Page 1

HYNIX SEMICONDUCTOR INC.
8-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCONTROLLERS
GMS90C3X
GMS90C5X
GMS97C5X
User’s Manual (Ver. 3.1a)
Page 2

Version 3.1a
Published by
MCU Application Team
2001 Hynix semiconductor All right reserved.
Additional information of this manual may beserved by Hynix semiconductor offices in Korea or Distributors
and Representatives listed at address directory.
Hynix semiconductor reserves the right to make changes to any information here in at any time without notice.
The information, diagrams and other data in this manual are correct and reliable; however, Hynix semiconduc-
tor is in no way responsible for any violations of patents or other rights of the third party generated by the use
of this manual.
Page 3

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
Device Naming Structure
GMS90X5X
Frequency
Package Type
Blank:
24:
40:
12MHz
24MHz
40MHz
Blank:
PL:
Q:
40PDIP
44PLCC
44MQFP
ROM Code serial No.
ROM size
1:
2:
4:
4k bytes
8k bytes
16k bytes
6:8:24k bytes
32k bytes
Operating Voltage
C:L:4.25~5.5V
2.7~3.6V
Hynix semiconductor MCU
-GBXXXXXXX
GMS97X5X
Frequency
Package Type
Blank:H:12/24(5V),12MHz(3V)
33MHz
Blank:
PL:
Q:
40PDIP
44PLCC
44MQFP
ROM size
1:
2:
4:
4k bytes
8k bytes
16k bytes
6:8:24k bytes
32k bytes
Operating Voltage
C:L:4.25~5.5V
2.7~3.6V
Hynix semiconductor MCU
XXX
Mask ROM version
OTP version
16: 16MHz
Page 4
GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
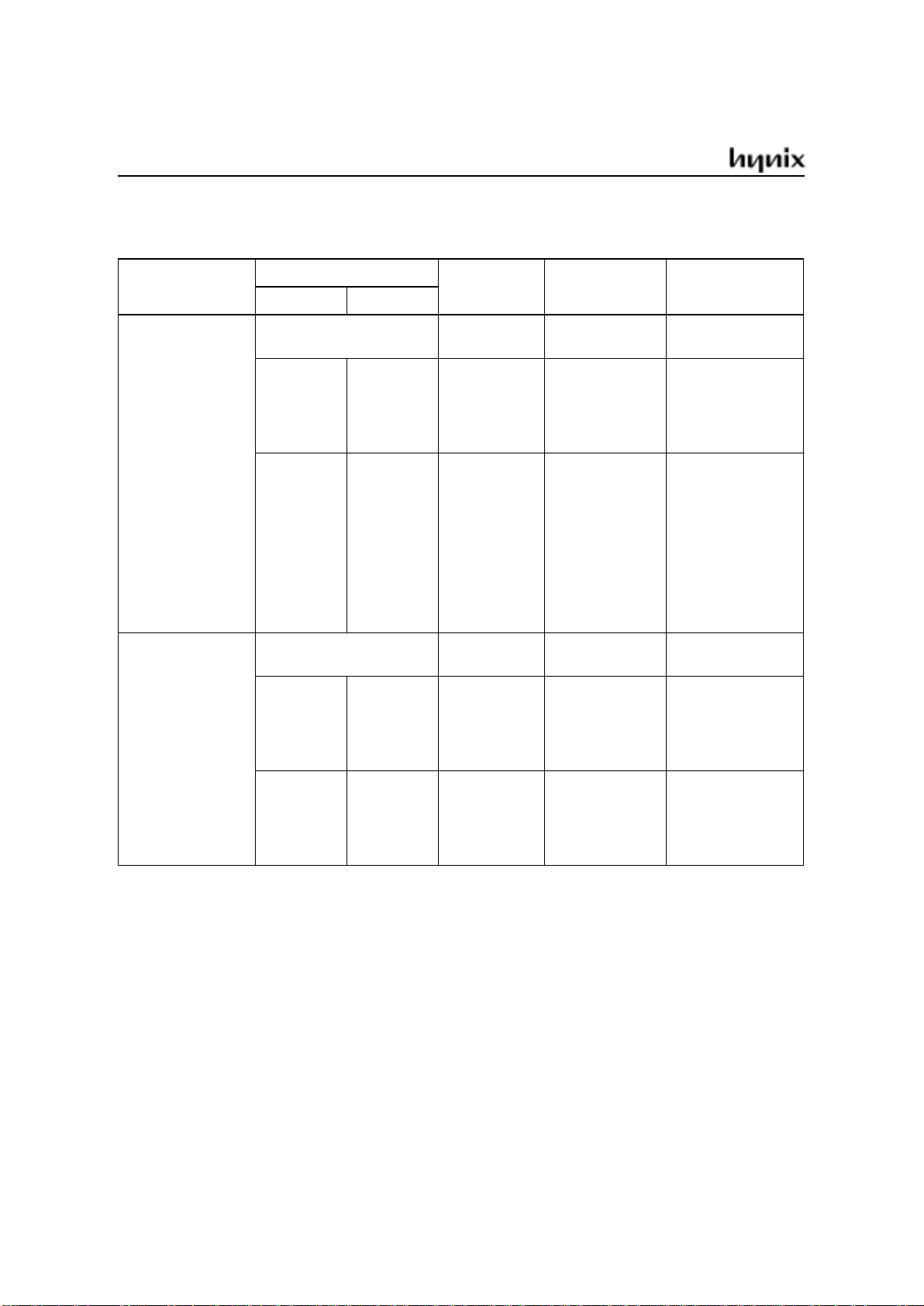
GMS90SeriesSelectionGuide
Operating
Voltage (V)
ROM size (bytes)
RAM size
(bytes)
Device Name
Operating
Frequency (MHz)
MASK OTP
4.25~5.5
ROM-less
128
256
GMS90C31
GMS90C32
12/24/40
12/24/40
4K
8K
16K
24K
32K
-
-
-
-
-
128
256
256
256
256
GMS90C51
GMS90C52
GMS90C54
GMS90C56
GMS90C58
12/24/40
12/24/40
12/24/40
12/24/40
12/24/40
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
4K
4K
8K
8K
16K
16K
24K
24K
32K
32K
128
128
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
GMS97C51
GMS97C51H
GMS97C52
GMS97C52H
GMS97C54
GMS97C54H
GMS97C56
GMS97C56H
GMS97C58
GMS97C58H
12/24
33
12/24
33
12/24
33
12/24
33
12/24
33
2.7~3.6
ROM-less
128
256
GMS90L31
GMS90L32
12/16
12/16
4K
8K
16K
24K
32K
-
-
-
-
-
128
256
256
256
256
GMS90L51
GMS90L52
GMS90L54
GMS90L56
GMS90L58
12/16
12/16
12/16
12/16
12/16
-
-
-
-
-
4K
8K
16K
24K
32K
128
256
256
256
256
GMS97L51
GMS97L52
GMS97L54
GMS97L56
GMS97L58
12
12
12
12
12
Page 5
GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 1
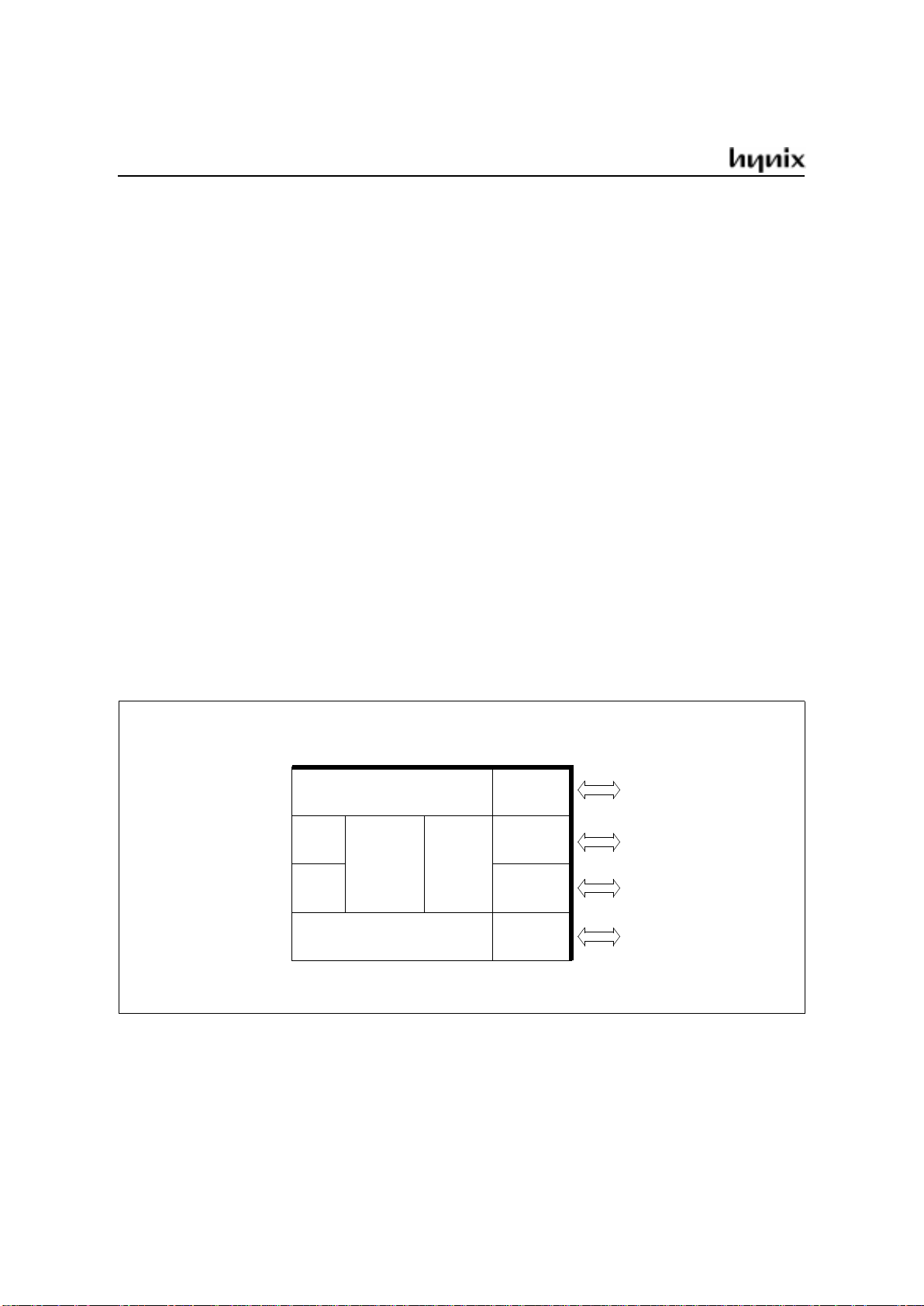
GMS90C31/51, 97C51
GMS90L31/51, 97L51 (Low voltage versions)
• Fully compatible to standard MCS-51 microcontroller
• Wide operating frequency up to 40MHz (for more detail, see “GMS90 Series Selection Guide”)
•4K× 8 (EP)ROM
•128× 8RAM
• 64K external program memory space
• 64K external data memory space
• Four 8-bit ports
• Two 16-bit Timers / Counters
• USART
• Five interrupt sources, two priority levels
• Power saving Idle and power down mode
• Quick pulse programming algorithm (in the OTPdevices)
• 2-level program memory lock (in the OTP devices)
• 2.7Volt low voltage version available
• P-DIP-40, P-LCC-44, P-MQFP-44 package
Block Diagram
RAM
128 × 8
PORT 0
PORT 1
PORT 3
PORT 2
8-BIT
USART
ROM / EPROM
4K × 8
CPU
T0
T1
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Page 6
GMS90 Series
2 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
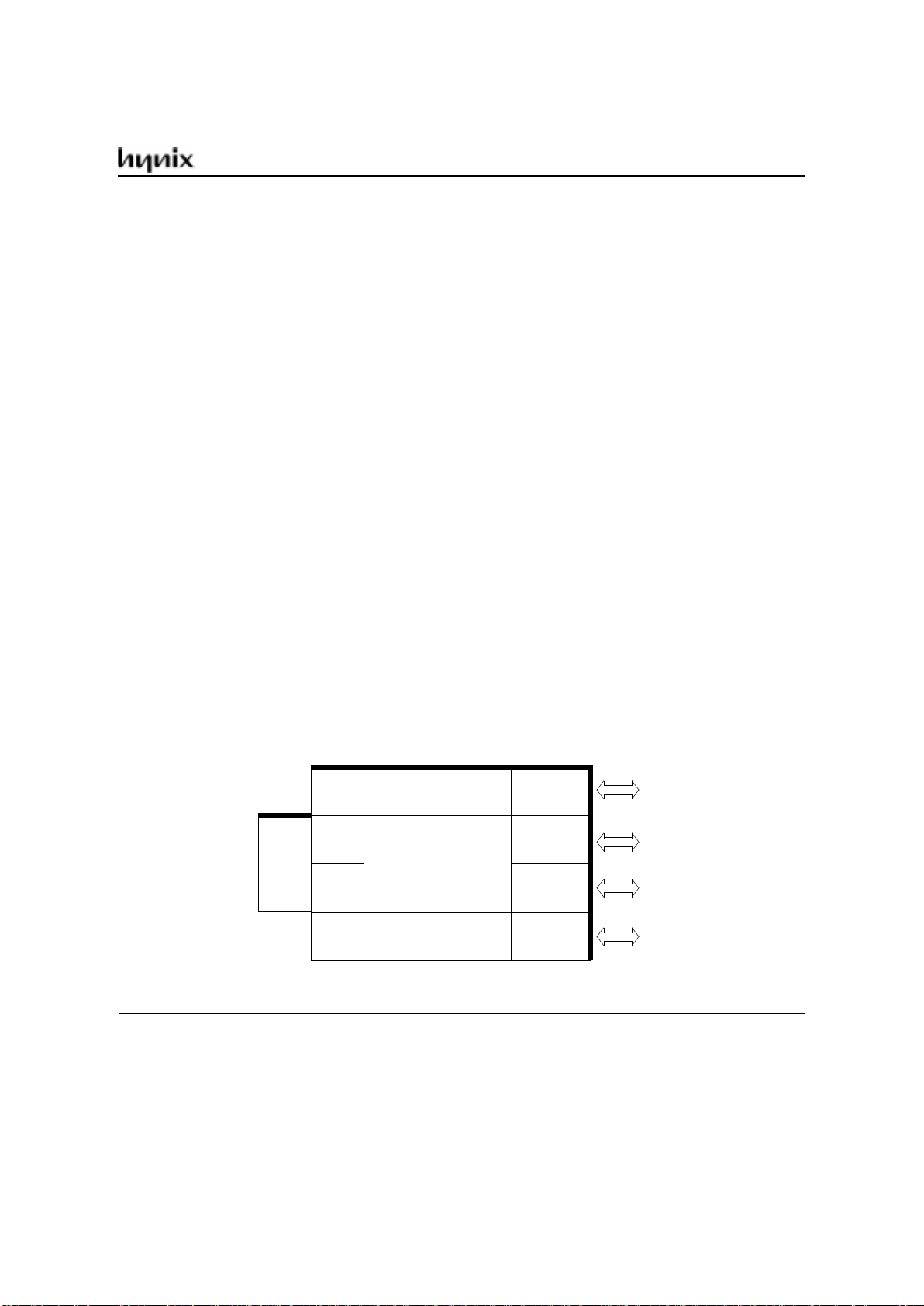
GMS90C32/52, 97C52
GMS90L32/52, 97L52 (Low voltage versions)
• Fully compatible to standard MCS-51 microcontroller
• Wide operating frequency up to 40MHz (for more detail, see “GMS90 Series Selection Guide”)
•8K× 8 (EP)ROM
•256× 8RAM
• 64K external program memory space
• 64K external data memory space
• Four 8-bit ports
• Three 16-bit Timers / Counters (Timer2 with up/down counter feature)
• USART
• Six interrupt sources, two priority levels
• Power saving Idle and power down mode
• Quick pulse programming algorithm (in the OTPdevices)
• 2-level program memory lock (in the OTP devices)
• 2.7Volt low voltage version available
• P-DIP-40, P-LCC-44, P-MQFP-44 package
Block Diagram
RAM
256 × 8
PORT 0
PORT 1
PORT 3
PORT 2
8-BIT
USART
ROM / EPROM
8K × 8
CPU
T0
T1
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
T2
Page 7
GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 3
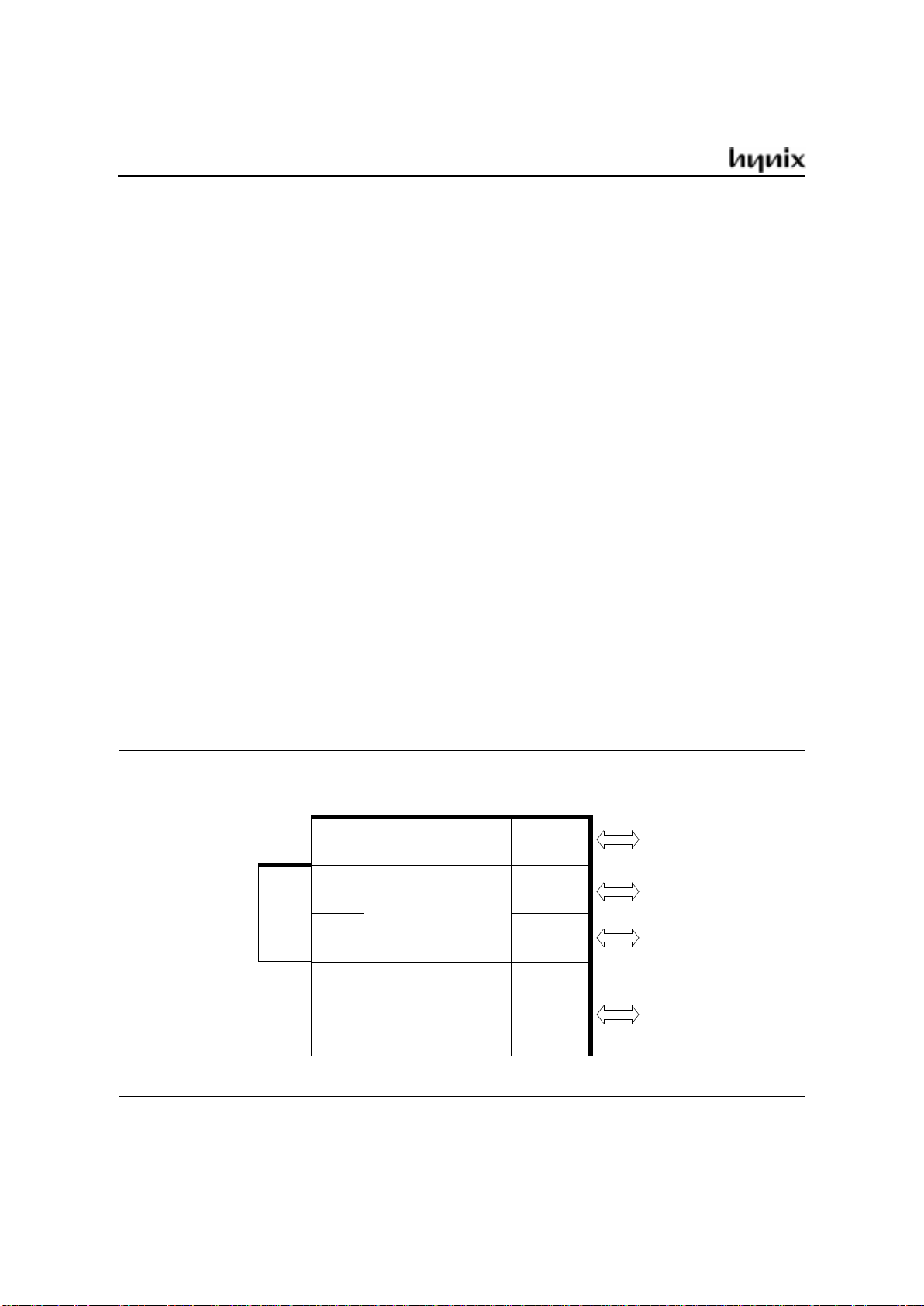
GMS90C54/56/58, 97C54/56/58
GMS90L54/56/58, 97L54/56/58 (Low voltage versions)
• Fully compatible to standard MCS-51 microcontroller
• Wide operating frequency up to 40MHz (for more detail, see “GMS90 Series Selection Guide”)
• 16K/24K/32K bytes (EP)ROM
•256× 8RAM
• 64K external program memory space
• 64K external data memory space
• Four 8-bit ports
• Three 16-bit Timers / Counters (Timer2 with up/down counter feature)
• USART
• One clock output port
• Programmable ALE pin enable / disable
• Six interrupt sources, two priority levels
• Power saving Idle and power down mode
• Quick pulse programming algorithm (in the OTPdevices)
• 2-level program memory lock (in the OTP devices)
• 2.7Volt low voltage version available
• P-DIP-40, P-LCC-44, P-MQFP-44 package
Block Diagram
RAM
256 × 8
PORT 0
PORT 1
PORT 3
PORT 2
8-BIT
USART
ROM / EPROM
GMS9XX54: 16K × 8
CPU
T0
T1
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
T2
GMS9XX56: 24K × 8
GMS9XX58: 32K × 8
Page 8
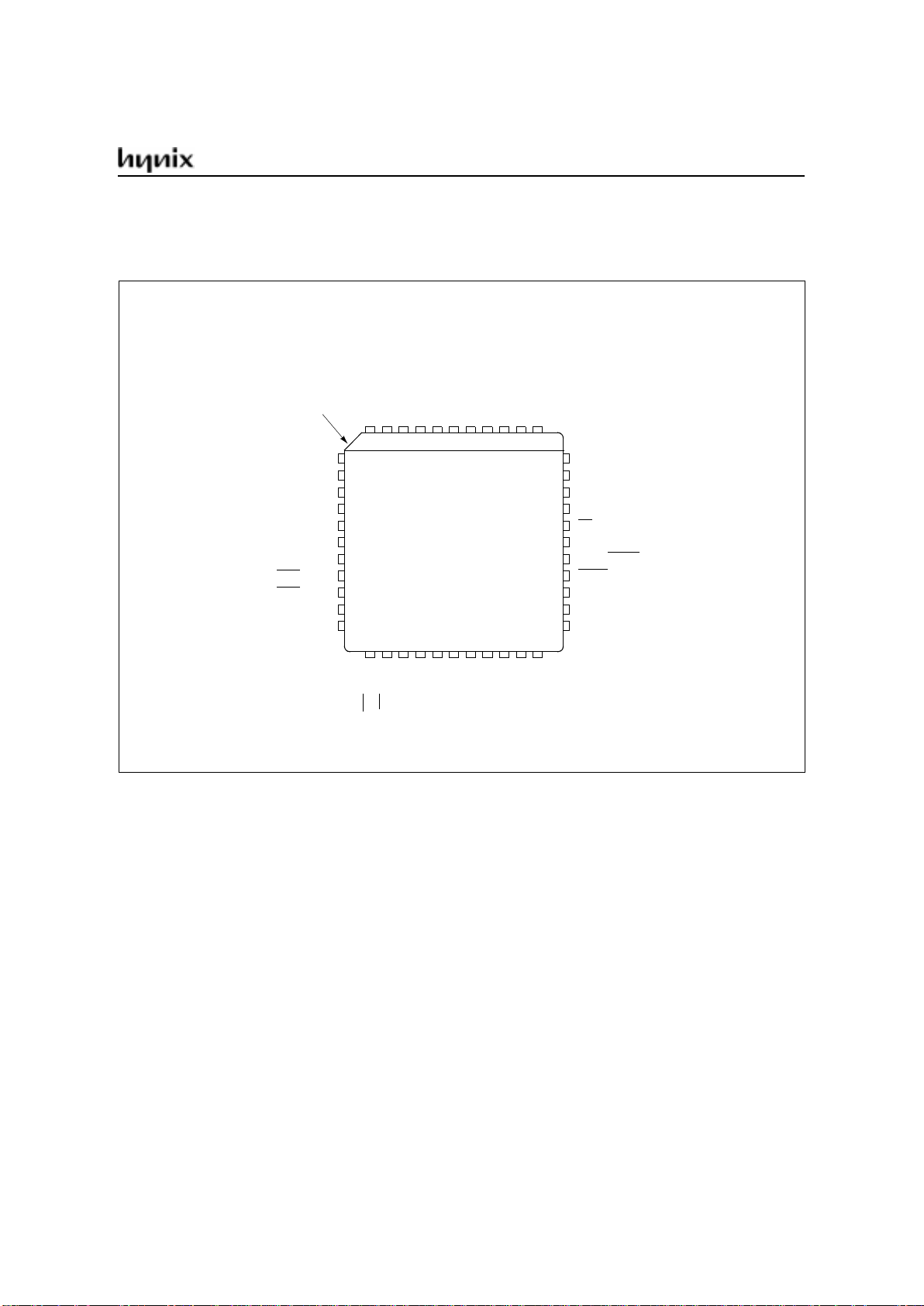
GMS90 Series
4 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
PIN CONFIGURATION
44-PLCC Pin Configuration (top view)
P0.4 / AD4
P0.5 / AD5
P0.6 / AD6
P0.7 / AD7
EA
/V
PP
N.C.*
ALE / PROG
PSEN
P2.7 / A15
P2.6 / A14
P2.5 / A13
P1.5
P1.6
P1.7
RESET
RxD / P3.0
N.C.*
TxD / P3.1
INT0
/P3.2
INT1
/P3.3
T0 / P3.4
T1 / P3.5
WR /P3.6
RD
/P3.7
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
SS
N.C.*
P2.0 / A8
P2.1 / A9
P2.2 / A10
P2.3 / A11
P2.4 / A12
P1.4
P1.3
P1.2
P1.1 / T2EX
P1.0 / T2
N.C.*
V
CC
P0.0 / AD0
P0.1 / AD1
P0.2 / AD2
P0.3 / AD3
65432
1
4443424140
1819202122232425262728
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
INDEX
CORNER
N.C.: Do not connect.
Page 9
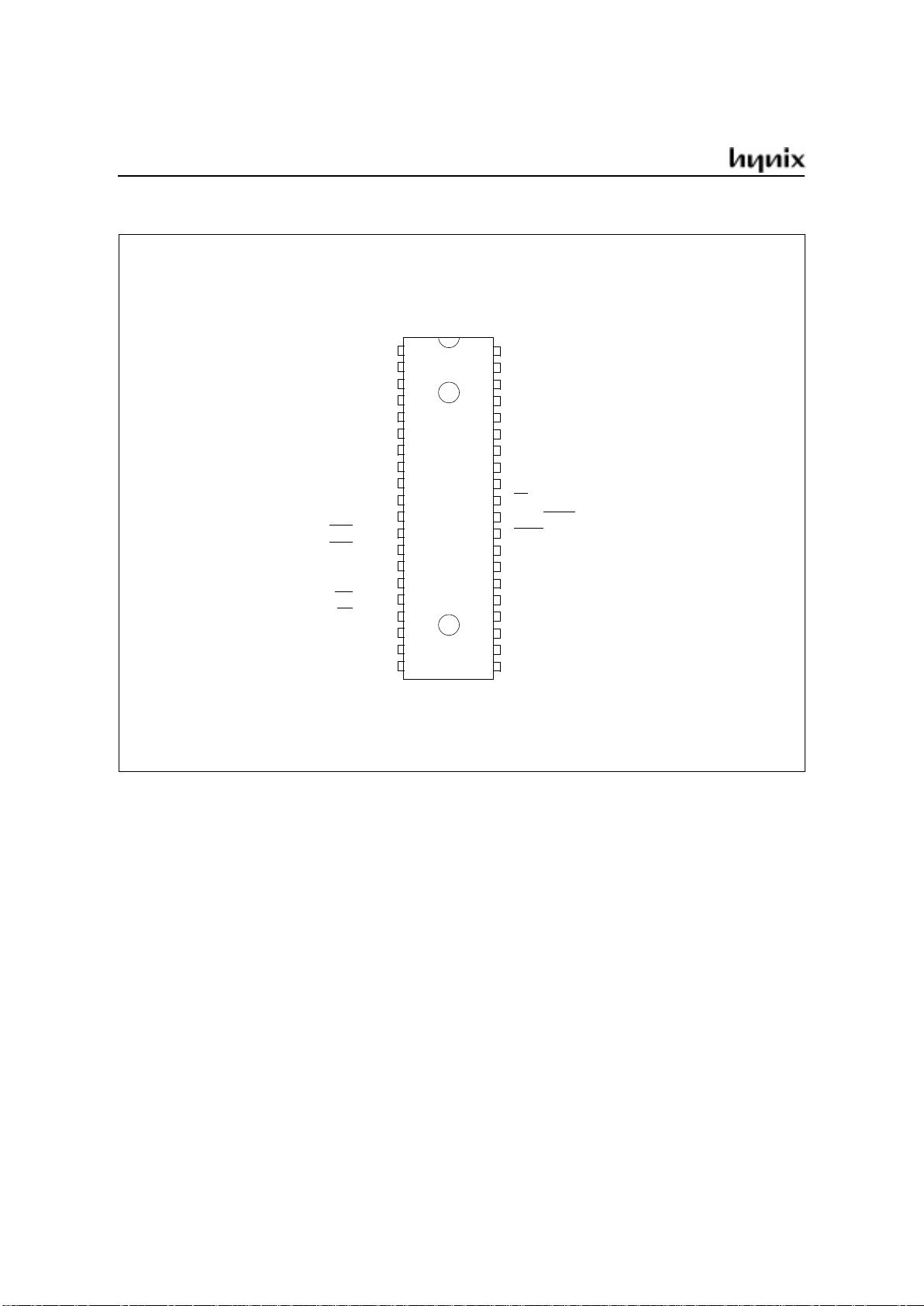
GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 5
40-PDIP Pin Configuration (top view)
P0.4 / AD4
P0.5 / AD5
P0.6 / AD6
P0.7 / AD7
EA
/V
PP
ALE / PROG
PSEN
P2.7 / A15
P2.6 / A14
P2.5 / A13
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
40
P2.4 / A12
P2.3 / A11
P2.2 / A10
P2.1 / A9
P2.0 / A8
P0.0 / AD0
P0.1 / AD1
P0.2 / AD2
P0.3 / AD3
V
CC
T2EX / P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
T2 / P1.0
P1.5
P1.6
P1.7
RESET
RxD / P3.0
TxD / P3.1
INT0
/P3.2
INT1
/P3.3
T0 / P3.4
T1 / P3.5
WR
/P3.6
RD
/P3.7
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
SS
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1
Page 10
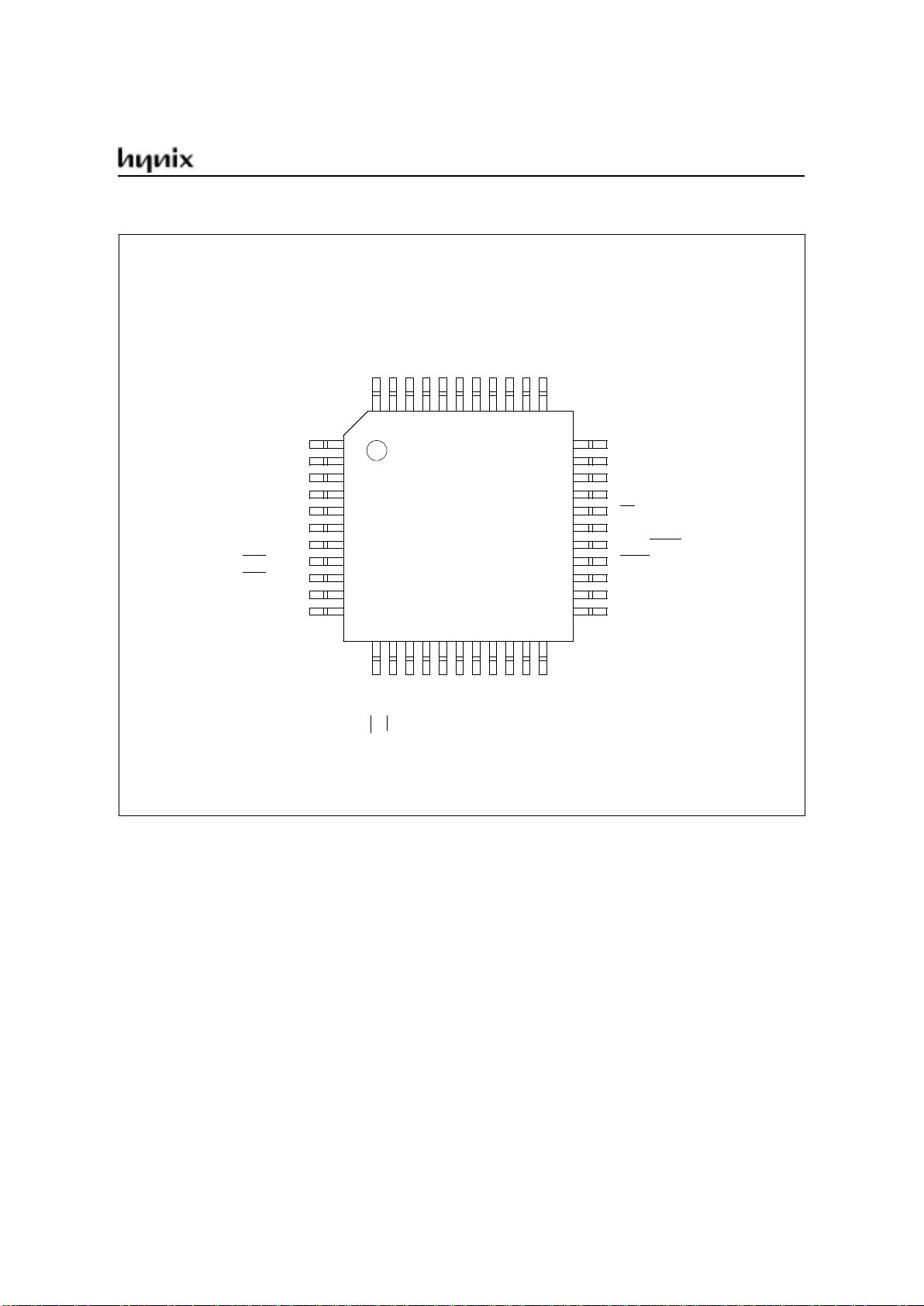
GMS90 Series
6 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
44-MQFP Pin Configuration (top view)
P0.4 / AD4
P0.5 / AD5
P0.6 / AD6
P0.7 / AD7
EA
/V
PP
N.C.*
ALE / PROG
PSEN
P2.7 / A15
P2.6 / A14
P2.5 / A13
P1.5
P1.6
P1.7
RESET
RxD / P3.0
N.C.*
TxD / P3.1
INT0
/P3.2
INT1
/P3.3
T0 / P3.4
T1 / P3.5
WR /P3.6
RD
/P3.7
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
SS
N.C.*
P2.0 / A8
P2.1 / A9
P2.2 / A10
P2.3 / A11
P2.4 / A12
P1.4
P1.3
P1.2
P1.1 / T2EX
P1.0 / T2
N.C.*
V
CC
P0.0 / AD0
P0.1 / AD1
P0.2 / AD2
P0.3 / AD3
4443424140393837363534
1213141516171819202122
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
N.C.: Do not connect.
Page 11
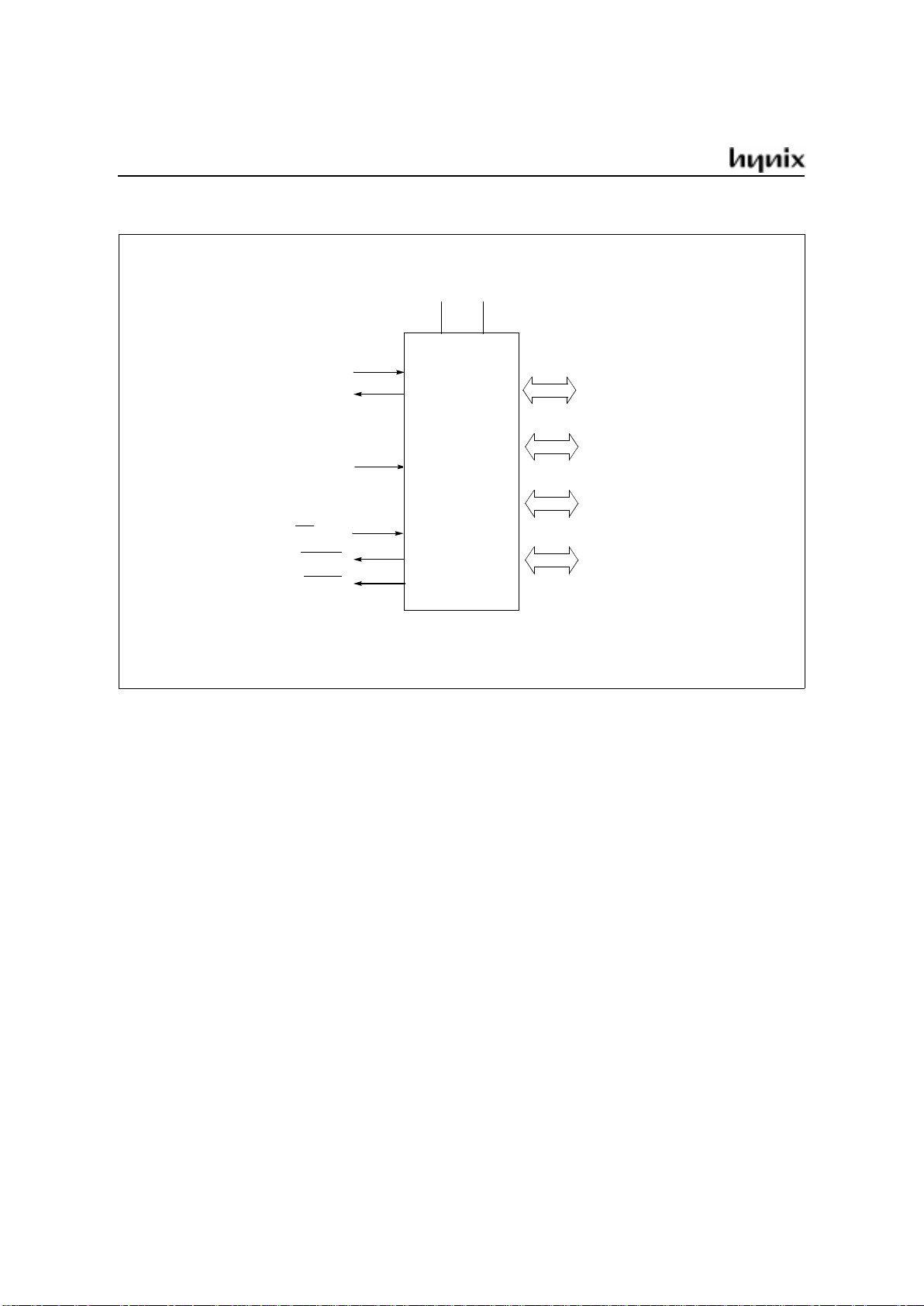
GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 7
Logic Symbol
XTAL1
XTAL2
RESET
Port 0
8-bit Digital I/O
Port 1
8-bit Digital I/O
Port 2
8-bit Digital I/O
Port 3
8-bit Digital I/O
EA/V
PP
ALE/PROG
PSEN
V
CCVSS
Page 12
GMS90 Series
8 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
PIN DEFINITIONS AND FUNCTIONS
Symbol
Pin Number
Input/
Output
Function
PLCC-44PDIP-40MQFP-
44
P1.0-P1.7 2-9
2
3
2
1-8
1
2
1
40-44,
1-3
40
41
40
I/O Port1
Port 1 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal
pull-ups. Port 1 pins that have 1s written to them are
pulled high by the internal pull-up resistors and can be
used as inputs. As inputs, port 1 pins that are
externally pulled low will source current because of
the pulls-ups (IIL, in the DC characteristics). Pins P1.0
and P1.1 also. Port1 also receives the low-order
address byte during program memory verification.
Port1 also serves alternate functions of Timer 2.
P1.0 / T2 : Timer/counter 2 external count input
P1.1 / T2EX : Timer/counter 2 trigger input
In GMS9XC54/56/58:
P1.0 / T2, Clock Out : Timer/counter 2 external count
input, Clock Out
P3.0-P3.7 11,
13-19
10-17 5, 7-13 I/O Port 3
Port 3 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal
pull-ups. Port 3 pins that have 1s written to them are
pulled high by the internal pull-up resistors and can be
used as inputs. As inputs, port 3 pins that are
externally pulled low will source current because of
the pulls-ups (IIL, in the DC characteristics). Port 3 also
serves the special features of the 80C51 family, as
listed below.
11
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
5
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
P3.0 / RxD
P3.1 / TxD
P3.2 /INT0
P3.3 / INT1
P3.4 /T0
P3.5 /T1
P3.6 / WR
P3.7 /RD
receiver data input (asynchronous) or
data input output(synchronous) of serial
interface 0
transmitter data output (asynchronous)
or clock output (synchronous) of the
serial interface 0
interrupt 0 input/timer 0 gate control
interrupt 1 input/timer 1 gate control
counter 0 input
counter 1 input
the write control signal latches the data
byte from port 0 into the external data
memory
the read control signal enables the
external data memory to port 0
XTAL2 20 18 14 O XTAL2
Output of the inverting oscillator amplifier.
Page 13
GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 9
XTAL1 21 19 15 I XTAL1
Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to
the internal clock generator circuits.To drive the
device from an external clock source, XTAL1 should
be driven, while XTAL2 is left unconnected. There are
no requirements on the duty cycle of the external
clock signal, since the input to the internal clocking
circuitry is divided down by a divide-by-two flip-flop.
Minimum and maximum high and low times as well as
rise fall times specified in the AC characteristics must
be observed.
P2.0-P2.7 24-31 21-28 18-25 I/O Port 2
Port 2 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal
pull-ups. Port 2 pins that have 1s written to them are
pulled high by the internal pull-up resistors and can be
used as inputs. As inputs, port 2 pins that are
externally pulled low will source current because of
the pulls-ups (IIL, in the DC characteristics).Port 2
emits the high-order address byte during fetches from
external program memory and during accesses to
external data memory that use 16-bit addresses
(MOVX @DPTR). In this application it uses strong
internal pull-ups when emitting 1s. During accesses to
external data memory that use 8-bit addresses
(MOVX @Ri), port 2 emits the contents of the P2
special function register.
PSEN 32 29 26 O The Program Store Enable
The read strobe to external program memory when
the device is executing code from the external
program memory. PSEN is activated twice each
machine cycle, except that two PSEN activations are
skipped during each access to external data memory.
PSEN is not activated during fetches from internal
program memory.
RESET 10 9 4 I RESET
A high level on this pin for two machine cycles while
the oscillator is running resets the device. An internal
diffused resistor to VSSpermits power-on reset using
only an external capacitor to VCC.
Symbol
Pin Number
Input/
Output
Function
PLCC-44PDIP-40MQFP-
44
Page 14
GMS90 Series
10 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
ALE /
PROG
33 30 27 O The Address Latch Enable / Program pulse
Output pulse for latching the low byte of the address
during an access to external memory. In normal
operation, ALE is emitted at a constant rate of 1/6 the
oscillator frequency, and can be used for external
timing or clocking. Note that one ALE pulse is skipped
during each access to external data memory. This pin
is also the program pulse input (PROG)during
EPROM programming.
In GMS9XC54/56/58:
If desired, ALE operation can be disabled by setting
bit 0 of SFR location 8EH. With this bit set, the pin is
weakly pulled high. The ALE disable feature will be
terminated by reset. Setting the ALE-disable bit has
no affect if the microcontroller is in external execution
mode.
EA /V
PP
35 31 29 I External Access Enable / Program Supply Voltage
EA must be external held low to enable the device to
fetch code from external program memory locations
0000Hto FFFFH.IfEAis held high, the device
executes from internal program memory unless the
program counter contains an address greater than its
internal memory size. This pin also receives the
12.75V programming supply voltage (VPP)during
EPROM programming.
Note; however, that if any of the Lock bits are
programmed, EA will be internally
latched on reset.
P0.0-P0.7 36-43 32-39 30-37 I/O Port 0
Port 0 is an 8-bit open-drain bidirectional I/O port.
Port 0 pins that have 1s written to them float and can
be used as high-impedance inputs.
Port 0 is also the multiplexed low-order address and
data bus during accesses to external program and
data memory. In this application it uses strong internal
pull-ups when emitting 1s. Port 0 also outputs the
code bytes during program verification in the
GMS97X5X. External pull-up resistors are required
during program verification.
V
SS
22 20 16 -
Circuit ground potential
V
CC
44 40 38 -
Supply terminal for all operating modes
N.C. 1,12
23,34
-6,17
28,39
-
No connection
Symbol
Pin Number
Input/
Output
Function
PLCC-44PDIP-40MQFP-
44
Page 15
GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 11
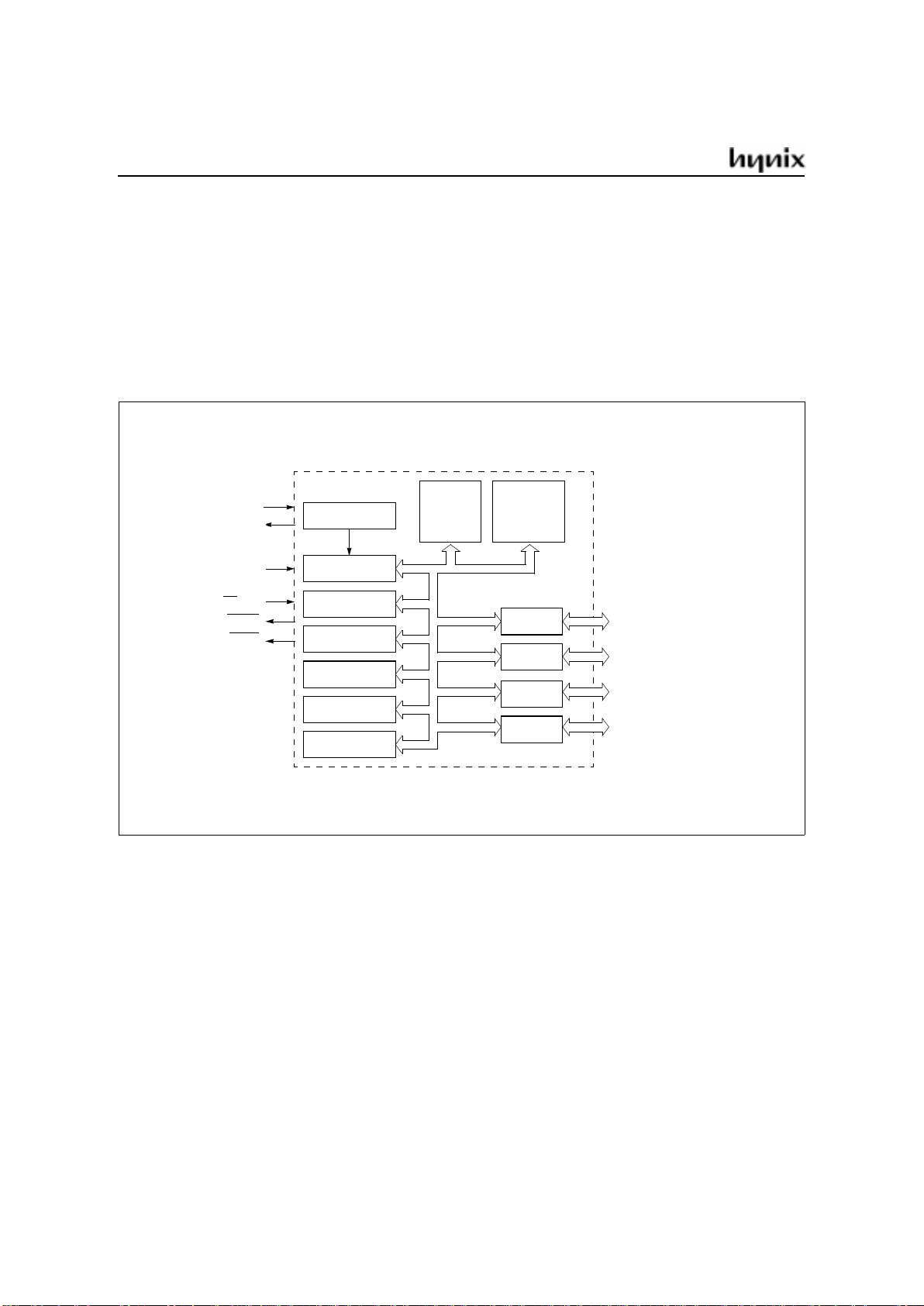
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The GMS90 series is fully compatible to the standard 8051 microcontroller family.
It is compatible with the general 8051 family. While maintaining all architectural and operational characteristics
of the general 8051 family.
Figure 1 shows a block diagram of the GMS90 series
Figure 1. Block Diagram of the GMS90 series
ROM/EPROM
4K/8K/16K
24K/32K
RAM
128/256×8
OSC & TIMING
CPU
Timer 0
Timer 1
Timer 2
Interrupt Unit
Serial Channel
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 0
8-bit Digit. I/O
Port 1
8-bit Digit. I/O
Port 2
8-bit Digit. I/O
Port 3
8-bit Digit. I/O
XTAL1
XTAL2
RESET
EA
/V
PP
ALE/PROG
PSEN
Page 16
GMS90 Series
12 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
CPU
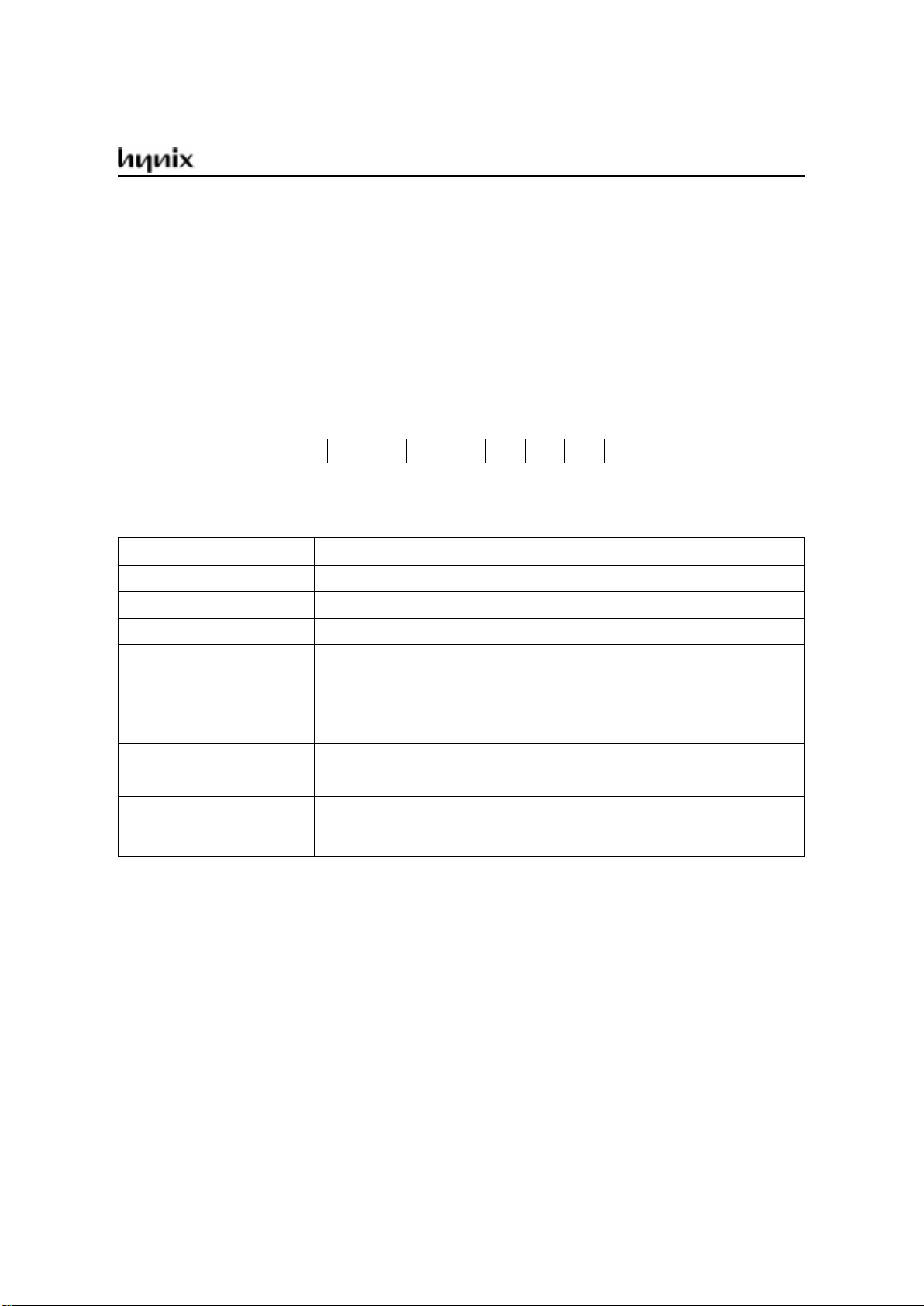
The GMS90 series is efficient both as a controller and as an arithmetic processor. It has extensive facilities for
binary and BCD arithmetic and excels in its bit-handling capabilities. Efficient use of program memory results
from an instruction set consisting of 44% one-byte,41% two-byte, and 15% three-byte instructions. With a 12
MHz crystal, 58% of the instructions are executed in 1.0µs (40MHz: 300ns).
Special Function Register PSW
Reset value of PSW is 00H.
Bit Function
CY
Carry Flag
AC
Auxiliary Carry Flag (for BCD operations)
F0
General Purpose Flag
RS1
0
0
1
1
RS0
0
1
0
1
Register Bank select control bits
Bank 0 selected, data address 00H-07
H
Bank 1 selected, data address 08H-0F
H
Bank 2 selected, data address 10H-17
H
Bank 3 selected, data address 18H-1F
H
OV
Overflow Flag
F1
General Purpose Flag
P
Parity Flag
Set/cleared by hardware each instruction cycle to indicate an odd/even
number of "one" bits in the accumulator, i.e. even parity.
CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV F1 P
76543210
LSB
MSB
Bit No.
Addr. D0
H
PSW
Page 17
GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 13
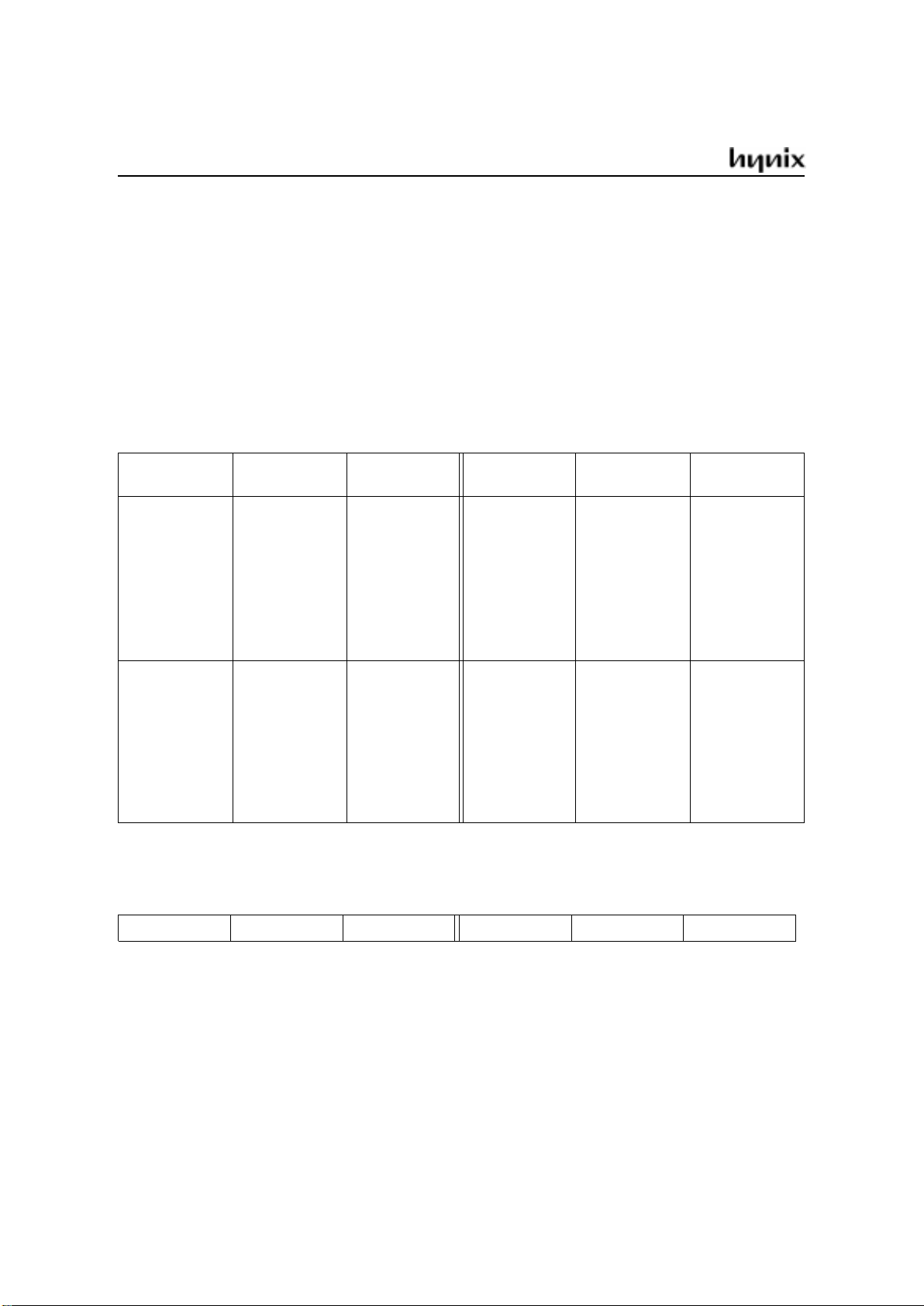
SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTERS
All registers, except the program counter and the four general purpose register banks, reside in the special function register area.
The 28 special function registers (SFR) include pointers and registers that provide an interface between the CPU
and the other on-chip peripherals. There are also 128 directly addressable bits within the SFR area.
All SFRs are listed in Table 1, Table 1, and Table 3.
In Table 1 they are organized in numeric order of their addresses. In Table 2 they are organized in groups which
refer to the functional blocks of the GMS90 series. Table 3 illustrates the contents of the SFRs.
Table 1. Special Function Registers in Numeric Order of their Addresses
Address Register
Contentsafter
Reset
Address Register
Contentsafter
Reset
80H
81H
82H
83H
84H
85H
86H
87H
P0
1)
SP
DPL
DPH
reserved
reserved
reserved
PCON
1) Bit-addressable SpecialFunctionRegister.
FFH
07H
00H
00H
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
0XX0000
B
2)
2) X means that the value is indeterminate and the location is reserved.
90H
91H
92H
93H
94H
95H
96H
97H
P1
1)
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
FF
H
00
H
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
88H
89H
8AH
8BH
8CH
8DH
8EH
3)
8FH
3) The GMS9XX54/56/58 have the AUXR0 register at address 8EH.
TCON
1)
TMOD
TL0
TL1
TH0
TH1
+
3)
reserved
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
+
3)
XXH
2)
98H
99H
9AH
9BH
9CH
9DH
9EH
9FH
SCON
1)
SBUF
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
00H
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
8E
H
reserved XXXXXXX0
B
2)
8E
H
AUXR0
GMS9XX51/52 GMS9XX54/56/58
XXXXXXXX
B
2)
Page 18
GMS90 Series
14 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
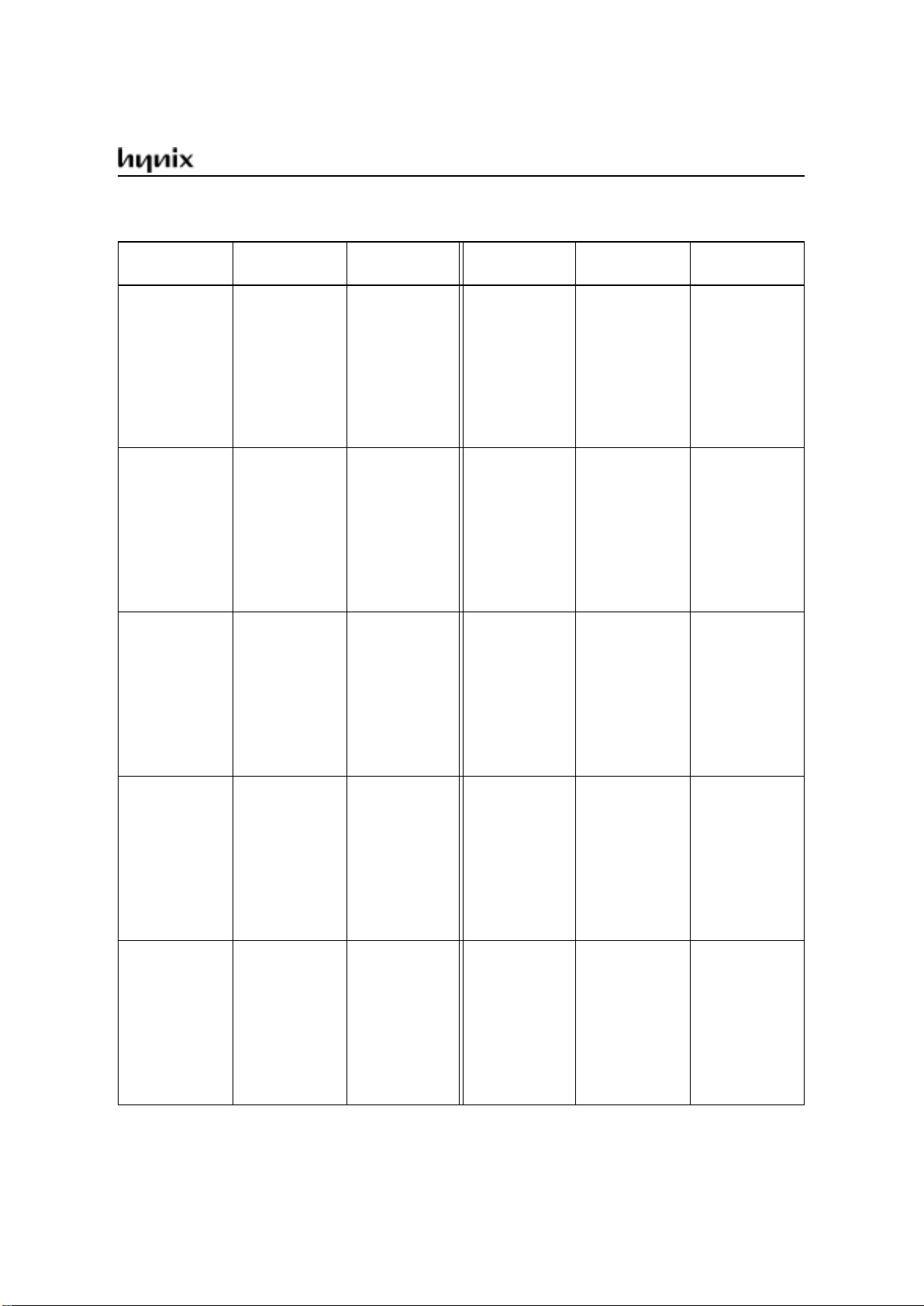
Table 1. Special Function Registers in Numeric Order of their Addresses (cont’d)
Address Register
Contentsafter
Reset
Address Register
Contentsafter
Reset
A0H
A1H
A2H
A3H
A4H
A5H
A6H
A7H
P2
1)
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
FFH
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
C8H
C9H
3)
CAH
CBH
CCH
CDH
CEH
CFH
T2CON
1)
T2MOD
RC2L
RC2H
TL2
TH2
reserved
reserved
00H
+
3)
00H
00H
00H
00H
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
A8H
A9H
AAH
ABH
ACH
ADH
AEH
AFH
IE
1)
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
0X000000B
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
D0H
D1H
D2H
D3H
D4H
D5H
D6H
D7H
PSW
1)
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
00H
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
B0H
B1H
B2H
B3H
B4H
B5H
B6H
B7H
P3
1)
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
FFH
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
D8H
D9H
DAH
DBH
DCH
DDH
DEH
DFH
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
B8H
B9H
BAH
BBH
BCH
BDH
BEH
BFH
IP
1)
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
XX000000B
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
E0H
E1H
E2H
E3H
E4H
E5H
E6H
E7H
ACC
1)
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
00H
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
C0H
C1H
C2H
C3H
C4H
C5H
C6H
C7H
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
XX
H
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
E8H
E9H
EAH
EBH
ECH
EDH
EEH
EFH
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
Page 19

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 15
F0H
F1H
F2H
F3H
F4H
F5H
F6H
F7H
B
1)
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
00H
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
F8H
F9H
FAH
FBH
FCH
FDH
FEH
FFH
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
XXH
2)
1) Bit-addressable SpecialFunctionRegister.
2) X means that the value is indeterminate and the location is reserved.
3) Address C9
H
is configured as below.
Table 1. Special Function Registers in Numeric Order of their Addresses (cont’d)
Address Register
Contentsafter
Reset
Address Register
Contentsafter
Reset
C9
H
reserved XXXXXX00
B
2)
XXXXXXX0
B
2)
C9
H
T2MOD
GMS9XX51/52 GMS9XX54/56/58
Page 20

GMS90 Series
16 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
Table 2. Special Function Registers - Functional Blocks
Block Symbol Name Address
Contents
after Reset
CPU ACC
B
DPH
DPL
PSW
SP
Accumulator
B-Register
Data Pointer, High Byte
Data Pointer, Low Byte
Program Status Word Register
Stack Pointer
E0H
1)
F0H
1)
83H
82H
D0H
1)
81H
1) Bit-addressable SpecialFunction register
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
07H
Interrupt System IE
IP
Interrupt Enable Register
Interrupt Priority Register
A8H
1)
B8H
1)
0X000000B
2)
XX000000B
2)
2) X means that the value is indeterminate and the location is reserved
Ports P0
P1
P2
P3
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
80H
1)
90H
1)
A0H
1)
B0H
1)
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
Serial Channels
PCON
3)
SBUF
SCON
3) This special function register is listed repeatedly since some bit of it also belong to other functional blocks
Power Control Register
Serial Channel Buffer Reg.
Serial Channel 0 Control Reg.
87H
99H
98H
1)
0XXX0000B
2)
XXH
2)
00H
Timer 0/ Timer 1 TCON
TH0
TH1
TL0
TL1
TMOD
Timer 0/1 Control Register
Timer 0, High Byte
Timer 1, High Byte
Timer 0, Low Byte
Timer 1, Low Byte
Timer Mode Register
88H
1)
8CH
8DH
8AH
8BH
89H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
Timer 2 T2CON
T2MOD
RC2H
RC2L
TH2
TL2
AUXR0
4)
4) The AUX R0 is in the GMS9XX54/56/58 only.
Timer 2 Control Register
Timer 2 Mode Register
Timer 2 Reload Capture Reg., High Byte
Timer 2 Reload Capture Reg., Low Byte
Timer 2, High Byte
Timer 2, Low Byte
Aux. Register 0
C8H
1)
C9H
CBH
CAH
CDH
CCH
8EH
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
XXXXXXX0B
2)
Power Saving
Modes
PCON
3)
Power Control Register 87H
0XXX0000B
2)
Page 21

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 17
† indicates resident in the GMS9XX54/56/58, not in 9XX51/52.
Table 3. Contents of SFRs, SFRs in Numeric Order
Address Register
Bit76543210
80H P0
81H SP
82H DPL
83H DPH
87H PCON
SMOD
---GF1GF0PDEIDLE
88H TCON TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0
89H TMOD GATE C/T M1 MT GATE C/T M1 M0
8AH TL0
8BH TL1
8CH TH0
8DH TH1
8EH
AUXR0
†
-------
A0
†
90H P1
98H SCON SM0 SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI
99H SBUF
A0H P2
A8H IE EA - ET2 ES ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0
B0H P3
B8H IP - - PT2 PS PT1 PX1 PT0 PX0
SFR bit and byte addressable
SFR not bit addressable
- : this bit locationis reserved
Page 22

GMS90 Series
18 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
† indicates resident in the GMS9XX54/56/58, not in 9XX51/52.
Table 3. Contents of SFRs, SFRs in Numeric Order (cont’d)
Address Register
Bit76543210
C8H T2CON TF2 EXF2 RCLK TCLK
EXEN2
TR2 C/T2
CP/RL2
C9HT2MOD ------
T2OE
†
DCEN
CAH RC2L
CBH RC2H
CCH TL2
CDH TH2
D0H PSW CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV
F1
P
E0H ACC
F0H B
A0
8EH
0 : Enable ALE Signal (Generated ALE Signal)
C9H
1 : Disable ALE Signal (Not Generated ALE Signal)
T2OE
0 : Disable Timer2 Output
1 : Enable Timer2 Output
†
†
T2OE : Timer2 Output Enable bit
A0 : ALE Signal Disable bit
SFR bit and byte addressable
SFR not bit addressable
- : this bit location is reserved
Page 23

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 19
TIMER / COUNTER 0 AND 1
Timer/Counter 0 and 1 can be used in four operating modes as listed in Table 4:
In the "timer" function (C/T
= "0") the register is incremented every machine cycle. Therefore the count rate is
f
OSC
/12.
In the "counter" function the register is incremented in response to a 1-to-0 transition at its corresponding external input pin (P3.4/T0, P3.5/T1). Since it takes two machine cycles to detect a falling edge the max. count rate
is f
OSC
/24. External inputs INT0 and INT1 (P3.2, P3.3) can be programmed to function as a gate to facilitate
pulse width measurements. Figure 2 illustrates the input clock logic.
Figure 2. Timer/Counter 0 and 1 Input Clock Logic
Table 4. Timer/Counter 0 and 1 Operating Modes
Mode Description
TMOD Input Clock
Gate C/T M1 M0 internal external (Max.)
0
8-bit timer/counter with a
divide-by-32 prescaler
XX00
f
OSC
÷(12×32) f
OSC
÷(24×32)
1 16-bit timer/counter X X 0 1
f
OSC
÷12 f
OSC
÷24
2
8-bit timer/counter with
8-bit auto-reload
XX10
f
OSC
÷12 f
OSC
÷24
3
Timer/counter 0 used as
one 8-bit timer/counter and
one 8-bit timer Timer 1
stops
XX11
f
OSC
÷12 f
OSC
÷24
f
OSC
÷ 12
TMOD
f
OSC
÷ 12
P3.4/T0
P3.5/T1
Max.
f
OSC
/24
C/T
=1
≥1
TCON
TR0 / 1
TMOD
Gate
&
P3.2 / INT0
P3.3 / INT1
Timer 0/1
Input Clock
0
1
Page 24

GMS90 Series
20 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
TIMER 2
Timer 2 is a 16-bit timer/Counter with an up/down count feature. It can operate either as timer or as an event
counter which is selected by bit C/T2
(T2CON.1). It has three operating modes as shown in Table 5.
Note: ↓ = falling edge
Table 5. Timer/Counter 2 Operating Modes
Mode
T2CON
T2MO
D
T2CON
P1.1/
T2EX
Remarks
Input Clock
RCLKor
TCLK
CP/RL2
TR2 DCEN EXEN2 internal
external
(P1.0/T2)
16-bit AutoReload
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
X
X
X
↓
0
1
reload upon overflow
reload trigger (falling edge)
Down counting
Up counting
f
OSC
÷ 12
Max.
f
OSC
÷24
16-bit
Capture
0
0
1
1
1
1
X
X
0
1
X↓16 bit Timer/ Coun-
ter (only up-counting)
capture TH2,TL2
→ RC2H,RC2L
f
OSC
÷ 12
Max.
f
OSC
÷ 24
Baud Rate
Generator
1
1
X
X
1
1
X
X
0
1
X↓no overflow
interrupt request
(TF2)
extra external interrupt ("Timer 2")
f
OSC
÷ 12
Max.
f
OSC
÷ 24
Off X X 0 X X X Timer 2 stops - -
Page 25

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 21
SERIAL INTERFACE (USART)
The serial port is full duplex and can operate in four modes (one synchronous mode, three asynchronous modes)
as illustrated in Table 6. The possible baud rates can be calculated using the formulas given in Table 7.
Table 6. USART Operating Modes
Mode
SCON
Baudrate Description
SM0 SM1
000
Serial data enters and exits through RxD.
TxD outputs the shift clock. 8-bit are transmitted/received (LSB first)
1 0 1 Timer 1/2 overflow rate
8-bit UART
10 bits are transmitted (through TxD) or
received (RxD)
210
or
9-bit UART
11 bits are transmitted (TxD) or received (RxD)
3 1 1 Timer 1/2 overflow rate
9-bit UART
Like mode 2 except the variable baud rate
Table 7. Formulas for Calculating Baud rates
Baud Rate
derived from
Interface Mode Baudrate
Oscillator
0
2
Timer 1 (16-bit timer)
(8-bit timer with
8-bit auto reload)
1,3
1,3
Timer 2 1,3
f
OSC
12
----------- -
f
OSC
32
----------- -
f
OSC
64
----------- -
f
OSC
12
----------- -
2
SMOD
64
----------------- -
f
OSC
×
2
SMOD
32
----------------- -
Timer 1 overflow
()×
2
SMOD
32
----------------- -
f
OSC
12 256 TH1
()–[]×
------------------------------------------------- -
×
f
OSC
32 65536 RC2H RC2L
,()–[]×
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -
Page 26

GMS90 Series
22 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
INTERRUPT SYSTEM
The GMS90 series provides 5 (4K bytes ROM version) or 6 (above 8K bytes ROM version) interrupt sources
with two priority levels. Figure 3 gives a general overview of the interrupt sources and illustrates the request and
control flags.
Figure 3. Interrupt Request Sources
PT0
IP.1
PT1
IP.3
PT2
IP.5
PS
IP.4
PX0
IP.0
PX1
IP.2
EA
IE.7
ET0
IE.1
ET1
IE.3
ET2
IE.5
ES
IE.4
EX0
IE.0
EX1
IE.2
TF0
TCON.5
TF1
TCON.7
≥1
TF2
T2CON.7
EXF2
T2CON.6
≥1
RI
SCON.0
TI
SCON.1
IE0
TCON.1
IE1
TCON.3
IT0
TCON.0
IT1
TCON.2
P3.2/
INT0
P3.3/
INT1
EXEN2
T2CON.3
P1.1/
T2EX
Timer 2 Overflow
Timer 0 Overflow
Timer 1 Overflow
: Low level triggered
: Falling edge triggered
Low
Priority
High
Priority
UART
Page 27

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 23
A low-priority interrupt can itself be interrupted by a high-priority interrupt, but not by another low priority interrupt. A high-priority interrupt cannot be interrupted by any other interrupt source.
If two requests of different priority level are received simultaneously, the request of higher priority is serviced.
If requests of the same priority are received simultaneously, an internal polling sequence determines which request is serviced. Thus within each priority level there is a second priority structure determined by the polling
sequence as shown in Table 9.
Table 8. Interrupt Sources and their Corresponding Interrupt Vectors
Source (Request Flags) Vectors Vector Address
RESET
IE0
TF0
IE1
TF1
RI + TI
TF2 + EXF2
RESET
External interrupt 0
Timer 0 interrupt
External interrupt 1
Timer 1 interrupt
Serial port interrupt
Timer 2 interrupt
0000H
0003H
000BH
0013H
001BH
0023H
002BH
Table 9. Interrupt Priority-Within-Level
Interrupt Source Priority
External Interrupt 0
Timer 0 Interrupt
External Interrupt 1
Timer 1 Interrupt
Serial Channel
Timer 2 Interrupt
IE0
TF0
IE1
TF1
RI + TI
TF2 + EXF2
High
↓
↓
↓
↓
Low
Page 28

GMS90 Series
24 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
Power Saving Modes
Two power down modes are available, the Idle Mode and Power Down Mode.
The bits PDE and IDLE of the register PCON select the Power Down mode or the Idle mode, respectively. If
the Power Down mode and the Idle mode are set at the same time, the Power Down mode takes precedence.
Table 10 gives a general overview of the power saving modes.
In the Power Down modeofoperation,V
CC
can be reduced tominimize power consumption. It must be ensured,
however,that V
CC
is not reduced before the Power Down mode is invoked, and that VCCis restored to its normal
operating level, before the Power Down mode is terminated. The reset signal that terminates the Power Down
mode also restarts the oscillator. The reset should not be activated before V
CC
is restored to its normal operating
level and must be held active long enough to allow the oscillator to restart and stabilize (similar to power-on
reset).
Table 10. Power Saving Modes Overview
Mode
Entering
Instruction
Example
Leaving by Remarks
Idle mode ORL PCON, #01H - Enabled interrupt
- Hardware Reset
CPU is gated off
CPU status registers maintain their
data.
Peripherals are active
Power-Down mode ORL PCON, #02H Hardware Reset Oscillatoris stopped, contents of on-
chip RAM and SFR’s are maintained
(leaving Power Down Mode means
redefinition of SFR contents).
Page 29

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 25
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Ambient temperature under bias (TA)...................................................................................... -40 to + 85 °C
Storage temperature (T
ST
)......................................................................................................-65 to + 150 °C
Voltage on V
CC
pins with respect to ground (VSS) .................................................................-0.5V to 6.5V
Voltage on any pin with respect to ground (V
SS
) ..........................................................-0.5V to VCC+0.5V
Input c urrent on any pin during overload condition............................................................-15mA to +15mA
Absolute sum of all input currents during overload condition ...........................................................|100mA|
Power dissipation ....................................................................................................................................1.5W
Note: Stresses above those listed under "Absolute Maximum Ratings" may cause permanent damage of the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above
those indicated in the operational sections of this specificationis not implied.Exposureto absolute maximum rating conditions for longer periods may affect device reliability. During overload conditions (VIN>VCCor VIN<VSS)
the Voltage on VCCpins with respect to ground (VSS) must not exceed the values defined by the absolute maximum ratings.
Page 30

GMS90 Series
26 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
DC Characteristics
DC Characteristics for GMS90C31/32, GMS90C51/52/54/56/58
V
CC
=5V+10%,-15%;VSS=0V; TA=0°Cto70°C
Parameter Symbol
Limit Values
Unit Test Conditions
Min. Max.
Input low voltage
(except EA, RESET)
V
IL
-0.5
0.2VCC-0.1
V-
Input low voltage (EA)V
IL1
-0.5
0.2VCC-0.3
V-
Input low voltage (RESET) V
IL2
-0.5
0.2VCC+0.1
V-
Input high voltage (except
XTAL1, EA, RESET)
V
IH
0.2VCC+0.9 VCC+0.5
V-
Input high voltage to XTAL1 V
IH1
0.7V
CC
VCC+0.5
V-
Input high voltage to EA,
RESET
V
IH2
0.6V
CC
VCC+0.5
V-
Output low voltage
(ports 1, 2, 3)
V
OL
-0.45V
IOL=1.6mA
1)
Output low voltage
(port0,ALE,PSEN)
V
OL1
-0.45V
IOL=3.2mA
1)
Output high voltage
(ports 1, 2, 3)
V
OH
2.4
0.9V
CC
-V
IOH=-80µA
IOH=-10µA
Output high voltage
(port 0 in external bus
mode, ALE, PSEN)
V
OH1
2.4
0.9V
CC
-V
IOH=-800µA
2)
IOH=-80µA
2)
Logic 0 input current
(ports 1, 2, 3)
I
IL
-10 -50 µA
VIN=0.45V
Logical 1-to-0 transition current (ports 1, 2, 3)
I
TL
-65 -650 µA
VIN=2.0V
Input leakage current
(port 0, EA)
I
LI
- ±1 µA
0.45 < VIN< V
CC
Pin capacitance
C
IO
-10pF
fC=1MHz
TA=25°C
Power supply current:
Active mode, 12MHz
3)
Idle mode, 12MHz
3)
Active mode, 24 MHz
3)
Idle mode, 24MHz
3)
Active mode, 40 MHz
3)
Idle mode, 40 MHz
3)
Power Down Mode
3)
I
CC
I
CC
I
CC
I
CC
I
CC
I
CC
I
PD
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
21
4.8
36.2
8.2
58.5
12.5
50
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
µA
VCC=5V
4)
VCC=5V
5)
VCC=5V
4)
VCC=5V
5)
VCC=5V
4)
VCC=5V
5)
VCC=5V
6)
Page 31

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 27
1) Capacitive loading on ports 0 and 2 may cause spurious noise pulses to be superimposed on the VOLof ALE and port 3.
The noise is due to external bus capacitance discharg ing into the port 0 and port 2 pins when these pins make 1-to-0 transitions during bus operation. In the worst case (capacitive l oading: > 50pF at 3.3V, > 100pF at 5V), the noise pulse on ALE
line may exceed 0.8V. In such cases it may be desirable to qualif y ALE with a schmitt-trigger, or use an address l atch with
a schmitt-trigger strobe input.
2) Capacitive loading on ports 0 and 2 may cause the V
OH
on ALE and PSEN to momentarily fall below the 0.9VCCspecifica-
tion when the address lines are stabilizing.
3) I
CC
Max at other frequencies is given by:
active mode: I
CC
=1.27× f
OSC
+5.73
idle mode: I
CC
=0.28× f
OSC
+ 1.45 (except OTP devices)
where f
OSC
is the oscillator frequency in MHz. ICCvalues are given in mA and measured at VCC=5V.
4) I
CC
(active mode) is measured with:
XTAL1 driven with t
CLCH,tCHCL
=5ns,VIL=VSS+0.5V,VIH=VCC- 0.5V; XTAL2 = N.C.;
EA
= Port0 = RESET = VCC; all other pins are disconnected. ICCwould be slightly higher if a crystal oscillator is used (appr.
1mA).
5) I
CC
(Idle mode) is measured with all output pins disconnectedand with all peripheralsdisabled;
XTAL1 driven with t
CLCH,tCHCL
=5ns,VIL=VSS+0.5V,VIH=VCC- 0.5V; XTAL2 = N.C.;
RESET=EA
=VSS;Port0=VCC; all other pins are disconnected;
6) I
PD
(Power Down Mode) is measured under following conditions:
EA
=Port0=VCC; RESET = VSS; XTAL2 = N.C.; XTAL1 = VSS; all other pins are disconnected.
Page 32

GMS90 Series
28 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
DC Characteristics for GMS97C51/52/54/56/58 (H)
V
CC
=5V+10%,-15%;VSS=0V; TA=0°Cto70°C
Parameter Symbol
Limit Values
Unit Test Conditions
Min. Max.
Input low voltage
(except EA, RESET)
V
IL
-0.5
0.2VCC-0.1
V-
Input low voltage (EA)V
IL1
-0.5
0.2VCC-0.3
V-
Input low voltage (RESET) V
IL2
-0.5
0.2VCC+0.1
V-
Input high voltage (except
XTAL1, EA, RESET)
V
IH
0.2VCC+0.9 VCC+0.5
V-
Input high voltage to XTAL1 V
IH1
0.7V
CC
VCC+0.5
V-
Input high voltage to EA,
RESET
V
IH2
0.6V
CC
VCC+0.5
V-
Output low voltage
(ports 1, 2, 3)
V
OL
-0.45V
IOL=1.6mA
1)
Output low voltage
(port0,ALE,PSEN)
V
OL1
-0.45V
IOL=3.2mA
1)
Output high voltage
(ports 1, 2, 3)
V
OH
2.4
0.9V
CC
-V
IOH=-80µA
IOH=-10µA
Output high voltage
(port 0 in external bus
mode, ALE, PSEN)
V
OH1
2.4
0.9V
CC
-V
IOH=-800µA
2)
IOH=-80µA
2)
Logic 0 input current
(ports 1, 2, 3)
I
IL
-10 -50 µA
VIN=0.45V
Logical 1-to-0 transition current (ports 1, 2, 3)
I
TL
-65 -650 µA
VIN=2.0V
Input leakage current
(port 0, EA)
I
LI
- ±1 µA
0.45 < VIN< V
CC
Pin capacitance
C
IO
-10pF
fC=1MHz
TA=25°C
Power supply current:
Active mode, 12MHz
3)
Idle mode, 12MHz
3)
Active mode, 24 MHz
3)
Idle mode, 24MHz
3)
Active mode, 33 MHz
3)
Idle mode, 33 MHz
3)
Power Down Mode
3)
I
CC
I
CC
I
CC
I
CC
I
CC
I
CC
I
PD
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
21
4.8
36.2
8.2
45
10
50
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
µA
VCC=5V
4)
VCC=5V
5)
VCC=5V
4)
VCC=5V
5)
VCC=5V
4)
VCC=5V
5)
VCC=5V
6)
Page 33

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 29
DC Characteristics for GMS90L31/32, GMS90L51/52/54/56/58
V
CC
= 3.3V + 0.3V, -0.6V; VSS=0V; TA=0°Cto70°C
Parameter Symbol
Limit Values
Unit Test Conditions
Min. Max.
Input low voltage V
IL
-0.5 0.8 V -
Input high voltage V
IH
2.0
VCC+0.5
V-
Output low voltage
(ports 1, 2, 3)
V
OL
-
0.45
0.30
V
IOL=1.6mA
1)
IOL=100µA
1)
Output low voltage
(port0,ALE,PSEN)
V
OL1
-
0.45
0.30
V
IOL=3.2mA
1)
IOL=200µA
1)
Output high voltage
(ports 1, 2, 3)
V
OH
2.0
0.9V
CC
-V
IOH=-20µA
IOH=-10µA
Output high voltage
(port 0 in external bus
mode, ALE, PSEN)
V
OH1
2.0
0.9V
CC
-V
IOH=-800µA
2)
IOH=-80µA
2)
Logic 0 input current
(ports 1, 2, 3)
I
IL
-1 -50 µA
VIN=0.45V
Logical 1-to-0 transition current (ports 1, 2, 3)
I
TL
-25 -250 µA
VIN=2.0V
Input leakage current
(port 0, EA)
I
LI
- ±1 µA
0.45 < VIN< V
CC
Pin capacitance
C
IO
-10pF
fC=1MHz
TA=25°C
Power supply current:
Active mode, 16 MHz
3)
Idle mode, 16MHz
3)
Power Down Mode
3)
I
CC
I
CC
I
PD
-
-
-
15
5
10
mA
mA
µA
VCC=3.6V
4)
VCC=2.6V
5)
VCC=2~ 5.5V
6)
Page 34

GMS90 Series
30 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
DC Characteristics for GMS97L51/52/54/56/58
V
CC
= 3.3V + 0.3V, -0.6V; VSS=0V; TA=0°Cto70°C
Parameter Symbol
Limit Values
Unit Test Conditions
Min. max.
Input low voltage V
IL
-0.5 0.8 V -
Input high voltage V
IH
2.0
VCC+0.5
V-
Output low voltage
(ports 1, 2, 3)
V
OL
-
0.45
0.30
V
IOL=1.6mA
1)
IOL=100µA
1)
Output low voltage
(port0,ALE,PSEN)
V
OL1
-
0.45
0.30
V
IOL=3.2mA
1)
IOL=200µA
1)
Output high voltage
(ports 1, 2, 3)
V
OH
2.0
0.9V
CC
-V
IOH=-20µA
IOH=-10µA
Output high voltage
(port 0 in external bus
mode, ALE, PSEN)
V
OH1
2.0
0.9V
CC
-V
IOH=-800µA
2)
IOH=-80µA
2)
Logic 0 input current
(ports 1, 2, 3)
I
IL
-1 -50 µA
VIN=0.45V
Logical 1-to-0 transition current (ports 1, 2, 3)
I
TL
-25 -250 µA
VIN=2.0V
Input leakage current
(port 0, EA)
I
LI
- ±1 µA
0.45 < VIN< V
CC
Pin capacitance
C
IO
-10pF
fC=1MHz
TA=25°C
Power supply current:
Active mode, 12MHz
3)
Idle mode, 12MHz
3)
Power Down Mode
3)
I
CC
I
CC
I
PD
-
-
-
15
5
10
mA
mA
µA
VCC=3.6V
4)
VCC=2.6V
5)
VCC=2~ 5.5V
6)
Page 35

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 31
AC Characteristics
Explanation of the AC Symbols
Each timing symbol has 5 characters. The first character is always a ‘t’ (stand for time). The other characters,
depending on their positions, stand for the name of a signal or the logical status of that signal. The following is
a list of all the characters and what they stand for.
AC Characteristics for GMS90 series (12MHz version)
External Program Memory Characteristics
VCC=5V: VCC=5V+ 10%, − 15%; VSS=0V; TA=0°Cto70°C
(CLfor port 0. ALE and PSEN outputs = 100pF; CLfor all other outputs = 80pF)
VCC=3.3V: VCC=3.3V+ 0.3V, − 0.6V; VSS=0V; TA=0°Cto70°C
(CLforport0.ALEandPSENoutputs = 50pF; CLfor all other outputs = 50pF)
Variable clock : Vcc = 5V : 1/t
CLCL
=3.5MHzto12MHz
Vcc = 3.3V : 1/t
CLCL
=1MHzto12MHz
Parameter Symbol
12 MHz Oscillator
Variable Oscillator
1/t
CLCL
=3.5to12MHz
Unit
Min. Max. Min. Max.
ALE pulse width
t
LHLL
127 - 2t
CLCL
-40 -
ns
Address setup to ALE
t
AVLL
43 - t
CLCL
-40 - ns
Address hold after ALE
t
LLAX
30 - t
CLCL
-53 -
ns
ALE low to valid instruction in
t
LLIV
-233 -4t
CLCL
-100 ns
ALE to PSEN
t
LLPL
58 - t
CLCL
-25 -
ns
PSEN pulse width
t
PLPH
215 - 3t
CLCL
-35 - ns
PSEN to valid instruction in
t
PLIV
-150 -3t
CLCL
-100
ns
Input instruction hold after PSEN
t
PXIX
0- 0 - ns
Input instruction float after PSEN
t
PXIZ
†
-63 -t
CLCL
-20
ns
Address valid after PSEN
t
PXAV
†
75 - t
CLCL
-8 - ns
A: Address
C: Clock
D: Input Data
H: Logic level HIGH
I: Instruction (program memory contents)
L: Logic level LOW, or ALE
P: PSEN
Q: Output Data
R: RD signal
T: Time
V: Valid
W: WR signal
X: No longer a valid logic level
Z: Float
For example,
t
AVLL
= Time from Address Valid to ALE Low
t
LLPL
= Time from ALE Low to PSEN Low
Page 36
GMS90 Series
32 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
†
Interfacing the GMS90 series to devices with float times up to 75 ns is permissible. This limited bus contention will not cause
any damage to port 0 Drivers.
Address to valid instruction in
t
AVIV
-302 -5t
CLCL
-115
ns
Address float to PSEN
t
AZPL
0- 0 - ns
Parameter Symbol
12 MHz Oscillator
Variable Oscillator
1/t
CLCL
=3.5to12MHz
Unit
Min. Max. Min. Max.
Page 37

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 33
AC Characteristics for GMS90 series (12MHz)
External Data Memory Characteristics
Advance Information (12MHz)
External Clock Drive
Parameter Symbol
12 MHz Oscillator
Variable Oscillator
1/t
CLCL
=3.5to12MHz
Unit
Min. Max. Min. Max.
RD pulse width
t
RLRH
400 - 6t
CLCL
-100 -
ns
WR pulse width
t
WLWH
400 - 6t
CLCL
-100 - ns
Address hold after ALE
t
LLAX2
53 - t
CLCL
-30 -
ns
RD to valid data in
t
RLDV
-252 -5t
CLCL
-165 ns
Data hold after RD
t
RHDX
0- 0 -
ns
Data float after RD
t
RHDZ
-97 -2t
CLCL
-70 ns
ALE to valid data in
t
LLDV
-517 -8t
CLCL
-150
ns
Address to valid data in
t
AVDV
-585 -9t
CLCL
-165 ns
ALE to WR or RD
t
LLWL
200 300 3t
CLCL
-50 3t
CLCL
+50
ns
Address valid to WR or RD
t
AVWL
203 - 4t
CLCL
-130 - ns
WR or RD high to ALE high
t
WHLH
43 123 t
CLCL
-40 t
CLCL
+40
ns
Data valid to WR transition
t
QVWX
33 - t
CLCL
-50 - ns
Data setup before WR
t
QVWH
433 - 7t
CLCL
-150 - ns
Data hold after WR
t
WHQX
33 - t
CLCL
-50 -
ns
Address float after RD
t
RLAZ
-0 - 0 ns
Parameter Symbol
Variable Oscillator
(Freq. = 3.5 to 12MHz)
Unit
Min. Max.
Oscillator period (VCC=5V)
Oscillator period (VCC=3.3V)
t
CLCL
t
CLCL
83.3
83.3
285.7
1
ns
High time
t
CHCX
20 t
CLCL-tCLCX
ns
Low time
t
CLCX
20 t
CLCL-tCHCX
ns
Rise time
t
CLCH
-20ns
Fall time
t
CHCL
-20
ns
Page 38

GMS90 Series
34 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
AC Characteristics for GMS90 series (16MHz version)
V
CC
=3.3V+0.3V,−0.6V; VSS=0V; TA=0°Cto70°C
(CLfor port 0. ALE and PSEN outputs = 50pF; CLfor all other outputs = 50pF)
External Program Memory Characteristics
†
Interfacing the GMS90 series to devices with float times up to 35 ns is permissible. This limited bus contention will not cause
any damage to port 0 Drivers.
Parameter Symbol
16 MHz Oscillator
Variable Oscillator
1/t
CLCL
=3.5to16MHz
Unit
Min. Max. Min. Max.
ALE pulse width
t
LHLL
85 - 2t
CLCL
-40 -
ns
Address setup to ALE
t
AVLL
23 - t
CLCL
-40 - ns
Address hold after ALE
t
LLAX
23 - t
CLCL
-40 -
ns
ALE low to valid instruction in
t
LLIV
-150 -4t
CLCL
-100 ns
ALE to PSEN
t
LLPL
38 - t
CLCL
-25 -
ns
PSEN pulse width
t
PLPH
153 - 3t
CLCL
-35 - ns
PSEN to valid instruction in
t
PLIV
-88 -3t
CLCL
-100
ns
Input instruction hold after PSEN
t
PXIX
0- 0 - ns
Input instruction float after PSEN
t
PXIZ
†
-43 -t
CLCL
-20
ns
Address valid after PSEN
t
PXAV
†
55 - t
CLCL
-8 - ns
Address to valid instruction in
t
AVIV
-198 -5t
CLCL
-115
ns
Address float to PSEN
t
AZPL
0- 0 - ns
Page 39

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 35
AC Characteristics for GMS90 series (16MHz)
External Data Memory Characteristics
Advance Information (16MHz)
External Clock Drive
Parameter Symbol
16 MHz Oscillator
Variable Oscillator
1/t
CLCL
=3.5to16MHz
Unit
Min. Max. Min. Max.
RD pulse width
t
RLRH
275 - 6t
CLCL
-100 -
ns
WR pulse width
t
WLWH
275 - 6t
CLCL
-100 - ns
Address hold after ALE
t
LLAX2
23 - t
CLCL
-40 -
ns
RD to valid data in
t
RLDV
-183 -5t
CLCL
-130 ns
Data hold after RD
t
RHDX
0- 0 -
ns
Data float after RD
t
RHDZ
-75 -2t
CLCL
-50 ns
ALE to valid data in
t
LLDV
-350 -8t
CLCL
-150
ns
Address to valid data in
t
AVDV
-398 -9t
CLCL
-165 ns
ALE to WR or RD
t
LLWL
138 238 3t
CLCL
−50 3t
CLCL
+50
ns
Address valid to WR or RD
t
AVWL
120 - 4t
CLCL
-130 - ns
WR or RD high to ALE high
t
WHLH
28 97 t
CLCL
−35 t
CLCL
+35
ns
Data valid to WR transition
t
QVWX
13 - t
CLCL
−50 - ns
Data setup before WR
t
QVWH
288 - 7t
CLCL
-150 - ns
Data hold after WR
t
WHQX
23 - t
CLCL
−40 -
ns
Address float after RD
t
RLAZ
-0 - 0 ns
Parameter Symbol
Variable Oscillator
(Freq. = 3.5 to 16MHz)
Unit
Min. Max.
Oscillator period
t
CLCL
62.5 285.7
ns
High time
t
CHCX
17 t
CLCL-tCLCX
ns
Low time
t
CLCX
17 t
CLCL-tCHCX
ns
Rise time
t
CLCH
-17ns
Fall time
t
CHCL
-17
ns
Page 40

GMS90 Series
36 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
AC Characteristics for GMS90 series (24MHz version)
V
CC
=5V+10%,−15%; VSS=0V; TA=0°Cto70°C
(CLfor port 0. ALE and PSEN outputs = 100pF; CLfor all other outputs = 80pF)
External Program Memory Characteristics
†
Interfacing the GMS90 series to devices with float times up to 35 ns is permissible. This limited bus contention will not cause
any damage to port 0 Drivers.
Parameter Symbol
24 MHz Oscillator
Variable Oscillator
1/t
CLCL
=3.5to24MHz
Unit
Min. Max. Min. Max.
ALE pulse width
t
LHLL
43 - 2t
CLCL
-40 -
ns
Address setup to ALE
t
AVLL
17 - t
CLCL
-25 - ns
Address hold after ALE
t
LLAX
17 - t
CLCL
-25 -
ns
ALE low to valid instruction in
t
LLIV
-80 -4t
CLCL
-87 ns
ALE to PSEN
t
LLPL
22 - t
CLCL
-20 -
ns
PSEN pulse width
t
PLPH
95 - 3t
CLCL
-30 - ns
PSEN to valid instruction in
t
PLIV
-60 -3t
CLCL
-65
ns
Input instruction hold after PSEN
t
PXIX
0- 0 - ns
Input instruction float after PSEN
t
PXIZ
†
-32 -t
CLCL
-10
ns
Address valid after PSEN
t
PXAV
†
37 - t
CLCL
-5 - ns
Address to valid instruction in
t
AVIV
-148 -5t
CLCL
-60
ns
Address float to PSEN
t
AZPL
0- 0 - ns
Page 41

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 37
AC Characteristics for GMS90 series (24MHz)
External Data Memory Characteristics
Advance Information (24MHz)
External Clock Drive
Parameter Symbol
24 MHz Oscillator
Variable Oscillator
1/t
CLCL
=3.5to24MHz
Unit
Min. Max. Min. Max.
RD pulse width
t
RLRH
180 - 6t
CLCL
-70 -
ns
WR pulse width
t
WLWH
180 - 6t
CLCL
-70 - ns
Address hold after ALE
t
LLAX2
15 - t
CLCL
-27 -
ns
RD to valid data in
t
RLDV
-118 -5t
CLCL
-90 ns
Data hold after RD
t
RHDX
0- 0 -
ns
Data float after RD
t
RHDZ
-63 -2t
CLCL
-20 ns
ALE to valid data in
t
LLDV
-200 -8t
CLCL
-133
ns
Address to valid data in
t
AVDV
-220 -9t
CLCL
-155 ns
ALE to WR or RD
t
LLWL
75 175 3t
CLCL
-50 3t
CLCL
+50
ns
Address valid to WR or RD
t
AVWL
67 - 4t
CLCL
-97 - ns
WR or RD high to ALE high
t
WHLH
17 67 t
CLCL
-25 t
CLCL
+25
ns
Data valid to WR transition
t
QVWX
5-t
CLCL
-37 - ns
Data setup before WR
t
QVWH
170 - 7t
CLCL
-122 - ns
Data hold after WR
t
WHQX
15 - t
CLCL
-27 -
ns
Address float after RD
t
RLAZ
-0 - 0 ns
Parameter Symbol
Variable Oscillator
(Freq. = 3.5 to 24MHz)
Unit
Min. Max.
Oscillator period
t
CLCL
41.7 285.7
ns
High time
t
CHCX
12 t
CLCL-tCLCX
ns
Low time
t
CLCX
12 t
CLCL-tCHCX
ns
Rise time
t
CLCH
-12ns
Fall time
t
CHCL
-12
ns
Page 42

GMS90 Series
38 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
AC Characteristics for GMS90 series (33MHz version)
V
CC
=5V+10%,−15%; VSS=0V; TA=0°Cto70°C
(CLfor port 0. ALE and PSEN outputs = 100pF; CLfor all other outputs = 80pF)
External Program Memory Characteristics
†
Interfacing the GMS90 series to devices with float times up to 35 ns is permissible. This limited bus contention will not cause
any damage to port 0 Drivers.
Parameter Symbol
33 MHz Oscillator
Variable Oscillator
1/t
CLCL
=3.5to33MHz
Unit
Min. Max. Min. Max.
ALE pulse width
t
LHLL
40 - 2t
CLCL
-20 -
ns
Address setup to ALE
t
AVLL
10 - t
CLCL
-20 - ns
Address hold after ALE
t
LLAX
10 - t
CLCL
-20 -
ns
ALE low to valid instruction in
t
LLIV
-56 -4t
CLCL
-65 ns
ALE to PSEN
t
LLPL
15 - t
CLCL
-15 -
ns
PSEN pulse width
t
PLPH
80 - 3t
CLCL
-20 - ns
PSEN to valid instruction in
t
PLIV
-35 -3t
CLCL
-55
ns
Input instruction hold after PSEN
t
PXIX
0- 0 - ns
Input instruction float after PSEN
t
PXIZ
†
-20 -t
CLCL
-10
ns
Address valid after PSEN
t
PXAV
†
25 - t
CLCL
-5 - ns
Address to valid instruction in
t
AVIV
-91 -5t
CLCL
-60
ns
Address float to PSEN
t
AZPL
0- 0 - ns
Page 43

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 39
AC Characteristics for GMS90 series (33MHz)
External Data Memory Characteristics
Advance Information (33MHz)
External Clock Drive
Parameter Symbol
33 MHz Oscillator
Variable Oscillator
1/t
CLCL
=3.5to33MHz
Unit
Min. Max. Min. Max.
RD pulse width
t
RLRH
132 - 6t
CLCL
-50 -
ns
WR pulse width
t
WLWH
132 - 6t
CLCL
-50 - ns
Address hold after ALE
t
LLAX2
10 - t
CLCL
-20 -
ns
RD to valid data in
t
RLDV
-81 -5t
CLCL
-70 ns
Data hold after RD
t
RHDX
0- 0 -
ns
Data float after RD
t
RHDZ
-46 -2t
CLCL
-15 ns
ALE to valid data in
t
LLDV
-153 -8t
CLCL
-90
ns
Address to valid data in
t
AVDV
-183 -9t
CLCL
-90 ns
ALE to WR or RD
t
LLWL
71 111 3t
CLCL
-20 3t
CLCL
+20
ns
Address valid to WR or RD
t
AVWL
66 - 4t
CLCL
-55 - ns
WR or RD high to ALE high
t
WHLH
10 40 t
CLCL
-20 t
CLCL
+20
ns
Data valid to WR transition
t
QVWX
5-t
CLCL
-25 - ns
Data setup before WR
t
QVWH
142 - 7t
CLCL
-70 - ns
Data hold after WR
t
WHQX
10 - t
CLCL
-20 -
ns
Address float after RD
t
RLAZ
-0 - 0 ns
Parameter Symbol
Variable Oscillator
(Freq. = 3.5 to 24MHz)
Unit
Min. Max.
Oscillator period
t
CLCL
30.3 285.7
ns
High time
t
CHCX
11.5 t
CLCL-tCLCX
ns
Low time
t
CLCX
11.5 t
CLCL-tCHCX
ns
Rise time
t
CLCH
-5ns
Fall time
t
CHCL
-5
ns
Page 44

GMS90 Series
40 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
AC Characteristics for GMS90 series (40MHz version)
V
CC
=5V+10%,− 15%; VSS=0V; TA=0°Cto70°C
(CLfor port 0. ALE and PSEN outputs = 100pF; CLfor all other outputs = 80pF)
External Program Memory Characteristics
†
Interfacing the GMS90 series to devices with float times up to 20 ns is permissible. This limited bus contention will not cause
any damage to port 0 Drivers.
Parameter Symbol
40 MHz Oscillator
Variable Oscillator
1/t
CLCL
=3.5to40MHz
Unit
Min. Max. Min. Max.
ALE pulse width
t
LHLL
35 - 2t
CLCL
−15 -
ns
Address setup to ALE
t
AVLL
10 - t
CLCL
−15 - ns
Address hold after ALE
t
LLAX
10 - t
CLCL
−15 -
ns
ALE low to valid instruction in
t
LLIV
-55 -4t
CLCL
−45 ns
ALE to PSEN
t
LLPL
10 - t
CLCL
−15 -
ns
PSEN pulse width
t
PLPH
60 - 3t
CLCL
−15 - ns
PSEN to valid instruction in
t
PLIV
-25 -3t
CLCL
−50
ns
Input instruction hold after PSEN
t
PXIX
0- 0 - ns
Input instruction float after PSEN
t
PXIZ
†
-15 -t
CLCL
−10
ns
Address valid after PSEN
t
PXAV
†
20 - t
CLCL
−5- ns
Address to valid instruction in
t
AVIV
-65 -5t
CLCL
−60
ns
Address float to PSEN
t
AZPL
5- 5 - ns
Page 45

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 41
AC Characteristics for GMS90 series (40MHz)
External Data Memory Characteristics
Advance Information (40MHz)
External Clock Drive
Parameter Symbol
at 40 MHz Clock
Variable Clock
1/t
CLCL
=3.5to40MHz
Unit
Min. Max. Min. Max.
RD pulse width
t
RLRH
120 - 6t
CLCL
-30 -
ns
WR pulse width
t
WLWH
120 - 6t
CLCL
-30 - ns
Address hold after ALE
t
LLAX2
10 - t
CLCL
-15 -
ns
RD to valid data in
t
RLDV
-75 -5t
CLCL
-50 ns
Data hold after RD
t
RHDX
0- 0 -
ns
Data float after RD
t
RHDZ
-38 -2t
CLCL
-12 ns
ALE to valid data in
t
LLDV
-150 -8t
CLCL
-50
ns
Address to valid data in
t
AVDV
-150 -9t
CLCL
-75 ns
ALE to WR or RD
t
LLWL
60 90 3t
CLCL
-15 3t
CLCL
+15
ns
Address valid to WR or RD
t
AVWL
70 - 4t
CLCL
-30 - ns
WR or RD high to ALE high
t
WHLH
10 40 t
CLCL
-15 t
CLCL
+15
ns
Data valid to WR transition
t
QVWX
5-t
CLCL
-20 - ns
Data setup before WR
t
QVWH
125 - 7t
CLCL
-50 - ns
Data hold after WR
t
WHQX
5-t
CLCL
-20 -
ns
Address float after RD
t
RLAZ
-0 - 0 ns
Parameter Symbol
Variable Oscillator
(Freq. = 3.5 to 40MHz)
Unit
Min. Max.
Oscillator period
t
CLCL
25 285.7
ns
High time
t
CHCX
10 t
CLCL-tCLCX
ns
Low time
t
CLCX
10 t
CLCL-tCHCX
ns
Rise time
t
CLCH
-10ns
Fall time
t
CHCL
-10
ns
Page 46

GMS90 Series
42 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
Figure 4. External Program Memory Read Cycle
t
LHLL
t
PXAV
t
PXIZ
t
PXIX
t
LLAX
t
LLIV
t
PLIV
t
PLPH
t
AZPL
t
LLPL
t
AVLL
A0-A7
INSTR.
IN
A0-A7
A8-A15
A8-A15
t
AVIV
ALE
PSEN
PORT 0
PORT 2
Page 47

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 43
Figure 5. External Data Memory Read Cycle
Figure 6. External Data Memory Write Cycle
t
LHLL
P2.0-P2.7 or A8-A15 from DPH
A8-A15 from PCH
ALE
PSEN
PORT 0
PORT 2
RD
t
LLWL
DATA IN A0-A7 from PCL INSTR. IN
A0-A7 from
t
LLAX2
t
AVWL
t
AVLL
t
AVDV
t
RLAZ
t
LLDV
t
RLRH
t
RLDV
t
RHDX
t
RHDZ
t
WHLH
RI or DPL
t
LHLL
P2.0-P2.7 or A8-A15 from DPH
A8-A15 from PCH
ALE
PSEN
PORT 0
PORT 2
WR
t
LLWL
DATA OUT
A0-A7 from PCL
INSTR. IN
A0-A7 from
t
LLAX2
t
AVWL
t
AVLL
t
WLWH
t
WHQX
t
WHLH
RI or DPL
t
QVWX
t
QVWH
Page 48

GMS90 Series
44 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
Figure 7. AC Testing: Input, Output Waveforms
Figure 8. Float Waveforms
Figure 9. External Clock Cycle
AC Inputs during testing are driven at VCC−0.5V for a logic ‘1’ and 0.45V for a logic ‘0’.
0.2VCC+ 0.9
0.2V
CC
− 0.1
Test Points
V
CC
−0.5V
0.45V
Timing measurements are made a V
IHmin
for a logic ‘1’ and V
ILmax
for a logic ‘0’.
V
LOAD
+ 0.1
V
LOAD
− 0.1
Timing Reference Points
0.2VCC− 0.1
V
OH
− 0.1
V
OL
+ 0.1
V
LOAD
For timing purposes a port pin is no longer floating when a 100mV change from load voltage
IOL/IOH≥ 20mA.
occurs and begins to float when a 100mV change from the loaded VOH/VOLlevel occurs.
t
CHCL
t
CLCH
t
CHCX
t
CLCL
t
CLCX
0.2 VCC−0.1
0.7 V
CC
VCC−0.5V
0.45V
Page 49

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 45
OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT
Figure 10. Recommended Oscillator Circuits
Oscillation circuit is designed to be used either with a ceramic resonator or crystal oscillator. Since each crystal
and ceramic resonator have their own characteristics, the user should consult the crystal manufacturer for appropriate values of external components.
XTAL2
P-LCC-44/Pin 20
P-DIP-40/Pin 18
M-QFP-44/Pin 14
XTAL1
P-LCC-44/Pin 21
P-DIP-40/Pin 19
M-QFP-44/Pin 15
CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR MODE DRIVING FROM EXTERNAL SOURCE
XTAL2
P-LCC-44/Pin 20
P-DIP-40/Pin 18
M-QFP-44/Pin 14
XTAL1
P-LCC-44/Pin 21
P-DIP-40/Pin 19
M-QFP-44/Pin 15
External Oscillator
Signal
N.C.
C2
C1
C1, C2 = 30pF ±10pF for Crystals
For Ceramic Resonators, contact resonator manufacturer.
Page 50

GMS90 Series
46 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
OTP ROM Verification Characteristics
ROM Verification Mode 1
Figure 11. OTP ROM Verification Mode 1
Parameter Symbol
Limit Values
Unit
Min. Max.
Address to valid data
t
AVQV
-48t
CLCL
ENABLE to valid data
t
CLCL
-48t
CLCL
ns
Data float after ENABLE
t
EHQZ
048t
CLCL
Oscillator frequency
1/t
CLCL
46MHz
Address
Data Out
P1.0-P1.7
PORT 0
Address:
P2.7
P2.0-P2.4
ENABLE
t
EHQZ
t
ELQV
t
AVQV
P2.0-P2.5 = A8-A13
Data:
P1.0-P1.7 = A0-A7
P0.0-P0.7 = D0-D7
Input:
ALE = V
IH
P2.6-P2.7, PSEN =V
SS
EA, RESET = V
IH2
P3.4 = A14
Page 51

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 47
EPROM CHARACTERISTICS
The GMS97C5X, 97L5X are programmed by using a modified Quick-Pulse ProgrammingTMalgorithm. It differs from older methods in the value used for V
PP
(programming supply voltage) and in the width and number
of the ALE/PROG
pulses. The GMS97C5X, 97L5X contains two signature bytes that can be read and used by
an EPROM programming system to identify the device. The signature bytes identify the device as an manufactured by HME. Table 11 showsthe logic levels for reading the signature byte, and for programmingthe program
memory, the encryption table, and the security bits. The circuit configuration and waveforms for quick-pulse
programming are shown in Figure 12 and Figure 13. Figure 14 show the circuit configuration for normal program memory verification.
Reading the Signature Bytes :
The GMS97X51/52 signature bytes in locations 030
H
and 031H, the GMS97X54/56/58 signature bytes in loca-
tions 05E
H
and 07CH. To read these bytes follow the procedure for EPROM verify, except that P3.6 and P3.7
need to be pulled to a logic low.
The values are:
Quick-pulse programming
The set u p for microcont rol ler quick-pulse programming is shown in Figure 13. Note that the GMS97C5X,
97L5X is running with a 4 to 6MHz oscillator. The reason the oscillator needs to be running is that the device
is executing internal address and program data transfers.
The address of the EPROM location to be programmed is applied to ports 1 and 2, as shown in Figure 12. The
code byte to be programmed into that location is applied to port 0, RST, PSEN
andpinsofport2and3inTable
11 are held at the "Program Code Data" levels indicated in Table 11. The ALE/PROG
is pulsed low 25 times(10
times for 97X54/56/58) as shown Figure 13.
To program the encryption table, repeat the 25 pulses (10 pulses for 97X54/56/58) programming sequence for
addresses 0 through 1F
H
(3FHfor 97X54/56/58), using the "Program Encryption Table" levels. Do not forget
that after the encryption table is programmed, verification cycles will produce only encrypted data.
To program the security bits, repeat the 25 pulses (10 pulses for 97X54/56/58) programming sequence using the
"Pgm Security Bit" levels after one security bit is programmed, further programming of the code memory and
Device Location Contents Remarks
GMS97X51 30
H
31
H
E0
H
73
H
Manufacturer ID
Device ID
GMS97X52 30
H
31
H
E0
H
71
H
Manufacturer ID
Device ID
GMS97X54 5E
H
7C
H
E0
H
54
H
Manufacturer ID
Device ID
GMS97X56 5E
H
7C
H
E0
H
56
H
Manufacturer ID
Device ID
GMS97X58 5E
H
7C
H
E0
H
58
H
Manufacturer ID
Device ID
Page 52

GMS90 Series
48 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
encryption table is disabled. However, the other security bit can still be programmed. Note that the EA/VPPpin
must not be allowed to go above the maximum specified V
PP
level for any amount of time. Even a narrow glitch
above that voltage can cause permanent damage to the device. The V
PP
source should be well regulatedand free
glitches and overshoot.
Figure 12. Programming Configuration
Program Verification
If security bit 2 has not been programmed, the on-chip program memory can be read out for program verification. The address of the program memory location to be read is applied to ports 1 and 2 as shown in Figure 15.
The other pins are held at the "Verify Code Data" levels indicated in Table 11. The contents of the address location will be emitted on port 0 for this operation. If the encryption table has been programmed, the data presented at port 0 will be the exclusive NOR of the program byte with one of the encryption bytes. The user will
have to know the encryption table contents in order to correctly decode the verification data. The encryption
table itself cannot be read out.
P1
RST
P3.6
P3.7
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
SS
V
CC
P0
EA
/V
PP
ALE/PROG
PSEN
P2.7
P2.6
P2.0
-P2.5
A0-A7
1
1
1
4~6MHz
1
1
0
GMS97X51/52:
+12.75V
GMS97X54/56/58:
100µs × 25 pulses to GND
100µs × 10 pulses to GND
+NOTE
NOTE:
PROGRAM DATA
A8-A13
+5V
P3.4
A14
Page 53

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 49
Program Memory Lock Bits
The two-level Program Lock system consists of 2
Lock bits and a 32-byte (64-byte for GMS97X54/
56/58) Encryption Array which are used to protect
the program memory against software piracy.
Encryption Array:
Within the EPROM array are 32 bytes (64 bytes
for G MS 97X54/56/58) of Encryption Array that
are initi ally unprogrammed (all 1s). Every time
that a byte is addressed during a verify, address
lines are used to select a byte of the Encryption array. This byte is then exclusive-NORed (XNOR) with the code
byte, creating an Encrypted Verify byte.
The algorithm, with the array in the unprogrammed state (all 1s), will return the code in its original, unmodified
form, It is recommended that whenever the Encryption Array is used, at least one of the L ock Bits be programmed as well.
Program / Verify algorithms
Any algorithm in agreement with the conditions listed in Table 11, and which satisfies the timing specifications
is suitable.
Notes:
1. “0” = Valid low for that pin, "1" = valid high for that pin.
2. VPP=12.75V± 0.25V
3. VCC=5V± 10% during programming and verification.
4. ALE/PROG receives 25 (10 for GMS97X54/56/58) programming pulses while VPPis held at 12.75V.
Each programming pulse is low for 100us (± 10us) and high for a minimum of 10µs.
Table 11. EPROM programming modes
MODE
RST PSEN
ALE/
PROG
EA/
V
PP
P2.7 P2.6 P3.7 P3.6
ReadSignature 10110000
Program Code Data
100VPP1011
Verify Code Data 10110011
Program encryption table
100VPP1010
Program security bit 1
100VPP1111
Program security bit 2
100VPP1100
Lock Bit Protection Modes
U: unprogrammed, P: programmed
Mode LB1 LB2 Protection Type
1 U U No program lock features
2 P U Further programming of the
EPROM is disabled
3 P P Sameasmode2,alsoverifyis
disabled
Page 54

GMS90 Series
50 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
Figure 13. PROG Waveform
Figure 14. Program Verification
100µs ±10
Min. 10µs
100µs ±10
In the GMS97X51/52
ALE/PROG
In the GMS97X54/56/58
ALE/PROG
25 PULSES
10 PULSES
Enlarged View
P1
RST
P3.6
P3.7
XTAL2
XTAL1
V
SS
V
CC
P0
EA
/V
PP
ALE/PROG
PSEN
P2.7
P2.6
P2.0
-P2.5
A0-A7
1
1
1
4~6MHz
1
0
0
1
1
PROGRAM DATA
A8-A13
+5V
P3.4
A14
10kΩ
Page 55

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 51
EPROM Programming and Verification Characteristics
T
A
=21°Cto27°C, VCC=5V+10%,− 15%; VSS=0V;
Figure 15. EPROM Programming and Verification
Parameter Symbol
Limit Values
Unit
Min. Max.
Programming supply voltage
V
PP
12.5 13.0 V
Programming supply current
I
PP
-50mA
Oscillator frequency
1/t
CLCL
46MHz
Address setup to PROG low
t
AVGL
48t
CLCL
--
Address hold after PROG
t
GHAX
48t
CLCL
--
Data setup to PROG
t
DVGL
48t
CLCL
--
Data hold after PROG
t
GHDX
48t
CLCL
--
P2.7 (ENABLE)hightoV
PP
t
EHSH
48t
CLCL
--
VPPsetup to PROG t
SHGL
10 - µs
VPPhold after PROG t
GHSL
10 - µs
PROG width
t
GLGL
90 110 µs
Address to data valid
t
AVQV
-48t
CLCL
-
ENABLE low to data valid
t
ELQV
-48t
CLCL
-
Data float after ENABLE
t
EHQZ
048t
CLCL
-
PROG high to PROG low
t
GHGL
10 - µs
ADDRESS
ADDRESS
P1.0-P1.7
P2.0-P2.5
P3.4
DATA IN
DATA OUT
PORT 0
ALE/PROG
EA/V
PP
P2.7
t
GHSL
t
GHGL
t
AVGL
t
GHAX
t
GHDX
t
EHSH
t
SHGL
t
DVGL
25 or 10
PULSES
t
GLGL
t
AVQV
t
ELQV
t
EHQZ
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
V
PP
TTL HIGH
PROGRAMMING VERIFICATION
(ENABLE)
TTL HIGH
TTL HIGH
Page 56

GMS90 Series
52 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
Plastic Package P-LCC-44
(Plastic Leaded Chip-Carrier)
0.180
0.165
UNIT: INCH
44PLCC
0.012
0.0075
0.120
0.090
0.032
0.026
0.630
0.590
min. 0.020
0.656
0.650
0.695
0.685
0.656
0.650
0.695
0.685
0.050 BSC
0.021
0.013
Page 57

GMS90 Series
Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a 53
Plastic Package P-DIP-40
(Plastic Dual in-Line Package)
UNIT: INCH
2.075
2.045
0.200 max.
0.022
0.015
0.065
0.045
0.100 BSC
0.550
0.530
0.600 BSC
0-15°
0
.
0
1
2
0
.
0
0
8
40DIP
0.140
0.120
min. 0.015
Page 58

GMS90 Series
54 Oct. 2000 Ver 3.1a
Plastic Package P-MPQF-44
(Plastic Metric Quad Flat Package)
2.35 max.
SEE DETAIL "A"
1.03
0.73
0-7°
0.25
0.10
1.60
REF
DETAIL "A"
UNIT: MM
0.45
0.30
0.80 BSC
2.10
1.95
44MQFP
0
.
1
3
0
.
2
3
10.10
9.90
13.45
12.95
10.10
9.90
13.45
12.95
Page 59

MASK ORDER & VERIFICATION SHEET
GMS90X5X-GB
1. Customer Information
Company Name
2. Device Information
3. Marking Specification
4. Delivery Schedule
Customer Sample
Date
Risk Order
YYYY MM DD
Quantity
Hynix Confirmation
Application
Order Date
YYYY MM DD
Tel:
Fax:
Name &
Signature:
Package
HYNIX
YYWW KOREA
5. ROM Code Verification
Ve rific a tio n D ate:
YYYY MM DD
Approval Date:
YYYY MM DD
Please confirm our verification data.
I agree w ith your verification data and confirm you to
make mask set.
Check Sum:
Tel:
Fax:
Name &
Signature:
Tel:
Fax:
Name &
Signature:
Mask Data
HitelChollianInternet
File Name: ( .HEX)
(Please check mark into )
Hynix semiconductor
pcs
Check Sum:
Customer should write inside thick line box.
This box is written after “5.Verification”.
ROM size
4K
Vol./Freq.
GMS90
-G B
SIEMENS ’92
5
Customer’s part number
Without
HYNIX
YYWW KO REA
90
-G B
SIEMENS ’92
5
40PD IP or 44PLCC 44M QFP
Г
Д
C: 5V
L: 3V
ROM size
1: 4K
2: 8K
4: 16K
6: 24K
8: 32K
YYYY MM DD
pcs
8K
16K
24K
32K
44MQFP
44PLCC
40PDIP
12MHz
24MHz
40MHz
12MHz
16MHz
5V
3V
Normal Super
ROM: 16,24,32K
ROM: 4K,8K
ROM Protection
 Loading...
Loading...