Page 1
HIP0045
Data Sheet April 1999
1A/50V Octal Low Side Power Driver With
Serial Bus Control and Fault Protection
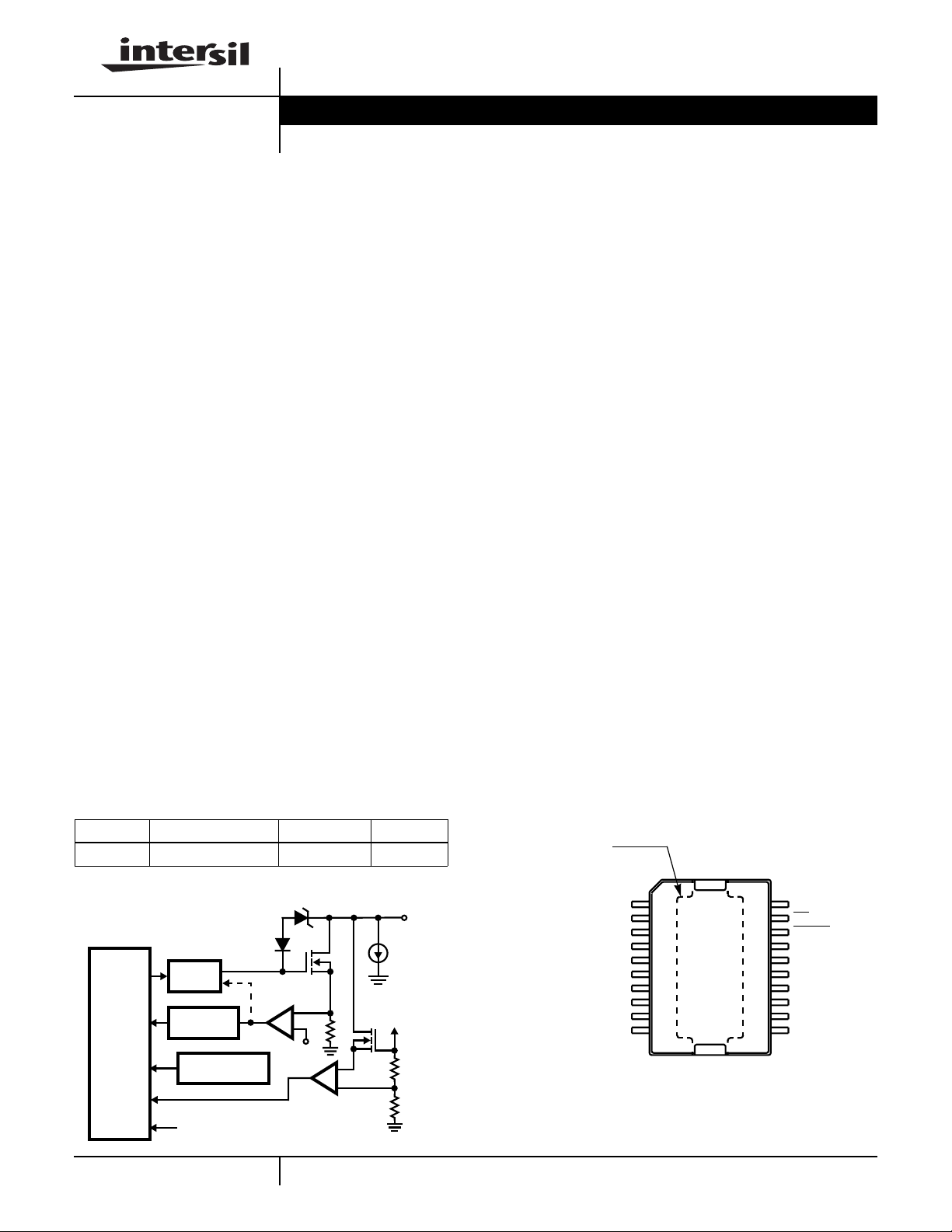
The HIP0045 is a logic controlled, eight channel Octal Serial
Pow er Low Side Driv er. The serial peripheral interface (SPI)
utilized by the HIP0045 is a serial synchronous bus compatible
with Intersil CDP68HC05, or equivalent, microcomputers. As
shown in the Block Diagram f or the HIP0045, each of the open
drain MOS Output Drivers have individual protection f or o v ervoltage and over-current. Each output channel has separate
output latch control with fault unlatch and diagnostic or status
feedback.Undernormal ON conditions, each output driveris in
a low voltage, high current state of saturated turn-on.
Comparators in the diagnostic circuitry monitor the output
drivers to determine if an out of saturation condition exists. If a
fault is sensed, the respective output driver f or Channels 0 - 5
haveovercurrentlatch-off .Channels6 and 7 are configured for
lamp drivers and have current limiting with ov er-temper ature
latch-off. Channels 0 and 1 have direct par allel drive control for
PWM applications and are ORed with the SPI Bus control. All
channels are SPI Bus controlled and sense the output states
for diagnostic feedbac k.
The HIP0045 is fabricated in a Power BiMOS IC process,
and is intended for use in automotive and other applications
having a wide range of temperature and electrical stress
conditions. It is particularly suited for driving relays,
solenoids and lamps in applications where low standby
power, high operating voltage, and high output current in
high ambient temperature conditions is required.
The HIP0045 is in a 20 lead plastic Pow er SOP (PSOP)
Packagewithanintegralcopper‘slug’toconductheatdirectly
to a PCB interface or heat sink on the bottom of the package.
Ordering Information
PART NO. TEMP. RANGE (oC) PACKAGE PKG. NO.
HIP0045AB -40 to 125 20 Ld PSOP M20.433
Driver Block Diagram
OUT
I
SK
V
CC
V
REF
SPI AND
DIRECT
INPUT
CONTROL
WITH
FAULT/
STATUS
OUTPUT
DRIVER
OC LATCH
(CH. 0-5)
OVER-TEMP.
DET. (CH. 6, 7)
RESET
OC LIMIT
(CH. 6, 7)
-
+
FAULT/STATUS
OC
REF
+
-
File Number
4047.2
Features
• Octal NDMOS Output Drivers in a High Voltage Power
BiMOS Process
• Over-Stress Protection - Each Output:
- Over-Current Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A Min
- Over-Voltage Clamp Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . 50V Typ
- Thermal Shutdown Protection (2 Channels)
• Open-Load Detection
• Power BiMOS Output Configuration
- Current Latch-Off Protection for 6 Channels; 2 with
External Drive Input and ORed with SPI Bus Control
- 2 Channels Configured for Lamp Drivers with Current
Limiting and Over-Temperature Latch-Off
• High Speed CMOS Logic Control
- SPI Bus Controlled Interface
- Individual Output Latch
- Individual Fault Unlatch and Feedback
- Common Reset Line
• Low Quiescent Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5mA Max
• Ambient Operating Temp. Range. . . . . . . -40
o
C to 125oC
Applications
• Automotive and Industrial Systems
• Solenoids, Relays and Lamp Drivers
• Logic and µP Controlled Drivers
• Robotic Controls
Pinout
HIP0045 (PSOP WITH HEAT SLUG)
TOP VIEW
INTEGRAL COPPER
HEAT SINK ‘SLUG’
FOR PCB CONTACT
OR EXT. HEAT SINK
GND
IN0
MISO
OUT0
OUT2
OUT4
OUT6
MOSI
SCK
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
GND
20
CE
19
RESET
18
OUT7
17
OUT5
16
OUT3
15
OUT1
14
V
13
12
11
CC
IN1
GND
4-1
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
http://www.intersil.com or 407-727-9207
| Copyright © Intersil Corporation 1999
Page 2
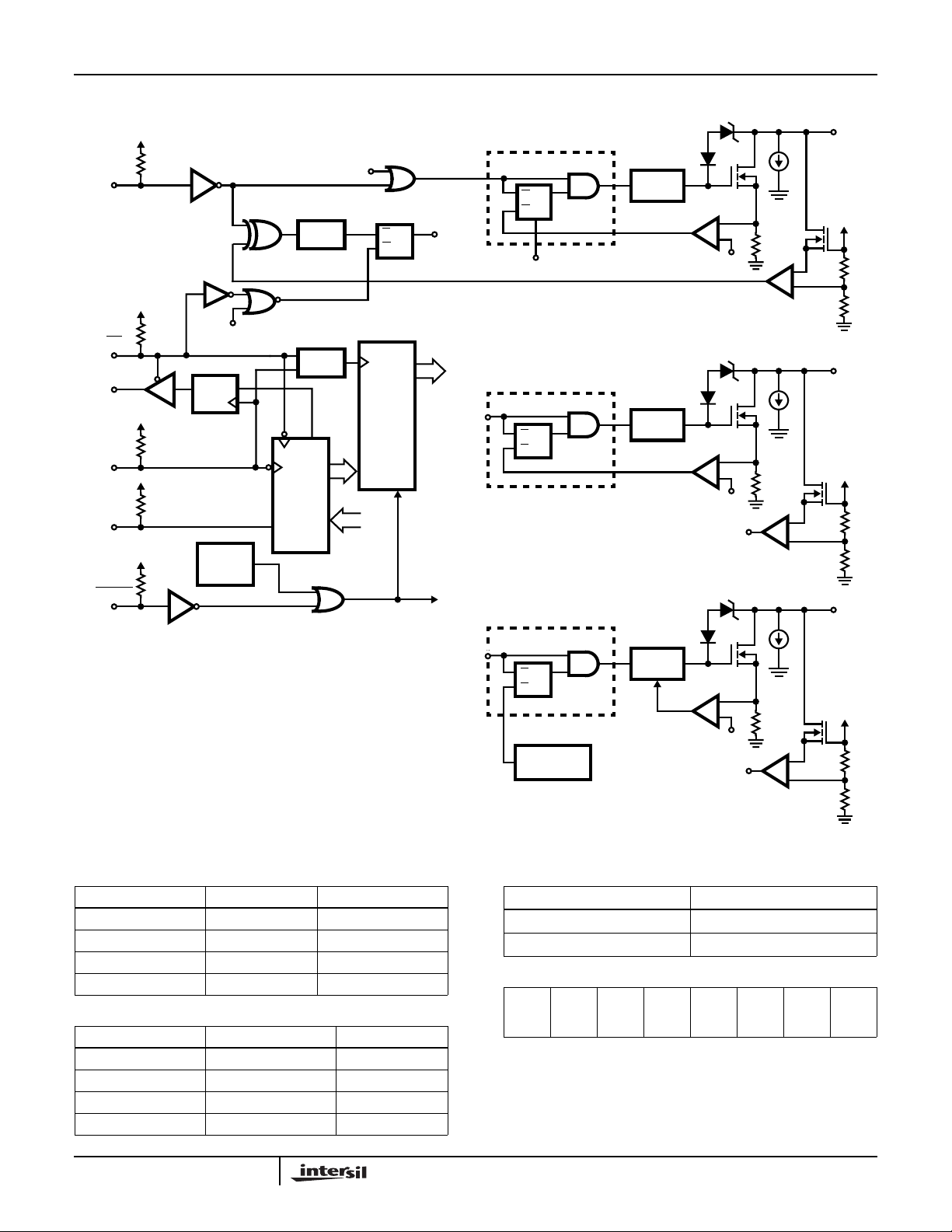
Detailed Block Diagram
HIP0045
SPI
REG
ON/OFF
FILTER
FILTER
OUT
Q0, 1
LATCH
FAULT LATCH
DIAG0-7
S
R
8-BIT
OUTPUT
LATCH
IN 0, 1
CE
MISO
SCK
MOSI
RESET
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
RESET
Q
LOW
VOTAGE
RESET
D
SHIFT
IN
NOTES:
1. OC = Over-Current Voltage Ref. = 1.8V Typ.
2. ISK = Current Sink Pull-Down = 500µA Typ.
3. Diag0, 1 = Status bit when Q0, 1 controlling OUT0, 1.
4. Diag0, 1 = Fault bit when IN1, 0 controlling OUT0, 1.
5. Refer to text and Tables 6, 7 for diagnostic information.
Q
DIAG0, 1
STATUS/
FAULT
Q0-7
ON/OFF
LATCH
RESET
ON/OFF
LATCH
Q2 - 5
Q6, 7
OVERLOAD LATCH
QS
R
RESET
OVERLOAD LATCH
QS
R
OVERLOAD LATCH
QS
R
OVER-TEMP.
DET.
DRIVER
DRIVER
DRIVER
-
+
OC
REF
-
+
OC
REF
DIAG2-5
STATUS
-
+
OC
REF
DIAG6, 7
STATUS
I
OUT0, 1
SK
V
CC
V
+
REF
-
I
OUT2-5
SK
V
CC
+
V
REF
-
I
OUT6, 7
SK
V
CC
+
V
REF
-
Input to Output Control Tables
TABLE 1. OUTPUT 0
SPI BIT 0 IN0 OUT0
0 1 OFF
00ON
10ON
11ON
TABLE 2. OUTPUT 1
SPI BIT 1 IN1 OUT1
0 1 OFF
00ON
10ON
11ON
4-2
TABLE 3. OUTPUT 2 - 7
SPI BIT 2 - 7 OUT2 - 7
0 OFF
1ON
TABLE 4. OUTPUT CONTROL REGISTER, Q0 - 7
Q1 Q3 Q5 Q7 Q0 Q2 Q4 Q6
(D7I) (D6I) (D5I) (D4I) (D3I) (D2I) (D1I) (D0I)
MSB LSB
NOTE: The OutputControl Register bitsQ0 -7 have thesame order
asthe Diagnostic FailureRegister bits Diag0- 7as definedin Table 5.
Data bits D0I - D7I give the MOSI SPI serial data input flow
sequence.
Page 3
HIP0045
Absolute Maximum Ratings Thermal Information
Maximum Output Voltage, V
Peak Output Load Current, I
Continuous Output Load Current, I
Continuous Output Load Current, I
Total Average Current, I
OUT
Reverse Peak Current Drive, Any one Output, IRD; t ≤ 2ms . . . -3A
DC Logic Supply, VCC. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.3 to 7V
Input Voltage, All Inputs and Data Lines . . . . . . . -0.3 to VCC+0.3V
Operating Conditions
Temperature Range. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -40oC to 125oC
Logic Supply Voltage, VCC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.5V to 5.5V
CAUTION: Stresses above those listed in “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress only rating and operationofthe
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
NOTE:
6. θJA Rated with standard PC Board, θJC rated with infinite heat sink.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-0.7 to V
OUT
. . . . . As Specified for ISC, I
LOAD
(All 8 Outputs ON) . . . . 0.5A
OUT
(Any one Output ON) . . 1A
OUT
OC
LIM
(All 8 Outputs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.5A
Thermal Resistance (Typical, Note 6) θJA (oC/W) θJC (oC/W)
PSOP Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 2
Maximum Junction Temperature, TJ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .150oC
Maximum Storage Temperature Range, T
. . . . -55oC to 150oC
STG
Maximum Lead Temperature (Soldering 10s) . . . . . . . . . . . . .265oC
Die Characteristics
Back Side Potential . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .V- (GND Pin, Heat Sink)
Electrical Specifications V
= 4.5V to 5.5V, TA = -40oC to 125oC, Unless Otherwise Specified
CC
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Standby Current, No Load I
Supply Current, Full Load I
Output Clamping Voltage (Note 7) V
Output Clamping Energy E
CCO
No Load - - 5 mA
All Outputs ON, 0.5A Load Per Output - - 5 mA
CC
OCILOAD
1ms Single Pulse Width, TA = 25oC,
OC
(Refer to Figure 4 for SOA)
Output Leakage Current 1 (Note 8) I
Output Leakage Current 2 (Note 8) I
Output Leakage Current 3 (Note 8) I
Drain-to-Source On Resistance, OUT0 - 7 r
Output Capacitance C
Turn-On Delay, OUT0, 1 t
Turn-On Delay, OUT2 - 7 t
Turn-Off Delay t
Turn-On Voltage Slew-Rate, OUT2 - 7 For V
Turn-On Voltage Slew-Rate, OUT0, 1 ForV
Turn-Off Voltage Slew-Rate, OUT0 - 7 For V
Turn-Off Voltage Slew-Rate, OUT0 - 7 For V
O LEAK1VOUT
O LEAK2VOUT
O LEAK3VOUT
DSONILOAD
OUTVOUT
d(ON)RL
d(ON)RL
d(OFF)RL
dV
-------------------
dV
-------------------
dV
----------------------
dV
----------------------
ON1
dt
ON2
dt
OFF1
dt
OFF2
dt
V
IN0,1
V
BATT
V
BATT
V
IN0,1
V
BATT
RL = 500Ω
RL = 500Ω
RL = 500Ω
V
BATT
FAULT PARAMETERS
Reverse Current Drive, OUT0 - 7 I
Reverse Voltage Drop, OUT0 - 7 V
∆ICC during Reverse Current Drive ∆I
RD
RDIOUT
CCIOUT
= 0.5A, Output Programmed OFF 45 - 62 V
20 45 - mJ
= 25V, Outputs OFF - - 100 µA
= 16V, Outputs OFF - - 100 µA
= 16V, Outputs OFF, VCC = 1V - - 10 µA
= 0.5A; TJ = 150oC - - 1.5 Ω
= 16V, f = 1MHz - - 20 pF
= 500Ω, VCE = 50% to V
= 50% to V
OUT
= 0.9 x V
OUT
= 0.9 x V
,
BATT
BATT
,
--5µs
= 16V
= 500Ω, VCE = 50% to V
OUT
= 0.9 x V
BATT
,
--10µs
= 16V
= 500Ω, VCE = 50% to V
= 50% to V
OUT
= 0.9 x V
OUT
= 0.1 x V
,
BATT
BATT
,
--10µs
= 16V
= 90%to 30% ofV
OUT
= 90% to30% of V
OUT
= 30% to90% of V
OUT
= 30% to 80% of V
OUT
BATT;VBATT
BATT;VBATT
BATT;VBATT
OC;
= 16V,
= 16V,
= 16V,
- 0.7 3.5 V/µs
- 2 10 V/µs
- 2 10 V/µs
- 2 15 V/µs
= 0.9 x VOC, RL = 500Ω
-500 - - mA
= -3A, t ≤2ms -1.5 - - V
= -3A, t ≤2ms - - 100 mA
4-3
Page 4

HIP0045
Electrical Specifications V
= 4.5V to 5.5V, TA = -40oC to 125oC, Unless Otherwise Specified (Continued)
CC
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Open Load Threshold Voltage V
Open Load Pull-Down Current I
Over-CurrentShutdown Threshold, OUT0 - 5 I
Short Circuit Current Limit, OUT6, 7 I
Short Circuit Shutdown Delay, OUT0 - 5 t
DisableFault DetectionTime,Channel IN0,
t
Open Load Fault Condition, Fault Detected If
REF
V
< V
OUT
REF
No Load, V
SK
VCC = 5V 1.05 1.4 2 A
SC
VCC = 5V 1.05 1.4 1.75 A
LIM
SC
DF
OUT
= V
= 16V 20 - 100 µA
BATT
0.32 x
V
CC
- 0.4x
0.2 - 12 µs
15 - 50 µs
IN1 After Input Switch Transition
Over-Temperature Detection Threshold T
OFF
155 165 175
LOGIC INPUTS (IN0, IN1, MOSI, SCK, RESET, CE)
Threshold Voltage at Falling Edge VT- 0.2xV
--V
CC
Threshold Voltage at Rising Edge VT+ - - 0.7xV
Hysteresis Voltage V
Input Current I
Input Pull-Up Resistance R
Input Capacitance C
Input Frequency, IN0, IN15 f
Active Supply Range for Reset State
V
HCC_RS
Change at RESET Pin
Low VCC Active Reset Threshold V
LCC_RST
VT+ - VT- 0.65 - - V
H
VIN = V
IN
IN
IN
IN
CC
RESET Pin Forced Reset. (Note: Normal V
Functional Operating Range is 4.0V to 5.5V)
T
Low VCC Forced Reset, (Low Voltage Reset
Active for 0 < VCC < V
LCC_RST
CC
)
- - +10 µA
50 80 200 kΩ
- - 10 pF
DC - 2 kHz
3.1 - 5.5 V
3.1 - 4 V
LOGIC OUTPUT (MISO)
Data Output LOW Voltage V
Data Output HIGH Voltage V
SOLISO
SOHISO
= -3.2mA - 0.2 0.4 V
= -4mA VCC-
--V
0.4V
Output Three-State Leakage Current I
Output Capacitance C
SOL
CE = High, 0V ≤ VSO≤ V
f
SO
= 3MHz - - 10 pF
OPER
CC
-10 - +10 µA
V
V
CC
o
C
V
CC
Serial Peripheral Interface Timing (MOSI, MISO Load Capacitor = 100pF, See Figure 1)
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITION MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Clock Frequency, 50% Duty Cycle f
Enable Lead Time
(SCK Change Low to High after CE = Low)
Enable Lag Time
(Time for SCK Low before CE goes High)
Minimum Time SCK = High t
Minimum Time SCK = Low t
Data Setup Time (SCK Change from High to Low
after MOSI Data Valid)
Data Hold Time (MOSI Data Hold Time SCK
Change from High to Low)
Enable Time from CE = Low to Data at MISO t
Disable Time
(Time for CE Low to High to Output Data Float)
4-4
CLK
t
LEAD
t
LAG
WSCKH
WSCKL
t
SU
t
H
EN
t
DIS
3 - - MHz
100 - - ns
150 - - ns
160 - - ns
160 - - ns
20 - - ns
-20ns
- - 100 ns
- - 100 ns
Page 5

HIP0045
Serial Peripheral Interface Timing (MOSI, MISO Load Capacitor = 100pF, See Figure 1)
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITION MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Data Valid Time, SCK to Data at MISO Valid t
Time forSCK Low beforeCE Low (SCKSetup Time
V
t
SCK_LEAD
before CE High to Low Change)
Time for SCK High after CE High t
SCK_LAG
CE Pulse Filter Time - Note 9 - ns
NOTES:
7. The MOSFET Output Drain is internally clamped with a Drain-to-Gate zener diode that turns-on the MOSFET; holdingthe Drain at the Output
Clamp Voltage, VOC.
8. The measurement ofOutput Leakage Current includesthe Output Pull-Down Current, ISK. EachOutput has a CurrentPull-Down which is used
to detect open load fault conditions.
9. The digital filter time for the output latch function determines if the output latch function will be enabled. The output latch function will only be
enabled if a positive CE slope occurs after 8 SCK clock cycles or a multiple of 8 SCK cycles since the last CE negative slope change.
VCC = 5V ±0.1V - - 100 ns
100 - - ns
150 - - ns
Timing Diagrams
CE
CE
(INPUT)
SCK
(INPUT)
MISO
(OUTPUT)
MOSI
(INPUT)
SCK
HIGH
Z
(CPOL = 0, CPHA = 1)
t
t
t
EN
WSCKH
LEAD
LAST BIT
TRANSMITTED
t
SU
MSB 6 5 4 3 2 1 LSB
INTERNAL STROBE FOR DATA CAPTURE
FIGURE 1A. DATA AND CLOCK TIMING DIAGRAM
t
LAG
t
WSCKL
D7O D6O D0O
t
V
D7I D6I D0I
t
H
t
DIS
FAULT-INDUCED
TURN-OFF
DRIVER
OUTPUT
OLD
4-5
FIGURE 1B. SPI TIMING DIAGRAM
t
DON
t
DOFF
NEW
t
DF
Page 6

HIP0045
Timing Diagrams
OUTPUTS
RESET
CE
SCK
MOSI
MISO
(Continued)
76543210
76543210
OLD NEW
FIGURE 2. BYTE TIMING DIAGRAM WITH ASYNCHRONOUS RESET
Signal Pin Descriptions
Power Output Drivers, OUT0 - OUT7 - The input and
output bits corresponding to Output 0 thru Output 7 are
transmitted and received most significant bit (MSB) first via
the SPI bus. Outputs OUT0 - 5 are provided with overcurrent shutdown. Current Limiting and Thermal Shutdown
are provided on OUT6, 7 for application use as Lamp
Drivers. After a fault shutdown, the control lines remain
active. The fault latches must be cleared by turning the
output off and on to reset the output to an ON state. OUT1, 2
latches may be cleared by the
RESET - Active low reset input. An internal pull-up is
provided on-chip. When this input line is low, all output
drivers are turned-off and the OUT1, 2 fault latches are
cleared. An internal low voltage reset is ORed with the
RESET input. When VCC is less than V
internal reset is active.
CE - Active low chip enable. The falling edge of CE loads the
shift register with the output status bits. Data is transferred
from the shift register to the outputs on the rising edge of CE.
The output driver for the MISO pin is enabled when CE goes
low .CE must be a logic low prior to the first serialclock(SCK)
and must remain low until after the last (eighth) serial clock
cycle. All eight MOSI bits of input data must be loaded in the
same sequence of SCK clock input. A digital filter is used in
the
CE line to insure that 8 (or a multiple of 8) clock cycles
occurs while
period, t
CE is active low. After SCK is low for a short
; CE maybe changed from low to high to latch the
LAG
input data. A lowlevel on CE alsoactivatesan internaldisable
circuit used for unlatching output states that are in a fault
mode as sensed by an out of saturation condition. A high on
CE forces MISO to a high impedance state. Also, when CE is
high, the octal driver ignores the SCK and MOSI signals.
IN0, 1 - IN0 and IN1 are Channels 0 and 1 direct parallel
input controls. Refer to ‘Special Input Conditions for Channel
0, 1‘ in the following te xt.
RESET pin.
LCC_RST
, the
RESET
FAULTS
SCK, MISO, MOSI - Refer to the ‘Serial Peripheral Interface’
(SPI) section in the following text.
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a serial synchronous
bus forcontrol and data transfers.The Clock (SCK), which is
generated by the microcomputer, is active only during data
transfers. In systems using CDP68HC05 family
microcomputers, the inactive clock polarity is determined by
the CPOL bit in the microcomputer’s control register. The
CPOL bit is used in conjunction with the clock phase bit,
CPHA to produce the desired clock data relationship
between the microcomputer and octal driver. The CPHA bit
in general selects the clock edge which captures data and
allows it to change states. For the HIP0045, the CPOL bit
must be set to a logic zero and the CPHA bit to a logic one.
Configured in this manner, MISO (output) data will appear
with every rising edge of the SCK clock pulse, and MOSI
(input) data will be latched into the shift register with every
falling edge of the SCK clock pulse. Also, the steady state
value of the inactive serial clock, SCK, will be at a low level.
Timing diagramsforthe serial peripheral interface are shown
in Figure 1.
SPI Signal Descriptions
MOSI (Master Out/Slave In) - Serial data input. Data bytes
are shifted in at this pin, most significant bit (MSB) first. The
data is passed directly to the shift register which in turn
controls the latches and output drivers.
MISO (Master In/Slave Out) -Serialdataoutput.Data bytes
are shifted out at this pin, most significant bit (MSB) first.
This pin is the serial output from the shift register and is
three stated when
information is given in Tables 6 and 7. Determination of the
fault condition may be done as a software sequence, based
on MOSI data latched into the shift register and subsequent
data clocked out of the MISO pin.
CE is high. Diagnostic Failure Register
4-6
Page 7

HIP0045
SCK - Serial clock input. The SCK signal clocks the shift
register and new MOSI (input) data will be latched into the
shift register on every falling edge of SCK. The SCK phase
bit, CPHA=1 and the polarity bit, CPOL=0, must be set in the
microcomputer’s control register.
Functional Descriptions
The HIP0045 is a low quiescent power, high voltage, high
current, octal, serial low side driver featuring eight channels
of open drain MOS output drivers. Referring to the Detailed
Block Diagram, the drivers have low r
saturation voltage with over-voltage drain-to-gate zener
clamp circuits. Each output is short circuit protected and
suited for driving resistive or inductive loads such as
solenoids, relays and lamps. Data is transmitted to the
device serially using the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
protocol. Each channel is independently controlled by an
output latch and a common
RESET line that disables all
eight outputs. Byte timing with asynchronous reset is shown
in Figure 2.
CDP68HC05C4
MICROCOMPUTER
PORT
MOSI
MISO
SCK
RESET
FIGURE 3. TYPICAL MICROCOMPUTER INTERFACE WITH
THE HIP0045
The circuitreceives8-bit serial data bymeans of the serial input
(MOSI), andstoresthis data in an internal registertocontrol the
output drivers. The serial output (MISO) provides 8-bit
diagnostic data representing the voltage lev el at the driver
output. This allows the microcomputer to diagnose the
condition at the output drivers. The deviceisselectedwhenthe
chip enable (
CE) line is low . When (CE) is high, the de vice is
deselected and the serial output (MISO) is placed in a threestate high impedance mode. The device shifts serial data on
the rising edge of the serial clock (SCK), and latches data on
the falling edge. On the rising edge of chip enable (
input data from the shift register is latched to control the output
drivers. The falling edge of chip enable (
output drivers fault information back to the shift register. The
output drivers have low ON v oltage at r ated current, and are
monitored by a comparator for an out of saturation condition, in
which case the output driver with the fault becomes unlatched
and diagnostic data is sent to the microcomputer via the MISO
line. A typical microcomputer interface circuit is shown in
Figure 3.
and low
DSON
HIP0045
CE
MOSI
MISO
SCK
RESET
CE), new
CE) transfers the
SPI Shift Register
The SPI shift register has both serial and parallel inputs and
outputs. Serial output and input data are simultaneously
transferred to and from the SPI bus. The serial input data is
parallel latched into the 8-Bit Output Latch of the HIP0045 at
the end of a data transfer. Diagnostic data, Diag0-7 is
transferred to the shift register when
CE goes low at the
beginning of a data transfer cycle.
8-Bit Output Latch
The 8-Bit Output Latch is used to control the output drivers.
New serial data is transferred from the shift register to the
8-Bit Output Latch when CE goes high. The 8-Bit Output
Latch is cleared by an active low
RESET signal.
Output Drivers
The output drivers provide an active low output of 500mA
nominal with current limiting set to greater than 1.05A to
allow for high inrush currents. In addition, each output is
provided with a voltage drain-to-gate clamp circuit to limit
inductive transients. Each output driver is also monitored by
a comparator for an out of saturation condition. If the output
voltage of an ON output pin exceeds the saturation voltage
limit, a fault latch turns off the output. The threshold
comparators are used to detect shorts to the power supply,
shorts to ground and open loads. Each comparator provides
status data to the shift register for diagnostic feedback. An
internal pull-down current, I
at each output will provide an
SK
indicator for low output voltage if the output is programmed
OFF and the output line is open. Refer to Tables 6 and 7 for
Fault information versus output control and V
V
is the out-of-saturation threshold for an ON state.
REF
When the output is switched off and V
REF
. Note that
REF
is low, an open-
load or ground fault is indicated.
CE High to Low Transition
When CE is low the three-state MISO pin is enabled. On the
falling edge of
CE, diagnostic and status data from the
output voltage comparators will be latched into the shift
register.Duringthetime that
CE is low,databytescontrolling
the output drivers are shifted in at the MOSI pin most
significant bit (MSB) first. Tables 1, 2 and 3 define the logic
state for control of each output and Table 4 defines the
control bit structure.
CE Low to High Transition
When the last serial data bit has been shifted into the MOSI
pin,
CE pinispulled high to transferdatafrom the shift register
into the 8-bit parallel output latch to activate the outputs. The
serial clock input pin (SCK) should be low during
transitionstoavoid falseclockingof the shift register.The SCK
input isgatedby
CE sothattheSCK input is ignored when CE
is high.
CE
4-7
Page 8

HIP0045
Detecting Fault Conditions
Fault conditions ma y be checked as follo ws: SCK is alw ays
low when
output is taken out of the three-state mode and the Output
status information is latched into the shift register.While
low , data bits in the shift register are tr ansferred to the MISO
output on each positive SCK clock transition and data bits
present at theMOSIinputare transferred into the shiftregister
on each negative transition of SCK. To verify Status and
Diagnostic conditions, clock in a new control byte and wait
approximately 150µs to allow the outputs to settle. Clock in
the same control byte and compare this to the data output at
the MISO pin. If there is a disparity , use Tables 5, 6 and 7 to
determine the faultorstatuscondition. (Use Tables 1,2,3and
4 to establish the ON/OFF conditions for each output).
Based on the needs of the application, a software sequence
should be programmed into the microcontroller to set the
corrective action of each fault condition.
Diag1 Diag3 Diag5 Diag7 Diag0 Diag2 Diag4 Diag6
(D7O) (D6O) (D5O) (D4O) (D3O) (D2O) (D1O) (D0O)
MSB LSB
NOTE:
10. The Diagnostic Failure Register bitsDiag0 -7 have the same
OUTPUT
STATE
CE is changing. When CE goes low, the MISO
CE is
TABLE 5. DIAGNOSTIC FAILURE REGISTER STRUCTURE
order as the Control Register bits Q0 - 7 as defined in Table 4.
Data bits D0O - D7O give the MISO SPI serial output flow
sequence.
TABLE 6. DEFINITION OF Diag0, 1 FAULT BITS FOR OUT0,
1 IN PARALLEL-CONTROLLED MODE
STATUS
OFF >V
OFF <V
ON <V
ON >V
V
REF
REF
REF
REF
REF
FAULT
BIT
H No Fault
L Open Load or GND Short
H No Fault
L Short to V
FAULT
MODE
BATT
Special Conditions for Channel 0, 1
Referring to the Detailed Block Diagram, Channel’s 0, 1 are
configured to externally provide control of the ON/OFF state.
The inputs, IN0 and IN1, are ORed with the SPI ON/OFF
control bit. In this configuration with IN0 and IN1 high, SPI
control latches Diag0andDiag1 as status bits. When the IN0
and IN1 inputs are active, a fault condition is detected by a
comparison of IN0 and IN1 to OUT0 and OUT1 respectively
causing the Fault Detector to latch a fault bit. The resulting
Faultoutputis latched as diagnostic bit, Diag0 or Diag1. The
Diag0 and Diag1 outputs give the status or fault condition of
the output drivers as shown in Table 6. Fault detection is
disabled during switching/settling time.
The Diag0 and Diag1 bits from Channel 0 and 1 respectively
indicate a fault when the FAULT BIT is Low, given IN1 and
IN0 control. Otherwise Diag0 and Diag1 are status bits when
controlled by the SPI input. Note that the SPI Bit, given in
Tables 1 and 2 overrides the ON state control from IN0
and IN1.
1000
100
ENERGY (mJ)
SAFE OPERATING AREA
BELOW LINE
10
0.1 1 10 100
TIME (ms)
FIGURE 4. MAXIMUM SINGLEPULSE ENERGY SAFE
OPERATING AREA FOR EACH CLAMPED
OUTPUT DRIVER, TA = 25oC
T ABLE 7. DEFINITION OF Diag0-7 STATUS BITS FOR OUT0-7
OUTPUT
STATE
OFF >V
OFF <V
ON <V
ON >V
NOTES:
11. For Channel 0 (Diag0) and Channel 1 (Diag1):
Fault Bit High = No Fault; Fault Bit Low = Fault Occurred.
12. V
REF
Refer to the Electrical Specification for the V
V
REF
STATUS
is thethreshold referencelevel for detectingan OpenLoad.
REF
REF
REF
REF
STATUS
BIT
H No Fault
L Open Load or GND Short
L No Fault
H Short to V
or Over-Temperature Fault
(Chan. 6, 7)
FAULT
MODE
(Chan. 0-7);
BATT
voltage level.
REF
4-8
Page 9

HIP0045
Power Small Outline Plastic Package (PSOP)
SEATING
PLANE
E2
2 PLACES
(DATUM
S
A
S
CB
M
0.25
A3
D1
0.15
REF.
SLUG
N
D2
3.10 REF.
HEAT
PLANE A)
2 PLACES
-B-
DETAIL "A"
PIN 1
MARKER
E3
E1
E
A1
o
3
2
1.10 MAX. X 45
-A-
1
A2
SEE DETAIL "A"
B
L
1.60 REF.
D
-HA
C0.10
SEATING
PLANE
L1
B
-C-
e
GAUGE
PLANE
o
0-8
S
B
S
CA
M
0.25
b
M20.433
20 LEAD POWER SMALL OUTLINE PLASTIC
PACKAGE
INCHES MILLIMETERS
SYMBOL
0.122 0.142 3.10 3.60
A
A1 0.004 0.012 0.10 0.30 A2 0.118 0.130 3.00 3.30 A3 0.000 0.004 0.00 0.10 -
b 0.016 0.021 0.40 0.53 6, 7
b1 0.016 0.020 0.40 0.50 6, 7
c 0.009 0.013 0.23 0.32 7
c1 0.009 0.011 0.23 0.29 7
D 0.622 0.630 15.80 16.00 3
D1 0.496 0.512 12.60 13.00 D2 - 0.043 - 1.10 -
E 0.547 0.571 13.90 14.50 E1 0.429 0.437 10.90 11.10 4
E2 - 0.114 - 2.90 E3 0.228 0.244 5.80 6.20 -
e 0.050 BSC 1.27 BSC -
L 0.031 0.043 0.80 1.10 5
L1 0.014 BSC 0.35 BSC -
N20 20-
NOTES:
1. Dimensioning and tolerancing per ANSI Y14.5M-1982.
2. "C" isa reference datum.Seating plane is definedby
lead tips only.
3. DimensionD doesnotinclude moldflash, protrusions
or gate burrs. Mold flash, protrusions or gate burrs
shall not exceed 0.15 per side. D measured at -H-.
4. Dimension E1 does not include interlead flash or protrusion. Interlead flash or protrusion shall not exceed
0.15 per side. E1 measured at -H-.
5. Dimension "L" isthe length of terminalfor soldering to
a substrate.
6. The lead width dimension doesnot include dambar
protrusion. Allowable dambar protrusion shall be
0.08mm total in excess ofthe lead width dimension at
maximum material condition.
7. Section"B-B" tobedeter mined at0.10mm to0.25mm
from the lead tip.
8. Controlling dimension: MILLIMETER.
9. Dimensions conform withJEDEC OutlineMO-166AA
Issue B.
17.15
N
13.92
NOTESMIN MAX MIN MAX
-
Rev. 0 3/96
4.09
1.52
b1
c
SECTION "B-B"
4-9
4.22
7.26
c1
b
2.87
0.71
1
e
LAND PATTERN
4.09
2.21
Page 10

HIP0045
All Intersil semiconductor products are manufactured, assembled and tested under ISO9000 quality systems certification.
Intersil semiconductor products are sold by description only .Intersil Corporation reserves the right to make changes in circuit design and/or specifications at any time without notice. Accordingly, the reader is cautioned to verify that data sheets are current before placing orders. Information furnished by Intersil is believed to be accurate and
reliable. Howe ver, no responsibility is assumed by Intersil or its subsidiaries for its use; nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result
from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Intersil or its subsidiaries.
For information regarding Intersil Corporation and its products, see web site http://www.intersil.com
Sales Office Headquarters
NORTH AMERICA
Intersil Corporation
P. O. Box 883, Mail Stop 53-204
Melbourne, FL 32902
TEL: (407) 724-7000
FAX: (407) 724-7240
4-10
EUROPE
Intersil SA
Mercure Center
100, Rue de la Fusee
1130 Brussels, Belgium
TEL: (32) 2.724.2111
FAX: (32) 2.724.22.05
ASIA
Intersil (Taiwan) Ltd.
7F-6, No. 101 Fu Hsing North Road
Taipei, Taiwan
Republic of China
TEL: (886) 2 2716 9310
FAX: (886) 2 2715 3029
 Loading...
Loading...