Datasheet GS881Z18BT-333, GS881Z18BT-300, GS881Z18BT-250, GS881Z18BT-200, GS881Z18BT-150 Datasheet (GSI TECHNOLOGY)
...Page 1

查询GS881Z18B供应商
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
100-Pin TQFP & 165-Bump BGA
9Mb Pipelined and Flow Through
Commercial Temp
Industrial Temp
Synchronous NBT SRAM
Features
• User-configurable Pipeline and Flow Through mode
• NBT (No Bus Turn Around) functionality allows zero wait
read-write-read bus utilization
• Fully pin-compatible with both pipelined and flow through
NtRAM™, NoBL™ and ZBT™ SRAMs
• IEEE 1149.1 JTAG-compatible Boundary Scan
• On-chip write parity checking; even or odd selectable
• 2.5 V or 3.3 V +10%/–10% core power supply
• 2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O supply
• LBO
pin for Linear or Interleave Burst mode
• Pin-compatible with 2M, 4M, and 18M devices
• Byte write operation (9-bit Bytes)
• 3 chip enable signals for easy depth expansion
• ZZ pin for automatic power-down
• JEDEC-standard packages
• Pb-Free 100-lead TQFP package available
Functional Description
The GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
is a 9Mbit Synchronous Static SRAM. GSI's NBT SRAMs,
like ZBT, NtRAM, NoBL or other pipelined read/double late
write or flow through read/single late write SRAMs, allow
utilization of all available bus bandwidth by eliminating the
need to insert deselect cycles when the device is switched from
read to write cycles.
333 MHz–150 MHz
2.5 V or 3.3 V V
DD
2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O
Because it is a synchronous device, address, data inputs, and
read/ write control inputs are captured on the rising edge of the
input clock. Burst order control (LBO
rail for proper operation. Asynchronous inputs include the
Sleep mode enable, ZZ and Output Enable. Output Enable can
be used to override the synchronous control of the output
drivers and turn the RAM's output drivers off at any time.
Write cycles are internally self-timed and initiated by the rising
edge of the clock input. This feature eliminates complex offchip write pulse generation required by asynchronous SRAMs
and simplifies input signal timing.
The GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
may be configured by the user to operate in Pipeline or Flow
Through mode. Operating as a pipelined synchronous device,
in addition to the rising-edge-triggered registers that capture
input signals, the device incorporates a rising-edge-triggered
output register. For read cycles, pipelined SRAM output data is
temporarily stored by the edge triggered output register during
the access cycle and then released to the output drivers at the
next rising edge of clock.
The GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
is implemented with GSI's high performance CMOS
technology and is available in a JEDEC-standard 100-pin
TQFP package.
) must be tied to a power
Paramter Synopsis
-333 -300 -250 -200 -150 Unit
t
KQ
Pipeline
3-1-1-1
Flow Through
2-1-1-1
tCycle
Curr (x18)
Curr (x32/x36)
t
KQ
tCycle
Curr (x18)
Curr (x32/x36)
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 1/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
2.5
3.0
250
290
4.5
4.5
200
230
2.5
3.3
230
265
5.0
5.0
185
210
2.5
4.0
200
230
5.5
5.5
160
185
3.0
5.0
170
195
6.5
6.5
140
160
3.8
6.7
140
160
7.5
7.5
128
145
ns
ns
mA
mA
ns
ns
mA
mA
Page 2
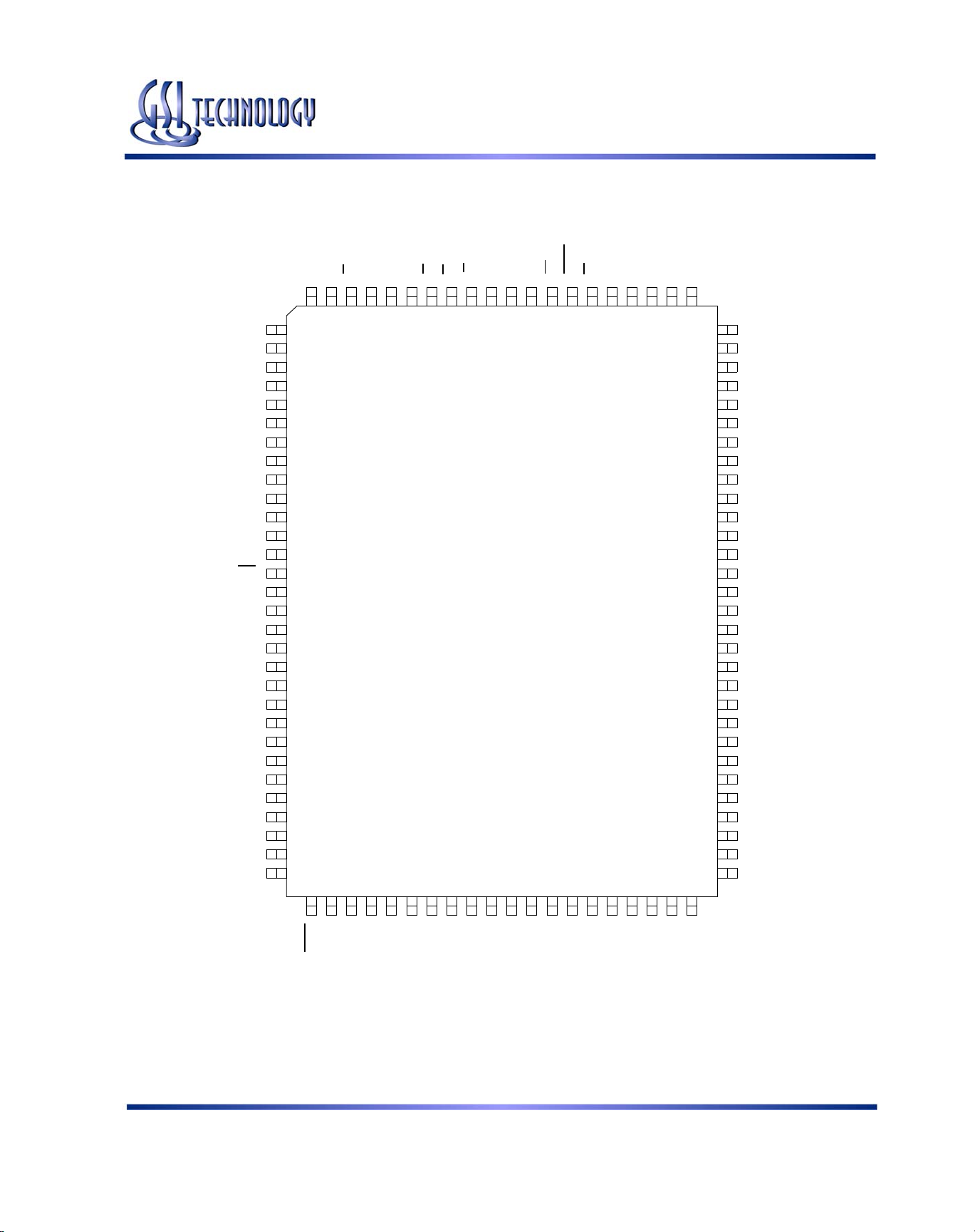
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
GS881Z18BT 100-Pin TQFP Pinout (Package T)
NC
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SS
NC
NC
DQB
DQB
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQB
DQB
FT
V
DD
NC
V
SS
DQB
DQB6
V
DD
V
SS
DQB
DQB
DQPB
NC
V
SS
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
NC
B
B
BA
NC
512K x 18
Top View
1
A
E
A
E2
10099989796959493929190898887868584838281
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
DD
E3
SS
V
V
CK
W
CKE
G
ADV
NC
A
A
A
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
A
NC
NC
V
DDQ
V
SS
NC
DQPA
DQA
DQA
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQA
DQA
V
SS
NC
V
DD
ZZ
DQ
A
DQA
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQA
DQA
NC
NC
V
SS
V
DDQ
NC
NC
NC
LBO
SS
A
A
A
A
A1A0
TDI
TMS
DD
V
V
A A A A A
TDO
TCK
A
1
A
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 2/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 3
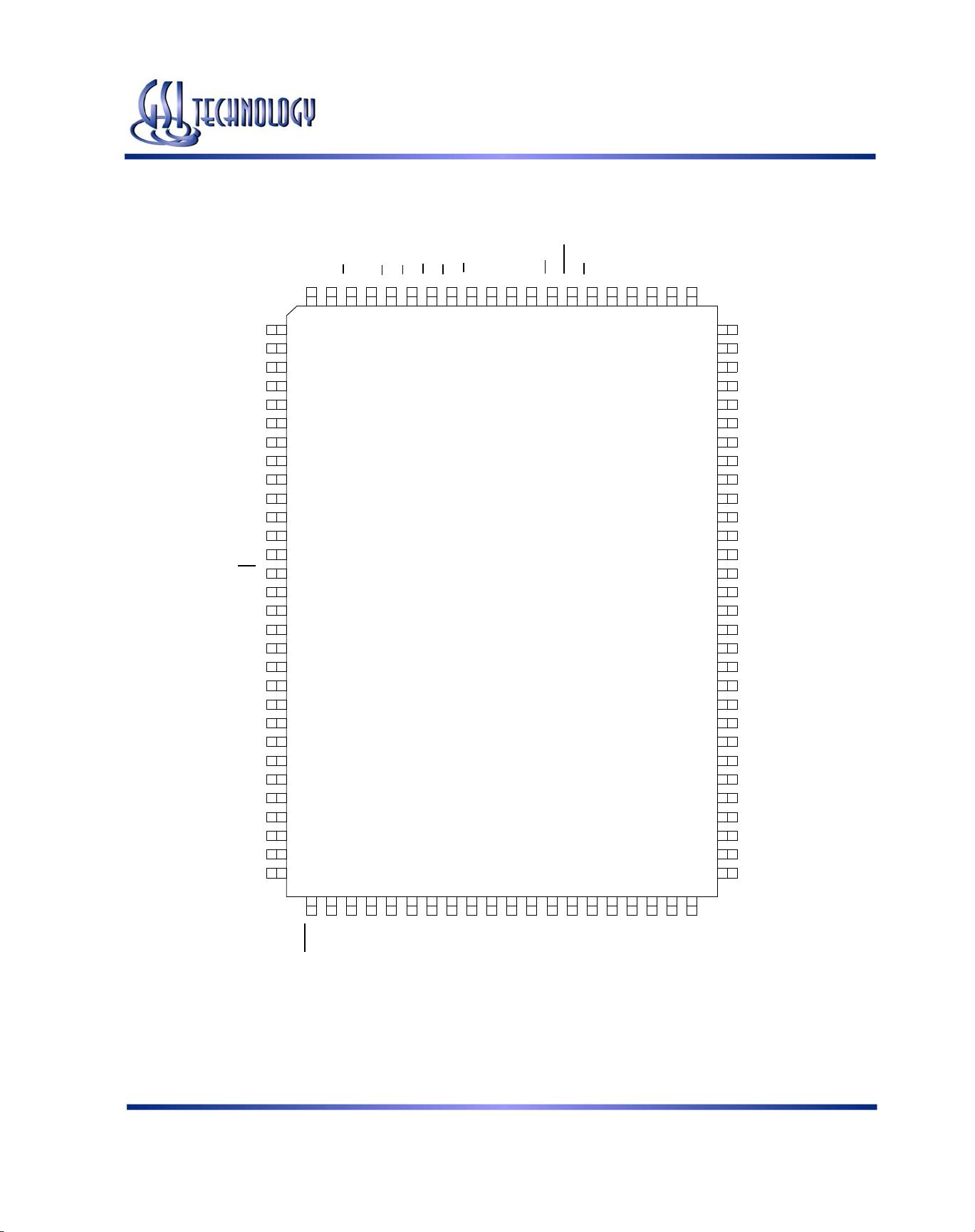
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
GS881Z32BT 100-Pin TQFP Pinout (Package T)
NC
DQC
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQC
DQ
DQC
DQC
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQC
DQC
FT
V
DD
NC
V
SS
DQD
DQD2
V
DDQ
V
DQD
DQD
DQD
DQD
V
V
DDQ
DQD
DQD
NC
SS
SS
1
A
A
10099989796959493929190898887868584838281
1
2
C
C
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
D
E
E2
BB
BA
BC
B
256K x 32
Top View
DD
E3
SS
V
V
CK
W
CKE
G
ADV
NC
A
A
A
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
NC
DQB
DQ
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQB
DQB
DQB
DQB
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQB
DQB
V
SS
NC
V
DD
ZZ
DQ
DQA
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQA
DQA
DQA
DQA
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQA
DQA
NC
B
A
SS
LBO
A
A
A
A
A1A0
TDI
TMS
DD
V
V
A A A A A
TCK
TDO
A
A
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 3/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 4
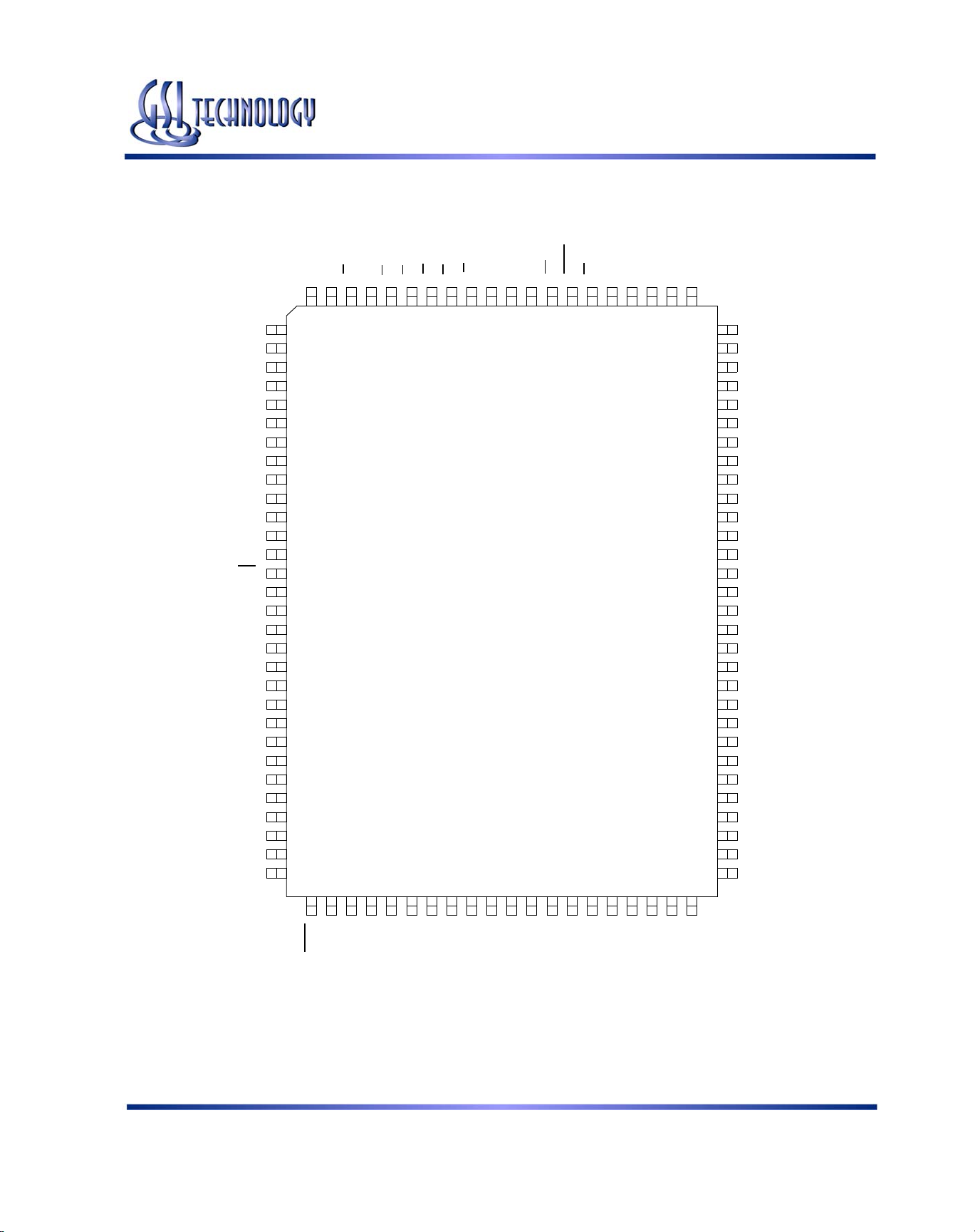
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
GS881Z36BT 100-Pin TQFP Pinout (Package T)
DQPC
DQC
DQC
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQC
DQC
DQC
DQC
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQC
DQC
FT
V
DD
NC
V
SS
DQD
DQD2
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQD
DQD
DQD
DQD
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQD
DQD
DQPD
1
A
A
10099989796959493929190898887868584838281
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
D
E
E2
BB
BA
BC
B
256K x 36
Top View
DD
E3
SS
V
V
CK
W
CKE
G
ADV
NC
A
A
A
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
DQPB
DQB
DQB
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQB
DQB
DQB
DQB
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQB
DQB
V
SS
NC
V
DD
ZZ
DQ
A
DQA
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQA
DQA
DQA
DQA
V
SS
V
DDQ
DQA
DQA
DQPA
SS
LBO
A
A
A
A
A1A0
TDI
TMS
DD
V
V
A A A A A
TCK
TDO
A
A
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 4/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 5

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
100-Pin TQFP Pin Descriptions
Symbol Type Description
A0, A1 In Burst Address Inputs; Preload the burst counter
A In Address Inputs
CK In Clock Input Signal
B
A In Byte Write signal for data inputs DQA1–DQA9; active low
B
B In Byte Write signal for data inputs DQB1–DQB9; active low
B
C In Byte Write signal for data inputs DQC1–DQC9; active low
B
D In Byte Write signal for data inputs DQD1–DQD9; active low
W
E
1 In Chip Enable; active low
E
2 In Chip Enable—Active High. For self decoded depth expansion
E
3 In Chip Enable—Active Low. For self decoded depth expansion
G
ADV In Advance/Load
CKE
NC — No Connect
DQ
A I/O Byte A Data Input and Output pins
DQ
B I/O Byte B Data Input and Output pins
DQ
C I/O Byte C Data Input and Output pins
DQ
D I/O Byte D Data Input and Output pins
ZZ In Power down control; active high
FT
LBO
V
DD
V
SS
V
DDQ
In Write Enable; active low
In Output Enable; active low
; Burst address counter control pin
In Clock Input Buffer Enable; active low
In Pipeline/Flow Through Mode Control; active low
In Linear Burst Order; active low.
In Core power supply
In Ground
In Output driver power supply
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 5/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 6
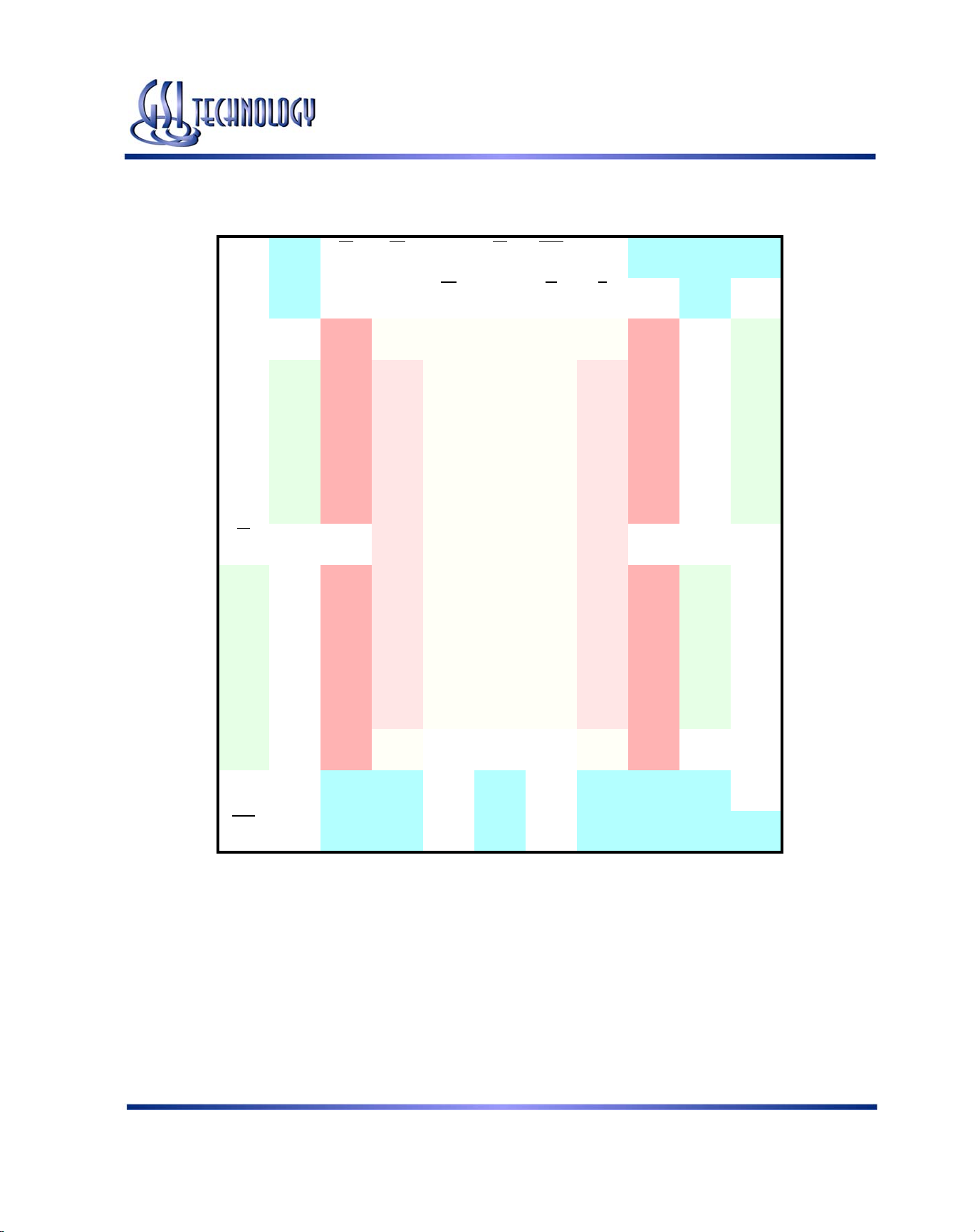
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
165 Bump BGA—x18 Commom I/O—Top View (Package D)
1234567891011
ANC
BNC
CNCNC
DNC
ENC
FNC
GNC
HFT
J
K
L
DQB NC V
DQB NC V
DQB NC V
AE1BB NC E3 CKE ADV A17 A AA
AE2NCBACK W G ANC B
V
DQB V
DQB V
DQB V
DQB V
MCH NC V
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
SS
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
SS
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
V
V
V
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
NC DQA C
NC DQA D
NC DQA E
NC DQA F
NC DQA G
NC NC ZZ H
V
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DQA NC J
DQA NC K
DQA NC L
M
N
DQB NC V
DQB NC V
PNCNC
RLBO
NC A ATMSA0 TCK A A A AR
11 x 15 Bump BGA—13 mm x 15 mm Body—1.0 mm Bump Pitch
DDQ
DDQ
V
V
DD
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC NC NC V
V
DD
SS
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
DQA NC M
NC NC N
A ATDIA1 TDO A A ANC P
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 6/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 7
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
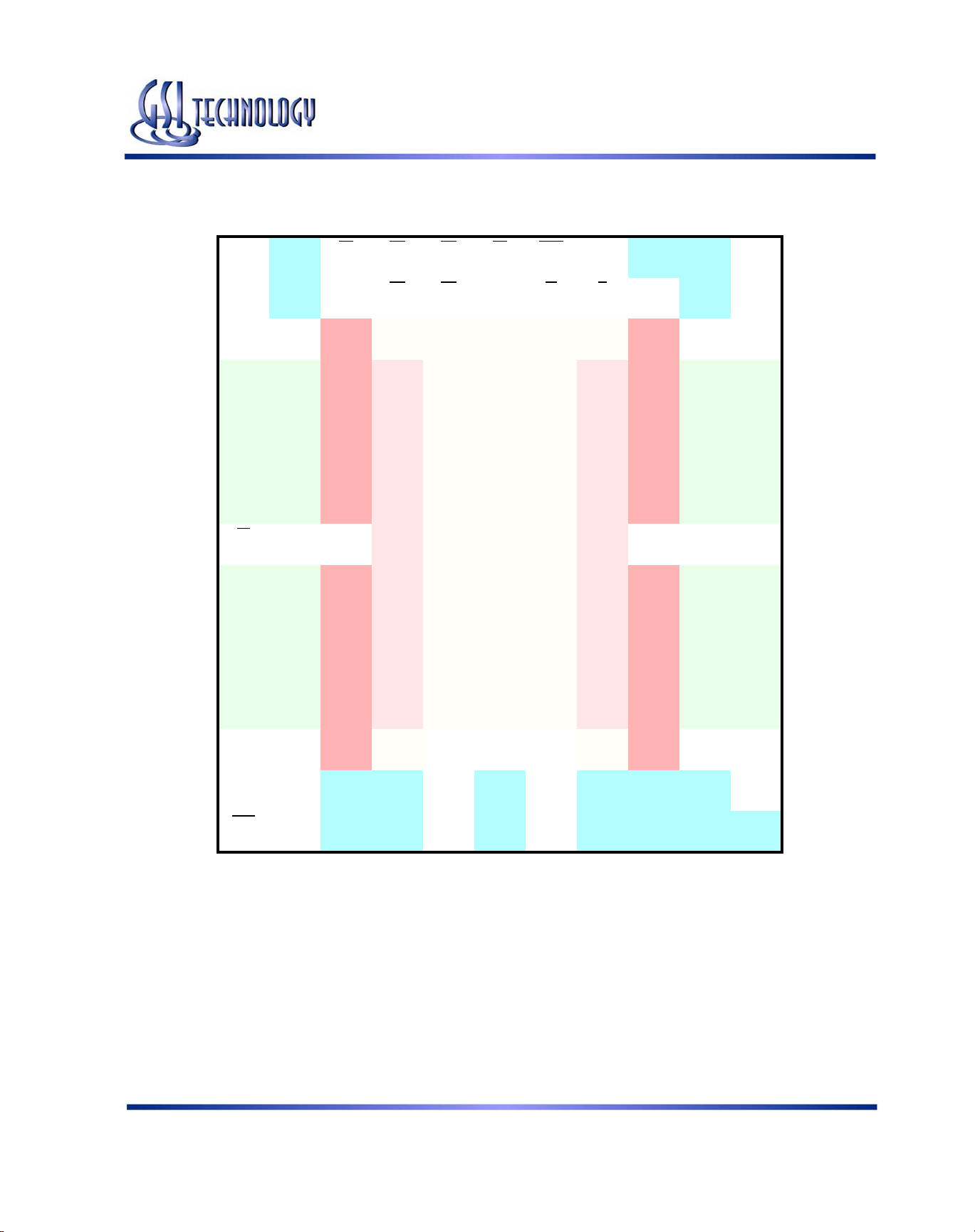
165 Bump BGA—x32 Common I/O—Top View (Package D)
1234567891011
ANC
BNC
CNCNC
D
E
F
G
DQC DQC V
DQC DQC V
DQC DQC V
DQC DQC V
HFT
J
K
L
DQD DQD V
DQD DQD V
DQD DQD V
AE1BC BB E3 CKE ADV A17 ANC A
AE2BDBA CK W G ANC B
V
MCH NC V
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
SS
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
SS
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
V
V
V
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
NC NC C
DQB DQB D
DQB DQB E
DQB DQB F
DQB DQB G
NC NC ZZ H
V
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DQA DQA J
DQA DQA K
DQA DQA L
M
NNCNC
DQD DQD V
V
PNCNC
RLBO
NC A ATMSA0 TCK A A A AR
11 x 15 Bump BGA—13 mm x 15 mm Body—1.0 mm Bump Pitch
DDQ
DDQ
V
V
DD
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC NC NC V
V
DD
SS
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
DQA DQA M
NC NC N
A ATDIA1 TDO A A ANC P
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 7/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 8
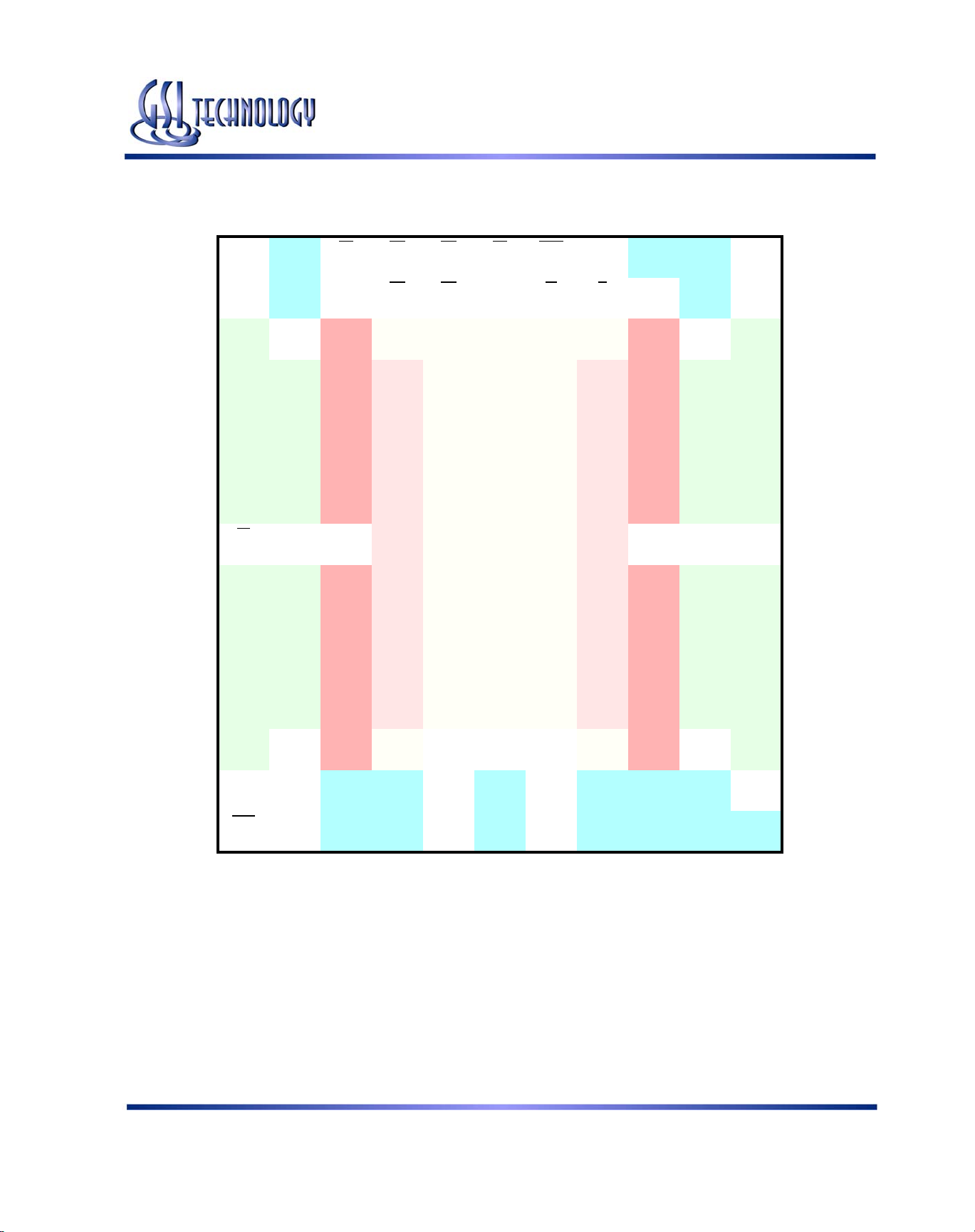
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
165 Bump BGA—x36 Common I/O—Top View (Package D)
1234567891011
ANC
BNC
C
D
E
F
G
HFT
K
L
DQPC NC V
DQC DQC V
DQC DQC V
DQC DQC V
DQC DQC V
J
DQD DQD V
DQD DQD V
DQD DQD V
MCH NC V
AE1BC BB E3 CKE ADV A ANC A
AE2BDBA CK W G ANC B
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
SS
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
SS
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
V
V
V
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
NC DQPB C
DQB DQB D
DQB DQB E
DQB DQB F
DQB DQB G
NC NC ZZ H
V
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DQA DQA J
DQA DQA K
DQA DQA L
M
N
DQD DQD V
DQPD NC V
PNCNC
RLBO
NC A ATMSA0 TCK A A A AR
11 x 15 Bump BGA—13 mm x 15 mm Body—1.0 mm Bump Pitch
DDQ
DDQ
V
V
DD
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
NC NC NC V
V
DD
SS
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
DQA DQA M
NC DQPA N
A ATDIA1 TDO A A ANC P
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 8/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 9
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
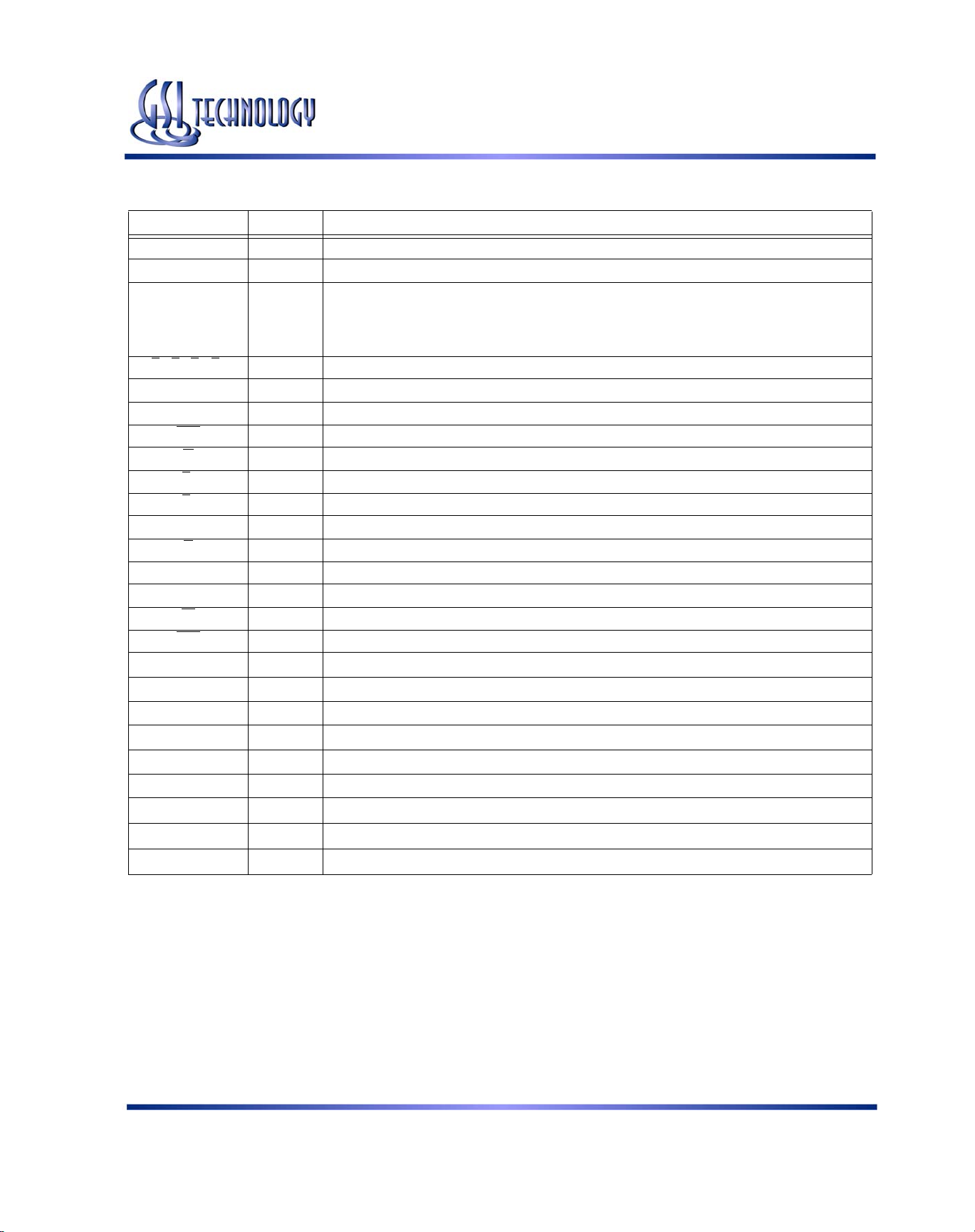
GS81Z18/32/36D 165-Bump BGA Pin Description
Symbol Type Description
A0, A1 I Address field LSBs and Address Counter Preset Inputs
A I Address Inputs
DQ
A
DQB
DQC
DQD
B
A, BB, BC, BD I Byte Write Enable for DQA, DQB, DQC, DQD I/Os; active low
NC — No Connect
CK I Clock Input Signal; active high
CKE
W
E
1 I Chip Enable; active low
E
3 I Chip Enable; active low
E
2 I Chip Enable; active high
G
ADV I Burst address counter advance enable; active high
ZZ I Sleep mode control; active high
FT
LBO
TMS
TDI
TDO
TCK
MCH
DNU
V
DD
V
SS
V
DDQ
I/O Data Input and Output pins
I Clock Enable; active low
I Write Enable; active low
I Output Enable; active low
I Flow Through or Pipeline mode; active low
I Linear Burst Order mode; active low
I Scan Test Mode Select
I Scan Test Data In
O Scan Test Data Out
I Scan Test Clock
— Must Connect High
—Do Not Use
I Core power supply
I I/O and Core Ground
I Output driver power supply
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 9/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 10
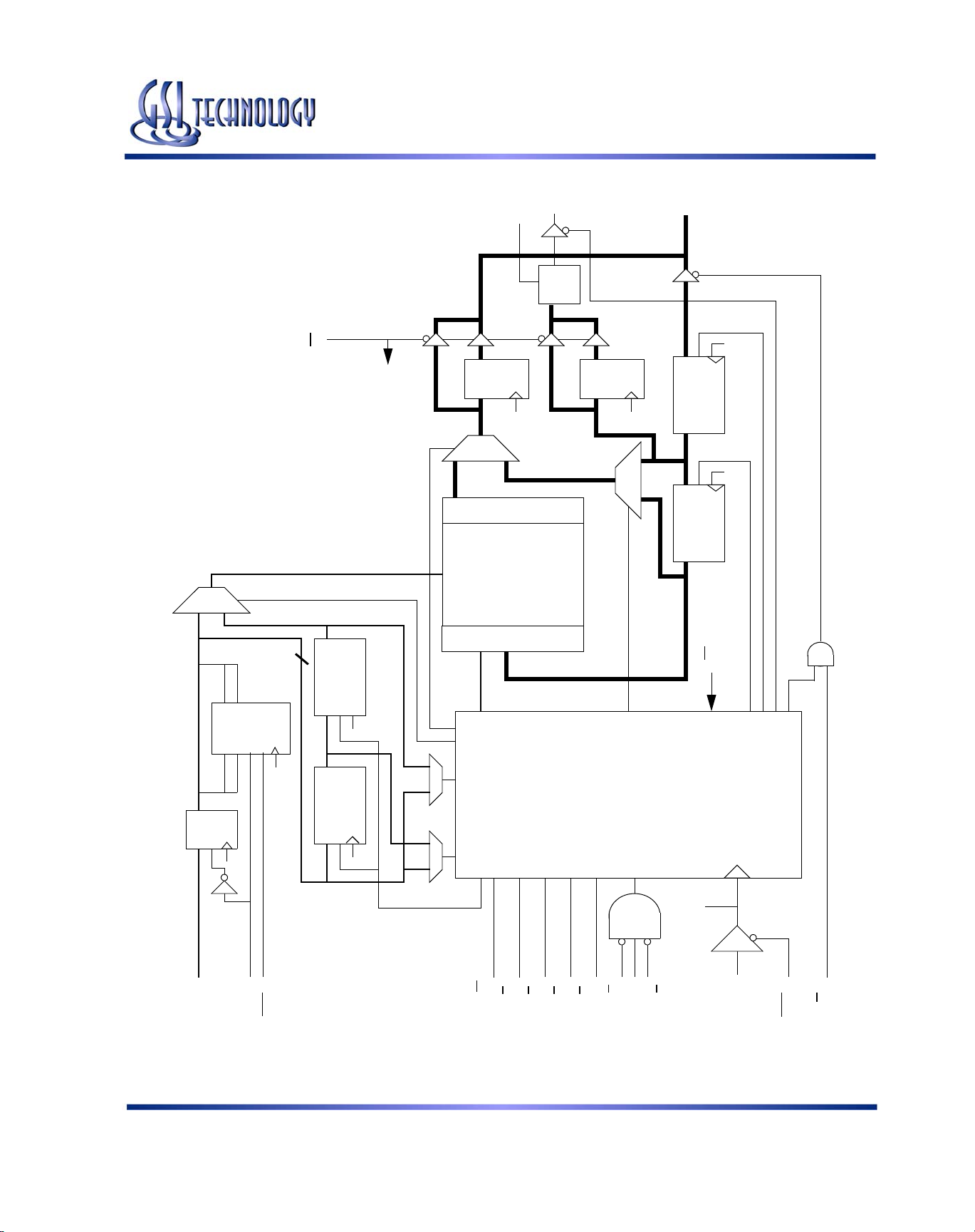
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
GS881Z18/32/36B NBT SRAM Functional Block Diagram
NC
NC
DQa–DQn
Parity
Check
SA1’
SA0’
Burst
Counter
18
FT
Write Address
Register 2
K
D Q
K
D Q
Register 1
K
Write Data
K
Sense Amps
Register 2
Write Data
Array
Memory
Write Drivers
FT
K
K
ADV
K
LBO
Write Address
Register 1
Match
Read, Write and
K
W
BA
Control Logic
Data Coherency
K
3
E2
BB
BC
E1
BD
E
CK
G
CKE
SA1
SA0
D Q
A0–An
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 10/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 11

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Functional Details
Clocking
Deassertion of the Clock Enable (CKE
suspend RAM operations. Failure to observe Clock Enable set-up or hold requirements will result in erratic operation.
Pipeline Mode Read and Write Operations
All inputs (with the exception of Output Enable, Linear Burst Order and Sleep) are synchronized to rising clock edges. Single cycle
read and write operations must be initiated with the Advance/Load
activation is accomplished by asserting all three of the Chip Enable inputs (E
inputs will deactivate the device.
) input blocks the Clock input from reaching the RAM's internal circuits. It may be used to
pin (ADV) held low, in order to load the new address. Device
1, E2 and E3). Deassertion of any one of the Enable
Function W
BA BB BC BD
Read H X X X X
Write Byte “a” L L H H H
Write Byte “b” L H L H H
Write Byte “c” L H H L H
Write Byte “d” L H H H L
Write all Bytes L L L L L
Write Abort/NOP L H H H H
Read operation is initiated when the following conditions are satisfied at the rising edge of clock: CKE
chip enables (E
1, E2, and E3) are active, the write enable input signals W is deasserted high, and ADV is asserted low. The address
is asserted low, all three
presented to the address inputs is latched in to address register and presented to the memory core and control logic. The control
logic determines that a read access is in progress and allows the requested data to propagate to the input of the output register. At
the next rising edge of clock the read data is allowed to propagate through the output register and onto the output pins.
Write operation occurs when the RAM is selected, CKE is active and the write input is sampled low at the rising edge of clock. The
Byte Write Enable inputs (B
A, BB, BC & BD) determine which bytes will be written. All or none may be activated. A write cycle
with no Byte Write inputs active is a no-op cycle. The pipelined NBT SRAM provides double late write functionality, matching the
write command versus data pipeline length (2 cycles) to the read command versus data pipeline length (2 cycles). At the first rising
edge of clock, Enable, Write, Byte Write(s), and Address are registered. The Data In associated with that address is required at the
third rising edge of clock.
Flow Through Mode Read and Write Operations
Operation of the RAM in Flow Through mode is very similar to operations in Pipeline mode. Activation of a read cycle and the use
of the Burst Address Counter is identical. In Flow Through mode the device may begin driving out new data immediately after new
address are clocked into the RAM, rather than holding new data until the following (second) clock edge. Therefore, in Flow
Through mode the read pipeline is one cycle shorter than in Pipeline mode.
Write operations are initiated in the same way, but differ in that the write pipeline is one cycle shorter as well, preserving the ability
to turn the bus from reads to writes without inserting any dead cycles. While the pipelined NBT RAMs implement a double late
write protocol, in Flow Through mode a single late write protocol mode is observed. Therefore, in Flow Through mode, address
and control are registered on the first rising edge of clock and data in is required at the data input pins at the second rising edge of
clock.
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 11/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 12
Synchronous Truth Table
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Operation Type Address CK CKE
Read Cycle, Begin Burst R External L-H L L H X L H L L L Q
Read Cycle, Continue Burst B Next L-H L H X X X X X L L Q 1,10
NOP/Read, Begin Burst R External L-H L L H X L H L H L High-Z 2
Dummy Read, Continue Burst B Next L-H L H X X X X X H L High-Z 1,2,10
Write Cycle, Begin Burst W External L-H L L L L L H L X L D 3
Write Cycle, Continue Burst B Next L-H L H X L X X X X L D 1,3,10
Write Abort, Continue Burst B Next L-H L H X H X X X X L High-Z 1,2,3,10
Deselect Cycle, Power Down D None L-H L L X X H X X X L High-Z
Deselect Cycle, Power Down D None L-H L L X X X X H X L High-Z
Deselect Cycle, Power Down D None L-H L L X X X L X X L High-Z
Deselect Cycle D None L-H L L L H L H L X L High-Z
Deselect Cycle, Continue D None L-H L H X X X X X X L High-Z 1
Sleep Mode None X X X X X X X X X H High-Z
Clock Edge Ignore, Stall Current L-H H X X X X X X X L - 4
ADV W Bx E1 E2 E3 G ZZ DQ Notes
1
Notes:
1. Continue Burst cycles, whether read or write, use the same control inputs. A Deselect continue cycle can only be entered into if a Deselect cycle is executed first.
2. Dummy Read and Write abort can be considered NOPs because the SRAM performs no operation. A Write abort occurs when the W
pin is sampled low but no Byte Write pins are active so no write operation is performed.
3. G
can be wired low to minimize the number of control signals provided to the SRAM. Output drivers will automatically turn off during
write cycles.
4. If CKE
5. X = Don’t Care; H = Logic High; L = Logic Low; Bx
6. All inputs, except G
7. Wait states can be inserted by setting CKE
8. This device contains circuitry that ensures all outputs are in High Z during power-up.
9. A 2-bit burst counter is incorporated.
10. The address counter is incriminated for all Burst continue cycles.
High occurs during a pipelined read cycle, the DQ bus will remain active (Low Z). If CKE High occurs during a write cycle, the bus
will remain in High Z.
= High = All Byte Write signals are high; Bx = Low = One or more Byte/Write
signals are Low
and ZZ must meet setup and hold times of rising clock edge.
high.
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 12/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 13

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Pipelined and Flow Through Read Write Control State Diagram
D
B
Deselect
R
D
W
New Read New Write
R
B
R
W
W
D
R
R
Burst Read Burst Write
B
Key Notes:
ƒ
Current State (n)
Input Command Code
Transition
Next State (n+1)
1. The Hold command (CKE Low) is not
shown because it prevents any state change.
2. W, R, B, and D represent input command
codes as indicated in the Synchronous Truth Table.
W
B
W
B
DD
n n+1 n+2 n+3
Clock (CK)
Command
Current State Next State
ƒ
ƒƒƒ
Current State and Next State Definition for Pipelined and Flow Through Read/Write Control State Diagram
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 13/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 14

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Pipeline Mode Data I/O State Diagram
Intermediate Intermediate
Key
ƒ
Transition
Current State (n) Next State (n+2)
W
B
High Z
(Data In)
Input Command Code
R
D
Intermediate
Transition
Intermediate State (N+1)
Intermediate
W
High Z
B
D
Intermediate
R
B
Data Out
W
(Q Valid)
Intermediate
R
D
Notes:
1. The Hold command (CKE Low) is not
shown because it prevents any state change.
2. W, R, B, and D represent input command
codes as indicated in the Truth Tables.
n n+1 n+2 n+3
Clock (CK)
Command
Current State
ƒ
ƒƒƒ
Intermediate
Next State
State
Current State and Next State Definition for Pipeline Mode Data I/O State Diagram
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 14/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 15

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Flow Through Mode Data I/O State Diagram
W
B
High Z
(Data In)
Key Notes:
ƒ
Current State (n)
Input Command Code
Transition
R
D
Next State (n+1)
W
R
High Z
B
D
1. The Hold command (CKE Low) is not
shown because it prevents any state change.
2. W, R, B, and D represent input command
codes as indicated in the Truth Tables.
R
B
Data Out
W
(Q Valid)
D
n n+1 n+2 n+3
Clock (CK)
Command
Current State Next State
ƒ
ƒƒƒ
Current State and Next State Definition for: Pipeline and Flow through Read Write Control State Diagram
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 15/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 16

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Burst Cycles
Although NBT RAMs are designed to sustain 100% bus bandwidth by eliminating turnaround cycle when there is transition from
read to write, multiple back-to-back reads or writes may also be performed. NBT SRAMs provide an on-chip burst address
generator that can be utilized, if desired, to further simplify burst read or write implementations. The ADV control pin, when
driven high, commands the SRAM to advance the internal address counter and use the counter generated address to read or write
the SRAM. The starting address for the first cycle in a burst cycle series is loaded into the SRAM by driving the ADV pin low, into
Load mode.
Burst Order
The burst address counter wraps around to its initial state after four addresses (the loaded address and three more) have been
accessed. The burst sequence is determined by the state of the Linear Burst Order pin (LBO
sequence is selected. When the RAM is installed with the LBO pin tied high, Interleaved burst sequence is selected. See the tables
below for details.
Mode Pin Functions
Mode Name Pin Name State Function
Burst Order Control LBO
Output Register Control FT
Power Down Control ZZ
Note:
There is a pull-up device on the FT
in the default states as specified in the above tables.
Burst Counter Sequences
pin and a pull-down device on the ZZ pin, so this input pin can be unconnected and the chip will operate
L Linear Burst
H Interleaved Burst
L Flow Through
H or NC Pipeline
L or NC Active
H
). When this pin is low, a linear burst
Standby, I
DD
= I
SB
Linear Burst Sequence
A[1:0] A[1:0] A[1:0] A[1:0]
1st address 00 01 10 11
2nd address 01 10 11 00
3rd address 10 11 00 01
4th address 11 00 01 10
Note:
The burst counter wraps to initial state on the 5th clock.
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 16/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Interleaved Burst Sequence
A[1:0] A[1:0] A[1:0] A[1:0]
1st address 00 01 10 11
2nd address 01 00 11 10
3rd address 10 11 00 01
4th address 11 10 01 00
Note:
The burst counter wraps to initial state on the 5th clock.
BPR 1999.05.18
Page 17

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Sleep Mode
During normal operation, ZZ must be pulled low, either by the user or by it’s internal pull down resistor. When ZZ is pulled high,
the SRAM will enter a Power Sleep mode after 2 cycles. At this time, internal state of the SRAM is preserved. When ZZ returns to
low, the SRAM operates normally after ZZ recovery time.
Sleep mode is a low current, power-down mode in which the device is deselected and current is reduced to I
2. The duration of
SB
Sleep mode is dictated by the length of time the ZZ is in a high state. After entering Sleep mode, all inputs except ZZ become
disabled and all outputs go to High-Z The ZZ pin is an asynchronous, active high input that causes the device to enter Sleep mode.
When the ZZ pin is driven high, I
2 is guaranteed after the time tZZI is met. Because ZZ is an asynchronous input, pending
SB
operations or operations in progress may not be properly completed if ZZ is asserted. Therefore, Sleep mode must not be initiated
until valid pending operations are completed. Similarly, when exiting Sleep mode during tZZR, only a Deselect or Read commands
may be applied while the SRAM is recovering from Sleep mode.
Sleep Mode Timing Diagram
tKHtKH
tKCtKC
CK
ZZ
Designing for Compatibility
The GSI NBT SRAMs offer users a configurable selection between Flow Through mode and Pipelinemode via the FT
on Pin 14. Not all vendors offer this option, however most mark Pin 14 as V
through parts. GSI NBT SRAMs are fully compatible with these sockets.
tKLtKL
tZZHtZZS
tZZR
signal found
DD
or V
on pipelined parts and VSS on flow
DDQ
Pin 66, a No Connect (NC) on GSI’s GS8160Z18/36 NBT SRAM, the Parity Error open drain output on GSI’s GS881Z18/36B
NBT SRAM, is often marked as a power pin on other vendor’s NBT compatible SRAMs. Specifically, it is marked V
on pipelined parts and V
on flow through parts. Users of GSI NBT devices who are not actually using the ByteSafe™ parity
SS
DD
or V
DDQ
feature may want to design the board site for the RAM with Pin 66 tied high through a 1k ohm resistor in Pipeline mode
applications or tied low in Flow Through mode applications in order to keep the option to use non-configurable devices open.
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 17/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 18

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Absolute Maximum Ratings
(All voltages reference to VSS)
Symbol Description Value Unit
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
I/O
V
IN
I
IN
I
OUT
P
D
T
STG
T
BIAS
Note:
Permanent damage to the device may occur if the Absolute Maximum Ratings are exceeded. Operation should be restricted to Recommended
Operating Conditions. Exposure to conditions exceeding the Absolute Maximum Ratings, for an extended period of time, may affect reliability of
this component.
Voltage on VDD Pins
Voltage in V
DDQ
Pins
Voltage on I/O Pins
Voltage on Other Input Pins
–0.5 to V
–0.5 to V
–0.5 to 4.6 V
–0.5 to 4.6 V
+0.5 (≤ 4.6 V max.)
DDQ
+0.5 (≤ 4.6 V max.)
DD
Input Current on Any Pin +/–20 mA
Output Current on Any I/O Pin +/–20 mA
Package Power Dissipation 1.5 W
Storage Temperature –55 to 125
Temperature Under Bias –55 to 125
o
o
V
V
C
C
Power Supply Voltage Ranges
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Notes
3.3 V Supply Voltage
2.5 V Supply Voltage
3.3 V V
2.5 V V
I/O Supply Voltage V
DDQ
I/O Supply Voltage V
DDQ
Notes:
1. The part numbers of Industrial Temperature Range versions end the character “I”. Unless otherwise noted, all performance specifications quoted are evaluated for worst case in the temperature range marked on the device.
2. Input Under/overshoot voltage must be –2 V > Vi < V
V
DD3
V
DD2
DDQ3
DDQ2
+2 V not to exceed 4.6 V maximum, with a pulse width not to exceed 20% tKC.
DDn
3.0 3.3 3.6 V
2.3 2.5 2.7 V
3.0 3.3 3.6 V
2.3 2.5 2.7 V
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 18/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 19

V
Range Logic Levels
DDQ3
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Notes
VDD Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
V
DD
I/O Input High Voltage V
V
DDQ
I/O Input Low Voltage V
V
DDQ
IH
IL
IHQ
ILQ
2.0 —
–0.3 — 0.8 V 1
2.0 —
–0.3 — 0.8 V 1,3
V
V
DD
DDQ
+ 0.3
+ 0.3
V1
V1,3
Notes:
1. The part numbers of Industrial Temperature Range versions end the character “I”. Unless otherwise noted, all performance specifications quoted are evaluated for worst case in the temperature range marked on the device.
2. Input Under/overshoot voltage must be –2 V > Vi < V
3. V
(max) is voltage on V
IHQ
pins plus 0.3 V.
DDQ
+2 V not to exceed 4.6 V maximum, with a pulse width not to exceed 20% tKC.
DDn
V
Range Logic Levels
DDQ2
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Notes
VDD Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
V
DD
V
I/O Input High Voltage V
DDQ
I/O Input Low Voltage V
V
DDQ
IH
IL
IHQ
ILQ
0.6*V
DD
–0.3 —
0.6*V
DD
–0.3 —
—
—
Notes:
1. The part numbers of Industrial Temperature Range versions end the character “I”. Unless otherwise noted, all performance specifications quoted are evaluated for worst case in the temperature range marked on the device.
2. Input Under/overshoot voltage must be –2 V > Vi < V
3. V
(max) is voltage on V
IHQ
pins plus 0.3 V.
DDQ
+2 V not to exceed 4.6 V maximum, with a pulse width not to exceed 20% tKC.
DDn
V
0.3*V
V
DDQ
0.3*V
DD
+ 0.3
DD
+ 0.3
DD
V1
V1
V1,3
V1,3
Recommended Operating Temperatures
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Notes
Ambient Temperature (Commercial Range Versions)
Ambient Temperature (Industrial Range Versions)
Notes:
1. The part numbers of Industrial Temperature Range versions end the character “I”. Unless otherwise noted, all performance specifications quoted are evaluated for worst case in the temperature range marked on the device.
2. Input Under/overshoot voltage must be –2 V > Vi < V
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 19/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
T
A
T
A
+2 V not to exceed 4.6 V maximum, with a pulse width not to exceed 20% tKC.
DDn
02570°C2
–40 25 85 °C2
Page 20

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Undershoot Measurement and Timing Overshoot Measurement and Timing
V
IH
+ 2.0 V
V
DD
V
SS
50%
50% tKC
50%
– 2.0 V
SS
50% tKC
Capacitance
(TA = 25oC, f = 1 MHZ, V
DD
= 2.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test conditions Typ. Max. Unit
Input Capacitance
Input/Output Capacitance
Note:
These parameters are sample tested.
C
IN
C
I/O
AC Test Conditions
Parameter Conditions
V
Input high level
Input low level 0.2 V
Input slew rate 1 V/ns
Input reference level
Output reference level
Output load Fig. 1
Notes:
1. Include scope and jig capacitance.
2. Test conditions as specified with output loading as shown in Fig. 1
unless otherwise noted.
3. Device is deselected as defined by the Truth Table.
– 0.2 V
DD
V
V
DDQ
DD
/2
/2
V
V
IN
OUT
= 0 V
= 0 V
V
DD
V
IL
45pF
67pF
Output Load 1
DQ
50Ω
V
DDQ/2
* Distributed Test Jig Capacitance
30pF
*
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 20/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 21

DC Electrical Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Max
Input Leakage Current
(except mode pins)
ZZ Input Current
FT
, SCD, ZQ Input Current
Output Leakage Current
Output High Voltage
Output High Voltage
Output Low Voltage
V
V
I
I
I
V
I
IL
IN1
IN2
OL
OH2
OH3
OL
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
V
= 0 to V
IN
V
DD ≥ VIN ≥ VIH
0 V ≤ V
V
DD ≥ VIN ≥ VIL
0 V ≤ V
Output Disable, V
I
= –8 mA, V
OH
I
= –8 mA, V
OH
I
= 8 mA
OL
IN
IN
OUT
DDQ
DDQ
≤ V
DD
IH
≤ V
IL
= 0 to V
= 2.375 V
= 3.135 V
DD
–1 uA 1 uA
–1 uA
–1 uA
–100 uA
–1 uA
1 uA
100 uA
1 uA
1 uA
–1 uA 1 uA
1.7 V —
2.4 V —
— 0.4 V
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 21/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 22

Operating Currents
Parameter Test Conditions Mode Symbol
Pipeline
(x32/
x36)
IL
(x18)
—
—
IL
Operating
Current
Standby
Current
Deselect
Current
Device Selected;
All other inputs
≥V
or ≤ V
IH
Output open
ZZ ≥ V
Device Deselected;
– 0.2 V
DD
All other inputs
≥ V
or ≤ V
IH
Notes:
1. I
DD
and I
apply to any combination of V
DDQ
2. All parameters listed are worst case scenario.
Flow
Through
Pipeline
Flow
Through
Pipeline
Flow
Through
Pipeline
Flow
Through
DD3
, V
DD2
I
I
I
I
I
DD
DDQ
I
DD
DDQ
I
DD
DDQ
I
DD
DDQ
I
SB
I
SB
I
DD
I
DD
, V
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
-333 -300 -250 -200 -150
0
–40
to
70°C
85°C
250402704023035250352003022030170251902514020160
205252252518525205251602518025140201602013015150
230202502021020230201851520515155151751513010150
18515205151701519015145151651513010150101208140
40 50 40 50 40 50 40 50 40 50 mA
40 50 40 50 40 50 40 50 40 50 mA
95 100 90 95 85 90 75 80 60 65 mA
65 60 60 65 60 65 50 55 50 55 mA
, and V
DDQ3
DDQ2
to
operation.
0
to
70°C
–40
to
85°C
0
to
70°C
–40
to
85°C
0
to
70°C
–40
to
85°C
0
to
70°C
–40
to
85°C
20
15
10
8
Unit
mA
mA
mA
mA
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 22/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 23

AC Electrical Characteristics
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Pipeline
Flow
Through
Parameter Symbol
Clock Cycle Time tKC 3.0 — 3.3 — 4.0 — 5.0 — 6.7 — ns
Clock to Output Valid tKQ — 2.5 — 2.5 — 2.5 — 3.0 — 3.8 ns
Clock to Output Invalid tKQX 1.5 — 1.5 — 1.5 — 1.5 — 1.5 — ns
Clock to Output in Low-Z
Setup time tS 1.0 — 1.0 — 1.2 — 1.4 — 1.5 — ns
Hold time tH 0.1 — 0.1 — 0.2 — 0.4 — 0.5 — ns
Clock Cycle Time tKC 4.5 — 5.0 — 5.5 — 6.5 — 7.5 — ns
Clock to Output Valid tKQ — 4.5 — 5.0 — 5.5 — 6.5 — 7.5 ns
Clock to Output Invalid tKQX 2.0 — 2.0 — 2.0 — 2.0 — 2.0 — ns
Clock to Output in Low-Z
Setup time tS 1.3 — 1.4 — 1.5 — 1.5 — 1.5 — ns
Hold time tH 0.3 — 0.4 — 0.5 — 0.5 — 0.5 — ns
Clock HIGH Time tKH 1.0 — 1.0 — 1.3 — 1.3 — 1.5 — ns
Clock LOW Time tKL 1.2 — 1.2 — 1.5 — 1.5 — 1.7 — ns
Clock to Output in
High-Z
to Output Valid tOE — 2.5 — 2.5 — 2.5 — 3.0 — 3.8 ns
G
G
to output in Low-Z
to output in High-Z
G
ZZ setup time
ZZ hold time
ZZ recovery tZZR 20 — 20 — 20 — 20 — 20 — ns
tLZ
tLZ
tHZ
tOLZ
tOHZ
tZZS
tZZH
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
-333 -300 -250 -200 -150
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
1.5 — 1.5 — 1.5 — 1.5 — 1.5 — ns
2.0 — 2.0 — 2.0 — 2.0 — 2.0 — ns
1.5 2.5 1.5 2.5 1.5 2.5 1.5 3.0 1.5 3.0 ns
0 — 0 — 0 — 0 — 0 — ns
— 2.5 — 2.5 — 2.5 — 3.0 — 3.8 ns
5 — 5 — 5 — 5 — 5 — ns
1 — 1 — 1 — 1 — 1 — ns
Unit
Notes:
1. These parameters are sampled and are not 100% tested.
2. ZZ is an asynchronous signal. However, in order to be recognized on any given clock cycle, ZZ must meet the specified setup and hold
times as specified above.
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 23/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 24

CK
CKE
E*
ADV
W
Bn
A0–An
DQa–DQd
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Pipeline Mode Timing (NBT)
Write A Write B Write B+1 Read C Cont Read D Write E Read F DESELECT
tKL
tKL
tKHtKH
tH
tS
tH
tS
tH
tS
tH
tS
tH
tS
tH
tS
AB C DEFG
tS
D(A) D(B) D(B+1) Q(C) Q(D) D(E) Q(F)
tKC
tKC
tLZtH
tHZ
tKQXtKQ
tOLZ
tOEtOHZ
G
*Note: E
=High(False) if E1 = 1 or E2 = 0 or E3 = 1
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 24/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 25

CK
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Flow Through Mode Timing (NBT)
Write A Write B Write B+1 Read C Cont Read D Write E Read F Write G
tKLtKL
tKHtKH
tKCtKC
CKE
ADV
Bn
A0–An
DQ
tS
tS
E
tS
tS
W
tS
tS
tH
tH
tH
tH
tH
tH
AB C DEFG
tH
tS
D(A) D(B) D(B+1) Q(C) Q(D) D(E) Q(F) D(G)
tLZ
tOLZ
tOE
tKQXtKQ
tKQ
tLZtHZ
tKQX
tOHZ
G
*Note: E
= High(False) if E1 = 1 or E2 = 0 or E3 = 1
JTAG Port Operation
Overview
The JTAG Port on this RAM operates in a manner that is compliant with IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990, a serial boundary scan
interface standard (commonly referred to as JTAG). The JTAG Port input interface levels scale with V
drivers are powered by V
DDQ
.
Disabling the JTAG Port
It is possible to use this device without utilizing the JTAG port. The port is reset at power-up and will remain inactive unless
clocked. TCK, TDI, and TMS are designed with internal pull-up circuits.To assure normal operation of the RAM with the JTAG
Port unused, TCK, TDI, and TMS may be left floating or tied to either V
or VSS. TDO should be left unconnected.
DD
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 25/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
. The JTAG output
DD
Page 26

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
JTAG Port Registers
JTAG Pin Descriptions
Pin Pin Name I/O Description
TCK Test Clock In
TMS Test Mode Select In
TDI Test Data In In
TDO Test Data Out Out
Note:
This device does not have a TRST (TAP Reset) pin. TRST is optional in IEEE 1149.1. The Test-Logic-Reset state is entered while TMS is
held high for five rising edges of TCK. The TAP Controller is also reset automaticly at power-up.
Overview
The various JTAG registers, refered to as Test Access Port orTAP Registers, are selected (one at a time) via the sequences of 1s
and 0s applied to TMS as TCK is strobed. Each of the TAP Registers is a serial shift register that captures serial input data on the
rising edge of TCK and pushes serial data out on the next falling edge of TCK. When a register is selected, it is placed between the
TDI and TDO pins.
Instruction Register
The Instruction Register holds the instructions that are executed by the TAP controller when it is moved into the Run, Test/Idle, or
the various data register states. Instructions are 3 bits long. The Instruction Register can be loaded when it is placed between the
TDI and TDO pins. The Instruction Register is automatically preloaded with the IDCODE instruction at power-up or whenever the
controller is placed in Test-Logic-Reset state.
Clocks all TAP events. All inputs are captured on the rising edge of TCK and all outputs propagate
from the falling edge of TCK.
The TMS input is sampled on the rising edge of TCK. This is the command input for the TAP
controller state machine. An undriven TMS input will produce the same result as a logic one input
level.
The TDI input is sampled on the rising edge of TCK. This is the input side of the serial registers
placed between TDI and TDO. The register placed between TDI and TDO is determined by the
state of the TAP Controller state machine and the instruction that is currently loaded in the TAP
Instruction Register (refer to the TAP Controller State Diagram). An undriven TDI pin will produce
the same result as a logic one input level.
Output that is active depending on the state of the TAP state machine. Output changes in
response to the falling edge of TCK. This is the output side of the serial registers placed between
TDI and TDO.
Bypass Register
The Bypass Register is a single bit register that can be placed between TDI and TDO. It allows serial test data to be passed through
the RAM’s JTAG Port to another device in the scan chain with as little delay as possible.
Boundary Scan Register
The Boundary Scan Register is a collection of flip flops that can be preset by the logic level found on the RAM’s input or I/O pins.
The flip flops are then daisy chained together so the levels found can be shifted serially out of the JTAG Port’s TDO pin. The
Boundary Scan Register also includes a number of place holder flip flops (always set to a logic 1). The relationship between the
device pins and the bits in the Boundary Scan Register is described in the Scan Order Table following. The Boundary Scan
Register, under the control of the TAP Controller, is loaded with the contents of the RAMs I/O ring when the controller is in
Capture-DR state and then is placed between the TDI and TDO pins when the controller is moved to Shift-DR state. SAMPLE-Z,
SAMPLE/PRELOAD and EXTEST instructions can be used to activate the Boundary Scan Register.
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 26/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 27

TDI
·· ······
·
·
108
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
JTAG TAP Block Diagram
Boundary Scan Register
0
Bypass Register
012
Instruction Register
ID Code Register
31 30 29 12
····
0
·
1
0
TDO
Control Signals
TMS
TCK
Test Access Port (TAP) Controller
Identification (ID) Register
The ID Register is a 32-bit register that is loaded with a device and vendor specific 32-bit code when the controller is put in
Capture-DR state with the IDCODE command loaded in the Instruction Register. The code is loaded from a 32-bit on-chip ROM.
It describes various attributes of the RAM as indicated below. The register is then placed between the TDI and TDO pins when the
controller is moved into Shift-DR state. Bit 0 in the register is the LSB and the first to reach TDO when shifting begins.
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 27/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 28

Tap Controller Instruction Set
ID Register Contents
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Die
Revision
Code
Bit # 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
x36 XXXX000000000000100000011011001 1
x32 XXXX0000000000001100000110110011
x18 XXXX0000000000001010000110110011
Overview
There are two classes of instructions defined in the Standard 1149.1-1990; the standard (Public) instructions, and device specific
(Private) instructions. Some Public instructions are mandatory for 1149.1 compliance. Optional Public instructions must be
implemented in prescribed ways. The TAP on this device may be used to monitor all input and I/O pads, and can be used to load
address, data or control signals into the RAM or to preload the I/O buffers.
When the TAP controller is placed in Capture-IR state the two least significant bits of the instruction register are loaded with 01.
When the controller is moved to the Shift-IR state the Instruction Register is placed between TDI and TDO. In this state the desired
instruction is serially loaded through the TDI input (while the previous contents are shifted out at TDO). For all instructions, the
TAP executes newly loaded instructions only when the controller is moved to Update-IR state. The TAP instruction set for this
device is listed in the following table.
Not Used
I/O
Configuration
GSI Technology
JEDEC Vendor
ID Code
Presence Register
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 28/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 29

Test Logic Reset
1
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
JTAG Tap Controller State Diagram
0
Run Test Idle
0
111
Select DR
1
Capture DR
0
Shift DR
1
Exit1 DR
Pause DR
Exit2 DR
Update DR
1
Select IR
0
1
0
Capture IR
0
Shift IR
1
0
0
1
1
Exit1 IR
0
Pause IR
1
1
0
0 0
1
Exit2 IR
1
Update IR
0
10
0
0
Instruction Descriptions
BYPASS
When the BYPASS instruction is loaded in the Instruction Register the Bypass Register is placed between TDI and TDO. This
occurs when the TAP controller is moved to the Shift-DR state. This allows the board level scan path to be shortened to facilitate testing of other devices in the scan path.
SAMPLE/PRELOAD
SAMPLE/PRELOAD is a Standard 1149.1 mandatory public instruction. When the SAMPLE / PRELOAD instruction is
loaded in the Instruction Register, moving the TAP controller into the Capture-DR state loads the data in the RAMs input and
I/O buffers into the Boundary Scan Register. Boundary Scan Register locations are not associated with an input or I/O pin, and
are loaded with the default state identified in the Boundary Scan Chain table at the end of this section of the datasheet. Because
the RAM clock is independent from the TAP Clock (TCK) it is possible for the TAP to attempt to capture the I/O ring contents
while the input buffers are in transition (i.e. in a metastable state). Although allowing the TAP to sample metastable inputs will
not harm the device, repeatable results cannot be expected. RAM input signals must be stabilized for long enough to meet the
TAPs input data capture set-up plus hold time (tTS plus tTH). The RAMs clock inputs need not be paused for any other TAP
operation except capturing the I/O ring contents into the Boundary Scan Register. Moving the controller to Shift-DR state then
places the boundary scan register between the TDI and TDO pins.
EXTEST
EXTEST is an IEEE 1149.1 mandatory public instruction. It is to be executed whenever the instruction register is loaded with
all logic 0s. The EXTEST command does not block or override the RAM’s input pins; therefore, the RAM’s internal state is
still determined by its input pins.
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 29/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 30

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Typically, the Boundary Scan Register is loaded with the desired pattern of data with the SAMPLE/PRELOAD command.
Then the EXTEST command is used to output the Boundary Scan Register’s contents, in parallel, on the RAM’s data output
drivers on the falling edge of TCK when the controller is in the Update-IR state.
Alternately, the Boundary Scan Register may be loaded in parallel using the EXTEST command. When the EXTEST instruction is selected, the sate of all the RAM’s input and I/O pins, as well as the default values at Scan Register locations not associated with a pin, are transferred in parallel into the Boundary Scan Register on the rising edge of TCK in the Capture-DR
state, the RAM’s output pins drive out the value of the Boundary Scan Register location with which each output pin is associated.
IDCODE
The IDCODE instruction causes the ID ROM to be loaded into the ID register when the controller is in Capture-DR mode and
places the ID register between the TDI and TDO pins in Shift-DR mode. The IDCODE instruction is the default instruction
loaded in at power up and any time the controller is placed in the Test-Logic-Reset state.
SAMPLE-Z
If the SAMPLE-Z instruction is loaded in the instruction register, all RAM outputs are forced to an inactive drive state (highZ) and the Boundary Scan Register is connected between TDI and TDO when the TAP controller is moved to the Shift-DR
state.
RFU
These instructions are Reserved for Future Use. In this device they replicate the BYPASS instruction.
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 30/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 31

JTAG Port AC Test Conditions
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Parameter Conditions
V
Input high level
– 0.2 V
DD
DQ
JTAG Port AC Test Load
Input low level 0.2 V
V
DDQ
50Ω
/2
Input slew rate 1 V/ns
Input reference level
Output reference level
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
/2
/2
* Distributed Test Jig Capacitance
Notes:
1. Include scope and jig capacitance.
2. Test conditions as as shown unless otherwise noted.
JTAG TAP Instruction Set Summary
Instruction Code Description Notes
EXTEST 000 Places the Boundary Scan Register between TDI and TDO. 1
IDCODE 001 Preloads ID Register and places it between TDI and TDO. 1, 2
Captures I/O ring contents. Places the Boundary Scan Register between TDI and
SAMPLE-Z 010
RFU 011
SAMPLE/
PRELOAD
100
GSI 101 GSI private instruction. 1
RFU 110
BYPASS 111 Places Bypass Register between TDI and TDO. 1
Notes:
1. Instruction codes expressed in binary, MSB on left, LSB on right.
2. Default instruction automatically loaded at power-up and in test-logic-reset state.
TDO.
Forces all RAM output drivers to High-Z.
Do not use this instruction; Reserved for Future Use.
Replicates BYPASS instruction. Places Bypass Register between TDI and TDO.
Captures I/O ring contents. Places the Boundary Scan Register between TDI and
TDO.
Do not use this instruction; Reserved for Future Use.
Replicates BYPASS instruction. Places Bypass Register between TDI and TDO.
30pF
*
1
1
1
1
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 31/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 32

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
JTAG Port Recommended Operating Conditions and DC Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Min. Max. Unit Notes
3.3 V Test Port Input High Voltage
3.3 V Test Port Input Low Voltage
2.5 V Test Port Input High Voltage
2.5 V Test Port Input Low Voltage
TMS, TCK and TDI Input Leakage Current
TMS, TCK and TDI Input Leakage Current
TDO Output Leakage Current
Test Port Output High Voltage
Test Port Output Low Voltage
Test Port Output CMOS High
Test Port Output CMOS Low
Notes:
1. Input Under/overshoot voltage must be –2 V > Vi < V
2. V
3. 0 V ≤ V
4. Output Disable, V
5. The TDO output driver is served by the V
6. I
7. I
8. I
9. I
ILJ
OHJ
OLJ
OHJC
OHJC
≤ V
IN
IN
= –4 mA
= + 4 mA
= –100 uA
= +100 uA
≤ V
≤ V
DDn
ILJn
OUT
= 0 to V
DDn
DDQ
supply.
JTAG Port Timing Diagram
+2 V not to exceed 4.6 V maximum, with a pulse width not to exceed 20% tTKC.
DDn
V
V
V
V
I
I
V
V
V
V
IHJ3
ILJ3
IHJ2
ILJ2
INHJ
INLJ
I
OLJ
OHJ
OLJ
OHJC
OLJC
V
DDQ
0.6 * V
V
2.0
DD3
+0.3
V1
–0.3 0.8 V 1
V
–0.3
DD2
DD2
0.3 * V
+0.3
DD2
V1
V1
–300 1 uA 2
–1 100 uA 3
–11uA4
1.7 — V5, 6
— 0.4 V 5, 7
– 100 mV
— V5, 8
— 100 mV V 5, 9
tTKLtTKLtTKHtTKHtTKCtTKC
TCK
tTH
tTS
TDI
tTH
tTS
TMS
tTKQ
TDO
tTH
tTS
Parallel SRAM input
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 32/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 33

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
JTAG Port AC Electrical Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit
TCK Cycle Time tTKC 50 — ns
TCK Low to TDO Valid tTKQ — 20 ns
TCK High Pulse Width tTKH 20 — ns
TCK Low Pulse Width tTKL 20 — ns
TDI & TMS Set Up Time tTS 10 — ns
TDI & TMS Hold Time tTH 10 — ns
Boundary Scan (BSDL Files)
For information regarding the Boundary Scan Chain, or to obtain BSDL files for this part, please contact our Applications
Engineering Department at: apps@gsitechnology.com
.
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 33/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 34

TQFP Package Drawing (Package T)
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Symbol Description Min. Nom. Max
A1 Standoff 0.05 0.10 0.15
A2 Body Thickness 1.35 1.40 1.45
b Lead Width 0.20 0.30 0.40
c Lead Thickness 0.09 — 0.20
D Terminal Dimension 21.9 22.0 22.1
D1 Package Body 19.9 20.0 20.1
E Terminal Dimension 15.9 16.0 16.1
E1 Package Body 13.9 14.0 14.1
e Lead Pitch — 0.65 —
L Foot Length 0.45 0.60 0.75
L1 Lead Length — 1.00 —
Y Coplanarity 0.10
θ Lead Angle 0° — 7°
L1
A1
θ
L
c
Pin 1
D1
D
e
b
A2
Y
E1
E
Notes:
1. All dimensions are in millimeters (mm).
2. Package width and length do not include mold protrusion.
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 34/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 35

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Package Dimensions—165-Bump FPBGA (Package D; Variation 1)
A1 CORNER
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
C
0.25
0.45±0.05
TOP VIEW
M
Ø0.10
C
M
Ø0.25
C A B
Ø0.40~0.50 (165x)
BOTTOM VIEW
A1 CORNER
11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
A
B
C
D
E
1.01.0
F
G
14.0
15±0.07
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
A
C
0.15
B
0.20(4x)
1.0 1.0
10.0
13±0.07
C
(0.26)
SEATING PLANE
1.20 MAX.
0.25~0.40
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 35/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 36

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
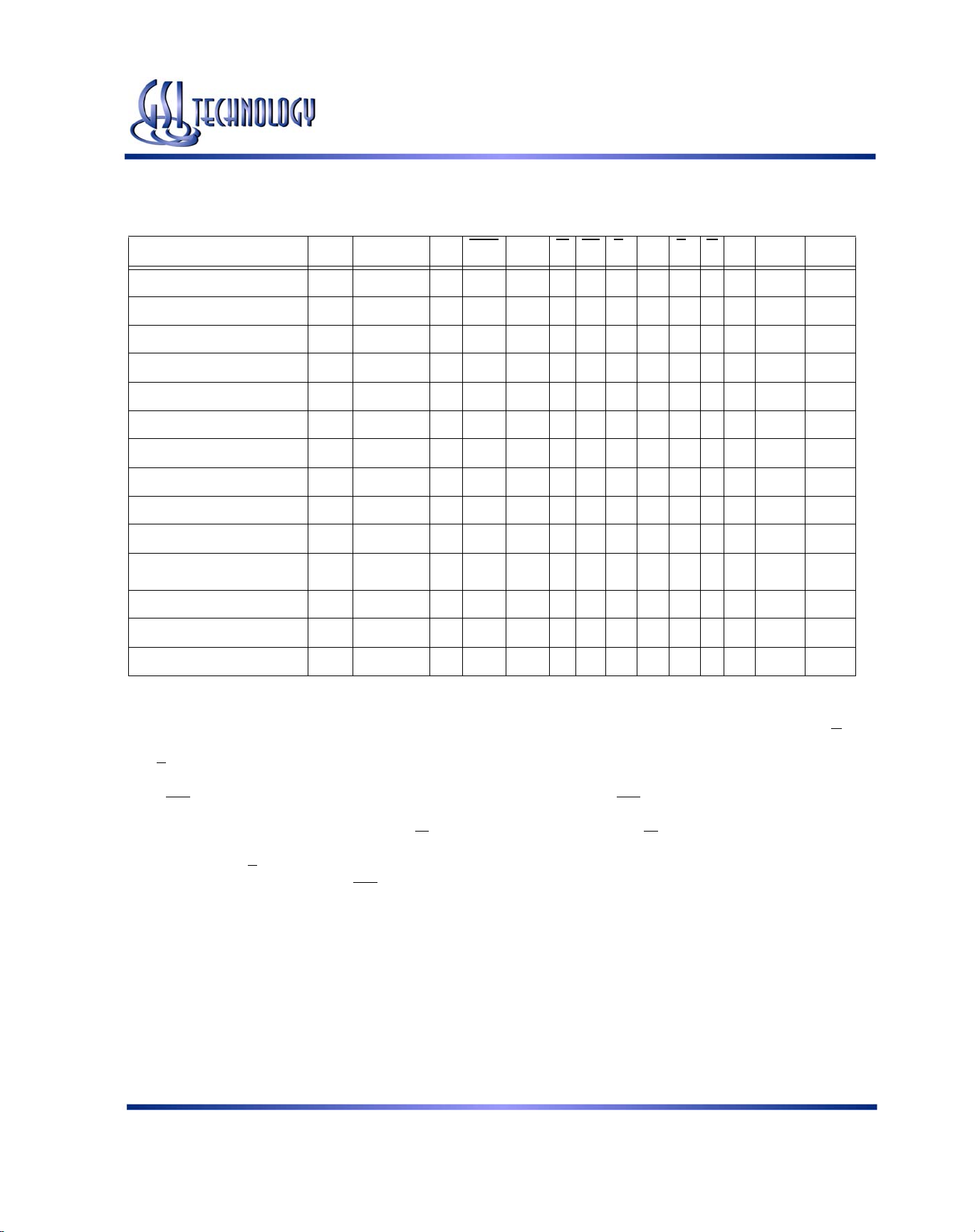
Ordering Information—GSI NBT Synchronous SRAM
2
Org
512K x 18 GS881Z18BT-333 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 333/4.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BT-300 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 300/5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BT-250 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 250/5.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BT-200 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 200/6.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BT-150 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 150/7.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BT-333 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 333/4.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BT-300 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 300/5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BT-250 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 250/5.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BT-200 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 200/6.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BT-150 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 150/7.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BT-333 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 333/4.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BT-300 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 300/5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BT-250 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 250/5.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BT-200 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 200/6.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BT-150 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 150/7.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BT-333I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 333/4.5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BT-300I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 300/5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BT-250I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 250/5.5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BT-200I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 200/6.5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BT-150I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 150/7.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BT-333I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 333/4.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BT-300I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 300/5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BT-250I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 250/5.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BT-200I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 200/6.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BT-150I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 150/7.5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BT-333I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 333/4.5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BT-300I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 300/5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BT-250I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 250/5.5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BT-200I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 200/6.5 I
Notes:
1. Customers requiring delivery in Tape and Reel should add the character “T” to the end of the part number. Example: GS881Z36B-150IT.
2. The speed column indicates the cycle frequency (MHz) of the device in Pipeline mode and the latency (ns) in Flow Through mode. Each
device is Pipeline/Flow through mode-selectable by the user .
3. T
= C = Commercial Temperature Range. TA = I = Industrial Temperature Range.
A
4. GSI offers other versions this type of device in many different configurations and with a variety of different features, only some
Part Number
1
Type Package
Speed
(MHz/ns)
of which are covered in this data sheet. See the GSI Technology web site (www.gsitechnology.com) for a complete listing of current
offerings
3
T
A
Status
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 36/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 37

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Ordering Information—GSI NBT Synchronous SRAM
2
Org
256K x 36 GS881Z36BT-150I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through TQFP 150/7.5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BGT-333 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 333/4.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BGT-300 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 300/5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BGT-250 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 250/5.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BGT-200 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 200/6.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BGT-150 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 150/7.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BGT-333 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 333/4.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BGT-300 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 300/5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BGT-250 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 250/5.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BGT-200 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 200/6.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BGT-150 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 150/7.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BGT-333 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 333/4.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BGT-300 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 300/5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BGT-250 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 250/5.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BGT-200 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 200/6.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BGT-150 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 150/7.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BGT-333I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 333/4.5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BGT-300I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 300/5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BGT-250I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 250/5.5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BGT-200I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 200/6.5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BGT-150I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 150/7.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BGT-333I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 333/4.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BGT-300I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 300/5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BGT-250I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 250/5.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BGT-200I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 200/6.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BGT-150I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 150/7.5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BGT-333I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 333/4.5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BGT-300I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 300/5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BGT-250I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 250/5.5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BGT-200I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 200/6.5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BGT-150I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through Pb-free TQFP 150/7.5 I
Notes:
1. Customers requiring delivery in Tape and Reel should add the character “T” to the end of the part number. Example: GS881Z36B-150IT.
2. The speed column indicates the cycle frequency (MHz) of the device in Pipeline mode and the latency (ns) in Flow Through mode. Each
device is Pipeline/Flow through mode-selectable by the user .
3. T
= C = Commercial Temperature Range. TA = I = Industrial Temperature Range.
A
4. GSI offers other versions this type of device in many different configurations and with a variety of different features, only some
Part Number
1
Type Package
Speed
(MHz/ns)
of which are covered in this data sheet. See the GSI Technology web site (www.gsitechnology.com) for a complete listing of current
offerings
3
T
A
Status
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 37/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 38

GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
Ordering Information—GSI NBT Synchronous SRAM
2
Org
512K x 18 GS881Z18BD-333 NBt Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 333/4.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BD-300 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 300/5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BD-250 NBt Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 250/5.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BD-200 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 200/6.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BD-150 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 150/7.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BD-333 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 333/4.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BD-300 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 300/5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BD-250 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 250/5.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BD-200 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 200/6.5 C
256K x 32 GS881Z32BD-150 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 150/7.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BD-333 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 333/4.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BD-300 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 300/5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BD-250 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 250/5.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BD-200 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 200/6.5 C
256K x 36 GS881Z36BD-150 NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 150/7.5 C
512K x 18 GS881Z18BD-333I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 333/4.5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BD-300I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 300/5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BD-250I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 250/5.5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BD-200I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 200/6.5 I
512K x 18 GS881Z18BD-150I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 150/7.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BD-333I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 250/5.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BD-300I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 225/6 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BD-250I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 250/5.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BD-200I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 200/6.5 I
256K x 32 GS881Z32BD-150I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 150/7.5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BD-333I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 250/5.5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BD-300I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 225/6 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BD-250I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 250/5.5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BD-200I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 200/6.5 I
256K x 36 GS881Z36BD-150I NBT Pipeline/Flow Through 165 BGA (var. 1) 150/7.5 I
Notes:
1. Customers requiring delivery in Tape and Reel should add the character “T” to the end of the part number. Example: GS881Z36B-150IT.
2. The speed column indicates the cycle frequency (MHz) of the device in Pipeline mode and the latency (ns) in Flow Through mode. Each
device is Pipeline/Flow through mode-selectable by the user .
3. T
= C = Commercial Temperature Range. TA = I = Industrial Temperature Range.
A
4. GSI offers other versions this type of device in many different configurations and with a variety of different features, only some
Part Number
1
Type Package
Speed
(MHz/ns)
of which are covered in this data sheet. See the GSI Technology web site (www.gsitechnology.com) for a complete listing of current
offerings
3
T
A
Status
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 38/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
Page 39

9Mb Sync SRAM Datasheet Revision History
GS881Z18B(T/D)/GS881Z32B(T/D)/GS881Z36B(T/D)
DS/DateRev. Code: Old;
New
881Z18B_r1
881Z18B_r1;
881Z18B_r1_01
881Z18B_r1_01;
881Z18B_r1_02
881Z18B_r1_02;
881Z18B_r1_03
881Z18B_r1_03;
881Z18B_r1_04
Types of Changes
Format or Content
Content
Content/Format
Content/Format
Content
Page;Revisions;Reason
• Creation of new datasheet
• Added x32 TQFP
• Removed address and DQ number designations
• Updated Current Numbers
• Basic page 1 format updates
• Updated Synchronous Truth Table
• Updated Package Thermal Table
• Removed erroneous speed bins
• Added 333/300 MHz speed bins
• Corrected 165 BGA mechanical drawing
• Format updates
• Added Pb-free information to TQFP
• Added variation information to 165 BGA
Rev: 1.04 10/2004 39/39 © 2002, GSI Technology
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
 Loading...
Loading...