Datasheet GMS81524BTQ, GMS81524BTLQ, GMS81524BTK, GMS81524BQ, GMS81524BLQ Datasheet (HEI)
...Page 1
HYUNDAI MICRO ELECTRONICS
8-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCONTROLLERS
GMS81508B
GMS81516B
GMS81524B
User’s Manual (Ver. 1.04)
+<81'$,
Semiconductor Group of Hyundai Electronics Industrial Co., Ltd.
MicroElectronics
Page 2
Version 1.04
Published by
MCU Application Team
1999 HYUNDAI Micro Electronics All right reserved.
Additional information of this manual may be served by HYUNDAI Micro Electronics offices in Korea or Distributors and
Representatives listed at address directory.
HYUNDAI Micro Electronics reserves the right to make changes to any information here in at any time without notice.
The information, diagrams and other data in this manual are co rrect and reliable; ho wever, HYUNDAI Micro Electronics is
in no way responsible for any violations of patents or other rights of the third party generated by the use of this manual.
Page 3

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
Table of Contents
1. OVERVIEW............................................1
Description .........................................................1
Features ............................... ..............................1
Development Tools ............................................2
Ordering Information ..........................................2
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM.................................3
3. PIN ASSIGNMENT ................................4
4. PACKAGE DIAGRAM............................6
5. PIN FUNCTION......................................8
6. PORT STRUCTURES..........................10
7. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS....12
Absolute Maximum Ratings .............................12
Recommended Operating Conditions ..............12
A/D Converter Characteristics .........................12
DC Electrical Characteristics ............ ...... ....... ..1 3
AC Characteristics ...........................................14
Serial Interface Timing Characteristics ............15
Typical Characteristic Curves ..........................16
8. MEMORY ORGANIZATION.................18
Registers ....................... ...................................18
Program Memory ....................... ....... ...............21
Data Memory ...................................................24
Addressing Mode .............................................27
9. I/O PORTS...........................................31
10. BASIC INTERVAL TIMER..................34
11. TIMER/EVENT COUNTER................36
8-bit Timer / Counter Mode ..............................38
16-bit Timer / Counter Mode ............................42
8-bit Capture Mode ..........................................43
16-bit Capture Mode .................. ....... ...... ....... ..4 4
12. ANALOG DIGITAL CONVERTER......46
13. SERIAL COMMUNICATION..............48
Transmission/Recei vi ng Timi ng ........... ........... 50
The Serial I/O operation by SRDY pin ............ 50
The method of Serial I/O ................................. 51
The Method to Test Correct Transmission ...... 51
14. PWM OUTPUT ..................................52
15. BUZZER FUNCTION.........................55
16. INTERRUPTS....................................57
Interrupt Sequence .......................................... 59
BRK Interrupt .................................................. 60
Multi Interrupt .................................................. 61
External Interrupt ............................................. 61
17. WATCHDOG TIMER .........................64
18. POWER DOWN OPERATION...........66
STOP Mode .................................................... 66
Minimizing Current Consumption .................... 67
19. OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT.....................69
20. RESET...............................................70
External Reset Input ........................................ 70
Watchdog Timer Reset ................................... 70
21. POWER FAIL PROCESSOR.............71
22. OTP PROGRAMMING.......................73
How to Program .............................................. 73
Pin Function .................................................... 73
Programming Specification ............................. 76
A. CONTROL REGISTER LIST..................i
B. SOFTWARE EXAMPLE....................... iii
7-segment LED display ....................................iii
C. INSTRUCTION....................................viii
Terminology List ..............................................viii
Instruction Map ..................................................ix
Instruction Set ....................................................x
D. MASK ORDER SHEET......................xvi
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 4
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
GMS81508B/16B/24B
CMOS SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
WITH A/D CONVERTER
1. OVERVIEW
1.1 Description
The GMS81508B/16B/24B are advanced CMOS 8-bi t microcon trollers with 8K/16K/24K byt es of ROM. The device is on e
of GMS800 family. This device using the GMS800 family CPU includes several peripheral functions such as Timer, A/D
converter, Programmable buzzer driver, Serial I/O communication, Pulse Width Mod ulation function, etc. The RAM, ROM,
and I/O are placed on the same memory map in addition to simple instruction set.
The GMS815xxB is functi onall y 10 0% com pati ble wit h earie r GMS81508/16 or GMS81508A/16A, h owever bet t er characteristics have such as strong EMS, wide operating voltage, temperature, frequency and fast programming time for the OTP.
Device name ROM Size RAM Size OTP Package
GMS81508B 8K bytes 448 bytes GMS81516BT
GMS81516B 16K bytes 448 bytes GMS81516BT
GMS81524B 24K bytes 448 bytes GMS81524BT
64SDIP, 64MQFP,
64LQFP
1.2 Features
• 8K/16K/24K Bytes On-chip Program Memory
• 448 Bytes of On-chip Data RAM
(Included stack memory)
• Minimum Instruction Execution Time
0.5
s at 8MHz
µµµµ
• One 8-bit Basic Interval Timer
• Four 8-bit Timer/Event counter
or Two 16-bit Timer/Event counter
• One 6-bit Watchdog timer
• Eight channel 8-bit A/D converter
• Two channel 8-bit PWM
• One 8-bit Serial Communication Interface
• Four External Interrupt input ports
• Buzzer Driving port
- 500Hz ~ 250kHz@8MHz
• 52 I/O Ports, 4 Input Ports
• Twelve Interrupt sources
- Basic Interval Timer: 1
- External input: 4
- Timer/Event counter: 4
- ADC: 1
- Serial Interface: 1
- WDT: 1
• Built in Noise Immunity Circuit
- Noise filter
- Power fail processor
• Power Down Mode
- STOP mode
• 2.2V to 5.5V Wide Operating Range
• 1~10MHz Wide Operating Frequency
• 64SDIP, 64MQFP, 64LQFP package types
• Available 16K, 24K bytes OTP version
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 1
Page 5
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
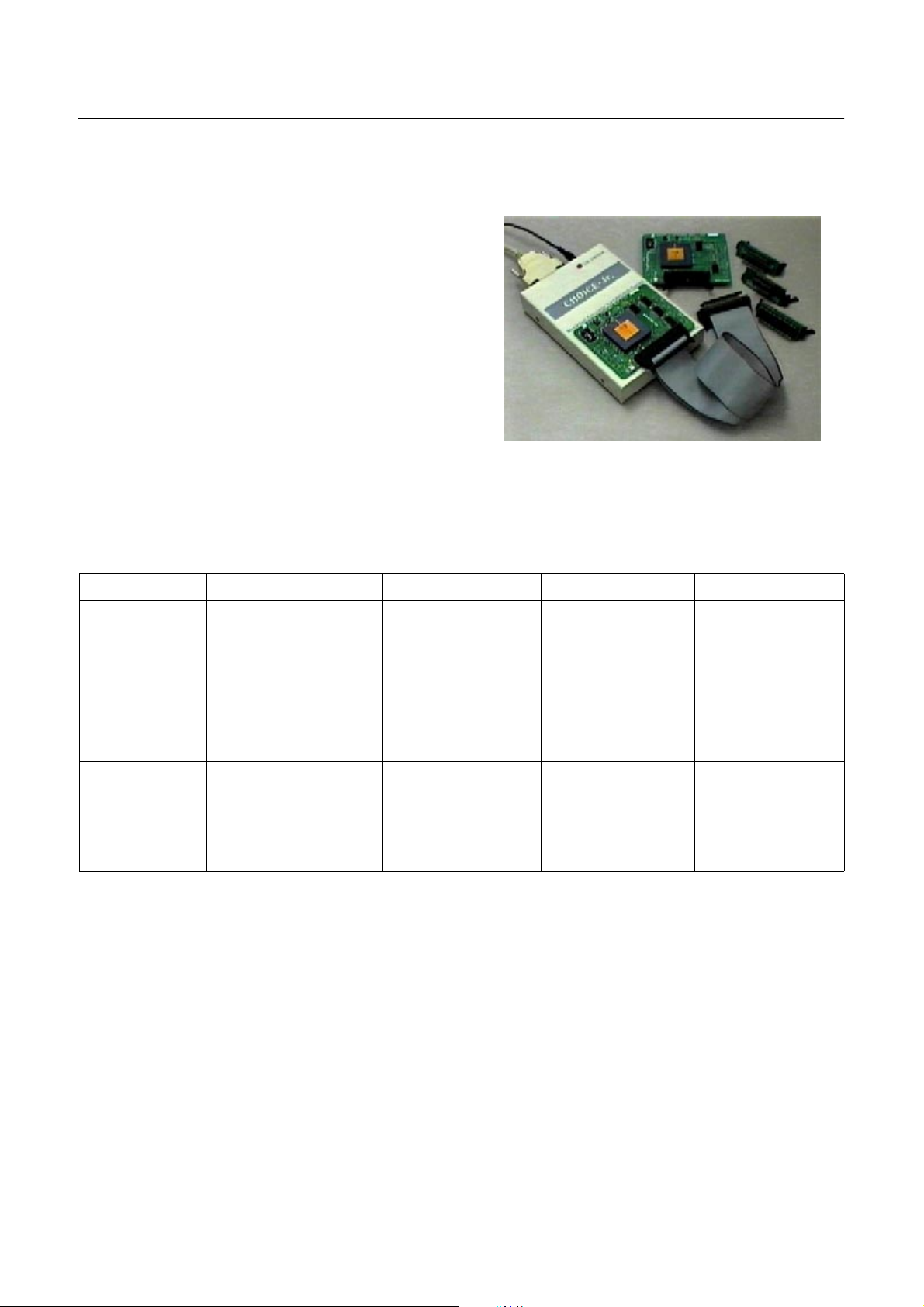
1.3 Development Tools
The GMS815xxB are supported by a full-featured macro
assembler, an in-circuit emulator CHOICE-Jr.
TM
and OTP
programmers. There are third different type programmers
such as emulator add-on board type, single type, gang
type. For mode detail, Refer to “22. OTP PROGRAMMING” on page 73. Macro assembler operates under the
MS-Windows 95/98
TM
.
Please contact sales part of Hyundai MicroElectronics.
1.4 Ordering Information
Device name ROM Size RAM size Package
Mask version
OTP version
GMS81508B K
GMS81508B Q
GMS81508B LQ
GMS81516B K
GMS81516B Q
GMS81516B LQ
GMS81524B K
GMS81524B Q
GMS81524B LQ
GMS81516BT K
GMS81516BT Q
GMS81516BT LQ
GMS81524BT K
GMS81524BT Q
GMS81524BT LQ
8K bytes
8K bytes
8K bytes
16K bytes
16K bytes
16K bytes
24K bytes
24K bytes
24K bytes
16K bytes OTP
16K bytes OTP
16K bytes OTP
24K bytes OTP
24K bytes OTP
24K bytes OTP
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
448 bytes
64SDIP
64MQFP
64LQFP
64SDIP
64MQFP
64LQFP
64SDIP
64MQFP
64LQFP
64SDIP
64MQFP
64LQFP
64SDIP
64MQFP
64LQFP
2 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 6
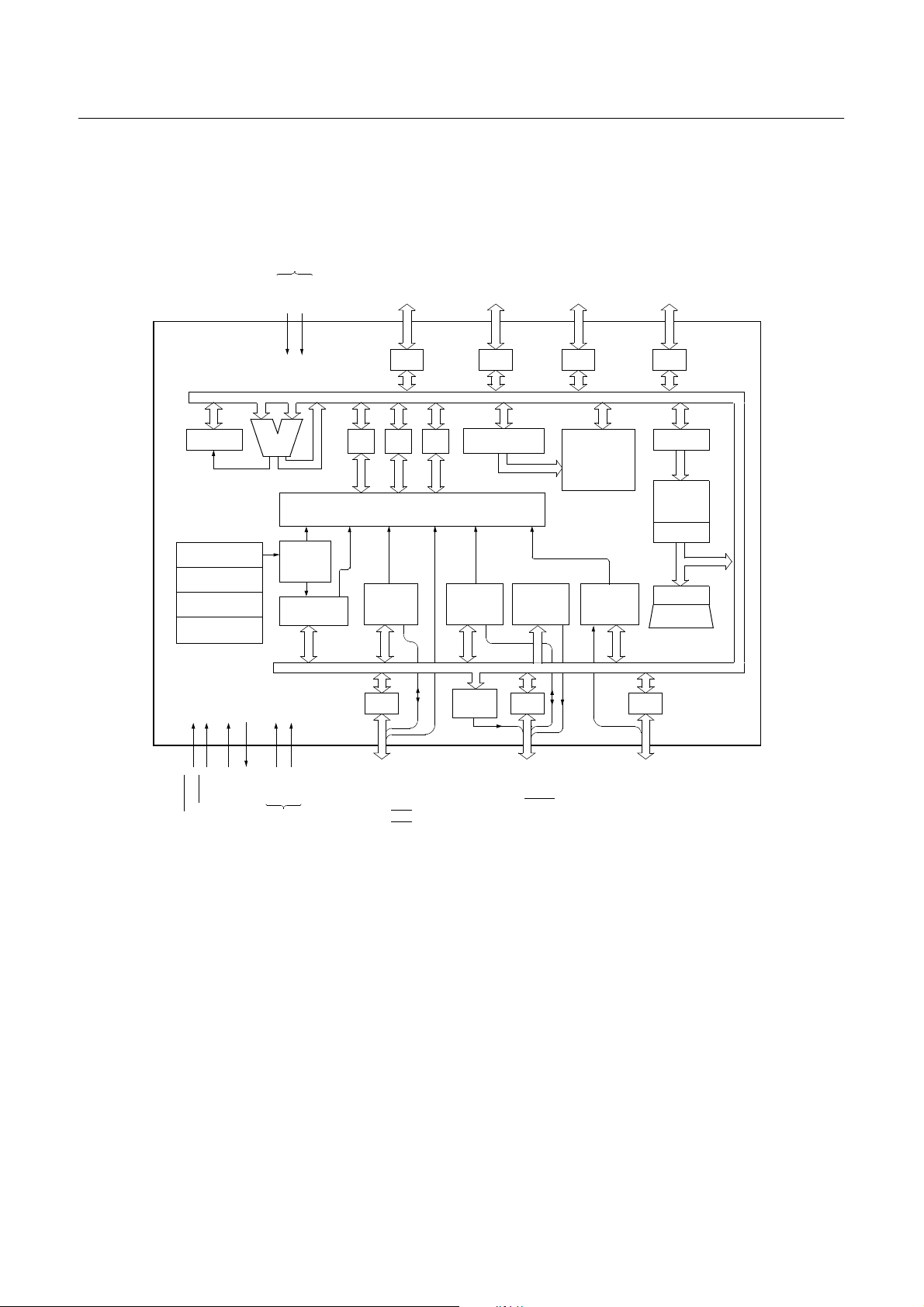
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM
ADC Power
Supply
PSW
System controller
System
Clock Controller
Timing generator
Clock
Generator
AVDDAV
ALU
8-bit Basic
Interval
Watchdog
Timer
Timer
SS
R00~R07
R0
A
X Y
Interrupt Controller
8-bit
Timer/
Counter
R4 R5
R10~R17
Stack Pointer
8-bit serial
Interface
Buzzer
Driver
R1
8-bit PWM
R20~R27
R2
Data Memor y
(448 bytes)
8-bit
ADC
R30~R37
R3
PC
Program
Memory
Data Table
PC
R6
TEST
RESET
IN
X
X
OUT
DD
V
Power
Supply
SS
V
R40 / INT0
R41 / INT1
R42 / INT2
R43 / INT3
R44 / EC0
R45 / EC2
R46 / T1O
R47 / T3O
R50 / SIN
R51 / SOUT
R52 / SCLK
R53 / SRDY
R54 / WDTO
R55 / BUZ
R56 / PWM0
R57 / PWM1
R60 / AN0
R61 / AN1
R62 / AN2
R63 / AN3
R64 / AN4
R65 / AN5
R66 / AN6
R67 / AN7
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 3
Page 7
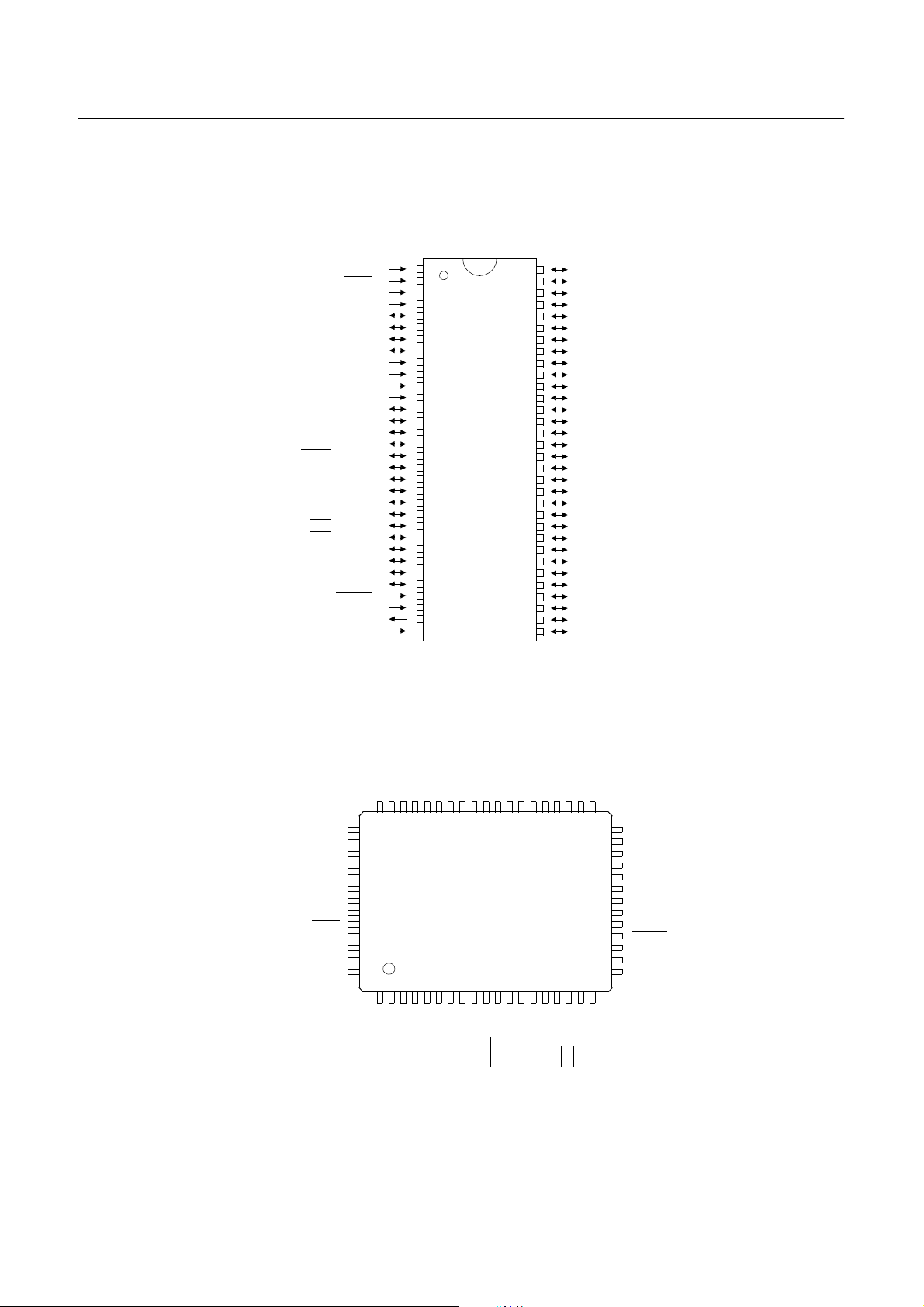
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
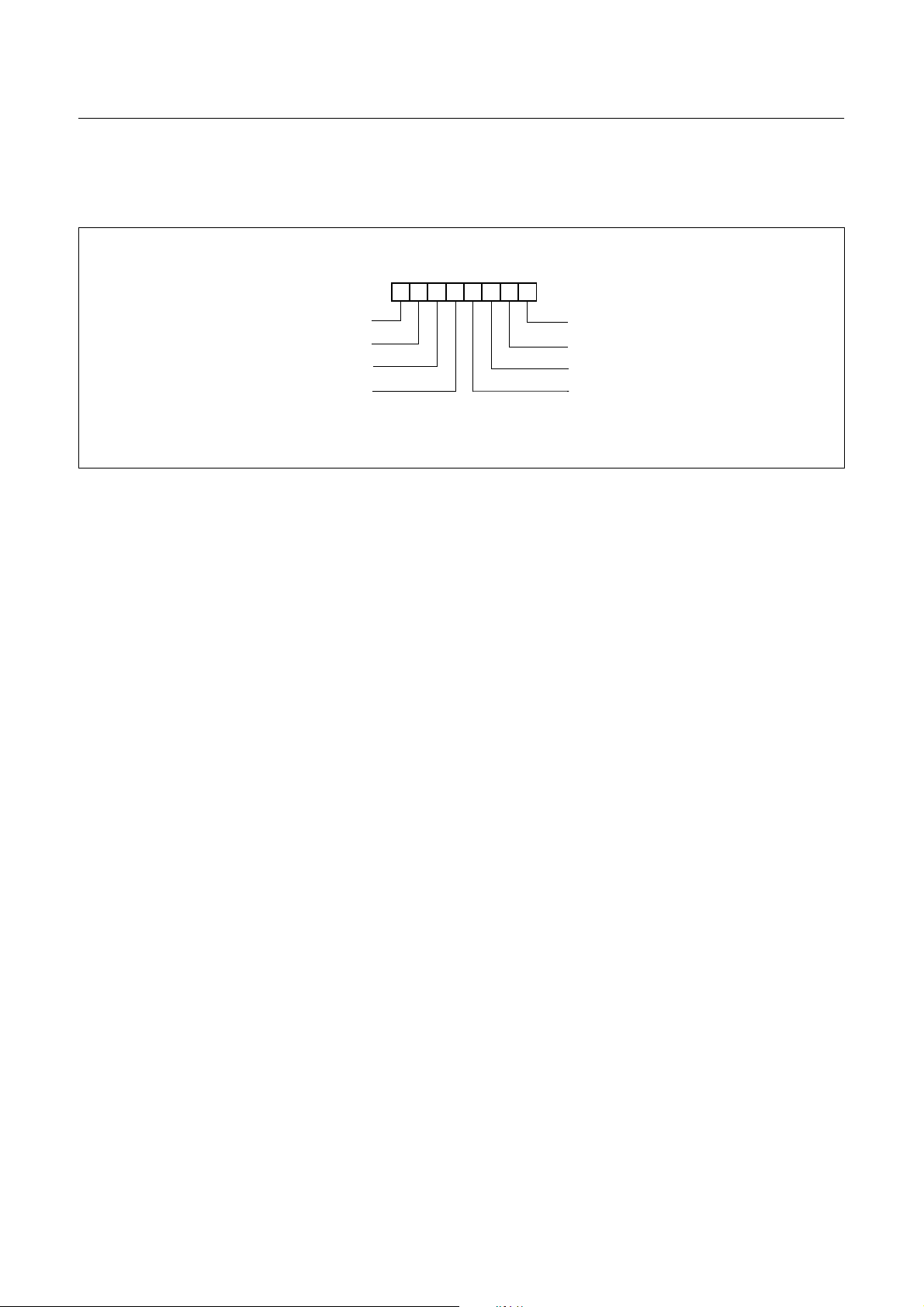
3. PIN ASSIGNMENT
64SDIP
(Top View)
AN7
AN6
AN5
AN4
AN3
AN2
AN1
AN0
PWM1
PWM0
BUZ
WDTO
SRDY
SCLK
SOUT
SIN
T3O
T1O
EC2
EC0
INT3
INT2
INT1
INT0
V
DD
TEST
AV
SS
AV
DD
R67
R66
R65
R64
R63
R62
R61
R60
R57
R56
R55
R54
R53
R52
R51
R50
R47
R46
R45
R44
R43
R42
R41
R40
RESET
XIN
XOUT
V
SS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
GMS81508B/16B/24B
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
R30
R31
R32
R33
R34
R35
R36
R37
R00
R01
R02
R03
R04
R05
R06
R07
R10
R11
R12
R13
R14
R15
R16
R17
R20
R21
R22
R23
R24
R25
R26
R27
64MQFP
(Top View)
AN7
AN6
R36
R35
R34
R33
R32
R31
R30
V
DD
TEST
AV
SS
AV
DD
R67
R66
R37
R01
R02
R03
R00
515049
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
484746
123456789
R65
R63
R62
R61
R64
AN5
AN3
AN2
AN1
AN4
R04
R05
R06
R07
R10
R11
R12
R13
45
4443424140
GMS81508B/16B/24B
R60
R57
R56
R55
AN0
PWM1
PWM0
BUZ
39
101112131415161718
R54
R53
R52
R51
SCLK
SOUT
SRDY
WDTO
R14
R15
R16
R17
3837363534
R50
R47
R46
R45
SIN
T3O
T1O
EC2
R20
R44
EC0
R21
33
R22
32
R23
31
R24
30
R25
29
R26
28
R27
27
V
26
SS
XOUT
25
XIN
24
23
RESET
R40
22
21
20
19
R43
INT3
R41
R42
INT0
INT1
INT2
4 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 8
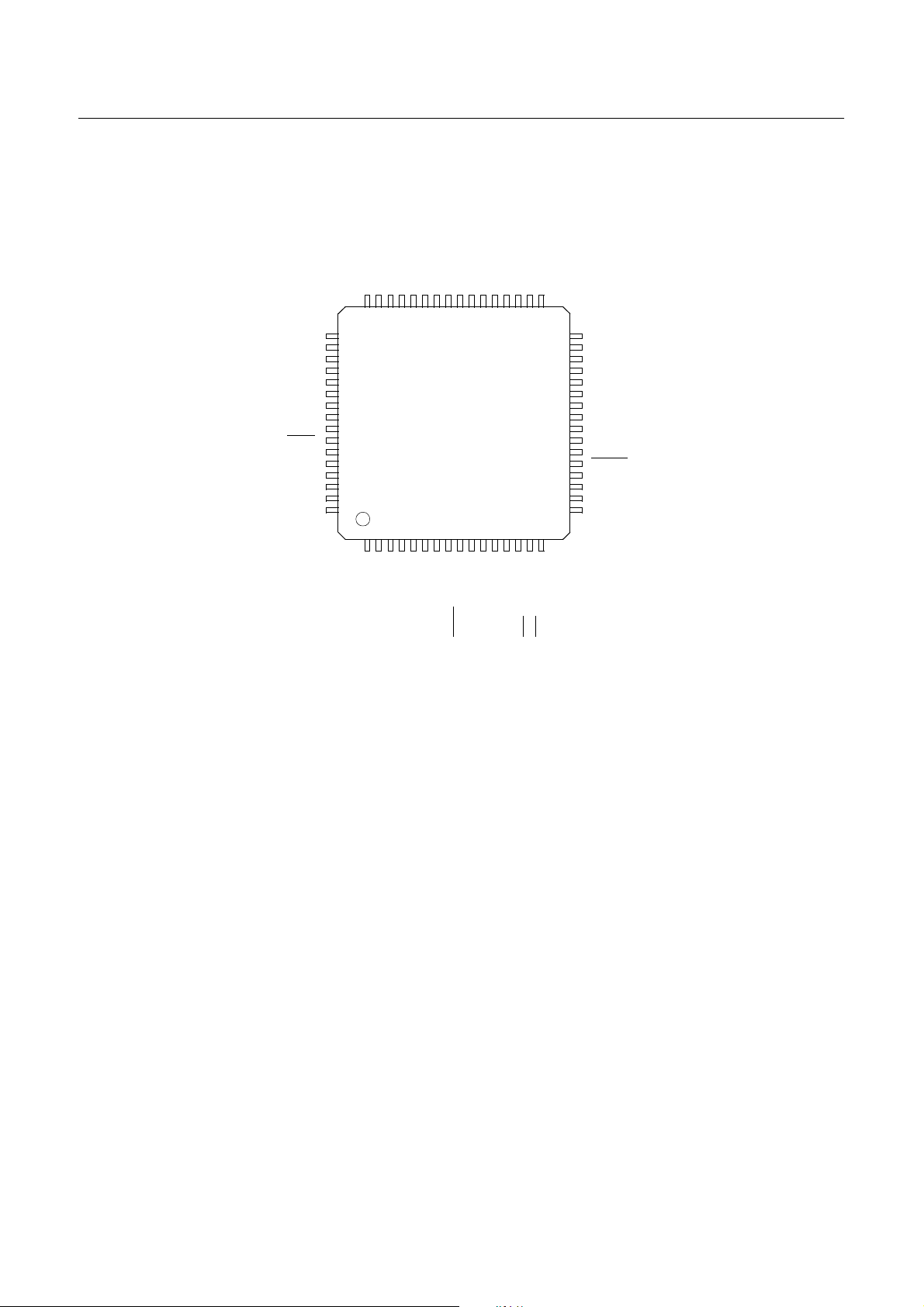
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
64LQFP
(Top View)
R00
R01
R02
R03
R04
R05
R06
R07
R10
R11
R12
R13
R14
R15
R16
R17
AN7
AN6
AN5
AN4
R37
R36
R35
R34
R33
R32
R31
R30
V
DD
TEST
AV
SS
AV
DD
R67
R66
R65
R64
484746454443424140393837363534
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
GMS81508B/16B/24B
123456789
R63
R62
R61
R60
R57
R56
R55
R54
AN3
AN2
AN1
AN0
PWM1
PWM0
BUZ
WDTO
10111213141516
R53
R52
SRDY
SCLK
R51
SOUT
33
32
R20
31
R21
30
R22
29
R23
28
R24
27
R25
26
R26
25
R27
24
V
SS
23
XOUT
XIN
22
21
RESET
20
R40
19
R41
18
R42
17
R43
R50
R47
R46
R45
R44
SIN
T3O
T1O
EC2
EC0
INT0
INT1
INT2
INT3
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 5
Page 9
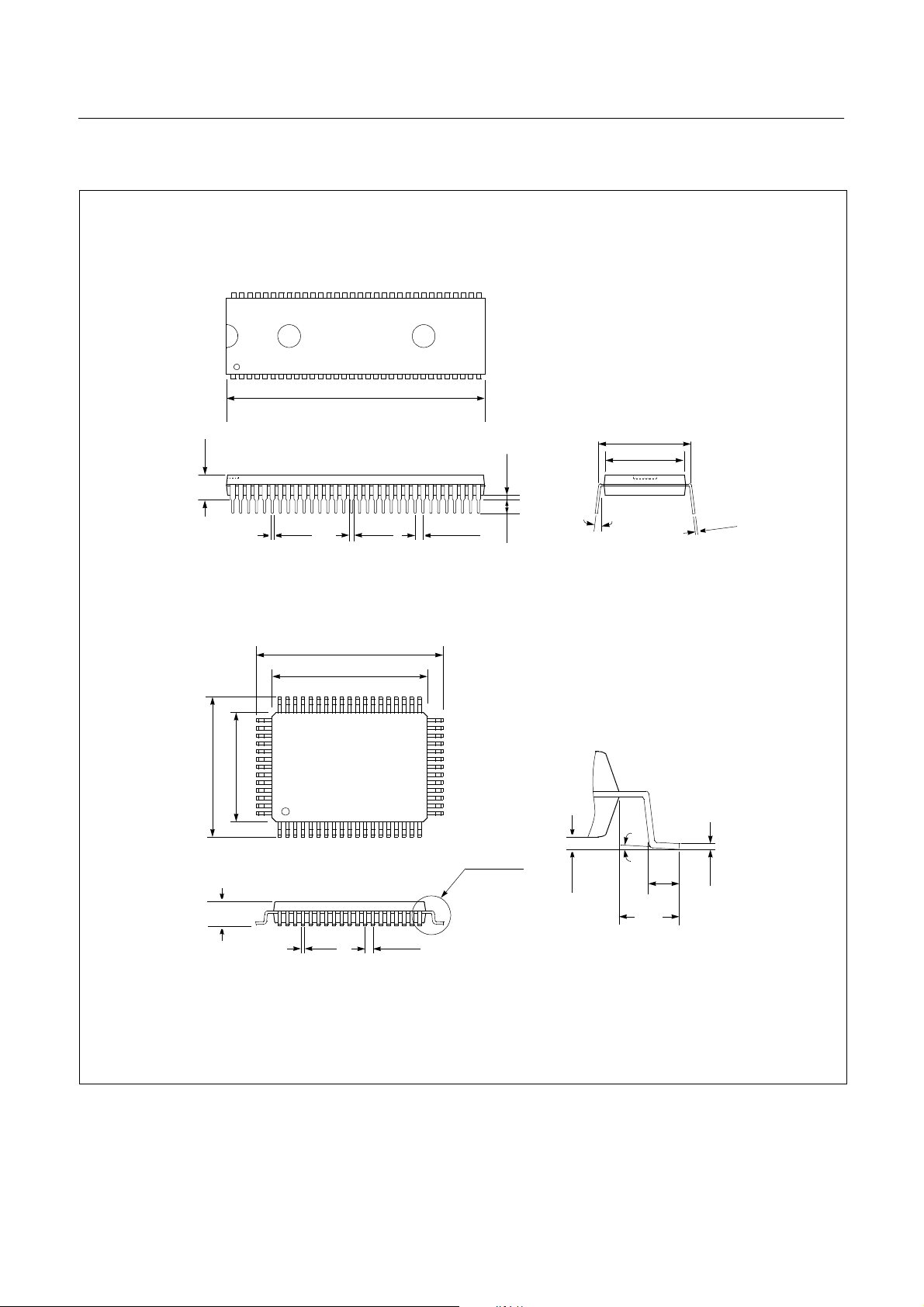
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
4. PACKAGE DIAGRAM
64SDIP
UNIT: INCH
2.280
2.260
0.750 Typ.
0.680
0-15
0.660
2
1
.0
0
8
0
.0
°
0
0.205 max.
min. 0.015
0.022
0.016
0.050
0.030
0.070 Typ.
0.140
0.120
64MQFP
18.15
17.65
3.18 max.
24.15
23.65
20.10
19.90
14.10
13.90
SEE DETAIL “A”
0.50
0.35
1.00 Typ.
0.36
0.10
UNIT: MM
0-7
°
1.95
REF
DETAIL “A”
1.03
0.73
0.23
0.13
6 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 10
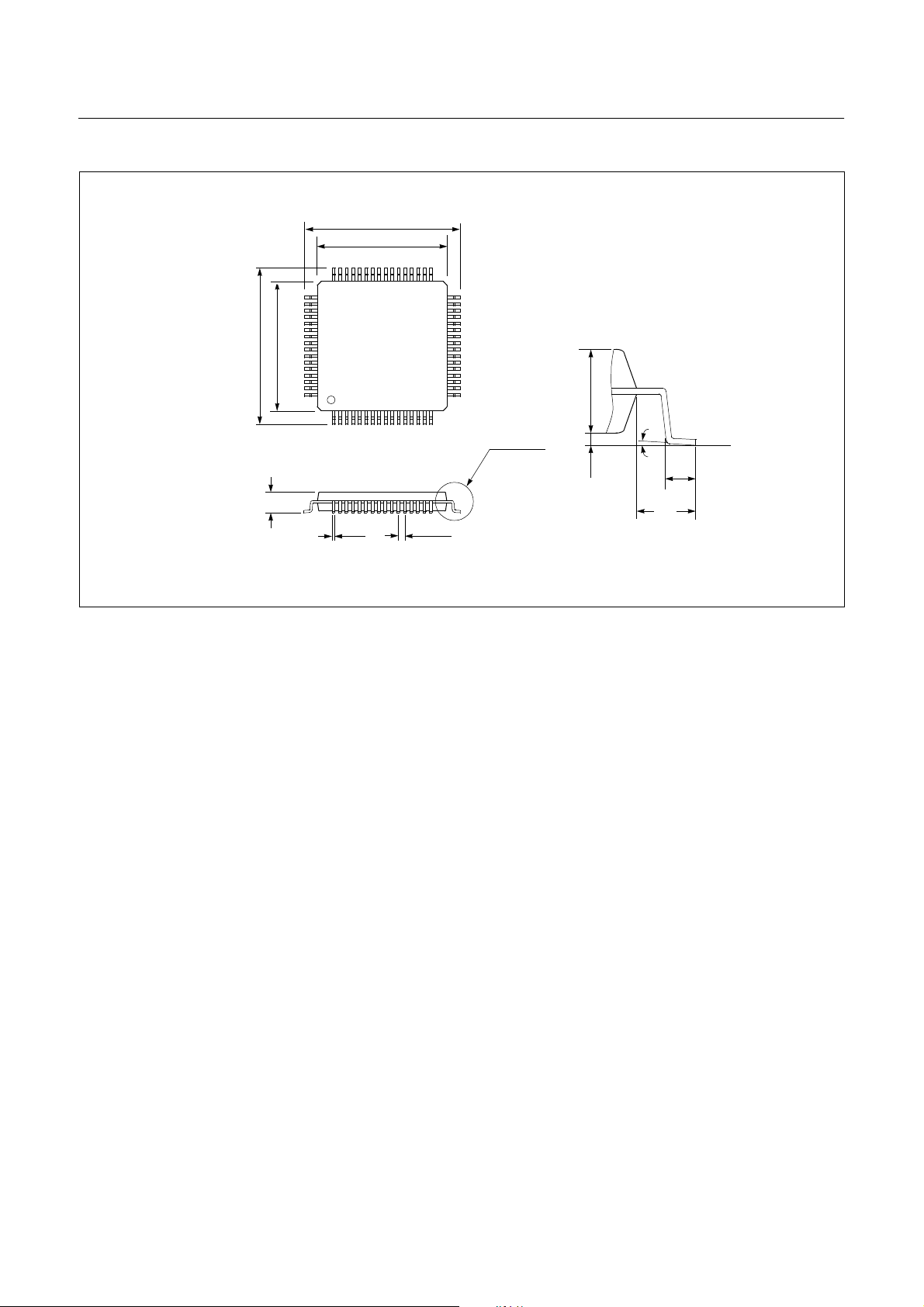
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
64LQFP
12.00 Typ.
10.00 Typ.
1.60 max.
12.00 Typ.
10.00 Typ.
0.38
0.22
0.50 Typ.
SEE DETAIL “A”
1.45
1.35
0.15
0.05
UNIT: MM
0-7
°
1.00
REF
DETAIL “A”
0.75
0.45
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 7
Page 11
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
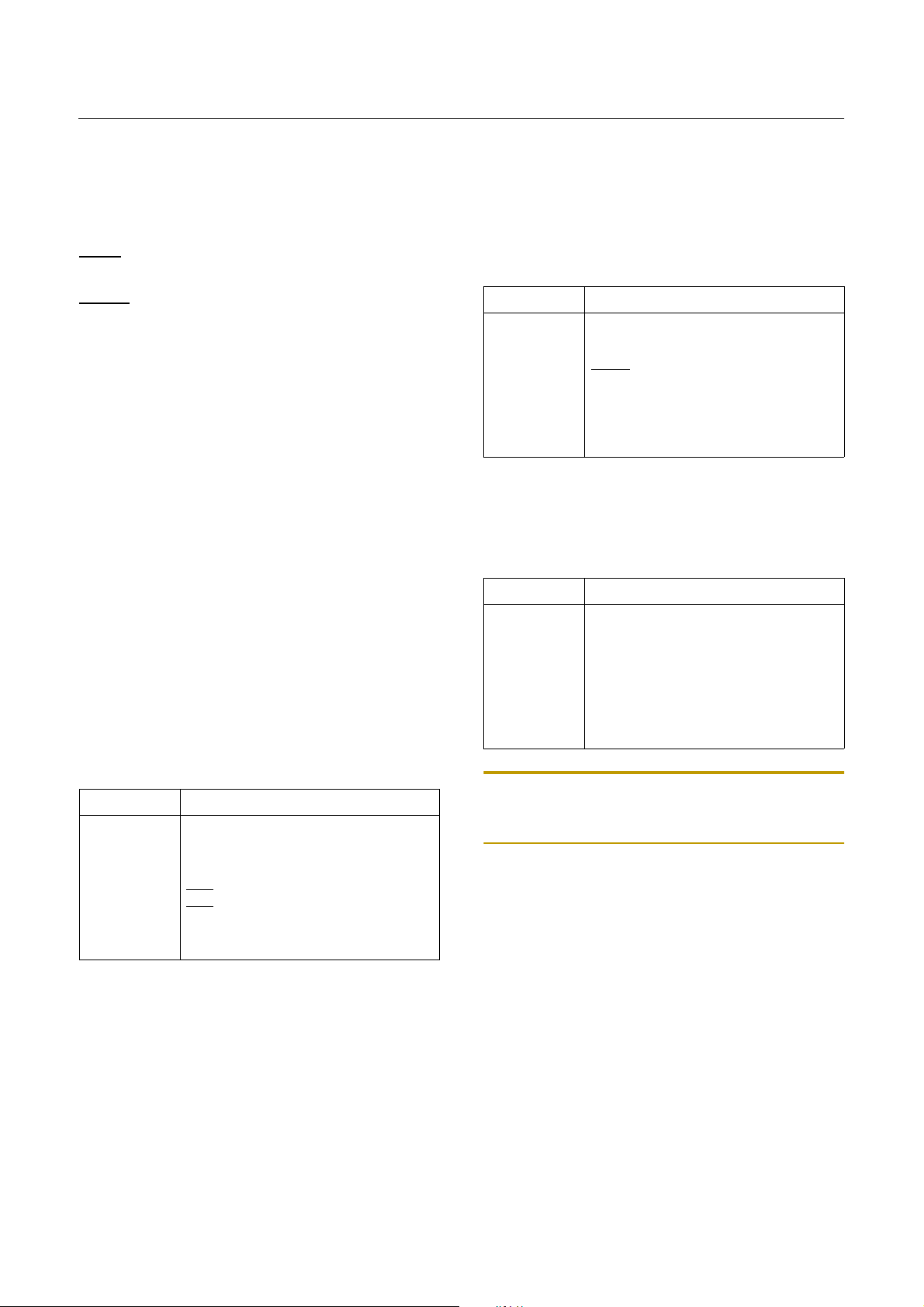
5. PIN FUNCTION
V
: Supply voltage.
DD
V
: Circuit ground.
SS
TEST
: Used for Test Mode. For normal operation, it
should be connected to V
RESET
X
: Reset the MCU.
: Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to
IN
DD
.
the internal main clock operating circuit.
X
: Output from the inverting oscillator amplifier.
OUT
R00~R07
: R0 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirectional I/O port. R0
pins 1 or 0 written to the Port Direction Register can be
used as output s or inputs.
R10~R17
: R1 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirectional I/O port. R1
pins 1 or 0 written to the Port Direction Register can be
used as output s or inputs.
R20~R27
: R2 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirectional I/O port. R2
pins 1 or 0 written to the Port Direction Register can be
used as output s or inputs.
R30~R37
: R3 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirectional I/O port. R3
pins 1 or 0 written to the Port Direction Register can be
used as output s or inputs.
R40~R47
: R4 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirectional I/O port. R4
pins 1 or 0 written to the Port Direction Register can be
used as output s or inputs.
In addition, R4 serves the functions of the various following special features.
used as outputs or inputs.
In addition, R5 serves the functions of the various follow -
ing special features.
Port pin Alternate function
R50
R51
R52
R53
R54
R55
R56
R57
R60~R67
SIN (Serial data input)
SOUT (Serial data output)
SCLK (Serial clock)
SRDY (Serial ready)
WDTO (Watchdog Timer output)
BUZ (Buzzer driver output)
PWM0 (PWM output 0)
PWM1 (PWM output 1)
: R6 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirectional I/O port. R6
pins 1 or 0 written to the Port Direction Register can be
used as outputs or inputs.
In addition, R6 is shared with the ADC input.
Port pin Alternate function
R60
R61
R62
R63
R64
R66
R66
R67
AN0 (Analog Input 0)
AN1 (Analog Input 1)
AN2 (Analog Input 2)
AN3 (Analog Input 3)
AN4 (Analog Input 4)
AN5 (Analog Input 5)
AN6 (Analog Input 6)
AN7 (Analog Input 7)
Port pin Alternate function
R40
R41
R42
R43
R44
R45
R46
R47
R50~R57
: R5 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirectional I/O port. R5
INT0 (External interrupt 0)
INT1 (External interrupt 1)
INT2 (External interrupt 2)
INT3 (External interrupt 3)
EC0
(Event counter input 0)
(Event counter input 2)
EC2
T1O (Timer/Counter 1 output)
T3O (Timer/Counter 3 output)
Note: On the MDS Ch oice, when the M CU is RESET, R60
can not be used digital input port. For more detail, refer to
"9. I/O PORTS" on page 31.
AV
: Supply voltage to the ladder resistor o f ADC cir-
DD
cuit. To enhance the resolution of analog to digital converter, use independent power source as well as possible, other
than digital power source.
AV
: ADC circuit ground.
SS
pins 1 or 0 written to the Port Direction Register can be
8 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 12
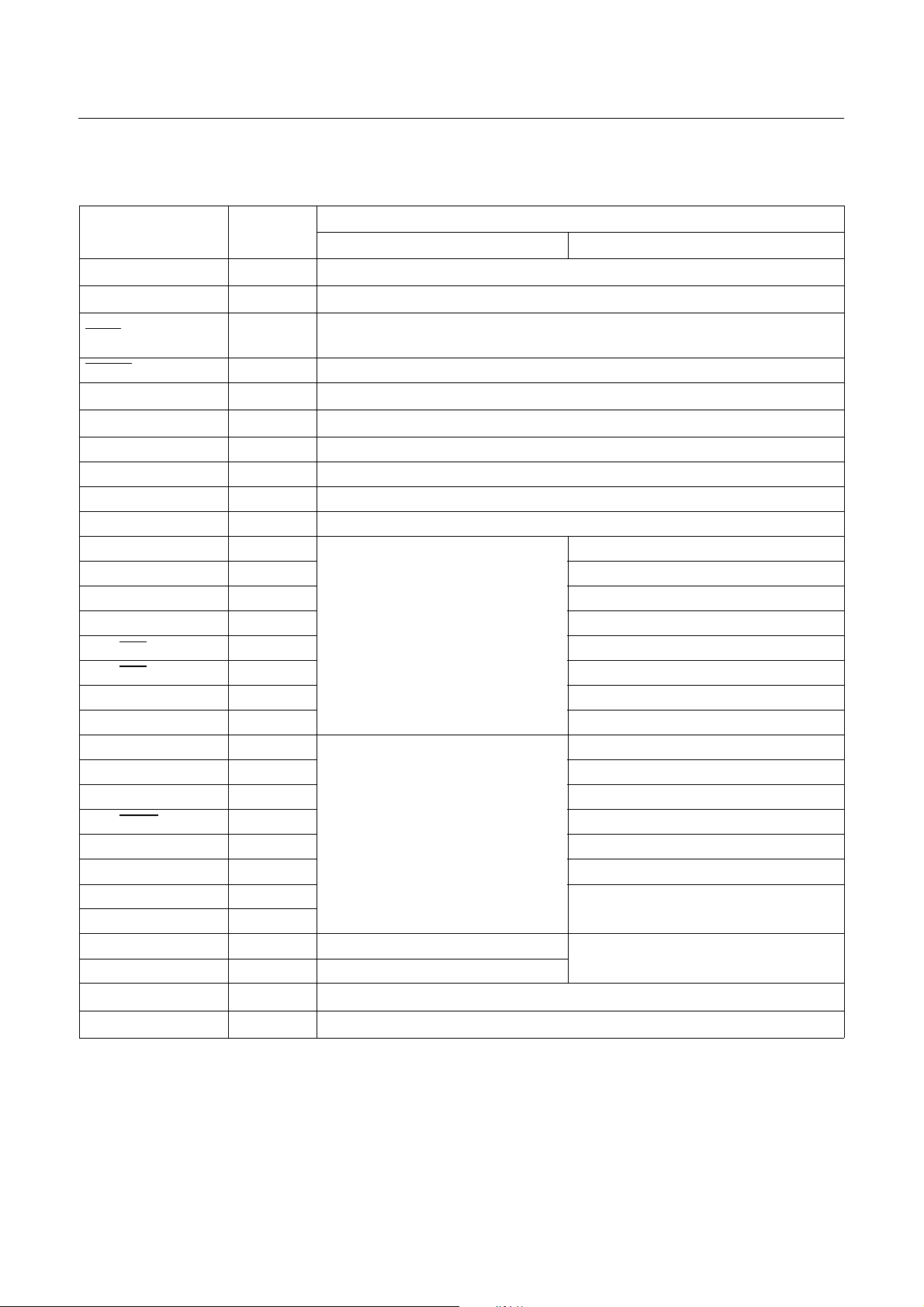
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
PIN NAME In/Out
Function
Basic Alternate
V
DD
V
SS
TEST
- Supply voltage
- Circuit ground
I
Controls test mode of the chip,
For normal operation, it should be connected at VDD.
RESET I Reset signal input
X
X
IN
OUT
I Oscillation input
O Oscillation output
R00~R07 I/O 8-bit general I/O ports
R10~R17 I/O 8-bit general I/O ports
R20~R27 I/O 8-bit general I/O ports
R30~R37 I/O 8-bit general I/O ports
R40 (INT0) I/O (I)
External interrupt 0 input
R41 (INT1) I/O (I) External interrupt 1 input
R42 (INT2) I/O (I) External interrupt 2 input
R43 (INT3) I/O (I) External interrupt 3 input
R44 (EC0
R45 (EC2
) I/O (I) Timer/Counter 0 external input
) I/O (I) Timer/Counter 2 external input
8-bit general I/O ports
R46 (T1O) I/O (O) Timer/Counter 1 output
R47 (T3O) I/O (O) Timer/Counter 3 output
R50 (SIN) I/O (I)
Serial data input
R51 (SOUT) I/O (O) Serial data output
R52 (SCLK) I/O (I/O) Serial clock I/O
R53 (SRDY) I/O (I/O) Receive enable I/O
8-bit general I/O ports
R54 (WDTO) I/O (O) Watchdog timer overflow output
R55 (BUZ) I/O (O) Buzzer driving output
R56 (PWM0) I/O (O)
PWM pulse output
R57 (PWM1) I/O (O)
R60~R63 (AN0~AN3) I (I) General input ports
Analog voltage input
R64~R67 (AN4~AN7) I/O (I) General I/O ports
AV
AV
SS
DD
- Groun d level input pin for ADC
- Supply voltage input pin for ADC
Table 5-1 Port Function Description
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 9
Page 13
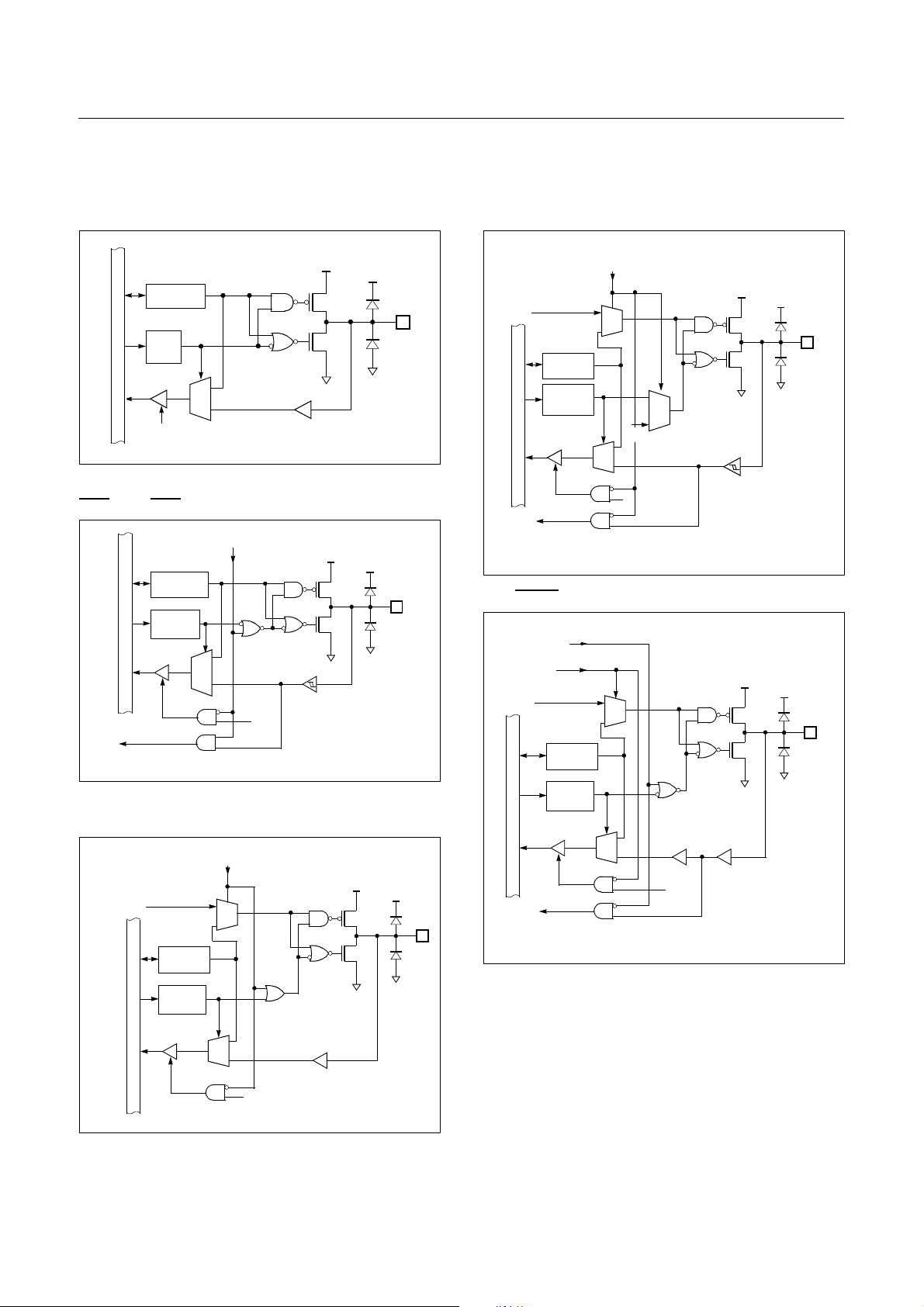
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
MUX
Data Bus
V
DD
V
SS
Pin
Data Reg.
Direction
Reg.
Rd
MUX
Selection
SCK Output
MUX
SCK Input
exck
MUX
Data Bus
V
DD
V
SS
Pin
Data Reg.
Direction
Reg.
Rd
MUX
Selection
SRDY Output
SRDY Input
SRDY
6. PORT STRUCTURES
R00~R07, R10~R17, R20~R27, R30~37
V
DD
Data Reg.
Dir.
Reg.
Data Bus
MUX
Rd
VSS
Pin
R40/INT0, R41/INT1, R42/INT2, R43/INT3, R44/
, R45/EC2, R50/SIN
EC0
Data Bus
Data Reg.
Direction
Reg.
PMR Selection
MUX
V
DD
Pin
V
SS
R52/SCLK
S53/SRDY
Rd
EX) INT0
Alternate Function
R46/T1O, R47/T3O, R51/SOUT, R54/WDTO
R55BUZ, R56/PWM0, R57/PWM1
Selection
Secondary function
MUX
Data Reg.
Data Bus
Direction
Reg.
MUX
Rd
V
DD
Pin
V
SS
10 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 14
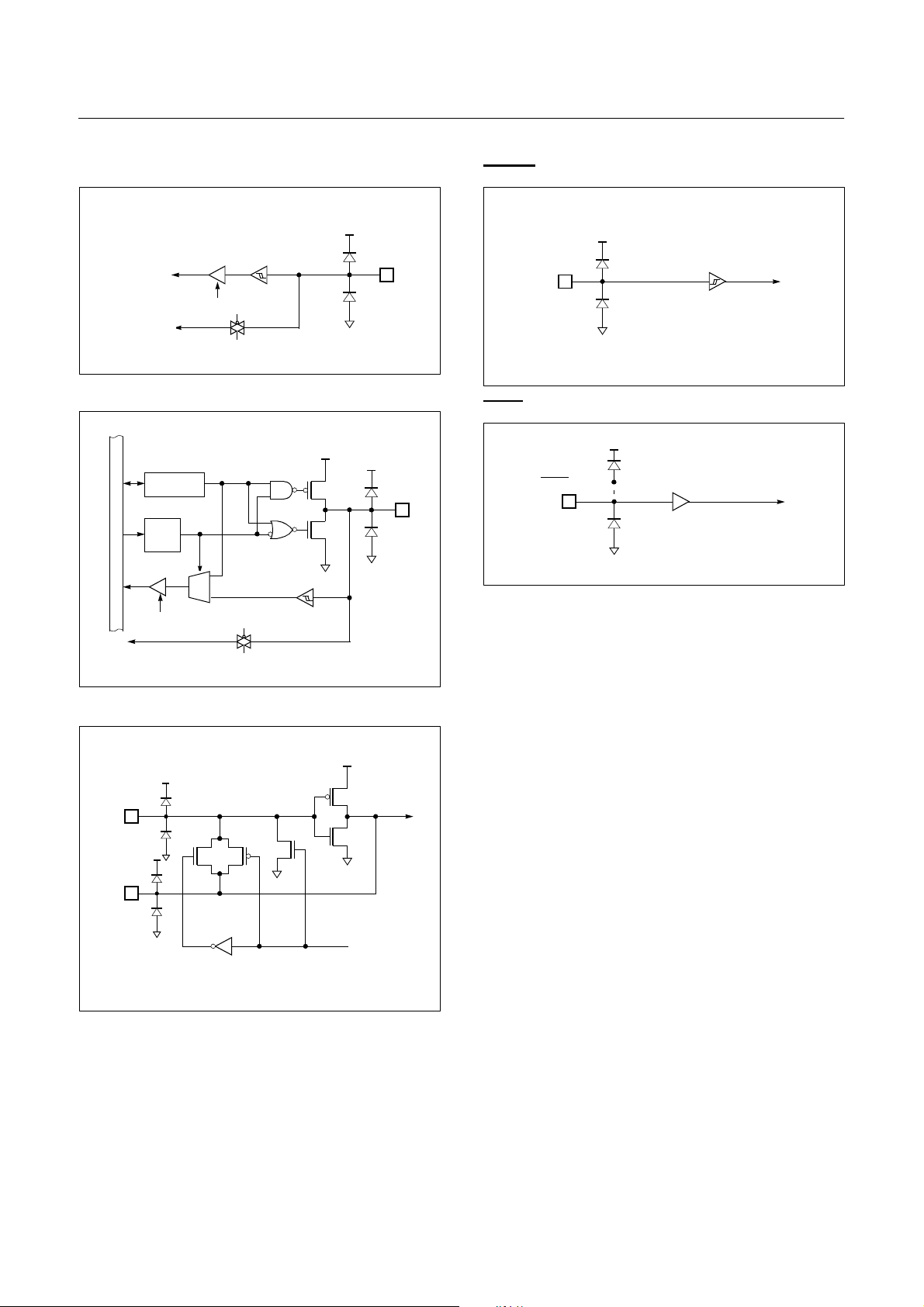
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
RESET
V
DD
V
SS
TEST
V
DD
V
SS
OTP version: disconnected
Mask version: connected
R60/AN0 ~ R63/AN3
Data bus
To A/D converter
R64/AN7 ~ R67/AN7
Data Reg.
Dir.
Reg.
Data Bus
MUX
Rd
Rd
RESET
V
DD
V
SS
TEST
V
DD
Pin
V
SS
X
, X
IN
XIN
XOUT
To A/D converter
OUT
V
DD
V
V
SS
SS
Stop
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 11
Page 15
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
7. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Supply voltage.............................................-0.3 to +7.0 V
Storage Temperature ..................................-40 to +125 °C
Voltage on any pin with respect to Ground (V
................................ ..................................-0.3 to V
Maximum current out of V
Maximum current into V
Maximum current sunk by (I
Maximum output current sourced by (I
pin..........................150 mA
SS
pin ..............................80 mA
DD
per I/O Pin) ..........20 mA
OL
OH
)
SS
DD
per I/O Pin)
+0.3
...................................................................................8 mA
7.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter Symbol Condition
f
=1 ~ 10 MHz
XIN
f
Supply Voltage
Operating Frequency
V
f
DD
XIN
=1 ~ 8 MHz
XIN
f
=1 ~ 4 MHz
XIN
VDD=4.5~5.5V
VDD=2.7~5.5V
VDD=2.2~5.5V
Maximum current (ΣI
Maximum current (ΣI
)......................................100 mA
OL
)........................................50 mA
OH
Note: Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause per manent damage to the d evice. This is a stress ra ting only and functional ope r ati on of
the device at any oth er c ond iti ons ab ov e tho se ind ic ated in
the oper ati o na l se c ti ons of this s pecificatio n i s no t i mp l ie d .
Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Specifications
Unit
Min. Max.
4.5
2.7
2.2
1
1
1
5.5
5.5
5.5
10
8
4
V
MHz
Operating Temperature
T
OPR
7.3 A/D Converter Characteristics
(TA=25°C, VSS=0V, VDD=5.12V@f
Parameter Symbol
Analog Input Voltage Range
Non-linearity Error
Differential Non-linearity Error
Zero Offset Error
Full Scale Error
Gain Error
Overall Accuracy
AV
Input Current I
DD
Conversion Time
=8MHz, VDD=3.072V@f
XIN
Normal Version
Temperature Extention Version
=4MHz)
XIN
Min.
V
N
N
N
N
N
N
T
CONV
AIN
NLE
DNLE
ZOE
FSE
GE
ACC
REF
V
SS
-
-
-
-
-
-
-0.51.01.0 mA
- - 40 20
-20
-40
85
85
Specifications
1
Typ.
f
XIN
-
1.0 ±1.5 ±1.5 LSB
±
1.0 ±1.5 ±1.5 LSB
±
0.5 ±1.5 ±1.5 LSB
±
0.35 ±0.5 ±0.5 LSB
±
1.0 ±1.5 ±1.5 LSB
±
1.0 ±1.5 ±1.5 LSB
±
Max.
=4MHz f
AV
DD
XIN
AV
=8MHz
DD
C
°
Unit
V
s
µ
12 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 16
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
Specifications
Parameter Symbol
Min.
Analog Power Supply Input Range
1. Data in “Typ” column is at 25°C unless otherwise stated. These parameters are for design guidance only and are not tested.
AV
DD
0.9V
DD
Typ.
V
DD
1
f
XIN
Max.
=4MHz f
1.1V
XIN
DD
Unit
=8MHz
V
7.4 DC Electrical Characteristics
(TA=-20~85°C, VDD=2.7~5.5V, Ta= -20~85°C, f
=8MHz, VSS=0V)
XIN
Parameter Symbol Condition
, RESET,
X
IN
R4, R5, R6
R0, R1, R2, R3
, RESET,
X
IN
R4, R5, R6
R0, R1, R2, R3 -
R0,R1,R2,R3,R4,R5
R6
R0,R1,R2,R3,R4,R5
R6
@ T
=25°C0.9V
A
All input pins -5.0 - 5.0
All input pins -5.0 - 5.0
RESET, EC0, EC2,
SIN, SCLK, INT0~INT3
SS
Input High Voltage
Input Low Voltage
Output High Voltage
Output Low Voltage
Power Fail Detect
Voltage
Input High
Leakage Current
Input Low
Leakage Current
Hysteresis
V
IH1
V
IH2
V
IL1
V
IL2
V
OH
V
OL
V
PFD
I
IH1
I
IL
, V
V
T+
T-
I
DD1fXIN
VDD=4.5
VDD=2.7
VDD=4.5
V
=2.7
DD
VDD=4.5
VDD=2.7
I
=-2mA
OH1
VDD=4.5
VDD=2.7
I
=5mA
OL1
V
=3.0V
PFD
V
=2.4V
PFD
VIN=V
DD
VIN=V
SS
= 8 MHz A ll inp ut = V
C ry s ta l Oscilla tor ,
Power Current
1. Data in “Typ.” column is at 4.5V, 25°C unless otherwise stated. These parameters are for design guidance only and are not tested.
I
DD2fXIN
I
STOP
=4MHz
L1=CL2
=30pF
C
A ll inp ut = V
SS
,
Specifications
Min.
0.8V
0.7V
DD
DD
Typ.
-
-
1
-
-1.0
V
DD
-
PFD
--V
-1.0V
0.3 0.8 V
-820mA
410mA
-110µA
Max.
V
DD
V
DD
0.2V
0.3V
1.1V
+0.3
+0.3
DD
DD
PFD
Unit
V
V
V
A
µ
A
µ
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 13
Page 17
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
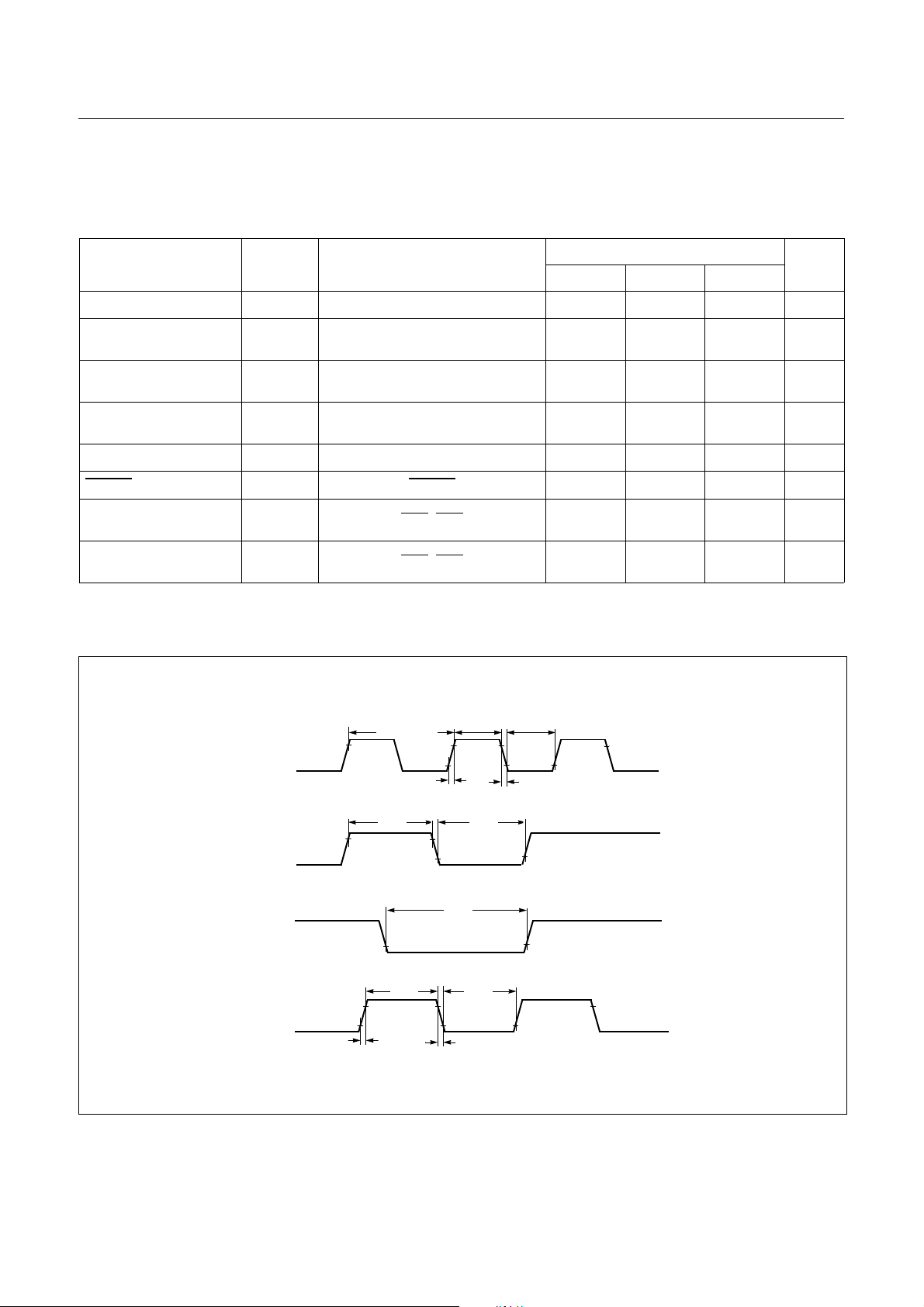
7.5 AC Characteristics
(TA=-20~+85°C, VDD=5V±10%, VSS=0V)
Parameter Symbol Pins
Operating Frequency
Oscillation Stabilizing
Time
External Clock Pulse
Width
External Clock Transi-
tion Time
Interrupt Pulse Width
RESET Input Width
Event Counter Input
Pulse Width
Event Counter Transi-
tion Time
f
XIN
t
ST
t
CPW
t
RCP,tFCP
t
IW
t
RST
t
ECW
t
REC,tFEC
Specifications
Min. Typ. Max.
X
XIN, X
X
X
IN
OUT
IN
IN
1.0 - 10.0 MHz
--20ms
40 - - ns
- - 20 ns
INT0, INT1, INT2, INT3 2 - -
RESET 8--
EC0, EC2 2--
EC0, EC2 - - 20 ns
Unit
t
SYS
t
SYS
t
SYS
XIN
INT0~INT3
RESET
EC1, EC2
t
0.8V
t
REC
SYS
DD
t
IW
= 1/f
t
ECW
XIN
t
FEC
t
RCP
t
t
RST
t
Figure 7-1 Timing Chart
CPW
t
ECW
t
CPW
-0.5V
V
DD
0.5V
t
FCP
IW
0.2V
DD
0.2V
DD
0.8V
DD
0.2V
DD
14 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 18
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
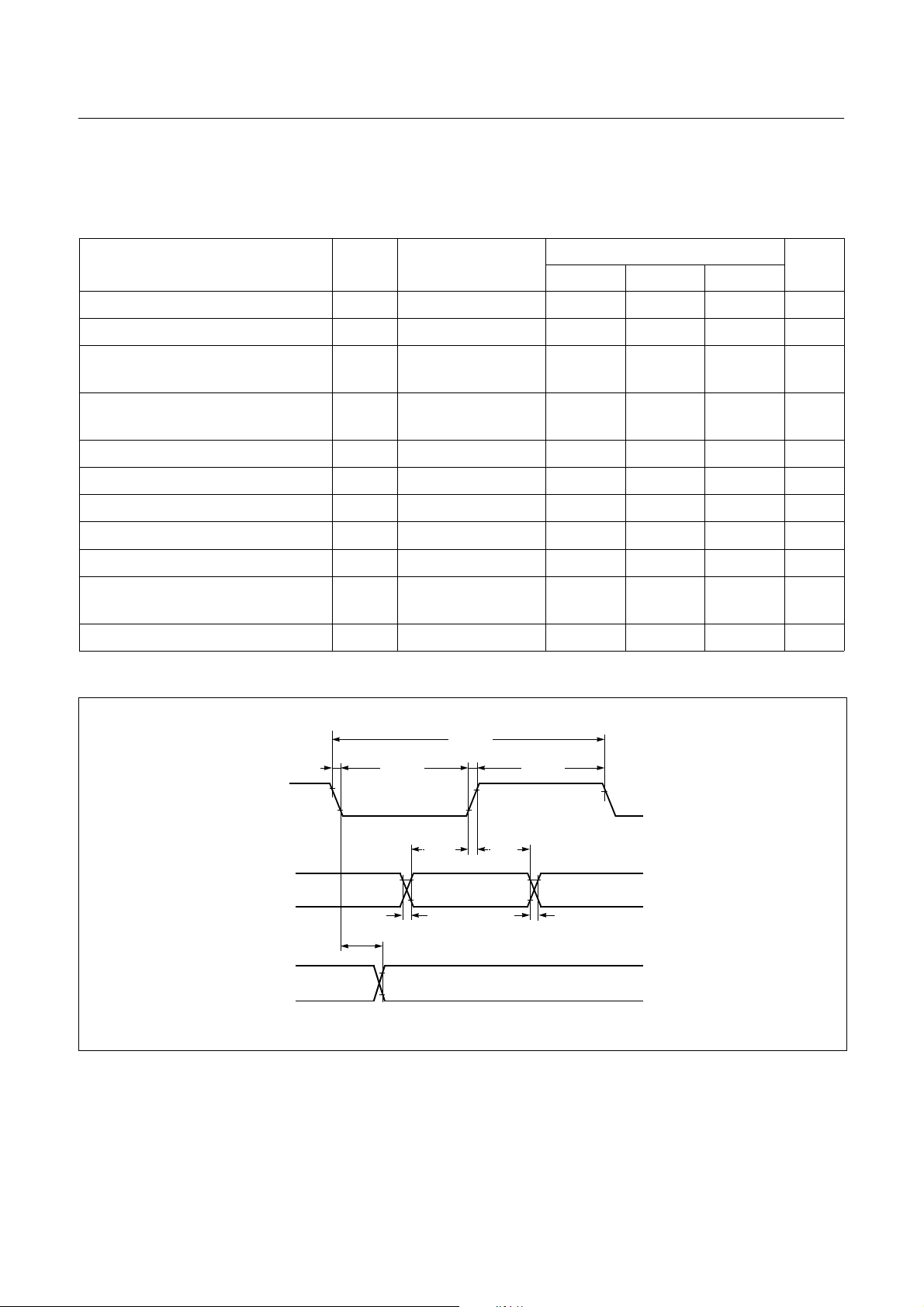
7.6 Serial Interface Timing Characteristics
(TA=-20~+85°C, VDD=5V±10%, VSS=0V, f
Parameter Symbol Pins
Serial Input Clock Pulse
Serial Input Clock Pulse Width
Serial Input Clock Pulse Transition
Time
SIN Input Pulse Transition Time
SIN Input Setup Time (External SCLK)
SIN Input Setup Time (Internal SCLK)
SIN Input Hold Time
Serial Output Clock Cycle Time
Serial Output Clock Pulse Width
Serial Output Clock Pulse Transition
Time
Serial Output Delay Time
XIN
t
SCYC
t
SCKW
t
FSCK
t
RSCK
t
FSIN
t
RSIN
t
SUS
t
SUS
t
HS
t
SCYC
t
SCKW
t
FSCK
t
RSCK
s
OUT
=8MHz)
Specifications
Unit
Min. Typ. Max.
SCLK
SCLK
2t
SYS
+70
t
SYS
-8ns
-8ns
+200
SCLK - - 30 ns
SIN - - 30 n s
SIN 100 - - ns
SIN 200 - ns
SIN
SCLK
SCLK
t
SYS
t
SYS
4t
SYS
-30
-ns
-
16t
SYS
ns
ns
+70
SCLK 30 ns
SOUT 100 ns
SCLK
SIN
SOUT
t
0.8V
0.2V
FSCK
t
SCYC
t
RSCK
SUS
DD
DD
t
SCKW
t
t
FSIN
t
DS
0.8V
DD
0.2V
DD
Figure 7-2 Serial I/O Timing Chart
t
SCKW
t
HS
0.8V
DD
0.2V
DD
t
RSIN
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 15
Page 19
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
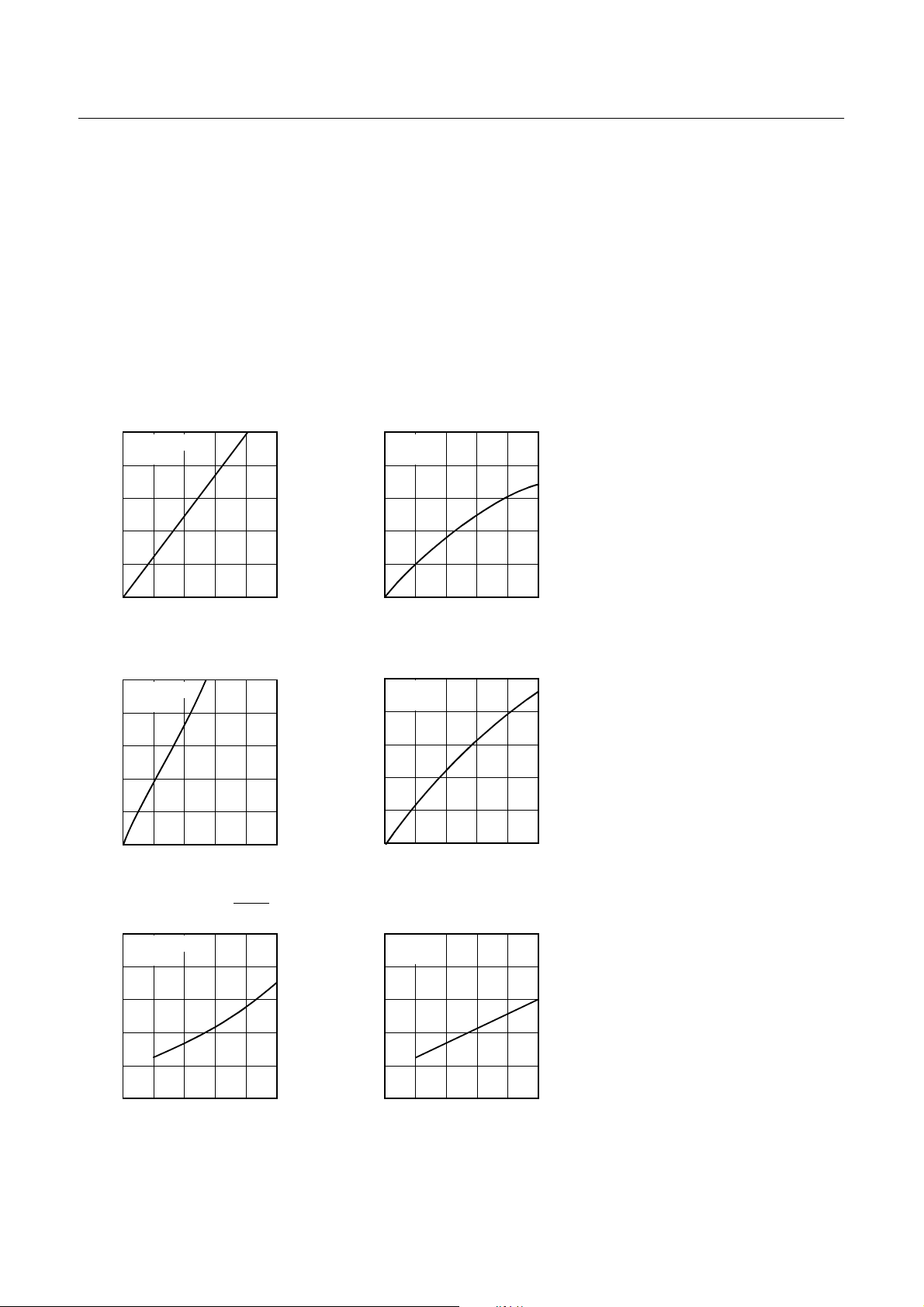
7.7 Typical Characteristic Curves
This graphs and tables provided in this section are for design guidance only and are not tested or guaranteed.
In some graphs or tables the data presented are outside specified operating range (e.g. outside specified
VDD range). This is for information only and devices
are guaranteed to operate properly only within the
specified range.
I
OH
(mA)
-12
-9
-6
-3
I
OH
VDD=4.5V
Ta=25°C
0
V
−
OH
0.3 0.6
R0~R6 pins
0.9 1.2
1.5
VDD-V
(V)
OH
I
OH
(mA)
-12
-9
-6
-3
I
0
V
−
OH
VDD=3.0V
Ta=25°C
0.3 0.6
OH
The data presented in this s ection is a statistical s ummary
of data collected on units from different lots over a period
of time. “Typical” represents the mean of the distribution
while “max” or “min” represents (mean + 3σ) and (mean
3σ) respectively where σ is standard deviation
R0~R6 pins
(V)
0.9 1.2
1.5
VDD-V
OH
−
V
I
OL
(mA)
20
15
10
IH1
(V)
0
I
5
0
V
4
3
2
1
V
−
OL
VDD=4.5V
Ta=25°C
0.2 0.4
V
−
DD
f
=8MHz
XIN
Ta=25°C
23
OL1
IH1
R0~R6 pins
0.6 0.8
XIN, RESET,
R4, R5, R6 pins
45
1.0
I
V
−
OL
VDD=3.0V
Ta=25°C
0.2 0.4
V
DD
f
=8MHz
XIN
Ta=25°C
1
OL2
V
−
IH2
23
I
OL
(mA)
20
15
10
5
V
OL
(V)
V
DD
(V)
6
0
V
IH2
(V)
4
3
2
1
0
R0~R6 pins
0.6 0.8
R0, R1, R2, R3 pins
45
1.0
6
V
V
(V)
(V)
OL
DD
16 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 20
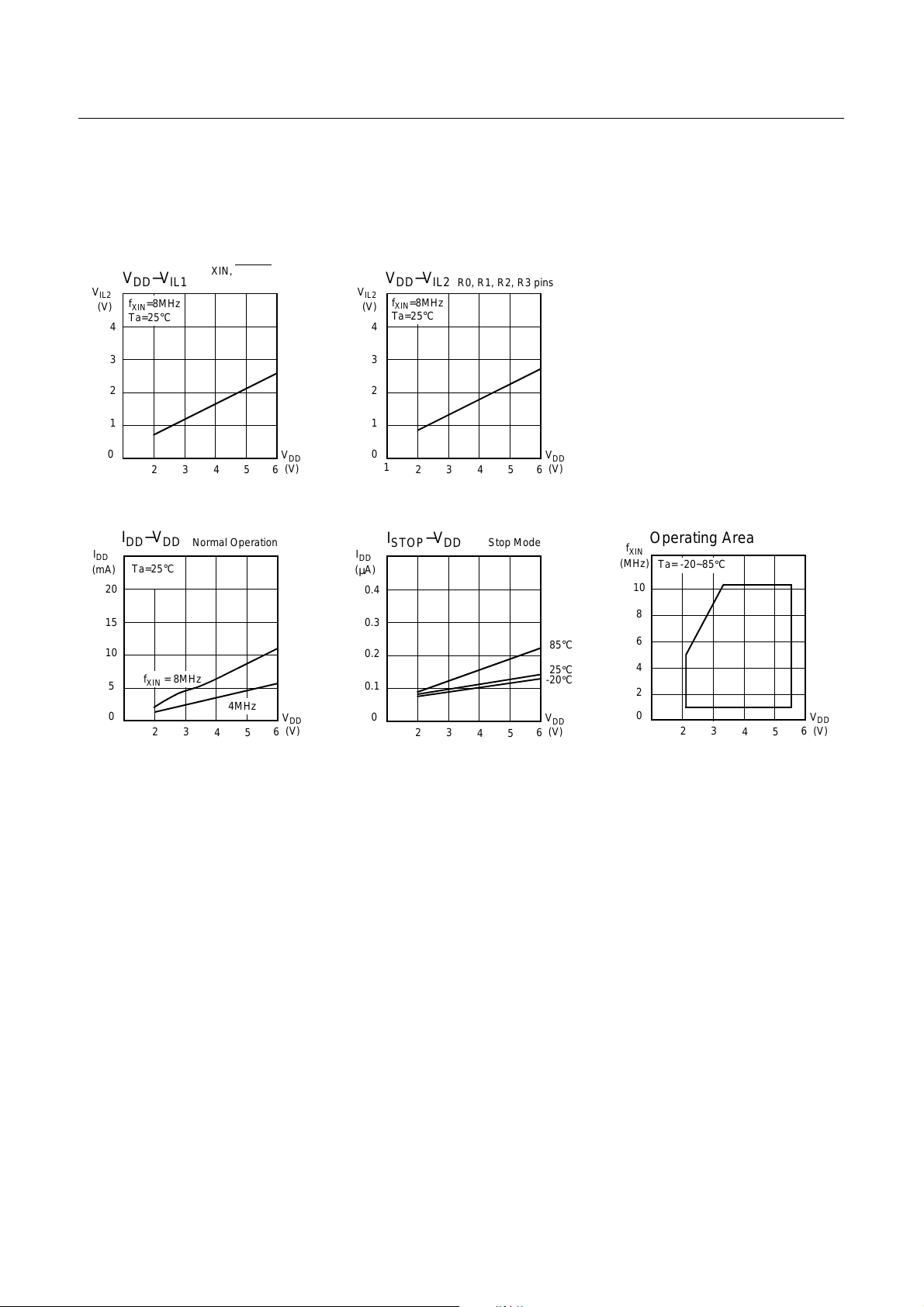
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
V
IL2
(V)
I
DD
(mA)
4
3
2
1
0
20
15
10
5
0
V
DD
f
XIN
Ta=25°C
I
−
DD
Ta=25°C
f
V
−
IL1
=8MHz
23
V
DD
= 8MHz
XIN
23
XIN, RESET
R4, R5, R6 pins
45
Normal Operation
4MHz
45
,
V
DD
(V)
6
V
DD
(V)
6
V
I
DD
(µA)
IL2
(V)
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
4
3
2
1
0
0
V
DD
f
XIN
Ta=25°C
1
I
STOP
V
−
IL2
=8MHz
23
V
−
DD
23
R0, R1, R2, R3 pins
45
Stop Mode
45
6
6
V
DD
(V)
85°C
25°C
-20°C
V
DD
(V)
Operating Area
f
XIN
(MHz)
Ta= -20~85°C
10
8
6
4
2
0
23
45
V
DD
(V)
6
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 17
Page 21
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
SP
01
H
Stack Address (100H ~ 1FEH)
Bit 15 Bit 087
Hardware fixed
00H~FE
H
8. MEMORY ORGANIZATION
The GMS81508B/16B/24B has separate address spaces
for Program memory and Data Memory. Pro gram memory
can only be read, not written to. It can be up to 24K bytes
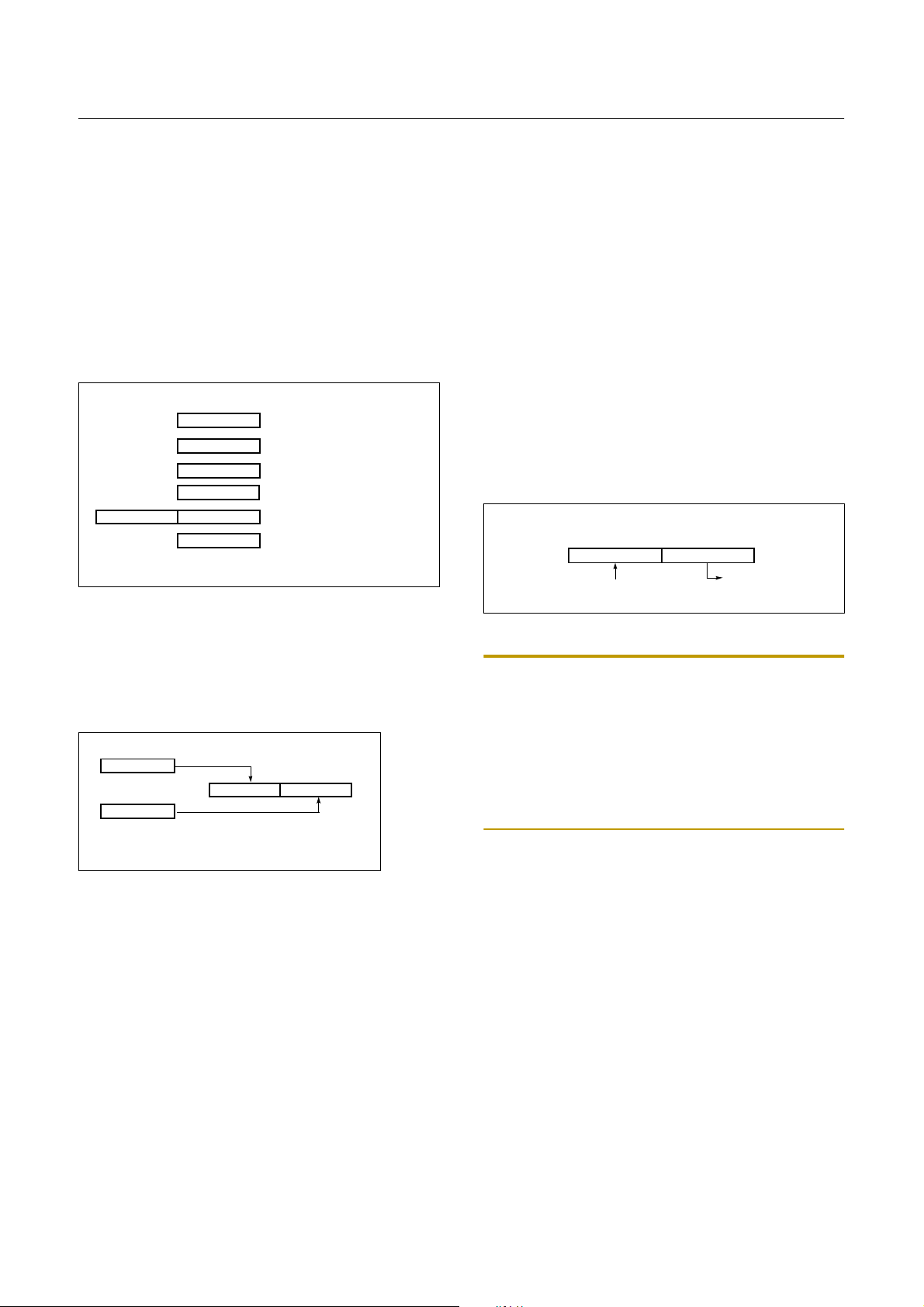
8.1 Registers
This device has six registers that are the Program Counter
(PC), a Accumulator (A), two index registers (X, Y), the
Stack Pointer (SP), and the Program Status Word (PSW).
The Program Counter consists of 16-bit register.
A
X
Y
SP
PCH
Figure 8-1 Configuration of Registers
Accumulator:
PCL
PSW
The Accumulator is the 8-bit general purpose register, used for data operation such as transfer, temporary saving, and conditional judgement, etc.
The Accumulator can be used as a 16-bit register with Y
Register as shown below.
Y
A
Two 8-bit Registers can be used as a “YA” 16-bit Register
Figure 8-2 Configuration of YA 16-bit Register
X, Y Registers
: In the addressing mode which uses these
index registers, the register conten ts a re added to the specified address, which becomes the actual address. These
modes are extremely effective for referencing subroutine
tables and memory tables . The index regi sters also h ave increment, decrement, comparison and data transfer functions, and they can be used as simple accumulators.
Stack Pointer
: The Stack Pointer is an 8-bit register used
for occurrence interrupts and calling out subroutines. Stack
Pointer identifies the location in the stack to be accessed
(save or restore).
Generally, SP is au to mat ic ally upda t ed wh e n a s ubr outin e
ACCUMULATOR
X REGISTER
Y REGISTER
STACK POINTER
PROGRAM COUNTER
PROGRAM STATUS
WORD
Y A
of Program memory. Data memory can be read and written
to up to 448 bytes including the stack area.
call is executed or an interrupt is accepted. However, if it
is used in excess of the stack area permitted by the data
memory allocating configuration, the user-processed data
may be lost.
The stack can be located at any position within 100
1FF
of the internal data memory. The SP is not initialized
H
to
H
by hardware, requiring to write the initial v alue (the lo cation with which the use of the stack starts) by using the initialization routine. Normally, the initial value of “F E
” is
H
used.
Note: The Stack Pointer must be initialized by software because its value is undefined after RESET.
Example: To initialize the SP
LDX #0FEH
TXSP ; SP ← FEH
Address 01FFH can not be used as stack. Don not use
1FFH, or malfunction would be occurred.
Program Counter
: The Program Counter is a 16-bit wide
which consists of two 8-bit registers, PCH and PCL. This
counter indicates the address of the next instruction to be
executed. In reset state, the program counter has reset routine address (PC
Program Status Word
:0FFH, PCL:0FEH).
H
: The Program Status Word (PSW)
contains several bits that reflect the current state of the
CPU. The PSW is described in Figure 8-3. It contains the
Negative flag, the Overflow flag, the Break flag the Half
Carry (for BCD operation), the Interrupt enable flag, the
Zero flag, and the Carry flag.
[Carry flag C]
This flag stores any carry or borrow from the ALU of CPU
after an arithmetic operation and is also changed by the
Shift Instruction or Rotate Instruction.
18 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 22
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
[Zero flag Z]
This flag is set when the result of an arithmetic operat ion
MSB LSB
N
V G B H I Z C
NEGATIVE FLAG
OVERFLOW FLAG
when G=1, page is selected to “page 1”
SELECT DIRECT PAGE
BRK FLAG
PSW
Figure 8-3 PSW (Program Status Word) Register
[Interrupt disable flag I]
This flag enables/disables all interrupts except interrupt
caused by Reset or software BRK instruction. All interrupts are disabled when cleared to “0”. This flag immediately becomes “0” when an interrupt is served. It is set by
the EI instruction and cleared by the DI instruction.
or data transfer is “0” and is cleared by any other result.
RESET VALUE: 00
CARRY FLAG RECEIVES
CARRY OUT
ZERO FLAG
INTERRUPT ENABLE FLAG
HALF CARRY FLAG RECEIVES
CARRY OUT FROM BIT 1 OF
ADDITION OPERLANDS
H
This flag assigns RAM page for direct addressing mode. In
the direct addressing mode, addressing area is from zero
page 00
addressing area is assigned 100
to 0FFH when this flag is "0". If it is set to "1",
H
to 1FFH. It is set by
H
SETG instruction and cleared by CLRG.
[Overflow flag V]
[Half carry flag H]
After operation, this is set when there is a carry from bit 3
of ALU or there is no borrow from bit 4 of ALU. This bit
can not be set or cleared except CLRV instruction with
Overflow flag (V).
[Break flag B]
This flag is set by software BRK instruction to distinguish
BRK from TCALL instruction with the same vector address.
[Direct page flag G]
This flag is set to “1” when an overflow occurs as the result
of an arithmetic operation involving signs. An overflow
occurs when the result of an addition or subtraction exceeds +127(7F
) or -128(80H). The CLRV instruction
H
clears the overflow flag. There is no set instruction. When
the BIT instruction is executed, bit 6 of memory is copied
to this flag.
[Negative flag N]
This flag is set to match the sign bit (bit 7) status of the re-
sult of a data or arithmetic operation. When the BIT instruction is executed, bit 7 of memory is copied to this flag.
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 19
Page 23
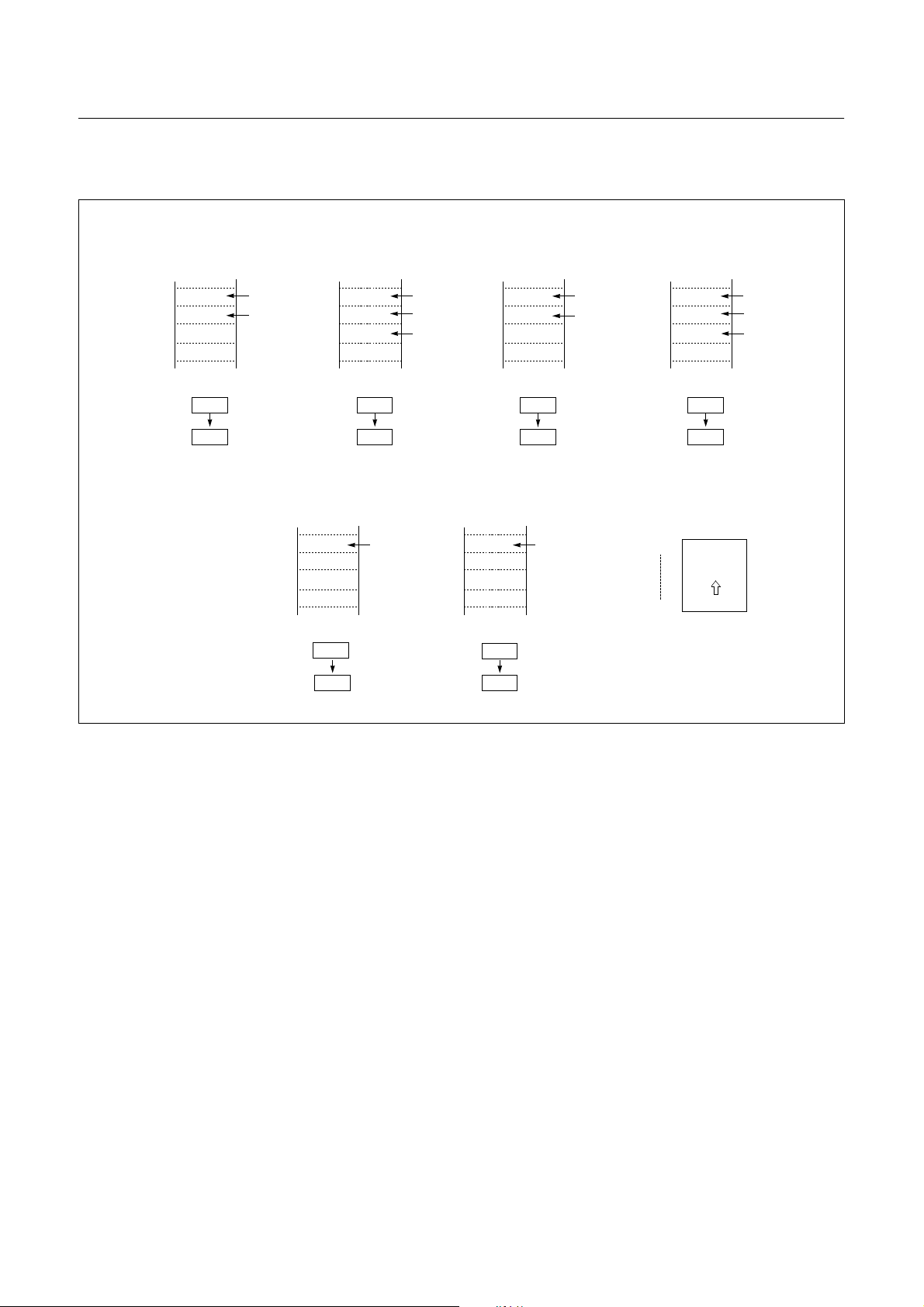
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
At execution of
a CALL/TCALL/PCALL
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FB
SP before
execution
SP after
execution
PCH
PCL
01FE
01FC
Push
down
SP before
execution
SP after
execution
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FB
At execution
of PUSH instruction
PUSH A (X,Y,PSW)
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FB
A
01FE
01FD
At acceptance
of interrupt
PCH
PCL
PSW
01FE
01FB
Push
down
Push
down
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FB
At execution
of RET instruction
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FB
At execution
of POP instruction
POP A (X,Y,PSW)
PCH
PCL
01FC
01FE
A
01FD
01FE
Pop
up
Pop
up
At execution
of RET instruction
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FB
0100H
01FEH
PCH
PCL
PSW
01FB
01FE
Stack
depth
Pop
up
Figure 8-4 Stack Operation
20 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 24

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
0FFE0H
E2
Address Vector Area Memory
E4
E6
E8
EA
EC
EE
F0
F2
F4
F6
F8
FA
FC
FE
-
-
Serial Communication Interface
Basic Interval Timer
-
-
-
External Interrupt 2
Timer/Counter 1 Interrupt
External Interrupt 0
-
RESET Vector Area
External Interrupt 1
Watchdog Timer Interrupt
“-” means reserved area.
NOTE:
Timer/Counter 2 Interrupt
External Interrupt 3
Timer/Counter 0 Interrupt
Timer/Counter 3 Interrupt
A/D Converter
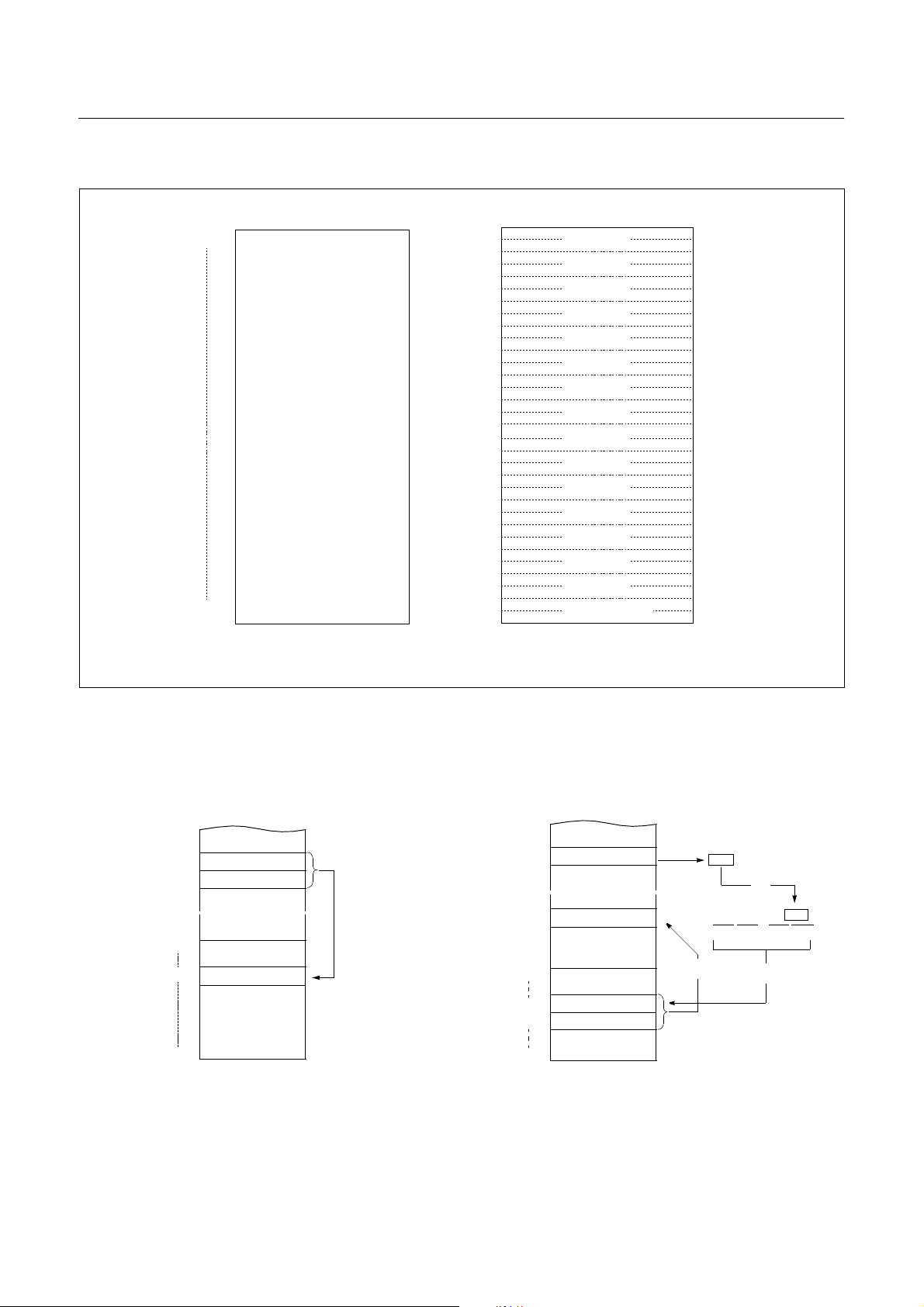
8.2 Program Memory
A 16-bit program counter is capable of addressing up to
64K bytes, but this device has 2 4K bytes program memory
space only physically implemented. Accessing a location
above FFFF
will cause a wrap-around to 0000H.
H
Figure 8-5, shows a map of Pr ogram Memory. After reset,
the CPU begins execution from reset vector which is stored
in address FFFE
and FFFFH as shown in Figure 8-6.
H
As shown in Figure 8-5, each area is assigned a fix ed location in Program Memory. Program Memory area contains
the user program.
A000
H
C000
H
E000
H
FEFF
H
FF00
FFC0
FFDF
FFE0
FFFF
H
H
H
H
H
TCALL area
Interrupt
Vector Area
PCALL area
GMS81508B, 8K ROM
GMS815024B, 24K ROM
GMS815016B, 16K ROM
it is more useful to save program byte length.
Table Call (TC ALL) causes the CP U to jump to each
TCALL address, where it commences the execution of the
service routine. The Table Call service area spaces 2-byte
for every TCALL: 0FFC0
for TCALL15, 0FFC2H for
H
TCALL14, etc., as shown in Figure 8-7.
Example: Usage of TCALL
The interrupt causes the CPU to jum p to specific location,
where it commences the execution of the service routine.
The External interrupt 0, for example, is assigned to location 0FFFA
interval: 0FFF8
0FFFA
Any area from 0FF00
. The interrupt service locations spaces 2-byte
H
and 0FFF9H for External Interru pt 1,
and 0FFFBH for External Interrupt 0, etc.
H
H
to 0FFFFH, if it is not going to be
H
used, its service location is available as general purpose
Program Memory.
Figure 8-5 Program Memory Map
Page Call (PCALL) area contains subroutine program to
reduce program byte length by using 2 bytes PCALL instead of 3 bytes CALL instruction. If it is frequently called,
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 21
Figure 8-6 Interrupt Vector Area
Page 25
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
11111111 11010110
01001010
PC:
FH FH DH 6H
4A
~
~
~
~
25
0FFD6
H
0FF00
H
0FFFF
H
D1
NEXT
0FFD7
H
➊
➋
➌
0D125
H
Reverse
Address
0FF00
0FFFF
PCALL Area Memory
H
PCALL Area
(256 Bytes)
H
Address P ro gra m Mem o r y
0FFC0
H
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
C8
C9
CA
CB
CC
CD
CE
CF
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
DA
DB
DC
DD
DE
DF
NOTE:
* means that the BRK software interrupt is using
same address with TCALL0.
TCALL 15
TCALL 14
TCALL 13
TCALL 12
TCALL 11
TCALL 10
TCALL 9
TCALL 8
TCALL 7
TCALL 6
TCALL 5
TCALL 4
TCALL 3
TCALL 2
TCALL 1
TCALL 0 / BRK *
PCALL
→
→
→ →
rel
4F35 PCALL 35H
0FF00
0FF35
0FFFF
Figure 8-7 PCALL and TCALL Memory Area
TCALL
→
→
→ →
n
4A TCALL 4
4F
35
~
~
H
H
NEXT
H
~
~
22 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 26

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
Example: The usage software example of Vector address for GMS81524B.
ORG 0FFE0H
DW NOT_USED
DW NOT_USED
DW SIO ; Serial Interface
DW BIT_TIMER ; Basic Interval Timer
DW WD_TIMER ; Watchdog Timer
DW ADC ; ADC
DW TIMER3 ; Timer-3
DW TIMER2 ; Timer-2
DW TIMER1 ; Timer-1
DW TIMER0 ; Timer-0
DW INT3 ; Int.3
DW INT2 ; Int.2
DW INT1 ; Int.1
DW INT0 ; Int.0
DW NOT_USED ; DW RESET ; Reset
; ORG 0C000H ; 16K ROM Start address
; ORG 0E000H ; 8K ROM Start address
;*******************************************
; MAIN PROGRAM *
;*******************************************
;
RESET: DI ;Disable All Interrupts
RAM_CLR: LDA #0 ;RAM Clear(!0000H->!00BFH)
;
;
ORG 0A000H ; 24K ROM Start address
CLRG
LDX #0
STA {X}+
CMPX #0C0H
BNE RAM_CLR
LDX #0FEH ;Stack Pointer Initialize
TXSP
LDM R0, #0 ;Normal Port 0
LDM R0DD,#82H ;Normal Port Direction
:
:
:
LDM TDR0,#250 ;8us x 250 = 2000us
LDM TM0,#1FH ;Start Timer0, 8us at 8MHz
LDM IRQH,#0
LDM IRQL,#0
LDM IENH,#0C8H ;Enable Timer0, INT0, INT1
LDM IENL,#0
LDM IEDS,#55H ;Select falling edge detect on INT pin
LDM PMR4,#3H ;Set external interrupt pin(INT0, INT1)
EI ;Enable master interrupt
:
:
:
:
NOT_USED:NOP
:
RETI
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 23
Page 27
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
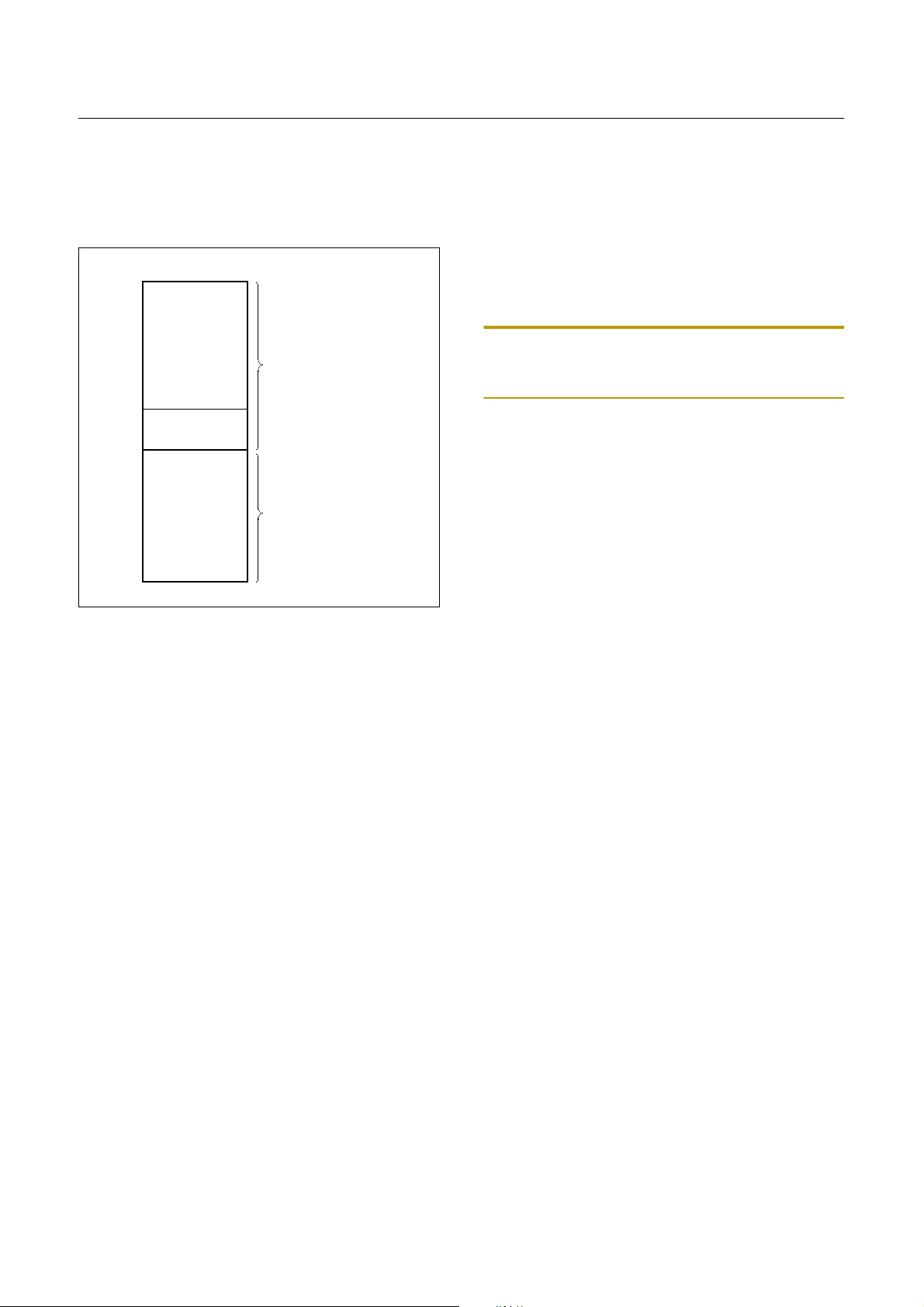
8.3 Data Memory
Figure 8-8 shows the internal Data Memory space available. Data Memory is divided in to four groups, a user RAM,
control registers, Stack, and LCD memory.
0000
H
Note that unoccupied addresses may not be implemented
on the chip. Read accesses to these addresses will in general return random data, and write accesses will have an indeterminate effect.
More detailed informations of each register are explained
in each peripheral section.
User Memory
00BF
00C0
00FF
0100
01FF
H
H
H
H
H
Control
Registers
User Memory
or Stack Area
PAGE0
PAGE1
When “G-flag=0”,
this page is selected
When “G-flag=1”
Figure 8-8 Data Memory Map
User Memory
The GMS815xxB has 448 × 8 bits for th e user me mory
(RAM).
Control Registers
The control registers are used by the CPU and Peripheral
function blocks for controlling the desired operation of the
device. Therefore these registers contain control and status
bits for the interrupt system, the timer/ counters, analog to
digital converters and I/O ports. The control registers are in
address range of 0C0
to 0FFH.
H
Note: Write only registers can not be accessed by bit manipulation instruction. Do not use read-modify-write instruction. Use byte manipulation instruction, for example “LDM”.
Example; To write at CKCTLR
LDM CLCTLR,#09H
;Divide ratio(÷32)
Stack Area
The stack provides the area where the return address is
saved before a jump is performed during the processing
routine at the execution of a subroutine call instruction or
the acceptance of an interrupt.
When returning from the processing routine, execu ting the
subroutine return instruction [RET] restores the contents of
the program counter from the stack; ex ecuting the interrupt
return instruction [RETI] restores the contents of the program counter and flags.
The save/restore locations in the stack are determined by
the stack pointed (SP). The SP is automatically decreased
after the saving, and increased before the restoring. This
means the value of the SP indicates the stack location
number for the next save. Refer to Figure 8-4 on page 20.
24 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 28
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
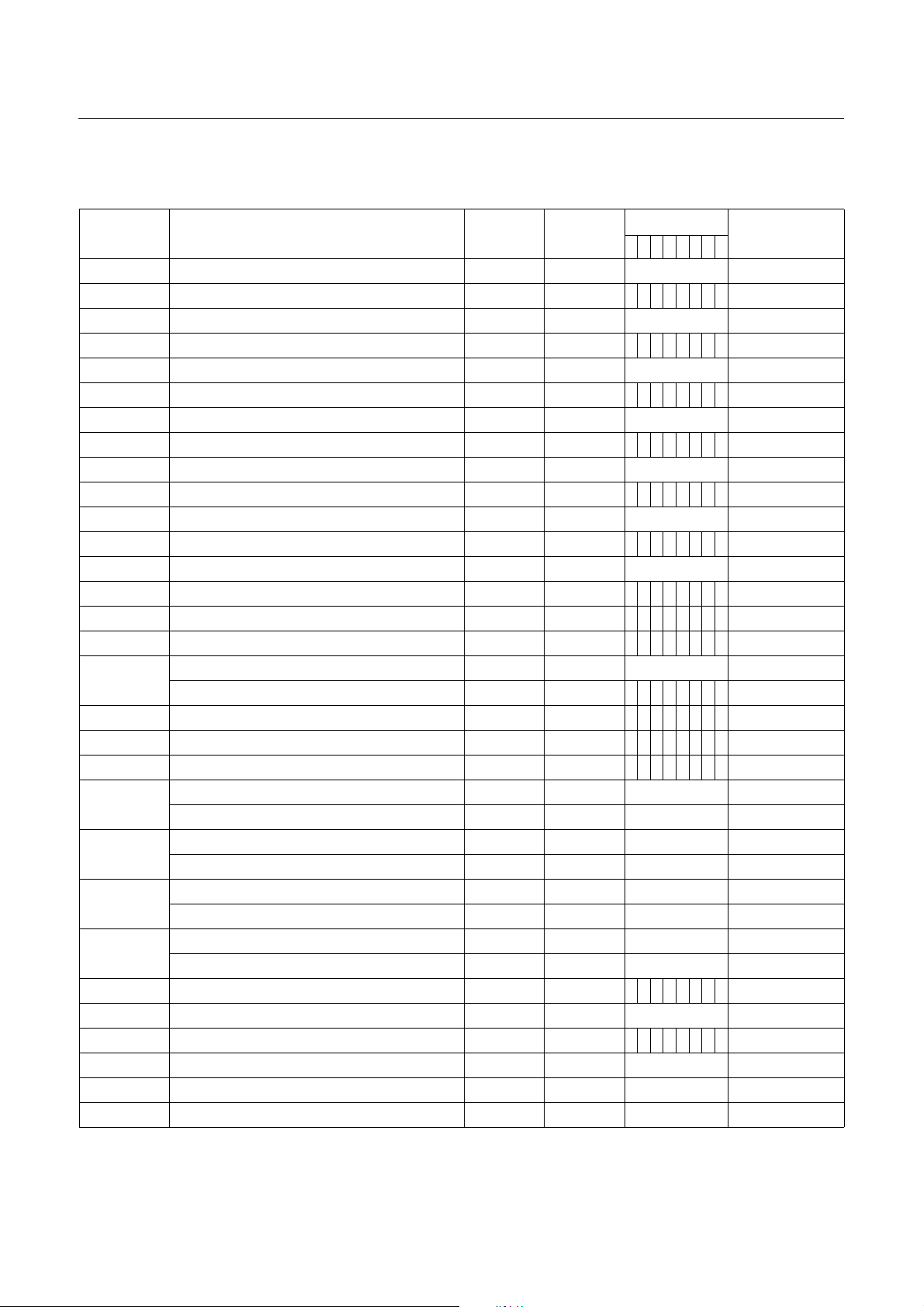
Address Register Name Symbol R/W
Initial Value
76543210
Page
00C0 R0 port data register R0 R/W Undefined page 31
00C1 R0 port I/O direction reg ister R0DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page 31
00C2 R1 port data register R1 R/W Undefined page 31
00C3 R1 port I/O direction reg ister R1DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page 31
00C4 R2 port data register R2 R/W Undefined page 31
00C5 R2 port I/O direction reg ister R2DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page 31
00C6 R3 port data register R3 R/W Undefined page 32
00C7 R3 port I/O direction reg ister R3DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page 32
00C8 R4 port data register R4 R/W Undefined page 32
00C9 R4 port I/O direction reg ister R4DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page 32
00CA R5 port data register R5 R/W Undefined page 33
00CB R5 port I/O direction register R5DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page 33
00CC R 6 port data register R6 R/W Undefined page 33
00CD R6 port I/O direction register R6DD W 0 0 0 0 - - - - page 33
00D0 R4 port mode register PMR4 W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
00D1 R5 port mode register PMR5 W - - 0 0 - - - -
page 32, page 63
page 33, page 55
Basic interval timer mode register BITR R Undefined page 35
00D3
Clock contr ol register CKCTLR W - - 0 1 0 1 1 1 page 35
00E0 Watchdog Timer Register WDTR W - 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 page 64
00E2 Timer mode register 0 TM0 R/W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page 37
00E3 Timer mode register 2 TM2 R/W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page 37
Timer 0 data register TDR0 W Undefined page 37
00E4
00E5
Timer 0 counter register T0 R Undefined page 37
Timer 1 data register TDR1 W Undefined page 37
Timer 1 counter register T1 R Undefined page 37
Timer 2 data register TDR2 W Undefined page 37
00E6
Timer 2 counter register T2 R Undefined page 37
Timer 3 data register TDR3 W Undefined page 37
00E7
Timer 3 counter register T3 R Undefined page 37
00E8 A/D converter mode register ADCM R/W - - 0 0 0 0 0 1 page 47
00E9 A/D converter data register ADR R Undefined page 47
00EA Serial I/O mode register SIOM R/W - 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 page 49
00EB Serial I/O register SIOR R/W Undefined page 49
00EC Buzzer driver regi ste r BUR W Undefined page 55
00F0 PWM0 duty register PWMR0 W Undefined page 53
Table 8-1 Control Registers
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 25
Page 29
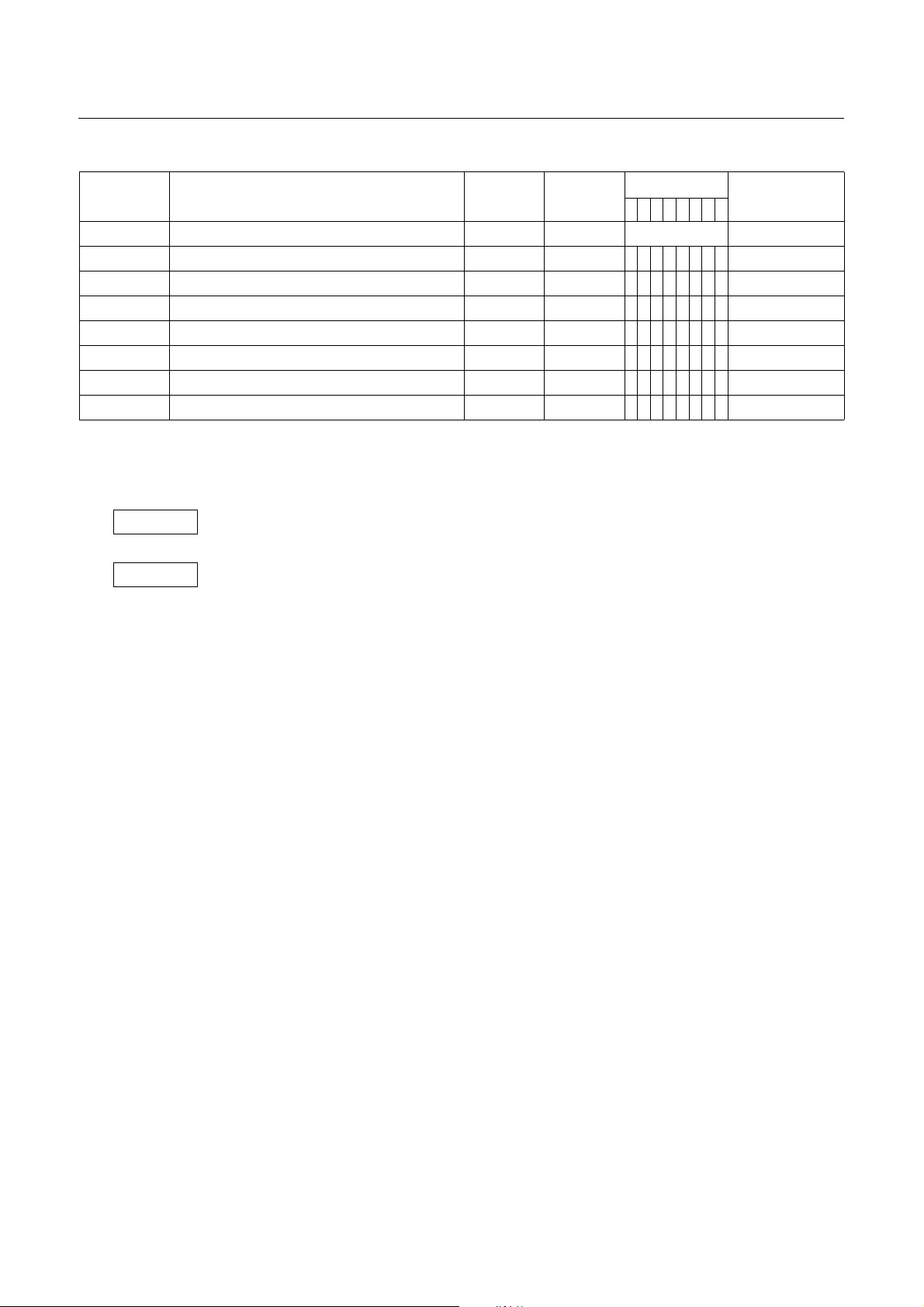
GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
Address Register Name Symbol R/W
Initial Value
76543210
Page
00F1 PWM1 duty register PWMR1 W Undefined page 53
00F2 PWM control register PWMCR W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page 53
00F4 Interrupt enable register low IENL R/W 0 0 0 0 - - - - page 58
00F5 Interrupt request flag register low IRQL R/W 0 0 0 0 - - - - page 57
00F6 Interrupt enable register high IENH R/W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page 58
00F7 Interrupt request flag register high IRQH R/W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page57
00F8 External interrupt edge selection register IEDS W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 page 63
00F9 Power fail detection register PFDR R/W - - - - 1 1 0 0 page 71
Table 8-1 Control Registers
W
R/W
- : this bit location is reserved.
Registers are controlled by byte manipulation instruction such as LDM etc., do not use bit manipulation
instruction such as SET1, CLR1 etc. If bit manipulation instruction is used on these registers,
content of other seven bits are may varied to unwanted value.
Registers are controlled by both bit and byte manipulation instruction.
26 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 30
HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
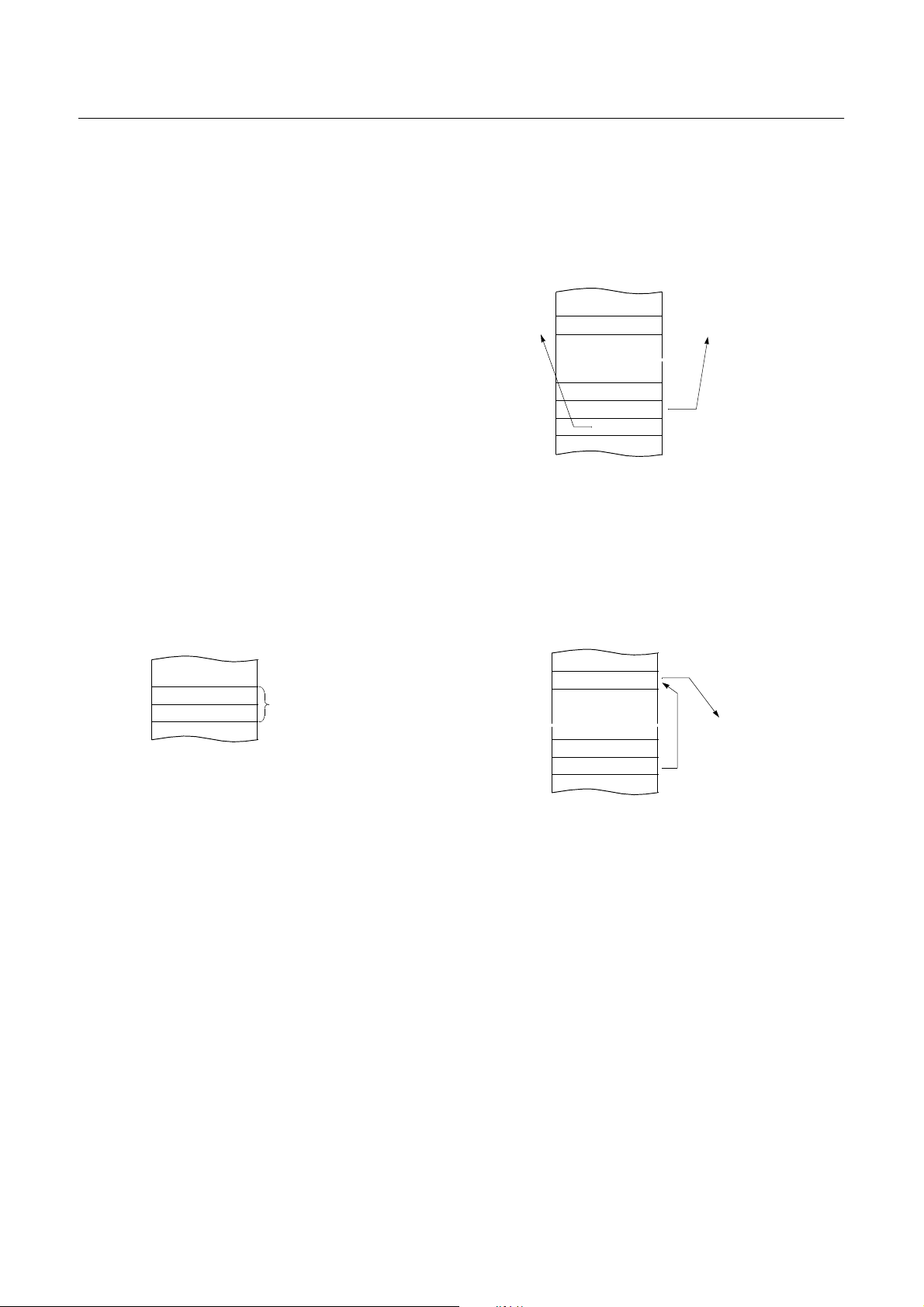
8.4 Addressing Mode
The GMS800 series MCU uses six addressing modes;
• Register addressing
• Immediate addressing
• Direct page addressing
• Absolute addressing
• Indexed addressing
• Register-indirect addressing
(1) Register Addressing
Register addressing accesses the A, X, Y, C and PSW.
(2) Immediate Addressing
→
→
→ →
#imm
In this mode, second byte (operand) is accessed as a data
immediate ly.
Example:
0435 ADC #35H
MEMORY
Example: G=1
E45535 LDM 35H,#55H
0135H
➊
0F100H
0F101H
0F102H
(3) Direct Page Addressing
data
~
~
~
~
data ¨ 55H
➋
E4
55
35
dp
→
→
→ →
In this mode, a address is specified within direct page.
Example; G=0
C535 LDA 35H ;A ←RAM[35H]
04
35
A+35H+C → A
When G-flag is 1, then RAM address is defined by 16-bit
address which is composed of 8-bit RAM paging register
(RPR) and 8-bit immediate data.
35H
0E550H
0E551H
data
➋
~
~
C5
35
~
~
data → A
➊
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 27
Page 31

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
(4) Absolute Addressing
→
→
→ →
!abs
Absolute addressing sets corresponding memory data to
Data, i.e. second byte (Operand I) of command becomes
lower level address and third byte (Operand II) becomes
upper level address.
With 3 bytes command, it is possible to access to whole
memory area.
ADC, AND, CMP, CMPX, CMPY, EOR, LDA, LDX,
LDY, OR, SBC, STA, STX, STY
Example;
0735F0 ADC !0F035H ;A ←ROM[0F035H]
0F035H
0F100H
0F101H
0F102H
data
~
~
07
35
F0
~
~
➋
A+data+C → A
➊
address: 0F035
The operation within data memory (RAM)
ASL, BIT, DEC, INC, LSR, ROL, ROR
ADC, AND, CMP, EOR, LDA, OR, SBC, STA, XMA
Example; X=15
D4 LDA {X} ;ACC←RAM[X].
115H
~
~
H
data
, G=1
➋
~
~
data → A
➊
0E550H
X indexed direct page, auto increment
D4
→
→
→ →
{X}+
In this mode, a address is specified within direct page by
the X register and the content of X is increased by 1.
LDA, STA
Example; G=0, X=35
DB LDA {X}+
H
Example; Addressing accesses the address 0135
regard-
H
less of G-flag.
983501 INC !0135H ;A ←ROM[135H]
135H
0F100H
0F101H
0F102H
data
~
~
98
35
01
~
~
➌
➋
data+1 → data
➊
address: 0135
(5) Indexed Addressing
X indexed direct page (no offset)
→
→
→ →
{X}
In this mode, a address is specified by the X register.
35H
X indexed direct page (8 bit offset)
data
~
~
DB
~
~
➊
➋
data Æ A
36H Æ X
→
→
→ →
dp+X
This address value is the second byte (Operand) of command plus the data of -register. And it assigns the memory in Direct page.
ADC, AND, CMP, EOR, LDA, LDY, OR, SBC, STA
STY, XMA, ASL, DEC, INC, LSR, ROL, ROR
Example; G=0, X=0F5
H
28 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 32

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
H
C645 LDA 45H+X
3AH
data
➌
~
~
0E550H
0E551H
C6
45
Y indexed direct page (8 bit offset)
~
~
➋
➊
45H+0F5H=13AH
data → A
→
→
→ →
dp+Y
This address value is the second byte (Operand) of command plus the data of Y- register, whic h assigns Memory in
Direct page.
This is same with above (2). Use Y register instead of X.
Y indexed absolute
!abs+Y
→
→
→ →
Sets the value of 16-bit absolute address plus Y-register
data as Memory.This addressing mode can specify memory in whole area.
Example; Y=55
D500FA LDA !0FA00H+Y
0F100H
0F101H
0F102H
~
~
0FA55H
H
D5
00
FA
data
➊
0FA00H+55H=0FA55H
~
~
➋
data → A
➌
Example; G=0
3F35 JMP [35H]
35H
36H
~
~
0E30AH
~
~
0FA00H
X indexed indirect
0A
E3
NEXT
3F
35
[dp+X]
→
→
→ →
~
~
~
~
➋
➊
jump to
address 0E30AH
Processes memory data as Data, assigned by 16-bit pair
memory which is determined by pair data
[dp+X+1][dp+X] Operand plusX-register data in Direct
page.
ADC, AND, CMP, EOR, LDA, OR, SBC, STA
Example; G=0, X=10
1625 ADC [25H+X]
35H
36H
~
~
0E005H
~
~
0FA00H
05
E0
data
16
25
H
0E005H
➋
~
~
25 + X(10) = 35
➊
~
~
A + data + C → A
➌
(6) Indirect Addressing
Direct page indirect
→
→
→ →
[dp]
Assigns data address to use for accomplishing command
which sets memory data (or pair memory) by Operand.
Also index can be used with Index register X,Y.
Y indexed indirect
Processes memory data as Data, assigned by the data
[dp+1][dp] of 16-bit pair memory paired by Operan d in Direct pageplus Y-register data.
ADC, AND, CMP, EOR, LDA, OR, SBC, STA
Example; G=0, Y=10
H
→
→
→ →
[dp]+Y
JMP, CALL
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 29
Page 33

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
1725 ADC [25H]+Y
25H
26H
~
~
0E015H
~
~
0FA00H
Absolute indirect
05
E0
data
17
25
→
→
→ →
~
~
~
~
[!abs]
➋
➊
0E005H + Y(10)
= 0E015H
➌
A + data + C → A
The program jumps to address specified by 16-bit absolute
address.
JMP
Example; G=0
1F25E0 JMP [!0C025H]
PROGRAM MEMORY
➊
0E025H
0E026H
0E725H
0FA00H
~
~
~
~
25
E7
NEXT
1F
25
E0
~
~
~
~
➋
jump to
address 0E30AH
30 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 34

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
R1 Data Register
R1
ADDRESS: 0C2
H
RESET VALUE: Undefined
R17
R16 R15 R14 R13
R12 R11 R10
Port Direction
R1 Direction Register
R1DD
ADDRESS: 0C3
H
RESET VALUE: 00
H
0: Input
1: Output
Input / Output data
R2 Data Register
R2
ADDRESS: 0C4
H
RESET VALUE: Undefined
R27 R26 R25 R24 R23 R22 R21 R20
Port Direction
R2 Direction Register
R2DD
ADDRESS: 0C5
H
RESET VALUE: 00
H
0: Input
1: Output
Input / Output data
9. I/O PORTS
The GMS815xxB has seve n ports (R0, R1, R2, R4, R5, and
R6).These ports pins may be multiplexed with an alternate
function for the peripheral features on the device.
All pins have data direction registers which can define
these ports as output or input. A “1” in the port direction
register configure the corresponding port pin as output.
Conversely, write “0” to the corresponding bit to specif y it
as input pin. For example, to use the even numbered bit of
R0 as output ports and the odd numbe red bits as input
ports, write “55
” to address 0C1H (R0 port direction reg-
H
ister) during initial setting as shown in Figure 9-1.
All the port direction registers in the GMS815xxB have 0
written to them by reset function. On the other hand, its initial status is input.
0C0
0C1
0C2
0C3
WRITE “55
H
R0 direction
H
H
R1 direction
H
R0 data
R1 data
” TO PORT R0 DIRECTION REGISTER
H
0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
76543210
I O I O I O I O
76543210
I: INPUT PORT
O: OUTPUT PORT
BIT
PORT
R1 and R1DD register:
al I/O port (address 0C2
R1 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirection-
). Each I/O pin can independently
H
used as an input or an output through the R1DD register
(address 0C3
R2 and R2DD register:
al I/O port (address 0C4
).
H
R2 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirection-
). Each I/O pin can independently
H
used as an input or an output through the R2DD register
(address 0C5
).
H
Figure 9-1 Example of port I/O assignment
R0 and R0DD register:
al I/O port (address 0C0
used as an input or an output through the R0DD register
(address 0C1
R0 Data Register
R0
R0 Direction Register
R0DD
R0 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirection-
). Each I/O pin can independently
H
).
H
ADDRESS: 0C0
RESET VALUE: Undefined
R07 R06 R05 R04 R03 R02 R01 R0 0
Input / Output data
ADDRESS: 0C1
RESET VALUE: 00
Port Direction
0: Input
1: Output
H
H
H
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 31
Page 35

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
R4 Port Mode Register
PMR4
ADDRESS: 0D0
H
RESET VALUE: 00
H
0: R40
1: INT0
0
0: R41
1: INT1
0: R42
1: INT2
0: R43
1: INT3
0: R44
1: EC0
0: R45
1: EC2
0: R46
1: T1O
0: R47
1: T3O
1234567
Edge Selection Register
IEDS
ADDRESS: 0F8H
RESET VALUE: 00H
01234567
INT0
INT1INT2INT3
External Interrupt Edge Select
00: Reserved
01: Falling (1-to-0 transition)
10: Rising (0-to-1 transition)
11: Both (Rising & Falling)
R4 Data Register
R4
ADDRESS: 0C8
H
RESET VALUE: Undefined
R47 R46 R45
R44
R43 R42 R41 R40
Port Direction
R4 Direction Register
R4DD
ADDRESS: 0C9
H
RESET VALUE: 00
H
0: Input
1: Output
Input / Output data
R3 and R3DD register:
al I/O port (address 0C6
used as an input or an output through the R0DD register
(address 0C7
R3 Data Register
R3
R3 Direction Register
R3DD
R4 and R4DD register:
al I/O port (address 0C8
used as an input or an output through the R4DD register
(address 0C9
In addition, Port R4 is multiplexed with va rious special
features. The control register PMR4 (address 0D0
trols the selection of alternate function. After reset, this
value is “0”, port may be used as normal I/O port.
To use alternate function such as external interrupt, external counter input or timer clock out, write “1” in the corresponding bit of PMR4.
Port Pin Alternate Function
R3 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirection-
). Each I/O pin can independently
H
).
H
ADDRESS: 0C6
RESET VALUE: Undefined
R37 R36 R35 R34 R33 R32 R31 R3 0
Input / Output data
ADDRESS: 0C7
RESET VALUE: 00
Port Direction
0: Input
1: Output
R4 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirection-
). Each I/O pin can independently
H
).
H
Regardless of the direction register R4DD, PMR4 is selected to use as alternate functions, port pin can be used as a
corresponding alternate features.
H
H
H
) con-
H
R40
R41
R42
R43
R44
R45
R46
R47
32 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
INT0 (External Interrupt 0)
INT1 (External Interrupt 1)
INT2 (External Interrupt 2)
INT3 (External Interrupt 3)
EC0
(External count input to Timer/
Counter 0)
(External count input to Timer/
EC2
Counter 2)
T1O (Timer 1 Clock-out)
T3O (Timer 3 Clock-out)
Page 36

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
R6 Data Register
R6
ADDRESS: 0CC
H
RESET VALUE: Undefined
R67 R66 R65 R64 R63 R62 R61 R6 0
Port Direction
R6 Direction Register
R6DD
ADDRESS: 0CD
H
RESET VALUE: 0000----
B
0: Input
1: Output
Input / Output data
----
R60~R63 are input
Input data
only
R5 and R5DD register:
al I/O port (addr ess 0 CA
R5 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirection-
). Each I/O pin can independent-
H
ly used as an input or an outp ut thro ugh th e R5DD register
(address 0CB
Port Pin
R54
R55
The control register PMR5 (address D1
).
H
Alternate Function
WDTO (Watchdog timer output)
BUZ (Square-wave output for buzzer)
) controls the se-
H
lection alternate function. After reset, this value is “0”, port
may be used as general I/O ports. To use buzzer function,
write “1” to the PMR5 and the pi n R 55 mus t be defined as
output mode (the bit 5 of R5DD=1)
R5 Data Register
R5
R57 R56 R55 R54 R53
R5 Direction Register
R5DD
ADDRESS: 0CA
RESET VALUE: Undefined
R52 R51
Input / Output data
ADDRESS: 0CB
RESET VALUE: 00
Port Direction
0: Input
1: Output
R50
H
H
H
R6 and R6DD register:
al I/O port (address 0CC
R6 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirection-
). Each I/O pin can independent-
H
ly used as an input or an output throu gh the R6DD regis ter
(address 0CD
Port Pin
R60
R61
R62
R63
R64
R65
R66
R67
R6DD (address CD
).
H
Alternate Function
AN0 (ADC input 0)
AN1 (ADC input 1)
AN2 (ADC input 2)
AN3 (ADC input 3)
AN4 (ADC input 4)
AN5 (ADC input 5)
AN6 (ADC input 6)
AN7 (ADC input 7)
) controls the direction of the R6 pins,
H
even when they are being used as analog inputs. The user
must make sure to keep the p ins conf igured as inputs when
using them as analog inputs.
Note: On the initial RESET, R60 can not be used di gital in put port, because this port is selected as an analog input
port by ADCM register. To use this port as a digital I/O port,
change the value of lower 4 bits of ADCM (address 0E8
H
On the other hand, R6 port, all eight pins can not be used
as digital I/O port simultaneously. At least one pin is used
as an analog input.
).
R5 Port Mode Register
PMR5
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 33
BUZ
WDTO
--
R54/WDTO Selection
0: R54
1: WDTO (Output)
R55/BUZ Selection
0: R55
1: BUZ (Output)
ADDRESS: 0D1
RESET VALUE: --00----
H
----
B
Page 37

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
10. BASIC INTERVAL TIMER
The GMS815xxB has one 8-bit Basic Interval Timer that
is free-run and can not stop. Bloc k diagram is shown in
Figure 10-1.
In addition, the Basic Interval Timer generates the time
base for watchdog timer counting. It also provides a Basic
interval timer interrupt (BITIF). As the count overflow
from FF
to 00H, this overflow causes th e interrupt to be
H
16
÷
32
÷
64
÷
128
PIN
X
IN
÷
256
÷
512
÷
Prescaler
1024
÷
2048
÷
Select Input clock
]
[0D3
H
Basic Interval Timer
clock control register
MUX
source
clock
3
BTS[2:0]
CKCTLR
[0F9
8-bit up-counter
BITR
]
H
clear
BTCL
Internal bus line
generated. The Basic Interval T imer is controlled by the
clock control register (CKCTLR) shown in Figure 10-2.
Source clock can be selected by lower 3 bits of CKCTLR.
BITR and CKCTLR are located at same address, and ad-
dress 0F9
overflow
Read
is read as a BITR, and written to CKCTLR.
H
BITIF
Basic Interval Timer Interrupt
To Watchdog timer (WDTCK)
CKCTLR
[2:0]
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
Figure 10-1 Block Diagram of Basic Interval Timer
Source clock
16
f
÷
XIN
f
32
÷
XIN
f
64
÷
XIN
f
128
÷
XIN
f
256
÷
XIN
f
512
÷
XIN
f
1024
÷
XIN
f
2048
÷
XIN
Interrupt (overflow) Period (ms)
= 8MHz
@ f
XIN
0.512
1.024
2.048
4.096
8.192
16.384
32.768
65.536
Table 10-1 Basic Interval Timer Interrupt Time
34 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 38

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
76543210
CKCTLR
--
Caution:
Both register are in same address,
when write, to be a CKCTLR,
when read, to be a BITR.
76543210
BITR
8-BIT FREE-RUN BINARY COUNTER
WDTON
ENPCK
BTCL
BTCL
BTCL
BTS1
BTS0BTS2
Basic Interval Timer source clock select
000: f
001: f
010: f
011: f
100: f
101: f
110: f
111: f
Clear bit
0: Normal operation (free-run)
1: Clear 8-bit counter (BITR) to “0”. This bit becomes 0 automatically
Enable Peripheral clock
If this bit is 0, all peripherals are disabled such as Timer, ADC, PWM, etc.
0: Operate as a 6-bit general timer
1: Enable Watchdog Timer ope rat ion
See the section “Watchdog Timer”.
Figure 10-2 BITR: Basic Interval Timer Mode Register
Example 1:
Interrupt request flag is generated every 8.19 2ms at 4MHz.
ADDRESS: 0D3
INITIAL VALUE: --01 0111
÷ 16
XIN
÷ 32
XIN
÷ 64
XIN
÷ 128
XIN
÷ 256
XIN
÷ 512
XIN
÷ 1024
XIN
÷ 2048
XIN
after one machine cycle, and starts counting.
ADDRESS: 0D3
INITIAL VALUE: Undefined
H
B
H
:
LDM CKCTLR,#1BH
SET1 BITE
EI
:
Example 2:
Interrupt request flag is generated every 8.19 2ms at 8MHz.
:
LDM CKCTLR,#1CH
SET1 BITE
EI
:
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 35
Page 39

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
11. TIMER/EVENT COUNTER
The GMS815xxB has four Timer/Counter registers. Each
module can generate an interrupt to indicate that an event
has occurred (i.e. timer match).
Timer 0 and Timer 1 are can be used either two 8-bit Timer/Counter or one 16-bit Timer/Counter with combine
them. Also Timer 2 and Timer 3 are same.
In the “timer” function, the register is increased every internal clock input. Thus , one can th ink of it as count ing in ternal clock input. Since a least clock consists of 4 and
most clock consists of 64 oscillator periods, the count rate
is 1/4 to 1/64 of the oscillator frequency.
In the “counter” function, the register is incremented in response to a 1-to-0 (falling edge) transition at its corre-
TM0
CAP
T1ST
0
0X
0 X X X 00 8-bit Event counter 8-bit Timer
1 X X X 01 or 10 or 11 8-bit Capture (internal clock) 8-bit Timer
1 X X X 00 8-bit Capture (external clock) 8-bit Timer
0X
0 X X X 00 16-bit Event counter
1 X X X 01 or 10 or 11 16-bit Capture (internal clock)
1 X X X 00 16-bit Capture (external clock)
T1SL
[1:0]
01 or
10 or
11
00
T0ST T0CN T0SL[1:0]
X X 01 or 10 or 11 8-bit Timer 8-bit Timer
X X 01 or 10 or 11 16-bit Timer
sponding external input pin, EC0
In addition the “capture” function, the register is incre-
mented in response external or internal clock sources same
with timer or counter function. When external clock edge
input, the count register is captured into Timer data register
correspondingly.
It has four oper ating modes: “8-bit timer/counter”, “16-bit
timer/counter”, “8-bit capture”, “16-bit capture” which are
selected by bit in Timer mode register TM0 and TM2 as
shown in Table 11-1.
In operation of Timer 2, Timer 3, their operations are same
with Timer 0, Timer 1, respectively as shown in Table 11-
2.
TIMER 0 TIMER 1
or EC2.
Table 11-1 TM0 Timer Mode Register
TM2
CAP
T3ST
2
0X
0 X X X 00 8-bit Event counter 8-bit Timer
1 X X X 01 or 10 or 11 8-bit Capture (internal clock) 8-bit Timer
1 X X X 00 8-bit Capture (external clock) 8-bit Timer
0X
0 X X X 00 16-bit Event counter
1 X X X 01 or 10 or 11 16-bit Capture (internal clock)
1 X X X 00 16-bit Capture (external clock)
T3SL
[1:0]
01 or
10 or
11
00
T2ST T2CN T2SL[1:0]
X X 01 or 10 or 11 8-bit Timer 8-bit Timer
X X 01 or 10 or 11 16-bit Timer
Table 11-2 TM2 Timer Mode Register
TIMER 2 TIMER 3
36 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 40

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
TM0
TIMER 1
TIMER 0
76543210
T1STCAP 0 T0SL1
BTCL
T0SL0T0CNT0STT1SL1 T1SL0
Bit Name Bit Position Description
CAP0 TM0.7 0: Timer/Counter mode
1: Capture mode selection flag
T1ST TM0.6 0: When cleared, stop the counting.
1: When set, Timer 1 count register is cleared and start again.
T1SL1
T1SL0
TM0.5
TM0.4
00: 16-bit mode (Clock source is sel ected by T0SL1, T0SL0)
01: 8-bit mode, Clock source is f
10: 8-bit mode, Clock source is f
11: 8-bit mode, Clock source is f
T0ST TM0.3 0: When cleared, stop the counting.
1: When set, Timer 0 Count Register is cleared and start again.
T0CN TM0.2 0: Stop the timer
1: A logic 1 starts the timer.
T0SL1
T0SL0
TM0.1
TM0.0
00: EC0 (External clock)
01: 8-bit Timer, Clock source is f
10: 8-bit Timer, Clock source is f
11: 8-bit Timer, Clock source is f
ADDRESS: 0E2
INITIAL VALUE: 00
÷ 4
XIN
÷ 16
XIN
÷ 64
XIN
÷ 4
XIN
÷ 16
XIN
÷ 64
XIN
H
H
TM2
TIMER 3
TIMER 2
TDR0~TDR3
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
76543210
T3STCAP2 T2SL1
Bit Name Bit Posi-
tion
BTCL
Description
T2SL0T2CNT2STT3SL1 T3SL0
CAP2 TM2.7 0: Timer/Coun ter mode
1: Capture mode selection flag
T3ST TM2.6 0: When cleared, stop the counting.
1: When set, Timer 3 count register is cleared and start again.
T3SL1
T3SL0
TM2.5
TM2.4
00: 16-bit mode (Clock source is selected by T2SL1, T2SL0)
01: 8-bit mode, Clock source is f
10: 8-bit mode, Clock source is f
11: 8-bit mode, Clock source is f
XIN
XIN
XIN
T2ST TM2.3 0: When cleared, stop the counting.
1: When set, Timer 2 Count Register is cleared and start again.
T2CN TM2.2 0: Stop the timer
1: A logic 1 starts the timer.
T2SL1
T2SL0
TM2.1
TM2.0
00: EC0 (External clock)
01: 8-bit T imer, Clock source is f
10: 8-bit T imer, Clock source is f
11: 8-bit T imer, Clock source is f
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
76543210
XIN
XIN
XIN
ADDRESS: 0E4
INITIAL VALUE: Undefined
ADDRESS: 0E3
INITIAL VALUE: 00
÷ 4
÷ 16
÷ 64
÷ 4
÷ 16
÷ 64
H
~ 0E7
H
H
H
Read: Count value read
Write: Compare data write
Figure 11-1 TM0, TM2 Registers
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 37
Page 41

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
11.1 8-bit Timer / Counter Mode
The GMS815xxB has four 8-bit Timer/Counters, Timer 0,
Timer 1, Timer 2, Timer 3. The Timer 0, Timer 1 are
shown in Figure .
The “timer” or “counter” function is selected by control
registers TM0, TM2 as shown in Table 11-1 and Table 11 -
2. To use as an 8-bit timer/counter mode, bit CAP0 of TM0
is cleared to “0” and bits T1SL1, T1SL0 of TM0 or bits
76543210
EC0 PIN
XIN PIN
TM0
T1STCAP0 T0SL1
0X XXXX
T0SL[1:0]
00
4
÷
#
01
16
÷
#
10
64
÷
#
Prescaler
11
MUX
BTCL
01 or 10 or 11
T0CN
TIMER 0
T3SL1, T3SL0 of TM2 shoul d not set to zero. Thes e timers
have each 8-bit count register and data register. The count
register is increased by every internal or external clock input. The internal clock has a prescaler divide ratio option
of 4, 16, 64 (selected by control bits TxSL1, TxSL0 of register TMx).
T0SL0T0CNT0STT1SL1 T1SL0
X means don’t care
T0ST
0: Stop
1: Clear and start
T0 (8-bit)
TDR0 (8-bit)
ADDRESS: 0E2
INITIAL VALUE: 00
clear
Comparator
T0IF
H
H
TIMER 0
INTERRUPT
T1SL[1:0]
4
÷
#
01
16
÷
#
10
64
÷
#
11
MUX
Example 1:
Timer0 = 4ms 8-bit timer mode at 4M Hz
Timer1 = 1ms 8-bit timer mode at 4M Hz
LDM TDR0,#250
LDM TDR1,#250
LDM TM0,#0110_1111B
SET1 T0E
SET1 T1E
EI
T1ST
0: Stop
1: Clear and start
T1 (8-bit)
clear
Comparator
TIMER 1
TDR1 (8-bit)
Figure 11-2 8-bit Timer/Counter 0, 1
Example 2:
Timer0 = 8-bit event counter mode
Timer1 = 1ms 8-bit timer mode at 4MHz
LDM TDR0,#250
LDM TDR1,#250
LDM TM0,#0110_1100B
SET1 T0E
SET1 T1E
EI
T1IF
F/F
TIMER 1
INTERRUPT
T1O PIN
38 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 42

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
Note: The contents of Timer data regist er TDRx shoul d be
initialized 1
~FFH, not 0H, because it is undefined after re-
H
set.
In the Timer 0, timer register T0 increments from 00H until
it matches TDR0 and then reset to 00H. The match output
of Timer 0 generates Timer 0 inter rupt (latched in T0IF bit)
As TDRx and Tx register are in same address, when read-
76543210
EC2 PIN
XIN PIN
TM2
Edge Detector
Prescaler
T3STCAP2 T2SL1
0X XXXX
T2SL[1:0]
00
4
÷
#
01
16
÷
#
10
64
÷
#
11
MUX
BTCL
01 or 10 or 11
T2CN
ing it as a Tx, written to TDRx.
In counter function, the counter is increased every 1-to-0
(falling edge) transition of EC0
or EC2 pin. In order to use
counter function, the bit 4, bit 5 of the Port mode register
PMR4 are set to “1”. The Timer 0 can be used as a counter
by pin EC0
Similarly, Timer 2 can be used b y pin EC2
input, but Timer 1 can input by internal clock.
input but Timer
3 can not.
T2SL0T2CNT2STT3SL1 T3SL0
X means don’t care
T2ST
0: Stop
1: Clear and start
T2 (8-bit)
Comparator
ADDRESS: 0E3
INITIAL VALUE: 00
clear
T2IF
H
H
TIMER 2
INTERRUPT
TIMER 2
T3SL[1:0]
4
÷
#
01
16
÷
#
10
64
÷
#
11
MUX
TIMER 3
Figure 11-3 8-bit Timer/Counter 2, 3
Example 3:
Timer2 = 8-bit timer mode, 2ms interval at 8MHz
Timer3 = 8-bit timer mode, 500us interval at 8MHz
LDM TDR2,#250
LDM TDR3,#250
LDM TM2,#0110_1111B
SET1 T2E
SET1 T3E
EI
TDR2 (8-bit)
T3ST
0: Stop
1: Clear and start
T3 (8-bit)
TDR3 (8-bit)
clear
Comparator
T3IF
F/F
TIMER 3
INTERRUPT
Example 4:
Timer2 = 8-bit event counter mode
Timer3 = 500us 8-bit timer mode at 8MHz
LDM TDR2,#250
LDM TDR3,#250
LDM TM2,#0110_1100B
SET1 T2E
SET1 T3E
EI
T3O PIN
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 39
Page 43

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
8-bit Timer Mode
In the timer mode, the internal clock is used for counting
up. Thus, you can think of it as counting internal clock input. The contents of TDRn are compared with the contents
of up-counter, Tn. If match is found, a timer 1 interrupt
(T1IF) is generated and the up-counter is cleared to 0.
Counting up is resumed after the up-counter is cleared.
As the value of TDRn is changeable by software, time interval is set as you want
Source clock
Up-counter
TDR1
T1IF interrupt
Start count
0
n
23
1
Figure 11-4 Timer Mode Timing Chart
Value of
TM[1:0]
00
01
10
11
Clock
Source
f
EC1
f
÷
XIN
f
÷
XIN
f
÷
XIN
4
16
64
Resolution
(At
=8 MHz)
f
XIN
1/f
EC1
0.5
2
8
Maximum Time
1/f
sec
us
us
us
Setting
(At
f
EC1
XIN
× 256
2048
=8 MH z)
128
512
sec
us
us
us
Table 11-1 Timer Source clock Interrupt Time
~
~
~
~
n-2
~
~
~
~
~
~
n-1
Match
Detect
n
0
Counter
Clear
2
1 4
3
Example:
When
INTERRUPT PERIOD =
TDR1
7D
0
Timer 1 (T1IF)
Interrupt
Make 1msinterrupt using by Timer0 at 8MHz
LDM TM0,#1FH ; divide by 64
LDM TDR0,#125 ; 8us x 125= 1ms
SET1 T0E ; Enable Timer 0 Interrupt
EI ; Enable Master Interrupt
TM0 = 0001 1111
TDR0 = 125
f
= 8 MHz
XIN
~
~
(8-bit Timer mode, Prescaler divide ratio = 64)
B
= 7D
D
H
1
8 × 106 Hz
1
0
Occur interrupt Occur interrupt Occur interrupt
×
MATCH
(TDR0 = T0)
cou
p-
u
4
3
2
Interrupt period
= 8 µs x 125
64 × 125 = 1 ms
7B
7A
nt
~
~
6
5
7C
7D
Count Pulse
Period
8 µs
~
~
TIME
Figure 11-5 Timer Count Example
40 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 44

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
8-bit Event Counter Mode
In this mode, counting up is started by an external trigger.
This trigger means falling edge of the EC0 or EC1 pin input. Source clock is used as an internal clock selected with
timer mode register TM0 or TM2. The contents of timer
data register TDRn (n = 0,1,2,3) are compared with the
contents of the up-counter Tn. If a match is found, an timer
interrupt request flag TnIF is generated, and the counter is
cleared to “0”. The counter is restart and count up continuously by every falling edge of the EC
The maximum frequency applied to the EC
n
pin input.
n
pin is f
XIN
/2
[Hz].
Start count
ECn pin input
Up-counter
TDR1
T1IF interrupt
0
1
n
2
Figure 11-6 Event Counter Mode Timing Chart
In order to use event counter function, the bit 4, 5 of the
Port Mode Register PMR4(add ress 0D0
) is required to be
H
set to “1”.
After reset, the value of timer data register TDRn is unde-
fined, it should b e initialized to between 1
H
"0"The interval period of Timer is calculated as below
equation.
1
---------- -
Period (sec)
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
n-1
=
0n
2 Divide Ratio TDRn
f
XIN
1
2
×××
~FF
H
not to
TDR1
Timer 1 (T1IF)
Interrupt
T1ST
Start & St op
T1CN
Control count
disable
clear & start
stop
~
~
Occur interrupt Occur interrupt
T1ST = 1
T1ST = 0
enable
~
~
up-count
T1CN = 1
T1CN = 0
Figure 11-7 Count Operation of Timer / Event counter
TIME
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 41
Page 45

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
11.2 16-bit Timer / Counter Mode
The Timer register is being run with all 16 bits . A 16-bit
timer/counter register T0, T1 are incremented from 0000
until it matches TDR0, TDR1 and then resets to 0000H.
The match output generates Timer 0 interrupt.
The clock source of the Timer 0 is selected either internal
or external clock by bit T0SL1, T0SL0.
76543210
TM0
EDGE DETECTOR
EC0 PIN
÷
XIN PIN
TIMER 0 + TIMER 1 → TIMER 0 (16-bit)
÷
÷
Prescaler
T1STCAP0 T0SL1
0X XXXX00
T0SL[1:0]
“00”
4
“01”
16
“10”
64
“11”
MUX
T0CN
T0STT1SL1 T1SL0
BTCL
X means don’t care
0
1
Higher byte
Even if the Timer 0 (including the Timer 1) is used as a 16-
H
bit timer, the Timer 2 and Timer 3 can still be used as either
two 8-bit timer or one 16-bit timer by setting the TM2. Reversely, even if the Timer 2 (including the Timer 3) is used
as a 16-bit timer, the Timer 0 and Timer 1 can still be used
as 8-bit timer independently.
T0ST
0: Stop
1: Clear and start
TDR1 + TDR0
(16-bit)
TDR1 + TDR0
(16-bit)
Lower byte
COMPARE DATA
T0SL0T0CN
clear
Comparator
ADDRESS: 0E2
INITIAL VALUE: 00
H
T0IF
H
TIMER 0
INTERRUPT
(Not Timer 1 interrupt)
76543210
TM2
EDGE DETECTOR
EC2 PIN
÷
XIN PIN
TIMER 2 + TIMER 3 → TIMER 2 (16-bit)
÷
÷
Prescaler
T3STCAP2 T2SL1
0X XXXX00
T2SL[1:0]
“00”
4
“01”
16
“10”
64
“11”
MUX
T2CN
T2STT3SL1 T3SL0
BTCL
X means don’t care
0
1
Higher byte
T2ST
TDR3 + TDR2
(16-bit)
TDR3 + TDR2
(16-bit)
COMPARE DATA
T2SL0T2CN
0: Stop
1: Clear and start
clear
Comparator
Lower byte
Figure 11-8 16-bit Timer/Counter
ADDRESS: 0E3
INITIAL VALUE: 00
H
T2IF
H
TIMER 2
INTERRUPT
(Not Timer 3 interrupt)
42 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 46

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
11.3 8-bit Capture Mode
The Timer 0 capture mode is set by bit CAP0 of timer
mode register TM0 (bi t CAP2 of tim er mode reg ister TM2
for Timer 2) as shown in Figure 21. In this mode, Timer 1
still operates as an 8-bit timer/counter.
As mentioned above, not on ly Timer 0 but Timer 2 can also
be used as a capture mode.
In 8-bit capture mode, Timer 1 and Timer 3 are can not be
used as a capture mode.
The Timer/Counter register is incremented in response internal or external input. This counting function is same
with normal timer mode, but Timer interrupt is not g ene rated. Timer/Counter still does the above, but with the added feature that a edge transition at external input INTn pin
76543210
EC0 PIN
XIN PIN
INT0 PIN
TM0
Edge Detector
Prescaler
IEDS[1:0]
“01”
“10”
“11”
T1STCAP0 T0SL1
1X XXXX
01 or 10 or 11
T0CN
TIMER 0
÷
÷
÷
4
16
64
T0SL[1:0]
“00”
“01”
“10”
“11”
MUX
To TIMER1
causes the current value in the Timer counter register
(T0,T2), to be captured into registers CDRn (CDR0,
CDR2), respectively. After captured, Timer counter register is cleared and restarts by hardware.
Note: The CDRn and TDRn are in same address.In the
capture mode, reading operation is read the CDRn, not
TDRn because path is opened to the CDRn.
It has three transition modes: "falling edge", "rising edge",
"both edge" which are selected by interrupt edge selection
register IEDS. Refer to “16.4 External Interrupt” on page
61. In addition, the transition at INTn pin generate an inte rrupt.
BTCL
T0STT1SL1 T1SL0
Capture
This figure is a example of using the Timer0.
In the Time r2, operation is same like Timer0, each register s and
flags may be changed with for Timer2.
T0SL0T0CN
X means don’t care
T0ST
0: Stop
1: Clear and start
T0 (8-bit)
CDR0 (8-bit)
ADDRESS: 0E2
INITIAL VALUE: 00
INT0IF
H
H
INT0
INTERRUPT
Figure 11-9 8-bit Capture Mode
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 43
Page 47

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
11.4 16-bit Capture Mode
16-bit capture mode is the same as 8-bit capture, except
that the Timer register is being run will 16 bits.
TM0
Edge Detector
EC0 PIN
XIN PIN
Prescaler
IEDS[1:0]
“01”
INT0 PIN
TIMER 0 + TIMER 1 → TIMER 0 (16-bit)
“10”
“11”
76543210
00
T0CN
BTCL
T0STT1SL1 T1SL0
X means don’t care
T0ST
TDR1 + TDR0
(16-bit)
Capture
TDR1 + TDR0
(16-bit)
Higher byte
CAPTURE DATA
This figure is a example of using the Timer0, 1.
In the Timer2, 3, operation is same like Timer0,1, each registers and
flags may be changed with for Timer2,3.
T1STCAP0 T0SL1
1X XXXX
T0SL[1:0]
“00”
4
÷
“01”
16
÷
“10”
64
÷
“11”
MUX
Figure 11-10 16-bit Capture Mode
T0SL0T0CN
0: Stop
1: Clear and start
Lower byte
ADDRESS: 0E2
INITIAL VALUE: 00
INT0IF
H
H
INT0
INTERRUPT
44 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 48

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
Example 1:
Timer0 = 16-bit timer mode, 0.5s at 8MHz
Timer2 = 2ms 8-bit timer mode at 8M Hz
Timer3 = 250us 8-bit timer mode at 8MHz
LDM TDR0,#23H
LDM TDR1,#0F4H
LDM TM0,#0FH
LDM TDR2,#249
LDM TDR3,#124
LDM TM2,#0110_1111B
SET1 T0E
SET1 T2E
SET1 T3E
EI
:
:
Example 2:
Timer0 = 8-bit timer mode, 2ms interval at 8MHz
Timer2 = 16-bit event counter mode
LDM TDR0,#249
LDM TM0,#0111_1111B
LDM TDR2,#3FH
LDM TDR3,#2AH
LDM TM2,#0100_1100B
SET1 T0E
SET1 T2E
EI
:
:
LDM TDR0,#250
LDM TM0,#0111_1111B
SET1 T0E
LDM TDR2,#40H
LDM TDR3,#2AH
LDM TM2,#1111_1111B
SET1 T2E
LDM IEDS,#XX11_XXXXB
LDM PMR4,#XXXX_X1XXB
SET1 INT2E
EI
:
:
X: don’t care.
Example 4:
Timer0 = 8-bit timer mode, 2ms interval at 8MHz
Timer2 = 16-bit capture mode
LDM TDR0,#249
LDM TM0,#0111_1111B
SET1 T0E
LDM TDR2,#40H
LDM TDR3,#2AH
LDM TM2,#1100_1111B
SET1 T2E
LDM IEDS,#XX11_XXXXB
LDM PMR4,#XXXX_X1XXB
SET1 INT2E
EI
:
:
Example 3:
Timer0 = 8-bit timer mode, 2ms interval at 8MHz
Timer2 = 8-bit capture mode
X: don’t care.
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 45
Page 49

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
12. ANALOG DIGITAL CONVERTER
The analog-to-digital converter (A/D) allows conversion
of an analog input signal to a corresponding 8-bit digital
value. The A/D module has eight analog inputs, which are
multiplexed into one sample and hold. The output of the
sample and hold is the input into the converter, which generates the result via successive approximation. The analog
supply voltage is connected to AV
of ladder resistance
DD
of A/D module.
The A/D module has two registers which are the control
register ADCM and A/D result register ADR. The register
ADCM, shown in Figure 12-2, controls the operation of
the A/D converter module. The port pins can be configured
as analog inputs or digital I/O. To use anal og input s, I/O is
selected input mode by R6DD direction register.
ADEN
ADS[2:0]
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
“0”
“1”
8-bit DAC
LADDER RESISTOR
S/H
Sample & Hold
AV
DD
R60/AN0
R61/AN1
R62/AN2
R63/AN3
R64/AN4
R65/AN5
R66/AN6
R67/AN7
How to Use A/D Converter
The processing of conversion is start when the start bit
ADST is set to “1”. After one cycle, it is cleared by hardware. The register ADR contains the results of the A/D
conversion. When the conversion is completed, the result
is loaded into the ADR, the A/D conversion status bit
ADSF is set to “1”, and the A/D interrup t flag AIF is set.
The block di agram of the A /D mo dule is shown in Figu re
12-1. The A/D status bit ADSF is set automatically when
A/D conversion is completed, cleared when A/D conversion is in process. The conversion time takes maximum 20
uS (at f
=8 MHz).
XIN
SUCCESSIVE
APPROXIMATION
CIRCUIT
ADR
A/D result register
ADIF
ADDRESS: E9
RESET VALUE: Undefined
H
A/D
INTERRUPT
Figure 12-1 A/D Block Diagram
Note: On the initial RESET, R60 port is selected as an an-
alog input by ADCM register. So it can not be used digital
input port. To use this port as a digital I/O port, change to
except “0” the value of ADCM. Finally all eight ports can not
be used as digita l I/O p ort simul tan eousl y. At le ast one po rt
must be in analog port.
46 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 50

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
ADCM
ADR
76543210
R
76543210
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R
--
RRRR RR
BTCL
BTCL
ADS1 ADS0ADEN ADS2
R
ADST
ADSF
ADDRESS: 0E9
INITIAL VALUE: Undefined
ADDRESS: 0E8
INITIAL VALUE: --00 0001
A/D status bit
0: A/D conversion is in progress
1: A/D conversion is completed
A/D start bit
Setting this bit starts an A/D conversion.
After one cycle, bit is cleared to “0” by hardware.
Analog input channel select
000: Channel 0 (AN0)
001: Channel 1 (AN1)
010: Channel 2 (AN2)
011: Channel 3 (AN3)
100: Channel 4 (AN4)
101: Channel 5 (AN5)
110: Channel 6 (AN6)
111: Channel 7 (AN7)
A/D converter Enable bit
0: A/D converter module turn off and
current is not flow.
1: Enable A/D converter
H
H
B
A/D Conversion Data
Figure 12-2 A/D Converter Control Register
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 47
Page 51

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
13. SERIAL COMMUNICATION
The serial iterface is used to transmit/receive 8-bit data serially. This consists of seri al I/O data register, seria l I/O
mode register, clock selection circuit octal counter and
control circuit as illustrated in Figure 13-1.Pin R50/SIN,
R51/SOUT, R52/SCLK and R53/SRDY pins ar e con-
SIOST
SCK[1:0]
Start
8
÷
00
16
Prescaler
SCK[1:0]
SRDY Out
÷
32
÷
“11”
not “11”
01
10
11
MUX
RSQ
CONTROL CIRCUIT
Clock
SRDY In
XIN PIN
SCLK PIN
SRDY PIN
trolled by the Serial Mode Register. The contents of the Serial I/O data register can be written into or re ad out by
software. The data in the Serial Data Register can be shifted synchronously with the transfer clock signal.
SIOSF
Complete
Clock
Complete
overflow
Octal
Counter
SIOIF
Serial communication
Interrupt
SOUT PIN
Input shift register
SIOR
Internal bus line
Figure 13-1 SCI Block Diagram
Shift
[0EB
SIN PIN
]
H
48 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 52

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
Serial I/O Mode Register(SIOM) controls serial I/O function. According to SCK1 and SCK0, the internal clock or
external clock can be selected.
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R
R/W
76543210
SIOM
-
SRDY
BTCL
SCK1 SCK0SM1 SM0
SIOST
Serial I/O Data Regist er(SIOR) is an 8-bit shift re gister.
First LSB is send or is received.
SIOSF
ADDRESS: 0EA
INITIAL VALUE: -000 0001
Serial transmission status bit
0: Serial transmission is in progress
1: Serial transmission is completed
Serial transmission start bit
Setting this bit starts an Serial transmission.
After one cycle, bit is cleared to “0” by hardware.
Serial transmission Clock selection
00: f
01: f
10: f
11: External Clock
Serial transmission Operation Mode
00: Normal Port(R52,R51,R50)
01: Sending Mode(SCLK,SOUT,R50)
10: Receiving Mode(SCLK,R51,SIN)
11: Sending & Receiving Mode(SCLK,SOUT,SIN)
4
÷
XIN
16
÷
XIN
32
÷
XIN
R53/SRDY Selection
0: R53
1: SRDY
H
B
SIOR
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
R/W
76543210
Sending Data at Sending Mode
Receiving Data at Receiving Mode
R/W
BTCL
Figure 13-2 SCI Control Register
ADDRESS: 0EB
INITIAL VALUE: Undefined
H
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 49
Page 53

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
13.1 Transmission/Receiving Timing
The serial transmission is started by setting SIOST(bit1 of
SIOM) to “1”. After one cycle of SCK, SIOST is cleared
automatically to “0”. The serial output data from 8-bit shift
register is output at falling edge of SCLK. And input data
Input Clock
SCLK PIN
SIOST FLAG
Output
D2
Latch
D1D0
D2
D1D0
SOUT PIN
SIN PIN
SIOIF
INTERRUPT SIGNAL
Figure 13-3 Timing Diagram of Serial I/O
is latched at rising edge of SCLK pin. When transmis sion
clock is counted 8 times, serial I/O counter is cleared as
‘0”. Transmission clock is halted in “H” state and serial I/
O interrupt(IFSIO) occurred.
D5
D5
D6
D7
D7D6
D4D3
D4D3
13.2 The Serial I/O operation by SRDY pin
Transmission clock = external clock
The SRDY
tells to the external system that this device is ready for se-
Transmission clock = internal clock
The I/O of SRDY
system is ready for serial transmission, The “L” level is in-
pin becomes “L” by SIOST = “1”. This signal
SIOST
SRDY(Output)
pin is input mode. When the external
SIOST
SRDY(Input)
rial transmission. The external system detects the “L” signal and starts transmission. The SRDY
pin becomes “H” at
the first rising edge of transmission clock.
putted at this pin. At this time this device starts serial transmission.
50 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 54

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
13.3 The method of Serial I/O
1. Select transmission/receiving mode.
2. In case of sending mode, wri te d at a t o be s e nd t o SIOR .
3. Set SIOST to “1” to start serial tran smission.
4. The SIO interrupt is generated at the completion of SIO
and SIOSF is set to “1”. In SIO interrupt service routine,
correct transmission should be tested .
5. In case of receiving mode, the received data is acquired
by reading the SIOR.
13.4 The Method to Test Correct Transmission
Serial I/O Interrupt
Service Routine
SIOSF
1
SE = 0
Write SIOM
Note: When external clock is used, the frequency should
be less than 1MHz and recommended duty is 50%. If both
transmission mode is sel ected and transmission is performed simultaneously it would be made error.
0
Abnormal
SR
Normal Operation
- SE: Interrupt Enable Register Low IENL(Bit3)
- SR: Interrupt Request Flag Register Low IRQL(Bit3)
0
1
Overrun Error
Figure 13-4 Serial Method to Test Transmission
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 51
Page 55

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
14. PWM OUTPUT
The GMS815xxB have two channels of built-in pulse
width modulation outputs. PWM outputs data are multiplex to the R56 and R57 port. Bit 6 and bit 7 of R5DD
should be set to “1” when PWM is used as an output port.
P0CK[1:0]
EN0
EN1
1
0
1
0
8-bit Counter
PWMR0
8-bit Coun ter
PWMR1
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
XIN
XIN
XIN
XIN
XIN
XIN
XIN
XIN
÷ 256
÷ 512
÷ 1024
÷ 2048
÷ 256
÷ 512
÷ 1024
÷ 2048
00
01
10
11
MUX
P1CK[1:0]
00
01
10
11
MUX
The input clock is selected by PWM Control Register
(PWMCR, address F2
) and the width of pulse is deter-
H
mined by the PWM Register (PWMR, address F0
F1
).
H
F/F
Overflow
Comparator
]
[0F0
H
Overflow
Comparator
]
[0F1
H
S
Q
R
POL0
F/F
S
Q
R
POL1
PWM0
PWM1
H
and
Figure 14-1 PWM block diagram
The pulse period according to input clock are shown as below.
Input clock Period of PWM
f
256
÷
÷
÷ ÷
f
f
f
XIN
XIN
XIN
XIN
÷
÷
÷ ÷
÷
÷
÷ ÷
÷
÷
÷ ÷
512
1024
2048
8.19 ms
16.38 ms
32.77 ms
65.54 ms
Bit 2 (EN0) and bit 3 (EN1) of PWMCR determine the operation channel of PWM. When EN0=0 and EN1=0, PWM
does not execute
It is a PWM output co ntrolled by PWMCR , PWMR0 a nd
PWMR1.
PWMR 1
+
Duty ratio
--------------------------- -
=
256
×
100%
52 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 56

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
PWMR0
PWMR1
ADDRESS: 0F0
WWWW WWWW
WWWW WWWW
RESET VALUE: Undefined
Duty data
ADDRESS: 0F1
RESET VALUE: Undefined
Duty data
Figure 14-2 PWM Duty Register
WWWWWW
76543210
PWMCR
PWM1 clock selection
÷ 256
00: f
XIN
÷ 512
01: f
XIN
10: f
÷ 1024
XIN
11: f
÷ 2048
XIN
P1CK0P1CK1 POL1
H
H
PWM0 clock selection
00: f
01: f
10: f
11: f
BTCL
EN1 EN0P0CK1 P0CK0
XIN
XIN
XIN
XIN
÷ 256
÷ 512
÷ 1024
÷ 2048
WW
POL0
ADDRESS: 0F2
INITIAL VALUE: 0000 0000
PWM0 output polarity
0: Active low
1: Active high
PWM1 output polarity
0: Active low
1: Active high
PWM enable flag
00: Disable
01: PWM0
10: PWM1
11: Both (PWM0 and PWM1)
H
B
Figure 14-3 PWM Control Register
Example:
PWM0: Period = 16.384ms, Duty = 20%
PWM1: Period = 8.192ms, Duty = 70%
LDM PWMCR,#0100_1111B
LDM PWMR0,#0B3H
LDM PWMR1,#33H
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 53
Page 57

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
3.264ms
PWM1
PWMR1
PWMCR
f
XIN
8MHz 512 256÷÷61.035Hz
16.384ms
×
16.384
33
------------ -
100
H
H
01
fixed
=
3.264ms
=
00
Figure 14-4 Example of Register Setting
enable
111 1
f
XIN
8MHz 256 256÷÷122.07Hz
PWM0
PWMR0
active high
fixed
=
8.192
8.192ms
5.728ms
B3
------------ -
×
100
H
H
5.728ms
=
54 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 58

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
15. BUZZER FUNCTION
The buzzer driver block consists of 6-bit binary counter,
buzzer register, and clock source selector. It generates
square-wave which has very wide range frequency (500Hz
~ 250kHz at f
= 8MHz) by user software.
XIN
A 50% duty pulse can be output to R55 /BUZ pin to use for
piezo-electric buzzer drive
of Buzzer driver by setting the bit 5 of PMR5 (address D1
“1”.
At this time, the pin R55 must be defined as output
. Pin R55 is assigned for output port
) to
H
mode (the bit 5 of R5DD=1).
Example: 2.4kHz output at 8MHz.
LDM R5DD,#XX1X_XXXXB
LDM BUR,#9AH
LDM PMR5,#XX1X_XXXXB
X means don’t care
6-bit binary
6-BIT COUNTER
Compare data
XIN PIN
Prescaler
÷
÷
÷
÷
128
16
00
32
01
64
10
11
MUX
2
The bit 0 to 5 of BUR determines output frequency for
buzzer driving.
Equation of frequency calcu lation is shown below .
f
f
f
: Buzzer frequency
BUZ
: Oscillator frequency
f
XIN
Divide Ratio: Prescaler divide ratio by BUCK[1:0]
BUR: Lower 6-bit value of BUR. Buzzer period value.
-------------------------------------------------------------
=
BUZ
2 DivideRatio BUR
XIN
××
The frequency of output signal is controlled by the buzzer
control register BUR.The bit 0 to bit 5 of BUR determine
output frequency for buzzer driving.
R55 port data
0
1
R55/BUZ PIN
Comparator
÷
F/F
2
PMR5
[0EC
]
H
6
BUR
Internal bus line
[0D1
H
PMR5
]
Port selection
Figure 15-1 Block Diagram of Buzzer Driver
ADDRESS: 0D1
RESET VALUE: --00 ----
W
W
--
---
R54/WDTO Selection
0: R54
1: WDTO (Output)
R55/BUZ Selection
0: R55 port (Turn off buzzer)
1: BUZ port (Turn on buzzer)
H
B
-
BUR
WW
BUCK1
BUCK0
WWWWWW
ADDRESS: 0EC
RESET VALUE: Undefined
BUR[5:0]
Buzzer Period Data
Source clock select
00: ÷16
01: ÷ 32
10: ÷ 64
11: ÷128
H
Figure 15-2 PMR5 and Buzzer Register
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 55
Page 59

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
Note: BUR is undefined after reset, s o it must be initi alized
to between 1
and 3FH by software.
H
Note that BUR is a write-only register.
BUR
[5:0]
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
0A
0B
0C
0D
0E
0F
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
1A
1B
1C
1D
1E
1F
00 01 10 11 00 01 10 11
-
250.000
125.000
83.333
62.500
50.000
41.667
35.714
31.250
27.778
25.000
22.727
20.833
19.231
17.857
16.667
15.625
14.706
13.889
13.158
12.500
11.905
11.364
10.870
10.417
10.000
9.615
9.259
8.929
8.621
8.333
8.065
BUR[7:6]
125.000
62.500
41.667
31.250
25.000
20.833
17.857
15.625
13.889
12.500
11.364
10.417
9.615
8.929
8.333
7.813
7.353
6.944
6.579
6.250
5.952
5.682
5.435
5.208
5.000
4.808
4.630
4.464
4.310
4.167
4.032
-
62.500
31.250
20.833
15.625
12.500
10.417
8.929
7.813
6.944
6.250
5.682
5.208
4.808
4.464
4.167
3.906
3.676
3.472
3.289
3.125
2.976
2.841
2.717
2.604
2.500
2.404
2.315
2.232
2.155
2.083
2.016
-
31.250
15.625
10.417
7.813
6.250
5.208
4.464
3.906
3.472
3.125
2.841
2.604
2.404
2.232
2.083
1.953
1.838
1.736
1.645
1.563
1.488
1.420
1.359
1.302
1.250
1.202
1.157
1.116
1.078
1.042
1.008
The 6-bit counter is cleared and starts the counting by writing signal at BUR register. It is incremental from 00
it matches 6-bit BUR value.
When main-frequency is 8MHz, buzzer frequency is
shown as below table.
BUR
[5:0]
-
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2A
2B
2C
2D
2E
2F
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
3A
3B
3C
3D
3E
3F
7.813
7.576
7.353
7.143
6.944
6.757
6.579
6.410
6.250
6.098
5.952
5.814
5.682
5.556
5.435
5.319
5.208
5.102
5.000
4.902
4.808
4.717
4.630
4.545
4.464
4.386
4.310
4.237
4.167
4.098
4.032
3.968
BUR[7:6]
3.906
3.788
3.676
3.571
3.472
3.378
3.289
3.205
3.125
3.049
2.976
2.907
2.841
2.778
2.717
2.660
2.604
2.551
2.500
2.451
2.404
2.358
2.315
2.273
2.232
2.193
2.155
2.119
2.083
2.049
2.016
1.984
1.953
1.894
1.838
1.786
1.736
1.689
1.645
1.603
1.563
1.524
1.488
1.453
1.420
1.389
1.359
1.330
1.302
1.276
1.250
1.225
1.202
1.179
1.157
1.136
1.116
1.096
1.078
1.059
1.042
1.025
1.008
0.992
until
H
0.977
0.947
0.919
0.893
0.868
0.845
0.822
0.801
0.781
0.762
0.744
0.727
0.710
0.694
0.679
0.665
0.651
0.638
0.625
0.613
0.601
0.590
0.579
0.568
0.558
0.548
0.539
0.530
0.521
0.512
0.504
0.496
Table 15-1 Buzzer Frequency
56 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 60

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
16. INTERRUPTS
The GMS815xxB interrup t cir cui ts cons ist of Interr upt enable register (IENH, IENL), Interrupt request flags of
IRQH, IRQL, Priority circuit, and Master enable flag (“I”
flag of PSW). Thirteen interrupt sources are provided. T he
configuration of interrupt circuit is shown in Figure 16-2.
The External Interrupts INT0 ~ INT3 each can be transition-activated (1-to-0 or 0-to -1 transition) by selection
IEDS.
The flags that actu ally generate these in terrupts are bit
INT0F, INT1F, INT2F and INT3F in register IRQH. When
an external interrupt is generated, the flag that generated it
is cleared by the hardware when the service routine is vectored to only if the interrupt was transition-activated.
The Timer 0 ~ Timer 3 Interrupts are generated by TxIF
which is set by a match in their respective timer/counter
register. The Basic Interval Timer Interrupt is generated by
BITIF which is set by an overflow in the timer register.
The AD converter Interrupt is generated by ADIF whi ch is
set by finishing the analog to digital conversion.
The Watchdog timer Interrupt is generated by WDTIF
which set by a match in Watchdog timer register.
The Basic Interval Timer INterrupt is generated by BITIF
which are set by a overflow in the timer counter register.
The interrupts are controlled by the interrupt master enable
flag I-flag (bit 2 of PSW on page 19), the interrupt enable
register (IENH, IENL), and the interrupt request flags (in
IRQH and IRQL) except Power-on reset and software
BRK interrupt. Below table shows the Interrupt priority.
Reset/Interrupt Symbol Priority
Hardware Reset
External Interrupt 0
External Interrupt 1
External Interrupt 2
External Interrupt 3
Timer/Counter 0
Timer/Counter 1
Timer/Counter 2
Timer/Counter 3
ADC Interrupt
Basic Interval Timer
Watchdog Timer
Serial Communication
RESET
INT0
INT1
INT2
INT3
Timer 0
Timer 1
Timer 2
Timer 3
ADC
BIT
WDT
SCI
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Vector addresses are shown in Figure 8-6 on page 21. Interrupt enable registers are shown in Figure 16-3. These
registers are composed of interrupt enab le flags of each interrupt source and these flags determines whether an interrupt will be accepted or not. When enable flag is “0”, a
corresponding interrupt source is prohibited. Note that
PSW contains also a master enable bit, I-flag, which disables all interrupts at once.
R/W
R/W R/W R/W
INT0IF
IRQH
MSB LSB
IRQL
MSB LSB
INT1IF
R/W R/W
ADIF
WDTIF
R/W R/W
INT2IF
INT3IF
R/W
R/W
SIOIF
BITIF
R/W R/W
T1IF
--
-
-
Figure 16-1 Interrupt Request Flag
T2IF
-
-
T3IFT0IF
-
-
ADDRESS: 0F7
INITIAL VALUE: 0000 0000
Timer/Counter 3 interr up t reque st fla g
Timer/Counter 2 interr up t reque st fla g
Timer/Counter 1 interr up t reque st fla g
Timer/Counter 0 interr up t reque st fla g
External interrupt 3 request flag
External interrupt 3 request flag
External interrupt 3 request flag
External interrupt 3 request flag
ADDRESS: 0F5
INITIAL VALUE: 0000 ----
Serial Communication interrupt request flag
Basic Interval Timer interrupt request flag
Watchdog timer interrupt request flag
A/D Converter interrupt request flag
H
B
H
B
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 57
Page 61

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
.
Internal bus line
INT0
INT1
INT2
INT3
Timer 0
Timer 1
Timer 2
Timer 3
A/D Converter
Watchdog Timer
BIT
Communication
Serial
IRQH
[0F7
IRQL
[0F5
]
H
]
H
INT0IF
INT1IF
INT2IF
INT3IF
T0IF
T1IF
T2IF
T3IF
ADIF
WDTIF
BITIF
SIOIF
[0F4
[0F6H]
]
H
IENH
IENL
Internal bus line
Interrupt Enable
Register (Higher byte)
Interrupt Enable
Register (Lower byte)
I-flag is in PSW, it is cleared by “DI”, set by
“EI” instruction. When it goes interrupt service,
I-flag is cleared by hardware, thus any other
interrupt are inhibited. When interrupt service is
completed by “RETI” instruction, I-flag is set to
“1” by hardware.
Release STOP
To CPU
I-flag
Priority Control
Interrupt Master
Enable Flag
Interrupt
Vector
Address
Generator
Figure 16-2 Block Diagram of Interrupt
R/W
IENH
R/W R/W R/W
INT0E
INT1E
R/W R/W
INT2E
INT3E
R/W R/W
T1E
MSB LSB
R/W
SIOE
--
-
-
IENL
R/W R/W
ADE
WDTE
R/W
BITE
MSB LSB
Figure 16-3 Interrupt Enable Flag
T2E
T3ET0E
ADDRESS: 0F6
INITIAL VALUE: 0000 0000
H
B
Timer/Counter 3 interrupt enable flag
Timer/Counter 2 interrupt enable flag
Timer/Counter 1 interrupt enable flag
Timer/Counter 0 interrupt enable flag
External interrupt 3 enable flag
External interrupt 2 enable flag
External interrupt 1 enable flag
External interrupt 0 enable flag
-
-
-
-
ADDRESS: 0F4
INITIAL VALUE: 0000 ----
H
B
VALUE
0: Disable
1: Enable
Serial Communication interrupt enable flag
Basic Interval Timer interrupt enable flag
Watchdog timer interrupt enable flag
A/D Converter interrupt enable flag
58 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 62

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
16.1 Interrupt Sequence
An interrupt request is held until the interrupt is accepted
or the interrupt latch is cleared to “0” by a reset or an instruction. Interrupt acceptance sequence requires 8
µ
s at f
=4.19MHz) after the completion of the current
MAIN
f
XIN
(2
instruction execution. The interrupt service task is term inated upon execution of an interrupt return instruction
[RETI].
Interrupt acceptance
1. The interrupt master enable flag (I-flag) is cleared to
“0” to temporarily disable the acceptance of any following maskable interrupts. When a non-maskable interrupt is accepted, the acceptance of any following
interrupts is temporarily disabled.
System clock
Instruction Fetch
Address Bus
PC
SP SP-1
2. Interrupt request flag for the interrupt source accepted is
cleared to “0”.
3. The contents of the program counter (return address)
and the program status word are saved (pushed) ont o the
stack area. The stack pointer decreases 3 times.
4. The entry address of the interrupt service program is
read from the vector table address and the entry address
is loaded to the program counter.
5. The instruction stored at the entry address of the interrupt service program is executed.
SP-2 V.H. New PC
V.L.
Data Bus
Internal Read
Internal Write
V.L. and V.H. are vector addresses.
ADL and ADH are start addresses of interrupt service routine as vector contents.
Not used
PCH PCL
Interrupt Processing Step Interrupt Service Task
Figure 16-4 Timing chart of Interrupt Acceptance and Interrupt Return Instruction
Basic Interval Timer
Vector Table Address
0FFE6
0FFE7
Correspondence between vector table address for BIT interrupt
and the entry address of the interrupt service program.
012
0E3
H
H
H
H
0E312
0E313
Entry Address
0E
2E
H
H
H
H
A interrupt request is not accepted until the I-flag is set to
“1” even if a requested interrupt has higher priority than
that of the current interrupt being serviced.
PSW ADL OP codeADH
V.L.
When nested interrupt service is required, the I -flag should
be set to “1” by “EI” instruction in the interrupt service
program. In this case, acceptable interrupt sources are selectively enabled by the individual interrupt enable flags.
Saving/Restoring General-purpose Register
During interrupt acceptance processing, the program
counter and the program status word are automatically
saved on the stack, but accumulator and other registers ar e
not saved itself. These registers are saved by the software
if necessary. Also, when multiple interrupt services are
nested, it is necessary to avoid using the same data memory
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 59
Page 63

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
B-FLAG
BRK
INTERRUPT
ROUTINE
RETI
TCALL0
ROUTINE
RET
BRK or
TCALL0
=0
=1
area for saving registers.
The following method is used to save/restore the general-
purpose registers.
Example: Register save using push and pop instructions
INTxx: PUSH A
PUSH X
PUSH Y
interrupt processing
POP Y
POP X
POP A
RETI
;SAVE ACC.
;SAVE X REG.
;SAVE Y REG.
;RESTORE Y REG.
;RESTORE X REG.
;RESTORE ACC.
;RETURN
General-purpose register save/restore using push and pop
instructions;
main task
acceptance of
interrupt
interrupt
service task
saving
registers
16.2 BRK Interrupt
Software interrupt can be invoked by BRK instruction,
which has the lowest priority order.
Interrupt vector address of BRK is shared with the vector
of TCALL 0 (Refer to Program Memory Section). When
BRK interrupt is generated, B-flag of PSW is set to distinguish BRK from TCALL 0.
Each processing step is determined by B-flag as shown in
Figure 16-5.
interrupt return
restoring
registers
Figure 16-5 Execution of BRK/TCALL0
60 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 64

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
16.3 Multi Interrupt
If two requests of different priority levels are received simultaneously, the request of higher priority level is serviced. If requests of the interrupt are received at the same
time simultaneously, an internal polling sequence determines by hardware which request is serviced.
Main Program
service
Occur
TIMER1 interrupt
Occur
INT0
TIMER 1
service
enable INT0
disable other
EI
enable INT0
enable other
INT0
service
However, multiple processing through software for special
features is possible. Generally when an interrupt is accepted, the I-flag is cleared to disable any further interru pt. But
as user sets I-flag in interrupt routine, some further interrupt can be serviced even if certain interrupt is in progress.
Example:
During Timer1 interrupt is in progress, INT0 in-
terrupt serviced without any suspen d.
TIMER1: PUSH A
PUSH X
PUSH Y
LDM IENH,#80H ;
LDM IENL,#0 ;
EI ;
:
:
:
:
:
:
LDM IENH,#0FFH ;
LDM IENL,#0F0H
POP Y
POP X
POP A
RETI
Enable INT0 only
Disable other
Enable Interrupt
Enable all interrupts
In this example, the INT0 interrupt can be serviced without any
pending, even TIMER1 is in progress.
Because of re-setting the interrupt enable registers IENH,IENL
and master enable “EI” in the TIMER1 routine.
Figure 16-6 Execution of Multi Interrupt
16.4 External Interrupt
The external interrupt on INT0, INT1, INT2 and INT3 pins
are edge triggered depending on the edge selecti on register
IEDS (address 0F8
) as shown in Figure 16-7.
H
The edge detection of external interrupt has three transition
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 61
Page 65

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
activated mode: rising edge, falling edge, and both edge.
INT0 pin
INT1 pin
INT2 pin
INT3 pin
2 2 2 2
IEDS
[0F8H]
Figure 16-7 External Interrupt Block Diagram
INT0IF
INT0 INTERRUPT
INT1IF
INT1 INTERRUPT
INT2IF
INT2 INTERRUPT
INT3IF
INT3 INTERRUPT
Edge selection
Register
INT0 ~ INT3 are multiplexed with general I/O ports
(R40~R43). To use as an external interrupt pin, the bit of
R4 port mode register PMR4 should be set to “1” corre -
spondingly.
Example:
**** Set port as an input port R40,R42
;
**** Set port as an external interrupt port
;
**** Set Falling-edge Detection
;
To use as an INT0 and INT2
:
:
LDM R4DD,#1111_1010B
;
LDM PMR4,#05H
;
LDM IEDS,#0001_0001B
:
:
:
Response Time
The INT0 ~ INT3 edge are latched into INT1IF ~ INT3IF
at every machine cycle. The values are not actually polled
by the circuitry until the next machine cycle. If a request is
active and conditions are right for it to be acknowledged, a
hardware subroutine call to the requested service routine
will be the next instruction to be executed. The DIV itself
takes twelve cycles. Thus, a minimum of twelve complete
machine cycles elapse between activation of an external
interrupt request and the begi nning of executio n of the first
instruction of the service routine.
Figure 16-8shows interrupt response timings.
8 f
XIN
Interrupt
processing
Interrupt
routine
Interrupt
goes
active
max. 12 f
Interrupt
latched
XIN
Figure 16-8 Interrupt Response Timing Diagram
62 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 66

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
PMR4
IEDS
0: R47
1: T3O
0: R46
1: T1O
0: R45
1: EC2
0: R44
1: EC0
WWWWWWWW
EC2ST1ST3S INT1S
WWWWWWWW
IED2HIED3LIED3H IED0H
Edge selection register
00: Reserved
01: Falling (1-to-0 transition)
10: Rising (0-to-1 transition)
11: Both (Rising & Falling)
BTCL
EC0S INT0SINT2SINT3S
BTCL
IED2L IED0LIED1LIED1H
LSBMSB
LSBMSB
INT1INT2INT3
INT0
Figure 16-9 PMR4 and IEDS Registers
ADDRESS: 0D0
INITIAL VALUE: 00
0: R40
1: INT0
0: R41
1: INT1
0: R42
1: INT2
0: R43
1: INT3
ADDRESS: 0F8
INITIAL VALUE: 00
H
H
H
H
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 63
Page 67

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
17. WATCHDOG TIMER
The watchdog timer rapidly detects the CPU malfunction
such as endless looping caused by noise or the like, and resumes the CPU to the normal state.
The watchdog timer signal for detecting malfunction can
be selected either a reset CPU or a interrupt request.
BASIC INTERVAL TIMER
OVERFLOW
WDTCL
Count source
[0E0
H
Watchdog
Counter (8-bit)
6-bit compare data
WDTR
]
Internal bus line
clear
6
When the watchdog tim er is not being us ed for malfunction detection, it can be used as a tim er to generate an interrupt at fixed intervals.
clear
comparato r
Watchdog Timer
Register
“0”
“1”
enable
WDTON in CKCTLR [0D3
WDTIF
to reset CPU
]
H
Watchdog Timer interrupt
Figure 17-1 Block Diagram of Watchdog Timer
Watchdog Timer Control
Figure 17-2 shows the watchdog timer control register.
The watchdog timer is automatically disab led aft e r reset.
The CPU malfunction is detected during setting of the detection time, selecting of output, and clearing of the binary
counter. Clearing the binary counter is repeated within the
detection time.
If the malfunction occurs for any cause, the watchdog tim-
WWWW
WDTR
WWWW
76543210
WDTCL-
Clear count flag
0: Free-run count
1: When the WDTCL is set to “1”, binary counter
is cleared to “0”. And the WDTCL becomes “0” automatically
after one machine cycle. Counter count up again.
er output will become active at the rising overflow from
the binary counters unless the binary counter is cleared. At
this time, when WDTON=1, a reset is generated, which
drives the RESET
pin to low to reset the internal hardware.
When WDTON=0, a watchdog timer interrupt (WDTIF) is
generated.
The watchdog timer temporarily stops counting in the
STOP mode, and when the STOP mode is released, it automatically restarts (continues counting).
ADDRESS: 0E0
INITIAL VALUE: -011_1111
6-bit compare data
H
NOTE:
The WDTON bit is in register CKCTLR.
B
Figure 17-2 WDTR: Watchdog Timer Data Register
64 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 68

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
Example: Sets the watchdog timer detection time to 0.5 sec at 4.19MHz
LDM CKCTLR,#3FH ;
LDM WDTR,#04FH
LDM WDTR,#04FH ;
:
Within WDT
detection time
:
:
:
LDM WDTR,#04FH ;
:
Within WDT
detection time
:
:
:
LDM WDTR,#04FH ;
Enable and Disable Watchdog
Watchdog timer is enabled by setting WDTON (bit 5 in
CKCTLR) to “1”. WDTON is initialized to “0” during reset and it should be set to “1” to operate after reset is released.
Example: Enables watchdog timer for Reset
:
LDM CKCTLR,#xx1x_xxxxB;
:
:
WDTON
← 1
Select 1/2048 clock source, WDTON ← 1, Clear Counter
Clear counter
Clear counter
Clear counter
Watchdog Timer Interrupt
The watchdog timer can be also used as a simple 6-bit timer by clearin g bit5 of CKCTLR to “0”. The in terval of
watchdog timer interrupt is decided by Basic Interval Timer. Interval equation is shown as below.
T WDTR Interval of BIT
=
×
The stack pointer (SP) should be initialized before using
the watchdog timer output as an interrupt source.
The watchdog timer is disabled by clearing bit 5 (WDTON) of CKCTLR. The watchdog timer is halted in STOP
mode and restarts automatically after STOP mode is released.
Source clock
BIT overflow
Binary-counter
WDTR
WDTIF interrupt
WDT reset reset
1
2
n
3
Figure 17-3 Watchdog timer Timing
If the watchdog timer output becomes active, a reset is generated, which drives the RESET
pin low to reset the inter-
nal hardware.
Example: 6-bit timer interrupt set up.
10
3
WDTR ← “0100_0011
The main clock oscillator also turns on wh en a watchdog
timer reset is generated in sub clock mode.
LDM CKCTLR,#xx0xxxxxB;
LDM WDTR,#7FH ;
WDTCL
:
2
”
B
30
Counter
Clear
Match
Detect
WDTON
←1
←0
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 65
Page 69

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
18. POWER DOWN OPERATION
GMS815xxB has a power-down mode. In power-down
mode, power consumption is reduced considerably that in
battery operation. Battery life can be extended a lot.
18.1 STOP Mode
For applications where power consumption is a critical
factor, device provides reduced power of STOP.
Start The Stop Operation
An instruction that STOP causes to be the last instruct ion
is executed before going into the STOP m ode. In the Stop
mode, the on-chip main-frequency oscillator is stopped.
With the clock frozen, all functions are stopped, but the onchip RAM and Control registers are held. The port pins
output the values held by their res pective port data registe r,
the port direction regis ters. The status of p eripherals during
Stop mode is shown below.
Peripheral STOP Mode
CPU All CPU operations are disabled
RAM Retain
PIN
X
IN
X
PIN
OUT
Oscillation Stop
I/O ports Retain
Control Registers Retain
Release method by RESET, by External interrupt
Low
High
STOP Mode is entered by STOP instruction.
Note: Sinc e the XIN pin is conn ecte d inte rnally to G ND to
avoid current leakage due to the crystal oscillator in STOP
mode, do not use STO P ins t ruc ti on w hen an e xte rnal c lo ck
is used as the main system clock.
In the Stop mode of operation, VDD can be reduced to minimize power consumption. Be careful, however, that V
DD
is not reduced before the Stop mode is invoked, and that
V
is restored to its normal operating level before the
DD
Stop mode is terminated.
The reset should not be activated before V
is restored to
DD
its normal operating level, and must be held active long
enough to allow the oscillator to restart and stabilize.
And after STOP instruction, at least two or more NOP in struction should be written as show n in example below.
Example:
LDM CKCTLR,#0000_1110B
STOP
NOP
NOP
:
The Interval Timer Register CKCTLR should be initialized (0F
or 0EH) by software in order that oscillation sta-
H
bilization time should be longer than 20ms before STOP
mode.
~
Oscillator
pin)
(X
IN
Internal Clock
External Interrupt
BIT Counter
~
~
~
~
~
~
STOP Instruction
Executed
n
n+1 n+2 n+3
Normal Operation Stop Operation Normal Operation
Figure 18-1 STOP Mode Release Timing by External Interrupt
~
~
~
~
Before executing Stop instruction, Basic Interval Timer must be set
properly by software to get stabilization time which is longer than 20ms.
0
Clear
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
~
1
~
~
tST > 20ms
by software
FE
FF
0
12
66 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 70

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
Release the STOP mode
The exit from STOP mode is using hardware reset or external interrupt.
To release STOP mode, corresponding interrupt should be
enabled before STOP mode.
the on-chip RAM. External interrupts allow both on-chip
RAM and Control registers to retain their values.
Start-up is performed to acquire the time for stabilizing oscillation. During the start-up, the internal operations are all
stopped.
Reset redefines all t he control regist ers but does not chan ge
Event MCU Status before event
RESET Don’t care Vector on
STOP instruction Normal operation N +1 off
External Interrupt Normal operation Vector on
External Interrupt Wake up
Table 18-1 Wake-up and Reset Function Table
STOP, I flag = 1
STOP, I flag = 0
Chip function after event
PC Oscillator Circuit
Vector
N + 1
18.2 Minimizing Current Consumption
The Stop mode is designed to reduce power consumption.
To minimize current drawn during Stop mode, the user
should turn-off output drivers that are sourcing or sinking
current, if it is practical.
Note: In the STOP operation, the power dissipation associated with the os cillato r and th e inter nal hard ware is lowered; however, the power dissipation associated with the
pin interface (depending on the external circuitry and program) is not directly determined by the hardware operation
of the STOP feature. T his point shou ld be little c urrent flows
when the input level is stable at the power voltage level
(V
than the power voltage level (by approximately 0.3V), a cu rrent begins to flow. Therefore, if cutting off the output transistor at an I/O port puts the pin signal into the highimpedance state, a curr ent flow across th e ports input transistor, requiring it to fix the level by pull-up or other means.
); however, when the input level becomes higher
DD/VSS
It should be set prop erl y in order that current flo w t hro ugh
port doesn't exist.
First conseider the setting to input mode. Be sure that there
is no current flow after considering its relationship with
external circuit. In inpu t mode, the pin impeda nce viewing
from external MCU is very high that the current doesn’t
flow.
But input voltage lev el shou ld be V
or VDD. Be careful
SS
that if unspecified voltage, i.e. if unfirmed voltage level
(not V
or VDD) is applied to input pin, there can be little
SS
current (max. 1mA at around 2V) flow.
If it is not appropriate to set as an input m ode, then set to
output mode considering th ere is no current flow. Settin g
to High or Low is decided considering its relationship with
external circuit. For example, if there is external pull-u p resistor then it is set to output mode, i.e. to High, and if there
on
on
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 67
Page 71

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
is external pull-down register, it is set to low.
V
DD
O
GND
O
INPUT PIN
V
DD
i
GND
X
Weak pull-up current flows
INPUT PIN
i
Very weak current flows
internal
pull-up
V
DD
V
DD
O
V
DD
X
OPEN
O
Figure 18-2 Application Example of Unused Input Port
When port is configure as an input, input level should
be closed to 0V or 5V to avoid power consumption.
i=0
OPEN
i=0
OUTPUT PIN
ON
ON
OFF
i
GND
X
In the left case, much current flows from port to GND.
OFF
ON
OFF
Figure 18-3 Application Example of Unused Output Port
O
O
OPEN
V
DD
OUTPUT PIN
V
DD
ON
OFF
i
X
In the left case, Tr. base current flows from port to GND.
To avoid power consumpt ion, there s hould be low output
to the port.
L
OFF
ON
GND
O
i=0
GND
V
DD
L
68 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 72

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
X
OUT
X
IN
19. OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT
The GMS815xxB has two oscillation circuits internally.
X
and X
IN
are input and output for frequency, respec-
OUT
C1
C2
Recommend
Crystal Oscillator
8MHz
X
OUT
X
IN
V
SS
C1,C2 = 30pF±10pF
Crystal or Ceramic Oscillator
Figure 19-1 Oscillation Circuit
Oscillation circuit is designed to be used either with a ceramic resonator or crystal oscillator. Since each crystal and
ceramic resonator have their own characteristics, the user
should consult the crystal manufacturer for appropriate
values of external components.
tively, inverting amplifier which can be configured for being used as an on-chip oscillator, as shown in Figure 19-1.
Open
External Clock
External Oscillator
X
OUT
X
IN
Oscillation circuit is designed to be used either with a ceramic resonator or crystal oscillator. Since each crystal and
ceramic resonator have their own characteristics, the user
should consult the crystal manufacturer for appropriate
values of external components.
In addition, see Figure 19-2 for the layout of the crystal.
Note: Minimize the wiring length. Do not allow the wiring to
intersect with other signa l cond uctors . Do not all ow the wiring to come near changing high current. Set the potential of
the grounding position of the oscillator capacitor to that of
SS
. Do not ground it to any g round pattern where high cur-
V
rent is present. Do not fetch signals from the oscillator.
Figure 19-2 Layout of Oscillator PCB circuit
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 69
Page 73

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
7036P
V
CC
10uF
+
10k
Ω
to the RESET pin
20. RESET
The GMS815xxB have two types of reset generation procedures; one is an external reset input, the other is a watch-
dog timer reset. Table 20-1 shows on-chip hardwar e initialization by reset action.
On-chip Hardware Initial Value On-chip Hardware Initial Value
Program counter (PC)
(FFFF
H
Watchdog timer Disable
) - (FFFEH)
G-flag (G) 0 Control registers Refer to Table 8-1 on page 25
Peripheral clock Off Power fail detector Disable
Table 20-1 Initializing Internal Status by Reset Action
20.1 External Reset Input
The reset input is the RESET pin, which is the input to a
Schmitt Trigger. A reset in accomplished by holding the
RESET pin low for at least 8 oscillator periods, within the
operating voltage range and oscillation stable, it is applied,
and the internal state is initialized. A fter reset, 64ms (at 4
MHz) add with 7 oscillator periods are required to start execution as shown in Figure 20-2.
Internal RAM is not affected by reset. When V
is turned
DD
on, the RAM content is indeterminate. Therefore, this
RAM should be initialized before read or tested it.
When the RESET pin input goes to high, the reset operation is released and the program execution starts at the vector address stored at addresses FFFE
- FFFFH.
H
A connection for simple p ower-on-reset is shown in Figure
20-1.
Figure 20-1 Simple Power-on-Reset Circuit
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
??
?
??
RESET Process Step
t
ST
1
= x 256
÷1024
f
MAIN
FFFE FFFF
FE?ADL
ADH
Start
OP
MAIN PROGRAM
Oscillator
pin)
(X
IN
RESET
ADDRESS
BUS
DATA
BUS
~
~
~
~
~
~
?
?
Stabilization Time
t
ST
~
~
~
~
~
~
= 62.5mS at 4.19MHz
Figure 20-2 Timing Diagram after RESET
20.2 Watchdog Timer Reset
Refer to “17. WATCHDOG TIMER” on page 64.
70 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 74

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
21. POWER FAIL PROCESSOR
The GMS815xxB has an on-chip power fail detection circuitry to immunize against power noise. A configuration
register, PFDR, can enable or disable the po wer fail detect
circuitry. Whenever V
falls close to or below power fail
DD
voltage for 100ns, the power fail situation may reset or
freeze MCU according to PFR bit of PFDR. Refer to “7.4
DC Electrical Characteri sti cs ” on page 13.
In the in-circuit emulator, power fail function is not implemented and user can not experiment with it. Theref ore, af ter final development of user program, this function may
be experimented or evaluated.
Note: User can select power fail voltag e leve l acco rding t o
PFV bit of PFDR at the OTP(GMS815xxBT) but must select
the power f ail vol tage le vel to de fine PF D optio n of “M ask
Order & Verification Sheet” at the mas k chip(GMS815 xxB).
Because the power fail voltage level of mask chip
(GMS815xxB ) is de termine d accor ding to mask op tion re gardless of PFV bit of PFDR
76543210
PFDR
R/W
PFV
Note: If power fail voltage is selected to 3.0V on 3V operation, MCU is freezed at all the times.
Power FailFunction OTP MASK
Enable/Disable by PFD flag by PFD flag
Level Selection by PFV flag by mask option
Table 21-1 Power fail processor
R/W R/W R/W
PFD
PFR
PFS
ADDRESS: 0 F9
INITIAL VALUE: ---- 1100
H
B
Power Fail Status
0: Normal operate
1: Set to “1” if power fail is detected
Operation Mode
0: Normal operation regardless of power fail
1: MCU will be reset by power fail detection
Disable Flag
0: Power fail detection enable
1: Power fail detection disable
Power Fail Voltage Selection Flag
0: 2.4V
1: 3.0V
Figure 21-1 Power Fail Voltage Detector Register
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 71
Page 75

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
RESET VECTOR
V
DD
Internal
RESET
PFS =1
NO
RAM CLEAR
INITIALIZE RAM DATA
INITIALIZE ALL PORTS
INITIALIZE REGISTERS
FUNTION
EXECUTION
YES
PFS = 0
initial routine
Figure 21-2 Example S/W of RESET flow by Power fail
64mS
Skip the
V
MAX
PFD
V
MIN
PFD
When PFR = 1
V
DD
Internal
RESET
V
DD
Internal
RESET
t <64mS
64mS
64mS
Figure 21-3 Power Fail Processor Situations
MAX
V
PFD
V
MIN
PFD
MAX
V
PFD
V
MIN
PFD
72 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 76

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
22. OTP PROGRAMMING
The GMS81516BT/24BT are OTP (One Time Programmable) microcontrollers. Its internal user memory is constructed with EPROM (Electrically Programmable Read
Only Memory).
The OTP micorcontroller is generally used for chip evaluation, first produ ctio n, small amo unt pr odu ction, fas t mass
production, etc.
Blank OTP’s internal EPROM is filled by 00
Note: In any case, you have to use *.OTP file, not *.HEX
file. After assemble, both OTP and HEX file are generated
by automatically. The HEX file is used during porgram emulation on emulator.
, not FFH.
H
22.1 How to Program
To program the OTP devices, user can use HME own programmer or third party universal programmer shown as
listed below.
HME own programmer list
Manufacturer: Hyundai MicroElectronics
Programmer:
The Choice-Dr Writer is single writer and physically addon adapter board type, it should be used with Choice-Dr
emulator. However, the Choice-Sigma is stand alone HME
universal single programmer for any HME OTP devices,
also the Choice-Gang4 can program four OTPs at once.
Ask to HME sales part which is listed on appen dix o f thi s
manual.
Third party programmer list
Manufacturer: Hi-Lo Systems
Programmer:
Website : http: //www.hilosystems.com.tw
Choice-Dr Writer
Choice-Sigma, Choice-Gang4
ALL-11, ALL-07
posed of Motorola-S1 format.
3. Set the programming address range as below table.
GMS81516BT
Address Set Value
Bufferstart address 4000H
Buffer end address 7FFFH
Device start address C000H
GMS81524BT
Address Set Value
Bufferstart address 2000H
Buffer end address 7FFFH
Device start address A000H
4. Mount the socket adapter on the programmer.
5. Start program/verify.
22.2 Pin Function
VPP (Program Voltage)
V
is the input for the program voltage for programming
PP
the EPROM.
(Chip Enable)
CE
CE is the input for programming and verifying internal
EPROM.
(Output Enable)
OE
OE is the input of data output control signal for verify.
A0~A15 (Address Bus)
A0~A15 are address input pins for internal EPROM.
O0~O7 (EPROM Data Bus)
These are data bus for internal EPROM.
Socket adapters are supported by third party pro grammer’s
manufacturer. The other third party will be registered and
being under development.
Programming Procedure
1. Select device GMS81516BT or GMS81524BT.
2. Load the *.OTP file to the programmer. The file is com-
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 73
Page 77

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
64SDIP
CE
OE
OPEN
V
DD
V
PP
V
DD
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
GMS81516BT/24BT
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
O0
O1
O2
O3
O4
O5
O6
O7
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
GND
64MQFP
O0O1O2O3O4O5O6O7A0A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8
515049
484746
45
52
53
54
55
V
DD
V
PP
GND
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
123456789
4443424140
GMS815016BT/24BT
39
3837363534
101112131415161718
V
DD
CE
OE
A9
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
OPEN
Table 22-1 Socket Adapter Pin Assignment
74 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 78

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
64LQFP
O0O1O2O3O4O5O6
484746454443424140393837363534
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
V
DD
V
PP
GND
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
GMS81516BT/24BT
123456789
A0A1A2A3A4A5A6
O7
10111213141516
V
DD
Table 22-2 Socket Adapter Pin Assignment
CE
A7
33
OE
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
OPEN
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 75
Page 79

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
22.3 Programming Specification
DEVICE OPERATION MODE
= 25°C ± 5°C)
(T
A
Mode CE OE A0~A15
Read Mode
Output Disable Mode
Programming Mode
X
V
V
Program Verify X
1. X = Either VIL or VIH.
2. See DC Characteristics Table for V
1
IH
IL
1
and VPP voltage during programming.
DD
V
IH
V
IH
V
PP
1
X
1
X
1
X
1
X
2
V
DD
2
V
DD
2
V
PP
2
V
PP
V
DD
O0~O7
5.0V DOUT
5.0V Hi-Z
2
V
DD
2
V
DD
DOUT
DEVICE CHARACTERISTICS
=0V, TA = 25°C ± 5°C)
(V
SS
Symbol Item Min Typ Max Unit Test condition
V
PP
V
DD
I
PP
I
DD
V
IH
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL
I
IL
1. VDD must be applied simultaneously or before VPP and removed simultaneously or after VPP.
2. The maximum current value is with outputs O0 to O7 unloaded.
Quick Pulse Programming 11.50 11.75 12.0 V
1
Quick Pulse Programming 5.75 6.0 6.25 V
2
VPP supply current
2
VDD supply current
Input high voltage
Input low voltage
Output high voltage
0.8V
V
DD
DD
0.2V
-0.1
Output low voltage 0.4 V
Input leakage current 5
50 mA
30 mA
V
DD
V
V
µ
A
CE=V
IL
IOH= -2.5mA
= 2.1mA
I
OL
DIN
76 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 80

HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS81508B/16B/24B
SWITCHING WAVEFORMS
WAVEFORM
READING WAVEFORMS
INPUTS OUTPUTS
Must be steady
May change Will be changing
from H to L from H to L
May change Will be changing
from L to H from L to H
Do not care any Changing state
change permitted unknown
Does not apply Center line is
Will be steady
high impedance “Off” state
V
IH
Addresses
V
IL
V
IH
Addresses Valid
See note (2)
OE
V
IL
V
IH
Output
V
IL
1. The input timing reference level is 1.0V for a VIL and 4.0V for a VIH at VDD=5.0V.
2. To read the output data, transition requires on the OE
t
AS
High-Z
t
OE
Valid Output
form the high to the low after address setup time tAS.
t
DH
DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04 77
Page 81

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
PROGRAMMING ALGORITHM WAVEFORMS
Addresses
Data In/Out
V
PP
V
DD
CE
OE
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
12.75V
V
DD
6.25V
5.0V
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
t
t
t
DS
VPS
VDS
t
AS
Program
Data in Stable
t
PW
Addresses Valid
t
DH
High-Z
t
OES
Program
t
OE
Verify
Data out valid
t
AH
t
DFP
1. The input timing reference level is 1.0V for a VIL and 4.0V for a VIH at VDD=5.0V.
78 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 82

AC READING CHARACTERISTICS
=0V, TA = 25°C ± 5°C)
(V
SS
Symbol Item Min Typ Max Unit Test condition
t
AS
t
OE
t
DH
Note: VDD must be applied simultaneously or before VPP and removed simultaneously or after VPP.
Address setup time 2
µ
Quick Pulse Programming 200 ns
VPP supply current
050ns
s
AC PROGRAMMING CHARACTERISTICS
=0V, TA = 25°C ± 5°C)
(V
SS
Symbol Item Min Typ Max Unit Test condition*
t
t
OES
t
t
t
t
DFP
t
VPS
t
VDS
t
t
AS
DS
AH
DH
PW
OE
Address setup time 2
OE setup time 2
Data setup time 2
Address hold time 0
Data hold time 2
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
Output delay disable time 0 130 ns
VPP setup time
VDD setup time
Program pulse width 95 100 105
2
2
µ
µ
µ
Data output delay time 150 ns
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
* AC CONDITION OF TEST
Input Rise and Fall Times (10% to 90%)...........................20ns
Input Pulse Levels.............................................................0.45V to 4.55V
Input Timing Reference Level............................................1.0V to 4.0V
Output Timing Reference Level......................................... 1.0V to 4.0V
must be applied simultaneously or before VPP and removed simultaneously or after VPP.
V
DD
Page 83

GMS81508B/16B/24B HYUNDAI MicroElectronics
START
ADDRESS=FIRST LOCATION
VCC=6.0V
=11.75
V
PP
X=0
PROGRAM ON E 100µs PULSE
INCREMENT X
INCREMENT
ADDRESS
NO
PASS
YES
PASS
YES
FAIL
VERIFY
BYTE
FAIL
NO
X=25?
VERIFY
ONE BYTE
LAST
ADDRESS?
VCC=VPP=5.0V
COMPARE
ALL BYTES TO
ORIGINAL
DATA
DEVICE
PASSED
Table 22-1 Programming Algorithm
PASS
FAIL
DEVICE
FAILED
80 DEC. 1999 Ver 1.04
Page 84

APPENDIX
Page 85

HYUNDAI Micro Electronics GMS800 Series
A. CONTROL REGISTER LIST
Address Register Name Symbol R/W
00C0 R0 port data register R0 R/W Undefined 31
00C1 R0 port I/O direction register R0DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 31
00C2 R1 port data register R1 R/W Undefined 31
00C3 R1 port I/O direction register R1DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 31
00C4 R2 port data register R2 R/W Undefined 31
00C5 R2 port I/O direction register R2DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 31
00C6 R3 port data register R3 R/W Undefined 32
00C7 R3 port I/O direction register R3DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 32
00C8 R4 port data register R4 R/W Undefined 32
00C9 R4 port I/O direction register R4DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 32
00CA R5 port data register R5 R/W Undefined 33
00CB R5 port I/O direction register R5DD W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 33
00CC R 6 port data register R6 R/W Undefined 33
00CD R6 port I/O direction register R6DD W 0 0 0 0 - - - - 33
00D0 R4 port mode register PMR4 W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 32, 63
00D1 R5 port mode register PMR5 W - - 0 0 - - - - 33, 55
00D3
00E0 Watchdog Timer Register WDTR W - 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 64
00E2 Timer mode register 0 TM0 R/W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 37
00E3 Timer mode register 2 TM2 R/W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 37
00E4
00E5
00E6
00E7
00E8 A/D converter mode register ADCM R/W - - 0 0 0 0 0 1 47
00E9 A/D converter data register ADR R Undefined 47
00EA Serial I/O mode register SIOM R/W - 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 49
00EB Serial I/O register SIOR R/W Undefined 49
00EC Buzzer driver regi ste r BUR W Undefined 55
00F0 PWM0 duty register PWMR0 W Undefined 53
00F1 PWM1 duty register PWMR1 W Undefined 53
Basic interval timer mode register BITR R Undefined 35
Clock contr ol register CKCTLR W - - 0 1 0 1 1 1 35
Timer 0 data register TDR0 W Undefined 37
Timer 0 counter register T0 R Undefined 37
Timer 1 data register TDR1 W Undefined 37
Timer 1 counter register T1 R Undefined 37
Timer 2 data register TDR2 W Undefined 37
Timer 2 counter register T2 R Undefined 37
Timer 3 data register TDR3 W Undefined 37
Timer 3 counter register T3 R Undefined 37
Initial Value
76543210
Page
DEC. 1999 i
Page 86

GMS800 Series HYUNDAI Micro Electronics
Address Register Name Symbol R/W
00F2 PWM control register PWMCR W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 53
00F4 Interrupt enable register low IENL R/W 0 0 0 0 - - - - 58
00F5 Interrupt request flag register low IRQL R/W 0 0 0 0 - - - - 57
00F6 Interrupt enable register high IENH R/W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 58
00F7 Interrupt request flag register high IRQH R/W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 57
00F8 External interrupt edge selection register IEDS W 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 63
00F9 Power fail detection register PFDR R/W - - - - 1 1 0 0 71
Initial Value
76543210
Page
ii DEC. 1999
Page 87

HYUNDAI Micro Electronics GMS800 Series
B. SOFTWARE EXAMPLE
B.1 7-segment LED display
V
UP/DOWN S/W
CLEAR S/W
GND
10k
Ω ×
DD
7
R20/INT0
R21/INT1
R00
R01
R02
R03
R04
R05
R06
R23
R22
330
4.7k
4.7k
Ω ×
7
Ω
Ω
LED Display
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
2N2222
2N2222
GMS81516
;*****************************************************************************
; Title: GMS81516 (GMS800 Series) Demonstration Program *
; Company: HYUNDAI Micro Electronics *
; Contents: Decimal Up/Down Counter *
; Programmer: HME MCU application team *
;*****************************************************************************
;
;******** DEFINE I/O PORT & FUNCTION REGISTER ADDRESS *********
;
R0 EQU 0C0H ;port R0 register
R0DD EQU 0C1H ;port R0 data I/O direction register
;
R1 EQU 0C2H ;port R1 register
R1DD EQU 0C3H ;port R1 data I/O direction register
;
R2 EQU 0C4H ;port R2 register
R2DD EQU 0C5H ;port R2 data I/O direction register
;
R3 EQU 0C6H ;port R3 register
R3DD EQU 0C7H ;port R3 data I/O direction register
;
R4 EQU 0C8H ;port R4 register
R4DD EQU 0C9H ;port R4 data I/O direction register
;
R5 EQU 0CAH ;port R5 register
R5DD EQU 0CBH ;port R5 data I/O direction register
;
R6 EQU 0CCH ;port R6 register
R6DD EQU 0CDH ;port R6 data I/O direction register
;
PMR4 EQU 0D0H ;port R4 mode register
T3S EQU 7,0D0H ;timer3 selection
DEC. 1999 iii
Page 88

GMS800 Series HYUNDAI Micro Electronics
T1S EQU 6,0D0H ;timer1 selection
EC2S EQU 5,0D0H ;event counter 2 selection
EC0S EQU 4,0D0H ;event counter 0 selection
INT3S EQU 3,0D0H ;external int.3 selection
INT2S EQU 2,0D0H ;external int.2 selection
INT1S EQU 1,0D0H ;external int.1 selection
INT0S EQU 0,0D0H ;external int.0 selection
;
PMR5 EQU 0D1H ;port R5 mode register
BUZS EQU 5,0D1H ;buzzer selection
WDTS EQU 4,0D1H ;watch dog timer selection
;
TMR EQU 0D2H ;test mode register
;
CKCTLR EQU 0D3H ;clock control register
BITR EQU 0D3H ;basic interval timer register
;
;WDTR EQU 0E0H ;watch dog timer register
;
TM0 EQU 0E2H ;timer0 mode register
TM2 EQU 0E3H ;timer2 mode register
;
TDR0 EQU 0E4H ;tomer0 data register
TDR1 EQU 0E5H ;tomer1 data register
TDR2 EQU 0E6H ;tomer2 data register
TDR3 EQU 0E7H ;tomer3 data register
;
ADCM EQU 0E8H ;A/D Converter mode register
ADR EQU 0E9H ;A/D con. register
;
SIOM EQU 0EAH ;serial I/O mode register
;SIOR EQU 0EBH ;serial I/O register
;
BUR EQU 0ECH ;buzzer data register
;
PWMR0 EQU 0F0H ;PWM0 data register
PWMR1 EQU 0F1H ;PWM1 data register
;
PWMCR EQU 0F2H ;PWM control register
;
IMOD EQU 0F3H ;interrupt mode register
IENL EQU 0F4H ;int. enable register low
AE EQU 7,0F4H ;A/D con. int. enable
WDTE EQU 6,0F4H ;W.D.T. int. enable
BITE EQU 5,0F4H ;B.I.T. int. enable
SE EQU 4,0F4H ;serial I/O int. enable
;
IRQL EQU 0F5H ;int. request flag register low
AR EQU 7,0F5H ;A/D con. int. request flag
WDTRF EQU 6,0F5H ;W.D.T. int. request flag
BITRF EQU 5,0F5H ;B.I.T. int. request flag
SR EQU 4,0F5H ;serial I/O int. request flag
;
IENH EQU 0F6H ;int. enable register high
INT0E EQU 7,0F6H ;external int.0 enable
INT1E EQU 6,0F6H ;external int.1 enable
INT2E EQU 5,0F6H ;external int.2 enable
INT3E EQU 4,0F6H ;external int.3 enable
T0E EQU 3,0F6H ;timer0 int. enable
T1E EQU 2,0F6H ;timer1 int. enable
T2E EQU 1,0F6H ;timer2 int. enable
T3E EQU 0,0F6H ;timer3 int. enable
;
IRQH EQU 0F7H ;int. request flag register high
INT0R EQU 7,0F7H ;external int.0 request flag
INT1R EQU 6,0F7H ;external int.1 request flag
INT2R EQU 5,0F7H ;external int.2 request flag
INT3R EQU 4,0F7H ;external int.3 request flag
T0R EQU 3,0F7H ;timer0 int. request flag
T1R EQU 2,0F7H ;timer1 int. request flag
T2R EQU 1,0F7H ;timer2 int. request flag
T3R EQU 0,0F7H ;timer3 int. request flag
;
IEDS EQU 0F8H ;external int. edge selection
;
;*********** MACRO DEFINITION ************
;
REG_SAVE MACRO ;Save Registers to Stacks
PUSH A
PUSH X
iv DEC. 1999
Page 89

HYUNDAI Micro Electronics GMS800 Series
PUSH Y
ENDM
;
REG_RESTORE MACRO ;Restore Register from Stacks
POP Y
POP X
POP A
ENDM
;
;*********** CONSTANT DEFINITION ***********
;
SEG_PORT EQU R0 ;7-Segment Output Port
STROBE_PORT EQU R2 ;Strobe Signal Port
;
;**************************************************************************
; RAM ALLOCATION *
;**************************************************************************
DIGIT10 DS 1 ;DIG10 Display Data
DIGIT1 DS 1 ;Seg1 Display Data
STROBE DS 1 ;Strobe Signal Data
TMR_500mS DS 1 ;500ms Time Counter
FLAGS DS 1 ;Function Flags
UP_F EQU 0,FLAGS ;1=Down,0=Up
F_500ms EQU 1,FLAGS ;
;
;**************************************************************************
; INTERRUPT VECTOR TABLE *
;**************************************************************************
;
ORG0FFE4H
DW NOT_USED ; Serial I/O
DW NOT_USED ; Basic Interval Timer
DW NOT_USED ; Watch Dog Timer
DW NOT_USED ; A/D CON.
DW NOT_USED ; Timer-3
DW NOT_USED ; Timer-2
DW NOT_USED ; Timer-1
DW TMR0_INT ; Timer-0
DW NOT_USED ; Int.3
DW NOT_USED ; Int.2
DW INT_1 ; Int.1
DW INT_0 ; Int.0
DW NOT_USED ;
DW RESET ; Reset
;
;**************************************************************************
; MAIN PROGRAM *
;**************************************************************************
;
ORG 0C000H ;Program Start Address
;
RESET: DI ;Disable All Interrupts
LDX #0
RAM_CLR: LDA #0 ;RAM Clear(!0000H->!00BFH)
STA {X}+ ;M(X) <- A, then X <- X+1
CMPX #0C0H ;X = #0C0H ?
BNE RAM_CLR
;
LDX #0FEH ;Stack Pointer Initial
TXSP ;SP. <- #0FEH
LDM R0,#0 ;I/O Port Data Clear
LDM R2,#0
LDM R0DD,#0FFH ;7-Seg. Data Output Mode
LDM R2DD,#00FH ;7-Seg. Strobe Output Mode
LDM STROBE,#0000_1011B
LDM TDR0,#250 ;8us x 250 = 2000us
LDM TM0,#0001_1111B ;Timer0(8bit),8us,Start Count-up
LDM IRQH,#0 ;Clear All Interrupts Requeat Flags
LDM IRQL,#0
LDM IENH,#1100_1000B ;EnableT0,Int0,Int1,Interrupt
LDM IENL,#00H
LDM IEDS,#0101_0101B ;External Int. Falling edge select
LDM PMR4,#03H ;General port OR Int?
SET1 UP_F
EI ;Enable Interrupts
DEC. 1999 v
Page 90

GMS800 Series HYUNDAI Micro Electronics
;
Loop: nop
IF F_500ms == 1
clr1 F_500ms
call INC_DEC
ENDIF
jmp Loop
;
;***********************************************
; Subject: Inc. or Dec. two digits *
;***********************************************
; Entry: UP_F *
; Return: UP_F=1, Increment two digits *
; UP_F=0, Decrement two digits *
;***********************************************
;
INC_DEC: BBC UP_F,DOWN ;Check Down mode or Up mode
;
;**************************
;* Up Count *
;**************************
;
SETC
LDA #0 ; DIGIT1 <- DIGIT1 + 1
ADC DIGIT1
IF A == #0AH
setc
lda #0
ENDIF
STA DIGIT1 ; Store result into DIGIT1
;
LDA #0 ; When Overflow is set,
ADC DIGIT10 ; DIGIT10 <- DIGIT10 + 1
IF A == #10
lda #0
ENDIF
STA DIGIT10
RET
;
;**************************
;* Down Count *
;**************************
;
DOWN: clrc
lda DIGIT1 ; DIGIT1 <- DIGIT1 - 1
sbc #0
IF A == #0FFH
lda #9
clrc
ELSE
setc
ENDIF
sta DIGIT1 ; Store result into DIGIT1
;
lda DIGIT10 ; When Overflow is set,
sbc #0 ; DIGIT10 <- DIGIT10 - 1
IF A == #0FFH
lda #9
ENDIF
STA DIGIT10
RET
;
;**************************************************************************
; TIMER0,INTERRUPT ROUTINE(2ms)& INT0,INT1 *
;**************************************************************************
;
TMR0_INT:
REG_SAVE ;Save Registers to Stacks
CALL DSPLY ;Segments Data Port Output
CALL Make_500msFalg ;250ms mesurement
REG_RESTORE ;Restore Registers from Stacks
RETI
;
;**************************************************************************
; EXTERNAL INTERRUPT 0 (UP/DOWN KEY) *
;**************************************************************************
;
INT_0: NOT1 UP_F ;INT0 Service routine
RETI ;Toggle the Up/Down mode
;
vi DEC. 1999
Page 91

HYUNDAI Micro Electronics GMS800 Series
;**************************************************************************
; EXTERNAL INTERRUPT 1 (CLEAR KEY) *
;**************************************************************************
;
INT_1: LDM DIGIT1,#0 ;INT1 Service routine
LDM DIGIT10,#0
LDM TMR_500MS,#0 ;0.5Sec Restart
RETI
;
;***********************************************************************
; Subject: Seven Segment Display (DSPLY) *
;***********************************************************************
; Entry: DIGIT10 or DIGIT1 *
; Return: Output SEG_PORT (R00~R07), *
; Strobe_port (R22,R23) *
; Scratch: STROBE *
;***********************************************************************
; Description: After read internal RAM data, output data to the port *
;***********************************************************************
;
DSPLY: LDM STROBE_PORT,#03H ;Segment All Turn Off
NOT1 STROBE.2 ;Toggle strobe0
NOT1 STROBE.3 ;Toggle strobe1
IF STROBE.3 = 1 ;Test if R23 is high.
ldy DIGIT1
ELSE
ldy DIGIT10
ENDIF
LDA !FONT+Y
STA SEG_PORT ;Segment Data output
LDA STROBE
STA STROBE_PORT ;Current Digit Turn On
RET ;Quit
;
;***********************************************
; Subject: Set falg at every 500ms *
;***********************************************
; Entry: None *
; Return: 500ms flag (F_500ms) *
;***********************************************
;
Make_500msFalg:
INC TMR_500MS ;count up every 2ms
LDA TMR_500MS
IF A == #250 ;Compare 0.5S
ldm TMR_500MS,#0 ;clear 0.5sec. counter
set1 F_500ms ;set 0.5sec. flag
ENDIF
RET
;
;**************************************************************************
; 7-SEGMENT PATTERN DATA *
; _a_ *
; f | g |b *
; |---| *
; e |___|c *
; d .h *
;**************************************************************************
; Segment: hgfe dcba To be displayed Digit Number
FONT DB 0011_1111B ; 0
DB 0000_0110B ; 1
DB 0101_1011B ; 2
DB 0100_1111B ; 3
DB 0110_0110B ; 4
DB 0110_1101B ; 5
DB 0111_1100B ; 6
DB 0000_0111B ; 7
DB 0111_1111B ; 8
DB 0110_0111B ; 9
;
;**************************************************************************
;
NOT_USED: nop ;Discard Unexpected Interrupts
reti
;
END ;Notice Program End
DEC. 1999 vii
Page 92

GMS800 Series HYUNDAI Micro Electronics
C. INSTRUCTION
C.1 Terminology List
Terminology Description
A Accumulator
X X - register
Y Y - register
PSW Program Status Word
#imm 8-bit Immediate data
dp Direct Page Offset Address
!abs Absolute Address
[ ] Indirect expression
{ } Register Indirect expression
{ }+ Register Indirect expression, after that, Register auto-increment
.bit Bit Position
A.bit Bit Position of Accumulator
dp.bit Bit Position of Direct Page Memory
M.bit
Bit Position of Memory Data (000
rel Relative Addressing Data
upage
U-page (0FF00H~0FFFFH) Offset Address
n Table CALL Number (0~15)
+ Addition
x
y
−
×
Subtraction
Multiplication
0
Bit Position
1
Bit Position
/ Division
( ) Contents Expression
∧
∨
⊕
AND
OR
Exclusive OR
~NOT
←
→
↔
Assignment / Transfer / Shift Left
Shift Right
Exchange
= Equal
≠
Not Equal
~0FFFH)
H
Upper Nibble Expression in Opcode
Upper Nibble Expression in Opcode
viii DEC. 1999
Page 93

HYUNDAI Micro Electronics GMS800 Series
C.2 Instruction Map
0000000000010100010020001103001000400101050011006001110701000080100109010100A010110B011000C011010D011100E01111
LOW
HIGH
0F
000 -
001 CLRC
010 CLRG
011 DI
100 CLRV
101 SETC
110 SETG
111 EI
LOW
HIGH
000
SET1
dp.bit
1000010100011110010121001113101001410101151011016101111711000181100119110101A110111B111001C111011D111101E11111
BPL
CLR1
rel
dp.bit
BBS
A.bit,rel
BBC
A.bit,rel
BBS
dp.bit,rel
BBC
dp.bit,rel
ADC
ADCdpADC
#imm
SBC
#imm
CMP
#imm
OR
#immORdpORdp+XOR!abs
AND
#imm
EOR
#imm
LDA
#imm
LDM
dp,#imm
ADC
{X}
!abs+Y
dp+X
SBCdpSBC
dp+X
CMPdpCMP
dp+X
ANDdpAND
dp+X
EORdpEOR
dp+X
LDAdpLDA
dp+X
STAdpSTA
dp+X
ADC
ADC
[dp+X]
ADC
!abs
SBC
!abs
CMP
!abs
AND
!abs
EOR
!abs
LDA
!abs
STA
!abs
ADC
[dp]+Y
ASLAASLdpTCALL0SETA1
ROLAROLdpTCALL2CLRA1
LSRALSRdpTCALL4NOT1
RORARORdpTCALL6OR1
INCAINCdpTCALL8AND1
DECADECdpTCALL10EOR1
LDYdpTCALL12LDC
TXA
STYdpTCALL14STC
TAX
ASL
ASL
dp+X
TCALL1JMP
!abs
.bit
.bit
M.bit
OR1B
AND1B
EOR1B
LDCB
M.bit
!abs
BITdpPOPAPUSH
COMdpPOPXPUSHXBRA
TSTdpPOPYPUSHYPCALL
CMPXdpPOP
CMPYdpCBNE
DBNEdpXMA
LDXdpLDX
STXdpSTX
BIT
!abs
PUSH
PSW
TXSP
dp+X
TSPX
dp+X
dp+Y
dp+Y
ADDWdpLDX
BRK
A
Upage
RET
PSW
INC
DEC
XCN DAS
XAX STOP
JMP
#imm
[!abs]
rel
X
X
1F
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
BVC
rel
BCC
rel
BNE
rel
BMI
rel
BVS
rel
BCS
rel
BEQ
rel
SBC
SBC
SBC
CMP
AND
EOR
LDA
STA
SBC
[dp]+Y
CMP
[dp]+Y
AND
[dp]+Y
EOR
[dp]+Y
LDA
[dp]+Y
STA
[dp]+Y
{X}
!abs+Y
[dp+X]
CMP
CMP
{X}
!abs+Y
[dp+X]
OR
{X}OR!abs+YOR[dp+X]OR[dp]+Y
AND
AND
{X}
!abs+Y
[dp+X]
EOR
EOR
{X}
!abs+Y
[dp+X]
LDA
LDA
{X}
!abs+Y
[dp+X]
STA
STA
{X}
!abs+Y
[dp+X]
ROL
!abs
LSR
!abs
ROR
!abs
INC
!abs
DEC
!abs
LDY
!abs
STY
!abs
ROL
TCALL3CALL
dp+X
LSR
TCALL
dp+X
ROR
dp+X
INC
dp+X
DEC
dp+X
LDY
dp+X
STY
dp+X
5
TCALL7DBNEYCMPX
TCALL
9
TCALL11XMA
TCALL13LDA
TCALL15STA
TEST
!abs
!abs
TCLR1
MUL
!abs
!abs
CMPY
DIV
!abs
XMAdpDECWdpDEC
{X}
LDX
{X}+
!abs
STX
{X}+
!abs
SUBWdpLDY
CMPWdpCMPX
INCWdpINC
CBNE
#imm
#imm
LDYAdpCMPY
#imm
Y
Y
STYA
dp
dp
XAY DAA
XYX NOP
JMP
[dp]
CALL
[dp]
RETI
TAY
TYA
DEC. 1999 ix
Page 94

GMS800 Series HYUNDAI Micro Electronics
C.3 Instruction Set
Arithmetic / Logic Operation
No. Mnemonic
1 ADC #imm 04 2 2 Add with carry.
2 ADC dp 05 2 3 A ← ( A ) + ( M ) + C
3 ADC dp + X 06 2 4
4 ADC !abs 07 3 4
5 ADC !abs + Y 15 3 5
6 ADC [ dp + X ] 16 2 6
7 ADC [ dp ] + Y 17 2 6
8 ADC { X } 14 1 3
9 AND #imm 84 2 2 Logical AND
10 A ND dp 85 2 3 A ← ( A ) ∧ ( M )
11 AND dp + X 86 2 4
12 AND !abs 87 3 4
13 AND !abs + Y 95 3 5
14 A ND [ dp + X ] 96 2 6
15 AND [ dp ] + Y 97 2 6
16 A ND { X } 94 1 3
17 ASL A 08 1 2
18 ASL dp 09 2 4
19 ASL dp + X 19 2 5
20 ASL !abs 18 3 5
21 CMP #imm 44 2 2
22 CMP dp 45 2 3
23 CMP dp + X 46 2 4
24 CM P !abs 47 3 4
25 CM P !abs + Y 55 3 5
26 CMP [ dp + X ] 56 2 6
27 CMP [ dp ] + Y 57 2 6
28 CM P { X } 54 1 3
29 CM PX #imm 5E 2 2 Compare X contents with memory contents
30 CM PX dp 6C 2 3 ( X ) - ( M )
31 CMPX !abs 7C 3 4
32 CM PY #imm 7E 2 2 Compare Y contents with memory contents
33 CM PY dp 8C 2 3 ( Y ) - ( M )
34 CMPY !abs 9C 3 4
35 COM dp 2C 2 4 1’S Complement : ( dp ) ← ~( dp )
36 DAA DF 1 3 Decimal adjust for addition
37 DAS CF 1 3 Decimal adjust for subtraction
38 DE C A A8 1 2 Decrement
39 DEC dp A9 2 4 M ← ( M ) - 1
40 DEC dp + X B9 2 5
41 DEC !abs B8 3 5
42 DEC X AF 1 2
43 DEC Y BE 1 2
Op
Code
ByteNoCycle
No
Operation
Arithmetic shift left
76543210
C
←
Compare accumulator contents with memory contents
( A ) - ( M )
“0”
←
←←←←←←←←
Flag
NVGBHIZC
NV--H-ZC
N-----Z-
N-----ZC
N-----ZC
N-----ZC
N-----ZC
N-----ZN-----ZC
N-----ZC
N-----ZN-----ZN-----ZN-----ZN-----ZN-----Z-
x DEC. 1999
Page 95

HYUNDAI Micro Electronics GMS800 Series
No. Mnemonic
Op
Code
ByteNoCycle
No
Operation
44 DIV 9B 1 12 Divide : YA / X Q: A, R: Y
45 E OR #imm A4 2 2 Exclusive OR
46 EOR dp A5 2 3 A ← ( A ) ⊕ ( M )
47 EOR dp + X A6 2 4
48 EOR !abs A 7 3 4
49 EOR !abs + Y B5 3 5
50 E OR [ dp + X ] B6 2 6
51 EOR [ dp ] + Y B7 2 6
52 EOR { X } B4 1 3
53 INC A 88 1 2 Increment
54 INC dp 89 2 4 M ← ( M ) + 1
55 INC dp + X 99 2 5
56 INC !abs 98 3 5
57 INC X 8F 1 2
58 INC Y 9E 1 2
59 LSR A 48 1 2
60 LS R dp 49 2 4
61 LSR dp + X 59 2 5
Logical shift right
76543210
“0”
→
62 LSR !abs 58 3 5
63 M UL 5B 1 9 Multiply : YA ← Y × A
64 OR #imm 64 2 2 Logical OR
65 OR dp 65 2 3 A ← ( A ) ∨ ( M )
66 OR dp + X 66 2 4
67 OR !abs 67 3 4
68 OR !abs + Y 75 3 5
69 OR [ dp + X ] 76 2 6
70 OR [ dp ] + Y 77 2 6
71 OR { X } 74 1 3
72 ROL A 28 1 2
73 ROL dp 29 2 4
Rotate left through Carry
76543210
C
74 ROL dp + X 39 2 5
75 ROL !abs 38 3 5
76 ROR A 68 1 2
77 ROR dp 69 2 4
Rotate right through Carry
76543210
78 ROR dp + X 79 2 5
79 ROR !abs 78 3 5
80 SBC #imm 24 2 2 Subtract with Carry
81 SBC dp 25 2 3 A ← ( A ) - ( M ) - ~( C )
82 SBC dp + X 26 2 4
83 SBC !abs 27 3 4
84 SBC !abs + Y 35 3 5
85 SBC [ dp + X ] 36 2 6
86 SBC [ dp ] + Y 37 2 6
87 S BC { X } 34 1 3
88 TST dp 4C 2 3
89 X CN CE 1 5
Test memory contents for negative or zero, ( dp ) - 00
Exchange nibbles within the accumulator
↔ A3~A
A
7~A4
0
Flag
NVGBHIZC
NV--H-Z-
N-----Z-
N-----ZC
N-----ZN-----ZN-----ZN-----ZN-----Z-
H
N-----ZC
N-----Z-
N-----Z-
N-----ZC
N-----ZC
NV--HZC
N-----Z-
N-----Z-
C
→→→→→→→→
→
←←←←←←←←
C
→→→→→→→→
DEC. 1999 xi
Page 96

GMS800 Series HYUNDAI Micro Electronics
Register / Memory Operation
No. Mnemonic
1 LDA #imm C4 2 2 Load accumulator
2 LDA dp C5 2 3 A ← ( M )
3 LDA dp + X C6 2 4
4 LDA !abs C7 3 4
5 LDA !abs + Y D5 3 5
6 LDA [ dp + X ] D6 2 6
7 LDA [ dp ] + Y D7 2 6
8 LDA { X } D4 1 3
9 LDA { X }+ DB 1 4 X- register auto-increment : A ← ( M ) , X ← X + 1
10 LDM dp,#imm E4 3 5 Load memory with immediate data : ( M ) ← imm
11 LDX #imm 1E 2 2 Load X-register
12 LDX dp CC 2 3 X ← ( M )
13 LDX dp + Y CD 2 4
14 LDX !abs DC 3 4
15 LDY #imm 3E 2 2 Load Y-register
16 LDY dp C9 2 3 Y ← ( M )
17 LDY dp + X D9 2 4
18 LDY !abs D8 3 4
19 S TA dp E 5 2 4 Store accumulator contents in memory
20 S TA dp + X E6 2 5 ( M ) ← A
21 STA !abs E7 3 5
22 STA !abs + Y F5 3 6
23 S TA [ dp + X ] F6 2 7
24 STA [ dp ] + Y F7 2 7
25 STA { X } F4 1 4
26 S TA { X }+ FB 1 4 X- register auto-increment : ( M ) ← A, X ← X + 1
27 S TX dp EC 2 4 Store X-register contents in memory
28 S TX dp + Y ED 2 5 ( M ) ← X
29 STX !abs FC 3 5
30 S TY dp E 9 2 4 Store Y-register contents in memory
31 S TY dp + X F9 2 5 ( M ) ← Y
32 STY !abs F8 3 5
33 T AX E8 1 2 Transf er accum ulator contents to X-register : X ← A
34 T AY 9F 1 2 Transfer accumulator contents to Y-register : Y ← A
35 TSP X AE 1 2 Transfer stack-pointer contents to X-register : X ← sp
36 TXA C8 1 2 Transfer X-register contents to accumulator: A ← X
37 T XSP 8E 1 2 Transfer X-register contents to stack-pointer: sp ← X
38 TYA BF 1 2 Transfer Y-register contents to accumulator: A ← Y
39 X AX EE 1 4 Exchange X-register contents with accumulator :X ↔ A
40 X AY DE 1 4 Exchange Y-register contents with accumulator :Y ↔ A
41 X MA dp BC 2 5 Exchange memory contents with accumulator
42 X MA dp+ X AD 2 6 ( M ) ↔ A
43 X MA {X} BB 1 5
44 X YX FE 1 4 Exchange X-register contents with Y-reg ister : X ↔ Y
Op
Code
ByteNoCycle
No
Operation
Flag
NVGBHIZC
N-----Z-
--------
N-----Z-
N-----Z-
--------
--------
--------
N-----ZN-----ZN-----ZN-----ZN-----ZN-----Z-
--------
--------
N-----Z-
--------
xii DEC. 1999
Page 97

HYUNDAI Micro Electronics GMS800 Series
16-BIT operation
No. Mnemonic
1 ADDW dp 1D 2 5
2CMPW dp 5D 2 4
3DECW dp BD 2 6
4 INCW dp 9D 2 6
5 LDYA dp 7D 2 5
6 STYA dp DD 2 5
7 SUBW dp 3D 2 5
Op
Code
ByteNoCycle
No
Operation
16-Bits add without Carry
YA ← ( YA ) + ( dp +1 ) ( dp )
Compare YA contents with memory pair contents :
(YA) − (dp+1)(dp)
Decrement memory pair
( dp+1)( dp) ← ( dp+1) ( dp) - 1
Increment memory pair
( dp+1) ( dp) ← ( dp+1) ( dp ) + 1
Load YA
YA ← ( dp +1 ) ( dp )
Store YA
( dp +1 ) ( dp ) ← YA
16-Bits subtract without carry
YA ← ( YA ) - ( dp +1) ( dp)
Bit Manipulation
No. Mnem onic
1 AND1 M.bit 8B 3 4 Bit AND C-flag : C ← ( C ) ∧ ( M .bit )
2 AND1B M.bit 8B 3 4 Bit AND C-flag and NOT : C ← ( C ) ∧ ~( M .bit )
3 BIT dp 0C 2 4 Bit test A with memory :
4 BIT !abs 1C 3 5
5 CLR1 dp.bit y1 2 4 Clear bit : ( M.bit ) ← “0”
6 CLRA1 A.bit 2B 2 2 Clear A bit : ( A.bit ) ← “0”
7 CLRC 20 1 2 Clear C-flag : C ← “0”
8 CLRG 40 1 2 Clear G-flag : G ← “0”
9 CLRV 80 1 2 Clear V-flag : V ← “0”
10 EOR1 M.bit AB 3 5 Bit exclusive-OR C-flag : C ← ( C ) ⊕ ( M .bit )
11 EOR1B M.bit AB 3 5 Bit exclusive-OR C-flag and NOT : C ← ( C ) ⊕ ~(M .bit)
12 LDC M.bit CB 3 4 Load C-flag : C ← ( M .bit )
13 LDCB M.bit CB 3 4 Load C-flag with NOT : C ← ~( M .bit )
14 NOT1 M.bit 4B 3 5 Bit complement : ( M .bit ) ← ~( M .bit )
15 OR1 M.bit 6B 3 5 Bit OR C-flag : C ← ( C ) ∨ ( M .bit )
16 OR1B M.bit 6B 3 5 Bit OR C-flag and NOT : C ← ( C ) ∨ ~( M .bit )
17 S ET1 dp.bit x1 2 4 Set bit : ( M.bit ) ← “1”
18 S ETA1 A.bit 0B 2 2 Set A bit : ( A.bit ) ← “1”
19 SETC A0 1 2 Set C-flag : C ← “1”
20 SETG C0 1 2 Set G-flag : G ← “1”
21 S TC M.bit EB 3 6 Store C-flag : ( M .bit ) ← C
22 TCLR1 !abs 5C 3 6
23 TSET1 !abs 3C 3 6
Op
Code
ByteNoCycle
No
Operation
Z ← ( A ) ∧ ( M ) , N ← ( M
Test and clear bits with A :
A - ( M ) , ( M ) ← ( M ) ∧ ~( A )
Test and set bits with A :
A - ( M ) , ( M ) ← ( M ) ∨ ( A )
) , V ← ( M6 )
7
Flag
NVGBHIZC
NV--H-ZC
N-----ZC
N-----Z-
N-----Z-
N-----Z-
--------
NV--H-ZC
Flag
NVGBHIZC
-------C
-------C
MM----Z-
--------
--------
-------0
--0-----
-0--0---
-------C
-------C
-------C
-------C
--------
-------C
-------C
--------
--------
-------1
--1-----
--------
N-----Z-
N-----Z-
DEC. 1999 xiii
Page 98

GMS800 Series HYUNDAI Micro Electronics
Branch / Jump Operation
No. Mnemonic
Op
Code
ByteNoCycle
No
Operation
1 BBC A.bit,rel y2 2 4/6 Branch if bit clear :
2 BBC dp.bit,rel y3 3 5/7 if ( bit ) = 0 , then pc ← ( pc ) + rel
3 BBS A.bit,rel x2 2 4/6 Branch if bit set :
4 BBS dp.bit,rel x3 3 5/7 if ( bit ) = 1 , then pc ← ( pc ) + rel
5 BCC rel 50 2 2/4
6 BCS rel D0 2 2/4
7 BEQ rel F0 2 2/4
8 BMI rel 90 2 2/4
9 BNE rel 70 2 2/4
10 BPL rel 10 2 2/4
11 BRA rel 2F 2 4
12 BVC rel 30 2 2/4
13 BVS rel B0 2 2/4
Branch if carry bit clear
if ( C ) = 0 , then pc ← ( pc ) + rel
Branch if carry bit set
if ( C ) = 1 , then pc ← ( pc ) + rel
Branch if equal
if ( Z ) = 1 , then pc ← ( pc ) + rel
Branch if minus
if ( N ) = 1 , then pc ← ( pc ) + rel
Branch if not equal
if ( Z ) = 0 , then pc ← ( pc ) + rel
Branch if minus
if ( N ) = 0 , then pc ← ( pc ) + rel
Branch always
pc ← ( pc ) + rel
Branch if overflow bit clear
if (V) = 0 , then pc ← ( pc) + rel
Branch if overflow bit set
if (V) = 1 , then pc ← ( pc ) + rel
14 CA LL !abs 3B 3 8 Subroutine call
15 CALL [dp] 5F 2 8
M( sp)←( pc
if !abs, pc← abs ; if [dp], pc
), sp←sp - 1, M(sp)← (pcL), sp ←sp - 1,
H
( dp ), pc
←
L
16 CBNE dp,rel FD 3 5/7 Compare and branch if not equal :
17 CB NE dp+X,rel 8D 3 6/8 if ( A ) ≠ ( M ) , then pc ← ( pc ) + rel.
18 DBNE dp,rel AC 3 5/7 Decrement and branch if not equal :
19 DB NE Y,rel 7B 2 4/6 if ( M ) ≠ 0 , then pc ← ( pc ) + rel.
20 JMP !abs 1B 3 3 Unconditional jump
21 JM P [!abs] 1F 3 5 pc ← jump address
22 JM P [dp] 3F 2 4
U-page call
23 P CALL upage 4F 2 6
24 TCALL n nA 1 8
M(sp) ←( pc
sp ← sp - 1, pc
Table call : (sp) ←( pc
M(sp) ← ( pc
← (Table vector L), pc
pc
L
), sp ←sp - 1, M(sp) ← ( pcL ),
H
( upage ), pc
←
L
), sp ← sp - 1,
H
),sp ← sp - 1,
L
←
H
(Table vector H)
←
H
”0FF
←
H
” .
H
( dp+1 ) .
Flag
NVGBHIZC
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
--------
xiv DEC. 1999
Page 99

HYUNDAI Micro Electronics GMS800 Series
Control Operation & Etc.
No. Mnemonic
1 BRK 0F 1 8
2 DI 60 1 3 Disable all interrupts : I ← “0”
3 EI E0 1 3 Enable all interrupt : I ← “1”
4 NOP FF 1 2 No operation
5 POP A 0D 1 4 sp ← sp + 1, A ← M( sp )
6 POP X 2D 1 4 sp ← sp + 1, X ← M( sp )
7 POP Y 4D 1 4 sp ← sp + 1, Y ← M( sp )
8 POP PSW 6D 1 4 sp ← sp + 1, PSW ← M( sp )
9 PUSH A 0E 1 4 M( sp ) ← A , sp ← sp - 1
10 PUSH X 2E 1 4 M( sp ) ← X , sp ← sp - 1
11 PUSH Y 4E 1 4 M( sp ) ← Y , sp ← sp - 1
12 PUSH PSW 6E 1 4 M( sp ) ← PSW , sp ← sp - 1
13 RE T 6F 1 5
14 RE TI 7F 1 6
15 S TOP EF 1 3 Stop mode ( halt CPU, stop oscillator )
Op
Code
ByteNoCycle
No
Operation
Software interrupt : B ← ”1”, M(sp)
M(s) ← (pc
pc
L
Return from subroutine
sp ← sp +1, pc
Return from interrupt
sp ← sp +1, PSW ← M( sp ), sp ← sp + 1,
← M( sp ), sp ← sp + 1, pcH ← M( sp )
pc
L
), sp ← sp - 1, M(sp) ← (PSW), sp ← sp -1,
L
( 0FFDE
←
) , pc
H
← M( sp ), sp ← sp +1, pcH ← M( sp )
L
←
H
←
( 0FFDF
(pc
) .
H
), sp ←sp-1,
H
Flag
NVGBHIZC
---1-0--
-----0--
-----1--
--------
--------
restored
--------
--------
restored
--------
DEC. 1999 xv
Page 100

D. MASK ORDER SHEET
MASK ORDER & VERIFICATION SHEET
Customer should write inside thick line box.
1. Customer Information
GMS81508B
GMS81516B
GMS81524B
-HF
2. Device Information
Company Name
Package
64SDIP 64MQFP
Application
Order Date
YYYY
MM DD
File Name
ROM Size (bytes)
Tel:
Fax:
Mask Data
Check Sum ( )
E-mail address:
Name &
Signature:
3. Marking Specification
HME
08 or 16 or 24
PFD Option
3.0V
2.4V
Not use
Customer’s logo
GMS815XXB-HF
YYWW
KOREA
If the customer logo must be used in the special mark, please submit a clean original of the logo.
Customer’s part number
GMS815XXB-HF
YYWW
Customer logo is not required.
( ) .OTP
(24K)
2000
(16K)
4000
(8K)
6000
Set “FFH” in blanked area
7FFF
(Please check mark
KOREA
H
H
H
.OT P file d a ta
H
64LQFP
ChollianInternet Hitel
24K8K 16K
√
into )
4. Delivery Schedule
Customer sample
Risk order
YYYY
YYYY
5. ROM Code Verification
Please confirm out verification data.
Verification date:
Check sum:
Tel:
E-mail address:
Name &
Signature:
DEC., 10. 1999
YYYY
Fax:
Date
MM DD
MM DD
MM DD
Quantity
HME Confirmation
pcs
pcs
Approval date:
YYYY
MM DD
I agree with your verification data and confirm you to
make mask set.
Tel:
Fax:
E-mail address:
Name &
Signature:
+<81'$,#0LFUR(OHFWURQLFV
Semiconductor Group of Hyundai Electronics Industries Co., Ltd.
 Loading...
Loading...