Page 1
DATA SH EET
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC04
January 1995
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
HEF4029B
MSI
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
•The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic
Family Specifications HEF, HEC
•The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic
Package Outlines/Information HEF, HEC
Page 2
January 1995 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
DESCRIPTION
The HEF4029B is a synchronous edge-triggered up/down
4-bit binary/BCD decade counter with a clock input (CP),
an active LOW count enable input (CE), an up/down
control input (UP/DN), a binary/decade control input
(BIN/DEC), an overriding asynchronous active HIGH
parallel load input (PL), four parallel data inputs (P0to P3),
four parallel buffered outputs (O0to O3) and an active
LOW terminal count output (TC).
Information on P
0
to P3is asynchronously loaded into the
counter while PL is HIGH, independent of CP.
The counter is advanced one count on the LOW to HIGH
transition of CP when CE and PL are LOW. TheTC signal
is normally HIGH and goes LOW when the counter
reaches its maximum count in the UP mode, or the
minimum count in the DOWN mode provided CE is LOW.
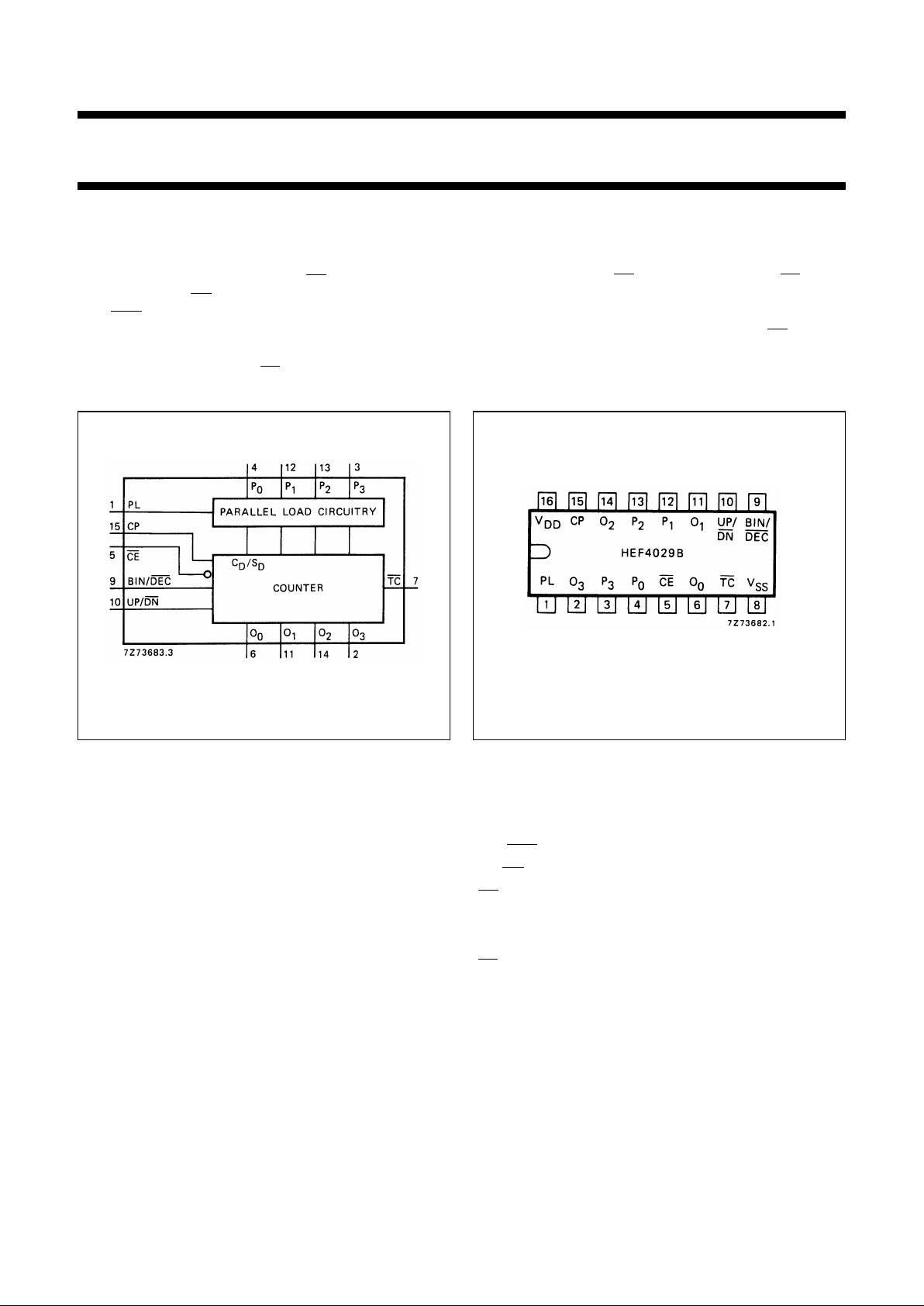
Fig.1 Functional diagram. Fig.2 Pinning diagram.
HEF4029BP(N): 16-lead DIL; plastic
(SOT38-1)
HEF4029BD(F): 16-lead DIL; ceramic (cerdip)
(SOT74)
HEF4029BT(D): 16-lead SO; plastic
(SOT109-1)
( ): Package Designator North America
PINNING
FAMILY DATA, I
DD
LIMITS category MSI
See Family Specifications
PL parallel load input
P
0
to P
3
parallel data inputs
BIN/
DEC binary/decade control input
UP/
DN up/down control input
CE count enable input (active LOW)
CP clock input (LOW to HIGH, edge triggered)
O
0
to O
3
buffered parallel outputs
TC terminal count output (active LOW)
Page 3
January 1995 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
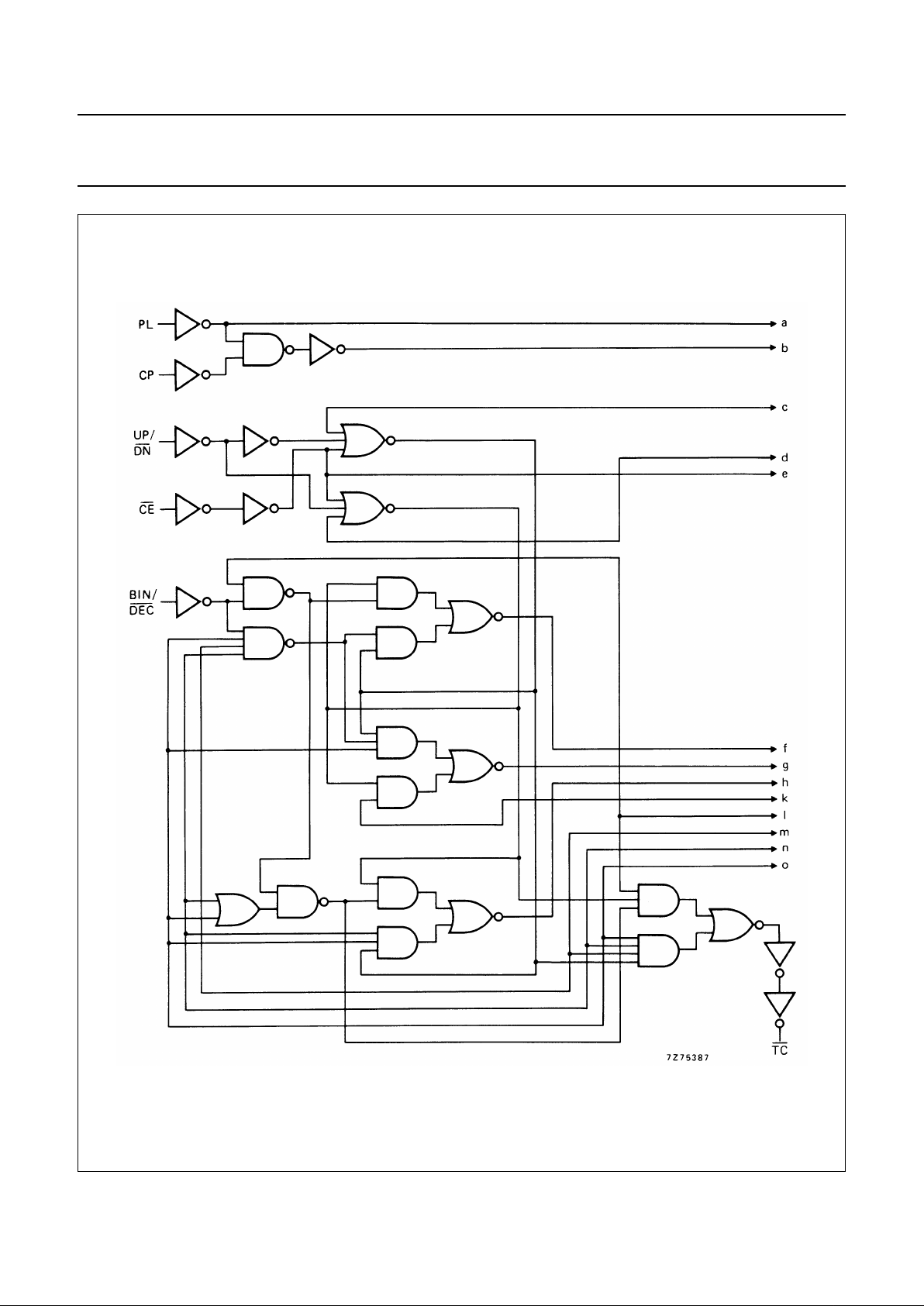
Fig.3 Logic diagram (continued in Fig.4).
Page 4
January 1995 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
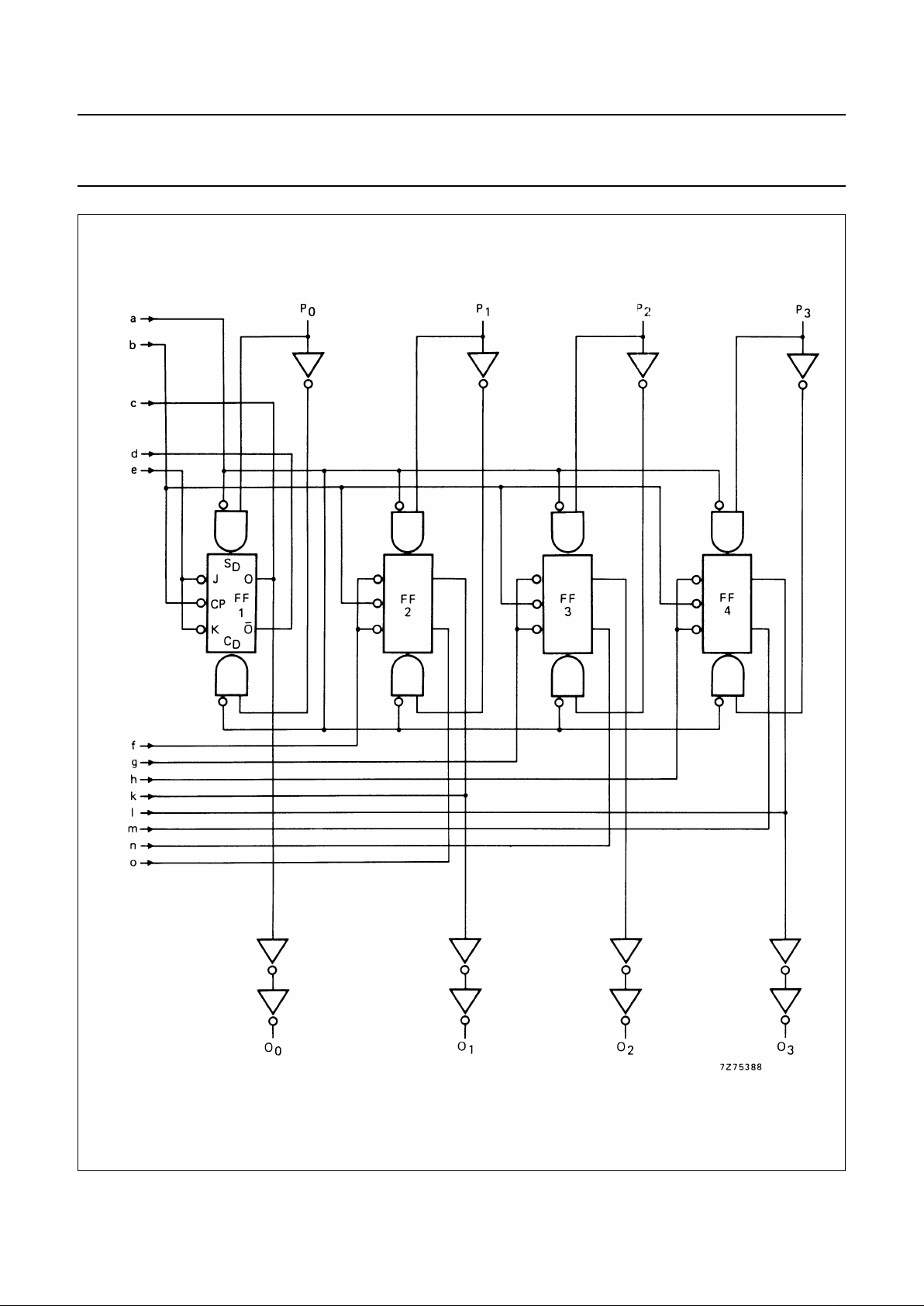
Fig.4 Logic diagram (continued from Fig.3).
Page 5
January 1995 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
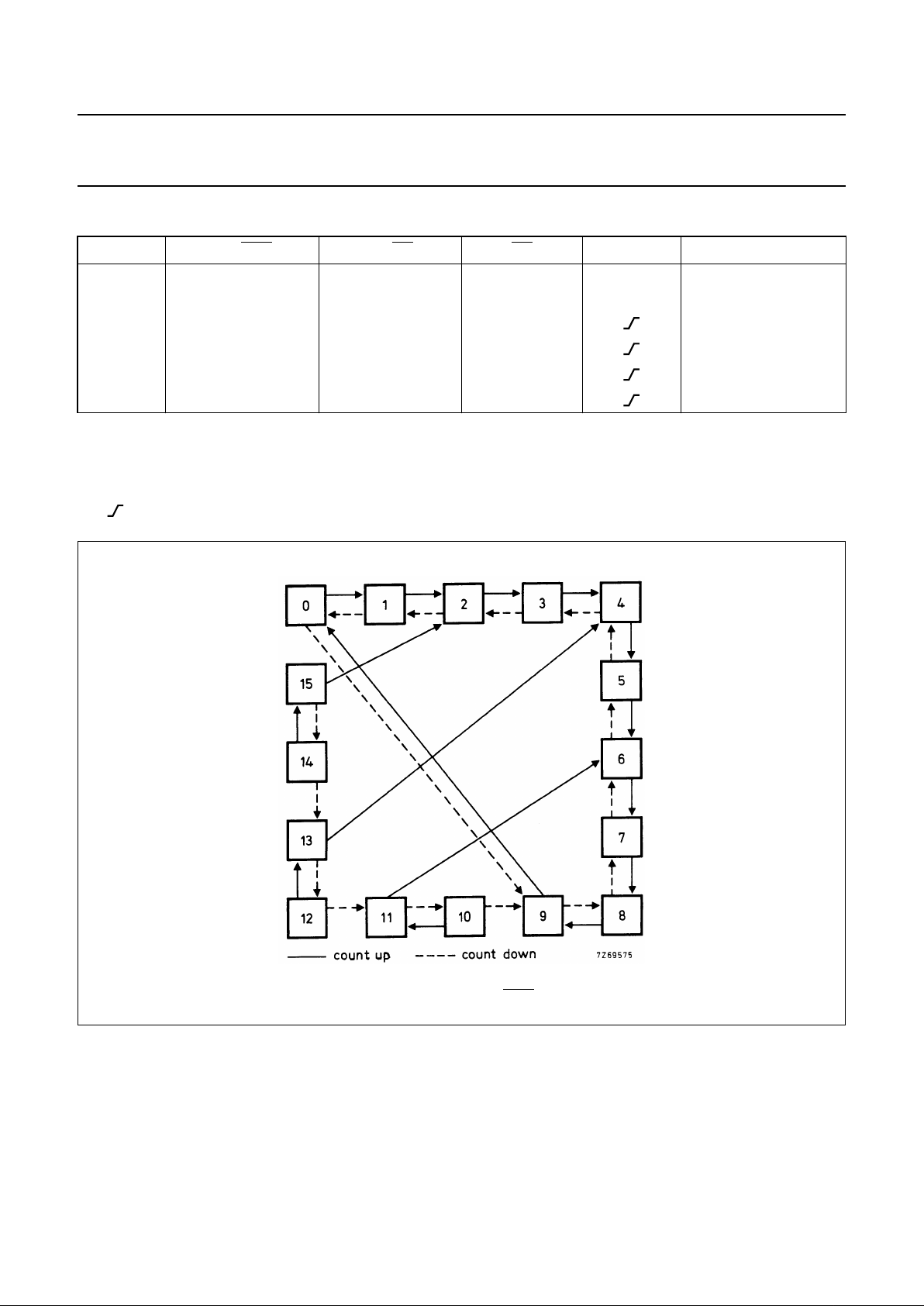
FUNCTION TABLE
Notes
1. H = HIGH state (the more positive voltage)
L = LOW state (the less positive voltage)
X = state is immaterial
= positive-going clock pulse edge
PL BIN/DEC UP/DN CE CP MODE
H X X X X parallel load (P
n
→ On)
L X X H X no change
L L L L count-down, decade
L L H L count-up, decade
L H L L count-down, binary
L H H L count-up, binary
Fig.5 State diagram; BIN/DEC = LOW.
Page 6

January 1995 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
Logic equation for terminal count:
Fig.6 State diagram; BIN/DEC = HIGH.
TC CE (BIN DEC⁄ UP DN⁄ O0O1O2O3BIN DEC UP DN⁄ O0O1O2O3+•••••⁄+•••••=
BIN DEC⁄ UP DN⁄ O0O3BIN DEC⁄ UP DN⁄ O0O1O2O3)•••••+•••
Page 7

January 1995 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
AC CHARACTERISTICS
V
SS
= 0 V; T
amb
=25°C; input transition times ≤ 20 ns
AC CHARACTERISTICS
V
SS
= 0 V; T
amb
=25°C; CL= 50 pF; input transition times ≤ 20 ns
V
DD
V
TYPICAL FORMULA FOR P (µW)
Dynamic power 5 1000 f
i
+∑(foCL) × V
DD
2
where
dissipation per 10 4500 f
i
+∑(foCL) × V
DD
2
fi= input freq. (MHz)
package (P) 15 11 500 f
i
+∑(foCL) × V
DD
2
fo= output freq. (MHz)
C
L
= load capacitance (pF)
∑(f
oCL
) = sum of outputs
V
DD
= supply voltage (V)
V
DD
V
SYMBOL MIN. TYP. MAX.
TYPICAL EXTRAPOLATION
FORMULA
Propagation delays
CP → O
n
5 145 290 ns 118 ns + (0,55 ns/pF) C
L
HIGH to LOW 10 t
PHL
55 110 ns 44 ns + (0,23 ns/pF) C
L
15 40 75 ns 32 ns + (0,16 ns/pF) C
L
5 160 315 ns 133 ns + (0,55 ns/pF) C
L
LOW to HIGH 10 t
PLH
60 120 ns 49 ns + (0,23 ns/pF) C
L
15 40 80 ns 32 ns + (0,16 ns/pF) C
L
CP → TC 5 280 560 ns 253 ns + (0,55 ns/pF) C
L
HIGH to LOW 10 t
PHL
105 205 ns 94 ns + (0,23 ns/pF) C
L
15 70 140 ns 62 ns + (0,16 ns/pF) C
L
5 195 385 ns 168 ns + (0,55 ns/pF) C
L
LOW to HIGH 10 t
PLH
75 150 ns 64 ns + (0,23 ns/pF) C
L
15 55 105 ns 47 ns + (0,16 ns/pF) C
L
PL → O
n
5 120 240 ns 93 ns + (0,55 ns/pF) C
L
HIGH to LOW 10 t
PHL
50 100 ns 39 ns + (0,23 ns/pF) C
L
15 35 70 ns 27 ns + (0,16 ns/pF) C
L
5 170 335 ns 143 ns + (0,55 ns/pF) C
L
LOW to HIGH 10 t
PLH
65 130 ns 54 ns + (0,23 ns/pF) C
L
15 45 90 ns 37 ns + (0,16 ns/pF) C
L
CE → TC 5 180 360 ns 153 ns + (0,55 ns/pF) C
L
HIGH to LOW 10 t
PHL
70 140 ns 59 ns + (0,23 ns/pF) C
L
15 50 100 ns 42 ns + (0,16 ns/pF) C
L
5 170 335 ns 143 ns + (0,55 ns/pF) C
L
LOW to HIGH 10 t
PLH
65 135 ns 54 ns + (0,23 ns/pF) C
L
15 50 100 ns 42 ns + (0,16 ns/pF) C
L
Page 8

January 1995 8
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
Output transition times 5 60 120 ns 10 ns + (1,0 ns/pF) C
L
HIGH to LOW 10 t
THL
30 60 ns 9 ns + (0,42 ns/pF) C
L
15 20 40 ns 6 ns + (0,28 ns/pF) C
L
5 60 120 ns 10 ns + (1,0 ns/pF) C
L
LOW to HIGH 10 t
TLH
30 60 ns 9 ns + (0,42 ns/pF) C
L
15 20 40 ns 6 ns + (0,28 ns/pF) C
L
V
DD
V
SYMBOL MIN. TYP. MAX.
TYPICAL EXTRAPOLATION
FORMULA
Page 9

January 1995 9
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
AC CHARACTERISTICS
V
SS
= 0 V; T
amb
=25°C; CL= 50 pF; input transition times ≤ 20 ns
V
DD
V
SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX
Minimum clock 5 110 55 ns
see also waveforms
Figs 7 and 8
pulse width; LOW 10 t
WCPL
35 20 ns
15 25 15 ns
Minimum PL 5 160 80 ns
pulse width; HIGH 10 t
WPLH
55 25 ns
15 35 15 ns
Recovery time 5 150 75 ns
for PL 10 t
RPL
50 25 ns
15 35 20 ns
Set-up times 5 270 135 ns
BIN/
DEC → CP 10 t
su
90 45 ns
15 60 30 ns
5 300 150 ns
UP/
DN → CP 10 t
su
105 55 ns
15 75 35 ns
5 240 120 ns
CE → CP 10 t
su
90 50 ns
15 70 40 ns
57035ns
P
n
→PL 10 t
su
20 10 ns
15 10 5 ns
Hold times 5 45 −90 ns
BIN/
DEC → CP 10 t
hold
15 −30 ns
15 10 −20 ns
515−135 ns
UP/
DN → CP 10 t
hold
0 −50 ns
15 −5 −35 ns
530−30 ns
CE → CP 10 t
hold
10 −10 ns
15 5 −10 ns
515−20 ns
P
n
→ PL 10 t
hold
0 −10 ns
15 0 −5ns
Maximum clock 5 2 4 MHz
pulse frequency 10 f
max
5 10 MHz
15 8 15 MHz
Page 10

January 1995 10
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
Fig.7 Waveforms showing minimum pulse width for CP, set-up and hold times for CE to CP, BIN/DEC to CP
and UP/DN to CP. Set-up and hold times are shown as positive values but may be specified as negative
values.
Fig.8 Waveforms showing minimum pulse width for PL, recovery time for PL, and set-up and hold times for P
n
to PL. Set-up and hold times are shown as positive values but may be specified as negative values.
Page 11

January 1995 11
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
Fig.9 Timing diagram; decade mode; P0= LOW; P3= LOW; BIN/DEC = LOW.
Page 12

January 1995 12
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
Fig.10 Timing diagram; binary mode; P0= HIGH; P1= LOW; BIN/DEC = HIGH.
Page 13

January 1995 13
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Some examples of applications for the HEF4029B are:
• Programmable binary and decade counting/frequency synthesizers - BCD output.
• Analogue-to-digital and digital-to-analogue conversion.
• Up/down binary counting.
• Magnitude and sign generation.
• Up/down decade counting.
• Difference counting.
Page 14

January 1995 14
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Synchronous up/down counter,
binary/decade counter
HEF4029B
MSI
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
Fig.11 Example of parallel clocking when cascading HEF4029B ICs.
Fig.12 Example of ripple clocking when cascading HEF4029B ICs. Ripple clocking mode: the up/down control can be changed at any count;
the only restriction on changing the up/down control is that the clock input to the first counting stage must be HIGH.
Note
TC lines at all stages after the first may have a negative-going glitch pulse resulting from differential delays of different HEF4029B ICs. These
negative-going glitches do not affect proper HEF4029B operation; however if the
TC signals are used to trigger other edge-sensitive logic devices,
such as flip-flops or counters, the
TC signals should be gated with the clock signal using a 2-input OR gate such as HEF4071B.
 Loading...
Loading...