Page 1

1 of 25 092299
FEATURES
§ Performs framing and monitoring functions
Supports Superframe and Extended Superframe formats
§ Four onboard error counters
– 16-bit bipolar violation
– 8-bit CRC
– 8-bit OOF
– 8-bit frame bit error
§ Indication of the following
– yellow and blue alarms
– incoming B8ZS code words
– 8 and 16 zero strings
– change of frame alignment
– loss of sync
– carrier loss
§ Simple serial interface used for config-
uration, control and status monitoring
§ Burst mode allows quick access to counters
for status updates
§ Automatic counter reset feature
§ Single 5V supply; low-power CMOS tech-
nology
§ Available in 28-pin DIP and 28-pin PLCC
§ The DS2182A is upward-compatible from
the original DS2182
The updated DS2182A includes the following
changes from the original DS2182:
§ Ability to count excessive zeros
§ Severely Errored Framing Event indication
§ Updated AIS detection
§ Updated RCL detection
§ AIS and RCL alarm clear indications
PIN ASSIGNMENT
DESCRIPTION
The DS2182A T1 Line Monitor Chip is a monolithic CMOS device designed to monitor real-time
performance on T1 lines. The DS2182A frames to the data on the line, counts errors, and supplies
detailed information about the status and condition of the line. Large on-board counters allow the
accumulation of errors for extended periods, which permits a single CPU to monitor a number of T1
lines. Output clocks that are synchronized to the incoming data stream are provided for easy extraction of
S-Bits, FDL bits, signaling bits, and channel data. The DS2182A meets the requirements of ANSI
T1.231.
DS2182A
T1 Line Monitor
www.dalsemi.com
INT 1 28 VDD
SDI 2 27 RLOS
SDO 3 26 RFER
CS 4 25 RBV
SCLK 5 24 RCL
NC 6 23 RNEG
RYEL 7 22 RPOS
RLINK 8 21 RST
RLCLK 9 20 TEST
RCLK 10 19 RSIGSEL
RCHCLK 11 18 RSIGFR
RSER 12 17 RABCD
NC 13 16 RMSYNC
VSS 14 15 RFSYNC
28-Pin DIP (600-mil)
Page 2

DS2182A
2 of 25
DS2182A BLOCK DIAGRAM Figure 1
Page 3

DS2182A
3 of 25
PIN DESCRIPTION Table 1
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
6 NC - No Connect. No internal connection. This pin can be tied to either
VSS or VDD, or it can be floated.
7 RYEL O Receive Yellow Alarm. Transitions high when yellow alarm
detected; goes low when alarm clears.
8 RLINK O
Receive Link Data. Updated with extracted FDL data one RCLK
before start of odd frames (193E) and held until next update.
Updated with extracted S-bit data one RCLK before start of even
frames (193S) and held until next update.
9 RLCLK O Receive Link Clock. 4 kHz demand clock for RLINK.
10 RCLK I Receive Clock. 1.544 MHz primary clock.
11 RCHCLK O Receive Channel Clock. 192 kHz clock; identifies time slot
(channel) boundaries.
12 RSER O Receive Serial Data. Received NRZ serial data; updated on rising
edges of RCLK.
13 NC -
No Connect. No internal connection. This pin can be tied to either
V
SS
or VDD, or it can be floated.
15 RFSYNC O
Receive Frame Sync. Extracted 8 kHz clock, one RCLK wide; Fbit position in each frame.
16 RMSYNC O Receive Multiframe Sync. Extracted multiframe sync; positive-
going edge indicates start of multiframe; 50% duty cycle.
17 RABCD O Receive ABCD Signaling. Extracted signaling data output; valid
for each channel in signaling frames. In non-signaling frames,
RABCD outputs the LSB of each channel word.
18 ESIGFR O Receive Signaling Frame. High during signaling frames; low
during non-signaling frames (and during resync).
19 RSIGSEL O Receive Signaling Select. In 193E framing, a .667 kHz clock that
identifies signaling frames A and C; a 1.33 kHz clock in 193S.
21
RST
I
Reset. A high-low transition clears all internal registers and resets
counters. A high-low-high transition initiates a resync.
22
23
RPOS
RNEG
I
Receive Bipolar Data Inputs. Sampled on falling of RCLK. Tie
together to receive NRZ data and disable bipolar violation
monitoring circuitry.
24 RCL O Receive Carrier Loss. High if 192 consecutive 0s appear at RPOS
and RNEG; goes low upon seeing 12.5% one’s density.
25 RBV O Receive Bipolar Violation. High during accused bit time at RSER.
If bipolar violation detected, low otherwise.
26 RFER O Receive Frame Error. High during F-bit time when FT or FS
errors occur (193S), or when FPS or CRC errors occur (193E). Low
during resync.
27 RLOS O
Receive Loss of Sync. Indicates sync status; high when internal
resync is in progress, low otherwise.
Page 4

DS2182A
4 of 25
PIN DESCRIPTION Table 2
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
1
INT
O
Receive Alarm Interrupt. Flags host controller during alarm conditions.
Active low; open drain output.
2 SDI I Serial Data In. Data for onboard registers. Sampled on rising edge of SCLK.
3 SDO O
Serial Data Out. Control and status information from onboard registers.
Updated on falling edge of SCLK; tri-stated during serial port write or
when CS is high.
4
CS
I Chip Select. Must be low to read or write the serial port.
5 SCLK I Serial Data Clock. Used to read or write the serial port registers.
POWER AND TEST PIN DESCRIPTION Table 3
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
14 V
SS
- Signal Ground. 0.0 volts.
20 TEST I Test Mode. Tie to VSS for normal operation.
28 V
DD
- Positive Supply. 5.0 volts.
REGISTER SUMMARY Table 4
REGISTER ADDRESS DESCRIPTION/FUNCTION
BVCR2 0000 Bipolar Violation Count Register 2. LSW of a 16-bit presettable counter that
records individual bipolar violations.
BVCR1 0001
Bipolar Violation Count Register 1. MSW of a 16-bit presettable counter that
records individual bipolar violations.
CRCCR 0010 CRC Error Count Register. 8-bit presettable counter that records CRC6 errored
words in the 193E frame mode.
OOFCR 0011
OOF Count Register. 8-bit presettable counter that records OOF events. OOF
events are defined by RCR1.5 and RCR1.6.
FECR 0100 Frame Error Count Register. 8-bit presettable counter that records individual
bit errors in the framing pattern.
RSR1 0101 Receive Status Register 1. Reports alarm conditions.
RIMR1 0110 Receive Interrupt Mask Register 1. Allows masking of individual alarm-
generated interrupts from RSR1.
RSR2 0111 Receive Status Register 2. Reports alarm conditions.
RIMR2 1000
Receive Interrupt Mask Register 2. Allows masking of individual alarmgenerated interrupts from RSR2.
RCR1 1001 Receive Control Register 1. Programs device operating characteristics.
RCR2 1010 Receive Control Register 2. Programs device operating characteristics.
SERIAL PORT INTERFACE
The port pins of the DS2182A serve as a microprocessor/ microcontroller-compatible serial port. Eleven
on-board registers allow the user to update operational characteristics and monitor device status via a host
controller, minimizing hardware interfaces. The port on the DS2182A can be read from or written to at
any time. Serial port reads and writes are independent of T1 line timing signals RCLK, RPOS, and
RNEG. However, RCLK is needed in order to clear RSR1 and RSR2 after reads.
ADDRESS/COMMAND
Reading or writing the control, configuration or status registers requires writing one address/command
byte prior to transferring register data. The first bit written (LSB) of the address/command word specifies
Page 5

DS2182A
5 of 25
register read or write. The following 4 bits identify the register address. The next 2 bits are reserved and
must be set to 0 for proper operation. The last bit of the address/ command word enables burst mode
when set; the burst mode causes all registers to be consecutively read or written to. Data is read and
written to the DS2182A LSB first.
CHIP SELECT AND CLOCK CONTROL
All data transfers are initiated by driving the CS input low. Input data is latched on the rising edge of
SCLK and must be valid during the previous low period of SCLK to prevent momentary corruption of
register data during writes. Data is output on the falling edge of SCLK and held to the next falling edge.
All data transfers are terminated if the CS input transitions high. Port control logic is disabled and SDO is
tri-stated when CS is high.
DATA I/O
Following the eight SCLK cycles that input an address/command byte to write, a data byte is strobed into
the addressed register on the rising edge of the next eight SCLK cycles. Following an address/command
word to read, contents of the selected register are output on the falling edges of the next eight SCLK
cycles. The SDO pin is tri-stated during device write and can be tied to SDI in applications where the host
processor has a bi-directional I/O pin.
BURST MODE
The burst mode allows all onboard registers to be consecutively written to or read by the host processor.
A burst read is used to poll all registers; RSR1 and RSR2 contents will be unaffected. This feature
minimizes device initialization time on system power-up or reset. Burst mode is initiated when ACB.7 is
set and the address is 0000. A burst is terminated by a low-high transition on CS .
ACB: ADDRESS COMMAND BYTE Figure 2
MSB LSB
BM - - ADD3 ADD2 ADD1 ADD0
R/W
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
BM ACB.7
Burst Mode.
If set (and register address is 0000) burst read or
write is enabled.
- ACB.6 Reserved, must be 0 for operation.
- ACB.5 Reserved, must be 0 for operation.
ADD3 ACB.4 MSB of register address.
ADD0 ACB.1 LSB of register address.
R/W ACB.0
Read/Write Select.
0 = write addressed register
1 = read addressed register
Page 6

DS2182A
6 of 25
SERIAL PORT READ/WRITE Figure 3
NOTES:
1. SDI is sampled on rising edge of SCLK.
2. SDO is updated on falling edge of SCLK.
OPERATION OF THE COUNTERS
All four of the counters in the DS2182A can be preset by the user to establish an event count interrupt
threshold. The counters count up from the preset value until they reach saturation. At saturation, each
additional event occurrence sets the appropriate bit in RSR2 and generates an interrupt if enabled by
RIMR2.
The DS2182A contains an auto counter reset feature in the burst read mode. If RCR1.4 is set, then the
user can burst read the four counters (five registers), and all four counters will be automatically reset to 0
after the read takes place. Since the burst mode can be terminated at any time by taking CS high, the user
has the option of reading all of the registers or only the counters. If RCR1.4 is set, then any read of the
registers, burst mode or not, will clear the count in all four counters. If the user wishes to read the port
and not clear the counters, then RCR1.4 must be cleared first.
The counter registers can be read or written to at any time with the serial port, which operates totally
asynchronously with the monitoring of the T1 line. Reading a register will not affect the count as long as
RCR1.4 is cleared. The dual buffer architecture of the DS2182A insures that no error events will be
missed while the serial port is being accessed for reads.
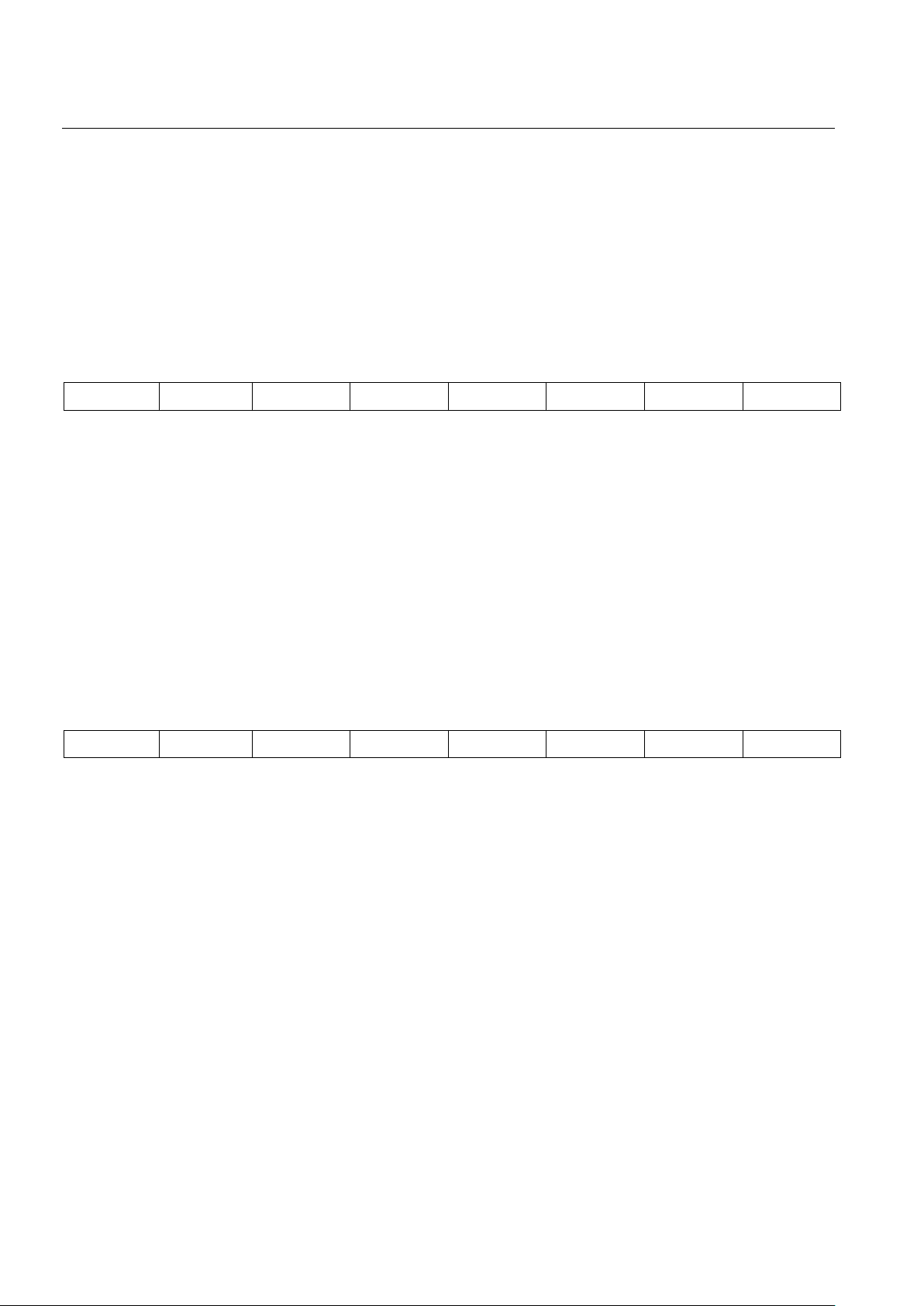
BVCR1: BIPOLAR VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER 1;
BVCR2: BIPOLAR VIOLATION COUNTER REGISTER 2 Figure 4
MSB LSB
BV7 BV6 BV5 BV4 BV3 BV2 BV1 BV0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
BV7 BVCR.7 MSB of bipolar violation count
BV0 BVCR.0 LSB of bipolar violation count
Bipolar Violation Count Register 1 (BVCR1) is the most significant word and BVCR2 is the least
significant word of a presettable 16-bit counter that records individual bipolar violations. If the B8ZS
mode is enabled (RCR2.2 = 1), then B8ZS code words are not counted. The BVCR can also be
programmed to count excessive zeros by setting the RCR2.5 bit. In this mode, the BVCR will count
Page 7
DS2182A
7 of 25
occurrences of 8 consecutive zeros when B8ZS is enabled or 16 consecutive zeros when B8Z5 is
disabled. This counter increments at all times and is not disabled by a loss of sync condition (RLOS = 1).
The counter saturates at 65,535 and generates an interrupt for each occurrence after saturation if RIMR2.0
is set.
NOTE:
1. In order to properly preset the Bipolar Violation Count Register, BVCR2 must be written to before
BVCR1 is written to.
CRCCR: CRC COUNT REGISTER 2 Figure 5
MSB LSB
CRC7 CRC6 CRC5 CRC4 CRC3 CRC2 CRC1 CRC0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CRC7 CRCCR.7 MSB of CRC6 word error count
CRC0 CRCCR.0 LSB of CRC6 word error count
The CRC Count Register (CRCCR) is an 8-bit presettable counter that records word errors in the Cyclic
Redundancy Check (CRC). This 8-bit binary counter saturates at 255 and generates an interrupt for each
occurrence after saturation if RIMR2.1 is set. The count in this register is only valid in the 193E framing
mode (RCR2.4 = 1) and is reset and disabled in the 193S framing mode (RCR2.4 = 0). The count is
disabled during a loss of sync condition (RLOS = 1).
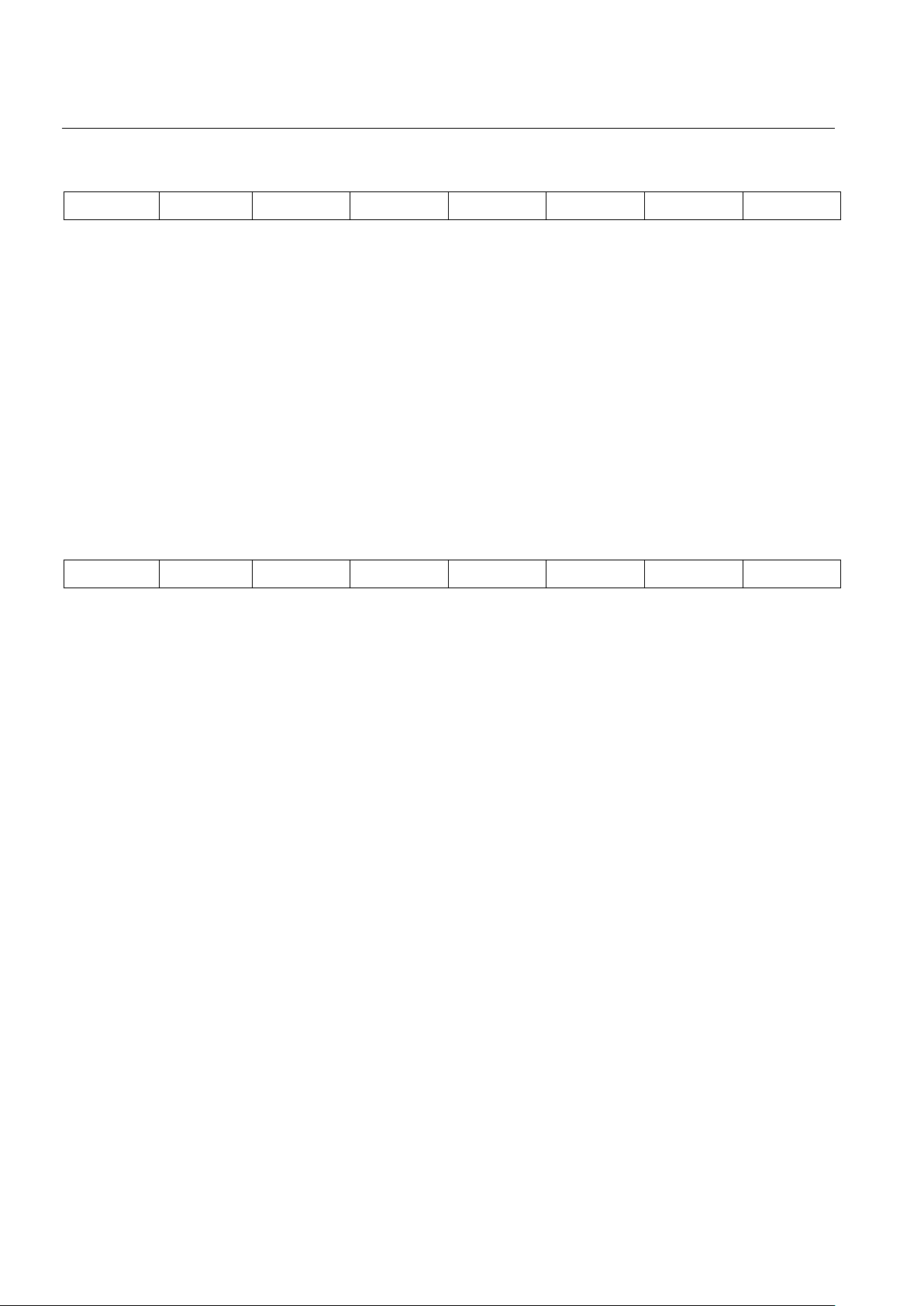
OOFCR: OOF COUNT REGISTER Figure 6
MSB LSB
OOF7 OOF6 OOF5 OOF4 OOF3 OOF2 OOF1 OOF0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
OOF7 OOFCR.7 MSB of OOF event count
OFF0 OOFCR.0 LSB of OOF of event count
The OOF Count Register (OOFCR) is an 8-bit presettable counter that records Out Of Frame (OOF)
events. OOF events are defined by RCR1.5 and RCR1.6. This 8-bit counter saturates at 255 and
generates an interrupt for each occurrence after saturation if RIMR2.2 is set. The count is disabled during
a loss of sync condition (RLOS = 1).
Page 8
DS2182A
8 of 25
FECR: FRAME ERROR COUNT REGISTER Figure 7
MSB LSB
FE7 FE6 FE5 FE4 FE3 FE2 FE1 FE0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
FE7 FECR.7 MSB of frame error count
FFE0 FECR.0 LSB of frame error count
The Frame Error Count Register (FECR) is an 8-bit pre-settable counter that records individual frame bit
errors. In the 193E mode (RCR2.4 = 1), the FECR records bit errors in the FPS framing pattern
(001011). In the 193S mode (RCR2.4 = 0), the FECR records bit errors in both the FT (101010) and FS
(001110) framing patterns if RCR1.3 is set. If RCR1.3 is cleared, then the FECR only records bit errors in
the FT pattern. This 8-bit counter saturates at 255 and generates an interrupt for each occurrence after
saturation if RIMR2.3 is set. The count is disabled during a loss of sync condition (RLOS = 1).
RSR1: RECEIVE STATUS REGISTER 1 Figure 8
MSB LSB
8ZD 16ZD RCL RYEL RLOS B8ZSD RBL COFA
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
8ZD RSR1.7 8 Zero Detect. Set when a string of eight consecutive 0s has
been received at RPOS and RNEG.
16ZD RSR1.6 16 Zero Detect. Set when a string of 16 consecutive 0s has
been received at RPOS and RNEG.
RCL RSR1.5 Receive Carrier Loss. Set when a string of 192 consecutive 0s has
been received at RPOS and RNEG. Cleared when 14 or more ones
out of 112 possible bit positions are received.
RYEL RSR1.4
Receive Yellow Alarm.
Set when yellow alarm is detected. The
format of yellow alarm is determined by RCR2.3 and RCR2.4.
RLOS RSR1.3 Receive Loss of Sync. Set when resync is in progress.
B8ZSD RSR1.2
B8ZS Code Word Detect.
Set when a B8ZS code word is
received at RPOS and RNEG independent of whether the B8ZS
mode is enabled or not (RCR2.2).
RBL RSR1.1
Receive Blue Alarm.
Set when over a 3 ms window, 5 or less
zeros are received. Cleared when over a 3 ms window, 6 or more
zeros are received.
COFA RSR1.0
Change of Frame Alignment.
Set when the last resync resulted in
a change of frame or multiframe alignment.
NOTE:
1. Alarm 8ZD and 16ZD are cleared on the next occurrence of a 1 at RPOS and RNEG.
Page 9

DS2182A
9 of 25
RECEIVE STATUS REGISTERS
The receive status registers (RSR1 and RSR2) can be used in either a polled or an interrupt configuration.
In a polled configuration, the user reads the RSR at regular intervals to check for alarms. In an interrupt
configuration, the user monitors the INT pin. When the INT pin goes low, an alarm condition has
occurred and has been reported in one of the RSRs. The processor can then read the RSRs to find which
bits have been set. All of the bits in the RSRs operate in a latched fashion. That is, once set, they remain
set until read. The bits in the RSR are cleared when read unless the read was performed in the burst mode
or the alarm condition still exists.
YELLOW ALARM
193S BIT 2. If RCR2.4 = 0 and RCR2.3 = 0, then the DS2182A examines bit 2 of all incoming channels
for the presence of a yellow alarm. If bit 2 is set to 0 in 256 consecutive channels, then the reception of a
yellow alarm is declared. The alarm is considered cleared when the first channel with bit 2 set to a 1 is
received.
193S S-BIT. If RCR2.4 = 0 and RCR2.3 = 1, then the DS2182A examines the S-bit position of frame 12
for the presence of a yellow alarm. The DS2182A declares the presence of a yellow alarm on the first
occurrence of the S-bit in frame 12 being set to 1. The alarm is considered cleared when this S-bit returns
to 0.
193E FDL. If RCR2.4 = 1, then the DS2182A examines the FDL for a repeating 00FF pattern. If this
pattern is received in the FDL 16 consecutive times without error, then a yellow alarm is declared. The
alarm is considered cleared as soon as any pattern other than 00FF is received.
Page 10

DS2182A
10 of 25
RIMR1: RECEIVE INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER 1 Figure 9
MSB LSB
8ZD 16ZD RCL RYEL RLOS B8ZSD RBL COFA
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
8ZD RIMR1.7
8 Zero Detect Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled.
0 = interrupt masked.
16ZD RIMR1.6
16 Zero Detect Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled.
0 = interrupt masked.
RCL RIMR1.5
Receive Carrier Loss Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled.
0 = interrupt masked.
RYEL RIMR1.4
Receive Yellow Alarm Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled.
0 = interrupt masked.
RLOS RIMR1.3
Receive Loss of Sync Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled.
0 = interrupt masked.
B8ZSD RIMR1.2
B8ZS Code Word Detect Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled.
0 = interrupt masked.
RBL RIMR1.1
Receive Blue Alarm Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled.
0 = interrupt masked.
COFA RIMR1.0
Change of Frame Alignment Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled.
0 = interrupt masked.
Page 11

DS2182A
11 of 25
RSR2: RECEIVE STATUS REGISTER 2 Figure 10
MSB LSB
SEFE RCLC RBLC FERR FECS OOFS CRCCS BPVCS
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
SEFE RSR2.7
Severely Errored Framing Event.
Set when 2 out of 6 framing
bits (Ft or FPS) are received in error.
RCLC RSR2.6
Receive Carrier Loss Clear.
Set when the carrier signal is
restored; will remain set until read.
RBLC RSR2.5
Receive Blue Alarm Clear.
Set when the Blue Alarm (AIS) is no
longer detected; will remain set until read.
FERR RSR2.4
Frame Bit Error.
Set when FT (193S) or FPS (193E) bit errors
occur.
FECS RSR2.3 Frame Error Count Saturation. Set on the next frame error event
after the 8-bit Frame Error Count Register (FECR) saturates at 255.
OOFCS RSR2.2
Out Of Frame Count Saturation.
Set on the next OOF event
after the 8-bit OOF Count Register (OOFCR) saturates at 255.
CRCCS RSR2.1
CRC Count Saturation.
Set on the next CRC error event after the
8-bit CRC Count Register (CRCCR) saturates at 255.
BPVCS RSR2.0
Bipolar Violation Count Saturation.
Set on the next BPV error
event after the 16-bit Bipolar Violation Count Register (BVCR)
saturates at 65,535.
RIMR2: RECEIVE INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER 2 Figure 11
MSB LSB
SEFE RCLC RBLC FERR FECS OOFS CRCCS BPVCS
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
SEFE RIMR2.7
Severely Errored Framing Event Mask.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
RCLC RIMR2.6
Receive Carrier Loss Clear Mask.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
RBLC RIMR2.5
Receive Blue Alarm Clear Mask.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Page 12

DS2182A
12 of 25
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
FERR RIMR2.4
Frame Bit Error Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
FECS RIMR2.3
Frame Error Count Saturation Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
OOFCS RIMR2.2
Out Of Frame Count Saturation Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
CRCCS RIMR2.1
CRC Count Saturation Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
BPVCS RIMR2.0
Bipolar Violation Count Saturation Mask.
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
RCR1: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 1 Figure 12
MSB LSB
ARC OOF1 OOF2 ACR SYNCC SYNCT SYNCE RESYNC
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
ARC RCR1.7 Auto Resync Criteria.
1 = resync on OOF event only
0 = resync on OOF event or Receive Carrier Loss (RCL)
OOF1 RCR1.6 Out Of Frame 1. OOF event description. Valid when RCR1.5 is
cleared
1 = 2 out of 5 frame bits (FT or FPS) in error
0 = 2 out of 4 frame bits (FT or FPS) in error
OOF2 RCR1.5 Out Of Frame 2. OOF event description.
1 = 2 out of 6 frame bits (FT or FPS) in error
0 = follow OOF event described in RCR1.6
ACR RCR1.4 Auto Counter Reset. When set, all four of the counters will be reset
to 0 when read.
Page 13

DS2182A
13 of 25
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
SYNCC RCR1.3
Sync Criteria.
Determines the type of algorithm utilized by the
receive synchronizer; differs for each frame mode.
193S Framing (RCR2.4 = 0)
0 = synchronize to frame boundaries using FT pattern, then search
for multiframe by using FS.
1 = cross couple FT and FS patterns in sync algorithm.
193E Framing (RCR2.4 = 1)
0 = normal sync (utilizes FPS only).
1 = validate new alignment with CRC before declaring sync.
SYNCT RCR1.2
Sync Time.
1 = validate 24 consecutive F-bits before declaring sync.
0 = validate 10 consecutive F-bits before declaring sync.
SYNCE RCR1.1
Sync Enable.
If clear, the DS2182A automatically begins a resync
if the conditions described in RCR1.7 are met. If set, no auto
resync occurs.
RESYNC RCR1.0 Resync. When toggled low to high, the DS2182A initiates a resync
immediately.
The bit must be cleared and set again for subsequent resyncs.
SYNCHRONIZER
The heart of the monitor is the receive synchronizer. This circuit serves two purposes: 1) monitors the
incoming data stream for loss of frame or multiframe alignment, and 2) searches for new frame alignment
pattern when sync loss is detected. When sync loss is detected, the synchronizer begins an off-line search
for the new alignment; all output timing signals remain at the old alignment with the exception of
RSIGFR, which is forced low during resync. When one and only one candidate is qualified, the output
timing moves to the new alignment at the beginning of the next multiframe. One frame later, RLOS will
transition low, indicating valid sync and the resumption of the normal sync monitoring mode. Several bits
in the RCR1 allow tailoring of the resync algorithm by the user. These bits are described below.
SYNC CRITERIA (RCR1.3)
193E. Bit RCR1.3 determines which sync algorithm is utilized when resync is in progress (RLOS = 1).
In 193E framing, when RCR1.3 = 0, the synchronizer will lock only to the FPS pattern and will move to
the new frame and multiframe alignment after the framing candidate is qualified. RLOS will go low one
frame after the move to the new alignment. When RCR1.3 = 1, the new alignment is further tested by a
CRC6 code match. RLOS will transition low after a CRC6 match occurs. If no CRC6 match occurs in
three attempts (three multiframes), the algorithm resets and a new search for the FPS pattern begins. It
takes 9 ms for the synchronizer to check the first CRC6 code after the new FPS alignment has been
loaded. Each additional CRC6 test takes 3 ms. Regardless of the state of RCR1.3, if more than one
candidate exists after 24 ms, the synchronizer begins eliminating emulators by testing their CRC6 codes
in order to find the true framing candidate.
193S. In 193S framing, when RCR1.3 = 1, the synchronizer cross-checks the FT pattern with the FS
pattern to help eliminate false framing candidates such as digital milliwatts. The FS patterns are
compared to the repeating pattern ...00111000111000...(00111x0 if RCR2.3 = 1). In this mode, FT and
FS must be correctly identified by the synchronizer before sync is declared. Clearing RCR1.3 causes the
synchronizer to search for the FT pattern (101010...) without cross-coupling the FS pattern. Frame sync
Page 14

DS2182A
14 of 25
is established using the FT information, while multiframe sync is established only if valid FS information
is present. If no valid FS pattern is identified, the synchronizer moves to the FT alignment, RLOS goes
low, and a false multiframe position may be indicated by RMSYNC. RFER indicates when the received
S-bit pattern does not match the assumed internal multiframe alignment. This mode will be used in
applications where non-standard S-bit patterns exist. In such applications, multiframe alignment
information can be decoded externally by using the S-bits present at RLINK.
SYNC TIME (RCR1.2)
Bit RCR1.2 determines the number of consecutive framing pattern bits to be qualified before SYNC is
declared. If RCR1.2 =1, the algorithm validates 24 bits; if RCR1.2 = 0, 10 bits are validated. Validating
24 bits results in superior false framing protection while 10-bit testing minimizes reframe time. In either
case, the synchronizer only establishes resync when one and only one candidate is found (see Table 5).
AVERAGE REFRAME TIME Table 5
RCR1.2=0 RCR1.2=1FRAME
MODE
MIN AVG. MAX. MIN. AVG. MAX
193S 3.0ms 3.75ms 4.5ms 6.5ms 7.25ms 8.0ms
193E 6.0ms 7.5ms 9.0ms 13.0ms 14.5ms 16.0ms
NOTE:
1. Average reframe time is defined here as the average time it takes from the start of resync (rising edge
of RLOS) to the actual loading of the new alignment (on a multiframe edge) into the output receive
timing.
SYNC ENABLE (RCR1.1)
When RCR1.1 is cleared, the receiver initiates automatic resync if an OOF event occurs or if carrier loss
(192 consecutive 0s) occurs (depends on RCR1.7). When RCR1.1 is set, the automatic resync circuitry is
disabled. In this case, resync can only be initiated by setting RCR1.0 to 1 or externally transitioning RST
from low to high. Note that using RST to initiate a resync resets the output timing while RST is low; use
of RCR1.1 will not affect the output timing until the new alignment is located.
RESYNC (RCR1.0)
A 0-to-1 transition of RCR1.0 causes the synchronizer to search for the framing pattern sequence
immediately, regardless of the internal sync status. In order to initiate another resync command, this bit
must be cleared and then set again.
Page 15

DS2182A
15 of 25
RCR2: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 2 Figure 13
MSB LSB
- - BVCRF FM SFYEL B8ZS - -
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
- RCR2.7 Reserved; must be 0 for proper operation.
- RCR2.6 Reserved; must be 0 for proper operation.
BVCRF RCR2.5
Bipolar Violation Count Register Function Select.
0 = do not count excessive 0s
1 = count excessive 0s
FM RCR2.4
Frame Mode.
1 = Extended Superframe (193E, 24 frames per Superframe).
0 = Superframe (193S or D4, 12 frames per Superframe).
SFYEL RCR2.3
SF Yellow Mode Select.
1 = 1 in the S-bit position of frame 12.
0 = 0 in bit 2 of all channels.
B8ZS RCR2.2
Bipolar Eight Zero Substitution.
1 = B8ZS enabled.
0 = B8ZS disabled.
- RCR2.1 Reserved; must be 0 for proper operation.
- RCR2.10 Reserved; must be 0 for proper operation.
193S RECEIVE MULTIFRAME TIMING Figure 14
NOTES:
1. Signaling data is updated during signaling frames on channel boundaries. Pin RABCD is the LSB of
each channel word in non-signaling frames.
2. RLINK data (S-bit) is updated one bit-time prior to S-bit frames and held for two frames.
Page 16

DS2182A
16 of 25
193E RECEIVE MULTIFRAME TIMING Figure 15
NOTES:
1. Signaling data is updated during signaling frames on channel boundaries. Pin RABCD is the LSB of
each channel word in non-signaling frames.
2. RLINK data (FDL data) is updated one bit-time prior to odd frames and held for two frames.
RECEIVE MULTIFRAME BOUNDARY TIMING Figure 16
NOTES:
1. RLINK timing is shown for 193E; in 193S, RLINK is updated on even frame boundaries and is held
across multiframe edges.
2. Total delay from RPOS and RNEG to RSER output is 13 RCLK periods.
Page 17

DS2182A
17 of 25
ALARM OUTPUTS
The transceiver also provides direct alarm outputs for applications when additional decoding and
demuxing are required to supplement the onboard alarm logic.
RLOS OUTPUT
The receive loss of sync output indicates the status of the receiver synchronizer circuitry; when high, an
off-line resynchronization is in progress and a high-low transition indicates that resync is complete. The
RLOS bit (RSR1.3) is a latched version of the RLOS output. If the auto-resync mode is selected (RCR1.1
= 0), RLOS is a real-time indication of a carrier loss or OOF event occurrence.
RYEL OUTPUT
The yellow alarm output transitions high when a yellow alarm is detected. A high-low transition indicates
the alarm condition has been cleared. The RYEL bit (RSR1.4) is a latched version of the RYEL output.
RBV OUTPUT
The bipolar violation output transitions high when the accused bit emerges at RSER. RBV goes low at the
next bit time if no additional violations are detected.
RFER OUTPUT
The receive frame error output transitions high at the F-bit time and is held high for 2 bit periods when a
frame bit error occurs. In 193S, framing FT and FS patterns are tested. The FPS pattern is tested in 193E
framing. Additionally, in 193E framing, RFER reports CRC6 code word errors by a low-high-low
transition (1 bit period-wide) one-half RCLK period before a low-high transition on RMSYNC (see
Figure 17).
RESET
A high-low transition on RST clears all registers and forces an immediate resync when RST returns high.
RST must be held low on system power-up to insure proper initialization of the counters and registers.
Following reset, the host processor should restore all control modes by writing appropriate registers with
control data.
ALARM OUTPUT TIMING Figure 17
Page 18

DS2182A
18 of 25
NOTES:
1. RFER transitions high during F-bit time if received framing pattern bit is in error. (Frame 12 F-bits in
193S are ignored if RCR2.3 = 1.) Also, in 193E, RFER transitions high 1/2 bit-time before rising
edge of RMSYNC to indicate a CRC6 error for the previous multiframe.
2. RBV indicates received bipolar violation and transitions high when accused bit emerges from RSER.
If B8ZS is enabled, RBV will not report the 0 replacement code.
3. RCL transitions high when 192 consecutive bits are 0; RCL transitions low upon reception of 12.5%
ones density.
4. RLOS transitions high during F-bit time that caused an OOF event if auto-resync is enabled (RCR1.1
= 0). Resync also occurs when loss of carrier is detected (RCL = 1) if RCR1.7 = 0. When RCR1.1 =
1, RLOS remains low until resync occurs, regardless of OOF or carrier loss flags. In this situation,
resync is initiated only when RCR1.0 transitions low-to-high or the RST pin transitions high-lowhigh.
Page 19

DS2182A
19 of 25
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Voltage on Any Pin Relative to Ground -0.1V to +7.0V
Operating Temperature 0° to 70°C
Storage Temperature -55°C to +125°C
Soldering Temperature 260°C for 10 seconds
* This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above
those indicated in the operation sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods of time may affect reliability.
RECOMMENDED DC OPERATING CONDITIONS (0°C to 70°C)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Input Logic 1 V
IH
2.0 VCC+0.3 V
Input Logic 0 V
IL
-0.3 +0.8 V
Supply V
DD
4.50 5.50 V
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (0°C to 70°C; VDD = 5V ± 10%)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Supply Current I
DD
3 mA 1,2
Input Leakage I
L
-1.0 +1.0 µA 3
Output Current (2.4V) I
OH
-1.0 mA 4
Output Current (0.4V) I
OL
+4.0 mA 5
Output Leakage I
LO
-1.0 +1.0 µA 6
CAPACITANCE (tA=25°C)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Input Capacitance C
IN
5 pF
Output Capacitance C
OUT
7 pF
NOTES:
1. RCLK = 1.544 MHz.
2. Outputs open.
3. 0V < V
IN
< V
DD
.
4. All outputs except INT which is open collector.
5. All outputs.
6. Applies to SDO when tri-stated.
Page 20

DS2182A
20 of 25
CHARACTERISTICS
1,2
SERIAL PORT (0°C to 70°C; VDD = 5V ± 10%)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
SDI to SCLK Setup t
DC
50 ns
SCLK to SDI Hold t
CHD
50 ns
SDI to SCLK Falling Edge t
CD
50 ns
SCLK Low Time t
CL
250 ns
SCLK High Time t
CH
250 ns
SCLK Rise and Fall Times tR, t
F
100 ns
CS to SCLK Setup
t
CC
50 ns
SCLK to CS Hold
t
CCH
50 ns
CS Inactive Time
t
CWH
2.5 µs
SCLK to SDO Valid t
CDV
200 ns
CS to SDO High Z
t
CDZ
75 ns
NOTES:
1. Measured at V
IH
= 2.0 or VIL = .8 and 10ns maximum rise and fall time.
2. Output load capacitance = 100 pF.
Page 21

DS2182A
21 of 25
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
1,2
RECEIVE
(0°C to 70°C; VDD = 5.0V ± 10%)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Propagation delay RCLK to
RMSYNC, RFSYNC,
RSISEL, RSIGFR, RLCLK,
RCHCLK
t
PRS
75 ns
Propagation delay RCLK to
RSER, RABCD, RLINK
t
PRD
75 ns
Transition Time All Outputs t
TTR
20 ns
RCLK Period t
P
648 ns
RCLK Pulse Width tR, t
F
324 ns
RCLK Rise and Fall Times t
CCH
20 ns
RPOS, RNEG Setup to RCLK
Falling
t
SRD
50 ns
RPOS, RNEG Hold to RCLK
Falling
t
HRD
50 ns
Propagation delay RCLK to
RLOS, RYEL, RBV, RCL,
RFER
t
PRA
75 ns
Minimum RST Pulse Width
t
RST
1 µs
NOTES:
1. Measured at V
IH
= 2.0 or VIL = .8 and 10ns maximum rise and fall time.
2. Output load capacitance = 100 pF.
Page 22

DS2182A
22 of 25
SERIAL PORT WRITE AC TIMING DIAGRAM Figure 18
NOTES:
1. Data byte bits must be valid across low clock periods to prevent transients in operating modes.
2. Shaded regions indicate “don’t care” states of input.
SERIAL PORT READ
1
AC TIMING DIAGRAM Figure 19
NOTES:
1. Serial port write must precede a port read to provide address information.
Page 23

DS2182A
23 of 25
RECEIVE AC TIMING DIAGRAM Figure 20
Page 24

DS2182A
24 of 25
DS2182A T1 LINE MONITOR 28-PIN DIP
INCHES
DIM
MIN. MAX.
A 1.445 1.470
B 0.530 0.550
C 0.140 0.160
D 0.600 0.625
E 0.015 0.040
F 0.120 0.145
G 0.090 0.110
H 0.600 0.680
J 0.008 0.012
K 0.015 0.022
Page 25

DS2182A
25 of 25
DS2182AQ T1 LINE MONITOR 28-PIN PLCC
INCHES
DIM
MIN. MAX.
A 0.165 0.180
A1 0.090 0.120
A2 0.020 -
B 0.026 0.033
B1 0.013 0.021
C 0.009 0.012
D 0.485 0.495
D1 0.450 0.456
D2 0.390 0.430
E 0.485 0.495
E1 0.450 0.456
E2 0.390 0.430
L1 0.060 -
N 28 -
e1 0.050 BSC
CH1 0.042 0.048
 Loading...
Loading...