Page 1
January 2007
FMS6502
8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers,
Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
Features
■ 8 x 6 Crosspoint Switch Matrix
■ Supports SD, PS, and HD 1080i / 1080p Video
■ Input Clamp and Bias Circuitry
■ Doubly Terminated 75Ω Cable Drivers
■ Programmable 0dB or 6dB Gain
■ AC- or DC-Coupled Inputs
■ AC- or DC-Coupled Outputs
■ One-to-One or One-to-Many Input-to-Output
Switching
2CTM
■ I
■ 3.3V or 5V Single Supply Operation
■ Pb-Free TSSOP-24 Package
-Compatible Digital Interface, Standard Mode
Applications
■ Cable and Satellite Set-Top Bo xes
■ TV and HDTV Sets
■ A / V Switchers
■ Personal Video Recorders (PVR)
■ Security and Surveillance
■ Video Distribution
■ Automotive (In-Cabin Entertainment)
Description
The FMS6502 provides eight inputs that can be routed to
any of six outputs. Each input can be routed to one or
more outputs, but only one input may be routed to any
output.
Each input supports an integrated clamp option to set the
output sync tip level of video with sync to ~300mV. Alternatively, the input may be internally biased to center output signals without sync (Chroma, Pb, Pr) at ~1.25V.
All outputs are designed to drive a 150Ω DC-coupled
load. Each output can be programmed to provide either
0dB or 6dB of signal gain.
Input-to-output routing and input bias mode functions are
controlled via an I
2
C-compatible digital interface.
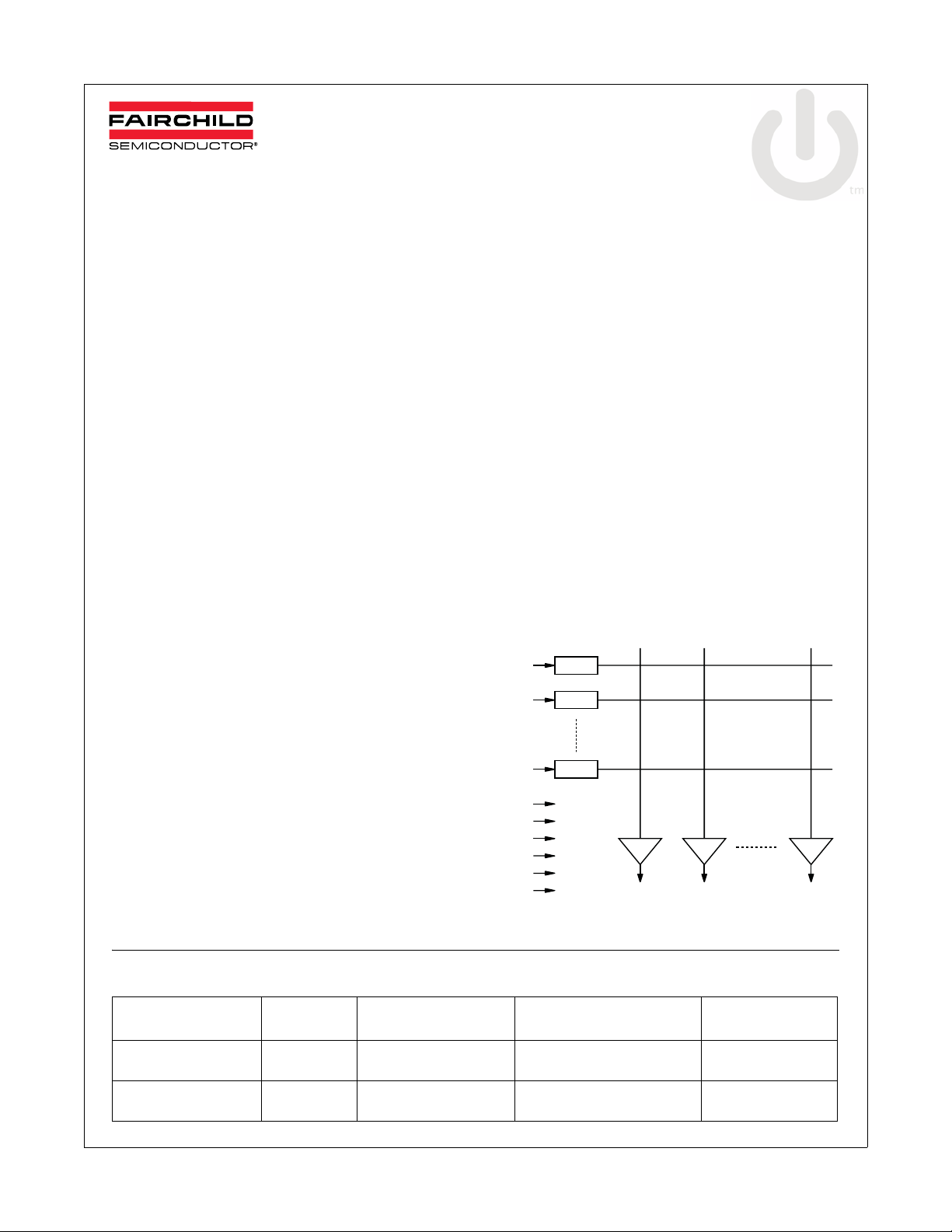
Block Diagram
IN1
IN2
IN8
C / B
C / B
C / B
SDA
SCL
ADDR0
ADDR1
VCC (2)
GND (4)
OUT1 OUT2 OUT6
Figure 1. Block Diagram
Ordering Information
Operating
Part Number Pb-Free
FMS6502MTC24 Yes -40°C to 85°C
FMS6502MTC24X Yes -40°C to 85°C
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
Rev. 1.0.0
Temperature Range Package Packing Method
24-Lead Thin Shrink Small
Ouline Package
24-Lead Thin Shrink Small
Ouline Package
Rail
Reel
Page 2
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
5
4
2
3
6
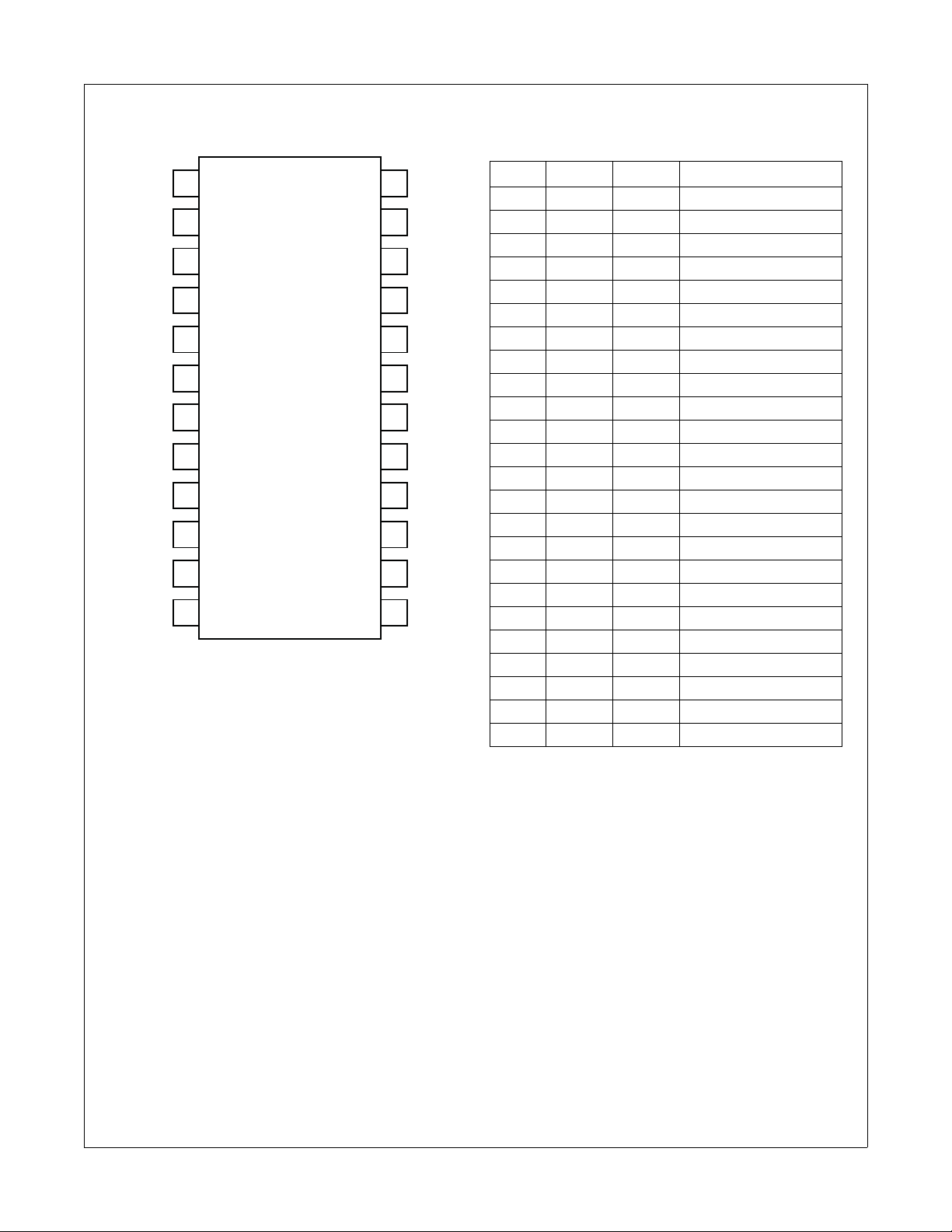
Pin Configuration
1
IN1
IN2
IN3
IN4
IN5
IN6
2
FAIRCHILD
3
FMS6502
4
24L TSSOP
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Figure 2. Pin Configuration
GND
VDD
GND
ADDR1
ADDR0
SCL
Pin Description
GND
24
OUT1
23
22
21
OUT
OUT
VDD
20
OUT
19
18
OUT
17
OUT
16
GND
15
IN8
14
13
SDA
IN7
Pin# Pin Type Description
1 IN1 Input Input, channel 1
2 GND Output Must be tied to ground
3 IN2 Input Input, channel 2
4 VDD Input Positive power supply
5 IN3 Input Input, channel 3
6 GND Output Must be tied to ground
7 IN4 Input Input, channel 4
2
8 ADDR1 Input Selects I
9 IN5 Input Input, channel 5
10 ADDR0 Input Selects I
1 1 IN6 Input Input, channel 6
12 SCL Input Serial clock for I
13 IN7 Input Input, channel 7
14 SDA Input Serial data for I
15 IN8 Input Input, channel 8
16 GND Output Must be tied to ground
17 OUT6 Output Output, channel 6
18 OUT5 Output Output, channel 5
19 OUT4 Output Output, channel 4
20 VDD Input Positive power supply
21 OUT3 Output Output, channel 3
22 OUT2 Output Output, channel 2
23 OUT1 Output Output, channel 1
24 GND Output Must be tied to ground
C address
2
C address
2
2
C port
C port
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 2
Page 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Stresses exceeding the absolute maximum ratings may damage the device. The device may not function or be operable above the recommended operating conditions and stressing the parts to these levels is not recommended. In addition, extended exposure to stresses above the recommended operating cond itions may affect device reliability. The
absolute maximum ratings are stress ratings only.
Parameter Min. Max. Unit
DC Supply Voltage -0.3 6 V
Analog and Digital I/O -0.3 V
Output Current Any One Channel, Do Not Exceed 40 mA
+ 0.3 V
cc
Reliability Information
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
T
Junction Temperature 150 °C
J
T
ΘJA
Storage Temperature Range -65 150 °C
STG
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10s) 300 °C
T
L
Thermal Resistance, JEDEC Standard Multi-Layer Test Boards,
Still Air
84 °C/W
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
Recommended Operating Conditions
The Recommended Operating Conditions table defines the conditions for actual device operation. Recommended
operating conditions are specified to ensure optimal perfor mance to the datasheet specifications. Fairchild does not
recommend exceeding them or designing to Absolute Maximum Ratings.
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
T
Operating Temperature Range -40 85 °C
A
V
Supply Voltage Range 3.135 5.0 5.25 V
CC
Electrostatic Discharge Information
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
HBM Human Body Model (JEDEC: JESD22-A114) 10 kV
CDM Charged Device Model (JEDEC: JESD22-A101) 2 kV
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 3
Page 4
Digital Interface
The I2C-compatibe interface is used to program output
enables, input-to-output routing, and input bias configuration. The I
2
C address of the FMS6502 is 0x06 (0000
ADDR1 ADDR0 Binary Hex
0 0 0000 0110 0x06
0 1 0100 0110 0x46
1 0 1000 0110 0x86
1 1 1100 0110 0xC6
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
0110) with the ability to offset based upon the valu es of
the ADDR0 and ADDR1 inputs. Offset addresses are
defined below:
Data and address data of eight bits each are written to
the FMS6502 I
functions.
For efficiency, a single data register is shared between
two outputs for input selection. More than one output can
select the same input channel for one-to-many routing.
2
C address register to access control
The clamp / bias control bits are written to their own
internal address since they should remain the same
regardless of signal routing. They are set based on the
input signal that is connected to the FMS6502.
All undefined addresses may be written without effect.
Output Control Register Contents and Defaults
Control Name Wid th Type Default Bit(s) Description
In-A 4 bits Write 0 3:0
In-B 4 bits Write 0 7:4
Input selected to drive this output:
0000=OFF
Input selected to drive this output:
0000=OFF
1
, 0001=IN1, 0010=IN2, 1000=IN8
1
, 0001=IN1, 0010=IN2, 1000=IN8
Output Control Register MAP
Name Address Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
OUT1,2 0x00 B3-Out2 B2-Out2 B1-Out2 B0-Out2 B3-Out1 B2-Out1 B1-Out1 B0-Out1
OUT3,4 0x01 B3-Out4 B2-Out4 B1-Out4 B0-Out4 B3-Out3 B2-Out3 B1-Out3 B0-Out3
OUT5,6 0x02 B3-Out6 B2-Out6 B1-Out6 B0-Out6 B3-Out5 B2-Out5 B1-Out5 B0-Out5
Clamp Control Register Contents and Defaults
Control Name Wid th Type Default Bit(s) Description
Clmp 1 bit Write 0 7:0 Clamp / Bias selection: 1 = Clamp, 0 = Bias
Clamp Control Register Map
Name Address Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
CLAMP 0x03 Clmp8 Clmp7 Clmp6 Clmp5 Clmp4 Clmp3 Clmp2 Clmp1
Gain Control Register Contents and Defaults
Control Name Wid th Type Default Bit(s) Description
Gain 1 bit Write 0 7:0 Output Gain selection: 0 = 6dB, 1 = 0dB
Gain Control Register Map
Name Address Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
GAIN 0x04 Unused Unused Gain6 Gain5 Gain4 Gain3 Gain2 Gain1
Note:
1. When the OFF input selection is used, the output amplifier is powered down and enters a high-impedance state.
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 4
Page 5

DC Electrical Characteristics
TA = 25°C, Vcc = 5V, Vin = 1Vpp, input bias mode, one-to-one routing, 6dB gain, all inputs AC-coupled with 0.1μF,
unused inputs AC-terminated through 75Ω to GND, all outputs AC-coupled with 220μF into 150Ω, referenced to
400kHz unless otherwise noted.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
No Load, All Outputs Enabled 55 75 mA
pp
Clamp Mode, All Gain Settings 0.10 0.15 0.20 V
Clamp Mode, 0dB Gain Setting 0.10 0.15 0.20 V
Clamp Mode, 6dB Gain Setting 0.20 0.30 0.40 V
Bias Mode, All Gain Settings 0.575 0.625 0.675 V
Bias Mode, 0dB Gain Setting 0.575 0.625 0.700 V
Bias Mode, 6dB Gain Setting 1.150 1.250 1.400 V
V
I
CC
OUT
Supply Current
Video Output Range 2.8 V
DC Input Level
V
clamp
DC Output Level
DC Output Level
DC Input Level
V
bias
DC Output Level
DC Output Level
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio All Channels, DC 90 dB
Note:
1. 100% tested at 25°C.
AC Electrical Characteristics
TA= 25°C, Vcc = 5V, Vin = 1Vpp, input bias mode, one-to-one routing, 6dB gain, all inputs AC-coupled with 0.1μF,
unused inputs AC-terminated through 75Ω to GND, all outputs AC-coupled with 220μF into 150Ω, referenced to
400kHz unless otherwise noted.
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
AV
AV
f
f
+1dB
-1dB
f
Channel Gain
0dB
Channel Gain
6dB
+1dB Peaking Bandwidth V
-1dB Bandwidth V
-3dB Bandwidth V
C
dG Differential Gain V
dφ Differential Phase V
THD
THD
X
TALK1
X
TALK2
X
TALK3
X
TALK4
X
TALK5
SNR
V
NOISE
AMP
SD Output Distortion V
SD
HD Output Distortion V
HD
Input Crosstalk 1MHz, V
Input Crosstalk 15MHz, V
Output Crosstalk 1MHz, V
Output Crosstalk 15MHz, V
Multi-Channel Crosstalk Standard Video, V
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
SD
Channel Noise 400kHz to 100MHz, Input Referred 20
Amplifier Recovery Time Post I2C Programming 300 ns
ON
Notes:
1. 100% tested at 25°C.
2. Adjacent input pair to adjacent output pair. Interfering input is through an open switch.
3. Adjacent input pair to adjacent output pair. Interfering input is through a closed switch.
4. Crosstalk of eight synchronous switching outputs onto single, asynchronous switching output.
5. SNR = 20 * log (714mV / rms noise).
(1)
(1)
DC, All Channels, 0dB Gain Setting -0.2 0 +0.2 dB
DC, All Channels, 6dB Gain Setting 5.8 6 6.2 dB
= 1.4V
OUT
OUT
OUT
= 5.0V , 3.58MHz 0.1 %
CC
= 5.0V , 3.58MHz 0.2 °
CC
OUT
OUT
(5)
NTC-7 Weighting, 4.2MHz LP,
pp
= 1.4V
pp
= 1.4V
pp
= 1.4Vpp, 5MHz, VCC = 5.0V 0.05 %
= 1.4Vpp, 22MHz, VCC = 5.0V 0.4 %
= 2V
OUT
= 2V
OUT
= 2V
OUT
= 2V
OUT
pp
pp
pp
pp
OUT
(2)
(3)
(2)
(3)
= 2V
(4)
pp
65 MHz
90 MHz
115 MHz
-77 dB
-62 dB
-81 dB
-62 dB
-50 dB
78 dB
100kHz HP
nV/ Hz
√
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 5
Page 6

I2C BUS Characteristics
TA = 25°C, V
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
il
V
ih
f
SCL
tr Input Rise Time 1.5V to 3V 1000 ns
tf Input Fall Time 1.5V to 3V 300 ns
t
low
t
high
t
SU,DAT
t
HD,DAT
t
SU,STO
t
BUF
t
HD,STA
t
SU,STA
Note:
1. 100% tested at 25°C.
= 5V unless otherwise noted.
cc
Digital Input Low
Digital Input High
1
1
SDA,SCL,ADDR 0 1.5 V
SDA,SCL,ADDR 3.0 V
cc
Clock Frequency SCL 100 kHz
Clock Low Period 4.7 µs
Clock High Period 4.0 µs
Data Set-up Time 300 ns
Data Hold Time 0 ns
Set-up Time from Clock High to Stop 4 µs
Start Set-up Time following a Stop 4.7 µs
Start Hold Time 4 µs
Start Set-up Time following Clock Low to High 4.7 µs
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
V
SDA
SCL
SDA
t
BUF
t
HD,STA
t
LOW
t
r
Figure 3. I
t
SU,STA
2
C Bus Timing
t
HD,DATtHIGH
t
f
t
SU,DAT
t
SU,STO
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 6
Page 7

I2C Interface
O
T
c
w
s
c
t
w
peration
he I2C-compatible interface conforms to the I2C specifi-
ation for Standard Mode. Individual addresses may be
ritten, but there is no read capability. The interface conists of two lines: a serial data line (SDA) and a serial
lock line (SCL). Both lines must be connected to a posi-
ive supply through an external resistor. Data transfer
may be initiated only when the bus is not busy.
SCL
SDA
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
Bit Transfer
One data bit is transferred during each clock pulse. The
data on the SDA line must remain stable during the
HIGH period of the clock pulse. Changes in the data line
during this time are interpreted as control signals.
Data line
stable;
data valid
Figure 4. Bit Transfer
Change
of data
allowed
Start and Stop conditions
Both data and clock lines remain HIGH when the bus is
not busy. A HIGH-to-LOW transition of the data line,
hile the clock is HIGH, is defined as start condition (S).
A LOW-to-HIGH transition of the data line, while the
clock is HIGH, is defined as stop condition (P).
SCL
SP
SDA
START condition
Figure 5. START and STOP conditions
STOP condition
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 7
Page 8

Acknowledge
The number of data bytes transferred between the start
and stop conditions from transmitter to receiver is unlimited. Each byte of eight bits is followed by an acknowledge bit. The acknowledge bit is a HIGH level signal put
on the bus by the transmitter while the master generates
an extra acknowledge-related clock pulse. The slave
receiver addressed must generate an acknowledge after
the reception of each byte. A master receiver must generate an acknowledge after the reception of each byte
clocked out of the slave transmitter.
START
condition
SCL FROM
MASTER
DATA OUTPUT
BY TRANSMITTER
12 89
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
The device that acknowledges must pull down the SDA
line during the acknowledge clock pulse so the SDA line
is stable LOW during the HIGH period of the acknowledge-related clock pulse (set-up and hold times must be
taken into consideration). A master receiver must signal
an end of data to the transmitter by not generating an
acknowledge on the last byte clocked out of the slave. In
this event, the transmitter must leave the data line HIGH
to enable the master to generate a stop condition.
clock pulse for
acknowledgement
DATA OUTPUT
BY RECEIVER
Figure 6. Acknowledgement on the I2C Bus
I2C Bus Protocol
Before any data is transmitted on the I2C bus, the device
which is to respond is addressed first. The addressing is
always carried out with the first byte transmitted after the
1 9 1 9
SCL
START BY
MASTER
SDA
A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 R/W
A6
FRAME1
SERIAL BUS ADDRESS BYTE
SCL(CONTINUED)
SDA(CONTINUED)
start procedure. The I2C bus configuration for a data
write to the FMS6502 is shown in Figure 7.
D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
D4 D3 D2
FRAME 3
DATA BYTE
FRAME 2
D1 D0
ACK. BY
FMS6502
ADDRESS POINTER REGISTER BYTE
ACK. BY
FMS6502
9
STOP BY
MASTER
ACK. BY
FMS6502
1
D7 D6 D5
D7 D6 D5
Figure 7. Write Register Address to Pointer Register; Write Data to Selected Register
3.3V Operation
The FMS6502 operates from a single 3.3V supply. With
= 3.3V, the digital input low (Vil) is 0V to 1V and the
V
cc
digital input high (V
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 8
) is 1.8V to 2.9V.
ih
Page 9

Applications Information
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
Input Clamp / Bias Circuitry
The FMS6502 can accommodate AC- or DC-coupled
inputs. Internal clamping and bias circuitry are provided
to support AC-coupled inputs. These are selectable
through the CLMP bits via the I
For DC-coupled inputs, the device should be programmed to use the 'bias' input configuration. In this configuration, the input is internally biased to 625mV through
a 100kΩ resistor. Distortion is optimized with the output
levels set between 250mV above ground and 500mV
below the power supply.
With AC-coupled inputs, the FMS6502 uses a simple
clamp rather than a full DC-restore circuit. For video signals with and without sync; (Y,CV,R,G,B), the lowest voltage at the output pins is clamped to approximately
300mV above ground.
If symmetric AC-coupled input signals are used
(Chroma,Pb,Pr,Cb,Cr), the bias circuit can be used to
center them within the input common range. The average DC value at the output is approximately 1.27V.
Figure 8 shows the clamp mode input circuit and the
internally controlled voltage at the input pin for AC-coupled inputs.
Lowest voltage
set to 125mV
Video source must
be AC coupled
75
0.1µF
2
C-compatible interface.
FMS6502
Input
Clamp
Output Configuration
The FMS6502 outputs may be AC or DC-coupled. DCcoupled loads can drive a 150Ω load. AC-coupled outputs are capable of driving a single, doubly terminated
video load of 150Ω. An external transistor is needed to
drive DC low-impedance loads. DC-coupled outputs
should be connected as indicated in Figure 10.
75
FMS6502
Output
Amplifier
Figure 10. DC-Coupled Load Connection
Configure AC-coupled loads as shown in Figure 11.
FMS6502
Output
Amplifier
Figure 11. AC-Coupled Load Connection
75
75
220µF
75
Figure 8. Clamp Mode Input Circuit
Figure 9 shows the bias mode input circuit and the internally controlled voltage at the input pin for AC-coupled
input to that particular channel’s amplifier is forced to
approximately 150mV. The output amplifier is still active
unless specifically disabled by the I
2
C interface. Voltage
output levels depend on the programmed gain for that
channel.
inputs.
When an output channel is not connected to an input, the
Video source must
be AC coupled
Average voltage
set to 625m
0.1µF
75
V
FMS6502
Input
Bias
Driving Capacitive Loads
When driving capacitive loads, use a 10Ω-series resistance to buffer the output, as indicated in Figure 12.
FMS6502
Output
Amplifier
10
C
L
Figure 9. Bias Mode Input Circuit
Figure 12. Driving Capacitive Loads
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 9
Page 10

Crosstalk
A
Crosstalk is an important consideration when using the
FMS6502. Input and output crosstalk represent the two
major coupling modes that may be present in a typical
application. Input crosstalk is crosstalk in the input pins
and switches when the interfering signal drives an open
switch. It is dominated by inductive coupling in the package lead frame between adjacent leads. It decreases
rapidly as the interfering signal moves further away from
the pin adjacent to the input signal selected. Output
crosstalk is coupling from one driven output to another
active output. It decreases with increasing load impedance as it is caused mainly by ground and power co upling between output amplifiers. If a signal is driving an
open switch, its crosstalk is mainly input crosstalk. If it is
driving a load through an active output, its crosstalk is
mainly output crosstalk.
Input and output crosstalk measurements are performed
with the test configuration shown in Figure 13.
TERMINATION
Bias
IN1
Crosstalk from multiple sources into a given channel is
measured with the setup shown in Figure 14. Input In1 is
driven with a 1V
pulse source and connected to out-
pp
puts Out1 to Out8. Input In9 is driven with a secondary,
asynchronous gray field video signal and is connected to
Out9. All other inputs are AC terminated with 75Ω.
Crosstalk effects on the gray field are measured and calculated with respect to a standard 1V
output measured
pp
at the load.
If not all inputs and outputs are needed, avoid using
adjacent channels to reduce crosstalk.
TERMINATION
IN1
IN1 driven with
SD video 1V
IN6 driven with
asynchronous
SD video 1V
IN2,3,4,5,7,8 are
C-term to GND
with 75 .
Bias
.
PP
.
PP
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
IN2 - IN8 are
AC-Term to
Ground
w/75
IN1 = 1VPP
Open switch
for input
crosstalk.
Close switch
for output
crosstalk.
IN8
Bias
IN6
IN8
Figure 14. Test Configuration for Multi-Channel
Bias
Bias
OUT1
Measure crosstalk from
channels 1-5 into
channel 6
OUT6
Crosstalk
Gain = 6dB
Out1 = 2.0V
PP
OUT1
Input Crosstalk from IN1
to OUTx
Output Crosstalk from
OUT1 to OUTx
OUT6
Figure 13. Test Configuration for Crosstalk
For input crosstalk, the switch is open and all inputs are
in bias mode. Channel 1 input is driven with a 1V
pp
signal, while all other inputs are AC terminated with 75Ω. All
outputs are enabled and crosstalk is measured from IN1
to any output.
For output crosstalk, the switch is closed. Crosstalk from
OUT1 to any output is measured.
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 10
Page 11

Layout Considerations
General layout and supply bypassing play a major role in
high-frequency performance and thermal characteristics.
Fairchild offers a demonstration board to guide layout
and aid device evaluation. The demo board is a fourlayer board with full power and ground planes. Following
this layout configuration provides optimum performance
and thermal characteristics for the device. For the best
results, follow the steps and recommended routing rules
listed below.
Recommended Routing/Layout Rules
• Do not run analog and digital signals in parallel.
• Use separate analog and digital power planes to sup-
ply power.
• Traces should run on top of the ground plane at all
times.
• No trace should run over ground/power splits.
• Avoid routing at 90-degree angles.
• Minimize clock and video data trace length differ-
ences.
• Include 10µF and 0.1µF ceramic power supply bypass
capacitors.
• Place the 0.1µF capacitor within 0.1 inches of the
device power pin.
• Place the 10µF capacitor within 0.75 inches of the
device power pin.
• For multilayer boards, use a large ground plane to
help dissipate heat.
• For two-layer boards, use a ground plane that extends
beyond the device body by at least 0.5 inches on all
sides. Include a metal paddle under the device on the
top layer.
• Minimize all trace lengths to reduce series inductance.
Thermal Considerations
Since the interior of most systems, such as set-top
boxes, TVs, and DVD players, are at +70ºC; consideration must be given to providing an adequate heat sink
for the device package for maximum heat dissipation.
When designing a system board, determine how much
power each device dissipates. Ensure that devices of
high power are not placed in the same location, such as
directly above (top plane) or below (bottom plane) each
other on the PCB.
PCB Thermal Layout Considerations
• Understand the system power requirements and envi-
ronmental conditions.
• Maximize thermal performance of the PCB.
• Consider using 70µm of copper for high-power
designs.
• Make the PCB as thin as possible by reducing FR4
thickness.
• Use vias in power pad to tie adjacent layers together.
• Remember that baseline temperature is a function of
board area, not copper thickness.
• Modeling techniques can provide a first-order approximation.
Power Dissipation
Worst-case, additional die power due to DC loading can
be estimated at V
assumes a constant DC output voltage of V
Vcc with a dual DC video load, add 25/(4*75) = 83mW,
per channel.
2
/4R
cc
per output channel. This
load
/2. For 5V
cc
Applications for the FMS6502 Video Switch
Matrix
The increased demand for consumer multimedia systems has created a large challenge for system designers
to provide cost-effective solutions to capitalize on the
growth potential in graphics display technologies. Th ese
applications require cost-effective video switching and filtering solutions to deploy high-quality display technologies rapidly and effectively to the target audience. Areas
of specific interest include HDTV, media centers, and
automotive infotainment (such as navigation, in-cabin
entertainment, and back-up cameras). In all cases, the
advantages the integrated video switch matrix provides
are high-quality video switching specific to the application, as well as video input clamps and on-chip, lowimpedance output cable drivers with switchable gain.
Generally the largest application for a video switch is for
the front-end of an HDTV. This is used to take multiple
inputs and route them to their appropriate signal paths
(main picture and picture-in-picture, or PiP). These are
normally routed into ADCs that are followed by decoders. Technologies for HDTV include LCD, plasma, and
CRT, which have similar analog switching circuitry.
VIPDEMOTM Control Software
The FMS6502 is configured via an I2C-compatible digital
interface. To facilitate demonstration, Fairchild Semiconductor had developed the VIPDEMOTM GUI-based control software to write to the FMS6502 register map. This
software is included in the FMS6502DEMO kit. A parallel
2
C adapter and an interface cable to connect to the
port I
demo board are also included. Besides using the full
FMS6502 interface, the VIPDEMO
to control single register read and writes for I
TM
can also be used
2
C.
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 11
Page 12

Physical Dimensions
Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise noted.
FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
Figure 15. 24-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 12
Page 13

FMS6502 8-Input, 6-Output Video Switch Matrix with Output Drivers, Input Clamp, and Bias Circuitry
© 2006 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FMS6502 Rev. 1.0.0 13
 Loading...
Loading...