Datasheet HM5225405BLTT-75, HM5225405BLTT-A6, HM5225405BLTT-B6, HM5225405BTT-75, HM5225405BTT-A6 Datasheet (ELPID)
...Page 1

4-Mword × 16-bit × 4-bank/8-Mword × 8-bit × 4-bank
Description
HM5225165B-75/A6/B6
HM5225805B-75/A6/B6
HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
256M LVTTL interface SDRAM
133 MHz/100 MHz
/16-Mword × 4-bit × 4-bank
PC/133, PC/100 SDRAM
E0082H10 (1st edition)
(Previous ADE-203-1073B (Z))
Jan. 31, 2001
The HM5225165B is a 256-Mbit SDRAM organized as 4194304-word × 16-bit × 4 bank. The HM5225805B
is a 256-Mbit SDRAM organized as 8388608-word × 8-bit × 4 bank. The HM5225405B is a 256-Mbit
SDRAM organized as 16777216-word × 4-bit × 4 bank. All inputs and outputs are referred to the rising edge
of the clock input. It is packaged in standard 54-pin plastic TSOP II.
Features
• 3.3 V power supply
• Clock frequency: 133 MHz/100 MHz (max)
• LVTTL interface
• Single pulsed RAS
• 4 banks can operate simultaneously and independently
• Burst read/write operation and burst read/single write operation capability
• Programmable burst length: 1/2/4/8
• 2 variations of burst sequence
Sequential (BL = 1/2/4/8)
Interleave (BL = 1/2/4/8)
• Programmable CAS latency: 2/3
Elpida Memory, Inc. is a joint venture DRAM company of NEC Corporation and Hitachi, Ltd.
Page 2

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
• Byte control by DQM : DQM (HM5225805B/HM5225405B)
: DQMU/DQML (HM5225165B)
• Refresh cycles: 8192 refresh cycles/64 ms
• 2 variations of refresh
Auto refresh
Self refresh
Ordering Information
Type No. Frequency CAS latency Package
1
HM5225165BTT-75*
HM5225165BTT-A6
HM5225165BTT-B6*
HM5225165BLTT-75*
HM5225165BLTT-A6
HM5225165BLTT-B6*
HM5225805BTT-75*
HM5225805BTT-A6
HM5225805BTT-B6*
HM5225805BLTT-75*
HM5225805BLTT-A6
HM5225805BLTT-B6*
HM5225405BTT-75*
HM5225405BTT-A6
HM5225405BTT-B6*
HM5225405BLTT-75*
HM5225405BLTT-A6
HM5225405BLTT-B6*
133 MHz
100 MHz
2
100 MHz
1
133 MHz
100 MHz
2
100 MHz
1
133 MHz
100 MHz
2
100 MHz
1
133 MHz
100 MHz
2
100 MHz
1
133 MHz
100 MHz
2
100 MHz
1
133 MHz
100 MHz
2
100 MHz
Notes: 1. 100 MHz operation at CAS latency = 2.
2. 66 MHz operation at CAS latency = 2.
3
2/3
3
3
2/3
3
3
2/3
3
3
2/3
3
3
2/3
3
3
2/3
3
400-mil 54-pin plastic TSOP II (TTP-54D)
Data Sheet E0082H10
2
Page 3
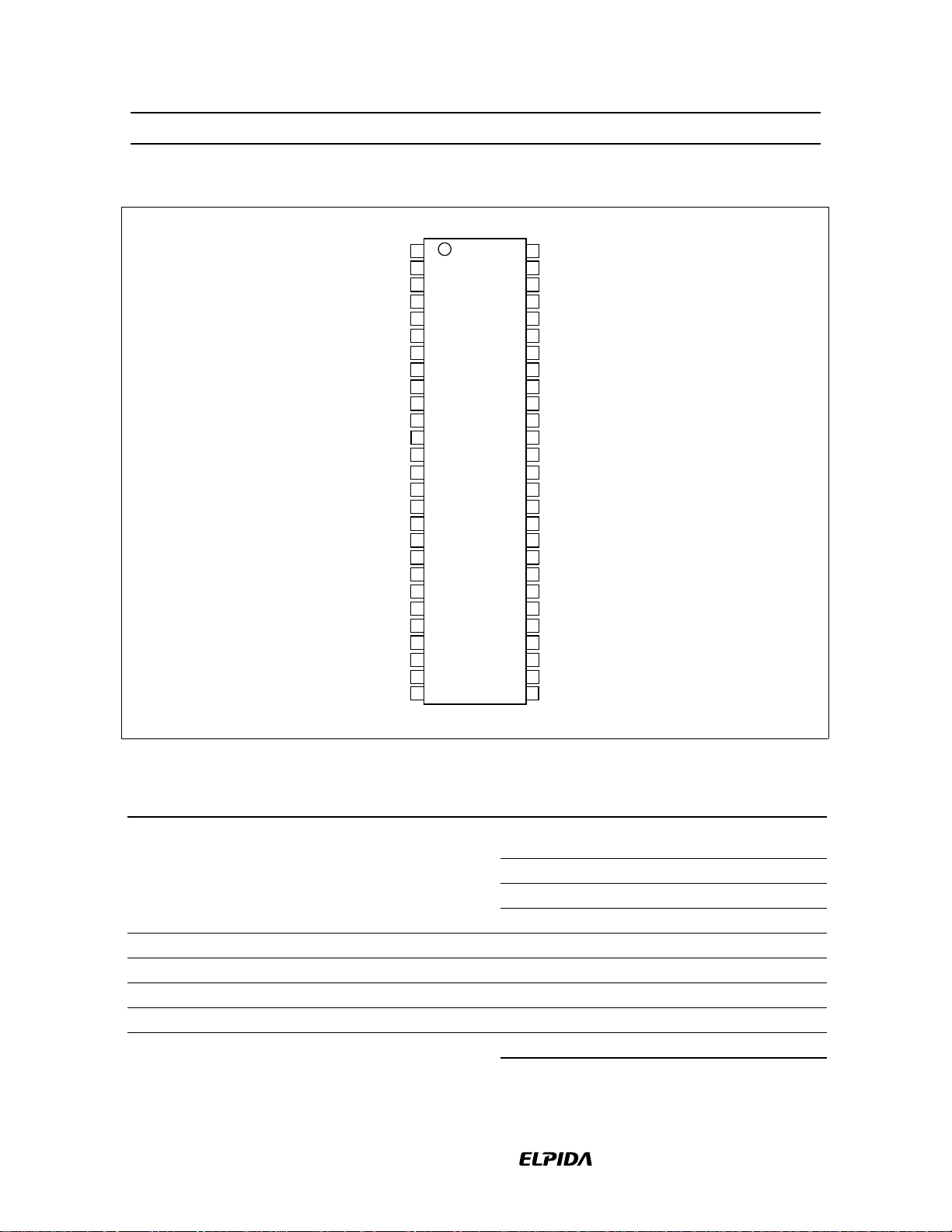
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Pin Arrangement (HM5225165B)
V
DQ0
V
CC
DQ1
DQ2
V
SS
DQ3
DQ4
V
CC
DQ5
DQ6
V
SS
DQ7
V
DQML
WE
CAS
RAS
BA0
BA1
A10
V
CC
CC
CS
A0
A1
A2
A3
CC
Q
Q
Q
Q
54-pin TSOP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
(Top view)
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
V
SS
DQ15
V
Q
SS
DQ14
DQ13
Q
V
CC
DQ12
DQ11
Q
V
SS
DQ10
DQ9
Q
V
CC
DQ8
V
SS
NC
DQMU
CLK
CKE
A12
A11
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
V
SS
Pin Description
Pin name Function Pin name Function
A0 to A12,
BA0, BA1
DQ0 to DQ15 Data-input/output V
CS Chip select V
RAS Row address strobe command VCCQ Power for DQ circuit
CAS Column address strobe command VSSQ Ground for DQ circuit
Address input WE Write enable
Row address A0 to A12 DQMU/DQML Input/output mask
Column address A0 to A8 CLK Clock input
Bank select address BA0/BA1 (BS) CKE Clock enable
CC
SS
Power for internal circuit
Ground for internal circuit
NC No connection
Data Sheet E0082H10
3
Page 4
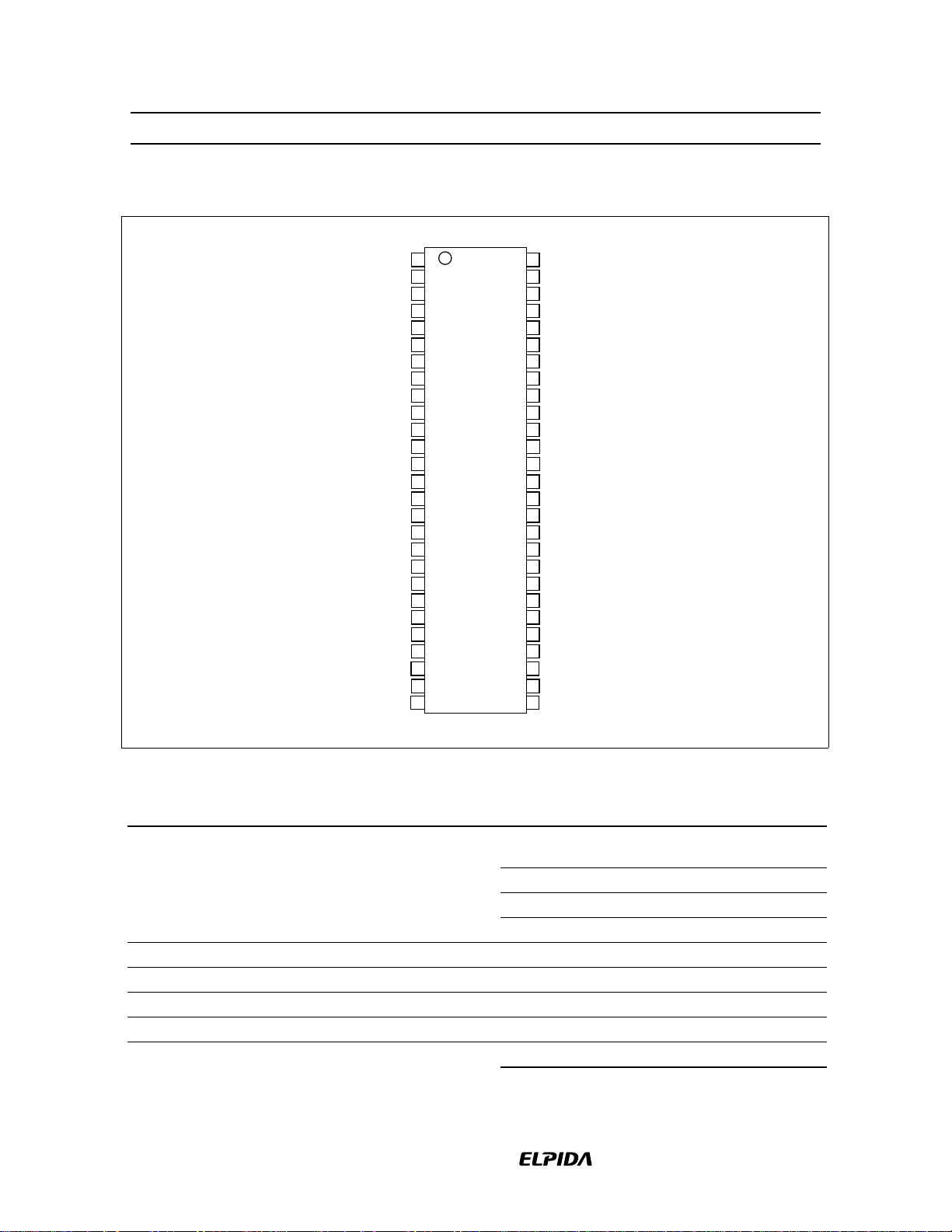
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Pin Arrangement (HM5225805B)
54-pin TSOP
CC
NC
NC
NC
NC
CC
NC
CS
A0
A1
A2
A3
CC
Q
Q
Q
Q
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
(Top view)
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
V
SS
DQ7
V
SS
NC
DQ6
V
CC
NC
DQ5
V
SS
NC
DQ4
V
CC
NC
V
SS
NC
DQM
CLK
CKE
A12
A11
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
V
SS
Q
Q
Q
Q
V
DQ0
V
CC
DQ1
V
DQ2
V
CC
DQ3
V
CAS
RAS
BA0
BA1
SS
SS
V
WE
A10
V
Pin Description
Pin name Function Pin name Function
A0 to A12,
BA0, BA1
DQ0 to DQ7 Data-input/output V
CS Chip select V
RAS Row address strobe command VCCQ Power for DQ circuit
CAS Column address strobe command VSSQ Ground for DQ circuit
4
Address input WE Write enable
Row address A0 to A12 DQM Input/output mask
Column address A0 to A9 CLK Clock input
Bank select address BA0/BA1 (BS) CKE Clock enable
CC
SS
Power for internal circuit
Ground for internal circuit
NC No connection
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 5
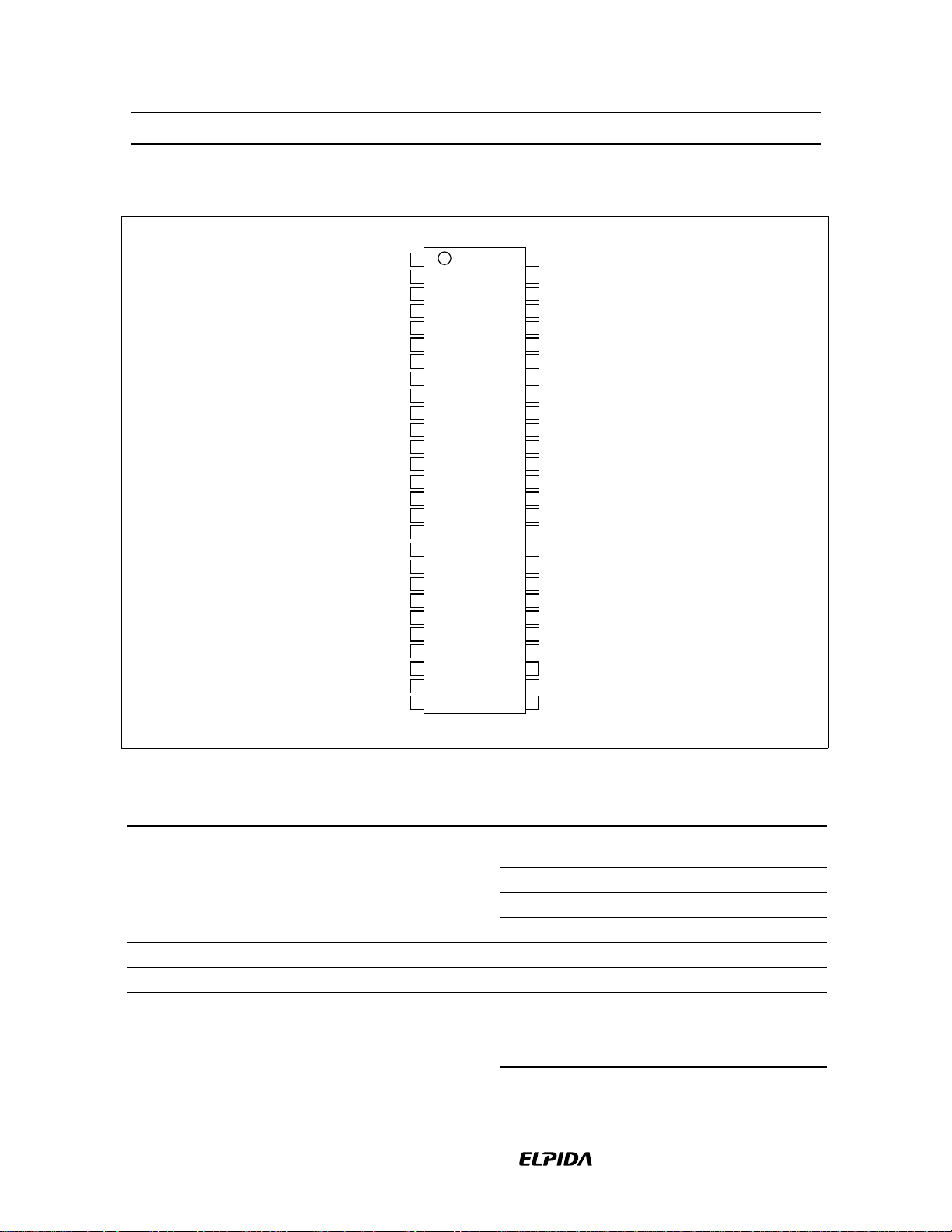
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Pin Arrangement (HM5225405B)
V
V
CC
DQ0
V
SS
V
CC
DQ1
V
SS
V
WE
CAS
RAS
BA0
BA1
A10
V
CC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
CC
NC
CS
A0
A1
A2
A3
CC
Q
Q
Q
Q
54-pin TSOP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
(Top view)
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
V
SS
NC
V
SS
NC
DQ3
V
CC
NC
NC
V
SS
NC
DQ2
V
CC
NC
V
SS
NC
DQM
CLK
CKE
A12
A11
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
V
SS
Q
Q
Q
Q
Pin Description
Pin name Function Pin name Function
A0 to A12,
BA0, BA1
DQ0 to DQ3 Data-input/output V
CS Chip select V
RAS Row address strobe command VCCQ Power for DQ circuit
CAS Column address strobe command VSSQ Ground for DQ circuit
Address input WE Write enable
Row address A0 to A12 DQM Input/output mask
Column address A0 to A9, A11 CLK Clock input
Bank select address BA0/BA1 (BS) CKE Clock enable
CC
SS
Power for internal circuit
Ground for internal circuit
NC No connection
Data Sheet E0082H10
5
Page 6
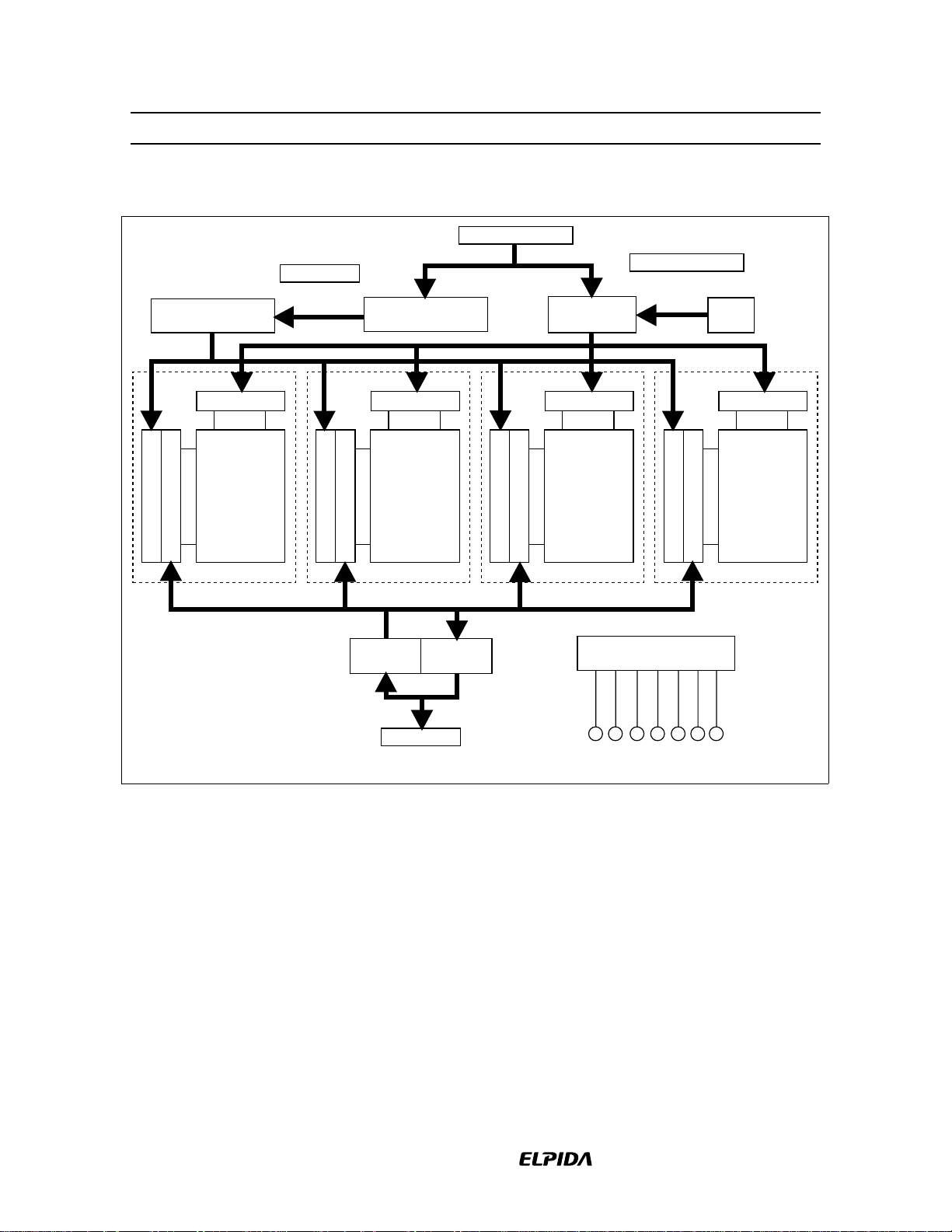
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
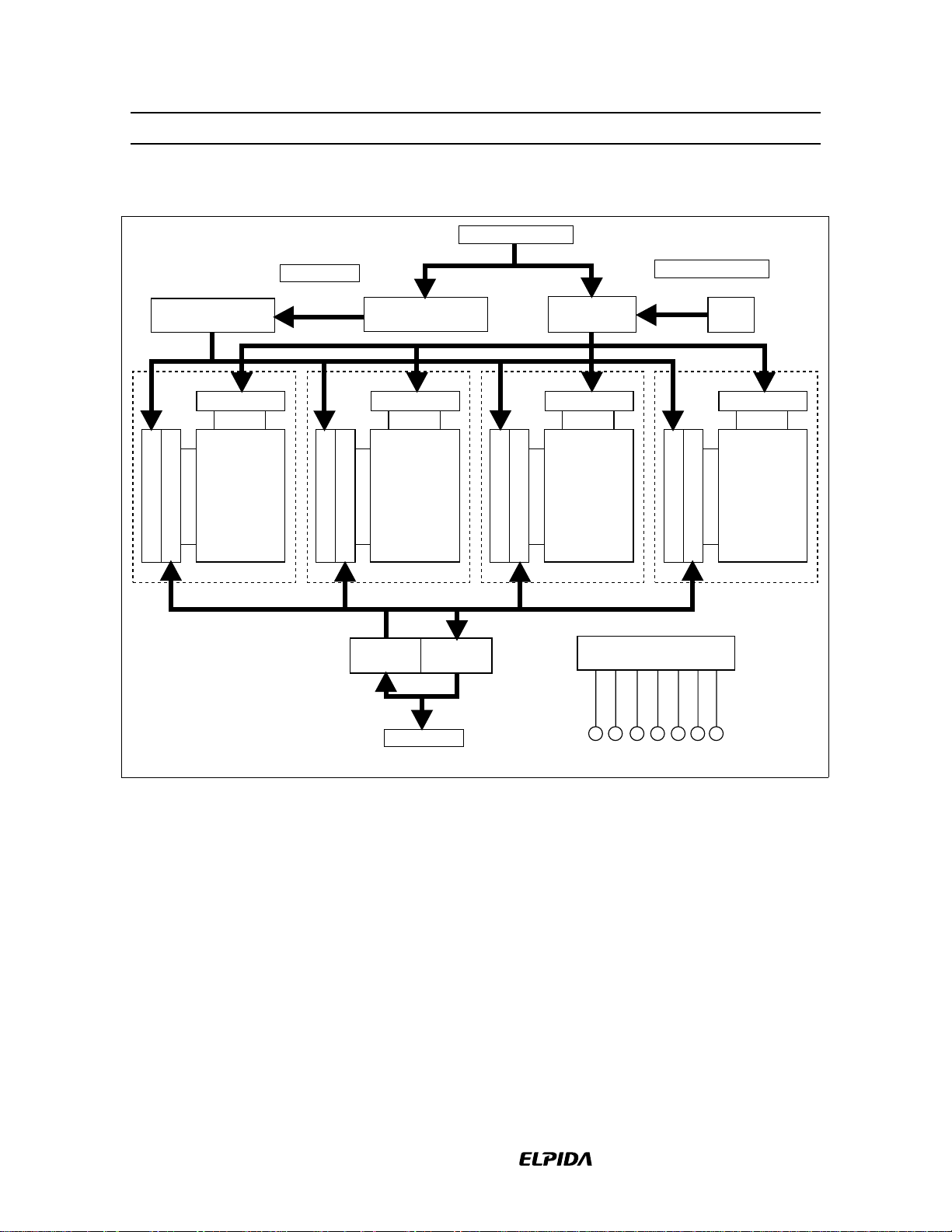
Block Diagram (HM5225165B)
A0 to A12, BA0, BA1
Column address
counter
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 0
Column decoder
8192 row
X 512 column
X 16 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
A0 to A8
Column address
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 1
Column decoder
8192 row
X 512 column
X 16 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
Input
buffer
buffer
Output
buffer
Row address
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 2
Column decoder
8192 row
X 512 column
X 16 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
buffer
A0 to A12, BA0, BA1
Control logic &
timing generator
Refresh
counter
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 3
Column decoder
8192 row
X 512 column
X 16 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
DQ0 to DQ15
CLK
CKECSRAS
CAS
WE
DQMU
/DQML
Data Sheet E0082H10
6
Page 7
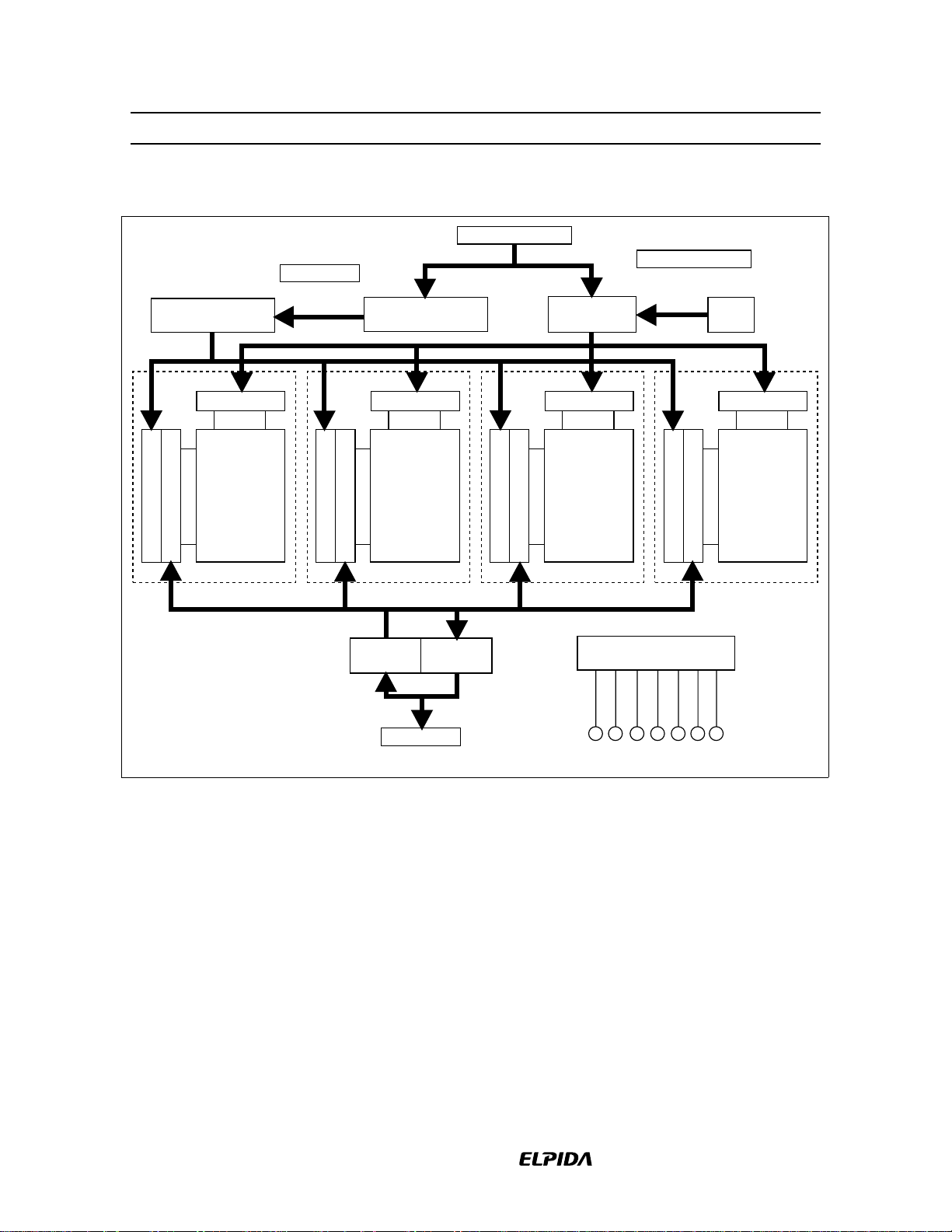
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Block Diagram (HM5225805B)
A0 to A12, BA0, BA1
Column address
counter
Row decoder
Memory array
Column decoder
8192 row
X 1024 column
X 8 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
Bank 0
A0 to A9
Column address
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 1
Column decoder
8192 row
X 1024 column
X 8 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
Input
buffer
buffer
Output
buffer
Row address
Row decoder
Memory array
Column decoder
8192 row
X 1024 column
X 8 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
buffer
Bank 2
A0 to A12, BA0, BA1
Control logic &
timing generator
Refresh
counter
Row decoder
Memory array
Column decoder
8192 row
X 1024 column
X 8 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
Bank 3
DQ0 to DQ7
Data Sheet E0082H10
CLK
CKECSRAS
CAS
WE
DQM
7
Page 8
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Block Diagram (HM5225405B)
A0 to A12, BA0, BA1
A0 to A9, A11
A0 to A12, BA0, BA1
Column address
counter
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 0
Column decoder
8192 row
X 2048 column
X 4 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
Column address
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 1
Column decoder
8192 row
X 2048 column
X 4 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
Input
buffer
DQ0 to DQ3
buffer
Output
buffer
Row address
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 2
Column decoder
8192 row
X 2048 column
X 4 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
buffer
Control logic &
timing generator
CLK
CKECSRAS
Refresh
counter
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 3
Column decoder
CAS
8192 row
X 2048 column
X 4 bit
Sense amplifier & I/O bus
WE
DQM
Data Sheet E0082H10
8
Page 9

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Pin Functions
CLK (input pin): CLK is the master clock input to this pin. The other input signals are referred at CLK
rising edge.
CS (input pin): When CS is Low, the command input cycle becomes valid. When CS is High, all inputs are
ignored. However, internal operations (bank active, burst operations, etc.) are held.
RAS, CAS, and WE (input pins): Although these pin names are the same as those of conventional DRAMs,
they function in a different way. These pins define operation commands (read, write, etc.) depending on the
combination of their voltage levels. For details, refer to the command operation section.
A0 to A12 (input pins): Row address (AX0 to AX12) is determined by A0 to A12 level at the bank active
command cycle CLK rising edge. Column address (AY0 to AY8; HM5225165B, AY0 to AY9;
HM5225805B, AY0 to AY9, AY11; HM5225405B) is determined by A0 to A8, A9 or A11 (A8;
HM5225165B, A9; HM5225805B, A9, A11; HM5225405B) level at the read or write command cycle CLK
rising edge. And this column address becomes burst access start address. A10 defines the precharge mode.
When A10 = High at the precharge command cycle, all banks are precharged. But when A10 = Low at the
precharge command cycle, only the bank that is selected by BA0/BA1 (BS) is precharged. For details refer to
the command operation section.
BA0/BA1 (input pin): BA0/BA1 are bank select signal (BS). The memory array of the HM5225165B,
HM5225805B, the HM5225405B is divided into bank 0, bank 1, bank 2 and bank 3. HM5225165B contain
8192-row × 512-column × 16-bit. HM5225805B contain 8192-row × 1024-column × 8-bit. HM5225405B
contain 8192-row × 2048-column × 4-bit. If BA0 is Low and BA1 is Low, bank 0 is selected. If BA0 is Low
and BA1 is High, bank 1 is selected. If BA0 is High and BA1 is Low, bank 2 is selected. If BA0 is High and
BA1 is High, bank 3 is selected.
CKE (input pin): This pin determines whether or not the next CLK is valid. If CKE is High, the next CLK
rising edge is valid. If CKE is Low, the next CLK rising edge is invalid. This pin is used for power-down
mode, clock suspend mode and self refresh mode.
DQM, DQMU/DQML (input pins): DQM, DQMU/DQML controls input/output buffers.
Read operation: If DQM, DQMU/DQML is High, the output buffer becomes High-Z. If the DQM,
DQMU/DQML is Low, the output buffer becomes Low-Z. (The latency of DQM, DQMU/DQML during
reading is 2 clocks.)
Write operation: If DQM, DQMU/DQML is High, the previous data is held (the new data is not written). If
DQM, DQMU/DQML is Low, the data is written. (The latency of DQM, DQMU/DQML during writing is 0
clock.)
DQ0 to DQ15 (DQ pins): Data is input to and output from these pins (DQ0 to DQ15; HM5225165B, DQ0
to DQ7; HM5225805B, DQ0 to DQ3; HM5225405B).
VCC and VCCQ (power supply pins): 3.3 V is applied. (VCC is for the internal circuit and VCCQ is for the
output buffer.)
Data Sheet E0082H10
9
Page 10

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
VSS and VSSQ (power supply pins): Ground is connected. (VSS is for the internal circuit and VSSQ is for the
output buffer.)
Command Operation
Command Truth Table
The SDRAM recognizes the following commands specified by the CS, RAS, CAS, WE and address pins.
CKE
Command Symbol n - 1 n CS RAS CAS WE BA0/BA1 A10A0to A12
Ignore command DESL H × H ×××× ××
No operation NOP H × LH H H×××
Column address and read command READ H × LH L HV L V
Read with auto-precharge READ A H × LH L HV H V
Column address and write command WRIT H × LH L L V L V
Write with auto-precharge WRIT A H × LH L L V H V
Row address strobe and bank active ACTV H × LL H HV V V
Precharge select bank PRE H × LL H L V L ×
Precharge all bank PALL H × LL H L × H ×
Refresh REF/SELF H V L L L H ×××
Mode register set MRS H × LL L L V V V
Note: H: VIH. L: VIL. ×: VIH or VIL. V: Valid address input
Ignore command [DESL]: When this command is set (CS is High), the SDRAM ignore command input at
the clock. However, the internal status is held.
No operation [NOP]: This command is not an execution command. However, the internal operations
continue.
Column address strobe and read command [READ]: This command starts a read operation. In addition,
the start address of burst read is determined by the column address (AY0 to AY8; HM5225165B, AY0 to
AY9; HM5225805B, AY0 to AY9, AY11; HM5225405B) and the bank select address (BS). After the read
operation, the output buffer becomes High-Z.
Read with auto-precharge [READ A]: This command automatically performs a precharge operation after a
burst read with a burst length of 1, 2, 4 or 8.
Data Sheet E0082H10
10
Page 11

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Column address strobe and write command [WRIT]: This command starts a write operation. When the
burst write mode is selected, the column address (AY0 to AY8; HM5225165B, AY0 to AY9; HM5225805B,
AY0 to AY9, AY11; HM5225405B) and the bank select address (BA0/BA1) become the burst write start
address. When the single write mode is selected, data is only written to the location specified by the column
address (AY0 to AY8; HM5225165B, AY0 to AY9; HM5225805B, AY0 to AY9, AY11; HM5225405B) and
the bank select address (BA0/BA1).
Write with auto-precharge [WRIT A]: This command automatically performs a precharge operation after a
burst write with a length of 1, 2, 4 or 8, or after a single write operation.
Row address strobe and bank activate [ACTV]: This command activates the bank that is selected by
BA0/BA1 (BS) and determines the row address (AX0 to AX12). When BA0 and BA1 are Low, bank 0 is
activated. When BA0 is Low and BA1 is High, bank 1 is activated. When BA0 is High and BA1 is Low,
bank 2 is activated. When BA0 and BA1 are High, bank 3 is activated.
Precharge selected bank [PRE]: This command starts precharge operation for the bank selected by
BA0/BA1. If BA0 and BA1 are Low, bank 0 is selected. If BA0 is Low and BA1 is High, bank 1 is selected.
If BA0 is High and BA1 is Low, bank 2 is selected. If BA0 and BA1 are High, bank 3 is selected.
Precharge all banks [PALL]: This command starts a precharge operation for all banks.
Refresh [REF/SELF]: This command starts the refresh operation. There are two types of refresh operation,
the one is auto-refresh, and the other is self-refresh. For details, refer to the CKE truth table section.
Mode register set [MRS]: The SDRAM has a mode register that defines how it operates. The mode register
is specified by the address pins (A0 to BA0 and BA1) at the mode register set cycle. For details, refer to the
mode register configuration. After power on, the contents of the mode register are undefined, execute the
mode register set command to set up the mode register.
Data Sheet E0082H10
11
Page 12

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
DQM Truth Table (HM5225165B)
CKE
Command Symbol n - 1 n DQMU DQML
Upper byte (DQ8 to DQ15) write enable/output enable ENBU H × L ×
Lower byte (DQ0 to DQ7) write enable/output enable ENBL H ××L
Upper byte (DQ8 to DQ15) write inhibit/output disable MASKU H × H ×
Lower byte (DQ0 to DQ7) write inhibit/output disable MASKL H ××H
Note: H: VIH. L: VIL. ×: VIH or VIL.
Write: I
Read: I
DQM Truth Table (HM5225805B/HM5225405B)
Command Symbol n - 1 n DQM
Write enable/output enable ENB H × L
Write inhibit/output disable MASK H × H
Note: H: VIH. L: VIL. ×: VIH or VIL.
Write: I
Read: I
is needed.
DID
is needed.
DOD
is needed.
DID
is needed.
DOD
CKE
The SDRAM can mask input/output data by means of DQM, DQMU/DQML.
DQMU masks the upper byte and DQML masks the lower byte. (HM5225165B)
During reading, the output buffer is set to Low-Z by setting DQM, DQMU/DQML to Low, enabling data
output. On the other hand, when DQM, DQMU/DQML is set to High, the output buffer becomes High-Z,
disabling data output.
During writing, data is written by setting DQM, DQMU/DQML to Low. When DQM, DQMU/DQML is set
to High, the previous data is held (the new data is not written). Desired data can be masked during burst read
or burst write by setting DQMU/DQML. For details, refer to the DQM, DQMU/DQML control section of the
SDRAM operating instructions.
12
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 13

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
CKE Truth Table
CKE
Current state Command n - 1 n CS RAS CAS WE Address
Active Clock suspend mode entry H L ЧЧЧЧЧ
Any Clock suspend L L ЧЧЧЧЧ
Clock suspend Clock suspend mode exit L H ЧЧЧЧЧ
Idle Auto-refresh command (REF) H H LLLH×
Idle Self-refresh entry (SELF) H LLLLH×
Idle Power down entry H L L H H H ×
HLH××××
Self refresh Self refresh exit (SELFX) L H L H H H ×
LHH××××
Power down Power down exit L H L H H H ×
LHH××××
Note: H: VIH. L: VIL. ×: VIH or VIL.
Clock suspend mode entry: The SDRAM enters clock suspend mode from active mode by setting CKE to
Low. If command is input in the clock suspend mode entry cycle, the command is valid. The clock suspend
mode changes depending on the current status (1 clock before) as shown below.
ACTIVE clock suspend: This suspend mode ignores inputs after the next clock by internally maintaining
the bank active status.
READ suspend and READ with Auto-precharge suspend: The data being output is held (and continues to
be output).
WRITE suspend and WRIT with Auto-precharge suspend: In this mode, external signals are not
accepted. However, the internal state is held.
Clock suspend: During clock suspend mode, keep the CKE to Low.
Clock suspend mode exit: The SDRAM exits from clock suspend mode by setting CKE to High during the
clock suspend state.
IDLE: In this state, all banks are not selected, and completed precharge operation.
Auto-refresh command [REF]: When this command is input from the IDLE state, the SDRAM starts auto-
refresh operation. (The auto-refresh is the same as the CBR refresh of conventional DRAMs.) During the
auto-refresh operation, refresh address and bank select address are generated inside the SDRAM. For every
auto-refresh cycle, the internal address counter is updated. Accordingly, 8192 times are required to refresh
the entire memory. Before executing the auto-refresh command, all the banks must be in the IDLE state. In
addition, since the precharge for all banks is automatically performed after auto-refresh, no precharge
command is required after auto-refresh.
Data Sheet E0082H10
13
Page 14

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Self-refresh entry [SELF]: When this command is input during the IDLE state, the SDRAM starts self-
refresh operation. After the execution of this command, self-refresh continues while CKE is Low. Since selfrefresh is performed internally and automatically, external refresh operations are unnecessary.
Power down mode entry: When this command is executed during the IDLE state, the SDRAM enters power
down mode. In power down mode, power consumption is suppressed by cutting off the initial input circuit.
Self-refresh exit: When this command is executed during self-refresh mode, the SDRAM can exit from selfrefresh mode. After exiting from self-refresh mode, the SDRAM enters the IDLE state.
Power down exit: When this command is executed at the power down mode, the SDRAM can exit from
power down mode. After exiting from power down mode, the SDRAM enters the IDLE state.
Function Truth Table
The following table shows the operations that are performed when each command is issued in each mode of
the SDRAM.
The following table assumes that CKE is high.
Current state CS RAS CAS WE Address Command Operation
Precharge H ×××× DESL Enter IDLE after t
LHHH× NOP Enter IDLE after t
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ/READ A ILLEGAL*
L H L L BA, CA, A10 WRIT/WRIT A ILLEGAL*
L L H H BA, RA ACTV ILLEGAL*
L L H L BA, A10 PRE, PALL NOP*
6
LLLH× REF, SELF ILLEGAL
L L L L MODE MRS ILLEGAL
Idle H ×××× DESL NOP
LHHH× NOP NOP
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ/READ A ILLEGAL*
L H L L BA, CA, A10 WRIT/WRIT A ILLEGAL*
L L H H BA, RA ACTV Bank and row active
L L H L BA, A10 PRE, PALL NOP
LLLH× REF, SELF Refresh
L L L L MODE MRS Mode register set
RP
RP
4
4
4
5
5
14
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 15

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Current state CS RAS CAS WE Address Command Operation
Row active H ×××× DESL NOP
LHHH× NOP NOP
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ/READ A Begin read
L H L L BA, CA, A10 WRIT/WRIT A Begin write
L L H H BA, RA ACTV Other bank active
ILLEGAL on same bank*
L L H L BA, A10 PRE, PALL Precharge
LLLH× REF, SELF ILLEGAL
L L L L MODE MRS ILLEGAL
Read H ×××× DESL Continue burst to end
LHHH× NOP Continue burst to end
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ/READ A Continue burst read to CAS
latency and New read
L H L L BA, CA, A10 WRIT/WRIT A Term burst read/start write
L L H H BA, RA ACTV Other bank active
ILLEGAL on same bank*
L L H L BA, A10 PRE, PALL Term burst read and
Precharge
LLLH× REF, SELF ILLEGAL
L L L L MODE MRS ILLEGAL
Read with autoprecharge
H ×××× DESL Continue burst to end and
precharge
LHHH× NOP Continue burst to end and
precharge
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ/READ A ILLEGAL*
L H L L BA, CA, A10 WRIT/WRIT A ILLEGAL*
4
4
L L H H BA, RA ACTV Other bank active
ILLEGAL on same bank*
L L H L BA, A10 PRE, PALL ILLEGAL*
4
LLLH× REF, SELF ILLEGAL
L L L L MODE MRS ILLEGAL
3
3
3
Data Sheet E0082H10
15
Page 16

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Current state CS RAS CAS WE Address Command Operation
Write H ×××× DESL Continue burst to end
LHHH× NOP Continue burst to end
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ/READ A Term burst and New read
L H L L BA, CA, A10 WRIT/WRIT A Term burst and New write
L L H H BA, RA ACTV Other bank active
ILLEGAL on same bank*
L L H L BA, A10 PRE, PALL Term burst write and
LLLH× REF, SELF ILLEGAL
L L L L MODE MRS ILLEGAL
Write with auto-
H ×××× DESL Continue burst to end and
precharge
LHHH× NOP Continue burst to end and
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ/READ A ILLEGAL*
L H L L BA, CA, A10 WRIT/WRIT A ILLEGAL*
L L H H BA, RA ACTV Other bank active
L L H L BA, A10 PRE, PALL ILLEGAL*
LLLH× REF, SELF ILLEGAL
L L L L MODE MRS ILLEGAL
Refresh (auto-
H ×××× DESL Enter IDLE after t
refresh)
LHHH× NOP Enter IDLE after t
L H L H BA, CA, A10 READ/READ A ILLEGAL*
L H L L BA, CA, A10 WRIT/WRIT A ILLEGAL*
L L H H BA, RA ACTV ILLEGAL*
L L H L BA, A10 PRE, PALL ILLEGAL*
LLLH× REF, SELF ILLEGAL
L L L L MODE MRS ILLEGAL
Notes: 1. H: VIH. L: VIL. ×: VIH or VIL. The other combinations are inhibit.
2. An interval of t
3. If t
is not satisfied, this operation is illegal.
RRD
is required between the final valid data input and the precharge command.
DPL
4. Illegal for same bank, except for another bank.
5. Illegal for all banks.
6. NOP for same bank, except for another bank.
Precharge*
precharge
precharge
ILLEGAL on same bank*
2
4
4
4
RC
RC
5
5
5
5
3
3
16
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 17

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
From PRECHARGE state, command operation
To [DESL], [NOP]: When these commands are executed, the SDRAM enters the IDLE state after tRP has
elapsed from the completion of precharge.
From IDLE state, command operation
To [DESL], [NOP], [PRE] or [PALL]: These commands result in no operation.
To [ACTV]: The bank specified by the address pins and the ROW address is activated.
To [REF], [SELF]: The SDRAM enters refresh mode (auto-refresh or self-refresh).
To [MRS]: The synchronous DRAM enters the mode register set cycle.
From ROW ACTIVE state, command operation
To [DESL], [NOP]: These commands result in no operation.
To [READ], [READ A]: A read operation starts. (However, an interval of t
To [WRIT], [WRIT A]: A write operation starts. (However, an interval of t
To [ACTV]: This command makes the other bank active. (However, an interval of t
is required.)
RCD
is required.)
RCD
is required.)
RRD
Attempting to make the currently active bank active results in an illegal command.
To [PRE], [PALL]: These commands set the SDRAM to precharge mode. (However, an interval of t
RAS
is
required.)
From READ state, command operation
To [DESL], [NOP]: These commands continue read operations until the burst operation is completed.
To [READ], [READ A]: Data output by the previous read command continues to be output. After CAS
latency, the data output resulting from the next command will start.
To [WRIT], [WRIT A]: These commands stop a burst read, and start a write cycle.
To [ACTV]: This command makes other banks bank active. (However, an interval of t
is required.)
RRD
Attempting to make the currently active bank active results in an illegal command.
To [PRE], [PALL]: These commands stop a burst read, and the SDRAM enters precharge mode.
From READ with AUTO-PRECHARGE state, command operation
Data Sheet E0082H10
17
Page 18

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
To [DESL], [NOP]: These commands continue read operations until the burst operation is completed, and
the SDRAM then enters precharge mode.
To [ACTV]: This command makes other banks bank active. (However, an interval of t
is required.)
RRD
Attempting to make the currently active bank active results in an illegal command.
From WRITE state, command operation
To [DESL], [NOP]: These commands continue write operations until the burst operation is completed.
To [READ], [READ A]: These commands stop a burst and start a read cycle.
To [WRIT], [WRIT A]: These commands stop a burst and start the next write cycle.
To [ACTV]: This command makes the other bank active. (However, an interval of t
is required.)
RRD
Attempting to make the currently active bank active results in an illegal command.
To [PRE], [PALL]: These commands stop burst write and the SDRAM then enters precharge mode.
From WRITE with AUTO-PRECHARGE state, command operation
To [DESL], [NOP]: These commands continue write operations until the burst is completed, and the
synchronous DRAM enters precharge mode.
To [ACTV]: This command makes the other bank active. (However, an interval of t
is required.)
RRD
Attempting to make the currently active bank active results in an illegal command.
From REFRESH state, command operation
To [DESL], [NOP]: After an auto-refresh cycle (after tRC), the SDRAM automatically enters the IDLE state.
18
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 19
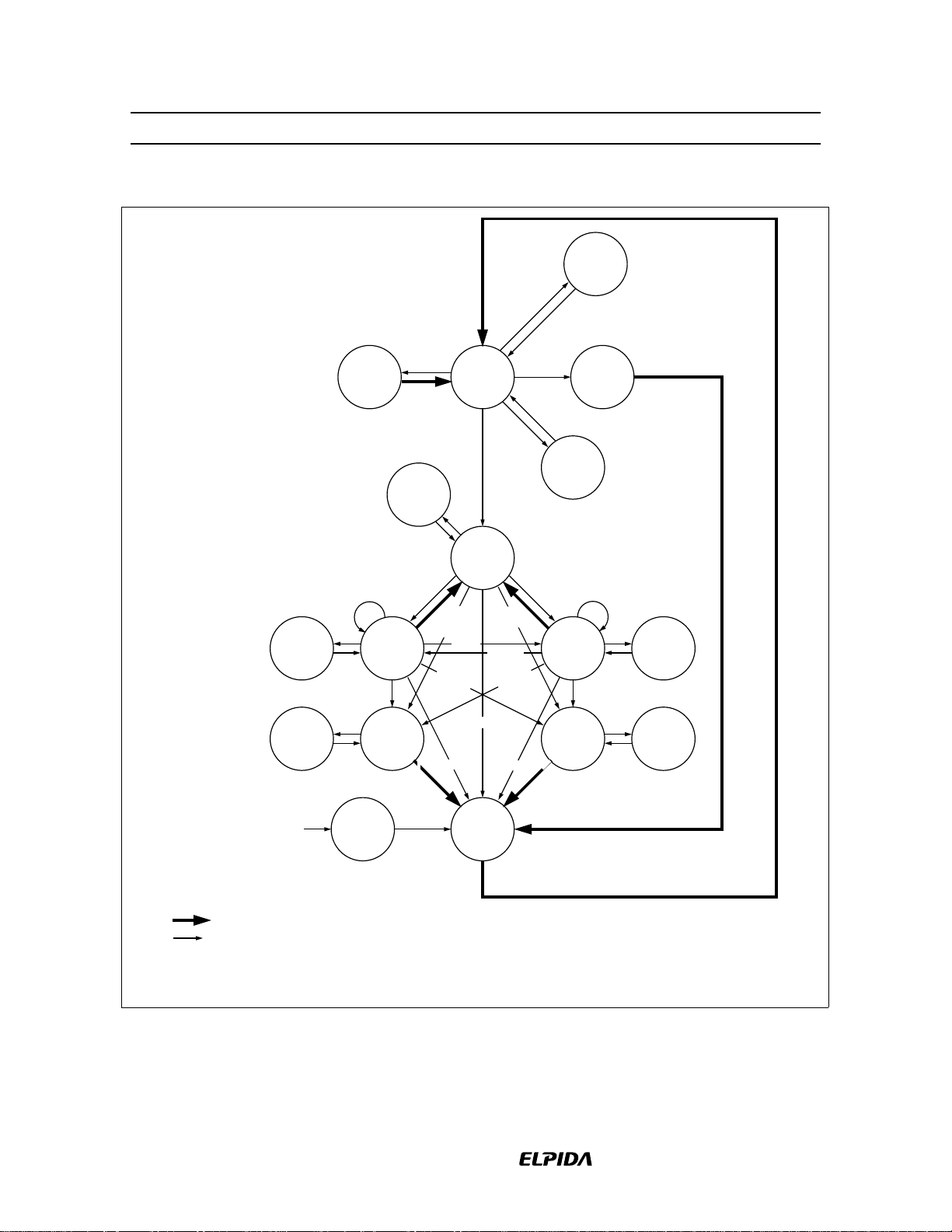
Simplified State Diagram
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
SELF
REFRESH
SR ENTRY
SR EXIT
WRITE
SUSPEND
WRITEA
SUSPEND
MODE
REGISTER
SET
Write
CKE_
CKE
WRITE
WITH AP
CKE_
CKE
MRS
ACTIVE
CLOCK
SUSPEND
CKE
WRITE
WRITE
WITH
AP
WRITE
READ
WITH AP
WRITEA
PRECHARGE PRECHARGE
IDLE
ACTIVE
CKE_
ROW
ACTIVE
READ
WRITE
PRECHARGE
CKE_
READ
WITH
AP
WRITE
WITH AP
REFRESH
CKE
READ
AUTO
REFRESH
IDLE
POWER
DOWN
READ
READA
CKE_
READ
WITH AP
CKE_
*1
Read
CKE
CKE
READ
SUSPEND
READA
SUSPEND
POWER
APPLIED
POWER
ON
PRECHARGE
PRECHARGE
Automatic transition after completion of command.
Transition resulting from command input.
Note: 1. After the auto-refresh operation, precharge operation is performed automatically and
enter the IDLE state.
Data Sheet E0082H10
19
Page 20

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Mode Register Configuration
The mode register is set by the input to the address pins (A0 to A12, BA0 and BA1) during mode register set
cycles. The mode register consists of five sections, each of which is assigned to address pins.
BA1, BA0, A11, A10, A12, A9, A8: (OPCODE): The SDRAM has two types of write modes. One is the
burst write mode, and the other is the single write mode. These bits specify write mode.
Burst read and burst write: Burst write is performed for the specified burst length starting from the column
address specified in the write cycle.
Burst read and single write: Data is only written to the column address specified during the write cycle,
regardless of the burst length.
A7: Keep this bit Low at the mode register set cycle. If this pin is high, the vender test mode is set.
A6, A5, A4: (LMODE): These pins specify the CAS latency.
A3: (BT): A burst type is specified.
A2, A1, A0: (BL): These pins specify the burst length.
BA1
0
X
X
X
BA0BA1
BA0
0
X
X
X
A12
A12
0
X
X
X
A11
A10
A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
OPCODE 0 LMODE BT BL
A3
A10
A11
00
X
X
X
X
X
X
000
001
010
011 3
1XX R
A9
0
0R
1 Burst read and single write
1R
Write mode
A8
0
Burst read and burst write
1
0
1
R
R
2
0 Sequential
1 Interleave
Burst typeA6 A5 A4 CAS latency
R is Reserved (inhibit)
X: 0 or 1
A2 A1 A0
000
001
010
011 8
100 R
101 R R
110 R
111
Burst length
BT=0 BT=1
1
1
2
2
4
4
8
R
R
R
R
20
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 21

Burst Sequence
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Burst length = 2
Starting Ad.
A0
0
1
Burst length = 8
Starting Ad.
A2 A1 A0
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
Addressing(decimal)
InterleaveSequential
0, 1,
1, 0,
Addressing(decimal)
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
4, 5, 6, 7,
5, 6, 7,
6, 7,
7,
0, 1,
1, 0,
0, 1, 2, 3,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
Burst length = 4
Starting Ad.
A1 A0
00
01
10
11
0,
0, 1,
0, 1, 2,
Addressing(decimal)
InterleaveSequential
0, 1, 2, 3,
1, 2, 3, 0,
2, 3, 0, 1,
3,
0, 1, 2,
InterleaveSequential
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
1, 0, 3, 2, 5, 4, 7,
2, 3, 0, 1, 6, 7,
3, 2, 1, 0, 7,
4, 5, 6, 7,
5, 4, 7,
6, 7,
7,
6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0,
0, 1, 2, 3,
6, 1, 0, 3, 2,
4, 5, 2, 3, 0, 1,
0, 1, 2, 3,
1, 0, 3, 2,
2, 3, 0, 1,
3, 2, 1, 0,
4, 5,
6, 5, 4,
6,
Data Sheet E0082H10
21
Page 22

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Operation of the SDRAM
The following chapter shows operation example of the products below.
Organization Input/output mask CAS latency
4-Mword × 16-bit × 4 bank DQMU/DQML 2/3
8-Mword × 8-bit × 4 bank DQM
16-Mword × 4-bit × 4 bank DQM
Note: The SDRAM should be used according to the product capability (See “Features”, “Pin Description”
and “AC Characteristics”).
Read/Write Operations
Bank active: Before executing a read or write operation, the corresponding bank and the row address must be
activated by the bank active (ACTV) command. An interval of t
command input and the following read/write command input.
Read operation: A read operation starts when a read command is input. Output buffer becomes Low-Z in
the (CAS Latency - 1) cycle after read command set. The SDRAM can perform a burst read operation.
is required between the bank active
RCD
The burst length can be set to 1, 2, 4, 8. The start address for a burst read is specified by the column address
and the bank select address (BA0/BA1) at the read command set cycle. In a read operation, data output starts
after the number of clocks specified by the CAS Latency. The CAS Latency can be set to 2 or 3.
When the burst length is 1, 2, 4, 8, the Dout buffer automatically becomes High-Z at the next clock after the
successive burst-length data has been output.
The CAS latency and burst length must be specified at the mode register.
22
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 23

CAS Latency
CLK
Command
ACTV
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
t
RCD
READ
Address
Dout
Burst Length
CLK
Command
Address
BL = 1
Dout
BL = 2
BL = 4
BL = 8
CL = 2
CL = 3
ACTV
Row
t
RCD
Row
READ
Column
Column
out 0
out 0 out 1
out 0 out 1 out 2
out 0 out 1 out 2
out 0 out 1 out 2
out 0 out 1 out 2
out 3
out 6 out 7
out 4
out 5
out 3
out 3
out 3
CL = CAS latency
Burst Length = 4
Data Sheet E0082H10
BL : Burst Length
CAS Latency = 2
23
Page 24

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Write operation: Burst write or single write mode is selected by the OPCODE (BA1, BA0, A12, A11, A10,
A9, A8) of the mode register.
1. Burst write: A burst write operation is enabled by setting OPCODE (A9, A8) to (0, 0). A burst write
starts in the same clock as a write command set. (The latency of data input is 0 clock.) The burst length can
be set to 1, 2, 4 and 8, like burst read operations. The write start address is specified by the column address
and the bank select address (BA0/BA1) at the write command set cycle.
CLK
Command
Address
Din
BL = 1
BL = 2
BL = 4
BL = 8
ACTV
Row
t
RCD
WRIT
Column
in 0
in 0
in 0
in 0
in 1
in 1
in 1
in 2
in 2
in 3
in 3
in 4
in 5
in 6 in 7
CAS Latency = 2, 3
2. Single write: A single write operation is enabled by setting OPCODE (A9, A8) to (1, 0). In a single write
operation, data is only written to the column address and the bank select address (BA0/BA1) specified by the
write command set cycle without regard to the burst length setting. (The latency of data input is 0 clock).
CLK
t
RCD
24
Command
Address
Din
ACTV
Row
WRIT
Column
in 0
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 25

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Auto Precharge
Read with auto-precharge: In this operation, since precharge is automatically performed after completing a
read operation, a precharge command need not be executed after each read operation. The command executed
for the same bank after the execution of this command must be the bank active (ACTV) command. In
addition, an interval defined by l
CAS latency Precharge start cycle
3 2 cycle before the final data is output
2 1 cycle before the final data is output
Burst Read (Burst Length = 4)
CLK
CL=2 Command
DQ (input)
CL=3 Command
DQ (input)
ACTV READ A ACTV
ACTV READ A ACTV
is required before execution of the next command.
APR
l
RAS
l
RAS
out3out2out1out0
l
APR
out3out2out1out0
Note: Internal auto-precharge starts at the timing indicated by " ".
And an interval of t
(l
) is required between previous active (ACTV) command and internal precharge " ".
RAS
RAS
l
APR
Data Sheet E0082H10
25
Page 26

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Write with auto-precharge: In this operation, since precharge is automatically performed after completing
a burst write or single write operation, a precharge command need not be executed after each write operation.
The command executed for the same bank after the execution of this command must be the bank active
(ACTV) command. In addition, an interval of l
next command.
Burst Write (Burst Length = 4)
CLK
is required between the final valid data input and input of
APW
Command
DQ (input)
Note: Internal auto-precharge starts at the timing indicated by " ".
Single Write
Command
DQ (input)
ACTV
and an interval of t
RAS
(l
RAS
and internal precharge " ".
CLK
ACTV
I
RAS
WRIT A
ACTV
in0 in1 in2 in3
l
APW
) is required between previous active (ACTV) command
I
RAS
WRIT A
ACTV
in
26
l
APW
Note: Internal auto-precharge starts at the timing indicated by " ".
and an interval of t
RAS
(l
) is required between previous active (ACTV) command
RAS
and internal precharge " ".
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 27

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Command Intervals
Read command to Read command interval:
1. Same bank, same ROW address: When another read command is executed at the same ROW address
of the same bank as the preceding read command execution, the second read can be performed after an
interval of no less than 1 clock. Even when the first command is a burst read that is not yet finished, the data
read by the second command will be valid.
READ to READ Command Interval (same ROW address in same bank)
CLK
Command
Address
BS
Dout
ACTV
Row
Bank0
Active
Column =A
Read
READ
Column A
READ
Column B
Column =B
Read
out A0
Column =A
Dout
out B1
out B0
Column =B
Dout
out B2
out B3
CAS Latency = 3
Burst Length = 4
Bank 0
2. Same bank, different ROW address: When the ROW address changes on same bank, consecutive read
commands cannot be executed; it is necessary to separate the two read commands with a precharge command
and a bank-active command.
3. Different bank: When the bank changes, the second read can be performed after an interval of no less
than 1 clock, provided that the other bank is in the bank-active state. Even when the first command is a burst
read that is not yet finished, the data read by the second command will be valid.
READ to READ Command Interval (different bank)
CLK
Command
Address
BS
Dout
ACTV
Row 0
Bank0
Active
ACTV
Row 1
Bank3
Active
READ
Column A
Bank0
Read
READ
Column B
Bank3
Read
out A0
Bank0
Dout
out B0
Bank3
Dout
out B1
out B2
out B3
CAS Latency = 3
Burst Length = 4
Data Sheet E0082H10
27
Page 28

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Write command to Write command interval:
1. Same bank, same ROW address: When another write command is executed at the same ROW address
of the same bank as the preceding write command, the second write can be performed after an interval of no
less than 1 clock. In the case of burst writes, the second write command has priority.
WRITE to WRITE Command Interval (same ROW address in same bank)
CLK
Command
Address
ACTV
Row
WRIT
Column A
WRIT
Column B
BS
Din
Bank0
Active
in A0
Column =A
Write
in B0
Column =B
Write
in B1
in B2
Burst Write Mode
Burst Length = 4
in B3
Bank 0
2. Same bank, different ROW address: When the ROW address changes, consecutive write commands
cannot be executed; it is necessary to separate the two write commands with a precharge command and a
bank-active command.
3. Different bank: When the bank changes, the second write can be performed after an interval of no less
than 1 clock, provided that the other bank is in the bank-active state. In the case of burst write, the second
write command has priority.
WRITE to WRITE Command Interval (different bank)
CLK
28
Command
Address
BS
Din
ACTV
Row 0
Bank0
Active
WRIT
Column A
in A0
Bank0
Write
WRIT
Column B
in B0
Bank3
Write
ACTV
Row 1
Bank3
Active
Data Sheet E0082H10
in B1
in B2
in B3
Burst Write Mode
Burst Length = 4
Page 29

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Read command to Write command interval:
1. Same bank, same ROW address: When the write command is executed at the same ROW address of the
same bank as the preceding read command, the write command can be performed after an interval of no less
than 1 clock. However, DQM, DQMU/DQML must be set High so that the output buffer becomes High-Z
before data input.
READ to WRITE Command Interval (1)
CLK
Command
DQM,
DQMU
/DQML
CL=2
CL=3
READ
Din
Dout
READ to WRITE Command Interval (2)
CLK
Command
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
CL=2
Dout
CL=3
Din
READ
WRIT
in B0
High-Z
in B1
in B2
in B3
Burst Length = 4
Burst write
WRIT
2 clock
High-Z
High-Z
2. Same bank, different ROW address: When the ROW address changes, consecutive write commands
cannot be executed; it is necessary to separate the two commands with a precharge command and a bankactive command.
3. Different bank: When the bank changes, the write command can be performed after an interval of no less
than 1 cycle, provided that the other bank is in the bank-active state. However, DQM, DQMU/DQML must
be set High so that the output buffer becomes High-Z before data input.
Data Sheet E0082H10
29
Page 30

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Write command to Read command interval:
1. Same bank, same ROW address: When the read command is executed at the same ROW address of the
same bank as the preceding write command, the read command can be performed after an interval of no less
than 1 clock. However, in the case of a burst write, data will continue to be written until one clock before the
read command is executed.
WRITE to READ Command Interval (1)
CLK
Command
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
Din
Dout
WRIT READ
in A0
Column = A
Write
Column = B
Read
WRITE to READ Command Interval (2)
CLK
Command
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
Din
WRIT
in A0
Column = A
Write
in A1
READ
Column = B
Read
out B0
CAS Latency
Column = B
Dout
out B0Dout
CAS Latency
Column = B
Dout
out B1 out B2 out B3
Burst Write Mode
CAS Latency = 2
Burst Length = 4
Bank 0
out B1 out B2 out B3
Burst Write Mode
CAS Latency = 2
Burst Length = 4
Bank 0
2. Same bank, different ROW address: When the ROW address changes, consecutive read commands
cannot be executed; it is necessary to separate the two commands with a precharge command and a bankactive command.
3. Different bank: When the bank changes, the read command can be performed after an interval of no less
than 1 clock, provided that the other bank is in the bank-active state. However, in the case of a burst write,
data will continue to be written until one clock before the read command is executed (as in the case of the
same bank and the same address).
Data Sheet E0082H10
30
Page 31

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Read with auto precharge to Read command interval
1. Different bank: When some banks are in the active state, the second read command (another bank) is
executed. Even when the first read with auto-precharge is a burst read that is not yet finished, the data read by
the second command is valid. The internal auto-precharge of one bank starts at the next clock of the second
command.
Read with Auto Precharge to Read Command Interval (Different bank)
CLK
Command
BS
READ A READ
Dout
bank0
Read A
Note: Internal auto-precharge starts at the timing indicated by " ".
bank3
Read
out A0 out A1 out B0 out B1
CAS Latency = 3
Burst Length = 4
2. Same bank: The consecutive read command (the same bank) is illegal.
Write with auto precharge to Write command interval
1. Different bank: When some banks are in the active state, the second write command (another bank) is
executed. In the case of burst writes, the second write command has priority. The internal auto-precharge of
one bank starts at the next clock of the second command .
Write with Auto Precharge to Write Command Interval (Different bank)
CLK
Command
BS
Din
WRIT A WRIT
bank0
Write A
bank3
Write
in B1 in B2 in B3in A0 in A1 in B0
Burst Length = 4
Note: Internal auto-precharge starts at the timing indicated by " ".
2. Same bank: The consecutive write command (the same bank) is illegal.
Data Sheet E0082H10
31
Page 32

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Read with auto precharge to Write command interval
1. Different bank: When some banks are in the active state, the second write command (another bank) is
executed. However, DQM, DQMU/DQML must be set High so that the output buffer becomes High-Z before
data input. The internal auto-precharge of one bank starts at the next clock of the second command.
Read with Auto Precharge to Write Command Interval (Different bank)
CLK
Command
BS
READ A WRIT
DQMU/DQML
DQM,
CL = 2
CL = 3
Din
Dout
bank0
Read A
Note: Internal auto-precharge starts at the timing indicated by " ".
in B0 in B1 in B2 in B3
High-Z
bank3
Write
Burst Length = 4
2. Same bank: The consecutive write command from read with auto precharge (the same bank) is illegal. It
is necessary to separate the two commands with a bank active command.
32
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 33

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Write with auto precharge to Read command interval
1. Different bank: When some banks are in the active state, the second read command (another bank) is
executed. However, in case of a burst write, data will continue to be written until one clock before the read
command is executed. The internal auto-precharge of one bank starts at the next clock of the second
command.
Write with Auto Precharge to Read Command Interval (Different bank)
CLK
Command
BS
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
WRIT A READ
Din
Dout
Note: Internal auto-precharge starts at the timing indicated by " ".
in A0
bank0
Write A
bank3
Read
out B0 out B1 out B2 out B3
CAS Latency = 3
Burst Length = 4
2. Same bank: The consecutive read command from write with auto precharge (the same bank) is illegal. It
is necessary to separate the two commands with a bank active command.
Data Sheet E0082H10
33
Page 34

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Read command to Precharge command interval (same bank):
When the precharge command is executed for the same bank as the read command that preceded it, the
minimum interval between the two commands is one clock. However, since the output buffer then becomes
High-Z after the clocks defined by l
interrupted, if the precharge command is input during burst read. To read all data by burst read, the clocks
defined by lEP must be assured as an interval from the final data output to precharge command execution.
READ to PRECHARGE Command Interval (same bank): To output all data
CAS Latency = 2, Burst Length = 4
CLK
, there is a case of interruption to burst read data output will be
HZP
Command
Dout
READ
CL=2
CAS Latency = 3, Burst Length = 4
CLK
Command
Dout
READ
PRE/PALL
out A0 out A1 out A2 out A3
l = -1 cycle
EP
PRE/PALL
out A0 out A1 out A2 out A3
CL=3 l = -2 cycle
EP
34
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 35

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
READ to PRECHARGE Command Interval (same bank): To stop output data
CAS Latency = 2, Burst Length = 1, 2, 4, 8
CLK
Command
Dout
READ
PRE/PALL
l
HZP
CAS Latency = 3, Burst Length = 1, 2, 4, 8
CLK
Command
Dout
READ
PRE/PALL
out A0
=2
l
HZP
=3
High-Z
out A0
High-Z
Data Sheet E0082H10
35
Page 36

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Write command to Precharge command interval (same bank): When the precharge command is executed
for the same bank as the write command that preceded it, the minimum interval between the two commands is
1 clock. However, if the burst write operation is unfinished, the input data must be masked by means of
DQM, DQMU/DQML for assurance of the clock defined by t
WRITE to PRECHARGE Command Interval (same bank)
Burst Length = 4 (To stop write operation)
CLK
DPL
.
Command
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
Din
CLK
Command
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
Din
WRIT
t
DPL
WRIT
in A0 in A1
Burst Length = 4 (To write all data)
CLK
Command
WRIT
PRE/PALL
t
DPL
PRE/PALL
PRE/PALL
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
Din
36
in A0 in A1 in A2
Data Sheet E0082H10
in A3
t
DPL
Page 37

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Bank active command interval:
1. Same bank: The interval between the two bank-active commands must be no less than tRC.
2. In the case of different bank-active commands: The interval between the two bank-active commands
must be no less than t
Bank Active to Bank Active for Same Bank
CLK
RRD
.
Command
Address
BS
ACTV
ROW
Bank 0
Active
Bank Active to Bank Active for Different Bank
CLK
Command
Address
BS
ACTV
ROW:0
t
RC
ROW:1
ACTV
ACTV
ROW
Bank 0
Active
t
RRD
Bank 0
Active
Data Sheet E0082H10
Bank 3
Active
37
Page 38

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Mode register set to Bank-active command interval: The interval between setting the mode register and
executing a bank-active command must be no less than l
CLK
RSA
.
Command
Address
MRS ACTV
BS & ROWCODE
I
RSA
Mode
Register Set
Bank
Active
38
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 39

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
DQM Control
The DQM mask the DQ data. The DQMU and DQML mask the upper and lower bytes of the DQ data,
respectively. The timing of DQMU/DQML is different during reading and writing.
Reading: When data is read, the output buffer can be controlled by DQM, DQMU/DQML. By setting
DQM, DQMU/DQML to Low, the output buffer becomes Low-Z, enabling data output. By setting DQM,
DQMU/DQML to High, the output buffer becomes High-Z, and the corresponding data is not output.
However, internal reading operations continue. The latency of DQM, DQMU/DQML during reading is 2
clocks.
Writing: Input data can be masked by DQM, DQMU/DQML. By setting DQM, DQMU/DQML to Low,
data can be written. In addition, when DQM, DQMU/DQML is set to High, the corresponding data is not
written, and the previous data is held. The latency of DQM, DQMU/DQML during writing is 0 clock.
Reading
CLK
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
Writing
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (output)
CLK
DQ (input)
out 0 out 1
l = 2 Latency
DOD
in 0 in 1
High-Z
l = 0 Latency
DID
out 3
in 3
Data Sheet E0082H10
39
Page 40

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Refresh
Auto-refresh: All the banks must be precharged before executing an auto-refresh command. Since the auto-
refresh command updates the internal counter every time it is executed and determines the banks and the
ROW addresses to be refreshed, external address specification is not required. The refresh cycle is 8192
cycles/64 ms. (8192 cycles are required to refresh all the ROW addresses.) The output buffer becomes HighZ after auto-refresh start. In addition, since a precharge has been completed by an internal operation after the
auto-refresh, an additional precharge operation by the precharge command is not required.
Self-refresh: After executing a self-refresh command, the self-refresh operation continues while CKE is held
Low. During self-refresh operation, all ROW addresses are refreshed by the internal refresh timer. A selfrefresh is terminated by a self-refresh exit command. Before and after self-refresh mode, execute auto-refresh
to all refresh addresses in or within 64 ms period on the condition (1) and (2) below.
(1) Enter self-refresh mode within 7.8 µs after either burst refresh or distributed refresh at equal interval to all
refresh addresses are completed.
(2) Start burst refresh or distributed refresh at equal interval to all refresh addresses within 7.8 µs after exiting
from self-refresh mode.
Others
Power-down mode: The SDRAM enters power-down mode when CKE goes Low in the IDLE state. In
power down mode, power consumption is suppressed by deactivating the input initial circuit. Power down
mode continues while CKE is held Low. In addition, by setting CKE to High, the SDRAM exits from the
power down mode, and command input is enabled from the next clock. In this mode, internal refresh is not
performed.
Clock suspend mode: By driving CKE to Low during a bank-active or read/write operation, the SDRAM
enters clock suspend mode. During clock suspend mode, external input signals are ignored and the internal
state is maintained. When CKE is driven High, the SDRAM terminates clock suspend mode, and command
input is enabled from the next clock. For details, refer to the "CKE Truth Table".
Power-up sequence: The SDRAM should be goes on the following sequence with power up.
The CLK, CKE, CS, DQM, DQMU/DQML and DQ pins keep low till power stabilizes.
The CLK pin is stabilized within 100 µs after power stabilizes before the following initialization sequence.
The CKE and DQM, DQMU/DQML is driven to high between power stabilizes and the initialization
sequence.
This SDRAM has VCC clamp diodes for CLK, CKE, CS DQM, DQMU/DQML and DQ pins. If these pins go
high before power up, the large current flows from these pins to VCC through the diodes.
Initialization sequence: When 200 µs or more has past after the above power-up sequence, all banks must be
precharged using the precharge command (PALL). After tRP delay, set 8 or more auto refresh commands
(REF). Set the mode register set command (MRS) to initialize the mode register. We recommend that by
keeping DQM, DQMU/DQML and CKE to High, the output buffer becomes High-Z during Initialization
sequence, to avoid DQ bus contention on memory system formed with a number of device.
40
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 41

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Initialization sequence
200 µs
VCC, VCCQ
CKE, DQM,
DQMU/DQML
CLK
CS, DQ
Power up sequence
100 µs
0 V
Low
Low
Low
Power stabilize
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Value Unit Note
Voltage on any pin relative to V
Supply voltage relative to V
SS
SS
V
T
V
CC
Short circuit output current Iout 50 mA
Power dissipation P
T
Operating temperature Topr 0 to +70 °C
Storage temperature Tstg –55 to +125 °C
Note: 1. Respect to VSS.
–0.5 to VCC + 0.5
V1
(≤ 4.6 (max))
–0.5 to +4.6 V 1
1.0 W
DC Operating Conditions (Ta = 0 to +70˚C)
Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit Notes
Supply voltage V
Input high voltage V
Input low voltage V
Notes: 1. All voltage referred to VSS.
2. The supply voltage with all V
3. The supply voltage with all V
4. V
(max) = VCC + 2.0 V for pulse width ≤ 3 ns at VCC.
IH
5. V
(min) = VSS – 2.0 V for pulse width ≤ 3 ns at VSS.
IL
, VCCQ 3.0 3.6 V 1, 2
CC
VSS, VSSQ0 0 V 3
IH
IL
CC and V
SS and V
CC
SS
2.0 VCC + 0.3 V 1, 4
–0.3 0.8 V 1, 5
Q pins must be on the same level.
Q pins must be on the same level.
Data Sheet E0082H10
41
Page 42

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
VIL/VIH Clamp
This SDRAM has VIL and V
Minimum V
VIL (V) I (mA)
–2 –32
–1.8 –25
–1.6 –19
–1.4 –13
–1.2 –8
–1 –4
–0.9 –2
–0.8 –0.6
–0.6 0
–0.4 0
–0.2 0
00
Clamp Current
IL
clamp for CLK, CKE, CS, DQM and DQ pins.
IH
–5
–10
–15
–20
I (mA)
–25
–30
–35
0
–2
–1.5 –1 –0.5
VIL (V)
0
42
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 43

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Minimum VIH Clamp Current
VIH (V) I (mA)
+ 2 10
V
CC
VCC + 1.8 8
VCC + 1.6 5.5
VCC + 1.4 3.5
VCC + 1.2 1.5
VCC + 1 0.3
VCC + 0.8 0
VCC + 0.6 0
VCC + 0.4 0
VCC + 0.2 0
VCC + 0 0
10
8
6
I (mA)
4
2
0
V
+ 0 VCC + 1 VCC + 2VCC + 0.5 VCC + 1.5
CC
VIH (V)
Data Sheet E0082H10
43
Page 44

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
IOL/IOH Characteristics
Output Low Current (IOL)
I
OL
I
OL
Vout (V) Min (mA) Max (mA)
000
0.4 27 71
0.65 41 108
0.85 51 134
1 58 151
1.4 70 188
1.5 72 194
1.65 75 203
1.8 77 209
1.95 77 212
3 80 220
3.45 81 223
250
44
200
150
(mA)
OL
I
100
50
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5
Vout (V)
Data Sheet E0082H10
min
max
Page 45

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Output High Current (IOH) (Ta = 0 to +70˚C, VCC, VCCQ = 3.0 V to 3.45 V, VSS, VSSQ = 0 V)
I
OH
I
OH
Vout (V) Min (mA) Max (mA)
3.45 —–3
3.3 —–28
30–75
2.6 –21 –130
2.4 –34 –154
2 –59 –197
1.8 –67 –227
1.65 –73 –248
1.5 –78 –270
1.4 –81 –285
1 –89 –345
0 –93 –503
0
0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
–100
3.50
–200
(mA)
OH
I
–300
–400
–500
–600
min
max
Vout (V)
Data Sheet E0082H10
45
Page 46

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
DC Characteristics (Ta = 0 to +70˚C, VCC, VCCQ = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V, VSS, VSSQ = 0 V)
(HM5225165B)
HM5225165B
-75 -A6 -B6
Parameter Symbol Min Max Min Max Min Max Unit Test conditions Notes
Operating current
(CAS latency = 2) I
(CAS latency = 3) I
Standby current in power
down
Standby current in power
down (input signal stable)
Standby current in non
power down
Standby current in non
power down (input signal
stable)
Active standby current in
power down
Active standby current in
power down (input signal
stable)
Active standby current in
non power down
Active standby current in
non power down (input
signal stable)
Burst operating current
(CAS latency = 2) I
(CAS latency = 3) I
Refresh current I
Self refresh current I
Self refresh current
(L-version)
Input leakage current I
Output leakage current I
Output high voltage V
Output low voltage V
CC1
CC1
I
CC2P
I
CC2PS
I
CC2N
I
CC2NS
I
CC3P
I
CC3PS
I
CC3N
I
CC3NS
CC4
CC4
CC5
CC6
I
CC6
LI
LO
— 115 — 100 — 80 mA
— 115 — 100 — 100 mA
— 3 — 3 — 3 mA CKE = VIL,
— 2 — 2 — 2 mA CKE = V
— 20 — 20 — 20 mA CKE, CS = VIH,
— 9 — 9 — 9 mA CKE = VIH, tCK = ∞ 9
— 4 — 4 — 4 mA CKE = VIL,
— 3 — 3 — 3 mA CKE = VIL, tCK = ∞ 2, 7
— 30 — 30 — 30 mA CKE, CS = VIH,
— 15 — 15 — 15 mA CKE = VIH, tCK = ∞ 2, 9
— 110 — 110 — 85 mA tCK = min, BL = 4 1, 2, 5
— 145 — 110 — 110 mA
— 220 — 220 — 220 mA tRC = min 3
— 3 — 3 — 3mAVIH ≥ VCC – 0.2 V
— 2 — 2 — 2mA
–11 –11 –1 1 µA 0 ≤ Vin ≤ V
–1.5 1.5 –1.5 1.5 –1.5 1.5 µA 0 ≤ Vout ≤ V
OH
OL
2.4 — 2.4 — 2.4 — VIOH = –4 mA
— 0.4 — 0.4 — 0.4 V IOL = 4 mA
Burst length = 1
tRC = min
t
= 12 ns
CK
, t
= ∞ 7
IL
CK
t
= 12 ns
CK
t
= 12 ns
CK
t
= 12 ns
CK
V
≤ 0.2 V
IL
CC
CC
DQ = disable
1, 2, 3
6
4
1, 2, 6
1, 2, 4
8
46
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 47

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
DC Characteristics (Ta = 0 to +70˚C, VCC, VCCQ = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V, VSS, VSSQ = 0 V)
(HM5225805B)
HM5225805B
-75 -A6 -B6
Parameter Symbol Min Max Min Max Min Max Unit Test conditions Notes
Operating current
(CAS latency = 2) I
(CAS latency = 3) I
Standby current in power
down
Standby current in power
down (input signal stable)
Standby current in non
power down
Standby current in non
power down (input signal
stable)
Active standby current in
power down
Active standby current in
power down (input signal
stable)
Active standby current in
non power down
Active standby current in
non power down (input
signal stable)
Burst operating current
(CAS latency = 2) I
(CAS latency = 3) I
Refresh current I
Self refresh current I
Self refresh current
(L-version)
Input leakage current I
Output leakage current I
Output high voltage V
Output low voltage V
CC1
CC1
I
CC2P
I
CC2PS
I
CC2N
I
CC2NS
I
CC3P
I
CC3PS
I
CC3N
I
CC3NS
CC4
CC4
CC5
CC6
I
CC6
LI
LO
— 110 — 95 — 75 mA
— 110 — 95 — 95 mA
— 3 — 3 — 3 mA CKE = VIL,
— 2 — 2 — 2 mA CKE = VIL, tCK = ∞ 7
— 20 — 20 — 20 mA CKE, CS = VIH,
— 9 — 9 — 9 mA CKE = VIH, tCK = ∞ 9
— 4 — 4 — 4 mA CKE = VIL,
— 3 — 3 — 3 mA CKE = VIL, tCK = ∞ 2, 7
— 30 — 30 — 30 mA CKE, CS = VIH,
— 15 — 15 — 15 mA CKE = VIH, tCK = ∞ 2, 9
— 100 — 100 — 75 mA tCK = min, BL = 4 1, 2, 5
— 135 — 100 — 100 mA
— 220 — 220 — 220 mA t
— 3 — 3 — 3mAVIH ≥ VCC – 0.2 V
— 2 — 2 — 2mA
–11 –11 –1 1 µA 0 ≤ Vin ≤ V
–1.5 1.5 –1.5 1.5 –1.5 1.5 µA 0 ≤ Vout ≤ V
OH
OL
2.4 — 2.4 — 2.4 — VIOH = –4 mA
— 0.4 — 0.4 — 0.4 V IOL = 4 mA
Burst length = 1
tRC = min
t
= 12 ns
CK
t
= 12 ns
CK
t
= 12 ns
CK
t
= 12 ns
CK
= min 3
RC
V
≤ 0.2 V
IL
CC
CC
DQ = disable
1, 2, 3
6
4
1, 2, 6
1, 2, 4
8
Data Sheet E0082H10
47
Page 48

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
DC Characteristics (Ta = 0 to +70˚C, VCC, VCCQ = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V, VSS, VSSQ = 0 V)
(HM5225405B)
HM5225405B
-75 -A6 -B6
Parameter Symbol Min Max Min Max Min Max Unit Test conditions Notes
Operating current
(CAS latency = 2) I
(CAS latency = 3) I
Standby current in power
down
Standby current in power
down (input signal stable)
Standby current in non
power down
Standby current in non
power down (input signal
stable)
Active standby current in
power down
Active standby current in
power down (input signal
stable)
Active standby current in
non power down
Active standby current in
non power down (input
signal stable)
Burst operating current
(CAS latency = 2) I
(CAS latency = 3) I
Refresh current I
Self refresh current I
Self refresh current
(L-version)
Input leakage current I
Output leakage current I
Output high voltage V
Output low voltage V
CC1
CC1
I
CC2P
I
CC2PS
I
CC2N
I
CC2NS
I
CC3P
I
CC3PS
I
CC3N
I
CC3NS
CC4
CC4
CC5
CC6
I
CC6
LI
LO
— 110 — 95 — 75 mA
— 110 — 95 — 95 mA
— 3 — 3 — 3 mA CKE = VIL,
— 2 — 2 — 2 mA CKE = VIL, tCK = ∞ 7
— 20 — 20 — 20 mA CKE, CS = VIH,
— 9 — 9 — 9 mA CKE = VIH, tCK = ∞ 9
— 4 — 4 — 4 mA CKE = VIL,
— 3 — 3 — 3 mA CKE = VIL, tCK = ∞ 2, 7
— 30 — 30 — 30 mA CKE, CS = VIH,
— 15 — 15 — 15 mA CKE = VIH, tCK = ∞ 2, 9
— 95 — 95 — 70 mA tCK = min, BL = 4 1, 2, 5
— 130 — 95 — 95 mA
— 220 — 220 — 220 mA t
— 3 — 3 — 3mAVIH ≥ VCC – 0.2 V
— 2 — 2 — 2mA
–11 –11 –1 1 µA 0 ≤ Vin ≤ V
–1.5 1.5 –1.5 1.5 –1.5 1.5 µA 0 ≤ Vout ≤ V
OH
OL
2.4 — 2.4 — 2.4 — VIOH = –4 mA
— 0.4 — 0.4 — 0.4 V IOL = 4 mA
Burst length = 1
tRC = min
t
= 12 ns
CK
t
= 12 ns
CK
t
= 12 ns
CK
t
= 12 ns
CK
= min 3
RC
V
≤ 0.2 V
IL
CC
CC
DQ = disable
1, 2, 3
6
4
1, 2, 6
1, 2, 4
8
48
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 49

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Notes: 1. I
depends on output load condition when the device is selected. ICC (max) is specified at the
CC
output open condition.
2. One bank operation.
3. Input signals are changed once per one clock.
4. Input signals are changed once per two clocks.
5. Input signals are changed once per four clocks.
6. After power down mode, CLK operating current.
7. After power down mode, no CLK operating current.
8. After self refresh mode set, self refresh current.
9. Input signals are V
or VIL fixed.
IH
Capacitance (Ta = 25°C, VCC, VCCQ = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V)
Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit Notes
Input capacitance (CLK) C
Input capacitance (Input) C
Output capacitance (DQ) C
I1
I2
O
Notes: 1. Capacitance measured with Boonton Meter or effective capacitance measuring method.
2. Measurement condition: f = 1 MHz, 1.4 V bias, 200 mV swing.
3. DQM, DQMU/DQML = V
to disable Dout.
IH
4. This parameter is sampled and not 100% tested.
2.5 3.5 pF 1, 2, 4
2.5 3.8 pF 1, 2, 4
4 6.5 pF 1, 2, 3, 4
Data Sheet E0082H10
49
Page 50

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
AC Characteristics (Ta = 0 to +70°C, VCC, VCCQ = 3.3 V ± 0.3 V, VSS, VSSQ = 0 V)
HM5225165B/
HM5225805B/
HM5225405B
-75 -A6 -B6
PC/100
Parameter Symbol
System clock cycle time
(CAS latency = 2) t
(CAS latency = 3) t
CLK high pulse width t
CLK low pulse width t
CK
CK
CKH
CKL
Access time from CLK
(CAS latency = 2) t
(CAS latency = 3) t
Data-out hold time t
CLK to Data-out low
AC
AC
OH
t
LZ
impedance
CLK to Data-out high
t
HZ
impedance
(CAS latency = 2, 3)
Input setup time tAS, tCS, tDS,
t
CES
CKE setup time for power
t
CESP
down exit
Input hold time tAH, tCH, tDH,
t
CEH
Ref/Active to Ref/Active
t
RC
command period
Active to Precharge
t
RAS
command period
Active command to column
t
RCD
command (same bank)
Precharge to active
t
RP
command period
Write recovery or data-in to
t
DPL
precharge lead time
Active (a) to Active (b)
t
RRD
command period
Transition time (rise and fall) t
Refresh period t
T
REF
Symbol Min Max Min Max Min Max Unit Notes
Tclk 10 — 10 — 15 — ns 1
Tclk 7.5 — 10 — 10 — ns
Tch 2.5 — 3 — 3 — ns 1
Tcl 2.5 — 3 — 3 — ns 1
Tac — 6 — 6 — 8 ns 1, 2
Tac — 5.4 — 6 — 6ns
Toh 2.7 — 3 — 3 — ns 1, 2
2 — 2 — 2 — ns 1, 2, 3
— 5.4 — 6 — 6 ns 1, 4
Tsi 1.5 — 2 — 2 — ns 1, 5, 6
Tpde 1.5 — 2 — 2 — ns 1
Thi 0.8 — 1 — 1 — ns 1, 6
Trc 67.5 — 70 — 70 — ns 1
Tras 45 120000 50 120000 50 120000 ns 1
Trcd 20 — 20 — 20 — ns 1
Trp 20 — 20 — 20 — ns 1
Tdpl 15 — 20 — 20 — ns 1
Trrd 15 — 20 — 20 — ns 1
15 15 15 ns
— 64 — 64 — 64 ms
50
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 51

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Notes: 1. AC measurement assumes t
= 1 ns. Reference level for timing of input signals is 1.5 V.
T
2. Access time is measured at 1.5 V. Load condition is CL = 50 pF.
(min) defines the time at which the outputs achieves the low impedance state.
3. t
LZ
4. t
(max) defines the time at which the outputs achieves the high impedance state.
HZ
5. t
define CKE setup time to CLK rising edge except power down exit command.
CES
6. t
: Address, tCS/tCH: CS, RAS, CAS, WE, DQM, DQMU/DQML.
AS/tAH
t
DS/tDH
: Data-in, t
CES/tCEH
: CKE.
Test Conditions
• Input and output timing reference levels: 1.5 V
• Input waveform and output load: See following figures
2.4 V
0.4 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
t
T
t
input
I/O
CL
T
Data Sheet E0082H10
51
Page 52

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Relationship Between Frequency and Minimum Latency
HM5225165B/
HM5225805B/
HM5225405B
Parameter -75 -A6/B6
Frequency (MHz) 133 100
PC/100
tCK (ns) Symbol
Active command to column command
l
RCD
(same bank)
Active command to active command
l
RC
(same bank)
Active command to precharge command
l
RAS
(same bank)
Precharge command to active command
l
RP
(same bank)
Write recovery or data-in to precharge
l
DPL
command (same bank)
Active command to active command
l
RRD
(different bank)
Self refresh exit time l
Last data in to active command
SREX
l
APW
(Auto precharge, same bank)
Self refresh exit to command input l
SEC
Precharge command to high impedance
(CAS latency = 2) l
(CAS latency = 3) l
Last data out to active command
l
HZP
HZP
APR
(Auto precharge, same bank)
Last data out to precharge (early precharge)
(CAS latency = 2) l
(CAS latency = 3) l
Column command to column command l
Write command to data in latency l
DQM to data in l
DQM to data out l
CKE to CLK disable l
Register set to active command l
EP
EP
CCD
WCD
DID
DOD
CLE
RSA
Symbol 7.5 10 Notes
321
97= [l
651
321
Tdpl 2 2 1
221
Tsrx 1 1 2
Tdal 5 4 = [l
97= [l
Troh 2 2
Troh 3 3
11
–1 –1
–2 –2
Tccd 1 1
Tdwd 0 0
Tdqm 0 0
Tdqz 2 2
Tcke 1 1
Tmrd 1 1
+ lRP]
RAS
1
+ lRP]
DPL
]
RC
3
52
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 53

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
HM5225165B/
HM5225805B/
HM5225405B
Parameter -75 -A6/B6
Frequency (MHz) 133 100
PC/100
tCK (ns) Symbol
CS to command disable l
Power down exit to command input l
Notes: 1. l
RCD
to l
are recommended value.
RRD
CDD
PEC
2. Be valid [DESL] or [NOP] at next command of self refresh exit.
3. Except [DESL] and [NOP]
Symbol 7.5 10 Notes
00
11
Data Sheet E0082H10
53
Page 54

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Timing Waveforms
Read Cycle
t
CK
t
t
CKL
CKH
CLK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
A10
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
BS
V
IH
t
RCD
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
t
CS
t
RAS
t
RC
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
t
CH
t
RP
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
54
DQ (input)
DQ (output)
Bank 0
Active
t
AC
t
Bank 0
Read
AC
t
OH
t
LZ
Data Sheet E0082H10
t
AC
t
OH
t
AC
t
OH
Bank 0
Precharge
t
HZ
t
OH
CAS latency = 2
Burst length = 4
Bank 0 access
= V or V
IH
IL
Page 55

Write Cycle
CLK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
A10
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (input)
DQ (output)
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
t
CK
t
t
CKL
CKH
t
V
IH
t
RCD
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
CS
t
t
CS
t
t
CS
t
t
CS
t
t
AS
t
t
AS
t
t
AS
t
CS
t
t
DS
t
RAS
CH
CH
CH
CH
AH
AH
AH
t
t
t
t
DS
DS
DH
DH
RC
t
RP
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
t
CH
t
t
DS
DH
DH
t
DPL
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CH
CS
t
t
CS
CH
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
t
t
AH
AS
Bank 0
Active
Bank 0
Write
Data Sheet E0082H10
Bank 0
Precharge
CAS latency = 2
Burst length = 4
Bank 0 access
= V or V
IH
IL
55
Page 56

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Mode Register Set Cycle
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
CLK
V
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (output)
DQ (input)
IH
valid
Precharge
If needed
code
R: b
C: b
C: b’
b
High-Z
l
Mode
register
Set
RSA
l
RP
Bank 3
Active
l
RCD
Bank 3
Read
Output mask
b+3
b’+1
b’
b’+3
b’+2
l = 3
RCD
CAS latency = 3
Burst length = 4
= V or V
IH
IL
Read Cycle/Write Cycle
CLK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (output)
DQ (input)
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (output)
DQ (input)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1011121314151617181920
V
IH
R:a C:a R:b C:b C:b' C:b"
Bank 0
Active
V
IH
R:a C:a R:b C:b C:b' C:b"
Bank 0
Active
Bank 0
Read
a a+1 a+2 a+3 b b+1 b+2 b+3 b' b'+1 b" b"+1 b"+2 b"+3
Bank 3
Active
Bank 3
Read
Bank 0
Precharge
High-Z
High-Z
Bank 3
Read
Bank 3
Read
a a+1 a+2 a+3 b b+1 b+2 b+3 b' b'+1 b" b"+1b"+2 b"+3
Bank 0
Write
Bank 3
Active
Bank 3
Write
Bank 0
Precharge
Bank 3
Write
Bank 3
Write
Bank 3
Precharge
Bank 3
Precharge
Read cycle
RAS-CAS delay = 3
CAS latency = 3
Burst length = 4
= V or V
Write cycle
RAS-CAS delay = 3
CAS latency = 3
Burst length = 4
= V or V
IL
IH
IL
IH
56
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 57

Read/Single Write Cycle
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
CLK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (input)
DQ (output)
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (input)
DQ (output)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
V
IH
R:a C:a R:b C:a'
C:a
a
a
Bank 0
Active
V
IH
R:a C:a C:a
Bank 0
Active
Bank 0
Read
Bank 0
Read
Bank 3
Active
R:b
Bank 3
Active
a+1 a+2 a+3
a
a+1 a+3
Bank 0
Write
a
Bank 0
Write
Bank 0
Read
C:b
bc
Bank 0
Write
a a+1 a+2 a+3
C:c
Bank 0
Write
Bank 0
Precharge
Bank 0
Precharge
Read/Single write
RAS-CAS delay = 3
CAS latency = 3
Burst length = 4
= V or V
IH
Bank 3
Precharge
IL
Data Sheet E0082H10
57
Page 58

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Read/Burst Write Cycle
CLK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (input)
DQ (output)
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (input)
DQ (output)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
R:a C:a R:b C:a'
a a+1 a+2 a+3
a+1 a+2 a+3
Bank 0
Active
V
IH
R:a C:a C:a
Bank 0
Read
Bank 3
Active
R:b
a
Clock
suspend
Bank 0
Write
Bank 0
Precharge
a a+1 a+2 a+3
a+1
a a+3
Bank 0
Active
Bank 0
Read
Bank 3
Active
Bank 0
Write
Bank 0
Precharge
Read/Burst write
RAS-CAS delay = 3
CAS latency = 3
Burst length = 4
= V or V
IH
Bank 3
Precharge
IL
58
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 59

Auto Refresh Cycle
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
CLK
CKE
V
IH
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (input)
DQ (output)
Precharge
If needed
Self Refresh Cycle
CLK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (input)
DQ (output)
Precharge command
If needed
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
RC
Next
clock
enable
C:a
Read
Bank 0
Auto
refresh
A10=1
t RC
RP
Auto Refresh
A10=1
t
RP
Self refresh entry
command
CKE Low
t
Auto Refresh
l
SREX
High-Z
Self refresh exit
ignore command
or No operation
High-Z
t
RC
Next
clock
enable
t
RC
Self refresh entry
command
R:a
Active
Bank 0
t
20
19
a a+1
Refresh cycle and
Read cycle
RAS-CAS delay = 2
CAS latency = 2
Burst length = 4
= V or V
Self refresh cycle
RAS-CAS delay = 3
CAS latency = 3
Burst length = 4
= V or V
IL
IH
IL
IH
Data Sheet E0082H10
59
Page 60

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Clock Suspend Mode
CLK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (output)
DQ (input)
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (output)
DQ (input)
t
CES
t
CEH
t
CES
01234 5 6 7 8 9 1011121314151617181920
R:a C:a R:b
Bank0
Active clock
Active
suspend start
R:a C:a
Active clock
suspend end
Bank0
Read
R:b
a a+1 a+2 a+3 b b+1 b+2
Read suspend
Bank3
Active
start
High-Z
Read suspend
end
C:b
C:b
Bank3
Read
Bank0
Precharge
b+3
Earliest Bank3
Precharge
High-Z
a a+1
Bank0
Active
Active clock
suspend start
Active clock
supend end
Bank0
Write
Bank3
Active
a+2
Write suspend
start
a+3
Write suspend
b b+1 b+2 b+3
Bank0
Bank3
Precharge
end
Write
Earliest Bank3
Precharge
Read cycle
RAS-CAS delay = 2
CAS latency = 2
Burst length = 4
= V or V
Write cycle
RAS-CAS delay = 2
CAS latency = 2
Burst length = 4
= V or V
IL
IH
IL
IH
60
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 61

Power Down Mode
CLK
HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
BS
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ (input)
DQ (output)
A10=1
t
Precharge command
If needed
RP
Power down entry
CKE Low
High-Z
Power down
mode exit
R: a
Active Bank 0
Power down cycle
RAS-CAS delay = 3
CAS latency = 3
Burst length = 4
= V or V
IL
IH
Initialization Sequence
CLK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
Address
DQM,
DQMU/DQML
DQ
V
IH
V
IH
All banks
Precharge
0123456
valid
t
RP
Auto Refresh
t
RC
Data Sheet E0082H10
78910
Auto Refresh
48 49 50 51
High-Z
t
RC
Mode register
Set
code
53
52
t
RSA
Bank active
If needed
Valid
55
54
61
Page 62

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Package Dimensions
HM5225165BTT/BLTT
HM5225805BTT/BLTT
HM5225405BTT/BLTT Series (TTP-54D)
22.22
22.72 Max
54 28
10.16
Unit: mm
127
+0.10
*0.30
–0.05
0.28 ± 0.05
0.80
0.13
M
0.91 Max
0.10
1.20 Max
*Dimension including the plating thickness
Base material dimension
0.125 ± 0.04
*0.145 ± 0.05
11.76 ± 0.20
0.13 ± 0.05
Hitachi Code
JEDEC
EIAJ
Weight
0° – 5°
0.50 ± 0.10
(reference value)
0.80
0.68
TTP-54D
—
—
0.53 g
62
Data Sheet E0082H10
Page 63

HM5225165B/HM5225805B/HM5225405B-75/A6/B6
Cautions
1. Elpida Memory, Inc. neither warrants nor grants licenses of any rights of Elpida Memory, Inc.’s or any
third party’s patent, copyright, trademark, or other intellectual property rights for information contained in
this document. Elpida Memory, Inc. bears no responsibility for problems that may arise with third party’s
rights, including intellectual property rights, in connection with use of the information contained in this
document.
2. Products and product specifications may be subject to change without notice. Confirm that you have
received the latest product standards or specifications before final design, purchase or use.
3. Elpida Memory, Inc. makes every attempt to ensure that its products are of high quality and reliability.
However, contact Elpida Memory, Inc. before using the product in an application that demands especially
high quality and reliability or where its failure or malfunction may directly threaten human life or cause
risk of bodily injury, such as aerospace, aeronautics, nuclear power, combustion control, transportation,
traffic, safety equipment or medical equipment for life support.
4. Design your application so that the product is used within the ranges guaranteed by Elpida Memory, Inc.
particularly for maximum rating, operating supply voltage range, heat radiation characteristics, installation
conditions and other characteristics. Elpida Memory, Inc. bears no responsibility for failure or damage
when used beyond the guaranteed ranges. Even within the guaranteed ranges, consider normally
foreseeable failure rates or failure modes in semiconductor devices and employ systemic measures such as
fail-safes, so that the equipment incorporating Elpida Memory, Inc. product does not cause bodily injury,
fire or other consequential damage due to operation of the Elpida Memory, Inc. product.
5. This product is not designed to be radiation resistant.
6. No one is permitted to reproduce or duplicate, in any form, the whole or part of this document without
written approval from Elpida Memory, Inc..
7. Contact Elpida Memory, Inc. for any questions regarding this document or Elpida Memory, Inc.
semiconductor products.
Data Sheet E0082H10
63
 Loading...
Loading...