICC + ∆ICC DHNT + ICCD (fiN)
ICC = Quiescent Current
∆ICC = Power Supply Current for a TTL High Input (VIN = 3.4V)
DH = Duty Cycle for TTL Inputs High
NT = Number of TTL Inputs at DH
ICCD = Dynamic Current Caused by an Input Transition Pair (HLH or LHL)
fi = Input Frequency
N = Number of Switches Toggling at fi
All currents are in milliamps and all frequencies are in megahertz.
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions
(1)
Min. Typ.
(2)
Max. Unit
∆ICC Quiescent Power Supply Current
TTL Inputs HIGH
VCC = Max.
V
IN = 3.4V
(3)
— 0.5 1.5 mA
ICCD Dynamic Power Supply
Current
(4)
VCC = Max.
Outputs Open
VIN = VCC
VIN = GND
—3040µA/
MHz/
Enable Pin Toggling
50% Duty Cycle
Switch
IC Total Power Supply Current
(6)
VCC = Max.
Outputs Open
Enable Pins Toggling
VIN = VCC
VIN = GND
— 7.2 9.6 mA
(24 Switches Toggling)
fi = 10MHz
50% Duty Cycle
VIN = 3.4
V
IN = GND
— 7.7 11.1
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS OVER OPERATING RANGE
Following Conditions Apply Unless Otherwise Specified:
Commercial: TA = –40°C to +85°C, VCC = 5.0V ±10%
Symbol Description Condition
(1)
Min.
(2)
Typ. Max. Unit
tPLH
tPHL
Data Propagation Delay
A to B, B to A
(3,4)
CL = 50pF
R
L = 500Ω
— — 0.25 ns
tBX Switch Multiplex Delay
S to A, B
1.5 — 6.5 ns
tPZH
tPZL
Switch Turn on Delay
S to A, B
1.5 — 6.5 ns
tPHZ
tPLZ
Switch Turn off Delay
S to A, B
(3)
1.5 — 7 ns
|QCI| Charge Injection, Typical
(5,7)
— 1.5 — pC
|QDCI| Charge Injection, Typical
(6,7)
— 0.5 —
NOTES:
1. See test circuit and waveforms.
2. Minimum limits guaranteed but not tested.
3. This parameter is guaranteed by design but not tested.
4. The bus switch contributes no propagation delay other than the RC delay of the on resistance of the switch and the load capacitance. The time constant
for the switch alone is of the order of 2.5ns for 50pF load. Since this time is constant and much smaller than the rise/fall times of typical driving signals,
it adds very little propagation delay to the system. Propagation delay on the bus switch when used in a system is determined by the driving circuit on the
driving side of the switch and its interaction with the load on the driven side.
5. Measured at switch turn off, load = 50 pF in parallel with 10 MΩ scope probe, VIN = 0.0 volts.
6. Measured at switch turn off through bus multiplexer, (e.g.- A1 to B1 = >A1 to B2), load = 50 pF in parallel with 10 MΩ scope probe, VIN at A = 0.0 volts.
Charge injection is reduced because the injection from the turn off of the A1 to B1 switch is compensated by the turn on of the A1 to B2 switch.
7. Characterized parameter. Not 100% tested.
3684 tbl 07
Page 5

DT74FST163213
24-BIT BUS EXCHANGE SWITCH COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
5
TEST CIRCUITS AND WAVEFORMS
TEST CIRCUITS FOR ALL OUTPUTS
SWITCH POSITION
SET-UP, HOLD AND RELEASE TIMES
PULSE WIDTH
Pulse
Generator
R
T
D.U.T.
V
CC
V
IN
C L
V
OUT
50pF
500Ω
500Ω
7.0V
3V
1.5V
0V
3V
1.5V
0V
3V
1.5V
0V
3V
1.5V
0V
DATA
INPUT
TIMING
INPUT
ASYNCHRONOUS CONTROL
PRESET
CLEAR
ETC.
SYNCHRONOUS CONTROL
tSU
tH
tREM
tSU
tH
HIGH-LOW-HIGH
PULSE
LOW-HIGH-LOW
PULSE
tW
1.5V
1.5V
SAME PHASE
INPUT TRANSITION
3V
1.5V
0V
1.5V
V
OH
tPLH
OUTPUT
OPPOSITE PHASE
INPUT TRANSITION
3V
1.5V
0V
tPLH tPHL
tPHL
VOL
CONTROL
INPUT
3V
1.5V
0V
3.5V
0V
OUTPUT
NORMALLY
LOW
OUTPUT
NORMALLY
HIGH
SWITCH
CLOSED
SWITCH
OPEN
VOL
0.3V
0.3V
t
PLZtPZL
tPZH tPHZ
3.5V
0V
1.5V
1.5V
ENABLE DISABLE
VOH
PRESET
CLEAR
CLOCK ENABLE
ETC.
PROPAGATION DELAY
ENABLE AND DISABLE TIMES
Test Switch
Disable Low
Enable Low
Closed
All Other Tests
Open
Open Drain
DEFINITIONS:
CL= Load capacitance: includes jig and probe capacitance.
RT = Termination resistance: should be equal to ZOUT of the Pulse
Generator.
3684 lnk 08
3684 drw 03
3684 drw 04
3684 drw 05
3684 drw 06
3684 drw 07
NOTES:
1. Diagram shown for input Control Enable-LOW and input Control DisableHIGH
2. Pulse Generator for All Pulses: Rate ≤ 1.0MHz; tF ≤ 2.5ns; tR ≤ 2.5ns
Page 6

6
IDT74FST163213
24-BIT BUS EXCHANGE SWITCH COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
3684 drw 08
IDT XX
Temp. Range
16 XX
Device Type
X
Package
74 –40°C to +85°C
PV
PA
PF
163213
Shrink Small Outline Package (SO56-1)
Thin Shrink Small Outline Package (SO56-2)
Thin Very Small Outline Package (SO56-3)
24-Bit Bus Exchange Switch
FST
ORDERING INFORMATION
 Loading...
Loading...