Page 1

www.dalsemi.com
A
DS2172
Bit Error Rate Tester (BERT)
FEATURES
Generates/Detects digital bit patterns for
analyzing, evaluating and troubleshooting
digital communications systems
Operates at speeds from DC to 52 MHz
Programmable polynomial length and
feedback taps for generation of any other
pseudorandom pattern up to 32 bits in length
including: 26-1, 29-1, 211-1, 215-1, 220-1, 223-1,
and 232-1
Programmable user-defined pattern and
length for generation of any repetitive pattern
up to 32 bits in length
Large 32-bit error count and bit count
registers
Software programmable bit error insertion
Fully independent transmit and receive
sections
8-bit parallel control port
Detects test patterns with bit error rates up to
-2
10
PIN ASSIGNMENT
TDATA
TDIS
TCLK
VSS
VDD
RCLK
RDIS
RDATA
TL
AD0
AD1
TEST
VSS
AD2
AD3
AD4
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25
1
2
3
4
DS2172
32-Pin TQFP
5
6
7
8
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
AD5
AD6
AD7
BTS
VSS
VDD
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
RD(DS)
RL
RLOS
LC
VSS
VDD
INT
WR(R/W)
LE(AS)
CS
ORDERING INFORMATION
DS2172T (00 C to 700 C)
DS2172TN (-400 C to + 850 C)
DESCRIPTION
The DS2172 Bit Error Rate Tester (BERT) is a software programmable test pattern generator, receiver,
and analyzer capable of meeting the most stringent error performance requirements of digital
transmission facilities. Two categories of test pattern generation (Pseudo-random and Repetitive)
conform to CCITT/ITU O.151, O.152, O.153, and O.161 standards. The DS2172 operates at clock rates
ranging from DC to 52 MHz. This wide range of operating frequenc y allows the DS2172 to be used in
existing and future test equipment, transmission facilities, switching equipment, multiplexers, DACs,
Routers, Bridges, CSUs, DSUs, and CPE equipment.
The DS2172 user-programmable pattern registers provide the unique ability to generate loopback patterns
required for T1, Fractional-T1, Smart Jack, and other test procedures. Hence the DS2172 can initiate the
loopback, run the test, check for errors, and finally deactivate the loopback.
The DS2172 consists of four functional blocks: the pattern generator, pattern detector, error counter, and
control interface. The DS2172 can be programmed to generate an y pseudorandom pattern with length up
32
-1 bits (see Table 5, Note 9) or any user programmable bit pattern from 1 to 32 bits in length. Logic
to 2
inputs can be used to configure the DS2172 for applications requiring gap clocking such as Fractional-T1,
Switched-56, DDS, normal framing requirements, and per-channel test procedures. In addition, the
DS2172 can insert single or 10-1 to 10-7 bit errors to verify equipment operation and connectivity.
1 of 21 051700
Page 2

DS2172
1.0 GENERAL OPERATION
1.1 PATTERN GENERATION
The DS2172 is programmed to generate a particular test pattern by programming the following registers:
- Pattern Set Registers (PSR)
- Pattern Length Register (PLR)
- Polynomial Tap Register (PTR)
- Pattern Control Register (PCR)
- Error Insertion Register (EIR)
Please see Tables 4 and 5 for examples of how to program these registers in order to generate some
standard test patterns. Once these registers are programmed, the user will then toggle the TL (Transmit
Load) bit or pin to load the pattern into the onboard pattern generation circuitry and the pattern will begin
appearing at the TDATA pin.
1.2 PATTERN SYNCHRONIZATION
The DS2172 expects to receive the same pattern that it transmitted. The synchronizer examines the data at
RDATA and looks for characteristics of the transmitted pattern. The user can control the onboard
synchronizer with the Sync Enable and Resync bits in the Pattern Control Register.
In pseudorandom mode, the received pattern is tested to see if it fits the polynomial generator as defined
in the transmit side. For pseudorandom patterns, only the original pattern and an all ones pattern or an all
0s pattern will satisfy this test. Synchronization in pseudorandom pattern mode should be qualified by
using the RA1 and RA0 indicators in the Status Register. Synchronization is declared after 34 + n bits are
received without error, where n is the exponent in the polynomial from table 4. Once in synchronization
(SR0. = 1) any deviation from this pattern will be counted by the Bit Error Count Register.
In repetitive pattern mode a received pattern of the same length as being transmitted will satisfy this test.
Synchronization in repetitive pattern mode should be qualified by using the RA1 and RA0 indicators in
the Status Register and examining the Pattern Receive Register (PRR0--3). See section 10 for an
explanation of the Pattern Receive Register. Once in synchronization (SR.0 = 1) an y deviation from this
pattern will be counted by the Bit Error Count Register.
1.3 BER CALCULATION
Users can calculate the actual Bit Error Rate (BER) of the digital communications channel by reading the
bit error count out of the Bit Error Count Register (BECR) and reading the bit count out of the Bit Count
Register (BCR) and then dividing the BECR value with the BCR value. The user has total control over
the integration period of the measurement. The LC (Load Count) bit or pin is used to set the integration
period.
1.4 GENERATING ERRORS
Via the Error Insertion Register (EIR), the user can intentionally inject a particular error rate into the
transmitted data stream. Injecting errors allows users to stress communication links and to check the
functionality of error monitoring equipment along the path.
1.5 POWER-UP SEQUENCE
On power-up, the registers in the DS2172 will be in a random state. The user must program all the
internal registers to a known state before proper operation can be insured.
2 of 21
Page 3
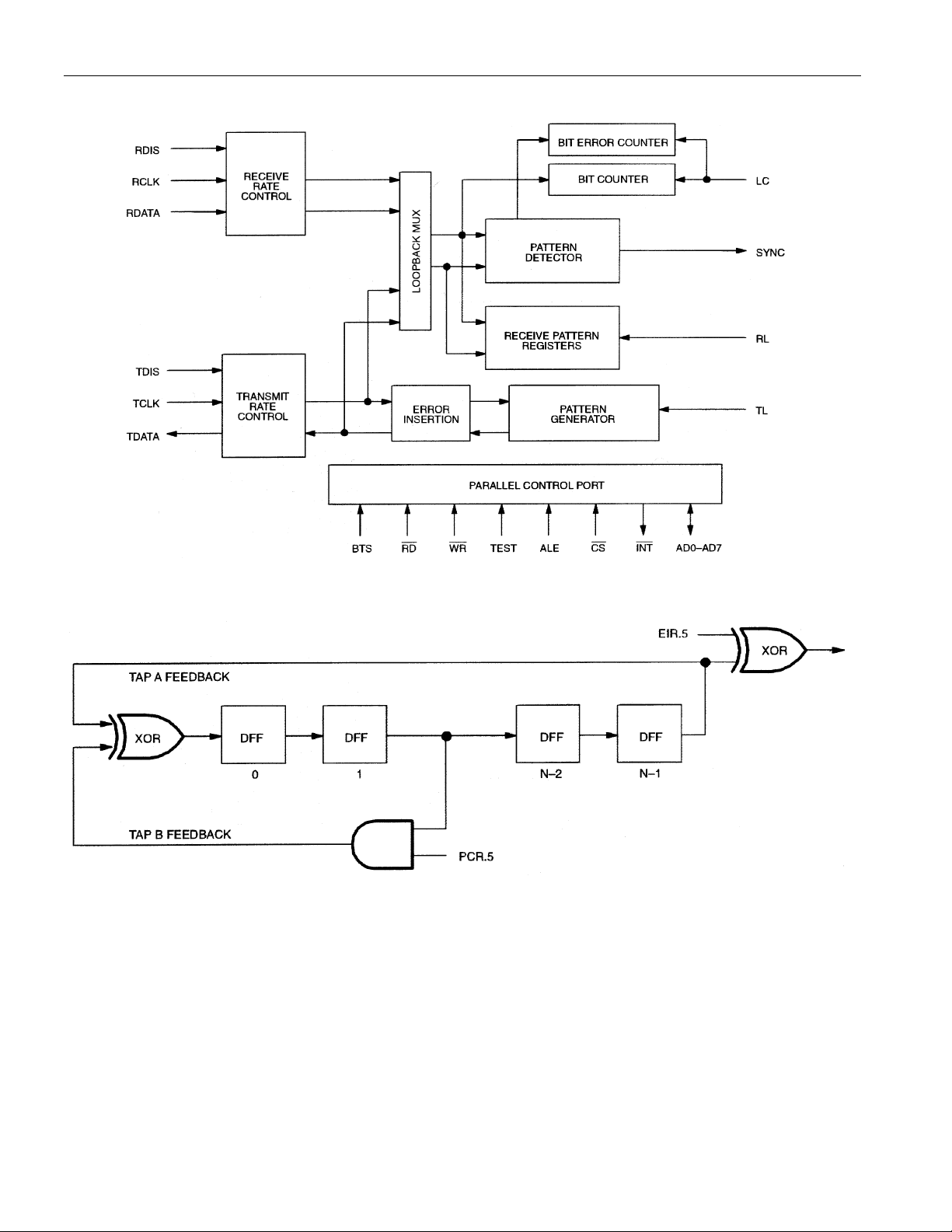
DS2172 FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM Figure 1
DS2172
DS2172 PATTERN GENERATION BLOCK DIAGRAM Figure 2
NOTES:
1. Tap A always equals length (N-1) of pseudorandom or repetitive pattern.
2. Tab B can be programmed to any feedback tap for pseudorandom pattern generation.
3 of 21
Page 4
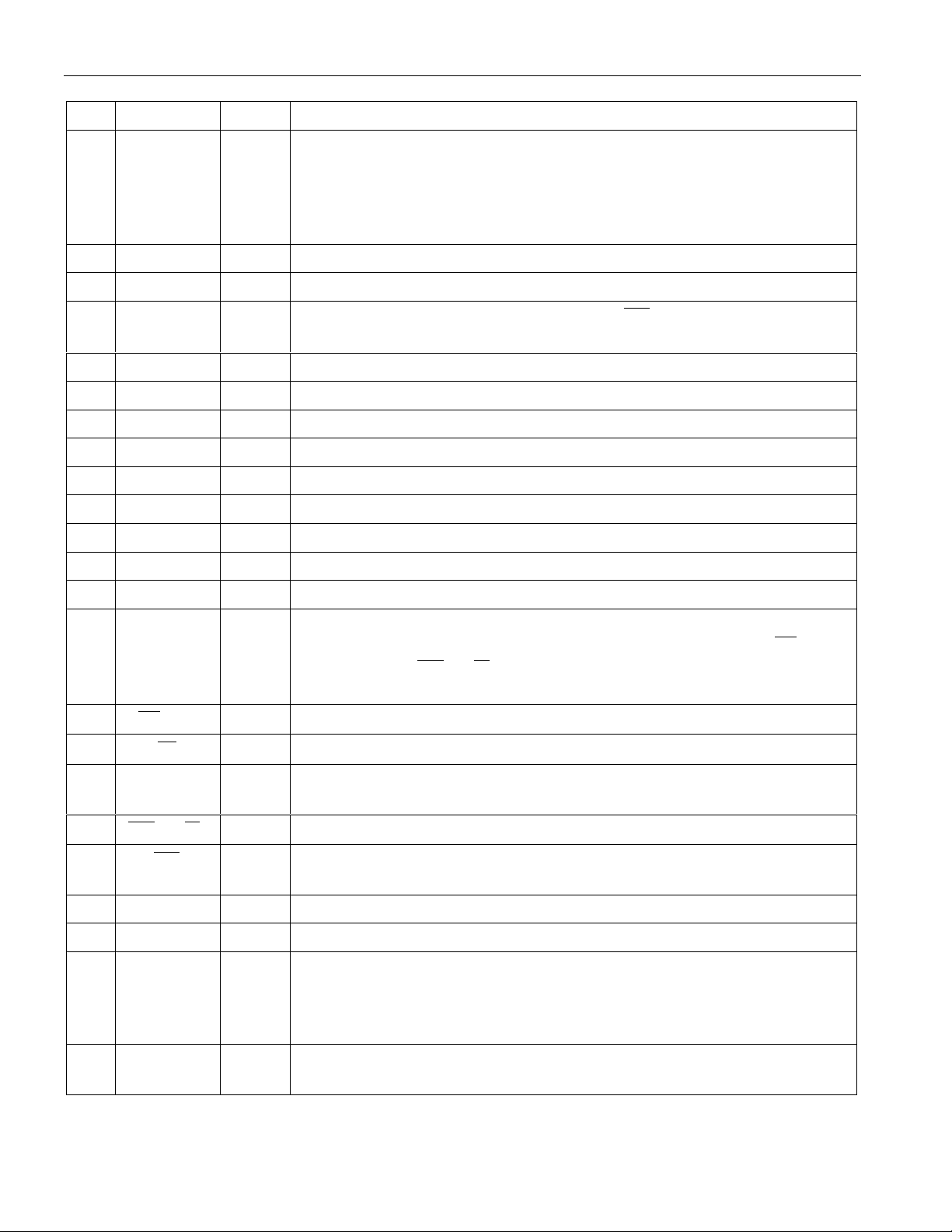
DETAILED PIN DESCRIPTION Table 1
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
DS2172
1TL I
Transmit Load. A positive-going edge loads the pattern generator with
the contents of the Pattern Set Registers. The MSB of the repetitive or
pseudorandom pattern appears at TDATA after the third positive edge of
TCLK from asserting TL. TL is logically OR’ed with PCR.7 and should
be tied to VSS if not used. See Figure 8 for timing information.
2 AD0 I/O Data Bus. An 8-bit multiplexed address/data bus.
3 AD1 I/O Data Bus. An 8-bit multiplexed address/data bus.
4 TEST I
Test. Set high to 3-state all output pins ( INT , ADx, TDATA, RLOS).
Should be tied to VSS to enable all outputs.
5VSS- Signal Ground. 0.0V. Should be tied to local ground plane.
6 AD2 I/O Data Bus. An 8-bit multiplexed address/data bus.
7 AD3 I/O Data Bus. An 8-bit multiplexed address/data bus.
8 AD4 I/O Data Bus. An 8-bit multiplexed address/data bus.
9 AD5 I/O Data Bus. An 8-bit multiplexed address/data bus.
10 AD6 I/O Data Bus. An 8-bit multiplexed address/data bus.
11 AD7 I/O Data Bus. An 8-bit multiplexed address/data bus.
12 V
13 V
SS
DD
- Signal Ground. 0.0V. Should be tied to local ground plane.
- Positive Supply. 5.0V.
14 BTS I Bus Type Select. Strap high to select Motorola bus timing; strap low to
select Intel bus timing. This pin controls the function of the RD (DS),
ALE(AS), and WR (R/W ) pins. If BTS = 1, then these pins assume the
function listed in parenthesis ().
15
16
RD (DS)
CS
I
Read Input (Data Strobe).
I Chip Select. Must be low to read or write the port.
17 ALE(AS) I Address Latch Enable (Address Strobe). A positive going edge serves
to demultiplex the bus.
18
19
WR (R/W )
INT
I
Write Input (Read/Write).
O Alarm Interrupt. Flags host controller during conditions defined in
Status Register. Active low, open drain output.
20 V
21 V
DD
SS
- Positive Supply. 5.0V.
- Signal Ground. 0.0V. Should be tied to local ground plane.
22 LC I Load Count. A positive-going edge latches the current bit and bit error
count into the user accessible BCR and BECR registers and clears the
internal count registers. LC is logically OR’ed with control bit PCR.4.
Should be tied to VSS if not used.
23 RLOS O
Receive Loss Of Sync. Indicates the real time status of the receive
synchronizer. Active high output.
4 of 21
Page 5
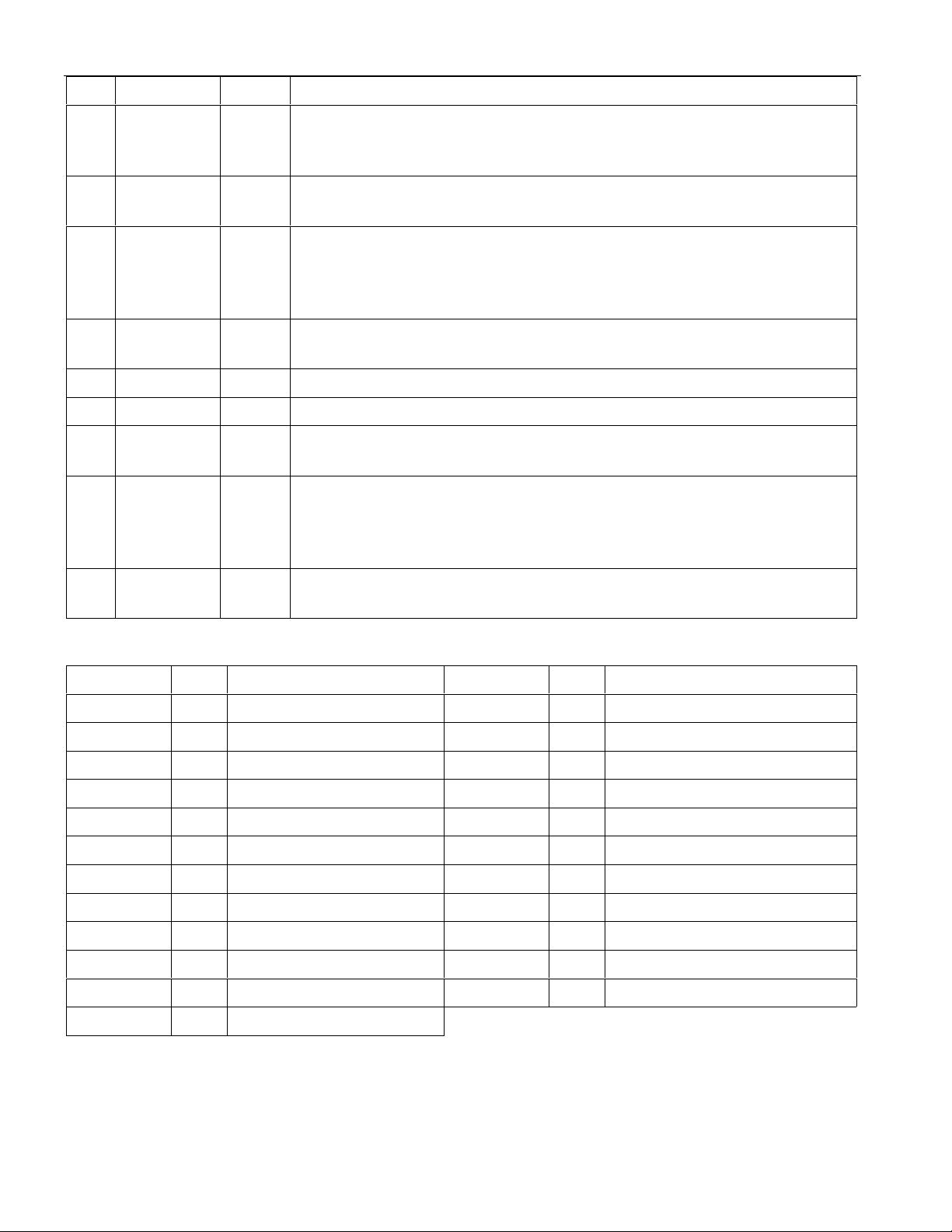
DS2172
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
24 RL I Receive Load. A positive-going edge loads the previous 32 bits of data
received at RDATA into the Pattern Receive Registers. RL is logicall y
OR’ed with control bit PCR.3. Should be tied to VSS if not used.
25 RDATA I Receive Data. Received NRZ serial data, s ampled on the rising edge of
RCLK.
26 RDIS I Receive Disable. Set high to prevent the data at RDATA from being
sampled. Set low to allow bits at RDATA to be sampled. Should be tied
to VSS if not used. See Figure 6 for timing information. All receive side
operations are disabled when RDIS is high.
27 RCLK I Receive Clock. Input clock from transmission link. 0 to 52 MHz. Can be
a gapped clock. Fully independent from TCLK.
28 V
29 V
DD
SS
- Positive Supply. 5.0V.
- Signal Ground. 0.0V. Should be tied to local ground plane.
30 TCLK I Transmit Clock. Transmit demand clock. 0 to 52 MHz. Can be a gapped
clock. Fully independent of RCLK.
31 TDIS I
Transmit Disable. Set high to hold the current bit being transmitted at
TDATA. Set low to allow the next bit to appear at TD ATA. Should be
tied to VSS if not used. See Figure 7 for timing information. All transmit
side operations are disabled when TDIS is high.
32 TDATA O Transmit Data. Transmit NRZ serial data, updated on the rising ed ge of
TCLK.
DS2172 REGISTER MAP Table 2
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME
00 R/W Pattern Set Register 3. 0C R Bit Error Counter Register 3.
01 R/W Pattern Set Register 2. 0D R Bit Error Counter Register 2.
02 R/W Pattern Set Register 1. 0E R Bit Error Counter Register 1.
03 R/W Pattern Set Register 0. 0F R Bit Error Counter Register 0.
04 R/W Pattern Length Register. 10 R Pattern Receive Register 3.
05 R/W Polynomial Tap Register. 11 R Pattern Receive Register 2.
06 R/W Pattern Control Register. 12 R Pattern Receive Register 1.
07 R/W Error Insert Register. 13 R Pattern Receive Register 0.
08 R Bit Counter Register 3. 14 R Status Register.
09 R Bit Counter Register 2. 15 R/W Interrupt Mask Register.
0A R Bit Counter Register 1. 1C R/W Test Register (see note 1)
0B R Bit Counter Register 0.
NOTE:
1. The Test Register must be set to 00 hex to insure proper operation of the DS2172.
5 of 21
Page 6
DS2172
2.0 PARALLEL CONTROL INTERFACE
The DS2172 is controlled via a multiplexed bi-directional address/data bus by an external microcontroller
or microprocessor. The DS2172 can operate with either Intel or Motorola bus timin g configurations. If
the BTS pin is tied low, Intel timing will be selected; if tied high, Motorola timing will be selected. All
Motorola bus signals are listed in parenthesis (). See the timing diagrams in the A.C. Electrical
Characteristics for more details. The multiplexed bus on the DS2172 saves pins because the address
information and data information share the same signal paths. The addresses are presented to the pins in
the first portion of the bus cycle and data will be transferred on the pins durin g second portion of the bus
cycle. Addresses must be valid prior to the falling edge of ALE(AS), at which time the DS2172 latches
the address from the AD0 to AD7 pins. Valid write data must be present and held stable during the later
portion of the DS or WR pulses. In a read cycle, the DS2172 outputs a byte of data during the latter
portion of the DS or RD pulses. The read cycle is terminated and the bus returns to a high impedance
state as RD transitions high in Intel timing or as DS transitions low in Motorola timing. The DS2172 can
also be easily connected to non-multiplexed buses. RCLK and TCLK are used to update counters and
load transmit and receive pattern registers. At slow clock rates, sufficient time must be allowed for these
port operations.
3.0 PATTERN SET REGISTERS
The Pattern Set Registers (PSR) are loaded each time a new pattern (whether it be pseudorandom or
repetitive) is to be generated. When a pseudorandom pattern is generated, all four PSRs must be loaded
with FF Hex. When a repetitive pattern is to be created, the four PSRs are loaded with the pattern that is
to be repeated. Please see Tables 4 and 5 for some programming examples.
PATTERN SET REGISTERS
(MSB) (LSB)
PS31 PS30 PS29 PS28 PS27 PS26 PS25 PS24 PSR3 (addr.=00 Hex)
PS23 PS22 PS21 PS20 PS19 PS18 PS17 PS16 PSR2 (addr.=01 Hex)
PS15 PS14 PS13 PS12 PS11 PS10 PS9 PS8 PSR1 (addr.=02 Hex)
PS7 PS6 PS5 PS4 PS3 PS2 PS1 PS0 PSR0 (addr.=03 Hex)
4.0 PATTERN LENGTH REGISTER
Length Bits LB4 to LB0 determine the length of the pseudorandom polynomial or programmable
repetitive pattern that is generated and detected. With the pseudorandom patterns, the “Tap A” feedback
position of the pattern generator is always equal to the value in the Pattern Length Register (PLR). Please
refer to Figure 2 for a block diagram of the pattern generator and to Tables 4 and 5 for some
programming examples.
6 of 21
Page 7

DS2172
PLR: PATTERN LENGTH REGISTER (Address=04 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
- - - LB4 LB3 LB2 LB1 LB0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
- PLR1.7 Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
- PLR1.6 Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
- PLR1.5 Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
LB4 PLR1.4
LB3 PLR1.3
LB2 PLR1.2
LB1 PLR1.1
LB0 PLR1.0
Length Bit 4.
Length Bit 3.
Length Bit 2.
Length Bit 1.
Length Bit 0.
5.0 POLYNOMIAL TAP REGISTER
Polynomial Tap Bits PT4 - PT0 determine the feedback position of Tap B connected to the XOR input of
the pattern generator. Feedback Tap B provides one of two feedback paths within the pattern generator.
Please refer to Figure 2 for a block diagram of the pattern generator and to Tables 4 and 5 for register
programming examples.
PTR: POLYNOMIAL TAP REGISTER (Address=05 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
- - - PT4 PT3 PT2 PT1 PT0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
-PTR.7Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
-PTR.6Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
-PTR.5Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
PT4 PTR.4
PT3 PTR.3
PT2 PTR.2
PT1 PTR.1
PT0 PTR.0
Polynomial Tap Bit 4.
Polynomial Tap Bit 3.
Polynomial Tap Bit 2.
Polynomial Tap Bit 1.
Polynomial Tap Bit 0.
7 of 21
Page 8

DS2172
6.0 PATTERN CONTROL REGISTER
The Pattern Control Register (PCR) is used to configure the operating parameters of the DS2172 and to
control the patterns being generated and received. Also the PCR is used to control the pattern
synchronizer and the error and bit counters.
PCR: PATTERN CONTROL REGISTER (Address=06 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TL QRSS PS LC RL SYNCE RESYNC LPBK
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TL PCR.7 Transmit Load. A low to high transition loads the pattern
generator with the contents of the Pattern Set Registers. PCR.7 is
logically ORed with the input pin TL. Must be cleared and set
again for subsequent loads.
QRSS PCR.6 Zero Suppression Select. Forces a 1 into the pattern whenever
the next 14 bit positions are all 0s. Should only be set when
using the QRSS pattern.
0 = Zero suppression disabled
1 = Zero suppression enabled
PS PCR.5
LC PCR.4 Latch Count Registers. A low to high transition latches the bit
RL PCR.3 Receive Data Load. A transition from low to high loads the
SYNCE PCR.2
RESYNC PCR.1 Initiate Manual Resync Process. A low to high transition will
Pattern Select.
0 = Repetitive Pattern
1 = Pseudorandom Pattern
and error counts into the user accessible registers BCR and
BECR and clears the internal register count. PCR.4 is logically
OR’ed with input pin LC. Must be cleared and set again for
subsequent loads.
previous 32 bits of data received at RDATA into the Pattern
Receive Registers (PRR). PCR.3 is logically OR’ed with input
pin RL. Must be cleared and set again for subsequent latches.
SYNC Enable.
0 = auto resync is enabled.
1 = auto resync is disabled.
force the DS2172 to resynchronize to the incoming pattern at
RDATA. Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent resync.
LPBK PCR.0 Transmit/Receive Loopback Select. When enabled, the
RDATA input is disabled; TDATA continues to output data as
normal. See Figure 1.
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
8 of 21
Page 9

DS2172
7.0 ERROR INSERT REGISTER
The Error Insertion Register (EIR) controls circuitry within the DS2172 that allows the generated pattern
to be intentionally corrupted. Bit errors can be inserted automatically at regular intervals by properly
programming the EIR0 to EIR2 bits or bit errors can be inserted at random (under microcontroller
control) via the EIR.3 bit.
EIR: ERROR INSERT REGISTER (Address=07 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
- - TINV RINV SBE EIR2 EIR1 EIR0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
-EIR.7Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
-EIR.6Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
TINV EIR.5
Transmit Data Inversion Select.
0 = do not invert data to be transmitted at TDATA
1 = invert data to be transmitted at TDATA
RINV EIR.4
Receive Data Inversion Select.
0 = do not invert data received at RDATA
1 = invert data received at RDATA
SBE EIR.3 Single Bit Error Insert. A low to high transition will create a
single bit error. Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent
bit error to be inserted. Can be used to accomplish rates not
addressed in Table 3 (e.g., BER of less than 10-7).
EIB2 EIR.2 Error Insert Bit 2. See Table 3.
EIB1 EIR.1 Error Insert Bit 1. See Table 3.
EIB0 EIR.0 Error Insert Bit 0. See Table 3.
ERROR BIT INSERTION Table 3
EIB2 EIB1 EIB0 ERROR RATE INSERTED
0 0 0 no errors automatically inserted
00 110
01 010
01 110
10 010
10 110
11 010
11 110
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
-6
-7
9 of 21
Page 10

DS2172
PSEUDORANDOM PATTERN GENERATION (PCR.5=1) Table 4
PATTERN TYPE PTR PLR PSR3 PSR2 PSR1 PSR0 TINV RINV
23 - 1 0002FFFFFFFF 0 0
24 - 1 0003FFFFFFFF 0 0
25 - 1 0104FFFFFFFF 0 0
26 - 1 0405FFFFFFFF 0 0
27 - 1 0006FFFFFFFF 0 0
27 - 1 Fractional T1 LB Activate 03 06 FF FF FF FF 0 0
27 - 1 Fractional T1 LB Deactivate 03 06 FF FF FF FF 1 1
29 - 1 O.153 (511 type) 04 08 FF FF FF FF 0 0
210 - 1 0209FFFFFFFF 0 0
211 - 1 O.152 and O.153 (2047 type) 08 0A FF FF FF FF 0 0
215 - 1 O.151 0D 0E FF FF FF FF 1 1
217 - 1 0210FFFFFFFF 0 0
218 - 1 0611FFFFFFFF 0 0
220 - 1 O.153 02 13 FF FF FF FF 0 0
220 - 1 O.151 QRSS (PCR.6=1) 10 13 FF FF FF FF 0 0
221 - 1 0114FFFFFFFF 0 0
222 - 1 0015FFFFFFFF 0 0
223 - 1 O.151 11 16 FF FF FF FF 1 1
225 - 1 0218FFFFFFFF 0 0
228 - 1 021BFFFFFFFF 0 0
229 - 1 011CFFFFFFFF 0 0
231 - 1 021EFFFFFFFF 0 0
232 - 1 (see note below) 10 1F FF FF FF FF 0 0
REPETITIVE PATTERN GENERATION (PCR.5=0) Table 5
PATTERN TYPE PTR PLR PSR3 PSR2 PSR1 PSR0 TINV RINV
all 1s 00 00 FF FF FF FF 0 0
all 0s 00 00 FF FF FF FE 0 0
alternating 1s and 0s 00 01 FF FF FF FE 0 0
double alternating 1s and 0s 00 03 FF FF FF FC 0 0
3 in 24 00 17 FF 20 00 22 0 0
1 in 16 00 0F FF FF 00 01 0 0
1 in 8 00 07 FF FF FF 01 0 0
1 in 4 00 03 FF FF FF F1 0 0
D4 Line Loopback Activate 00 04 FF FF FF F0 0 0
D4 Line Loopback Deactivate 00 02 FF FF FF FC 0 0
10 of 21
Page 11

DS2172
NOTES FOR TABLES 4 AND 5:
1. PTR = Polynomial Tap Register (address = 05)
2. PLR = Pattern Length Register (address = 04)
3. PSR3 = Pattern Set Register 3 (address = 00)
4. PSR2 = Pattern Set Register 2 (address = 01)
5. PSR1 = Pattern Set Register 1 (address = 02)
6. PSR0 = Pattern Set Register 0 (address = 03)
7. TINV = Transmit Data Inversion Select Bit (EIR.5)
8. RINV = Receive Data Inversion Select Bit (EIR.4)
32
9. For the 2
32
2
- 1.
-1 pattern, the random pattern actually repeats every (4093 x 220) + 1046529 bits instead of
8.0 BIT COUNT REGISTERS
The Bit Count Registers (BCR3 to BCR0) comprise a 32-bit count of bits (actually RCLK cycles)
received at RDATA. BC31 is the MSB of the 32-bit count. The bit counter increments for each c ycle of
RCLK when input pin RDIS is low. The bit counter is disabled during loss of SYNC. The Status Register
bit BCOF is set when this 32-bit register overflows. Upon an overflow condition, the user must clear the
BCR by either toggling the LC bit or pin. The DS2172 latches the bit count into the BCR registers and
clears the internal bit count when either the PCR.4 bit or the LC input pin toggles f rom low to high. The
bit count and bit error count (available via the BECRs) are used by an external processor to compute the
BER performance on a loop or channel basis.
BIT COUNT REGISTERS
(MSB) (LSB)
BC31 BC30 BC29 BC28 BC27 BC26 BC25 BC24 BCR3 (addr.=08 Hex)
BC23 BC22 BC21 BC20 BC19 BC18 BC17 BC16 BCR2 (addr.=09 Hex)
BC15 BC14 BC13 BC12 BC11 BC10 BC9 BC8 BCR1 (addr.=0A Hex)
BC7 BC6 BC5 BC4 BC3 BC2 BC1 BC0 BCR0 (addr.=0B Hex)
9.0 BIT ERROR COUNT REGISTERS
The Bit Error Count Registers (BECR3 to BECR0) comprise a 32-bit count of bits received in error at
RDATA. The bit error counter is disabled during loss of SYNC. BEC31 is the MSB of th e 32-bit count.
The Status Register bit BECOF is set when this 32-bit register overflows. Upon an overflow condition,
the user must clear the BECR by either toggling the LC bit or pin. The DS2172 latches the bit error count
into the BECR registers and clears the internal bit error count when either the PCR.4 bit or the LC input
pin toggles from low to high. The bit count (available via the BCRs) and bit error count are used by an
external processor to compute the BER performance on a loop or channel basis.
11 of 21
Page 12

DS2172
BIT ERROR COUNT REGISTERS
(MSB) (LSB)
BEC31 BEC30 BEC29 BEC28 BEC27 BEC26 BEC25 BEC24 BECR3
(addr.=0C Hex)
BEC23 BEC22 BEC21 BEC20 BEC19 BEC18 BEC17 BEC16 BECR2
(addr.=0D Hex)
BEC15 BEC14 BEC13 BEC12 BEC11 BEC10 BEC9 BEC8 BECR1
(addr.=0E Hex)
BEC7 BEC6 BEC5 BEC4 BEC3 BEC2 BEC1 BEC0 BECR0
(addr.=0F Hex)
10.0 PATTERN RECEIVE REGISTERS
The Pattern Receive Register (PRR) provides access to the data patterns received at RDATA. The
operation of these registers depends on the synchronization status of the DS2172. Asserting the RL bit
(PCR.3) or pin during an out-of -sync condition (SR.0 = 0) will latch the previous 32 bits of data received
at RDATA into the PRR registers. When the DS2172 is in sync (SR.0 = 1) asserting RL will latch the
pattern that to which the device has established synchronization. Since the receiver has no knowledge of
the start or end of the pattern, the data in the PRR registers will have no particular alignment. As an
example, if the receiver has synchronized to the pattern 00100110, PRR1 may report 10011000,
11000100 or any rotation thereof. Once synchronization is established, bit errors cannot be viewed in the
PRR registers.
PATTERN RECEIVE REGISTERS
(MSB) (LSB)
PR31 PR30 PR29 PR28 PR27 PR26 PR25 PR24 PRR3 (addr.=10 Hex)
PR23 PR22 PR21 PR20 PR19 PR18 PR17 PR16 PRR2 (addr.=11 Hex)
PR15 PR14 PR13 PR12 PR11 PR10 PR9 PR8 PRR1 (addr.=12 Hex)
PR7 PR6 PR5 PR4 PR3 PR2 PR1 PR0 PRR0 (addr.=13 Hex)
11.0 STATUS REGISTER AND INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER
The Status Register (SR) contains information on the current real time status of the DS2172. When a
particular event has occurred, the appropriate bit in the register will be set to a 1. All of the bits in these
registers (except for the SYNC bit) operate in a latched fashion. This means that if an ev ent occu rs and a
bit is set to a 1 in any of the registers, it will remain set until the user reads that bit. For the BED, BCOF,
and BECOF status bits, they will be cleared when read and will not be set again until the event has
occurred again. For RLOS, RA0, and RA1 status bits, they will be cleared when read if the condition no
longer persists.
The SR register has the unique ability to initiate a hardware interrupt via the INT pin. Each of the alarms
and events in the SR can be either masked or unmasked from the interrupt pins via the Interrupt Mask
Register (IMR).
12 of 21
Page 13

DS2172
SR: STATUS REGISTER (Address=14 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
- RA1 RA0 RLOS BED BCOF BECOF SYNC
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
-SR.7Not Assigned. Could be any value when read.
RA1 SR.6 Receive All Ones. Set when 32 consecutive 1s are received;
allowed to be cleared when a 0 is received.
RA0 SR.5 Receive All Zeros. Set when 32 consecutive 0s are received;
allowed to be cleared when a 1 is received.
RLOS SR.4 Receive Loss Of Sync. Set when the device is searchin g for
synchronization. Once sync is achieved, will remain set until
read.
BED SR.3 Bit Error Detection. Set when bit errors are detected.
BCOF SR.2 Bit Counter Overflow. Set when the 32-bit BCR overflows.
BECOF SR.1 Bit Error Count Overflow. Set when the 32-bit BECR
overflows.
SYNC SR.0 Sync. Real time status of the synchronizer (this bit is not
latched). Will be set when synchronization is declared. Will be
cleared when 6 or more bits out of 64 ar e received in error (if
PCR.2 = 0).
13 of 21
Page 14

DS2172
IMR: INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER (Address=15 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
- RA1 RA0 RLOS BED BCOF BECOF SYNC
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
-IMR.7Not Assigned. Should be set to 0 when written to.
RA1 IMR.6
RA0 IMR.5
RLOS IMR.4
BED IMR.3
BCOF IMR.2
BECOF IMR.1
Receive All 1s.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive All 0s.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Receive Loss Of Sync.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit Error Detection.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit Counter Overflow.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit Error Count Overflow.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
SYNC IMR.0
Sync.
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
14 of 21
Page 15

DS2172
12.0 AC TIMING AND DC OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Voltage on Any Pin Relative to Ground -1.0V to +7.0V
Operating Temperature for DS2172TN -40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature -55°C to +125°C
Soldering Temperature See J-STD-020A specification
* This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above
those indicated in the operation sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods of time may affect reliability.
RECOMMENDED DC OPERATING CONDITIONS
(0ºC TO 70ºC for DS2172T;
-40ºC TO +85ºC for DS2172TN)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Logic 1 V
Logic 0 V
Supply V
IH
IL
DD
2.0 VDD+0.3 V
-0.3 +0.8 V
4.50 5.50 V
CAPACITANCE (tA=25ºC)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Input Capacitance C
Output Capacitance C
IN
OUT
5pF
7pF
DC CHARACTERISTICS (0ºC TO 70ºC for DS2172T; VDD=5V±10%;
-40ºC TO +85ºC for DS2172TN; VDD=5V±10%)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Supply Current @ 5V I
Input Leakage I
Output Leakage I
Output Current @ 2.4V I
Output Current @ 0.4V I
DD
IL
LO
OH
OL
-1.0 +1.0
-1.0 mA
+4.0 mA
10 mA 1
µA
1.0
µA
2
3
NOTES:
1. TCLK = RCLK = 1.544 MHz; outputs open circuited.
2. 0.0V < VIN < VDD.
3. Applies to
INT when tri-stated.
15 of 21
Page 16

AC CHARACTERISTICS - PARALLEL PORT
DS2172
(0ºC to 70ºC for DS2172T; V
-40ºC to +85ºC for DS2172TN; V
=5V±10%;
DD
=5V±10%)
DD
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Cycle Time t
Pulse Width, DS Low or RD High
Pulse Width, DS High or RD Lo w
CYC
PW
PW
Input Rise/Fall Times tR, t
R/W Hold Times
R/W Setup Time Before DS High
CS Setup Time Before DS, WR or RD
t
RWH
t
RWS
t
CS
EL
EH
F
200 ns
100 ns
100 ns
20 ns
10 ns
50 ns
20 ns
Active
CS Hold Time
Read Data Hold Time t
Write Data Hold Time t
Mux'ed Address Valid to AS or ALE
t
CH
DHR
DHW
t
ASL
0ns
550ns
0ns
15 ns
Fall
Mux'ed Address Hold Time t
Delay Time DS, WR or RD to AS or
t
ALE Rise
Pulse Width AS or ALE High PW
Delay Time, AS or ALE to DS, WR or
RD
Output Data Delay Time from DS or
RD
t
ASED
t
Data Setup Time t
AHL
ASD
ASH
DDR
DSW
10 ns
20 ns
30 ns
10 ns
550ns
50 ns
16 of 21
Page 17

INTEL BUS READ AC TIMING (BTS=0) Figure 3
DS2172
17 of 21
Page 18

INTEL BUS WRITE AC TIMING (BTS=0) Figure 4
MOTOROLA BUS AC TIMING (BTS=1) Figure 5
DS2172
18 of 21
Page 19

DS2172
AC CHARACTERISTICS - RECEIVE SIDE
(0ºC TO 70ºC for DS2172T; VDD=5V±10%;
-40ºC TO +85ºC for DS2172TN; VDD=5V±10%)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
RCLK Period t
RCLK Pulse Width t
RDATA Set Up to RCLK Rising t
RDATA Hold from RCLK Rising t
RDIS Set Up to RCLK Rising t
RDIS Hold from RCLK Rising t
RL and LC Pulse Width t
CP
CH
t
CL
SU1
HD1
SU2
HD2
WRL
RCLK Rise and Fall Times tR, t
F
19 ns
8
8
ns
ns
4ns
0ns
4ns
0ns
25 ns
10 ns 1
AC CHARACTER ISTIC S - TRAN SMIT SIDE
(0ºC TO 70ºC for DS2172T; VDD=5V±10%;
-40ºC TO +85ºC for DS2172TN; VDD=5V±10%)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
TCLK Period t
TCLK Pulse Width t
TDATA Delay from TCLK Rising t
TDIS Set Up to TCLK Rising t
TDIS Hold from TCLK Rising t
TL Pulse Width t
TL Set Up to TCLK Rising t
TL Hold Off from TCLK Rising t
CP
CH
t
CL
DD
SU
HD
WTL
STL
HTL
TCLK Rise and Fall Time tR, t
F
19 ns
8
8
ns
ns
9ns
4ns
0ns
15 ns
4ns
0ns
10 ns 1
NOTE:
1. The maximum rise and fall time is either 10 ns or 10% of tCP whichever is less.
19 of 21
Page 20

RECEIVE AC TIMING Figure 6
TR AN SMIT AC TIMING Figure 7
DS2172
NOTE:
When TDIS is high about the rising edge of TCLK, TDATA will not be updated and will be held with the
previous valve until TDIS is low about the rising edge of TCLK.
TRANSMIT AC TIMING FOR THE TL INPUT Figure 8
NOTE:
The rising edge of TL causes the internal pattern generation circuitry to be reloaded; the first bit of the
new pattern (the shaded one) will appear after two TCLK periods.
20 of 21
Page 21

DS2172 32-PIN TQFP
DS2172
DIM MIN MAX
A
A1
A2
D
D1
E
E1
L
e
B
C
-1.20
0.05 0.15
0.95 1.05
8.80 9.20
7.00 BSC
8.80 9.20
7.00 BSC
0.45 0.75
0.80 BSC
0.30 0.45
0.09 0.20
21 of 21
 Loading...
Loading...