Datasheet IA80C152JA-PDW48I, IA80C152JA-PDW68I, IA80C152JA-PLC68I, IA80C152JB-PLC68C, IA80C152JB-PLC68I Datasheet (INOVC)
...Page 1
Page 1 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
FEATURES
• Form, Fit, and Function Compatible
with the Intel 80C152
• Packaging options available
− 48 Pin Plastic or Ceramic DIP
− 68 Pin Plastic or Ceramic LCC
• 8051 Core with:
− Direct Memory Access(DMA)
− Global Serial Channel (GSC)
− MCS- 51 Compatible UART
− Two Timers/Counters
− Maskable Interrupts
• Memory
− 256 Bytes Internal RAM
− 64K Bytes Program Memory
− 64K Bytes Data Memory
• 5 or 7 I/O Ports
• Up to 16.5 MHz Clock Frequency
• Two-Channel DMA With Multiple
Transfer Modes
• GSC Provides Support for Multiple
Protocols
− CSMA/CD
− SDLC/HDLC
− User Definable
• Separate Transmit & Receive FIFOs
• Special Protocol Features
− Up to 2.0625 Mbps Serial
Operation
− CSMA and SDLC Frame Formats
with CRC Checking
− Manchester, NRZ, & NRZI Data
Encoding
− Collision Detection & Resolution
in CSMA Mode
− Selectable Full/Half Duplex
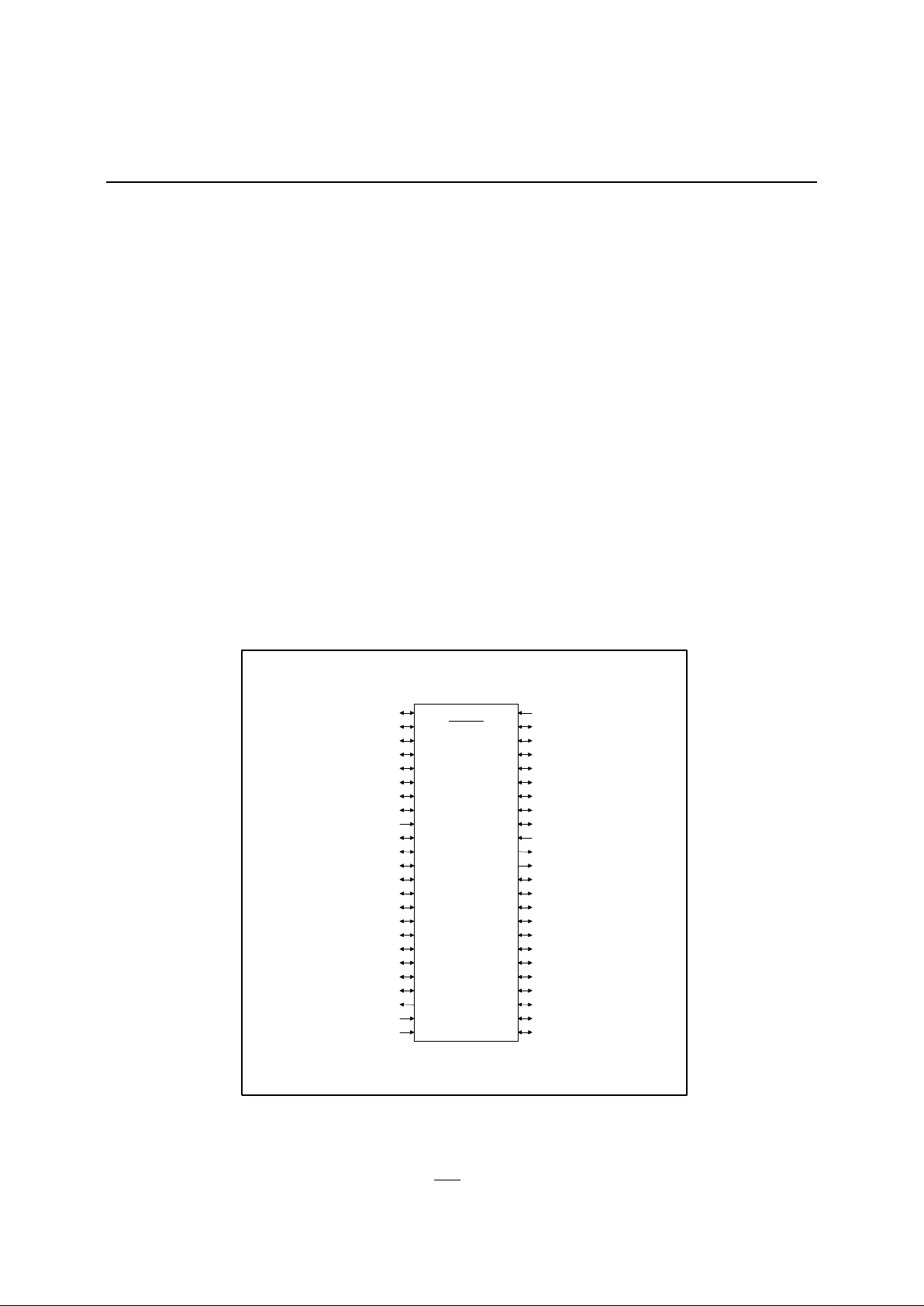
Figure 1 - 48 Pin DIP Pinout
(6)(HLDn) P1.5
(1)(GRXD) P1.0
(2)(GTXD) P1.1
(3)(DENn) P1.2
(4)(TXCn) P1.3
(5)(RXCn) P1.4
(7)(HLDAn) P1.6
(8)P1.7
(9)RESETn
(10)(RXD) P3.0
(11)(TXD) P3.1
(12)(INT0n) P3.2
(13)(INT1n) P3.3
(14)(T0) P3.4
48 Pin DIP
JA/JC
IA80152
(48) VDD
(47)
(46)
(45)
(44)
(43)
(42)
(41)
(40) P4.7
(39) EA
(38) ALE
(37) PSENn
(36) P2.7 (A15)
(35) P2.6 (A14)
(20)(A / D2) P0.2
(15)(T1) P3.5
(16)(WRn) P3.6
(17)(RDn) P3.7
(18)(A / D0) P0.0
(19)(A / D1) P0.1
(21)(A / D3) P0.3
(22)XTAL2
(23)XTAL1
(24)Vss
(34)
(33)
(32)
(31)
(30)
(29)
(28)
(27)
(26)
(25)
P2.5 (A13)
P2.4 (A12)
P2.3 (A11)
P2.2 (A10)
P2.1 (A9)
P2.0 (A8)
P0.7 (A / D7)
P0.6 (A / D6)
P0.5 (A / D5)
P0.4 (A / D4)
P4.6
P4.5
P4.4
P4.3
P4.2
P4.1
P4.0
Page 2
Page 2 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
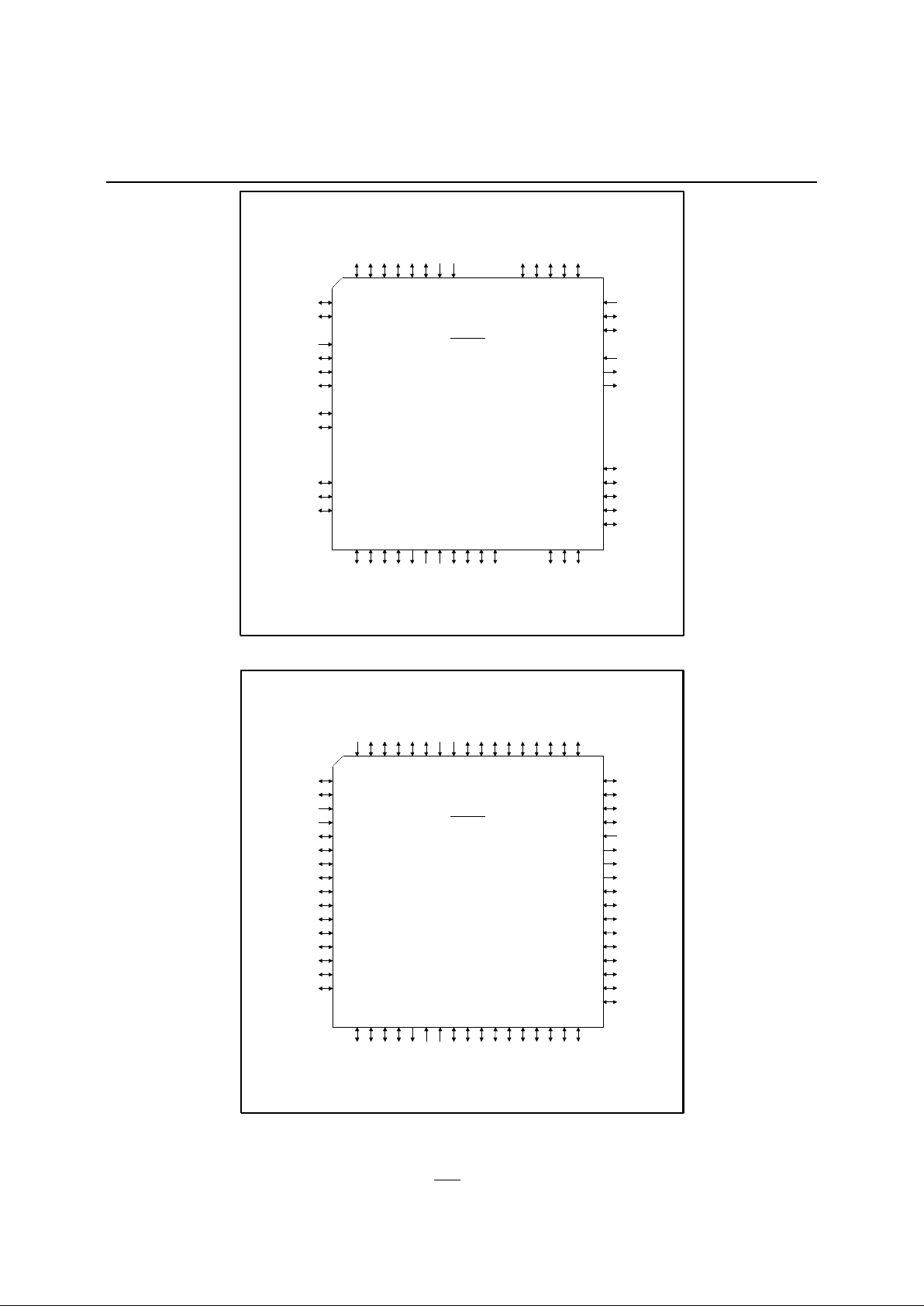
Figure 2 - 68 Lead LCC Pinout - JA/JC Versions
Figure 3 - 68 Lead LCC Pinout - JB/JD Versions
68 Pin LCC
JA/JC
IA82510
(15)(TXD) P3.1
(10)(HLDAn) P1.6
(11)P1.7
(12)N.C.
(13)RESETn
(14)(RXD) P3.0
(16)(INT0n) P3.2
(17)N.C.
(18)(INT1n) P3.3
(19)(T0) P3.4
(20)N.C.
(21)N.C.
(22)N.C.
(23)(T1) P3.5
(24)(WRn) P3.6
(25)(RDn) P3.7
(26)N.C.
(60) P4.5
(59)
(58)
(57)
(56)
(55)
(54)
(53)
(52) N.C.
(51) N.C.
(50) N.C.
(49) N.C.
(48) P2.7 (A15)
(47) P2.6 (A14)
(46)
(45)
(44)
P2.5 (A13)
P2.4 (A12)
P2.3 (A11)
N.C.
PSENn
ALE
EA
N.C.
P4.7
P4.6
(32)XTAL1
(27)(A / D0) P0.0
(28)(A / D1) P0.1
(29)(A / D2) P0.2
(30)(A / D3) P0.3
(31)XTAL2
(33)Vss
(34)(A / D4) P0.4
(35)(A / D5) P0.5
(36)(A / D6) P0.6
(37)(A / D7) P0.7
(38)N.C.
(39)N.C.
(40)N.C.
(41)(A8) P2.0
(42)(A9) P2.1
(43)(A10) P2.2
(9) P1.5 (HLDn)
(8)
(7)
(6)
(5)
(4)
(3)
(2)
(1) N.C.
(68) N.C.
(67) N.C.
(66) N.C.
(65) P4.0
(64) P4.1
(63)
(62)
(61)
P4.2
P4.3
P4.4
VDD
Vss
P1.0 (GRXD)
P1.1 (GTXD)
P1.2 (DENn)
P1.3 (TXCn)
P1.4 (RXCn)
68 Pin LCC
JB/JD
IA82510
(15)(TXD) P3.1
(10)(HLDAn) P1.6
(11)P1.7
(12)EBEN
(13)RESETn
(14)(RXD) P3.0
(16)(INT0n) P3.2
(17)P5.0
(18)(INT1n) P3.3
(19)(T0) P3.4
(20)P5.1
(21)P5.2
(22)P5.3
(23)(T1) P3.5
(24)(WRn) P3.6
(25)(RDn) P3.7
(26)
N.C.
(60) P4.5
(59)
(58)
(57)
(56)
(55)
(54)
(53)
(52) P6.2
(51) P6.7
(50) P6.4
(49) P5.7
(48) P2.7 (A15)
(47) P2.6 (A14)
(46)
(45)
(44)
P2.5 (A13)
P2.4 (A12)
P2.3 (A11)
EPSENn
PSENn
ALE
EA
P6.3
P4.7
P4.6
(32)XTAL1
(27)(A / D0) P0.0
(28)(A / D1) P0.1
(29)(A / D2) P0.2
(30)(A / D3) P0.3
(31)XTAL2
(33)Vss
(34)(A / D4) P0.4
(35)(A / D5) P0.5
(36)(A / D6) P0.6
(37)(A / D7) P0.7
(38)P5.4
(39)P5.5
(40)P5.6
(41)(A8) P2.0
(42)(A9) P2.1
(43)(A10) P2.2
(9) P1.5 (HLDn)
(8)
(7)
(6)
(5)
(4)
(3)
(2)
(1) P6.6
(68) P6.5
(67) P6.0
(66) P6.1
(65) P4.0
(64) P4.1
(63)
(62)
(61)
P4.2
P4.3
P4.4
VDD
Vss
P1.0 (GRXD)
P1.1 (GTXD)
P1.2 (DENn)
P1.3 (TXCn)
P1.4 (RXCn)
Page 3
Page 3 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
The IA80C152 is a "plug-and-play" drop-in replacement for the original IC. innovASIC produces
replacement ICs using its MILESTM, or Managed IC Lifetime Extension System, cloning technology.
This technology produces replacement ICs far more complex than "emulation" while ensuring they
are compatible with the original IC. MILESTM captures the design of a clone so it can be produced
even as silicon technology advances. MILESTM also verifies the clone against the original IC so that
even the "undocumented features" are duplicated. This data sheet documents all necessary
engineering information about the IA80C152 including functional and I/O descriptions, electrical
characteristics, and applicable timing.
INTEL is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation
DESCRIPTION
The IA80C152 is a Universal Communications Controller (UCC) that is pin-for-pin compatible
with the Intel 80C152. This version of the UCC is a ROMless version. The ROM version is
identified as the 83C152 and can be easily derived from the 80C152 using a customer furnished
ROM program. The IA80C152 can be programmed with the same software development tools and
can transmit and receive using the same communication protocols as the Intel 80C152 making the
IA80C152 a drop-in replacement. Table 1 below cross-references IA80C152 versions with
protocol, package, and I/O Port capability. Pinout diagrams are provided in figures 1, 2, and 3.
Table 1 - IC Version Differences
innovASIC
Part Number
CSMA/CD,
SDLC/HDLC,
User-Defined
5 I/O
Ports
7 I/O
Ports 48 Pin DIP 68 Lead LCC
IA80C152JA
√ √ √ √
IA80C152JB
√ √ √
IA80C152JC
√ √ √ √
IA80C152JD
√ √ √
The only difference between The innovASIC 80C152 and the Intel 80C152 is that all protocols
are available in all IC versions. Originally, the Intel 80C152 JC and JD versions were limited to
SDLC/HDLC only. Also, innovASIC will support a ROM version (83152) in any of the JA, JB, JC,
or JD versions.
The IA80C152 is partitioned into three major functional units identified as the C8051, the Direct
Memory Access (DMA) Controller, and the Global Serial Channel (GSC). The C8051 is
implemented using a CAST, Inc. Intellectual Property (IP) core. This core is instruction set
compatible with the 80C51BH, and contains compatible peripherals including a UART interface
and timers. The special function registers (SFRs) and interrupts are modified from the original
8051BH to accommodate the additional DMA controller and GSC peripherals.
The DMA Controller is a 2 channel, 8-bit device that is 16-bit addressable. Either channel can
access any combination of reads and writes to external memory, internal memory, or the SFR's.
Various modes allow the DMA to access the UART, GSC, SFRs, and internal and external memory
as well as provide for external control. Since there is only 1 data/program memory bus, only one
DMA channel or the microcontroller can have control at any give time. Arbitration within the
device makes this control transparent to the programmer.
Page 4
Page 4 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
The GSC is a serial interface that can be programmed to support CSMA/CD, SDLC, user definable
protocols, and limited HDLC. Protocol specific features are supported in hardware such as address
recognition, collision resolution, CRC generation and errors, automatic re-transmission, and
hardware acknowledge. The CSMA/CD protocol meets the requirements of ISO/IEC 8802-3 and
ANSI/IEEE Std 802.3 to the extent implemented in the original IC. The SDLC protocol meets
the requirements of IBM GA27-3093-04 to the extent implemented in the original IC.
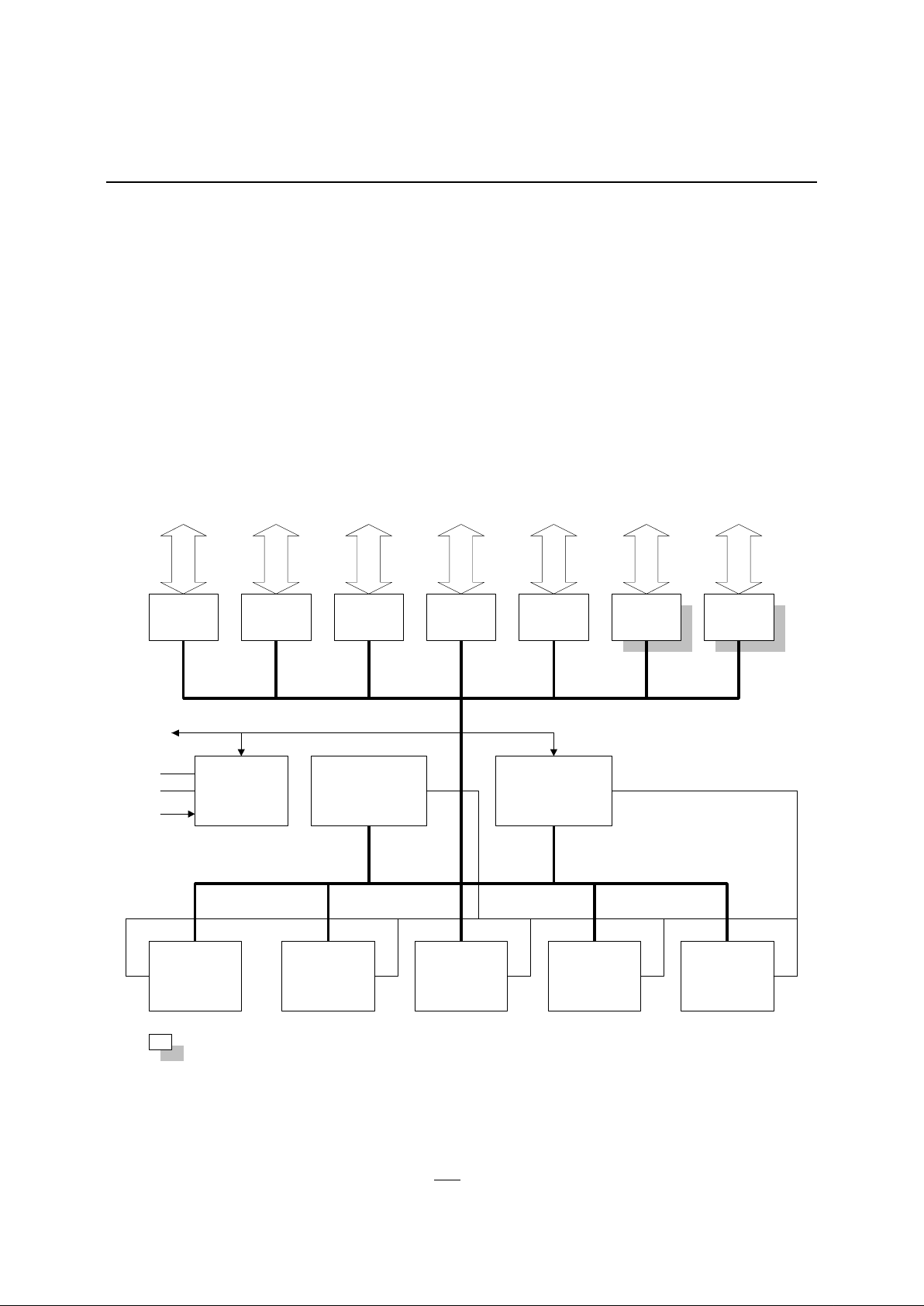
Functional Block Diagram
Figure 4 shows the major functional blocks of the IA80C152. Each version of the IA80C152
function identically to each other with the exception of the 2 additional I/O ports (Port 5 and
Port 6) in the JB and JD versions.
Figure 4 - Functional Block Diagram
256x8 RAM
C8051
CPU
UART DMA GSC
Port 0 Port 1 Port 2 Port 4Port 3 Port 5 Port 6
Interrupts Timers
Control
Address/Data
Clock Gen.
& Timing
XTAL
Reset
Memory
Control
I/O for Memory, GSC, DMA, UART, Interrupts, Timers
= JB and JD Versions Only
Page 5
Page 5 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
I/O Signal Description
Table 2 below describes the I/O characteristics for each signal on the IC. The signal names
correspond to the signal names on the pinout diagrams provided above. (!) Denotes active Low.
Table 2 - I/O Signal Descriptions
Signal Name Description
!EA External Access enable. Since there is no internal ROM in the
80C152, this signal has no function in the JA and JC versions. For
the JB and JD versions, controls program memory fetch locations.
!EPSEN E-bus Program Store ENable. When EBEN is 1, this signal is the
read strobe for external program memory.
!PSEN Program Store ENable. When EBEN is 0, this signal is the read
strobe for external program memory.
!RESET Reset. When this signal is low for 3 machine cycles, the device is put
into reset. The GSC may continue transmitting after reset is applied.
An internal pull-up allow the use of an external capacitor to generate
a power-on reset.
ALE Address Latch Enable. Latches the low-byte of external memory.
EBEN E-Bus ENable. In conjunction with EA, EBEN designates program
memory fetches from either Port 0,2 or Port 5,6.
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2
P0.3
P0.4
P0.5
P0.6
P0.7
Port 0 - open drain 8-bit bi-directional port that bit addressable and
can drive up to 8 LS TTL inputs. The port signals can be used as
high impedance inputs.
This port also provides the low-byte of the multiplexed address and
data bus depending on the state of !EBEN.
P1.0 - GRXD, GSC Receive
P1.1 - GTXD, GSC Transmit
P1.2 - !DEN, Driver Enable
P1.3 - !TXC, External Transmit Clock
P1.4 - !RXC, External Receive Clock
P1.5 - !HLD, DMA Hold
P1.6 - !HLDA, DMA Hold Acknowledge
P1.7
Port 1 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is bit addressable. To use a port
signal as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups pull
the input high and source current when the input is driven low. To
use a port signal as an output, a 1 or 0 written to the port location is
presented at the output.
Port signals in this port also serve as I/O for 80C152 functions.
These I/O signals are defined next to the port name.
P2.0
P2.1
P2.2
P2.3
P2.4
P2.5
P2.6
P2.7
Port 2 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is bit addressable. To use a port
signal as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups pull
the input high and source current when the input is driven low. To
use a port signal as an output, a 1 or 0 written to the port location is
presented at the output.
This port also provides the high-byte of the multiplexed address and
data bus depending on the state of !EBEN.
P3.0 - RXD, UART Receive
P3.1 - TXD, UART Transmit
P3.2 - !INT0, External Interrupt 0
P3.3 - !INT1, External Interrupt 1
P3.4 - T0, Timer 0 External Input
P3.5 - T1, Timer 1 External Input
P3.6 - !WR, External Data Memory Write Strobe
P3.7 - !RD, External Data Memory Read Strobe
Port 3 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is bit addressable. To use a port
signal as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups pull
the input high and source current when the input is driven low. To
use a port signal as an output, a 1 or 0 written to the port location is
presented at the output.
Port signals in this port also serve as I/O for 80C152 functions.
These I/O signals are defined next to the port name.
P4.0
P4.1
P4.2
Port 4 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is bit addressable. To use a port
signal as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups pull
the input high and source current when the input is driven low. To
Page 6
Page 6 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Table 2 - I/O Signal Descriptions
Signal Name Description
P4.3
P4.4
P4.5
P4.6
P4.7
use a port signal as an output, a 1 or 0 written to the port location is
presented at the output.
P5.0
P5.1
P5.2
P5.3
P5.4
P5.5
P5.6
P5.7
Port 5 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is NOT bit addressable. To use
the port as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups
pull the input high and source current when the input is driven low.
To use the port as an output, 1s or 0s written to the port are
presented at the output.
This port also provides the low-byte of the multiplexed address and
data bus depending on the state of !EBEN.
P6.0
P6.1
P6.2
P6.3
P6.4
P6.5
P6.6
P6.7
Port 6 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is NOT bit addressable. To use
the port as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups
pull the input high and source current when the input is driven low.
To use the port as an output, 1s or 0s written to the port are
presented at the output.
This port also provides the high-byte of the multiplexed address and
data bus depending on the state of !EBEN.
VCC Supply Voltage
VSS Device Ground
XTAL1 Input to the internal clock generator
XTAL2 Output from the internal oscillator amplifier
Memory Space
Memory space is divided up into program and data memory. Program memory is all external to the
IA80C152. Data memory is divided up into external and internal data memory. There can be up to
64K bytes of external program and data memory. Internal data memory is 256 bytes that is
mapped between RAM, SFRs, and Register Banks. Figure 5 diagrams the organization of the
IA80C152 memory space. See the C8051 section for further details.
Program memory is accessed using control signals and ports. On the JA and JC versions of the
IA80C152 this access is performed through ports P0 and P2. Further, since there is no internal
ROM, the entire program memory space is accessed via ports P0 and P2. On the JB and JD
version of the IA80C152, program memory access can be through either ports P0 and P2, or ports
P5 and P6. Which set of ports program memory fetches are made is controlled by the input signals
!EA and !EBEN. Table 3 summarizes the IA80C152 versions and the relationship to program
memory fetches.
Page 7

Page 7 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Figure 5 - Memory Space
Table 3 - Summary of Program Memory Fetches
Fetch Control Fetch Signal
Version
EBEN EA
Fetch Ports
PSEN EPSEN
Memory Space
JA, JC N/A 0 or 1 P0, P2 Active - 0h - FFFFh
0 0 P0, P2 Active - 0h - FFFFh
1 0 P5, P6 - Active 0h - FFFFh
P5, P6 - Active 0h - 1FFFh
JB, JD
1 1
P0, P2 Active - 2000h - FFFFh
Summary of the 80C152 Registers and Interrupts
The 80C152 combines the register set of the 8051BH and additional SFRs for the DMA and GSC
functions. Likewise, the 80C152 combines the interrupts of the 8051BH and the interrupts
required by the DMA and GSC. Table 4 contains a summary of the 80C152 registers, and table 5
contains a summary of the 80C152 interrupts.
External RAM
00H
FFFFH
0000H
Internal RAM
7FH
8000H
4000H
C000H
80H
FFH
Lower 128
Bytes
Upper 128
Bytes
SFR Space
Page 8
Page 8 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Table 4 - SFR Summary
Item
Register
Name
Register
Address
Functional
Block Description
Initial
Value
1. A 0E0h C8051 Accumulator 00h
2. ADR0 095h GSC Address Match 0 00h
3. ADR1 0A5h GSC Address Match 1 00h
4. ADR2 0B5h GSC Address Match 2 00h
5. ADR3 0C5h GSC Address Match 3 00h
6. AMSK0 0D5h GSC Address Mask 0 00h
7. AMSK1 0E5h GSC Address Mask 1 00h
8. B 0F0h C8051 B Register 00h
9. BAUD 094h GSC Baud Rate 00h
10. BCRL0 0E2h DMA Byte Count Register (Low) 0 X
11. BCRH0 0E3h DMA Byte Count Register (High) 0 X
12. BCRL1 0F2h DMA Byte Count Register (Low) 1 X
13. BCRH1 0F3h DMA Byte Count Register (High) 1 X
14. BKOFF 0C4h GSC Backoff Timer X
15. DARL0 0C2h DMA Destination Address Register (Low) 0 X
16. DARH0 0C3h DMA Destination Address Register (High) 0 X
17. DARL1 0D2h DMA Destination Address Register (Low) 1 X
18. DARH1 0D3h DMA Destination Address Register (High) 1 X
19. DCON0 092h DMA DMA Control 0 00h
20. DCON1 093h DMA DMA Control 1 00h
21. DPH 083h C8051 Data Pointer High 00h
22. DPL 082h C8051 Data Pointer Low 00h
23. GMOD 084h GSC GSC Mode X0000000b
24. IE 0A8h C8051 Interrupt Enable 0XX00000b
25. IEN1 0C8h DMA, GSC Interrupt Enable 1 XX000000b
26. IFS 0A4h GSC Interframe Space 00h
27. IP 0B8h C8051 Interrupt Priority XXX00000b
28. IPN1 0F8h DMA, GSC Interrupt Priority 1 XX000000b
29. MYSLOT 0F5h GSC GSC Slot Address 00h
30. P0 080h C8051 Port 0 0FFh
31. P1 090h C8051 Port 1 0FFh
32. P2 0A0h C8051 Port 2 0FFh
33. P3 0B0h C8051 Port 3 0FFh
34. P4 0C0h C8051 Port 4 0FFh
35. P5 091h C8051 Port 5 0FFh
36. P6 0A1h C8051 Port 6 0FFh
37. PCON 087h C8051 Power Control 0XXX0000b
38. PRBS 0E4h GSC Pseudo-Random Sequence 00h
39. PSW 0D0h C8051 Program Status Word 00h
40. RFIFO 0F4h GSC Receive FIFO X
41. RSTAT 0E8h GSC Receive Status 00h
42. SARL0 0A2h DMA Source Address Register (Low) 0 X
43. SARH0 0A3h DMA Source Address Register (High) 0 X
44. SARL1 0B2h DMA Source Address Register (Low) 1 X
45. SARH1 0B3h DMA Source Address Register (High) 1 X
46. SBUF 099h C8051 Serial Channel Buffer (UART) X
47. SCON 098h C8051 Serial Channel Control (UART) 00h
48. SLOTTM 0B4h GSC GSC Slot Time 00h
49. SP 081h C8051 Stack Pointer 07h
50. TCDCNT 0D4h GSC Transmit Collision Counter X
51. TCON 088h C8051 Timer Control 00h
Page 9
Page 9 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Table 4 - SFR Summary
Item
Register
Name
Register
Address
Functional
Block Description
Initial
Value
52. TFIFO 085h GSC Transmit FIFO X
53. TH0 08Ch C8051 Timer (High) 0 00h
54. TH1 08Dh C8051 Timer (High) 1 00h
55. TL0 08Ah C8051 Timer (Low) 0 00h
56. TL1 08Bh C8051 Timer (Low) 1 00h
57. TMOD 089h C8051 Timer Mode 00h
58. TSTAT 0D8h GSC Transmit Status XX000100b
Table 5 - Interrupt Summary
Interrupt
Priority
Interrupt
Name
Priority
Symbol
Name
Enable
Symbol
Name
Priority
Address
Enable
Address
Vector
Address
- Enable All Interrupts - EA - 0AFh 1 External Interrupt 0 PX0 EX0 0B8h 0A8h 03h
2 GSC Receive Valid PGSRV EGSRV 0F8h 0C8h 2Bh
3 Timer 0 Overflow PT0 ET0 0B9h 0A9h 0Bh
4 GSC Receive Error PGSRE EGSRE 0F9h 0C9h 33h
5 DMA Channel 0 Done PDMA0 EDMA0 0FAh 0CAh 3Bh
6 External Interrupt 1 PX1 EX1 0BAh 0AAh 13h
7 GSC Transmit Valid PGSTV EGSTV 0FBh 0CBh 43h
8 DMA Channel 1 Done PDMA1 EDMA1 0FCh 0CCh 53h
9 Timer 1 Overflow PT1 ET1 0BBh 0ABh 1Bh
10 GSC Transmit Error PGSRE EGSRE 0FDh 0CDh 4Bh
11 UART Transmit/Receive PS ES 0BCh 0ACh 23h
Power Conservation Modes
There are 2 power conservation modes identified as Idle Mode and Power Down Mode. The
IA80C152 pins will have values according to the Table 6 below.
Idle Mode is entered through software control of the PCON register. Idle halts processor
execution and the DMA. The GSC continue to operate to the extent that it can without the
processor or DMA servicing its requests. Idle mode is exited upon receipt of any enabled interrupt
or invoking a hardware reset.
Power Down Mode is entered through software control of the PCON register. Power Down
disables the oscillator causing all functions to stop. RAM data is maintained since power is not
removed from the device. The only way to exit power down mode is to invoke a hardware reset.
Page 10
Page 10 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
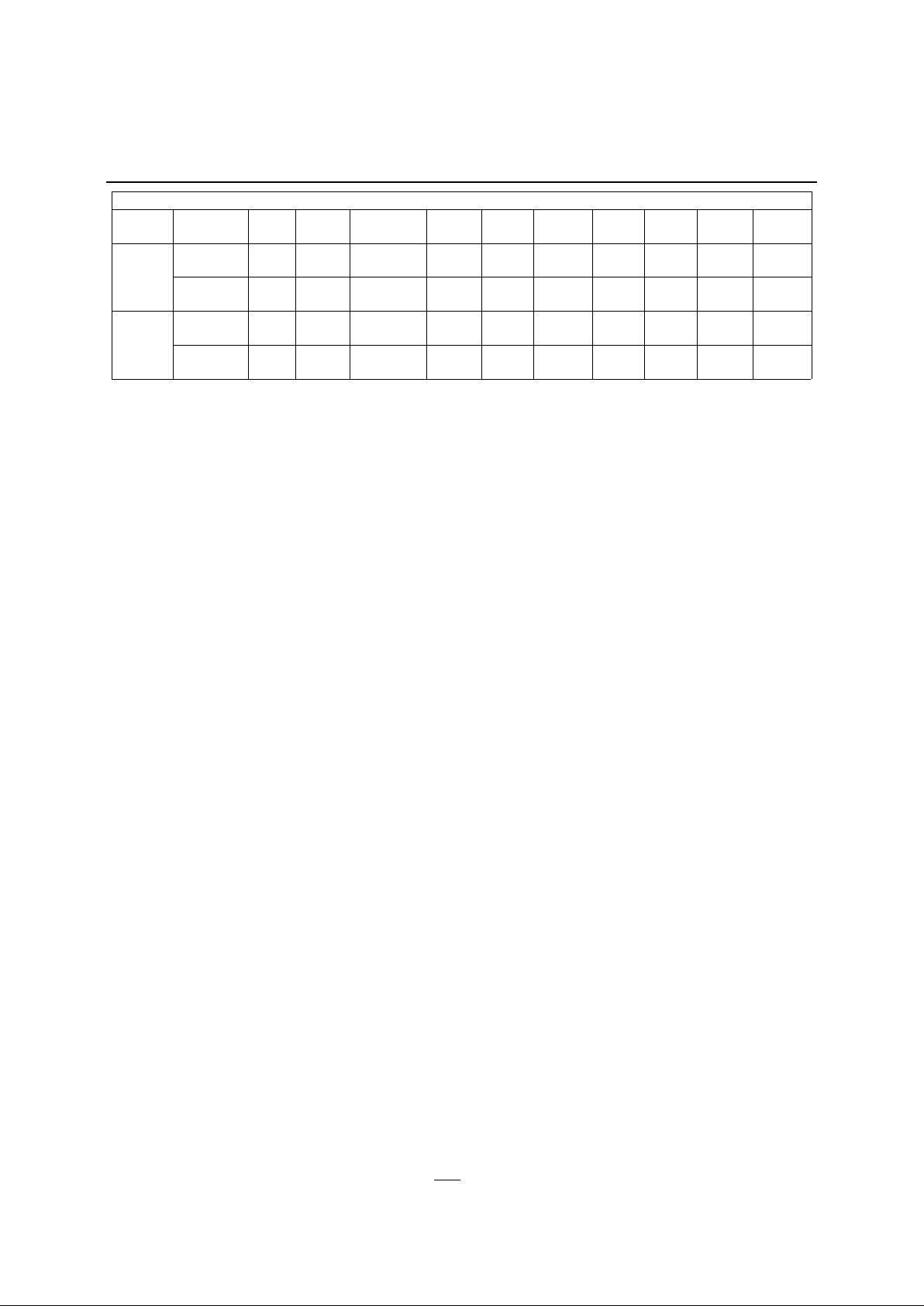
Table 6 - Power Conservation Modes
Mode
Program
Fetch ALE PSEN EPSEN*
Port0Port1Port2Port3Port4Port
5*
Port
6*
P0, P2 1 1 1 Float Data Addr. Data Data 0FFh 0FFhIdle
P5, P6* 1 1 1 Data Data Data Data Data 0FFh Addr.
P0, P2 0 0 1 Float Data Data Data Data 0FFh 0FFhPower
Down
P5, P6* 0 1 0 Data Data Data Data Data 0FFh 0FFh
*JB and JD Versions Only
Oscillator Pins
There are 2 methods for providing a clock to the 80C152. One method is to provide a crystal
oscillator and the other method is to provide an external clock source. When providing a crystal
oscillator, the XTAL1 pin is the input and XTAL2 is the output. The min and max crystal
frequencies are 3.5 MHz and 16.5 MHz, respectively.
When providing an external clock source, XTAL1 is the input and XTAL has no connection. Duty
cycle does not matter to the device, however, the external clock source requires a minimum pulse
width of 20 ns.
Summary of the 8051 Instruction Set
Table 7 provides a summary of the instruction set organized by hexadecimal opcode. Please refer
to the original Intel Data Book for individual instruction set details.
Page 11

Page 11 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Table 7 - Instruction Set Summary
Opcode Mnemonic Opcode Mnemonic Opcode Mnemonic
00 H NOP 30 H JNB bit.rel 60 H JZ rel
01 H AJMP addr11 31 H ACALL addr11 61 H AJMP addr11
02 H LJMP addr16 32 H RETI 62 H XRL direct,A
03 H RR A 33 H RLC A 63 H XRL direct,#data
04 H INC A 34 H ADDC A,#data 64 H XRL A,#data
05 H INC direct 35 H ADDC A,direct 65 H XRL A,direct
06 H INC @R0 36 H ADDC A,@R0 66 H XRL A,@R0
07 H INC @R1 37 H ADDC A,@R1 67 H XRL A,@R1
08 H INC R0 38 H ADDC A,R0 68 H XRL A,R0
09 H INC R1 39 H ADDC A,R1 69 H XRL A,R1
0A H INC R2 3A H ADDC A,R2 6A H XRL A,R2
0B H INC R3 3B H ADDC A,R3 6B H XRL A,R3
0C H INC R4 3C H ADDC A,R4 6C H XRL A,R4
0D H INC R5 3D H ADDC A,R5 6D H XRL A,R5
0E H INC R6 3E H ADDC A,R6 6E H XRL A,R6
0F H INC R7 3F H ADDC A,R7 6F H XRL A,R7
10 H JBC bit,rel 40 H JC rel 70 H JNZ rel
11 H ACALL addr11 41 H AJMP addr11 71 H ACALL addr11
12 H LCALL addr16 42 H ORL direct,A 72 H ORL C,direct
13 H RRC A 43 H ORL direct,#data 73 H JMP @A+DPTR
14 H DEC A 44 H ORL A,#data 74 H MOV A,#data
15 H DEC direct 45 H ORL A,direct 75 H MOV direct,#data
16 H DEC @R0 46 H ORL A,@R0 76 H MOV @R0,#data
17 H DEC @R1 47 H ORL A,@R1 77 H MOV @R1,#data
18 H DEC R0 48 H ORL A,R0 78 H MOV R0.#data
19 H DEC R1 49 H ORL A,R1 79 H MOV R1.#data
1A H DEC R2 4A H ORL A,R2 7A H MOV R2.#data
1B H DEC R3 4B H ORL A,R3 7B H MOV R3.#data
1C H DEC R4 4C H ORL A,R4 7C H MOV R4.#data
1D H DEC R5 4D H ORL A,R5 7D H MOV R5.#data
1E H DEC R6 4E H ORL A,R6 7E H MOV R6.#data
1F H DEC R7 4F H ORL A,R7 7F H MOV R7.#data
20 H JB bit.rel 50 H JNC rel 80 H SJMP rel
21 H AJMP addr11 51 H ACALL addr11 81 H AJMP addr11
22 H RET 52 H ANL direct,A 82 H ANL C,bit
23 H RL A 53 H ANL direct,#data 83 H MOVC A,@A+PC
24 H ADD A,#data 54 H ANL A,#data 84 H DIV AB
25 H ADD A,direct 55 H ANL A,direct 85 H MOV direct,direct
26 H ADD A,@R0 56 H ANL A,@R0 86 H MOV direct,@R0
27 H ADD A,@R1 57 H ANL A,@R1 87 H MOV direct,@R1
28 H ADD A,R0 58 H ANL A,R0 88 H MOV direct,R0
29 H ADD A,R1 59 H ANL A,R1 89 H MOV direct,R1
2A H ADD A,R2 5A H ANL A,R2 8A H MOV direct,R2
2B H ADD A,R3 5B H ANL A,R3 8B H MOV direct,R3
2C H ADD A,R4 5C H ANL A,R4 8C H MOV direct,R4
2D H ADD A,R5 5D H ANL A,R5 8D H MOV direct,R5
2E H ADD A,R6 5E H ANL A,R6 8E H MOV direct,R6
2F H ADD A,R7 5F H ANL A,R7 8F H MOV direct,R7
90 H
MOV DPTR,#data16 C0 H PUSH direct
F0 H MOVX @DPTR,A
91 H
ACALL addr11 C1 H AJMP addr11
F1 H ACALL addr11
92 H MOV bit,C C2 H CLR bit F2 H MOVX @R0,A
Page 12

Page 12 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Table 7 - Instruction Set Summary
Opcode Mnemonic Opcode Mnemonic Opcode Mnemonic
93 H MOVC A,@A+DPTR C3 H CLR C F3 H MOVX @R1,A
94 H SUBB A,#data C4 H SWAP A F4 H CPL A
95 H SUBB A,direct C5 H XCH A,direct F5 H MOV direct,A
96 H SUBB A,@R0 C6 H XCH A,@R0 F6 H MOV @R0,A
97 H SUBB A,@R1 C7 H XCH A,@R1 F7 H MOV @R1,A
98 H SUBB A,R0 C8 H XCH A,R0 F8 H MOV R0,A
99 H SUBB A,R1 C9 H XCH A,R1 F9 H MOV R1,A
9A H SUBB A,R2 CA H XCH A,R2 FA H MOV R2,A
9B H SUBB A,R3 CB H XCH A,R3 FB H MOV R3,A
9C H SUBB A,R4 CC H XCH A,R4 FC H MOV R4,A
9D H SUBB A,R5 CD H XCH A,R5 FD H MOV R5,A
9E H SUBB A,R6 CE H XCH A,R6 FE H MOV R6,A
9F H SUBB A,R7 CF H XCH A,R7 FF H MOV R7,A
A0 H ORL C,bit D0 H POP direct
A1 H AJMP addr11 D1 H ACALL addr11
A2 H MOV C,bit D2 H SETB bit
A3 H INC DPTR D3 H SETB C
A4 H MUL AB D4 H DA A
A5 H - D5 H DJNZ direct,rel
A6 H MOV @R0,direct D6 H XCHD A,@R0
A7 H MOV @R1,direct D7 H XCHD A,@R1
A8 H MOV R0,direct D8 H DJNZ R0,rel
A9 H MOV R1,direct D9 H DJNZ R1,rel
AA H MOV R2,direct DA H DJNZ R2,rel
AB H MOV R3,direct DB H DJNZ R3,rel
AC H MOV R4,direct DC H DJNZ R4,rel
AD H MOV R5,direct DD H DJNZ R5,rel
AE H MOV R6,direct DE H DJNZ R6,rel
AF H MOV R7,direct DF H DJNZ R7,rel
B0 H ANL C,bit E0 H MOVX A,@DPTR
B1 H ACALL addr11 E1 H AJMP addr11
B2 H CPL bit E2 H MOVX A,@R0
B3 H CPL C E3 H MOVX A,@R1
B4 H CJNE A,#data,rel E4 H CLR A
B5 H CJNE A,direct,rel E5 H MOV A,direct
B6 H CJNE @R0,#data,rel E6 H MOV A,@R0
B7 H CJNE @R1,#data,rel E7 H MOV A,@R1
B8 H CJNE R0,#data,rel E8 H MOV A,R0
B9 H CJNE R1,#data,rel E9 H MOV A,R1
BA H CJNE R2,#data,rel EA H MOV A,R2
BB H CJNE R3,#data,rel EB H MOV A,R3
BC H CJNE R4,#data,rel EC H MOV A,R4
BD H CJNE R5,#data,rel ED H MOV A,R5
BE H CJNE R6,#data,rel EE H MOV A,R6
BF H CJNE R7,#data,rel EF H MOV A,R7
Page 13

Page 13 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
80C152 Register Set Descriptions
The following are detailed descriptions for the IA80C152 register set. This register set is the same
for all versions of the IA80C152. There is no difference between the IA80C152 register set and the
register set for the original device.
In addition to the registers listed below, there are four banks of eight general purpose registers (R0
through R7) which reside within internal RAM space. Selection of these register banks is controlled
through the Program Status Word (PSW).
The register descriptions are listed in alphanumeric order. The asterisk (*) indicates the register is bit
addressable.
A* (0E0h) - Accumulator register used for various memory, arithmetic, and logic operations.
ADR0,1,2,3 (095h, 0A5h, 0B5h, 0c5h) - Address match registers contain the values which determine which data will be
accepted as valid. If using 8 bit addressing mode a match with any of the four registers will cause the data to be accepted.
If using 16 bit addressing mode a match with the pairs ADR1 and ADR2 or ADR3 and ADR2 will cause the data to be
accepted. A received address of all 1s will be accepted regardless of whether the address mode is 16 bit or 8 bit.
B* (0F0h) - B register used for multiply and divide instructions. May also be used as a general purpose register.
AMSK0,1 (0D5h, 0E5h) - Address Match Mask registers are used to set the corresponding bit in Address match registers
to don’t care. Setting the bit to a one in the AMSK register sets the corresponding bit in the ADR register to don’t care.
BAUD (094h) - Contains the value to be used by the baud rate determining equation. The value written to BAUD will
actually be stored in a reload register. When the BAUD register contents are decremented to 00H the BAUD register will
be reloaded from the reload register. Reading the BAUD register yields the current baud rate timer value. A read during a
GSC operation may not give the current value since the value in BAUD could decrement after it is read and before the
read value can be stored in its destination.
BCRL0, BCRH0 (0E2h, 0E3h) - Byte count register high and low bytes for DMA channel 0. The two registers provide
a 16-bit value representing for the number of DMA transfers via channel 0. Valid count range is from 0 to 65535.
BCRL0, BCRH0 (0F2h, 0F3h) - Byte count register high and low bytes for DMA channel 1. The two registers provide
a 16-bit value representing for the number of DMA transfers via channel 1. Valid count range is from 0 to 65535.
BKOFF (0C4h) - An 8 bit count down timer with a clock period equal to one slot time. A user may read the register, but
the register is clocked asynchronously to the CPU so invalid data can result. Writing to BKOFF will have no effect.
DARL0, DARH0 (0C2h, 0C3h) - Destination address register high and low bytes for DMA channel 0. The two
registers provide a 16-bit value representing the address of the destination for a DMA transfer via channel 0. Valid
address range is from 0 to 65535.
DARL0, DARH0 (0D2h, 0D3h) - Destination address register high and low bytes for DMA channel 1. The two
registers provide a 16-bit value representing the address of the destination for a DMA transfer via channel 1. Valid
address range is from 0 to 65535.
DCON0,1 (092h, 093h) - DCON0 and DCON1 control DMA channel 0 or 1, respectively. Each bit in these 8-bit
registers control the DMA transfer as described below.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
DAS IDA SAS ISA DM TM DONE GO
DAS - This bit in conjunction with IDA determine the destination address space.
Page 14

Page 14 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
IDA - If IDA is set to 1 then the destination address is automatically incremented after the transfer of each byte.
DAS IDA Destination Auto-Increment
0 0 External Ram NO
0 1 External Ram YES
1 0 SFR NO
1 1 Internal RAM YES
SAS - This bit in conjunction with ISA determine the source address space.
ISA - If ISA is set to 1 then the source address is automatically incremented after the transfer of each byte.
SAS ISA Source Auto-Increment
0 0 External Ram NO
0 1 External Ram YES
1 0 SFR NO
1 1 Internal RAM YES
DM - If this bit is set to a 1 then the DMA channel operates in demand mode. In this mode the DMA is initiated by
either an external signal or by a serial port flag depending on the value of the TM bit. If the DM bit is set to a 0 then
DMA is initiated by setting the GO bit.
TM - If DM is 1 then TM selects if DMA is initiated by an external signal (TM=1) or by a serial port bit (TM=0). If
DM is 0 then TM selects whether DMA transfers are in burst mode (TM=1) or in alternate cycles mode (TM=0).
DM TM Mode
0 0 Alternate Cycles
0 1 Burst
1 0 Serial Port Demand
1 1 External Demand
DONE - This bit indicates that the DMA operation has completed. It also causes an interrupt. This bit is set to 1
when BCRn equals 0 and is set to 0 when the interrupt is vectored to. The user can also set and clear this bit.
GO - If this bit is set to 1 it enables the DMA channel.
DPL, DPH (082h, 083h) - DPTR, or the "data pointer" consists of the two 8-bit registers, DPL and DPH. The DPTR
must be used for accesses to external memory requiring 16-bit addresses.
GMOD (084h) - An 8-bit register that controls the GSC Modes as described below.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
XTCLK M1 M0 AL CT PL1 PL0 PR
PR - If set to a 1 the GSC is in SDLC mode. If set to a 0 the GSC is in CSMA/CD mode.
PL0,1 - Preamble length:
PL1 PL0 Preamble length in bits
0 0 0
0 1 8
1 0 32
1 1 64
The length noted in the table includes the two bit BOF in CSMA/CD mode but not the SDLC flag. Zero length
preamble is not compatible with CSMA/CD mode.
CT - This bit determines the CRC type used. If set to a 1 the 32 bit AUTODIN II-32 is used. If set to a 0 the 16 bit
Page 15

Page 15 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
CRC-CCITT is used.
AL - This bit determines the address length used. If set to a 1 the 16 bit addressing is used. If set to a 0 the 8 bit
addressing is used.
M1,M0 - These bits contain the backoff mode select bits as defined in the following table.
M1 M0 Mode
0 0 Normal
0 1 Raw Transmit
1 0 Raw Receive
1 1 Alternate Backoff
In Raw Receive mode the transmitter operates normally. The receiver operates normally except that all the bytes
following the BOF are loaded into the receive FIFO including the CRC.
In the Raw Transmit mode the receiver operates as normal and zero bit detection is performed. The transmit output
is driven from the receiver input. Data transmitted is done so without a preamble, flag or zero bit insertion and
without a CRC.
In the Alternate Backoff mode the backoff is modified so it is delayed until the end of the IFS. Since the IFS time is
generally longer than the slot time this should help to prevent collisions.
XTCLK - This bit enables the use of an external transmit clock. A 1 enables the external clock (input on port 1, bit 3),
a zero enables the internal baud rate generator.
IE* (0A8h) - The Interrupt Enable register allows the software to select which interrupts are enabled per the table below.
If a bit is 0, the interrupt is disabled. If a bit is 1, the interrupt is enabled.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
EA - - ES ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0
EA - Enable All interrupts. This bit globally enables or disables all interrupts regardless of the state of the individual
bits.
ES - Enable or disable serial port interrupt.
ET1 - Enable or disable Timer 1 overflow interrupt.
EX1 - Enable or disable External Interrupt 1.
ET0 - Enable or disable Timer 0 overflow interrupt.
EX0 - Enable or disable External Interrupt 0.
IEN1* (0C8h) - The Interrupt Enable Number 1 register allows the software to select which interrupts are enabled per
the table below. If a bit is 0, the interrupt is disabled. If a bit is 1, the interrupt is enabled.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - EGSTE EDMA1 EGSTV EDMA0 EGSRE EGSRV
EGSTE - Enable or disable GSC Transmit Error interrupt.
EDMA1 - Enable or disable DMA channel 1 interrupt.
EGSTV - Enable or disable GSC Transmit Valid interrupt.
EDMA0 - Enable or disable DMA channel 0 interrupt.
Page 16

Page 16 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
EGSRE - Enable or disable GSC Receive Error interrupt.
EGSRV - Enable or disable GSC Receive Valid interrupt.
IFS (0A4h) - The Interframe Spacing register determines the number of bit times between transmitted frames in both
CSMA/CD and SDLC. Only even bit times can be used. The number written to this register is divided by two and
loaded into the seven most significant bits. An interframe space is created by counting down this seven bit number twice.
The value read from this register is the current count value in the upper seven bits and the first or second count down in
the LSB. A 1 indicates the first count down and a 0 indicates the second count down. The value may not be valid since
the register is clocked asynchronously to the CPU.
IP* (0B8h) - The Interrupt Priority register allows the software to select which interrupts have a higher than normal
priority. If a bit is 0, the interrupt has normal priority. If a bit is 1, the interrupt has a higher priority. When multiple bits
are set to higher priority, interrupts are resolved in the same order as their normal priority setting.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - - PS PT1 PX1 PT0 PX0
PS - Set normal or higher priority level for serial port interrupt.
PT1 - Set normal or higher priority level for Timer 1 overflow interrupt.
PX1 - Set normal or higher priority level for External Interrupt 1.
PT0 - Set normal or higher priority level for Timer 0 overflow interrupt.
PX0 - Set normal or higher priority level for External Interrupt 0.
IPN1* (0F8h) - The Interrupt Enable Number 1 register allows the software to select which interrupts have a higher than
normal priority. If a bit is 0, the interrupt has normal priority. If a bit is 1, the interrupt has a higher priority. When
multiple bits are set to higher priority, interrupts are resolved in the same order as their normal priority setting.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - PGSTE PDMA1 PGSTV PDMA0 PGSRE PGSRV
PGSTE - Set normal or higher priority level for GSC Transmit Error interrupt.
PDMA1 - Set normal or higher priority level for DMA channel 1 interrupt.
PGSTV - Set normal or higher priority level for GSC Transmit Valid interrupt.
PDMA0 - Set normal or higher priority level for DMA channel 0 interrupt.
PGSRE - Set normal or higher priority level for GSC Receive Error interrupt.
PGSRV - Set normal or higher priority level for GSC Receive Valid interrupt.
MYSLOT (0F5h) - Register that controls the slot address for the devices as well as the type of Jam used and which
backoff algorithm is used during a collision.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
DCJ DCR SA5 SA4 SA3 SA2 SA1 SA0
SA5-0 - The six slot address bits determine not only the address but also the priority. Addresses 0 through 63 are
available with 63 having the highest priority and 1 the lowest. An address of 0 will prevent a station from transmitting
during the collision resolution period.
DCR - The Deterministic Collision Resolution register determines which resolution algorithm to use. Setting this bit
Page 17

Page 17 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
to a 1 selects the alternate collision resolution algorithm. Also disabled by setting this bit is the retriggering of the IFS
on the reappearance of the carrier. Alternate Backoff mode must be used with this feature. The user must initialize
TCDCNT with the maximum number of slots that are appropriate for the system. To disable the PBRS this register
must be set to all 1s.
DCJ - A 1 selects DC type jam. A 0 selects AC type jam.
P0*, P1*, P2*, P3*, P4*, P5, P6 (080h, 090h, 0A0h, 0C0h, 091h, 0A1h) - These registers are for I/O as defined in the
table below. Most registers have a dual function. P5 and P6 are not bit addressable and are only available in the JB and JD
versions of the IC.
Port Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Function Multiplexed Address/DataP0
Bit Address 087h 086h 085h 084h 083h 082h 081h 080h
Function - HLDA HLD RXCn TXCn DENn GTXD GRXDP1
Bit Address 097h 096h 095h 094h 093h 092h 091h 090h
Function Address and User DefinedP2
Bit Address 0A7h 0A6h 0A5h 0A4h 0A3h 0A2h 0A1h 0A0h
Function RDn WRn T1 T0 INT1n INT0n TXD RXDP3
Bit Address 0B7h 0B6h 0B5h 0B4h 0B3h 0B2h 0B1h 0B0h
Function User DefinedP4
Bit Address 0C7h 0C6h 0C5h 0C4h 0C3h 0C2h 0C1h 0C0h
Function User DefinedP5
Bit Address 091h
Function User DefinedP6
Address 0A1h
PCON (087h) - The POwer CONtrol register controls the power down and idle states of the 80C152 as well as various
UART, GSC, and DMA functions as defined below.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SMOD ARB REQ GAREN XRCLK GFIEN PD IDL
SMOD - Doubles the baud rate of the UART if the bit is set to 1.
ARB - The DMA (both channels) is put into ARBiter mode if the bit is set to 1.
REQ - The DMA (both channels) is put into REQuester mode if the bit is set to 1.
GAREN - The GSC Auxiliary Receive Enable allows the GSC to receive back-to-back SDLC frames by setting the bit
to 1. This bit has no effect in CSMA mode.
XRCLK - Setting this bit enables the External Receive Clock to be used by the receiver portion of the GSC.
GFIEN - The GSC Flag Idle Enable bit generates idle flags between transmitted SDLC frames when this bit is set to a
1. This bit has no effect in CSMA mode.
PD - The Power Down bit puts the 80C152 into the power down power saving mode by setting this bit to a 1.
IDL - The IDLe bit puts the 80C152 into the idle power saving mode by setting this bit to a 1.
PRBS (0E4h) - This register contains the pseudo-random number to be used in the CSMA/CD backoff algorithm. The
number is generated by using a feedback shift register clocked by the CPU phase clocks. Writing all 1s to this register will
cause the register to freeze at all 1s. Writing any other value to it will cause it to start again. A read of this register will not
always give the seed value due to the register being clocked by the CPUs phase clocks.
Page 18

Page 18 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
PSW* (0D0h) - The Program Status Word register provides arithmetic and other microcontroller status as well as control
for the selection of register banks 0 through 4.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV - P
CY - Carry Flag set to 1 if an instruction execution results in a carry.
AC - Auxiliary Carry Flag set to 1 if an instruction execution results in a carry.
F0 - Flag 0 available for user defined general purpose.
RS1, RS0 - Register bank Select 1 bit and Register bank Select 0 bit in combination define the current register bank to
be used by the microprocessor. See table below.
Register Bank RS1 RS0 Register Bank Addresses
0 0 0 00h-07h
1 0 1 08h-0Fh
2 1 0 10h-17h
3 1 1 18h-1fh
OV - The OVerflow bit indicates an arithmetic overflow when set to a 1.
P - Parity flag set or cleared by the hardware each instruction to indicate odd or even number of 1's in the
accumulator.
RFIFO (0F4h) - This is a 3 byte buffer which points to the oldest data in the buffer. The buffer is loaded with receive
data every time the receiver receives a new byte of data.
RSTAT* (0E8h) - This register provides status of the GSC receiver as defined below.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
OR RCABT AE CRCE RDN RFNE GREN HABEN
HABEN - The Hardware Based Acknowledge Enable when set to a 1 enables this feature.
GREN - When this bit is set the receiver is enabled to accept incoming frames. RFIFO should be cleared before
setting this bit by reading RFIFO until RFNE = 0. This should be done since setting GREN to a 1 clears RFIFO. It
takes twelve clock cycles for the status of RFNE to be updated after a read of RFIFO. Setting GREN also clears
RDN, CRCE, AE and RCABT. GREN is cleared by hardware at the end of a reception or if receive errors are
encountered. The user is responsible for setting this bit to a 1. The user or the GSC can set this bit to a 0. In
CSMA/CD mode the status of GREN has no effect on whether the receiver detects a collision since the receiver
always monitors the receive pin.
RFNE - This bit if set indicates that the receive FIFO is not empty. This flag is controlled by the GSC. If all the data
is read from the FIFO the GSC will clear the bit.
RDN - This bit is controlled by the GSC and if set indicates a successful receive operation has occurred. This bit will
not be set if a CRC, alignment, abort, or FIFO overrun error occurred.
CRCE - This bit is controlled by the GSC and if set indicates that a properly aligned frame was received without a
mismatched CRC.
AE - This bit is set by the GSC in CSMA/CD mode to indicate that the receiver shift register is not full and the CRC
is bad when the EOF was detected. If the CRC is correct AE will not be set and a misalignment will be assumed to
be caused by ‘dribble bits’ as the line went idle. In SDLC mode AE is set if a non-byte aligned flag is received. CRCE
may also be set.
RCABT - This bit is set by the GSC when a collision is detected after data has been loaded into the receive FIFO in
Page 19

Page 19 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
CSMA/CD mode. In SDLC mode this bit indicates that 7 consecutive 1s were detected before an end flag but after
data was loaded into the receive FIFO. AE may also be set.
OR - This bit is set by the GSC to indicate that the receive FIFO was full and then new data was shifted into it. AE
and /or CRCE may also be set. This flag is cleared by the user.
SARL0, SARH0 (0A2h, 0A3h) - Source address register high and low bytes for DMA channel 0. The two registers
provide a 16-bit value representing the address of the source for a DMA transfer via channel 0. Valid address range is
from 0 to 65535.
SARL1, SARH1 (0B2h, 0B3h) - Source address register high and low bytes for DMA channel 1. The two registers
provide a 16-bit value representing the address of the source for a DMA transfer via channel 1. Valid address range is
from 0 to 65535.
SBUF (099h) - Writes to this register load the transmit register, and reads access the receive register.
SCON* (098h) - This register controls the set up of the UART as defined by the table below.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SM0 SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI
SM0, SM - The combination of these 2 bits controls the mode and type of baud rate.
Mode SM0 SM1 Description Baud Rate
0 0 0 Shift Register (Osc. Freq.)/12
1 0 1 8-bit UART Variable
2 1 0 9-bit UART (Osc. Freq.)/64 or (Osc. Freq.)/32
3 1 1 9-bit UART Variable
SM2 - When this bit is set and the UART mode is 1, RI will not be activated unless a valid stop bit is received. When
this bit is set and the UART mode is 2 or 3, RI will not be activated if the 9th bit is 0.
REN - Setting this bit enables the UART to receive. Clearing this bit disables UART reception.
TB8 - In modes 2 and 3, the value of this bit is transmitted during the 9th bit time. This bit is set or cleared by
software.
RB8 - In modes 2 and 3, this bit is the value of the 9th bit that was received by the UART. In mode 1, this bit is the
value of the stop bit received by the UART.
TI - Transmit Interrupt flag set by hardware upon at the end of the 8th bit in mode 0 or at the beginning of the stop
bit in modes 1, 2, or 3. This bit must be cleared by software to clear the interrupt.
RI - Receive Interrupt flag set by hardware at the end of the 8th bit in mode 0 or halfway through the stop bit in
modes 1, 2, or 3. This bit must be cleared by software to clear the interrupt.
SLOTTM (0B4h) - Determines the length of the slot time in CSMA/CD mode. A slot time equals SLOTTM * (1 /
baud rate). Reads from this location are unreliable since this register is clocked asynchronously to the CPU. Loading a
value of 0 results in a slot time of 256 bit times.
SP (081h) - This register is the stack pointer. Its value points to the memory location that is the beginning of the stack.
TCDCNT (0D4h) - If probabilistic CSMA/CD is used this register contains the number of collisions. The user must
clear this register before transmitting a new frame so the GSC can distinguish between a new frame and the retransmit of a
frame. In deterministic backoff mode TCDCNT is used to hold the maximum number of slots.
TCON* (088h) - This register controls the operation of the Timers 0 and 1 and External Interrupts 0 and 1 as defined by
the table below.
Page 20

Page 20 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0
TF1 - Timer overFlow 1 interrupt flag set by hardware when timer 1 overflows. Hardware clears this flag when the
processor vectors to the interrupt service routine.
TR1 - Timer Run 1 flag set by software to turn on timer 1 and cleared by software to turn off timer 1.
TF0 - Timer overFlow 0 interrupt flag set by hardware when timer 0 overflows. Hardware clears this flag when the
processor vectors to the interrupt service routine.
TR0 - Timer Run 0 flag set by software to turn on timer 0 and cleared by software to turn off timer 0.
IE1 - Interrupt External 1 flag set by hardware when an edge is detected on External Interrupt 1. Hardware clears
this flag when the processor vectors to the interrupt service routine.
IT1 - Interrupt Trigger 1 flag is set by software to specify a falling edge triggered interrupt for External Interrupt 1.
The flag is cleared by software to specify a low level triggered interrupt for External Interrupt 1.
IE0 - Interrupt External 0 flag set by hardware when an edge is detected on External Interrupt 0. Hardware clears
this flag when the processor vectors to the interrupt service routine.
IT0 - Interrupt Trigger 0 flag is set by software to specify a falling edge triggered interrupt for External Interrupt 0.
The flag is cleared by software to specify a low level triggered interrupt for External Interrupt 0.
TFIFO (085h) - This is the 3 byte buffer used for storing transmit data. If TEN is set to a 1 transmission begins as soon
as data is written to TFIFO.
TH0, TL0 (08Ch, 08Ah) - These registers provide the high byte (TH0) and low byte (TL0) values for Timer 0. These
registers may be used together or separately depending on Timer 0 mode bits.
TH1, TL1 (08Dh, 08Bh) - These registers provide the high byte (TH0) and low byte (TL0) values for Timer 0. These
registers may be used together or separately depending on Timer 0 mode bits.
TMOD (089h) - This register controls the set up and modes of Timers 0 and 1 as defined by the table below.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Timer 1 Timer 0
GATE C/Tn M1 M0 GATE C/Tn M1 M0
GATE - When this bit is set, Timers/Counters may be turned on or off by the corresponding External Interrupt, if
the appropriate TR bit is set. When this bit is cleared, Timers/Counters may only be turned on or off by the
appropriate TR bit.
C/Tn - Counter/Timer flag. Set by software for Counter operation, cleared by software for Timer operation.
M1, M0 - Set the mode of the Timers/Counters as defined by the table below.
Mode M1 M0 Description
0 0 0 13-bit Timer
1 0 1 16-bit Timer/Counter
2 1 0 8-bit Auto Reload Timer/Counter
3 1 1 One 8-bit Timer/Counter (TL0) controlled by Timer 0 control bits.
One 8-bit Timer/Counter (TH0) controlled by Timer 1 control bits.
TSTAT* (0D8h) - This register provides status of the GSC transmitter as defined below.
Page 21

Page 21 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
LNI NOACK UR TCDT TDN TFNF TEN DMA
DMA - If this bit is set it indicates that the DMA channels are used to service the RFIFO and TFIFO and that GSC
interrupts occur on TDN and RDN. If set it also enables UR to become set. If this bit is cleared it indicates that the
GSC is operating in normal mode and interrupts occur on TFNF and RFNE.
TEN - When TEN is set it will cause TDN, UR, TCDT and NOACK to be reset and the TFIFO to be cleared. The
transmitter will clear TEN after a successful transmission, a collision during data, CRC or end flag. The user sets the
bit and the user of the GSC can clear the bit. If the bit is cleared during a transmission the transmit pin goes to a high
level. This is the method used to send an abort character in SDLC. DEN is also forced to a high level. An end of
transmission occurs whenever the TFIFO is emptied.
TFNF - If this bit is a 1 TFIFO is not full and new data may be written to it.
TDN - The GSC sets this bit to indicate that a frame transmission completed successfully. If HABEN is set, TDN
will not be set until the end of the IFS so that the acknowledge can be checked. TDN will not be set if an
acknowledge is expected but not received. An acknowledge will not be expected after a broadcast or a multi-cast
packet.
TCDT - The GSC sets this bit to indicate that the transmission stopped due to a collision. The bit is set by a collision
occurring during the data, the CRC or if there are more than 8 collisions.
UR - The GSC sets this bit to indicate that in DMA mode the last bit was shifted out of the transmit register and that
the DMA byte count did not equal 0. When this occurs the transmitter stops without sending the CRC and the end
flag.
NOACK - The GSC sets this bit to indicate that an acknowledge was not received for the previous frame. This bit
will be set only if HABEN is set and no acknowledge is received before the end of the IFS. NOACK will not be set
following a broadcast or a multi-cast packet.
LNI - The GSC sets this bit to indicate that the receive line is idle. In CSMA/CD mode LNI is set if GRXD remains
high for ~ 1.6 bit times. LNI is cleared after a transition on GRXD. In SDLC node LNI is set if 15 consecutive ones
are received.
Page 22

Page 22 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Absolute Maximum Ratings
AC/DC Parameters
Ambient temperature under bias....................................-40°C to +85°C
(2)
Operating temperature…………………………..…-40°C to +85°C
Storage temperature..................................…...................-65°C to +150°C
Voltage on any pin to VSS.............................................-0.3 to (VDD +0.3)
Power dissipation.................................................…........391.1 mW (95°C, 16MHz, 15% Toggle)
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. Operating the
device beyond the conditions indicated in the “recommended operating conditions” section is not recommended. Operation
at the “absolute maximum ratings” may adversely affect device reliability.
Notes: Design, Static and Dynamic Timing Characterization in Progress.
Table 8: DC Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
V
IL
Input Low Voltage
(All Except EAn, EBEN) V
V
IL1
Input Low Voltage
(EAn, EBEN) V
V
IH
Input High Voltage
( Except XTAL1, RSTn) V
V
IH1
Input High Voltage
( XTAL1 RSTn) V
V
OL
Output Low Voltage
(Ports 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) V
V
OL1
Output Low Voltage
(Ports 0, ALE.PSENn, EPSENn) V
V
V
V
V
I
IL
Logical 0 Input Current
(Ports 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) µA
I
TL
Logical 1 to 0
Transition Current
(Ports 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) µA
I
LI
Input Leakage
( Port 0, EAn) µA
RRST Reset Pull-up Resistor k
Ω
I
IH
Logical 1 Input Current (EBEN) µA
mA
100 µA (1)
mA
Power Supply Current:
Active (16.5 MHz)
Idle(16.5 MHz)
Power Down Mode
I
DD
V
OH
Output High Voltage
(Ports 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, COMM9
ALE, PSENn, EPSENn)
V
OH1
Output High Voltage
(Port 0 in External
Bus Mode)
Notes:
(1) Static Idd current is exclusive of input/output drive requirements and is measured with the clocks stopped and all inputs
tied to Vdd or Vss, configured to draw minimum current.
(2) The input and output parametric values in section VII-B, parts 1, 2, and 3, are directly related to ambient temperature and
DC supply voltage. A temperature or supply voltage range other than those specified in the Operating Conditions above will
affect these values and part performance is not guaranteed by innovASIC.
Page 23

Page 23 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
A. C. Characteristics
Table 9:External Program and Data Memory Characteristics
Min Max Min Max
Oscillator Frequency
80C152JA/JC
83C152JA/JC
83C152JB/JD
3.5 12
MHZ
80C152JA/JC-1
83C152JA/JC-1
80C152JB/JD-1
3.5 16.5
MHZ
TLHLL
ALE Pulse Width
ns
TAVLL
Address Valid to ALE Low
ns
TLLAX
Address Hold After ALE Low
ns
TLLIV ALE Low to Valid
Instruction In
ns
TLLPL
ALE Low to PSENn Low
ns
TPLPH PSENn Pulse Width ns
TPLIV
PSENn Low to Valid
Instruction In
ns
TPXIX
Input Instruction
Hold After PSENn
0 0
ns
TPXIZ
Input Instruction
Float After PSENn
ns
TAVIV
Address to Valid
Instruction In
ns
TPLAZ
PSENn Low to Address
Float
ns
TRLRH RDn Pulse Width ns
TWLWH
WRn Pulse Width
ns
TRLDV
RDn Low to Valid
Data In
ns
TRHDX
Data Hold After RDn
0 0 ns
TRHDZ
Data Float After RDn
ns
TLLDV
ALE Low to Valid
Data In
ns
TAVDV
Address to Valid
Data In
ns
TLLWL
ALE Low to RDn or
WRn Low
ns
TAVWL
Address to RDn or
WRn Low
ns
TQVWX Data Valid to WRn
Transition
ns
TWHQX
Data Hold After WRn
ns
TRLAZ
RDn Low to Address
Float
0 0
ns
TWHLH
RDn or WRn High to
ALE High
ns
1/TCLCL
Unit
Variable Oscillator
Symbol Parameter
16.5 MHz
Input leakage is ± 1µA
Page 24

Page 24 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Figure 6: External Program Memory Read Cycle
ALE
PSENn/EPSENn
PORT0/PORT5
PORT2/PORT6
A0-A7 INSTR IN A0-A7
A8-A15 A8-A15A8-A15
TLHLL
TLLPL
TPLPHTAVLL
TLLIV
TPLIV
TPLAZ
TLLAX TPXIX
TPXIZ
TAVIV
Figure 7: External Data Memory Read Cycle
ALE
PSENn
RDn
PORT0
PORT2
A0-A7 FROM R OR DPL
DATA IN
A0-A7 FROM PCL
INSTR. IN
P2.0-P2.7 OR A8-A15 FROM DPH A8-A15 FROM PCHP2.0-P2.7 OR A8-A15 FROM DPH
TWHLHTLLDV
TLLWL TRLRH
TAVLL
TLLAX
TRLDV
TRLAZ
TRHDX
TRHDZ
TAVDV
TAVWL
Page 25

Page 25 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Figure 8: External Data Memory Write Cycle
ALE
PSENn
WRn
PORT0
PORT2
A0-A7 FROM R OR DPL
DATA OUT
A0-A7 FROM PCL
INSTR. IN
P2.0-P2.7 OR A8-A15 FROM DPH A8-A15 FROM PCHP2.0-P2.7 OR A8-A15 FROM DPH
TWHLHTLLWL TWLWH
TQVWXTAVLL
TLLAX
TWHQX
TAVWL
Table 10: External Clock Drive
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units
1/TCLCL Oscillator Frequency
3.5 16.5
MHz
TCHCX High Time
20
ns
TCLCX Low Time
20
ns
TCLCH Rise Time
20
ns
TCHCL Fall Time
20
ns
Figure 9: External Clock Drive Waveform
Vcc - 0.5
0.7 V
cc
0.2 V
cc
- 0.1
0.45V
TCHCL TCLCX
TCHCX
TCLCH
TCLCL
Page 26

Page 26 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Table 11: Local Serial Channel Timing - Shift Register Mode
Min Max Min Max
TXLXL
Serial Port Clock Cycle
Time
12TCLCL ns
TQVXH
Output Data Setup to
Clock Rising Edge
ns
TXHQX
Output Data Hold After
Clock Rising Edge
ns
TXHDX
Input Data Hold After
Clock Rising Edge
ns
TXHDV
Clock Rising Edge to
Input Data Valid
ns
16.5 MHz Variable Oscillator
UnitsSymbol
Parameter
Figure 10: Shift Register Mode Timing Waveforms
INSTRUCTION
ALE
CLOCK
OUTPUT_DATA
INPUT_DATA
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 77
VALID VALID VALID VALID VALID VALID VALID VALIDVALID
TXLXL
TXHQX
TQVXH
TXHDX
TXHDV
| 0 | | | | | | | | |1 2 3 4 5 6
7
8
|____________|
|_________|
^
|
WRITE TO SBUF
CLEAR R1
^
|
^
|
^
|
SET T1
SET R1
Page 27

Page 27 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Table 12: Global Serial Port Timings - Internal Baud Rate Generator
Min Max Min Max
HBTJR
Allowable jitter on
the Receiver for 1/2
bit time (Manchester
encoding only)
0.0375
µs
FBTJR
Allowable jitter on
the Receiver for one
full bit time (NRZI
and Manchester)
0.10
µs
HBTJT
Jitter of data from
Transmitter for 1/2
bit time (Manchester
encoding only)
± 10 ± 10
ns
FBTJT
Jitter of data from
Transmitter for one
full bit time (NRZI
and Manchester)
± 10 ± 10
ns
DRTR
Data rise time for
Receiver
20.00 20.00
ns
DFTR
Data fall time for
Receiver
20.00 20.00
ns
UnitSymbol Parameter
16.5 MHz (BAUD = 0) Variable Oscillator
Figure 11: GSC Receiver Timings (Internal Baud Rate Generator)
MANCHESTER
NRZI
BT
HBTJR
HBTJR FBTJR
FBTJR
FBTJR
FBTJR
GRxD
GRxD
Figure 12: GSC Transmit Timings (Internal Baud Rate Generator)
MANCHESTER
NRZI
BT
HBTJT FBTJT
FBTJT
FBTJT
FBTJT
HBTJT
GTxD
GTxD
Page 28

Page 28 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Table 13: Global Serical Port Timings - External Clock
Min Max Min Max Unit
1/ECBT
GSC Frequency with an
External Clock
2.4 0.009
MHz
ECH
External Clock High ns
ECL
External Clock Low ns
ECRT
External Clock Rise
Time
ns
ECFT
External Clock Fall
Time
ns
ECDVT
External Clock to Data
Valid Out - Transmit
(To External Clock
Negative Edge)
ns
ECDHT
External Clock to Data
Hold - Transmit
(To External Clock
Negative Edge)
ns
ECDSR
External Clock to Data
Set-up - Receiver
(To External Clock
Positive Edge)
ns
ECDHR
External Clock to Data
Hold - Receiver
(To External Clock
Positive Edge)
ns
Symbol Parameter
16.5 MHz Variable Oscillator
Figure 13: GSC Timings (External Clock)
EXTERNAL_CLOCK
TRANSMIT_DATA
EXTERNAL_CLOCK
RECEIVE_DATA
ECBT
ECBT
ECL ECH
ECDHT
ECDVT
ECDSR
ECDHR
Page 29

Page 29 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
.10
.51 MIN.
R 1.14 / .64
SEATING PLANE
A1
e
.81 / .66
A
.53 / .33
D2 / E2
SIDE VIEW
PLCC Packaging Dimensions (Theta J = TBD)
LEAD COUNT
68 (in Millimeters)
Symbol
MIN MAX
A 4.20 5.08
A1 2.29 3.30
D1 24.13 24.33
D2 22.61 23.62
D3 20.32 BSC
E1 24.13 24.33
E2 22.61 23.62
E3 20.32 BSC
e 1.27 BSC
D 25.02 25.27
E 25.02 25.27
D
D1
E
E1
BOTTOM VIEW
D3
E3
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER & ZONE
1.22/1.07
2 PLCS
TOP VIEW
Page 30

Page 30 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
PDIP Packaging Dimensions (Theta J = TBD)
Lead Count
48 (in Inches)
Symbol
MIN MAX
A - .200
A1 .015 -
B .015 .020
B1 .040 .060
C .008 .012
D 2.455 2.460
E .580 .610
E1 .520 .560
e .100 TYP
eA .580 eB - .686
L .100 MIN
B2 - -
S - -
D
L
A1
A
B
B1
e
SIDE VIEW (LENGTH)
LEAD 1
IDENTIFIER
1
LEAD COUNT
DIRECTION
E1
E
TOP
eA
eB
C
SIDE VIEW (WIDTH)
Page 31

Page 31 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Packaging Options
The IA80C152 is available in four versions, two package styles, and two environmental classes as
shown in the table below.
Package Type Version Environment Order Number
Industrial IA80C152JA/JC-PDW48I48 Lead Plastic DIP, 600 mil wide JA/JC
Commercial IA80C152JA/JC-PDW48C
Industrial IA80C152JA/JC-PLC68IJA/JC
Commercial IA80C152JA/JC-PLC68C
Industrial IA80C152JB/JD-PLC68I
68 Lead Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier
JB/JD
Commercial IA80C152JB/JD-PLC68C
The following diagram depicts the innovASIC Product Identification Number.
IAXXXXX-PPPPNNNT/SP
Special Processing:
S = Space
Q = MIL-STD-883
Temperature:
C = Commercial
I = Industrial
M = Military
Number of Leads
Package Type:
Per Package Designator Table
IC Base Number
innovASIC Designator
Page 32

Page 32 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Package Designator Table
Package Type innovASIC Designator
Ceramic side brazed Dual In-line CDB
Cerdip with window CDW
Ceramic leaded chip carrier CLC
Cerdip without window CD
Ceramic leadless chip carrier CLL
PLCC PLC
Plastic DIP standard (300 mil) PD
Plastic DIP standard (600 mil) PDW
Plastic metric quad flat pack PQF
Plastic thin quad flat pack PTQ
Skinny Cerdip CDS
Small outline plastic gull-wing(150 mil body) PSO
Small outline medium plastic gull-wing (207 mil body) PSM
Small outline narrow plastic gull wing (150 mil body) PSN
Small outline wide plastic gull wing (300 mil body) PSW
Skinny Plastic Dip PDS
Shrink small outline plastic (5.3mm .208 body) PS
Thin shrink small outline plastic PTS
Small outline large plastic gull wing (330 mil body) PSL
Thin small outline plastic gull-wing (8 x 20mm) [TSOP] PST
PGA CPGA
BGA CBGA
Contact innovASIC for other package and processing options.
 Loading...
Loading...